Two-Step Equations
Two step equations are equations that can be solved within exactly two steps. Two step equations are extremely easy to solve. As the name suggests, two step equations take only two steps to solve. These equations are just a little complicated than the one step equations. While solving a two step equation, we need to perform the operation on both sides of the equals to sign.
In this article, we will understand the meaning of two step equations with integers, decimals, and fractions, how to solve them, the golden rule to solve two step equations along with some examples for a better understanding.

What are Two Step Equations?
Two step equations are algebraic problems that take just two steps to solve. The two step equation is a linear equation in one variable . While performing an operation for solving a two step equation, we need to perform the same operation on both sides of the equation. We isolate the variable on one side of the equation to determine its value.
Two Step Equations Definition
Two step equations are algebraic equations and are the equations that can be solved in exactly two steps and gives the final value of the variable in two steps. Generally, two step equations are of the form ax + b = c, where a, b, c are real numbers. A few examples of two step equations are:
- 0.3y + 5 = 1
- (2/3)z - 12 = 10
Solving Two Step Equations
Two step equations are very easy to solve. It includes just one extra step as compared to one-step equations to solve. We can solve a two-step equation by isolating the variable (usually represented by an alphabet or letter) on one side of the equation and all other values on the other side. The general two steps to solve the two-step equations are:
- Step 1: Addition and subtraction to isolate the variable.
- Step 2: Multiplication or division to determine the value of the variable.
Let us consider a few examples and solve two-step equations to understand the concept of solving two-step equations.
Example 1: Solve the equation 2x + 6 = 12.
To solve the two step equation 2x + 6 = 12, we need to determine the value of x. Let us solve it step-wise.
Step 1: Subtract -6 from both sides of the equation to isolate the variable x.
2x + 6 - 6 = 12 - 6
Step 2: Divide both sides of the equation by 2 to solve for x.
Hence, we have solved the equation 2x + 3 = 12 in just two steps.

Thus the two-step equation can be easily solved in a sequence of steps, as presented above.
Two-Step Equations with Decimals and Fractions
Two step equations that have decimals and fractions as the coefficient of the variable and constant term are said to be two step equations with decimals and fractions. A few examples of two step equations with fractions and decimals are:
- 0.3 x + 2/3 = 1
- 3x - 0.5 = 1.2
- (1/3) x + 4/5 = 3/4
These equations are solved in the same manner as the general two steps equations and the same steps are followed to determine the value of the variable.
Golden Rule to Solve Two Step Equations
The golden rule to solve two step equations is to perform all operations simultaneously on both sides of the equation. To isolate the variable on one side of the equation and to determine its value, we first add or subtract on both sides of the equation and then multiply or divide on both sides to get the final solution of the two step equation.
Important Notes on Two Step Equations
- Remove the parentheses and combine like terms to simplify each side of the two-step equation.
- Always remove the constant first by adding or subtracting the appropriate number.
- Always verify the solution in the end.
Topics Related to Two Step Equations
- Equations in Math
- Simple equations
- Algebraic formulas
Two Step Equations Examples
Example 1: Solve the two step equation (x/6) - 7 = 11
Solution: To solve the given two step equation, we will follow the steps discussed above in the article.
Step 1: Add 7 to both sides of the given two step equation
(x/6) - 7 + 7 = 11 + 7
⇒ (x/6) = 18
Step 2: Multiply both sides of the equation by 6.
6 × x/6 = 6 × 18
Answer: Hence the solution to the given two step equation (x/6) - 7 = 11 is x = 108.
Example 2: Determine the solution of the two step equation (2/3) z + 0.8 = 1.5
Step 1: Subtract 0.8 from both sides of the given two step equation
(2/3) z + 0.8 - 0.8 = 1.5 - 0.8
⇒ (2/3) z = 0.7
Step 2: Multiply both sides of the equation by (3/2).
(3/2) × (2/3) z = (3/2) × 0.7
Answer: Hence the solution to the given two step equation (2/3) z + 0.8 = 1.5 is x = 1.05
go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Two Step Equations
Faqs on two step equations, what are two step equations in algebra.
Two step equations are algebraic equations that take just two steps to solve.First, the variable is isolated by adding or subtracting a numeric value on both sides of the equation. Secondly, the value of the variable is computed by multiplying or dividing the variable by an appropriate number.
What are the Steps to Solve Two Step Equations?
The general two steps to solve two step equations are:
- Step 1: Simplify the given equation by removing all brackets and parenthesis:
- Step 2: Add or subtract to isolate the variable.
- Step 2: Multiply or divide to determine the value of the variable.
- Step: Verify the answer by substituting it in the given equation .
How to Solve Two Step Equations?
Two step equations can be solved by following two quick steps:
- Step 1: Add or subtract numbers on either sides, to isolate the variable.
IS Two Step Equation the Same as A Multi-Step Equation?
Two-step equation can also be called a multi-step equation since it involves more than one step. And a multi-step equation can have two or more steps, in the process of solving the equation.
What is the Difference Between One Step and Two Step Equations?
One step equations take just one step to solve whereas two steps equations take two steps to get to the solution. Two-step equations include just one extra step as compared to one step equations to solve.
What is the Goal of Solving Two Step Equations?
The goal of solving two step equations is to isolate the variable and determine the value of the variable. And in the end, the variable should satisfy the given two step equation.

Solving Two-Step Equations: Explanations, Review, and Examples
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: February 16, 2023

So, we’ve made it past one-step equations! Woo-hoo!
Our reward? Solving two-step equations !
Don’t worry: whether this is your first experience with two-step equations, or you are reviewing for an exam, this blog will guide you through defining two-step equations, examples of two-step equations, and how to solve two-step equations (including fractions and word problems). Let’s get started!
What We Review
What is a two-step equation?
Remember, an equation is a mathematical sentence that uses an equal sign, = , to show that two expressions are equal.
Very similar to one-step equations , a two-step equation is an equation that only requires two steps to solve. We will use a mix of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to solve these equations.
Examples of two-step equations
Two-step equations come in many types. You might have some equations that require subtraction, then division to solve, or an equation that requires multiplication, then division to solve.
Here are some examples of two-step equations:
Return to the Table of Contents
How to solve two-step equations
Remember: To solve equations, we must use inverse operations to isolate the variable. Examples of inverse operations are:
We must first eliminate any constants from the side of the equation with the variable. Additionally, whatever we do to one side of the equation, we must also do to the other. Here are two examples of how to solve two-step equations:
First, let’s solve for x in the following equation:
To check your answer, you can substitute 4 into the variable to see if the equation is true:
Thus, x = 4 is the correct solution.
Now, we can trying solving for y in the following equation:
To check you answer, you can simplify substitute 7 into the variable to see if the equation is true:
Thus, y = 7 is the correct solution.
For more, watch the video from mathantics below showing how the solve 2-step equations:

How to solve two-step equations with fractions
Unfortunately, equations do not always contain only whole numbers. Never fear! We can still solve two-step equations even when fractions are involved.
Here is an example of solving a two-step equation with a fraction:
Solve for m in the following equation:
To check you answer, you can simplify substitute 9 into the variable to see if the equation is true:
Thus, m = 9 is the correct solution.
Is there a way to make solving two-step equations with fractions easier? I’m glad you asked! If you want to eliminate fractions completely when solving a two-step equation, you can simply multiply the whole equation by the Least Common Denominator . Here is an example showing this method:
Solve for x in the following equation:
Since the denominators are 2, 3, \text{and } 6 , the least common denominator would be 6 . Therefore, to eliminate all fractions from the problem, we would multiply each term by 6 .
To check you answer, you can simplify substitute 1 into the variable to see if the equation is true:
Here’s a video from Brian McLogan on how to solve two-step equations with fractions:
Two-step equation word problems
Similar to One-Step Equations , we can model real-life scenarios with two-step equations. Once we model the situation with an equation, we simply solve as we have above.
For instance, model the following situations with an equation and find a solution that makes the situation true.
To solve for c , we will first subtract 10 from each side:
Then to find the cost of one ticket, we will divide each side by 3
To solve for t , we must first multiply each side by 4 to eliminate the denominator
Solving Two-Step Equations: Keys to Remember

Remember, just like solving One-Step Equations there are some key facts to remember:
- A two-step equation is an equation that requires two steps to solve
- We must eliminate any constant that is on the same side as the variable first
- To solve, use the inverse operations to isolate the variable by itself
- Remember whatever you do to one side, you must do to the other
- To check the solution, simply substitute the value into the variable to see if the equation is true
- You can model real-life situations with an equation and solve for a correct solution
Read these other helpful posts:
- Solving One-Step Equations
- Solving Multi-Step Equations
- Forms of Linear Equations
- View ALL Algebra 1 Review Guides
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score

Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
Interested in a school license?

Bring Albert to your school and empower all teachers with the world's best question bank for: ➜ SAT® & ACT® ➜ AP® ➜ ELA, Math, Science, & Social Studies aligned to state standards ➜ State assessments Options for teachers, schools, and districts.
Free Printable Solving 2 Step Equations Worksheets
Solving two-step equations is one of the most important skills that you need to master in studies of algebra. This is truly a skill that comes up over and over again throughout studies of mathematics. And that’s why I’ve put together this collection of solving 2 step equations worksheets for you!
These free printable worksheets will help you practice solving for the value of the unknown variables in linear equations. Practicing multi-step equations is important to help you develop foundational skills that will be built upon in further studies of mathematics.
Throughout my career as a math teacher I have seen many students struggle with much more advanced equation solving as a result of missing foundations. Completing additional practice by using practice worksheets like those found below will help you avoid encountering further struggles down the road!
Let’s dig into this two step equations worksheet collection!
How to Solve Two-Step Equations
Two-step equations contain a combination of algebraic expressions that form math sentences. These types of equations require you to perform two steps in order to determine the value of the unknown variables.
If this is your first time solving a 2-step equation, don’t worry! Two-step equations are solved using a similar process to solving one-step equations. However, there is the obvious addition of an extra step.
A 2-step equation problem will require you to apply two operations in order to determine the value of the variable that is unknown. You will be given two sides of the equation, an unknown variable, and a series of operations.
The first step is to identify the side of the equation that has the unknown variable on it. In simple terms, this will be whichever side has the “letter” on it. Your main goal will be to isolate this unknown variable.
The second step is to “undo” whatever the operations are that are keeping the variable from being isolated. To do this, we apply inverse operations. This is just a fancy way of saying “do the opposite of whichever operations are there”. Typically this involves completing order of operations in reverse.
After you have performed each step, you will be able to identify the value of the variable!
Solving Two-Step Equations Example
In order to help you get ready for the math worksheets linked below, I wanted to share an example of a two-step equation. Consider the following 2-step equation:
As you can see, this equation has an unknown variable on the left hand side of the equation that is multiplied by 3 before being subtracted by 4. Because of this, unlike one-step equations, this equation cannot be solved in a single step.
To begin, we apply an inverse operation to “undo” the subtraction by 4. This inverse operation is addition by 4. We do this on both sides of the equation to ensure that we do not unbalance the equation:
$$3p-4+4=8+4$$
We now have a single step equation! Since the variable is multiplied by 3, the inverse operation will be to divide both sides by 3. This results in:
$$\frac{3p}{3}=\frac{12}{3}$$
We have now successfully solved this 2-step equation for the value of the unknown variable!
Remember that you can always check your answer by taking the value of the variable and placing it back into the original equation. If the left hand side of the equation is equal to the right hand side, you have solved the equation correctly!
For example, replacing p with \(p = 4\) results in:
$$3(4)-4=8$$
So we can confirm that the equation was solved correctly! Checking your answer is a fun activity that can give you a boost of confidence if this is your first time solving a 2-step equation!
Solving 2 Step Equations Worksheets
Now that you have completed some additional practice using the example above, it’s time to dig into these solving 2 step equations worksheets! I have included a wide variety of problem types across three worksheets to help you develop a deep understanding of the equation solving process.
Solving Two-Step Equations: Positive and Negative Integers
The two step equations worksheet linked below is an excellent resource if this is your first time solving algebraic equations. Positive and negative integers are familiar to most mathematics students, so it makes sense to try solving these linear equations first!
After solving each equation, be sure to check the answer key to verify that you fully understand the process for solving two-step equations involving positive integers and negative integers.
After you have had some time to practice with equations involving integers, move forward with decimals and fractions to deepen your understanding!
Download the PDF worksheet by clicking below!
Solving 2-Step Equations Involving Decimals
After you have spent some time familiarizing yourself with 2-step equations involving negative and positive integers, take a look at the following practice worksheets. Next up is a PDF worksheet that focuses on solving equations involving decimals.
You will see that the equations found in this PDF worksheet include decimal coefficients. The process that you use to solve these 2-step equations is exactly the same as the steps you completed previously.
I have included a wide variety of types of decimal answers throughout these problems. You will see examples of terminating decimals as well as non-terminating decimals !
Be sure to review the answer key after you complete each problem and take note of each type of decimal number!
Solving Two Step Equations Involving Fractions
The last of the practice worksheets that I have included focuses on solving equations involving fractions. These types of equations are the most challenging of this set. Fractions are something that many students find intimidating. However, the process to solve a two-step equation that contains fractions is the same!
After you complete this worksheet, check the answer key to make sure you fully understand how to solve 2-step equations involving fractions!
Using These Solving 2 Step Equations Worksheets
Equation solving is one of the most important skills that you can develop as a student who is studying mathematics. Whether you are learning to use algebra to solve real-world word problems or a tricky test question, understanding how to solve 2-step equations is your first step toward developing a strong foundation of basic algebra skills.
And it is important to remember that you will need strong algebra skills as you move forward to start solving much more complex problems such as quadratic equations, linear inequalities , and exponential equations .
I hope you found these practice worksheets to be useful additional practice problems as you work to deepen your understanding of two-step equation solving!
If you are looking to apply your understanding of linear equations to word problems, check out this linear equations word problems worksheet !
Did you find this breakdown of two-step equations helpful? Share this post with a friend and subscribe to Math By The Pixel on YouTube for more helpful mathematics content!
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Linear Equations Word Problems Worksheet with Solutions
Free Linear Inequalities Word Problems Worksheet

Two-Step Word Problems (Grade 3)
Suggested learning target.
- I can choose the correct operation to perform the first computation, and choose the correct operation to perform the second computation in order to solve two-step word problems.
- I can write equations using a letter for the unknown number.
- I can decide if my answers are reasonable using mental math and estimation strategies including rounding.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- Two-step equations – word problems
Simply put, two-step equations – word problems are two step equations expressed using words instead of just numbers and mathematical symbols. They are just a bit more complicated than one-step equations with word problems and they demand just a bit more effort to solve. If you are not confident in your abilities to solve two-step equations with word problems, you can go to one-step equations – word problems and practice some more before continuing with this lesson. But if you feel ready, we will show you how to solve it using this example:
Hermione’s Bikes rents bikes for $10 plus $4per hour. Janice paid $30 to rent a bike. For how many hours did she rent the bike?
First thing we have to do in this assignment is to find the variable and see what its connection is with the other values. The thing we do not know is the number of hours Janice rented the bike for and we have been asked to find that out. That means the number of hours is our variable.
The cost of renting a bike is 10$ to take the bike and 4$ for every hour it spends in our possession. The final sum Janice paid is $30. Let us write that down as an equation.
4 * x + 10 = 30
Now, in order to make things neater and more clear, let us move all the numbers (except for the number 4 – we have to get rid of it in a different way) to the right side of the equation. Like this:
4 * x = 30 – 10
To simplify things further, let us perform the subtraction.
The next thing to do is to get rid of the number 4 in front of the variable. We will do that by dividing the whole equation by 4.
4 * x = 20 |:4
Now that we have calculated the value of the variable, we can tell that Janice rented that bike for 5 hours. If you want to check the result – you can. If you multiply $4 that Janice paid per hour by the 5 hours she spend with that bike and then add the $10 she had to pay regardless of the time she spent with the bike, you will get a total sum of $30 that is indeed the full sum she paid.

These word problems are called two-step because you have to perform two mathematical operations in order to solve them. In this case – addition (subtraction) and multiplication (division). To practice solving two-step equations – word problems, feel free to use the worksheets below.
Two-step equations – word problems exams for teachers
Two-step equations – word problems worksheets for students.
Basic Mathematical Operations
- Addition and subtraction
- Multiplying
- Divisibility and factors
- Order of operations
- Greatest common factor
- Least common multiple
- Squares and square roots
- Naming decimal places
- Write numbers with words
- Verbal expressions in algebra
- Rounding numbers
- Convert percents, decimals and fractions
- Simplifying numerical fractions
- Proportions and similarity
- Calculating percents
- The Pythagorean theorem
- Quadrilaterals
- Solid figures
- One-step equations
- One-step equations – word problems
- Two-step equations
- Multi-step equations
- Multiplying polynomials
- Inequalities
- One-step inequalities
- Two-step inequalities
- Multi-step inequalities
- Coordinates
- Graphing linear equations
- The distance formula
Linear Equations
- Writing a linear equation
- Systems of linear equations
- Linear systems – word problems
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- x^{2}-x-6=0
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- line\:(1,\:2),\:(3,\:1)
- prove\:\tan^2(x)-\sin^2(x)=\tan^2(x)\sin^2(x)
- \frac{d}{dx}(\frac{3x+9}{2-x})
- (\sin^2(\theta))'
- \lim _{x\to 0}(x\ln (x))
- \int e^x\cos (x)dx
- \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx
- \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n}
- Is there a step by step calculator for math?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. It shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations for each problem.
- Is there a step by step calculator for physics?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of physics problems, including mechanics, electricity and magnetism, and thermodynamics. It shows you the steps and explanations for each problem, so you can learn as you go.
- How to solve math problems step-by-step?
- To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
- Practice, practice, practice Math can be an intimidating subject. Each new topic we learn has symbols and problems we have never seen. The unknowing...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: 3rd grade > Unit 8
- Setting up 2-step word problems
- Represent 2-step word problems with equations
- 2-step word problem: truffles
2-step word problem: running
- 2-step word problem: theater
- 2-step word problems

Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page
Video transcript
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Free Printable Two-Step Word Problems Worksheets for 3rd Grade
Math: Discover a collection of free printable worksheets for Grade 3 students, focusing on two-step word problems to enhance their problem-solving skills and mathematical understanding.

Explore Two-Step Word Problems Worksheets by Grades
- kindergarten
Explore Other Subject Worksheets for grade 3
- Social studies
- Social emotional
- Foreign language
- Reading & Writing
Explore printable Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for 3rd Grade
Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for Grade 3 are an essential tool for teachers who want to help their students develop strong problem-solving skills in math. These worksheets provide a variety of math word problems that require students to use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to find the solutions. By incorporating real-life scenarios and engaging themes, these worksheets make learning fun and relatable for young learners. Teachers can use these Grade 3 math worksheets to reinforce classroom lessons, provide extra practice for struggling students, or as a homework assignment to keep math skills sharp. With a wide range of topics and difficulty levels, these Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for Grade 3 are an invaluable resource for educators looking to challenge and inspire their students in the world of mathematics.
Quizizz is an innovative platform that offers a variety of educational resources, including Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for Grade 3, to help teachers create engaging and interactive learning experiences for their students. In addition to math word problems, Quizizz also provides resources for other subjects such as science, social studies, and language arts. Teachers can easily customize and assign quizzes, worksheets, and other activities to their students, making it simple to track progress and provide targeted support. The platform also offers gamified quizzes and competitions, which can help motivate students and make learning more enjoyable. By incorporating Quizizz into their lesson plans, teachers can provide a well-rounded and dynamic educational experience for their Grade 3 students, ensuring they develop a strong foundation in math and other essential subjects.

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)

Game Central
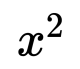
- Our Mission
3 Simple Strategies to Improve Students’ Problem-Solving Skills
These strategies are designed to make sure students have a good understanding of problems before attempting to solve them.

Research provides a striking revelation about problem solvers. The best problem solvers approach problems much differently than novices. For instance, one meta-study showed that when experts evaluate graphs , they tend to spend less time on tasks and answer choices and more time on evaluating the axes’ labels and the relationships of variables within the graphs. In other words, they spend more time up front making sense of the data before moving to addressing the task.
While slower in solving problems, experts use this additional up-front time to more efficiently and effectively solve the problem. In one study, researchers found that experts were much better at “information extraction” or pulling the information they needed to solve the problem later in the problem than novices. This was due to the fact that they started a problem-solving process by evaluating specific assumptions within problems, asking predictive questions, and then comparing and contrasting their predictions with results. For example, expert problem solvers look at the problem context and ask a number of questions:
- What do we know about the context of the problem?
- What assumptions are underlying the problem? What’s the story here?
- What qualitative and quantitative information is pertinent?
- What might the problem context be telling us? What questions arise from the information we are reading or reviewing?
- What are important trends and patterns?
As such, expert problem solvers don’t jump to the presented problem or rush to solutions. They invest the time necessary to make sense of the problem.
Now, think about your own students: Do they immediately jump to the question, or do they take time to understand the problem context? Do they identify the relevant variables, look for patterns, and then focus on the specific tasks?
If your students are struggling to develop the habit of sense-making in a problem- solving context, this is a perfect time to incorporate a few short and sharp strategies to support them.
3 Ways to Improve Student Problem-Solving
1. Slow reveal graphs: The brilliant strategy crafted by K–8 math specialist Jenna Laib and her colleagues provides teachers with an opportunity to gradually display complex graphical information and build students’ questioning, sense-making, and evaluating predictions.
For instance, in one third-grade class, students are given a bar graph without any labels or identifying information except for bars emerging from a horizontal line on the bottom of the slide. Over time, students learn about the categories on the x -axis (types of animals) and the quantities specified on the y -axis (number of baby teeth).
The graphs and the topics range in complexity from studying the standard deviation of temperatures in Antarctica to the use of scatterplots to compare working hours across OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) countries. The website offers a number of graphs on Google Slides and suggests questions that teachers may ask students. Furthermore, this site allows teachers to search by type of graph (e.g., scatterplot) or topic (e.g., social justice).
2. Three reads: The three-reads strategy tasks students with evaluating a word problem in three different ways . First, students encounter a problem without having access to the question—for instance, “There are 20 kangaroos on the grassland. Three hop away.” Students are expected to discuss the context of the problem without emphasizing the quantities. For instance, a student may say, “We know that there are a total amount of kangaroos, and the total shrinks because some kangaroos hop away.”
Next, students discuss the important quantities and what questions may be generated. Finally, students receive and address the actual problem. Here they can both evaluate how close their predicted questions were from the actual questions and solve the actual problem.
To get started, consider using the numberless word problems on educator Brian Bushart’s site . For those teaching high school, consider using your own textbook word problems for this activity. Simply create three slides to present to students that include context (e.g., on the first slide state, “A salesman sold twice as much pears in the afternoon as in the morning”). The second slide would include quantities (e.g., “He sold 360 kilograms of pears”), and the third slide would include the actual question (e.g., “How many kilograms did he sell in the morning and how many in the afternoon?”). One additional suggestion for teams to consider is to have students solve the questions they generated before revealing the actual question.
3. Three-Act Tasks: Originally created by Dan Meyer, three-act tasks follow the three acts of a story . The first act is typically called the “setup,” followed by the “confrontation” and then the “resolution.”
This storyline process can be used in mathematics in which students encounter a contextual problem (e.g., a pool is being filled with soda). Here students work to identify the important aspects of the problem. During the second act, students build knowledge and skill to solve the problem (e.g., they learn how to calculate the volume of particular spaces). Finally, students solve the problem and evaluate their answers (e.g., how close were their calculations to the actual specifications of the pool and the amount of liquid that filled it).
Often, teachers add a fourth act (i.e., “the sequel”), in which students encounter a similar problem but in a different context (e.g., they have to estimate the volume of a lava lamp). There are also a number of elementary examples that have been developed by math teachers including GFletchy , which offers pre-kindergarten to middle school activities including counting squares , peas in a pod , and shark bait .
Students need to learn how to slow down and think through a problem context. The aforementioned strategies are quick ways teachers can begin to support students in developing the habits needed to effectively and efficiently tackle complex problem-solving.
Follow Polygon online:
- Follow Polygon on Facebook
- Follow Polygon on Youtube
- Follow Polygon on Instagram
Site search
- What to Watch
- What to Play
- PlayStation
- All Entertainment
- Dragon’s Dogma 2
- FF7 Rebirth
- Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
- Baldur’s Gate 3
- Buyer’s Guides
- Galaxy Brains
- All Podcasts
Filed under:
- Entertainment
The 3-body problem is real, and it’s really unsolvable
Oh god don’t make me explain math
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: The 3-body problem is real, and it’s really unsolvable
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73224177/3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E4_00_26_53_00RC.jpg_3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E4_00_26_53_00RC.0.jpg)
Everybody seems to be talking about 3 Body Problem , the new Netflix series based on Cixin Liu’s Remembrance of Earth’s Past book trilogy . Fewer people are talking about the two series’ namesake: The unsolvable physics problem of the same name.
This makes sense, because it’s confusing . In physics, the three-body problem attempts to find a way to predict the movements of three objects whose gravity interacts with each of the others — like three stars that are close together in space. Sounds simple enough, right? Yet I myself recently pulled up the Wikipedia article on the three-body problem and closed the tab in the same manner that a person might stagger away from a bright light. Apparently the Earth, sun, and moon are a three-body system? Are you telling me we don’t know how the moon moves ? Scientists have published multiple solutions for the three-body problem? Are you telling me Cixin Liu’s books are out of date?
All I’d wanted to know was why the problem was considered unsolvable, and now memories of my one semester of high school physics were swimming before my eyes like so many glowing doom numbers. However, despite my pains, I have readied several ways that we non-physicists can be confident that the three-body problem is, in fact, unsolvable.
Reason 1: This is a special definition of ‘unsolvable’
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25343152/3BP_103_Unit_03306RC.jpg_3BP_103_Unit_03306RC.jpg)
The three-body problem is extra confusing, because scientists are seemingly constantly finding new solutions to the three-body problem! They just don’t mean a one-solution-for-all solution. Such a formula does exist for a two-body system, and apparently Isaac Newton figured it out in 1687 . But systems with more than two bodies are, according to physicists, too chaotic (i.e., not in the sense of a child’s messy bedroom, but in the sense of “chaos theory”) to be corralled by a single solution.
When physicists say they have a new solution to the three-body problem, they mean that they’ve found a specific solution for three-body systems that have certain theoretical parameters. Don’t ask me to explain those parameters, because they’re all things like “the three masses are collinear at each instant” or “a zero angular momentum solution with three equal masses moving around a figure-eight shape.” But basically: By narrowing the focus of the problem to certain arrangements of three-body systems, physicists have been able to derive formulas that predict the movements of some of them, like in our solar system. The mass of the Earth and the sun create a “ restricted three-body problem ,” where a less-big body (in this case, the moon) moves under the influence of two massive ones (the Earth and the sun).
What physicists mean when they say the three-body problem has no solution is simply that there isn’t a one-formula-fits-all solution to every way that the gravity of three objects might cause those objects to move — which is exactly what Three-Body Problem bases its whole premise on.
Reason 2: 3 Body Problem picked an unsolved three-body system on purpose
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25325944/3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E3_00_34_33_04RC.jpg_3_Body_Problem_n_S1_E3_00_34_33_04RC.jpg)
Henri Poincaré’s research into a general solution to the three-body problem formed the basis of what would become known as chaos theory (you might know it from its co-starring role in Jurassic Park ). And 3 Body Problem itself isn’t about any old three-body system. It’s specifically about an extremely chaotic three-body system, the exact kind of arrangement of bodies that Poincaré was focused on when he showed that the problem is “unsolvable.”
[ Ed. note: The rest of this section includes some spoilers for 3 Body Problem .]
In both Liu’s books and Netflix’s 3 Body Problem , humanity faces an invasion by aliens (called Trisolarans in the English translation of the books, and San-Ti in the TV series) whose home solar system features three suns in a chaotic three-body relationship. It is a world where, unlike ours, the heavens are fundamentally unpredictable. Periods of icy cold give way to searing heat that give way to swings in gravity that turn into temporary reprieves that can never be trusted. The unpredictable nature of the San-Ti environment is the source of every detail of their physicality, their philosophy, and their desire to claim Earth for their own.
In other words, 3 Body Problem ’s three-body problem is unsolvable because Liu wanted to write a story with an unsolvable three-body system, so he chose one of the three-body systems for which we have not discovered a solution, and might never.
Reason 3: Scientists are still working on the three-body problem
Perhaps the best reason I can give you to believe that the three-body problem is real, and is really unsolvable, is that some scientists published a whole set of new solutions for specific three-body systems very recently .
If physicists are still working on the three-body problem, we can safely assume that it has not been solved. Scientists, after all, are the real experts. And I am definitely not.
The next level of puzzles.
Take a break from your day by playing a puzzle or two! We’ve got SpellTower, Typeshift, crosswords, and more.
Sign up for the newsletter Patch Notes
A weekly roundup of the best things from Polygon
Just one more thing!
Please check your email to find a confirmation email, and follow the steps to confirm your humanity.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Loading comments...

Don’t have the time to read (or watch) Shōgun? Get the audiobooks for just $10

Cloud’s unreliable narration only makes Final Fantasy 7 Rebirth’s ending more confusing

Imaginary, Lisa Frankenstein, Netflix’s The Beautiful Game, and every new movie to watch at home this weekend

- Dragon’s Dogma 2 guides, walkthroughs, and explainers
Should you give the grimoires to Myrddin or Trysha in Dragon’s Dogma 2?

All maister skills in Dragon’s Dogma 2 and how to get them

How to get a house in FFXIV

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Two step equations are algebraic problems that take just two steps to solve. The two step equation is a linear equation in one variable. While performing an operation for solving a two step equation, we need to perform the same operation on both sides of the equation. We isolate the variable on one side of the equation to determine its value.
Hone your skills in solving two-step equations because it will serve as your foundation when solving multi-step equations. I prepared eight (8) two-step equations problems with complete solutions to get you rolling. My advice is for you to solve them by hand using a pencil or pen and paper. Believe me, you get the most benefit from this ...
The answer is c = 1. You would first combine all the like terms in the parenthesis. The only like terms are -5 and 6. The sum of those numbers gets you 1, then by subtracting 1 from both sides you are left with c = 1. You can even check it by putting 1 in c's place: 2= (1-5+6). 10 comments.
Two-Step Word Problems. Two-step word problems have three numbers which must be operated on separately, and in the right order. They take much more understanding of the problem than simple word problems because they provide the information in a less structured form. Two-Step Word Problems. Addition, then Subtraction. Addition, then Multiplication.
What is a two-step equation? Remember, an equation is a mathematical sentence that uses an equal sign, = , to show that two expressions are equal.. Very similar to one-step equations, a two-step equation is an equation that only requires two steps to solve. We will use a mix of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to solve these equations.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. ... Two-step equations intro. Same thing to both sides of equations. Intro to two-step equations. ... Report a problem. Stuck? Review related articles/videos or use a hint. ...
2-step word problems. The cash register at the ice cream store started the day with $ 120 . During the day, the store earned $ 56 selling ice cream. The manager also paid for a delivery out of the cash register. At the end of the day, the cash register had $ 141 . How much did the delivery cost?
The USUAL way of solving a two-step equation: Note: This is the "usual" method because most of the two-step equations are solved this way.Notice that Step 2 can alternatively be replaced by Step 3 which are the same essentially. 1) First, add or subtract both sides of the linear equation by the same number. 2) Secondly, multiply or divide both sides of the linear equation by the same number.
If this is your first time solving a 2-step equation, don't worry! Two-step equations are solved using a similar process to solving one-step equations. However, there is the obvious addition of an extra step. A 2-step equation problem will require you to apply two operations in order to determine the value of the variable that is unknown. You ...
Learn how to solve word problems using two-step equations.For more Math help visit our websitehttp://www.moomoomath.com/
Solving Two-Step Word Problems (II) - Lesson Plan. In this lesson, students will learn how to solve two-step word problems using various strategies. They will practice solving problems involving shopping and changes in quantities. The class aims to develop problem-solving skills and mathematical thinking. Go to Lesson Plan. See full lesson plan.
Two step word problems - Common Core Standard (CCSS: 3.OA.8) Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. In this lesson you will learn to identify the operations in two step word problems. Example: The Davis family drove a total of 720 miles, starting on Friday and ending on Sunday. They drove 255 miles on Friday and 229 miles on ...
Welcome to Solving Two-Step Equations with Mr. J! Need help with how to solve two-step equations? You're in the right place!Whether you're just starting out,...
These word problems are called two-step because you have to perform two mathematical operations in order to solve them. In this case - addition (subtraction) and multiplication (division). To practice solving two-step equations - word problems, feel free to use the worksheets below. Two-step equations - word problems exams for teachers
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem. Show more; en. Related Symbolab blog posts.
The game requires players to solve two-step, mixed operation word problems during their turn. Similar to Connect Four, each solved problem earns the player an X or O. 3rd grade. Math. Worksheet. Vocabulary Cards: Word Problem Comprehension. Worksheet. Vocabulary Cards: Word Problem Comprehension.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Well, this is essentially 9 plus 9 plus 9 plus 9. So we could just add up the 9's. 9 plus 9 is 18, plus 9 is 27, plus 9 is 36. So he ran a total of 36 kilometers. Now, that's not what they're asking us for. They're asking us for the number of kilometers Beth ran that week. And they tell us that she ran 15 fewer kilometers than Abe.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Explore printable Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for 5th Grade. Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for Grade 5 are an essential resource for teachers looking to challenge their students in the realm of Math. These worksheets provide a variety of Math Word Problems that require students to use their critical thinking skills and apply their ...
Integrating two-step word problems with other math concepts to reinforce understanding. Utilizing technology and interactive resources, such as online simulations or math apps, to enhance engagement and provide additional practice. Assessing and Monitoring Progress. To ensure students' progress while teaching two step word problems, you can:
Two-Step Word Problems worksheets for Grade 3 are an essential tool for teachers who want to help their students develop strong problem-solving skills in math. These worksheets provide a variety of math word problems that require students to use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to find the solutions.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
dxd (x − 5)(3x2 − 2) Integration. ∫ 01 xe−x2dx. Limits. x→−3lim x2 + 2x − 3x2 − 9. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
SFBT includes positive psychology principles, such as being a solution-building approach rather than a problem-solving one. This forward-moving methodology can offer a clear path to achieving therapy goals — and the motivation to do so. Focusing on solving concerns means you have to wade through them first before coming up with solutions.
While slower in solving problems, experts use this additional up-front time to more efficiently and effectively solve the problem. In one study, researchers found that experts were much better at "information extraction" or pulling the information they needed to solve the problem later in the problem than novices. This was due to the fact that they started a problem-solving process by ...
In other words, 3 Body Problem 's three-body problem is unsolvable because Liu wanted to write a story with an unsolvable three-body system, so he chose one of the three-body systems for which ...