- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

Communication →

- 16 Feb 2024
- Research & Ideas
Is Your Workplace Biased Against Introverts?
Extroverts are more likely to express their passion outwardly, giving them a leg up when it comes to raises and promotions, according to research by Jon Jachimowicz. Introverts are just as motivated and excited about their work, but show it differently. How can managers challenge their assumptions?

- 06 Nov 2023
Did You Hear What I Said? How to Listen Better
People who seem like they're paying attention often aren't—even when they're smiling and nodding toward the speaker. Research by Alison Wood Brooks, Hanne Collins, and colleagues reveals just how prone the mind is to wandering, and sheds light on ways to stay tuned in to the conversation.
.jpg)
- 31 Oct 2023
Checking Your Ethics: Would You Speak Up in These 3 Sticky Situations?
Would you complain about a client who verbally abuses their staff? Would you admit to cutting corners on your work? The answers aren't always clear, says David Fubini, who tackles tricky scenarios in a series of case studies and offers his advice from the field.

- 24 Jul 2023
Part-Time Employees Want More Hours. Can Companies Tap This ‘Hidden’ Talent Pool?
Businesses need more staff and employees need more work, so what's standing in the way? A report by Joseph Fuller and colleagues shows how algorithms and inflexibility prevent companies from accessing valuable talent in a long-term shortage.

- 23 Jun 2023
This Company Lets Employees Take Charge—Even with Life and Death Decisions
Dutch home health care organization Buurtzorg avoids middle management positions and instead empowers its nurses to care for patients as they see fit. Tatiana Sandino and Ethan Bernstein explore how removing organizational layers and allowing employees to make decisions can boost performance.

- 24 Jan 2023
Passion at Work Is a Good Thing—But Only If Bosses Know How to Manage It
Does showing passion mean doing whatever it takes to get the job done? Employees and managers often disagree, says research by Jon Jachimowicz. He offers four pieces of advice for leaders who yearn for more spirit and intensity at their companies.

- 10 Jan 2023
How to Live Happier in 2023: Diversify Your Social Circle
People need all kinds of relationships to thrive: partners, acquaintances, colleagues, and family. Research by Michael Norton and Alison Wood Brooks offers new reasons to pick up the phone and reconnect with that old friend from home.

- 15 Nov 2022
Why TikTok Is Beating YouTube for Eyeball Time (It’s Not Just the Dance Videos)
Quirky amateur video clips might draw people to TikTok, but its algorithm keeps them watching. John Deighton and Leora Kornfeld explore the factors that helped propel TikTok ahead of established social platforms, and where it might go next.

- 03 Nov 2022
Feeling Separation Anxiety at Your Startup? 5 Tips to Soothe These Growing Pains
As startups mature and introduce more managers, early employees may lose the easy closeness they once had with founders. However, with transparency and healthy boundaries, entrepreneurs can help employees weather this transition and build trust, says Julia Austin.

- 15 Sep 2022
Looking For a Job? Some LinkedIn Connections Matter More Than Others
Debating whether to connect on LinkedIn with that more senior executive you met at that conference? You should, says new research about professional networks by Iavor Bojinov and colleagues. That person just might help you land your next job.

- 08 Sep 2022
Gen Xers and Millennials, It’s Time To Lead. Are You Ready?
Generation X and Millennials—eagerly waiting to succeed Baby Boom leaders—have the opportunity to bring more collaboration and purpose to business. In the book True North: Emerging Leader Edition, Bill George offers advice for the next wave of CEOs.

- 05 Aug 2022
Why People Crave Feedback—and Why We’re Afraid to Give It
How am I doing? Research by Francesca Gino and colleagues shows just how badly employees want to know. Is it time for managers to get over their discomfort and get the conversation going at work?

- 23 Jun 2022
All Those Zoom Meetings May Boost Connection and Curb Loneliness
Zoom fatigue became a thing during the height of the pandemic, but research by Amit Goldenberg shows how virtual interactions can provide a salve for isolation. What does this mean for remote and hybrid workplaces?

- 13 Jun 2022
Extroverts, Your Colleagues Wish You Would Just Shut Up and Listen
Extroverts may be the life of the party, but at work, they're often viewed as phony and self-centered, says research by Julian Zlatev and colleagues. Here's how extroverts can show others that they're listening, without muting themselves.

- 24 May 2022
Career Advice for Minorities and Women: Sharing Your Identity Can Open Doors
Women and people of color tend to minimize their identities in professional situations, but highlighting who they are often forces others to check their own biases. Research by Edward Chang and colleagues.

- 12 May 2022
Why Digital Is a State of Mind, Not Just a Skill Set
You don't have to be a machine learning expert to manage a successful digital transformation. In fact, you only need 30 percent fluency in a handful of technical topics, say Tsedal Neeley and Paul Leonardi in their book, The Digital Mindset.

- 08 Feb 2022
Silos That Work: How the Pandemic Changed the Way We Collaborate
A study of 360 billion emails shows how remote work isolated teams, but also led to more intense communication within siloed groups. Will these shifts outlast the pandemic? Research by Tiona Zuzul and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- Cold Call Podcast
What’s Next for Nigerian Production Studio EbonyLife Media?
After more than 20 years in the media industry in the UK and Nigeria, EbonyLife Media CEO Mo Abudu is considering several strategic changes for her media company’s future. Will her mission to tell authentic African stories to the world be advanced by distributing films and TV shows direct to customers? Or should EbonyLife instead distribute its content through third-party streaming services, like Netflix? Assistant Professor Andy Wu discusses Abudu’s plans for her company in his case, EbonyLife Media. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
.jpg)
- 11 Jan 2022
Feeling Seen: What to Say When Your Employees Are Not OK
Pandemic life continues to take its toll. Managers who let down their guard and acknowledge their employees' emotions can ease distress and build trust, says research by Julian Zlatev and colleagues. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 Jan 2022
Scrap the Big New Year's Resolutions. Make 6 Simple Changes Instead.
Self-improvement doesn't need to be painful, especially during a pandemic. Rather than set yet another gym goal, look inward, retrain your brain, and get outside, says Hirotaka Takeuchi. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review
- Open access
- Published: 02 February 2021
- Volume 25 , pages 971–993, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Yogesh K. Dwivedi 1 ,
- Elvira Ismagilova 2 ,
- Nripendra P. Rana 2 &
- Ramakrishnan Raman 3
96k Accesses
65 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses. This research provides a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by business-to-business (B2B) companies. The current study focuses on the number of aspects of social media such as the effect of social media, social media tools, social media use, adoption of social media use and its barriers, social media strategies, and measuring the effectiveness of use of social media. This research provides a valuable synthesis of the relevant literature on social media in B2B context by analysing, performing weight analysis and discussing the key findings from existing research on social media. The findings of this study can be used as an informative framework on social media for both, academic and practitioners.
Similar content being viewed by others

The future of social media in marketing
Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda
Social media influencer marketing: foundations, trends, and ways forward
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The Internet has changed social communications and social behaviour, which lead to the development of new forms of communication channels and platforms (Ismagilova et al. 2017 ). Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses (Kunsman 2018 ). Digital transformation refers to the globally accelerated process of technical adaptation by companies and communities as a result of digitalisation (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ; Westerman et al. 2014 ). Web is developed from a tool used to provide passive information into the collaborative web, which allows and encourages active user engagement and contribution. If before social networks were used to provide the information about a company or brand, nowadays businesses use social media in their marketing aims and strategies to improve consumers’ involvement, relationship with customers and get useful consumers’ insights (Alalwan et al. 2017 ). Business-to-consumer (B2C) companies widely use social media as part of their digital transformation and enjoy its benefits such as an increase in sales, brand awareness, and customer engagement to name a few (Barreda et al. 2015 ; Chatterjee and Kar 2020 ; Harrigan et al. 2020 ; Kamboj et al. 2018 ; Kapoor et al. 2018 ).
From a marketing and sales research perspective, social media is defined as “the technological component of the communication, transaction and relationship building functions of a business which leverages the network of customers and prospects to promote value co-creation” (Andzulis et al. 2012 p.308). Industrial buyers use social media for their purchase as they compare products, research the market and build relationships with salesperson (Itani et al. 2017 ). Social media changed the way how buyers and sellers interact (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ) by enabling open and broad communications and cooperation between them (Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). Social media is an important facilitator of relationships between a company and customers (Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Tedeschi 2006 ). Customers are more connected to companies, which make them more knowledgable about product selection and more powerful in buyer-seller relationships (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ). Social media also helps companies to increase business exposure, traffic and providing marketplace insight (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Stelzner 2011 ). As a result, the use of social media supports business decision processes and helps to improve companies’ performance (Rossmann and Stei 2015 ).
Due to digitalisation customers are becoming more informed and rely less on traditional selling initiatives (Ancillai et al. 2019 ). Buyers are relying more on digital resources and their buying process more often involves the use of social media. For example, in the research B2B buyer survey, 82% of buyers stated that social media content has a significant impact on the purchase decision (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Minsky and Quesenberry 2016 ). As a result, these changes in consumer behaviour place high pressure on B2B salespeople and traditional sales companies (Ancillai et al. 2019 ). By using evidence from major B2B companies and consultancy report some studies claim that social media can be applied in sales to establish effective dialogues with buyers (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Kovac 2016 ; McKinsey and Company 2015 ).
Now, business-to-business (B2B) companies started using social media as part of their digital transformation. 83% of B2B companies use social media, which makes it the most common marketing tactic (Pulizzi and Handley 2017 ; Sobal 2017 ). More than 70% of B2B companies use at least one of the “big 4” social media sites such as LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook and YouTube. Additionally, 50% of the companies stated that social media has improved their marketing optimization and customer experience, while 25% stated that their revenue went up (Gregorio 2017 ; Sobal 2017 ). Even though B2B companies are benefitting from social media used by marketers, it is argued that research on that area is still in the embryonic stage and future research is needed (Salo 2017 ; Siamagka et al. 2015 ; Juntunen et al. 2020 ; Iannacci et al. 2020 ). There is a limited understanding of how B2B companies need to change to embrace recent technological innovations and how it can lead to business and societal transformation (Chen et al. 2012 ; Loebbecke and Picot 2015 ; Pappas et al. 2018 ).
The topic of social media in the context of B2B companies has started attracting attention from both academics and practitioners. This is evidenced by the growing number of research output within academic journals and conference proceedings. Some studies provided a comprehensive literature review on social media use by B2B companies (Pascucci et al. 2018 ; Salo 2017 ), but focused only on adoption of social media by B2B or social media influence, without providing the whole picture of the use of social media by B2B companies. Thus, this study aims to close this gap in the literature by conducting a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by B2B companies and discuss its role in the digital transformation of B2B companies. The findings of this study can provide an informative framework for research on social media in the context of B2B companies for academics and practitioners.
The remaining sections of the study are organised as follows. Section 2 offers a brief overview of the methods used to identify relevant studies to be included in this review. Section 3 synthesises the studies identified in the previous section and provides a detailed overview. Section 4 presents weight analysis and its findings. Next section discusses the key aspects of the research, highlights any limitations within existing studies and explores the potential directions for future research. Finally, the paper is concluded in Section 6 .
2 Literature Search Method
The approach utilised in this study aligns with the recommendations in Webster and Watson ( 2002 ). This study used a keyword search-based approach for identifying relevant articles (Dwivedi et al. 2019b ; Ismagilova et al. 2020a ; Ismagilova et al. 2019 ; Jeyaraj and Dwivedi 2020 ; Williams et al. 2015 ). Keywords such as “Advertising” OR “Marketing” OR “Sales” AND TITLE (“Social Media” OR “Web 2.0” OR “Facebook” OR “LinkedIn” OR “Instagram” OR “Twitter” OR “Snapchat” OR “Pinterest” OR “WhatsApp” OR “Social Networking Sites”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“B2B” OR “B to B” OR “Business to Business” OR “Business 2 Business”) were searched via the Scopus database. Scopus database was chosen to ensure the inclusion of only high quality studies. Use of online databases for conducting a systematic literature review became an emerging culture used by a number of information systems research studies (Dwivedi et al. 2019a ; Gupta et al. 2019 ; Ismagilova et al. 2020b ; Muhammad et al. 2018 ; Rana et al. 2019 ). The search resulted in 80 articles. All studies were processed by the authors in order to ensure relevance and that the research offered a contribution to the social media in the context B2B discussion. The search and review resulted in 70 articles and conference papers that formed the literature review for this study. The selected studies appeared in 33 separate journals and conference proceedings, including journals such as Industrial Marketing Management, Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing and Journal of Business Research.
3 Literature Synthesis
The studies on social media research in the context of B2B companies were divided into the following themes: effect of social media, adoption of social media, social media strategies, social media use, measuring the effectiveness of use of social media, and social media tools (see Table 1 ). The following subsections provide an overview of each theme.
3.1 Effect of Social Media
Some studies focus on the effect of social media for B2B companies, which include customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, building relationships with customers, brand awareness, knowledge creation, perceived corporate credibility, acquiring of new customers, salesperson performance, employee brand engagement, and sustainability (Table 2 ).
3.1.1 Customer Satisfaction
Some studies investigated how the use of social media affected customer satisfaction (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). For example, Agnihotri et al. ( 2016 ) investigated how the implementation of social media by B2B salesperson affects consumer satisfaction. Salesperson’s social media use is defined as a “salesperson’s utilization and integration of social media technology to perform his or her job” (Agnihotri et al. 2016 , p.2). The study used data from 111 sales professionals involved in B2B industrial selling to test the proposed hypotheses. It was found that a salesperson’s use of social media will have a positive effect on information communication, which will, in turn, lead to improved customer satisfaction with the salesperson. Also, it was investigated that information communication will be positively related to responsiveness, which impacts customer satisfaction.
Another study by Rossmann and Stei ( 2015 ) looked at the antecedents of social media use, social media use by B2B companies and their effect on customers. By using data from 362 chief information officers of B2B companies the study found the following. Social media usage of sales representative has a positive impact on customer satisfaction. Age has a negative effect on content generation. It seems that older salespeople use social media in passive ways or interacting with the customer rather than creating their own content. It was found that the quality of corporate social media strategy has a positive impact on social media usage in terms of the consumption of information, content generation, and active interaction with customers. Also, the expertise of a salesperson in the area of social media has a positive impact on social media usage.
3.1.2 Value Creation
Research in B2B found that social media can create value for customers and salesperson (Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Agnihotri et al. 2017 ). Agnihotri et al. ( 2012 ) proposed a theoretical framework to explain the mechanisms through which salespeople’s use of social media operates to create value and propose a strategic approach to social media use to achieve competitive goals. The study draws on the existing literature on relationship marketing, task–technology fit theory, and sales service behavior to sketch a social media strategy for business-to-business sales organizations with relational selling objectives. The proposed framework describes how social media tools can help salespeople perform service behaviors (information sharing, customer service, and trust-building) leading to value creation.
Some researchers investigated the role of the salesperson in the value creation process after closing the sale. By employing salesperson-customer data within a business-to-business context, Agnihotri et al. ( 2017 ) analysed the direct effects of sales-based CRM technology on the post-sale service behaviors: diligence, information communication, inducements, empathy, and sportsmanship. Additionally, the study examines the interactive effects of sales-based CRM technology and social media on these behaviors. The results indicate that sales-based CRM technology has a positive influence on salesperson service behaviors and that salespeople using CRM technology in conjunction with social media are more likely to exhibit higher levels of SSBs than their counterparts with low social media technology use. Data were collected from 162 salespeople from India. SmartPLS was used to analyse the data.
3.1.3 Intention to Buy and Sales
Another group of studies investigated the effect of social media on the level of sales and consumer purchase intention (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Salo 2017 ; Hsiao et al. 2020 ; Mahrous 2013 ). For example, Itani et al. ( 2017 ) used the theory of reasoned actions to develop a model that tests the factors affecting the use of social media by salesperson and its impact. By collecting data from 120 salespersons from different industries and using SmartPLS to analyse the data, it was found that attitude towards social media usefulness did not affect the use of social media. It was found that social media use positively affects competitive intelligence collection, adaptive selling behaviour, which in turn influenced sales performance. Another study by Ancillai et al. ( 2019 ) used in-depth interviews with social selling professionals. The findings suggest that the use of social media improves not only the level of sales but also affects relationship and customer performance (trust, customer satisfaction, customer referrals); and organisational performance (organisational selling performance and brand performance).
It was investigated that social media has a positive effect on the intention to purchase (Hsiao et al. 2020 ; Mahrous 2013 ). For instance, Mahrous ( 2013 ) by reviewing the literature on B2B and B2C companies concluded that social media has a significant influence on consumer buying behaviour.
3.1.4 Customer Relationships
Another group of studies focused on the effect of social media on customer relationships (Bhattacharjya and Ellison 2015 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gruner and Power 2018 ; Hollebeek 2019 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Jussila et al. 2011 ; Kho 2008 ; Niedermeier et al. 2016 ; Ogilvie et al. 2018 ). For example, Bhattacharjya and Ellison ( 2015 ) investigated the way companies build relationships with customers by using responsive customer relationship management. The study analysed customer relationship management activities from Twitter account of a Canadian company Shopify (B2B service provider). The company uses Twitter to engage with small business customers, develops and consumers. Jussila et al. ( 2011 ), by reviewing the literature, found that social media leads to increased customer focus and understanding, increased level of customer service and decreased time-to-market.
Gáti et al. ( 2018 ) focused their research efforts on social media use in customer relationship performance, particularly in customer relations. The study investigated the adoption and impact of social media by salespeople of B2B companies. By using data of 112 salespeople from several industries the study found that the intensity of technology use positively affects attitude towards social media, which positively affects social media use. Intensive technology use in turn positively affects customer relationship performance (customer retention). PLS-SEM was applied for analysis.
Another study by Gruner and Power ( 2018 ) investigated the effectiveness of the use of multiple social media platforms in communications with customers. By using data from 208 large Australian organisations, the paper explores how companies’ investment in one form of social media impacts activity on another form of social media. A regression analysis was performed to analyse the data. It was found that widespread activities on LinkedIn, Twitter and YouTube have a negative effect on a company’s marketing activity on Facebook. Thus, having it is more effective for the company to focus on a specific social media platform in forming successful inter-organisational relationships with customers.
Hollebeek ( 2019 ) proposed an integrative S-D logic/resource-based view (RBV) model of customer engagement. The proposed model considers business customer actors and resources in driving business customer resource integration, business customer resource integration effectiveness and business customer resource integration efficiency, which are antecedents of business customer engagement. Business customer engagement, in turn, results in business customer co-creation and relationship productivity.
Niedermeier et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the use of social media among salespeople in the pharmaceutical industry in China. Also, the study investigated the impact of social media on building culturally specific Guanxi relationships-it involves the exchange of factors to build trust and connection for business purpose. By using in-depth interviews with 3 sales managers and a survey of 42 pharmaceutical sales representatives that study found that WeChat is the most common social media platform used by businesses. Also, it was found to be an important tool in building Guanxi. Future studies should focus on other industries and other types of cultural features in doing business.
Ogilvie et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the effect of social media technologies on customer relationship performance and objective sales performance by using two empirical studies conducted in the United States. The first study used 375 salespeople from 1200 B2B companies. The second study used 181 respondents from the energy solution company. It was found that social media significantly affects salesperson product information communication, diligence, product knowledge and adaptability, which in turn affect customer relationship performance. It was also found that the use of social media technologies without training on technology will not lead to good results. Thus, the results propose that companies should allocate the resources required for the proper implementation of social media strategies. Future research should examine how the personality traits of a salesperson can moderate the implementation of social media technologies.
While most of the studies focused on a single country, Iankova et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the perceived effectiveness of social media by different types of businesses in two countries. By using 449 respondents from the US and the UK businesses, it was found that social media is potentially less important, at the present time, for managing ongoing relationships in B2B organizations than for B2C, Mixed or B2B2C organizations. All types of businesses ascribe similar importance to social media for acquisition-related activities. Also it was found that B2B organizations see social media as a less effective communication channel, and to have less potential as a channel for the business.
3.1.5 Brand Awareness
Some researchers argued that social media can influence brand awareness (Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Hsiao et al. 2020 ). For instance, Hsiao et al. ( 2020 ) investigated the effect of social media in the fashion industry. By collecting 1395 posts from lookbook.nu and employing regression analysis it was found that the inclusion of national brand and private fashion brands in the post increased the level of popularity which leads to purchasing interest and brand awareness.
3.1.6 Knowledge Creation
Multiple types of collaborative web tools can help and significantly increase the collaboration and the use of the distributed knowledge inside and outside of the company (McAfee 2006 ). Kärkkäinen et al. ( 2011 ) by analysing previous literature on social media proposed that social media use has a positive effect on sharing and creation of customer information and knowledge in the case of B2B companies.
3.1.7 Corporate Credibility
Another study by Kho ( 2008 ) states the advantages of using social media by B2B companies, which include faster and more personalised communications between customer and vendor, which can improve corporate credibility and strengthen the relationships. Thanks to social media companies can provide more detailed information about their products and services. Kho ( 2008 ) also mentions that customer forums and blog comments in the B2B environment should be carefully monitored in order to make sure that inappropriate discussions are taken offline and negative eWOM communications should be addressed in a timely manner.
3.1.8 Acquiring New Customers
Meire et al. ( 2017 ) investigated the impact of social media on acquiring B2B customers. By using commercially purchased prospecting data, website data and Facebook data from beverage companies the study conducted an experiment and found that social media us an effective tool in acquiring B2B customers. Future work might assess the added value of social media pages for profitability prediction instead of prospect conversion. When a longer timeframe becomes available (e.g., after one year), the profitability of the converted prospects can be assessed.
3.1.9 Salesperson Performance
Moncrief et al. ( 2015 ) investigated the impact of social media technologies on the role of salesperson position. It was found that social media affects sales management functions (supervision, selection, training, compensation, and deployment) and salesperson performance (role, skill, and motivation). Another study by Rodriguez et al. ( 2012 ) examines the effect of social media on B2B sales performance by using social capital theory and collecting data from 1699 B2B salespeople from over 25 different industries. By employing SEM AMOS, the study found that social media usage has a positive significant relationship with selling companies’ ability to create opportunities and manage relationships. The study also found that social media usage has a positive and significant relationship with sales performance (based on relational measurers of sales that focus on behaviours that strengthen the relationship between buyers and sellers), but not with outcome-based sales performance (reflected by quota achievement, growth in average billing size, and overall revenue gain).
3.1.10 Employee Brand Management
The study by Pitt et al. ( 2018 ) focuses on employee engagement with B2B companies on social media. By using results from Glassdoor (2315 five-star and 1983 one-star reviews for the highest-ranked firms, and 1013 five star and 1025 one-star reviews for lowest ranked firms) on employee brand engagement on social media, two key drivers of employee brand engagement by using the content analysis tool DICTION were identified-optimism and commonality. Individuals working in top-ranked companies expressed a higher level of optimism and commonality in comparison with individuals working in low-ranked companies. As a result, a 2 × 2 matrix was constructed which can help managers to choose strategies in order to increase and improve employee brand engagement. Another study by Pitt et al. ( 2017 ) focused on employee engagement of B2B companies on social media. By using a conceptual framework based on a theory of word choice and verbal tone and 6300 reviews collected from Glassdoor and analysed using DICTION. The study found that employees of highly ranked B2B companies are more positive about their employer brand and talk more optimistically about these brands. For low ranked B2B companies it was found that employees express a greater level of activity, certainty, and realism. Also, it was found that they used more aggressive language.
3.1.11 Sustainability
Sustainability refers to the strategy that helps a business “to meet its current requirements without compromising its ability to meet future needs” (World Commission Report on Environment and Development 1987 , p 41). Two studies out of 70 focused on the role of social media for B2B sustainability (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ). For example, Sivarajah et al. ( 2019 ) argued that big data and social media within a participatory web environment to enable B2B organisations to become profitable and remain sustainable through strategic operations and marketing related business activities.
Another study by Kasper et al. ( 2015 ) proposed the Social Media Matrix which helps companies to decide which social media activities to execute based on their corporate and communication goals. The matrix includes three parts. The first part is focusing on social media goals and task areas, which were identified and matched. The second part consists of five types of social media activities (content, interaction/dialog, listening and analysing, application and networking). The third part provides a structure to assess the suitability of each activity type on each social media platform for each goal. The matrix was successfully tested by assessing the German B2B sector by using expert interviews with practitioners.
Based on the reviewed studies, it can be seen that if used appropriately social media have positive effect on B2B companies before and after sales, such as customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, customer relationships, brand awareness, knowledge creation, corporate credibility, acquiring new customers, salesperson performance, employee brand management, and sustainability. However, limited research is done on the negative effect of social media on b2b companies.
3.2 Adoption of Social Media
Some scholars investigated factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies (Buratti et al. 2018 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gazal et al. 2016 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Kumar and Möller 2018 ; Lacka and Chong 2016 ). For instance, Lacka and Chong ( 2016 ) investigated factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies from different industries in China. The study collected the data from 181 respondents and used the technology acceptance model with Nielsen’s model of attributes of system acceptability as a theoretical framework. By using SEM AMOS for analysis the study found that perceived usability, perceived usefulness, and perceived utility positively affect adoption and use of social media by B2B marketing professionals. The usefulness is subject to the assessment of whether social media sites are suitable means through which marketing activities can be conducted. The ability to use social media sites for B2B marketing purposes, in turn, is due to those sites learnability and memorability attributes.
Another study by Müller et al. ( 2018 ) investigated factors affecting the usage of social media. By using survey data from 100 Polish and 39 German sensor suppliers, it was found that buying frequency, the function of a buyer, the industry sector and the country does not affect the usage of social media in the context of sensor technology from Poland and Germany. The study used correlation analysis and ANOVA.
Lashgari et al. ( 2018 ) studied the adoption and use of social media by using face-to-face interviews with key managers of four multinational corporations and observations from companies’ websites and social media platforms. It was found that that the elements essential in forming the B2B firm’s social media adoption strategies are content (depth and diversity), corresponding social media platform, the structure of social media channels, the role of moderators, information accessibility approaches (public vs. gated-content), and online communities. These elements are customized to the goals and target group the firm sets to pursue. Similarly, integration of social media into other promotional channels can fall under an ad-hoc or continuous approach depending on the scope and the breadth of the communication plan, derived from the goal.
Similar to Lashgari et al. ( 2018 ), Shaltoni ( 2017 ) used data from managers. The study applied technology organisational environmental framework and diffusion of innovations to investigate factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies. By using data from marketing managers or business owners of 480 SMEs, the study found that perceived relative advance, perceive compatibility, organizational innovativeness, competitor pressure, and customer pressure influence the adoption of social media by B2B companies. The findings also suggest that many decision-makers in B2B companies think that Internet marketing is not beneficial, as it is not compatible with the nature of B2B markets.
Buratti et al. ( 2018 ) investigated the adoption of social media by tanker shipping companies and ocean carriers. By using data from 60 companies the following was found. LinkedIn is the most used tool, with a 93.3% adoption rate. Firm size emerges as a predictor of Twitter’s adoption: big companies unveil a higher attitude to use it. Finally, the country of origin is not a strong influential factor in the adoption rate. Nonetheless, Asian firms clearly show a lower attitude to join SM tools such as Facebook (70%) and LinkedIn (86.7%), probably also due to governmental web restrictions imposed in China. External dimensions such as the core business, the firm size, the geographic area of origin, etc., seem to affect network wideness. Firm size, also, discriminates the capacity of firms to build relational networks. Bigger firms create networks larger than small firms do. Looking at geographical dimensions, Asian firms confirm to be far less active on SM respect to European and North American firms. Finally, the study analyzed the format of the contents disclosed by sample firms, observing quite limited use of photos and videos: in the sample industries, informational contents seem more appropriate for activating a dialogue with stakeholders and communication still appears formulated in a very traditional manner. Preliminary findings suggest that companies operating in conservative B2B services pursue different strategic approaches toward SMM and develop ad hoc communication tactics. Nonetheless, to be successful in managing SM tools, a high degree of commitment and a clear vision concerning the role of SM within communication and marketing strategy is necessary.
Gazal et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption and measuring of the effectiveness of social media in the context of the US forest industry by using organisational-level adoption framework and TAM. By using data from 166 companies and performing regression analysis, the following results were received. Years in business, new sales revenue, product type, amount of available information on a company website, perceived importance of e-commerce and perceived ease of use of social media significantly affected social media use. Also, it was found that companies’ strategies and internal resources and capabilities and influence a company’s decision to adopt social media. Also, it was found that 94 of respondents do not measure the ROI from social media use. The reason is that the use of social media in marketing is relatively new and companies do not possess the knowledge of measuring ROI from the use of social media. Companies mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with the key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers. Facebook was found to be the most effective social media platform reported by the US forest industry.
The study by Kumar and Möller ( 2018 ) investigated the role of social media for B2B companies in their recruitment practices. By using data from international B2B company with headquarter in Helsinki, Finland comprised of 139 respondents it was found that brand familiarity encourages them to adopt social media platforms for a job search; however, the effect of the persuasiveness of recruitment messages on users’ adoption of social media platforms for their job search behavior is negative. The study used correlation analysis and descriptive analysis to analyse the data.
Nunan et al. ( 2018 ) identified areas for future research such as patterns of social media adoption, the role of social media platforms within the sales process, B2B consumer engagement and social media, modeling the ROI of social media, and the risks of social media within B2B sales relationships.
The study by Pascucci et al. ( 2018 ) conducted a systematic literature review on antecedents affecting the adoption and use of social media by B2B companies. By reviewing 29 studies published in academic journal and conferences from 2001 to 2017, the study identified external (pressure from customers, competitors, availability of external information about social media) and internal factors (personal characteristics -managers age, individual commitment, perceptions of social media-perceived ease of use, perceived usefulness, perceived utility), which can affect adoption of social media.
The study by Siamagka et al. ( 2015 ) aims to investigate factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B organisations. The conceptual model was based on the technology acceptance model and the resource-based theory. AMOS software and Structural equation modelling were employed to test the proposed hypotheses. By using a sample of 105 UK companies, the study found that perceived usefulness of social media is influenced by image, perceived ease of use and perceived barriers. Also, it was found that social media adoption is significantly determined by organisational innovativeness and perceived usefulness. Additionally, the study tested the moderating role of organisational innovativeness and found that it does not affect the adoption of social media by B2B organisations. The study also identified that perceived barriers to SNS (uncertainty about how to use SNS to achieve objectives, employee’s lack of knowledge about SNS, high cost of investment needed to adopt the technology) have a negative impact on perceived usefulness of social media by B2B organisations. The study also used nine in-depth interviews with B2B senior managers and social media specialists about adoption of social media by B2B. It was found that perceived pressure from stakeholders influences B2B organisations’ adoption intention of social media. Future research should test it by using quantitative methods.
While most of the studies focused on the antecedents of social media adoption by B2B companies, Michaelidou et al. ( 2011 ) investigated the usage, perceived barriers and measuring the effectiveness of social media. By using data from 92 SMEs the study found that over a quarter of B2B SMEs in the UK are currently using SNS to achieve brand objectives, the most popular of which is to attract new customers. The barriers that prevent SMEs from using social media to support their brands were lack of staff familiarity and technical skills. Innovativeness of a company determined the adoption of social media. It was found that most of the companies do not evaluate the effectiveness of their SNS in supporting their brand. The most popular measures were the number of users joining the groups/discussion and the number of comments made. The findings showed that the size of the company does not influence the usage of social media for small and medium-sized companies. Future research should investigate the usage of social media in large companies and determine if the size can have and influence on the use. The benefits of using social media include increasing awareness and communicating the brand online. B2B companies can employ social media to create customer value in the form of interacting with customers, as well as building and fostering customer relationships. Future research should investigate the reasons why most of the users do not assess the effectiveness of their SNS. Future research should also investigate how the attitude towards technology can influence the adoption of social media.
Based on the reviewed studies it can be seen that the main factors affecting the adoption of social media by B2B companies are perceived usability, technical skills of employees, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness and innovativeness.
3.3 Social Media Strategies
Another group of studies investigated types of strategies B2B companies apply (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ; Huotari et al. 2015 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ; McShane et al. 2019 ; Mudambi et al. 2019 ; Swani et al. 2013 ; Swani et al. 2014 ; Swani et al. 2017 ; Watt 2010 ). For example, Cawsey and Rowley ( 2016 ) focused on the social media strategies of B2B companies. By conducting semi-structured interviews with marketing professionals from France, Ireland, the UK and the USA it was found that enhancing brand image, extending brand awareness and facilitating customer engagement were considered the most common social media objective. The study proposed the B2B social media strategy framework, which includes six components of a social media strategy: 1) monitoring and listening 2) empowering and engaging employees 3) creating compelling content 4) stimulating eWOM 5) evaluating and selecting channels 6) enhancing brand presence through integrating social media.
Chirumalla et al. ( 2018 ) focused on the social media engagement strategies of manufacturing companies. By using semi-structured interviews (36), observations (4), focus group meetings (6), and documentation, the study developed the process of social media adoption through a three-phase engagement strategy which includes coordination, cooperation, and co-production.
McShane et al. ( 2019 ) proposed social media strategies to influence online users’ engagement with B2B companies. Taking into consideration fluency lens the study analysed Twitter feeds of top 50 social B2B brands to examine the influence of hashtags, text difficulty embedded media and message timing on user engagement, which was evaluated in terms of likes and retweets. It was found that hashtags and text difficulty are connected to lower levels of engagement while embedded media such as images and videos improve the level of engagement.
Swani et al. ( 2014 ) investigate the use of Twitter by B2B and B2C companies and predict factors that influence message strategies. The study conducted a longitudinal content analysis by collecting 7000 tweets from Fortune 500 companies. It was found that B2B and B2C companies used different message appeals, cues, links and hashtags. B2B companies tend to use more emotional than functional appeals. It was found that B2B and B2C companies do not use hard-sell message strategies.
Another study by Swani et al. ( 2013 ) aimed to investigate message strategies that can help in promoting eWOM activity for B2B companies. By applying content analysis and hierarchical linear modeling the study analysed 1143 wall post messages from 193 fortune 500 Facebook accounts. The study found that B2B account posts will be more effective if they include corporate brand names and avoid hard sell or explicitly commercial statement. Also, companies should use emotional sentiment in Facebook posts.
Huotari et al. ( 2015 ) aimed to investigate how B2B marketers can influence content creation in social media. By conducting four face-to-face interviews with B2B marketers, it was found that a B2B company can influence content creation in social media directly by adding new content, participating in a discussion and removing content through corporate user accounts and controlling employees social media behaviour. Also, it can influence it indirectly by training employees to create desired content and perfuming marketing activities that influence other users to create content that is favorable for the company.
Most of the studies investigated the strategies and content of social media communications of B2B companies. However, the limited number of studies investigated the importance of CEO engagement on social media in the company’s strategies. Mudambi et al. ( 2019 ) emphasise the importance of the CEO of B2B companies to be present and active on social media. The study discusses the advantages of social media presence for the CEO and how it will benefit the company. For example, one of the benefits for the CEO can be perceived as being more trustworthy and effective than non-social CEOs, which will benefit the company in increased customer trust. Mudambi et al. ( 2019 ) also discussed the platforms the CEO should use and posting frequencies depending on the content of the post.
From the above review of the studies, it can be seen that B2B companies social media strategies include enhancing brand image, extending brand awareness and facilitating customer engagement. Companies use various message strategies, such as using emotional appeal, use of brand names, and use of hashtags. Majority of the companies avoid hard sell or explicitly commercial statement.
3.4 Social Media Use
Studies investigated the way how companies used social media and factors affecting the use of social media by B2B (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Habibi et al. 2015 ). For example, Vasudevan and Kumar ( 2018 ) investigated how B2B companies use social media by analysing 325 brand posts of Canon India, Epson India, and HP India on Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter. By employing content analysis the study found that most of the posts had a combination of text and message. More than 50% of the posts were about product or brand-centric. The study argued that likes proved to be an unreliable measure of engagement, while shares were considered a more reliable metric. The reason was that likes had high spikes when brand posts were boosted during promotional activities.
Andersson and Wikström ( 2017 ) used case studies of three B2B companies to investigate reasons for using social media. It was found that companies use social media to enhance customer relationships, support sales and build their brands. Also, social media is used as a recruiting tool, a seeking tool, and a product information and service tool.
Bell and Shirzad ( 2013 ) aimed to conduct social media use analysis in the context of pharmaceutical companies. The study analysed 54,365 tweets from the top five pharmaceutical companies. The study analysed the popular time slots, the average number of positive and negative tweets and its content by using Nvivo9.
Bernard ( 2016 ) aims to examine how chief marketing officers use social media. By using case studies from IBM experience with social media it was found that B2B CMO’s are not ready to make use of social media. It was proposed that social media can be used for after-sales service, getting sales leads, engaging with key influencers, building the company’s reputation and enhancing the industry status of key individuals. B2B firms need to exploit the capabilities of processing massive amounts of data to get the most from social media.
Bolat et al. ( 2016 ) explore how companies apply mobile social media. By employing a grounded theory approach to analyse interviews from 26 B2B company representatives from UK advertising and marketing sector companies. It was found that companies use social media for branding, sensing market, managing relationships, and developing content.
Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü ( 2018 ) investigated how social media usage influence stakeholder engagement focusing on the corporate Facebook page of 30 3PLs companies. In total 1532 Facebook posts were analysed. It was found that the number of followers, post sharing frequency, negatively affect stakeholder engagement. It was found that content including photos facilitates more stakeholder engagement (likes, comment, share) in comparison with other forms. Vivid posts and special day celebration posts strengthen relationships with stakeholders.
Dyck ( 2010 ) discussed the advantages of using social media for the device industry. Social media can be used for product innovation and development, to build a team and collaborate globally. Also, there is an opportunity to connect with all of the stakeholders needed in order to deliver the device to the market. Additionally, it provides to receive feedback from customers (doctors, hospitals) in real-time.
The study by Guesalaga ( 2016 ) draws on interactional psychology theory to propose and test a model of usage of social media in sales, analysing individual, organizational, and customer-related factors. It was found that organizational competence and commitment to social media are key determinants of social media usage in sales, as well as individual commitment. Customer engagement with social media also predicts social media usage in sales, both directly and (mostly) through the individual and organizational factors analysed, especially organizational competence and commitment. Finally, the study found evidence of synergistic effects between individual competence and commitment, which is not found at the organizational level. The data obtained by surveying 220 sales executives in the United States were analysed using regression analysis.
Habibi et al. ( 2015 ) proposed a conceptual model for the implementation of social media by B2B companies. Based on existing B2B marketing, social media and organisational orientational literature the study proposed that four components of electronic market orientation (philosophical, initiation, implementation and adoption) address different implementation issues faced in implementing social media.
Katona and Sarvary ( 2014 ) presented a case of using social media by Maersk-the largest container shipping company in the world. The case provided details on the program launch and the integration strategy which focused on integrating the largest independent social media operation into the company’s broader marketing efforts.
Moore et al. ( 2013 ) provided insights into the understanding of the use of social media by salespersons. 395 salespeople in B2B and B2C markets, utilization of relationship-oriented social media applications are presented and examined. Overall, findings show that B2B practitioners tend to use media targeted at professionals whereas their B2C counterparts tend to utilize more sites targeted to the general public for engaging in one-on-one dialogue with their customers. Moreover, B2B professionals tend to use relationship-oriented social media technologies more than B2C professionals for the purpose of prospecting, handling objections, and after-sale follow-up.
Moore et al. ( 2015 ) investigated the use of social media between B2B and B2C salespeople. By using survey data from 395 sales professionals from different industries they found that B2B sales managers use social selling tools significantly more frequently than B2C managers and B2C sales representatives while conducting sales presentations. Also, it was found that B2B managers used social selling tools significantly more frequently than all sales representatives while closing sales.
Müller et al. ( 2013 ) investigated social media use in the German automotive market. By using online analysis of 10 most popular car manufacturers online social networks and surveys of six manufacturers, 42 car dealers, 199 buyers the study found that social media communication relations are widely established between manufacturers and (prospective) buyers and only partially established between car dealers and prospective buyers. In contrast to that, on the B2B side, social media communication is rarely used. Social Online Networks (SONs) are the most popular social media channels employed by businesses. Manufacturers and car dealers focus their social media engagement, especially on Facebook. From the perspective of prospective buyers, however, forums are the most important source of information.
Sułkowski and Kaczorowska-Spychalska ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption of social media by companies in the Polish textile-clothing industry. By interviewing seven companies representatives of small and medium-sized enterprises the study found that companies started implementing social media activities in their marketing activities.
Vukanovic ( 2013 ) by reviewing previous literature on social media outlined advantages of using social media for B2B companies, which include: increase customer loyalty and trust, building and improving corporate reputation, facilitating open communications, improvement in customer engagement to name a few.
Keinänen and Kuivalainen ( 2015 ) investigated factors affecting the use of social media by B2B customers by conducting an online survey among 82 key customer accounts of an information technology service company. Partial least squares path modelling was used to analysed the proposed hypotheses. It was found that social media private use, colleague support for using SM, age, job position affected the use of social media by B2B customers. The study also found that corporate culture, gender, easiness to use, and perception of usability did not affect the use of social media by B2B customers.
By using interviews and survey social media research found that mostly B2B companies use social media to enhance customer relationships, support sales, build their brands, sense market, manage relationships, and develop content. Additionally, some companies use it social media as a recruitment tool. The main difference between B2B and B2C was that B2B sales managers use social selling tools significantly more frequently than B2C managers.

3.5 Measuring the Effectiveness of Social Media
It is important for a business to be able to measure the effectiveness of social media by calculating return on investment (ROI). ROI is the relationship between profit and the investment that generate that profit. Some studies focused on the ways B2B companies can measure ROI and the challenges they face (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ). For example, Gazal et al. ( 2016 ) investigated the adoption and measuring of the effectiveness of social media in the context of the US forest industry by using organisational-level adoption framework and TAM. By using data from 166 companies it was found that 94% of respondents do not measure the ROI from social media use. The reason is that the use of social media in marketing is relatively new and companies do not possess the knowledge of measuring ROI from the use of social media. Companies mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with the key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers).
Another study by Michaelidou et al. ( 2011 ) found that most of the companies do not evaluate the effectiveness of their SNS in supporting their brand. The most popular measures were the number of users joining the groups/discussion and the number of comments made.
Vasudevan and Kumar ( 2018 ) investigated how B2B companies use social media and measure ROI from social media by analysing 325 brand posts of Canon India, Epson India, and HP India on Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter. By employing content analysis the study found that most of the post has a combination of text and message. More than 50% of the posts were about product or brand-centric. The study argued that likes proved to be an unreliable measure of engagement, while shares were considered a more reliable metric. The reason was that likes had high spikes when brand posts were boosted during promotional activities. Future research should conduct longitudinal studies.
By reviewing the above studies, it can be concluded that companies still struggle to find ways of measuring ROI and applying correct metrics. By gaining knowledge in how to measure ROI from social media activities, B2B companies will be able to produce valuable insights leading to better marketing strategies (Lal et al. 2020 ).
3.6 Social Media Tools
Some studies proposed tools that could be employed by companies to advance their use of social media. For example, Mehmet and Clarke ( 2016 ) proposed a social semiotic multimodal (SSMM) framework that improved the analysis of social media communications. This framework employs multimodal extensions to systemic functional linguistics enabling it to be applying to analysing non-language as well as language constituents of social media messages. Furthermore, the framework also utilises expansion theory to identify, categorise and analyse various marketing communication resources associated with marketing messages and also to reveal how conversations are chained together to form extended online marketing conversations. This semantic approach is exemplified using a Fairtrade Australia B2B case study demonstrating how marketing conversations can be mapped and analysed. The framework emphasises the importance of acknowledging the impact of all stakeholders, particularly messages that may distract or confuse the original purpose of the conversation.
Yang et al. ( 2012 ) proposed the temporal analysis technique to identify user relationships on social media platforms. The experiment was conducted by using data from Digg.com . The results showed that the proposed techniques achieved substantially higher recall but not very good at precision. This technique will help companies to identify their future consumers based on their user relationships.
Based on the literature review, it can be seen that B2B companies can benefit by using the discussed tools. However, it is important to consider that employee should have some technical skills and knowledge to use these tools successfully. As a result, companies will need to invest some resources in staff training.
4 Weight Analysis
Weight analysis enables scrutiny of the predictive power of independent variables in studied relationships and the degree of effectiveness of the relationships (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ; Rana et al. 2015 ; Ismagilova et al. 2020a ). The results of weight analysis are depicted in Table 3 providing information about an independent variable, dependent variable, number of significant relationships, number of non-significant relationships, the total number of relationships and weight. To perform weight analysis, the number of significant relationships was divided by the total number of analysed relationships between the independent variable and the dependent variable (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ; Rana et al. 2015 ). For example, the weight for the relationship between attitude towards social media and social media is calculated by dividing ‘1’ (the number of significant relationships) by ‘2’ (the total number of relationships) which equals 0.5.
A predictor is defined as well-utilised if it was examined five or more times, otherwise, it is defined as experimental. It can be seen from Table 3 that all relationships were examined less than five times. Thus all studied predictors are experimental. The predictor is defined as promising when it has been examined less than five times by existing studies but has a weight equal to ‘1’ (Jeyaraj et al. 2006 ). From the predictors affecting the adoption of social media, it can be seen that two are promising, technical skills of employees and pressure from stakeholders. Social media usage is a promising predictor for acquiring new customers, sales, stakeholder engagement and customer satisfaction. Perceived ease of use and age of salesperson are promising predictors of social media usage. Even though this relationship was found to be significant every time it was examined, it is suggested that this variable, which can also be referred to as experimental, will need to be further tested in order to qualify as the best predictor. Another predictor, average rating of product/service, was examined less than five times with a weight equal to 0.75, thus it is considered as an experimental predictor.
Figure 1 shows the diagrammatic representation of the factors affecting different relationships in B2B social media with their corresponding weights, based on the results of weight analysis. The findings suggest that promising predictors should be included in further empirical studies to determine their overall performance.
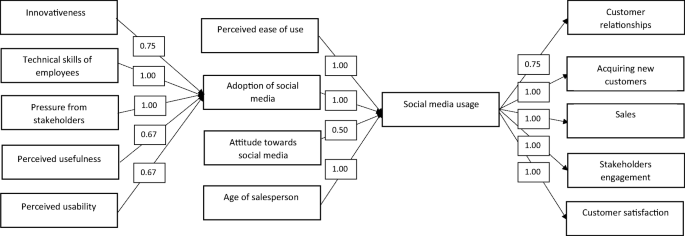
Diagrammatic representation of results of weight analysis. Note: experimental predictors
It can be seen from Fig. 1 that social media usage is affected by internal (e.g. attitude towards social media, technical skills of employees) and external factors (e.g. pressure from stakeholders) of the company. Also, the figure depicts the effect of social media on the business (e.g. sales) and society (e.g. customer satisfaction).
5 Discussion
In reviewing the publications gathered for this paper, the following themes were identified. Some studies investigated the effect of social media use by B2B companies. By using mostly survey to collect the data from salespeople and managers, the studies found that social media has a positive effect on number of outcomes important for the business such as customer satisfaction, value creation, intention to buy and sales, customer relationships, brand awareness, knowledge creation, corporate credibility, acquiring new customers, salespersons performance, employee brand management, and sustainability. Most of the outcomes are similar to the research on social media in the context of B2C companies. However, some of the outcomes are unique for B2B context (e.g. employee brand management, company credibility). Just recently, studies started investigating the impact of the use of social media on sustainability.
Another group of studies looked at the adoption of social media by B2B companies (Buratti et al. 2018 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gazal et al. 2016 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Kumar and Möller 2018 ). The studies investigated it mostly from the perspectives of salespersons and identify some of the key factors which affect the adoption, such as innovativeness, technical skills of employees, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness, and perceived usability. As these factors are derived mostly from surveys conducted with salespersons findings can be different for other individuals working in the organisation. This it is important to conduct studies that will examine factors affecting the adoption of social media across the entire organisation, in different departments. Using social media as part of the digital transformation is much bigger than sales and marketing, it encompasses the entire company. Additionally, most of the studies were cross-sectional, which limits the understanding of the adoption of social media by B2B over time depending on the outcomes and environment (e.g. competitors using social media).
Some studies looked at social media strategies of B2B companies (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ; Huotari et al. 2015 ; Kasper et al. 2015 ; McShane et al. 2019 ; Mudambi et al. 2019 ). By employing interviews with companies’ managers and analysing its social media platforms (e.g. Twitter) it was found that most of the companies follow the following strategies: 1) monitoring and listening 2) empowering and engaging employees 3) creating compelling content 4) stimulating eWOM 5) evaluating and selecting channels 6) enhancing brand presence through integrating social media (Cawsey and Rowley 2016 ). Some studies investigated the difference between social media strategies of B2B and B2C companies. For example, a study by Swani et al. ( 2017 ) focused on effective social media strategies. By applying psychological motivation theory the study examined the key differences in B2B and B2C social media message strategies in terms of branding, message appeals, selling, and information search. The study used Facebook posts on brand pages of 280 Fortune companies. In total, 1467 posts were analysed. By using Bayesian models, the results showed that the inclusion of corporate brand names, functional and emotional appeals and information search cues increases the popularity of B2B messages in comparison with B2C messages. Also, it was found that readers of B2B content show a higher message liking rate and lower message commenting rate in comparison with readers of B2C messages.
The next group of studies looked at social media use by B2B companies (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ; Habibi et al. 2015 ). B2B companies use social media for enhancing and managing customer relationships (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Bolat et al. ( 2016 ); branding (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ), sensing market (Bolat et al. 2016 ) and co-production (Chirumalla et al. 2018 ). Additionally, it was mentioned that some of the B2B companies use social media as a recruiting tool, and tool which helps to collaborate globally (Andersson and Wikström 2017 ; Dyck 2010 ).
It is important for companies to not only use social media to achieve positive business outcomes but also it is important to measure their achievements. As a result, some of the studies focused on the measuring effectiveness of social media (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ). Surprisingly, it was found that not so many companies measure ROI from social media (Gazal et al. 2016 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ). The ones who do it mostly use quantitative metrics (number of site visits, number of social network friends, number of comments and profile views) and qualitative metrics (growth of relationships with key audience, audience participation, moving from monologue to dialogue with consumers) (Gazal et al. 2016 ). Some future studies should investigate how ROI influences the strategy of B2B companies over period of time.
The last group of studies focused on social media tools used by B2B companies (Keinänen and Kuivalainen 2015 ; Mehmet and Clarke 2016 ; Yang et al. 2012 ). By using number of social media tools (Social Semiotic Multimodal) companies are able to improve their analysis of social media communications and identify their future consumers based on their user relationships. Studies investigating barriers and factors adoption of various social media tools by B2B companies are needed.
After reviewing studies on b2B social media, weight analysis was performed. Based on the results of weight analysis the conceptual model for future studies was proposed (Fig. 2 ). It is important to note that a limited number of studies focused and empirically tested factors affecting the adoption, use, and effect of social media. As a result, identified factors were considered as experimental (examined less than five times). It is too early to label these experimental predictors as worst or best, thus their further investigation is encouraged.
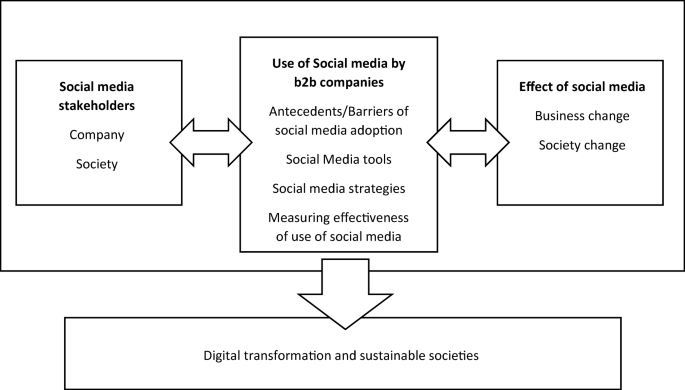
Social media impact on digital transformation and sustainable societies
Additionally, our review of the literature on B2B social media identified dominant research methods used by scholars. Qualitative and quantitative techniques were used by most of these studies. Closer analysis of 70 publications reviewed in this study revealed the multiple techniques applied for gathering data. Quantitative methods used in the studies mostly used surveys (see Table 4 ).
The data was mostly gathered from salespersons, managers and data from social media platforms (e.g. Twitter, Facebook). Just a limited number of studies employed consumer reported data (see Table 5 ).
On the other hand, publications using qualitative methods mainly used interviews and web scraping for the collection of the required data. To analyse the data studies used a variety of techniques including SEM, regression analysis and content analysis being one of the most used (see Table 6 ).
5.1 Digital Transformation and Sustainability Model
Based on the conducted literature review and adapting the model by Pappas et al. ( 2018 ) Fig. 2 presents the digital transformation and sustainability model in the context of B2B companies, which conceptualise the social media ecosystems, and the factors that need to collaborate to enable the use of social media towards the achievement of digital transformation and the creation of sustainable societies. The model comprises of social media stakeholders, the use of social media by B2B companies, and effect of social media on business and society.
5.1.1 Social Media Stakeholders
Building on the discussion and model provided by Pappas et al. ( 2018 ), this paper posits that the social media ecosystem comprises of the data stakeholders (company, society), who engage on social media (posting, reading, using information from social media). The use of social media by different stakeholders will lead to different effects affecting companies, customers and society. This is an iterative process based on which the stakeholders use their experience to constantly improve and evolve their use of social media, which has impacts on both, business and society. The successful implementation of this process is key to digital transformation and the creation of sustainable societies. Most of the current studies (Andersson et al. 2013 ; Bernard 2016 ; Bolat et al. 2016 ; Denktaş-Şakar and Sürücü 2018 ; Dyck 2010 ; Guesalaga 2016 ) focus mostly on the company as a stakeholder. However, more research is needed on other types of stakeholders (e.g. society).
5.1.2 Use of Social Media by B2B Companies
Social media affects not only ways how companies connect with their clients, but it is also changing their business models, the way how the value is delivered and profit is made. To successfully implement and use social media, B2B companies need to consider various social media tools, antecedents/barriers of its adoption, identify suitable social media strategies which are in line with the company’s overall strategy, and measure effectiveness of the use of social media. There are various factors that affect the use of social media by B2B companies. The study found that social media usage is influenced by perceived ease of use, adoption of social media, attitude towards social media and age of salesperson.
The majority of the studies focus on the management of the marketing department. However, digital transformation is much bigger than just marketing as it encompasses the entire organisation. As a result, future studies should look like the entire organisation and investigate barriers and factors affecting the use of social media.
It is crucial for companies to design content which will be noticed on social media by their potential, actual and former customers. Social media content should be interesting and offer some beneficial information, rather than just focus on services the company provides. Companies could use fresh views on relevant industry news, provide information how they are contributing to society and environment, include humour in their posts, share information about the team, make it more personal. It is also useful to use images, infographics, and video content.
It is also important for companies to measure digital marketing actions. More studies are needed on how to isolate the impact of specific media marketing actions to demonstrate their impact on the desired business outcomes (Salo 2017 ). Thus, future studies can consider how particular social media channels (e.g. Facebook, LinkedIn) in a campaign of a new product/ service influence brand awareness and sales level. Also, a limited number of studies discussed the way B2B companies can measure ROI. Future research should investigate how companies can measure intangible ROI, such as eWOM, brand awareness, and customer engagement (Kumar and Mirchandani 2012 ). Also, future research should investigate the reasons why most of the users do not assess the effectiveness of their SNS. Furthermore, most of the studies focused on likes, shares, and comments to evaluate social media engagement. Future research should focus on other types of measures. More research needs considering the impact of legislation on the use of social media by companies. Recent B2B studies did not consider recent legislation (General Data Protection Regulation 2018 ) in the context B2B (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ).
5.1.3 Effect of Social Media on Business and Society
Social media plays an important part in the company’s decision-making process. Social media can bring positive changes into company, which will result in improving customer satisfaction, value creation, increase in sales, building relationships with customers, knowledge creation, improve the perception of corporate credibility, acquisition of new customers, and improve employment brand engagement. Using information collected from social media can help companies to have a set of reliable attributes that comprise social, economic and environmental aspects in their decision-making process (Tseng 2017 ). Additionally, by using social media B2B companies can provide information to other stakeholders on their sustainability activities. By using data from social media companies will be able to provide products and services which are demanded by society. It will improve the quality of life and result in less waste. Additionally, social media can be considered as a tool that helps managers to integrate business practices with sustainability (Sivarajah et al. 2019 ). As a result, social media use by B2B companies can lead to business and societal changes.
A limited number of studies investigated the effect of social media on word of mouth communications in the B2B context. Future research should investigate the differences and similarities between B2C and B2B eWOM communications. Also, studies should investigate how these types of communications can be improved and ways to deal with negative eWOM. It is important for companies to respond to comments on social media. Additionally, future research should investigate its perceived helpfulness by customers.
Majority of studies (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ; Agnihotri et al. 2012 ; Agnihotri et al. 2017 ; Itani et al. 2017 ; Salo 2017 ; Bhattacharjya and Ellison 2015 ; Gáti et al. 2018 ; Gruner and Power 2018 ; Hollebeek 2019 ) investigated positive effect of social media such consumer satisfaction, consumer engagement, and brand awareness. However, it will be interesting to consider the dark side of social media use such as an excessive number of requests on social media to salespeople (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ), which can result in the reduction of the responsiveness; spread of misinformation which can damage the reputation of the company.
Studies were performed in China (Lacka and Chong 2016 ; Niedermeier et al. 2016 ), the USA (Guesalaga 2016 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Ogilvie et al. 2018 ), India (Agnihotri et al. 2017 ; Vasudevan and Kumar 2018 ), the UK (Bolat et al. 2016 ; Iankova et al. 2018 ; Michaelidou et al. 2011 ). It is strongly advised that future studies conduct research in other countries as findings can be different due to the culture and social media adoption rates. Future studies should pay particular attention to other emerging markets (such as Russia, Brazil, and South Africa) as they suffer from the slow adoption rate of social media marketing. Some companies in these countries still rely more on traditional media for advertising of their products and services, as they are more trusted in comparison with social media channels (Olotewo 2016 ). The majority of studies investigate the effect of social media in B2B or B2C context. Future studies should pay attention to other contexts (e.g. B2B2B, B2B2C). Another limitation of the current research on B2B companies is that most of the studies on social media in the context of B2B focus on the effect of social media use only on business outcomes. It is important for future research to focus on societal outcomes.
Lastly, most of the studies on social media in the context of B2B companies use a cross-sectional approach to collect the data. Future research can use the longitudinal approach in order to advance understanding of social media use and its impact over time.
5.2 Research Propositions
Based on the social media research in the context of B2B companies and the discussion above the following is proposed, which could serve as a foundation for future empirical work.
Social media is a powerful tool to deliver information to customers. However, social media can be used to get consumer and market insights (Kazienko et al. 2013 ). A number of studies highlighted how information obtained from a number of social media platforms could be used for various marketing purposes, such as understanding the needs and preferences of consumers, marketing potential for new products/services, and current market trends (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Constantinides et al. 2008 ). It is advised that future research employs a longitudinal approach to study the impact of social media use on understanding customers. Therefore, the following proposition can be formulated:
Proposition 1
Social media usage of B2B companies has a positive influence on understanding its customers.
By using social media companies can examiner valuable information on competitors. It can help to understand competitors’ habits and strategies, which can lead to the competitive advantage and help strategic planning (Dey et al. 2011 ; Eid et al. 2019 ; Teo and Choo 2001 ). It is advised that future research employs a longitudinal approach to study the impact of social media use on understanding its competitors. As a result, using social media to understand customers and competitors can create business value (Mikalef et al. 2020a ) for key stakeholders and lead to positive changes in the business and societies. The above discussion leads to the following proposition:
Proposition 2
Social media usage of B2B companies has a positive influence on understanding its competitors.
Proposition 3
Culture influences the adoption and use of social media by B2B companies.
Usage of social media can result in some positive marketing outcomes such as building new customer relationships, increasing brand awareness, and level of sales to name a few (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ; Ancillai et al. 2019 ; Dwivedi et al. 2020 ; Rossmann and Stei 2015 ). However, when social media is not used appropriately it can lead to negative consequences. If a company does not have enough resources to implement social media tools the burden usually comes on a salesperson. A high number of customer inquiries, the pressure to engage with customers on social media, and monitor communications happening on various social media platforms can result in the increased workload of a salesperson putting extra pressure (Agnihotri et al. 2016 ). As a result, a salesperson might not have enough time to engage with all the customers online promptly or engage in reactive and proactive web care. As a result, customer satisfaction can be affected as well as company reputation. To investigate the negative impact of social media research could apply novel methods for data collection and analysis such as fsQCA (Pappas et al. 2020 ), or implying eye-tracking (Mikalef et al. 2020b ). This leads to the following proposition:
Proposition 4
Inappropriate use of social media by B2B companies has a negative effect on a) customer satisfaction and b) company reputation.
According to Technology-Organisation-Environment (TOE) framework environmental context significantly affects a company’s use of innovations (Abed 2020 ; Oliveira and Martins 2011 ). Environment refers to the factors which affect companies from outside, including competitors and customers. Adopting innovation can help companies to change the rules of the competition and reach a competitive advantage (Porter and Millar 1985 ). In a competitive environment, companies have a tendency to adopt an innovation. AlSharji et al. ( 2018 ) argued that the adoption of innovation can be extended to social media use by companies. A study by AlSharji et al. ( 2018 ) by using data from 1700 SMEs operating in the United Arab Emirates found that competitive pressure significantly affects the use of social media by SMEs. It can be explained by the fact that companies could feel pressure when other companies in the industry start adopting a particular technology and as a result adopt it to remain competitive (Kuan and Chau 2001 ). Based on the above discussion, the following proposition can be formulated:
Proposition 5
Competitive pressure positively affects the adoption of social media by B2B companies.
Companies might feel that they are forced to adopt and use IT innovations because their customers would expect them to do so. Meeting customers’ expectations could result in adoption of new technologies by B2B companies. Some research studies investigated the impact of customer pressure on companies (AlSharji et al. 2018 ; Maduku et al. 2016 ). For example, a study by Maduku et al. ( 2016 ) found that customer pressure has a positive effect on SMEs adoption of mobile marketing in the context of South Africa. Future research could implement longitudinal approach to investigate how environment affects adoption of social media by B2B companies. This leads to the formulation of the following proposition:
Proposition 6
Customer pressure positively affects the adoption of social media by B2B companies.
6 Conclusion
The aim of this research was to provide a comprehensive systematic review of the literature on social media in the context of B2B companies and propose the framework outlining the role of social media in the digital transformation of B2B companies. It was found that B2B companies use social media, but not all companies consider it as part of their marketing strategies. The studies on social media in the B2B context focused on the effect of social media, antecedents, and barriers of adoption of social media, social media strategies, social media use, and measuring the effectiveness of social media. Academics and practitioners can employ the current study as an informative framework for research on the use of social media by B2B companies. The summary of the key observations provided from this literature review is the following: [i] Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn are the most famous social media platforms used by B2B companies, [ii] Social media has a positive effect on customer satisfaction, acquisition of new customers, sales, stakeholder engagement, and customer relationships, [iii] In systematically reviewing 70 publications on social media in the context of B2B companies it was observed that most of the studies use online surveys and online content analysis, [iv] Companies still look for ways to evaluate the effectiveness of social media, [v] Innovativeness, pressure from stakeholders, perceived usefulness, and perceived usability have a significant positive effect on companies’ adoption to use social media, [vi] Lack of staff familiarity and technical skills are the main barriers that affect the adoption of social media by B2B, [vii] Social media has an impact not only on business but also on society, [viii] There is a dark side of social media: fake online reviews, an excessive number of requests on social media to salespeople, distribution of misinformation, negative eWOM, [ix] Use of social media by companies has a positive effect on sustainability, and [x] For successful digital transformation social media should change not only the way how companies integrate it into their marketing strategies but the way how companies deliver values to their customers and conduct their business. This research has a number of limitations. First, only publications from the Scopus database were included in literature analysis and synthesis. Second, this research did not use meta-analysis. To provide a broader picture of the research on social media in the B2B context and reconcile conflicting findings of the existing studies future research should conduct a meta-analysis (Ismagilova et al. 2020c ). It will advance knowledge of the social media domain.
Abed, S. S. (2020). Social commerce adoption using TOE framework: An empirical investigation of Saudi Arabian SMEs. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102118.
Article Google Scholar
Agnihotri, R., Kothandaraman, P., Kashyap, R., & Singh, R. (2012). Bringing “social” into sales: The impact of salespeople’s social media use on service behaviors and value creation. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 32 (3), 333–348. https://doi.org/10.2753/PSS0885-3134320304 .
Agnihotri, R., Dingus, R., Hu, M. Y., & Krush, M. T. (2016). Social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales. Industrial Marketing Management, 53 , 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.09.003 .
Agnihotri, R., Trainor, K. J., Itani, O. S., & Rodriguez, M. (2017). Examining the role of sales-based CRM technology and social media use on post-sale service behaviors in India. Journal of Business Research, 81 , 144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.08.021 .
Alalwan, A. A., Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Algharabat, R. (2017). Social media in marketing: A review and analysis of the existing literature. Telematics and Informatics, 34 (7), 1177–1190.
AlSharji, A., Ahmad, S. Z., & Bakar, A. R. A. (2018). Understanding social media adoption in SMEs. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 10 (2), 302–328.
Ancillai, C., Terho, H., Cardinali, S., & Pascucci, F. (2019). Advancing social media driven sales research: Establishing conceptual foundations for B-to-B social selling. Industrial Marketing Management, 82 , 293–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.01.002 .
Andersson, S., & Wikström, N. (2017). Why and how are social media used in a B2B context, and which stakeholders are involved? Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (8), 1098–1108. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-07-2016-0148 .
Andersson, S., Evers, N., & Griot, C. (2013). Local and international networks in small firm internationalization: Cases from the Rhône-Alpes medical technology regional cluster. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 25 (9–10), 867–888.
Andzulis, J. M., Panagopoulos, N. G., & Rapp, A. (2012). A review of social media and implications for the sales process. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 32 (3), 305–316.
Barreda, A. A., Bilgihan, A., Nusair, K., & Okumus, F. (2015). Generating brand awareness in online social networks. Computers in Human Behavior, 50 , 600–609.
Bell, D., & Shirzad, S, R. (2013). Social media domain analysis (SoMeDoA): A pharmaceutical study. 9th international conference on web information systems and technologies, 561–570. https://doi.org/10.5220/0004499105610570 .
Bernard, M. (2016). The impact of social media on the B2B CMO. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 31 (8), 955–960. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-268 .
Bhattacharjya, J., & Ellison, A, B. (2015). Building business resilience with social media in B2B environments: The emergence of responsive customer relationship management processes on twitter. Working Conference on Virtual Enterprises doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24141-8_15 .
Bolat, E., Kooli, K., & Wright, L. T. (2016). Businesses and mobile social media capability. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 31 (8), 971–981. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-270 .
Buratti, N., Parola, F., & Satta, G. (2018). Insights on the adoption of social media marketing in B2B services. TQM Journal, 30 (5), 490–529. https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-11-2017-0136 .
Cawsey, T., & Rowley, J. (2016). Social media brand building strategies in B2B companies. Marketing Intelligence and Planning, 34 (6), 754–776. https://doi.org/10.1108/MIP-04-2015-0079 .
Chatterjee, S., & Kar, A. K. (2020). Why do small and medium enterprises use social media marketing and what is the impact: Empirical insights from India. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102103.
Chen, H., Chiang, R. H., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS Quarterly, 36 , 1165–1188.
Chirumalla, K., Oghazi, P., & Parida, V. (2018). Social media engagement strategy: Investigation of marketing and R&D interfaces in manufacturing industry. Industrial Marketing Management, 74 , 138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.10.001 .
Constantinides, E., Romero, C. L., & Boria, M. A. G. (2008). Social media: A new frontier for retailers?. In European retail research (pp. 1–28) . Wiesbaden: Gabler Verlag.
Google Scholar
Denktaş-Şakar, G., & Sürücü, E. (2018). Stakeholder engagement via social media: An analysis of third-party logistics companies. Service Industries Journal, 40 , 866–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642069.2018.1561874 .
Dey, L., Haque, S, M., Khurdiya, A., & Shroff, G. (2011). Acquiring competitive intelligence from social media. In proceedings of the 2011 joint workshop on multilingual OCR and analytics for noisy unstructured text data (pp. 1-9) . https://doi.org/10.1145/2034617.2034621 .
Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., Jeyaraj, A., Clement, M., & Williams, M. D. (2019a). Re-examining the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): Towards a revised theoretical model. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 719–734.
Dwivedi, Y, K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., ... & Galanos, V. (2019b). Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International Journal of Information Management , 101994, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.08.002 .
Dwivedi, Y, K., Ismagilova, E., Hughes, D. L., Carlson, J., Filieri, R., Jacobson, J., ... & Kumar, V. (2020). Setting the future of digital and social media marketing research: Perspectives and research propositions. International Journal of Information Management , 102168, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102168 .
Dyck, P. V. (2010). As social media evolves, the device industry must also. Medical Device and Diagnostic Industry, 32 (8).
Eid, R., Abdelmoety, Z., & Agag, G. (2019). Antecedents and consequences of social media marketing use: An empirical study of the UK exporting B2B SMEs. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing., 35 , 284–305.
Gáti, M., Mitev, A., & Bauer, A. (2018). Investigating the impact of salespersons’ use of technology and social media on their customer relationship performance in B2B settings. Trziste, 30 (2), 165–176. https://doi.org/10.22598/mt/2018.30.2.165 .
Gazal, K., Montague, I., Poudel, R., & Wiedenbeck, J. (2016). Forest products industry in a digital age: Factors affecting social media adoption. Forest Products Journal, 66 (5-6), 343–353. https://doi.org/10.13073/FPJ-D-15-00007 .
General Data Protection Regulation (2018). Guide to the General Data Protection Regulation. Available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/guide-to-the-general-data-protection-regulation . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Gregorio, J. (2017). 10 reasons to diversify your digital marketing efforts. Digital marketing Philippines. Available at https://digitalmarketingphilippines.com/10-reasons-to-diversify-your-digital-marketing-efforts// Accessed on April , 27 , 2019.
Gruner, R. L., & Power, D. (2018). To integrate or not to integrate? Understanding B2B social media communications. Online Information Review, 42 (1), 73–92. https://doi.org/10.1108/OIR-04-2016-0116 .
Guesalaga, R. (2016). The use of social media in sales: Individual and organizational antecedents, and the role of customer engagement in social media. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.12.002 .
Gupta, P., Chauhan, S., & Jaiswal, M. P. (2019). Classification of smart city research-a descriptive literature review and future research agenda. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 661–685.
Habibi, F., Hamilton, C. A., Valos, M. J., & Callaghan, M. (2015). E-marketing orientation and social media implementation in B2B marketing. European Business Review, 27 (6), 638–655. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBR-03-2015-0026 .
Harrigan, P., Miles, M. P., Fang, Y., & Roy, S. K. (2020). The role of social media in the engagement and information processes of social CRM. International Journal of Information Management, 54 , 102151.
Hollebeek, L. D. (2019). Developing business customer engagement through social media engagement-platforms: An integrative SD logic/RBV-informed model. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 89–98.
Hsiao, S. H., Wang, Y. Y., Wang, T., & Kao, T. W. (2020). How social media shapes the fashion industry: The spillover effects between private labels and national brands. Industrial Marketing Management, 86 , 40–51.
Huotari, L., Ulkuniemi, P., Saraniemi, S., & Mäläskä, M. (2015). Analysis of content creation in social media by B2B companies. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30 (6), 761–770. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-05-2013-0118 .
Iankova, S., Davies, I., Archer-Brown, C., Marder, B., & Yau, A. (2018). A comparison of social media marketing between B2B, B2C and mixed business models. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.001 .
Iannacci, F., Fearon, C., & Pole, K. (2020). From acceptance to adaptive acceptance of social media policy change: A set-theoretic analysis of b2b SMEs. Information Systems Frontiers , 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-09988-1 .
Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y. K., Slade, E., & Williams, M. D. (2017). Electronic word of mouth (eWOM) in the marketing context: A state of the art analysis and future directions . Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-52459-7 .
Ismagilova, E., Hughes, L., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Raman, K. R. (2019). Smart cities: Advances in research—An information systems perspective. International Journal of Information Management, 47 , 88–100.
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E. L., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020a). The effect of electronic word of mouth communications on intention to buy: A meta-analysis. Information Systems Frontiers, 22 , 1203–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-019-09924-y .
Ismagilova, E., Slade, E., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020b). The effect of characteristics of source credibility on consumer behaviour: A meta-analysis. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 53 , 101736.
Ismagilova, E., Rana, N, P., Slade, E., & Dwivedi, Y, K. (2020c). A meta-analysis of the factors affecting eWOM providing behaviour. European Journal of Marketing. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/EJM-07-2018-0472 , ahead-of-print.
Itani, O. S., Agnihotri, R., & Dingus, R. (2017). Social media use in B2b sales and its impact on competitive intelligence collection and adaptive selling: Examining the role of learning orientation as an enabler. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 64–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.06.012 .
Jeyaraj, A., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020). Meta-analysis in information systems research: Review and recommendations. International Journal of Information Management, 55 , 102226.
Jeyaraj, A., Rottman, J. W., & Lacity, M. C. (2006). A review of the predictors, linkages, and biases in IT innovation adoption research. Journal of Information Technology, 21 (1), 1–23.
Juntunen, M., Ismagilova, E., & Oikarinen, E. L. (2020). B2B brands on twitter: Engaging users with a varying combination of social media content objectives, strategies, and tactics. Industrial Marketing Management, 89 , 630–641.
Jussila, J. J., Kärkkäinen, H., & Leino, M. (2011). Benefits of social media in business-to-business customer interface in innovation. 15th International Academic MindTrek Conference: Envisioning Future Media Environments . MindTrek, 2011 , 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1145/2181037.2181065 .
Kamboj, S., Sarmah, B., Gupta, S., & Dwivedi, Y. (2018). Examining branding co-creation in brand communities on social media: Applying the paradigm of stimulus-organism-response. International Journal of Information Management, 39 , 169–185.
Kapoor, K. K., Tamilmani, K., Rana, N. P., Patil, P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Nerur, S. (2018). Advances in social media research: Past, present and future. Information Systems Frontiers, 20 (3), 531–558.
Kärkkäinen, H., Jussila, J., & Janhonen, J. (2011). Managing customer information and knowledge with social media in business-to-business companies. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/2024288.2024309 .
Kasper, H., Koleva, I., & Kett, H. (2015). Social media matrix matching corporate goals with external social media activities doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46641-4_17 .
Katona, Z., & Sarvary, M. (2014). Maersk line: B2B social media-“it’s communication, not marketing. California Management Review , 56(3), 142–156. doi: https://doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2014.56.3.142 .
Kazienko, P., Szozda, N., Filipowski, T., & Blysz, W. (2013). New business client acquisition using social networking sites. Electronic Markets, 23 (2), 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12525-013-0123-9 .
Keinänen, H., & Kuivalainen, O. (2015). Antecedents of social media B2B use in industrial marketing context: Customers’ view. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30 (6), 711–722. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-04-2013-0095 .
Kho, N. D. (2008). B2B gets social media. EContent, 31 (3), 26–30.
Kovac, M. (2016). Social media works for B2B sales, too. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2016/01/social-media-worksfor-b2b-sales-too . Accessed on April , 27 , 2020 .
Kuan, K. K., & Chau, P. Y. (2001). A perception-based model for EDI adoption in small businesses using a technology–organization–environment framework. Information & Management, 38 (8), 507–521.
Kumar, V., & Mirchandani, R. (2012). Increasing the ROI of social media marketing. MIT Sloan Management Review, 54 (1), 55–61.
Kumar, A., & Möller, K. (2018). Extending the boundaries of corporate branding: An exploratory study of the influence of brand familiarity in recruitment practices through social media by B2B firms. Corporate Reputation Review, 21 (3), 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41299-018-0046-7 .
Kunsman, T. (2018). Internal marketing: Why your company should prioritize it. https://everyonesocial.com/blog/internal-marketing/ . Accessed on September, 25, 2019.
Lacka, E., & Chong, A. (2016). Usability perspective on social media sites' adoption in the B2B context. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.01.001 .
Lal, B., Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y.,. K., & Kwayu, S. (2020). Return on Investment in Social Media Marketing: Literature review and suggestions for future research. In Digital and Social Media Marketing (pp. 3–17) . Cham: Springer.
Lashgari, M., Sutton-Brady, C., Solberg Søilen, K., & Ulfvengren, P. (2018). Adoption strategies of social media in B2B firms: A multiple case study approach. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 33 (5), 730–743. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-0242 .
Loebbecke, C., & Picot, A. (2015). Reflections on societal and business model transformation arising from digitization and big data analytics: A research agenda. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (3), 149–157.
Maduku, D. K., Mpinganjira, M., & Duh, H. (2016). Understanding mobile marketing adoption intention by south African SMEs: A multi-perspective framework. International Journal of Information Management, 36 (5), 711–723.
Mahrous, A, A. (2013). Social media marketing: Prospects for marketing theory and practice on the social web. E-marketing in developed and developing countries: Emerging practices (pp. 56-68) doi: https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-3954-6.ch004 Retrieved from www.scopus.com .
McAfee, A. P. (2006). Enterprise 2.0: The dawn of emergent collaboration. Enterprise, 2 , 15–26.
McKinsey & Company (2015). Transforming the business through social tools. McKinsey.com , ( http://www.mckinsey.com/industries/high-tech/our-insights/transformingthe-business-through-social-tools ).
McShane, L., Pancer, E., & Poole, M. (2019). The influence of B to B social media message features on brand engagement: A fluency perspective. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26 (1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565132 .
Mehmet, M. I., & Clarke, R. J. (2016). B2B social media semantics: Analysing multimodal online meanings in marketing conversations. Industrial Marketing Management, 54 , 92–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.12.006 .
Meire, M., Ballings, M., & Van den Poel, D. (2017). The added value of social media data in B2B customer acquisition systems: A real-life experiment. Decision Support Systems, 104 , 26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.09.010 .
Michaelidou, N., Siamagka, N. T., & Christodoulides, G. (2011). Usage, barriers and measurement of social media marketing: An exploratory investigation of small and medium B2B brands. Industrial Marketing Management, 40 (7), 1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2011.09.009 .
Mikalef, P., Pappas, I. O., Krogstie, J., & Pavlou, P. A. (2020a). Big data and business analytics: A research agenda for realizing business value. Information & Management, 57 (1), 103237.
Mikalef, P., Sharma, K., Pappas, I, O., & Giannakos, M. (2020b). Seeking information on social commerce: An examination of the impact of user-and marketer-generated content through an eye-tracking study. Information Systems Frontiers , 1-14, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-020-10034-3 .
Minsky, L., & Quesenberry, K, A. (2016). How B2B sales can benefit from social selling . Harvard Business Review. Available at https://hbr.org/2016/11/84-of-b2b-sales-start-with-a-referral-not-a-salesperson . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Moncrief, W. C., Marshall, G. W., & Rudd, J. M. (2015). Social media and related technology: Drivers of change in managing the contemporary sales force. Business Horizons, 58 (1), 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2014.09.009 .
Moore, J. N., Hopkins, C. D., & Raymond, M. A. (2013). Utilization of relationship-oriented social media in the selling process: A comparison of consumer (B2C) and industrial (B2B) salespeople. Journal of Internet Commerce, 12 (1), 48–75. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332861.2013.763694 .
Moore, J. N., Raymond, M. A., & Hopkins, C. D. (2015). Social selling: A comparison of social media usage across process stage, markets, and sales job functions. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 23 (1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10696679.2015.980163 .
Mudambi, S. M., Sinha, J. I., & Taylor, D. S. (2019). Why B-to-B CEOs should be more social on social media. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26 (1), 103–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565144 .
Muhammad, S. S., Dey, B. L., & Weerakkody, V. (2018). Analysis of factors that influence customers’ willingness to leave big data digital footprints on social media: A systematic review of literature. Information Systems Frontiers, 20 (3), 559–576.
Müller, L., Griesbaum, J., & Mandl, T. (2013). Social media relations in the german automotive market. Paper presented at the proceedings of the IADIS international conference ICT, society and human beings 2013, Proceedings of the IADIS International Conference e-Commerce 2013, 19–26.
Müller, J. M., Pommeranz, B., Weisser, J., & Voigt, K. I. (2018). Digital, social media, and Mobile marketing in industrial buying: Still in need of customer segmentation? Empirical evidence from Poland and Germany. Industrial Marketing Management, 73 , 70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.033 .
Niedermeier, K. E., Wang, E., & Zhang, X. (2016). The use of social media among business-to-business sales professionals in China: How social media helps create and solidify guanxi relationships between sales professionals and customers. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 10 (1), 33–49. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-08-2015-0054 .
Nunan, D., Sibai, O., Schivinski, B., & Christodoulides, G. (2018). Reflections on “social media: Influencing customer satisfaction in B2B sales” and a research agenda. Industrial Marketing Management, 75 , 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.03.009 .
Ogilvie, J., Agnihotri, R., Rapp, A., & Trainor, K. (2018). Social media technology use and salesperson performance: A two study examination of the role of salesperson behaviors, characteristics, and training. Industrial Marketing Management, 75 , 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.03.007 .
Oliveira, T., & Martins, M. F. (2011). Literature review of information technology adoption models at firm level. Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, 14 (1), 110.
Olotewo, J. (2016). Social media marketing in emerging markets. International Journal of Online Marketing Research, 2 (2), 10–18.
Pappas, I. O., Mikalef, P., Giannakos, M. N., Krogstie, J., & Lekakos, G. (2018). Big data and business analytics ecosystems: Paving the way towards digital transformation and sustainable societies. Information Systems and e-Business Management, 16 , 479–491.
Pappas, I. O., Papavlasopoulou, S., Mikalef, P., & Giannakos, M. N. (2020). Identifying the combinations of motivations and emotions for creating satisfied users in SNSs: An fsQCA approach. International Journal of Information Management, 53 , 102128.
Pascucci, F., Ancillai, C., & Cardinali, S. (2018). Exploring antecedents of social media usage in B2B: A systematic review. Management Research Review, 41 (6), 629–656. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-07-2017-0212 .
Pitt, C. S., Plangger, K. A., Botha, E., Kietzmann, J., & Pitt, L. (2017). How employees engage with B2B brands on social media: Word choice and verbal tone. Industrial Marketing Management, 81 , 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.09.012 .
Pitt, C. S., Botha, E., Ferreira, J. J., & Kietzmann, J. (2018). Employee brand engagement on social media: Managing optimism and commonality. Business Horizons, 61 (4), 635–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2018.04.001 .
Porter, M. E., & Millar, V. E. (1985). How information gives you competitive advantage. Harvard Business Review, 63 (4), 149–160.
Pulizzi, J., & Handley, A. (2017). B2C content marketing-2018 benchmarks, budgets, and trends—North America. Available at https://contentmarketinginstitute.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/2017_B2B_Research_FINAL.pdf Accessed on April , 27 , 2020.
Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Williams, M. D. (2015). A meta-analysis of existing research on citizen adoption of e-government. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (3), 547–563.
Rana, N. P., Luthra, S., Mangla, S. K., Islam, R., Roderick, S., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2019). Barriers to the development of smart cities in Indian context. Information Systems Frontiers, 21 (3), 503–525.
Rodriguez, M., Peterson, R. M., & Krishnan, V. (2012). Social media's influence on business-to-business sales performance. Journal of Personal Selling and Sales Management, 32 (3), 365–378. https://doi.org/10.2753/PSS0885-3134320306 .
Rossmann, A., & Stei, G. (2015). Sales 2.0 in business-to-business (B2B) networks: Conceptualization and impact of social media in B2B sales relationships . Paper presented at the Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI), Proceedings - Series of the Gesellschaft Fur Informatik (GI), 244 67–78. Available at https://subs.emis.de/LNI/Proceedings/Proceedings244/67.pdf . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Salo, J. (2017). Social media research in the industrial marketing field: Review of literature and future research directions. Industrial Marketing Management, 66 , 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.07.013 .
Shaltoni, A. M. (2017). From websites to social media: Exploring the adoption of internet marketing in emerging industrial markets. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (7), 1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-06-2016-0122 .
Siamagka, N. T., Christodoulides, G., Michaelidou, N., & Valvi, A. (2015). Determinants of social media adoption by B2B organizations. Industrial Marketing Management, 51 , 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.05.005 .
Sivarajah, U., Irani, Z., Gupta, S., & Mahroof, K. (2019). Role of big data and social media analytics for business to business sustainability: A participatory web context. Industrial Marketing Management . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2019.04.005 .
Sobal, A. (2017). 30 statistics about B2B social media usage. Available at https://www.weidert.com/blog/statistics-about-b2b-social-media-usage Accessed on April , 27 , 2020.
Stelzner, M. (2011). 2012 social media marketing industry report. Social media examiner . Available at https://www.socialmediaexaminer.com/socialmedia-marketing-industry-report-2012/ . Accessed 28 Jan 2021.
Sułkowski, Ł., & Kaczorowska-Spychalska, D. (2016). Social media in the process of marketing evolution in polish textile-clothing industry. Fibres and Textiles in Eastern Europe, 24 (5), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.5604/12303666.1215521 .
Swani, K., Milne, G., & Brown, B. P. (2013). Spreading the word through likes on facebook: Evaluating the message strategy effectiveness of fortune 500 companies. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7 (4), 269–294. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-05-2013-0026 .
Swani, K., Brown, B. P., & Milne, G. R. (2014). Should tweets differ for B2B and B2C? An analysis of fortune 500 companies' twitter communications. Industrial Marketing Management, 43 (5), 873–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2014.04.012 .
Swani, K., Milne, G. R., Brown, B. P., Assaf, A. G., & Donthu, N. (2017). What messages to post? Evaluating the popularity of social media communications in business versus consumer markets. Industrial Marketing Management, 62 , 77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.07.006 .
Tedeschi, B. (2006). Like shopping? Social networking? Try social shopping. New York Times, 11 , 09.
Teo, T. S., & Choo, W. Y. (2001). Assessing the impact of using the internet for competitive intelligence. Information & Management, 39 (1), 67–83.
Tseng, M. L. (2017). Using social media and qualitative and quantitative information scales to benchmark corporate sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142 , 727–738.
Vasudevan, S., & Kumar, F. J. P. (2018). Social media and B2B brands: An Indian perspective. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology, 9 (9), 767–775.
Vukanovic, Z. (2013). Managing social media value networks: From publisher (broadcast) to user-centric (broadband-narrowcast) business models. Handbook of social media management: Value chain and business models in changing media markets (pp. 269-288) doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28897-5_16 .
Wang, Y., Rod, M., Ji, S., & Deng, Q. (2017). Social media capability in B2B marketing: Toward a definition and a research model. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32 (8), 1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-10-2016-0250 .
Watt, I. (2010). Changing visions of parliamentary libraries: From the enlightenment to Facebook. IFLA Journal, 36 (1), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1177/0340035209359574 .
Webster, J., & Watson, R.,. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS quarterly, 26 (2), xiii–xxiii.
Westerman, G., Bonnet, D., & McAfee, A. (2014). Leading digital: Turning technology into business transformation . Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
Williams, M. D., Rana, N. P., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2015). The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): A literature review. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 28 (3), 443–488.
World Commission Report on Environment and Development. (1987). Our Common Future . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Yang, C. C., Yang, H., Tang, X., & Jiang, L. (2012). Identifying implicit relationships between social media users to support social commerce. In ACM international conference proceeding series (pp. 41–47). https://doi.org/10.1145/2346536.2346544 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Emerging Markets Research Centre (EMaRC), School of Management, Swansea University, Bay Campus, Swansea, UK
Yogesh K. Dwivedi
School of Management, University of Bradford, Bradford, UK
Elvira Ismagilova & Nripendra P. Rana
Symbiosis Institute of Business Management, Pune & Symbiosis International, Deemed University, Pune, India
Ramakrishnan Raman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yogesh K. Dwivedi .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Dwivedi, Y.K., Ismagilova, E., Rana, N.P. et al. Social Media Adoption, Usage And Impact In Business-To-Business (B2B) Context: A State-Of-The-Art Literature Review. Inf Syst Front 25 , 971–993 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Download citation
Accepted : 07 January 2021
Published : 02 February 2021
Issue Date : June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Business-to-business
- Digital transformation
- Information systems
- Literature review
- Social media
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Social Media: Changing the World of Business Communication

Related Papers
Journal of Information Technology Education: Innovations in Practice
Merrill Warkentin
The ways people connect, interact, share, and communicate have changed due to recent developments in information technology. These developments, categorized as social media, have captured the attention of business executives, technologists, and education professionals alike, and have altered many business models. Additionally, the concept of social media impacts numerous sub-disciplines within business and has become an important issue with operational, tactical, and strategic considerations. Despite this interest, many business schools do not have courses involving social media technologies and applications. In those that do, the placement and focus of the course varies considerably. This article provides motivation and insight into the process of developing an approach for effectively teaching social media use in business. Additionally, it offers implementation examples of courses taught at three major universities. The article concludes with lessons-learned that will give instruc...
International Journal of Online Pedagogy and Course Design
Corie Haylett
This study reviews the literature on the advantages, disadvantages, best practices, communication challenges, and benefits of using social media for teaching online, particularly the enhancement of essential business communication skills. Social media tools for teaching online are varied, plentiful, and easily accessible to teachers and students. Nevertheless, educators cannot assume because social media is an appropriate technology, it will essentially involve learners and enhance student achievement. This study, therefore, will examine the literature that reported positive effects of social media for teaching online, as it relates to learners' achievement and engagement, as well as literature showing a negative relationship or showing no conclusive evidence that there exists any relationship between the two. The findings of the review will reveal there is irrefutable evidence to suggest the use of social media for teaching online has a positive relationship to learner engageme...
AICTE Sponsored two day National Conference on Management and Social Sciences it’s Impact on Sustainable Development held at Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of Technology (CBIT), Hyderabad, India, from October 25-26, 2013.
Sambaji Rao
The term ‘communication’ comes from Latin word communis which means common. Communication has been defined in several ways as people have different impression about it. Communication essentially means transmission of commonly meaningful information. Communication has a rich history and its traditions can still be seen in modern day business activities. Much like life itself, communication is a process. That means it is dynamic, ever-changing never ending process. The salient features of communication are interchange of information, continuous process, mutual understanding, response or reaction, constructive feedback, universal function, social activity etc. Basically, there are two models namely: a) Linear Model b) Interpersonal or interactional Model. The present study shows that when compared to traditional means of communication, today in the 21st century there has been a drastic change in the modern means of communication. The advancements in ICT had left its impact on everyone. As a result, today the whole world is viewed as a “global village” and we could see rapid progress in every sector-education, politics, and economy.
ijhssnet.com
Casimir Barczyk
20th Annual European Council for Business Education (ECBE) Conference, Metropolis Palace, Belgrade, Serbia ISSN 1534-9373.
Dennis Blanco
The article offers a synthesis integrative review on the various implications and repercussion of social media in the field of business and higher education. It also narrates how Social Media transcends organizations irrespective of whether it is a private corporation engage in business or academic institutions involve in the delivery of quality education. In the field of business, the article analyzes and discusses the issues with revolves around the role of social media in specific business concepts and practices such as corporate social responsibility, social media listening, social media monitoring, social media selling and attempts to provide a comparative insights on their similarities and disparities with the plethora of voices culled from various authors and literatures as reference points. In the context of higher education, the article breakdown and posit concrete and the tangible effects of social media to the vital components of higher education institutions such as administration, faculty and student service offices with library, student affairs and admissions in particular. In the process of analyzing and philosophizing, the article raises few questions on social media such as who shall decide which specific social media tools and platforms would perfectly blend and fit to organisations. Will social media be the panacea of the education for the future or the future for education? In the end, the article concludes that there is not stopping media in coming to our workplace, schools, college and universities. The inevitability of both private corporations and higher education institutions searching for a social media solution lies on the very fabric of their rational choices and decisional –methods on which social media network sites can best fit and work to their business context and educational paradigms.
Jetlira Hoxha
In assessing the application of social media on the teaching of business communication, this article looks at MBA student use of blogs, online photo database contributions, and video contributions to YouTube channels. These assignments were part of their course activities, which included a 2-week study tour in China. The article looks at these activities within the context of the social constructivist view on learning in general. The student work provides evidence of the positive results that come from the use of social media, when viewed from the perspective of social constructivist theories for learning. THIS ARTICLE DISCUSSES SOME of the effects of social media on business communication pedagogy. Specifically, we will be sharing the experience and providing some analysis related to implementation of social media into MBA courses at the University of Texas at Austin. We begin by placing the use of social media within the broader theoretical context of social constructivism. Many principles of social constructivism coincide with the ways that social media enhances learning in our everyday lives. Second, we present the background and strategy behind the implementation of blogs, photo databases, and student-generated video clips assigned in an MBA course that included a 2-week study tour in China. We then end with some recommendations and observations for further implementation.
Cynthia Nichols
Dr. Ephraim Okoro
FOCUS ON TEACHING 435 presentations focusing on social networking, blogs, wikis, and various Web 2.0 technologies have captured our attention. We have oftentimes felt deep anxiety about staying up-to-date and responding effectively to the needs of our students. We sense that this anxiety, almost panic, is widespread among many of us business communication instructors.
International Journal of Technology and Educational Marketing
Pamela A Lemoine
The technological revolution of the past two decades has changed communication in contemporary higher education settings. Consequently, there is now a wide gulf between the unlimited use of technology and higher education, particularly with respect to digital communications and the rapid increase in the use of social media in instructional applications. Technology offers college students an array of options to socialize, network, stay informed and connected, but technology proficiency may not be the same for instructors. As social media use by students becomes more established, educators in higher education are pursuing methods to parlay expertise in instruction to advertise and market higher education institutions. Can social media be used in higher education to improve learning through student and faculty collaboration, and just as importantly can the use of social media be used as a recruiting tool for higher education institutions?
Academy of Strategic Management Journal
Ahmad Zamil
RELATED PAPERS
muhammad babar
Aerobiologia
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences
Anubhuti Sharma
Anales De Pediatria
Clara Cavero-Carbonell
Akindele Michael Okedoye
Segundo Félix Salvador Quezada
Journal of Krishi Vigyan
Noorjehan K A Hanif
Yuka Kitano
Gastroenterology
sambit nanda
Critical Care Medicine
Douglas Sloane
Bulletin of Materials Science
Reda Hassanien
martin garcia
Elisabeth Larsson
Window of Health : Jurnal Kesehatan
lestari tampubolon
Tatiana Pikuz
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids
Pavel Laktionov
EJVES Vascular Forum
Alexandru Florea
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology
Costas Apostolis
Rune Ellefsen
Munir Tarazi
International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology
Ramya Gowda
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology
Sneha Shree
International Journal of Communication Systems
Rony Kumer Saha, Ph.D.
hgvfgd ghtgf
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- About the Journal
- Aims and Scope
- Editorial Board
- Subscription Information
- Copyright & Open Access
- Crossmark Policy
- Contact Information
- Current Issue
- Most Read Articles
- Most Cited Articles
- Advanced Search
- Author Guidelines
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Submission of Manuscript
- Copyright Transfer Agreement
- Free Email Alerts
QR Code of this Article:
- E-Submission
- Journal Archive
Bus. Commun. Res. Pract. 2019 ; 2 ( 1 ): 28 - 33
pISSN: 2586-5293, eISSN: 2586-534X
DOI: https://doi.org/10.22682/bcrp.2019.2.1.28
Uses of Rhetorical Reasoning Theories in Business Communication Researches
Copyright © 2019 Korean Association for Business Communication. This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ ) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: Oct 10, 2018 ; Revised: Nov 02, 2018 ; Accepted: Nov 08, 2018
Published Online: Mar 31, 2019
By literature review, this paper tries to find how rhetorical reasoning models and theories have been used in business communication both in industry and academia and answer the following questions: 1) Is rhetorical reasoning important for persuasion in business? 2) What kinds of rhetorical reasoning methods have been used in business communication?
Dissertations and journal articles from RISS (Research Information Sharing Service) and Google Scholar were gathered. Academic sources were reviewed based on the basic frame of research: Domain, Method, and Results.
Theories and models of Perelman, Toulmin, and van Eemeren have been used to explain various phenomena in the field of business. Business fields in this paper include advertising, bank annual reports, downsizing reports, and policy decision making processes.
Rhetorical reasoning is a widely used method in business communication. Several suggestions for future researches are: First, more rhetorical theories and models are needed to be used to business communication research. Second, existing rhetorical reasoning models like the argumentation model of Toulmin need to be tested in more diverse fields of business communication. Third, in addition to text, rhetorical, content analysis, other kinds of research methods such as experiments will be useful for expanding the boundaries of business communication research based on rhetorical reasoning theories.
Introduction
Persuasion is an essential part of business communication. Rhetoric is the study of finding the best ways of persuasion. Since the time of classical rhetoricians such as Aristotle (1991) , rhetoric has only focused on ways of expression in literature and has departed from the field of logical persuasion ( Choi, 2013 ). But since the 1950s, when Perelman (1982) and Toulmin (2003) opened the Neo-Rhetoric age, rhetoric regained a connection with logical persuasion. While the ancient rhetoric basically focused on politics and public speeches, Neo-Rhetoric expanded its boundaries to the daily lives of people such as in debate ( Lee, 2018 ). Advertising goods to customers, justifying a need for downsizing to internal and external members of a company, pitching to get investments, and many other daily practices exist in the field of business communication and persuasion. Persuasion in business communication does not require absolute truth or mathematically perfect logic. Rather, it requires rhetorical reasoning. Since business communication also addresses mass public and diverse groups, so the communicators need to decide what should be explicitly expressed and what is implicitly considered. Without logic, even colorful advertisements and beautiful models are not effective because there are no clear messages to persuade customers.
Therefore, So this paper needs to seek a strategically organized way to use logical methods of persuasion. To do this, we consider Toulmin’s argument model, as Toulmin’s argument model has been considered to be universally applicable for daily persuasion. We consider two more, those of which are Perelman, who started the era of New Rhetoric, and van Eemeren, Grootendorst, Johnson, Plantin, and Williard (1996) , who also suggested other universally applicable reasoning models. Although other rhetoricians can potentially contribute to expand the boundaries of rhetoric ( Park, 2012 ), our paper deals with these three rhetoricians. In this paper, we will see how rhetoric has been expanding the boundaries of the very fields of business communication.
This paper finds rhetorical reasoning theories in business communication research first from RISS (Research Information Sharing Service, www.riss.kr), the Korean government supported academic information service. There are many articles and dissertations for ‘business communication’ or ‘rhetorical reasoning,’ but a few articles and dissertations are for ‘business communication’ and ‘rhetorical reasoning.’ So we expanded boundaries to Google Scholar and found a few more articles for ‘business communication’ and ‘rhetorical reasoning’.
The combinations of search words were as follows. In RISS, ‘Toulmin,’ ‘Perelman,’ ‘Eemeren,’ ‘Rhetoric, business,’ and ‘Business, communication, and reasoning,’ etc. were used in Korean. In RISS Foreign DB Searching Service, ‘Toulmin, business,’ ‘Perelman, business, and communication,’ ‘Business, communication, rhetoric, reasoning,’ and ‘Eemeren, business,’ etc. were used. In Google Scholar, there were ‘Toulmin, business,’ ‘Perelman, business, and communication,’ and ‘Business, communication, rhetoric, and reasoning,’ etc. were used. In RISS, we found 53 dissertations and 92 journal articles. In RISS Foreign DB Searching Service, we found 341 journal articles. In Google Scholar, we searched from the first to eleventh page of results of Google Scholar about each combination of search words mentioned above. To narrow down the boundaries, only articles mentioning both keywords are excluded.
This paper selected 12 articles satisfying the following conditions ( Table 1 ): First, the papers provide ample explanations of certain rhetorical reasoning models or at least a certain amount of introduction to rhetorical reasoning. Second, the papers use the rhetorical reasoning models as a key tool for researching their domains. This paper emphasizes the importance of logical reasoning in business communication, so it is excludes other elements of persuasion such as ethos and pathos as well as cases in non-business communication fields with rhetorical reasoning models. Based on the twelve articles, the review consists of three parts: domain, method, and results. In domain, we will see what cases, stakeholders, and issues get attention from the researchers. In method, we will analyze what models and theories of rhetoricians are used in the frame of research. In results, we observe what results come out, what limitations are remaining, and what directions for future researches are suggested.
Corporations need business communication when dealing with their main stakeholders (e.g., consumers, inner members, investors, societies, government). To consumers, corporations need to sell their products and gain a higher level of trust and loyalty from consumers ( Choi, 2013 ; Jaganathan, Mayr, & Nagaratnam, 2014 ; Kang, 2014 ; Kim & Benbasat, 2006 ; Kisicek, 2018 ). For example, they need to persuade inner members of the necessity of structural reform of the organization such as downsizing and relieve the dissatisfaction of members for smoother structural reform ( Hossfeld, 2018 ). Corporations also need to get support from investors in two different scenarios; 1) When corporations need to keep and sustain their business, as they need to show how their business is healthy, they need to maintain their trust and loyalty ( Al-Hindawi & Naji, 2018 ), and 2) When corporations need to start their new a project or business, they need to show how their plan is plausible and possible and how they can guarantee profits for investors ( Spinuzzi et al., 2014 ; van Werven, Bouwmeester, & Cornelissen, 2019 ). Society and governments can implement and abolish laws and policies that can decide the rise and fall of a specific market ( Schmidt, 1986 ). Corporations can support pro-corporation governmental officials, social groups, and opinion leaders to influence laws and policies for them.
Choi (2013) , Jaganathan et al. (2014) , Kang (2014) , Kim and Benbasat (2006 , 2009 ) and Kisicek (2018) focus on consumers. They use printed and textual advertisements because it is easy to find logical relationships among the parts of advertisements. The goods are varied from cars to hairsprays. When advertising their products, advertisers need to consider the differences among the diverse backgrounds of customers. Jaganathan et al. (2014) investigate the differences of emphasis to English and German customers even though corporations run the same automobile advertisements. The focus of Kim and Benbasat (2006) differs from that of others. Their study focuses on Internet stores, which need to seek safety and security in the transaction process. Unlike offline stores, customers cannot see the appearance of goods and the flow of money. Online stores thus need to show policies that will guarantee safe transactions and gain the trust of customers. As the trust of customers in Internet stores is relatively low, these stores need to communicate in a logical and clear manner about how their policies can provide safe and secure transactions. Kim and Benbasat (2009) also focus on the trust from consumers in online stores. But the factors differ from those of the previous paper. This paper picks up high and low prices of products as the factor and stores themselves and the third parties as the interesting groups. Based on this, the paper tries to compare the persuasive power between claim-only arguments and claims with supporting arguments. Hossfeld (2018) focuses on organizational communication. Manuals and rules cannot cover every situation in a certain organization. As uncertainties exist, people communicate and persuade each other to seek the best way to solve the problems. When changes such as downsizing, which aims to reduce their budget by eliminating employees, the uncertainties become bigger. Germany, unlike the United States, pursues more stability in the job market than flexibility, and the efforts of persuading members to accept downsizing should be more serious (p. 13).
Al-Hindawi and Naji (2018) focus on investors, especially in the case of banks. Annual reports are not only for investors, but also for analysts, workers, shareholders, and other parties (p. 212). By publishing annual reports, the bank shows the stability and potential of the firm in order to gain trust and supports. Management earning forecasts also play a similar role to that of annual reports. Hursti (2011) selects the German engineering group Siemens and the Swiss-Swedish engineering group ABB to show what kinds of forecasts from corporations can and cannot gain trust from investors.
Spinuzzi et al. (2014) and van Werven et al. (2019) focus on investors of start-up companies. Spinuzzi et al. (2014) use the case of Gyeonggi-UT Innovation Program in Korea, the training and competing program for business people to build up their pitch. Their study explores how the preparation of teams has been better following the progress of the program. van Werven et al. (2019) also examine a similar context, the educational environment for start-up businesses, but they use the case of Amsterdam-based business incubator. Schmidt (1986) deals with society and government using the case of in vitro fertilization (IVF). Although this paper basically deals with the issues of religion, philosophy, and ethics, allowing or banning IVF has a massive impact on related medical industries. As churches were against IVF, they campaigned to ban IVF. But from the point of view of medical industries, they wanted to pass the policy. These examples show that business communication is not limited only to the business sector. Business communication also needs to consider government regulations and the social atmosphere.
This paper aims to review how theories have been applied in the field of business communication. As the aim of this paper is not to review what the rhetorical reasoning models are, the basic explanation of reasoning models mentioned in the body was omitted.
Perelman’s reasoning schemes are used in Choi (2013) . Choi (2013) uses the ‘quasi-logical reasoning,’ ‘reasoning based on already associated,’ ‘reasoning making new association,’ and the ‘technique of dissociation’ ( Park, 2012 ) suggested by Perelman (1982) and analyzes the reasoning structures of advertisements. Choi (2013) suggests that the ‘quasi-logical reasoning’ represents enthymeme. Unlike pure logic, this is more flexible in terms of logical structure; some premises can be omitted for the sake of customer persuasion. As reasoning in advertisements demands probabilistic reasoning rather than absolute correctness, some level of overemphasis can be allowed.
The argumentation model of Toulmin is used in Al-Hindawi and Naji (2018) , Jaganathan et al. (2014) , Hossfeld (2018) , Kang (2014) , Kim and Benbasat (2006 , 2009 ), Kišiček (2018) , Schmidt (1986) , and Spinuzzi et al. (2014) . Most of them use only claim, data, and warrant and sometimes add backing. It is interesting to see that none of them used all the six elements (Claim, Data, Warrant, Backing, Rebuttal, and Qualifier) of Toulmin’s argument model in an explicit manner. The reasons can be explained as follows.
First, it seems that the researchers were unknowingly influenced by the enthymeme of Aristotle, as their background is theoretical. Toulmin’s argument model can actually cover reasoning schemes suggested by Aristotle, that is, both inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning ( Kang, 2014 ). Second, the researchers wanted to focus on the explicit parts of reasoning. Backing, Rebuttal, and Qualifiers are neither explicit nor basic parts of Toulmin’s argument model from their point of view. Only Jaganathan et al. (2014) mention that backing, rebuttal, and qualifiers are not the ones for the demonstrator, the company in business communication. Rather, as these elements are basically for their opponents and from the advertising industry, according to them, it is unethical to use these strategies (p. 154). But even in an exceptional case such as Hursti (2011) trying to use all the elements of Toulmin, it is quite difficult to reflect on these equally as in the case of unwarranted claims by Siemens (p. 401).
Kišiček (2018) is the perfect example for using only the three basic elements as mentioned above. The starting point of the paper is not reasoning. Instead, the paper introduces simulataneously the basic elements of persuasion such as ethos, pathos, and logos and also incorporates Toulmin’s model explaining logos in persuasion. Toulmin’s argument model is used to analyze the logical structure of an automobile advertisement (p. 347).
Schmidt (1986) uses claim, data, warrant, backing and omits rebuttals and qualifiers because of the simplicity of the analysis. In the paper, claim and data are explicit, and warrant and backing are implicit. Although warrant and backing are also sometimes explicit, it still depends on the domain and the requirement of certainty. Using the four of the six elements of Toulmin’s model, the paper tries to find that both philosophy and theology meaningfully contribute to business ethics.
Kim and Benbasat (2006) also use the same four elements of Toulmin. Their paper sees backing as an element that supports both data and claim while Toulmin originally explains that backing supports warrant and gives grounds on why we can accept warrant as legitimate. As we see in their paper, Toulmin’s model can be modified depending on the characteristics of the research object. It shows the flexibility and possibility of expanding the application of Toulmin’s Model.
Kim and Benbasat (2009) does not use warrant compared to their previous research, but it make two pairs of comparison in two contrasting situations. The first comparison is between the third party and the store. The second comparison is between claim, data, and backing and claim-only. Combining the previous 4 elements to form 4 pairs, the paper applies the pairs in situations of high and low price product.
Spinuzzi et al. (2014) uses not only claim and data, but also rebuttal and qualifiers to explain the logical elements of pitching decks. It explains rebuttal as a tool for mitigation from possible comments of judges and qualifiers as a tool for making limitations how much boundaries their arguments can apply (p. 16). Using rebuttals and qualifiers are important because arguments made by the recognition of possible rebuttals and own limitations have a higher plausibility than arguments without any consideration of these elements. Omitting ‘warrant’ and ‘backing’ makes additional limitations of the research although the authors do not mention this as its own limitation.
In terms of using Toulmin’s Argument Model holistically, Hursti (2011) cannot be excluded. Starting by introducing all 6 elements of Toulmin’s Model, the paper compares two randomly selected management earnings forecasts from the groups mentioned in the ‘II. Domain’ section for analyzing their plausibility (p. 399). Although some of six elements such as warrant and backing are not clearly shown in the results section, the paper tried to make the link between all the elements of Toulmin’s Model in the interpretation of the results.
van Werven et al. (2019) mentions Perelman, Toulmin, and van Eemeren at the same time and analyzes the structure of argumentation at the micro level. When their paper mentions Toulmin, it emphasizes ‘arguments’ and ‘grounds.’ The paper tries to figure out which kinds of arguments were made by new ventures and what kinds of data supported their arguments. In its mention of van Eemeren, it shows the two kinds of argumentation: explicit and implicit. It tries to use these criteria to compare pre-launch entrepreneurs and post-launch entrepreneurs.
According to Hossfeld (2018) , the best situation is one in which only arguments and assertions are explicitly expressed and which persuade effectively. But in most of our daily lives, there are many situations in which stakeholders do not agree on certain arguments but rather demand further support to judge the arguments. In this situation, arguments should be supported by plausible warrants and solid data. Kim and Benbasat (2006) show that claims with supporting materials can gain higher trust from customers. To prove this, Kim and Benbasat (2006) also consider the possible use of ‘rebuttal’ and explain this successfully through further analysis.
As many uncertainties and problems exist in business communication, persuaders need to prepare possible rebuttals and know whether or not their plan will work. The general tendency is maintained in the experiment of Kim and Benbasat (2009) without exception. According to Kim and Benbasat (2009 , p. 200), claim-only arguments from the 3rd party have higher credibility from the perspective of consumers than claims with supporting materials from the store in the case of low-price products. Even in the previous situation, claims with supporting materials of each party still have higher credibility than their claim-only materials, but we also need to consider the non-content factor when we apply reasoning models in business communication.
Most of research we review are the qualitative analysis of texts, contents, and cases. A few of them go further to analyze the relationship between the type of contents and responses of consumers by experiments ( Kim & Benbasat, 2006 , 2009 ). Hossfeld (2018) analyzes media and workers who oppose downsizing and how they hinder corporate efforts to justify downsizing.
Pitchers modify their decks based on the possible rebuttal from the market. But the way they do so is basically based on experience rather than a systematic approach ( Spinuzzi et al., 2014 ). The authors claim that education based on a systematic approach is necessary. Pitchers who confront journalists, investors, judges, the public, and senior entrepreneurs try to argue that there is a well-prepared team and that customers and environments that are hospitable for the team and its performance can bring be beneficial, so investors must invest in the venture ( van Werven et al., 2019 ). To support these kinds of claims, explicit arguments and data are not always better than their implicit counterparts ( van Werven et al., 2019 ). Although it looks more like back-up and clarity make arguments more plausible, more materials often make room for audiences to find their weaknesses. The rhetorical reasoning model does not only find a way of persuasion. It can be the bridge for business people to reach business ethics originating from philosophy and theology ( Schmidt, 1986 ). Formal logic, which was developed by moral philosophers in the isolation of the ivory tower has made the wall between theory and practice ( Schmidt, 1986 ).
It was found that rhetorical reasoning has already been in use in business communication. Most papers deal with Toulmin’s, but we also found the research addressing Perelman’s and van Eemeren’s. Corporations make various efforts to persuade various stakeholders such as customers, investors, journalists, and workers. One limitation of our research stems from the result of reviewing only 12 articles. If we had access to more research, we could have acknowledged that rhetorical reasoning is not limited to Aristotle and academia but has a strong impact on the larger field of business communication regardless of time and space.
There are a few suggestions for future research. First, this review just found the influence of Toulmin, Perelman, and van Eemeren. As there are numerous other rhetoricians and rhetorical reasoning theories yet untouched, future researches needs to use them to test the explanatory power of these theories in the field of business communication. Second, although this paper found diverse stakeholders already influenced by rhetorical reasoning, future researchers will be able to divide each stakeholder group to sub-groups and find untouched stakeholders to expand the boundaries of rhetorical reasoning application. Third, text, case, and content analysis are the traditional research methods for the application of rhetorical reasoning models and theories. But the usage of various research methods such as the experiments done by Kim and Benbasat (2006 , 2009 ) will open new possibilities of rhetorical reasoning applied to business communication research.
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
178 Communication Research Topics For Your Paper

Imagine what the world would be without communication! How would we get along? I guess there would be no sense in existing after all. That is just a tiny snippet of how important communication is in everyday life. Exchanging information is a key component of coexistence as it creates order and a sense of satisfaction in the end.
However, communication as a discipline cuts across all other niches in the academic world. Students from an Engineering course would also take up communication as a unit of study. Students delve into the transmission, representation, reception, and decoding of information communicated to a greater extent.
Situations When You May Need To Write A Communication Paper
Various scenarios call for a communication paper either as an assignment or a research project in college. The communication papers needed for every situation vary in format and outline. Here are some of the cases when communication papers are necessary:
When writing a resume or cover letter In presentations and reports Internal or external communication in a company Writing a thesis statement
When writing communication papers in these different scenarios, students can develop the following aspects:
Understand the various communication phenomena Ability to direct communication messages towards accomplishing individual and organizational goals Understand various types of communication such as rhetoric, interpersonal or organizational
Such an assignment is peculiar because it deals with students’ communication processes. Therefore, the student can easily relate a communication assignment to the real-world environment.
You will have to conduct extensive digging before writing your paper like any other research project. In writing a communication research paper, you will benefit from the importance of communication in general, such as building better relationships and finding the right solutions to various problems.
It takes a lot of time to create a high-quality writing, so you have all the right to ask dissertation writers for hire to help.
Guidelines On Structure And Step By Step Tips On Writing
To have an award-winning communication paper, you need to understand that structure is always at the heart of it all. A great communication paper follows the structure below:
Solid intro : Begin by presenting a captivating introduction by highlighting the facts, questions, or problems that you will explore in the body. The reader should find more than a million reasons to proceed with your essay by reading the first two lines. A strong thesis statement is also necessary for the introduction. An insightful literature review : It shows the theoretical basis of your research project, thus giving it validity. An in-depth literature review will give room for exploration and further research. Main body : This is where we expect to find all your findings, methodological steps, concepts, analyses, and the outcome. Discussion and conclusion : Depending on your professor’s instructions, you can divide this into two parts or put it as one. In either case, this section will consist of the strengths and weaknesses of your research and any future development or improvements. You could also compare the results found in your research with what other authors have discovered.
Provided you have all your facts at hand, a communication research paper will be the easiest you will ever handle in college. Nonetheless, you can order a custom paper from various online writing experts.
If you want to make an impression with your communication research paper, here are some tips to consider:
Select a thought-provoking and captivating research topic Have a working outline with all the arguments and examples/evidence in place Ensure that you exhaust reading all the possible research materials on your topic Such papers are always in the first person except in unique cases
You can review some of the samples on our essay writer to familiarize yourself with the structure and outline of a communication research paper.
Let’s now explore 178 of the hottest communication research topics to ace your project:
Top Interpersonal Communication Research Topics
- Evaluate the different relational patterns of interaction theory
- How to achieve coordinated management of meaning
- Discuss the fundamentals of pedagogical communication
- How does technology relate to interpersonal communication?
- Key constructs of openness and closeness
- Establishing identities in the identity management theory
- Evaluate the contribution of interpersonal communication scholars
- How mental representations influence how people interpret information
- Conceptualizing the process of social interaction
- Discuss the various behavioral interaction patterns among siblings
- Why do individuals modify their communicative behavior?
- Describe why new environments present a challenge for most people to communicate effectively
- The role of eye contact and gestures in interpersonal communication
- Varying effects of nonverbal and verbal acts of interpersonal communication
- Effects of different cultures on interpersonal communication strategies
World-Class Communication Research Topics For College Students
- Understanding the historical research methods in communication
- Discuss the relationship between technology, media, and culture
- Evaluate the various revolutions in human communication
- Discuss the developments made in the invention of human speech and language
- The role of image-making, cinema, and media entertainment in communication
- How to overcome communication barriers among students
- Steps in encouraging participation in meetings
- How employees contribute to the information flow in organizations
- How to evaluate a report based on its findings
- Sources of error during nonverbal communication
- How the media can match the channels of communication to their audience
- Ensuring audience attention during a presentation
- The impact of graphics in communication strategies
- How to interpret non-verbal signals
- Developing communication methods that match a given purpose
Possible Topics For Communication Research
- How to develop realistic communication strategies
- Discuss the economics of finance in communication processes
- How exposure to radio and TV impacts communication
- How to manage controversial issues in communication
- Why speaking with confidence is still difficult for many people
- The effectiveness of communicating with words and body language
- Why defining your purpose is key in any communication process
- Why explanatory communication is more difficult than informative communication
- The place of communication in long-distance relationships
- Communication strategies that influence people
- How to use communication effectively for conflict resolution
- Developing your self-esteem for effective communication
- Effects of redundancy in communication processes
- The place of responsibility in developing communication messages
- How to acquire effective communication skills in college
Latest Communication Topic For Research
- The role of persuasive dialogue in negotiations
- Why everyone must learn proper expression strategies
- Effects of emoji and other characters in enhancing textual conversations
- The role of propaganda in shaping communication tones
- Evaluate the unique political language used in America versus Africa
- The continuing impact of the internet on interpersonal communication
- How images are enhancing communication
- Discuss the effects of gender victimization on communication
- Evaluate the development of modern digital communication
- How to effectively communicate during a war or crisis
- How hacking is transforming communication of encrypted messages
- Effects of stereotyping in developing communication messages
- Is virtual reality ruining effective communication?
- Evaluate language as a barrier in communicating messages
- The role of empathy in communicating to victims of a disaster
Top-Notch Communication Research Paper Topics
- The role of diplomacy in fostering better relations among countries
- Why aided communication may not achieve the intended purpose
- Effects of using a translator in the communication of critical messages
- Evaluate the development of audio-visual devices for communication
- The dangers of failing to notice barriers to communication
- How stigma and prejudice impact effective communication
- Discuss the impact of having a common language in a country
- How social classes affect communication messages
- Factors that hinder communication between fighting political sides
- How to develop strong communication skills in a marketplace
- Why opinions may prevent one from seeing the true picture
- Discuss the role of fantasy and exaggeration in communication
- Differences between oral and verbal messages in conveying information
- The role of attitude and mood in enhancing effective message delivery
- How the media sets the communication pattern of a given society
Highly Rated Mass Communication Research Topics
- Discuss the essence of social media among PR practitioners
- The role of mass media in rebranding a nation
- Challenges to media freedom and their impact on proper communication
- Discuss the effects of news commercialization and their credibility
- How TV advertisements impact children and their development
- Compare and contrast between animation and real-people adverts in mass media
- How the internet affects professionalization in news media
- How mass media messages contribute to the development of religion in Africa
- Evaluate the radio listenership patterns between men and women
- How does mass media contribute to an emerging democracy
- Discuss how the media enlightens the public on issues of concern
- The role of mass media in communicating development messages
- Why mass media is critical before, during, and after elections
- Assess the influence of community radio in remote areas
- How mass media contributes to national integration
Good Communication Research Topics
- What determines consumer preference patterns in the 21 st century?
- Effective communication strategies for creating awareness against drug abuse
- Prospects and challenges of local dialects in communication
- Evaluate the influence of television on public opinion
- Discuss the growing cyberactivism in the digital age
- How social media is contributing to misleading information
- Challenges facing teachers when communicating to pre-school students
- Discuss the impact of information overload on the credibility of information
- Evaluate communication patterns among the youth in the US
- Assess the effects of the Russia-Ukraine conflict on communication patterns
- How public perception influences communication strategies
- Explain how mothers learn to communicate with and understand their babies at such a tender age
- The role of music in shaping communication models
- How to overcome the challenge of top-down communication in companies
- Management of information on online media for effective use
Business Communication Research Paper Topics
- Discuss the increasing role of influencers on brand marketing
- Why company blogs are essential in attracting new clients
- Evaluate the differences between face to face and virtual business meetings
- The growing popularity of social media in business marketing
- Why every company should have a partner relations department
- Dealing with complaints in a relaxed and useful manner
- Why online project management is the future of business
- Discuss why it is necessary to have company retreats
- Explore the role of digital document sharing in speeding up business communication
- Effects of relying on online communication at the expense of physical meetings
- The role of effective business management in the performance of an organization
- How staff motivation improve the overall working environment
- Discuss the place of corporate social responsibility in a company
- Effective ways of handling crisis in a large company
- Explain why trust is important in any business partnerships
Intercultural Communication Research Topics
- Discuss how Muslims interact with Christians at a social level
- Evaluate the reception of instructions from a man to a woman
- How Americans interact with Africans at the basic level
- Discuss how an American Democrat would associate with a Chinese politician
- Discuss the impact of marginalization in developing communication messages
- How migration and immigration affect communication patterns
- Effects of social stereotyping in communication
- How do Western communication models differ from those of Africa?
- Impact of discriminatory communication messages
- How to organize an effective intergroup come-together
- How the media represents various groups in its communication
- Effects of the growing intercultural norms
- The role of language attitudes in inhibiting effective communication
- Evaluate how ethnographic perspectives affect communication messages
- Why it is difficult to solve intercultural conflicts
Additional Interpersonal Communication Topics For Research Paper
- The role of interpersonal communication in team member satisfaction
- How collaboration and teamwork enhances business success
- Discuss how interpersonal communication enhances problem-solving skills
- The role of trust in interpersonal communication
- Effects of confusion, negativity, and conflicts on interpersonal communication
- How to deal with workplace miscommunication effectively
- The role of personalizing information
- How to improve internal communication channels in a company
- Discuss the role of interests in communication patterns
- Challenges when implementing modern communication solutions
- Evaluate how jargon and inattention make internal communication difficult
- The role of feedback in interpreting messages correctly
- Discuss the influence of environmental factors in communication
- Why miscommunication may result in a disconnect among a group of people
- Discuss the role of skills and knowledge in effective communication among leaders
Interesting Communication Research Topics
- How can effective interpersonal communication be a catalyst for action
- Why a focused and intentional approach is necessary for effective communication
- Discuss why online dating is not successful in most cases
- Evaluate the role of non-verbal communication and customer satisfaction
- Why is it important to have a list of communication networks?
- Effects of lack of personal contact when it comes to communication
- Discuss the various forms of human interactions and their influence on communication
- The role of clear communication during an organizational change process
- Why online communication is not as effective as physical meetings
- Evaluate the roles and issues involved in a nurse-patient communication
- The role of TV shows in determining how people relate to each other in the society
- Effects of the digital divide in communication paradigms
- The relationship between quality leadership and effective communication
- Why is email still not yet an effective communication medium?
- Effects of integrating marketing communication
General Communication Studies Research Topics
- Discuss the differences in body language between male and female
- The role of communication in familiarizing with someone
- How online gaming communication affects one’s interpersonal communication
- Why a leader without proper communication skills may not succeed
- The role of communication in achieving an organization’s vision
- How mobile phone conversations are turning around interpersonal communication
- Discuss the role of different personality types in communication
- Is there a difference between language and communication?
- Discuss how communication in the military is different from that in a normal setting
- Compare and contrast between written and spoken forms of communication
- Why family communication is critical for a peaceful coexistence
- Shortcomings to understanding foreign languages
- Discuss the effectiveness of web-based communication
Professional Help On Research Paper Writing
If you are still unsure which writing idea to use for your project, your expert paper writing help might be what you need. Our service has a team of select paper writers who can crush any task in a snap. You can pay for dissertation today or request a writer to help you with your incomplete task.
Let us help you brainstorm great ideas that will turn your project into a world-class paper!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
International Journal of Business Communication (IJBC), peer-reviewed and published quarterly, provides rigorous original research that contributes to the knowledge and theory of business communication as a distinct, multifaceted field, approached through the administrative disciplines, the liberal arts, and the social sciences.IJBC is the official publication of the Association for Business ...
by Michael Blanding. People who seem like they're paying attention often aren't—even when they're smiling and nodding toward the speaker. Research by Alison Wood Brooks, Hanne Collins, and colleagues reveals just how prone the mind is to wandering, and sheds light on ways to stay tuned in to the conversation. 31 Oct 2023. HBS Case.
Abstract. This article introduces the special issue on crisis communication, whose aim is to bring together diverse approaches and methods of analysis in the field. The article overviews the field by discussing two main frameworks, dealing with postcrisis (reputation management) and precrisis (issue management) communication, respectively.
The importance of communication in business management. Paper presented at the 7th International Scientific Conference on Employment, Education and Entrepreneurship, At Belgrade, Serbia.. ... 513-1 Orbis Hall, Business Communication Center, Management Research Institute, 26 Kyungheedaero, Dongdaemoon-gu, Seoul 02447, Korea
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on BUSINESS COMMUNICATION. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review ...
The centrality of communication in international business (IB) is undeniable; yet our understanding of the phenomenon is partially constrained by a cross-cultural comparative focus as opposed to intercultural, process-oriented research designs that capture the dynamic nature of communicative interactions. Our brief review of studies at the ...
HTML PDF PubReader. Business Communication Research and Practice (BCRP) is the official journal of the Korean Association for Business Communication (KABC) and is published in English. The journal publishes original research articles, reviews, case reports, tutorials, communications, editorials, and book reviews that contribute to the knowledge ...
Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Jim Suchan, Naval Postgraduate School, Graduate School of Business and Public Policy, Monterey, CA 93943; e-mail: [email protected]. Journal of Business Communication, Volume 43, Number 4, October 2006 389-397. DOI: 10.1177/0021943606291714.
Three Streams in Business Communication Research and Theory. Culture, language, and international business are the three constructs chosen to be the focal point of this discussion because of their important role in shaping Asian business communication research and practice. Culture is an important concept and is most researched when ...
business communication (Haase, 2012). Moreover, Forman (1993) espoused factors that may. profitably influence research in business communication: 1) the historical and theoretical study of ...
Social media plays an important part in the digital transformation of businesses. This research provides a comprehensive analysis of the use of social media by business-to-business (B2B) companies. The current study focuses on the number of aspects of social media such as the effect of social media, social media tools, social media use, adoption of social media use and its barriers, social ...
2. ABSTRACT. Communication, as a management function is the process of creating, communicating and interpreting ideas, facts, opinions and feelings abou t work. performance, organisational ...
The status of the business communication course at U.S. colleges and universities. Business Communication Quarterly, 72(4), 395-413. doi: 10.1177/ 1080569909349524. Shao, G. (2009). Understanding the appeal of user-generated media: A uses and gratification perspective. Internet Research, 19(1), 7-25. doi: 10.1108/10662240910927795. SheSpeaks.
Business and Professional Communication Quarterly (BPCQ) is the only refereed journal devoted to research that advances the teaching of communication in the workplace.BPCQ publishes scholarship that advances knowledge about business and professional communication pedagogy and praxis in both academic and workplace settings. Articles in BPCQ present a variety of theoretical, applied, and ...
Business fields in this paper include advertising, bank annual reports, downsizing reports, and policy decision making processes. Rhetorical reasoning is a widely used method in business communication. Several suggestions for future researches are: First, more rhetorical theories and models are needed to be used to business communication research.
This paper then is an attempt toward analyzing the significance and role of intercultural communication and etiquette in international business. Recommendations for appropriate practices and ...
Advertising research topics. Communicating with the public through advertising. Creating effective messaging through advertising. Creating a positive corporate image through advertising. Impact of advertising on consumers. Impact of technology on the advertising industry.
Business Communication Research Paper Topics. Discuss the increasing role of influencers on brand marketing; Why company blogs are essential in attracting new clients; Evaluate the differences between face to face and virtual business meetings; The growing popularity of social media in business marketing
This paper discusses the communication process, barriers to communication, and provides guideline for administrators to improve communication effectiveness. Discover the world's research 25 ...
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION 2 Abstract The purpose of this paper is to explain how business communication is significant to organizational businesses. Communication can be defined as the transmission of a message form a sender to a receiver in understandable manner. (Sanchez, 2009). Business communication is essential so organizations can keep a high level of quality and service.
This book is about, how important is Communication in our work life, what are the various forms of communication and how effective communication plays an importantant in career. This book also ...