Subject Guide


Search for Databases by Subject or Keyword
Purdue Libraries provides access to many other databases in Education and other related disciplines. A full list of databases is available at the A-Z Databases home page.
- To see databases of particular interest to Education research, choose "Education" from the subject drop-down menu
- To search by keyword, use the search box in the upper-right corner of the guide
Key Education Databases
This list includes some of the most frequently-used databases in Education research.
Looking for the full text of articles in these databases? If an article does not have a direct HTML full-text or PDF link, look for the FIND IT @ Purdue Libraries icon or search for the article from the Purdue Libraries catalog to see if full-text access is provided through another source.
- Education Full Text This full-text source of education scholarship provides coverage for a wide range of topics, including adult education, continuing education, literacy standards, multicultural/ethnic education, secondary education, teaching methods and much more.
- Educational Administration Abstracts Provides bibliographic records and many full-text articles covering areas related to educational administration, including educational leadership, educational management, educational research, and other areas of key relevance to the discipline.
- Teacher Reference Center (TRC) Free database. Indexes 260+ titles: popular teacher and administrator trade journals, periodicals, and books. Provides coverage on topics such as Assessment, Continuing Education, Current Pedagogical Research, Curriculum Development, Instructional Media, Language Arts, Literacy Standards, Science & Mathematics, and more for K-12 Teachers & Librarians.
- ERIC from US Gov't Use this version ONLY if you are not a Purdue student or faculty member. more... less... https://eric.ed.gov
Major Databases from Education-Related Fields
- PsycINFO This database contains more than one million citations and summaries of journal articles, book chapters, books, dissertations and technical reports, all in the field of psychology. It also includes information about the psychological aspects of related disciplines such as medicine, psychiatry, nursing, sociology, education, pharmacology, physiology, linguistics, anthropology, business and law. Journal coverage, which spans from 1887 to present, includes international material selected from more than 1,700 periodicals in over 35 languages.
- Dissertations and Theses (Native ProQuest interface) With more than 2 million entries, PQD&T is the single, central, authoritative resource for information about doctoral dissertations and master's theses.
- << Previous: Tutorials for Searching Education Topics
- Next: ERIC Documents and Database >>
- Last Edited: Apr 5, 2024 9:55 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/education

- Articles, Journals & Databases
- Books & Media
- Curriculum Materials Center | Children's Literature
- Dissertations & Theses
- Research Support
Looking for numbers? Use the tools below to help you with your statistical needs.
- NC Department of Public Instruction The North Carolina Department of Public Instruction website provides data & reports on information such as testing results, teacher performance, school report cards and more!
- Data.gov A U.S. government website that aims to improve public access to high value, datasets generated by the Executive Branch of the Federal Government. The site is a repository for federal, state, local, and tribal government data, made available to the public.
- EDDIE The Educational Directory and Demographical Information Exchange (EDDIE) is an online application containing The Educational Directory and Demographical Information Exchange (EDDIE) is an online application containing LEA (school district) and school information such as LEA numbers, school numbers, select administrative contacts, addresses, grade levels, calendar types, and more.
- NC School Report Cards NC School Report Cards is a user-friendly interactive site that provides data on all NC Public Schools report cards. This site was created by the NC Department of Public Instruction
- Statistical Profile The Statistical Profile Online provides a collection of statistical information about North Carolina's elementary and secondary schools.
Use the search tools on this page to locate articles, journals, and a complete list of databases recommended for education. We have a ton of education databases that will help you with your research. Below are a few databases you can explore that are specific to education.
- Academic Search Premier This link opens in a new window Academic Search Premier covers the expansive academic disciplines offered in colleges and universities. It provides comprehensive content, including PDF backfiles to 1975 for many journals and searchable cited references for more than 1,000 titles.
- Education Source This link opens in a new window Education Source is the world's largest full-text research database designed for education students, professionals and policymakers. It provides full text, indexing and abstracts for thousands of education journals, books and education-related conference papers. Coverage spans all levels of education and includes educational specialties such as multilingual education, health education and testing.
- ERIC (Educational Resources Information Center) This link opens in a new window Provides access to education literature and resources from journals included in the Current Index of Journals in Education and Resources in Education Index. The database contains more than 1,194,000 records and links to more than 100,000 full-text documents from ERIC. Links to available full text.
- Google Scholar This link opens in a new window Google Scholar is a web search engine that finds scholarly literature, including papers, theses, books, and reports. By searching Google Scholar from the library’s webpage, you will have free linked access to the library’s subscription holdings. Other links from Google Scholar may prompt you to pay for articles, but DO NOT PAY for articles. We will help you get the articles you need.
- Literature Resource Center This link opens in a new window Find biographical information and excerpts of criticism in this online reference tool covering more than 130,000 novelists, poets, essayists, journalists, and other writers.
- SIRS Discoverer This link opens in a new window Designed specifically for elementary and middle school students, SIRS Discoverer offers articles, nonfiction books, images, activities and websites curated for educational relevance, age appropriateness, and readability.
To find scholarly, peer-reviewed journals from various disciplines and databases, use the EBSCO Databases Quick Search.
For best results, follow these simple tips:
- Use only the major terms for your topic. For example, if you want to research the relationship between high-stakes testing and student achievement, the keywords are high-stakes tests and student achievement
- Put phrases (and only phrases) in quotes. For example: "high-stakes tests" and "student achievement"
- Put the word and in between each of your keywords: "high-stakes tests" and "student achievement"
- Use an * to truncate your search: comput* will retrieve computer, computing, computes, etc. . .
Introduction to Literature Reviews
Graduate research methods courses commonly require either a research proposal or an applied research project. In either case, a major component of the assignment, and your grade, will be a review of the existing literature on your topic, including empirical research studies. This guide offers an overview of literature reviews and features library resources and services that will help you be successful.
Because literature reviews differ significantly from a standard research paper or annotated bibliography, it helps a lot to gain a basic understanding of what a literature review is. The resources below can help.
This short video used with permission from North Carolina State University Libraries offers an overview of literature review assignments.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Books & Media >>
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.wcu.edu/education
HUNTER LIBRARY
176 Central Drive Cullowhee, NC 28723 Administration: 828-227-7485 Reference: 828-227-7465 Circulation: 828-227-7485

QUICK LINKS
Ask-A-Librarian Reserve a Study Room My Account Library Catalog Article Databases Interlibrary Loan
- Skip to Guides Search
- Skip to breadcrumb
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
- Skip to chat link
- Report accessibility issues and get help
- Go to Penn Libraries Home
- Go to Franklin catalog
Education: Articles in Education Databases
- Handbooks, Encyclopedias, Dictionaries
- Books and Searchable E-Book Collections
- Articles in Education Databases
- Articles in Subject Databases
- Articles in Multidisciplinary Databases
- Full-text Dissertations
- Open Access
- Publications, Reports, Working Papers
- Literature Reviews
- Research Methods
- How to Search Better
- Manage your Citations
- Journal Info / Metrics
- Author Citation Metrics
- ERIC - Education Resources Information Center (ProQuest interface) Indexes education journals (most comprehensively, some selectively), as well as education-related materials from scholarly organizations, professional associations, research centers, policy organizations, university presses, the U.S. Department of Education and other federal agencies, and state and local agencies. Individual contributors submit conference papers, dissertations, and theses. Sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES), U.S. Department of Education. Covers 1966-present. See ERIC Selection Policy . Combine searches with other ProQuest databases like PsycINFO or LLBA. (PennKey required). more... less... Of the journal content, c. 260 journals offer full-text and c. 50 provide full-text after an embargo period.
- Education Source Ultimate (EBSCO) “Education Source Ultimate is the world's largest and most comprehensive full-text research database designed for education students, researchers, professionals and policymakers. Coverage of education studies spans all levels of education and includes educational specialties ranging from educational assessment and education ethics to educational technology, literacy, research methodology and more." more... less... Education Source Ultimate includes: - 658 active full-text, non-open access journals not available in any version of Academic Search - 2,544 active indexed and abstracted journals. 2,289 of them are peer-reviewed - rigorous curation and indexing of open access (OA) journals, which has resulted in a growing collection of 923 active global OA journals - more than 4,400 full-text education-related conference papers. - a collection of 415 videos from SimpleK12 to provide practical online teacher training that addresses the evolving landscape of education. See Education Source Ultimate Journal Coverage List . Education Source Ultimate includes the content in EBSCO's Professional Development Collection, Education Index Retrospective: 1929-1983, and Education Index Full-text (H.W. Wilson). (PennKey required).
- ERIC - Education Resources Information Center (EBSCO interface) Same content and similar functionality to ERIC (ProQuest), on the EBSCOhost platform, shared with Education Source database.
- ERIC - Education Resources Information Center - Public version While the public version of ERIC will only take you to full-text ERIC documents and does not have linking to PennText articles, unique features available here include different limiters for: specific source, author, and identifiers for laws, assessments, and location.
- ERIC ED Microfiche Collection Many ERIC Documents (ED accession numbers) are now accessible online, for those that are not, Penn Libraries holds a complete collection of ERIC fIche. Use this Franklin Catalog record to request fiche.
Additional Education Databases
- Oxford Bibliographies Online - Education Annotated bibliographies on specific topics, identifying useful overview and reference works, classic works, controversial works, and other significant books and articles on the topic. Bibliographic articles are frequently updated.
- LearnTechLib - The Learning and Technology Library Covers more than 25+ years and indexes journals, conference proceedings, reports, presentations on educational technologies and e-learning.
- Educational Administration Abstracts A bibliographic database covering all areas of educational administration, including educational leadership, educational management and educational research.
- NCES Bibliography Identifies journal articles that use data from National Center for Education Statistics research programs, 1973-present. Assembled by NCES from searching online bibliographic databases (e.g., ERIC, JSTOR, EconLit, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses).
- UNESDOC (UNESBIB) / UNESCO UNESDOC, the UNESCO Digital Library, is the repository for UNESCO publications and UNESCO-sponsored publications, and also for UNESCO Director-General speeches and documents of UNESCO's governing bodies, drawn from the UNESCO Library, UNESCO Archives, and documentation centers in UNESCO field offices and institutes.
- Library, Information Science & Technology Abstracts Useful for research on academic, school, and public libraries.
- Children's Literature Comprehensive Database Search for children and young adult works by age, grade, genre, awards, language, series, and reading metrics. Includes some reviews.
- Observatory on Borderless Higher Education Tracks news, issues, and provides commissioned reports on higher education issues.
History of Education
- Past Masters Includes the full-text of The Collected Works of John Dewey, 1882-1953 (First release) and Correspondence .
- Education Index Retrospective Covers 1929-1983. Choose document type: Book Review.
- Record of current educational publications / US Bureau of Education A classified bibliography, quarterly with annual index. Covers 1921-1932.
- Monthly record of current educational publications / US Bureau of Education. A classified bibliography, monthly with annual index. Covers 1912-1921.
- Bibliography of education. US Bureau of Education. A classified bibliography. Covers 1899-1912.
- L'Année pédagogique. French-language annual bibliography, covering 1911-1913.
- << Previous: Books and Searchable E-Book Collections
- Next: Articles in Subject Databases >>
- Last Updated: Apr 16, 2024 8:23 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.upenn.edu/education
Databases: Education: Education Databases
- Education Databases
- All Databases by Subject
Core Resources
- Education Source This link opens in a new window Includes Education Abstracts and Education Index back to 1929, with full text for 1,700+ journals, 550 books and monographs, and education-related conference papers, plus citations for over 4 million articles and book reviews. Coverage spans all levels of education from early childhood to higher education.
- ERIC (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Index and abstracts, with some full-text included. The premier bibliographic database covering the literature on education. Covers both journal articles and unpublished research documents. Updates: Ongoing
- JSTOR This link opens in a new window Back issues of core scholarly journals in subjects including African-American studies, anthropology, Asian studies, classics, ecology, economics, education, finance, history, literature, mathematics, philosophy, political science, population studies, sociology, and statistics. Includes free Early-Journal Content, journals published before 1923 in the U.S. and before 1870 outside of the U.S.
- Web of Science (WOS) This link opens in a new window Includes several citation indices covering sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities. Search by a specific index, or across all indices. Citations to articles in more than 8,000 major research journals. Also permits cited reference searching (searching for articles that cite a particular author or work).
Additional Resources
- Academic Search Complete This link opens in a new window This academic multi-disciplinary database provides than 8,500 full-text periodicals, including more than 7,300 peer-reviewed journals. In addition, it offers indexing and abstracts for more than 12,500 journals and a total of more than 13,200 publications including monographs, reports, conference proceedings, etc. Coverage spans virtually every area of academic study and offers information dating as far back as 1887.
- Cabell's Directory of Publishing Opportunities This link opens in a new window Cabell's Directories helps scholars identify journals for publication and guides users in evaluating journal quality. Entries include contact information, manuscript guidelines, acceptance rates, review process, number of reviewers, and audience.
- Career and Technical Education This link opens in a new window Covers vocational and technical periodicals relevant to a vocational curriculum. Fields covered include technology, healthcare, building trades, auto mechanics, sales and retail, accounting, graphic design, photography, forestry, criminal justice, nursing, and more.
- Chronicle of Higher Education This link opens in a new window The Chronicle's online version features the complete contents of the latest issue; daily news and advice columns; thousands of current job listings; discussion forums; and career-building tools such as online CV management, salary databases, and more. To access Premium features, you must be on campus or logged into the GW VPN, or else create a free personal account using your GW email address.
- Counseling and Therapy in Video (Volumes I and IV) This link opens in a new window Counseling and Therapy in Video is an online collection of video for the study of social work, psychotherapy, psychology, and psychiatric counseling. It provides a firsthand look at the realities of working with clients and the challenges associated with putting theoretical concepts into practice. GW has access to Volumes I and IV.
- Dissertations and Theses Online This link opens in a new window Contains information about doctoral dissertations and master's theses from over 1,000 North American and European universities. Includes citations ranging from the first U.S. dissertation, accepted in 1861, to ones accepted as recently as last semester. Of over 1.5 million titles listed, Proquest offers over a million in full text. For these titles, the citation includes the Proquest order number.
- EBL (Ebooks) This link opens in a new window Now part of Ebook Central.
- Emerald Library This link opens in a new window Full-text articles from management journals. Note that current content is not being added to this database.
- ERIC.gov This link opens in a new window ERIC - the Education Resources Information Center - is an online digital library of education research and information. ERIC is sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education. ERIC provides ready access to education literature to support the use of educational research and information to improve practice in learning, teaching, educational decision-making, and research.
- Films on Demand This link opens in a new window Films on Demand is a streaming video platform for educational content from the Films Media Group. Films are provided as Flash Video streams, with Windows Media and QuickTime also available for most titles.
- Grant Forward This link opens in a new window Grant Forward (formerly called IRIS, the Illinois Researcher Information Service) contains over 9,000 active federal and private funding opportunities in the sciences, social sciences, arts, and humanities. In addition to funding opportunities for faculty, Grant Forward also contains fellowships and scholarships for grad students and undergrads. Users can search by sponsor, deadline date, keyword, and other criteria. Most records contain live links to sponsor Web sites or portals. It also displays upcoming deadlines in 25 subject areas.
- LearnTechLib This link opens in a new window Online resource for aggregated, peer-reviewed research on the latest developments and applications in Learning and Technology.
- LexisNexis Academic: please use Nexis Uni This link opens in a new window This database has been replaced by Nexis Uni.
- Mental Measurements Yearbook with Tests in Print Internacional This link opens in a new window Version of Mental Measurements Yearbook with Tests in Print that includes Spanish-language as well as English-language content. Produced by the Buros Institute at the University of Nebraska, it provides a comprehensive guide to over 2,000 contemporary testing instruments. Contains information for evaluating test products within such diverse areas as psychology, education, business, and leadership. Simultaneous users: 4
- Nexis Uni This link opens in a new window Formerly LexisNexis Academic. Access to major newspapers from around the world, as well as: industry and market news; company financial information; general medical topics; accounting, auditing, and tax information; legal news, law reviews, and case law; and the U.S. and state codes. Please use Google Chrome or IE browsers with this database.
- Policy File Index This link opens in a new window Policy File Index includes full-text report, paper, document and other sources on U.S. public policy research including over 75 public policy topics (both foreign and domestic) from over 350 public policy think tanks, nongovernmental organizations, research institutes, university centers, advocacy groups, and other entities.
- Primary Search (Articles for Children) This link opens in a new window Access to more than 60 popular magazines for elementary school research.
- Project Muse This link opens in a new window Articles and reviews from peer-reviewed, scholarly journals in the humanities and social sciences.
- ProQuest Education Database This link opens in a new window Abstracts and indexing of over 900 education journals, many in full-text.
- ProQuest Research Library Plus This link opens in a new window Covers a wide range of subject matter in both popular and scholarly periodicals. Also includes Proquest's Computing, Education, Religion, Science, Social Science and Telecommunication Journal modules.
- PsycINFO 1887-Current This link opens in a new window Contains citations and summaries of journal articles, book chapters, books, dissertations and technical reports in the field of psychology. Includes information about the psychological aspects of related disciplines such as medicine, psychiatry, nursing, sociology, education, linguistics, business, law and more. Journal coverage, spanning from 1887 to present, includes international material.
- Qualitative Data Repository This link opens in a new window The Qualitative Data Repository (QDR) is a dedicated archive for storing and sharing digital data (and accompanying documentation) generated or collected through qualitative and multi-method research in the social sciences and related disciplines.
- SAGE Research Methods Core This link opens in a new window Comprehensive online resource providing material to guide users through every step of the research process, including datasets, cases, books, articles and videos. For more information, see Sage Research Methods Libguide
- Teacher Reference Center This link opens in a new window Indexes over 260 titles from the teacher and administrator trade journals, periodicals, and books. This database provides coverage on key education topics such as Assessment, Continuing Education, Current Pedagogical Research, Curriculum Development, Instructional Media, Language Arts, Literacy Standards, Science & Mathematics, and more for K-12 Teachers & Librarians.
- TeachingBooks.net Original This link opens in a new window Includes thousands of resources about fiction and nonfiction books used in the K–12 environment, with every resource selected to encourage the integration of multimedia author and book materials into reading and library activities.
Related Research Guides
- Education Leadership & Administration by Shmuel Ben-Gad Last Updated Aug 14, 2023 143 views this year
Ask a Librarian
- Next: All Databases by Subject >>
- Last Updated: Dec 7, 2023 11:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gwu.edu/educationdatabases

- Brandeis Library
- Research Guides
- Find Articles & Databases
Education Guide
What is peer review, find education articles, select education journals.
- Reference Works
- Find Data & Statistics
- Find Empirical Studies
- Search Strategies

This guide highlights general education resources available at Brandeis, tips for effective research, and more. Please email or book an appointment with our Education Librarian, Zoe Weinstein ([email protected]) if you have questions about these resources or need help with your research.
These databases are a great place to start when you're looking for articles related to education, teaching, and related topics.
- ERIC (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window Database sponsored by the U.S. Department of Education that provides access to scholarly journals, curriculum and teaching guides, research reports, and other materials related to the field of education.
- Education Database (ProQuest) This link opens in a new window Scholarly journal articles, dissertations, and other materials on early childhood education through higher education topics. Most items are from 1980-present.
- Education Research Complete (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Scholarly journal articles, dissertations, professional development resources, and other materials on topics related to the field of education. Coverage includes early childhood through adult education and all education specialties.
- JSTOR This link opens in a new window Archive of scholarly journals and ebooks spanning many disciplines, primarily in the humanities and social sciences. Often does not have the last 1-3 years of a publication. Use Advanced Search to select specific subject areas.
- APA PsycInfo (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Citations and summaries of journal articles, book chapters, books, dissertations and technical reports in psychology. Includes information about the psychological aspects of related disciplines such as medicine, psychiatry, nursing, sociology, education, pharmacology, physiology, linguistics, anthropology, business and law. Coverage 1887 to present, includes 1,700+ international sources in over 35 languages.
- ScienceDirect (Elsevier) This link opens in a new window Contains over 25% of the world's science, technology and medicine full text and bibliographic publications. Search across all content, limit to a single title, or choose by subject subsets.
- Teacher Reference Center (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window Freely available database that provides access to articles from popular teacher and administrator journals on topics relating to professional development and all levels of education.
Find more on our A-Z Databases: Education page .
The following education journals are great places to browse if you'd like to find ideas for research topics or read some of the latest scholarship.
- American Educational Research Journal Articles include original empirical and theoretical studies and analyses in education. The editors seek to publish articles from a wide variety of academic disciplines and substantive fields. Older issues (1964-2012) are available in JSTOR .
- Elementary School Journal ESJ publishes peer-reviewed articles that pertain to both education theory and research and their implications for teaching practice. In addition, ESJ presents articles that relate the latest research in child development, cognitive psychology, and sociology to school learning and teaching. Older issues (1912-2012) are available in JSTOR .
- Harvard Educational Review Scholarly journal of opinion and research in education. It provides an interdisciplinary forum for discussion and debate about the field's most vital issues.
- Review of Research in Education Provides an overview and descriptive analysis of selected topics of relevant research literature through critical and synthesizing essays (coverage: 1973-present).
- Teaching and Teacher Education International journal concerned primarily with teachers, teaching, or teacher education situated in an international perspective or in an international context.
- Urban Education Articles cover topics such as mental health needs of urban students, student motivation and teacher practice, school-to-work programs and community economic development, restructuring in large urban schools and health and social services
- Next: Reference Works >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 11:43 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.brandeis.edu/education
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
Education Research Guide
- Articles Databases and News
- Introduction to Education
- Articles Databases
- Books and Reference Sources
- Data and Statistics
- Government Sources
- Dissertations and Theses
- Ethnic Resources
- Historical Textbooks Collections
- Journal Metrics and Cited References
- K-12 Resources
- Research Centers and Policy Reports
- Tests and Measurements
- EndNote This link opens in a new window
- Zotero This link opens in a new window
- Additional Resources
- Citation Styles and Research Management

Education News
- EdSurge Award-winning education news organization that reports on the people, ideas and technologies shaping the future of learning. An independent news and research initiative of the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE).
- Newsroom: CA Department of Education Current news releases, editorials, and letters from the California Department of Education's (CDE) Communications Division.
Leading & General Papers
Full text (no ads or pictures) from 1985 to the present. For access to older issues, see Proquest Historical Newspapers: Chicago Tribune [1849-2013] .
News Databases
- Independent Voices This link opens in a new window Full text of 1,000+ alternative publications covering feminists, dissident GIs, campus radicals, Native Americans, anti-war activists, Black Power advocates, Latinos, LGBTQ+ activists, etc., 1960s-1980s.
Also see: NEWS GUIDE to all UCLA news subscriptions.
- Locating Full Text
- Interlibrary Loans
- ERIC Documents (U.S. Department of Education) Access to the full text of ERIC Documents.
Multidiscipinary
- Google Scholar This link opens in a new window Searches articles, theses, books, abstracts, patents, and court opinions from academic publishers, professional societies, online repositories, universities, and other web sites.
Art, Music, STEM
- PubMed This link opens in a new window Citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. Citations may include links to full-text content from PubMed Central and publisher web sites. Also searches NCBI's integrated molecular biology databases, including nucleotide sequences, protein sequences, 3-D protein structure data, population study data sets, and assemblies of complete genomes in an integrated system. Note: This link uses a special address which turns on Get it at UC . Without that, PubMed does not link to UCLA's online subscriptions. pumed, pucmed, pubmced, pubmedd, pubmedf
Sociology and Social Issues
Ethnic studies, gender studies, law, business, policy, language and linguistics.
- Language and Linguistics Compass Online-only journal publishing original, peer-reviewed surveys of current research from across the entire discipline. In Wiley Online, 2007-present; monthly.
- Citation Linker Locate an article from your citation in journals within UCLA Library holdings.
- UC Library Search This link opens in a new window Search the UC Library Search catalog when looking for online OR print materials. Contains journal titles, books, conference proceedings and more, in print or electronic form, representing all Library holdings. Click on Online Access to get to full-text items. Here's a guide to learn more about searching UC Library Search .
If UCLA does not own an item , UC students, faculty, and staff can request it through the Interlibrary Loan (ILL) service . There is no charge for this service for UCLA students, faculty and staff.
- Your UCLA Library account number is the nine-digit number (aka your Bruin ID) that appears on the front of your BruinCard, plus the single digit that appears on the back side, lower righthand corner of your BruinCard. Enter all ten digits without any spaces.
- Only a University of California e-mail address or an address registered in your library account is valid.
- Submit an Interlibrary Loan Request . The Interlibrary Loan Service enables UC students, faculty, and staff to borrow materials not available in UCLA Libraries . You don't have to specify a location, UCLA will automatically search for availability in other libraries, both in this country and abroad.
- Check the status of your Interlibrary Loan Request . Sign in to your UCLA Library Account to determine the status of your ILL requests.
OFF-CAMPUS ACCESS
A program you install on your computer, the UCLA VPN allows you to surf websites privately and securely as well as gain access to UCLA subscription websites and sources.
A simple browser setting which will automatically divert you to a UCLA logon page when you first access a restricted site.
An extra layer of online protection for your access and account.
Your UCLA IT experts, available for UCLA students, faculty and staff to contact with ANY access problem.
ON-CAMPUS ACCESS
Provides the highest level of security and is the recommended network for UCLA faculty, students, and staff. Devices must be configured in advance before using this network. Logon is [email protected]. This is the only network that allows wireless printing from CLICC laptops.
- UCLA Wireless Networks
Note: Sign into EDUroam using your UCLA Logon ID with @ucla.edu appended ( [email protected] ) and password.
- << Previous: Finding Various Source Types
- Next: Books and Reference Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 18, 2024 11:55 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/education

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 17 April 2024
How popularising higher education affects economic growth and poverty alleviation: empirical evidence from 38 countries
- Jian Li ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3228-8163 1 na1 ,
- Eryong Xue ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7079-5027 2 na1 ,
- Yukai Wei ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5202-7307 2 &
- Yunshu He ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4814-9835 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 520 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
141 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
The popularisation of higher education supports UNESCO’s aim of developing inclusive and equitable quality education to achieve the fourth Sustainable Development Goal. However, the effect of popularising higher education on economic growth and poverty alleviation remains unexplored. Therefore, this study investigated the effects of higher education and adult education within populations (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (gross domestic product; GDP) and the poverty line using panel data from 38 countries. OLS and quantile regression were performed using data for the period 1995–2021 extracted from the OECD and World Bank databases. The results showed that the population segments with higher education had a significantly positive impact on GDP growth. Moreover, an increased proportion of the population with higher education, of working age, was found to be a contributing factor to GDP growth. Popularising higher education also played a positive role during the initial stage of social and economic development. This study also highlighted that popularising higher education play a key role to influence a country’s educational development and scientific and technological innovation drives the deepening of a country’s economy. It suggested that both national and local governments worldwide should pay much attention to the popularisation degree of higher education to greatly improve the innovative ability of talents and scientific and technological innovation in higher education for both the economic growth and poverty alleviation.
Similar content being viewed by others
The effect of intergenerational mobility on family education investment: evidence from China
Nan Zhao, Wanqing Liao, … Zizhe Zhang
Dynamics of returns to vocational education in China: 2010–2017
Jie Chen & Francesco Pastore

Measuring and forecasting progress in education: what about early childhood?
Linda M. Richter, Jere R. Behrman, … Hirokazu Yoshikawa
Introduction
The popularisation of higher education critically contributes to UNESCO’s efforts to realise the fourth Sustainable Development Goal of inclusive and equitable quality education (Ainscow, 2020 ; Bamberger and Kim, 2022 ).Popularisation of higher education expands the scale of higher education and its high growth rate introduces considerable challenges to the management structure of higher education, triggering a series of theoretical and practical concerns relating to the nature and function of higher education (Balestra and Ruiz, 2015 ; Brand, 2021 ). Given that education and social and economic development are mutually reinforcing, the expansion of higher education leads to an ascending spiral of development for individuals and/or economies. By contrast, a lack of education or early withdrawal from education leads to a downward spiral for them (Camilla, 2023 ). This relationship between education and development undergirds the model of poverty alleviation based on the return on education (Decancq, 2017 ). The previous studies emphasise the importance of the return on education as a multidimensional anti-poverty mechanism and thus a key factor in poverty alleviation (Fang et al., 2022 ; Chelli et al., 2022 ; Garritzmann, 2016 ). For example, return on education is the key factor enabling a transition from poverty alleviation through education to poverty alleviation through education (Gillian et al., 2021 ; Gong and Hong, 2021 ). Poverty alleviation is realised through an interlinking of these two processes and the promotion of the latter (Granata, 2022 ; Habibi and Zabardast, 2020 ). The educational resources can meet the needs of the poor mainly through the return on education at the levels of survival and life quality. In addition, the previous studies highlighted that, with a continuous expansion in the scale of higher education, its economic effect gradually appears to become marginal (Hoeller et al., 2014 ). The density of colleges and universities worldwide has increased considerably in recent years, but it is still inadequate to meet increasing demands resulting from the ongoing popularisation of higher education (Jericho, 2016 ). The increase in the number of colleges and universities has a positive effect in promoting economic development but with marginal benefits. (Julian, 2018 ).
Through reviewed the current relevant studies, it is found that there have limited studies that have simultaneously explored the effects of popularising higher education on economic growth and poverty alleviation. The previous research revealed that most studies have focused on the relations between popularisation of higher education and economic growth. However, a few empirical investigations have examined the effect of population segments with higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and poverty reduction. Considering the scope and limitations of previous studies, it aimed to address the above research gap by investigating the effect of a population segment with high levels of higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and the poverty line at a wide scale using panel data from 38 countries. The main research questions addressed in this study are as follows.
Q1: What is the effect of a population segment with higher education on GDP growth?
Q2: What is the effect of adult education on GDP growth?
Q3: What impact does a population segment with higher education have on reducing the proportion of those experiencing poverty?
Q4: What is the relation between an increased level of adult education and the proportion of the population experiencing poverty?
All these questions are relevant to an exploration of the effect of the population segment with higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and the poverty line. This study is divided into several sections: the first section concentrates on examining the effect of popularising higher education on economic growth and the poverty line, the relationship between popularisation of higher education and poverty alleviation, and the relationship between popularisation of higher education and poverty alleviation. In the second section of method, to address this research gap, this study performed OLS and quantile regressions using data extracted from the OECD and World Bank databases for the period 1995–2021. An OLS regression model and a panel quantile model were used to analyse the effect of a population segment with higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and the poverty line within 38 OECD countries. The impact of the proportion of people aged 24–64 years and 25–34 years who had completed higher education in relation to their peers on GDP and the proportion of people living in poverty in 38 OECD countries have been measured and analysed. The results and discussion have been provided at the last.
Literature review
The effect of popularising higher education on economic growth.
The population segment with higher education is regarded as an important contributor to economic growth, generating scientific knowledge and providing labour, which in turn increases human capital and productivity (Jungblut, 2017 ; Kalamova, 2020 ; Liu, 2017 ). As the scale of higher education expands, the emergence of knowledge power as a large-scale global phenomenon reflects the important role of an expanded educated labour force in the advancement of science and technology and the economy. For example, the relationship between higher education and economic development in European Union countries between 1997 and 2016 was analysed. Their findings revealed a statistically significant correlation between expanding higher education and economic growth in the selected countries. The one-way cause-and-effect relationship between education and economic development in these countries suggests that an increase in the proportion of the population enroled in higher education boosts economic performance. In addition, using a survey sample of 35 households, a retrospective study in Brazil, examined the role of educational expansion in reducing income inequality and poverty. Its findings suggest that it would take decades to reduce inequality and poverty in this country and that this outcome could only be achieved through a major expansion of the higher education sector. The growth needed to achieve this outcome would be considerable (Lamichhane et al., 2021 ). This reduction in inequality and poverty could only be achieved if optimistic assumptions about growth, matching job skills and the return on education do not fall short. In brief, education is not a panacea for reducing poverty and inequality. How three major stages of education contributed to the growth in labour productivity in 125 countries during the period 1999–2014 was also explored. They found that human capital is consistent with the educational returns of an average number of years of formal education at the levels of primary, secondary, and higher education. Their analysis showed that higher education had the greatest impact on labour productivity in the economies under study (Ledger et al., 2019 ). In addition, popularising higher education plays an important role in promoting economic growth, as the scale of higher education can guarantee the scale of human resources development by improving the quality of human resources and cultivating and distributing innovative scientific and technological talents. The scale of higher education guarantees the spread of science and technology and the popularisation of scientific and technological achievements (Mathias, 2023 ; Megyesiova and Lieskovska, 2018 ). The expanded scale of higher education worldwide has a spatial spillover effect on economic growth, which is strengthened through international cooperation in the fields of science and technology.
Popularising higher education also plays a direct role in cultivating and transporting scientific and technological talents to promote international scientific and technological cooperation (Mitic, 2018 ; Özdoğan Özbal, 2021 ; OECD, 2022 ; Pinheiro and Pillay, 2016 ). The scale of postgraduate education inhibited the total number of scientific and technological innovation achievements, indicating that there may be a trade-off between ‘quantity expansion’ and ‘quality upgrading’ of scientific and technological innovation achievements. Nevertheless, the positive effect on the number of high-tech innovation outcomes is significant, indicating that the supporting effect of graduate education on scientific and technological innovation is mainly concentrated in the high-tech fields (Pinheiro and Pillay, 2016 ; Rowe, 2019 ; Sahnoun and Abdennadher, 2022 ). The ‘talent increment’ of regional expansion and the ‘resource stock’ of graduate education have a combined promoting effect on high-tech innovation. There are differences in the effect of graduate education supporting high-tech innovation among provinces with different characteristics relating to the development of graduate education. The incremental expansion of high-quality talent is essential for enhancing the efficiency of material capital and stabilising the advantage of resource stocks. Using education statistics from OECD countries, Russia, and several other countries that participate in OECD education research, comparative and correlational analysis methods were applied to analyse how the scale of growth in young people’s participation in higher education is reflected in changes in their employment and economic activity. The results of their analysis showed that the growth in economic activity involving young graduates with a master’s degree exceeded that of college graduates after the 2009 financial crisis, and graduates fared better in the 2020 crisis, which was triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic.
The effect of popularisation of higher education on poverty alleviation
Popularisation of higher education is regarded as an essential factor contributing to poverty alleviation (Samo, 2022 ; Adams, 2013 ; Zapp, 2022 ). The higher education’s role in promoting economic growth can only be fully realised through the cultivation of talents suitable for the actual development situation of the country. Countries with food shortages, for example in Africa, also need to procure and train the right agricultural talent. Key drivers of sustainable agricultural production include access to improved technologies, sustainable growth of human, biological and natural resource capital, improvements in institutional performance and a favourable economic policy environment. Higher education graduates with the necessary ‘soft skills and business skills constitute an important pillar. Chakeredza ( 2008 ), who explored the effect of popularising higher education on poverty alleviation, suggested that the number of hungry people in Africa will continue to increase. Higher education in agriculture must be transformed, and efforts must focus on retaining faculty and on reviewing and redesigning institutional management systems, curriculum content and education delivery.
There are many reasons for poverty, with a lack of education being an important one. Insufficient quality education leads to educational poverty. Using PISA data, Agasisti et al. ( 2021 ) investigated the extent of educational poverty in European countries, considering its incidence, breadth, depth and severity. For this study, they adopted an additive multidimensional poverty measure proposed by Alkirew and Foster. Their findings indicated that between 2006 and 2015, the depth and severity of poverty decreased in most of the countries under study. Moreover, the incidence of educational poverty in many European countries was related mainly to student characteristics and school factors. The expansion of higher education has a positive effect on economic development and poverty reduction by improving work skills within the labour force. Increased enrolment in higher education encourages individuals born in families with low education levels to avail of higher education opportunities. Evidently, the expanded scale of higher education in the process of promoting economic growth has enhanced the equity effect of intergenerational social mobility. The expansion of higher education improves total factor productivity, thus promoting economic transformation and advancement globally (Samo, 2022 ; Adams, 2013 ; Zapp, 2022 ). Furthermore, the previous studies have shown that the structure of higher education talent training has a significant impact on economic development. Therefore, government departments need to make constant efforts to improve relevant systems and promote the optimisation and upgrading of the structure of higher education talent training to meet the needs of future economic development.
Theoretical underpinnings
The relationship between education and economic growth is a classic issue in the study of educational economics. For example, in Solow’s view, the growth of per capita output comes from per capita capital stock and technological progress, but capital investment has the problem of diminishing marginal returns, and the long-term sustainable development of the economy depends on technological progress (Solow, 1957 ). The emphasis on technological progress is a very important point in Solow’s growth theory. It was Schultz who systematically analyzed the contribution of education to economic growth. Influenced by the progress of economic growth theory and national accounting methods, Schulz proposed human capital theory in the process of explaining Solow residuals (Schultz, 1961 ). believes that once human capital is included in economic growth, it will solve the paradoxes and puzzles faced in economic growth research. Starting with the difference in income of different types of workers in the labour market, he found that education and health factors are the main reasons for the income difference, and further clarified that the reason for the income difference is the difference in labor productivity (Schultz, 1961 ). Schultz ( 1961 ) believes that human resources include the quantity and quality of labor, and he mainly focuses on the skills and knowledge of people who can improve labor productivity. As for how to measure human capital investment, Schulz believes that the cost of human capital can be measured in the same way as physical capital. Lucas ( 1988 ) focuses on the mechanism of human capital accumulation and why human capital does not show diminishing marginal returns like physical capital. Lucas divides the effect of human capital into internal effect and external effect. Romer ( 1990 ) internalised technological progress, revealed the relationship between human capital and technological progress, and proposed that the stock of human capital determines the economic growth rate, and it is human capital rather than population that determines economic growth. Romer starts with three hypotheses: first, technological progress is central to long-term economic growth; Second, technological progress is formed by people’s response to market incentives, and market incentives determine technological progress. Third, technology is a special kind of product, and once the cost of the initial input is produced, the technology can be reproduced indefinitely at no cost or very low cost.
In other words, higher education is more about improving students’ ability and productivity, thereby increasing students’ income, and promoting economic growth. Higher education mainly affects economic growth through two aspects: one is the same as Schulz’s improvement of individual ability, and the internal effect of human capital, which directly affects the production process (Schultz, 1961 ). Second, Lucas emphasised the external effect of human capital, and the comprehensive effect of human capital on the whole society, which has the characteristics of increasing marginal benefit (Lucas, 1988 ). It emphasises that the human capital invested in technological innovation and the existing knowledge and technology stock of the whole society jointly determine technological innovation.
Research hypotheses and analytical model
In this study, an OLS regression model and a panel quantile model were used to analyse the effect of a population segment with higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and the poverty line within 38 OECD countries. The study’s hypotheses were as follows:
Hypothesis 1: The effect of a population segment with higher education has a positive impact on GDP growth.
Hypothesis 2: Some level of adult education has a positive impact on GDP growth.
Hypothesis 3: A population segment with higher education has a positive impact by reducing the proportion of the population experiencing poverty.
Hypothesis 4: An increase in the level of adult education has a positive impact by reducing the proportion of the population experiencing poverty.
The widely used Mankiw-Romer-Weil model was applied in this study. The overall level of development of higher education and the popularisation of higher education were considered core elements that independently promote economic development and alleviate poverty. The following model was constructed by incorporating the variable of quality higher education into the Solow model:
where Y it refers to the output of i country in t year. The independent variables Qit and P it respectively represent the scale of development and the degree of popularisation of higher education in i country in t year. The following specific model was constructed:
The independent variables were the proportion of people aged 25–64 years with higher education (A) and the proportion of people aged 25–34 years with higher education within the same age group (B). The first variable reflects the population segment that has completed higher education and can work in the corresponding age group. The second reflects the degree of popularisation of higher education. The proportion of those who have completed higher education in relation to their peers is in the normal state, which can reflect the enrolment rate for the previous process of higher education, thus indicating the degree of popularisation of higher education.
The dependent variables were GDP and the poverty line (D). GDP is a measure the overall level of a country’s economic and social development. The poverty line refers to the proportion of people living on less than US$1.25 a day as a percentage of the country’s total population or the proportion of people living in poverty. Thus, it reflects the level of equity in social development. The figure of US$2.15 is used in the World Bank’s index and is based on the purchasing power parity in 2017 (see Table 1 ).
Data sources and selection of variables
This study measured the impact of the proportion of people aged 24–64 years and 25–34 years who had completed higher education in relation to their peers on GDP and the proportion of people living in poverty in 28 OECD countries. Specifically, this study assessed the impact of the overall level of development of higher education and the degree of its popularisation (the breadth of development of higher education) on GDP (the height of development of economic and social development) and the poverty line (the breadth of development of economic and social development). Data were sourced from the OECD database and the World Bank website covering the period 1995–2021. This study selected 38 OECD countries for this study: the United States, UK, France, Germany, Italy, Canada, Ireland, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, Austria, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, Denmark, Sweden, Spain, Portugal, Greece, Turkey, Japan, Finland, Australia, New Zealand, Mexico, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, South Korea, Slovakia, Chile, Slovenia, Estonia, Israel, Latvia, Lithuania Colombia and Costa Rica. Figure 1 shows the distribution of the 38 OECD countries. Of these countries, 20 were founding members of the OECD when it was established in 1961, while the remaining 18 subsequently became members. After 1994, OECD membership expanded rapidly. Five new members were added within three years. OECD then entered a period of accelerated development, and its operations and advancement reached an optimal stage. Therefore, this study selected data from the OECD database and the World Bank website covering the period 1995–2021 to explore the relationship between higher education and economic and social development in OECD member countries.
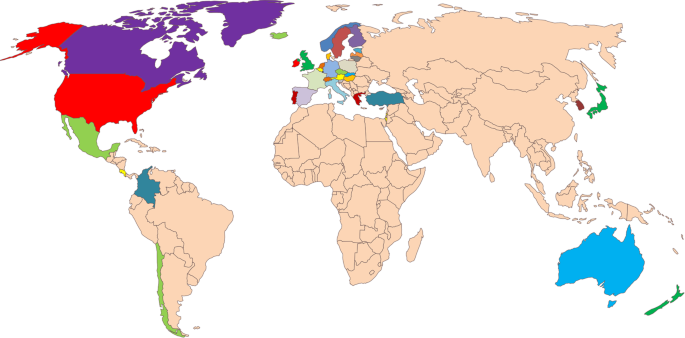
It expresses the geographical relations of the Atlantic region and simplifies the latitude and longitude lines and country symbols, highlighting the geographical distribution by highlighting OECD countries in color and other countries in apricot color.
The impact of the population segment with higher education on GDP growth
This study explored the impact of the population segment with higher education on GDP, taking the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education (B) and the proportion of people aged 25–64 years who had completed higher education (A) as the independent variables for the OLS regression. The square value of model R was 0.097, indicating that the two independent variables could explain 9.73% of the change in GDP. The model passed an F test ( F = 46.137, p = 0.000 < 0.05), indicating that at least one of the two independent variables impacted the GDP regression coefficient (C). The following formula was used:
The final analysis revealed that the regression coefficient value of A was 1.553 and the significance level was 0.01 ( t = 7.141, p = 0.000 < 0.01). Therefore, A had a significantly positive influence on C. Accordingly, the proportion of the population aged 25–64 years who had completed higher education, that is, the overall level of development of higher education was found to have a positive impact on GDP. The influence coefficient value was 1.533, indicating that an increase in the proportion of the population with completed higher education led to an increase in GDP.
The regression coefficient value of B was −0.813 at a 0.01 level of significance ( t = −4.300, p = 0.000 < 0.01), indicating that B had a significantly negative influence on C. The proportion of the population aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education, that is, the degree of popularisation of higher education had a negative effect on GDP, and the influence coefficient value was −0.813.
The negative impact on economic and social development caused by an increase in the popularity of higher education and the proportion of young people’s higher education experience may be attributed to the excess capacity of higher education. The development of higher education should be adapted to the national context. An excess of higher education and a lack of investment lead to a rise in the social cost of education and a decline in social outputs, which hinder social and economic development. At the same time, young people aged between 25 and 34 years occupy the position of’ export’ in the education process. With the increasing popularity of higher education, the supply of talents in the labour market generated through the recruitment of former higher education exceeds the demand for graduates with higher education within recruiting organisations. Consequently, issues such as wasted educational resources and knowledge, unemployment, excessive education, excess talents, an imbalance in the structure of higher education, excessive expansion and decreasing compatibility undermine economic operations and hinder GDP growth.
In this study, the variance decomposition and Pearson coefficient based on covariance calculation were analyzed. The variable of the number of 25–34-year-old who have completed higher education as a percentage of their peers explains 50.74% of the change in GDP. The variable of the proportion of 25–64-year-old who have completed higher education explains 49.26% of the change in GDP. The variable of 25- to 34-year-olds who completed higher education as a percentage of their peers explained 45.88% of the change in poverty line. The variable of the proportion of people aged 25–64 who have completed higher education explains 54.12% of the change in GDP (See Table 2 ).
The proportion of people aged 25–34 who have completed higher education in their peers and the proportion of people aged 25–64 who have completed higher education in their peers, GDP and poverty line showed significant correlation coefficients. The correlation between the proportion of people who have completed higher education at the age of 25–34 and the proportion of people who have completed higher education at the age of 25–64 is 0.931, and shows a significance of 0.01, which indicates that there is a significant positive correlation between the proportion of people who have completed higher education at the age of 25–34 and the proportion of people who have completed higher education at the age of 25–64. The correlation between the proportion of the number of people who have completed higher education at the age of 25–34 and the GDP is 0.209, and the significance is 0.01, which indicates that there is a significant positive correlation between the number of people who have completed higher education at the age of 25–34 and the GDP. The correlation between the number of people who have completed higher education and the poverty line at the age of 25–34 is −0.365, with a significance of 0.01, indicating a significant negative correlation between the number of people who have completed higher education and the poverty line at the age of 25–34 (See Table 2 ).
White test and BP test were used in this study. The test null hypothesis is that the model has no heteroscedasticity. The table above shows that both tests reject the null hypothesis ( p < 0.05), indicating that the model does have heteroscedasticity. When there is a heteroscedasticity problem, Robust and robust standard false regression is used (See Table 3 ).
The impact of a population segment with higher education on the poverty line
This study also explored the impact of a population segment with higher education on the poverty line. Specifically, this study performed an OLS regression in which the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education (B) and the proportion of those aged 25–64 years who had completed higher education (A) were the independent variables. As Table 2 shows, the R squared value was 0.134. This means that variables A and B could explain 13.37% of the change in the poverty line (D). The model passed the F test ( F = 48.771, p = 0.000 < 0.05), which means that at least one variable (A or B) had an impact on the poverty line. The formula for the change in the poverty line was expressed as follows:
The final analysis revealed that the regression coefficient value of the proportion of people aged 25–64 years who had completed higher education (A) was 0.005 but with no significance ( t = 0.428, p = 0.669 > 0.05), indicating that the population segment with higher education did not have an impact on the poverty line.
The regression coefficient value of the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education (B) was −0.048 at a significance level of 0.01 ( t = −4.305, p = 0.000 < 0.01), which means that in relation to their peers, the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education had a significantly negative impact on the proportion of poor people. A higher proportion of people aged 25–34-years who had completed higher education corresponded to a higher penetration rate of higher education and a lower proportion of those living in poverty. This phenomenon can be attributed to OECD’s support for the development of higher education in various countries. When the development of higher education reaches a certain level, the reduction of the proportion of the population segment experiencing poverty will no longer be affected by a simple expansion of the scale of extended higher education and the superposition of the total number of highly educated human resources. It will be influenced more by the reasonable distribution of educational resources and educational equity within higher education and its popularisation, that is, the increase in the proportion of the school-aged population aged 25–34 years based on the increase of the previous enrolment rate (see Table 4 ).
The effect of adult education on GDP growth
For quantile regression analysis, a total of nine models (with decimal points ranging from 0.10 to 0.90 and at intervals of 0.10) were estimated in this analysis, which aimed to explore the impact of the independent variables A and B on the dependent variable, GDP (C). When the quantile value was between 0.1 and 0.3, the proportion of the population aged 25–64 years who had completed higher education (A) had no significant positive impact on GDP growth, indicating that the development of higher education did not significantly affect economic and social development in poorer OECD countries. When the quantile value was between 0.4 and 0.6, the level of development of higher education had a significantly negative impact on economic and social development. Thus, for a country that had developed over a period, the advancement of higher education required multiple inputs, such as capital, material, and human resources.
During the early stage of the development of higher education, such inputs may, however, have a negative and weakening impact on social and economic development. The added cost of education and the lag between the output of educational achievements and the input of talents puts increased pressure on economic and social development during a certain period. When the quantile value was 0.7 or higher, the improvement of the overall level of higher education had a significantly positive impact on GDP growth, indicating the realisation of the talent training outcomes of higher education. Teaching and research outcomes were thus transformed into socially productive resources and power, with talents with higher education contributing to economic and social development.
When the quantile value was 0.1, the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education in relation to their peers (variable B), indicating the popularisation of higher education, had no significant impact on GDP growth. Thus, in extremely backward countries, the popularisation of higher education had little effect on economic and social development. When the quantile value ranged between 0.2 and 0.6, the popularisation of higher education had a significantly positive effect on GDP growth, indicating its contribution to economic growth.
When the quantile value was 0.7, the influence of variable B on variable C was no longer significant, indicating that social development would soon face the problem of overcapacity in higher education. When it exceeded 0.7, the ratio of eligible people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education in relation to their peers had a significantly negative impact on GDP growth, revealing that with the development of the economy, society and education, higher education had become overexpanded. Thus, the cost of investing in education exceeded the social benefits, leading to overcapacity whereby the supply of higher education talents exceeded the demand. This situation led to wasted educational resources and excessive competition of talents, hindering economic growth (See Table 5 ).
The increased level of adult education and the proportion of the population experiencing poverty
Using the same model, this study explored the influence of the independent variables, A and B, on the poverty line (dependent variable D). The proportion of the population aged 25–64 years who had completed higher education (independent variable A) had no significant influence on the proportion of the population living in poverty, indicating that popularisation of education and economic and social development have been achieved to a certain extent in OECD countries, and improvements targeting the population experiencing poverty could no longer be achieved simply by increasing the volume and quantity of higher education. When the quantile value was 0.1, the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who had completed higher education in relation to their peers (independent variable B) had no significant effect on the proportion of the population experiencing poverty (dependent variable D). Therefore, the strategy of increasing higher education enrolment and the ratio of the eligible population through the fair allocation of educational resources, and thus the popularisation of education, would not be effective for a small population segment experiencing poverty. In other words, the population segment experiencing poverty in highly developed countries is less receptive to the popularisation of higher education. When the quantile value was 0.2, the independent variable, B, had a significantly positive impact on the dependent variable D, that is, an increase in the popularity of higher education led to an increase in the population segment experiencing poverty. This phenomenon can be interpreted as reflecting the inherent disadvantages of the welfare state in the field of education. A rise in the number of eligible young people aged 25–34 years who have completed higher education reflects the development trend of higher education towards fairness and popularisation following the redistribution of higher education resources.
The fair distribution of higher education resources leads to a lack of competition in the areas of teaching and career development. To a certain extent, reducing students’ willingness and enthusiasm to work may lead to poverty caused by the failure to achieve teaching results. When the quantile value was between 0.3 and 0.4, the independent variable, B, had no significant influence on the dependent variable D. In relatively poor countries, the popularisation of higher education contributes little to reducing the degree of poverty, so it may be necessary to explore ways of alleviating poverty from the perspective of improving the overall level and expanding the scale of basic higher education. When the quantile value was 0.5 or above, the independent variable B had a significantly negative impact on the dependent variable D, indicating that for countries with a relatively high proportion of their population experiencing poverty, the following strategy would be more effective.
Considering the quantile data, this study deemed that the degree of sensitivity of countries at different stages of economic development to the level of development and popularisation of higher education could be more intuitively evaluated using a radar map (see Fig. 2 ). Countries with sub-points 0.1–0.9 were defined along a spectrum as extremely backward, backward, moderately backward, slightly backward, moderate, preliminarily developed, moderately developed, developed, and highly developed. From the perspective of economic development, increasing the proportion of young people who complete higher education and popularising higher education had an obvious positive effect in backward and medium-developed countries, whereas the effect in highly developed countries was not obvious. Overall, the sensitivity of OECD countries to the high level of education penetration was found to be higher than the level of development of higher education. From the perspective of equitable economic development, the overall level of development of higher education had no significant impact on the poverty link in OECD countries, whereas OECD countries with differing economic development backgrounds and at varying stages of development evidenced relatively significant and stable sensitivity to the proportion of young and middle-aged people who completed higher education and the popularisation of higher education.
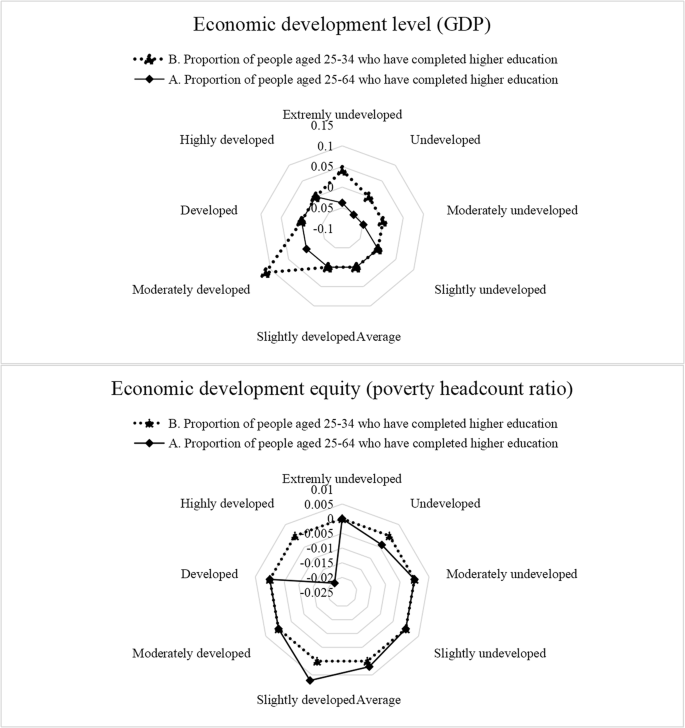
The dashed line represents the proportion of people aged 25–34 years who have completed higher education. The solid line represents the proportion of people aged 25–64 years who have completed higher education, the impact of the overall level of higher education.
Our findings indicated that population segments with higher education had a significantly positive impact on GDP growth in 38 OECD countries. An increase in the proportion of the population segment of working age who completed higher education was found to contribute to GDP growth. Moreover, an improvement in the popularity of higher education played a positive role during the initial stage of economic and social development.
At the same time, oversupply and overcapacity may result from a continuous improvement of higher education. A very large number of young people who have completed higher education can lead to excessive competition and wasted academic qualifications (Mathias, 2023 ; Megyesiova and Lieskovska, 2018 ). In turn, higher education knowledge unemployment, overinvestment, a structural imbalance, disorderly expansion and wasted resources can occur, which have detrimental impacts on economic operations.
Some studies have shown that strengthening the quality of higher education helps to improve cognitive abilities within the labour force, thereby enhancing the growth of the knowledge economy (Ainscow, 2020 ; Bamberger and Kim, 2022 ). Other studies have reported regional heterogeneity relating to the marginal effect of improving the quality of higher education on economic growth. Some scholars have analysed the influence of the quality of higher education on economic development from the perspective of human capital investment theory. Their findings indicate that the quality of higher education determines the composition and growth trend of social human capital. Because of differences in the degrees of development of different economies, the quality of higher education has a phased influence on economic growth (Balestra and Ruiz, 2015 ; Brand, 2021 ). Case studies of African developing countries by international scholars have revealed that quality factors are key to realising the economic development function of higher education. From the perspectives of both efficient financial investments by states in education poverty alleviation and the effects of economic, time and emotional investments of poor families and individuals in education poverty alleviation, it is necessary to take the return on education into consideration. Moreover, it is important to respond to reasonable concerns regarding the return on education for poor people and to strengthen their cognitive capacities to rationalise as well as their expectations regarding returns on education (Li et al., 2023 ). In this way, the intention to participate and behaviour of anti-poverty education will be generated, and the strategic upgrading of poverty alleviation combined with the promotion of aspirations and cognitive capacities will be emphasised.
Implications
Our use of panel data from 38 countries to deepen understanding of the effect of popularising higher education on economic growth and poverty reduction also has practical implications. The economic, social, and higher education undertakings in OECD countries evidence a certain level of development. The population segment with higher education has no significant impact on reducing the proportion of the population segment experiencing poverty. Simply increasing the proportion of people who complete higher education and expanding the scale of higher education will not effectively reduce poverty (Li and Xue, 2021 ). Providing more educational opportunities to poor people through the slanting of educational resources can help to reduce the proportion of poor people (Ainscow, 2020 ; Bamberger and Kim, 2022 ). For example, popularising higher education plays a key role to influence a country’s development level and scientific and technological innovation drives the deepening of a country’s economy (Bamberger and Kim, 2022 ). Technological progress is the core of economic growth, scientific and technological innovation brings technological change and development in all aspects, human capital promotes economic growth, and higher education trains talents and improves the capital attribute of human (Camilla, 2023 ). For endogenous economic growth theory, the economy does not rely on external forces to achieve sustained growth, and endogenous technological progress determines sustained economic growth. Popularising higher education worldwide brings the accumulation of human capital, improves the quality of workers, and scientific and technological innovation makes technological progress and high-quality economic development, practically. Human capital accumulation is also the process of continuous input of labour force, which covers the accumulation of human capital by labour force factors in formal education, training, and other learning processes. From the perspective of human capital, popularising higher education is the most direct and efficient way to promote the accumulation of human capital and improve the quality of labour force (Balestra and Ruiz, 2015 ; Brand, 2021 ). The popularisation degree of higher education is one of the important indicators to measure the development level of a country’s economic, and it is also the common trend of the development of higher education in all countries after World War II. In this transitional era, how to continue the achievements of higher education in the popular era and solve the existing problems as soon as possible is the heavy responsibility of our times. Therefore, at the initial stage of popularisation of higher education, it is necessary to re-examine the process of higher education popularisation globally and explore the internal logics between the popularisation of higher education and Sustainable Development Goal of inclusive and equitable quality education (Ainscow, 2020 ; Bamberger and Kim, 2022 ).
For policy suggestions, this study suggests that both national and local governments worldwide should pay much attention to the popularisation degree of higher education to greatly improve the innovative ability of talents and scientific and technological innovation in higher education. For example, they could promote scientific and technological innovation in an organised manner to serve national and regional economic and social development. Faced with the current situation in which global higher education has entered a stage of popularisation and new challenges and problems in serving regional economic and social development, national governments should continue to optimise the distribution and structure of higher education resources to support different regions, focusing on the major strategy of enhancing national competitiveness, serving economic and social development, and promoting common prosperity.
Contributions
This study novelty contributes on examining how popularising higher education affects economic growth and poverty alleviation, conceptually, methodologically, and practically. For instance, this study focuses on epitomising the conceptual and analytical model to explore the effects of higher education and adult education within populations (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (gross domestic product; GDP) and the poverty line. In addition, this study novelty combines both Mankiw-Romer-Weil model Solow model to investigate the effects of higher education and adult education within populations on economic growth and the poverty through OLS regression model and quantile model. For the practical aspect, this study practically uncovers the implicit significance of the popularisation of higher education for advocating UNESCO’s aim of developing inclusive and equitable quality education to achieve the fourth Sustainable Development Goal.
Limitations
This study had some limitations. Data could have been collected from a larger sample of OECD countries to explore the effect of population segments with higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and the poverty line. In addition, a qualitative component could be included in future studies to uncover the cultural and historical contexts of the effect of popularising higher education on economic growth and poverty reduction at the local level. Future studies should also investigate the causal relationship between the popularisation of higher education and economic growth. Additional empirical data and advanced research methods can be used to enable a shift from correlation to causality.
In conclusion, this study examined the effect of the population segment with higher education and adult education (popularisation of higher education) on economic growth (GDP) and the poverty line using panel data from 38 countries. The population segment with higher education was found to have a significant positive impact on promoting GDP growth. An increase in the proportion of the working-age population segment that had completed higher education was evidently conducive to GDP growth. Popularisation of higher education was also found to play a positive role in the initial stage of economic and social development.
Data availability
The data of OECD country GDP is retrieved from https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?locations=1W , The data of OECD country poverty line is retrieved from https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.DDAY?locations=1W&start=1984&view=chart , The data of OECD country Population with tertiary education 25–34-year-old is retrieved from https://data.oecd.org/eduatt/population-with-tertiary-education.htm#indicator-chart , The data of OECD country Percentage of 25–64-year old’s who have completed higher education (%) is retrieved from https://data.oecd.org/eduatt/adult-education-level.htm#indicator-chart , The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in Harvard Dataverse https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/TP43QS .
Adams, R (2013). Education: poverty and inequality blamed as UK sinks in adult literacy league: OECD survey flags up big problems for England: Post-16 education blamed for failure to address issue. The Guardian . (2013, October 9). London, England
Agasisti T, Longobardi S, Prete V, Russo F (2021) The relevance of educational poverty in europe: determinants and remedies. J Policy Model 43(3):692–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2020.03.015
Article Google Scholar
Ainscow M (2020) Promoting inclusion and equity in education: lessons from international experiences. Nord J Stud Educ Policy 6(1):7–16
Balestra C, Ruiz N (2015) Scale-invariant measurement of inequality and welfare in ordinal achievements: an application to subjective well-being and education in OECD Countries. Soc Indic Res 123(2):479–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-014-0751-2
Bamberger, A, & Kim, MJ (2022) The OECD’s influence on national higher education policies: internationalisation in Israel and South Korea. Comp Educ 18. https://doi.org/10.1080/03050068.2022.2147635
Brand M (2021) The OECD poverty rate: lessons from the russian case. Glob Soc Policy 21(1):144–147
Camilla S. (2023) The design of upper secondary education across OECD countries: Managing choice, coherence and specialisation. OECD Education Working Papers. https://doi.org/10.1787/158101f0-en
Chakeredza S, Temu A, Saka J, Munthali D, Muir-Leresche K, Akinnifesi F, Ajayi O, Sileshi G (2008) Tailoring Tertiary Agricultural Education for Sustainable Development in Sub-Saharan Africa: Opportunities and Challenges. J Sci Res Essay 3(8):326–332
Google Scholar
Chelli F, Ciommi M, Mariani F, Polinesi G, Recchioni MC, Lamonica GR, Salvati L (2022) A story of strengths and weaknesses in tertiary education: evaluating “Mobility” and “Opportunities” in OECD countries with composite indicators. Sustainability 14(24):16463. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416463
Decancq, K (2017) Measuring multidimensional inequality in the OECD member countries with a distribution-sensitive better life index. Soc Indic Res 131(3):1057–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-016-1289-2
Fang W, Farooq U, Liu Z, Lan J, Iram R (2022) Measuring energy efficiency financing: a way forward for reducing energy poverty through financial inclusion in OECD. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(47):71923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20139-8
Garritzmann, JL (2016) The political economy of higher education finance: the politics of tuition fees and subsidies in OECD Countries, 1945–2015. Garritzmann. Germany, Berlin: Springer International Publishing
Gillian G, Lisa T, & Thomas W (2021) How are higher education systems in OECD countries resourced?: Evidence from an OECD Policy Survey.OCDE. https://doi.org/10.1787/0ac1fbad-en
Gong HJ, Hong JE (2021) Does postsecondary education attainment matter in community service engagement? Evidence from Across 18 OECD Countries. Educ Sci 11(3):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11030096
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Granata, M (2022) The OECD and technical education in post-war Mediterranean Europe. Labor History. https://doi.org/10.1080/0023656X.2022.2057459
Habibi, F & Zabardast, MA (2020) Digitalization, education and economic growth: a comparative analysis of Middle East and OECD countries. Technol Soc 63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101370
Hoeller P, Joumard I, Koske I (2014) Reducing income inequality while boosting economic growth: can it be done? Evidence from OECD Countries. Singap Econ Rev 59(1):1–22
Jericho, G (2016) Australia didn’t have a ‘great recession’? Tell that to young people; an OECD report has found a rise in youth not in employment, education or training (Neets) since 2008. While historically the rate isn’t high, benefits are so low that youth are now more likely to be living in poverty. Guardian. London, England. https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A463552813/AONE?u=unimelb&sid=bookmark-AONE&xid=701996a9
Julian LG (2018) The political economy of higher education finance. the politics of tuition fees and subsidies in OECD Countries, 1945–2015. Czech Sociol Rev 54(3):479–482
Jungblut J (2017) The political economy of higher education finance. The politics of tuition fees and subsidies in OECD countries, 1945–2015. Eur J High Educ 7(1):96–99. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568235.2017.1265789
Kalamova, M (2020) Resourcing higher education: challenges, choices and consequences. Higher Education Policy Team. Paris: OECD Publishing
Lamichhane, S, Egilmez, G, Gedik, R, Bhutta, MKS, & Erenay, B (2021) Benchmarking OECD countries’ sustainable development performance: a goal-specific principal component analysis approach. J Clea Prod 287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125040
Ledger, S, Thier, M, Bailey, L, & Pitts, C (2019) OECD’s approach to measuring global competency: powerful voices shaping education. Teachers College Record, 121(8):1–40
Li, J & Xue. E (2021) Returnee faculty responses to internationalizing “Academic Ecology” for Creating World-class Universities in China’ Elite Universities. Higher Education. 81(5), 1063–1078
Li, J, & Xue. E, Liu, C, Li, X (2023) Integrated macro and micro analyses of student burden reduction policies in China: call for a collaborative “family–school–society” model. Humanities & Social Sciences Communications. 10, 184 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01695-x
Liu, L (2017) Exploring the relationship between education economy and individual civic attitudes: a cross-national analysis in England, Spain, Sweden, Poland and Chinese Taipei
Lucas R (1988) On the mechanics of economic development. J. Monetary Econ 22(1):342
Mathias B (2023). The assessment of students’ creative and critical thinking skills in higher education across OECD countries: a review of policies and related practices. OECD Education Working Papers. https://doi.org/10.1787/35dbd439-en
Megyesiova, S, & Lieskovska, V (2018) Analysis of the sustainable development indicators in the OECD Countries. Sustainability 10(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124554
Mitic RR (2018) The political economy of higher education finance: the politics of tuition fees and subsidies in OECD Countries, 1945-2015. Rev High Educ 41(3):484–487
OECD (2022) Education at a Glance 2022: OECD Indicators, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/3197152b-en
Özdoğan Özbal E (2021) Dynamic effects of higher education expenditures on human capital and economic growth: an evaluation of OECD countries. Policy Rev High Educ 5(2):174–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/23322969.2021.1893125
Pinheiro R, Pillay P (2016) Higher education and economic development in the OECD: policy lessons for other countries and regions. J High Educ Policy Manag 38(2):150
Romer M (1990) Endogenous technological change. J Political Econ 98(5):S71–S102
Rowe E (2019) Capitalism without capital: the intangible economy of education reform. Discourse 40(2):271
Sahnoun M, Abdennadher C (2022) Returns to investment in education in the OECD Countries: does governance quality matter? J Knowldege Econ 13(3):1819–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00783-0
Samo V. (2022). A snapshot of equity and inclusion in OECD education systems: findings from the Strength through Diversity Policy Survey. OECD Eduction Working Papers. https://doi.org/10.1787/801dd29b-en
Schultz (1961) Investment in human capital. Am Econ Rev 51(1):1–17
Solow RM (1957) Technical change and the aggregate production function. Rev Econ Stat 39(3):312–320
Zapp M (2022) Revisiting the global knowledge economy: the worldwide expansion of research and development personnel, 1980–2015. Minerva 60(2):181–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11024-021-09455-4
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by 2021 National Social Science Foundation of Higher Education Ideological and Political Course research (Key project) Ideological and Political Education System Construction System Mechanism Research in New Era (No.: 21VSZ004).
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Jian Li, Eryong Xue.
Authors and Affiliations
Institute of International and Comparative Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875, China
China Institute of Education Policy, Faculty of Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875, China
Eryong Xue, Yukai Wei & Yunshu He
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work: Jian Li and Eryong Xue; the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work: Jian Li and Eryong Xue; drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content: Eryong Xue, Jian Li, Yukai Wei, and Yunshu He; final approval of the version to be published: Eryong Xue and Jian Li.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Jian Li or Eryong Xue .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants. It was not required as this article used published data.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, J., Xue, E., Wei, Y. et al. How popularising higher education affects economic growth and poverty alleviation: empirical evidence from 38 countries. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 520 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03013-5
Download citation
Received : 29 June 2023
Accepted : 02 April 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03013-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Open access
- Published: 15 April 2024

Medical, dental, and nursing students’ attitudes and knowledge towards artificial intelligence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hamidreza Amiri 1 na1 ,
- Samira Peiravi 2 na1 ,
- Seyedeh sara rezazadeh shojaee 3 na1 ,
- Motahareh Rouhparvarzamin 4 ,
- Mohammad Naser Nateghi 5 ,
- Mohammad Hossein Etemadi 6 ,
- Mahdie ShojaeiBaghini 7 ,
- Farhan Musaie 8 ,
- Mohammad Hossein Anvari 9 &
- Mahsa Asadi Anar 10
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 412 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
285 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Nowadays, Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the most popular topics that can be integrated into healthcare activities. Currently, AI is used in specialized fields such as radiology, pathology, and ophthalmology. Despite the advantages of AI, the fear of human labor being replaced by this technology makes some students reluctant to choose specific fields. This meta-analysis aims to investigate the knowledge and attitude of medical, dental, and nursing students and experts in this field about AI and its application.
This study was designed based on PRISMA guidelines. PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases were searched with relevant keywords. After study selection according to inclusion criteria, data of knowledge and attitude were extracted for meta-analysis.
Twenty-two studies included 8491 participants were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled analysis revealed a proportion of 0.44 (95%CI = [0.34, 0.54], P < 0.01, I2 = 98.95%) for knowledge. Moreover, the proportion of attitude was 0.65 (95%CI = [0.55, 0.75], P < 0.01, I2 = 99.47%). The studies did not show any publication bias with a symmetrical funnel plot.
Average levels of knowledge indicate the necessity of including relevant educational programs in the student’s academic curriculum. The positive attitude of students promises the acceptance of AI technology. However, dealing with ethics education in AI and the aspects of human-AI cooperation are discussed. Future longitudinal studies could follow students to provide more data to guide how AI can be incorporated into education.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The term "artificial intelligence (AI)" was coined nearly 70 years ago to refer to using of computers to imitate human reasoning [ 1 ]. The first application of AI was in mathematics in 1956 when it was utilized for proving theorems [ 2 ]. Integrating of AI in medicine was a gradual process [ 3 ] that began with the development of a software program that guided doctors on appropriate antimicrobial therapy [ 4 ].
AI is a trending topic that is currently at the forefront of technological advancements [ 5 ] and has the potential to influence the healthcare industry significantly [ 6 ]. The term AI refers to a scientific and engineering discipline that deals with developing computer-based systems capable of exhibiting intelligent behavior, as well as understanding and replicating human-like cognitive processes [ 7 ]. Recent advancements in computer and informatics technologies have paved the way for integrating of AI technologies, such as machine learning and deep learning, into healthcare information systems [ 8 , 9 ]. AI has been extensively integrated into decision support systems (DSSs) in data-intensive medical specialties like radiology, pathology, and ophthalmology [ 10 ].
Several experts have expressed their opinions on the future of radiology in light of AI's emergence [ 11 , 12 ]. Radiological societies have also published white papers promoting their views [ 13 , 14 ]. Studies have indicated that medical students do not express significant concern or fear about being replaced by AI in their profession [ 15 ]. However, some students may experience anxiety related to the possibility of being displaced by AI, which may discourage them from considering certain medical specialties [ 16 ]. Indeed, there are positive and negative perspectives on the impact of AI on daily human life. Pessimistic views suggest that AI may replace humans in various sectors. On the other hand, optimistic views highlight that individuals with AI support will have increased opportunities to leverage future advancements [ 17 ]. To the best of our knowledge, this study aimed to evaluate the attitudes, knowledge, and skills of medical, dental, and nursing students toward AI and to gather information about their opinions on the use of AI.
This systematic review and meta-analysis study was based on the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis) guidelines. The protocol of this study was registered on PROSPERO with the ID of CRD42024521006.
Literature search
A structured literature search was applied up to 12th September 2023 to collect appropriate articles from PubMed /MEDLINE, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases. Search tactics included two main subgroups of keywords. One subgroup was the concepts related to artificial intelligence, and the other group was the perspective of health care and dentists; then, Subgroups were mixed by using ‘AND.’ More specifically, we searched the above databases for (artificial intelligence or machine learning) and (Medical or dentistry or nursing) (Table 1 ). The search process was done according to the query options of each database. In addition, we searched the reference lists of appropriate systematic reviews to prevent missing data. Two reviewers accomplished all strategies in a solitary state, and any controversy between the reviewers was resolved by negotiation.
Criteria for selecting studies
The main goal was to evaluate the attitudes of students and graduates working in dentistry, nursing, or medical (health care providers) fields toward AI and machine learning. We didn't use any restrictions on date and language, but to make the search more specific, we restricted the keyword search to the title. Articles with irrelevant subject matter and studies utilizing animal models were excluded during the initial phase of document selection. Additionally, duplicate documents were eliminated.
Data extraction and study quality assessment
Two reviewers independently assessed the title and abstract of each study to ascertain its suitability for inclusion in this meta-analysis. We excluded studies that didn’t fulfill our criteria. The complete text of the remaining studies was reviewed, and studies that met the criteria were included in the data extraction step. After that, the subsequent items were acquired for extraction and divided into four sets:
1. Study characteristics include authors, type of study, year, location, and follow-up duration.
2. Participant variables (average age, gender).
3. Research Methodology (e.g., participant sample size).
4. Results and outcomes (the attitude, knowledge, and skill toward artificial intelligence).
Two previously mentioned reviewers utilized the critical appraisal checklists for cohort, case–control, and analytical cross-sectional studies created by the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI). The checklists can be found at the following website: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools . If there were any inconsistencies, a third author was involved in the process.
Statistical analysis
Our data analysis was conducted using the STATA 13.1 software developed by StataCorp LP in College Station, TX, USA. The findings were presented as combined odds ratios (ORs) and a 95% confidence interval displayed in a forest plot. Heterogeneity among the eligible studies was assessed using the I2 statistic. The random effects model was employed when significant heterogeneity was observed (I2 > 50%). In addition, we performed a sensitivity analysis by systematically excluding one study at a time and repeating the meta-analysis. This allowed us to guarantee the consistency of our conclusions. To assess the possibility of publication bias, we visually examined the symmetry of the funnel plot and conducted Egger’s regression analysis.
Search strategy
We obtained 2426 from PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, and Google Scholar in the initial search. Seventeen studies were found by manual search. After the automatic removal of duplicated reports, 2292 studies remained. Two thousand sixty-five studies were excluded in the title and abstract evaluation. Two hundred twenty-seven remaining studies underwent additional assessment through full-text, causing 205 papers to be excluded due to ineligibility to inclusion criteria. Finally, 22 studies were included in this systematic review and meta-analysis (Fig. 1 ).
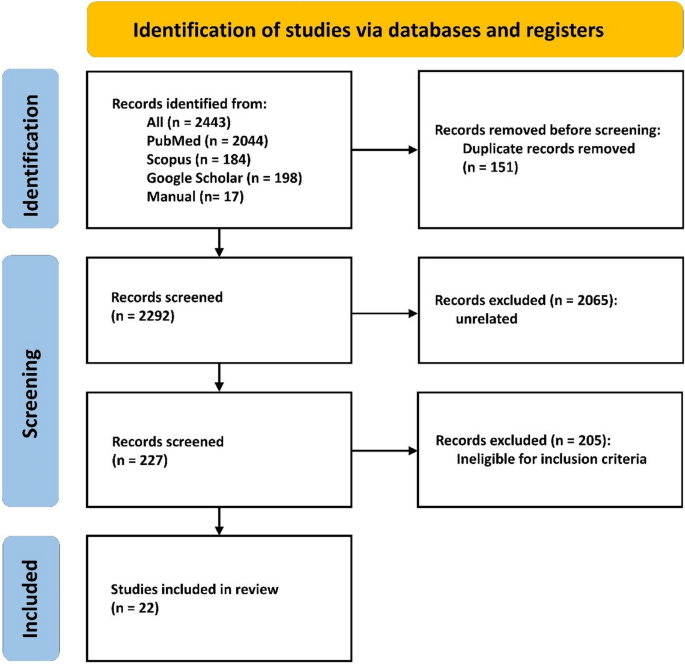
Prisma diagram for study selection process in this study
Baseline characteristic
This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the attitude, knowledge, and skills of medical, dental, and nursing students toward artificial intelligence. We included 22 original articles published from 2020–2023. These studies were performed in several countries, including the U.S.A [ 18 ], Germany [ 19 , 20 ], Lebanon [ 21 ], Pakistan [ 22 ], Canada [ 23 ], The U.K. [ 24 ], United Arab Emirates [ 25 ], Nigeria [ 26 ], Turkey [ 27 , 28 ], Spain [ 29 ] Saudi Arabia [ 30 ], India [ 31 , 32 , 33 ], Egypt [ 34 ], Peru [ 35 ], Nepal [ 36 ], Kuwait [ 37 ], Syria [ 38 ], and multiple countries [ 39 ]. The study design of 19 studies was cross-sectional [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 ], and the rest followed a mixed methodology [ 18 , 19 , 39 ]. This study included 8491 participants, with a mean age of 19–30 years (Table 2 ).
We performed a meta-analysis on 22 studies for attitude of students toward AI. The proportion for attitude was 0.65 (95%CI = [0.55, 0.75], P < 0.01) according to 22 studies. This means that 65% of all students were agree with the use of AI in medicine and had a favorable view. Similarly, the heterogeneity was severe with I2 of 99.47%, and H2 = 189.47 (Fig. 2 ).
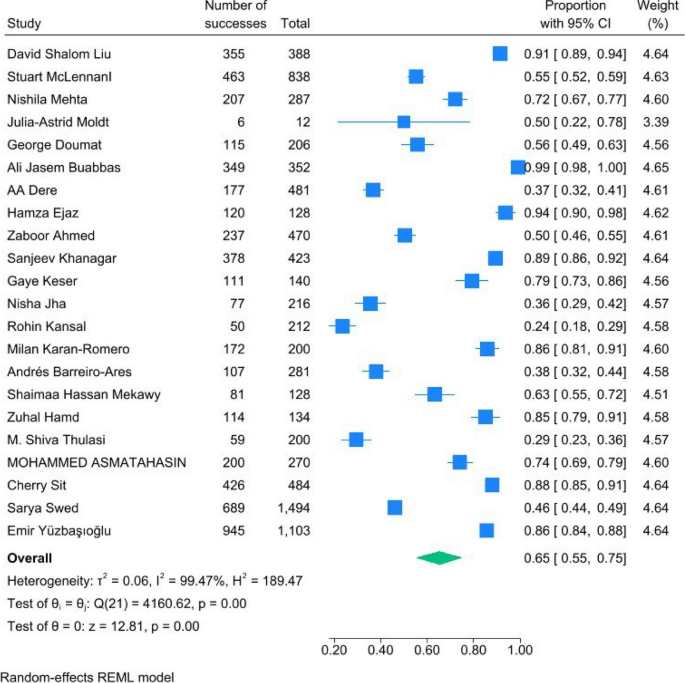
Forest plot of proportion of attitude showed a significant effect of 0.44 (0.34, 0.54)
In comparison between various countries, students in the U.S.A. Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, and England showed a higher rate of attitude toward AI than those in Germany, Lebanon, Nigeria, Pakistan, and India. Additionally, the Attitudes of Spanish and United Arab Emirates students varied in different studies. Finally, students in Canada and Egypt displayed a medium rate of positive attitude (Fig. 3 ).
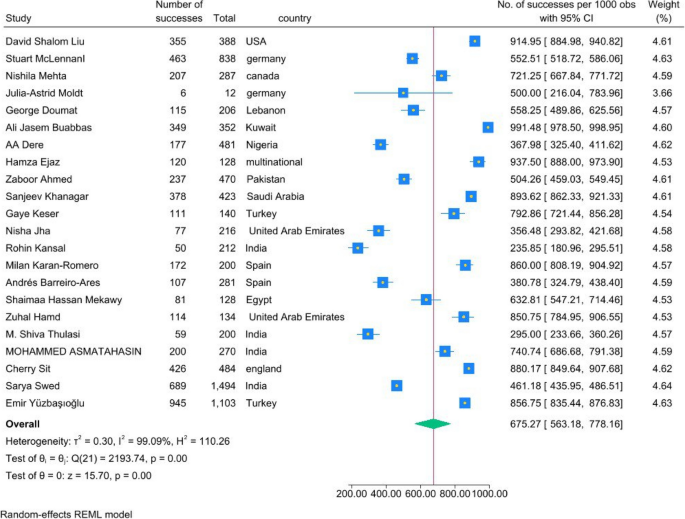
Forest plot for comparing countries in terms of their students' attitudes toward AI
A total of 17 studies had provided the knowledge data. The pooled analysis showed a proportion for knowledge of 0.44 (95%CI = [0.34, 0.54], P < 0.01). This shows that 44% of the total population of included students had a relatively good knowledge about AI, either in the field of theory or practical. The studies showed a high heterogeneity with an I2 of 98.95% and H2 of 93.35 (Fig. 4 ).
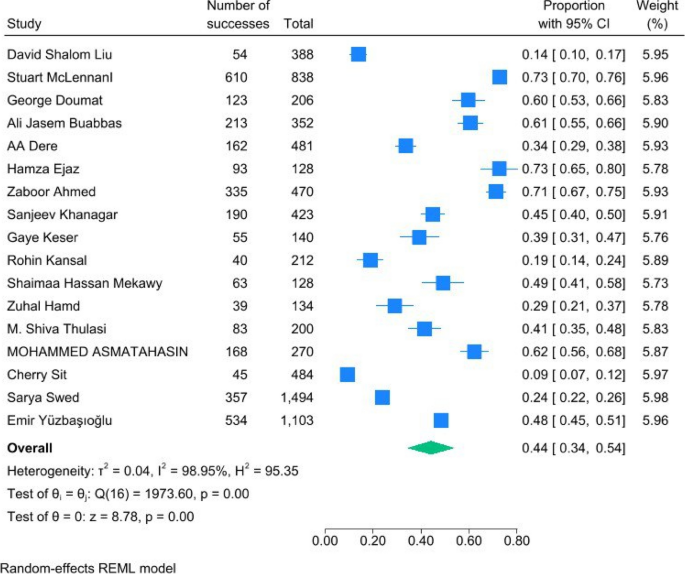
Forest plot of proportion of knowledge showed a significant effect of 0.65 (0.55, 0.75)
Students from Germany, Lebanon, Kuwait, and Pakistan had higher levels of knowledge in the field of AI. In contrast, students from the U.S.A., Nigeria, the United Arab Emirates, and England showed a relatively lower knowledge level. Additionally, the level of knowledge in Indian students varied across different studies. Finally, students from Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey showed moderate knowledge (Fig. 5 ).
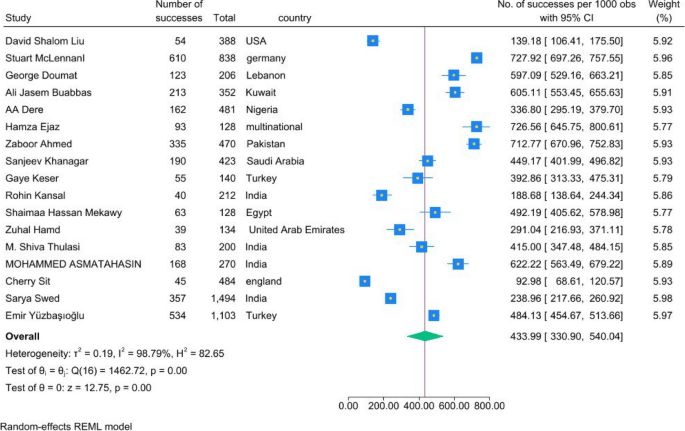
Forest plot for comparing countries in terms of their students' knowledge of AI
Publication bias
The publication bias was evaluated through the funnel plot and Egger’s test. The funnel plot (Fig. 6 ) showed a symmetrical pattern, indicating no publication bias. This was supported by Egger’s test result ( P = 0.75).
Funnel plot of included studies showed a symmetrical pattern including no publication bias (Egger’s test P -value = 0.75)
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to provide evidence on medical, dental, and nursing students’ attitudes, knowledge, and skills regarding AI. Across 24 studies with 5789 participants, students demonstrated moderate knowledge but generally positive attitudes towards AI.
Overall, 44% of students exhibited medium to high knowledge of AI principles and applications. Knowledge encompassed theoretical understanding of AI algorithms, practical abilities to implement AI systems, and programming proficiency. However, the majority of students had limited AI knowledge. This knowledge gap signals an urgent need to incorporate comprehensive AI education into healthcare curricula. Studies show that students support this idea [ 40 , 41 ]. Curricula should cover foundational concepts like machine learning and neural networks as well as applied skills in utilizing AI tools for tasks like diagnostic imaging interpretation. Hands-on experiential learning with real-world case examples could prove highly effective. Other reason is that lack of knowledge is an important barrier to the use of AI [ 42 ]. Notably, students from developed countries demonstrated greater AI knowledge than peers in developing nations. This has been shown in previous studies as well [ 43 ]. This discrepancy highlights concerning global digital divides in accessing AI skills training. Targeted investments and capacity building programs are critical to ensuring students worldwide can gain applied AI competencies.
In contrast to their variable knowledge, 65% of students expressed positive attitudes regarding AI utilization in education and clinical practice. This was also showed in previous studies that most of healthcare students have a positive attitude towards AI [ 19 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 ]. Students recognized potential benefits of AI for enhancing diagnostic accuracy, improving healthcare access, and relieving clinical workloads. In contrast there are negative perceptions too [ 44 , 48 , 49 ].
Attitudinal measures had substantial heterogeneity, reflecting divergent perceptions across student subgroups. In particular, developing world students held more skeptical views, fearing AI could dehumanize care or render healthcare jobs obsolete. Curricula must address these valid ethical and social concerns through discussions of AI bias, transparency, and impacts on healthcare roles. It should be noted that patient privacy and autonomy, informed consent, transparency, equality and biases are some of major concerns [ 50 ]. Refining attitudinal measures with more granular subsets and exploring predictors of AI acceptance would further inform targeted educational initiatives based on students’ specific concerns.
Enthusiasm and optimism vs. expertise gaps
Overall students showed enthusiasm and optimism about AI's role in medicine, yet the majority lacked substantial expertise and practical abilities in utilizing AI technology. A similar pattern exists in other majors too. A study by Busch et al. involving 387 pharmacy students from 12 countries found that 58% of students held positive attitudes towards AI in medicine, while 63% reported limited general knowledge of AI [ 51 ]. Bridging these attitude-knowledge gaps represents a key challenge for AI readiness. Curricula must not only transfer technical knowledge but also address values, ethics, and societal impacts. Education should emphasize AI as a collaborative tool to augment human capabilities rather than replace them. Again, having students directly experience AI’s benefits for care quality could show its potential for enhancing work rather than displacing workers. Additionally, equitable access to AI upskilling is imperative, particularly for students from disadvantaged regions who may have heightened concerns about AI’s risks.
Strength and limitations
The strength of our study is the review of articles from three large databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Also, we used the random effect model to ensure the robustness of the results. Also, our study had some limitations. We included only studies in English. In addition, most of the included studies used their own questionnaires to evaluate the knowledge and approach of the participants toward artificial intelligence. Finally, it is necessary to mention that there were not enough studies to extract the skill results and perform a meta-analysis.
Future research directions
Future research should investigate the long-term knowledge and attitudinal trajectories of students after graduation. As AI becomes further embedded into real-world practice, how do provider perspectives evolve? Do knowledge gaps persist or does on-the-job exposure improve understanding? How do early attitudinal concerns translate to technology adoption patterns? Longitudinal data tracking cohorts of students into practice could provide pivotal insights to guide continuing education and change management interventions.
Follow-up studies should also assess the durability of AI skills training. Can one-time education produce lasting competencies or is ongoing reinforcement needed? Comparisons of different pedagogical approaches for AI instruction could illuminate best practices as well. And crucially, future work must evaluate links from AI education to concrete improvements in clinical processes and patient outcomes. Demonstrating benefits to care quality represents the strongest incentive for curriculum reform.
AI is rapidly transforming healthcare and medical education. However, the extent to which healthcare students are prepared for this transformation remains unclear. The moderate knowledge levels indicate substantial room for improvement through curricular enhancement. Hands-on experiential learning focused on applied AI skills shows promise for durably improving competencies. Positive baseline attitudes bode well for acceptance, but targeted education around AI ethics, impacts, and human-AI collaboration will be key to realizing this potential.
Important gaps remain in understanding long-term knowledge retention, optimal pedagogies, impacts of improved education on clinical processes and outcomes, and equitable global access. Follow-up longitudinal studies tracking cohorts of students into practice could offer pivotal data to guide continuing education. Comparisons of instructional approaches may illuminate best practices.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Artificial intelligence
Larentzakis A, Lygeros N. Artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine as a strategic valuable tool. Pan Afr Med J. 2021;38:184.
Article Google Scholar
Russell S, Norvig P. Artificial Intelligence, A Modern Approach. Second Edition. 2003. p 1081.
Kaul V, Enslin S, Gross SA. History of artificial intelligence in medicine. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92(4):807–12.
Shortliffe EH, et al. Computer-based consultations in clinical therapeutics: Explanation and rule acquisition capabilities of the MYCIN system. Comput Biomed Res. 1975;8(4):303–20.
Morris K, Schlenoff C, Srinivasan V. A Remarkable Resurgence of Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Automation and Autonomy. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. 2017;14:407–9.
Hinton G. Deep Learning-A Technology With the Potential to Transform Health Care. JAMA. 2018;320(11):1101–2.
Shapiro, S.C., Artificial intelligence (AI), in Encyclopedia of Computer Science. 2003, John Wiley and Sons Ltd. p. 89–93.
Miotto R, et al. Deep learning for healthcare: review, opportunities and challenges. Brief Bioinform. 2018;19(6):1236–46.
Xiao C, Choi E, Sun J. Opportunities and challenges in developing deep learning models using electronic health records data: a systematic review. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018;25(10):1419–28.
Yu KH, Kohane IS. Framing the challenges of artificial intelligence in medicine. BMJ Qual Saf. 2019;28(3):238–41.
Moehrle A. “Radiology” Is Going Away . . . and That’s Okay: Titles Change, A Profession Evolves. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(3):499–500.
Schier R. Artificial Intelligence and the Practice of Radiology: An Alternative View. J Am Coll Radiol. 2018;15(7):1004–7.
Beregi JP, et al. Radiology and artificial intelligence: An opportunity for our specialty. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2018;99(11):677–8.
Tang A, et al. Canadian Association of Radiologists White Paper on Artificial Intelligence in Radiology. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2018;69(2):120–35.
Pinto Dos Santos D, et al. Medical students’ attitude towards artificial intelligence: a multicentre survey. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(4):1640–6.
Gong B, et al. Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Canadian Medical Students’ Preference for Radiology Specialty: ANational Survey Study. Acad Radiol. 2019;26(4):566–77.
Johnston SC. Anticipating and Training the Physician of the Future: The Importance of Caring in an Age of Artificial Intelligence. Acad Med. 2018;93(8):1105–6.
Liu DS, et al. Perceptions of US medical students on artificial intelligence in medicine: mixed methods survey study. JMIR Medical Education. 2022;8(4): e38325.
Moldt J-A, et al. Chatbots for future docs: exploring medical students’ attitudes and knowledge towards artificial intelligence and medical chatbots. Med Educ Online. 2023;28(1):2182659.
McLennan S, et al. German medical students´ views regarding artificial intelligence in medicine: A cross-sectional survey. PLOS Digital Health. 2022;1(10): e0000114.
Doumat G, et al. Knowledge and attitudes of medical students in Lebanon toward artificial intelligence: A national survey study. Frontiers in artificial intelligence. 2022;5:1015418.
Ahmed Z, et al. Knowledge, attitude, and practice of artificial intelligence among doctors and medical students in Pakistan: A cross-sectional online survey. Annals of Medicine and Surgery. 2022;76: 103493.
Mehta N, et al. Knowledge and Attitudes on Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A Provincial Survey Study of Medical Students. MedEdPublish. 2021;10:75.
Sit C, et al. Attitudes and perceptions of UK medical students towards artificial intelligence and radiology: a multicentre survey. Insights Imaging. 2020;11:1–6.
Hamd Z, et al. A closer look at the current knowledge and prospects of artificial intelligence integration in dentistry practice: A cross-sectional study. Heliyon. 2023;9(6):e17089.
Dere, A.A., Knowledge and Attitude of Medical Students and Doctors towards Artificial Intelligence: A study of University of Ilorin. 2023.
Yüzbaşıoğlu E. Attitudes and perceptions of dental students towards artificial intelligence. J Dent Educ. 2021;85(1):60–8.
Keser G, PEKİNER F.M.N. Attitudes, perceptions and knowledge regarding the future of artificial intelligence in oral radiology among a group of dental students in Turkey: a survey. Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences. 2021;11(4):637–41.
Barreiro-Ares A, et al. Impact of the rise of artificial intelligence in radiology: what do students think? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(2):1589.
Khanagar S, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of dental students towards artificial intelligence in Riyadh. Saudi Arabia Med Sci. 2021;25(114):1857–67.
Google Scholar
Kansal R, et al. Differences in knowledge and perspectives on the usage of artificial intelligence among doctors and medical students of a developing country: a cross-sectional study. Cureus. 2022;14(1):e21434.
Asmatahasin M, et al. Attitude and perception of dental students towards artificial intelligence. Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research. 2021;10(3):305–14.
Thulasi MS, et al. Knowledge attitude and practices of dental students and dental practitioners towards artificial intelligence. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering. 2022;10(1s):248–53.
Hassan Mekawy S, Ali Mohamed Ismail S, Zayed Mohamed M. Digital Health Literacy (DHL) Levels Among Nursing Baccalaureate Students And Their Perception And Attitudes Toward The Application Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Nursing. Egyptian Journal of Health Care. 2020;11(1):1266–77.
Karan-Romero M, Salazar-Gamarra RE, Leon-Rios XA. Evaluation of Attitudes and Perceptions in Students about the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry. Dentistry Journal. 2023;11(5):125.
Jha N, et al. Undergraduate medical Students’ and Interns’ knowledge and perception of artificial intelligence in medicine. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2022;(13):927–37.
Buabbas, A.J., et al. Investigating Students’ Perceptions towards Artificial Intelligence in Medical Education. in Healthcare. 2023. MDPI.
Swed S, et al. Knowledge, attitude, and practice of artificial intelligence among doctors and medical students in Syria: a cross-sectional online survey. Frontiers in artificial intelligence. 2022;5:1011524.
Ejaz H, et al. Artificial intelligence and medical education: A global mixed-methods study of medical students’ perspectives. Digital Health. 2022;8:20552076221089100.
Banerjee M, et al. The impact of artificial intelligence on clinical education: perceptions of postgraduate trainee doctors in London (UK) and recommendations for trainers. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):429.
Pupic N, et al. An evidence-based approach to artificial intelligence education for medical students: A systematic review. PLOS Digit Health. 2023;2(11): e0000255.
Singh N, et al. Attitude, perception and barriers of dental professionals towards artificial intelligence. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(5):584–8.
Mousavi Baigi SF, et al. Attitudes, knowledge, and skills towards artificial intelligence among healthcare students: A systematic review. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6(3): e1138.
AlZaabi A, AlMaskari S, AalAbdulsalam A. Are physicians and medical students ready for artificial intelligence applications in healthcare? DIGITAL HEALTH. 2023;9:20552076231152170.
Chen, M., et al., Acceptance of clinical artificial intelligence among physicians and medical students: A systematic review with cross-sectional survey. Frontiers in Medicine, 2022. 9.
Gillissen A, Kochanek T, Zupanic M, Ehlers E. "Medical students’ perceptions towards digitization and artificial intelligence: a mixed-methods study." Healthcare. 2022;10(4):723.
Karan-Romero M, Salazar-Gamarra RE,Leon-Rios XA. Evaluation of attitudes and perceptions in students about the use of artificial intelligence in dentistry. Dent J. 2023;11(5):125.
Sheela J. Attitude of Nursing Students towards Artificial Intelligence. Int J Sci Healthc Res. 2022;7(2):344-347.
Jussupow E, Spohrer K, Heinzl A. Identity Threats as a Reason for Resistance to Artificial Intelligence: Survey Study With Medical Students and Professionals. JMIR Form Res. 2022;6(3): e28750.
Prakash S, et al. Ethical Conundrums in the Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare-A Scoping Review of Reviews. J Pers Med. 2022;12(11):1914.
Busch F, et al. International pharmacy students' perceptions towards artificial intelligence in medicine-A multinational, multicentre cross-sectional study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2023;90(3):649–61.
Liu DS, et al. Perceptions of US Medical Students on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine: Mixed Methods Survey Study. JMIR Med Educ. 2022;8(4): e38325.
McLennan S, et al. German medical students´ views regarding artificial intelligence in medicine: A cross-sectional survey. PLOS Digit Health. 2022;1(10): e0000114.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all the authors of included studies.
Author information
Hamidreza Amiri, Samira Peiravi and Seyedeh sara rezazadeh shojaee contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Student Research Committee, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran
Hamidreza Amiri
Department of Emergency Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
Samira Peiravi
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Mashhad Medical Sciences, Islamic Azad University, Mashhad, Iran
Seyedeh sara rezazadeh shojaee
Student Research Committee, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran
Motahareh Rouhparvarzamin
Student Research Committee, Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
Mohammad Naser Nateghi
Students Research Committee, School of Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Mohammad Hossein Etemadi
Medical Informatics Research Center, Institute for Futures Studies in Health, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran
Mahdie ShojaeiBaghini
Dentistry Student, Dental Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
Farhan Musaie
Master of Health Science, Faculty of Health Sciences, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Mohammad Hossein Anvari
Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, SBUMS, Arabi Ave, Daneshjoo Blvd, Velenjak, Tehran, 19839-63113, Iran
Mahsa Asadi Anar
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Study design and conception: M.AA; Search & study selection: H.A, S.P; Data extraction: SS.RS, M.P; Quality assessment: MN.N, MH.E; Statistical analysis and interpretation: M.S, F.M; Drafting the manuscript: H.A, S.P, SS.RS, M.P, MN.N, MH.E, M.S, F.M, MH.A; Critical revision: M.AA. All authors were approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mahsa Asadi Anar .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary materials 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Amiri, H., Peiravi, S., rezazadeh shojaee, S. et al. Medical, dental, and nursing students’ attitudes and knowledge towards artificial intelligence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Educ 24 , 412 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05406-1
Download citation
Received : 13 February 2024
Accepted : 09 April 2024
Published : 15 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05406-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical students
- Dental students
- Nursing students
- Meta-analysis
- Systematic review
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
How to Write a Data Analyst Job Description: Important Skills and Role Responsibilities
Use these job description examples to guide your writing.
The terms may sound similar, but data analysts , data engineers and data scientists are actually very different roles.
Here’s the simplified version: Data analysts are responsible for collecting, cleaning, analyzing and reporting data; meanwhile, data engineers create and maintain architectural systems for collecting, storing, analyzing and managing large quantities of raw data; and finally, data scientists handle data collection, analysis and visualization — and sometimes build things like machine learning models.
To write a stellar job description for data analysts — and attract top candidates — you’ll need to understand their role more specifically. That’s where this guide comes in.
Table of Contents
What Does a Data Analyst Do?
Types of data analyst jobs.
- Data Analyst Skills
Data Analyst Salary Information
Data analyst job description template.
Access our entire library of templates for your open roles.
Data analysts gather data across a business, analyze it and translate the results into non-technical language for team members of all backgrounds.
Data analysts are typically early in their careers and may be seeking their first job after completing a bachelor’s degree or gaining the equivalent professional experience. Common degrees include statistics, math, computer science, physics, finance, business administration, economics or a related field.
What Is a Data Analyst?
Data analysts may be responsible for building data models to organize important data for different teams across the business and for monitoring and handling data. With large quantities of data comes endless possibilities for mistakes, requiring data analysts to constantly be on the lookout for information that needs cleansing and updating.
In addition to gathering, analyzing and cleansing information, data analysts create business reports for teams and individuals across the business. They also help translate analytics into non-technical insights to help all teams make well-informed decisions based on empirical evidence.
As they progress in their careers, data analysts may continue their education and become data engineers and eventually data scientists.
There are many different careers and jobs that data analysts can hold. Some of the most common fields for data analysts to work in include healthcare, big data , market research, operations and intelligence.
Let’s take a closer look at a few different types of data analyst jobs and what they do.
1. Business Intelligence Analyst
The primary job of a business intelligence analyst is to extract valuable insights from company data. Someone in this role should be comfortable with SQL, analyzing data, as well as creating data models.
2. Marketing Analyst
Marketing analysts help their team track the success of campaigns by using Google Analytics, custom reporting tools or other traffic analytics sites to determine the impact advertisements are making. Marketing analysts are key to marketing departments as they help understand what efforts are working and what advertisements to spend company money on.
3. Transportation Logistics Specialist
Transportation logistics specialists can utilize a data analytics background in a variety of ways. This role relies heavily on the ability to identify efficient delivery routes for products and services. Someone in this role uses large datasets to eliminate transit bottlenecks.
4. Operations Analyst
An operations analyst’s primary job is to organize a company’s internal processes. This role focuses on general operations as well as internal reporting and product manufacturing and distribution. Operations analysts can work for nearly every type of business, including supermarket chains, delivery providers or even government agencies.
5. Healthcare Analyst
Healthcare data analysts collect, organize and interpret data from sources like electronic health records, billing claims, cost reports and surveys. The purpose of this role is to assist healthcare providers in order to improve the quality of care, lower costs and improve patient experiences. Someone in this field might have duties like automating internal and external reports, creating data dashboards or being responsible for presenting information to hospital executives.
Related Reading Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Similarities and Differences Explained
Data Analyst Skills
Data analysts employ a variety of soft and technical skills throughout their careers. Like many positions, having clear communication skills and the ability to present complex information is crucial to this role. Critical thinking skills are an essential part of many jobs, and data analysts are no exception. These soft skills are especially important to data analysts because they are often responsible for presenting data to stakeholders and other teams in ways that everyone can understand.
Along with communication and critical thinking skills, data analysts will need to understand different visualization tools, coding languages and mathematical principles.
Top Data Analyst Skills
- Data visualization
- Data cleaning
- Critical thinking
- Communication
Coding Languages
Mastering coding languages like R and Python is important as they are standard in the industry. These languages also provide advanced analyses and predictive analytics on large data sets. Some coding languages data analysts need to know are:
Data Visualization
A key element of a data analyst’s job is data visualization. Data visualization allows analysts to identify patterns and showcase their findings to stakeholders and other teams. This skill is crucial in shaping company decisions and roadmaps. Some data visualization tools that data analysts use include:
- Google Analytics & Google Tag Manager
- Microsoft Power BI
Data analysts rely on databases to store, maintain and organize data. There are several types of database languages that analysts may need to learn early on in their career. SQL , one of the first database languages created in 1970, is still a standard for querying and handling data today. Some common database languages for data analysis include:
- Apache Cassandra
Data Warehouses
Data analysts use data warehouses to perform queries and analysis on historical data. The information contained in a data warehouse can include data such as application log files and transaction applications. These tools are useful to analysts because they consolidate large datasets from many sources. Often called a “single source of truth,” a data warehouse allows a company to improve decision making based on historical insights over time. Some types of data warehouses are:
- Amazon Redshift
- Apache Hive
- Microsoft Azure SQL Database
- Oracle Database
- Oracle Warehouse Builder
- SAP NetWeaver Business Warehouse
Data Analyst Education Requirements
Although it may be possible to get a job in data analytics without a degree, having a bachelor’s degree can help candidates stand out and is often a requirement for many positions. Majoring in data analytics in an undergraduate program is a great place to start but not all universities offer this. Some alternative majors to look into include data science, computer science, applied mathematics or statistics.
Whatever major you choose, taking courses on statistics, calculus and linear algebra will help you develop crucial skills for your career. Computer science courses with a focus on databases and statistical software will also provide a solid background to draw from. For those that have an idea of what field they’d like to work in, it’s always a good idea to take a course or two in a specific industry like healthcare or finance.
Obtaining a master’s degree in analytics or a related field will open up more opportunities as well as senior positions. In fact, approximately 50 percent of professionals in the data science and analytics industry hold master’s degrees. Master’s degrees can help data analysts advance their visualization skills, understand how to use data in an ethical way and learn the best practices for data security.
More on Job Descriptions How to Write a Job Description: Data Driven Results
To help determine what candidates expect, we’ve gathered average data analyst salary information from seven major hiring markets in the United States.
- Austin, TX: $78,469
- Boston, MA: $83,313
- Chicago, IL: $78,462
- Colorado: $77,359
- Los Angeles, CA: $89,517
- New York, NY: $86,392
- Seattle, WA: $83,224
Below are some resources to help you write a job description that will attract candidates with the skills needed to be successful in their role. It includes a data analyst job description template for you to alter and customize so that it includes the necessary responsibilities and requirements while reflecting your unique company culture.
Company Bio
Use this section to provide a high level overview of your company, culture, perks and benefits, career development opportunities and anything else that will get candidates excited about your company.
Responsibilities
- Collaborate with various stakeholders and teams including product, engineering and finance.
- Provide teams and stakeholders with actionable insights and analysis reports based on data to support decision making efforts.
- Collect data from numerous data sources, clean data and analyze data to identify trends.
- Build and analyze automated dataset dashboards to predict issues before they arise, identify bugs in data and resolve them.
- Support individual team members by creating customizable tabular or visual reports with ad hoc reporting via SQL.
- Communicate and present technical information with non-technical team members and stakeholders.
Requirements
- Bachelor’s degree in computer science, mathematics, finance, economics, statistics or a related field.
- [X] years experience working in technical data analysis, data science, data warehousing in [insert industry] or a related industry.
- Experience with designing reports and dashboards on [insert tools].
- Experience with [insert relevant databases].
- Strong knowledge of [insert coding languages].
- Excellent communication skills including written, verbal and presentation.
Recent Job Descriptions Articles

Librarians/Admins
- EBSCOhost Collection Manager
- EBSCO Experience Manager
- EBSCO Connect
- Start your research
- EBSCO Mobile App
Clinical Decisions Users
- DynaMed Decisions
- Dynamic Health
- Waiting Rooms
- NoveList Blog
Education Full Text
Education Full Text is a research database for education students, professionals and policymakers. It includes full-text education journals that cover the essentials of education and related fields of study, including in-depth coverage of special education.
Education Full Text offers a selection of 260 active full-text journals covering the essentials of education and related fields of study. With a journal retail value of $39,186.13, it is the fourth largest database within the Education Source family.
Strengthen Exposure to Open Access Journals
Education Full Text includes rigorous curation and indexing of open access (OA) journals, which has resulted in a growing collection of 693 active global OA journals. Once validated and certified for inclusion, these OA journals are treated with high-quality subject indexing and sophisticated, precise/accurate full-text linking.
NOTE: EBSCOhost databases and EBSCO Discovery Service generate a lot more referrals for DOAJ than any other online platform .
Unique Full-Text Journals
Education Full Text includes 151 active full-text journals not available in any version of Academic Search.
The Highest Quality Subject Indexing
EBSCO has the premier and most highly regarded scholarly vocabularies curated by subject matter experts, covering all disciplines and major publishers.
EBSCO believes in breaking down barriers to information through Enhanced Subject Precision (ESP) mapping, bridging the gap between content and end users through inclusion of natural languages.
EBSCO databases support all learning types through textual and visual subject browse and information literacy training through subject access points in more than 30 languages. Watch video to learn more .
Education Full Text includes 2,069 active indexed and abstracted journals. 1,861 of them are peer-reviewed.
Customers also bought:


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ERIC is an online library of education research and information, sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education.
Comprehensively indexed journals contain an average of 80% or more education-related articles; ERIC creates a bibliographic record for all articles in every acquired issue. Selectively indexed journals contain an average of 50-79% education-related articles and are critical to topic area coverage; ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
NCEE Projects: Education Resources Information Center (ERIC) provides free public access to education research and information through an electronic database of over 1.2 million bibliographic records of journal articles and other education-related materials and, if available, includes links to full text spanning the period 1966 to the present.
ERIC (Education Resources Information Center) is an authoritative database of indexed and full-text education literature and resources. Sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences of the U.S. Department of Education, it is an essential tool for education researchers of all kinds.
Education Abstracts. Education Abstracts is an education research database providing high-quality indexing and abstracts for hundreds of journals. Coverage spans all levels of education and includes adult education, multicultural education and teaching methods. Education Source · Full Text. Education Source is a leading full-text research ...
The Education Resources Information Center (ERIC) is a national information system providing educators, researchers, and the general public with access to education literature and resources. ERIC is the world's largest and most frequently used education digital library, composed of more than 1.3 million bibliographic records beginning with 1966 ...
The American Educational Research Journal (AERJ) is the flagship journal of AERA, with articles that advance the empirical, theoretical, and methodological understanding of education and learning. It publishes original peer-reviewed analyses spanning the field of education research across all subfields and disciplines and all levels of analysis, all levels of education throughout the life span ...
EBSCO databases support all learning types through textual and visual subject browse and information literacy training through subject access points in more than 30 languages. Watch video to learn more. Education Research Complete includes 2,034 active indexed and abstracted journals. 1,825 of them are peer-reviewed.
Please Read This Once - Ordering Documents - ERIC Search Strategies - ERIC Education Search. Education Resources - Education Information - Department of Education - Adult Education Resources. Spanish Education - German Education - Chinese Education - Special Education Resources. ERIC Database Information - Education Resources Information Center.
Journal of Education. The oldest educational publication in the country, the Journal of Education's mission is to disseminate knowledge that informs practice in PK-12, higher, and professional education. A refereed publication, the Journal offers … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication ...
Education Database. Education Database includes full-text scholarly journals and dissertations, supporting research on the theory and practice of education. Education Database covers not only the literature on primary, secondary, and higher education but also special education, home schooling, adult education, and hundreds of related topics.
Education Research Abstracts Online (ERA) is an exciting and comprehensive database, comprising fully indexed abstracts which cover the current international research in education. A versatile research tool, ERA is supported by a fully-flexible search engine, and comprises links to the full-text online versions of articles where possible.
Purdue Libraries provides access to many other databases in Education and other related disciplines. A full list of databases is available at the A-Z Databases home page. To see databases of particular interest to Education research, choose "Education" from the subject drop-down menu. To search by keyword, use the search box in the upper-right ...
Education Source is the world's largest full-text research database designed for education students, professionals and policymakers. It provides full text, indexing and abstracts for thousands of education journals, books and education-related conference papers.
A bibliographic database covering all areas of educational administration, including educational leadership, educational management and educational research. Identifies journal articles that use data from National Center for Education Statistics research programs, 1973-present.
This academic multi-disciplinary database provides than 8,500 full-text periodicals, including more than 7,300 peer-reviewed journals. In addition, it offers indexing and abstracts for more than 12,500 journals and a total of more than 13,200 publications including monographs, reports, conference proceedings, etc. Coverage spans virtually every area of academic study and offers information ...
American Educational Research Journal. Articles include original empirical and theoretical studies and analyses in education. The editors seek to publish articles from a wide variety of academic disciplines and substantive fields. Older issues (1964-2012) are available in JSTOR. Elementary School Journal.
Includes more than 2,850 education journals, 550 books, and education-related conference papers. Index to journal articles and gray literature on educational research and practice from 1969 to the present and ERIC documents since 1966. Index of education journals from 1929 to 1983.
Databases for School Educators. Education databases give K-12 teachers the opportunity to expand learning in exciting new ways. Our school databases are visually appealing, highly intuitive, and a trustworthy resource where students can find vetted, age-appropriate content. By helping students develop the right research skills early on ...
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Aim/Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the extant research on data science education (DSE) to identify the existing gaps, opportunities, and challenges, and make recommendations for current and future DSE. Background: There has been an increase in the number of data science programs especially because of the increased appreciation of data as a multidisciplinary strategic resource.
Research hypotheses and analytical model. In this study, an OLS regression model and a panel quantile model were used to analyse the effect of a population segment with higher education and adult ...
Errors included confusing conference papers with academic articles and mixing up institution names. Commercial databases such as the Web of Science had some of these problems at inception, she says, but have eliminated many thanks to corrections provided by the institutions—work that would have to be repeated with the new databases.
Freely Accessible: Unlike many academic databases, it is free. This makes it a valuable resource for students and educators at all levels. What Can Be Improved. Full-Text Access: Not all articles listed by this tool are freely available. Integration with library resources or paid databases for full-text access would be a big win.
Background Nowadays, Artificial intelligence (AI) is one of the most popular topics that can be integrated into healthcare activities. Currently, AI is used in specialized fields such as radiology, pathology, and ophthalmology. Despite the advantages of AI, the fear of human labor being replaced by this technology makes some students reluctant to choose specific fields. This meta-analysis aims ...
Going Beyond the "Self" in Self-Control (PDF, 262KB) Washington — People who use willpower to overcome temptations and achieve their goals are perceived as more trustworthy than those who use strategies that involve external incentives or deterrents—such as swear jars or internet-blocking apps—according to research published by the ...
Education Source is a valuable full-text database covering all levels of education research and specialities such as multilingual education, health education and testing. With access to 1,217 active full-text education journals valued at $378,968.20, it is the second largest database in the Education Source family.
Databases. Data analysts rely on databases to store, maintain and organize data. There are several types of database languages that analysts may need to learn early on in their career. SQL, one of the first database languages created in 1970, is still a standard for querying and handling data today. Some common database languages for data ...
Education Full Text offers a selection of 260 active full-text journals covering the essentials of education and related fields of study. With a journal retail value of $39,186.13, it is the fourth largest database within the Education Source family. Strengthen Exposure to Open Access Journals