- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both

Writing objectively How and when to use an impersonal tone
For another look at the same content, check out the video on YouTube (also available on Youku ). There is a worksheet (with answers and teacher's notes) for this video.
Academic writing is generally impersonal and objective in tone. This section considers what objective writing is , how objective academic writing is , then presents several ways to make your writing more objective . There is also an academic article , to show authentic examples of objective language, and a checklist at the end, that you can use to check the objectivity of your own writing.
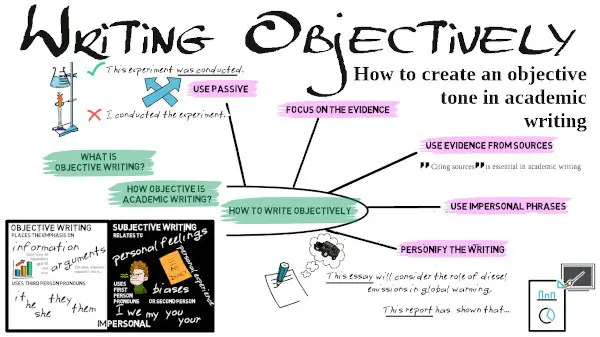
What is objective writing?
Objective writing places the emphasis on facts, information and arguments, and can be contrasted with subjective writing which relates to personal feelings and biases. Objective writing uses third person pronouns (it, he, she, they), in contrast to subjective writing which uses first person pronouns (I, we) or second person pronoun (you).
How objective is academic writing?
Although many academic writers believe that objectivity is an essential feature of academic writing, conventions are changing and how much this is true depends on the subject of study. An objective, impersonal tone remains essential in the natural sciences (chemistry, biology, physics), which deal with quantitative (i.e. numerical) methods and data. In such subjects, the research is written from the perspective of an impartial observer, who has no emotional connection to the research. Use of a more subjective tone is increasingly acceptable in areas such as naturalist research, business, management, literary studies, theology and philosophical writing, which tend to make greater use of qualitative rather than quantitative data. Reflective writing is increasingly used on university courses and is highly subjective in nature.
How to write objectively
There are many aspects of writing which contribute to an objective tone. The following are some of the main ones.
Use passive
Objective tone is most often connected with the use of passive, which removes the actor from the sentence. For example:
- The experiment was conducted.
- I conducted the experiment.
- The length of the string was measured using a ruler.
- I measured the length of the string with a ruler.
Most academic writers agree that passive should not be overused, and it is generally preferrable for writing to use the active instead, though this is not always possible if the tone is to remain impersonal without use of I or other pronouns. There is, however, a special group of verbs in English called ergative verbs , which are used in the active voice without the actor of the sentence. Examples are dissolve, increase, decrease, lower, and start . For example:
- The white powder dissolved in the liquid.
- I dissolved the white powder in the liquid.
- The white powder was dissolved in the liquid.
- The tax rate increased in 2010.
- We increased the tax rate in 2010.
- The tax rate was increased in 2010.
- The building work started six months ago.
- The workers started the building work six months ago.
- The building work was started six months ago.
Focus on the evidence
Another way to use active voice while remaining objective is to focus on the evidence, and make this the subject of the sentence. For example:
- The findings show...
- The data illustrate...
- The graph displays...
- The literature indicates...
Use evidence from sources
Evidence from sources is a common feature of objective academic writing. This generally uses the third person active. For example:
- Newbold (2021) shows that... He further demonstrates the relationship between...
- Greene and Atwood (2013) suggest that...
Use impersonal constructions
Impersonal constructions with It and There are common ways to write objectively. These structures are often used with hedges (to soften the information) and boosters (to strengthen it) . This kind of language allows the writer to show how strongly they feel about the information, without using emotive language, which should be avoided in academic writing.
- It is clear that... (booster)
- It appears that... (hedge)
- I believe that...
- There are three reasons for this.
- I have identified three reasons for this.
- There are several disadvantages of this approach.
- This is a terrible idea.
Personify the writing
Another way to write objectively is to personify the writing (essay, report, etc.) and make this the subject of the sentence.
- This essay considers the role of diesel emissions in global warming.
- I will discuss the role of diesel emissions in global warming.
- This report has shown that...
- I have shown that...
In short, objective writing means focusing on the information and evidence. While it remains a common feature of academic writing, especially in natural sciences, a subjective tone is increasingly acceptable in fields which make use of qualitative data, as well as in reflective writing. Objectivity in writing can be achieved by:
- using passive;
- focusing on the evidence ( The findings show... );
- referring to sources ( Newbold (2021) shows... );
- using impersonal constructions with It and There ;
- using hedges and boosters to show strength of feeling, rather than emotive language;
- personifying the writing ( This report shows... ).
Bailey, S. (2000). Academic Writing. Abingdon: RoutledgeFalmer
Bennett, K. (2009) 'English academic style manuals: A survey', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 8 (2009) 43-54.
Cottrell, S. (2013). The Study Skills Handbook (4th ed.) , Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan.
Hinkel, E. (2004). Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers.
Hyland, K. (2006) English for Academic Purposes: An advanced resource book . Abingdon: Routledge.
Jordan, R. R. (1997) English for academic purposes: A guide and resource book for teachers . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Example article
Below is an authentic academic article. It has been abbreviated by using the abstract and extracts from the article; however, the language is unchanged from the original. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes) to highlight the different objective features.
Title: Obesity bias and stigma, attitudes and beliefs among entry-level physiotherapy students in the Republic of Ireland: a cross sectional study. Source: : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031940621000353

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for using objectivity in academic writing. Use it to check your writing, or as a peer to help. Note: you do not need to use all the ways given here.
Next section
Read more about writing critically in the next section.
- Critical writing
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about using complex grammar .
- Complex grammar

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 05 February 2024.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
Subjective vs. Objective Essay: Examples, Writing Guides, & Topics
Subjective or objective essay writing is a common task students have to deal with. On the initial stage of completing the assignment, you should learn how to differentiate these two types of papers. Their goals, methods, as well as language, tone, and voice, are different.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
A subjective essay focuses on the writer’s personal opinion, while an objective one represents valid facts. So, be careful when composing an objective paragraph or paper. Don’t let your beliefs take over real arguments supported by substantial evidence.
In short, differences between these styles concern the following:
- The ground for objective essays is facts; for subjective essays – personal opinions and beliefs.
- Objective papers report the findings from scientific sources, while subjective ones describe the writer’s thoughts.
- The objective essay’s goal is to help the reader make a decision. Subjective writing aims to reflect the author’s vision of the issue.
So, if you face this task for the first time, you may need some explanations. Custom-writing.org experts prepared a list of tips on how to write objective and subjective essays. Some topics, as well as objective and subjective writing examples, will also be useful.
- 🆚 Subjective vs. Objective
🔗 References
🆚 subjective vs. objective essays.
First and foremost, let’s find out the critical differences between the writing styles. Take a look at the following table and shed light on this issue.
An objective essay is a presentation of the material with no independent opinion involved. Only facts matter in this paper, and only facts can back up some assertions. Writing subjective essays implies introducing your standpoint on a particular problem.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
📋 How to Write an Objective Essay
Writing any essay consists of three parts: preparation, the actual writing, and revision. During the first one, you need to decide on your topic and do a little research. You can see how it looks in a real example.
Objective Essay Example: The Portrayal of Odysseus
In Odyssey, Homer portrays Odysseus, the king of Ithaca, as the true epic hero. The depiction of Odysseus is thoughtfully knitted together with the themes of love and loyalty that further magnify it, painting a holistic picture of a long 10-year journey home. Although it can be argued that some of Odysseus’s personality traits he displays cannot be applied to a true hero, he is still depicted following a very specific heroic archetype.
Now, let’s get into more detail!
Objective Essay Topics
If you’ve decided to write an objective essay, you need to come up with a topic. The topic gives a reader a brief overview of what will be covered in the paper.
Here are ten great examples:
- While the differences between Italy and Spain are evident, the resemblances are striking.
- There are several similarities between the movies “Deep Impact” and “Armageddon.”
- Compare and contrast the capitals of two English-speaking countries.
- Somatic symptoms in people with PTSD can be influenced by age, gender, and avoidance.
- Some might argue, but being overweight carries a social stigma.
- Environmental factors contribute to the phenotypic expression of psychological disorders.
- Although the exact reason remains unclear, depression is affected by sex, gender, hormonal changes, and age.
- When comparing and contrasting the Bible and Quran, it seems that they have more similarities than differences.
- Musical ability is the result of influence on the person from outside.
- In comparison to extroverts, introverts draw power from within themselves to use it in future activities.
Objective Essay Structure
We shall continue with exploring an essay structure. Note that the parts described below are essential for any essay.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
- Introduction . The introduction is usually the part that broadly describes the topic and gets the interest of the reader. This part of the paper should cover some background information and present the purpose.
- Hypothesis . In case your essay has one, state it in your introduction. A hypothesis includes information about how you intend to prove or refute the claim. It briefly describes the way you intend to do so.
- Arguments . Present one side of the argument. In the next paragraph, present the opposing one, using such words as “however,” “nevertheless,” and “although.” The task is to provide the readers with two sides of the argument.
- Evidence . Provide the evidence for all of your points. Keep the balance in providing proof and refutal. Omit your personal opinion, rather than include the evidence you find informative and convincing.
- Conclusion . Summarize the arguments both for and against the position. While remaining objective, shortly go over the information you presented as evidence. If the instructions require a personal opinion, in conclusion, you might write one. In other cases, briefly recap the parts of the essay. Shorten sentence generator would be greatly beneficial in such endeavor.
📜 How to Write a Subjective Essay
As we’ve mentioned earlier, a subjective essay represents the author’s vision of a particular issue. You have an opportunity to introduce your point of view without supporting your ideas with evidence from the primary sources. However, make sure your arguments are still logical and adequate.
Now see how to write a subjective essay in the sections below.
Subjective Writing Example
A well-chosen topic is the vital determinant of a successful essay. Yet, the process of selecting an idea for your paper might be challenging. That’s why you may find our example helpful.
The rapid pace of development of modern technologies increases the demand for oil and gas every year. A considerable amount of these resources is necessary to maintain both industrial enterprises and private equipment. Despite active production, there are still many unexplored places on Earth, potentially rich in oil and gas deposits. However, while making them public would help solve the existing problem, I’m afraid I disagree with this proposal.
Subjective Essay Topics
Check our list of subjective essay topics, choose the one you like the most, or inspire and come up with your idea!
- The fake and too glamorous life presented in social media leads to the development of an inferiority complex among teenagers.
- The information flows within the country should not be controlled by the governments.
- Since developed nations provoked the climate crisis, they should take full responsibility for their past actions and reduce carbon emissions in the atmosphere.
- Cyberbullying should be a matter of the same importance as physical abuse.
- Remote learning opens more opportunities and expands the students’ horizons.
- Instead of catching up with fashion trends, it is better to develop your unique style.
- People should have enough rest to reduce the levels of anxiety and decrease the chances of depression.
- Studying abroad is an experience worth trying.
- Planning and scheduling are perfect strategies to deal with procrastination.
- While applying for a job position, work experience is more significant than having a degree.
📝 Subjective Essay Structure
When you deal with this task, you have full freedom of choice. You can decide for yourself what idea to support and what arguments to present. Still, you have to structure even a subjective essay properly.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Here are the elements you have to include in your paper:
- grab the readers’ attention;
- introduce your subject;
- state your position in the thesis statement.
Important note: your thesis should be clear and straightforward. Let your audience understand your opinion.
- Description . Dive deeper into your topic and describe your issue in detail. However, don’t go too far. Avoid including irrelevant facts and unnecessary information. Follow the principle “quality over quantity” to keep your reader engaged.
- Opinion . After describing your issue, move to the most crucial part of your essay—opinion. State it clearly and concisely. Although you don’t need to provide any evidence from scholarly sources, your ideas should be supported by substantial arguments or examples from your personal life.
- Conclusion . In the last paragraph of your subjective essay, restate your thesis statement. Don’t introduce any other ideas here. To make your paper more dynamic, ask a provocative question at the end. It may motivate your reader for further investigation of your subject.
A helpful tip:
Before submitting your work, make sure it is coherent. Check if all of your ideas follow the logical flow. To avoid redundancy and wordiness, mix shorter sentences with longer ones and apply transitional phrases. Polish your essay, turn it in, and wait for your perfect grade.
Thanks for reading the page! Share it with your peers who may need some guidance as well. Our writers are ready to explain any other essay type , not only objective or subjective ones.
Learn more on this topic:
- How to Write an Expository Essay in Simple Steps
- Nursing Reflective Essay Example and Guidelines for Students
- Essay on Dengue Fever: How to Write + Free Examples
- French Essay Writing: How-to Guide and Examples
- How to Write a Rebuttal Essay: Jackie Michael, Pen and the Pad
- Writing Objectively: OWLL, Massey University
- Subjective vs Objective: Difference and Comparison, Diffen
- Objective and Subjective Claims: TIP Sheet, Butte College
- Evidence: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Organizing Your Argument: Purdue Online Writing Lab, College of Liberal Arts, University of Purdue
- Argumentative Paper Format: Courtesy the Odegaard Writing & Research Center, University of Washington
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph: LSA Sweetland Center for Writing, the University of Michigan
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Writing All About Me paragraph is probably one of the most usual assignments. For example, students might write it when entering an academic institution. Such work gives an opportunity to introduce yourself, your skills, and goals. However, it is not the only possible situation.

Coral reefs can be called one of the most amazing things created by nature. These structures can be found in tropical and temperate waters. Like many other unique natural phenomena, coral reefs are influenced by human activity these days. This negative impact is one of the significant issues to consider when...

An ambition essay focuses on one’s strong desire to achieve success in one or several areas. It might be one’s career, finance, family, art, health, or all at once. Writing an ambition essay, you might want to consider your own life or examples from the world literature. You can describe...
![objectives essay Essay for Primary School: Simple Guide for Kids [with Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/pupils-raising-hand-classroom-284x153.jpg)
The age of primary school students ranges from 5 to 11 years. At this stage of education, children start developing their writing skills. They make their first steps to analyzing and proving their points of view. Besides, they study how to write an essay for elementary school. Correctly preparing all...

Canadian identity is something that has become really important for many Canadians in the past fifty years. Canada is a big, multinational country with its own traditions, culture, and history. However, because of quite a large number of foreigners and even Americans, its culture and people are associated with the...

Let’s say you received a task to write an essay about cars. The topic might be interesting for you, but you may still have no idea how to organize your paper. Well, this article is for you.

Smoking can be viewed as one of the trendy habits. Numerous teenagers try it since they think that it is cool or can help them socialize. Often students start smoking due to stress or mental illnesses. But is it okay? Educators tend to give different written assignments, which may disclose...
![objectives essay Child Labor Essay: Thesis, Examples, & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/child-working-in-cambodia-e1565628499749-284x153.jpg)
Children have always been apprentices and servants all over human history. However, the Industrial Revolution increased the use of child labor in the world. It became a global problem that is relevant even today when such employment is illegal.

Dissertation critique writing develops the students’ critical and logical thinking abilities. When composing, the students learn to analyze the works conducted by other researchers. To critique a dissertation, you should: Thoroughly read the paper.Take notes and summarize the text (you can even try and use auto summarizer for that).Interpret and...

An opinion essay is a formal piece of writing which presents the author’s point of view on a particular subject supported by reasoning and examples. The opposing viewpoint is also suggested, but it is followed by arguments that show its inconsistency. Take a look at the guide prepared by Custom-writing experts to...

So, you need to accomplish your discursive essay writing. The typical questions most students ask are: How do you write it? What is discursive essay? A discursive essay is an academic paper that involves a discussion on a particular topic. It is usually assigned to college students. You may be...

How to write a narrative essay? To do that, you need to know what a narrative essay is. It is an academic text usually written as a story and containing all the usual elements of a story. Narrative essays are often personal, experiential, and creative. Still, they should be made...
Very helpful to make my assignment. Thank you so much!

Glad to know that. Thank you very much, Farhana!
Subjective and reflective.
That’s right, Raj 🙂
Thank you for this information. I submitted my subjective essay, which was rejected by my teacher for lack of an attractive hook. After reading your info on writing subjective essays, I know what I should change in my paper to get a good grade.
Thank you so sweet for these wonderful tips for objective essays! I love your blog, and it’s really helpful one online! Keep it up!
This is what I need to complete my paper. Your subjective essay writing secrets are appropriate for students who can’t cope with their essays themselves. Even those who write a paper for the first time will complete their subjective essays without any problems.
I really appreciate your help in posting all this information for students — this time you’ve taught me how to write an objective essay. You’re real specialists in writing all types of papers!

How to Write Objectives | A Step-to-step Guide | 2024 Updates
Astrid Tran • 22 Apr 2024 • 6 min read
Objectives are needed for every aspect of life, work and education.
Whether you are setting objectives for academic research, teaching and learning, courses and training, personal development, professional growth, a project, or more, having clear objectives like having a compass to help you stay on track.
So, how to write objectives? Check out this article to get a complete guide on writing realistic and impactful objectives.
Table of Contents
How to write objectives of a project
How to write objectives for a presentation, how to write objectives for lesson plan, how to write objectives for a research, how to write objectives for personal growth.
More tips on how to write objectives
Frequently Asked Questions
Project objectives often focus on tangible results, such as completing specific tasks, delivering products, or achieving certain milestones within a defined timeframe.
Writing project objectives should follow these principles:
Start early : It is important to set your project objectives at the beginning of your project to avoid unexpected situations and employees misunderstanding.
Changes : Project objectives can be determined to address challenges of previous projects experience and seek to minimize potential risks prior to the project begins.
Achievement : An objective of a project should mention what success is. Different success is measured by specific and measurable objectives.
OKR : OKR stands for “objectives and key results,” a managerial model that aims to set goals and identify metrics to measure progress. Objectives are your destination, while key results contribute to the path that will get you there.
Focus : Different project objectives might consist of related issues such as:
- Customer satisfaction
- Turnover and Retention
- Sales and Revenue
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Sustainability
- Productivity
For example :
- The goal of the campaign is to improve the traffic by 15% before the end of the first quarter.
- This project aims to produce 5,000 units of products in the next three months.
- Add five new methods for clients to seek the feedback form in-product within the next three months.
- Increase click through rate (CTR) engagement on email by 20% by the end of the second quarter.

Presentation objectives outline what you intend to accomplish with your presentation, which might involve informing, persuading, educating, or inspiring your audience. They guide the content creation process and shape how you engage your listeners during the presentation.
When it comes to writing presentation objectives, there are some notes to look at:
The questions “Why” : To write a good presentation objective, start with answering why questions, such as Why is this presentation important to your audience? Why should people invest time and money to attend this presentation? Why is your content important to the organization?
What do you want the audience to know, feel and do ? Another important of writing objectives for a presentation is considering the comprehensive impact your presentation has on the audience. This pertains to the informational, emotional, and actionable aspect.
Rule of three : When you write your objectives in your PPT, don’t forget to express no more than three key points per slide.
Some examples of objectives:
- Ensure the managers understand that without additional funding of $10,000, the project will fail.
- Get commitment from the director of sales to a three-tier pricing proposal for customer Prime.
- Get the audience to commit to reducing their personal plastic usage by signing a pledge to avoid single-use plastics for at least a week.
- Participants will feel empowered and confident about managing their finances, replacing financial anxiety with a sense of control and informed decision-making.

Get your Students Engaged
Start meaningful discussion, get useful feedback and educate your students. Sign up to take free AhaSlides template
Learning objectives, often used in education and training, specify what learners are expected to gain from a learning experience. These objectives are written to guide curriculum development, instructional design, and assessment.
A guide on writing an objective for learning and lesson plan described as follows:
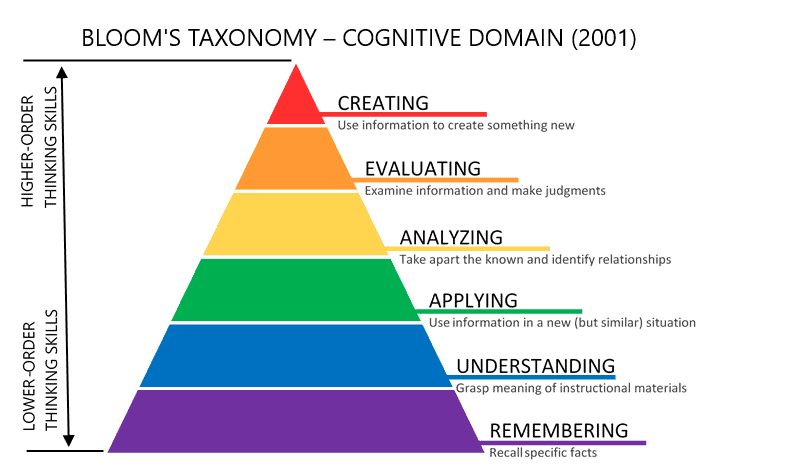
Learning objectives verbs : There is no better way to have learning objectives start with measurable verbs collected by Benjamin Bloom based on level of cognition.
- Knowledge level: tell, uncover, show, state, define, name, write, recall,…
- Comprehension level: indicate, illustrate, represent, formulate, explain, classify, translate,…
- Application level: perform, make a chart, put into action, build, report, employ, draw, adapt, apply,…
- Analysis Level: analyze, study, combine, separate, categorize, detect, examine,…
- Synthesis Level: integrate, conclude, adapt, compose, construct, create, design,…
- Evaluation Level: evaluate, interpret, decide, solve, rate, appraise, verify,…
Student-centered : Objectives should reflect the unique aspirations, strengths and weaknesses of each student, emphasize what students will know or be able to do, not what you will teach or cover.
Learning Objective Examples:
- To recognize the power of different types of language
- By the end of this course, students will be able to identify and develop data collection instruments and measures for planning and conducting sociological research.
- By the end of this course, students will be able to identify their own position on the political spectrum.
The purpose of research objectives is congruent with research study outcomes.They articulate the purpose of the research, what the researcher intends to investigate, and the expected outcomes.
There are severals principles to follow to ensure a well-written research objectives:
Academic language : It is important to note that research writing is strict on the use of language. It is held to a high standard of clarity, precision, and formality.
Avoid using first-person references to state the objectives. Replace “I will” with neutral phrasing that emphasizes the research’s intention. Avoid emotional language, personal opinions, or subjective judgments.
Pinpoint the Focus : Your research objectives should clearly articulate what your study aims to investigate, analyze, or uncover.
Specify the Scope : Outline the boundaries of your research by specifying the scope. Clearly delineate what aspects or variables will be examined, and what will not be addressed.
Maintain Consistency with Research Questions : Ensure your research objectives align with your research questions.
Frequently used phrases in research objectives
- …contribute to the knowledge of…
- …search for…
- Our study will also document….
- The primary objective is to integrate…
- The purposes of this research include:
- We attempt to…
- We formulated these objective based on
- This study searches for
- The second gold is to test
Objectives for personal growth often focus on individual improvement on skills, knowledge, well-being, and overall development.
Personal growth objectives encompass various aspects of life, including emotional, intellectual, physical, and interpersonal dimensions. They serve as roadmaps for continuous learning, growth, and self-awareness.
- Read one non-fiction book each month to expand knowledge in areas of personal interest.
- Incorporate regular exercise into the routine by walking or jogging for at least 30 minutes five times a week.
Tips to write objectives for personal growth from AhaSlides.
💡 Development Goals For Work: A Step-By-Step Guide For Beginners with Examples
💡 What is Personal Growth? Set Up Personal Goals For Work | Updated in 2023
💡 Work Goals Examples For Evaluation with +5 Steps To Create in 2023
How to write objectives in general? Here are common tips for setting objectives of any field.

#1. Be concise and straightforward
Keep the words as simple and straightforward as much as possible. It is much better to remove unnecessary or ambiguous words that might lead to misunderstanding.
#2. Keep your number of objectives limited
Don’t confuse your learners or readers with too many objectives. Concentrating on a few key objectives can effectively maintain focus and clarity and prevent overwhelming.
#3. Use action verbs
You can start each objective with one of the following measurable verbs: Describe, Explain, Identify, Discuss, Compare, Define, Differentiate, List, and more.
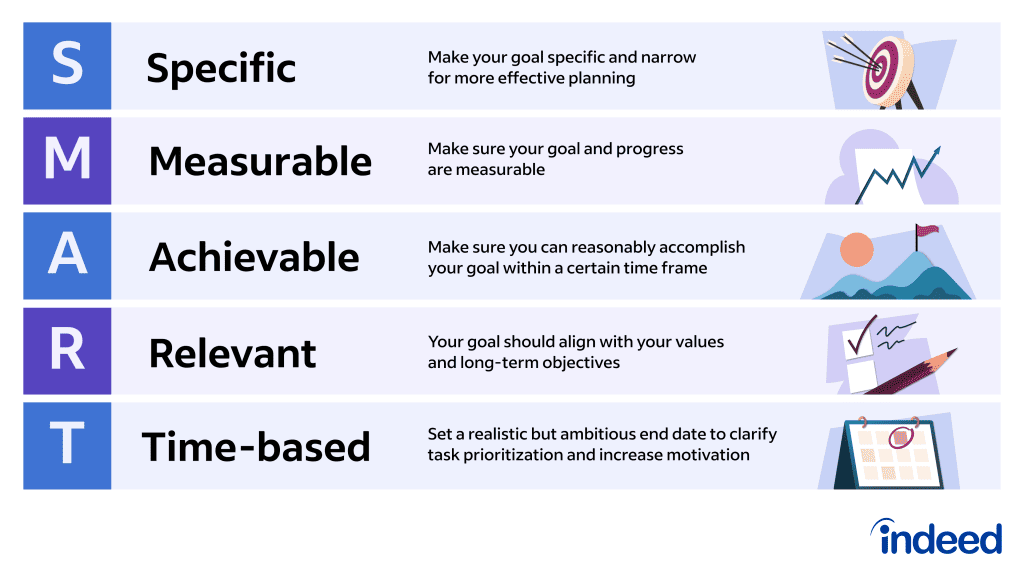
#4. Be SMART
SMART objectives framework can be defined with specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. These objectives are clearer and easier to understand and achieve.
⭐ Want more inspiration? Check out AhaSlides to explore the innovative way to get presentations and lesson engaging and fun!
What are the 3 parts of an objective?
According to Mager (1997), objective statements contain three parts: behavior (or, performance), conditions, and criteria.
What are the 4 elements of a well-written objective?
The four elements of an objective are Audience, Behavior, Condition, and Degree, called A-B-C-D method. They are used to identify what a student is expected to know and how to test them.
What are the 4 components of objective writing?
There are four components of an objective include: (1) the action verb, (2) conditions, (3) standard, and (4) the intended audience (always the students)
Ref: Indeed | Batchwood |

Astrid Tran
I've got my rhythm with words
More from AhaSlides

- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
How to Write an Objective Essay
Objectivity in essay writing is important in order for the writer to clearly state both sides of an argument without displaying a bias toward one side or the other. When students are given essay titles to complete, not all titles call for objectivity, but the main question will always point to a pro-and-con situation. Personal opinions in essays are not usually accepted unless they are written with objectivity and backed up by references and proof.
Begin your essay with an introductory paragraph that presents the purpose of the essay. If there is a hypothesis involved, state how you intend to prove or disprove the hypothesis and broadly explain how you intend to do so. Details at this point are not necessary, as they will be covered in the main body of your essay.
State one side of the argument and report the evidence and findings that support the statement you are making. Leave out how you personally feel about the issue but do bring in supporting evidence that you find compelling. Remain objective when you compose an essay by keeping your arguments balanced in support or for rebuttal of the hypothesis.
Read back over the essay as you write and remain focused on your objectivity. To be objective is the opposite of being subjective. Being objective is being able to remove yourself from the personal emotions and thoughts you may have about the subject, while being able to examine fairly and critique both sides of the argument you are discussing.
State the opposing argument in your next paragraph or chapter. Use words and phrases that express the change of direction within the essay, such as “however,” “although” and “on the other hand.” Include comments that contrast the preceding paragraphs. For example, you may be writing about Freud, and your contrasting statement would include something like “While Freud argued that ... Jung disagreed with this by stating ...” Your goal in the rebuttal argument is to compel readers to see both sides and draw their own conclusions.
Conclude your essay by summing up the arguments both for and against the position. Again, remaining objective means reiterating your argument in a simplified form to remind readers what they have heard and, hopefully, learned from your statements. Your aim is to gear the readers up for a short evaluation of the topic of discussion. State the facts you have laid out and remind the readers of your own objectivity by using an equal number of references and arguments from both sides. If your essay requires you to conclude with an opinion, then you should compose and add one. If the essay simply requests an argumentative approach, then lay out the two sides and state the conclusion as the recap of the elements of the essay.
Jackie Michael has been a freelance writer since 2007. Her work has appeared on various websites, including Autos.com and CarsDirect. She holds a Bachelor of Arts in psychology and sociology from East London University.
Skip to Content
Massey University
- Search OWLL
- Handouts (Printable)
- Pre-reading Service
- StudyUp Recordings
- StudyUp Postgraduate
- Academic writing
- Intro to academic writing
- What is academic writing?
Writing objectively
- Writing concisely
- 1st vs. 3rd person
- Inclusive language
- Te Reo Māori
- Assignment planning
- Assignment planning calculator
- Interpreting the assignment question
- Command words
- Organising points
- Researching
- Identifying academic sources
- Evaluating source quality
- Editing & proofreading
- Apostrophes
- Other punctuation
- Active voice
- American vs. British spelling
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Pronoun Reference
- Sentence fragments
- Sentence Structure
- Subject-verb agreement
- Formatting and layout
- Word limits and assignment length
- Commonly confused words
- How assignments are marked
- Marking guides
- Getting an A
- Levels of assessment
- Using feedback
- Professional emails
- Forum posts
- Forum netiquette guidelines
- Sharing personal information
- Writing about personal experiences
- Assignment types
- What is an essay?
- Essay planning and structure
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body paragraphs
- Essay revision
- Essay writing resources
- What is a report?
- Report structure
- Analysing issues for a report
- Business report
- What is a business report?
- Business report structure
- Inductive vs. deductive reports
- Other kinds of business communication
- Business report format and layout
- What is a lab report?
- Lab report structure
- Science lab report writing resources
- Psychology lab report writing resources
- Lab report body paragraphs
- Literature review
- What is a literature review?
- Writing a literature review
- Literature review structure
- Literature review writing resources
- Research proposal
- Writing a research proposal
- Research proposal structure
- Other types
- Article critique
- Book review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- Oral presentation
- Thesis / dissertation
- Article / conference paper
- Shorter responses
- Computer skills
- Microsoft Word
- Basic formatting
- Images, tables, & figures
- Long documents
- Microsoft Excel
- Basic spreadsheets
- Navigating & printing spreadsheets
- Charts / graphs & formulas
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Basic skills
- Advanced skills
- Distance study
- Getting started
- How to study
- Online study techniques
- Distance support
- Reading & writing
- Reading strategies
- Writing strategies
- Grammar resources
- Listening & speaking
- Listening strategies
- Speaking strategies
- Maths & statistics
- Trigonometry
- Finance formulas
- Postgraduate study
- Intro to postgrad study
- Planning postgrad study
- Postgrad resources
- Postgrad assignment types
- Referencing
- Intro to referencing
- What is referencing?
- Why reference?
- Common knowledge
- Referencing styles
- What type of source is this?
- Reference list vs. bibliography
- Referencing software
- Quoting & paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing & summarising
- Paraphrasing techniques
- APA Interactive
- In-text citation
- Reference list
- Online material
- Other material
- Headings in APA
- Tables and Figures
- Referencing elements
- 5th vs. 6th edition
- 6th vs. 7th edition
- Chicago style
- Chicago Interactive
- About notes system
- Notes referencing elements
- Quoting and paraphrasing
- Author-date system
- MLA Interactive
- Abbreviations
- List of works cited
- Captions for images
- 8th vs 9th edition
- Oxford style
- Other styles
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- Legal citations
- Visual material
- Sample assignments
- Sample essay 1
- Sample essay 2
- Sample annotated bibliography
- Sample book review
- Study skills
- Time management
- Intro to time management
- Procrastination & perfectionism
- Goals & motivation
- Time management for internal students
- Time management for distance students
- Memory skills
- Principles of good memory
- Memory strategies
- Note-taking
- Note-taking methods
- Note-taking in lectures
- Note-taking while reading
- Digital note-taking
- Reading styles
- In-depth reading
- Reading comprehension
- Reading academic material
- Reading a journal article
- Reading an academic book
- Critical thinking
- What is critical thinking?
- Constructing an argument
- Critical reading
- Logical fallacies
- Tests & exams
- Exam & test study
- Planning exam study
- Gathering & sorting information
- Reviewing past exams
- Phases of revision
- Last-minute study strategies
- Question types
- Short answer
- Multi-choice
- Problem / computational
- Case-study / scenario
- Open book exam
- Open web exam or test
- Take home test
- In the exam
- Online exam
- Physical exam
Being objective suggests that you are concerned about facts and are not influenced by personal feelings or biases. Part of being objective is being fair in your work. Try to consider both sides of an argument and avoid making value judgements by using words such as wonderful or appalling. Being objective also makes your work more professional and credible.
Techniques for making your writing more objective
Be explicit in expressing your ideas:.
- several ⇒ 10
- most of the population ⇒ 70%
- some time ago ⇒ three years ago; or in 2006
Avoid intensifiers which can tend to exaggerate your writing in an imprecise, subjective way:
- For example, awfully, very, really.
Part of being objective is being balanced in your work, professional and believable:
- Try to avoid making value judgements through use of words such as amazing or dreadful.
First vs. third person
Pronouns are a set of words that replace nouns. They can be used to make your work less complicated and less repetitive. Examples of pronouns include:
- First person: I, we, me, us
- Second person: you
- Third person: he, she, it, they, him, her, them
For some assignments, it is appropriate to use the first person (e.g. reflective writing). However, for other assignments the third person is preferred. Sometimes a mixture of the first and third person should be used for different purposes. So, check your assignment guidelines for each assignment, as it will differ for different assignment types , different style guides, and different disciplines. If you are unsure, then check with your course coordinator. For more on this see 1st person vs. 3rd person .
Page authorised by Director - Centre for Learner Success Last updated on 29 November, 2018
- Academic Q+A
Have a study or assignment writing question? Ask an expert at Academic Q+A
Live online workshops
- StudyUp (undergraduate)
- Campus workshops
- Albany (undergraduate)
- Albany (postgraduate)
- Albany (distance)
- Manawatu (undergraduate)
- Manawatu (postgraduate)
Upcoming events
- All upcoming events
- Academic writing and learning support
- 0800 MASSEY | (+64 6 350 5701)
- [email protected]
- Online form
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write Research Objectives

3-minute read
- 22nd November 2021
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation ? If so, you’ll want to state your research objectives in the introduction of your paper to make it clear to your readers what you’re trying to accomplish. But how do you write effective research objectives? In this post, we’ll look at two key topics to help you do this:
- How to use your research aims as a basis for developing objectives.
- How to use SMART criteria to refine your research objectives.
For more advice on how to write strong research objectives, see below.
Research Aims and Objectives
There is an important difference between research aims and research objectives:
- A research aim defines the main purpose of your research. As such, you can think of your research aim as answering the question “What are you doing?”
- Research objectives (as most studies will have more than one) are the steps you will take to fulfil your aims. As such, your objectives should answer the question “How are you conducting your research?”
For instance, an example research aim could be:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
- Replicat ing a small Singaporean study into the role of dehydration in UTIs in hospital patients (Sepe, 2018) in a larger Australian cohort.
- Trialing the use of intravenous fluids for intensive care patients to prevent dehydration.
- Assessing the relationship between the age of patients and quantities of intravenous fluids needed to counter dehydration.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Note that the objectives don’t go into any great detail here. The key is to briefly summarize each component of your study. You can save details for how you will conduct the research for the methodology section of your paper.
Make Your Research Objectives SMART
A great way to refine your research objectives is to use SMART criteria . Borrowed from the world of project management, there are many versions of this system. However, we’re going to focus on developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timebound objectives.
In other words, a good research objective should be all of the following:
- S pecific – Is the objective clear and well-defined?
- M easurable – How will you know when the objective has been achieved? Is there a way to measure the thing you’re seeking to do?
- A chievable – Do you have the support and resources necessary to undertake this action? Are you being overly ambitious with this objective?
- R elevant – Is this objective vital for fulfilling your research aim?
- T imebound – Can this action be realistically undertaken in the time you have?
If you follow this system, your research objectives will be much stronger.
Expert Research Proofreading
Whatever your research aims and objectives, make sure to have your academic writing proofread by the experts!
Our academic editors can help you with research papers and proposals , as well as any other scholarly document you need checking. And this will help to ensure that your academic writing is always clear, concise, and precise.
Submit a free sample document today to trial our services and find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Scholarly Voice: Objectivity
Try to present your argument in as objective a way as possible. Avoid judgmental and emotive language, as this often reveals that you are presenting an opinion rather than evidence or a logical argument. Note, however, that whether a phrase or word is judgmental or emotive often depends on the context. It is best to avoid phrases like "it is right , " "I believe," or "I feel . " Often these types of statements lead the writer into bias , a mistake that academic writing avoids. Remember to back up your arguments with sources and facts in order to give you credibility and a more objective tone.
For example, take a look at this sentence:
I feel that childhood obesity is unhealthy, and children’s eating habits are not right.
Note the use of "I" and the judgmental phrase "not right." Try to think of a way to portray the same information without inserting yourself or your opinion. For example, instead of saying I feel, ask yourself, "Is this a fact?" If it is a fact, write it as a statement:
Childhood obesity is unhealthy.
With this statement, you are stating a fact and removing yourself to maintain your authorial distance. Also, rather than saying their eating habits are not right (after all, who is to judge what is right and wrong in eating?), you can use statistics and valid sources to back up your ideas:
Two major causes of childhood obesity are poor nutrition and uneducated food choices (Fredricks, 2010).
Here you are giving information rather than giving a judgment. See APA 7, Chapter 5 for more guidelines for reducing bias.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Second-Person Point of View
- Next Page: Avoiding Bias
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills

Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
English that goes straight to the heart
What is an essay?
Aldous Huxley described an essay as “A literary device for saying almost everything about almost anything”.
What is an Essay?
An essay is a piece of writing that revolves around a particular theme and contains the academic opinions of the person writing it.
Daily Test - Attempt Now
An essay can perform one or more of the following functions:
- Analyses and critically evaluates a topic
- Presents the writer‘s argument for or against an idea
- Describes something
- Narrates a story
- Persuades the reader

Also, Read 6 Types of Essay
Characteristics of a Good Essay
- Brevity: Express what you want concisely. Do not beat around the bush.
- Coherence: Every sentence and paragraph should flow smoothly and logically from the previous one. A clumsily written essay reflects not only the lack of preparation but also the absence of clarity of thought.
- Unity: The essay should never stray from its main purpose. Different points of view can be introduced, but they should all be used for the same subject.
- Lucidity: The essay should be easy to read and understand. Using tough words or difficult phrases may impress a few but can confuse many others. Great writers are praised not only for their beautiful ideas but also for the simplicity of their language.
Also, Read Top 10 Essay Examples
The objective of Essay Writing
Essay writing often forms a part of English written exams to test the ability of students to
- Think critically: Critical thinking involves understanding the task at hand and evaluating it appropriately.
- Structure the ideas logically: The essay has to be structured and coherent. The ideas have to neatly flow from one paragraph to the other.
- Express views eloquently: The student should be fluent in the language he or she is writing in. Ideas when presented shoddily may not make the right impact.
Parts of an Essay
Introduction.
It constitutes the opening paragraph of the essay.
- It helps the reader get oriented with the topic.
- It states the purpose of the essay.
- It captures the interest of the reader.
- It presents the general idea of the essay.
- It often ends with the thesis or the main idea of the essay.
Body (Supporting Paragraphs)
They constitute the supporting sentences and ideas.
- They provide the reader with additional details about the main idea.
- They support the thesis of the writer.
- There is no fixed number of supporting paragraphs.
- Ideally, every supporting paragraph should contain a different idea.
It constitutes the ending paragraph(s) of the essay.
- It ties up loose ends of the paragraph.
- It helps in reiterating or highlighting the main idea.
- It summarises all the arguments.
- It brings the essay to a logical close.
- It never ends in detail.
Also, Read Short Essay Examples
Tips for Writing an Essay
Preparation.
- Read: The more you read, the better you get. Reading essays will give you the inspiration to write. It will fill you with knowledge that you can use to enrich your writing.
- Write: Practise writing essays. This will give you the necessary confidence that you require during the exams. Writing also sharpens your thought process preparing you to deal with essay questions with much ease.
1. Think about the idea given in the title or the prompt.
- What type of essay will be appropriate?
- What could be the main ideas?
- How to write the introduction, the body and the conclusion?
- Write all the ideas.
2. Structure your essay.
- Create an outline of your essay.
- Do not use more than two sentences for the introduction and conclusion, respectively.
- Therefore, it is important to plan your essay before instead of writing spontaneously.
- Arrange the ideas in chronological order if you are attempting a narrative essay.
- Arrange them in increasing order of importance while attempting a descriptive or expository essay.
- Remember to conclude the essay.
3. Use a consistent tense form while writing the essay.
4. Express clearly.
5. Be original in your ideas. Don‘t be afraid to think out of the box.
6. Use your own memories or your experiences to add to the essay.
7. Recheck for any grammatical errors after finishing the essay.
Also, Read Summarizing an Essay
Example of Essay
My native place.
My parents hail from a small village in Kerala which is nestled among mountains in a scenic district of the state. Every year, I visit my native place with my family. It is a trip that I look forward to all year. My father books the ticket two months in advance as it is difficult to procure reservations on short notice. Although I have lived in the city all my life, I feel that I never belonged to it. I have always felt at home in the quaint mountain village that is far removed from the hustle and bustle of city life.
It takes us 18 hours by train to reach the railway station that is closest to my village. The journey is usually gruelling in the summers but very pleasant in the winters and in the monsoons. We plan our trip in the summer months since we get a two-month vacation in April. In order to beat the heat, we travel by air-conditioned coaches every year. We board the train at noon and we reach our destination at 6 am the next day.
The morning air is heavy with the scent of flowers and wet foliage. The temple bells start ringing at 6:30 am and the sound of bhajans fills the air. The village is only a 20-minute rickshaw ride away from the station. When we enter my grandmother‘s house, we are welcomed by her diminutive figure holding a lamp.
According to her, it is auspicious to welcome loved ones by lighting the lamp at the altar of God. The moment we set foot into the house, we are filled with a sense of nostalgia and love. After a sumptuous yet simple breakfast, we relax with our family in the courtyard.
The cool mountain air is laden with scents of the rustic countryside. From afar, we hear the sounds of birds. My sister and I make paper boats and run to the little babbling brook that flows southwards. We set the boats on the water and watch them bob up and down. Far away from the world of video games and television, we seek fun in a world of simplicity.
The house itself has a personality. Simple, two-storeyed, made of stone walls and a thatched roof, the house is an old friend who warmly embraces you every time you meet. The rooms are small but well-maintained. On the ground floor is a room that my grandmother uses for storing condiments and grains. It is illuminated with a single light bulb and an old-fashioned lock-and-key style door. In its corner is a small bed.
The calming silence of the room soothes my ears and transports me into a magical place. I feel weightless. The smell of spices envelops me. On many occasions, I have spent hours sprawled on that bed reading a book or listening to music. If I ever have to pick a favourite place, then I have no doubt this would be it.
When twilight descends on the little hamlet, large clusters of stars start appearing in the sky. Such a sight is never seen in the city as the lights obscure the stars that appear in the sky. My grandmother lights the lamp again and we all gather around her to say our evening prayers. After enjoying her simple, rustic yet delicious meal, we retire for the night.
Sometimes when I am upset, I think of my quaint little house in the village, my grandmother‘s warm embrace, and the small room that smells of spices. They immediately help me put my worries away and bring a smile to my face.
You Asked, We Listened – Get Free Access to All Writing Lists 😍😍

6 Types of Essays
Read More »

Top 30 Essay Examples

Essay Writing Format

Long Essays
Daily reading comprehension test - attempt now, 1 thought on “what is an essay”.
How to finish or sum up essay in formal way? Thank you
Comments are closed.
Discover more from English Luv
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Goals and Objectives Analytical Essay
Introduction, need to differentiate goals and objectives, strategies to achieve goals and objectives, implementation of the strategies.
The terms goals and objectives have been used interchangeably as though to imply they are synonymous. Although the line that distinguishes these two is very thin, there is a difference between these two concepts.
This discussion focuses on the differences between goals and objectives and why each of them is important to an organization. This discussion will further focus on strategies to achieve goals and objectives and the implementation of these strategies.
A mission also referred to as a mission statement in most organizations is a short phrase or number of words which states the purpose for which an organization or a company was set up. The mission statement acts as guide to the organization’s employees in their activities by ensuring that they keep within the mission of the company.
Mission and vision though often confused as to mean the same things are different in that mission is the purpose of existence of an organization while vision is what the organization hopes to achieve.
It is important that the line between goals and objectives is recognized. Goals on one hand are aims that are set on a long term basis which an individuals or an organization hopes to achieve after a given period of time.
Objectives on the other hand are more concrete and specific and their attainability is set for a relatively shorter time. This means that it is easy to validate objectives than it is to validate goals.
Goals also tend to be broad while objectives are limited in their scope. Due to the short time span that objectives are expected to be attained, they are considered tangible while goals are intangible and always considered as intentions to do something as opposed to objectives which are precise.
If you have a proposal that you are making, being able to clearly draw the line between goals and objectives is important if your proposal is to be accepted.
Both objectives and goals are important in any organizations as they are tools that help an organization get to where it wants to be. An organization should therefore have both aspects for the forward movement of the company and to be able to ensure whether or not accomplishments have been achieved.
It is of paramount importance for any organization to have well laid down strategies to help the organization achieve its goals and objectives. The first strategy is to be clear on what you want. An organization cannot come up with an effective strategy of attaining goals and objectives if they do not know what they want to achieve.
The next important thing is to be committed in whatever it is that the organization wants to achieve. (Vurnum, 2010). Setting goals and objectives is the easy part, attaining them, is the most difficult and challenging part. This means that an organization must work towards the set goals and objectives without relenting or looking back. It is only through putting considerable efforts that expected outcome will be realized.
Be S.M.A.R.T is the other strategy that organizations must embrace so as to succeed in the attainment of their goals and objectives. S.M.A.R.T is an acronym for specific, measurable, achievable, and relevant and time bound. This means that the goals and objectives that a company sets must be specific. If the goals and objectives are general, then it will be difficult in the end to determine whether or not they have been achieved. Goals and objectives must also be measurable.
It should be possible to measure and determine the extent to which the goals and objectives have been attained and what is remaining for the two to be fully achieved. (Rouillard, 2003).The goals and objectives set must also be relevant to the core business of the company.
If they go outside the scope of the business then they may not be attained. Goals and objectives must also be time bound meaning that they must be achieved within a specific period of time. An organization cannot set goals and objectives which it hopes to achieve within an indefinite period of time.
Once the strategies have been developed, the next thing is to implement these strategies. This is done by considering six important factors which are:
- Action planning- this involves coming up with a number of actions that need to be carried out, estimating the finances that will be required for these actions to be successful and giving a time limit within which these actions should be complete.
- Organizational structure- This is taking into consideration the manner in which the organization is structured.
- Considering human resource needs so that the people in charge of the implementation process do fully understand what they are expected to do.
- Annual business plan- having the picture of the organization on a long term basis.
- Monitoring and Control- This is an evaluation to ensure that the organization is still on track.
- Linkage- This is ensuring that all the above factors are interconnected and working in harmony.
The success of an organization is highly dependent on the kind of goals and objectives that have been set by the management and also the laid down mechanisms that are meant to oversee the implementation. With these tips in mind, an organization cannot go wrong.
Rouillard, L. (2003). Goals and goal setting: achieving measured objectives . London: Cengage Learning.
Vurnum, G. (2010). Goals and Objectives: 92 Affirmations That Apply Smart Goal Setting to Achieve Your Goals in Life. NY : Create Space.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 24). Goals and Objectives. https://ivypanda.com/essays/goals-and-objectives/
"Goals and Objectives." IvyPanda , 24 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/goals-and-objectives/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Goals and Objectives'. 24 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Goals and Objectives." October 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/goals-and-objectives/.
1. IvyPanda . "Goals and Objectives." October 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/goals-and-objectives/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Goals and Objectives." October 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/goals-and-objectives/.
- Testing Methodologies to Validate Functionalities
- Statistics in Marketing Research: Does Statistical Precision Validate Results?
- Measurable Learning Outcomes After Any Course
- Stream of Consciousness: Mary the Measurable Woman
- Attaining Power and Influence in a Group
- The Business Strategy Elements and Principles
- The Faith and Ethics Course: Attaining Ethical Maturity
- Cultural Changes and Attaining Organizational Goals
- Employee Performance Management
- Employee Development Plan
- Small Businesses Attractivity
- Strategic Planning: Achieving Away-From-Home Experience
- Globalization Theory, Its Benefits and Shortcomings
- Optimizing Organization Design for the Future
- Formal Planning's Strengths and Weakness

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.3: The Argumentative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58378
- Lumen Learning
Learning Objectives
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you argue that something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the causes of the decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean and make a case for your cause.
Evaluation Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your education class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you must propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a proposal that would increase retention rates at your college.
Narrative Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past.
Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/20277
Essay Examples
- Click here to read an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contributors and Attributions
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
- How it works
How to Write the Dissertation Aims and Objectives – Guide & Examples
Published by Grace Graffin at January 27th, 2023 , Revised On October 9, 2023
Aims and objectives are among the essential aspects of a dissertation. If you write aims and objectives effectively, they can act as a foundation to give your research clarity and focus.
This article will provide you with all the necessary information regarding aims and objectives, their differences, writing tips , and the common mistakes you should avoid while writing them.
The aim is often a single sentence or a short paragraph that describes your dissertation’s main goal and intent. It tells what you hope to achieve at the end. You should write the aim so that it becomes identifiable when it is achieved with the completion of your dissertation .
The aim is written in a subsection of the introduction to clarify the overall purpose of the dissertation .
Example: It is often observed that employees in culturally diverse workplaces struggle to work effectively in a team. A probable cause of this issue is bullying at the workplace. This research investigates the impact of bullying on employee job satisfaction at culturally diverse workplaces and the resulting loss of employee productivity. This research will use surveys and case study analysis to analyze the impact of bullying on employees.
The objectives in a dissertation describe the ways through which you intend to achieve the research aim. They are specific statements that break down the aim into several smaller key sections of the overall research. Suitable objectives can help you stay focused and conduct research in the direction of your aim.
The number of objectives should be realistic; usually, between three to six, and each one should be possible to achieve. The following example shows the objectives for the previously-mentioned dissertation aim.
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace
The objectives of a dissertation should be SMART.
- Specific: should be precise, focused, and well-defined
- Measurable: the progress should be measurable, and you should be able to determine when you have achieved an objective.
- Achievable: you should be able to carry out the required action within your available resources
- Relevant: should be related to the dissertation aim
- Time-bound: should be possible within the available time
Differences between aims and objectives
Aims and objectives are often mixed, but there are clear differences between them.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

How to write aims and objectives?
There is no particular way or standard to write the aims and objectives. Different researchers have different writing styles, and often it can be influenced by your research supervisor. However, you should follow certain basic principles while writing aims and objectives in a dissertation.
Writing the aim statement
The aim statement should cover the following essential elements.
- Why is the research necessary? (covers the underlying problem on which the study is to be conducted)
- What is the research about? (description of the research title)
- How are you going to conduct it? (a brief statement of intended research methods)
An appropriate aim clearly defines the research purpose without confusing the reader. If you struggle to explain your research and its importance in simpler terms, you should consider refining your research to clarify it further.
Writing objectives
The objectives describe how you would achieve your research aim. You can do this through the following steps,
- The first one to two objectives can be applied to the literature review . (Verbs to be used: investigate, examine, study)
- One objective can be applied to the methodology portion. (Verbs to be used: collect, select, demonstrate, estimate)
- Two to three objectives can cover the critical evaluation or discussion chapters (Verbs to be used: analyze, compare, evaluate)
- The final objective will cover the conclusion or recommendation portion. (Verbs to be used: conclude, recommend)
Instead of writing like a paragraph, the objectives should be written as a numbered list to give them more clarity.
How many aims and objectives should be there?
It depends upon the topic of your research and mainly upon your supervisor’s requirements. Generally, a dissertation has a single broad statement as the research aim. However, it is acceptable to include a main aim along with two to three subsidiary aims.
Similarly, the number of objectives should be realistic and sufficient to measure the progress regarding the achievement of the research aim. Their number can generally vary from three to six depending upon the aim.
Common mistakes to avoid while writing research aims and objectives
- Writing a broad research aim
Writing a broad research aim is a common mistake, and it often becomes difficult to achieve. It may create a problem when you are asked to prove how you have achieved your aims during your viva defense . It would be best to narrow your study to a specific area in the early stages of the dissertation.
- Formulating overlapping research objectives
The objectives should be written such that they are measurable and distinct from each other. If they overlap, it makes it difficult to structure your dissertation properly in specific chapters.
- Setting unrealistic aims
Students often get over-ambitious while describing the research aim and face problems afterward in achieving those aims. You should avoid this mistake and be realistic about what you can achieve in the available time and resources.
Aims and objectives are the sections that require significant time and attention to avoid future hassles while conducting research and writing your dissertation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to set dissertation aims and objectives.
To set dissertation aims and objectives, define your research goals clearly. Aims state what you want to achieve, while objectives outline specific, measurable steps to reach those goals. Ensure they align with your research question and contribute to your study’s significance.
You May Also Like
Elevate your professional profile with the CapCut Creative Suite! Craft compelling video resumes that captivate employers in the job market.
It can be difficult to choose a suitable topic for your dissertation. Find out the tips to help you to decide the best dissertation topic in this article.
We have identified the most common dissertation questionnaire mistakes made by researchers that need to be avoided for good dissertations and thesis
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
How to Write an Awesome Essay About Your Career Goals
- Before you begin, ask yourself a few key questions like:
- What are my short-term and long-term career goals?
- Where do I see myself in ten years?
- What events in my life have led me to have these goals?
- What major will help me reach my goals?
- What skills do I need to reach my goals?
- What impact do I want to have on society?
Career Goals Essay Template
Need more inspiration.
After you brainstorm the responses to these questions, look for common themes, or pick out the most interesting stories. You can build your main essay “thesis” or idea around this.
Once you’ve got the main idea, create an outline to put your ideas into essay format. This will give you a general idea of structure.
You can use the career essays template below to give you some ideas. But remember that some rules are meant to be broken, so don’t be afraid to be innovative and think outside the box!
Also, when you’re done, head over to Going Merry to apply for the Career Goals scholarship essay bundle (one essay, one application, multiple scholarships!). You might as well make that essay count. Sign up for Going Merry to apply for scholarships more efficiently.

Here’s a paragraph-by-paragraph breakdown:
Paragraph 1 : Establish the main theme of what you’re going to talk about. It should also grab the reader’s attention. For example, instead of starting your essay with something generic (e.g. Ever since I was a little girl, I wanted to be a zoologist), get creative with it! Try something like My greatest memory as a young girl was going to the zoo for the first time or While most kids play house or school, I always wanted to play zookeeper.
Paragraph 2 : Elaborate on what inspired your career goals. Perhaps it was a relative, a TV show, or simply an experience that you had. Remember that old writing adage, “Show, don’t tell.” In other words, try to demonstrate your interest with story or description.
Paragraph 3 : Discuss your short-term career goals and your intended major. How will your intended major help you reach these goals? What skills do you need to learn to reach them? At the end of the paragraph, try discussing how your short-term goals can help you achieve your long-term goals.
Paragraph 4 : Focus on your long-term goals and the impact that you hope to have on society. If you’re not sure what your long-term goals are, don’t sweat it; they’ll probably change anyways. You can instead focus on the difference you’d like to make overall. And don’t worry too much about the size of the impact…remember that just doing what you’re truly passionate about has a massive impact on those around you.
The last paragraph is your conclusion. You can use this paragraph to summarize what you discussed in the previous few paragraphs. If you want to be even more creative, try ending your essay with a question for your readers or a new insight. Good luck!
And now that you’re ready with that essay, put it to good use! You can recycle that same essay, when applying for the Career Goals Scholarship Bundle. We’ve joined together multiple scholarships (all requesting essays on career goals), into just ONE simple application! See more info here , or just sign up to get going.
Check out examples from other students just like you. Here are links to some great career goal essay examples:
- Example 1
- Example 2
- Example 3
Or maybe you’re looking for help with an academic goals essay — we’ve got you covered there too.
Also, check out this helpful list of the 10 most common scholarship essay topics !

Sign up for Going Merry today, and upload your career goal essay right to your profile. It’s that easy!
- Recent Posts
- 7 Outstanding Oregon Scholarships for 2021 - November 6, 2020
- Great Scholarships for Students in Ohio for 2021 - November 4, 2020
- 38 Weird Scholarships for Unique Students in 2023 - August 2, 2020
Ready to find scholarships that are a match for you?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Objective writing places the emphasis on facts, information and arguments, and can be contrasted with subjective writing which relates to personal feelings and biases. ... Another way to write objectively is to personify the writing (essay, report, etc.) and make this the subject of the sentence. This essay considers the role of diesel ...
In short, differences between these styles concern the following: The ground for objective essays is facts; for subjective essays - personal opinions and beliefs. Objective papers report the findings from scientific sources, while subjective ones describe the writer's thoughts. The objective essay's goal is to help the reader make a decision.
When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a source or collection of sources, you will have the chance to wrestle with some of the
Objectives for Writing an Essay. An essay does more than inform or persuade a reader. The process of writing an essay teaches a student how to research a topic and organize her thoughts into an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Essay writing objectives apply to expository and persuasive essays on a variety of topics.
Concentrating on a few key objectives can effectively maintain focus and clarity and prevent overwhelming. #3. Use action verbs. You can start each objective with one of the following measurable verbs: Describe, Explain, Identify, Discuss, Compare, Define, Differentiate, List, and more.
Remain objective when you compose an essay by keeping your arguments balanced in support or for rebuttal of the hypothesis. Step 3. Read back over the essay as you write and remain focused on your objectivity. To be objective is the opposite of being subjective. Being objective is being able to remove yourself from the personal emotions and ...
Objective is a word to describe something that is purely factual and not influenced by personal feelings. Therefore, objective writing is writing that can be verified through evidence and facts ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Writing objectively. Being objective suggests that you are concerned about facts and are not influenced by personal feelings or biases. Part of being objective is being fair in your work. Try to consider both sides of an argument and avoid making value judgements by using words such as wonderful or appalling.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example: This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
Try to present your argument in as objective a way as possible. Avoid judgmental and emotive language, as this often reveals that you are presenting an opinion rather than evidence or a logical argument. Note, however, that whether a phrase or word is judgmental or emotive often depends on the context. It is best to avoid phrases like "it is ...
The objective of Essay Writing. Essay writing often forms a part of English written exams to test the ability of students to. Think critically: Critical thinking involves understanding the task at hand and evaluating it appropriately. Structure the ideas logically: The essay has to be structured and coherent.
Summary. One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and ...
Be S.M.A.R.T is the other strategy that organizations must embrace so as to succeed in the attainment of their goals and objectives. S.M.A.R.T is an acronym for specific, measurable, achievable, and relevant and time bound. This means that the goals and objectives that a company sets must be specific. If the goals and objectives are general ...
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
In 100 words, tell us about your career goals. 100-word essays, while short, can take careful planning and thought. With so little space to communicate your ideas, it's important to ensure you maximize the strength of every sentence. Scholarship teams might give you this prompt to assess your future goals quickly or to supplement some of the ...
Learning Objectives. Examine types of argumentative essays; Argumentative Essays. You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you're writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you'll be asked to ...
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying. 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace. 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees. 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Remember the goal of the career goals essay. Demonstrate a passion for a problem, and convince the admissions committee that you are the type of person who can solve it. You can show off that passion in 1,000 words or 250 words. No matter the essay's length, the heart of your approach is the same. The introduction.
Career Goals Essay Template. Here's a paragraph-by-paragraph breakdown: Paragraph 1: Establish the main theme of what you're going to talk about.It should also grab the reader's attention. For example, instead of starting your essay with something generic (e.g. Ever since I was a little girl, I wanted to be a zoologist), get creative with it!