- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In

Definition of synthesis
- amalgamation
- combination
- intermixture
Examples of synthesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'synthesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Greek, from syntithenai to put together, from syn- + tithenai to put, place — more at do
1589, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing synthesis
synthesis gas
Dictionary Entries Near synthesis
Cite this entry.
“Synthesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/synthesis. Accessed 1 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of synthesis, medical definition, medical definition of synthesis, more from merriam-webster on synthesis.
Nglish: Translation of synthesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of synthesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about synthesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
The tangled history of 'it's' and 'its', more commonly misspelled words, why does english have so many silent letters, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - mar. 29, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Grammar Coach ™
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
the combining of the constituent elements of separate material or abstract entities into a single or unified entity (opposed to analysis ).
a complex whole formed by combining.
Chemistry . the forming or building of a more complex substance or compound from elements or simpler compounds.
Philosophy . the third stage of argument in Hegelian dialectic , which reconciles the mutually contradictory first two propositions, thesis and antithesis.
Biology . modern synthesis , a consolidation of the results of various lines of investigation from the 1920s through the 1950s that supported and reconciled the Darwinian theory of evolution and the Mendelian laws of inheritance in terms of natural selection acting on genetic variation.
Psychology , Psychiatry . the integration of traits, attitudes, and impulses to create a total personality.
Origin of synthesis
Other words from synthesis.
- syn·the·sist, noun
- non·syn·the·sis, noun, plural non·syn·the·ses.
- re·syn·the·sis, noun, plural re·syn·the·ses.
Words that may be confused with synthesis
- antithesis , synthesis , thesis
Words Nearby synthesis
- syntax language
- synthesis gas
- synthesizer
- synthespian
Dictionary.com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2024
How to use synthesis in a sentence
Journalists and watchdogs have been pointing out these issues for years, but the film’s value isn’t its novelty—it’s that it’s a polished and cohesive synthesis of various threads of the conversation.
According to a 2017 paper on BCAAs and muscle protein synthesis , leucine triggers the necessary chemical reactions needed to fuse together muscle fibers, perhaps making this process more efficient.
Like everything our bodies do, muscle protein synthesis is chemically complicated, and can be affected by a variety of compounds, including hormones like testosterone and certain amino acids.
In particular, none of the genes involved in the synthesis , modification or degradation of retinoic acid were present.
In late 2018, for example, Insilico was generating novel molecules in fewer than 46 days, and this included not just the initial discovery, but also the synthesis of the drug and its experimental validation in computer simulations.
Palmer's inability to reach a synthesis in almost any area of his life is what makes him exasperating.
I may get the whole synthesis of something, or most of it, an initial impact.
David Frum on Allen Guelzo's compendious synthesis of new thinking about slavery and its aftermath.
Almost all Christians, even most textualists, accept the need for exegesis, synthesis , and theological application.
This was code: the Hebrew writers of Zionism were now reprising this Hellenizing genius and synthesis .
But where there is no existing relation between the words or ideas, it is a case for synthesis , to be taught hereafter.
In such cases, synthesis , which is taught hereafter, develops an indirect relation.
synthesis will be sometimes hereafter resorted to to connect in our minds an event to its date.
Recollective synthesis or Thoughtive Unification is used where no relation exists.
Dorlands Dictionary: synthesis —The artificial building up of a chemic compound by the union of its elements.
British Dictionary definitions for synthesis
/ ( ˈsɪnθɪsɪs ) /
the process of combining objects or ideas into a complex whole : Compare analysis
the combination or whole produced by such a process
the process of producing a compound by a chemical reaction or series of reactions, usually from simpler or commonly available starting materials
linguistics the use of inflections rather than word order and function words to express the syntactic relations in a language : Compare analysis (def. 5)
philosophy archaic synthetic reasoning
(in the writings of Kant) the unification of one concept with another not contained in it : Compare analysis (def. 7)
the final stage in the Hegelian dialectic, that resolves the contradiction between thesis and antithesis
Derived forms of synthesis
- synthesist , noun
Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Scientific definitions for synthesis
[ sĭn ′ thĭ-sĭs ]
The formation of a chemical compound through the combination of simpler compounds or elements.
- synthesize verb
The American Heritage® Science Dictionary Copyright © 2011. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of synthesis noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- synthesis of A with B the synthesis of art with everyday life
- synthesis of A and B a synthesis of traditional and modern values
Definitions on the go
Look up any word in the dictionary offline, anytime, anywhere with the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app.

Definition of 'synthesis'

Video: pronunciation of synthesis

synthesis in British English
Synthesis in american english, synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry, examples of 'synthesis' in a sentence synthesis, cobuild collocations synthesis, trends of synthesis.
View usage for: All Years Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
In other languages synthesis
- American English : synthesis / ˈsɪnθɪsɪs /
- Brazilian Portuguese : síntese
- Chinese : 结合体
- European Spanish : síntesis
- French : synthèse
- German : Synthese
- Italian : sintesi
- Japanese : 総合体
- Korean : 종합
- European Portuguese : síntese
- Latin American Spanish : síntesis
- Thai : การสังเคราะห์
Browse alphabetically synthesis
- synthase activity
- synthesis gas
- synthesis pathway
- synthesiser
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'S'
Related terms of synthesis
- lipid synthesis
- voice synthesis
- aperture synthesis
- chemical synthesis
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5
Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of synthesis – Learner’s Dictionary
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
(Definition of synthesis from the Cambridge Learner's Dictionary © Cambridge University Press)
Translations of synthesis
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
null and void
having no legal force

Sitting on the fence (Newspaper idioms)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- Learner’s Dictionary Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add synthesis to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Synthesis Reaction Definition and Examples
Overview of a Synthesis or Direct Combination Reaction
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction is one of the most common types of chemical reaction.
In a synthesis reaction, two or more chemical species combine to form a more complex product: A + B → AB.
In this form, a synthesis reaction is easy to recognize because you have more reactants than products. Two or more reactants combine to make one larger compound.
One way to think of synthesis reactions is that they are the reverse of a decomposition reaction .
Synthesis Reaction Examples
In the simplest synthesis reactions, two elements combine to form a binary compound (a compound made of two elements). The combination of iron and sulfur to form iron (II) sulfide is an example of a synthesis reaction :
8 Fe + S 8 → 8 FeS
Another example of a synthesis reaction is the formation of potassium chloride from potassium and chlorine gas :
2K (s) + Cl 2(g) → 2KCl (s)
As in these reactions, it's common for a metal to react with a nonmetal. One typical nonmetal is oxygen, as in the everyday synthesis reaction of rust formation :
4 Fe (s) + 3 O 2 (g) → 2 Fe 2 O 3 (s)
Direct combination reactions aren't always just simple elements reacting to form compounds: Another everyday synthesis reaction, for example, is the reaction that forms hydrogen sulfate, a component of acid rain. Here, the sulfur oxide compound reacts with water to form a single product:
SO 3 (g) + H 2 O (l) → H 2 SO 4 (aq)
Multiple Products
So far, the reactions you have seen have only one product molecule on the right-hand side of the chemical equation. Let's take a look at more complex reactions with multiple products. For example, the overall equation for photosynthesis:
CO 2 + H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2
The glucose molecule is more complex than either carbon dioxide or water.
Remember, the key to identifying a synthesis or direct combination reaction is to recognize two or more reactants form a more complex product molecule.
Predictable Products
Certain synthesis reactions form predictable products. For example:
- Combining two pure elements will form a binary compound.
- A metallic oxide and carbon dioxide will form a carbonate.
- Binary salts combined with oxygen form a chlorate.
- Synthesis Reaction Description Plus Examples
- Chemical Reaction Definition and Examples
- Types of Chemical Reactions
- How Many Types of Chemical Reactions Are There?
- 4 Types of Inorganic Chemical Reactions
- Decomposition Reaction Definition
- What Is a Chemical Reaction?
- Single-Displacement Reaction Definition and Examples
- Examples of Chemical Reactions in Everyday Life
- Simple Chemical Reactions
- Chemistry Vocabulary Terms You Should Know
- Chemosynthesis Definition and Examples
- What Are the Products of Photosynthesis?
- Chemical Reaction Classification Practice Test
- Combustion Reactions in Chemistry
- Catalysts Definition and How They Work
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
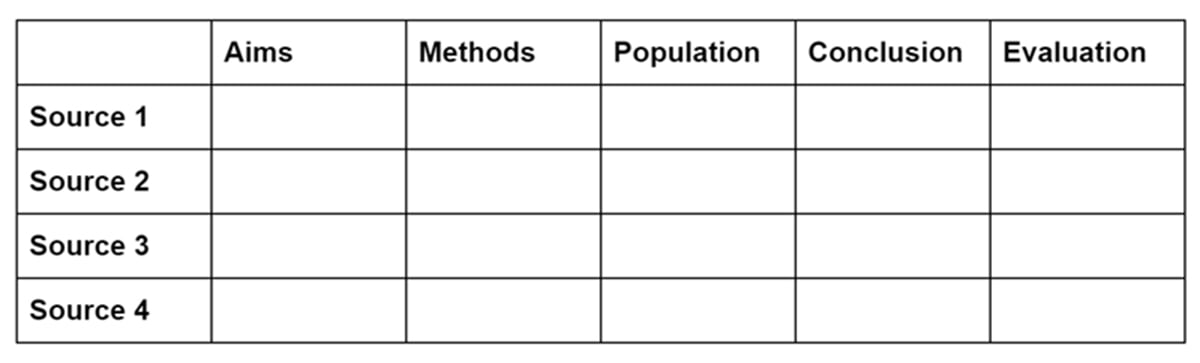
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.

Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
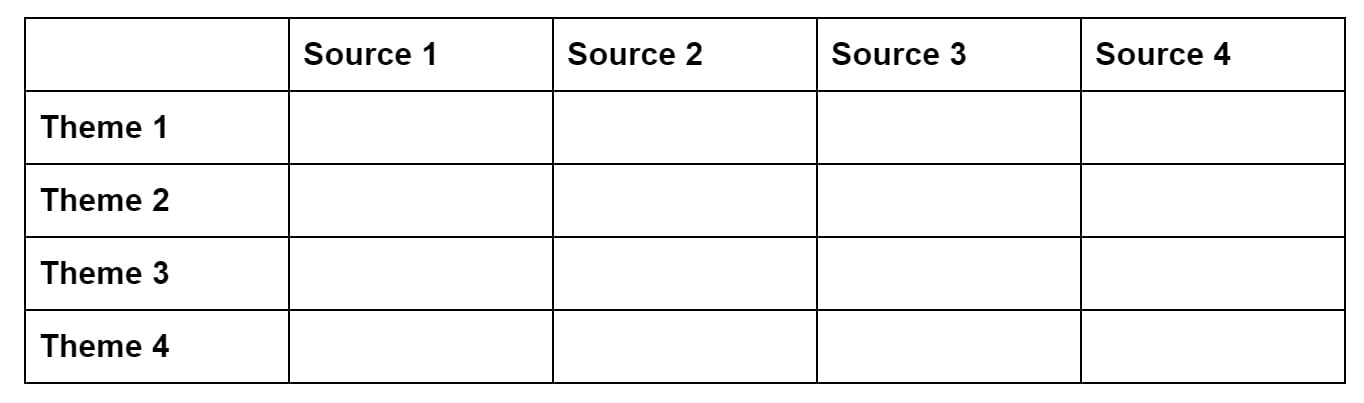
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
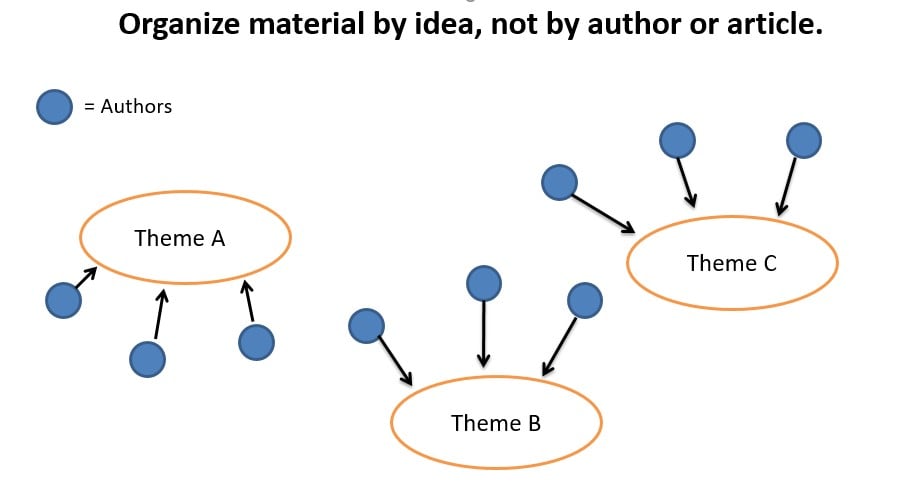
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Definition noun, plural: syntheses ( biochemistry ) The production of an organic compound in a living thing, especially as aided by enzymes Supplement In general, the term synthesis pertains to the creation of something. It is the process of combining two or more components to produce an entity. In biochemistry, it refers to the production of an organic compound in a living thing, especially as aided by enzymes. There are several syntheses occurring in the cell or organism. The creation of an organic compound in a living organism is referred to as biosynthesis. One of them is photosynthesis, a synthesis of complex organic material using carbon dioxide, water, inorganic salts, and light energy (from sunlight) captured by light-absorbing pigments, such as chlorophyll and other accessory pigments. In other relevant fields, such as chemistry, the term refers to the act or process of forming a complex substance by combining or integrating two or more chemical entities, especially through a chemical reaction. In psychiatry, synthesis pertains to the integration of different elements of the personality, in opposition to analysis. Word origin: Latin synthesis , from Ancient Greek synthesis (a putting together) See also:
- biosynthesis
Related term(s):
- photosynthesis
- Kiliani-fischer synthesis
- Merrifield synthesis
- Protein synthesis
- Dna synthesis
- Gene synthesis
- Synthesis of continuity
- Synthesis period
Related form(s):
- synthesize or synthesise ( verb , to produce substance by combining chemical precursors)
Last updated on July 23rd, 2021
You will also like...

Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis

Protein Synthesis

Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis

Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism

Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance

Animal Growth Hormones
Related articles....

Tools and Methods for Data Collection in Ethnobotanical Studies of Homegardens

Biodiversity

Sex Reversal – When Males Grew Ovaries Instead of Testes

A Protein Being Born – a live cell imaging of RNA translation
Cells know when to separate at mitosis

OASIS: Writing Center
Video transcripts, analyzing & synthesizing sources: synthesis: definition and examples.
Last updated 11/8/2016
Video Length: 2:50
Visual: The screen shows the Walden University Writing Center logo along with a pencil and notebook. “Walden University Writing Center.” “Your writing, grammar, and APA experts” appears in center of screen. The background changes to the title of the video with open books in the background.
Audio: Guitar music plays.
Visual: Slide changes to the title “Moving Towards Synthesis” and the following:
Interpreting, commenting on, explaining, discussion of, or making connections between MULTIPLE ideas and sources for the reader.
Often answers questions such as:
- What do these things mean when put together?
- How do you as the author interpret what you’ve presented?
Audio : Synthesis is a lot like, I like to say it's like analysis on steroids. It's a lot like analysis, where analysis is you're commenting or interpreting one piece of evidence or one idea, one paraphrase or one quote. Synthesis is where you take multiple pieces of evidence or multiple sources and their ideas and you talk about the connections between those ideas or those sources. And you talk about where they intersect or where they have commonalities or where they differ. And that's what synthesis is. But really, in synthesis, when we have synthesis, it really means we're working with multiple pieces of evidence and analyzing them.
Visual: Slide changes to the title “Examples of Synthesis” and the following example:
Ang (2016) found that small businesses that followed the theory of financial management reduced business costs by 12%, while Sonfield (2015) found that this theory reduced costs by 17%. These studies together confirmed that adopting the theory of financial management reduces costs for U.S. small businesses.
Audio: So here's an example for you. In this eaxmple we have Ang (2016), that's source number 1, right? Then Sonfield (2015), that's source number 2. They are both using this theory and found that it reduced costs by both 12% and 17%. So this is my evidence, right?
I have one sentence, but two pieces of evidence, because we're working with two different sources, Ang and Sonfield, one and two. In my next sentence, my last sentence here, we have my piece of synthesis. Because I'm taking these two sources and saying that they both found something very similar. They confirmed that adopting the theory for financial management reduces costs for small businesses. So I'm showing the commonality between these two sources. So it's a very, sort of, not simple, but, you know, clean approach to synthesis. It's a very direct approach to kind of showing the similarities between these two sources. So that's an example of synthesis, okay.
Visual : The following example is added to the slide:
Sharpe (2016) observed an increase in students’ ability to focus after they had recess. Similarly, Barnes (2015) found that hands-on activities also helped students focus. Both of these techniques have worked well in my classroom, helping me to keep my students engaged in learning.
Audio: Another example here. So Sharpe found that one thing helps students. Barnes found another thing helps students focus. Two different sources, two different ideas. In the bold sentence of synthesis, I'm taking these two ideas together and talking about how they have both worked well in my classroom.
The synthesis that we have here kind of take two different approaches. The first example is more about how these studies confirm something. The second example is about how these two ideas can be useful in my own practice, I'm applying it to my own practice, or the author is applying it to their own practice in the classroom. But they both are examples of synthesis and taking different pieces of evidence showing how they work together or relate, okay.
I kind of like to think of synthesis as taking two pieces of a puzzle. So each piece of evidence is a piece of the puzzle. And you're putting together those pieces for the reader and saying, look, this is the overall picture, right? This is what we can see, when these two pieces--or three pieces--of the puzzle are put together. So it's kind of like putting together a puzzle.
Visual: “Walden University Writing Center. Questions? E-mail [email protected] ” appears in center of screen.
- Previous Page: Analyzing & Synthesizing Sources: Analysis in Paragraphs
- Next Page: Analyzing & Synthesizing Sources: Synthesis in Paragraphs
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix
Published on July 4, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It’s a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research.
Synthesizing sources involves more than just summarizing . You must emphasize how each source contributes to current debates, highlighting points of (dis)agreement and putting the sources in conversation with each other.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field or throughout your research paper when you want to position your work in relation to existing research.
Table of contents
Example of synthesizing sources, how to synthesize sources, synthesis matrix, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about synthesizing sources.
Let’s take a look at an example where sources are not properly synthesized, and then see what can be done to improve it.
This paragraph provides no context for the information and does not explain the relationships between the sources described. It also doesn’t analyze the sources or consider gaps in existing research.
Research on the barriers to second language acquisition has primarily focused on age-related difficulties. Building on Lenneberg’s (1967) theory of a critical period of language acquisition, Johnson and Newport (1988) tested Lenneberg’s idea in the context of second language acquisition. Their research seemed to confirm that young learners acquire a second language more easily than older learners. Recent research has considered other potential barriers to language acquisition. Schepens, van Hout, and van der Slik (2022) have revealed that the difficulties of learning a second language at an older age are compounded by dissimilarity between a learner’s first language and the language they aim to acquire. Further research needs to be carried out to determine whether the difficulty faced by adult monoglot speakers is also faced by adults who acquired a second language during the “critical period.”
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

To synthesize sources, group them around a specific theme or point of contention.
As you read sources, ask:
- What questions or ideas recur? Do the sources focus on the same points, or do they look at the issue from different angles?
- How does each source relate to others? Does it confirm or challenge the findings of past research?
- Where do the sources agree or disagree?
Once you have a clear idea of how each source positions itself, put them in conversation with each other. Analyze and interpret their points of agreement and disagreement. This displays the relationships among sources and creates a sense of coherence.
Consider both implicit and explicit (dis)agreements. Whether one source specifically refutes another or just happens to come to different conclusions without specifically engaging with it, you can mention it in your synthesis either way.
Synthesize your sources using:
- Topic sentences to introduce the relationship between the sources
- Signal phrases to attribute ideas to their authors
- Transition words and phrases to link together different ideas
To more easily determine the similarities and dissimilarities among your sources, you can create a visual representation of their main ideas with a synthesis matrix . This is a tool that you can use when researching and writing your paper, not a part of the final text.
In a synthesis matrix, each column represents one source, and each row represents a common theme or idea among the sources. In the relevant rows, fill in a short summary of how the source treats each theme or topic.
This helps you to clearly see the commonalities or points of divergence among your sources. You can then synthesize these sources in your work by explaining their relationship.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Synthesizing sources means comparing and contrasting the work of other scholars to provide new insights.
It involves analyzing and interpreting the points of agreement and disagreement among sources.
You might synthesize sources in your literature review to give an overview of the field of research or throughout your paper when you want to contribute something new to existing research.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). Synthesizing Sources | Examples & Synthesis Matrix. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/synthesizing-sources/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, signal phrases | definition, explanation & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, how to find sources | scholarly articles, books, etc., "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Chemistry Learner
It's all about chemistry.
- Chemical Bonds
- Chemical Reactions
- Materials Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Periodic Trends
- Periodic Table Groups
- How to Read Periodic Table
- Naming Covalent Compounds Worksheets
- Net Ionic Equation Worksheets
- Types of Chemical Reactions Worksheets
- Word Equations Worksheets
- Valence Electrons Worksheets
- Graphing Periodic Trends Worksheets
- Periodic Trends Ionization Energy Worksheets
- Atomic Structure And Isotopes Worksheets
Synthesis Reaction (Combination Reaction)
What is a synthesis reaction, how to identify a synthesis reaction, example of synthesis reaction, different types of synthesis reaction, examples of synthesis reactions in everyday life.
A synthesis reaction is a reaction in which two or more reactants chemically bond and combine to form a product. A synthesis reaction is also known as a combination reaction. Most synthesis reactions are exothermic reactions, i.e., heat is released during the reaction.
General Equation
The general chemical equation for a synthesis reaction is given by the following equation.
When writing an actual reaction, the reaction must be balanced.

A synthesis reaction combines all the reactants of the reaction to form a product. To recognize a synthesis reaction, look for a product that contains all the reactant atoms.
An example of a combination reaction is the combination of aluminum (Al) and oxygen (O 2 ) to aluminum oxide (Al 2 O 3 ).
4 Al (s) + 3 O 2 (g) → 2 Al 2 O 3 (s)
There are three types of synthesis reaction.
1. Reaction between two elements
- The reaction between hydrogen (H 2 ) and nitrogen (N 2 ) to form ammonia (NH 3 )
N 2 (g) + 3 H 2 (g) → 2 NH 3 (g)
- The reaction between carbon (C) and oxygen (O 2 ) to form carbon dioxide (CO 2 )
C (s) + O 2 (g) → CO 2 (g)
- When sodium (Na) metal reacts with chlorine (Cl 2 ) gas, the reaction results in sodium chloride (NaCl), also known as common salt
2 Na (s) + Cl 2 (g) → 2 NaCl (s)
- The reaction between iron (Fe) and oxygen (O 2 ) results in iron (III) oxide (Fe 2 O 3 ), commonly known as rust. Rusting is a naturally occurring phenomenon.
4 Fe (s) + 3 O 2 (g) → 2 Fe 2 O 3 (s)
2. Reaction between two compounds
- When magnesium oxide (MgO) and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) combine, the resulting product is magnesium carbonate (MgCO 3 )
MgO (s) + CO 2 (s) → MgCO 3 (s)
3. Reaction between an element and a compound
- The reaction between carbon monoxide (CO) and oxygen (O 2 ) yields carbon dioxide (CO 2 ).
2 CO (g) + O 2 (g) → 2 CO 2 (g)

There are a few examples of the synthesis reaction in real and daily life. Almost all real-life examples are seen in the industry. During industrial production, the synthesis reaction plays a significant part in synthesizing new compounds.
- Synthesis of ammonia
- Commercial production of slaked lime (calcium hydroxide)
- Production of sodium chloride or common salt
- Preparation of hydrochloric acid and ammonium chloride
Other examples include
- Photosynthesis
Ans. A decomposition reaction is one when a substance decomposes into two or more products. This reaction is the opposite of what a combination does.
Ans. Yes. In fact, most common oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions are combination reactions.
Ans. Yes, a combination reaction can be an oxidation reaction if one of the reactants is oxygen.
Ans. While all combination reactions are exothermic, there can be an exception. The production of nitric oxide (NO) from nitrogen and oxygen is an endothermic reaction.
Ans. Dehydration synthesis is the formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants, followed by the loss of a water molecule.
Ans. Dehydration synthesis reactions build up the molecules and generally require energy, while hydrolysis reactions break down the molecules and generally release energy. The two are opposite to one another.
- Opentextbc.ca
- Chem.wisc.edu
- Cpanhd.sitehost.iu.edu
- Amrita.olabs.edu.in
- Chem.libretexts.org
Trending Topics
© 2024 ( Chemistry Learner )
Synthesis Reactions — Definition & Examples - Expii
Synthesis reactions — definition & examples.
In a synthesis reaction, or combination reaction, simpler reactants combine to form more complex products. The general equation is A + B → AB.
Explanations (4)
Synthesis reactions.
What are Synthesis Reactions?
- Synthesis reactions are reactions that involve multiple reactants reacting to form one single product.
Example: A + B → AB
- Synthesis reactions are exothermic reactions. So, they release energy as heat or light .
They involve the formation of either ionic or covalent bonds. The formation of a bond releases energy and increases stability. In contrast, breaking bonds requires energy.

Image source: Caroline Monahan
Synthesis Reaction Practice Problem
Which of the following are synthesis reactions?
2S + 3O2 → 2SO3
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O
MgO + CO2 → MgCO3
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
2Ni2O3 → 4Ni + 3O2
Related Lessons
(Video) Synthesis Reactions: Chemical Reaction (5 of 11) Synthesis Reactions, an Explanation
By Step by Step Science
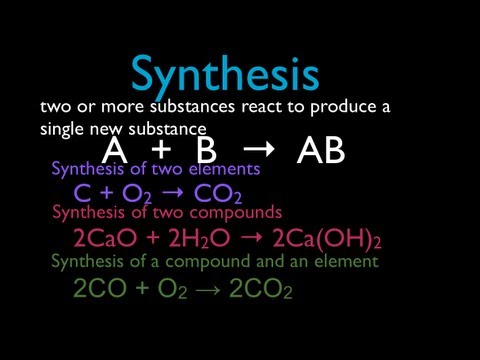
In this video, you will learn that a synthesis reaction occurs when two or more compounds or elements react with each other to form a singular compound. You will also learn different examples of synthesis reactions in this video.
Synthesis Reactions: What are synthesis reactions?
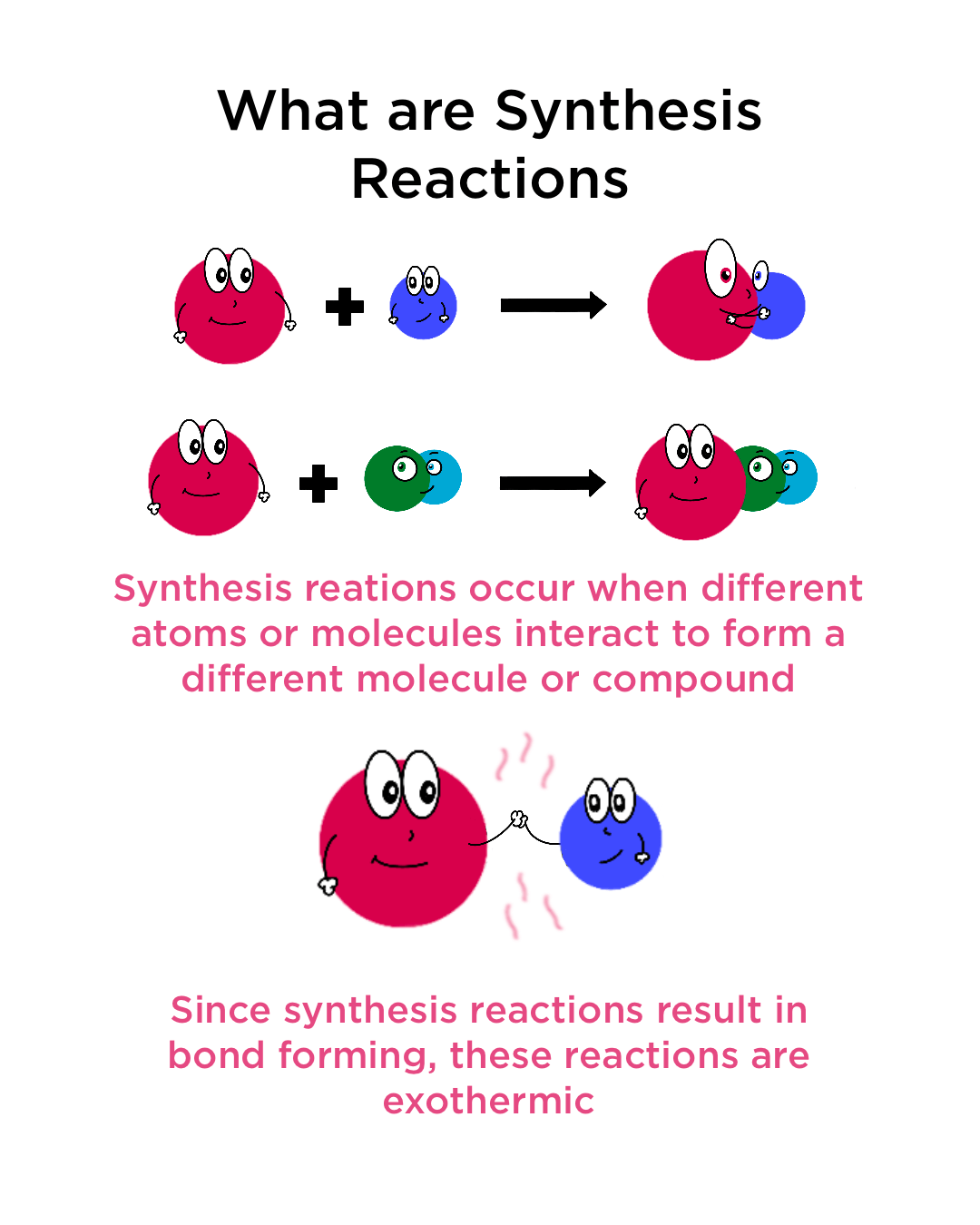
Image Source: Leo Dong
What is Chemical Synthesis like for Professional Chemists?
In general chemistry, synthesis reactions are the least complicated chemical reaction. You take two reactants and make one product. A generic balanced chemical equation would be A+B→AB. Unfortunately, in the real world, chemical synthesis is rarely so straightforward.
I remember a nightmare scenario from my organic chemistry class. I had one question left on our online homework. I was so close to finishing! I clicked the next button and saw the final problem. It was a fifteen-step synthesis! When you're learning organic chemistry, that's not a short puzzle. Often in chemical synthesis, there are many steps. Why? There are a couple of possible reasons. Sometimes, the reactants that produce an easy synthesis reaction are expensive. So, you might have to start with cheap reactants and build up your molecules. Other times, the reaction intermediates may be unstable. They only form during a series of chemical reactions. So, again we have to build up our reactants.
Planning a Chemical Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is the heart of applied chemistry . The chemist works to develop a procedure to produce their desired compound. What's the result? They construct the reaction mechanism , piece by piece. Along the way, they often have to manipulate specific steps to achieve their goals. They use their knowledge of chemistry principles to influence the reaction.
How would a chemist go about planning a synthesis? Most often, they start at the final product and work backward. Each step focuses on changing one specific bond or group of atoms . In organic chemistry, a compound's reactivity comes from functional groups. They are groupings of atoms with set chemical properties . For example, a carbon - oxygen - hydrogen set is the alcohol group. Because oxygen is bound to hydrogen, it is always a polar group . The oxygen-hydrogen bond is also a weak acid . So, we might manipulate it with a strong base . Other chemists, like inorganic chemists, often focus on individual atoms. But they also have to consider the reactivity of the element .
Performing the Lab Work
In college, I had a friend that was doing a research project. One of the steps in his synthesis formed a hydrate . But, before he could proceed to the next step, he needed to remove the water. So, his compound had to sit in a chemical oven for twelve hours. He didn't get it in until after his afternoon classes. So, he had to return to the lab at 3:00 am to take it out! In chemical synthesis, the lab work is often the most challenging part. Why? A chemical reaction gets influenced by so many factors! We must consider temperature , pressure , pH , time, and other factors. Often we have to manipulate many factors along the way.
Sometimes, we use chemical manipulation . For example, maybe step seven of a fifteen-step reaction is the rate-limiting step . What could we do? We might try to develop a catalyst . Remember, they lower a reaction's activation energy and improve its rate . Sometimes, we can research the published work of other chemists for possible catalysts. Other times, we may need to use theoretical modeling to develop a catalyst. Sometimes, we even have to synthesize the catalyst!
Other times, we need to use physical manipulations. For example, one of our steps could be an equilibrium reaction. But we want it to go to completion. How do we manipulate the equilibrium? We take advantage of Le' Chatlier's principle . If the reaction is endothermic, we could apply heat. What if it's exothermic? We could cool it. Sometimes we can physically separate our products. By removing the products, we alter the equilibrium.
What are Your Results?
Chemistry is complex. For example, sometimes, a reaction can produce multiple products. So, even if we successfully implement our plan, we may not get our desired result. Why? We also have to worry about the percent yield . Part of planning the mechanism is calculating the theoretical yield . But often, one of the steps will act as a limiting reagent . So, very rarely are the theoretical and actual yields equivalent. Sometimes, experimental errors mean we don't produce our desired amount.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
synthesis: [noun] the composition or combination of parts or elements so as to form a whole. the production of a substance by the union of chemical elements, groups, or simpler compounds or by the degradation of a complex compound.
Synthesis definition: . See examples of SYNTHESIS used in a sentence.
SYNTHESIS definition: 1. the production of a substance from simpler materials after a chemical reaction 2. the mixing of…. Learn more.
A synthesis reaction or direct combination reaction reacts two or more simple elements or compounds to form a more complex product. A synthesis reaction is one of the four main types of chemical reactions, along with decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement reactions. Here is the synthesis reaction definition, examples of the reaction using elements and compounds, a look at ...
SYNTHESIS meaning: 1. the production of a substance from simpler materials after a chemical reaction 2. the mixing of…. Learn more.
When asked to synthesize sources and research, many writers start to summarize individual sources. However, this is not the same as synthesis. In a summary, you share the key points from an individual source and then move on and summarize another source. In synthesis, you need to combine the information from those multiple sources and add your ...
synthesis: 1 n the combination of ideas into a complex whole Synonyms: synthetic thinking Antonyms: analysis , analytic thinking the abstract separation of a whole into its constituent parts in order to study the parts and their relations Type of: abstract thought , logical thinking , reasoning thinking that is coherent and logical n the ...
Definition of synthesis noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
6 meanings: 1. the process of combining objects or ideas into a complex whole → Compare analysis 2. the combination or whole.... Click for more definitions.
SYNTHESIS definition: the mixing of several things to make another whole new thing. Learn more.
Synthesis is a crucial skill for academic writing, as it allows you to use evidence from multiple sources to support your own arguments. In this guide, you will learn how to summarize, paraphrase, cite, and integrate sources in your papers. You will also find video tutorials, examples, and exercises to help you master synthesis.
Synthesis Reaction Examples. In the simplest synthesis reactions, two elements combine to form a binary compound (a compound made of two elements). The combination of iron and sulfur to form iron (II) sulfide is an example of a synthesis reaction : 8 Fe + S 8 → 8 FeS. Another example of a synthesis reaction is the formation of potassium ...
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
By definition, in an argumentative synthesis essay, a writer argues or persuades a reader of a main claim or thesis statement by using information gained through research. A synthesis essay can be ...
Learn what synthesis is with a definition and examples.
chemical synthesis, the construction of complex chemical compounds from simpler ones. It is the process by which many substances important to daily life are obtained. It is applied to all types of chemical compounds, but most syntheses are of organic molecules. Chemists synthesize chemical compounds that occur in nature in order to gain a ...
Definition. noun, plural: syntheses. ( biochemistry) The production of an organic compound in a living thing, especially as aided by enzymes. Supplement. In general, the term synthesis pertains to the creation of something. It is the process of combining two or more components to produce an entity. In biochemistry, it refers to the production ...
So I'm showing the commonality between these two sources. So it's a very, sort of, not simple, but, you know, clean approach to synthesis. It's a very direct approach to kind of showing the similarities between these two sources. So that's an example of synthesis, okay. Visual: The following example is added to the slide:
The chemical synthesis definition introduces the concept of creating new substances by causing a chemical change in the starting materials. A chemical synthesis involves chemical reactions, which ...
Example of synthesizing sources. Let's take a look at an example where sources are not properly synthesized, and then see what can be done to improve it. Example: Poor synthesis. Lenneberg (1967) theorized that language acquisition could occur only within a critical period of development between infancy and puberty.
A synthesis reaction is a reaction in which two or more reactants chemically bond and combine to form a product. A synthesis reaction is also known as a combination reaction. Most synthesis reactions are exothermic reactions, i.e., heat is released during the reaction.
Synthesis reactions are reactions that involve multiple reactants reacting to form one single product. Example: A + B → AB. Synthesis reactions are exothermic reactions. So, they release energy as heat or light. They involve the formation of either ionic or covalent bonds. The formation of a bond releases energy and increases stability.