

13 Tips to Prepare for Your PhD Dissertation Defense
How well do you know your project? Years of experiments, analysis of results, and tons of literature study, leads you to how well you know your research study. And, PhD dissertation defense is a finale to your PhD years. Often, researchers question how to excel at their thesis defense and spend countless hours on it. Days, weeks, months, and probably years of practice to complete your doctorate, needs to surpass the dissertation defense hurdle.
In this article, we will discuss details of how to excel at PhD dissertation defense and list down some interesting tips to prepare for your thesis defense.
Table of Contents
What Is Dissertation Defense?
Dissertation defense or Thesis defense is an opportunity to defend your research study amidst the academic professionals who will evaluate of your academic work. While a thesis defense can sometimes be like a cross-examination session, but in reality you need not fear the thesis defense process and be well prepared.
Source: https://www.youtube.com/c/JamesHaytonPhDacademy
What are the expectations of committee members.
Choosing the dissertation committee is one of the most important decision for a research student. However, putting your dissertation committee becomes easier once you understand the expectations of committee members.
The basic function of your dissertation committee is to guide you through the process of proposing, writing, and revising your dissertation. Moreover, the committee members serve as mentors, giving constructive feedback on your writing and research, also guiding your revision efforts.
The dissertation committee is usually formed once the academic coursework is completed. Furthermore, by the time you begin your dissertation research, you get acquainted to the faculty members who will serve on your dissertation committee. Ultimately, who serves on your dissertation committee depends upon you.
Some universities allow an outside expert (a former professor or academic mentor) to serve on your committee. It is advisable to choose a faculty member who knows you and your research work.
How to Choose a Dissertation Committee Member?
- Avoid popular and eminent faculty member
- Choose the one you know very well and can approach whenever you need them
- A faculty member whom you can learn from is apt.
- Members of the committee can be your future mentors, co-authors, and research collaborators. Choose them keeping your future in mind.
How to Prepare for Dissertation Defense?

1. Start Your Preparations Early
Thesis defense is not a 3 or 6 months’ exercise. Don’t wait until you have completed all your research objectives. Start your preparation well in advance, and make sure you know all the intricacies of your thesis and reasons to all the research experiments you conducted.
2. Attend Presentations by Other Candidates
Look out for open dissertation presentations at your university. In fact, you can attend open dissertation presentations at other universities too. Firstly, this will help you realize how thesis defense is not a scary process. Secondly, you will get the tricks and hacks on how other researchers are defending their thesis. Finally, you will understand why dissertation defense is necessary for the university, as well as the scientific community.
3. Take Enough Time to Prepare the Slides
Dissertation defense process harder than submitting your thesis well before the deadline. Ideally, you could start preparing the slides after finalizing your thesis. Spend more time in preparing the slides. Make sure you got the right data on the slides and rephrase your inferences, to create a logical flow to your presentation.
4. Structure the Presentation
Do not be haphazard in designing your presentation. Take time to create a good structured presentation. Furthermore, create high-quality slides which impresses the committee members. Make slides that hold your audience’s attention. Keep the presentation thorough and accurate, and use smart art to create better slides.
5. Practice Breathing Techniques
Watch a few TED talk videos and you will notice that speakers and orators are very fluent at their speech. In fact, you will not notice them taking a breath or falling short of breath. The only reason behind such effortless oratory skill is practice — practice in breathing technique.
Moreover, every speaker knows how to control their breath. Long and steady breaths are crucial. Pay attention to your breathing and slow it down. All you need I some practice prior to this moment.
6. Create an Impactful Introduction
The audience expects a lot from you. So your opening statement should enthrall the audience. Furthermore, your thesis should create an impact on the members; they should be thrilled by your thesis and the way you expose it.
The introduction answers most important questions, and most important of all “Is this presentation worth the time?” Therefore, it is important to make a good first impression , because the first few minutes sets the tone for your entire presentation.
7. Maintain Your Own List of Questions
While preparing for the presentation, make a note of all the questions that you ask yourself. Try to approach all the questions from a reader’s point of view. You could pretend like you do not know the topic and think of questions that could help you know the topic much better.
The list of questions will prepare you for the questions the members may pose while trying to understand your research. Attending other candidates’ open discussion will also help you assume the dissertation defense questions.
8. Practice Speech and Body Language
After successfully preparing your slides and practicing, you could start focusing on how you look while presenting your thesis. This exercise is not for your appearance but to know your body language and relax if need be.
Pay attention to your body language. Stand with your back straight, but relax your shoulders. The correct posture will give you the feel of self-confidence. So, observe yourself in the mirror and pay attention to movements you make.
9. Give Mock Presentation
Giving a trial defense in advance is a good practice. The most important factor for the mock defense is its similarity to your real defense, so that you get the experience that prepares for the actual defense.
10. Learn How to Handle Mistakes
Everyone makes mistakes. However, it is important to carry on. Do not let the mistakes affect your thesis defense. Take a deep breath and move on to the next point.
11. Do Not Run Through the Presentation
If you are nervous, you would want to end the presentation as soon as possible. However, this situation will give rise to anxiety and you will speak too fast, skipping the essential details. Eventually, creating a fiasco of your dissertation defense .
12. Get Plenty of Rest
Out of the dissertation defense preparation points, this one is extremely important. Obviously, sleeping a day before your big event is hard, but you have to focus and go to bed early, with the clear intentions of getting the rest you deserve.
13. Visualize Yourself Defending Your Thesis
This simple exercise creates an immense impact on your self-confidence. All you have to do is visualize yourself giving a successful presentation each evening before going to sleep. Everyday till the day of your thesis defense, see yourself standing in front of the audience and going from one point to another.
This exercise takes a lot of commitment and persistence, but the results in the end are worth it. Visualization makes you see yourself doing the scary thing of defending your thesis.
If you have taken all these points into consideration, you are ready for your big day. You have worked relentlessly for your PhD degree , and you will definitely give your best in this final step.
Have you completed your thesis defense? How did you prepare for it and how was your experience throughout your dissertation defense ? Do write to us or comment below.
The tips are very useful.I will recomend it to our students.
Excellent. As a therapist trying to help a parent of a candidate, I am very impressed and thankful your concise, clear, action-oriented article. Thank you.
Thanks for your sharing. It is so good. I can learn a lot from your ideas. Hope that in my dissertation defense next time I can pass
The tips are effective. Will definitely apply them in my dissertation.
My dissertation defense is coming up in less than two weeks from now, I find this tips quite instructive, I’ll definitely apply them. Thank you so much.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Mitigating Survivorship Bias in Scholarly Research: 10 tips to enhance data integrity
The Power of Proofreading: Taking your academic work to the next level
Facing Difficulty Writing an Academic Essay? — Here is your one-stop solution!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
PhD Defence Process: A Comprehensive Guide

Embarking on the journey toward a PhD is an intellectual odyssey marked by tireless research, countless hours of contemplation, and a fervent commitment to contributing to the body of knowledge in one’s field. As the culmination of this formidable journey, the PhD defence stands as the final frontier, the proverbial bridge between student and scholar.
In this comprehensive guide, we unravel the intricacies of the PhD defence—a momentous occasion that is both a celebration of scholarly achievement and a rigorous evaluation of academic prowess. Join us as we explore the nuances of the defence process, addressing questions about its duration, contemplating the possibility of failure, and delving into the subtle distinctions of language that surround it.
Beyond the formalities, we aim to shed light on the significance of this rite of passage, dispelling misconceptions about its nature. Moreover, we’ll consider the impact of one’s attire on this critical day and share personal experiences and practical tips from those who have successfully navigated the defence journey.
Whether you are on the precipice of your own defence or are simply curious about the process, this guide seeks to demystify the PhD defence, providing a roadmap for success and a nuanced understanding of the pivotal event that marks the transition from student to scholar.
Introduction
A. definition and purpose:, b. overview of the oral examination:, a. general duration of a typical defense, b. factors influencing the duration:, c. preparation and flexibility:, a. preparation and thorough understanding of the research:, b. handling questions effectively:, c. confidence and composure during the presentation:, d. posture of continuous improvement:, a. exploring the possibility of failure:, b. common reasons for failure:, c. steps to mitigate the risk of failure:, d. post-failure resilience:, a. addressing the language variation:, b. conforming to regional preferences:, c. consistency in usage:, d. flexibility and adaptability:, e. navigating language in a globalized academic landscape:, a. debunking myths around the formality of the defense:, b. significance in validating research contributions:, c. post-defense impact:, a. appropriate attire for different settings:, b. professionalism and the impact of appearance:, c. practical tips for dressing success:, b. practical tips for a successful defense:, c. post-defense reflections:, career options after phd.
Embarking on the doctoral journey is a formidable undertaking, where aspiring scholars immerse themselves in the pursuit of knowledge, contributing new insights to their respective fields. At the pinnacle of this academic odyssey lies the PhD defence—a culmination that transcends the boundaries of a mere formality, symbolizing the transformation from a student of a discipline to a recognized contributor to the academic tapestry.
The PhD defence, also known as the viva voce or oral examination, is a pivotal moment in the life of a doctoral candidate.
PhD defence is not merely a ritualistic ceremony; rather, it serves as a platform for scholars to present, defend, and elucidate the findings and implications of their research. The defence is the crucible where ideas are tested, hypotheses scrutinized, and the depth of scholarly understanding is laid bare.
The importance of the PhD defence reverberates throughout the academic landscape. It is not just a capstone event; it is the juncture where academic rigour meets real-world application. The defence is the litmus test of a researcher’s ability to articulate, defend, and contextualize their work—an evaluation that extends beyond the pages of a dissertation.
Beyond its evaluative nature, the defence serves as a rite of passage, validating the years of dedication, perseverance, and intellectual rigour invested in the research endeavour. Success in the defence is a testament to the candidate’s mastery of their subject matter and the originality and impact of their contributions to the academic community.
Furthermore, a successful defence paves the way for future contributions, positioning the scholar as a recognized authority in their field. The defence is not just an endpoint; it is a launchpad, propelling researchers into the next phase of their academic journey as they continue to shape and redefine the boundaries of knowledge.
In essence, the PhD defence is more than a ceremonial checkpoint—it is a transformative experience that validates the intellectual journey, underscores the significance of scholarly contributions, and sets the stage for a continued legacy of academic excellence. As we navigate the intricacies of this process, we invite you to explore the multifaceted dimensions that make the PhD defence an indispensable chapter in the narrative of academic achievement.
What is a PhD Defence?
At its core, a PhD defence is a rigorous and comprehensive examination that marks the culmination of a doctoral candidate’s research journey. It is an essential component of the doctoral process in which the candidate is required to defend their dissertation before a committee of experts in the field. The defence serves multiple purposes, acting as both a showcase of the candidate’s work and an evaluative measure of their understanding, critical thinking, and contributions to the academic domain.
The primary goals of a PhD defence include:
- Presentation of Research: The candidate presents the key findings, methodology, and significance of their research.
- Demonstration of Mastery: The defence assesses the candidate’s depth of understanding, mastery of the subject matter, and ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
- Critical Examination: Committee members rigorously question the candidate, challenging assumptions, testing methodologies, and probing the boundaries of the research.
- Validation of Originality: The defence validates the originality and contribution of the candidate’s work to the existing body of knowledge.
The PhD defence often takes the form of an oral examination, commonly referred to as the viva voce. This oral component adds a dynamic and interactive dimension to the evaluation process. Key elements of the oral examination include:
- Presentation: The candidate typically begins with a formal presentation, summarizing the dissertation’s main components, methodology, and findings. This presentation is an opportunity to showcase the significance and novelty of the research.
- Questioning and Discussion: Following the presentation, the candidate engages in a thorough questioning session with the examination committee. Committee members explore various aspects of the research, challenging the candidates to articulate their rationale, defend their conclusions, and respond to critiques.
- Defence of Methodology: The candidate is often required to defend the chosen research methodology, demonstrating its appropriateness, rigour, and contribution to the field.
- Evaluation of Contributions: Committee members assess the originality and impact of the candidate’s contributions to the academic discipline, seeking to understand how the research advances existing knowledge.
The oral examination is not a mere formality; it is a dynamic exchange that tests the candidate’s intellectual acumen, research skills, and capacity to contribute meaningfully to the scholarly community.
In essence, the PhD defence is a comprehensive and interactive evaluation that encapsulates the essence of a candidate’s research journey, demanding a synthesis of knowledge, clarity of expression, and the ability to navigate the complexities of academic inquiry. As we delve into the specifics of the defence process, we will unravel the layers of preparation and skill required to navigate this transformative academic milestone.
How Long is a PhD Defence?
The duration of a PhD defence can vary widely, but it typically ranges from two to three hours. This time frame encompasses the candidate’s presentation of their research, questioning and discussions with the examination committee, and any additional deliberations or decisions by the committee. However, it’s essential to note that this is a general guideline, and actual defence durations may vary based on numerous factors.
- Sciences and Engineering: Defenses in these fields might lean towards the shorter end of the spectrum, often around two hours. The focus is often on the methodology, results, and technical aspects.
- Humanities and Social Sciences: Given the theoretical and interpretive nature of research in these fields, defences might extend closer to three hours or more. Discussions may delve into philosophical underpinnings and nuanced interpretations.
- Simple vs. Complex Studies: The complexity of the research itself plays a role. Elaborate experiments, extensive datasets, or intricate theoretical frameworks may necessitate a more extended defence.
- Number of Committee Members: A larger committee or one with diverse expertise may lead to more extensive discussions and varied perspectives, potentially elongating the defence.
- Committee Engagement: The level of engagement and probing by committee members can influence the overall duration. In-depth discussions or debates may extend the defence time.
- Cultural Norms: In some countries, the oral defence might be more ceremonial, with less emphasis on intense questioning. In others, a rigorous and extended defence might be the norm.
- Evaluation Practices: Different academic systems have varying evaluation criteria, which can impact the duration of the defence.
- Institutional Guidelines: Some institutions may have specific guidelines on defence durations, influencing the overall time allotted for the process.
Candidates should be well-prepared for a defence of any duration. Adequate preparation not only involves a concise presentation of the research but also anticipates potential questions and engages in thoughtful discussions. Additionally, candidates should be flexible and responsive to the dynamics of the defense, adapting to the pace set by the committee.
Success Factors in a PhD Defence
- Successful defence begins with a deep and comprehensive understanding of the research. Candidates should be well-versed in every aspect of their study, from the theoretical framework to the methodology and findings.
- Thorough preparation involves anticipating potential questions from the examination committee. Candidates should consider the strengths and limitations of their research and be ready to address queries related to methodology, data analysis, and theoretical underpinnings.
- Conducting mock defences with peers or mentors can be invaluable. It helps refine the presentation, exposes potential areas of weakness, and provides an opportunity to practice responding to challenging questions.
- Actively listen to questions without interruption. Understanding the nuances of each question is crucial for providing precise and relevant responses.
- Responses should be clear, concise, and directly address the question. Avoid unnecessary jargon, and strive to convey complex concepts in a manner that is accessible to the entire committee.
- It’s acceptable not to have all the answers. If faced with a question that stumps you, acknowledge it honestly. Expressing a willingness to explore the topic further demonstrates intellectual humility.
- Use questions as opportunities to reinforce key messages from the research. Skillfully link responses back to the core contributions of the study, emphasizing its significance.
- Rehearse the presentation multiple times to build familiarity with the material. This enhances confidence, reduces nervousness, and ensures a smooth and engaging delivery.
- Maintain confident and open body language. Stand tall, make eye contact, and use gestures judiciously. A composed demeanour contributes to a positive impression.
- Acknowledge and manage nervousness. It’s natural to feel some anxiety, but channelling that energy into enthusiasm for presenting your research can turn nervousness into a positive force.
- Engage with the committee through a dynamic and interactive presentation. Invite questions during the presentation to create a more conversational atmosphere.
- Utilize visual aids effectively. Slides or other visual elements should complement the spoken presentation, reinforcing key points without overwhelming the audience.
- View the defence not only as an evaluation but also as an opportunity for continuous improvement. Feedback received during the defence can inform future research endeavours and scholarly pursuits.
In essence, success in a PhD defence hinges on meticulous preparation, adept handling of questions, and projecting confidence and composure during the presentation. A well-prepared and resilient candidate is better positioned to navigate the challenges of the defence, transforming it from a moment of evaluation into an affirmation of scholarly achievement.
Failure in PhD Defence
- While the prospect of failing a PhD defence is relatively rare, it’s essential for candidates to acknowledge that the possibility exists. Understanding this reality can motivate diligent preparation and a proactive approach to mitigate potential risks.
- Failure, if it occurs, should be seen as a learning opportunity rather than a definitive endpoint. It may highlight areas for improvement and offer insights into refining the research and presentation.
- Lack of thorough preparation, including a weak grasp of the research content, inadequate rehearsal, and failure to anticipate potential questions, can contribute to failure.
- Inability to effectively defend the chosen research methodology, including justifying its appropriateness and demonstrating its rigour, can be a critical factor.
- Failing to clearly articulate the original contributions of the research and its significance to the field may lead to a negative assessment.
- Responding defensively to questions, exhibiting a lack of openness to critique, or being unwilling to acknowledge limitations can impact the overall impression.
- Inability to address committee concerns or incorporate constructive feedback received during the defense may contribute to a negative outcome.
- Comprehensive preparation is the cornerstone of success. Candidates should dedicate ample time to understanding every facet of their research, conducting mock defences, and seeking feedback.
- Identify potential weaknesses in the research and address them proactively. Being aware of limitations and articulating plans for addressing them in future work demonstrates foresight.
- Engage with mentors, peers, or advisors before the defence. Solicit constructive feedback on both the content and delivery of the presentation to refine and strengthen the defence.
- Develop strategies to manage stress and nervousness. Techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, or visualization can be effective in maintaining composure during the defence.
- Conduct a pre-defense review of all materials, ensuring that the presentation aligns with the dissertation and that visual aids are clear and supportive.
- Approach the defence with an open and reflective attitude. Embrace critique as an opportunity for improvement rather than as a personal affront.
- Clarify expectations with the examination committee beforehand. Understanding the committee’s focus areas and preferences can guide preparation efforts.
- In the event of failure, candidates should approach the situation with resilience. Seek feedback from the committee, understand the reasons for the outcome, and use the experience as a springboard for improvement.
In summary, while the prospect of failing a PhD defence is uncommon, acknowledging its possibility and taking proactive steps to mitigate risks are crucial elements of a well-rounded defence strategy. By addressing common failure factors through thorough preparation, openness to critique, and a resilient attitude, candidates can increase their chances of a successful defence outcome.
PhD Defense or Defence?
- The choice between “defense” and “defence” is primarily a matter of British English versus American English spelling conventions. “Defense” is the preferred spelling in American English, while “defence” is the British English spelling.
- In the global academic community, both spellings are generally understood and accepted. However, the choice of spelling may be influenced by the academic institution’s language conventions or the preferences of individual scholars.
- Academic institutions may have specific guidelines regarding language conventions, and candidates are often expected to adhere to the institution’s preferred spelling.
- Candidates may also consider the preferences of their advisors or committee members. If there is a consistent spelling convention used within the academic department, it is advisable to align with those preferences.
- Consideration should be given to the spelling conventions of scholarly journals in the candidate’s field. If intending to publish research stemming from the dissertation, aligning with the conventions of target journals is prudent.
- If the defense presentation or dissertation will be shared with an international audience, using a more universally recognized spelling (such as “defense”) may be preferred to ensure clarity and accessibility.
- Regardless of the chosen spelling, it’s crucial to maintain consistency throughout the document. Mixing spellings can distract from the content and may be perceived as an oversight.
- In oral presentations and written correspondence related to the defence, including emails, it’s advisable to maintain consistency with the chosen spelling to present a professional and polished image.
- Recognizing that language conventions can vary, candidates should approach the choice of spelling with flexibility. Being adaptable to the preferences of the academic context and demonstrating an awareness of regional variations reflects a nuanced understanding of language usage.
- With the increasing globalization of academia, an awareness of language variations becomes essential. Scholars often collaborate across borders, and an inclusive approach to language conventions contributes to effective communication and collaboration.
In summary, the choice between “PhD defense” and “PhD defence” boils down to regional language conventions and institutional preferences. Maintaining consistency, being mindful of the target audience, and adapting to the expectations of the academic community contribute to a polished and professional presentation, whether in written documents or oral defences.
Is PhD Defense a Formality?
- While the PhD defence is a structured and ritualistic event, it is far from being a mere formality. It is a critical and substantive part of the doctoral journey, designed to rigorously evaluate the candidate’s research contributions, understanding of the field, and ability to engage in scholarly discourse.
- The defence is not a checkbox to be marked but rather a dynamic process where the candidate’s research is evaluated for its scholarly merit. The committee scrutinizes the originality, significance, and methodology of the research, aiming to ensure it meets the standards of advanced academic work.
- Far from a passive or purely ceremonial event, the defence involves active engagement between the candidate and the examination committee. Questions, discussions, and debates are integral components that enrich the scholarly exchange during the defence.
- The defence serves as a platform for the candidate to demonstrate the originality of their research. Committee members assess the novelty of the contributions, ensuring that the work adds value to the existing body of knowledge.
- Beyond the content, the defence evaluates the methodological rigour of the research. Committee members assess whether the chosen methodology is appropriate, well-executed, and contributes to the validity of the findings.
- Successful completion of the defence affirms the candidate’s ability to contribute meaningfully to the academic discourse in their field. It is an endorsement of the candidate’s position as a knowledgeable and respected scholar.
- The defence process acts as a quality assurance mechanism in academia. It ensures that individuals awarded a doctoral degree have undergone a thorough and rigorous evaluation, upholding the standards of excellence in research and scholarly inquiry.
- Institutions have specific criteria and standards for awarding a PhD. The defence process aligns with these institutional and academic standards, providing a consistent and transparent mechanism for evaluating candidates.
- Successful completion of the defence is a pivotal moment that marks the transition from a doctoral candidate to a recognized scholar. It opens doors to further contributions, collaborations, and opportunities within the academic community.
- Research presented during the defence often forms the basis for future publications. The validation received in the defence enhances the credibility of the research, facilitating its dissemination and impact within the academic community.
- Beyond the academic realm, a successfully defended PhD is a key credential for professional advancement. It enhances one’s standing in the broader professional landscape, opening doors to research positions, teaching opportunities, and leadership roles.
In essence, the PhD defence is a rigorous and meaningful process that goes beyond formalities, playing a crucial role in affirming the academic merit of a candidate’s research and marking the culmination of their journey toward scholarly recognition.
Dressing for Success: PhD Defense Outfit
- For Men: A well-fitted suit in neutral colours (black, navy, grey), a collared dress shirt, a tie, and formal dress shoes.
- For Women: A tailored suit, a blouse or button-down shirt, and closed-toe dress shoes.
- Dress codes can vary based on cultural expectations. It’s advisable to be aware of any cultural nuances within the academic institution and to adapt attire accordingly.
- With the rise of virtual defenses, considerations for attire remain relevant. Even in online settings, dressing professionally contributes to a polished and serious demeanor. Virtual attire can mirror what one would wear in-person, focusing on the upper body visible on camera.
- The attire chosen for a PhD defense contributes to the first impression that a candidate makes on the examination committee. A professional and polished appearance sets a positive tone for the defense.
- Dressing appropriately reflects respect for the gravity of the occasion. It acknowledges the significance of the defense as a formal evaluation of one’s scholarly contributions.
- Wearing professional attire can contribute to a boost in confidence. When individuals feel well-dressed and put-together, it can positively impact their mindset and overall presentation.
- The PhD defense is a serious academic event, and dressing professionally fosters an atmosphere of seriousness and commitment to the scholarly process. It aligns with the respect one accords to academic traditions.
- Institutional norms may influence dress expectations. Some academic institutions may have specific guidelines regarding attire for formal events, and candidates should be aware of and adhere to these norms.
- While adhering to the formality expected in academic settings, individuals can also express their personal style within the bounds of professionalism. It’s about finding a balance between institutional expectations and personal comfort.
- Select and prepare the outfit well in advance to avoid last-minute stress. Ensure that the attire is clean, well-ironed, and in good condition.
- Accessories such as ties, scarves, or jewelry should complement the outfit. However, it’s advisable to keep accessories subtle to maintain a professional appearance.
- While dressing professionally, prioritize comfort. PhD defenses can be mentally demanding, and comfortable attire can contribute to a more confident and composed demeanor.
- Pay attention to grooming, including personal hygiene and haircare. A well-groomed appearance contributes to an overall polished look.
- Start preparation well in advance of the defense date. Know your research inside out, anticipate potential questions, and be ready to discuss the nuances of your methodology, findings, and contributions.
- Conduct mock defenses with peers, mentors, or colleagues. Mock defenses provide an opportunity to receive constructive feedback, practice responses to potential questions, and refine your presentation.
- Strike a balance between confidence and humility. Confidence in presenting your research is essential, but being open to acknowledging limitations and areas for improvement demonstrates intellectual honesty.
- Actively engage with the examination committee during the defense. Listen carefully to questions, respond thoughtfully, and view the defense as a scholarly exchange rather than a mere formality.
- Understand the expertise and backgrounds of the committee members. Tailor your presentation and responses to align with the interests and expectations of your specific audience.
- Practice time management during your presentation. Ensure that you allocate sufficient time to cover key aspects of your research, leaving ample time for questions and discussions.
- It’s normal to feel nervous, but practicing mindfulness and staying calm under pressure is crucial. Take deep breaths, maintain eye contact, and focus on delivering a clear and composed presentation.
- Have a plan for post-defense activities. Whether it’s revisions to the dissertation, publications, or future research endeavors, having a roadmap for what comes next demonstrates foresight and commitment to ongoing scholarly contributions.
- After successfully defending, individuals often emphasize the importance of taking time to reflect on the entire doctoral journey. Acknowledge personal and academic growth, celebrate achievements, and use the experience to inform future scholarly pursuits.
In summary, learning from the experiences of others who have successfully defended offers a wealth of practical wisdom. These insights, combined with thoughtful preparation and a proactive approach, contribute to a successful and fulfilling defense experience.
You have plenty of career options after completing a PhD. For more details, visit my blog posts:
7 Essential Steps for Building a Robust Research Portfolio
Exciting Career Opportunities for PhD Researchers and Research Scholars
Freelance Writing or Editing Opportunities for Researchers A Comprehensive Guide
Research Consultancy: An Alternate Career for Researchers
The Insider’s Guide to Becoming a Patent Agent: Opportunities, Requirements, and Challenges
The journey from a curious researcher to a recognized scholar culminates in the PhD defence—an intellectual odyssey marked by dedication, resilience, and a relentless pursuit of knowledge. As we navigate the intricacies of this pivotal event, it becomes evident that the PhD defence is far more than a ceremonial rite; it is a substantive evaluation that validates the contributions of a researcher to the academic landscape.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Recent Posts
- How to End Your Academic/Research Internship?
- PhD or Industry Job? A Comprehensive Career Guide
- Post Doc Positions in India
- 04 Reasons for Outsourcing Academic Conference Management
- How to Put Research Grants on Your CV ?
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

Preparing For Your Dissertation Defense
13 Key Questions To Expect In The Viva Voce
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & David Phair (PhD) . Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2021
Preparing for your dissertation or thesis defense (also called a “viva voce”) is a formidable task . All your hard work over the years leads you to this one point, and you’ll need to defend yourself against some of the most experienced researchers you’ve encountered so far.
It’s natural to feel a little nervous.
In this post, we’ll cover some of the most important questions you should be able to answer in your viva voce, whether it’s for a Masters or PhD degree. Naturally, they might not arise in exactly the same form (some may not come up at all), but if you can answer these questions well, it means you’re in a good position to tackle your oral defense.

Viva Voce Prep: 13 Essential Questions
- What is your study about and why did you choose to research this in particular?
- How did your research questions evolve during the research process?
- How did you decide on which sources to include in your literature review?
- How did you design your study and why did you take this approach?
- How generalisable and valid are the findings?
- What were the main shortcomings and limitations created by your research design?
- How did your findings relate to the existing literature?
- What were your key findings in relation to the research questions?
- Were there any findings that surprised you?
- What biases may exist in your research?
- How can your findings be put into practice?
- How has your research contributed to current thinking in the field?
- If you could redo your research, how would you alter your approach?
#1: What is your study about and why did you choose to research this in particular?
This question, a classic party starter, is pretty straightforward.
What the dissertation or thesis committee is assessing here is your ability to clearly articulate your research aims, objectives and research questions in a concise manner. Concise is the keyword here – you need to clearly explain your research topic without rambling on for a half-hour. Don’t feel the need to go into the weeds here – you’ll have many opportunities to unpack the details later on.
In the second half of the question, they’re looking for a brief explanation of the justification of your research. In other words, why was this particular set of research aims, objectives and questions worth addressing? To address this question well in your oral defense, you need to make it clear what gap existed within the research and why that gap was worth filling.
#2: How did your research questions evolve during the research process?
Good research generally follows a long and winding path . It’s seldom a straight line (unless you got really lucky). What they’re assessing here is your ability to follow that path and let the research process unfold.
Specifically, they’ll want to hear about the impact that the literature review process had on you in terms of shaping the research aims, objectives and research questions . For example, you may have started with a certain set of aims, but then as you immersed yourself in the literature, you may have changed direction. Similarly, your initial fieldwork findings may have turned out some unexpected data that drove you to adjust or expand on your initial research questions.
Long story short – a good defense involves clearly describing your research journey , including all the twists and turns. Adjusting your direction based on findings in the literature or the fieldwork shows that you’re responsive , which is essential for high-quality research.

#3: How did you decide on which sources to include in your literature review?
A comprehensive literature review is the foundation of any high-quality piece of research. With this question, your dissertation or thesis committee are trying to assess which quality criteria and approach you used to select the sources for your literature review.
Typically, good research draws on both the seminal work in the respective field and more recent sources . In other words, a combination of the older landmark studies and pivotal work, along with up-to-date sources that build on to those older studies. This combination ensures that the study has a rock-solid foundation but is not out of date.
So, make sure that your study draws on a mix of both the “classics” and new kids on the block, and take note of any major evolutions in the literature that you can use as an example when asked this question in your viva voce.
#4: How did you design your study and why did you take this approach?
This is a classic methodological question that you can almost certainly expect in some or other shape.
What they’re looking for here is a clear articulation of the research design and methodology, as well as a strong justification of each choice . So, you need to be able to walk through each methodological choice and clearly explain both what you did and why you did it. The why is particularly important – you need to be able to justify each choice you made by clearly linking your design back to your research aims, objectives and research questions, while also taking into account practical constraints.
To ensure you cover every base, check out our research methodology vlog post , as well as our post covering the Research Onion .

#5: How generalizable and valid are the findings?
This question is aimed at specifically digging into your understanding of the sample and how that relates to the population, as well as potential validity issues in your methodology.
To answer question this well, you’ll need to critically assess your sample and findings and consider if they truly apply to the entire population, as well as whether they assessed what they set out to. Note that there are two components here – generalizability and validity . Generalizability is about how well the sample represents the population. Validity is about how accurately you’ve measured what you intended to measure .
To ace this part of your dissertation defense, make sure that you’re very familiar with the concepts of generalizability , validity and reliability , and how these apply to your research. Remember, you don’t need to achieve perfection – you just need to be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of your research (and how the weaknesses could be improved upon).
Need a helping hand?
#6: What were the main shortcomings and limitations created by your research design?
This question picks up where the last one left off.
As I mentioned, it’s perfectly natural that your research will have shortcomings and limitations as a result of your chosen design and methodology. No piece of research is flawless. Therefore, a good dissertation defense is not about arguing that your work is perfect, but rather it’s about clearly articulating the strengths and weaknesses of your approach.
To address this question well, you need to think critically about all of the potential weaknesses your design may have, as well as potential responses to these (which could be adopted in future research) to ensure you’re well prepared for this question. For a list of common methodological limitations, check out our video about research limitations here .
#7: How did your findings relate to the existing literature?
This common dissertation defense question links directly to your discussion chapter , where you would have presented and discussed the findings in relation to your literature review.
What your dissertation or thesis committee is assessing here is your ability to compare your study’s findings to the findings of existing research . Specifically, you need to discuss which findings aligned with existing research and which findings did not. For those findings that contrasted against existing research, you should also explain what you believe to be the reasons for this.
As with many questions in a viva voce, it’s both the what and the why that matter here. So, you need to think deeply about what the underlying reasons may be for both the similarities and differences between your findings and those of similar studies.

#8: What were your key findings in relation to the research questions?
This question is similar to the last one in that it too focuses on your research findings. However, here the focus is specifically on the findings that directly relate to your research questions (as opposed to findings in general).
So, a good way to prepare for this question is to step back and revisit your research questions . Ask yourself the following:
- What exactly were you asking in those questions, and what did your research uncover concerning them?
- Which questions were well answered by your study and which ones were lacking?
- Why were they lacking and what more could be done to address this in future research?
Conquering this part dissertation defense requires that you focus squarely on the research questions. Your study will have provided many findings (hopefully!), and not all of these will link directly to the research questions. Therefore, you need to clear your mind of all of the fascinating side paths your study may have lead you down and regain a clear focus on the research questions .
#9: Were there any findings that surprised you?
This question is two-pronged.
First, you should discuss the surprising findings that were directly related to the original research questions . Going into your research, you likely had some expectations in terms of what you would find, so this is your opportunity to discuss the outcomes that emerged as contrary to what you initially expected. You’ll also want to think about what the reasons for these contrasts may be.
Second, you should discuss the findings that weren’t directly related to the research questions, but that emerged from the data set . You may have a few or you may have none – although generally there are a handful of interesting musings that you can glean from the data set. Again, make sure you can articulate why you find these interesting and what it means for future research in the area.
What the committee is looking for in this type of question is your ability to interpret the findings holistically and comprehensively , and to respond to unexpected data. So, take the time to zoom out and reflect on your findings thoroughly.

#10: What biases may exist in your research?
Biases… we all have them.
For this question, you’ll need to think about potential biases in your research , in the data itself but also in your interpretation of the data. With this question, your committee is assessing whether you have considered your own potential biases and the biases inherent in your analysis approach (i.e. your methodology). So, think carefully about these research biases and be ready to explain how these may exist in your study.
In an oral defense, this question is often followed up with a question on how the biases were mitigated or could be mitigated in future research. So, give some thought not just to what biases may exist, but also the mitigation measures (in your own study and for future research).
#11: How can your findings be put into practice?
Another classic question in the typical viva voce.
With this question, your committee is assessing your ability to bring your findings back down to earth and demonstrate their practical value and application. Importantly, this question is not about the contribution to academia or the overall field of research (we’ll get to that next) – it is specifically asking about how this newly created knowledge can be used in the real world.
Naturally, the actionability of your findings will vary depending on the nature of your research topic. Some studies will produce many action points and some won’t. If you’re researching marketing strategies within an industry, for example, you should be able to make some very specific recommendations for marketing practitioners in that industry.
To help you flesh out points for this question, look back at your original justification for the research (i.e. in your introduction and literature review chapters). What were the driving forces that led you to research your specific topic? That justification should help you identify ways in which your findings can be put into practice.
#12: How has your research contributed to current thinking in the field?
While the previous question was aimed at practical contribution, this question is aimed at theoretical contribution . In other words, what is the significance of your study within the current body of research? How does it fit into the existing research and what does it add to it?
This question is often asked by a field specialist and is used to assess whether you’re able to place your findings into the research field to critically convey what your research contributed. This argument needs to be well justified – in other words, you can’t just discuss what your research contributed, you need to also back each proposition up with a strong why .
To answer this question well, you need to humbly consider the quality and impact of your work and to be realistic in your response. You don’t want to come across as arrogant (“my work is groundbreaking”), nor do you want to undersell the impact of your work. So, it’s important to strike the right balance between realistic and pessimistic .
This question also opens the door to questions about potential future research . So, think about what future research opportunities your study has created and which of these you feel are of the highest priority.

#13: If you could redo your research, how would you alter your approach?
This question is often used to wrap up a viva voce as it brings the discussion full circle.
Here, your committee is again assessing your ability to clearly identify and articulate the limitations and shortcomings of your research, both in terms of research design and topic focus . Perhaps, in hindsight, it would have been better to use a different analysis method or data set. Perhaps the research questions should have leaned in a slightly different direction. And so on.
This question intends to assess whether you’re able to look at your work critically , assess where the weaknesses are and make recommendations for the future. This question often sets apart those who did the research purely because it was required, from those that genuinely engaged with their research. So, don’t hold back here – reflect on your entire research journey ask yourself how you’d do things differently if you were starting with a blank canvas today.
Recap: The 13 Key Dissertation Defense Questions
To recap, here are the 13 questions you need to be ready for to ace your dissertation or thesis oral defense:
As I mentioned, this list of dissertation defense questions is certainly not exhaustive – don’t assume that we’ve covered every possible question here. However, these questions are quite likely to come up in some shape or form in a typical dissertation or thesis defense, whether it’s for a Master’s degree, PhD or any other research degree. So, you should take the time to make sure you can answer them well.
If you need assistance preparing for your dissertation defense or viva voce, get in touch with us to discuss 1-on-1 coaching. We can critically review your research and identify potential issues and responses, as well as undertake a mock oral defense to prepare you for the pressures and stresses on the day.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

12 Comments
Very interesting
Interesting. I appreciate!
Really appreciating
My field is International Trade
Interesting
This is a full course on defence. I was fabulously enlightened and I gained enough confidence for my upcoming Masters Defence.
There are many lessons to learn and the simplicity in presentationmakes thee reader say “YesI can”
This is so helping… it has Enlightened me on how to answer specific questions. I pray to make it through for my upcoming defense
Lovely to hear that 🙂
Really educative and beneficial
Interesting. On-point and elaborate. And comforting too! Thanks.
Thank you very much for the enlightening me, be blessed
Thankyou so much. I am planning to defend my thesis soon and I found this very useful
Very interesting and useful to all masters and PhD students
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Defending Your Dissertation: A Guide
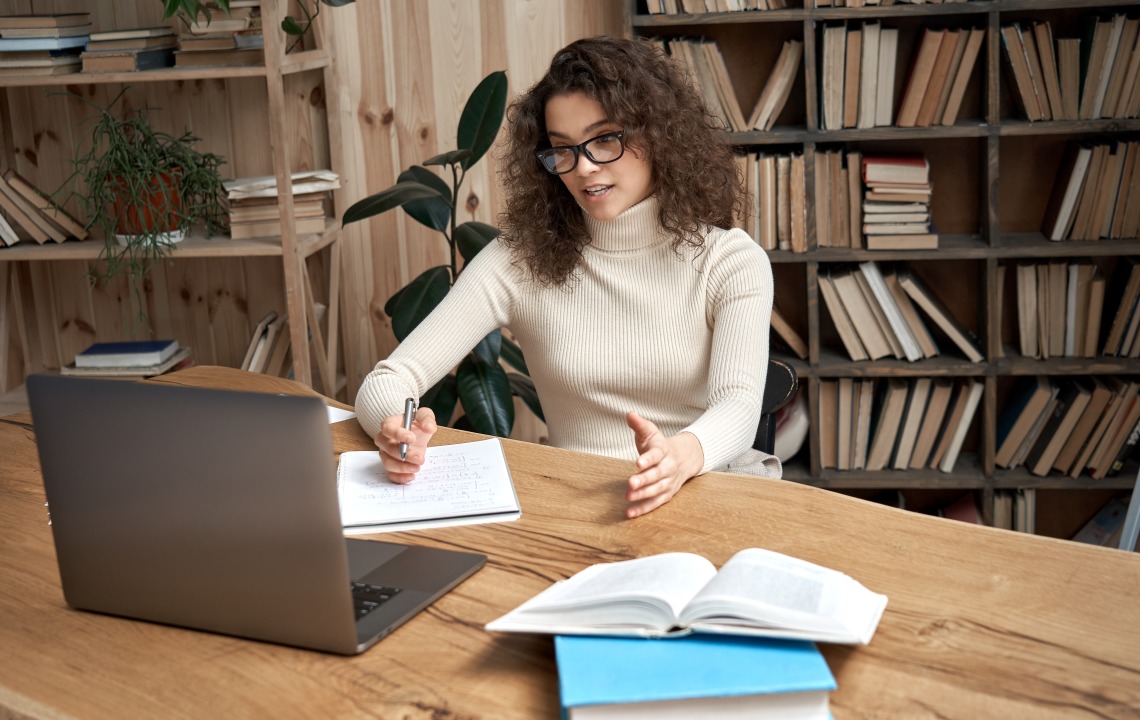

Written by Luke Wink-Moran | Photo by insta_photos
Dissertation defenses are daunting, and no wonder; it’s not a “dissertation discussion,” or a “dissertation dialogue.” The name alone implies that the dissertation you’ve spent the last x number of years working on is subject to attack. And if you don’t feel trepidation for semantic reasons, you might be nervous because you don’t know what to expect. Our imaginations are great at making The Unknown scarier than reality. The good news is that you’ll find in this newsletter article experts who can shed light on what dissertations defenses are really like, and what you can do to prepare for them.
The first thing you should know is that your defense has already begun. It started the minute you began working on your dissertation— maybe even in some of the classes you took beforehand that helped you formulate your ideas. This, according to Dr. Celeste Atkins, is why it’s so important to identify a good mentor early in graduate school.
“To me,” noted Dr. Atkins, who wrote her dissertation on how sociology faculty from traditionally marginalized backgrounds teach about privilege and inequality, “the most important part of the doctoral journey was finding an advisor who understood and supported what I wanted from my education and who was willing to challenge me and push me, while not delaying me. I would encourage future PhDs to really take the time to get to know the faculty before choosing an advisor and to make sure that the members of their committee work well together.”
Your advisor will be the one who helps you refine arguments and strengthen your work so that by the time it reaches your dissertation committee, it’s ready. Next comes the writing process, which many students have said was the hardest part of their PhD. I’ve included this section on the writing process because this is where you’ll create all the material you’ll present during your defense, so it’s important to navigate it successfully. The writing process is intellectually grueling, it eats time and energy, and it’s where many students find themselves paddling frantically to avoid languishing in the “All-But-Dissertation” doldrums. The writing process is also likely to encroach on other parts of your life. For instance, Dr. Cynthia Trejo wrote her dissertation on college preparation for Latin American students while caring for a twelve-year-old, two adult children, and her aging parents—in the middle of a pandemic. When I asked Dr. Trejo how she did this, she replied:
“I don’t take the privilege of education for granted. My son knew I got up at 4:00 a.m. every morning, even on weekends, even on holidays; and it’s a blessing that he’s seen that work ethic and that dedication and the end result.”
Importantly, Dr. Trejo also exercised regularly and joined several online writing groups at UArizona. She mobilized her support network— her partner, parents, and even friends from high school to help care for her son.
The challenges you face during the writing process can vary by discipline. Jessika Iwanski is an MD/PhD student who in 2022 defended her dissertation on genetic mutations in sarcomeric proteins that lead to severe, neonatal dilated cardiomyopathy. She described her writing experience as “an intricate process of balancing many things at once with a deadline (defense day) that seems to be creeping up faster and faster— finishing up experiments, drafting the dissertation, preparing your presentation, filling out all the necessary documents for your defense and also, for MD/PhD students, beginning to reintegrate into the clinical world (reviewing your clinical knowledge and skill sets)!”
But no matter what your unique challenges are, writing a dissertation can take a toll on your mental health. Almost every student I spoke with said they saw a therapist and found their sessions enormously helpful. They also looked to the people in their lives for support. Dr. Betsy Labiner, who wrote her dissertation on Interiority, Truth, and Violence in Early Modern Drama, recommended, “Keep your loved ones close! This is so hard – the dissertation lends itself to isolation, especially in the final stages. Plus, a huge number of your family and friends simply won’t understand what you’re going through. But they love you and want to help and are great for getting you out of your head and into a space where you can enjoy life even when you feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash.”
While you might sometimes feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash, remember: a) no it’s not, you brilliant scholar, and b) the best dissertations aren’t necessarily perfect dissertations. According to Dr. Trejo, “The best dissertation is a done dissertation.” So don’t get hung up on perfecting every detail of your work. Think of your dissertation as a long-form assignment that you need to finish in order to move onto the next stage of your career. Many students continue revising after graduation and submit their work for publication or other professional objectives.
When you do finish writing your dissertation, it’s time to schedule your defense and invite friends and family to the part of the exam that’s open to the public. When that moment comes, how do you prepare to present your work and field questions about it?
“I reread my dissertation in full in one sitting,” said Dr. Labiner. “During all my time writing it, I’d never read more than one complete chapter at a time! It was a huge confidence boost to read my work in full and realize that I had produced a compelling, engaging, original argument.”
There are many other ways to prepare: create presentation slides and practice presenting them to friends or alone; think of questions you might be asked and answer them; think about what you want to wear or where you might want to sit (if you’re presenting on Zoom) that might give you a confidence boost. Iwanksi practiced presenting with her mentor and reviewed current papers to anticipate what questions her committee might ask. If you want to really get in the zone, you can emulate Dr. Labiner and do a full dress rehearsal on Zoom the day before your defense.
But no matter what you do, you’ll still be nervous:
“I had a sense of the logistics, the timing, and so on, but I didn’t really have clear expectations outside of the structure. It was a sort of nebulous three hours in which I expected to be nauseatingly terrified,” recalled Dr. Labiner.
“I expected it to be terrifying, with lots of difficult questions and constructive criticism/comments given,” agreed Iwanski.
“I expected it to be very scary,” said Dr. Trejo.
“I expected it to be like I was on trial, and I’d have to defend myself and prove I deserved a PhD,” said Dr Atkins.
And, eventually, inexorably, it will be time to present.
“It was actually very enjoyable” said Iwanski. “It was more of a celebration of years of work put into this project—not only by me but by my mentor, colleagues, lab members and collaborators! I felt very supported by all my committee members and, rather than it being a rapid fire of questions, it was more of a scientific discussion amongst colleagues who are passionate about heart disease and muscle biology.”
“I was anxious right when I logged on to the Zoom call for it,” said Dr. Labiner, “but I was blown away by the number of family and friends that showed up to support me. I had invited a lot of people who I didn’t at all think would come, but every single person I invited was there! Having about 40 guests – many of them joining from different states and several from different countries! – made me feel so loved and celebrated that my nerves were steadied very quickly. It also helped me go into ‘teaching mode’ about my work, so it felt like getting to lead a seminar on my most favorite literature.”
“In reality, my dissertation defense was similar to presenting at an academic conference,” said Dr. Atkins. “I went over my research in a practiced and organized way, and I fielded questions from the audience.
“It was a celebration and an important benchmark for me,” said Dr. Trejo. “It was a pretty happy day. Like the punctuation at the end of your sentence: this sentence is done; this journey is done. You can start the next sentence.”
If you want to learn more about dissertations in your own discipline, don’t hesitate to reach out to graduates from your program and ask them about their experiences. If you’d like to avail yourself of some of the resources that helped students in this article while they wrote and defended their dissertations, check out these links:
The Graduate Writing Lab
https://thinktank.arizona.edu/writing-center/graduate-writing-lab
The Writing Skills Improvement Program
https://wsip.arizona.edu
Campus Health Counseling and Psych Services
https://caps.arizona.edu
https://www.scribbr.com/
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
8 Top Tips for Crushing Your PhD Oral Defense
3-minute read
- 27th January 2016
Once you’ve submitted your PhD dissertation , most of the hard work is done. The one big thing standing between you and your shiny new doctorate is your oral dissertation defense .
The exact format this takes will depend on your grad school, but the general idea is that you present your thesis to a committee who have read your dissertation. The committee members then ask questions about your work , which you have to defend to prove your academic credentials. You may be asked to make revisions to your dissertation based on the discussion.
This might sound a bit like a scholastic Spanish Inquisition , but as long as you prepare thoroughly, your oral defense doesn’t have to be a stressful experience:
1. Ask Around
The first thing to do when preparing for your oral defense is to ask your PhD advisor what to expect and check your grad school’s requirements. You could also ask colleagues who have already completed their defense.
2. Practice Makes Perfect
If you get the chance, sit in on other people’s oral defense sessions. Even better, if you have some willing friends available, try practicing your defense presentation in front of them, including having them ask you questions.
3. Re-read Your Dissertation
You don’t have to memorize every detail, but re-familiarizing yourself with your work before your oral defense is definitely a good idea.
4. Arrive Early
On the day, make sure you know where and when your oral defense is scheduled to take place. Get there at least fifteen minutes early so you have time to set up and settle down.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
5. Your Thesis Statement
Make sure you have a clear thesis statement to begin your presentation. This will usually include the problem you’re addressing, why it’s important and what your research has achieved.
6. Use Visual Aids
Having handouts or a PowerPoint slideshow to accompany your talk is pretty much standard these days and can enhance your presentation.
7. Don’t Fear the Committee
It’s easy to feel like the committee members are out to get you once the questions start flying, but try not to panic. It’s perfectly fine to ask for clarification if you’re unsure about something.
Likewise, be honest if you don’t have an immediate response; it’s far better to say you’d need to do more research before answering than it is to try and bluff your way through the conversation.
Similarly, don’t feel like you have to rush. Taking a moment to think before answering a question will help you to formulate a considered answer.
8. Believe in Yourself!
The most important thing to remember is that your advisor will not have let you submit your dissertation unless they thought it was a good piece of work. As such you have every reason to be confident, which will make your presentation more convincing. Try to dress smart too, as you want to make a good first impression.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
How to insert a text box in a google doc.
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Before you go, check this out!
We have lots more on the site to show you. You've only seen one page. Check out this post which is one of the most popular of all time.
PhD Oral Defense Tips (You Need These)
When you first start your PhD, the required oral defense seems so far away. But then you blink and the time to defend is now !
This is the last step and the only thing standing between you and the title of “doctor.” Ya, baby!
So, what exactly is an oral defense?
After you hand in your dissertation (you know, that large paper you spent the last year pouring your blood, sweat and tears into), your committee will take time to review your work and then assign a date when you will go and “defend” your research.
A PhD oral defense is usually a day-long event where you give a public presentation and/ or a private presentation to some examiners. These examiners will be people from your University or from other universities.
You will spend your time presenting your findings, answering questions about your work and proving to your committee that you have a solid understanding of your field of study and focus area.
If you are in a PhD program, defending your dissertation is most likely the final requirement.
Keep reading for some valuable tips for your PhD oral defense (or sometimes called the Viva).
This post was written by a recent doctoral graduate (it is anonymous to keep the discussion frank) on behalf of Dave Maslach. This is part of the R3ciprocity project (Check out the YouTube Channel or the writing feedback software ). R3ciprocity helps students, faculty, and research folk by providing a real and authentic look into doing research. It provides solutions and hope to researchers around the world. For more on this topic and to see what Dave has to say, watch this video:
* This video provides some oral defense tips that will be important during your PhD or doctorate. It’s especially relevant for people that are doing a PhD in Business Administration.
Know What They Are Looking For
Generally, by the time you get to your defense you have made any required, last minute edits to your paper. You have received feedback from your committee members and are prepared to present your final product and answer questions.
The exact format of your defense will depend on your university and the requirements of your grad school. So, make sure you check your grad school’s website and speak with your advisor to get as many details about necessities in order to prepare.
Find out if you need to put together a presentation to go along with your speech. If so, you can prepare presentation slides by using information from your first chapter to design an outline.
Substantive information from your dissertation should be included on your slides and correspond with the important aspects highlighted in your paper.
If you are still unsure of exactly what to expect, ask around- ask colleagues that have already successfully defended their dissertation, ask other committee members or see if you can sit in on someone else’s defense.
Gaining insight into the defense process and knowing what to expect can provide you with confidence and reassurance.
Be Honest with Yourself.
You’ve recently spent day in and day out working on your dissertation and you can probably cite all the literature used during your research, in your sleep. You are an expert on your topic and you’re passionate about your research.
However, you likely don’t know it all. And that’s ok!
One of the most nerve-wracking things about preparing for a defense is thinking about being asked a question that you can’t answer. While we can attend defenses, talk to colleagues, and practice over and over, there is no way to predict every question that the committee will ask.
Luckily for you, once upon a time, your committee was in your same shoes. They know there will be gaps in your knowledge. Your defense is not about being perfect. You aren’t expected to know everything. If you get asked a question and you don’t know the answer, it is ok to just say, “I don’t know.”
You can try to have them rephrase the question or ask for clarification if you aren’t quite sure, but chances are they have asked the question out of curiosity and may not even know the answer themselves.
It is completely acceptable to let them know you haven’t thought of that before but that you’d be happy to do a little more research to find the answer to their question.
Try to create discussions among the examiners. If the examiner asks you a question that you simply can’t answer, you can ask them for their input in what they would do in this circumstance. Show them that you have the ability to think as a scholar.
Be Prepared to Answer Questions
Since your paper has already been evaluated, the questions your committee asks are typically not designed to trick or stump you. Some committees may provide you with the questions before your defense in order to prepare, while others will wait until after you have finished your presentation to decide what to ask.
Questions are usually open-ended and revolve around the core content of your dissertation. They will require you to describe the reasons you chose your topic, summarize your findings and explain how your work will contribute to the current knowledge surrounding your topic. These questions are designed to allow you to show what you know, as well as to have you think critically about your work.
One question that I feel very certain you will be asked in one way or another is, “So what?” Now that you have completed this research and conducted your studies, what have you accomplished? What is your field of study gaining with the completion of your work?
Another question may be, “What’s next?” They may want to see if your study has influenced your future plans or if this process has brought forward any areas of interest for future research.
You may be able to anticipate some of the other questions you’ll be asked by reviewing the work of your committee members. Then, take another look at your own dissertation through the lens of your committee, keeping in consideration their areas of expertise. You can also try to prepare for possible questions by sitting in other defenses with these committee members to get a better feel for what they will ask.
When you answer questions, don’t rush your responses. It is completely ok to take a few seconds to think before answering. They are looking for solid responses, not quick ones. Also, make your answers concise and to the point; state enough to show you have understanding without going all over the map.
Keep the Discussion Moving
PhDs (professors) have a tendency to be full of hot air and probably could ask a lot of questions. if you feel like they’re focusing too much on one particular area you can guide the conversation on to another topic by continuing forward with the discussion.
Designing an outline of your dissertation and starting your defense with a clear thesis statement can get the discussion off on the right foot.
Try to be crystal clear with your construct definitions and what you did in your study. Many of the questions will be focused on what you did or didn’t do in the limitations of what you chose to do. Understand that every study has limitations and that is okay.
Visual aids, such as PowerPoint presentations with bulleted lists and clearly labeled graphs, can accompany your talk and enhance the flow of your presentation. This will save you if you find yourself rambling or getting off topic; just look back to your current slide, refocus and move to the next.
Just make sure that your presentation isn’t overloaded with too much text or too many graphics. Your slides should highlight the main points of your research, and include visual representations of data, or other important findings from your study. You may need to sacrifice details from your slides, and just work them into your conversation, if you feel they are vital in telling the story of your research.
Also know that just reading off of your slides isn’t going to impress anyone. Even the most impressive visuals aren’t going to save you if you haven’t practiced what you are going to say.
The goal with the PhD oral defense is just to make sure that you are comfortable with doing research. It’s a lot like getting the blessing from your examiners, and other people that are going to be your peers, that you are capable of doing research.
It’s All About the Mindset
The biggest hurdle with the PhD oral defense is remembering to view it as a way to improve your thoughts. Your examiners are there to work with you not against you.
Don’t fear your committee. It may seem like they are out to get you once their questions and need for clarification begin, but don’t let that intimidate you. Your advisor or committee chair would not have let you submit your dissertation, or get this far, without thinking that you were ready for the defense.
Believe in yourself!
It’s best to enter your oral defense with a proactive and positive mindset.
If you begin to feel stressed or panicked, take a moment to think before formulating a response. Take a deep breath and remind yourself that you are there because you are an expert on your topic.
It’s impossible to completely anticipate how your committee will respond to your thoughts but taking the time to reread your dissertation and re-familiarize yourself with your work will make you better prepared and more at ease.
( Read here for more advice on how to stay calm and productive during the dissertation process.)
Also, getting in lots of practice and plenty of rest will help reduce stress levels, allow you to think more clearly, and be able to reply to questions in a satisfactory way.
Practice Makes Perfect (Better)
Once you submit your dissertation to your committee, most of the hard work is done. Now all that is left is to practice, practice, practice.
Don’t just write down your presentation plan or potential questions and responses; you need to practice saying it aloud. By speaking your thoughts, you will get more comfortable with the flow of your ideas and it will make it easier to identify areas that may need a little more focus.
It may feel silly presenting to an empty room, or to people that are unfamiliar with the process, but this practice will help rid some of the discomfort that comes with talking in front of an audience. You may also be able to get some feedback that will make your defense day even more successful. (Read this interesting blog post on how to get feedback on your writing).
Make sure to check if there are any time restrictions with your presentation so that you can prepare accordingly. You wouldn’t want to waste your time preparing for a two-hour defense when you only have thirty minutes, nor do you want to show up with only enough material for a short presentation when you need to fill a longer time-slot.
If there are time restrictions, this makes it even more imperative that you are practicing aloud and that you are timing yourself while you do it. Run through your presentation several times so that you can get a solid feel for transitions and pacing.
Most likely, you will be nervous before your presentation and with nervousness, comes the inadvertent fast talking. Nerves can also cause logical thoughts to come out as long streams of babbling. So, try to also practice taking pauses and giving yourself time to process and breath.
Practice on your own and practice with an audience if possible. Practice your presentation on your best friend, your mirror, your dog, or whatever you have available.
As your defense date gets closer, you should be getting to the point where you can go through most of your presentation without your notes. The goal is to become so familiar with what you are going to say that everything comes out smooth and natural without making it appear that you have just memorized a speech.
Don’t Procrastinate
If there was ever a time to NOT procrastinate, that time is now.
You don’t want to wait until the last minute to start practicing. You need time to formally practice all aspects of your presentation, get feedback, and integrate any changes into your slides and your talk.
You need time to check out the room where you will be presenting and try out any of the equipment you may use on defense day. Decide if you’ll need a microphone, projector or any other technology. Take note of any tools that are available in that room and make your request to ensure they will be present for your big day. Depending on what is available already in the room, you may need to line up other resources to bring with you. You don’t want the added stress of trying to figure out logistics just minutes before you begin your presentation.
While you’re in this space, take the time to practice your presentation just as you would do it on the day of your defense. This will help you work out any kinks and gain more confidence for the real event.
You will also need a well-developed backup plan.
You won’t have time to run around on the morning of your defense trying to find another laptop or an extension cord. We know that even in the 21 st century, technology can be unpredictable. There is no guarantee that your presentation plan will actually unfold the way you have envisioned it.
It’s Defense Day- Now What?
You know your material inside and out; you have practiced in front of anyone that will listen, and your visual presentation is golden.
The day has finally arrived, and it is now time for you to present the work that has been such a huge part of your life for the past few years.
Dress the part and don’t forget your notes. Both of these things will give you confidence and feel prepared.
On the day of your defense, make sure to arrive at least fifteen minutes before your defense is scheduled to begin. This will give you time to set up your presentation, do one last, quick run through and then try to calm your nerves.
Lastly, make sure to have printed handouts in case your technology fails, water for when your mouth goes dry from all the talking, and definitely have tissues for the tears of joy that come after you rock your presentation !
If you liked this blog post and we hope you did, be sure to read these other helpful posts:
- How to (stay calm) when writing your dissertation. Yikes! That is difficult.
- These tips on editing your dissertation will greatly help your research!
- Productivity tips that all PhDs and Professors need to know.
R3ciprocity_Team
Recent Posts
Rethinking Success and Embracing the Journey: Lessons from the R3ciprocity Project
The Surprising Lesson of Going It Alone When I launched the R3ciprocity Project, I anticipated an outpouring of support from various groups like scientists, researchers, universities, and...
Navigating Academia As A Parent Or Caregiver: The Dual Challenge of PhDs and Parenthood
PhD students and highly-educated individuals face a unique set of challenges. Among these, balancing the rigorous demands of academic life with personal responsibilities, such as single parenthood or...


- PhD Viva Voces – A Complete Guide
- Doing a PhD
- A PhD viva involves defending your thesis in an oral examination with at least two examiners.
- The aim of a PhD viva is to confirm that the work is your own , that you have a deep understanding of your project and, overall, that you are a competent researcher .
- There are no standard durations, but they usually range from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours .
- There are six outcomes of a PhD viva: (1) pass without corrections (2) pass subject to minor corrections, (3) pass subject to major corrections, (4) downgrade to MPhil with no amendments, (5) downgrade to MPhil subject to amendments, (6) immediate fail.
- Almost all students who sit their viva pass it, with the most common outcome being ‘(2) – pass subject to minor corrections’.
What Is a PhD Viva?
A viva voce , more commonly referred to as ‘viva’, is an oral examination conducted at the end of your PhD and is essentially the final hurdle on the path to a doctorate. It is the period in which a student’s knowledge and work are evaluated by independent examiners.
In order to assess the student and their work around their research question, a viva sets out to determine:
- you understand the ideas and theories that you have put forward,
- you can answer questions about elements of your work that the examiners have questions about,
- you understand the broader research in your field and how your work contributes to this,
- you are aware of the limitations of your work and understand how it can be developed further,
- your work makes an original contribution, is your own and has not been plagiarised.
Note: A viva is a compulsory procedure for all PhD students, with the only exception being when a PhD is obtained through publication as opposed to the conventional route of study.
Who Will Attend a Viva?
In the UK, at least two examiners must take part in all vivas. Although you could have more than two examiners, most will not in an attempt to facilitate a smoother questioning process.
One of the two examiners will be internal, i.e. from your university, and the other will be external, i.e. from another university. Regardless, both will be knowledgeable in your research field and have read your thesis beforehand.
In addition to your two examiners, two other people may be present. The first is a chairperson. This is an individual who will be responsible for monitoring the interview and for ensuring proper conduct is followed at all times. The need for an external chairperson will vary between universities, as one of the examiners can also take on this role. The second is your supervisor, whose attendance is decided upon by you in agreement with your examiners. If your supervisor attends, they are prohibited from asking questions or from influencing the outcome of the viva.
To avoid any misunderstandings, we have summarised the above in a table:
Note: In some countries, such as in the United States, a viva is known as a ‘PhD defense’ and is performed publicly in front of a panel or board of examiners and an open audience. In these situations, the student presents their work in the form of a lecture and then faces questions from the examiners and audience which almost acts as a critical appraisal.
How Long Does a Viva Last?
Since all universities have different guidelines , and since all PhDs are unique, there are no standard durations. Typically, however, the duration ranges from one to three hours, with most lasting approximately two hours.
Your examiners will also influence the duration of your viva as some will favour a lengthy discussion, while others may not. Usually, your university will consult your examiners in advance and notify you of the likely duration closer to the day of your viva.
What Happens During a Viva?
Regardless of the subject area, all PhD vivas follow the same examination process format as below.
Introductions
You will introduce yourselves to each other, with the internal examiner normally introducing the external examiner. If an external chairperson is present, they too are introduced; otherwise, this role will be assumed by one of the examiners.
Procedure Explained
After the introductions, the appointed chair will explain the viva process. Although it should already be known to everyone, it will be repeated to ensure the viva remains on track during the forthcoming discussion.
Warm-Up Questions
The examiners will then begin the questioning process. This usually starts with a few simple opening questions, such as asking you to summarise your PhD thesis and what motivated you to carry out the research project.
In-Depth Questions
The viva questions will then naturally increase in difficulty as the examiners go further into the details of your thesis. These may include questions such as “What was the most critical decision you made when determining your research methodology ?”, “Do your findings agree with the current published work?” and “How do your findings impact existing theories or literature? ”. In addition to asking open-ended questions, they will also ask specific questions about the methodology, results and analysis on which your thesis is based.
Closing the Viva
Once the examiners are satisfied that they have thoroughly evaluated your knowledge and thesis, they will invite you to ask any questions you may have, and then bring the oral examination to a close.
What Happens After the Viva?
Once your viva has officially ended, your examiners will ask you to leave the room so that they can discuss your performance. Once a mutual agreement has been reached, which can take anywhere from 10 minutes to an hour, you will be invited back inside and informed of your outcome.
PhD Viva Outcomes
There are six possible outcomes to a viva:
- Immediate award of degree: A rare recommendation – congratulations, you are one of the few people who completely satisfied your examiners the first time around. You do not have to do anything further at this point.
- Minor amendments required: The most common recommendation – you obtain a pass on the condition that you make a number of minor amendments to your thesis, such as clarifying certain points and correcting grammatical errors. The time you have to make these changes depends on the number of them, but is usually one to six months.
- Major amendments required: A somewhat uncommon recommendation – you are requested to make major amendments to your thesis, ranging from further research to collecting more data or rewriting entire sections. Again, the time you have to complete this will depend on the number of changes required, but will usually be six months to one year. You will be awarded your degree once your amended thesis has been reviewed and accepted.
- Immediate award of MPhil: An uncommon recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree but meets the standard for an MPhil (Master of Philosophy), a lower Master’s degree.
- Amendments required for MPhil: A rare recommendation – your examiners believe your thesis does not meet the standard for a doctoral degree, but with several amendments will meet the standard for an MPhil.
- Immediate fail: A very rare recommendation – you are given an immediate fail without the ability to resubmit and without entitlement to an MPhil.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
What Is the Pass Rate for Vivas?
Based on an analysis of 26,076 PhD students who took their viva exam between 2006 and 2017, the PhD viva pass rate in the UK is 96%; of those who passed, about 80% were required to make minor amendments to their thesis. The reason for this high pass rate is that supervisors will only put their students forward for a viva once they confidently believe they are ready for it. As a result, most candidates who sit a viva are already well-versed in their PhD topic before they even start preparing for the exam.
How Do I Arrange a Viva?
Your viva will be arranged either by the examiners or by the chairperson. The viva will be arranged at least one to two months after you have submitted your thesis and will arrange a viva date and venue that is suitable for all participants.
Can I Choose My Examiners?
At most universities, you and your supervisor will choose the internal and external examiners yourselves. This is because the examiners must have extensive knowledge of the thesis topic in order to be able to examine you and, as the author of the thesis in question, who else could better determine who they might be than you and your supervisor. The internal examiner is usually quite easy to find given they will be from your institution, but the external examiner may end up being your second or third preference depending on availability.
Can I Take Notes Into a Viva?
A viva is about testing your competence, not your memory. As such, you are allowed to take notes and other supporting material in with you. However, keep in mind that your examiners will not be overly impressed if you constantly have to refer to your notes to answer each question. Because of this, many students prefer to take an annotated copy of their thesis, with important points already highlighted and key chapters marked with post-it notes.
In addition to an annotated copy of a thesis, some students also take:
- a list of questions they would like to ask the examiners,
- notes that were created during their preparation,
- a list of minor corrections they have already identified from their viva prep work.
How Do I Prepare for a PhD Viva?
There are several ways to prepare for a PhD viva, one of the most effective being a mock viva voce examination . This allows you to familiarise yourself with the type of viva questions you will be asked and identify any weak areas you need to improve. They also give you the opportunity to practise without the pressure, giving you more time to think about your answers which will help to make sure that you know your thesis inside out. However, a mock viva exam is just one of many methods available to you – some of the other viva preparation methods can be found on our “ How to Prepare for a PhD Viva ” page.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
How Do I Prepare for a Successful Defence?
Vivas and Presentations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
273 Accesses
Once you have submitted your dissertation, you may be asked to do a defence of your dissertation. This could be in the form of an oral presentation, a poster presentation of your findings, or you could be invited to a viva voce. Vivas, as they are usually known, are particularly common for research degrees such as MPhils or PhDs and are essentially a verbal defence of your thesis that is conducted in an interview style format. At a minimum, the viva is a way of checking you authored the thesis yourself and understand the detail, but it is also an opportunity to discuss your research findings and interpretations in depth with experts. Preparation is key for defending your thesis in a viva or a presentation format. With a bit of groundwork, you could even enjoy the discussion, after all the thesis is the culmination of all your hard work, and no one knows it better than you.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Ratcliffe R (2015) How to survive a PhD viva: 17 top tips. https://www.theguardian.com/higher-education-network/2015/jan/08/how-to-survive-a-phd-viva-17-top-tips. Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Levin P, Topping G (2006) Perfect presentations. Open University Press
Google Scholar
Smith P (2014) The PhD viva: how to prepare for your oral examination. Macmillan, New York
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Prepare for a Successful Defence?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_14
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_14
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Top things to do while preparing for your dissertation defense
You’ve written the defining work of your academic career – and now it’s time to defend it. The prospect of explaining your research and answering questions about it in front of a committee of experts can certainly be daunting. Fortunately, you know the subject matter deeply, so success is mostly a matter of presentation and preparation.
With that in mind, here are eight of the top things to do when preparing for your dissertation defense – from the beginning of your program to the day of your defense.
Attend other people’s defenses: Within the first year or two of your program, start attending the dissertation defenses of other students. [i] This will help you better understand what to expect.
Read your department’s guidelines: Every department has slightly different guidelines for the timeline and preparation of a thesis defense. Read yours early and often, and discuss them with your advisor.
Start your dissertation: This should take between three and four months to write, and you’ll want to submit a completed draft a month before your defense. This means you should start writing your thesis at least five months ahead of time.
Schedule your defense: You should coordinate the date, time and place of your defense as soon as possible, long before your dissertation is completed. [ii]
Submit dissertation and any required paperwork: About a month before your defense, you should submit the final draft of your dissertation for faculty to read. [iii] Your committee members will need time to fully read it and come up with questions.
Research committee members: Talk to other people whose committees they’ve served on, and ask what types of questions they tend to ask, and what their experiences were like. [iv] Read members’ feedback to get an idea of possible questions.
Attend a pre-defense meeting: At the meeting, raise any issues or concerns you have, and ask what questions and issues might be raised during the defense. [v]
Prepare your presentation: Prepare a 15-30 minute PowerPoint presentation, and make it as polished and professional as possible. [vi] Practice giving the presentation, including to friends and family if possible.
Select comfortable, professional clothes: Select your outfit – including accessories – a couple of weeks in advance. You don’t want to worry about what to wear the day before your presentation.
Organize a small reception: If it’s considered appropriate in your department, organize a small celebration following your defense for committee members, friends and family. [vii]
Take a break for a few days: You’re an expert, and you’re prepared. Psychologists believe taking a short break can enhance memory, creativity and problem solving. [viii]
Review everything one last time: The day before your defense, go through your information one last time, and practice your presentation again.
Defend, and amend: Remember, you are an expert presenting your research findings. You likely know more about your topic at this point than the committee members. Do your requested revisions the next day. [ix]
[i] http://www.proquest.com/researchers/graduate-student/expert-advice-thesisdissertation/Defending-your-Dissertation.html
[ii] http://www.proquest.com/researchers/graduate-student/expert-advice-thesisdissertation/Defending-your-Dissertation.html
[iii] http://asq.org/edu/2010/01/career-development/preparing-for-the-oral-defense-of-a-dissertation.pdf
[iv] https://graduate.asu.edu/sites/default/files/dissertation-defense.pdf
[v] http://www.proquest.com/researchers/graduate-student/expert-advice-thesisdissertation/Defending-your-Dissertation.html
[vi] https://graduate.asu.edu/sites/default/files/dissertation-defense.pdf
[vii] http://www.proquest.com/researchers/graduate-student/expert-advice-thesisdissertation/Defending-your-Dissertation.html
[viii] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3990058/
[ix] https://graduate.asu.edu/sites/default/files/dissertation-defense.pdf
Related posts
Clarivate welcomes the barcelona declaration on open research information.

Demonstrating socioeconomic impact – a historical perspective of ancient wisdom and modern challenges

Unlocking U.K. research excellence: Key insights from the Research Professional News Live summit


PhD Dissertation Defense Slides Design: Start
- Tips for designing the slides
- Presentation checklist
- Example slides
- Additional Resources
Purpose of the Guide
This guide was created to help ph.d. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. the guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from ph.d. graduates. the tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can be used in designing other types of presentations such as conference talks, qualification and proposal exams, and technical seminars., the tips and examples are used to help students to design effective presentation. the technical contents in all examples are subject to copyright, please do not replicate. , if you need help in designing your presentation, please contact julie chen ([email protected]) for individual consultation. .
- Example Slides Repository
- Defense slides examples Link to examples dissertation defense slides.
Useful Links
- CIT Thesis and dissertation standards
- Dissertations and Theses @ Carnegie Mellon This link opens in a new window Covers 1920-present. Full text of some dissertations may be available 1997-present. Citations and abstracts of dissertations and theses CMU graduate students have published through UMI Dissertation Publishing. In addition to citations and abstracts, the service provides free access to 24 page previews and the full text in PDF format, when available. In most cases, this will be works published in 1997 forward.
- Communicate your research data Data visualization is very important in communicating your data effectively. Check out these do's and don'ts for designing figures.
Power Point Template and other Resources
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 1
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 2
Source: CEE Department Resources https://www.cmu.edu/cee/resources/index.html
- CMU Powerpoint Slide Template
Source: CMU Marketing and Communications
https://www.cmu.edu/marcom/brand-standards/downloads/index.html
- Use of CMU logos, marks, and Unitmarks
Email me for questions and schedule an appointment

Top 7 tips for your defense presentation
1. show why your study is important, remember, your audience is your committee members, researchers in other fields, and even the general public. you want to convince all of them why you deserve a ph.d. degree. you need to talk about why your study is important to the world. in the engineering field, you also need to talk about how your study is useful. try to discuss why current practice is problematic or not good enough, what needs to be solved, and what the potential benefits will be. , see how dr. posen and dr. malings explained the importance of their studies..
- Carl Malings Defense Slides with Notes
- I. Daniel Posen Defense Slides with Notes
2. Emphasize YOUR contribution
Having a ph.d. means that you have made some novel contributions to the grand field. this is about you and your research. you need to keep emphasizing your contributions throughout your presentation. after talking about what needs to be solved, try to focus on emphasizing the novelty of your work. what problems can be solved using your research outcomes what breakthroughs have you made to the field why are your methods and outcomes outstanding you need to incorporate answers to these questions in your presentation. , be clear what your contributions are in the introduction section; separate what was done by others and what was done by you. , 3. connect your projects into a whole piece of work, you might have been doing multiple projects that are not strongly connected. to figure out how to connect them into a whole piece, use visualizations such as flow charts to convince your audience. the two slides below are two examples. in the first slide, which was presented in the introduction section, the presenter used a flow diagram to show the connection between the three projects. in the second slide, the presenter used key figures and a unique color for each project to show the connection..

- Xiaoju Chen Defense Slides with Notes
4. Tell a good story
The committee members do not necessarily have the same background knowledge as you. plus, there could be researchers from other fields and even the general public in the room. you want to make sure all of your audience can understand as much as possible. focus on the big picture rather than technical details; make sure you use simple language to explain your methods and results. your committee has read your dissertation before your defense, but others have not. , dr. cook and dr. velibeyoglu did a good job explaining their research to everyone. the introduction sessions in their presentations are well designed for this purpose. .
- Laren M. Cook Defense Slides with Notes
- Irem Velibeyoglu Defense with Notes
5. Transition, transition, transition
Use transition slides to connect projects , it's a long presentation with different research projects. you want to use some sort of transition to remind your audience what you have been talking about and what is next. you may use a slide that is designed for this purpose throughout your presentation. , below are two examples. these slides were presented after the introduction section. the presenters used the same slides and highlighted the items for project one to indicate that they were moving on to the first project. throughout the presentation, they used these slides and highlighted different sections to indicate how these projects fit into the whole dissertation. .

You can also use some other indications on your slides, but remember not to make your slides too busy. Below are two examples. In the first example, the presenter used chapter numbers to indicate what he was talking about. In the second example, the presenter used a progress bar with keywords for each chapter as the indicator.

Use transition sentences to connect slides
Remember transition sentences are also important; use them to summarize what you have said and tell your audience what they will expect next. if you keep forgetting the transition sentence, write a note on your presentation. you can either write down a full sentence of what you want to say or some keywords., 6. be brief, put details in backup slides , you won't have time to explain all of the details. if your defense presentation is scheduled for 45 minutes, you can only spend around 10 minutes for each project - that's shorter than a normal research conference presentation focus on the big picture and leave details behind. you can put the details in your backup slides, so you might find them useful when your committee (and other members of the audience) ask questions regarding these details., 7. show your presentation to your advisor and colleagues, make sure to ask your advisor(s) for their comments. they might have a different view on what should be emphasized and what should be elaborated. , you also want to practice at least once in front of your colleagues. they can be your lab mates, people who work in your research group, and/or your friends. they do not have to be experts in your field. ask them to give you some feedback - their comments can be extremely helpful to improve your presentation. , below are some other tips and resources to design your defense presentation. .
- Tips for designing your defense presentation
How important is your presentation, and cookies?

- Next: Tips for designing the slides >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 11:18 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/c.php?g=883178
University of Rochester
Search Rochester.edu
Popular Searches
Resources for
- Prospective students
- Current students
- Faculty and staff
Arts, Sciences & Engineering
Graduate Education and Postdoctoral Affairs
- PhD Defense
Preparing for a PhD Defense
Table of contents, preparing to start, nominate a faculty member to serve as chair for your defense, selecting a defense date, international students and work visas, registration categories for defense, dissertation writing and guidelines, preparing your dissertation for defense, registering your dissertation for the final oral exam, know the rituals.
- Use PowerPoint
Public Lecture
Dress Professionally
Items to Bring to the Defense
The Closed Examination
Address Questions with Confidence
Student Status
Final corrected copies of the dissertation, publishing your final dissertation, binding your final dissertation, before defense.
Before you can start your thesis you must:
- Complete all courses, exams, and research requirements
- Meet with your advisory committee to ensure that everyone agrees that the work is ready to defend
- Decide on a date for the defense
- Inform your graduate administrator that you have started the process to prepare for your defense
A chair is appointed for each PhD oral defense to monitor and promote fairness and rigor in the conduct of the defense. To help eliminate pre-established judgments on the candidate’s work, the chair should be from a different program/department than the student. For more information about chair responsibilities, read the instructions for the chair .
You must identify a faculty member to serve as chair for your defense. The chair must be:
- A current full-time faculty member at assistant professor rank or higher
- Outside the department offering the degree program, or outside your advisor's department (interdisciplinary degree programs only)
- Someone who has not had prior involvement in your research
The selection of the chair is subject to the approval of the department/program, th Arts, Sciences and Engineering dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs, and the University dean of graduate studies.
The chair must be physically present during the entire defense, including the public oral presentation (if applicable) and the questioning session. The chair is welcome to read and comment on the dissertation and/or the defense presentation, but this is not required. The chair does not need to be an expert in your research area.
It is your responsibility to get a copy of the final dissertation to the chair at least one week prior to the defense.
You should begin scheduling the actual defense date three months in advance to ensure that your advisor, committee members, and chair are able to be present and that rooms are available on the date and time selected.
Defenses can be held on any day the University’s Graduate Studies Office is open (not weekends, evenings, holidays, or the days between Christmas and New Year’s). Check the academic calendar for important dates and deadlines.
Use the PhD calendar to determine the deadline dates for getting your paperwork to the Office of Graduate Education and Postdoctoral Affairs and department committee.
When all committee members and your chair agree to a specific date and time for the defense, inform your graduate administrator as soon as you possibly can, but no later than six weeks prior to your defense date . Your graduate administrator will advise you of any program-specific requirements for the defense as well as work with you to prepare for your thesis defense. They will also help you determine who will schedule the room for your thesis defense.
You should provide your committee members at least two weeks to read and comment on your dissertation before the date you need to register your dissertation.
Participating Via Video Conferencing
While you, your advisor, and the chair must all be physically present in the room for the defense, other committee members are allowed to participate in the defense remotely via Skype or other video conferencing technology so long as all committee members agree to the arrangement. This must also be approved by the AS&E dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs and the University dean of graduate studies before the dissertation is registered for defense.
Someone other than you and your committee must handle the IT setup and be on standby for any problems. If anyone involved finds that remote participation is interfering with the defense, he or she can request that the defense be rescheduled.
We strongly recommend that international students meet with an International Services Office (ISO) representative as soon as permission to start writing is granted. The ISO will provide information on visa options, documentation, and timelines for applying for a visa for employment in the United States.
You will register for one of the following categories while preparing your defense:
- 999: Dissertation —Indicates the PhD student has completed all of the requirements for the degree except the dissertation and is in residence as a full-time student
- 995 : Continuation of Enrollment —Indicates the PhD student has completed all of the requirements for the degree except the dissertation and is not in residence as a full-time student
See the registration page for more information about these categories.
The Preparing Your Doctoral Dissertation manual is a great resource to help you bring your dissertation up to the required standard of organization, appearance, and format for the University of Rochester. Before preparing the defense copy of your dissertation, check the contents of the manual carefully to help avoid mistakes that can be time-consuming and costly to correct.
Before beginning your dissertation, you should consult with your advisor for your department or program’s preferred style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago).
Including material produced by other authors in your dissertation can serve a legitimate research purpose, but you want to avoid copyright infringement in the process. For detailed instructions on avoiding copyright infringement, please see ProQuest’s Copyright Guide .
The University requires that you provide copies of the dissertation to your committee members and exam chair. You should check with your committee members to see if they prefer printed or electronic copies (or both). Printed copies do not need to be printed on heavyweight, expensive paper unless there is the need to do so for figures and images.
Printing and binding a dissertation can be expensive. You can use the Copy Center or FedEx Office to print and bind your dissertation.
In order to register your dissertation, you or your graduate administrator will need to create a record on the Graduate Studies PhD Completion website . This record will include:
- Degree information
- Past degrees
- Contact information
- The defense version of your dissertation as a PDF
- Other relevant documents
The version of your dissertation attached to your online record is considered the registration copy.
When your PhD completion record is finalized, committee members will receive emails with links to access your record and approve your dissertation to progress to defense. You’ll need to provide copies of the dissertation identical to the registration copy to all members of your committee, including the chair, at least two weeks before the record is finalized. Everyone but the chair is required to comment or sign off on the dissertation before it is submitted.
There may be deadlines for registering your dissertation specific to your program. Consult with your graduate administrator to ascertain those deadlines and follow them carefully.
After all committee members have provided their approval, your thesis will be reviewed by your faculty director/department chair, the AS&E dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs, and the office of the University dean of graduate studies. When all of these officials have approved your committee and dissertation for defense, your dissertation is considered registered. You will be able to track these approvals in your online record and will receive a confirmation email when approvals are complete.
The GEPA Office and the AS&E dean of graduate education and postdoctoral affairs, as well as the University Graduate Studies Office, may make corrections to the PDF of your dissertation. This annotated copy of your dissertation, along with the original version, will be stored in the PhD completion website. You are not allow to distribute updated versions of your dissertation prior to the defense, but be sure to incorporate any corrections before uploading your final dissertation to ProQuest®.
After the defense, if the committee has required major revisions to be approved by one or more of its members, it is your responsibility to provide them with the corrected final version for their approval. They will be asked to submit written confirmation of that approval to the University Graduate Studies Office. Failure to do so could delay conferral of your degree.
After the defense, you will receive additional instructions by email for completion of all PhD degree requirements.
It is important to walk into the defense knowing that your committee wants you to pass. Even if criticism is harsh, it is meant to be constructive. The defense is not solely an opportunity for the committee to compliment and congratulate you for the work you have done. It is also meant to challenge you and force you to consider tough questions.

The Defense
The best way to prepare for your defense is to regularly attend the defenses of your colleagues throughout your graduate program, not just several weeks prior to your own defense.
You can also talk to people in your department who already defended to find out what their defenses were like. You should also speak with your advisor to get a sense of his/her specific expectations of a defense.
Guidelines for Presentations
Use PowerPoint or Other Software to Create Slides
You should prepare a presentation of the research that comprises the thesis. Your slides should encapsulate the work and focus on its most salient contributions. In preparing, ask yourself these questions: “What do I want people to know about my thesis? What is the most important information that I can present and talk about?”
Here are some basic tips:
- Use text large enough to be read by the audience (especially text from figures)
- Ensure graphics and tables are clear
- Don’t clutter your slides—if necessary, have things come up on mouse clicks
- Use spell check and proofread your slides
- Practice your presentation with your peers
- Work on pronunciation, if required
- Time your presentation to ensure it will fit the allotted time while allowing time for questions
If your defense includes a public lecture, we recommended that you do a trial run a day or two before in the room that has been booked for your lecture. This will allow you to familiarize yourself with the space and the equipment and to address any problems that arise during the trial run.
Plan your public lecture to allow enough time for questions. Present enough information so that the audience understands what you did, why you did it, what the implications are, and what your suggestions are for future research.
Friends and family are welcome to attend your public lecture. Faculty and students in the audience are given the opportunity to ask questions.
Plan to dress professionally for the defense in the same way you would if presenting a paper at a conference or for a job interview. You will be standing for a long time on the day of your defense. You might want to keep this in mind when selecting the shoes you will wear for your defense.
Essentials for your public lecture include:
- Your presentation
- A laser pointer
- A copy of your dissertation
- A pen or pencil
- A bottle of water
You will be asked to leave the room while your committee reviews your program of study, and decides whether:
- The thesis is acceptable/not acceptable
- Whether members will ask sequential questions or whether each member will be allotted a specific time period for questioning
The person to start the questioning is designated. You will be called back into the examining room and questioning will begin. After all questions have been addressed, you will be asked to leave the room while your committee decides the outcome of the exam. You will be asked to return to the room to be informed of the outcome by the chair of your exam committee.
- Listen to the entire question no matter how long it takes the faculty member or student to ask it (take notes if necessary).
- Pause and think about the question before answering.
- Rephrase the question.
- Answer the question to the best of your ability; if you do not know the answer, remain calm and say so in a professional way.
- Remember that no one will know the ins and outs of the thesis and your research materials as well as you. You are the foremost expert in the thesis topic and YOU know the research involved. Be positive!
Possible outcomes include:
- Acceptable with minor or no revisions (no further approval required)
- Acceptable with major revisions in content or format (in this case, one or more committee members must be responsible for overseeing and approving the major revisions before the final copies are submitted)
- Not acceptable
After the Defense
You can submit the final corrected copies of your dissertation as soon as you address any remaining comments that were brought up during the defense or noted in the registration copy of your dissertation, which will be returned to you usually within a few days before or after the defense. You can take up to one semester following the defense to address any comments, during which you can remain a full-time student. Your degree conferral date will depend on when you submit the final corrected copies of your dissertation.
The day after your defense, you will receive an email from the University dean of graduate studies that provides instructions on how to:
- Submit the final corrected copies of your dissertation through ProQuest
- Provide authorization for the release of your dissertation through UR Research
- Complete a mandatory online exit survey
- Verify to the University dean of graduate studies’ office that the dissertation has been submitted
The University of Rochester requires all doctoral candidates to deposit their dissertations for publication with ProQuest Dissertation Publishing and with the University libraries. Hard copies are not required. The library receives an electronic copy of the dissertation from ProQuest, but students must give the University permission to obtain it.
For questions regarding publishing through ProQuest, contact Author Relations at [email protected] or (800) 521-0600 ext. 77020.
Check with your graduate administrator to see if your department wants a bound copy of your dissertation, and, if so, how the cost of binding is covered.
If you want a bound copy for yourself or your family, you can purchase one through ProQuest .
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to prepare an excellent thesis defense
What is a thesis defense?
How long is a thesis defense, what happens at a thesis defense, your presentation, questions from the committee, 6 tips to help you prepare for your thesis defense, 1. anticipate questions and prepare for them, 2. dress for success, 3. ask for help, as needed, 4. have a backup plan, 5. prepare for the possibility that you might not know an answer, 6. de-stress before, during, and after, frequently asked questions about preparing an excellent thesis defense, related articles.
If you're about to complete, or have ever completed a graduate degree, you have most likely come across the term "thesis defense." In many countries, to finish a graduate degree, you have to write a thesis .
A thesis is a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
Once you hand in your thesis, you will be assigned a date to defend your work. Your thesis defense meeting usually consists of you and a committee of two or more professors working in your program. It may also include other people, like professionals from other colleges or those who are working in your field.
During your thesis defense, you will be asked questions about your work. The main purpose of your thesis defense is for the committee to make sure that you actually understand your field and focus area.
The questions are usually open-ended and require the student to think critically about their work. By the time of your thesis defense, your paper has already been evaluated. The questions asked are not designed so that you actually have to aggressively "defend" your work; often, your thesis defense is more of a formality required so that you can get your degree.
- Check with your department about requirements and timing.
- Re-read your thesis.
- Anticipate questions and prepare for them.
- Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups.
- Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
How long your oral thesis defense is depends largely on the institution and requirements of your degree. It is best to consult your department or institution about this. In general, a thesis defense may take only 20 minutes, but it may also take two hours or more. The length also depends on how much time is allocated to the presentation and questioning part.
Tip: Check with your department or institution as soon as possible to determine the approved length for a thesis defense.
First of all, be aware that a thesis defense varies from country to country. This is just a general overview, but a thesis defense can take many different formats. Some are closed, others are public defenses. Some take place with two committee members, some with more examiners.
The same goes for the length of your thesis defense, as mentioned above. The most important first step for you is to clarify with your department what the structure of your thesis defense will look like. In general, your thesis defense will include:
- your presentation of around 20-30 minutes
- questions from the committee
- questions from the audience (if the defense is public and the department allows it)
You might have to give a presentation, often with Powerpoint, Google slides, or Keynote slides. Make sure to prepare an appropriate amount of slides. A general rule is to use about 10 slides for a 20-minute presentation.
But that also depends on your specific topic and the way you present. The good news is that there will be plenty of time ahead of your thesis defense to prepare your slides and practice your presentation alone and in front of friends or family.
Tip: Practice delivering your thesis presentation in front of family, friends, or colleagues.
You can prepare your slides by using information from your thesis' first chapter (the overview of your thesis) as a framework or outline. Substantive information in your thesis should correspond with your slides.
Make sure your slides are of good quality— both in terms of the integrity of the information and the appearance. If you need more help with how to prepare your presentation slides, both the ASQ Higher Education Brief and James Hayton have good guidelines on the topic.
The committee will ask questions about your work after you finish your presentation. The questions will most likely be about the core content of your thesis, such as what you learned from the study you conducted. They may also ask you to summarize certain findings and to discuss how your work will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
Tip: Read your entire thesis in preparation of the questions, so you have a refreshed perspective on your work.
While you are preparing, you can create a list of possible questions and try to answer them. You can foresee many of the questions you will get by simply spending some time rereading your thesis.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense:
You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions. In addition, since you will know who will be on the committee, look at the academic expertise of the committee members. In what areas would they most likely be focused?
If possible, sit at other thesis defenses with these committee members to get a feel for how they ask and what they ask. As a graduate student, you should generally be adept at anticipating test questions, so use this advantage to gather as much information as possible before your thesis defense meeting.
Your thesis defense is a formal event, often the entire department or university is invited to participate. It signals a critical rite of passage for graduate students and faculty who have supported them throughout a long and challenging process.
While most universities don't have specific rules on how to dress for that event, do regard it with dignity and respect. This one might be a no-brainer, but know that you should dress as if you were on a job interview or delivering a paper at a conference.
It might help you deal with your stress before your thesis defense to entrust someone with the smaller but important responsibilities of your defense well ahead of schedule. This trusted person could be responsible for:
- preparing the room of the day of defense
- setting up equipment for the presentation
- preparing and distributing handouts
Technology is unpredictable. Life is too. There are no guarantees that your Powerpoint presentation will work at all or look the way it is supposed to on the big screen. We've all been there. Make sure to have a plan B for these situations. Handouts can help when technology fails, and an additional clean shirt can save the day if you have a spill.
One of the scariest aspects of the defense is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. While you can prepare for some questions, you can never know exactly what the committee will ask.
There will always be gaps in your knowledge. But your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. You are not expected to know everything.
James Hayton writes on his blog that examiners will sometimes even ask questions they don't know the answer to, out of curiosity, or because they want to see how you think. While it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, but you would need to do [...] in order to find out.” This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
You will be nervous. But your examiners will expect you to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions, for example. Dora Farkas at finishyourthesis.com notes that it’s a myth that thesis committees are out to get you.
Two common symptoms of being nervous are talking really fast and nervous laughs. Try to slow yourself down and take a deep breath. Remember what feels like hours to you are just a few seconds in real life.
- Try meditational breathing right before your defense.
- Get plenty of exercise and sleep in the weeks prior to your defense.
- Have your clothes or other items you need ready to go the night before.
- During your defense, allow yourself to process each question before answering.
- Go to dinner with friends and family, or to a fun activity like mini-golf, after your defense.
Allow yourself to process each question, respond to it, and stop talking once you have responded. While a smile can often help dissolve a difficult situation, remember that nervous laughs can be irritating for your audience.
We all make mistakes and your thesis defense will not be perfect. However, careful preparation, mindfulness, and confidence can help you feel less stressful both before, and during, your defense.
Finally, consider planning something fun that you can look forward to after your defense.
It is completely normal to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions for example if needed. Slow yourself down, and take a deep breath.
Your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. James Hayton writes on his blog that it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", but he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, you would need to do [...] in order to find out".
Your Powerpoint presentation can get stuck or not look the way it is supposed to do on the big screen. It can happen and your supervisors know it. In general, handouts can always save the day when technology fails.
- Dress for success.
- Ask for help setting up.
- Have a backup plan (in case technology fails you).
- Deal with your nerves.

How to Prepare for the Oral Defense of Your Thesis/Dissertation
© Paul T. P. Wong , Ph.D., C.Psych., Former Research Director, Graduate Program in Counselling Psychology, Trinity Western University, Langley, BC, Canada
Use the following steps when preparing for the oral defense of your thesis/dissertation.
1. Evaluation of oral examination is based on your presentation and your answers to questions from the examining committee.
2. Be well prepared for your presentation—academically, mentally and physically. Try to be well rested and focused before your oral defense.
3. In your preparation, don’t try to memorize all the studies cited in your thesis, but you do need to know the details of the few key studies that form the basis of your investigation.
4. You need to be familiar with larger issues, such as the basic assumptions, theoretical framework, paradigm, cross-cultural perspectives, Christian integration, etc.
5. More importantly, you need to have a deep understanding of the nature of your research problem and the major issues involved.
6. You may bring with you important materials for easy reference in the course of your defense; these may include key articles, computer print-outs of results, etc.
7. Your presentation is evaluated in terms of content and clarity as well as style.
8. Don’t speak too fast and don’t read from your notes.
9. Treat your presentation as a public address because there may be non-psychologists present at your defense. Therefore, don’t use too many jargons and don’t pack it with details. You need to tell people in simple, concise language:
- What you did,
- Why you did it,
- How you did it,
- What you found, and
- What the results mean.
10. Prepare handouts or power-points. Typically, they should include
- An overview or outline of your presentation,
- Introduction (including research question, rationale and hypothesis, if any, and definition of key constructs),
- Method (including design, methodology, sample, instruments or questionnaires, and procedure,
- Results (including tables or figures summarizing your findings), and
- Discussion (including reasons for new or unexpected findings, contributions and limitations, and practical implications).
11. Make sure that you space yourself well. Don’t spend too much time on one section. For example, you should not spend more than 5 minutes on introduction, since you are allowed only 20 minutes for your presentation.
12. Most of the questions are rather general and broad, dealing with substantial methodological, theoretical and application issues. However, some questions focus on specific points regarding sampling, statistical analysis, or some questionable conclusions.
13. Be prepared to clarify or elaborate on your assumptions, theoretical positions, methods, and conclusions. Often, an examiner plays the devil’s advocate to see how well you can think on your feet and defend yourself.
14. Occasionally, an examiner may ask a question which is unfair or cannot be adequately answered. After a few futile attempts, feel free to say that you don’t know the answer. You may even be bold enough to say, “Since none of my answers are acceptable, I would really appreciate it if you could give me some pointers or tell me what would be a correct answer.”
15. Here are some common questions:
- If you were to do it all over again, what changes would you make?
- What specific aspects of your findings can be utilized by counselors or psychologists in their practice?
- What is the most important contribution of your thesis? Can you say it in one or two sentences?
- What are some of the competing hypotheses? Could you think of an alternative interpretation of your findings?
16. Don’t rush to any answers. It is perfectly acceptable to think for a couple of seconds, or ask if you are on the right track. If you are not clear about the question, you are entitled to ask for clarification.
17. Try to be concise and to the point, but at the same time demonstrate that you have a good grasp of the complex issues involved. In other words, do not give superficial answers, but at the same time, do not go all over the map.
18. Put up a good defense without being defensive. Be confident without being cocky. A good defense means that you can provide strong logical arguments as well as empirical support o defend your position or conclusion. However, don’t be defensive when people criticize your study. If they are able to point out some real flaws or weaknesses in your study, accept their criticisms with humility, grace and gratitude.
19. Before the oral defense, talk to your advisor about areas of concerns based on external examiner’s comments. Then, discuss with your advisor how to best address these concerns. (Your advisor cannot tell you the specific questions the examiners will ask, but s/he can direct your attention to issues or areas that require some thinking or additional research.)
20. After the oral defense, meet with your advisor for debriefing and seek advice on how to revise your thesis.
- President’s Annual Report 2023: Founder’s Vision and Last Wishes
- Editorial: A New Science of Suffering, Existential Intelligence, and the New Behavioral Economics of Happiness—Toward a General Theory of Wellbeing
- Meaning-Centered Positive Education (PE 2.0) Based on the New Paradigm of Existential Positive Psychology (EPP)
- What is the meaning of suffering?
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Dissertation Defense: Steps To Follow To Succeed

A dissertation defense is arguably one of the most important milestones in every student’s career. While it signals that your tenure as a student is soon about to close, it validates all your efforts towards your thesis.
Being cautious about including all the necessary details is very important to successfully complete your dissertation proposal defense. This article tells you everything that you need to know about writing a defense that can add great credibility to you as a student.
What is A Dissertation Defense?
The first thing that you need to learn is what is a dissertation defense and what is its purpose. In simple terms, it is a presentation made by a student to defend all the ideas and views that are presented in a dissertation.
The presenter must include details like what is the reason for choosing specific research methods, the theory that has been selected for the paper, and other such points. This presentation is made before an audience that comprises of the university committee, professors and even fellow-students. It is met with questions and answers that gives the student an opportunity to provide more clarity on the dissertation in order to convince the committee to approve it.
Stages of a Dissertation Defense
One of the most important dissertation defense tips provided by several professors is to breakdown the process into three steps:
- Preparation : This stage involves collection of all the necessary information that must be included in the defense dissertation and making all the arrangements for the actual meeting.
- The defense meeting : This is where you decide how you will present the defense. The actual meeting is hugely reliant on the performance, body language and the confidence in your oral defense.
- After the defense meeting : This stage, also known as the follow up, requires you to make the necessary revisions suggested by the university committee. You can even provide bound copies of the whole dissertation to distribute among different members of your departments. In the follow up stage, one must also think about expense that are related to publishing the Ph.D. dissertation defense as well as printing additional copies of the manuscript, if required.
How Long is a Dissertation Defense?
The first thing that a student should know is how long does a dissertation defense last? The length has to be carefully calculated to make the impact that you want. One of the most important steps in the dissertation preparation is to understand how much time each department allocates to the closing oral defense. When you plan in the early stages of your dissertation itself, you can write it in a manner that allows you to defend it in the allocated time.
Usually these meetings including the presentation, the oral defense and the question and answer session last for about two hours. In most cases, these two hours also encompass the time needed by members of the committee to deliberate.
How to Prepare for the Dissertation Defense
Now that you know how long is a dissertation defense, the next step is to prepare well enough to make your presentation impressive.
Here are some tips on how to prepare for a dissertation defense:
- Watch other students in action to learn about different presentation styles. You can attend defenses of different colleagues in your department as well as other departments in your university.
- Get all the details about the deadlines and the rules of your college or university about scheduling your defense.
- Scheduling is also a very important part of your preparation. It is important to note that members of the committee and University chairs need to make time for these defences in a very packed schedule. Coordinate the date, venue and time of your defense as early as possible.
- Prepare a manuscript adhering to the necessary formatting rules. Review your manuscript thoroughly before you hand it in. During your PH.D, your faculty will also assist you with the defense. For this, they must have a crisp and polished copy of your manuscript.
- Most colleges have the facility for a pre-defense meeting. This is the best opportunity to sort out any concerns that you may have about the actual meeting. It is a good idea to ask the chairs what types of questions may be put forward and if there are any problems with the defense that need to be resolved. When you prepare for a pre-defense meeting, think of it as the final one and give it your all.
- Put together all the material that you need for the defense. A detailed, yet to-the-point presentation must be prepared.
- The final stage of preparation is practicing your presentation over and over again. It is not just the presentation but also the approach towards the questions that you must practice.
Tips To Nail Your Actual Meeting
With these tips you will be one step closer towards a successful defense that will help your dissertation pass and be approved:
- All meetings should begin by addressing the chair. Make sure you thank all the committee members and the advisors for the efforts that they have put it. This gives you a professional start to the presentation.
- The presentation should cover the following subjects in brief:
- The research topic
- Literature review
- The methods used for analysis
- The primary findings of the research
- Recommendations of additional research on the subject in the focus.
- Do not get rattled by any discussions among the chairs. They will deliberate on any disagreements or topics of interest. This is a part of the process and is not a reflection of the presentation itself.
- There are two questions that are commonly asked that you should be prepared for. This includes the weaknesses of the dissertation and the research plans that you have made post-dissertation.
- Use subtle gestures when you are talking. Do not overuse your hands when doing so. The whole meeting including the question and answer session should have a very formal appeal.
- The tone of your voice must be assertive without making it seem like you are trying to hard. Be clear and enunciate when you speak.
Once the questions have been answered, the committee will leave the room. Then, after the deliberation, you will be informed if your dissertation has passed or not.
For affordable thesis writing assistance , get in touch our team today. The pricing is cheap but students can be assured of top notch quality in all our final products.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
- Alumni and Friends
- Directories
- News and Events
- Prospective Student Information
Search form
- International Students
- Non-Degree Visiting Students
- Newly Admitted Students
- Financial Aid
- Student Registration Policies
- Student Employment
- Satisfactory Academic Progress
- Incomplete Coursework
- Language Exam Requirements
- Joint Degree Programs
- Transfer Course Credits
Dissertation and Defense
- Information on Academic Disputes and Formal Grievance Policy
- Leave of Absence and Withdrawal
- Faculty Departures: Impact on Student Advising
- Academic Requirements and Milestones
- Course Enrollment
- Receiving Your Degree
- Resources for Students
- BA/MA programs in the Humanities
- Student Leadership Opportunities
Dissertation Committee
Dissertation defense process.
The dissertation defense is one of the most important moments in a graduate student’s career. When a student is deemed to be ready to defend the doctoral thesis, the student is the expert in a particular research area. At the defense the student is expected to cogently and clearly explain their research and how it fits with other scholarship in the field of study. The exact nature of the oral defense may vary by discipline and department, so it is important that the student talk to the dissertation committee chair about what to expect and how to prepare.
The defense typically lasts about two hours and may be open to the public. The defense aims to accomplish two goals. First, it will provide an occasion for the presentation and recognition of the completed doctoral work. Second, it will furnish the opportunity for discussion and formal evaluation of the dissertation.
The timing of the defense will be set by the student in consultation with the dissertation committee. Students should contact their departments to schedule the dissertation defense. Note that some departments do not schedule examinations in summer. The student should send copies of the dissertation to the members of the committee no later than three weeks prior to the defense. The time and place of the defense shall be announced on the department’s calendar of events.
The chair of the student's dissertation committee and at least one other committee member must be present in person. In the case that a committee member is unable to attend in person, the committee member may participate by Skype or other teleconference media. The defense must be open to all faculty within the department. Broader attendance will be left to the discretion of the student in consultation with the committee.
Please note: Departments will be allowed to have in-person defenses. Additionally, there is no reason to limit remote defenses if that is what the participants want and the department/committee approves.
The dissertation defense shall be an open presentation by the student on the main aspects of the research reported in the dissertation, followed by questions, comments, and discussion. The chair of the dissertation committee or a designee shall act as the moderator of this discussion and shall have discretion to decide whether questions are germane to the topic of the dissertation. After discussion is completed, the departmental faculty in attendance and the dissertation committee will decide privately whether the dissertation defense has been satisfactory.
The dissertation chair or designee will report the results as soon as possible after the dissertation defense to the Dean of Students office by submitting a signed Report of Final Examination and a Dissertation Defense Form. If the manuscript is to undergo revisions, the student will be informed of the timeframe in which the revisions are to be completed.
Dissertation Submission
A final copy of the dissertation must be submitted following the procedure outlined on the Dissertation Office website by Friday of the seventh week of the quarter in which a student is graduating, sixth week in summer quarter. The defense should be held in sufficient advance of this deadline to allow revisions recommended by the student's dissertation committee.
Students should contact the Dissertation Office no later than early in the quarter in which they intend to graduate in order to resolve any questions or problems they may have in preparing the dissertation. The Dissertation Office staff is willing to look at a draft of the dissertation. Having them do so avoids both the expense and headache of having to re-format the dissertation. They offer a schedule to help students plan for a smooth process to meet these deadlines.
Office of the Dean of Students [email protected] 773.702.1552

Capstone Documents: Oral Defense
- Supplemental Resources for the PhD Social Work
- DBA Capstone: Traditional Capstone Options
- DBA Capstone: Portfolio Project Options
- DBA Capstone: Consulting Capstone Option
- DHA Doctoral Study (Summer 2021 or before)
- DIT Doctoral Study
- DNP Doctoral Project
- Doctor of Nursing Program Capstone Resources
- DNP Capstone Resources NURS 8702 and NURS 8703
- DPA Doctoral Study
- DrPH Doctoral Study
- DSW Doctoral Study
- EdD Doctoral Study
- PsyD Doctoral Study
- Doctoral Prospectus Resources This link opens in a new window
- Oral Defense
- Capstone Committee Process
- Doctoral Prospectus Resources
- DHS Doctoral Study
- DHA Doctoral Study Landing Page
- DHA Doctoral Study (Fall 2021 or after)
- Previous Page: Doctoral Prospectus Resources
- Next Page: Capstone Committee Process
Oral Defense Information
- Conference Call Request Form (Faculty Only)
Please submit this form at least three business days prior to the requested conference call date. This form is used when the necessary approvals are in place to hold a conference call for one of the following: For Student and Committee Members (sessions are recorded):
- Proposal Oral Presentation - The Proposal Oral Presentation should only be scheduled after committee approval of the proposal has been finalized .
- Final Oral Presentation - The Final Oral Presentation should only be scheduled after Form & Style approval has been finalized . When scheduling the Final Oral Presentation, the requested day/time should take place no sooner than the day following the Form & Style due date or date of return if completed before the due date.
- Faculty Only Oral Defense Resources
Presentation Templates
Here are a few oral presentation templates to get you started in preparing for your oral presentation. If a template is not listed for your program; this program currently does not provide generic models for the oral presentation. Please, reach out to your committee chair to determine the appropriate materials to prepare and the process that will be used in the call
- PhD Dissertation Proposal Oral Defense Template
- PhD Dissertation Final Oral Defense Template
- DBA Presentation Template
- DBA Consulting Capstone Oral Defense Template
- DHA Oral Defense Template
- DHS Proposal Oral Defense Template
- DHS Final Oral Template
- DIT Proposal Oral Presentation Template
- DIT Final Oral Presentation Template
- DrPH Oral Proposal Defense PowerPoint Template
- DrPH Oral Final Defense PowerPoint Template
- DSW Proposal Defense Template
- DSW Final Oral Defense Template
- DNP Final Project Defense Template
Oral Defense Archives (Listen to Oral Defenses)
- Oral Defense Recordings (Student Access Only)
Social Media
Connect with the office of research and doctoral services.
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Current Students
- Brightspace
- UWinsite Student
- Campus Bookstore
- Faculty + Staff
- UWinsite Finance
- Alumni + Donors
- Industry + Community Partners
- About UWindsor
- Office of the President
- People, Equity and Inclusion
- Virtual Tour
- Visitor Information
- Campus Maps
- VIEW Magazine
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- International Programs
- Co-operative Education
- Continuing Education
- Office of the Registrar
- Financial Matters
- Office of the Provost
- Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences
- Engineering
- Graduate Studies
- Human Kinetics
- Vice-President, Research & Innovation
- Research & Innovation Services
- Research Partnerships
- Research Appointments
- Research Ethics
- Research Safety
- Animal Care
- Research Finance
- Leddy Library
- UWill Discover!
- About Student Life
- UWindsor Events
- SoCA Concerts & Events
- Lancers Varsity Sports
- University Players
- Athletics + Recreation Services
- Student Accessibility Services
- Food Services
- Student Support
- UWindsor Home
- Faculty of Graduate Studies
Final oral defense: John Boamah (M.A.Sc.)
"Effect of incidence angle on the wake flow of a wallmounted cylinder with a slot immersed in a shallow flow"
Location: Room 3001 CEI
- Follow us on X (Twitter)
Trump immunity case highlights: Ex-president's lawyers and DOJ argue before Supreme Court
Highlights from today's supreme court arguments.
- The Supreme Court heard arguments on former President Donald Trump ’s claim of presidential immunity from prosecution in special counsel Jack Smith's election interference case against him.
- Trump's lawyers argue that his efforts to overturn the 2020 election were “official acts” taken in office. His attorney D. John Sauer argued Trump's case before the court. Michael Dreeben responded for the U.S.
- Arguments began at 10 a.m. ET and ran for just under three hours. Conservative justices raised concerns about going too far in restricting a president while liberals worried about what a president unrestricted by the fear of criminal prosecution might do.
- The court, which has a 6-3 conservative majority, including three justices appointed by Trump, has come under criticism for the delay in considering the former president's appeal as the November presidential election approaches.
Follow live coverage of testimony in Trump's ongoing hush money criminal trial in New York.
Supreme Court signals further delay in Trump election interference case as it weighs immunity claims
Lawrence Hurley Supreme Court reporter
Ryan J. Reilly
WASHINGTON — The Supreme Court on Thursday indicated that any trial in former President Donald Trump’s election interference case is unlikely to take place anytime soon, with justices expressing concerns about whether certain presidential acts should be off-limits.
Although the court appears likely to reject Trump’s expansive claim of absolute immunity, it could remand the case for further proceedings, further delaying the chance of a trial taking place before the election.
The court is weighing the novel legal question of whether a former president can be prosecuted for what Trump’s attorneys say were “official acts” taken in office, though much of the focus remains on whether the justices will rule quickly so a trial can take place before the November election .
With most legal experts questioning Trump’s broad argument that the entire election interference indictment should be dismissed based on immunity, the court’s eventual ruling on the extent to which official acts are protected and how quickly it rules will be of equal importance.
While the court’s three liberal justices appeared most sympathetic to prosecutors, the court’s conservatives seems to have differing views on the scope of presidential immunity, making it unclear exactly how the court will rule.
Several justices raised concerns about the broad implications for future presidents, with most steering clear of discussing the specific allegations against Trump.
“If an incumbent who loses a very close, hotly contested election, knows that a real possibility after leaving office is not that the president is going to be able to go off into a peaceful retirement, but that the president may be criminally prosecuted by a bitter political opponent, will that not lead us into a cycle that destabilizes the functioning of our country as a democracy?” asked conservative Justice Samuel Alito.
Read the full story here .
Jack Smith was in court today
The special counsel was in the courtroom and present for arguments this morning.
Jackson expressed concerns about the prosecutions of future presidents
Summer Concepcion
At the close of arguments, Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson said there are real concerns about future presidents being prosecuted and asked Dreeben to comment on whether some of the caution from the Justice Department and prosecutors comes from an understanding that presidents will soon be former presidents as well.
Dreeben replied, “absolutely,” adding that her point is a “structural argument that’s built into the Constitution itself.”
Jackson went on to say that she views that as an “equal” argument to concerns that presidents wouldn’t be burdened by the fear about criminal prosecutions for their actions.
Court is adjourned
Alexandra Marquez is based in Washington, D.C.
Oral arguments are complete and court has adjourned for the day.
Government would still raise private conduct to jury, Dreeben says
During her questioning, Barrett asked whether the special counsel lawyers would still pursue prosecution of Trump's private acts even they weren't allowed to prosecute him for his official acts as president.
"There's really an integrated conspiracy here that had different components, as alleged in the indictment, working with with private lawyers to achieve the goals of the fraud, and ... the petitioner reaching for his official powers to try to make the conspiracies more likely to succeed," Dreeben answered.
Dreeben added, "We would like to present that as an integrated picture to the jury so that it sees the sequence and the gravity of the conduct and why each step occurred," but if the court ruled that much of Trump's conduct was private, "we would take a jury instruction that would say, you may not impose criminal culpability for the actions that he took, however, you may consider it insofar as it bears on knowledge and intent."
Dreeben says government aims for a system that 'preserves the effective functioning of the presidency'
Dreeben acknowledged that "no perfect system" exists, but that the government is "trying to design a system that preserves the effective functioning of the presidency and the accountability of a former president under the rule of law."
"And the perfect system that calibrates all of those values probably has not been devised," he said. "I think that the system that we have works pretty well, maybe it needs some, a few ancillary rules. It is different from the radical proposal” of my friend who argues absolute immunity.
Barrett replied that she agrees with that sentiment.
Kavanaugh presses Dreeben on Obama drone strikes
In response to a question from Kavanaugh about why former President Barack Obama was never prosecuted for drone strikes, Dreeben answered, in part, "this is actually the way that the system should function."
"So, the Office of Legal Counsel looked at this very carefully and determined that number one, the federal murder statute does apply to the executive branch, [but] the president wasn’t personally carrying out the strike," Dreeben said. He added, "But the aiding and abetting laws are broad, and it’s determined that a public authority exception that’s built into statutes and that applied — particularly the murder statute, because it talks about unlawful killing, did not apply to the drone strike. So this is actually the way that the system should function."
Kavanaugh also expresses concerns over potential breadth of ruling
Justice Brett Kavanaugh said that, like Gorsuch, he’s “very concerned about the future,” as opposed to this particular case.
“That’s the concern going forward, is that the system will, when former presidents are subject to prosecution ... the history of Morrison v. Olson tells us it’s not going to stop,” Kavanaugh said. “It’s going to cycle back and be used against the current president or the next president and the next president after that.”
“I want you to try to allay that concern — why is this not Morrison v. Olson redux if we agree with you?” Kavanaugh asked Dreeben.
Referring to the case Kavanaugh cited, Dreeben responded that "the independent counsel regime did have many structural features that emphasized the independence at the expense of accountability. We don’t have that regime now."
Gorsuch seems worried about writing a decision too broadly
In his questioning, Gorsuch said, “I’m not concerned about this case, but I am concerned about future uses of the criminal law to target political opponents based on accusations about their motives, whether it’s re-election or who knows.”
Dreeben: Trump using his presidential powers 'makes the crime ... worse'
Dreeben clarified that the U.S. isn’t charging Trump for seeking to appoint favorable figures to his Cabinet, but for seeking to remove those who wouldn't help him overturn the election and for seeking to appoint those who would help him.
“For an incumbent president to then use his presidential powers to try to enhance the likelihood that it succeeds, makes the crime in our view worse," Dreeben said.
He added, "We’re not seeking to impose criminal liability on the president for exercising or talking about exercising the appointment and removal power. No, what we’re seeking to impose criminal liability for is a conspiracy to use fraud to subvert the election.”
Dreeben lists things Sauer said were official but government believes are private acts
Dreeben listed out what Suaer said constitutes official acts but the government considers private.
“Organizing fraudulent slates of electors, creating false documentation that says, ‘I’m an elector, I was appointed properly,’” Dreeben said. “I’m going to send a vote off to Congress that reflects that petitioner won rather than the candidate that actually got the most votes and who was ascertained by the governor and whose electors were appointed to cast votes.”
“That is not an official conduct, that is campaign conduct,” Dreeben added.
Alito asks about what an incumbent who lost can do
Alito further pressed Dreeben with a question on the peaceful transfer of power between presidencies, asking, “If an incumbent who loses a very close, hotly contested election and knows that a real possibility after leaving office is not that the president is going to be able to go off into a peaceful retirement, but that the president may be criminally prosecuted by a bitter political opponent, will that not lead us into a cycle that destabilizes the functioning of our country as a democracy?”
“I think it’s exactly the opposite, Justice Alito,” Dreeben answered, saying, “There are lawful mechanisms to contest the results in an election.”
Alito and Dreeben go back and forth over self-pardoning
Alito brings up the issue of self-pardoning, which other justices had previously raised.
If the court agrees that presidents can pardon themselves, "won't the predictable result be that presidents in the last couple of days of office are going to pardon themselves from anything that they might have been conceivably charged with committing?" Alito asked.
"I really doubt that, Justice Alito," Dreeben answered, adding later: "That seems to contradict a bedrock principle of our law, that no person shall be the judge in their own case."
Dreeben argues a president is constitutionally protected when attorney general says an action is lawful
Alito asked Dreeben, "If the president gets advice from the attorney general, that something is lawful, is that an absolute defense?"
Dreeben replied, "Yes."
"Wouldn’t that give presidents an incentive to be sure to pick an attorney general who can, who will reliably tell the president that it is lawful to do whatever the president wants to do if there’s any possibly conceivable argument in favor of it?" Alito pressed Dreeben.
Dreeben contended that "the constitutional structure protects against that risk."
"The president nominates the attorney general, and the Senate provides advice and consent," Dreeben said.
Alito invokes internment of Japanese Americans during World War II
As he questioned Dreeben, Alito asked, "What about President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s decision to intern Japanese Americans during World War II, could [he] in fact have been charged under 18 U.S.C. 241 conspiracy against civil rights today?"
Dreeben agreed that, "Yes," he could have been charged if that happened today, "given this court’s decision in ... Trump v. Hawaii."
Alito: 'You don't think he's in a peculiarly precarious position?'
During his questioning, Alito seems skeptical of Dreeben's argument, asking him, "Did I understand you to say, 'Well, you know, if he makes a mistake, he makes a mistake. He's subject to the criminal laws just like anybody else.' You don't think he's in a peculiarly precarious position?"
In response, Dreeben told Alito, "He's under a constitutional obligation. ... He's supposed to be faithful to the laws of the United States and the Constitution of the United States."
He added, "And making a mistake is not what lands you in a criminal prosecution."
Dreeben notes the president lacks 'functions with respect to' certifying the winner of the presidential election
Dreeben circled back to a point the court discussed earlier regarding the "distinction between a public official acting to achieve public ends and a public official acting to achieve private ends" as applied to this case.
"The president has no functions with respect to the certification of the winner of the presidential election," he said. "It seems likely that the framers designed the Constitution that way because at that time of the founding, presidents had no two-term limit, they could run again and again."
"So the potential for self-interest would explain why the state’s conduct, the elections, they send electors to certify who won those elections and to provide votes," he added. "And then Congress, in a joint extraordinary joint session, certifies the vote and the president doesn’t have an official role in that proceeding."
Gorsuch presses Dreeben on a president leading a peaceful protest
Gorsuch pressed Deeben about a potential scenario where a president leads a mostly peaceful protest or sit-in in front of Congress because he objects to a piece of legislation that’s going through, which leads to delays of proceedings in Congress.
Dreeben said he doesn’t think that would lead to prosecution.
“But without a clear statement that applies to the president ... it’s not core, the core kinds of activities that the court has acknowledged," Dreeben said. But things like the pardon power, the power to recognize foreign nations the power to veto legislation, the power to make appointments, these are things that the Constitution specifically allocates to the president.”
Sotomayor: President not mentioned in many federal laws
Sotomayor points out that the president is only explicitly mentioned in a few federal statutes, adding that, "Justice Barrett made the point that if we say a president can’t be included in a criminal law unless explicitly named, then that would bar the Senate from impeaching him for high crimes or misdemeanor because that means that he’s not subject to the law at all.”
Dreeben pushes back on 'taking away immunity' from Trump
Addressing Roberts, Dreeben said, "I would take issue, Mr. Chief Justice, with the idea of taking away immunity. There is no immunity that is in the Constitution unless this court creates it today."
"What is important is that no public official has ever had the kind of absolute criminal immunity that my friend speaks of," he added.
Jackson questions whether Trump thinks every law needs to say it applies to the president
During questioning of Sauer, Jackson asked whether he believed that Congress would have to write "and the president is included" in every law it passed.
"I thought that was the sort of background understanding that if they’re enacting a generally applicable criminal statute, it applies to the president just like everyone else," Jackson said. "So, what is the clear statement that would have to be made?”
Sauer said that he believes "Congress has to speak clearly before it interferes with the president’s powers."
Thomas asks why past presidents have not been prosecuted for overseas operations
Thomas said that in the not so distant past, presidents who have engaged in various activities such as coups have not faced prosecution, specifically mentioning Operation Mongoose, which aimed to remove the Castro regime from power in Cuba.
“If what you’re saying is right, it would seem that that would have been ripe for criminal prosecution,” Thomas asked Dreeben.
Dreeben replied, “The reason why there have not been prior criminal prosecutions is that there were not crimes.”
“And I want to explain why there are layers of safeguards that assure that former presidents do not have to lightly assume criminal liability for any of their official acts,” Dreeben said.
Trump's team is done. Now it's the U.S.'s turn.
Trump's attorneys are done with their arguments. Michael Dreeben has taken over with arguments for the U.S. now.
Jackson asks why 'the president would not be required to follow the law'
Amid her questioning, Jackson asks, "Why .... [would] the president ... not be required to follow the law when he is performing his official acts? Everyone else — there are lots of folks who have very high-powered jobs and they do so against the backdrop of potential criminal prosecution."
She further posited that perhaps presidents don't commit criminal acts because they're afraid of prosecution. That may not be case, she said, "once we say 'no criminal liability. Mr. President, you can do what you want.'"
In response, Sauer argued that presidents haven't been under credible threat of criminal prosecution since the founding of the U.S.
"The regime you've described is the one we've operated under for over 240 years," Sauer said.
Jackson tells Sauer that if a president weren't 'chilled,' then there would be no potential penalty for committing crimes
Jackson told Sauer that he seems to be "worried about the president being chilled."
She then argued that in reality, a "really significant opposite problem" would emerge.
"If the president wasn’t chilled, if someone with those kinds of powers, the most powerful person in the world with the greatest amount of authority, could go into office knowing that there would be no potential penalty for committing crimes, I’m trying to understand what the disincentive is from turning the Oval Office into, you know, the seat of criminal activity in this country,” she said.
Barrett presses Sauer on impeachment clause
“You’ve argued that the impeachment clause suggests or requires impeachment to be a gateway to criminal prosecution, right?” Barrett asked.
Sauer replied, “Yes, I think that’s the plain meaning of that second phrase in the clause.”
“OK, so there are many other people who are subject to impeachment, including the nine sitting on this bench, and I don’t think anyone has ever suggested that impeachment would have to be the gateway to criminal prosecution for any of the many other officers subject to impeachment,” Barrett pressed. “So why is the president different when the impeachment clause doesn’t say so?”
Sauer replied that then-U.S. Solicitor General Robert Bork in 1973 argued that “the sequence is mandatory only as to the president.”
Gorsuch asks if a president can pardon himself
Asked by Justice Neil Gorsuch whether a president can pardon himself, Sauer responded, "Perhaps if he feels he has to, he'll pardon himself every every four years from now on."
Kagan presses Sauer on whether a president ordering his generals to stage a coup would be an official act
Kagan repeated the hypothetical situation of a president "who ordered the military to stage a coup — he’s no longer president, he wasn’t impeached, he couldn’t be impeached, but ordered the military to stage a coup, and you’re saying that’s an official act?” Kagan asked.
Sauer replied that “would depend on the circumstances whether it was an official act.”
Sauer says Trump made two official acts
Under questioning by Justice Elena Kagan, Sauer said two actions taken by Trump while in office were official, and thus he was ineligible to be criminally prosecuted for them.
First, Kagan asked about the "defendant [calling] the chairwoman of the Republican National Committee" and asking her "to gather electors in targeted states."
Then, she said, "The defendant asked the Arizona House speaker to call the Legislature into session to hold a hearing based on their claims of election fraud."
On the second point, Sauer said it was "absolutely an official act for the president to communicate with state officials."
Alito clarifies with Sauer that they want all official acts removed from the indictment
"When you say that the official acts should be expunged from the indictment, that in itself would not achieve very much unless evidence of those official acts were precluded at trial. So is that what you’re saying?" Alito asked Sauer. "That the prosecution should not be permitted at trial to prove the official acts as part of the conspiracies that are alleged?"
Sauer confirmed that was the premise of his argument.
"Absolutely, and we think that’s just the clear implications of Brewster and Johnson and their discussion. It’s very, very analogous context," Sauer said.
What's Blassingame?
Oral arguments have repeatedly referred to Blassingame, a decision from the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit that involved numerous lawsuits against Trump in his personal capacity. The decision , which came out in December , denied Trump's claims of presidential immunity for now.
“The sole issue before us is whether President Trump has demonstrated an entitlement to official-act immunity for his actions leading up to and on January 6 as alleged in the complaints. We answer no, at least at this stage of the proceedings,” a panel of judges ruled.
The case is named after James Blassingame, a Capitol Police officer who was injured in the Jan. 6, 2021, riot .
Barrett asks Sauer a list of 'hypothetical 'acts
Daniel Barnes is reporting from the federal courthouse.
During her questions, Justice Amy Coney Barrett asked Sauer to "agree or disagree with the characterization of these acts as private." He agreed that all were private acts:
- Petitioner turned to a private attorney who was willing to spread knowingly false claims of election fraud to spearhead his challenges to the election results.
- Petitioner conspired with another private attorney who caused the filing in court of a verification signed by petitioner that contain false allegations to support a challenge.
- Three private actors — two attorneys, including those mentioned above, and a political consultant — helped implement a plan to submit fraudulent slates of presidential electors to obstruct the certification proceeding.
Sotomayor asks Sauer about false electors scheme
“What is plausible about the president insisting and creating a fraudulent slate of electoral candidates. ... Is that plausible that that would be within his right to do?” Sotomayor asked.
Sauer replied “absolutely,” saying there was historical precedent in President Ulysses S. Grant sending federal troops to Louisiana and Mississippi in 1876 to make sure that the Republican electors got certified.
“The notion that it’s completely implausible, it just can’t be supported based on the face of this indictment, or even knowing that the slate is fake ... that they weren’t actually elected, that they weren’t certified by the state.”
Sauer then disputed the characterization of the word “fraudulent” electors in the indictment.
“On the face of the indictment, it appears that there was no deceit about who had emerged from the relevant state conventions, and this was being done as an alternative basis,” he said.
Alito asks Sauer a hypothetical about 'plausible justification' as a standard for official acts
Justice Samuel Alito posed a question to Sauer: "Suppose the rule were that a former president cannot be prosecuted for official acts unless no plausible justification could be imagined for what the president did. ... Would that be sufficient or if it is insufficient?"
In response, Sauer said he believed that would be insufficient, adding "that might be a much better rule than what emerged in the lower courts."
Jackson presses Sauer on Nixon's pardon
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson posed the question to Sauer that if presidents can’t be prosecuted, why was former President Richard Nixon pardoned?
“What was up with the pardon for President Nixon? I think that if everybody thought that presidents couldn’t be prosecuted, then what was that about?” she said.
Sauer replied, “Well, he was under investigation for both private and public conduct at the time.”
Roberts' bribery hypothetical ties into Trump's first impeachment
Chief Justice John Roberts asked a hypothetical question about whether a president could be prosecuted for appointing someone ambassador after being paid a $1 million bribe.
One million dollars is exactly the amount of money that Gordon Sondland , who was at the center of Trump's first impeachment trial, gave to Trump's inauguration fund before he was named ambassador to the European Union.
Presidents of both parties have named donors to ambassadorships. The money that Sondland, a wealthy hotelier, donated went to Trump's inauguration fund, not Trump directly, so it wasn't a personal bribe.
“Do you know what a quid pro quo is?” Rep. Jim Jordan asked Sondland during a hearing in November 2019. "I do," Sondland responded.
NBC News’ Shaquille Brewster reports from outside the Supreme Court where protesters are demonstrating as the court is set to hear arguments over former President Trump’s claim of presidential immunity in the election interference case against him.
Sotomayor points out that founders had state constitutions that granted some criminal immunity to governors
Sotomayor pointed out that the founders had discussed whether to grant immunity to the president, adding that they had state constitutions that granted some criminal immunity to governors, but yet they didn’t take it up.
Instead, she said, they passed an impeachment clause that says you can’t remove the president from office except through a trial in the Senate and can impose criminal liability after.
Sotomayor seems skeptical of Sauer's argument
As she questioned Sauer, Sotomayor told him, "I am having a hard time thinking that creating false documents, that submitting false documents, that ordering the assassination of a rival, that accepting a bribe and countless other laws that could be broken for personal gain, that anyone would say that it would be reasonable for a president or any public official to do that.”
Sotomayor poses a hypothetical to Sauer about a president assasinating a rival
In a question to Sauer, Justice Sonia Sotomayor posed a hypothetical: If the president ordered the military to assassinate a rival he views as corrupt, "is that within his official act for which he can get immunity?"
Sauer answered that, "it would depend," but "we can see that could well be an official act."
Sauer argues against a president being imprisoned for 'controversial decisions'
Sauer argues in his opening that if a president can be charged, put on trial and imprisoned for “controversial decisions” upon leaving office, “that looming threat will distort the president’s decision-making precisely when bold and fearless action is most needed.”
“Could President George W. Bush be sent to prison for obstructing an official proceeding or allegedly lying to Congress to induce war in Iraq?” he asked. “Could President Obama be charged with murder for killing U.S. citizens abroad by drone strike? Could President Biden someday be charged with unlawfully inducing immigrants to enter the country illegally for his border policies?”
Thomas asks the first question
Justice Clarence Thomas asks the first question, to Sauer. He asks Sauer to detail where presidential immunity is founded in law.
Oral arguments are underway
Oral arguments in front of the justices have begun.
Arguments come a day after Trump and allies face fallout from 'fake elector' scheme
Megan Lebowitz
Today's arguments come after several Trump aides and allies were indicted yesterday as part of an Arizona investigation into alleged efforts to overturn Biden's 2020 win in the swing state.
The former president was also described as an "unindicted coconspirator" in the indictment from the Arizona state grand jury.
Trump was also labeled an uncharged co-conspirator in the 2020 "false electors" scheme in Michigan, according to a state investigator's testimony , which also occurred on Wednesday.
Trump again asserts presidential immunity ahead of arguments
Jillian Frankel
In a series of posts to his Truth Social platform this morning, Trump again asserted that he has presidential immunity from criminal charges over his efforts to overturn the 2020 election results.
“Without Presidential Immunity, the Presidency will lose its power and prestige, and under some Leaders, have no power at all. The Presidency will be consumed by the other Branches of Government,” he wrote . “That is not what our founders wanted!”
Trump’s lawyers argue that their client is being prosecuted for “official acts” during his time in office. In his post, Trump argues that if a president does not have total immunity, then the opposing party can “extort and blackmail ” the president during his or her term in office.
“If a President does not have Immunity, the Opposing Party, during his/her term in Office, can extort and blackmail the President by saying that, ‘if you don’t give us everything we want, we will Indict you for things you did while in Office,’ even if everything done was totally Legal and Appropriate,” he wrote. “That would be the end of the Presidency, and our Country, as we know it, and is just one of the many Traps there would be for a President without Presidential Immunity.”
Here's the central question in this case
The justices will directly address the following question when they issue their opinion in this case: “Whether and, if so, to what extent does a former President enjoy presidential immunity from criminal prosecution for conduct alleged to involve official acts during his tenure in office?"
Former Missouri Solicitor General D. John Sauer will be arguing on behalf of Trump. He's argued in front of the Supreme Court once before, in a case he won 5-4.
On the opposing side, former deputy U.S. Solicitor General Michael Dreeben will argue for the U.S. He worked for special counsel Robert Mueller on the Russia probe and has argued in front of the Supreme Court over 100 times before.
Media is setting up outside the court amid a few protest banners
Media is gathered at the Supreme Court, preparing for arguments today. There are a few protest banners outside the fence, including a large sign in the style of Trump's campaign banners that reads: “LOSER."
Lead prosecutor is here
Thomas Windom, the lead prosecutor on Trump’s Washington election interference case, is attending arguments today. Stands to reason others from the special counsel’s office will be here as well.
Trump will be in N.Y. court as Supreme Court arguments play out
The former president will be in court in New York as today's arguments play out before the Supreme Court.
Trump faces 34 counts of falsifying business records tied to hush money payments to adult film star Stormy Daniels. He has pleaded not guilty.
David Pecker is expected to return to the Manhattan courthouse for witness testimony today, and Judge Juan Merchan is expected at some point to issue a decision on whether the former president willfully violated a gag order.
NBC News legal analyst Joyce Vance joins "Meet the Press NOW" to discuss what to expect as the Supreme Court is set to hear arguments on former President Donald Trump’s presidential immunity claims.
How judges previously responded to Trump's immunity arguments
Trump's presidential immunity arguments have been winding through courts for months ahead of today's arguments — with discouraging results for the former president.
In December, Judge Tanya Chutkan dismissed two of Trump's motions to toss out the D.C. election interference case against him, ruling that presidents do not have absolute immunity. Trump's lawyers had argued in an October filing to Chutkan that he should be shielded by presidential immunity.
Similarly, a federal appeals court ruled in February against Trump's assertion that he is immune from prosecution.
“For the purpose of this criminal case, former President Trump has become citizen Trump, with all of the defenses of any other criminal defendant. But any executive immunity that may have protected him while he served as President no longer protects him against this prosecution,” the appeals court said in the ruling .
Supreme Court tackles Trump’s broad claim of presidential immunity in election interference case
WASHINGTON — Tackling an unprecedented and politically fraught issue, the Supreme Court on Thursday considers former President Donald Trump ’s assertion of total immunity from criminal charges over his attempt to overturn the 2020 election results.
The court will take on the novel legal question of whether a former president can be prosecuted for what Trump’s attorneys say were “official acts” taken in office, though much of the focus remains on whether the justices will rule quickly so a trial could take place before the November election .
The case puts considerable scrutiny on the court, which has a 6-3 conservative majority that includes three justices Trump appointed. The court already handed Trump an election-year boost when it ruled last month that Colorado could not kick him off the ballot .
Read the full story here
Supreme Court immunity case: Updates of oral arguments in Trump's fight for immunity
Lawyers for the former president argue trump can't be criminally charged for any action he took in office..
- Justice Department special counsel Jack Smith has charged Trump with conspiring to overturn his 2020 loss to Joe Biden.
- Trump is currently on trial in New York, charged with covering up hush money payments made to to porn star Stormy Daniels before the 2016 election.
- Trump is the first former president to face criminal trial.
Can presidents get away with murder?
Nine Supreme Court justices heard Donald Trump’s arguments today that yes, maybe they can.
The former president's lawyers say all presidents are immune from prosecution for anything they do in office – even murder, bribery, and corruption . The only way to hold one criminally accountable, Trump's attorneys will argue today, is if a president is first impeached in the House of Representatives and then convicted by two-thirds of the Senate.
Here are USA TODAY's live updates from Trump’s remarkable stand at the Supreme Court .
The case is submitted
The historic arguments wrapped up after more than two-and-a-half hours of debate with Trump’s attorney, John Sauer, forgoing his opportunity for a final rebuttal after the Justice Department made its case.
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
“I have nothing further,” Sauer said.
And with that, Chief Justice John Roberts declared that the case is submitted.
--Maureen Groppe
Jackson pushes for quick, narrow decision
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson appeared to be trying to convince her colleagues to decide the case quickly and narrowly.
If the court wanted to use the case to decide all the possible times when a president does or doesn’t have immunity, she asked the Justice Department, “is this the right vehicle to hammer out that test?”
“I don’t see any need in this case for the court to embark on that analysis,” Justice Department Michael Dreeben responded.
Barrett looks for way for Trump trial to proceed
Justice Amy Coney Barrett asks the Justice Department whether the government can get to trial faster by prosecuting only on the Trump acts that his lawyer agrees are private conduct so are not immune.
Michael Dreeben, the Justice Department attorney, said Trump’s official and private acts are part of an “integrated conspiracy.”
But he added that a trial could proceed by allowing the government to introduce anything considered an official act as information that has relevance even if not a crime itself.
Does presidential motive matter?
Justice Neil Gorsuch pressed the Justice Department on whether the court should consider the motive of a president when deciding whether a presidential act deserves immunity. Everything a president does can be seen through the prism of his interest in getting re-elected, he said.
Michael Dreeben, the Justice Department’s attorney, said motive doesn’t have to be considered for a core presidential act – such as a veto, or appointment – which is protected from prosecution.
“None is involved in this case,” Dreeben said.
Gorsuch said he’s not asking so much about Trump’s case but whether accusations about a president’s motives can be a future basis for prosecution.
“We’re writing a rule for the ages,” Gorsuch said.
Dreeben said wanting to get re-elected is not an illegal motive.
“And you don’t have to worry about prosecuting presidents for that,” he said.
Ham sandwiches, grand juries and solar eclipses: Alito has questions
Justice Samuel Alito asked Justice Department attorney Michael Dreeben if a former president should be left to the mercy of prosecutors, noting the old saying on the pliability of grand juries: That grand jurors would indict a ham sandwich if a prosecutor asked them to.
Alito asked Dreeben if he knew of a single case in which a federal prosecutor had asked a grand jury to indict a suspect “and the grand jury refused to do so.”
Drebeen said it had happened.
“Every once in a while there’s an eclipse too,” Alito replied. No prosecutor wants to indict without sufficient evidence, Drebeen said, because the case would end in an acquittal.
--Dan Morrison
More: What does 'SCOTUS' mean? Here's a brief rundown on the country's highest court.
Trump back in New York courtroom
As attorneys at the Supreme Court argued over a president’s ability to escape prosecution for official acts, Donald Trump returned to the Manhattan courtroom where he is on trial on charges he doctored business records to cover up a $130,000 hush money payment to adult film star Stormy Daniels. Trump entered the courtroom at 11:22 a.m. ET, taking a look at reporters in the audience as he walked past them to the defense table.
– Aysha Bagchi
Trump named unindicted co-conspirator in Arizona election case
Former President Donald Trump was named an unindicted co-conspirator in the Arizona fake elector case unsealed yesterday. The indictment charges 18 state Republicans and former Trump aides including former White House chief of staff Mark Meadows, former New York mayor Rudolph Giuliani and attorney John Eastman.
The defendants are charged with crimes including conspiracy and forgery for falsely claiming they were presidential electors and that Trump won the state in the 2020 election. Trump was identified as “unindicted coconspirator 1" in the indictment.
--Bart Jansen
All That Jazz: Demonstrators drum, clang, and sing their views of Trump
As justices and lawyers solemnly discussed the finer points of law inside the Supreme Court, the scene outside featured the clang of bells, the shrill of whistles, the throb of electric music, and the chants of demonstrators - most of them anti-Trump.
“The whole world is watching!” a crowd of demonstrators chanted at one point. A small brass band serenaded the crowd of three-to-four dozen with jazz-like tunes.
In addition to attacking Trump, the crowd also weighed in on other issues, particularly abortion rights and the campaign between Trump and President Joe Biden. “Feminists vs. Fascists,” said one sign.
The two sides exchanged a few f-bombs, but nothing serious broke out and the dozen or so police officers who watched the proceedings had little to do.
-- David Jackson
Roberts asks what protects against political prosecutions
Chief Justice John Roberts pressed on whether there are enough protections against retaliatory or harassing prosecutions for presidents.
Dreeben, the Justice Department’s lawyer, said politically driven prosecutions would violate the Constitution.
The chilling effect of prosecutions is one of Trump’s main arguments for why presidents should have immunity.
Who are the conservative Supreme Court justices?
There are six conservative-leaning justices, making up the majority of the Supreme Court bench : Chief Justice John Roberts, along with Justices Samuel Alito, Brett Kavanaugh, Neil Gorsuch, Amy Coney Barrett and Clarence Thomas.
Thomas is the longest serving of the group, nominated by former President George H. W. Bush in 1991. Former President George W. Bush nominated Roberts and Alito in 2005, while former President Donald Trump nominated Kavanaugh, Gorsuch and Barrett.
– Savannah Kuchar
More: Who are the current Supreme Court justices? Get to know the bench in 2024.
Thomas raises the 1961 Bay of Pigs invasion of Cuba
Apparently picking up on Justice Elena Kagan’s earlier questions touching on a military coup in the U.S., Justice Clarence Thomas asked why past presidents haven’t faced criminal charges for fomenting coups in foreign countries, using Operation Mongoose, the failed 1961 CIA attempt to overthrow Fidel Castro in Cuba, as an example.
“There were no prosecutions” after the so-called Bay of Pigs affair, Thomas said. (President John F. Kennedy, who ordered the operation, was assassinated before the end of his first term.)
Michael Dreeben, arguing for the Justice Department, replied that U.S. law has a “public authority defense” that protects a president from prosecution for overseas acts. The defense “would prevent it from being a violation of law.”
–Dan Morrison
Who are the liberal Supreme Court justices?
There are three liberal-leaning justices on the Supreme Court bench: Justices Sonya Sotomayor, Ketanji Brown Jackson and Elena Kagan.
Sotomayor and Kagan were nominees of former President Barack Obama, while Jackson was nominated by President Joe Biden in 2022, becoming the first Black woman to serve as a justice on the Supreme Court.
J ustice Department: `Such presidential immunity has no foundation in the Constitution’
Opening his argument for the Justice Department, Michael Dreeben said the Supreme Court has never recognized absolute criminal immunity for any public official.
But Trump, Dreeben said, is asking that presidents be protected from prosecution for bribery, treason, sedition, murder and for conspiring to use fraud to overturn an election.
“Such presidential immunity has no foundation in the Constitution,” Dreeben said. “The framers knew too well the danger of a king who could do no wrong.”
Immunity for official acts versus private
Although Trump’s lawyer concedes that presidents can be prosecuted for private acts, Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson pressed why that should be different for official acts.
“If there’s no threat to criminal prosecution, what prevents the president from doing whatever he wants?” she asked.
Sauer said the president is required to follow the law for his official acts. But the question is whether the punishment for not doing so is impeachment or criminal prosecution.
Jackson asked how Trump's argument didn't "risk turning the oval office into the center of criminality in this country."
--Maureen Groppe and Dan Morrison
How to watch today’s Supreme Court case live
Cameras are not allowed inside the nation’s highest court, so there is no televised coverage of today’s oral arguments.
But the justices and lawyers can be listened to live on USA TODAY’s broadcast or via C-SPAN.
Coup could be an official act, Trump lawyer says
Trump lawyer D. John Sauer, speaking in a notable rasp, found himself cornered by Justice Elena Kagan as she pushed him to draw a line between a president’s official and unofficial acts.
Kagan asked Sauer whether a president could officially order the military to stage a coup at the end of their term. “Is it an official act?”
“It could well be,” Sauer replied.
“It certainly sounds very bad,” Kagan said.
Sauer said the Constitution and the military’s code of justice prevents “that very extreme hypothetical.”
Can presidents self pardon?
Justice Neil Gorsuch raised the issue of whether presidents can pardon themselves.
“Happily,” Gorsuch said of that issue, “it’s never been presented to us.”
Sauer, Trump’s lawyers, said if the court agrees with him that presidents have absolute immunity, they will never have to decide if presidents can self pardon.
Should trial be further delayed for fact finding?
The Justice Department has urged the court not to delay the trial further even if the justices find presidents have immunity in some circumstances.
Justice Sonia Sotomayor appeared to side with that position, pressing Trump’s lawyer on why fact-finding questions about immunity in Trump’s particular case can’t be done at trial.
Sauer said it would be difficult to do that.
Sotomayor asks about fake electors
Justice Sonia Sotomayor asked Trump’s lawyer why he can claim that Trump’s actions were part of his official duties instead of being done for personal gain. Trump, she said, created a fraudulent list of presidential electors.
“Is that plausible that that would be within his right to do?” she asked.
Sauer, Trump’s lawyer, disputed Sotomayor’s characterization that Trump was doing anything fraudulent with the electors he was pushing.
“This was being done on an alternative basis,” Sauer said.
-- Maureen Groppe
Justice Alito stands up for Navy SEALs
Amid a blizzard of hypothetical questions over whether a president can order Navy SEALs to assassinate a rival, Justice Samuel Alito took a moment to stand up for the armed forces.
“I don’t want to slander SEAL Team Six,” Alito said. “They are honorable officers, bound by the military code of justice not to obey an illegal order.”
Sotomayor: 'Fundamentally evil' acts must be prosecuted
Challenging former President Donald Trump’s argument that a president is entitled to complete immunity, Justice Sonia Sotomayor said, “there are some things that are so fundamentally evil that they have to be protected against.”
“Immunity says even if you did it for personal gain,” Sotomayor told attorney D. John Sauer, president’s actions, including murder and bribery, ”cannot be prosecuted.”
-- Dan Morrison
Sotomayor brings up assassination of political rival
Justice Sonia Sotomayor goes right to a key issue that came up during the appeals court review: does a president have immunity if he orders the assassination of a political rival?
Sauer, Trump’s lawyer, said that depends on the situation, but it could well be an official act for which a president is immune.
Sotomayor said Trump wants the court to find that presidents are entitled to use the trappings of their office for total personal gain without facing criminal liability.
Kangaroo masks and revolutionary war hats
More than two dozen demonstrators organized by the group Women’s March protested Trump’s immunity claim, and criticized the Supreme Court for even considering the matter.
“We’re here to demand that they wrap this up,” said Amanda Chavez Barnes, senior program director for Women’s March, protesting that the court’s decision to take up the case delayed Trump’s trial on Jan. 6-related charges.
Some of the protesters wore kangaroo masks in order to mock the “Kangaroo Court.” They rang cowbells, banged on small drums, and chanted slogans like “lock him up!”
Just a few Trump supporters counter-demonstrated. Matthew Atwood, 62, a local DJ and classical pianist, mounted a sign describing other people as “the real authoritarians.” Wearing a Revolutionary War-style uniform, Atwood described himself as “pro-American.”
He also sought to engage the anti-Trump faction in debate, asking members of three crowd at one point, “are you better off now than you were three years ago?”
“Yes we are,” replied a Trump opponent.
Trump lawyer: Without immunity, `there can be no presidency as we know it.’
In his opening argument, Trump lawyer John Sauer told the justices presidents should be immune from prosecution because otherwise “there can be no presidency as we know it.”
No president has ever been prosecuted for their official acts, he said.
Without immunity, he continued, the threat of prosecution will “distort the president’s decision making.”
Every president will face defacto blackmail and distortion from his political rivals while he’s still in office, Sauer said.
Could Supreme Court presidential immunity arguments impact Trump's New York case?
Early this month, New York trial Judge Juan Merchan rejected an argument from Trump to delay Trump's New York criminal trial until after the Supreme Court rules on the scope of presidential immunity in Trump's federal election interference case. Merchan said Trump raised the immunity defense in his New York case too late.
If Trump is found guilty in the New York criminal trial, he could challenge Merchan's immunity ruling on appeal, and potentially point to a Supreme Court immunity ruling as a basis for re-trying the New York case.
Where is Donald Trump today?
Trump held a campaign event en route to the courthouse in New York, stopping at a nearby construction site to speak with supportive union members .
Reporters asked the former president about the Supreme Court’s immunity hearing, but his comments were drowned out by the cheers of his audience.
What are the charges against Trump?
Justice Department special counsel Jack Smith indicted Trump last August on four charges, to which he’s pleaded not guilty.
Trump is charged with conspiring to try to steal the 2020 election and remain in power by spreading lies about election fraud that fueled the Capitol attack on Jan. 6, 2021. Trump is also charged with obstructing Congress because the riot interrupted lawmakers counting Electoral College votes to certify that President Joe Biden won the election.
Protesting 'fake news' and tyranny
Outside the Supreme Court, protestors who traveled from Minnesota, Florida, and other states to register their support and concern about the historic Trump case.“Absolute Immunity = Absolute Tyranny,” reads the sign carried by Demitri Morgan, 38, who said he traveled from his home in Montana for the high court hearing.
Another hand-painted sign says “Loser.”
“Yo, fake news! What’s up with fake news?,” chanted Jim Whalen, 61, an ad salesman who said he came up from his home in West Palm Beach, Fla.-- David Jackson
Trump immunity argument ‘ridiculous’: Schumer
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., called former President Donald Trump’s immunity argument “ridiculous” and said the Supreme Court shouldn’t have agreed to hear the case.
“Today, SCOTUS hears Trump’s ridiculous claim of total immunity. He's obviously not immune,” Schumer wrote on X , formerly Twitter. “SCOTUS is only protecting Trump and slowing his trial. SCOTUS should not have taken this case or frozen the district court.”
What is presidential immunity?
The Supreme Court ruled in 1982 that presidents are immune both while in office and after from civil damages for official acts, including those on the “outer perimeter of a president’s official responsibilities.”
In 1997, the court said presidents can be sued for their private acts.
The court has also said presidents have no broad immunity from complying with subpoenas in criminal cases brought by states or the federal government.
The Justice Department has long argued that presidents can’t be criminally prosecuted while in office.
But the court has never weighed in on whether former presidents are immune from criminal prosecution.
What is Donald Trump trying to do with his Supreme Court immunity argument?
Donald Trump is trying to quash federal charges that he conspired to overturn the 2020 election after his bitter loss to President Joe Biden .
Without sweeping immunity, a president “will always be concerned, and even paralyzed, by the prospect of wrongful prosecution and retaliation after they leave office,” Trump wrote on Truth Social Sunday.
Is Donald Trump at the Supreme Court today?
The presumptive Republican nominee won’t be at the Supreme Court for today’s blockbuster arguments.
Trump is on trial in New York , charged with doctoring records to hide $130,000 in hush money paid to an adult film star . Trump also faces two other criminal indictments.
The judge in his New York trial told him he was required to be in court , which meant he was not able to attend his historic hearing.
Significance of being the first president to face criminal charges
What should the justices make of the fact that Donald Trump is the first president – former or current – to face criminal charges?
Trump’s lawyers say it’s evidence that presidents can’t be prosecuted.
“The long history of not prosecuting Presidents for official acts, despite ample motive and opportunity to do so over the years, demonstrates that the newly discovered alleged power to do so does not exist,” they wrote in their main brief previewing their oral argument.
Special counsel Jack Smith counters that the fact that no previous president has been prosecuted underscores the unprecedented nature of Trump’s alleged crimes.
Recent ruling: Supreme Court snubbed House Republicans who dodged metal detectors after Jan. 6
Justices Seem Ready to Limit the 2020 Election Case Against Trump
Such a ruling in the case, on whether the former president is immune from prosecution, would probably send it back to a lower court and could delay any trial until after the November election.
- Share full article

Charlie Savage and Alan Feuer
Charlie Savage reported from Washington, and Alan Feuer from New York.
Here are four takeaways from the Supreme Court hearing on Trump’s claim to immunity.
The Supreme Court heard arguments on Thursday about Donald J. Trump’s claim that the federal charges accusing him of plotting to overturn the 2020 election must be thrown out because he is immune from being prosecuted for any official act he took as president.
Here are some takeaways.
Several justices seemed to want to define some level of official act as immune.
Although Mr. Trump’s claim of near-absolute immunity was seen as a long shot intended primarily to slow the proceedings, several members of the Republican-appointed majority seemed to indicate that some immunity was needed. Some of them expressed worry about the long-term consequences of leaving future former presidents open to prosecution for their official actions.
Among others, Justice Brett Kavanaugh compared the threat of prosecution for official acts to how a series of presidents were “hampered” by independent counsel investigations, criticizing a 1984 ruling that upheld a now-defunct law creating such prosecutors as one of the Supreme Court’s biggest mistakes. Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. criticized an appeals court ruling rejecting immunity for Mr. Trump, saying he was concerned that it “did not get into a focused consideration of what acts we are talking about or what documents are talking about.”
“It’s a serious constitutional question whether a statute can be applied to the president’s official acts. So wouldn’t you always interpret the statute not to apply to the president, even under your formulation, unless Congress had spoken with some clarity?” “I don’t think across the board that as serious constitutional question exists on applying any criminal statute to the president.” “The problem is the vague statute — obstruction and 371, conspiracy to defraud the United States can be used against a lot of presidential activities historically with a creative prosecutor who wants to go after a president.” “I think that the question about the risk is very serious. And obviously it is a question that this court has to evaluate. For the executive branch, our view is that there is a balanced protection that better serves the interests of the Constitution that incorporates both accountability and protection for the president.”

The Democrat-appointed justices — Sonia Sotomayor, Elena Kagan and Ketanji Brown Jackson — asked questions indicating greater concern about opening the door for presidents to commit official crimes with impunity.
“This is what you’re asking us to say, which is that a president is entitled not to make a mistake — but more than that, a president is entitled for total personal gain to use the trappings of his office. That’s what you’re trying to get us to hold — without facing criminal liability.” “Your honor, I would say three things in response to that. First, the doctrine that immunity does not turn on the allegedly improper motivation or purpose is something that this court has reaffirmed in at least nine or 10 —” “That’s absolute immunity. But qualified immunity does say that whatever act you take has to be within what a reasonable person would do. I’m having a hard time thinking that creating false documents, that submitting false documents, that ordering the assassination of a rival, that accepting a bribe, and countless other laws that could be broken for personal gain, that anyone would say that it would be reasonable for a president or any public official to do that.”

The arguments signaled further delay and complications for a Trump trial.
If the Supreme Court does place limits on the ability of prosecutors to charge Mr. Trump over his official actions, it could alter the shape of his trial.
A decision to send all or part of the case back to the lower courts could further slow progress toward a trial, increasing the odds that it does not start before Election Day.
Of the matters listed in the indictment, some — like working with private lawyers to gin up slates of fraudulent electors — seem like the private actions of a candidate. Others — like pressuring the Justice Department and Vice President Mike Pence to do things — seem more like official acts he took in his role as president.
At one point, Justice Amy Coney Barrett suggested that prosecutors could simply drop Mr. Trump’s arguably official actions from their case and proceed to a swift trial focused only on his private actions. And D. John Sauer, the lawyer for Mr. Trump, told the court that no evidence of Mr. Trump’s official actions should be allowed into the trial.
But Michael R. Dreeben, a Justice Department lawyer arguing on behalf of the special counsel’s office, said the indictment laid out an “integrated conspiracy” in which Mr. Trump took the official actions to bolster the chances that his other efforts to overturn the election would succeed.
He argued that even if the court holds that Mr. Trump has immunity from liability for his official actions, prosecutors should still be allowed to present evidence about them to the jury because the actions are relevant to assessing his larger knowledge and intentions — just as speech that is protected by the First Amendment can still be used as evidence in a conspiracy case.
The hearing revolved around two very different ways of looking at the issue.
Looming over the hearing was a sweeping moral question: What effect might executive immunity have on the future of American politics?
Not surprisingly, the two sides saw things very differently.
Mr. Sauer claimed that without immunity, all presidents would be paralyzed by the knowledge that once they were out of office, they could face an onslaught of charges from their rivals based on the tough calls they had to make while in power. He pictured a dystopian world of ceaseless tit-for-tat political prosecutions that would destroy the “presidency as we know it.”
If a president can be charged, put on trial and imprisoned for his most controversial decisions as soon as he leaves office, that looming threat will distort the president’s decision-making precisely when bold and fearless action is most needed. Every current president will face de facto blackmail and extortion by his political rivals while he is still in office. The implications of the court’s decision here extend far beyond the facts of this case. Could President George W. Bush have been sent to prison for obstructing an official proceeding or allegedly lying to Congress to induce war in Iraq? Could President Obama be charged with murder for killing U.S. citizens abroad by drone strike? Could President Biden someday be charged with unlawfully inducing immigrants to enter the country illegally for his border policies? The answer to all these questions is no.

Envisioning the opposite scenario, Mr. Dreeben worried that any form of blanket immunity would place presidents entirely outside of the rule of law and encourage them to commit crimes, including “bribery, treason, sedition, even murder,” with impunity.
“The framers knew too well the dangers of a king who could do no wrong,” he said.
This court has never recognized absolute criminal immunity for any public official. Petitioner, however, claims that a former president has permanent criminal immunity for his official acts unless he was first impeached and convicted. His novel theory would immunize former presidents for criminal liability; for bribery, treason, sedition, murder and here, conspiring to use fraud to overturn the results of an election and perpetuate himself in power. Such presidential immunity has no foundation in the Constitution. The framers knew too well the dangers of a king who could do no wrong.

Both sides found advocates for their positions on the court.
Justice Samuel A. Alito Jr. clearly seemed worried that without some form of criminal immunity, former presidents would be vulnerable to partisan warfare as their successors used the courts to go after them once they were out of office. And that, he added, could lead to endless cycles of retribution that would be a risk to “stable, democratic society.”
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson appeared more concerned that if presidents were in fact shielded by immunity, they would be unbounded by the law and could turn the Oval Office into what she described as “the seat of criminality.”
If someone with those kinds of powers, the most powerful person in the world with the greatest amount of authority, could go into office knowing that there would be no potential penalty for committing crimes, I’m trying to understand what the disincentive is from turning the Oval Office into the seat of criminal activity in this country? If the potential for criminal liability is taken off the table, wouldn’t there be a significant risk that future presidents would be emboldened to commit crimes with abandon while they’re in office? It’s right now the fact that we’re having this debate, because O.L.C. has said that presidents might be prosecuted. Presidents from the beginning of time have understood that that’s a possibility. That might be what has kept this office from turning into the kind of crime center that I’m envisioning. But once we say no criminal liability, Mr. President, you can do whatever you want, I’m worried that we would have a worse problem than the problem of the president feeling constrained to follow the law while he’s in office.

What happens next?
There did not seem to be a lot of urgency among the justices — especially the conservative ones — to ensure that the immunity question was resolved quickly. That left open the possibility that Mr. Trump could avoid being tried on charges of plotting to overturn the last election until well after voters went to the polls to decide whether to choose him as president in this election.
And if he is elected, any trial could be put off while he is in office, or he could order the charges against him dropped.
It could take some time for the court to do its own analysis of what presidential acts should qualify for the protections of immunity. And even if the justices determine that at least some of the allegations against Mr. Trump are fair game for prosecution, if they do not issue a ruling until late June or early July, it could be difficult to hold a trial before November.
That would become all but impossible if the court took a different route and sent the analysis back to the trial judge, Tanya S. Chutkan. If Judge Chutkan were ordered to hold further hearings on which of the indictment’s numerous allegations were official acts of Mr. Trump’s presidency and which were private acts he took as a candidate for office, the process could take months and last well into 2025.
Aishvarya Kavi
Reporting from Washington
A spectacle outside the Supreme Court for Trump’s defenders and detractors.
Just as the Supreme Court began considering on Thursday morning whether former President Donald J. Trump was entitled to absolute immunity, rap music started blaring outside the court.
The lyrics, laced with expletives, denounced Mr. Trump, and several dozen demonstrators began chanting, “Trump is not above the law!”
Mr. Trump was not in Washington on Thursday morning — in fact, he was in another courtroom , in New York. But the spectacle that pierced the relative tranquillity outside the court was typical of events that involve him: demonstrations, homemade signs, police, news media, and lots and lots of curious onlookers.
One man, Stephen Parlato, a retired mental health counselor from Boulder, Colo., held a roughly 6-foot-long sign with a blown-up photo of Mr. Trump scowling that read, “Toxic loser.” The back of the sign featured the famous painting by Cassius Marcellus Coolidge of dogs playing poker, adorned with the words, “Faith erodes … in a court with no binding ethics code.” He made the sign at FedEx, he said.
The Supreme Court’s decision to even hear the case, which has delayed Mr. Trump’s election interference trial , was “absurd,” he said.
“I’m a child of the late ’60s and early ’70s and the Vietnam War,” said Mr. Parlato, dressed in a leather jacket and cowboy hat. “I remember protesting that while in high school. But this is very different. I’m here because I’m terrified of the possibility of a second Trump presidency.”
Inside the court, Jack Smith sat to the far right of the lawyer arguing on behalf of his team of prosecutors, Michael R. Dreeben, a leading expert in criminal law who has worked for another special counsel who investigated Mr. Trump, Robert S. Mueller III.
Among those in attendance were Jane Sullivan Roberts, who is married to Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr., and Ashley Estes Kavanaugh, who is married to Justice Brett M. Kavanaugh.
In an orderly line outside along the side of the court, people were calmly waiting to listen to the arguments from the court’s public gallery. More than 100 people, many of them supporters of Mr. Trump, were in line as of 8:30 a.m. Reagan Pendarvis, 19, who had been waiting there since the middle of the night, said the first person in line had gotten there more than a day before the arguments began.
Mr. Pendarvis, a sophomore at the University of California, San Diego who is living in Washington for the spring semester, was wearing a black suit and bright red bow tie. He said he had been struggling to keep warm since he took his place in line.
Mr. Pendarvis, a supporter of Mr. Trump, said he thought that the cases brought against the former president were an uneven application of the law.
“I think a lot of the cases, especially that happen for Donald Trump, don’t really happen for Democrats on the other side,” he said. “That’s just my take on it.”
David Bolls, 42, and his brother, Jonathan, 43, both of Springfield, Va., also in line for the arguments, also contended that the prosecutions against Mr. Trump were an abuse of judicial power.
“For me, I want to see an even application of justice,” David Bolls said.
For others in line, the Supreme Court’s deliberations were not the main draw. Ellen Murphy, a longtime Washington resident, was trying to sell buttons she designs, though she acknowledged that it was unlikely she would be allowed in with all of her merchandise.
Dozens of the buttons, which said, “Immunize democracy now” and “Trump is toast” over a toaster with two slices of bread, were pinned to a green apron she was wearing.
“We lose our democracy,” Ms. Murphy said, “if the president can do whatever he wants just because he’s president.”
Eileen Sullivan contributed reporting.
Advertisement
Adam Liptak
What’s next: Much will turn on how quickly the court acts.
The justices heard arguments in the immunity case at a special session, the day after what had been the last scheduled argument of its term. Arguments heard in late April almost always yield decisions near the end of the court’s term, in late June or early July.
But a ruling in early summer, even if it categorically rejected Mr. Trump’s position, would make it hard to complete his trial before the election. Should Mr. Trump win at the polls, there is every reason to think he would scuttle the prosecution.
In cases that directly affected elections — in which the mechanisms of voting were at issue — the court has sometimes acted with unusual speed.
In 2000, in Bush v. Gore, the court issued its decision handing the presidency to George W. Bush the day after the justices heard arguments.
In a recent case concerning Mr. Trump’s eligibility to appear on Colorado’s primary ballot, the justices moved more slowly, but still at a relatively brisk pace. The court granted Mr. Trump’s petition seeking review just two days after he filed it , scheduled arguments for about a month later and issued its decision in his favor about a month after that.
In United States v. Nixon, the 1974 decision that ordered President Richard M. Nixon to comply with a subpoena for audiotapes of conversations with aides in the White House, the court also moved quickly , granting the special prosecutor’s request to bypass the appeals court a week after it was filed.
The court heard arguments about five weeks later — compared with some eight weeks in Mr. Trump’s immunity case. It issued its decision 16 days after the argument , and the trial was not delayed.
Abbie VanSickle
The oral argument lasted nearly three hours, as the justices tangled with a lawyer for the former president and a Justice Department lawyer. A majority of the justices appeared skeptical of the idea of sweeping presidential immunity. However, several of them suggested an interest in drawing out what actions may be immune and what may not — a move that could delay the former president’s trial if the Supreme Court asks a lower court to revisit the issues.
Many of the justices seemed to be considering the idea that presidents should enjoy some form of protection against criminal prosecution. The devil, however, will be in the details: How should that protection extend?
And that question will have profound relevance not only for future presidents, but much more immediately for Donald Trump. The court could decide to draw those rules itself in a broad way for history. Or it could send this case back to a lower court to set the rules of what form immunity could take. If the case is sent back for further proceedings, it could have a dramatic effect on the timing of Trump’s trial, pushing it well past the election in November.
Looking back, one of the main points of discussion turned on the question of which situation would be worse: a world in which presidents, shorn of any legal protections against prosecution, were ceaselessly pursued in the courts by their rivals in a never-ending cycle of political retribution, or allowing presidents to be unbounded by criminal law and permitted to do whatever they wanted with impunity.
Charlie Savage
Sauer, Trump’s attorney, declines to offer a rebuttal. The argument is over.
If the court finds that there is some immunity for official actions, one of the most important questions will be whether prosecutors can still present evidence to the jury of Trump’s official actions (like pressuring the Justice Department and Vice President Mike Pence to do certain things) as evidence that helps illuminate Trump’s knowledge and intent for his private acts as a candidate. Dreeben says the jury needs to understand the whole “integrated conspiracy” but prosecutors would accept a jury instruction in which the judge would say they cannot impose liability for the official actions but may consider them as evidence of his knowledge and intent for the other actions. That’s how courts handle protected speech that is evidence to a larger conspiracy, he notes.
Justice Barrett picks up the question of timing again. She suggests that if prosecutors want to take Trump quickly to trial, they could simply drop those parts of the indictment that seem to be his official acts as president and proceed with only those parts of the indictment that reflect Trump’s private actions taken as a candidate for office. Dreeben is not wild about that idea.
Dreeben suggests that allegations in the “private acts bucket,” as Justice Jackson just called it, would include things like the scheme to create fake electors and the way in which Trump fomented a mob of his supporters to violently attack the Capitol on Jan. 6.
Justice Barrett seems to signal that she is less likely to find that presidents have blanket immunity for their official acts. When Dreeben says the system needs to balance the effective functioning of the presidency and accountability for a former president under the rule of law, and the existing system does that pretty well or maybe needs a few ancillary rules but that is different from the “radical proposal” put forward by Trump’s legal team, she says: “I agree.”
Dreeben, in a balancing act that seems to acknowledge that the court is looking for some form of criminal immunity for presidents, says he is trying to do two things at once, neither of them easy. He wants to design a system to find some rules that preserve the “effective functioning of the presidency” but that still allows for “accountability” if presidents violated the law.
Kavanaugh asks Dreeben about Obama’s drone strike that killed an American citizen suspected of terrorism, Anwar al-Awlaki, which Trump’s lawyer invoked in his opening. Dreeben notes that the Office of Legal Counsel analyzed the question and found that the murder statute did not apply to presidents when they were acting under public authority, so authorizing the strike was lawful. This is the way the system can function, he said — the Justice Department analyzes laws carefully and with established principles.
Justice Kavanaugh signals that he is likely to find that presidents must have immunity for their official actions. He talks about how the threat of prosecution by independent counsels (under a law that lapsed in 1999) hampered Presidents Reagan, George H.W. Bush and Clinton, and says a 1984 ruling upholding that structure as constitutional was one of the Supreme Court’s biggest mistakes. (Notably, Kavanaugh was a prosecutor on the staff of independent counsel Ken Starr during his investigation into President Bill Clinton, before becoming a White House lawyer under President George W. Bush.)
Dreeben tries to push back on Kavanaugh’s argument by saying that even after Watergate, even after all of the independent counsel investigations mentioned above, the legal system has survived without “having gone off on a runaway train” of actual criminal prosecutions against former presidents.
The Supreme Court rejected Bill Clinton’s claim of immunity.
In Clinton v. Jones in 1997, the Supreme Court unanimously allowed a sexual harassment suit against President Bill Clinton to proceed while he was in office, discounting concerns that it would distract him from his official responsibilities. Both of his appointees, Justices Ruth Bader Ginsburg and Stephen G. Breyer, voted against him.
“The president is subject to judicial process in appropriate circumstances,” Justice John Paul Stevens wrote for the court, adding, “We have never suggested that the president, or any other official, has an immunity that extends beyond the scope of any action taken in an official capacity.”
The case was in one sense harder than the one against Mr. Trump, as it involved a sitting president. In another sense, though, it was easier, as it concerned an episode said to have taken place before Mr. Clinton took office (Paula Jones, an Arkansas state employee, said Mr. Clinton had made lewd advances in a hotel room when he was governor of the state).
The case is best remembered for a prediction in Justice Stevens’s majority opinion that “it appears to us highly unlikely to occupy any substantial amount of petitioner’s time.” In fact, it led to Mr. Clinton’s impeachment.
In the same paragraph, Justice Stevens made a second prediction.
“In the more than 200-year history of the Republic, only three sitting presidents have been subjected to suits for their private actions,” he wrote. “If the past is any indicator, it seems unlikely that a deluge of such litigation will ever engulf the presidency.”
Suits against Presidents Theodore Roosevelt and Harry S. Truman were dismissed, and one against President John F. Kennedy involving a car accident during his 1960 campaign was settled. The case against Mr. Clinton added a fourth.
Justice Stevens, who died in 2019, failed to anticipate the enormous volume of civil and criminal litigation in which Mr. Trump and his businesses have been named as defendants.
We are now over the two-hour mark of the Supreme Court’s arguments in the Trump immunity case. The Justice Department lawyer has continued to face skeptical questions from many of the court’s conservatives, several of whom appear particularly focused on how to draw the line between a president’s core powers and non-core powers. In other words, what actions by a president might be shielded from prosecution and what would not. The questioning suggests that some of the justices may favor a ruling that could lead to more lower-court proceedings, perhaps delaying the trial.
The Supreme Court’s relatively new process (coming out of Covid) of letting each justice ask questions at the end in order of seniority has an interesting consequence, as seen here. Dreeben kept wanting to say these things about government legal memos and to go into the details about the actions Trump is accused of taking, but the Republican-appointed justices kept cutting him off. It’s the turn of Kagan, a Democratic appointee, to ask any final questions she wants, and she is letting him talk on and on.
Much of the discussion this morning has swirled around the question of whether, without immunity, presidents will be hounded by their rivals with malicious charges after leaving office. Alito and other conservatives on the court seem concerned that the Trump prosecutions will open the door to endless attacks against future presidents.
The other main topic of discussion has been whether presidents enjoy some form of immunity for carrying out their official duties and, if so, how those official actions are defined. That’s an important question for the Trump election case because Trump has claimed he was acting in his role as president when, by his own account, he sought to root out fraud in the 2020 vote count. It’s also important for a different reason: the justices could send the official acts question back to a lower court to sort out, and that process could take a long time, delaying the case's trial until after this year’s election.
Justice Alito suggests that there is a risk to our stable democracy if presidents who lose close elections would not be allowed to retire in peace but could face prosecution. He has essentially flipped the situation under consideration upside down: that Trump is being prosecuted for having used fraud to remain in power after losing a close election.
A part of this exchange between Justice Alito and the Justice Department's lawyer, Dreeben, gets at a pressure point in American-style democracy and the rule of law. One of the safeguards against illegitimate prosecutions of ex-presidents, Dreeben says, is that if the Justice Department has advised the president that doing something would be lawful, the department could not later turn around and prosecute the now-former president for relying on that advice and doing that thing.
Alito points out that this creates an incentive for presidents to appoint attorneys general who will just tell them that anything they want to do would be legal. Indeed — that is a critique of the Office of Legal Counsel system, in which politically appointed lawyers decide what the law means for the executive branch.
An example: During the George W. Bush administration, memos about post-9/11 surveillance and torture were written by a politically appointed lawyer with idiosyncratically broad views of a president’s supposed power, as commander in chief, to authorize violations of surveillance and torture laws. The Justice Department later withdrew those memos as espousing a false view of the law, but held that officials who had taken action based on those memos could not be charged with crimes.
Justice Alito suggests there are not enough legal safeguards in place to protect presidents against malicious prosecution if they don’t have some form of immunity. He tells Dreeben that the grand jury process isn’t much of a protection because prosecutors, as the saying goes, can indict a ham sandwich. When Dreeben tries to argue that prosecutors sometimes don’t indict people who don’t deserve it, Alito dismissively says, “Every once in a while there’s an eclipse too.”
If you are just joining in, the justices are questioning the Justice Department lawyer, Michael Dreeben, about the government’s argument that former President Trump is not absolutely immune from prosecution on charges that he plotted to subvert the 2020 election. Dreeben has faced skeptical questions from several of the conservative justices, including both Justices Alito and Kavanaugh, who have suggested that the fraud conspiracy statute being used against the former president is vague. That statute is central to the government’s case against Trump.
Justice Alito now joins Justice Kavanaugh in suggesting that the fraud conspiracy statute is very vague and broadly drawn. That is bad news for the indictment brought against Trump by Jack Smith, the special counsel.
The scope and viability of this fraud statute, which is absolutely central to the Trump indictment, wasn’t on the menu of issues seemingly at play in this hearing. Kavanaugh and Alito appear to have gone out of their way to question its use in the Trump case.
Justice Sotomayor points out that under the Trump team’s theory that a criminal statute has to clearly state that it applies to the presidency for it to cover a president’s official actions, there would essentially be no accountability at all. Because only a tiny handful of laws mention the president, that means a president could act contrary to them without violating them. As a result, the Senate could not even impeach a president for violating criminal statutes, she says — because he would not be violating those laws if they don’t apply to the president.
Dreeben is under heavy fire from the court’s conservatives.
The precedent most helpful to Trump: Nixon v. Fitzgerald.
In 1982, in Nixon v. Fitzgerald , the Supreme Court ruled that former President Richard M. Nixon had absolute immunity from civil lawsuits — ones brought by private litigants seeking money — for conduct “within the ‘outer perimeter’ of his official responsibility.”
The ruling is helpful to former President Donald J. Trump, establishing as it does that immunity can be expansive, lives on after a president leaves office and extends to the very limits of what may be said to be official conduct.
But the decision also falls well short of dictating the outcome in the case that is being argued on Thursday, which concerns a criminal prosecution, not a civil suit.
The 1982 case arose from a lawsuit brought by an Air Force analyst, A. Ernest Fitzgerald, who said he was fired in 1970 in retaliation for his criticism of cost overruns. By the time the Supreme Court acted, Nixon had been out of office for several years.
“In view of the special nature of the president’s constitutional office and functions,” Justice Lewis F. Powell Jr. wrote for the majority 5-to-4 decision, “we think it appropriate to recognize absolute presidential immunity from damages liability” for Nixon’s official conduct, broadly defined.
But the decision drew a sharp line between civil suits, which it said can be abusive and harassing, and criminal prosecutions like the one Mr. Trump is facing.
“In view of the visibility of his office and the effect of his actions on countless people, the president would be an easily identifiable target for suits for civil damages,” Justice Powell wrote, adding, “The court has recognized before that there is a lesser public interest in actions for civil damages than, for example, in criminal prosecutions.”
Chief Justice Warren E. Burger underscored the point in a concurring opinion. “The immunity is limited to civil damages claims,” he wrote.
Even in the context of civil suits, Nixon v. Fitzgerald conferred immunity only on conduct within the “outer perimeter” of a president’s official duties. Jack Smith, the special counsel, has said that Mr. Trump’s efforts to subvert democracy are well outside that line.
The Justice Department has already granted sitting presidents immunity while they are in office.
Former President Donald J. Trump’s claim that former presidents must enjoy “complete immunity” from prosecution for any crimes they committed in office would significantly expand the temporary immunity that sitting presidents already have.
Nothing in the Constitution or federal statutes says that presidents are shielded from being prosecuted while in office, and no court has ever ruled that way. But political appointees in the Justice Department’s Office of Legal Counsel, whose interpretations are binding on the executive branch, have declared that the Constitution implicitly establishes such immunity.
This argument boils down to practicalities of governance: The stigma of being indicted and the burden of a trial would unduly interfere with a president’s ability to carry out his duties, Robert G. Dixon Jr. , then the head of the Justice Department’s Office of Legal Counsel, wrote in a memo in September 1973 . This would prevent the executive branch “from accomplishing its constitutional functions” in a way that cannot “be justified by an overriding need,” he added.
Mr. Dixon, an appointee of President Richard M. Nixon, wrote his memo against the backdrop of the Watergate scandal, when Mr. Nixon faced a criminal investigation by a special counsel, Archibald Cox. The next month, Nixon’s solicitor general, Robert H. Bork , in a court brief , similarly argued for an “inference” that the Constitution makes sitting presidents immune from indictment and trial.
(That same month, Mr. Nixon had Mr. Cox fired in the so-called Saturday Night Massacre. Mr. Nixon’s attorney general and deputy attorney general resigned rather than carry out his orders to oust the prosecutor; Mr. Nixon then turned to Mr. Bork, the department’s No. 3, who proved willing to do it. Amid a political backlash, Mr. Nixon was forced to allow a new special counsel, Leon Jaworski , to resume the investigation.)
The question arose again a generation later, when President Bill Clinton faced an investigation by Kenneth Starr, an independent counsel, into the Whitewater land deal that morphed into an inquiry into his affair with Monica Lewinsky, a White House intern. Randolph D. Moss , Mr. Clinton’s appointee to lead the Office of Legal Counsel, reviewed the Justice Department’s 1973 opinions and reaffirmed their conclusions .
Legal scholars, as well as staff for prosecutors investigating presidents, have disputed the legitimacy of that constitutional theory. In 1974, Mr. Jaworski received a memo from his staff saying he could, in fact, indict Mr. Nixon while he was in office, and he later made that case in a court brief .
And in a 56-page memo in 1998, Ronald Rotunda, a prominent conservative constitutional scholar whom Mr. Starr hired as a consultant on his legal team, rejected the view that presidents are immune from prosecution while in office. Mr. Starr later said that he had concluded that he could indict Mr. Clinton.
“It is proper, constitutional, and legal for a federal grand jury to indict a sitting president for serious criminal acts that are not part of, and are contrary to, the president’s official duties,” Mr. Rotunda wrote. “In this country, no one, even President Clinton, is above the law.”
Mr. Starr commissioned the Rotunda memo as he was drafting a potential indictment of Mr. Clinton, and Mr. Starr decided that he could charge the president while in office. In the end, however, both Mr. Jaworski and Mr. Starr decided to let congressional impeachment proceedings play out and did not try to bring indictments while Mr. Nixon and Mr. Clinton remained in office.
The question may never be definitively tested in the courts. In 1999, Congress allowed a law that created independent counsels like Mr. Starr — prosecutors who do not report to the attorney general — to expire, and the Justice Department issued regulations to allow for the appointment of semiautonomous special counsels for inquiries into potential high-level wrongdoing in the executive branch.
Special counsels are, however, bound by Justice Departments policies and practices — including the Office of Legal Counsel’s proclamation that sitting presidents are temporarily immune from criminal indictment or trial.
Alan Feuer and Charlie Savage
Is there such a thing as executive immunity?
There are no direct precedents on the broad question of whether presidents have criminal immunity for their official actions.
The Supreme Court has held that presidents are absolutely immune from civil lawsuits related to their official acts , in part to protect them against ceaseless harassment and judicial scrutiny of their day-to-day decisions. The court has also held that presidents can be sued over their personal actions .
The Supreme Court has further found that while presidents are sometimes immune from judicial subpoenas requesting internal executive branch information, that privilege is not absolute. Even presidents, the court has decided, can be forced to obey a subpoena in a criminal case if the need for information is great enough.
But until Mr. Trump wound up in court, the Supreme Court has never had a reason to decide whether former presidents are protected from being prosecuted for official actions. The Justice Department has long maintained that sitting presidents are temporarily immune from prosecution because criminal charges would distract them from their constitutional functions. But since Mr. Trump is not in office, that is not an issue.
The closest the country has come to the prosecution of a former president over official actions came in 1974, when Richard M. Nixon resigned to avoid being impeached over the Watergate scandal. But a pardon by his successor, President Gerald R. Ford, protected Nixon from indictment by the Watergate special prosecutor.
Mr. Smith’s team has argued that Ford’s pardon — and Nixon’s acceptance of it — demonstrates that both men understood that Nixon was not already immune. Mr. Trump’s team has sought to counter that point by arguing — inaccurately — that Nixon faced potential criminal charges only over private actions, like tax fraud. But the special prosecutor weighed charging Nixon with abusing his office to obstruct justice.
Mr. Trump’s team has argued that denying his claims risks unleashing a routine practice of prosecuting former presidents for partisan reasons. But Mr. Smith’s team has argued that if courts endorse Mr. Trump’s theory, then future presidents who are confident of surviving impeachment could, with impunity, commit any number of crimes in connection with their official actions.
“Such a result would severely undermine the compelling public interest in the rule of law and criminal accountability,” prosecutors wrote.
Hypothetical questions test the limits of Trump’s immunity claim.
An exchange during an appeals court argument in January about a hypothetical political assassination tested former President Donald J. Trump’s claim that he is absolutely immune from prosecution for his official conduct.
His lawyer, D. John Sauer, has urged the justices to consider only what he is actually accused of: plotting to subvert the 2020 election. But hypothetical questions are routine at the Supreme Court, and they have a way of illuminating the contours and implications of legal theories.
That is what happened in January, when Judge Florence Y. Pan of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia had to press Mr. Sauer to get an answer to a hypothetical question: Are former presidents absolutely immune from prosecution, even for murders they ordered while in office?
“I asked you a yes-or-no question,” Judge Pan said. “Could a president who ordered SEAL Team 6 to assassinate a political rival, who was not impeached, would he be subject to criminal prosecution?”
Mr. Sauer said his answer was a “qualified yes,” by which he meant no. He explained that prosecution would be permitted only if the president were first impeached by the House and convicted by the Senate.
Impeachments of presidents are rare: There have been four in the history of the Republic, two of them of Mr. Trump. The number of convictions, which require a two-thirds majority of the Senate: zero.
Mr. Sauer’s statement called to mind a 2019 federal appeals court argument over whether Mr. Trump could block state prosecutors from obtaining his tax and business records. He maintained that he was immune not only from prosecution but also from criminal investigation so long as he was president.
At that time, Judge Denny Chin of the Second Circuit pressed William S. Consovoy, a lawyer for Mr. Trump, asking about his client’s famous statement that he could shoot someone on Fifth Avenue without losing political support.
“Local authorities couldn’t investigate?” Judge Chin asked, adding: “Nothing could be done? That’s your position?”
“That is correct,” said Mr. Consovoy. “That is correct.”
This headline followed: “If Trump Shoots Someone on 5th Ave., Does He Have Immunity? His Lawyer Says Yes.”
For his part, Mr. Sauer does not seem eager to revisit the question about assassinations. Indeed, in asking the Supreme Court to hear Mr. Trump’s appeal, Mr. Sauer urged the justices not to be distracted by “lurid hypotheticals” that “almost certainly never will occur.”
What counts as an official act as president?
Another issue that has come up in lower courts in this case was what counted as an official act for a president, as opposed to a private action that was not connected to his constitutional responsibilities.
If the justices want to dispose of the dispute without definitively ruling on whether presidents are immune from prosecution for official acts, they could do so by finding that the specific steps former President Donald J. Trump took to remain in office that are cited in the federal indictment were not official actions. If so, the broader immunity question would not matter, and the prosecution could proceed.
The acts by Mr. Trump cited in the indictment include using deceit to organize fake slates of electors and to try to get state officials to subvert legitimate election results; trying to get the Justice Department and Vice President Mike Pence to help fraudulently alter the results; directing his supporters to the Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021; and exploiting the violence and chaos of their ensuing riot.
In its court filings, Mr. Trump’s team has sought to reframe those accusations not only as official actions, but innocuous or even admirable ones.
“All five types of conduct alleged in the indictment constitute official acts,” they wrote. “They all reflect President Trump’s efforts and duties, squarely as chief executive of the United States, to advocate for and defend the integrity of the federal election, in accord with his view that it was tainted by fraud and irregularity.”
Mr. Smith’s team has argued that they should be seen as the efforts of a person seeking office, not of an officeholder carrying out government responsibilities.
“Those alleged acts were carried out by and on behalf of the defendant in his capacity as a candidate, and the extensive involvement of private attorneys and campaign staff in procuring the fraudulent slates as alleged in the indictment underscores that those activities were not within the outer perimeter of the office of the presidency,” they wrote.
Judge Tanya S. Chutkan, who is overseeing Mr. Trump’s case in Federal District Court in Washington, issued her ruling rejecting Mr. Trump’s immunity claim without including any detailed analysis of whether his acts were “official.”
If the Supreme Court were to send the matter back to her to take a stab at answering that question before restarting the appeals process, Mr. Trump will, at a minimum, have used up additional valuable time that could help push any trial past the election.
Noah Weiland and Alan Feuer
Here are the lawyers arguing before the Supreme Court.
The two lawyers arguing before the Supreme Court on Thursday have each played a role in some of the defining legal battles stemming from Mr. Trump’s term in office.
Arguing the case for the special counsel Jack Smith will be Michael Dreeben, who worked for a different special counsel’s office that scrutinized Mr. Trump’s presidency: Robert S. Mueller III’s investigation into links between Russia and associates of Mr. Trump. Mr. Dreeben, one of the nation’s leading criminal law experts, has made more than 100 oral arguments before the Supreme Court, including when he served as deputy solicitor general.
On Mr. Mueller’s team, he handled pretrial litigation, defending the scope of the investigation and preventing the office from losing cases on appeal. He also helped with a second part of Mr. Mueller’s investigation, examining whether Mr. Trump had tried to obstruct the inquiry in his dealings with associates involved in the case.
Mr. Dreeben, who was heavily involved in the writing of Mr. Mueller’s final report on his investigation, supported an interpretation of presidential power that emphasized limits on what a president could do while exercising his or her powers, according to “Where Law Ends,” a book written by Andrew Weissmann, another prosecutor on Mr. Mueller’s team.
After Mr. Mueller’s investigation concluded, Mr. Dreeben took a teaching position at Georgetown University’s law school and returned to private practice at O’Melveny, arguing in front of the Supreme Court on behalf of the city of Austin over a First Amendment dispute about the placement of digital billboards.
Opposing Mr. Dreeben in front of the Supreme Court will be D. John Sauer, a lawyer based in St. Louis who once served as the solicitor general of Missouri. Mr. Sauer joined Mr. Trump’s legal team late last year to handle appellate matters, including his challenge to a gag order imposed on him in the election case in Washington.
As Missouri’s solicitor general, Mr. Sauer took part in a last-ditch effort to keep Mr. Trump in power after his defeat in the 2020 election, filing a motion on behalf of his state and five others in support of an attempt by Texas to have the Supreme Court toss out the results of the vote count in several key swing states.
He also joined in an unsuccessful bid with Texas in asking the Supreme Court to stop the Biden administration from rescinding a Trump-era immigration program that forces certain asylum seekers arriving at the southwestern border to await approval in Mexico.
When he left the solicitor general’s office last January, Mr. Sauer, who once clerked for Justice Antonin Scalia, returned to his private firm, the James Otis Law Group. The firm is named after a prominent Revolutionary War-era lawyer who built a career out of challenging abuses by British colonial forces.
To justify his defense in the immunity case, Trump turns to a familiar tactic.
When the Supreme Court considers Donald J. Trump’s sweeping claims of executive immunity on Thursday, it will break new legal ground, mulling for the first time the question of whether a former president can avoid being prosecuted for things he did in office.
But in coming up with the argument, Mr. Trump used a tactic on which he has often leaned in his life as a businessman and politician: He flipped the facts on their head in an effort to create a different reality.
At the core of his immunity defense is a claim that seeks to upend the story told by federal prosecutors in an indictment charging him with plotting to overturn the 2020 election. In that indictment, prosecutors described a criminal conspiracy by Mr. Trump to subvert the election results and stay in power.
In Mr. Trump’s telling, however, those same events are official acts that he undertook as president to safeguard the integrity of the race and cannot be subject to prosecution.
In many ways, Mr. Trump’s immunity claim is breathtaking. In one instance, his lawyers went so far as to say that a president could not be prosecuted even for using the military to assassinate a rival unless he was first impeached.
But the wholesale rewriting of the government’s accusations — which first appeared six months ago in Mr. Trump’s motion to dismiss the election interference case — may be the most audacious part of his defense. It was certainly a requisite step his lawyers had to take to advance the immunity argument.
Other courts have ruled that presidents enjoy limited immunity from civil lawsuits for things they did as part of the formal responsibilities of their job. To extend that legal concept to criminal charges, Mr. Trump’s lawyers needed to reframe all of the allegations lodged against him in the election interference case as official acts of his presidency rather than as the actions of a candidate misusing his power.

Title: Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Discusses International Conflict, Defense and Leadership on the Hilltop
On Thursday April 25, 2024 Georgetown students gathered in the Healey Family Student Center Social Room to hear from General Charles Q. Brown, Jr., Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff about the role of the U.S. military in U.S. politics and the world. As the most senior-ranking military officer in the U.S. and military advisor to the President , General Brown shared his experiences as a military leader and students had the opportunity to ask questions.
Vilda Westh Blanc (SFS‘27), a student who was on Dan Lamothe’s Student Strategy Team this semester, introduced the event. She welcomed Brown to the stage as well as current GU Politics Fellow Dan Lamothe to moderate the conversation.
Lamothe started the conversation by asking Brown about the current state of U.S. military operations and the threats to national security. “What makes this time uniquely dangerous, uniquely challenging?” Lamothe asked.
Brown emphasized the complex dynamics of this moment for U.S. national security, noting the significance of threats from North Korea, China, Russia and Iran. He explained that before coming to his current position he championed the phrase “Accelerate change or lose.”
“Personally and professionally, I do not play for second place. And I am very focused on ensuring we have all the capabilities to ensure our national security,” Brown said.
Outlining his priorities for the U.S. military, Brown highlighted the importance of training skilled service members, embracing the modernization of capabilities, and creating a foundation of trust with communities and elected officials.
On the importance of maintaining trust with American people, Brown said “Having that trust is hugely important to ensure that we do the things the nation calls us to do as military members.”
Next, Lamothe asked Brown how the Israel-Hamas conflict shapes the priorities of the U.S. military.
On the tension between current crises and future threats, Brown said “You’ve got to balance risk over time.”
“You never want to take short-term satisfaction at the expense of your long-term goals,” Brown said.
Continuing to discuss the conflict in the Middle East, Lamothe asked Brown about what it takes to deal with such a volatile situation and what strategies the military is utilizing to keep the conflict contained.
“From the very beginning, we looked at how do we deter a future conflict and at the same time protect our armed forces and support Israel to defend itself,” Brown said. “In addition to that is making sure we were providing humanitarian assistance and minimizing collateral damage.”
“This has been a theme throughout: how do we deter a broader conflict,” Brown said. Brown further emphasized the military’s preparedness, the efforts of the U.S. National Security Council, and the role of other foreign nations.
Lamothe then asked about what initial concerns Brown had regarding Iran’s attack on Israel on April 13th.
“First thing I’ll tell you is that I didn’t have a lot of concern because I have complete confidence in our force and they were well-prepared,” Brown said. He emphasized the work of the U.S. military in the week leading up to the April 13th attack and explained the communication and collaboration between the Pentagon and White House that happened the day of.
Turning to the topic of Ukraine, Lamothe noted that despite the recent aid package approved by the U.S. Congress, many think that “Ukraine will continue to be outgunned this year. What do you see as the likely outcome this summer?”
“When Ukraine is supplied, they have been able to be effective,” Brown said, stressing the importance of continuing to provide support.
“Even broader than this: what happens in one corner of the world does not stay in one corner of the world,” Brown added. “Unchecked aggression provides opportunity for future aggression.”
Next, Lamothe asked about building trust in the U.S. military. “We’re in a time where there is dwindling support for the U.S. military in a lot of polls. There are concerns about American democracy at large. What does it take to build new faith in the American military?” Lamothe asked.
“Trust is the foundation of our profession. And part of that, my focus, is not only maintaining the trust we have but to continue to build upon it.” Brown added, “I think the most important thing I can do is lead by example.”
Brown also emphasized the importance of being non-partisan as a military member. “Our oath is to the Constitution of the United States, to an ideal— not to a leader, not to an office,” Brown said.
Students then had the opportunity to ask Brown questions.
Captain Trevor Barton, Omar Bradley Fellow and McCourt Student studying national security issues asked: “What is your assessment, as the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs, of the current health of the defense industrial base related to our production capability, and what can policymakers do to increase the resiliency of the defense industrial base?”
“There’s key things, from a policymaker standpoint, that I think are very important. Consistency is probably top of the notch,” Brown said. “What I mean by that is that there’s consistency in our demand signal from the Department of Defense in what we need. And then consistency in resourcing. When you have that consistency, that helps predictability for the defense industrial base.”
MJ Ninal (C’24), a cadet in the Air Force ROTC , asked Brown about his advice for young lieutenants in this unique time of international threats and political polarization.
“Whatever job you’re going into, get really good at it. That’s probably the most important thing you can do. I’d also say ask a lot of questions. There are no dumb questions,” Brown said. “And when you ask tough questions of your leaders, it challenges us.”
One student asked Brown about the challenges of advising political leaders and what his advice was for fostering mutual understanding of perspectives and positions.
“When providing advice, you need to understand your boss, and your boss’s boss, and their intent and what their focused on,” Brown said. He emphasized that the perfect military solution does not always line up with what is going on geopolitically, economically and diplomatically, but understanding the bigger picture is key to effective conversations and problem-solving.
Lewis Williams III (S’28), a student studying applied intelligence at Georgetown’s School of Continuing Studies asked Brown, “What are some of your role models or individuals that have inspired you, whether civilian or military?”
Brown talked about the influence of his father, who was in the Army and encouraged Brown to apply. “This is all his idea,” Brown said.
“I think the other thing that has been an inspiration to me has been the Tuskegee Airmen,” Brown said, referring to the first African American military aviators in the U.S. “Just in general, what they were able to do leading up to World War II and during World War II.”
Brown recounted his experience getting to talk to some of the Tuskegee Airmen and hear their stories. He remembered Brigadier General Charles McGee and reflected on the honor it was to meet him.
Brown also answered student questions about cybersecurity, use of innovative technologies in Ukraine, climate change as a national security threat, and promoting cooperation between branches of the U.S. military.
Luke Hughes (SFS‘27) asked Brown what his message would be to incoming Georgetown students who are considering joining the ROTC.
On reasons to join, “I would say two things: One, the opportunity to serve your nation but the opportunity to gain some valuable experience,” Brown noted.
Brown emphasized the opportunities for growing as a leader, building meaningful relationships, and giving back to your community through involvement in the military.
“We need you, whether you serve in uniform or you serve in some other part of government, that’s what makes our democracy so strong,” Brown said.
GU Politics extends its gratitude to the Walsh School of Foreign Service , the SFS Security Studies Program , the Georgetown University Military and Veterans Resource Center and the National Defense Policy Initiative for co-sponsoring this event.
This article was written by Jane Wright , a first-year graduate student in the McCourt School of Public Policy.
Watch the full recording below.

The Hoya: Panelists Discuss Ranked-Choice Voting and Polarization With GU Politics
Panelists argued ranked-choice voting produces more democratic elections and decreases polarization and apathy in a Georgetown University Institute of Politics and Public Service (GU Politics) event April 17.

Maxwell Frost Discusses Advocacy, Activism and Running for Office at Georgetown
On Wednesday, April 10, 2024 students gathered in the ICC Auditorium to hear from U.S. Representative Maxwell Frost (D-FL) about his experience as an organizer and elected official,…

Boris Johnson Talks Democracy Around World at Gaston Hall
On Thursday April, 11 Georgetown students filled Gaston Hall to hear former Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Boris Johnson have a conversation about global politics and democracy…

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
So, observe yourself in the mirror and pay attention to movements you make. 9. Give Mock Presentation. Giving a trial defense in advance is a good practice. The most important factor for the mock defense is its similarity to your real defense, so that you get the experience that prepares for the actual defense. 10.
The PhD defence, also known as the viva voce or oral examination, is a pivotal moment in the life of a doctoral candidate. PhD defence is not merely a ritualistic ceremony; rather, it serves as a platform for scholars to present, defend, and elucidate the findings and implications of their research. The defence is the crucible where ideas are ...
Preparing for your dissertation or thesis defense (also called a "viva voce") is a formidable task. All your hard work over the years leads you to this one point, and you'll need to defend yourself against some of the most experienced researchers you've encountered so far. It's natural to feel a little nervous.
She described her writing experience as "an intricate process of balancing many things at once with a deadline (defense day) that seems to be creeping up faster and faster— finishing up experiments, drafting the dissertation, preparing your presentation, filling out all the necessary documents for your defense and also, for MD/PhD students ...
1. Ask Around. The first thing to do when preparing for your oral defense is to ask your PhD advisor what to expect and check your grad school's requirements. You could also ask colleagues who have already completed their defense. 2. Practice Makes Perfect.
A PhD oral defense is usually a day-long event where you give a public presentation and/ or a private presentation to some examiners. These examiners will be people from your University or from other universities. You will spend your time presenting your findings, answering questions about your work and proving to your committee that you have a ...
Second, the Oral Defense may be one of the few times in the individual's life that a group of thoughtful and able people will devote their full attention to his or her ideas and work. Students often remember the Dissertation Oral Defense as a stimulating, challenging, and even exhilarating experience. Preparation of the Dissertation Manuscript
A viva voce, more commonly referred to as 'viva', is an oral examination conducted at the end of your PhD and is essentially the final hurdle on the path to a doctorate. It is the period in which a student's knowledge and work are evaluated by independent examiners. In order to assess the student and their work around their research ...
If you are doing a PhD or an MPhil then you will definitely need to do a viva, and this will be conducted by at least two examiners, usually one from inside the university and one external to the university who is an expert in the field. At BSc or MSc level you may be asked to do a viva, however you may be expected to do an oral or a poster ...
Learn about the 9 critical questions you need to be ready for as you prepare for your dissertation or thesis defense (also called a viva voce or oral defense...
Attend a pre-defense meeting: At the meeting, raise any issues or concerns you have, and ask what questions and issues might be raised during the defense. [v] Prepare your presentation: Prepare a 15-30 minute PowerPoint presentation, and make it as polished and professional as possible. [vi] Practice giving the presentation, including to ...
Graduate Administrator that you have started the process to prepare for your defense. Nominate a Faculty Member to Serve as Chair for Your Defense A Chair is appointed for each PhD oral defense exam to monitor and promote fairness and rigor in the conduct of the defense. Instructions for the Chair. can be accessed on the AS&E Intranet by faculty
This Guide was created to help Ph.D. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. The Guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from Ph.D. graduates. The tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can ...
Lesson 6 of 6 for how to prepare for and pass a doctoral proposal and dissertation oral defense. I conclude this 7 video min-library with 12 expert tips on h...
Decide on a date for the defense; Inform your graduate administrator that you have started the process to prepare for your defense; Nominate a Faculty Member to Serve as Chair for Your Defense. A chair is appointed for each PhD oral defense to monitor and promote fairness and rigor in the conduct of the defense.
Dr. Valerie Balester of Texas A&M University talks about how to prepare and what to expect when defending your dissertation.#tamu #Dissertation #Defensehttp:...
Preparing the oral presentation Rehearse the presentation - use an audience (colleague or a recent grad) Get feedback from audience Adjust the presentation to fit time available - better to be less than 20 minutes in rehearsal The defense Stand up is usual - sitting down is acceptable
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense: 1. Anticipate questions and prepare for them. You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions.
2. Be well prepared for your presentation—academically, mentally and physically. Try to be well rested and focused before your oral defense. 3. In your preparation, don't try to memorize all the studies cited in your thesis, but you do need to know the details of the few key studies that form the basis of your investigation. 4.
The defense meeting: This is where you decide how you will present the defense. The actual meeting is hugely reliant on the performance, body language and the confidence in your oral defense. After the defense meeting: This stage, also known as the follow up, requires you to make the necessary revisions suggested by the university committee ...
The defense aims to accomplish two goals. First, it will provide an occasion for the presentation and recognition of the completed doctoral work. Second, it will furnish the opportunity for discussion and formal evaluation of the dissertation. The timing of the defense will be set by the student in consultation with the dissertation committee.
23. Generally speaking, PhD defenses come in two flavors, and it is not possible to say a priori which one yours will fall into: A real thesis "defense" focuses on the thesis, and all questions will relate to the scope of the research work. In this case, knowing your own work and its context well enough should be sufficient, but it is of course ...
Oral Defense Information. Conference Call Request Form. (Faculty Only) Please submit this form at least three business days prior to the requested conference call date. This form is used when the necessary approvals are in place to hold a conference call for one of the following: For Student and Committee Members (sessions are recorded):
Final oral defense: John Boamah (M.A.Sc.) Wednesday, May 1, 2024 - 16:00. "Effect of incidence angle on the wake flow of a wallmounted cylinder with a slot immersed in a shallow flow". Location: Room 3001 CEI. (519)253-3000. share. post. save.
Oral arguments have repeatedly referred to Blassingame, a decision from the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit that involved numerous lawsuits against Trump in his personal ...
Trump entered the courtroom at 11:22 a.m. ET, taking a look at reporters in the audience as he walked past them to the defense table. - Aysha Bagchi Trump named unindicted co-conspirator in ...
The oral argument lasted nearly three hours, as the justices tangled with a lawyer for the former president and a Justice Department lawyer. A majority of the justices appeared skeptical of the ...
Consistency is probably top of the notch," Brown said. "What I mean by that is that there's consistency in our demand signal from the Department of Defense in what we need. And then consistency in resourcing. When you have that consistency, that helps predictability for the defense industrial base."