Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Fall 2022)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper, single-point rubric, more examples:.
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
Search the blog
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Vibrant Teaching
Teaching Resources Creator and Blogger
3 Types of Writing Rubrics for Effective Assessments
There are so many different writing rubrics out there and it may be difficult to find the right one. Below you will find a guide with 3 types of effective writing rubrics. Choosing the right one depends on the writing genre and your needs for the assessment.
Student-Friendly Rubrics
There are two ways to think about student-friendly rubrics. The first way is to use a rubric that students can complete as a self-assessment. The second way is to use a rubric that is completed by the teacher but is easy for students to understand. These rubrics are often based on the standards but shown in a different way. Instead of writing the actual standard on the rubric, include a one or two-word category.
See the example below of a third grade informative writing rubric. The first rubric uses the words introduction, content, linking words, closing, and mechanics for the categories. The second rubric lists each standard that goes with those categories. As you can see, the first option covers the same information but uses fewer words and is much easier for students to use and understand.
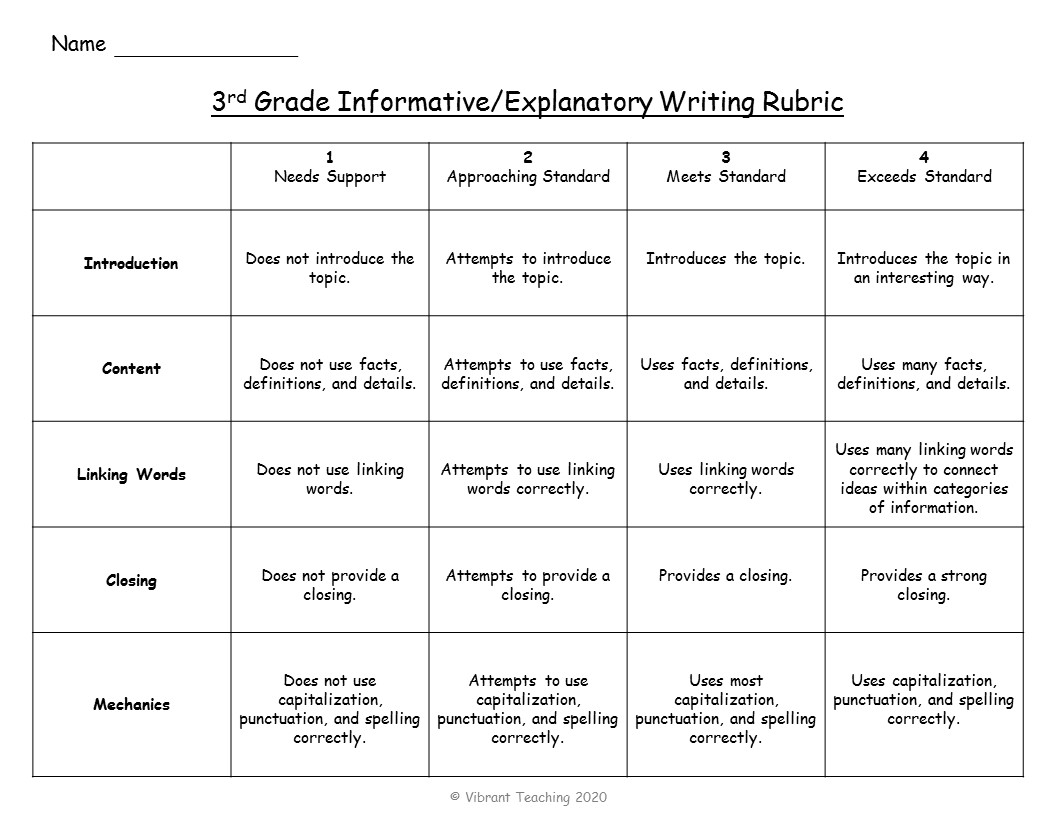
When do you use student-friendly rubrics? These are great for students to assess themselves. The student and teacher can fill out the rubric separately and then meet for a conference to discuss any differences. This same strategy can also be done with two students, but instead of a conference, they will meet to edit and revise their work. Another option is for teachers to fill out the writing rubric and hand it back to students with feedback. The student-friendly rubrics are easy for kids to understand and are still aligned with the standards.

Teacher-Friendly Rubrics
Teacher-friendly rubrics list each standard and use more details in the descriptions. This helps teachers know what to look for when assessing a writing piece. It will be very clear from the rubric whether or not the student is meeting or exceeding the standard. These writing rubrics are also quick and easy for teachers to use but may be more difficult for students to understand.
The examples below are standards based teacher-friendly rubrics. On the left side, you will see each Common Core Standard. The descriptions on the right side match each standard accordingly. These rubrics are used for assessing narrative writing in 1st grade, 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade, and 5th grade.
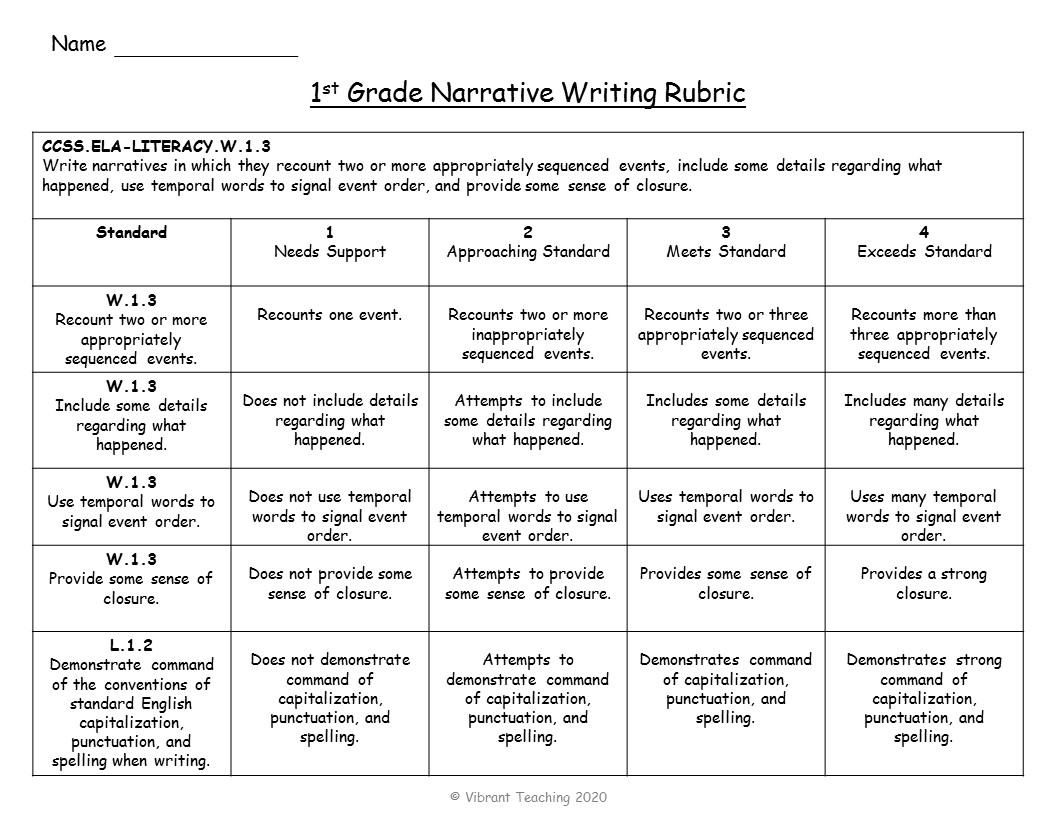
When do you use teacher-friendly rubrics? These are ideal when a teacher needs to get an accurate assessment for recording grades or writing report cards. They can choose whether or not to hand these rubrics back to students or use them for their records. Teacher-friendly rubrics are also helpful to show parents, especially at conferences.
Time-Saving Rubrics
Time-saving rubrics are a combination of student-friendly and teacher-friendly rubrics. These are standards based and list each standard on the left side. The difference is that instead of a description there is a number in each box such as 1, 2, 3, or 4. These numbers tell whether or not the student is meeting the standard.
1= needs support
2 = approaching standard, 3 = meets standard, 4 = exceeds standard.
The benefits of these rubrics are that they save time and energy by easily circling the number for each standard. It is quick for teachers to use but also easy for students to understand. Some teachers may also choose to include a section for the total score and comments depending on their needs. Check out some of the examples below for opinion writing.
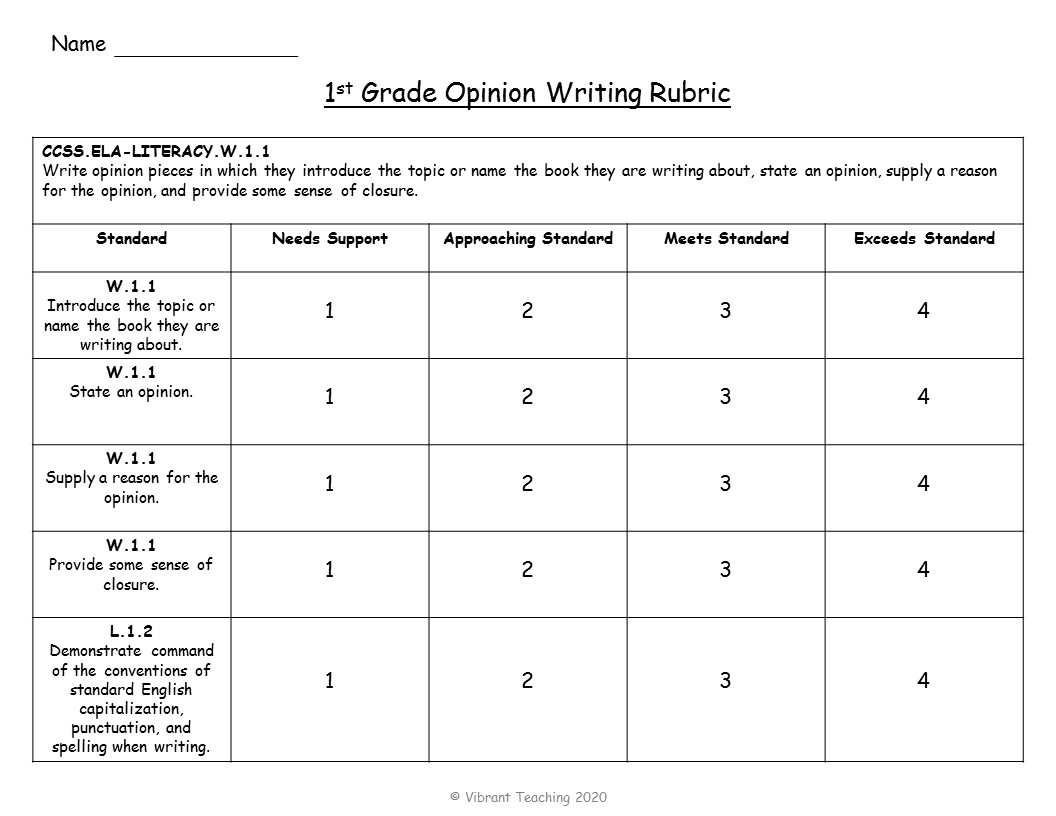
When do you use time-saving rubrics? Well of course these are helpful when teachers want to save time. The best part is the rubrics are still standards based but also very easy for students and parents to understand. Use these anytime!
Writing Rubrics Conclusion
I hope you have found these 3 types of writing rubrics helpful and will utilize them with your class. Think about what your goal is with the assessment and choose the best rubric for both you and your students. You may find that a mix of all three is beneficial throughout the school year.
Writing Rubrics by Grade Level
Grab these standards based writing rubrics. Each grade level includes 9 rubrics in 3 different options . Choose from student-friendly, teacher-friendly, and time-saving rubrics. These are ideal for assessing narrative, opinion, and informative pieces. Click each grade level below to learn more. Also, check out this Monthly Writing Prompts blog post for more resources and ideas.

Middle School Writing Rubrics

Angela Sutton
Related posts.

How to Use Writing Prompts Daily

How to Find Perimeter in 3 Easy Ways

6 Important Writing Prompt Examples for the Classroom
No comments, leave a reply cancel reply.
I accept the Privacy Policy

I specialize in helping elementary teachers with writing resources, tips, and ideas. My goal is to save teachers time and energy so they can be vibrant inside and outside of the classroom! Read More
SEARCH THE BLOG
Subscribe to our mailing list.
Get the news right in your inbox!
Health and Wellness
Sample Essay Rubric for Elementary Teachers
- Grading Students for Assessment
- Lesson Plans
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
An essay rubric is a way teachers assess students' essay writing by using specific criteria to grade assignments. Essay rubrics save teachers time because all of the criteria are listed and organized into one convenient paper. If used effectively, rubrics can help improve students' writing .
How to Use an Essay Rubric
- The best way to use an essay rubric is to give the rubric to the students before they begin their writing assignment. Review each criterion with the students and give them specific examples of what you want so they will know what is expected of them.
- Next, assign students to write the essay, reminding them of the criteria and your expectations for the assignment.
- Once students complete the essay have them first score their own essay using the rubric, and then switch with a partner. (This peer-editing process is a quick and reliable way to see how well the student did on their assignment. It's also good practice to learn criticism and become a more efficient writer.)
- Once peer-editing is complete, have students hand in their essay's. Now it is your turn to evaluate the assignment according to the criteria on the rubric. Make sure to offer students examples if they did not meet the criteria listed.
Informal Essay Rubric
Formal essay rubric.
- How to Create a Rubric in 6 Steps
- Writing Rubrics
- What Is a Rubric?
- Holistic Grading (Composition)
- How to Make a Rubric for Differentiation
- A Simple Guide to Grading Elementary Students
- How to Write a Philosophy of Education for Elementary Teachers
- Tips to Cut Writing Assignment Grading Time
- Assignment Biography: Student Criteria and Rubric for Writing
- Rubrics - Quick Guide for all Content Areas
- How to Teach the Compare and Contrast Essay
- How to Calculate a Percentage and Letter Grade
- Stage a Debate in Class
- Rubric Template Samples for Teachers
- Group Project Grading Tip: Students Determine Fair Grade
- Grading for Proficiency in the World of 4.0 GPAs
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects
In the end, they actually make grading easier.

When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student’s knowledge, and the answers are either right or wrong. But often, assessing a student’s performance is much less clear-cut. In these situations, a scoring rubric is often the way to go, especially if you’re using standards-based grading . Here’s what you need to know about this useful tool, along with lots of rubric examples to get you started.
What is a scoring rubric?
In the United States, a rubric is a guide that lays out the performance expectations for an assignment. It helps students understand what’s required of them, and guides teachers through the evaluation process. (Note that in other countries, the term “rubric” may instead refer to the set of instructions at the beginning of an exam. To avoid confusion, some people use the term “scoring rubric” instead.)
A rubric generally has three parts:
- Performance criteria: These are the various aspects on which the assignment will be evaluated. They should align with the desired learning outcomes for the assignment.
- Rating scale: This could be a number system (often 1 to 4) or words like “exceeds expectations, meets expectations, below expectations,” etc.
- Indicators: These describe the qualities needed to earn a specific rating for each of the performance criteria. The level of detail may vary depending on the assignment and the purpose of the rubric itself.
Rubrics take more time to develop up front, but they help ensure more consistent assessment, especially when the skills being assessed are more subjective. A well-developed rubric can actually save teachers a lot of time when it comes to grading. What’s more, sharing your scoring rubric with students in advance often helps improve performance . This way, students have a clear picture of what’s expected of them and what they need to do to achieve a specific grade or performance rating.
Learn more about why and how to use a rubric here.
Types of Rubric
There are three basic rubric categories, each with its own purpose.
Holistic Rubric

Source: Cambrian College
This type of rubric combines all the scoring criteria in a single scale. They’re quick to create and use, but they have drawbacks. If a student’s work spans different levels, it can be difficult to decide which score to assign. They also make it harder to provide feedback on specific aspects.
Traditional letter grades are a type of holistic rubric. So are the popular “hamburger rubric” and “ cupcake rubric ” examples. Learn more about holistic rubrics here.
Analytic Rubric
Source: University of Nebraska
Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. Each rating is assigned a point value, and the total number of points earned determines the overall grade for the assignment.
Though they’re more time-intensive to create, analytic rubrics actually save time while grading. Teachers can simply circle or highlight any relevant phrases in each rating, and add a comment or two if needed. They also help ensure consistency in grading, and make it much easier for students to understand what’s expected of them.
Learn more about analytic rubrics here.
Developmental Rubric
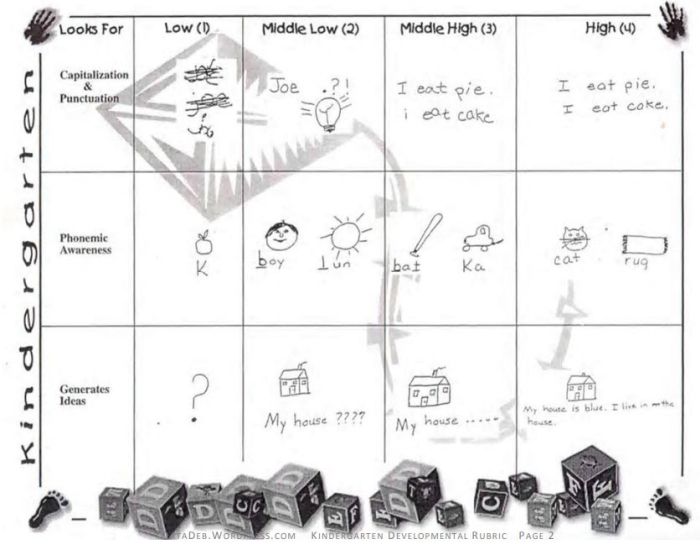
Source: Deb’s Data Digest
A developmental rubric is a type of analytic rubric, but it’s used to assess progress along the way rather than determining a final score on an assignment. The details in these rubrics help students understand their achievements, as well as highlight the specific skills they still need to improve.
Developmental rubrics are essentially a subset of analytic rubrics. They leave off the point values, though, and focus instead on giving feedback using the criteria and indicators of performance.
Learn how to use developmental rubrics here.
Ready to create your own rubrics? Find general tips on designing rubrics here. Then, check out these examples across all grades and subjects to inspire you.
Elementary School Rubric Examples
These elementary school rubric examples come from real teachers who use them with their students. Adapt them to fit your needs and grade level.
Reading Fluency Rubric
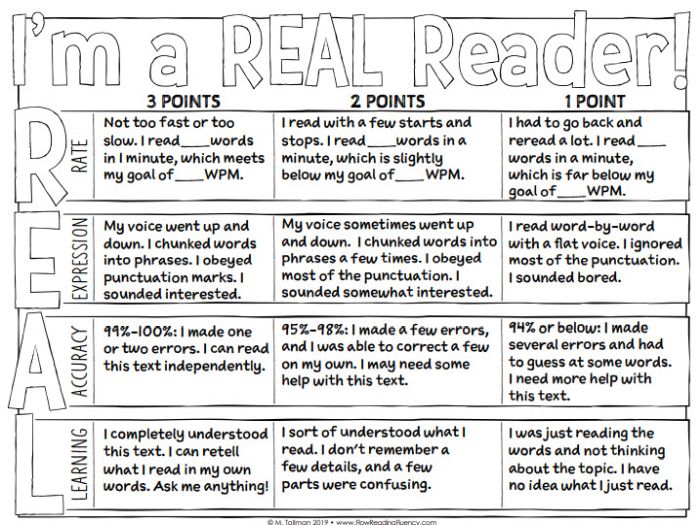
You can use this one as an analytic rubric by counting up points to earn a final score, or just to provide developmental feedback. There’s a second rubric page available specifically to assess prosody (reading with expression).
Learn more: Teacher Thrive
Reading Comprehension Rubric
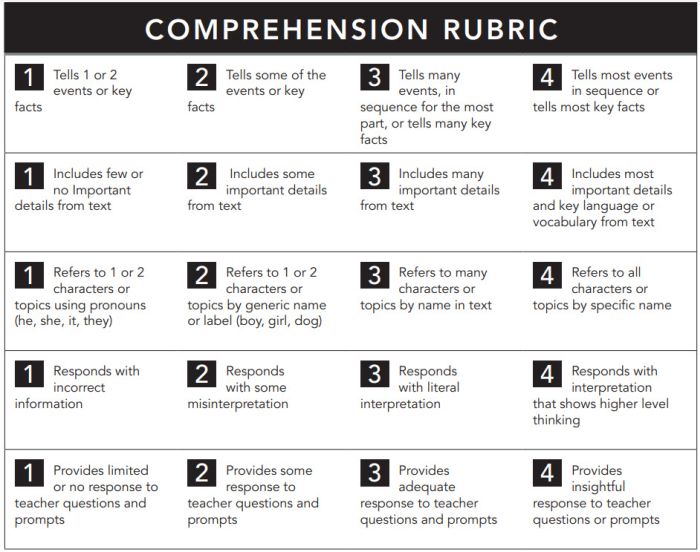
The nice thing about this rubric is that you can use it at any grade level, for any text. If you like this style, you can get a reading fluency rubric here too.
Learn more: Pawprints Resource Center
Written Response Rubric

Rubrics aren’t just for huge projects. They can also help kids work on very specific skills, like this one for improving written responses on assessments.
Learn more: Dianna Radcliffe: Teaching Upper Elementary and More
Interactive Notebook Rubric
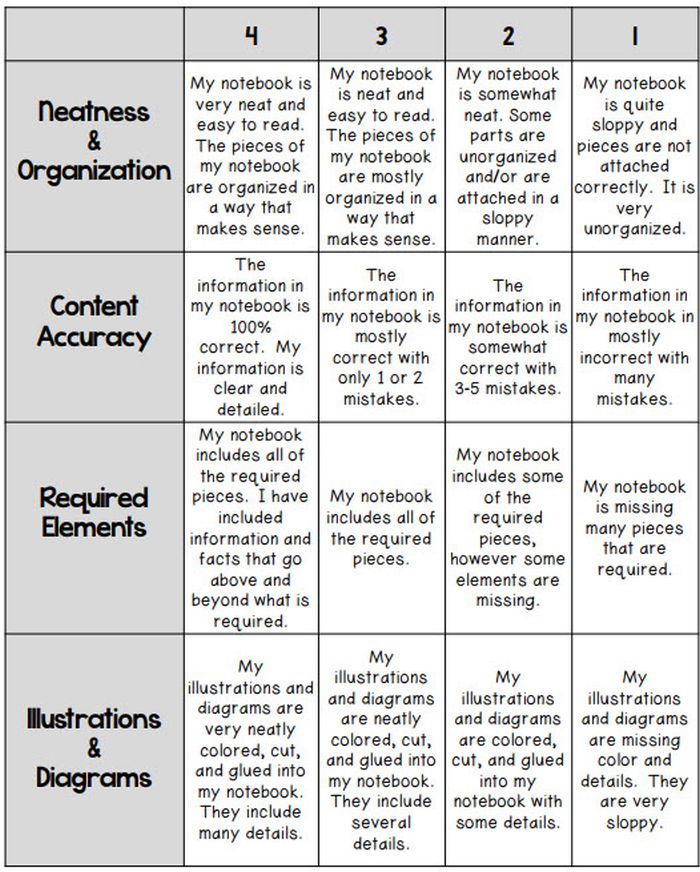
If you use interactive notebooks as a learning tool , this rubric can help kids stay on track and meet your expectations.
Learn more: Classroom Nook
Project Rubric
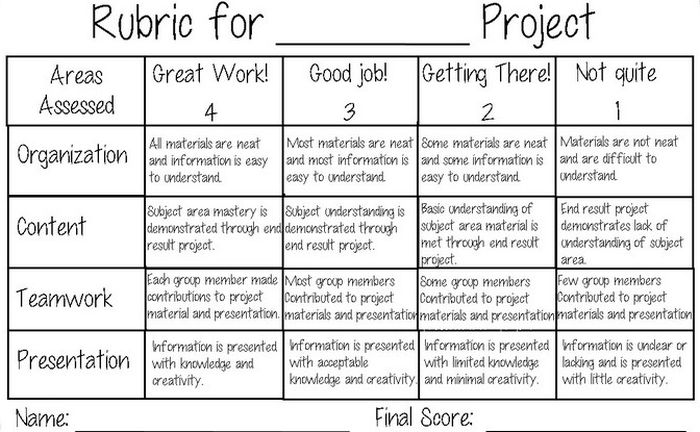
Use this simple rubric as it is, or tweak it to include more specific indicators for the project you have in mind.
Learn more: Tales of a Title One Teacher
Behavior Rubric
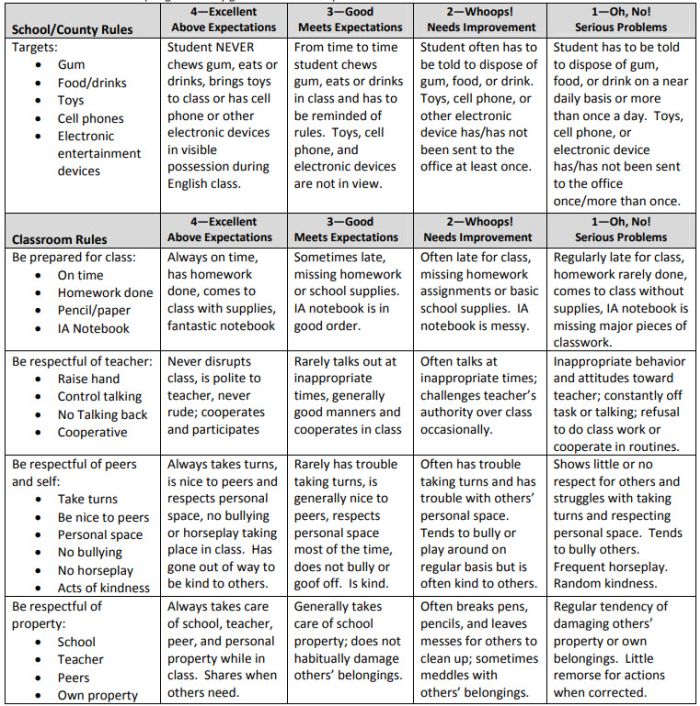
Developmental rubrics are perfect for assessing behavior and helping students identify opportunities for improvement. Send these home regularly to keep parents in the loop.
Learn more: Teachers.net Gazette
Middle School Rubric Examples
In middle school, use rubrics to offer detailed feedback on projects, presentations, and more. Be sure to share them with students in advance, and encourage them to use them as they work so they’ll know if they’re meeting expectations.
Argumentative Writing Rubric
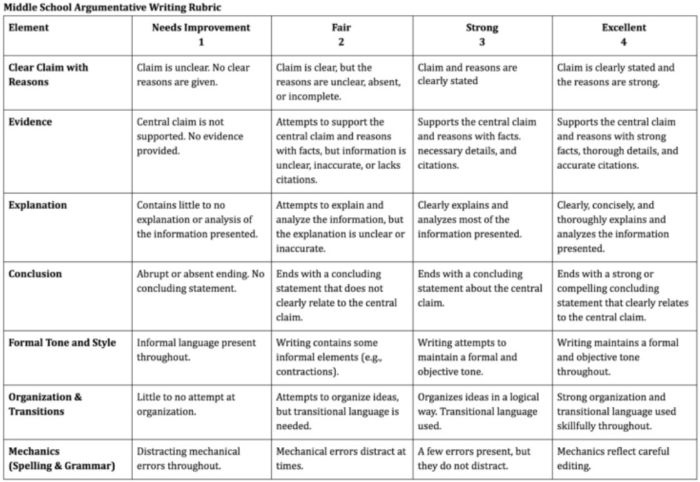
Argumentative writing is a part of language arts, social studies, science, and more. That makes this rubric especially useful.
Learn more: Dr. Caitlyn Tucker
Role-Play Rubric
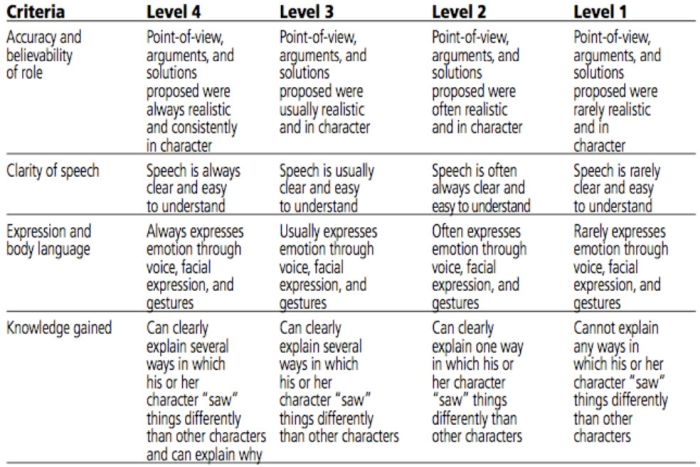
Role-plays can be really useful when teaching social and critical thinking skills, but it’s hard to assess them. Try a rubric like this one to evaluate and provide useful feedback.
Learn more: A Question of Influence
Art Project Rubric
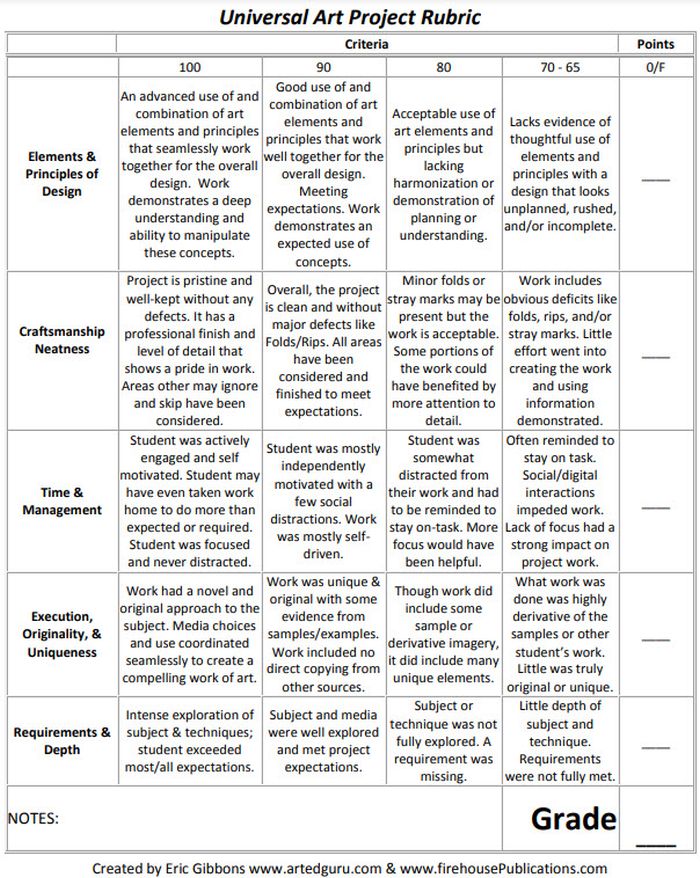
Art is one of those subjects where grading can feel very subjective. Bring some objectivity to the process with a rubric like this.
Source: Art Ed Guru
Diorama Project Rubric
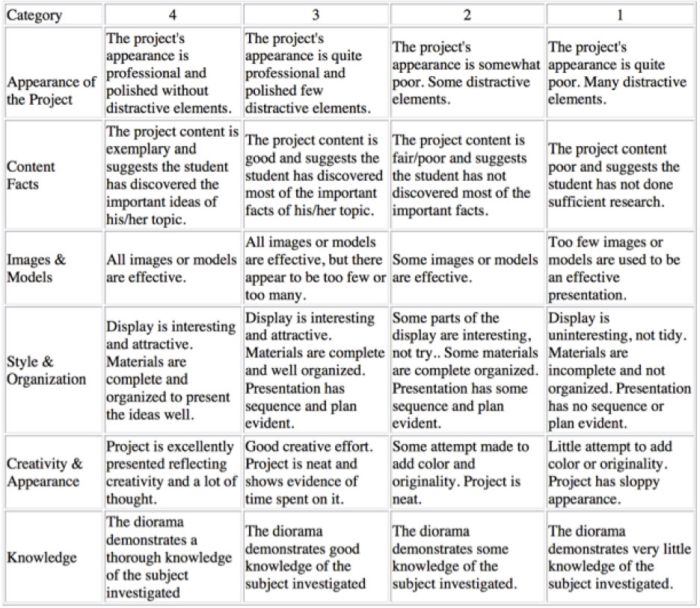
You can use diorama projects in almost any subject, and they’re a great chance to encourage creativity. Simplify the grading process and help kids know how to make their projects shine with this scoring rubric.
Learn more: Historyourstory.com
Oral Presentation Rubric
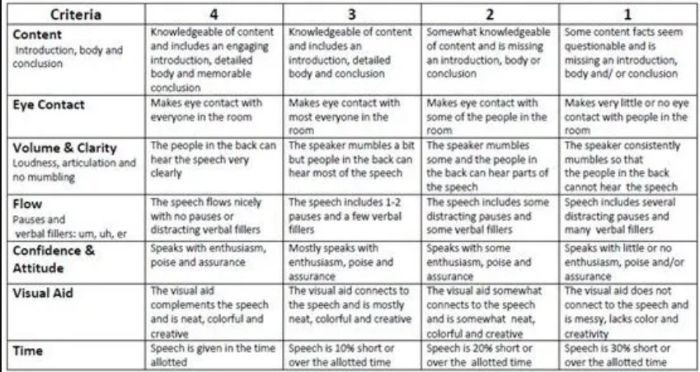
Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. Consider letting students use a rubric like this to offer peer feedback too.
Learn more: Bright Hub Education
High School Rubric Examples
In high school, it’s important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so helping them become familiar with them now will help in the future.
Presentation Rubric
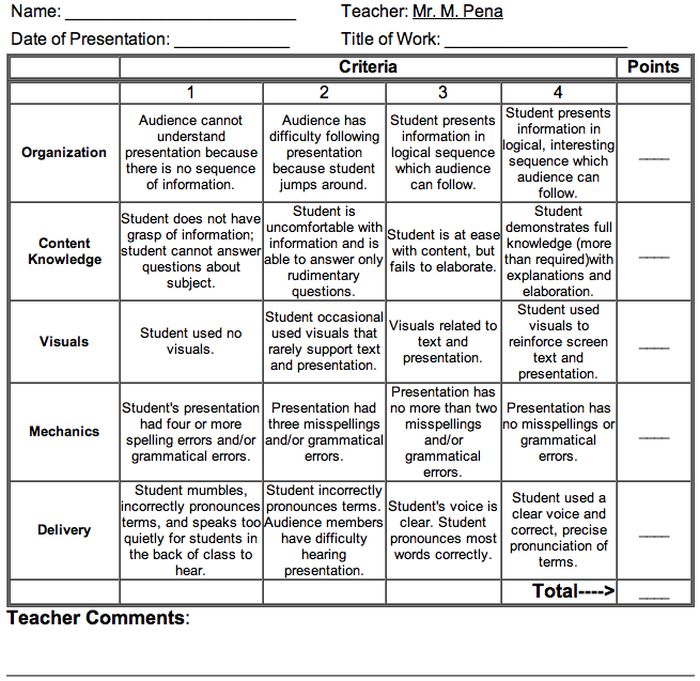
Analyze a student’s presentation both for content and communication skills with a rubric like this one. If needed, create a separate one for content knowledge with even more criteria and indicators.
Learn more: Michael A. Pena Jr.
Debate Rubric
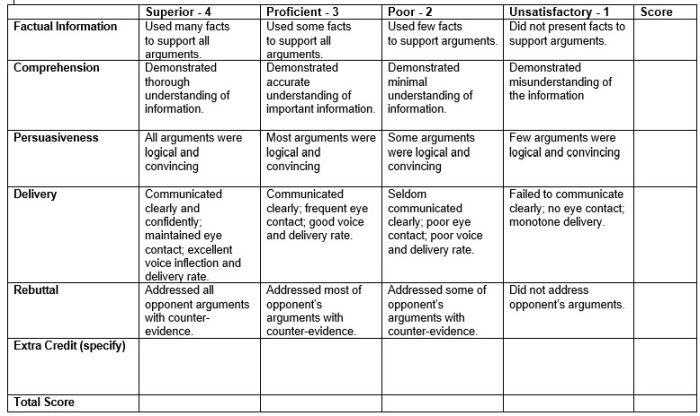
Debate is a valuable learning tool that encourages critical thinking and oral communication skills. This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively.
Learn more: Education World
Project-Based Learning Rubric
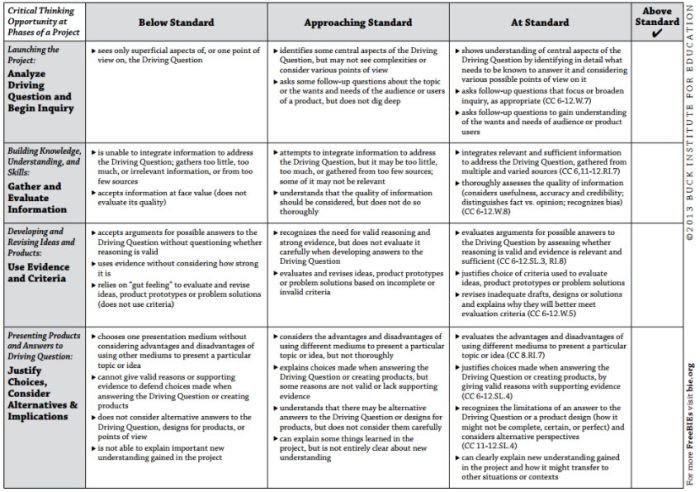
Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier.
Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers
100-Point Essay Rubric
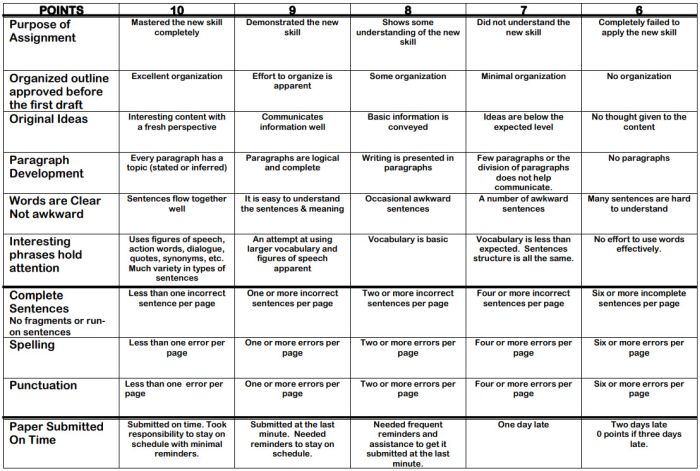
Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points.
Learn more: Learn for Your Life
Drama Performance Rubric
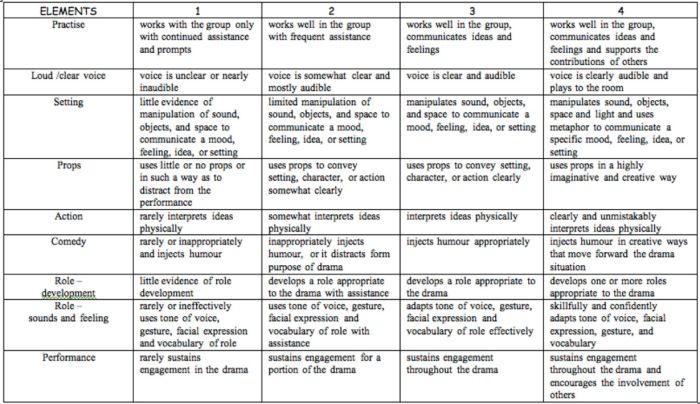
If you’re unsure how to grade a student’s participation and performance in drama class, consider this example. It offers lots of objective criteria and indicators to evaluate.
Learn more: Chase March
How do you use rubrics in your classroom? Come share your thoughts and exchange ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, 25 of the best alternative assessment ideas ..

You Might Also Like
I Switched to Standards-Based Grading—Why I’m Loving It
Reduced grading time? Yes, please! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Compare and Contrast Rubric

About this printout
Students and teachers can use this rubric when doing writing that compares and contrasts two things, as well as when assessing the writing.
Teaching with this printout
More ideas to try.
When assigning a compare and contrast writing assignment, students need to be aware of what makes an outstanding written work. This rubric is a great tool to show students what is expected of them in a concrete way. Additionally, this rubric will help teachers assess this student writing and inform further instruction. This Comparison and Contrast Rubric is also a great way to introduce different rubrics that are used to assess student writing on many state tests.
- Have students work with a partner or a group and grade each others' papers using the rubric (the entire group should grade the same paper at one time). Students can then compare their scores with those of other students, as well as the author, to see how they are similar and different. Feedback from group members will help students when editing their own papers and looking to see if they have included what is required of the assignment.
- Before turning in the writing assignment, have students assess his/her own writing using the rubric. After the teacher has assessed the assignment, the student and teacher could have a one-on-one conference to discuss how their assessed rubrics differ and what improvements could be made.
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, act writing rubric: full analysis and essay strategies.
ACT Writing

What time is it? It's essay time! In this article, I'm going to get into the details of the newly transformed ACT Writing by discussing the ACT essay rubric and how the essay is graded based on that. You'll learn what each item on the rubric means for your essay writing and what you need to do to meet those requirements.
feature image credit: A study in human nature, being an interpretation with character analysis chart of Hoffman's master painting "Christ in the temple"; (1920) by CircaSassy , used under CC BY 2.0 /Resized from original.
ACT Essay Grading: The Basics
If you've chosen to take the ACT Plus Writing , you'll have 40 minutes to write an essay (after completing the English, Math, Reading, and Science sections of the ACT, of course). Your essay will be evaluated by two graders , who score your essay from 1-6 on each of 4 domains, leading to scores out of 12 for each domain. Your Writing score is calculated by averaging your four domain scores, leading to a total ACT Writing score from 2-12.
NOTE : From September 2015 to June 2016, ACT Writing scores were calculated by adding together your domain scores and scaling to a score of 1-36; the change to an averaged 2-12 ACT Writing score was announced June 28, 2016 and put into action September 2016.
The Complete ACT Grading Rubric
Based on ACT, Inc's stated grading criteria, I've gathered all the relevant essay-grading criteria into a chart. The information itself is available on the ACT's website , and there's more general information about each of the domains here . The columns in this rubric are titled as per the ACT's own domain areas, with the addition of another category that I named ("Mastery Level").
ACT Writing Rubric: Item-by-Item Breakdown
Whew. That rubric might be a little overwhelming—there's so much information to process! Below, I've broken down the essay rubric by domain, with examples of what a 3- and a 6-scoring essay might look like.
Ideas and Analysis
The Ideas and Analysis domain is the rubric area most intimately linked with the basic ACT essay task itself. Here's what the ACT website has to say about this domain:
Scores in this domain reflect the ability to generate productive ideas and engage critically with multiple perspectives on the given issue. Competent writers understand the issue they are invited to address, the purpose for writing, and the audience. They generate ideas that are relevant to the situation.
Based on this description, I've extracted the three key things you need to do in your essay to score well in the Ideas and Analysis domain.
#1: Choose a perspective on this issue and state it clearly. #2: Compare at least one other perspective to the perspective you have chosen. #3: Demonstrate understanding of the ways the perspectives relate to one another. #4: Analyze the implications of each perspective you choose to discuss.
There's no cool acronym, sorry. I guess a case could be made for "ACCE," but I wanted to list the points in the order of importance, so "CEAC" it is.
Fortunately, the ACT Writing Test provides you with the three perspectives to analyze and choose from, which will save you some of the time of "generating productive ideas." In addition, "analyzing each perspective" does not mean that you need to argue from each of the points of view. Instead, you need to choose one perspective to argue as your own and explain how your point of view relates to at least one other perspective by evaluating how correct the perspectives you discuss are and analyzing the implications of each perspective.
Note: While it is technically allowable for you to come up with a fourth perspective as your own and to then discuss that point of view in relation to another perspective, we do not recommend it. 40 minutes is already a pretty short time to discuss and compare multiple points of view in a thorough and coherent manner—coming up with new, clearly-articulated perspectives takes time that could be better spend devising a thorough analysis of the relationship between multiple perspectives.
To get deeper into what things fall in the Ideas and Analysis domain, I'll use a sample ACT Writing prompt and the three perspectives provided:
Many of the goods and services we depend on daily are now supplied by intelligent, automated machines rather than human beings. Robots build cars and other goods on assembly lines, where once there were human workers. Many of our phone conversations are now conducted not with people but with sophisticated technologies. We can now buy goods at a variety of stores without the help of a human cashier. Automation is generally seen as a sign of progress, but what is lost when we replace humans with machines? Given the accelerating variety and prevalence of intelligent machines, it is worth examining the implications and meaning of their presence in our lives.
Perspective One : What we lose with the replacement of people by machines is some part of our own humanity. Even our mundane daily encounters no longer require from us basic courtesy, respect, and tolerance for other people.
Perspective Two : Machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs, and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases they work better than humans. This efficiency leads to a more prosperous and progressive world for everyone.
Perspective Three : Intelligent machines challenge our long-standing ideas about what humans are or can be. This is good because it pushes both humans and machines toward new, unimagined possibilities.
First, in order to "clearly state your own perspective on the issue," you need to figure out what your point of view, or perspective, on this issue is going to be. For the sake of argument, let's say that you agree the most with the second perspective. A essay that scores a 3 in this domain might simply restate this perspective:
I agree that machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs, and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases they work better than humans. This efficiency leads to a more prosperous and progressive world for everyone.
In contrast, an essay scoring a 6 in this domain would likely have a more complex point of view (with what the rubric calls "nuance and precision in thought and purpose"):
Machines will never be able to replace humans entirely, as creativity is not something that can be mechanized. Because machines can perform delicate and repetitive tasks with precision, however, they are able to take over for humans with regards to low-skill, repetitive jobs and high-skill, extremely precise jobs. This then frees up humans to do what we do best—think, create, and move the world forward.
Next, you must compare at least one other perspective to your perspective throughout your essay, including in your initial argument. Here's what a 3-scoring essay's argument would look like:
I agree that machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs, and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases they work better than humans. This efficiency leads to a more prosperous and progressive world for everyone. Machines do not cause us to lose our humanity or challenge our long-standing ideas about what humans are or can be.
And here, in contrast, is what a 6-scoring essay's argument (that includes multiple perspectives) would look like:
Machines will never be able to replace humans entirely, as creativity is not something that can be mechanized, which means that our humanity is safe. Because machines can perform delicate and repetitive tasks with precision, however, they are able to take over for humans with regards to low-skill, repetitive jobs and high-skill, extremely precise jobs. Rather than forcing us to challenge our ideas about what humans are or could be, machines simply allow us to BE, without distractions. This then frees up humans to do what we do best—think, create, and move the world forward.
You also need to demonstrate a nuanced understanding of the way in which the two perspectives relate to each other. A 3-scoring essay in this domain would likely be absolute, stating that Perspective Two is completely correct, while the other two perspectives are absolutely incorrect. By contrast, a 6-scoring essay in this domain would provide a more insightful context within which to consider the issue:
In the future, machines might lead us to lose our humanity; alternatively, machines might lead us to unimaginable pinnacles of achievement. I would argue, however, projecting possible futures does not make them true, and that the evidence we have at present supports the perspective that machines are, above all else, efficient and effective completing repetitive and precise tasks.
Finally, to analyze the perspectives, you need to consider each aspect of each perspective. In the case of Perspective Two, this means you must discuss that machines are good at two types of jobs, that they're better than humans at both types of jobs, and that their efficiency creates a better world. The analysis in a 3-scoring essay is usually "simplistic or somewhat unclear." By contrast, the analysis of a 6-scoring essay "examines implications, complexities and tensions, and/or underlying values and assumptions."
- Choose a perspective that you can support.
- Compare at least one other perspective to the perspective you have chosen.
- Demonstrate understanding of the ways the perspectives relate to one another.
- Analyze the implications of each perspective you choose to discuss.
To score well on the ACT essay overall, however, it's not enough to just state your opinions about each part of the perspective; you need to actually back up your claims with evidence to develop your own point of view. This leads straight into the next domain: Development and Support.
Development and Support
Another important component of your essay is that you explain your thinking. While it's obviously important to clearly state what your ideas are in the first place, the ACT essay requires you to demonstrate evidence-based reasoning. As per the description on ACT.org [bolding mine]:
Scores in this domain reflect the ability to discuss ideas, offer rationale, and bolster an argument. Competent writers explain and explore their ideas, discuss implications, and illustrate through examples . They help the reader understand their thinking about the issue.
"Machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs, and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases they work better than humans. This efficiency leads to a more prosperous and progressive world for everyone."
In your essay, you might start out by copying the perspective directly into your essay as your point of view, which is fine for the Ideas and Analysis domain. To score well in the Development and Support domain and develop your point of view with logical reasoning and detailed examples, however, you're going to have to come up with reasons for why you agree with this perspective and examples that support your thinking.
Here's an example from an essay that would score a 3 in this domain:
Machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases, they work better than humans. For example, machines are better at printing things quickly and clearly than people are. Prior to the invention of the printing press by Gutenberg people had to write everything by hand. The printing press made it faster and easier to get things printed because things didn't have to be written by hand all the time. In the world today we have even better machines like laser printers that print things quickly.
Essays scoring a 3 in this domain tend to have relatively simple development and tend to be overly general, with imprecise or repetitive reasoning or illustration. Contrast this with an example from an essay that would score a 6:
Machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases, they work better than humans. Take, for instance, the example of printing. As a composer, I need to be able to create many copies of my sheet music to give to my musicians. If I were to copy out each part by hand, it would take days, and would most likely contain inaccuracies. On the other hand, my printer (a machine) is able to print out multiple copies of parts with extreme precision. If it turns out I made an error when I was entering in the sheet music onto the computer (another machine), I can easily correct this error and print out more copies quickly.
The above example of the importance of machines to composers uses "an integrated line of skillful reasoning and illustration" to support my claim ("Machines are good at low-skill, repetitive jobs and at high-speed, extremely precise jobs. In both cases, they work better than humans"). To develop this example further (and incorporate the "This efficiency leads to a more prosperous and progressive world for everyone" facet of the perspective), I would need to expand my example to explain why it's so important that multiple copies of precisely replicated documents be available, and how this affects the world.
World Map - Abstract Acrylic by Nicolas Raymond , used under CC BY 2.0 /Resized from original.
Organization
Essay organization has always been integral to doing well on the ACT essay, so it makes sense that the ACT Writing rubric has an entire domain devoted to this. The organization of your essay refers not just to the order in which you present your ideas in the essay, but also to the order in which you present your ideas in each paragraph. Here's the formal description from the ACT website :
Scores in this domain reflect the ability to organize ideas with clarity and purpose. Organizational choices are integral to effective writing. Competent writers arrange their essay in a way that clearly shows the relationship between ideas, and they guide the reader through their discussion.
Making sure your essay is logically organized relates back to the "development" part of the previous domain. As the above description states, you can't just throw examples and information into your essay willy-nilly, without any regard for the order; part of constructing and developing a convincing argument is making sure it flows logically. A lot of this organization should happen while you are in the planning phase, before you even begin to write your essay.
Let's go back to the machine intelligence essay example again. I've decided to argue for Perspective Two, which is:
An essay that scores a 3 in this domain would show a "basic organizational structure," which is to say that each perspective analyzed would be discussed in its own paragraph, "with most ideas logically grouped." A possible organization for a 3-scoring essay:
An essay that scores a 6 in this domain, on the other hand, has a lot more to accomplish. The "controlling idea or purpose" behind the essay should be clearly expressed in every paragraph, and ideas should be ordered in a logical fashion so that there is a clear progression from the beginning to the end. Here's a possible organization for a 6-scoring essay:
In this example, the unifying idea is that machines are helpful (and it's mentioned in each paragraph) and the progression of ideas makes more sense. This is certainly not the only way to organize an essay on this particular topic, or even using this particular perspective. Your essay does, however, have to be organized, rather than consist of a bunch of ideas thrown together.
Here are my Top 5 ACT Writing Organization Rules to follow:
#1: Be sure to include an introduction (with your thesis stating your point of view), paragraphs in which you make your case, and a conclusion that sums up your argument
#2: When planning your essay, make sure to present your ideas in an order that makes sense (and follows a logical progression that will be easy for the grader to follow).
#3: Make sure that you unify your essay with one main idea . Do not switch arguments partway through your essay.
#4: Don't write everything in one huge paragraph. If you're worried you're going to run out of space to write and can't make your handwriting any smaller and still legible, you can try using a paragraph symbol, ¶, at the beginning of each paragraph as a last resort to show the organization of your essay.
#5: Use transitions between paragraphs (usually the last line of the previous paragraph and the first line of the paragraph) to "strengthen the relationships among ideas" ( source ). This means going above and beyond "First of all...Second...Lastly" at the beginning of each paragraph. Instead, use the transitions between paragraphs as an opportunity to describe how that paragraph relates to your main argument.

Language Use
The final domain on the ACT Writing rubric is Language Use and Conventions. This the item that includes grammar, punctuation, and general sentence structure issues. Here's what the ACT website has to say about Language Use:
Scores in this domain reflect the ability to use written language to convey arguments with clarity. Competent writers make use of the conventions of grammar, syntax, word usage, and mechanics. They are also aware of their audience and adjust the style and tone of their writing to communicate effectively.
I tend to think of this as the "be a good writer" category, since many of the standards covered in the above description are ones that good writers will automatically meet in their writing. On the other hand, this is probably the area non-native English speakers will struggle the most, as you must have a fairly solid grasp of English to score above a 2 on this domain. The good news is that by reading this article, you're already one step closer to improving your "Language Use" on ACT Writing.
There are three main parts of this domain:
#1: Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics #2: Sentence Structure #3: Vocabulary and Word Choice
I've listed them (and will cover them) from lowest to highest level. If you're struggling with multiple areas, I highly recommend starting out with the lowest-level issue, as the components tend to build on each other. For instance, if you're struggling with grammar and usage, you need to focus on fixing that before you start to think about precision of vocabulary/word choice.
Grammar, Usage, and Mechanics
At the most basic level, you need to be able to "effectively communicate your ideas in standard written English" ( ACT.org ). First and foremost, this means that your grammar and punctuation need to be correct. On ACT Writing, it's all right to make a few minor errors if the meaning is clear, even on essays that score a 6 in the Language Use domain; however, the more errors you make, the more your score will drop.
Here's an example from an essay that scored a 3 in Language Use:
Machines are good at doing there jobs quickly and precisely. Also because machines aren't human or self-aware they don't get bored so they can do the same thing over & over again without getting worse.
While the meaning of the sentences is clear, there are several errors: the first sentence uses "there" instead of "their," the second sentence is a run-on sentence, and the second sentence also uses the abbreviation "&" in place of "and." Now take a look at an example from a 6-scoring essay:
Machines excel at performing their jobs both quickly and precisely. In addition, since machines are not self-aware they are unable to get "bored." This means that they can perform the same task over and over without a decrease in quality.
This example solves the abbreviation and "there/their" issue. The second sentence is missing a comma (after "self-aware"), but the worse of the run-on sentence issue is absent.
Our Complete Guide to ACT Grammar might be helpful if you just need a general refresh on grammar rules. In addition, we have several articles that focus in on specific grammar rules, as they are tested on ACT English; while the specific ways in which ACT English tests you on these rules isn't something you'll need to know for the essay, the explanations of the grammar rules themselves are quite helpful.
Sentence Structure
Once you've gotten down basic grammar, usage, and mechanics, you can turn your attention to sentence structure. Here's an example of what a 3-scoring essay in Language Use (based on sentence structure alone) might look like:
Machines are more efficient than humans at many tasks. Machines are not causing us to lose our humanity. Instead, machines help us to be human by making things more efficient so that we can, for example, feed the needy with technological advances.
The sentence structures in the above example are not particularly varied (two sentences in a row start with "Machines are"), and the last sentence has a very complicated/convoluted structure, which makes it hard to understand. For comparison, here's a 6-scoring essay:
Machines are more efficient than humans at many tasks, but that does not mean that machines are causing us to lose our humanity. In fact, machines may even assist us in maintaining our humanity by providing more effective and efficient ways to feed the needy.
For whatever reason, I find that when I'm under time pressure, my sentences maintain variety in their structures but end up getting really awkward and strange. A real life example: once I described a method of counteracting dementia as "supporting persons of the elderly persuasion" during a hastily written psychology paper. I've found the best ways to counteract this are as follows:
#1: Look over what you've written and change any weird wordings that you notice.
#2: If you're just writing a practice essay, get a friend/teacher/relative who is good at writing (in English) to look over what you've written and point out issues (this is how my own awkward wording was caught before I handed in the paper). This point obviously does not apply when you're actually taking the ACT, but it very helpful to ask for someone else to take a look over any practice essays you write to point out issues you may not notice yourself.
Vocabulary and Word Choice
The icing on the "Language Use" domain cake is skilled use of vocabulary and correct word choice. Part of this means using more complicated vocabulary in your essay. Once more, look at this this example from a 3-scoring essay (spelling corrected):
Machines are good at doing their jobs quickly and precisely.
Compare that to this sentence from a 6-scoring essay:
Machines excel at performing their jobs both quickly and precisely.
The 6-scoring essay uses "excel" and "performing" in place of "are good at" and "doing." This is an example of using language that is both more skillful ("excel" is more advanced than "are good at") and more precise ("performing" is a more precise word than "doing"). It's important to make sure that, when you do use more advanced words, you use them correctly. Consider the below sentence:
"Machines are often instrumental in ramifying safety features."
The sentence uses a couple of advanced vocabulary words, but since "ramifying" is used incorrectly, the language use in this sentence is neither skillful nor precise. Above all, your word choice and vocabulary should make your ideas clearer, not make them harder to understand.

untitled is also an adjective by Procsilas Moscas , used under CC BY 2.0 /Resized and cropped from original.
How Do I Use the ACT Writing Grading Rubric?
Okay, we've taken a look at the ACTual ACT Writing grading rubric and gone over each domain in detail. To finish up, I'll go over a couple of ways the scoring rubric can be useful to you in your ACT essay prep.
Use the ACT Writing Rubric To...Shape Your Essays
Now that you know what the ACT is looking for in an essay, you can use that to guide what you write about in your essays...and how develop and organize what you say!
Because I'm an Old™ (not actually trademarked), and because I'm from the East Coast, I didn't really know much about the ACT prior to starting my job at PrepScholar. People didn't really take it in my high school, so when I looked at the grading rubric for the first time, I was shocked to see how different the ACT essay was (as compared to the more familiar SAT essay ).
Basically, by reading this article, you're already doing better than high school me.

An artist's impression of L. Staffaroni, age 16 (look, junior year was/is hard for everyone).
Use the ACT Writing Rubric To...Grade Your Practice Essays
The ACT can't really give you an answer key to the essay the way it can give you an answer key to the other sections (Reading, Math, etc). There are some examples of essays at each score point on the ACT website , but these examples assume that students will be at an equal level in each of domains, which will not necessarily be true for you. Even if a sample essay is provided as part of a practice test answer key, it will probably use different context, have a different logical progression, or maybe even argue a different viewpoint.
The ACT Writing rubric is the next best thing to an essay answer key. Use it as a filter through which to view your essay . Naturally, you don't have the time to become an expert at applying the rubric criteria to your essay to make sure you're in line with the ACT's grading principles and standards. That is not your job. Your job is to write the best essay that you can. If you're not confident in your ability to spot grammar, usage, and mechanics issues, I highly recommend asking a friend, teacher, or family member who is really good at (English) writing to take a look over your practice essays and point out the mistakes.
If you really want custom feedback on your practice essays from experienced essay graders, may I also suggest the PrepScholar test prep platform ? As I manage all essay grading, I happen to know a bit about the essay part of this platform, which provides you with both an essay grade and custom feedback. Learn more about PrepScholar ACT Prep and our essay grading here!
What's Next?
Desirous of some more sweet sweet ACT essay articles? Why not start with our comprehensive guide to the ACT Writing test and how to write an ACT essay, step-by-step ? (Trick question: obviously you should do this.)
Round out your dive into the details of the ACT Writing test with tips and strategies to raise your essay score , information about the best ACT Writing template , and advice on how to get a perfect score on the ACT essay .
Want actual feedback on your essay? Then consider signing up for our PrepScholar test prep platform . Included in the platform are practice tests and practice essays graded by experts here at PrepScholar.
Want to improve your ACT score by 4 points?
Check out our best-in-class online ACT prep program . We guarantee your money back if you don't improve your ACT score by 4 points or more.
Our program is entirely online, and it customizes what you study to your strengths and weaknesses . If you liked this Writing lesson, you'll love our program. Along with more detailed lessons, you'll get thousands of practice problems organized by individual skills so you learn most effectively. We're special in having expert instructors grade your essays and give you custom feedback on how to improve . We'll also give you a step-by-step program to follow so you'll never be confused about what to study next.
Check out our 5-day free trial:

Laura graduated magna cum laude from Wellesley College with a BA in Music and Psychology, and earned a Master's degree in Composition from the Longy School of Music of Bard College. She scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and GRE and loves advising students on how to excel in high school.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
- Introduction : Curriculum Components
- Writing: Skills-Based Writing Instruction
- Routines: Instruction
- For All Learners : Access
- Unit 1: Identity
- Unit 2: Personality
Unit 3: Society and its Structure
- Unit 4: Otherness
- Unit 5: Challenging Truths/Coming-of-Age
- Unit 6: Establishing Truths/Coming-of-Age
- Unit 1: The Quest
- Unit 2: The Unlikely Hero
- Unit 3: Dystopia
- Unit 4: The Anti-Hero
- Unit 5: The Monster
- Unit 6: The Tragic Hero
- Unit 1: The Contemporary American Experience
- Unit 2: The Creation of the American
- Unit 3: The American and the Changing Landscape
- Unit 4: The Reawakening of the American
- ELA Regents: Resources
- ELA Regents: Multiple Choice
- ELA Regents: Writing from Sources Essay
- ELA Regents : Text Analysis Essay
- Find Resources
Establishing Truths/Coming-of-Age
Student-Friendly Rubric for the Writing from Sources Essay
Identity Archive
Developing Skills : Student-Friendly Writing from Sources Rubric

Teacher Feedback
Please comment below with questions, feedback, suggestions, or descriptions of your experience using this resource with students.
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Free 6th grade writing rubrics

Reading Comprehension Strategies MEGA Bundle + Differentiated Reading Passages!

Words Matter: A Poem About Animal-Friendly Idioms

Kindergarten Decodable Sentence Activities MEGA Bundle

Poetry Writing Bundle with Interactive Notebook & Lapbook

CAASPP Test Prep & Academic Testing Vocabulary Bundle for Reading ELA Test Prep

6th Grade SPRING / April MATH PACKET {Review/Assessments of Standards}

Solar Eclipse Activities 2024 Reading Comprehension Worksheets & Color By Code

ANNE FRANK Biography Resources BUNDLE of 3 PRINT and EASEL

FREE Narrative Writing Checklists | Rubrics | All Ages | Editing Assessment

Writing Rubric - Expository, Argumentative, Narrative (Common Core)

RACE Strategy Grading Rubric

Creative Writing - Student Peer/Self Editing Checklist and Rubric

Persuasive Essay Rubric (Common Core Aligned)

ESL Writing Activities: Quick Write Rubric & Prompt

Tools For Writers: Peer Editing Checklist, Feedback Rubric, Reference List

Narrative Writing Checklist - FREE - Primary Exploration - Grade 1, 2, 3, 4, 5

Writing Rubric and Student Response Sheet

Argumentative Writing Essay Rubric and Peer Review FREE

- Easel Activity

Presentation & Partner Peer Review Rubric

Paragraph Writing Rubric

CUPS Checklist for Editing Narrative/Writing Stories

Middle School Writing Rubric

FREE Writing Rubrics for Secondary English

Paragraph Writing Checklist

CUPS and ARMS checklist

- Word Document File

Opinion Writing Rubric Form - Self Editing Template - 3rd - 5th FREEBIE

Argument Essay Rubric and Score Card

WIDA Writing Rubric: SCAFFOLDED and STUDENT-FRIENDLY

Ontario Writing Rubric & Achievment Chart Grade 1-8

Free Persuasive Writing Rubric

ELL Writing Rubric

PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL MODELS

Find Writing resources | TPT
Learn more about writing resources.
Writing worksheets can help your child develop essential writing and literacy skills needed for school and life. If you’re a teacher or parent looking for printable and digital writing resources to help your student learn a writing concept, look no further! TPT has an extensive collection of resources, created by other teachers, that are designed to help with any need across grade levels.
For elementary students who are just learning to write, you can use worksheets to practice letter formation. Students in middle and high school can use learning stations to learn how to write and revise essays. With plenty of TPT resources at your fingertips, you can sharpen your student's writing skills in no time. Extend writing activities beyond the classroom and observe as your child nurtures their imagination, enriches their vocabulary, and enhances their storytelling prowess.
Fun and engaging writing activities to try
Here are a few ideas for writing activities — from our teacher-created resources — that you can find on TPT and that are designed to teach students how to write effectively. (Pro tip: These worksheets serve as an excellent complement to our reading materials.)
Encourage students to keep daily journals where they can freely express their thoughts, feelings, and experiences. This practice helps them develop their writing style and build the habit of writing regularly.
Writing Prompts
Provide engaging prompts that encourage imaginative storytelling. For instance, you could ask students to write about a world without the internet, or ask them to describe something only using one of their five senses (sight, sound, smell, touch, or taste).
Peer Editing
Have students exchange their written work with a peer for feedback. This helps them strengthen their ability to identify and correct mistakes in grammar, punctuation, and spelling; give constructive criticism; and revise their writing based on feedback.
Sentence and Paragraph Construction
Provide sentence and paragraph building exercises to help students understand the basic structure of writing and how to organize their ideas coherently.
Letter Writing
Ask students to write letters to real or fictional recipients. They could compose formal letters, persuasive letters on specific topics, thank-you notes, or postcards.
Create a classroom blog where students can publish their writing for a wider audience. This teaches them to write for a purpose and consider their audience's perspective.
Research Papers
Guide students through the process of researching and writing informative or argumentative essays. Teach them how to construct persuasive arguments and counterarguments on various topics, include evidence, and cite sources.
Poetry Writing
Explore different forms of poetry, such as haikus, sonnets, and free verse. Encourage students to experiment with imagery, rhythm, and metaphor.
By incorporating these (and other!) writing activities into your lesson plans, you can nurture a love for writing.
Frequently asked questions about teaching writing
What types of writing resources are available on tpt.
There are many different types of writing resources sold by Sellers on TPT. Some popular writing lessons include creative writing, poetry, writing essays, writing expository, and handwriting.
How do I find writing lessons on TPT?
Educators can save time preparing writing lessons with resources created by experienced teachers. Simply start a search for writing resources on the TPT marketplace, and filter by grade level, price, and/or resource type to find materials that've been proven to work in classrooms like yours. No matter what you’re teaching, there are plenty of writing lessons and activities sold by Sellers on TPT that are tailored to meet your students' skill levels.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Teaching Students to Use Rubrics. Using student-friendly language was a good first step, but it was useless if my students didn't even read the rubrics. I had good reason for concern. In an informal show of hands, over half of my 8th grade students admitted they had never read the rubrics on prior French projects . I was incredulous.
The Rubric for Narrative Writing (Personal Narrative) is similar to the rubric for Expository Writing, but with a few important differences (style, voice, and presentation of ideas). Students should become familiar with the expectations for high-quality writing in each genre, and the AISD Student-Friendly Rubric is a good way to introduce the ...
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates. A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects ...
Holistic scoring is a quick method of evaluating a composition based on the reader's general impression of the overall quality of the writing—you can generally read a student's composition and assign a score to it in two or three minutes. Holistic scoring is usually based on a scale of 0-4, 0-5, or 0-6.
Rubrics are tools for communicating grading criteria and assessing student progress. Rubrics take a variety of forms, from grids to checklists, and measure a range of writing tasks, from conceptual design to sentence-level considerations. As with any assessment tool, a rubric's effectiveness is entirely dependent upon its design and its ...
The first rubric uses the words introduction, content, linking words, closing, and mechanics for the categories. The second rubric lists each standard that goes with those categories. As you can see, the first option covers the same information but uses fewer words and is much easier for students to use and understand. Student-Friendly Rubric.
Student Friendly Version Argumentative Writing Rubric 6 12. My writing purposefully argues a claim asked for by the prompt. My writing keeps a tight focus by fully supporting the claim/thesis statement and having effective organization. It is complete and easily understood.
essay and is not mere summary. ___ My essay's order makes complete sense. ___ I am writing in a way that fits my audience and my purpose. ___My writing shows my personal voice; while completely avoiding slang. __My essay has no loosely related material. My writing gives my audience complete evidence
Student-Friendly Rubric for the Text Analysis Essay. Identity Archive. Unit 6: Establishing Truths/Coming-of-Age. Developing Skills: Student-Friendly Text Analysis Rubric. Preview Resource Add a Copy of Resource to my Google Drive.
Argumentative Essay Student-Friendly Writing Rubric (Grade 6) Statement of Purpose/Focus and Organization. Evidence and Elaboration. Conventions/Editing. The response is focused and complete. the claim is clearly stated and focused throughout. the claim is communicated clearly and appropriately for the purpose, audience, and task.
STEP 3: Create a Student-Friendly Rubric. Especially if your students are new to extended constructed responses, they will likely get overwhelmed by a traditional teacher-centric rubric. ... Letting students read and score sample student essays (both good and bad) by using the rubric is a wonderful way for students to internalize the goal.
Student Friendly Writing Rubric (From a School Using the 6 Traits of Writing) ORGANIZATION. VOICE. SENTENCE FLUENCY. 5 - Clear and compelling. I have chosen an order that works well and makes the reader want to find out what comes next. My beginning grabs the reader's attention and gives clues about what is coming.
Sample Essay Rubric for Elementary Teachers. An essay rubric is a way teachers assess students' essay writing by using specific criteria to grade assignments. Essay rubrics save teachers time because all of the criteria are listed and organized into one convenient paper. If used effectively, rubrics can help improve students' writing .
This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively. Learn more: Education World. Project-Based Learning Rubric. Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier. Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers. 100 ...
Teaching with this printout. When assigning a compare and contrast writing assignment, students need to be aware of what makes an outstanding written work. This rubric is a great tool to show students what is expected of them in a concrete way. Additionally, this rubric will help teachers assess this student writing and inform further instruction.
1. demonstrate little or no skill in writing an argumentative essay. The writer fails to generate an argument that responds intelligibly to the task. The writer's intentions are difficult to discern. Attempts at analysis are unclear or irrelevant. Ideas lack development, and claims lack support.
Sample College Essay 2 with Feedback. This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org. College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay.
Student-Friendly Rubric for the Writing from Sources Essay ... Student-Friendly Rubric for the Writing from Sources Essay Identity Archive. Unit 3: Society and its Structure. Developing Skills : Student-Friendly Writing from Sources Rubric. Preview Resource Add a Copy of Resource to my Google Drive.
RLA ER Rubric - Trait 1 The Reasoning Through Language Arts Extended Response Rubric for Trait 1 appears below: ... students must employ a great deal of advanced vocabulary. Advanced vocabulary used correctly is often associated with a higher score on Trait 2, but responses that reflect a precision in word choice are just as likely to score ...
Ashlei Mosher. Use this rubric to assess any type of writing! It has categories that focus on ideas, organization, voice, and word choice for example. A student can score in the Not Yet, Developing, or Strong category. This can be used for a variety of writing types such as expository, argumentative, and narrative.
Student-Friendly Rubric for the Writing from Sources Essay ... Student-Friendly Rubric for the Writing from Sources Essay Identity Archive. Unit 3: Society and its Structure. Developing Skills : Student-Friendly Writing from Sources Rubric. Preview Resource Add a Copy of Resource to my Google Drive.
SBAC Aligned Narrative Writing E- Rubric ( student - friendly language) Gr. 3-8. This multi-use rubric uses student - friendly language, helping you to clearly communicate expectations and scores to students. It can be used for students to self-assess or for you to quickly grade narrative writing assignments.
2nd grade writing rubrics that are easy to use AND kid-friendly for writing assessments can be hard to find. These tried and true student friendly writing rubrics include formative assessments for informative writing, opinion writing, and narrative writing that have a Common Core Standard linked with each task. They are written as "I can" statements to make it very kid-friendly.These are the ...
Best used for students learning to write basic paragraphs. Can be used a tool to guide students in the revision process. Bonus: Just updated to add a 6 point writing rubric and time order/transitional words reference chart for your. Subjects: English Language Arts, Grammar, Writing. Grades: 2 nd - 6 th.