College Students’ Time Management: a Self-Regulated Learning Perspective
- Review Article
- Published: 27 October 2020
- Volume 33 , pages 1319–1351, ( 2021 )

Cite this article

- Christopher A. Wolters ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8406-038X 1 &
- Anna C. Brady 1
25k Accesses
59 Citations
10 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Despite its recognized importance for academic success, much of the research investigating time management has proceeded without regard to a comprehensive theoretical model for understanding its connections to students’ engagement, learning, or achievement. Our central argument is that self-regulated learning provides the rich conceptual framework necessary for understanding college students’ time management and for guiding research examining its relationship to their academic success. We advance this larger purpose through four major sections. We begin by describing work supporting the significance of time management within post-secondary contexts. Next, we review the limited empirical findings linking time management and the motivational and strategic processes viewed as central to self-regulated learning. We then evaluate conceptual ties between time management and processes critical to the forethought, performance, and post-performance phases of self-regulated learning. Finally, we discuss commonalities in the antecedents and contextual determinants of self-regulated learning and time management. Throughout these sections, we identify avenues of research that would contribute to a greater understanding of time management and its fit within the framework of self-regulated learning. Together, these efforts demonstrate that time management is a significant self-regulatory process through which students actively manage when and for how long they engage in the activities deemed necessary for reaching their academic goals.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Examining the relations of time management and procrastination within a model of self-regulated learning
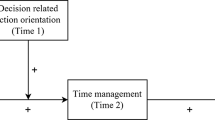
Willing, able, and engaged: roles of action-state orientation, intrinsic academic motivation, and time management on academic engagement
Are Mastery-Oriented College Students Better Time Managers?
Adams, G. A., & Jex, S. M. (1999). Relationships between time management, control, work family conflict, and strain. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 4 (1), 72–77.
Google Scholar
Aeon, B., & Aguinis, H. (2017). It’s about time: new perspectives and insights on time management. Academy of Management Perspectives, 31 , 309–330.
Ames, C. (1992). Classrooms: goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84 , 261–271.
Asikainen, H., & Gijbels, D. (2017). Do students develop towards more deep approaches to learning during studies? A systematic review on the development of students’ deep and surface approaches to learning in higher education. Educational Psychology Review, 29 , 205–234.
Balduf, M. (2009). Underachievement among college students. Journal of Advanced Academics, 20 , 274–294.
Banahan, L., & Mullendore, R. (2014). Navigating the first college year. A guide for parents and families . Columbia: University of South Carolina, National Resource Center for The First-Year Experience and Students in Transition.
Bandura, A. (1986). The explanatory and predictive scope of self-efficacy theory. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 4 , 359–373.
Bartels, J. M., Magun-Jackson, S., & Ryan, J. J. (2010). Dispositional approach-avoidance achievement motivation and cognitive self-regulated learning: the mediation of achievement goals. Individual Differences Research, 8 , 97–110.
Basila, C. (2014). Good time management and motivation level predict student academic success in college on-line courses. International Journal of Cyber Behavior, Psychology and Learning, 4 , 45–52.
Bembenutty, H. (2009). Academic delay of gratification, self-regulation of learning, gender differences, and expectancy-value. Personality and Individual Differences, 46 , 347–352.
Beuhler, R., Griffin, D., & Peetz, J. (2010). The planning fallacy: cognitive, motivational, and social origins. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 43 , 1–62.
Bidjerano, T., & Dai, D. Y. (2007). The relationship between the big-five model of personality and self-regulated learning strategies. Learning and Individual Differences, 17 , 69–81.
Boekaerts, M. (1996). Self-regulated learning at the junction of cognition and motivation. European Psychologist, 1 , 100–112.
Boekaerts, M., & Corno, L. (2005). Self-regulation in the classroom: a perspective on assessment and intervention. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 54 , 199–231.
Bond, M. J., & Feather, N. T. (1988). Some correlates of structure and purpose in the use of time. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 321–329.
Britton, B. K., & Glynn, S. M. (1989). Mental management and creativity: a cognitive model of time management for intellectual productivity. In J. Glover, R. Ronning, & C. Reynolds (Eds.), Handbook of creativity (pp. 429–440). New York: Plenum.
Britton, B. K., & Tesser, A. (1991). Effects of time-management practices on college grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 83 , 405–410.
Buehler, R., & Griffin, D. (2015). When plans lead to optimistic forecasts. In M. D. Mumford & M. Frese (Eds.), The psychology in planning in organizations: research and applications (pp. 31–57). New York: Routledge.
Burlison, J. D., Murphy, C. S., & Dwyer, W. O. (2009). Evaluation of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire for predicting academic performance in college students of varying scholastic aptitude. College Student Journal, 43 , 1313–1323.
Burnette, J., O’Boyle, E., VanEpps, E., Pollack, J., & Finkel, E. (2013). Mind-sets matter: a meta-analytic review of implicit theories and self-regulation. Psychological Bulletin, 139 (3), 655–701.
Burt, C. D., Weststrate, A., Brown, C., & Champion, F. (2010). Development of the time management environment (TiME) scale. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 25 , 649–668.
Butler, D., & Winne, P. (1995). Feedback and self-regulated learning: a theoretical synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 65 , 245–281.
Cano, F. (2006). An in-depth analysis of the Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI). Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66 , 1023–1038.
Capdeferro, N., Romero, M., & Barberà, E. (2014). Polychronicity: review of the literature and a new configuration for the study of this hidden dimension of online learning. Distance Education, 35 , 294–310.
Cassidy, S. (2011). Self-regulated learning in higher education: identifying key component processes. Studies in Higher Education, 36 , 989–1000.
Chang, A., & Nguyen, L. T. (2011). The mediating effects of time structure on the relationships between time management behaviour, job satisfaction, and psychological well-being. Australian Journal of Psychology, 63 , 187–197.
Choi, B. (2016). How people learn in an asynchronous online learning environment: the relationships between graduate students’ learning strategies and learning satisfaction. Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology, 42 , 1–15.
Chuderski, A. (2016). Time pressure prevents relational learning. Learning and Individual Differences, 49 , 361–365.
Claessens, B. J. C., van Eerde, W., Rutte, C. G., & Roe, R. A. (2007). A review of the time management literature. Personnel Review, 36 , 255–276.
Conti, R. (2001). Time flies: investigating the connection between intrinsic motivation and the experience of time. Journal of Personality, 69 (1), 1–26.
Corno, L., Cronbach, L. J., Kupermintz, H., Lohman, D. F., Mandinach, E. B., Porteus, A. W., & Talbert, J. E. (2002). Remaking the concept of aptitude: extending the legacy of Richard E Snow . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Crede, M., & Kuncel, N. R. (2008). Study habits, skills, and attitudes: the third pillar supporting collegiate academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3 (6), 425–453.
Crede, M., & Phillips, L. A. (2011). A meta-analytic review of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. Learning and Individual Differences, 21 , 337–346.
Crede, M., Roch, S. G., & Kieszczynka, U. M. (2010). Class attendance in college: a meta-analytic review of the relationship of class attendance with grades and student characteristics. Review of Educational Research, 80 , 272–295.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996). Creativity: flow and the psychology of discovery and invention . New York: HarperCollins Publishers.
Dembo, M. H., & Eaton, M. J. (2000). Self-regulation of academic learning in middle-level schools. The Elementary School Journal, 100 , 473–490.
Dent, A., & Koenka, A. (2016). The relation between self-regulated learning and academic achievement across childhood and adolescence: a meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 28 , 425–474.
Díaz-Morales, J. F., Ferrari, J. R., & Cohen, J. R. (2008). Indecision and avoidant procrastination: the role of morningness—eveningness and time perspective in chronic delay lifestyles. The Journal of General Psychology, 135 (3), 228–240.
Donker, A., de Boer, H., Kostons, D., Dignath van Ewijk, C., & van der Werf, M. (2014). Effectiveness of learning strategy instruction on academic performance: a meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 11 , 1–26.
Douglas, H. E., Bore, M., & Munro, D. (2016). Coping with university education: the relationships of time management behaviour and work engagement with the five factor model aspects. Learning and Individual Differences, 45 , 268–274.
Doumen, S., Broeckmans, J., & Masui, C. (2014). The role of self-study time in freshmen’s achievement. Educational Psychology, 34 , 385–402.
Duncan, T. G., & McKeachie, W. J. (2005). The making of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire. Educational Psychologist, 40 , 117–128.
Duncheon, J. C., & Tierney, W. G. (2013). Changing conceptions of time: implications for educational research and practice. Review of Educational Research, 83 , 236–272.
Dunlosky, J., & Ariel, R. (2011). Self-regulated learning and the allocation of study time. In B. Ross (Ed.), Psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 54, pp. 103–140). San Diego: Academic Press.
Dunning, D., Heath, C., & Suls, J. (2004). Flawed self-assessments. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 5 (3), 69–106.
Efklides, A. (2011). Interactions of metacognition with motivation and affect in self-regulated learning: the MASRL model. Educational Psychologist, 46 , 6–25.
Eilam, B., & Aharon, I. (2003). Students’ planning in the process of self-regulated learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 28 , 304–334.
Ferrari, J. R., & Díaz-Morales, J. F. (2007). Procrastination: different time orientations reflect different motives. Journal of Research in Personality, 41 , 707–714.
Flake, J. K., Barron, K. E., Hulleman, C., McCoach, B. D., & Welsh, M. E. (2015). Measuring cost: the forgotten component of expectancy-value theory. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 41 , 232–244.
Flanigan, A. E., & Kiewra, K. A. (2018). What college instructors can do about student cyber-slacking. Educational Psychology Review, 30 , 585–597.
Francis-Smythe, J. A., & Robertson, I. T. (1999a). On the relationship between time management and time estimation. British Journal of Psychology, 90 , 333–347.
Francis-Smythe, J. A., & Robertson, I. T. (1999b). Time-related individual differences. Time & Society, 8 , 273–292.
Fromme, K., Corbin, W., & Kruse, M. (2008). Behavioral risks during the transition from high school to college. Developmental Psychology, 44 (5), 1497–1504.
Gable, P. A., & Poole, B. D. (2012). Time flies when you’re having approach-motivated fun: effects of motivational intensity on time perception. Psychological Science, 23 (8), 879–886.
Gevers, J. M., Rutte, C. G., & Van Eerde, W. (2006). Meeting deadlines in work groups: implicit and explicit mechanisms. Applied Psychology, 55 , 52–72.
Green, P., & Skinner, D. (2005). Does time management training work? An evaluation. International Journal of Training and Development, 9 , 124–139.
Gulec, M., Selvi, Y., Boysan, M., Aydin, A., Oral, E., & Aydin, E. F. (2013). Chronotype effects on general well-being and psychopathology levels in healthy young adults. Biological Rhythm Research, 44 , 457–468.
Guzman, G., Goldberg, T., & Swanson, H. (2018). A meta-analysis of self-monitoring on reading performance of K-12 students. School Psychology Quarterly, 33 (1), 160–168.
Hadwin, A., & Oshige, M. (2011). Self-regulation, coregulation, and socially shared regulation: exploring perspectives of social in self-regulated learning theory. Teachers College Record, 113 , 240–264.
Hafner, A., Stock, A., Pinneker, L., & Strohle, S. (2014). Stress prevention through a time management training intervention: an experimental study. Educational Psychology, 34 , 403–416.
Hahn, C., Cowell, J. M., Wiprzycka, U. J., Goldstein, D., Ralph, M., Hasher, L., & Zelazo, P. D. (2012). Circadian rhythms in executive function during the transition to adolescence: the effect of synchrony between chronotype and time of day. Developmental Science, 15 (3), 408–416.
Harkin, B., Webb, T. L., Chang, B. P. I., Prestwich, A., Conner, M., Kellar, I., et al. (2016). Does monitoring goal progress promote goal attainment? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Psychological Bulletin, 142 (2), 198–229.
Hattie, J., Biggs, J., & Purdie, N. (1996). Effects of learning skills interventions on student learning: a meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 66 , 99–136.
Haynes, N., Comer, J., & Hamilton-Lee, M. (1988). Gender and achievement status differences on learning factors among Black high school students. Journal of Educational Research, 81 , 233–237.
Hensley, L. C., Wolters, C. A., Won, S., & Brady, A. C. (2018). Academic probation, time management, and time use in a college success course. Journal of College Reading and Learning, 48 , 105–123.
Hicks, T., & Heastie, S. (2008). High school to college transition: a profile of the stressors, physical and psychological health issues that affect the first-year on-campus college students. Journal of Cultural Diversity, 15 (3), 143–147.
Hilbrecht, M., Zuzanek, J., & Mannell, R. C. (2008). Time use, time pressure and gendered behavior in early and late adolescence. Sex Roles, 58 , 342–357.
Hofer, B. K., Yu, S. L., & Pintrich, P. R. (1998). Teaching college students to be self-regulated learners. In D. H. Schunk & B. J. Zimmerman (Eds.), Self-regulated learning: from teaching to self-reflective practice (pp. 57–85). New York: Guilford Press.
Horstmanshof, L., & Zimitat, C. (2007). Future time orientation predicts academic engagement among first-year university students. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77 (Pt 3), 703–718.
Huie, F. C., Winsler, A., & Kitsantas, A. (2014). Employment and first-year college achievement: the role of self-regulation and motivation. Journal of Education and Work, 27 , 110–135.
Husman, J., & Lens, W. (1999). The role of the future in student motivation. Educational Psychologist, 34 , 113–125.
Kanfer, R., Frese, M., & Johnson, R. (2017). Motivation related to work: a century of progress. Journal of Applied Psychology, 102 (3), 338–355.
Kantrowitz, T. M., Grelle, D. M., Beaty, J. C., & Wolf, M. B. (2012). Time is money: polychronicity as a predictor of performance across job levels. Human Performance, 25 , 114–137.
Kauderer, S., & Randler, C. (2013). Differences in time use among chronotypes in adolescents. Biological Rhythm Research, 44 , 601–608.
Kaufman-Scarborough, C., & Lindquist, J. D. (1999). Time management and polychronicity: comparisons, contrasts, and insights for the workplace. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 14 , 288–312.
Keating, D. P. (2012). Cognitive and brain development in adolescence. Enfance, 64 , 267–279.
Kesici, Ş., Baloğlu, M., & Deniz, M. E. (2011). Self-regulated learning strategies in relation with statistics anxiety. Learning and Individual Differences, 21 , 472–477.
Kim, K. R., & Seo, E. H. (2015). The relationship between procrastination and academic performance: a meta-analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 82 , 26–33.
Kitsantas, A., Winsler, A., & Huie, F. (2008). Self-regulation and ability predictors of academic success during college: a predictive validity study. Journal of Advanced Academics, 20 , 42–68.
Koch, C. J., & Kleinmann, M. (2002). A stitch in time saves nine: behavioural decision-making explanations for time management problem. European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology, 11 , 199–217.
Komarraju, M., Karau, S. J., & Schmeck, R. R. (2009). Role of the Big Five personality traits in predicting college students’ academic motivation and achievement. Learning and Individual Differences, 19 , 47–52.
Konig, C. J., & Waller, M. J. (2010). Time for reflection: a critical examination of polychronicity. Human Performance, 23 , 173–190.
Kooij, D. T. A. M., Kanfer, R., Betts, M., & Rudolph, C. W. (2018). Future time perspective: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology, 103 (8), 867–893.
Krumrei-Mancuso, E. J., Newton, F. B., Kim, E., & Wilcox, D. (2013). Psychosocial factors predicting first-year college student success. Journal of College Student Development, 54 , 247–266.
Landrum, R. E., Turrisi, R., & Brandel, J. M. (2006). College students’ study time: course level, time of semester, and grade earned. Psychological Reports, 98 (3), 675–682.
Liborius, P., Bellhauser, H., & Schmitz, B. (2017). What makes a good study day? An intraindividual study on university students’ time investment by means of time-series analyses. Learning and Instruction.
Linnenbrink-Garcia, L., & Patall, E. (2016). Motivation. In L. Corno & E. Anderman (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (3rd ed., pp. 91–1030). New York: Routledge.
Liu, O. L., Rijmen, F., MacCann, C., & Roberts, R. (2009). The assessment of time management in middle-school students. Personality and Individual Differences, 47 , 174–179.
Locke, E., & Latham, G. (2019). The development of goal setting theory: a half-century retrospective. Motivation Science, 5 , 93–105.
Loureiro, F., & Garcia-Marques, T. (2015). Morning or evening person? Which type are you? Self-assessment of chronotype. Personality and Individual Differences, 86 , 168–171.
Lynch, D. J. (2010). Application of online discussion and cooperative learning strategies to online and blended college courses. College Student Journal, 44 , 920–927.
Macan, T. H. (1994). Time management: test of a process model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 , 381–391.
Macan, T. H., Shahani, C., Dipboye, R. L., & Phillips, A. P. (1990). College students’ time management: correlations with academic performance and stress. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82 , 760–768.
MacCann, C., & Roberts, R. D. (2010). Do time management, grit, and self-control relate to academic achievement independently of conscientiousness? In R. E. Hicks (Ed.), Personality and individual differences: current directions (pp. 79–90). Bowen Hills: Australian Academic Press.
MacCann, C., Fogarty, G. J., & Roberts, R. D. (2012). Strategies for success in education: time management is more important for part-time than full-time community college students. Learning and Individual Differences, 22 , 618–623.
McCrae, R., & Lockenhoff, C. (2010). Self-regulation and the five-factor model of personality traits. In R. Hoyle (Ed.), Handbook of personality and self-regulation (pp. 143–168). New York: Wiley.
McInerney, D., & King, R. (2018). Culture and self-regulation in educational contexts. In D. Schunk & J. Greene (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (2nd ed., pp. 485–502). New York: Routledge.
Meeuwisse, M., Born, M. P., & Severiens, S. E. (2013). Academic performance differences among ethnic groups: do the daily use and management of time offer explanations? Social Psychology of Education, 16 , 599–615.
Melancon, J. G. (2002). Reliability, structure, and correlates of Learning and Study Strategies Inventory scores. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 62 , 1020–1027.
Miele, D. B., & Scholer, A. A. (2018). The role of metamotivational monitoring in motivation regulation. Educational Psychologist, 53 , 1–21.
Miller, R. B., & Brickman, S. J. (2004). A model of future-oriented motivation and self-regulation. Educational Psychology Review, 16 , 9–33.
Muis, K. R. (2007). The role of epistemic beliefs in self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 42 , 173–190.
Nelson, T., & Narens, L. (1990). Metamemory: a theoretical framework and some new findings. In G. H. Bower (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation (pp. 125–173). New York: Academic Press.
Nonis, S., Teng, J., & Ford, C. (2005). A cross-cultural investigation of time management practices and job outcomes. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 29 , 409–428.
Nonis, S. A., Philhours, M. J., & Hudson, G. I. (2006). Where does the time go? A diary approach to business and marketing students’ time use. Journal of Marketing Education, 28 , 121–134.
Olaussen, B. S., & Bråten, I. (1998). Identifying latent variables measured by the Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI) in Norwegian college students. The Journal of Experimental Education, 67 , 82–96.
Olejnik, S., & Nist, S. L. (1992). Identifying latent variables measured by the Learning and Study Strategies Inventory (LASSI). The Journal of Experimental Education, 60 , 151–159.
Panadero, E. (2017). A review of self-regulated learning: six models and four directions for research. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , 1–28.
Panadero, E., Brown, G., & Strijbos, J. (2016). The future of student self-assessment: a review of known and unknowns and potential directions. Educational Psychology Review, 28 (803), 830.
Panek, E. (2014). Left to their own devices: college students’ “guilty pleasure” media use and time management. Communication Research, 41 , 561–577.
Pekrun, R., Goetz, T., Titz, W., & Perry, R. P. (2002). Academic emotions in students’ self-regulated learning and achievement: a program of qualitative and quantitative research. Educational Psychologist, 37 , 91–105.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–502). San Diego: Academic.
Pintrich, P. R. (2004). A conceptual framework for assessing motivation and self-regulated learning in college students. Educational Psychology Review, 16 , 385–407.
Pintrich, P. R., & Zusho, A. (2007). Student motivation and self-regulated learning in the college classroom. In R. P. Perry & J. C. Smart (Eds.), The scholarship of teaching and learning in higher education: an evidence based perspective (pp. 731–810). New York: Springer.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A., Garcia, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1993). Reliability and predictive validity of the Motivated Strategies for Learning Questionnaire. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 53 , 801–813.
Pintrich, P. R., Wolters, C. A., & Baxter, G. P. (2000). Assessing metacognition and self-regulated learning. In G. Schraw & J. Impara (Eds.), Issues in the measurement of metacognition (pp. 43–97). Lincoln: Buros Institute of Mental Measurement.
Plant, E. A., Ericsson, K. A., Hill, L., & Asberg, K. (2005). Why study time does not predict grade point average across college students: implications of deliberate practice for academic performance. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30 , 96–116.
Prevatt, F., Petscher, Y., Proctor, B. E., Hurst, A., & Adams, K. (2006). The revised Learning and Study Strategies Inventory: an evaluation of competing models. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66 (3), 448–458.
Pychyl, T. A., Morin, R. W., & Salmon, B. R. (2000). Procrastination and the planning fallacy: an examination of the study habits of university students. Journal of Social Behavior and Personality, 15 , 135–150.
Ranellucci, J., Hall, N. C., & Goetz, T. (2015). Achievement goals, emotions, learning, and performance: a process model. Motivation Science, 1 , 98–120.
Rhodes, M., & Tauber, S. (2011). The influence of delaying judgments of learning on metacognitive accuracy: a meta-analytic review. Psychological Bulletin, 137 (1), 131–148.
Richards, J. H. (1987). Time management—a review. Work & Stress, 1 , 73–78.
Rickert, N. P., Meras, I. L., & Witkow, M. R. (2014). Theories of intelligence and students’ daily self-handicapping behaviors. Learning and Individual Differences, 36 , 1–8.
Roskes, M., Elliot, A. J., Nijstad, B. A., & De Dreu, C. K. (2013). Time pressure undermines performance more under avoidance than approach motivation. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 39 , 803–813.
Rytkonen, H., Parpala, A., Lindblom-Ylanne, S., Virtanen, V., & Postareff, L. (2012). Factors affecting bioscience students’ academic achievement. Instructional Science, 40 , 241–256.
Sanders, L., Reedy, D., & Frizell, M. (Eds.). (2018). Learning centers in the 21 st century: a modern guide for learning assistance professionals in higher education . Bentonville: AR. Iona Press.
Sansgiry, S. S., Bhosle, M., & Sail, K. (2006). Factors that affect academic performance among pharmacy students. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 70 , 1–9.
Schell, K. L., & Conte, J. M. (2008). Associations among polychronicity, goal orientation, and error orientation. Personality and Individual Differences, 44 , 288–298.
Schraw, G. (2006). Knowledge: structures and processes. In P. Alexander & P. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed., pp. 245–263). Mahwah: Erlbaum Associates.
Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (1997). Social origins of self-regulatory competence. Educational Psychologist, 32 , 195–208.
Schunk, D. H., & Zimmerman, B. J. (Eds.). (1998). Self-regulated learning: from teaching to self-reflective practice . New York: Guilford Press.
Sen, S., & Yilmaz, A. (2016). Devising a structural equation model of relationships between preservice teachers’ time and study environment management, effort regulation, self-efficacy, control of learning beliefs, and metacognitive self-regulation. Science Education International, 27 , 301–316.
Shaunessy-Dedrick, E., Suldo, S. M., Roth, R. A., & Fefer, S. A. (2015). Students’ perceptions of factors that contribute to risk and success in accelerated high school courses. The High School Journal, 98 , 109–137.
Shell, D. F., & Husman, J. (2001). The multivariate dimensionality of personal control and future time perspective beliefs in achievement and self-regulation. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 26 (4), 481–506.
Simons, J., Vansteenkiste, M., Lens, W., & Lacante, M. (2004). Placing motivation and future time perspective theory in a temporal perspective. Educational Psychology Review, 16 , 121–139.
Sinatra, G., Kienhues, D., & Hofer, B. (2014). Addressing challenges to public understanding of science: epistemic cognition, motivated reasoning, and conceptual change. Educational Psychologist, 49 , 123–138.
Sirois, F. M. (2014). Procrastination and stress: exploring the role of self-compassion. Self and Identity, 13 , 128–145.
Sitzmann, T., & Ely, K. (2011). A meta-analysis of self-regulated learning in work-related training and educational attainment: what we know and where we need to go. Psychological Bulletin, 137 (3), 421–442.
Sitzmann, T., Ely, K., Brown, K., & Bauer, K. (2010). Self-assessment of knowledge: a cognitive learning or affective measure? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 9 , 169–191.
Snow, R. (1989). Cognitive-conative aptitude interactions in learning. In R. Kanfer, P. Ackerman, & R. Cudeck (Eds.), Abilities, motivation, and methodology: the Minnesota symposium on learning and individual differences (pp. 435–474). Hillsdale: Erlbaum Associates.
Snow, R. E., Corno, L., & Jackson III, D. (1996). Individual differences in affective and conative functions. In D. C. Berliner & R. C. Calfee (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (pp. 243–310). New York: Macmillan Library Reference.
Soderstrom, N. C., & Bjork, R. A. (2014). Testing facilitates the regulation of subsequent study time. Journal of Memory and Language, 73 , 99–115.
Steel, P. (2007). The nature of procrastination: a meta-analytic and theoretical review of quintessential self-regulatory failure. Psychological Bulletin, 133 (1), 65–94.
Stevens, T., & Tallent-Runnels, M. K. (2004). The learning and study strategies inventory-high school version: issues of factorial invariance across gender and ethnicity. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 64 , 332–346.
Strunk, K. K., Cho, Y., Steele, M. R., & Bridges, S. L. (2013). Development and validation of a 2× 2 model of time-related academic behavior: procrastination and timely engagement. Learning and Individual Differences, 25 , 35–44.
Tanner, J. R., Stewart, G., Maples, G. M., & Totaro, M. W. (2009). How business students spend their time—do they really know? Research in Higher Education Journal, 3 , 1–9.
Terenzini, P., Rendon, L., Upcraft, M. L., Millar, S., Allison, K., Gregg, P., & Jalomo, R. (1994). The transition to college: diverse students, diverse stories. Research in Higher Education, 35 , 57–73.
Trueman, M., & Hartley, J. (1996). A comparison between the time-management skills and academic performance of mature and traditional-entry university students. Higher Education, 32 , 199–215.
Truschel, J., & Reedy, D. L. (2009). National survey—what is a learning center in the 21st century? Learning Assistance Review, 14 , 9–22.
Tsai, H. C., & Liu, S. H. (2015). Relationships between time-management skills, Facebook interpersonal skills and academic achievement among junior high school students. Social Psychology of Education, 18 , 503–516.
U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, What Works Clearinghouse (2016). Studies of interventions for students in developmental education intervention report: first year experience courses for students in developmental education . Retrieved from http://whatworks.ed.gov . Accessed 20 Jan 2020.
Urdan, T., & Schoenfelder, E. (2006). Classroom effects on student motivation: goal structures, social relationships, and competence beliefs. Journal of School Psychology, 44 , 331–349.
Usher, E. L., & Pajares, F. (2008). Sources of self-efficacy in school: critical review of the literature and future directions. Review of Educational Research, 78 , 751–796.
van Den Hurk, M. (2006). The relation between self-regulated strategies and individual study time, prepared participation and achievement in a problem-based curriculum. Active Learning in Higher Education, 7 , 155–169.
van der Meer, J., Jansen, E., & Torenbeek, M. (2010). ‘It’s almost a mindset that teachers need to change’: first-year students’ need to be inducted into time management. Studies in Higher Education, 35 , 777–791.
van Eerde, W. (2015). Time management and procrastination. In M. D. Mumford & M. Frese (Eds.), The psychology of planning in organizations: research and applications (pp. 312–333). New York: Routledge.
Wagner, P., Schober, B., & Spiel, C. (2008). Time students spend working at home for school. Learning and Instruction, 18 , 309–320.
Weiner, B. (2005). Motivation from an attribution perspective and the social psychology of perceived competence. In A. Elliot & C. Dweck (Eds.), Handbook of competence and motivation (pp. 73–84). New York: Guildford.
Weinstein, C. E., Palmer, D. R., & Acee, T. W. (2016). LASSI user’s manual (3th ed.). Clearwater: H & H Pub.
Winne, P. H. (1995). Inherent details in self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 30 , 173–187.
Winne, P. H., & Baker, R. (2013). The potentials of educational data mining for researching metacognition, motivation, and self-regulated learning. Journal of Educational Data Mining, 5 , 1–8.
Winne, P., & Hadwin, A. (1998). Studying as self-regulated learning. In D. Hacker, J. Dunlosky, & A. Graesser (Eds.), Metacognition in educational theory and practice (pp. 277–304). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Winne, P. H., & Hadwin, A. F. (2008). The weave of motivation and self-regulated learning. Motivation and self-regulated learning: theory, research, and applications (pp. 297–314). New York: Taylor & Francis.
Winne, P., & Perry, N. (2000). Measuring self-regulated learning. In M. Boekaerts, P. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 531–566). San Diego: Academic Press.
Witkow, M. R. (2009). Academic achievement and adolescents’ daily time use in the social and academic domains. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 19 , 151–172.
Wolters, C. A. (2003). Regulation of motivation: evaluating an underemphasized aspect of self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 38 , 189–205.
Wolters, C. A. (2011). Regulation of motivation: contextual and social aspects. Teachers College Record, 113 , 265–283.
Wolters, C. A., & Gonzalez, A. L. (2008). Classroom climate and motivation: a step toward integration. Advances in Motivation and Achievement: Social Psychological Influences, 15 , 493–519.
Wolters, C. A., & Hoops, L. D. (2015). Self-regulated learning interventions for motivationally disengaged college students. In T. L. Cleary (Ed.), Self-regulated learning interventions with at-risk youth: Enhancing adaptability, performance, and well-being (pp. 67–88). Washington: American Psychological Association.
Wolters, C., & Taylor, D. (2012). A self-regulated learning perspective on student engagement. In S. L. Christenson, A. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 635–651). New York: Springer.
Wolters, C. A., & Won, S. (2018). Validity and the use of self-report questionnaires to assess self-regulated learning. In D. H. Schunk & J. A. Greene (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 307–322). New York: Routledge.
Wolters, C. A., Won, S., & Hussain, M. (2017). Examining the relations of time management and procrastination within a model of self-regulated learning. Metacognition and Learning, 12 , 381–399.
Won, S., & Yu, S. L. (2018). Relations of perceived parental autonomy support and control with adolescents’ academic time management and procrastination. Learning and Individual Differences, 61 , 205–215.
Woolfolk, A. E., & Woolfolk, R. L. (1986). Time management: an experimental investigation. Journal of School Psychology, 24 , 267–275.
Xie, K., Heddy, B. C., & Greene, B. A. (2019). Affordances of using mobile technology to support experience-sampling method in examining college students’ engagement. Computers & Education, 128 , 183–198.
Xu, J. (2008). Models of secondary school students’ interest in homework: a multilevel analysis. American Educational Research Journal, 45 , 1180–1205.
Xu, J. (2010). Predicting homework time management at the secondary school level: a multilevel analysis. Learning and Individual Differences, 20 , 34–39.
Xu, J., Du, J., & Fan, X. (2013). “Finding our time”: predicting students’ time management in online collaborative groupwork. Computers & Education, 69 , 139–147.
Xu, J., Yuan, R., Xu, B., & Xu, M. (2014). Modeling students’ time management in math homework. Learning and Individual Differences, 34 , 33–42.
Yamada, M., Goda, Y., Matsuda, T., Saito, Y., Kato, H., & Miyagawa, H. (2016). How does self-regulated learning relate to active procrastination and other learning behaviors? Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 28 , 326–343.
Young, D. G., & Hopp, J. M. (2014). 2012-2013 national survey of first-year seminars: exploring high-impact practices in the first college year (Research report No. 4) . Columbia: University of South Carolina.
Zimbardo, P., & Boyd, J. (1999). Putting time in perspective: a valid, reliable individual-differences metric. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 77 , 1271–1288.
Zimmerman, B. J. (1989). A social cognitive view of self-regulated academic learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 81 , 329–339.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2000). Attaining self-regulation: a social cognitive perspective. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation: theory, research, and applications (pp. 13–29). San Diego: Academic Press.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Risemberg, R. (1997). Becoming a self-regulated writer: a social cognitive perspective. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 22 , 73–101.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. (2012). Motivation: an essential dimension of self-regulated learning. In D. Schunk & B. Zimmerman (Eds.), Motivation and self-regulated learning: theory, research and applications (pp. 1–30). New York: Routledge.
Zimmerman, B. J., Greenberg, D., & Weinstein, C. E. (1994). Self-regulating academic study time: a strategy approach. In D. H. Schunk & B. J. Zimmerman (Eds.), Self-regulation of learning and performance: issues and educational applications (pp. 181–199). Hillsdale: Erlbaum.
Zusho, A. (2017). Toward an integrated model of student learning in the college classroom. Educational Psychology Review, 29 , 301–324.
Zusho, A., & Pintrich, P. (2003). Skill and will: the role of motivation and cognition in the learning of college chemistry. International Journal of Science Education, 25 , 1081–1094.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Dennis Learning Center, The Ohio State University, 250B Younkin Success Building, 1640 Neil Ave., Columbus, OH, 43201, USA
Christopher A. Wolters & Anna C. Brady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christopher A. Wolters .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wolters, C.A., Brady, A.C. College Students’ Time Management: a Self-Regulated Learning Perspective. Educ Psychol Rev 33 , 1319–1351 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09519-z
Download citation
Published : 27 October 2020
Issue Date : December 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09519-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Self-regulated learning
- Time management
- Postsecondary students
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Does time management work? A meta-analysis
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Concordia University, Sir George Williams Campus, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Roles Methodology, Validation
Affiliation FSA Ulaval, Laval University, Quebec City, Quebec, Canada
Roles Validation, Writing – review & editing
- Brad Aeon,
- Aïda Faber,
- Alexandra Panaccio

- Published: January 11, 2021
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066
- Reader Comments
Does time management work? We conducted a meta-analysis to assess the impact of time management on performance and well-being. Results show that time management is moderately related to job performance, academic achievement, and wellbeing. Time management also shows a moderate, negative relationship with distress. Interestingly, individual differences and contextual factors have a much weaker association with time management, with the notable exception of conscientiousness. The extremely weak correlation with gender was unexpected: women seem to manage time better than men, but the difference is very slight. Further, we found that the link between time management and job performance seems to increase over the years: time management is more likely to get people a positive performance review at work today than in the early 1990s. The link between time management and gender, too, seems to intensify: women’s time management scores have been on the rise for the past few decades. We also note that time management seems to enhance wellbeing—in particular, life satisfaction—to a greater extent than it does performance. This challenges the common perception that time management first and foremost enhances work performance, and that wellbeing is simply a byproduct.
Citation: Aeon B, Faber A, Panaccio A (2021) Does time management work? A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 16(1): e0245066. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066
Editor: Juan-Carlos Pérez-González, Universidad Nacional de Educacion a Distancia (UNED), SPAIN
Received: October 27, 2020; Accepted: December 21, 2020; Published: January 11, 2021
Copyright: © 2021 Aeon et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Introduction
Stand-up comedian George Carlin once quipped that in the future a “time machine will be built, but no one will have time to use it” [ 1 ]. Portentously, booksellers now carry one-minute bedtime stories for time-starved parents [ 2 ] and people increasingly speed-watch videos and speed-listen to audio books [ 3 – 5 ]. These behaviors are symptomatic of an increasingly harried society suffering from chronic time poverty [ 6 ]. Work is intensifying—in 1965 about 50% of workers took breaks; in 2003, less than 2% [ 7 ]. Leisure, too, is intensifying: people strive to consume music, social media, vacations, and other leisure activities ever more efficiently [ 8 – 11 ].
In this frantic context, time management is often touted as a panacea for time pressure. Media outlets routinely extol the virtues of time management. Employers, educators, parents, and politicians exhort employees, students, children, and citizens to embrace more efficient ways to use time [ 12 – 16 ]. In light of this, it is not surprising that from 1960 to 2008 the frequency of books mentioning time management shot up by more than 2,700% [ 17 ].
Time management is defined as “a form of decision making used by individuals to structure, protect, and adapt their time to changing conditions” [ 18 ]. This means time management, as it is generally portrayed in the literature, comprises three components: structuring, protecting, and adapting time. Well-established time management measures reflect these concepts. Structuring time, for instance, is captured in such items as “Do you have a daily routine which you follow?” and “Do your main activities during the day fit together in a structured way?” [ 19 ]. Protecting time is reflected in items such as “Do you often find yourself doing things which interfere with your schoolwork simply because you hate to say ‘No’ to people?” [ 20 ]. And adapting time to changing conditions is seen in such items as “Uses waiting time” and “Evaluates daily schedule” [ 21 ].
Research has, furthermore, addressed several important aspects of time management, such as its relationship with work-life balance [ 22 ], whether gender differences in time management ability develop in early childhood [ 23 ], and whether organizations that encourage employees to manage their time experience less stress and turnover [ 24 ]. Despite the phenomenal popularity of this topic, however, academic research has yet to address some fundamental questions [ 25 – 27 ].
A critical gap in time management research is the question of whether time management works [ 28 , 29 ]. For instance, studies on the relationship between time management and job performance reveal mixed findings [ 30 , 31 ]. Furthermore, scholars’ attempts to synthesize the literature have so far been qualitative, precluding a quantitative overall assessment [ 18 , 32 , 33 ]. To tackle this gap in our understanding of time management, we conducted a meta-analysis. In addressing the question of whether time management works, we first clarify the criteria for effectiveness. In line with previous reviews, we find that virtually all studies focus on two broad outcomes: performance and wellbeing [ 32 ].
Overall, results suggest that time management enhances job performance, academic achievement, and wellbeing. Interestingly, individual differences (e.g., gender, age) and contextual factors (e.g., job autonomy, workload) were much less related to time management ability, with the notable exception of personality and, in particular, conscientiousness. Furthermore, the link between time management and job performance seems to grow stronger over the years, perhaps reflecting the growing need to manage time in increasingly autonomous and flexible jobs [ 34 – 37 ].
Overall, our findings provide academics, policymakers, and the general audience with better information to assess the value of time management. This information is all the more useful amid the growing doubts about the effectiveness of time management [ 38 ]. We elaborate on the contributions and implications of our findings in the discussion section.
What does it mean to say that time management works?
In the din of current debates over productivity, reduced workweeks, and flexible hours, time management comes to the fore as a major talking point. Given its popularity, it would seem rather pointless to question its effectiveness. Indeed, time management’s effectiveness is often taken for granted, presumably because time management offers a seemingly logical solution to a lifestyle that increasingly requires coordination and prioritization skills [ 39 , 40 ].
Yet, popular media outlets increasingly voice concern and frustration over time management, reflecting at least part of the population’s growing disenchantment [ 38 ]. This questioning of time management practices is becoming more common among academics as well [ 41 ]. As some have noted, the issue is not just whether time management works. Rather, the question is whether the techniques championed by time management gurus can be actually counterproductive or even harmful [ 26 , 42 ]. Other scholars have raised concerns that time management may foster an individualistic, quantitative, profit-oriented view of time that perpetuates social inequalities [ 43 , 44 ]. For instance, time management manuals beguile readers with promises of boundless productivity that may not be accessible to women, whose disproportionate share in care work, such as tending to young children, may not fit with typically male-oriented time management advice [ 45 ]. Similarly, bestselling time management books at times offer advice that reinforce global inequities. Some manuals, for instance, recommend delegating trivial tasks to private virtual assistants, who often work out of developing countries for measly wages [ 46 ]. Furthermore, time management manuals often ascribe a financial value to time—the most famous time management adage is that time is money. But recent studies show that thinking of time as money leads to a slew of negative outcomes, including time pressure, stress, impatience, inability to enjoy the moment, unwillingness to help others, and less concern with the environment [ 47 – 51 ]. What’s more, the pressure induced by thinking of time as money may ultimately undermine psychological and physical health [ 52 ].
Concerns over ethics and safety notwithstanding, a more prosaic question researchers have grappled with is whether time management works. Countless general-audience books and training programs have claimed that time management improves people’s lives in many ways, such as boosting performance at work [ 53 – 55 ]. Initial academic forays into addressing this question challenged those claims: time management didn’t seem to improve job performance [ 29 , 30 ]. Studies used a variety of research approaches, running the gamut from lab experiments, field experiments, longitudinal studies, and cross-sectional surveys to experience sampling [ 28 , 56 – 58 ]. Such studies occasionally did find an association between time management and performance, but only in highly motivated workers [ 59 ]; instances establishing a more straightforward link with performance were comparatively rare [ 31 ]. Summarizing these insights, reviews of the literature concluded that the link between time management and job performance is unclear; the link with wellbeing, however, seemed more compelling although not conclusive [ 18 , 32 ].
It is interesting to note that scholars often assess the effectiveness time management by its ability to influence some aspect of performance, wellbeing, or both. In other words, the question of whether time management works comes down to asking whether time management influences performance and wellbeing. The link between time management and performance at work can be traced historically to scientific management [ 60 ]. Nevertheless, even though modern time management can be traced to scientific management in male-dominated work settings, a feminist reading of time management history reveals that our modern idea of time management also descends from female time management thinkers of the same era, such as Lillian Gilbreth, who wrote treatises on efficient household management [ 43 , 61 , 62 ]. As the link between work output and time efficiency became clearer, industrialists went to great lengths to encourage workers to use their time more rationally [ 63 – 65 ]. Over time, people have internalized a duty to be productive and now see time management as a personal responsibility at work [ 43 , 66 , 67 ]. The link between time management and academic performance can be traced to schools’ historical emphasis on punctuality and timeliness. In more recent decades, however, homework expectations have soared [ 68 ] and parents, especially well-educated ones, have been spending more time preparing children for increasingly competitive college admissions [ 69 , 70 ]. In this context, time management is seen as a necessary skill for students to thrive in an increasingly cut-throat academic world. Finally, the link between time management and wellbeing harks back to ancient scholars, who emphasized that organizing one’s time was necessary to a life well-lived [ 71 , 72 ]. More recently, empirical studies in the 1980s examined the effect of time management on depressive symptoms that often plague unemployed people [ 19 , 73 ]. Subsequent studies surmised that the effective use of time might prevent a host of ills, such as work-life conflict and job stress [ 22 , 74 ].
Overall, then, various studies have looked into the effectiveness of time management. Yet, individual studies remain narrow in scope and reviews of the literature offer only a qualitative—and often inconclusive—assessment. To provide a more quantifiable answer to the question of whether time management works, we performed a meta-analysis, the methods of which we outline in what follows.
Literature search and inclusion criteria
We performed a comprehensive search using the keywords “time management” across the EBSCO databases Academic Search Complete , Business Source Complete , Computers & Applied Sciences Complete , Gender Studies Database , MEDLINE , Psychology and Behavioral Sciences Collection , PsycINFO , SocINDEX , and Education Source . The search had no restrictions regarding country and year of publication and included peer-reviewed articles up to 2019. To enhance comprehensiveness, we also ran a forward search on the three main time management measures: the Time Management Behavior Scale [ 21 ], the Time Structure Questionnaire [ 19 ], and the Time Management Questionnaire [ 20 ]. (A forward search tracks all the papers that have cited a particular work. In our case the forward search located all the papers citing the three time management scales available on Web of Science .)
Time management measures typically capture three aspects of time management: structuring, protecting, and adapting time to changing conditions. Structuring refers to how people map their activities to time using a schedule, a planner, or other devices that represent time in a systematic way [ 75 – 77 ]. Protecting refers to how people set boundaries around their time to repel intruders [ 78 , 79 ]. Examples include people saying no to time-consuming requests from colleagues or friends as well as turning off one’s work phone during family dinners. Finally, adapting one’s time to changing conditions means, simply put, to be responsive and flexible with one’s time structure [ 80 , 81 ]. Furthermore, time management measures typically probe behaviors related to these three dimensions (e.g., using a schedule to structure one’s day, making use of downtime), although they sometimes also capture people’s attitudes (e.g., whether people feel in control of their time).
As shown in Fig 1 , the initial search yielded 10,933 hits, excluding duplicates.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.g001
The search included no terms other than “time management” to afford the broadest possible coverage of time management correlates. Nevertheless, as shown in Table 1 , we focused exclusively on quantitative, empirical studies of time management in non-clinical samples. Successive rounds of screening, first by assessing paper titles and abstracts and then by perusing full-text articles, whittled down the number of eligible studies to 158 (see Fig 1 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t001
Data extraction and coding
We extracted eligible effect sizes from the final pool of studies; effect sizes were mostly based on means and correlations. In our initial data extraction, we coded time management correlates using the exact variable names found in each paper. For instance, “work-life imbalance” was initially coded in those exact terms, rather than “work-life conflict.” Virtually all time management correlates we extracted fell under the category of performance and/or wellbeing. This pattern tallies with previous reviews of the literature [ 18 , 32 ]. A sizable number of variables also fell under the category of individual differences and contextual factors, such as age, personality, and job autonomy. After careful assessment of the extracted variables, we developed a coding scheme using a nested structure shown in Table 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t002
Aeon and Aguinis suggested that time management influences performance, although the strength of that relationship may depend on how performance is defined [ 18 ]. Specifically, they proposed that time management may have a stronger impact on behaviors conducive to performance (e.g., motivation, proactiveness) compared to assessments of performance (e.g., supervisor rankings). For this reason, we distinguish between results- and behavior-based performance in our coding scheme, both in professional and academic settings. Furthermore, wellbeing indicators can be positive (e.g., life satisfaction) or negative (e.g., anxiety). We expect time management to influence these variables in opposite ways; it would thus make little sense to analyze them jointly. Accordingly, we differentiate between wellbeing (positive) and distress (negative).
In our second round of coding, we used the scheme shown in Table 2 to cluster together kindred variables. For instance, we grouped “work-life imbalance,” “work-life conflict” and “work-family conflict” under an overarching “work-life conflict” category. The authors reviewed each variable code and resolved rare discrepancies to ultimately agree on all coded variables. Note that certain variables, such as self-actualization, covered only one study (i.e., one effect size). While one or two effect sizes is not enough to conduct a meta-analysis, they can nonetheless be grouped with other effect sizes belonging to the same category (e.g., self-actualization and sense of purpose belong the broader category of overall wellbeing). For this reason, we included variables with one or two effect sizes for comprehensiveness.
Meta-analytic procedures
We conducted all meta-analyses following the variables and cluster of variables outlined in Table 2 . We opted to run all analyses with a random effects model. The alternative—a fixed effects model—assumes that all studies share a common true effect size (i.e., linking time management and a given outcome) which they approximate. This assumption is unrealistic because it implies that the factors influencing the effect size are the same in all studies [ 83 ]. In other words, a fixed effects model assumes that the factors affecting time management are similar across all studies—the fallacy underlying this assumption was the main theme of Aeon and Aguinis’s review [ 18 ]. To perform our analyses, we used Comprehensive Meta-Analysis v.3 [ 84 ], a program considered highly reliable and valid in various systematic assessments [ 85 , 86 ].
In many cases, studies reported how variables correlated with an overall time management score. In some cases, however, studies reported only correlations with discrete time management subscales (e.g., short-range planning, attitudes toward time, use of time management tools), leaving out the overall effect. In such cases, we averaged out the effect sizes of the subscales to compute a summary effect [ 83 ]. This was necessary not only because meta-analyses admit only one effect size per study, but also because our focus is on time management as a whole rather than on subscales. Similarly, when we analyzed the link between time management and a high-level cluster of variables (e.g., overall wellbeing rather than specific variables such as life satisfaction), there were studies with more than one relevant outcome (e.g., a study that captured both life satisfaction and job satisfaction). Again, because meta-analyses allow for only one effect size (i.e., variable) per study, we used the mean of different variables to compute an overall effect sizes in studies that featured more than one outcome [ 83 ].
Overall description of the literature
We analyzed 158 studies for a total number of 490 effect sizes. 21 studies explored performance in a professional context, 76 performance in an academic context, 30 investigated wellbeing (positive), and 58 distress. Interestingly, studies did not systematically report individual differences, as evidenced by the fact that only 21 studies reported correlations with age, and only between 10 and 15 studies measured personality (depending on the personality trait). Studies that measured contextual factors were fewer still—between 3 and 7 (depending on the contextual factor). These figures fit with Aeon and Aguinis’s observation that the time management literature often overlooks internal and external factors that can influence the way people manage time [ 18 ].
With one exception, we found no papers fitting our inclusion criteria before the mid-1980s. Publication trends also indicate an uptick in time management studies around the turn of the millennium, with an even higher number around the 2010s. This trend is consistent with the one Shipp and Cole identified, revealing a surge in time-related papers in organizational behavior around the end of the 1980s [ 87 ].
It is also interesting to note that the first modern time management books came out in the early 1970s, including the The Time Trap (1972), by Alec MacKenzie and How to Get Control of your Time and your Life (1973), by Alan Lakein. These books inspired early modern time management research [ 21 , 58 , 88 ]. It is thus very likely that the impetus for modern time management research came from popular practitioner manuals.
To assess potential bias in our sample of studies, we computed different estimates of publication bias (see Table 3 ). Overall, publication bias remains relatively low (see funnel plots in S1). Publication bias occurs when there is a bias against nonsignificant or even negative results because such results are seen as unsurprising and not counterintuitive. In this case, however, the fact that time management is generally expected to lead to positive outcomes offers an incentive to publish nonsignificant or negative results, which would be counterintuitive [ 89 ]. By the same token, the fact that some people feel that time management is ineffective [ 38 ] provides an incentive to publish papers that link time management with positive outcomes. In other words, opposite social expectations surrounding time management might reduce publication bias.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t003
Finally, we note that the link between time management and virtually all outcomes studied is highly heterogeneous (as measured, for instance, by Cochran’s Q and Higgins & Thompson’s I 2 ; see tables below). This high level of heterogeneity suggests that future research should pay more attention to moderating factors (e.g., individual differences).
Time management and performance in professional settings
Overall, time management has a moderate impact on performance at work, with correlations hovering around r = .25. We distinguish between results-based and behavior-based performance. The former measures performance as an outcome (e.g., performance appraisals by supervisors) whereas the latter measures performance as behavioral contributions (e.g., motivation, job involvement). Time management seems related to both types of performance. Although the effect size for results-based performance is lower than that of behavior-based performance, moderation analysis reveals the difference is not significant (p > .05), challenging Aeon and Aguinis’s conclusions [ 18 ].
Interestingly, the link between time management and performance displays much less heterogeneity (see Q and I 2 statistics in Table 4 ) than the link between time management and other outcomes (see tables below). The studies we summarize in Table 4 include both experimental and non-experimental designs; they also use different time management measures. As such, we can discount, to a certain extent, the effect of methodological diversity. We can perhaps explain the lower heterogeneity by the fact that when people hold a full-time job, they usually are at a relatively stable stage in life. In school, by contrast, a constellation of factors (e.g., financial stability and marital status, to name a few) conspire to affect time management outcomes. Furthermore, work contexts are a typically more closed system than life in general. For this reason, fewer factors stand to disrupt the link between time management and job performance than that between time management and, say, life satisfaction. Corroborating this, note how, in Table 6 below, the link between time management and job satisfaction ( I 2 = 58.70) is much less heterogeneous than the one between time management and life satisfaction ( I 2 = 95.45).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t004
Moreover, we note that the relationship between time management and job performance (see Fig 2 ) significantly increases over the years ( B = .0106, p < .01, Q model = 8.52(1), Q residual = 15.54(9), I 2 = 42.08, R 2 analog = .75).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.g002
Time management and performance in academic settings
Overall, the effect of time management on performance seems to be slightly higher in academic settings compared to work settings, although the magnitude of the effect remains moderate (see Table 5 ). Here again, we distinguish between results- and behavior-based performance. Time management’s impact on behavior-based performance seems much higher than on results-based performance—a much wider difference than the one we observed in professional settings. This suggests than results-based performance in academic settings depends less on time management than results-based performance in professional settings. This means that time management is more likely to get people a good performance review at work than a strong GPA in school.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t005
In particular, time management seems to be much more negatively related to procrastination in school than at work. Although we cannot establish causation in all studies, we note that some of them featured experimental designs that established a causal effect of time management on reducing procrastination [ 90 ].
Interestingly, time management was linked to all types of results-based performance except for standardized tests. This is perhaps due to the fact that standardized tests tap more into fluid intelligence, a measure of intelligence independent of acquired knowledge [ 91 ]. GPA and regular exam scores, in contrast, tap more into crystallized intelligence, which depends mostly on accumulated knowledge. Time management can thus assist students in organizing their time to acquire the knowledge necessary to ace a regular exam; for standardized exams that depend less on knowledge and more on intelligence, however, time management may be less helpful. Evidence from other studies bears this out: middle school students’ IQ predicts standardized achievement tests scores better than self-control while self-control predicts report card grades better than IQ [ 92 ]. (For our purposes, we can use self-control as a very rough proxy for time management.) Relatedly, we found no significant relationship between time management and cognitive ability in our meta-analysis (see Table 8 ).
Time management and wellbeing
On the whole, time management has a slightly stronger impact on wellbeing than on performance. This is unexpected, considering how the dominant discourse points to time management as a skill for professional career development. Of course, the dominant discourse also frames time management as necessary for wellbeing and stress reduction, but to a much lesser extent. Our finding that time management has a stronger influence on wellbeing in no way negates the importance of time management as a work skill. Rather, this finding challenges the intuitive notion that time management is more effective for work than for other life domains. As further evidence, notice how in Table 6 the effect of time management on life satisfaction is 72% stronger than that on job satisfaction.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t006
Time management and distress
Time management seems to allay various forms of distress, although to a lesser extent than it enhances wellbeing. The alleviating effect on psychological distress is particularly strong ( r = -0.358; see Table 7 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t007
That time management has a weaker effect on distress should not be surprising. First, wellbeing and distress are not two poles on opposite ends of a spectrum. Although related, wellbeing and distress are distinct [ 93 ]. Thus, there is no reason to expect time management to have a symmetrical effect on wellbeing and distress. Second, and relatedly, the factors that influence wellbeing and distress are also distinct. Specifically, self-efficacy (i.e., seeing oneself as capable) is a distinct predictor of wellbeing while neuroticism and life events in general are distinct predictors of distress [ 94 ]. It stands to reason that time management can enhance self-efficacy. (Or, alternatively, that people high in self-efficacy would be more likely to engage in time management, although experimental evidence suggests that time management training makes people feel more in control of their time [ 89 ]; it is thus plausible that time management may have a causal effect on self-efficacy. Relatedly, note how time management ability is strongly related to internal locus of control in Table 8 ) In contrast, time management can do considerably less in the way of tackling neuroticism and dampening the emotional impact of tragic life events. In other words, the factors that affect wellbeing may be much more within the purview of time management than the factors that affect distress. For this reason, time management may be less effective in alleviating distress than in improving wellbeing.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.t008
Time management and individual differences
Time management is, overall, less related to individual differences than to other variables.
Age, for instance, hardly correlates with time management (with a relatively high consistency between studies, I 2 = 55.79, see Table 8 above).
Similarly, gender only tenuously correlates with time management, although in the expected direction: women seem to have stronger time management abilities than men. The very weak association with gender ( r = -0.087) is particularly surprising given women’s well-documented superior self-regulation skills [ 95 ]. That being said, women’s time management abilities seem to grow stronger over the years ( N = 37, B = -.0049, p < .05, Q model = 3.89(1), Q residual = 218.42(35), I 2 = 83.98, R 2 analog = .03; also see Fig 3 below). More realistically, this increase may not be due to women’s time management abilities getting stronger per se but, rather, to the fact that women now have more freedom to manage their time [ 96 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.g003
Other demographic indicators, such as education and number of children, were nonsignificant. Similarly, the relationships between time management and personal attributes and attitudes were either weak or nonsignificant, save for two notable exceptions. First, the link between time management and internal locus of control (i.e., the extent to which people perceive they’re in control of their lives) is quite substantial. This is not surprising, because time management presupposes that people believe they can change their lives. Alternatively, it may be that time management helps people strengthen their internal locus of control, as experimental evidence suggests [ 89 ]. Second, the link between time management and self-esteem is equally substantial. Here again, one can make the argument either way: people with high self-esteem might be confident enough to manage their time or, conversely, time management may boost self-esteem. The two options are not mutually exclusive: people with internal loci of control and high self-esteem levels can feel even more in control of their lives and better about themselves through time management.
We also note a very weak but statistically significant negative association between time management and multitasking. It has almost become commonsense that multitasking does not lead to performance [ 97 ]. As a result, people with stronger time management skills might deliberately steer clear of this notoriously ineffective strategy.
In addition, time management was mildly related to hours spent studying but not hours spent working. (These variables cover only student samples working part- or full-time and thus do not apply to non-student populations.) This is consistent with time-use studies revealing that teenagers and young adults spend less time working and more time studying [ 98 ]. Students who manage their time likely have well-defined intentions, and trends suggest those intentions will target education over work because, it is hoped, education offers larger payoffs over the long-term [ 99 ].
In terms of contextual factors, time management does not correlate significantly with job autonomy. This is surprising, as we expected autonomy to be a prerequisite for time management (i.e., you can’t manage time if you don’t have the freedom to). Nevertheless, qualitative studies have shown how even in environments that afford little autonomy (e.g., restaurants), workers can carve out pockets of time freedom to momentarily cut loose [ 100 ]. Thus, time management behaviors may flourish even in the most stymying settings. In addition, the fact that time management is associated with less role overload and previous attendance of time management training programs makes sense: time management can mitigate the effect of heavy workloads and time management training, presumably, improves time management skills.
Finally, time management is linked to all personality traits. Moreover, previous reviews of the literature have commented on the link between time management and conscientiousness in particular [ 32 ]. What our study reveals is the substantial magnitude of the effect ( r = 0.451). The relationship is not surprising: conscientiousness entails orderliness and organization, which overlap significantly with time management. That time management correlates so strongly with personality (and so little with other individual differences) lends credence to the dispositional view of time management [ 101 – 103 ]. However, this finding should not be taken to mean that time management is a highly inheritable, fixed ability. Having a “you either have it or you don’t” view of time management is not only counterproductive [ 104 ] but also runs counter to evidence showing that time management training does, in fact, help people manage their time better.
Does time management work? It seems so. Time management has a moderate influence on job performance, academic achievement, and wellbeing. These three outcomes play an important role in people’s lives. Doing a good job at work, getting top grades in school, and nurturing psychological wellbeing contribute to a life well lived. Widespread exhortations to get better at time management are thus not unfounded: the importance of time management is hard to overstate.
Contributions
Beyond answering the question of whether time management works, this study contributes to the literature in three major ways. First, we quantify the impact of time management on several outcomes. We thus not only address the question of whether time management works, but also, and importantly, gauge to what extent time management works. Indeed, our meta-analysis covers 53,957 participants, which allows for a much more precise, quantified assessment of time management effectiveness compared to qualitative reviews.
Second, this meta-analysis systematically assesses relationships between time management and a host of individual differences and contextual factors. This helps us draw a more accurate portrait of potential antecedents of higher (or lower) scores on time management measures.
Third, our findings challenge intuitive ideas concerning what time management is for. Specifically, we found that time management enhances wellbeing—and in particular life satisfaction—to a greater extent than it does various types of performance. This runs against the popular belief that time management primarily helps people perform better and that wellbeing is simply a byproduct of better performance. Of course, it may be that wellbeing gains, even if higher than performance gains, hinge on performance; that is to say, people may need to perform better as a prerequisite to feeling happier. But this argument doesn’t jibe with experiments showing that even in the absence of performance gains, time management interventions do increase wellbeing [ 89 ]. This argument also founders in the face of evidence linking time management with wellbeing among the unemployed [ 105 ], unemployment being an environment where performance plays a negligible role, if any. As such, this meta-analysis lends support to definitions of time management that are not work- or performance-centric.
Future research and limitations
This meta-analysis questions whether time management should be seen chiefly as a performance device. Our questioning is neither novel nor subversive: historically people have managed time for other reasons than efficiency, such as spiritual devotion and philosophical contemplation [ 72 , 106 , 107 ]. It is only with relatively recent events, such as the Industrial Revolution and waves of corporate downsizing, that time management has become synonymous with productivity [ 43 , 65 ]. We hope future research will widen its scope and look more into outcomes other than performance, such as developing a sense of meaning in life [ 108 ]. One of the earliest time management studies, for instance, explored how time management relates to having a sense of purpose [ 73 ]. However, very few studies followed suit since. Time management thus stands to become a richer, more inclusive research area by investigating a wider array of outcomes.
In addition, despite the encouraging findings of this meta-analysis we must refrain from seeing time management as a panacea. Though time management can make people’s lives better, it is not clear how easy it is for people to learn how to manage their time adequately. More importantly, being “good” at time management is often a function of income, education, and various types of privilege [ 42 , 43 , 46 , 109 ]. The hackneyed maxim that “you have as many hours in a day as Beyoncé,” for instance, blames people for their “poor” time management in pointing out that successful people have just as much time but still manage to get ahead. Yet this ill-conceived maxim glosses over the fact that Beyoncé and her ilk do, in a sense, have more hours in a day than average people who can’t afford a nanny, chauffeur, in-house chefs, and a bevy of personal assistants. Future research should thus look into ways to make time management more accessible.
Furthermore, this meta-analysis rests on the assumption that time management training programs do enhance people’s time management skills. Previous reviews have noted the opacity surrounding time management interventions—studies often don’t explain what, exactly, is taught in time management training seminars [ 18 ]. As a result, comparing the effect of different interventions might come down to comparing apples and oranges. (This might partly account for the high heterogeneity between studies.) We hope that our definition of time management will spur future research into crafting more consistent, valid, and generalizable interventions that will allow for more meaningful comparisons.
Finally, most time management studies are cross-sectional. Yet it is very likely that the effect of time management compounds over time. If time management can help students get better grades, for instance, those grades can lead to better jobs down the line [ 110 ]. Crucially, learning a skill takes time, and if time management helps people make the time to learn a skill, then time management stands to dramatically enrich people’s lives. For this reason, longitudinal studies can track different cohorts to see how time management affects people’s lives over time. We expect that developing time management skills early on in life can create a compound effect whereby people acquire a variety of other skills thanks to their ability to make time.
Overall, this study offers the most comprehensive, precise, and fine-grained assessment of time management to date. We address the longstanding debate over whether time management influences job performance in revealing a positive, albeit moderate effect. Interestingly, we found that time management impacts wellbeing—and in particular life satisfaction—to a greater extent than performance. That means time management may be primarily a wellbeing enhancer, rather than a performance booster. Furthermore, individual and external factors played a minor role in time management, although this does not necessarily mean that time management’s effectiveness is universal. Rather, we need more research that focuses on the internal and external variables that affect time management outcomes. We hope this study will tantalize future research and guide practitioners in their attempt to make better use of their time.
Supporting information
S1 checklist. prisma 2009 checklist..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.s001
S1 File. Funnel plots.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.s002
S2 File. Dataset.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245066.s003
Acknowledgments
We would like to take this opportunity to acknowledge our colleagues for their invaluable help: Mengchan Gao, Talha Aziz, Elizabeth Eley, Robert Nason, Andrew Ryder, Tracy Hecht, and Caroline Aubé.
- 1. Carlin G. When will Jesus bring the pork chops? New York, NY: Hyperion; 2004.
- 2. Lewis S, O’Kun L. One-minute bedtime stories. New York, NY: Doubleday; 1982.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 8. Boerma J, Karabarbounis L. Labor Market Trends and the Changing Value of Time [Internet]. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research; 2019 Sep [cited 2019 Dec 20] p. w26301. Report No.: w26301. Available from: http://www.nber.org/papers/w26301.pdf
- 12. Clinton B. My life. New York, NY: Knopf; 2004. https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540400003425 pmid:15545218
- 16. Pausch R, Zaslow J. The last lecture. New York, NY: Hyperion; 2008.
- 17. Google Ngram Viewer. The rise of time management. Google Books. 2016.
- 40. Southerton D. Re-ordering temporal rhythms: Coordinating daily practices in the UK in 1937 and 2000. In: Shove E, Trentmann F, Wilk R, editors. Time, consumption, and everyday life: Practice, materiality and culture. New York, NY: Berg; 2009. p. 49–63.
- 41. Gregg M. Getting things done: Productivity, self-management, and the order of things. In: Hillis K, Paasonen S, Petit M, editors. Networked Affect. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2015. p. 187–202.
- 42. Reagle JM. Hacking life: Systematized living and its discontents. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press; 2019. 204 p. (Strong ideas series).
- 43. Gregg M. Counterproductive: Time management in the knowledge economy. Durham, NC: Duke University Press; 2018.
- 46. Costas J, Grey C. Outsourcing your life: Exploitation and exploration in “The 4-hour workweek.” In: Holmqvist M, Spicer A, editors. Managing ‘Human Resources’ by exploiting and exploring people’s potentials (Research in the sociology of organizations, volume 37). Bingley, UK: Emerald; 2013.
- 53. Allen D. Getting things done: The art of stress-free productivity. New York, NY: Penguin; 2001.
- 54. Lakein A. How to get control of your time and your Life. New York, NY: Signet; 1973.
- 55. Sutherland J. Scrum: The art of doing twice the work in half the time. New York, NY: Crown Business; 2014.
- 60. Taylor FW. The principles of scientific management. New York, NY: Harper & Brothers; 1911.
- 63. Landes DS. Revolution in time: Clocks and the making of the modern world. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press; 1983. 482 p.
- 64. Martineau J. Time, capitalism and alienation: A socio-historical inquiry into the making of modern time. Boston, MA: Brill; 2015.
- 66. Alvesson M, Deetz SA. Critical Theory and Postmodernism Approaches to Organizational Studies. In: Clegg SR, Hardy C, Lawrence TB, Nord WR, editors. The SAGE Handbook of Organization Studies. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2006. p. 255–83.
- 70. Ramey G, Ramey V. The Rug Rat Race [Internet]. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research; 2009 Aug [cited 2020 Feb 27] p. w15284. Report No.: w15284. Available from: http://www.nber.org/papers/w15284.pdf
- 71. Aurelius M. Meditations. In: Eliot CW, editor. Harvard Classics vol 2. New York, NY: P.F. Collier & Son; 1909. p. 193–306.
- 72. Seneca LA. On the shortness of life. In: Hardship and Happiness. Chicago, IL: University Of Chicago Press; 2014. p. 110–34.
- 76. Doob LW. Patterning of time. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press; 1971.
- 83. Borenstein M, editor. Introduction to meta-analysis. Chichester, U.K: John Wiley & Sons; 2009. 421 p.
- 84. Borenstein M, Hedges L, Higgins J, Rothstein H. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 3. Englewood, NJ: Biostat; 2013.
- 96. Goodin RE, Rice JM, Parpo A, Eriksson L. Discretionary time: A new measure of freedom. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2008.
- 101. Burrus A. What Does Time Management Mean to You? Exploring Measures of Time Management and Group Differences [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Missouri-St. Louis; 2019.
- 109. Sharma S. In the meantime: Temporality and cultural politics. Durham, NC: Duke University Press; 2014.
Accessibility Links
- Skip to content
- Skip to search IOPscience
- Skip to Journals list
- Accessibility help
- Accessibility Help
Click here to close this panel.
Purpose-led Publishing is a coalition of three not-for-profit publishers in the field of physical sciences: AIP Publishing, the American Physical Society and IOP Publishing.
Together, as publishers that will always put purpose above profit, we have defined a set of industry standards that underpin high-quality, ethical scholarly communications.
We are proudly declaring that science is our only shareholder.
The Impact of Time Management on Students' Academic Achievement
S N A M Razali 1 , M S Rusiman 1 , W S Gan 1 and N Arbin 2
Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd Journal of Physics: Conference Series , Volume 995 , International Seminar on Mathematics and Physics in Sciences and Technology 2017 (ISMAP 2017) 28–29 October 2017, Hotel Katerina, Malaysia Citation S N A M Razali et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 995 012042 DOI 10.1088/1742-6596/995/1/012042
Article metrics
112733 Total downloads
Share this article
Author affiliations.
1 Department of Mathematics and Statistic, Faculty of Applied Science and Technology University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia.
2 Department of Mathematic, Faculty of Science and Mathematics, Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, 35900 Perak, Malaysia.
Buy this article in print
Time management is very important and it may actually affect individual's overall performance and achievements. Students nowadays always commented that they do not have enough time to complete all the tasks assigned to them. In addition, a university environment's flexibility and freedom can derail students who have not mastered time management skills. Therefore, the aim of this study is to determine the relationship between the time management and academic achievement of the students. The factor analysis result showed three main factors associated with time management which can be classified as time planning, time attitudes and time wasting. The result also indicated that gender and races of students show no significant differences in time management behaviours. While year of study and faculty of students reveal the significant differences in the time management behaviours. Meanwhile, all the time management behaviours are significantly positively related to academic achievement of students although the relationship is weak. Time planning is the most significant correlated predictor.
Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS
Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence . Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI.

Disclosure: MyeLearningWorld is reader-supported. We may receive a commission if you purchase through our links.
25 Time Management Questions for Students Who Want to Get More Done
Last Updated: 10/17/2023
By Scott Winstead
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit
- Share on Pinterest

The further you get in school, the more papers, projects, and exams you’ll have to juggle. And of course, your responsibilities outside of school will continue to demand more and more attention as you get older. The journey through education is a whirlwind of lectures, assignments, social engagements, and personal pursuits, all vying for your attention.
With so many responsibilities, is it any surprise that a report from the Anxiety and Depression Association of America found 80% of students feel overwhelmed and stressed out?
That’s why effective time management is essential for students. It can spell the difference between academic triumph and mere survival.
But what does that actually mean? How can you make sure you’re using your time wisely to handle all of your academic responsibilies? How can you be more productive at school and in all areas of your life?
As someone who’s been working in eLearning for around 20 years and seeing how students perform, I’ve learned it all starts with taking the time to assess your current situation and figure out where you need to make some changes. And that’s what these time management questions for students are designed to help you do. Heck, I use many of these same questions to help me better manage my own time in my professional and personal life.
By asking yourself the following questions and answering honestly, you can start to get a better handle on your time management skills and find areas where you need to make some improvements. As you work your way through the questions below, remember that the destination isn’t perfection, but progress.

This time management course offers clear, proven strategies to help you prioritize tasks, cut out distractions, and get more accomplished.
1. What time do you wake up in the morning?
It’s important to make sure you’re waking up with enough time to get ready for the day without feeling rushed. If you’re constantly hitting the snooze button and starting your day in a rush, skipping breakfast, and not taking the time to mentally prepare for the day, it can set the tone for the rest of the day and make it harder to focus on what’s important. Getting up just a few minutes earlier could make a big difference.
2. What is your morning routine?
Do you have a set routine that you follow each morning, or do you just wing it? Having a set routine can help you better manage your time by ensuring that you’re taking care of all the important tasks before moving on to anything else.
3. How long does it take you to get to school?
Do you give yourself enough time to get to school, or are you always cutting it close? If you’re constantly running late, it can throw off your entire day and make it difficult to focus on your studies.
4. How are you spending your time in class?
Be honest here — are you paying attention and taking good notes , or are you daydreaming and not really absorbing the material? If you’re not paying attention in class, it’s going to be tough to do well on exams or projects, and you’re going to have to spend a lot more time studying outside of class. Use your time effectively when you’re in class.
5. Do you have any free periods during the school day?
If so, how are you spending that time? Are you using it to catch up on homework or get ahead on projects, or are you just socializing and goofing off? If you’re not using your free time effectively to handle your academic responsibilities, it can be a big drain on your productivity. Manage your time wisely and take advantage of moments where you can get things done.
6. Are you taking advantage of the resources your school offers?
Your school likely offers a number of resources that can help you with your studies, including tutoring, academic advising, and the library. If you’re not taking advantage of these resources, you may be falling behind in your coursework and costing yourself a lot of time.
7. What do you do when the school day ends?
Once you get out of school for the day, how do you spend your time? Do you head straight home to work on homework, or do you go out with friends and spend hours messing around? If you’re not using your time wisely after school, it can be tough to get all of your work done.
8. How long does it take you to finish your homework each night?
It’s important to have a good idea of how much time homework takes you on average so that you can plan your evenings accordingly. If it’s taking you much longer than it should, you may need to reevaluate how you’re approaching your work.
9. Do you have a study routine?
When it comes to studying, do you just sit down and wing it, or do you have a set routine that you follow? Using the right study methods can help you make better use of your time and ensure that you’re covering all the material you need to know.
10. How far in advance do you begin working on an assignment?
Do you wait until the last minute to start an assignment, or do you begin working on it as soon as you get it? If you’re constantly waiting until the last minute right before the due date, it can lead to a lot of stress and may cause you to rush through your work and make mistakes.
11. Do you have a good space for doing your school work?
Your work environment can have a big impact on your productivity. If you’re trying to study in a cluttered and noisy space, it’s going to be tough to focus on your work. Having a dedicated study space that’s quiet and free of distractions can make a world of difference.
12. What are some common distractions that lead you to procrastinate?
Do you find yourself getting easily distracted when you’re trying to work? do you have difficulty focusing? Maybe it’s a TV in the background or a game on your phone. Once you identify your common distractions, you can start working on strategies to avoid them.
13. What are your after-school activities?
Do you participate in any extracurricular activities, such as sports, clubs, or volunteering? If so, how much time are you dedicating to these activities? While it’s important to have a well-rounded life, too many after-school activities can take away from the time you have to focus on your studies. Take a step back and look at everything you have on your plate, prioritize tasks accordingly, and cut out something if you have too much going on.
14. Are you setting aside personal time for yourself?
It’s important to have some time for yourself outside of school and work. Whether it’s time to relax, watch TV, or go out with friends, make sure you’re taking some time for yourself each day. If you’re constantly working and never taking a break, it can lead to burnout.
15. How do you feel about your current time management skills?
Do you feel like you’re managing your time well, or are there areas you know you need to improve? If you’re not happy with your current skills, start brainstorming some ways you can make changes. Time management is a skill that takes practice, so don’t be discouraged if it doesn’t
16. Are there things you wish you could do but don’t have the time?
Do you have any hobbies or interests that you’re not able to pursue because of a lack of time? If so, start thinking about ways you can incorporate them into your life. Whether it’s taking up a new hobby or making time for an old one, find ways to fit the things you love into your schedule.
17. What are your goals for the future?
Do you have any specific goals related to time management that you want to achieve? Maybe you want to be able to finish your homework in less time or get better grades. Whatever your goals may be, start thinking about how you can achieve them.
18. Are there any changes you need to make in order to reach your goals?
If you have goals related to time management, there may be some changes you need to make in order to reach them. Perhaps you need to start setting aside more time for studying or working on assignments. Whatever the case may be, start making a plan for how you can reach your goals.
19. What time do you get to sleep each night?
It’s important to get enough sleep, but if you’re staying up too late it can take away from the time you have to focus on your studies. Make sure you’re going to bed at a reasonable hour so you can get enough rest and feel good the next day.
20. How do you typically spend your weekends?
Do you spend your weekends relaxing, or do you use them to catch up on work? If you’re spending most of your weekends working, it’s important to find a balance. Make sure you’re taking some time for yourself so you don’t get too burned out.
21. How do you prioritize your tasks?
Do you have a system for prioritizing your tasks? If not, it’s something you may want to consider. Having a plan for how you’ll tackle your work can help you stay organized and on track.
22. How would you rate your level of stress on a typical day?
Do you find yourself feeling stressed out often? If so, it’s important to find ways to reduce your stress. Maybe you need to start setting aside more time for relaxation or exercise. Or maybe you can take a stress management course online to learn techniques for reducing your stress. Whatever the case may be, make sure you’re taking care of yourself both mentally and physically.
23. How do you feel about your current workload?
Do you feel like you have too much on your plate? If so, it’s important to find ways to lighten your load. Maybe you need to start saying no to some commitments or delegate some tasks to others. Whatever the case may be, make sure you’re not taking on more than you can handle.
24. What are some things you can do to lighten your workload?
If you’re feeling overwhelmed by your current workload, there are some things you can do to make it more manageable. Perhaps you need to start setting aside more time for each task or break down your work into smaller chunks. Whatever the case may be, find ways to make your workload more manageable
25. Are you happy with how you’re currently spending your time?
It’s important to make sure you’re spending your time in a way that’s fulfilling and satisfying. That doesn’t mean you won’t have to do things you don’t want to do sometimes, but it does mean making sure you’re not sacrificing your happiness for other things. If you’re not happy with how you’re currently spending your time, start thinking about ways you can make changes. Maybe you need to start setting aside more time for the things you enjoy or find ways to incorporate your interests into your daily life.
A Final Word on Time Management Questions for Students
By taking the time to truly assess your relationship with time, you can set yourself up for success both now and in the future.
If you find that you need to make some changes, don’t be afraid to start small, incorporating simple productivity tips students can use to make a big impact.
I also highly recommend checking out the online course “ Time Management for Boosting Productivity ”. With this online time management class , you can learn some highly effective tactics for prioritizing tasks and getting more done. The time management techniques you’ll learn will help you set realistic goals and develop a productive routine.
Remember, the goal is to find what works best for you and your unique situation. With that in mind, don’t hesitate to experiment until you find a time management system that works for you.
Have any thoughts on these time management questions for students? Any questions you’d add to the list? Let us know by commenting below.
How to be More Productive at School: 12 Key Tips
The 9 best online personal development courses (2023 rankings), leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Exploring Students Attitude toward Time Management on Academic Pursuit (A Case Study of Gombe State University)

2023, AFRICAN JOURNAL OF EDUCATIONAL FOUNDATIONS
This study explored student attitude toward time management on their academic pursuit in Gombe state university. Descriptive survey research design was used for the study. The population of the study comprised of 14,532 in which 375 were used as the sample for the study. Four-point rating scale questionnaire consisting of 21 items were used for data collection. Data collected were analyzed using mean and Standard deviation. The result showed that a positive cognitive attitude of students towards time management on academic pursuit in Gombe State University. The result also revealed low affective attitude and poor behavioral attitude of students toward time management on academic pursuit in Gombe State University. It was recommended that Students should deliberately incorporate understanding of time and understanding of the things that occupy time with positive working habits, which will improve their academic pursuit. The universities should also introduce and encourage behaviour Engagement through activities that deliberately attracts efforts, persistence, attention and concentration on student’s academic pursuit.
Related Papers
Kehinde S . Busari
The problem investigated in this study was the relationship between students’ time management strategies, study habits and academic performance in Osun State Secondary Schools and the main purpose was to carry out the study titled “Students’ time management strategies, study habits and academic performance of secondary school students in Osun State” to help improve students’ learning and academic performance. Three research questions were asked, three null hypotheses were formulated that guided the study. Proportional, simple and stratified random sampling techniques were used in selecting 1920 respondents from 96 Osun State senior secondary schools in 240 Osun State senior secondary schools. Students’ academic performance pro-forma, students’ time management strategies questionnaire and students’ study habit questionnaire were used in the study. The instruments were reliable at the correlation coefficients of 0.757 and 0.733 for time management strategies and study habit respectively and were both significant at p < 0.05 indicating the consistency of the instruments for the study. The minimum, maximum value of responses, mean and standard deviation were used to analyse the research questions while the hypotheses were analysed using the multiple regression analysis statistics and the Pearson Product-Moment Correlation statistics. The value of students’ academic performance ranged from the minimum performance of 1.00 and the maximum performance of 5.00 and the average mean of 3.44 and standard deviation of 1.284 indicating that most of the students have at least 5 credits with either English language or mathematics with other relevant subjects. The main result of the study indicated the relationship of students’ time management strategies and students’ study habit with the academic performance of students in Osun State Secondary Schools with F = 2421.902 and significant at P < 0.05. The result showed the significant contribution of time management strategies with ß = 0.669; t = 27.092; p < 0.05 while the contribution of study habit stood at ß = 0.198; t = 8.024; p < 0.05. It was also found that there is a significant relationship between students’ time management strategies and academic performance in Osun State Secondary Schools with F = 958.345 and significant at P < 0.05.Study habit variables also as an independent variable has a significant relationship with the students’ academic performance in Osun State Secondary Schools with F = 1117.372 and significant at P < 0.05 while cramming and guessing of examination questions from the study habit reportedly have negative and significant correlation with academic performance. It was concluded that if the students practice effectively the time management strategies and adopt good study skills as a habit, their academic performance will improve. It was recommended in the study that time management strategies and study habits should be taught in the classroom to help students get familiar with them and practice them. Students should practice effectively the time management strategies and adopt good study skills as a habit and the excessive use of cramming and guessing of examination questions as study habit should be discourage.
International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research
Abaikpa U D E M E Anthony , Cornelia D Thomas
The study was designed to examine the relationship between time management and achievement of academic performance in Trinity Polytechnic, Uyo, Akwa Ibom State. To achieve this objective, survey research design was adopted for this study. The population of the study consisted of the nine departments of the institution with a sample size of 90. The study utilized a multi stage (random and purposive sampling techniques). The instrument used for data collection was Time Management and Achievement of Academic Performance Questionnaire (TMAAPQ). The questionnaire was used to obtain information with regards to independent variables. Tables, simple percentage and Pearson Product Moment Correlation Coefficient were adopted as analytical tools for this study. Three hypotheses were formulated and tested at 0.05 level of significance using tables and Simple percentage to answer the research questions and Pearson Product Moment Correlation Coefficient to test the hypotheses. The findings revealed that there is positive significant relationship between time management and academic performance of Trinity Polytechnic, uyo,
Al-Hikmah Management Review
Sodiq Babatunde
Deficiency in students' academic performance has become an issue of concern in the academic environment as the performance of these students suffer in relations to effective timing and lack of timely completion of school works and poor overall academic result. Hence, this study aimed at examining the effect of time management on the academic performance of students in selected universities in Kwara State, Nigeria. Additionally, this study has an accumulated population of seventy-two thousand (72,000) drawn from the three selected universities in Kwara State. However, a sample size of 382 was arrived at using the Krejcie and Morgan's Table of sample size. Also, this study employed the close ended questionnaire and retrieved two hundred and ninety-five (295) copies of questionnaire out of the 382 copies distributed. Furthermore, this study analysed the gathered data using the multiple regression analysis with the aid of Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, version 20). Thus, this study revealed that time management through effective prioritising and scheduling of activities by students have significant effect on students' timely completion of assignments and good CGPA achievements and in turn affect academic performance 2 2 with R of .635 (Sig. .000) and R 616 (Sig. .000) respectively. However, this study concludes that time management does influences students' academic performance in selected universities in Kwara State. Hence, this study recommends that students should pay attention to scheduling and prioritising tasks and also concentrate on important tasks in order to increase their academic performance via timely completion of assignments and CGPA accomplishment. Lastly, this study also recommends that students should make out a list of tasks to be attended to inform of schedules and to be supported with specific time bound attached to them, taking into consideration the major and minor tasks with priority as these will enhance their academic performance.
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Cornelia D Thomas
Journal of Business and Social Review in Emerging Economies
Ilyas Sharif
Effective time management leads to greater academic performance and reduces stress, strain and anxiety among students, however, students facing difficulties to keep a balance between their academic life and personal-social life. This study aims to examine the self-perceptions of undergraduate students’ time management behaviour by using Time Management Behaviour Scale (TMBS) developed by Macan, Shahani, Dipboye and Phillips (1990). The scale consisted of 34 rating items ranges from very often true to seldom true. The population of the study consisted of all undergraduate students studying in the academic session 2018-19 at public sector general category universities in Malakand division. By using stratified sampling technique a sample of 1050 undergraduate students were selected from the sampled universities. Students were also asked to provide their CGPA in their previous semester. Both descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the data. It was found that prospect...
Journal of Human Resource and Leadership
Bernice Tsitsia
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to examine the extent of effective time management practices of the teacher-trainees in the Colleges of Education in Ghana. Methodology: The population of the study comprised teacher-trainees (students) of the Public Colleges of Education in the Volta Region of Ghana. Two Colleges were chosen in the region based on convenience sampling technique. In all, a total of 336 participants completed the study survey questionnaire. Statistical data analysis was carried out using the Jamovi Statistical Data Analysis (JSDA) tool and the Microsoft Excel Application package. The instrument was pilot-tested on thirty students. The Cronbach’s Alpha (α) reliability analysis measures were computed. The returned α values obtained on the constructs include 0.95, 0.97 and 0.98, and with the overall α as 0.91. Findings: The findings revealed that the existence of time management strategies to check students’ time consciousness is of low rate in the Colleges. The r...
The British Journal of Administrative Management
Prof AVR Pandian , Aschalew Mulugeta
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of time management practicessuch as level of general time management behavior, attitude towards time management and goal setting behaviors (long range planning and short range planning) of the students ontheir academic achievementin Dire Dawa University. For this purpose, the researchers have selected a sample 610 students using stratified proportionate random sampling techniquefrom the six constituent colleges of
Research on humanities and social sciences
Juliana Dinko
The study was conducted in Nyankpala Campus of the University for Development Studies. The study examined the implementation/utilization of prioritization, planning and avoidance of procrastination as time management skills. The study used the descriptive survey. Proportional and simple random sampling techniques were used to select two hundred and twenty (220) level hundred students from a total of 476. Questionnaire was used to collect data from the respondents using a 5 point Likert-type scale ranging from 5 (strongly agree, SD), 4 (agree, A), 3 (not sure, NS), 2 (disagree, D) to 1 (strongly disagree, SD). The data were collected and analyzed using frequencies, percentages, means and standard deviations with the help of SPSS. A criterion score of 3.50 was used to compare with the mean of means to determine whether a time management skill was effectively utilized/ implemented or not by the students. The study revealed that prioritization and planning as time management skills we...
S i n g a p o r e a n J o u r n a l o f B u s i n e s s Economi c s and Management
Abaikpa U D E M E Anthony
The study examined the relationship between time planning and academic performance in Ritman University, Ikot Ekpene, Akwa Ibom State. A survey research design was adopted for the study. A sample of 228 respondents was drawn from a population of 600 using Taro Yamane's scientific sampling technique. For the objectives of the study to be achieved, four hypotheses were formulated and tested. The study utilized structured questionnaire and interview as major instruments for data collection. 240 questionnaires were distributed and 228 were usably returned. Data collected were analyzed using simple percentage and ordinal logistic regression. Results showed that, all the independent variables maintained insignificant relationship with academic performance in Ritman University, Ikot Ekpene, Akwa Ibom State. It was recommended that, students should have realistic expectations, which can decrease pressure, stress, anxiety and imbalance sense of well-being for them to perform at their best academically, students should avoid distracting factors such as noise or visual stimuli, or internal factors, such as thoughts or emotions whether from multitasking, technological devices, environmental factors, or non-academic activities for effective academic performance, students should manage interruptions effectively through good communication skills, planning, and the ability to prioritize tasks and activities. Finally, it was recommended that students should avoid procrastination by timely task completion, decreased stress levels, increased motivation and proper time planning management to achieve academic goals.
RELATED PAPERS
Elsa Sonya carentina
Miqdam Tariq Chaichan
Der Ophthalmologe
D. Pauleikhoff
Angel Mateos
Novas Reflexões Indigenistas
Rodrigo Ferreira Barros
Willy Putranta
Joaquim Fidalgo
Phill Davis
Placenta and Trophoblast
Norberto Mendoza Gonzalez
flavio bocarde
Alek Tarkowski
Julia Littell
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Juan Jimenez Felix
Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
The British Journal of Radiology
Dr Rahul Krishnatry
Francesco Graziano
Agricultura Sociedad y Desarrollo
Nancy Miguel
Dr. Sacide Çobanoğlu
Marine Pollution Bulletin
Ahmad Ismail
Nurse Media Journal of Nursing
Wenny Trisnaningtyas
Journal of Child Neurology
anna chilosi
tyghfg hjgfdfd
The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries
Ujjwala Gaikwad
Astrid Hamm
Journal of Biological Chemistry
Marzena Pazgier
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
The Daily MBA
Tips, Tools, and Techniques to be a Better Entrepreneur
Time-management Lessons for Research Students
September 14, 2020 Jarie Bolander

It is well known that those who are involved in the field of research multitask in a very competitive environment – they are responsible for several aspects of research. Despite trying their hardest to be in the headspace that allows them to boost their productivity to the maximum, researchers may well come across distractions that can hamper their efficiency.
This calls for strategized time management, which helps students retain focus while they work and hence boosts their productivity. Making sure and evaluating that one is making the most out of the precious time they have allows a student in the field of research to identify whether or not they are making progress. Additionally, they can even rectify their mistakes and figure out areas of improvement.
Eventually, every research student will be required to write a paper – a dissertation, thesis , an essay, whatever it may be. Sometimes, they may have trouble understanding the topic that they are assigned or may just be in a pinch regarding the time that they have been allotted. To help them out, there are several theses writing services that are available online that can ease their troubles, execute the main theme, and help them collate their ideas as a whole.
It is very important for students to invest their time and money in a trusted vendor, one that offers quality, legitimacy, and value for money. Ultimately, the work the produce will have an enormous impact on their future career ! It’s a good practice to request them to show you some of their previous work so that you know exactly what you are signing up for. There are also some sites available online that offer proofreading help – so that you can ensure that your write-up is free of errors and plagiarism!
Here are a couple of tips and strategies that you can keep in mind and implement as a research student to help you optimize the time you are given!
Table of Contents
1. Set Realistic and Attainable Goals
The first step to identifying goals or objectives is to link them with a defined process that you can follow through. They should be S.M.A.R.T – specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound.
Determine the factors that are directly under your control and do not waste time and effort chasing after those that aren’t – this helps you be more capable of actually completing the goals you have assigned for yourself.
For a long term plan, you can develop goals for things like scholarships, and for the short term, list down activities and achievements that you can attain within the near future. These will accrue to benefit you in the long term.
Make sure to periodically review your goals and identify if you have successfully been able to achieve them, or if there are certain obstacles in your path that prevent you from doing so.
2. Optimize your planning
One of the best tried and tested methods that organized students use to plan out their daily activities is to create a To-Do list. This helps them keep track of what needs to be done and also check off completed tasks.
Breaking down tasks that require multiple steps for completion helps manage deadlines in a more easy manner. You can also keep in mind to collect resources that are required for your work beforehand so that you have ample time to actually focus on your work.
Creating a detailed timeline of activities, jotting down notes after the completion of each session, and seeking assistance early on in the process all comprise of processes that should be done away with to help you stay on top of your schedule.
3. Prioritize!
Acknowledging that your word is of foremost importance will go a long way. Additionally, arranging the various tasks you have by their respective order of priority helps in being consistent with all your goals – this also helps you by not exhausting your energy in relatively unimportant tasks.
Understand your right to say “no” – you will come across several opportunities and requests that you may or may not be able to cater to. It’s alright to sometimes put your needs and responsibilities first.
4. Maintain and focus on a research program
Several options online allow you to create a schedule on an e-calendar that can be accessed by your friends and family so that they know when you are occupied – you can block sections for the time of the day during which you are taking part in research and related scholarly activities.
When you go to meet with other people, make sure that your appointment is limited by time – and that they understand your value for it.
Try to engage your fullest in activities that are in support of and supplement your academic research. Do hands-on work that furthers the effort you put in.
5. Manage potential distractions
Try and set up a workspace that is free from incoming distractions. While you devote a specific part of the day for research, try to switch to the Do Not Disturb feature of your phone – that silences all incoming calls and text messages.
It’s best to have the materials and tools you need for work set up and ready well in advance so that you are not spending time fumbling and looking for them.
Keep this in mind – although multitasking comes with its own set of charms, it is ultimately bound to set you up for unnecessary distractions and can quite possibly hamper your productivity .
6. Be smart about planning your workday
Working all day and neglecting the importance of good sleep and healthy eating will inadvertently cause burnout and make you tired less than halfway through the metaphorical marathon. Understand and imbibe the importance of your good health, incorporate exercise into your daily regimen. Also, ensure that you have sufficient time to relax and reboot for the next work session!
7. Analyze progress and time management strategies periodically
The reassessment of productivity after completing your research will help you better organize your work in the future. You will notice an increase in your efficiency and quality of work. Major goals should get taken looked at at least on a quarter-annum basis.
You can even consider investing in project management software that is quite readily available online.
8. Reward yourself for your achievements
Last, but most definitely not the least, rewarding yourself after the completion of tasks, however small, acts as a psychological incentive for continuing to improve your efforts in upcoming tasks.
So go ahead, enjoy that pint of your favorite ice cream, or binge-watch yet another episode of that show!
Author Bio:-
Mary Jones is the co-founder and editor-in-chief at TopMyGrades, which focuses on career counselling for university students in the US, Canada, UK and Australia. Mary also provides help with assignments for University students as an online service to guide them in with a range of University courses and certifications. When free, she loves to read inspirational novels and biographies.
Share this:
College & Research Libraries News ( C&RL News ) is the official newsmagazine and publication of record of the Association of College & Research Libraries, providing articles on the latest trends and practices affecting academic and research libraries.
C&RL News became an online-only publication beginning with the January 2022 issue.
C&RL News Reader Survey
Give us your feedback in the 2024 C&RL News reader survey ! The survey asks a series of questions today to gather your thoughts on the contents and presentation of the magazine and should only take approximately 5-7 minutes to complete. Thank you for taking the time to provide your feedback and suggestions for C&RL News , we greatly appreciate and value your input.
Jeanine Mazak-Kahne is associate professor at the Indiana University of Pennsylvania History Department, email: [email protected] .
Theresa McDevitt is government information and outreach librarian at Indiana University of Pennsylvania, email: [email protected] .
Lorilie Blose is currently a student in the Clarion University Department of Information and Library Science, email: [email protected] .
ALA JobLIST
Advertising Information
- Preparing great speeches: A 10-step approach (218608 views)
- The American Civil War: A collection of free online primary sources (201905 views)
- 2018 top trends in academic libraries: A review of the trends and issues affecting academic libraries in higher education (77728 views)
Jeanine Mazak-Kahne, Theresa McDevitt, and Lorilie Blose
Academic Libraries and Public Art
Engaging Students in a Timely Discussion
Jeanine Mazak-Kahne is associate professor at the Indiana University of Pennsylvania History Department, email: [email protected] . Theresa McDevitt is government information and outreach librarian at Indiana University of Pennsylvania, email: [email protected] . Lorilie Blose is currently a student in the Clarion University Department of Information and Library Science, email: [email protected] .
© 2024 Jeanine Mazak-Kahne, Theresa McDevitt, and Lorilie Blose
A cademic libraries are dynamic institutions that are constantly changing in response to the needs and wants of their users. At the same time, they are also the offices that house the institution’s archives and are responsible for preserving the records that document the institution’s past. While they strive to adopt best practices consistent with student needs, they also work to protect and preserve the past. Such roles can be at odds.
What do libraries do when current student and administrative priorities, tastes, and institutional missions clash with their interest in preserving the past? Are libraries’ users best served by exclusively supporting current taste and initiatives, or does preservation of the past serve students and institutions more? Can libraries use existing historic places to share significant historical stories about their institution and still be perceived as current and attractive? These questions are ones that librarians might struggle with, but they do not have to struggle alone.
Academic libraries exist in colleges and universities that are staffed by discipline-specific experts and the students who are training in these disciplines. Librarians, who work daily with faculty and students, have a ready opportunity to seek advice from both seasoned and budding experts and include them in discussions on authentic dilemmas that libraries face. Collaboration may result in more informed decision-making, as well as provide educational and professional benefits for students as they build work skills, develop more impressive vitas, and become more deeply engaged in their learning.
Public history programs provide students with civically engaged instruction, often incorporating practical projects into traditional classroom learning. Public history fields include librarianship and/or encourage strong relationships with libraries and librarians not only as a source of research, but also as tied to their nature as being public service–oriented. Both have a concern for ensuring information is preserved and shared, and shape community and identity, in shared, as well as unique ways.
During the 2022–2023 academic year, an Indiana University of Pennsylvania Libraries issue related to historic public art was brought to faculty and students with an expertise in public history when seeking a practical solution to a real-world problem. This article will describe the problem, the collaboration, and the manner in which the service-learning activity at once benefited the library, faculty, and students.
Mural tracing the evolution of communications, located in a stairwell of the IUP Stabley Library. The mural was installed c. 1960s by student and artist Wayne Hawxhurst. Photo by Rhonda Yeager.
The People and the Issue
Indiana University of Pennsylvania (IUP) is a mid-sized public university in Western Pennsylvania that began as a Normal School in 1875 to prepare teachers for common schools. Over the years, it developed into a university with an R2 or High Research Activity classification. In the summer of 2022, IUP Libraries were renovated to support student success by physically uniting a number of campus support services and creating a Learning Commons in the library facility. In the course of the renovations, a stairway previously available only to staff was again opened to the public and a mural painted in the late 1960s was rediscovered. The mural was painted as part of a course assignment by a graduate student who loved the library. It illustrated the evolution of information storage and sharing from the beginning of time to the 1960s. Although it survived for more than 50 years, in the fall of 2022 the new renovations and resulting altered traffic patterns drew attention to the mural and led some to question whether it should be preserved or painted over. Interesting in its time, and related to the library’s current and historical mission, it was not consistent with the more minimalist and standardized style of the renovated building. The question arose: should it be painted over, or should it be preserved?
Public History Instruction and Libraries
Theresa McDevitt is a librarian who has a PhD in history. Over the years she has developed several history-based initiatives in the library and university communities and long served as the embedded librarian for the History Department. In this role, McDevitt has worked closely with Jeanine Mazak-Kahne, a public history professor, to develop authentic public history assignments based upon existing local history records. Mazak-Kahne considers this relationship as essential in providing critical instruction to public history students, from information literacy to research practices in local history.
Instruction in public history is anchored in understanding and fostering the preservation of cultural heritage, whether it be on the local level or a national scale. Course materials and faculty instruction involve a historical understanding of community and memory, especially that fostered by cultural and heritage objects created (such as public art or memorials) for a given purpose and examining how purpose and meaning change over time. In contemporary discussions, the weight has fallen on monuments and memorials. Discussion is often lively and reflective; however, for many, these issues are abstract as students are removed by space and time from the objects and the surrounding debates.
Also critical to public history instruction is the understanding of community and memory. While typical case studies examined in the classroom are often part of larger debates over a national identity, in reality, peoples’ lives are most often rooted in the local identity, community, and memory. As students are part of a university community, public history professors recognize that student learning and engagement with material deepens when an understanding of place, identity, and memory is drawn from their immediate surroundings. This leads to the development of connections to the community in which they are immersed in new ways. Through projects that stem from authentic local issues, students apply what they have learned in the classroom to their immediate, discuss identity, memory, and community values and how they have changed over time.
Students in the IUP public history program comprise multiple disciplines from history and anthropology to art and English. Students continue to work in a variety of fields, including historic sites and museums, but also in archives and libraries, and they benefit from developing an understanding of how information is preserved and used in these different organizations. Therefore, it is an ideal situation to work with the embedded librarian and university library to develop authentic applications of theory at every opportunity possible.
The Assignment
Discussion of whether the library mural should be painted over came just at the time when instruction in the public history course shifted to the meaning of memory and identity as preserved and expressed in public monuments, memorials, and art. In this course, students are encouraged to think about how the meaning of public objects change over time and how evolving meaning and understanding of our past causes us to reinterpret these objects. They also seek to explore how objects have different meanings within the community and how public historians must navigate and negotiate these meanings among different groups and provide professional insight when called upon.
McDevitt and Mazak-Kahne felt that the discussion of whether the mural should be preserved or painted over would be a good authentic assignment for students. Students in two public history classes, Introduction to Public History and History Museums and Historic Sites, visited the library and read about the mural’s history in an alumni newsletter article. They were then asked to call upon what they had learned so far to provide advice to the libraries on the disposition of the mural. The mission of the libraries was shared, and the historical value of the mural and possible significance of its having been painted by an alumnus was considered. They were able to recommend that it be preserved or painted over. If they chose the latter, they were asked to suggest ways that the historical information intrinsic to the artifact could be preserved. Discussion prompts included those related to historical significance, historical content accuracy, artistic quality, and impact of ease of navigation when the space might be used for navigational signs.
While considering this real-world dilemma, they were asked to consider what the historical significance of the content of the mural was, and if it was accurate, and if that mattered. The students participated actively in the discussion, clearly drawing upon their training, and raised unanticipated issues that led to a deeper consideration of not just the mural, but of all public art in the library.
Some of the students in the classes were so intrigued with the mural that they volunteered to look more into its history. They wrote up their findings for library administration and prepared background documents that will be preserved in the Special Collections Department. They also provided wording for a plaque for the mural should it be preserved.
In reflecting on the assignment, Mazak-Kahne felt that the mural lesson enhanced student learning, immersing them in the immediate relationship between public art, public engagement, and institutional memory. She feels that it is important for students to learn that life is messy and that no solution is perfect, while giving them practice in making decisions for the common good, while not dismissing the past. She argues that engagement with this real-world problem helps students gain experience that may help them assess the complicated circumstances that professionals encounter in their field.
Based on this success, Mazak-Kahne intends to build upon this project in the future. IUP’s public history program spans multiple courses, and it is often the case that a project started in the Intro class is carried into the archives, museums, oral history, digital history, and family and local history courses. The documentation created during this project will, at the very least, be used to create a digital exhibit that will be housed on the program’s website, currently under construction.
Students who worked on the assignment echoed Mazak-Kahne’s sentiments. They reported that the mural project gave them insight and hands-on experience that corresponded to their field of interest, public history, and offered them a glimpse into the work often found within museums and archival sites.
They also agreed that the investigation of the mural led them to deepen their understanding of historical research by conducting thorough research into various primary and secondary sources in a manner that an actual public historian would. Although it was challenging, they felt that translating discovered information into an accurate and unique plaque strengthened their ability to communicate historical information effectively and efficiently.
Lorilie Blose, a student in the class, wrote, “Throughout the project, I learned about the meticulous research required to understand art and artifacts, the careful decision of what to preserve, and the significance of accurately documenting and contextualizing historical objects and art. . . . This hands-on experience helped me grasp the intricate workings of these institutions, preparing me for potential future roles in public history.” She continued that it “enhanced my academic experience but also gave me invaluable insights into the operational aspects of public history. Such projects help to bridge the gap between theory and practice, preparing students for careers in history and other related subjects.”
For the immediate future, the mural will continue to grace the walls of the stairway in the older part of the library building, and the students’ plaque text will be mounted near it in the stairway. Based on this experience, the curator of the University Museum was inspired to ask interns working at the University Museum the following semester to write descriptions for more of the art items in the library.
The decision of what to do with the historical mural presented a challenge to library personnel. Like most challenges though, it offered opportunities for learning and growth. By including history professors and students as advisors in the discussion-making process, librarian learning was extended, and students and faculty benefited as well.
Article Views (Last 12 Months)
Contact ACRL for article usage statistics from 2010-April 2017.
Article Views (By Year/Month)
© 2024 Association of College and Research Libraries , a division of the American Library Association
Print ISSN: 0099-0086 | Online ISSN: 2150-6698
ALA Privacy Policy
ISSN: 2150-6698
Health Science Center
What Can we help you find?
Popular Searches
- Academic Calendar
- Study Abroad
- Majors & Minors
- Request Info

UT Tyler Health Science Center
Build a healthier tomorrow.
Home to the region’s only academic medical center, The University of Texas at Tyler Health Science Center is one of the five campuses of UT Tyler. Two of UT Tyler’s four health-related schools have a presence on this campus: the School of Health Professions and the School of Medicine.
Campus History

Our Beginnings


Joining the University of Texas System

A Name Change

New Programs

Campus Programs and Facilities
The UT Tyler Health Science Center facility offers an array of crucial medical and healthcare education resources, fostering an environment dedicated to excellence in education. From cutting-edge simulation labs to dedicated research spaces, every aspect of the UT Tyler Health Science Center is designed to enhance the educational experience. This dynamic campus is not just a hub for learning; it’s a catalyst for progress in healthcare education and a testament to UT Tyler's commitment to shaping the future of healthcare in the East Texas region.

Office of Health Affairs

School of Health Professions

School of Medicine

Center for Biomedical Research
Simulation in Medicine and Immersive Learning Experience Center

Watson W. Wise Medical Research Library

Public Health Laboratory of East Texas

UT Health North Campus Tyler (UTHET)

HOPE Cancer Center

A Regional Leader in Health Research
UT Tyler pioneers solutions to improve health. Several research centers, including the Center for Mycobacterial Treatment and Discovery and the Center for Biomedical Research, are housed on this campus. The centers build on our history of innovative treatments for lung disease and focus on the health concerns of rural populations through projects funded by agencies like the National Institutes of Health and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Students benefit from hands-on research opportunities and instruction informed by the latest developments in the field.
Dr. Maolin Lu
Assistant Professor of Cellular and Molecular Biology
Meet Professor Lu
Community Outreach and Engagement
Ut health east texas.
In its regional network of hospitals, clinics and other facilities, UT Health East Texas delivers world-class care to thousands of patients each year while conducting clinical trials and training the next generation of professionals through UT Tyler’s unique programs. The UT Tyler Health Science Center is home to UT Health North Campus Tyler .
Public Health Programs
Faculty, staff and students at the UT Tyler Health Science Center campus connect their expertise with local community needs to assist traditionally underserved populations through an array of health and outreach programs, including behavioral health telemedicine services for rural populations, cancer screenings, parental education, lifestyle changes and more.
Regional Health Resources
To strengthen regional healthcare, we train community health workers, promote healthcare careers in underrepresented communities and support community health education and development efforts.
Connect With Us
The university of texas at tyler health science center.
Phone: 903.877.7777
We’re pioneering the future of healthcare in East Texas. Find out how you can join us.
11937 U.S. Hwy. 271 Tyler, TX 75708-3154

Discover CALS
See how our current work and research is bringing new thinking and new solutions to some of today's biggest challenges.
- Agriculture
- Applied Economics
- Climate Change
- Communication
- Environment
- Global Development
- Health + Nutrition

Rethinking the issue of solid household waste in Ethiopia
The Humphrey PACT (Practitioner - Assistant - Collaborative - Training) Program pairs undergraduate students in Global Development with Hubert H. Humphrey Fellows to work on a research endeavor in the fields of agriculture, rural development, and natural resource management. In this bilateral exchange, each undergrad is assigned as a research assistant, contributing to the Humphrey Fellow’s work from their home countries. Humphrey Fellows, who are mid-career professionals from around the world, gain support from students, while students get direct experiences with real-world development projects.
In this field note, Semira Beyan (Humphrey Fellow from Ethiopia) and Sadie Groberg ‘24 (Global Development), reflect on their research partnership which focused on rethinking the management of household solid waste in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Specifically, Semira and Sadie examined the methods of disposal and management which are employed by residential condominiums in the city. Together, they prepared a grant proposal aimed at reframing the way that individuals and systems approach waste management.
What are the big challenges that your PACT project confronted?
Sadie: The issue of improper management of solid waste is one that significantly impacts the health and wellbeing of Addis Ababa’s residents. Due to inadequate collection, organization, and treatment practices, the city lacks an effective system for removing waste from households. Until this issue is addressed through policy reforms and other interventions, the people of Addis Ababa will continue to suffer the consequences on their health and surroundings.
More than 60% of communicable diseases in Ethiopia are significantly linked to poor environmental conditions, particularly related to unsafe water and inadequate sanitation and hygiene. This high percentage underscores the critical impact of environmental factors on public health in the country.
When we say “domestic” or “household” waste, this refers to food scraps, ash, plastics, paper, packaging and any other household byproducts. As Addis Ababa's population grows rapidly, this waste is being produced in increasing quantities. The city's waste management system is overwhelmed, with only 65% of the daily waste generation actually being collected. The remaining 35% is either improperly dumped or accumulates around residences.
Through our research review, Semira and I identified a number of root causes to this issue — mainly, the lack of strong infrastructure, low enforcement of regulation, and lack of awareness about proper management. As a result, we explored the subsequent problems of environmental damage, economic burdens, and a multitude of negative health effects on residents.
Semira: The country doesn't have a well-established collection system where people can dump their household waste properly. The management is mainly handled by groups organized by the Woreda municipal office, while pickers are mostly women. The problem is severe in areas where people live in condominiums. For example, where I lived, we used to dump our unsegregated waste every Tuesday and Friday at a nearby location, basically into the road across from our residential building with no collection bin. Then the waste collector piles waste and puts it into a bigger waste collector vehicle and transfers it to a landfill. Individuals and organizations interested in waste recycling and reuse usually navigate the landfills to pick their preferences. It is not unusual to see women and children collecting/picking plastic cans/bottles — they transfer them to recycling companies.
This means of disposal has created a problem for the people living around the area, primarily the waste collectors. It has health, aesthetic, and environmental effects and impacts the overall well-being of communities.
Therefore, without major policy adjustments and infrastructure improvements to rebuild a waste management system that is capable of handling Addis Ababa's population growth, the city's residents will continue to suffer.
How can your PACT project make an impact on that challenge?
Semira: In the PACT partnership, Sadie and I developed a project that considers the huge health and environmental effects of improper waste disposal. The proposed project will contribute to waste management in the Tafo condominium residential areas of Addis Ababa.
This initiative is not just about improving household waste management. It's about empowering the community to recognize their role as the key stakeholders and take charge of their environment. By engaging the community and upgrading the infrastructure, we aim to boost local participation and awareness about responsible waste disposal, thereby minimizing health and environmental risks.
Key efforts include modernizing waste collection facilities, enhancing recycling processes, and educating residents via workshops and school programs. The project also plans to establish better-equipped waste collection sites and train waste pickers on safety and efficiency. The initiative hopes to replicate its success in other locations by demonstrating a scalable waste management model, ultimately fostering sustainable environmental practices.

Why did you want to get involved in the PACT program in the first place?
Semira: The issue of waste management has been in my mind for the longest period of my life since I became involved in the field of soil science. I would ask myself, how can we solve it? Who is responsible? And coming to Cornell and learning about the PACT program made me interested in learning about the solid waste management system of the US by using the opportunity to collaborate with a sustainability student like Sadie.
Sadie: As an undergraduate student in the Department of Global Development, I have long admired the Humphrey Fellowship participants for their regional expertise, diversity of interests, and the sacrifices that they make to further their research and pursuits. The PACT program provides a unique opportunity for undergraduate students to collaborate with someone who has a wealth of tailored knowledge as well as a nuanced understanding of global complexities. In my final semester at Cornell, I have been intentional about devoting my time to the GDEV community while also seizing any possible opportunity to hone my research and collaboration skills. Although I was impressed by the resumes of each of the Humphrey Fellows, I am so lucky to have been paired with Semira and able to work under her guidance. This experience has been educational as well as empowering for me as a researcher, and I look forward to following the progress of the program in the future.
What’s next?!
Semira: The next steps are executing the project plan by securing funding. I look forward to submitting the grant proposal that we were able to work on together.
What are you taking away from your time in this research partnership?
Sadie: My time working with Semira has had a significant impact on my research and collaboration skills. I was eager to learn from Semira, as an expert in her field with first-hand experience and a true recognition of how improper waste management impacts the lives of Ethiopian residents.
I was previously unaware of the crisis of improper household solid waste management, and was particularly struck by the personal perspective that Semira was able to provide. Not only does mismanaged waste have a negative impact on population health, but it also affects civilians’ relationships with their environment and society. Moving forward, I am eager to continue observing how the structures of disposal alter a region’s functionality and attractiveness.
Throughout our partnership, Semira encouraged me to take the lead on the direction of our research and the presentation of findings. Although she already knew many of the answers to my questions, she supported me in reaching my own conclusions. Despite the many contrasts in our personal backgrounds, Semira and I found common ground through the PACT partnership and I am grateful for her leadership and encouragement.
Semira: Working with Sadie was a wonderful experience; she is an amazing, hard-working student with a strong passion for community engagement. For me, key takeaways include the importance of simplifying complex ideas without losing essential content; the value of this connection for future collaborations and professional opportunities; and an understanding of the problem and its root causes.
About the authors

Humphrey Fellow, 2023-24 (Ethiopia) Specialization: Natural/soil resource management; environmental policy and climate change; gender in agricultural development and innovation

Major: Development Sociology with minors in Inequality Studies and Crime, Prison, Education, & Justice Research focus: The sociology of prisons
Keep Exploring

Mario Herrero, Timothy Ryan, M.S. ’86, Ph.D. ’89, Steven Strogatz and Peter Wolczanski are Cornell’s 2024 electees to the National Academy of Sciences, the academy announced April 30 at the close of its 161st annual meeting.
- Department of Global Development
- Cornell Atkinson

We openly share valuable knowledge.
Sign up for more insights, discoveries and solutions.
You’ve not added any courses yet!
When you find a course you like select 'Add to course compare' to compare it with up to two other courses.
- MSc Construction Project Management
- Construction and surveying

Construction Project Management
Join a fast-track course to develop the skills you'll need in construction project management for private or public sector clients and construction companies.
Everything you need to know...
What is the fee.
Home: £10,310 or £11,810 (with work experience) for the course International/EU: £17,205 or £18,705 (with work experience) for the course
How long will I study?
Where will i study, city campus, when do i start.
September 2024 January 2025
Work Placement Route
For international students wishing to undertake a placement as part of this course, you must apply to MSc Construction Project Management (Work Experience) route. Transferring to the work experience route later will not be possible due to visa restrictions.
Course summary
- Gain key managerial skills for a range of construction project management roles.
- Learn to plan, programme, procure, develop and manage construction projects, both logistically and contractually.
- Understand industry dynamics and fundamental economic principles, critical thinking and analysis.
- Develop the knowledge you’ll need to manage the context surrounding projects of all sizes.
This is a fast-track conversion course for first-degree holders from unrelated disciplines, and existing practitioners, who want to become Chartered Surveyors through the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) and Chartered Institute of Building (CIOB).
Accredited by

This course is accredited by the The Chartered Institute of Building (CIOB) and Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS).

Come to an open day
Find out more at our postgraduate open days. Book now for your place.
How you learn
All our courses are designed around a set of key principles based on engaging you with the world, collaborating with others, challenging you to think in new ways, and providing you with a supportive environment in which you can thrive.
You’ll benefit from a range of 'experiential' teaching, learning and reflective assessment techniques. The course has a hands-on focus – you’ll work frequently with other students on the Construction Project Management course and in the wider built environment disciplines.
You learn through
- lectures and seminars
- tutorials and dialogue
- presentations
- site visits
- visiting speakers
- experiential learning and roleplay
Course leaders and tutors

Ron Middleton
Senior Lecturer at Sheffield Hallam University
Applied learning
Work placements
You’ll have the chance to work on an international project – experiencing the project management of a real site and the challenges associated with working on a live project for a client. You’ll work with local practitioners and other experts, gaining insights from the professionals working in that location.
Live projects
You’ll complete intensive study weeks which allow you to work on complex, professional briefs with other students – further building your professional experience.
Field trips
Previously the international project has taken place in Canada, with assistance from international firms. You may also have the opportunity to study and work abroad and gain hands-on experience of the education environment – with the possibility of Erasmus funding being available to support costs for overseas study.
Networking opportunities
Our course content meets Chartered Institute of Building (CIOB) and Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) requirements and also reflects our long-standing relationships with placement and graduate employers in the sector.
Future careers
This course prepares you for a career in
- construction project management
- site management
- surveying
- business management
- the infrastructure sector
There are many employment opportunities for construction project managers with regional, national and international construction and civil engineering contractors.
After completing the course, you’ll be able to proceed to the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors’ Assessment of Professional Competence or the Chartered Institute of Building's professional development programme.
You study at City Campus through a structured mix of lectures, seminars and practical sessions as well as access to digital and online resources to support your learning.
City Campus is located in the heart of Sheffield, within minutes of the train and bus stations.
City Campus map | City Campus tour

Howard Street Sheffield S1 1WB

Adsetts library
Adsetts Library is located on our City Campus. It's open 24 hours a day, every day.
Learn more about your department
Natural and Built Environment Facilities Tour
Take a look around the natural and built environment facilities at Sheffield Hallam University with lecturer Camila Bassi.
Equipment and facilities
On this course you work with
- Microsoft Office suite such as Excel, Powerpoint, Word, Visio and Project
- other specialist packages used for construction
Entry requirements
All students, additional information for eu/international students.
Minimum 2:2 degree or equivalent in any discipline.
We welcome applications from candidates who may not meet the exact academic entry requirements but have significant relevant experience, on application you will be referred to our course leader, who will evaluate your experience, this may involve an informal conversation either in person or by other media.
If English is not your first language you typically need an IELTS 6.0 overall score with a minimum of 5.5 in all other skills or equivalent. If your English language skill is currently below IELTS 6.0 we recommend you consider a Sheffield Hallam University Pre-sessional English course which will enable you to achieve an equivalent English score.
If you are an International or non-UK European student, you can find out more about the country specific qualifications we accept on our international qualifications page.
For details of English language entry requirements (IELTS), please see the information for 'All students'.
Modules studied may differ depending on when you start your course.
Module and assessment information for future years is displayed as currently validated and may be liable to change. When selecting electives, your choices will be subject to the core requirements of the course. As a result, selections may be limited to a choice between one of two or more specified electives in some instances.
Compulsory modules
Applied construction production management, applied international project, applied research methods and dissertation, construction law & professional context, economics and the built environment, health and safety management, project planning and contractual issues, sustainable building technology, fees and funding, home students, international students.
Our tuition fee for UK students starting full-time study in 2024/25 is £10,310 for the course without work experience placement or £11,810 with work experience placement. The tuition fee displayed above is for the full course. If the full course is more than one year in duration, the fee will be divided into annual payments which will then be rounded. This may mean the total fee you pay is slightly higher than the fee stated above. If you take a break in study or have to re-take part of the course, you may also be charged an additional fee and will be notified of this at the time.
If you are studying an undergraduate course, postgraduate pre-registration course or postgraduate research course over more than one academic year then your tuition fees may increase in subsequent years in line with Government regulations or UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) published fees. More information can be found in our terms and conditions under student fees regulations.
Our tuition fee for International/EU students starting full-time study in 2024/25 is £17,205 for the course without work experience placement or £18,705 with work experience placement. The tuition fee displayed above is for the full course. If the full course is more than one year in duration, the fee will be divided into annual payments which will then be rounded. This may mean the total fee you pay is slightly higher than the fee stated above. If you take a break in study or have to re-take part of the course, you may also be charged an additional fee and will be notified of this at the time.

Postgraduate student loans
Up to £11,222 available for Home students on most masters courses.
Additional course costs
This link allows you to view estimated costs associated with the main activities on specific courses. These are estimates and, as such, are only an indication of additional course costs. Actual costs can vary greatly depending on the choices you make during your course.
Non-repayable grant of £3,000 per year for three years
Offering four scholarships for undergraduate students joining the department in September 2020 on an eligible course.
Legal information
Any offer of a place to study is subject to your acceptance of the University’s Terms and Conditions and Student Regulations .
Student success story

‘It was a really easy decision for me to stay on at Hallam, after the positive experience I had at undergrad. My main focus was on the management side of things, which has taught me to be more efficient in my work.’
David Ajala, MSc Construction Project Management
How do I apply?
You apply for this course via our online application form.
- Apply for January 2025
- Apply for September 2024
You can also use the application form above to apply for future years of entry.
Not ready to apply just yet?
Why not come to our next open day? Open days are the perfect place to talk to staff and students, visit our campuses and get all the information you need. Alternatively, feel free to ask us a question.
Why choose us?
We are Gold rated in the Teaching Excellence Framework (TEF) for the outstanding quality of our teaching and student outcomes
Accommodation
We guarantee to find you an affordable place to live that’s close to campus and comes with all bills included
95% of our UK graduates are in work or further study 15 months after graduating (2020/21 Graduate Outcomes Survey)
Where next?
Find out more about Sheffield Hallam's postgraduate opportunities and community.

You can chat to teaching and admissions staff, view our facilities and learn more about your funding options.

Sign up for updates
Receive emails about postgraduate study, including application reminders and alerts for open days.

Information for international students
Information for international students including entry requirements by country and funding.
You might also like
Other courses relating to this MSc Construction Project Management course.
Quantity Surveying
A fast-track course allowing graduates from a non-construction related degree or existing quantity surveyors to become chartered surveyors.
Cancel event
Are you sure you want to cancel your place on Saturday 12 November ?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Time management can be defined as clusters of behavioral skills that are important in the organization of study and course load (Lay & Schouwenburg, 1993).Empirical evidence suggests that effective time management is associated with greater academic achievement (McKenzie & Gow, 2004; Trueman & Hartley, 1996) as students learn coping strategies that allow them to negotiate competing demands.
Time mana gement pla ys a vital role in improving studen t's academic perfor mance and achievements. Each and. every student should have time management ability which includes setting goals ...
A critical gap in time management research is the question of whether time management works [28, 29]. ... Time management can thus assist students in organizing their time to acquire the knowledge necessary to ace a regular exam; for standardized exams that depend less on knowledge and more on intelligence, however, time management may be less ...
Research Questions In an attempt to examine the practices and insight of students in regard to time management and the links between time management and student outcomes, three areas of study were developed from the key messages in the literature. In explor - ing these areas, we ask the following three questions: 1. Research Question 1:
Abstract. This study assessed test-retest reliability and internal consistency of the Assessment of Time Management Skills (ATMS), a self-report questionnaire designed to assess awareness and ...
Despite its recognized importance for academic success, much of the research investigating time management has proceeded without regard to a comprehensive theoretical model for understanding its connections to students' engagement, learning, or achievement. Our central argument is that self-regulated learning provides the rich conceptual framework necessary for understanding college students ...
In a study conducted by Khanam N et al. (3) Showed that 51.90% of the participants possessed moderate to low level time management score. Participants who obtained higher percentages of mark (70 ...
To facilitate the process of learning and managing personal res ponsibilities of. students, this paper aims to teach practical methods of study a nd time management, supported from an empir ical ...
A critical gap in time management research is the question of whether time management works [28, 29]. ... Time management can thus assist students in organizing their time to acquire the knowledge necessary to ace a regular exam; for standardized exams that depend less on knowledge and more on intelligence, however, time management may be less ...
fellow students, time management, control over time, the pace of learning, motivation, and expectations of efficiency or effectiveness stand out as the most significant (Govindasamy, 2002; Fresen & Lesley, 2006; Goyal et al., 2010). Whatore, it is m even now, common digital competence frameworks already begin to exist, in which, at the
This research is valuable because instead of explaining that this is an important. skill, I will be able to prove that our mental health actually improves when we use it properly. This is a different kind of eye opener, as we are learning how important our mental health is. Section 3: Creative Thinking.
The Impact of Time Management on Students' Academic Achievement. S N A M Razali 1, M S Rusiman 1, W S Gan 1 and N Arbin 2. Published under licence by IOP Publishing Ltd Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Volume 995, International Seminar on Mathematics and Physics in Sciences and Technology 2017 (ISMAP 2017) 28-29 October 2017, Hotel Katerina, Malaysia Citation S N A M Razali et al 2018 ...
The aim of the study or the research was to assess general time management practice /behavior of regular program students of Dire Dawa University and its association with their academic achievement, gender, and year ... students score in time management (mean score=55.72) were higher than female (50.5) students. With respect to
Increased self-esteem: Every task completed on time is an accomplishment that boosts confidence and reinforces a student's belief in their abilities. Quality sleep: A well-managed schedule often aligns with better sleep routines, as students can avoid all-nighters and last-minute studying. Time management is the secret ingredient to living a ...
Results and Discussions. It is observed from Table 1, from the present investigation, 19.0% of higher secondary students have high level of time management and 23.8% of higher secondary students have high level of academic achievement. Moreover majority of the samples have moderate level of time management and Academic achievement.
Students should: • Schedule short breaks every 25-50 minutes to clear their minds and avoid fatigue. • Engage in different activities during breaks, such as stretching, walking, or a hobby, to mentally recharge. • Set boundaries for work and rest to ensure time off is truly relaxing and re-energizing.
Keywords: time management, academic stress, stressors, time organization. 1. Introduction. Higher education is a stressful period in the lives of students due to various reasons such as living away from families, a heavy curriculum or ineffectiveness in higher education programs (Bhujade, 2017). From the moment an individual enters college, he ...
Manage your time wisely and take advantage of moments where you can get things done. 6. Are you taking advantage of the resources your school offers? Your school likely offers a number of resources that can help you with your studies, including tutoring, academic advising, and the library.
This study explored student attitude toward time management on their academic pursuit in Gombe state university. Descriptive survey research design was used for the study. ... Research Question 3: What is the behavioural attitude of students towards time management on academic pursuit in Gombe state university? 64 VOL/ 4(1) 2023 AFRICAN JOURNAL ...
Maintain and focus on a research program. 5. Manage potential distractions. 6. Be smart about planning your workday. 7. Analyze progress and time management strategies periodically. 8. Reward yourself for your achievements.
Jeanine Mazak-Kahne, Theresa McDevitt, and Lorilie Boise. Academic Libraries and Public Art. Engaging Students in a Timely Discussion . Jeanine Mazak-Kahne is associate professor at the Indiana University of Pennsylvania History Department, email: [email protected] McDevitt is government information and outreach librarian at Indiana University of Pennsylvania, email: [email protected].
Students benefit from hands-on research opportunities and instruction informed by the latest developments in the field. Research During my interview in December 2020, when most of the U.S. was locked down, I felt very welcomed and grateful that other faculty members appreciated my research.
shows that 48.12% of the students study for more than 8. hours during the exam time, 34.7% of the students study. for less than 8 hours during exam time and 18.2% of. the students studied exactly ...
AP Seminar end-of-course exams are only available to students taking AP Seminar at a school participating in the AP Capstone Diploma Program. April 30, 2024 (11:59 p.m. ET) is the deadline for: AP Seminar and AP Research students to submit performance tasks as final and their presentations to be scored by their AP Seminar or AP Research teachers.
The Humphrey PACT (Practitioner - Assistant - Collaborative - Training) Program pairs undergraduate students in Global Development with Hubert H. Humphrey Fellows to work on a research endeavor in the fields of agriculture, rural development, and natural resource management. In this bilateral exchange, each undergrad is assigned as a research assistant, contributing to the Humphrey Fellow's ...
This is very large topic, some pointers: 1) In Cognitive Ergonomics there is a large literature about planning (organizational strategies to cope with time pressure). See for instance Xiao ...
International students. Our tuition fee for UK students starting full-time study in 2024/25 is £10,310 for the course without work experience placement or £11,810 with work experience placement. The tuition fee displayed above is for the full course.
The study on the relationship between time management skills and academic performance of students was conducted at Mariano Peralta National High School's Open High School Program.