Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )

Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
78k Accesses
28 Citations
72 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

Good Qualitative Research: Opening up the Debate
Beyond qualitative/quantitative structuralism: the positivist qualitative research and the paradigmatic disclaimer.

What is Qualitative in Research
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
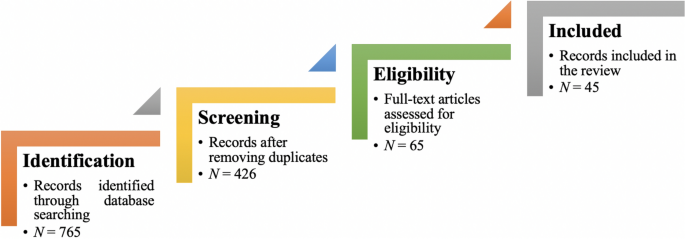
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
What makes a high quality clinical research paper?
Affiliation.
- 1 BMJ, London, UK. [email protected]
- PMID: 20233312
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2010.01663.x
The quality of a research paper depends primarily on the quality of the research study it reports. However, there is also much that authors can do to maximise the clarity and usefulness of their papers. Journals' instructions for authors often focus on the format, style, and length of articles but do not always emphasise the need to clearly explain the work's science and ethics: so this review reminds researchers that transparency is important too. The research question should be stated clearly, along with an explanation of where it came from and why it is important. The study methods must be reported fully and, where appropriate, in line with an evidence based reporting guideline such as the CONSORT statement for randomised controlled trials. If the study was a trial the paper should state where and when the study was registered and state its registration identifier. Finally, any relevant conflicts of interest should be declared.
Publication types
- Clinical Trials as Topic*
- Ethics, Research*
- Guidelines as Topic
- Journalism, Medical / standards*
- Periodicals as Topic
- Publishing / standards*
- Writing / standards*
Research Paper
29 December 2023
last updated
A research paper is a product of seeking information, analysis, human thinking, and time. Basically, when scholars want to get answers to questions, they start to search for information to expand, use, approve, or deny findings. In simple words, research papers are results of processes by considering writing works and following specific requirements. Besides, scientists research and expand many theories, developing social or technological aspects of human science. However, in order to write relevant papers, they need to know a definition of the research, structure, characteristics, and types.
Definition of What Is a Research Paper and Its Meaning
A research paper is a common assignment. It comes to a situation when students, scholars, and scientists need to answer specific questions by using sources. Basically, a research paper is one of the types of papers where scholars analyze questions or topics , look for secondary sources , and write papers on defined themes. For example, if an assignment is to write a research paper on some causes of global warming or any other topic, a person must write a research proposal on it, analyzing important points and credible sources . Although essays focus on personal knowledge, writing a research paper means analyzing sources by following academic standards. Moreover, scientists must meet the structure of research papers. Therefore, writers need to analyze their research paper topics , start to research, cover key aspects, process credible articles, and organize final studies properly.
The Structure of a Research Work
The structure of research papers depends on assignment requirements. In fact, when students get their assignments and instructions, they need to analyze specific research questions or topics, find reliable sources , and write final works. Basically, the structure of research papers consists of the abstract , outline , introduction , literature review , methodology, results , discussion, recommendations, limitations, conclusion , acknowledgments , and references. However, students may not include some of these sections because of assigned instructions that they have and specific types of research papers. For instance, if instructions of papers do not suppose to conduct real experiments, the methodology section can be skipped because of the data’s absence. In turn, the structure of the final work consists of:

Join our satisfied customers who have received perfect papers from Wr1ter Team.
🔸 The First Part of a Research Study
Abstract or an executive summary means the first section of a research paper that provides the study’s purpose, research questions or suggestions, main findings with conclusions. Moreover, this paragraph of about 150 words should be written when the whole work is finished already. Hence, abstract sections should describe key aspects of studies, including discussions about the relevance of findings.
Outline serves as a clear map of the structure of a research study.
Introduction provides the main information on problem statements, the indication of methodology, important findings, and principal conclusion. Basically, this section of a research paper covers rationales behind the work or background research, explanation of the importance, defending its relevance, a brief description of experimental designs, defined research questions, hypotheses, or key aspects.
🔸 Literature Review and Research or Experiment
Literature Review is needed for the analysis of past studies or scholarly articles to be familiar with research questions or topics. Hence, this section summarizes and synthesizes arguments and ideas from scholarly sources without adding new contributions. In turn, this part is organized around arguments or ideas, not sources.
Methodology or Materials and Methods covers explanations of research designs. Basically, techniques for gathering information and other aspects related to experiments must be described in a research paper. For instance, students and scholars document all specialized materials and general procedures. In this case, individuals may use some or all of the methods in further studies or judge the scientific merit of the work. Moreover, scientists should explain how they are going to conduct their experiments.
Results mean the gained information or data after the research or experiment. Basically, scholars should present and illustrate their findings. Moreover, this section may include tables or figures.
🔸 Analysis of Findings
Discussion is a section of a research paper where scientists review the information in the introduction part, evaluate gained results, or compare it with past studies. In particular, students and scholars interpret gained data or findings in appropriate depth. For example, if results differ from expectations at the beginning, scientists should explain why that may have happened. However, if results agree with rationales, scientists should describe theories that the evidence is supported.
Recommendations take its roots from a discussion section where scholars propose potential solutions or new ideas based on obtained results in a research paper. In this case, if scientists have any recommendations on how to improve this research so that other scholars can use evidence in further studies, they must write what they think in this section.
Limitations mean a consideration of research weaknesses and results to get new directions. For instance, if researchers found any limitations of studies that could affect experiments, scholars must not use such knowledge because of the same mistakes. Moreover, scientists should avoid contradicting results, and, even more, they must write it in this section.
🔸 The Final Part of a Conducted Research
Conclusion includes final claims of a research paper based on findings. Basically, this section covers final thoughts and the summary of the whole work. Moreover, this section may be used instead of limitations and recommendations that would be too small by themselves. In this case, scientists do not need to use headings for recommendations and limitations. Also, check out conclusion examples .
Acknowledgments or Appendix may take different forms, from paragraphs to charts. In this section, scholars include additional information on a research paper.
References mean a section where students, scholars, or scientists provide all used sources by following the format and academic rules.
Research Characteristics
Any type of work must meet some standards. By considering a research paper, this work must be written accordingly. In this case, the main characteristics of research papers are the length, style, format, and sources. Firstly, the length of research work defines the number of needed sources to analyze. Then, the style must be formal and covers impersonal and inclusive language. In turn, the format means academic standards of how to organize final works, including its structure and norms. Finally, sources and their number define works as research papers because of the volume of analyzed information. Hence, these characteristics must be considered while writing research papers.
Types of Research Papers
In general, the length of assignments can be different because of instructions. For example, there are two main types of research papers, such as typical and serious works. Firstly, a typical research paper may include definitive, argumentative, interpretive, and other works. In this case, typical papers are from 2 to 10 pages, where students analyze research questions or specific topics. Then, a serious research study is the expanded version of typical works. In turn, the length of such a paper is more than 10 pages. Basically, such works cover a serious analysis with many sources. Therefore, typical and serious works are two types of research papers.
Typical Research Papers
Basically, typical research works depend on assignments, the number of sources, and the paper’s length. So, a typical research paper is usually a long essay with the analyzed evidence. For example, students in high school and colleges get such assignments to learn how to research and analyze topics. In this case, they do not need to conduct serious experiments with the analysis and calculation of data. Moreover, students must use the Internet or libraries in searching for credible secondary sources to find potential answers to specific questions. As a result, students gather information on topics and learn how to take defined sides, present unique positions, or explain new directions. Hence, typical research papers require an analysis of primary and secondary sources without serious experiments or data.
Serious Research Studies
Although long papers require a lot of time for finding and analyzing credible sources, real experiments are an integral part of research work. Firstly, scholars at universities need to analyze the information from past studies to expand or disapprove of researched topics. Then, if scholars want to prove specific positions or ideas, they must get real evidence. In this case, experiments can be surveys, calculations, or other types of data that scholars do personally. Moreover, a dissertation is a typical serious research paper that young scientists write based on the research analysis of topics, data from conducted experiments, and conclusions at the end of work. Thus, serious research papers are studies that take a lot of time, analysis of sources with gained data, and interpretation of results.

What Should Be the Characteristics of a Good Research Paper?
by team@blp
In miscellaneous.
When people want to get answers to various issues, they search for information on the problems. From their findings, they expand them, aiming to agree or refute them. Research papers are common assignments in colleges.
They follow specific research and writing guidelines to answer particular questions or assigned topics. They look into the critical topic of credible research sources and argue their findings in an orderly manner. To be termed as good, the research paper must bear the following characteristics.
In this Article
Gives credit to previous research work on the topic
- It’s hooked on a relevant research question.
It must be based on appropriate, systematic research methods
- The information must be accurate and controlled.
- It must be verifiable and rigorous.
Be careful with the topic you choose
Decide the sources you want to use, create your thesis statement , plan your points, write your paper, characteristics of a good research paper.
Writing a research paper aims to discover new knowledge, but the knowledge must have a base. Its base is the research done previously by other scholars. The student must acknowledge the previous research and avoid duplicating it in their writing process.
A college student must engage in deep research work to create a credible research paper. This makes the process lengthy and complex when choosing your topic, selecting sources, and developing its design. In addition, it requires a great deal of knowledge to piece everything together. Fortunately, Studyclerk will give you professional help anytime you need it. If you do not have enough knowledge and time to write a paper on your own, you can ask for research paper help by StudyClerk, where experienced paper writers will write your paper in no time. You can trust their expert writers to handle your assignment well and get a well-written paper in a short time.
It’s hooked on a relevant research question .
All the time a student spends researching multiple sources is to answer a specific research question. The question must be relevant to the current needs. This question guides them into the information they use or the line of argument they take.
The methodology of research a student chooses will determine the value of the information they get or give. The methods must be valid and credible to provide reliable outcomes. Whether the student chooses a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed approach, they must all be valuable and relevant.
The information must be accurate and controlled .
A good research paper cannot be generalized information but specific, scientific information. That is why they must include references and record tests or information accurately. Moreover, they must keep the information controlled by staying within the topic from the first step of research to the last.
It must be verifiable and rigorous .
The student must use information or write arguments that can be verified. If it’s a test, it must be replicable by another researcher. The sources must be verifiable and accurate. Without rigorous deep research strategies , the paper cannot be good. They must put a lot of labor into both the writing and research processes to ensure the information is credible, clear, concise, original, and precise.
How to write a good research paper
To write a good research paper, you must first understand what kind of question you have been assigned. Then, you will choose the best topic that you will love to write about. The following points will help you write a good research paper.
You must select a topic you love. Go for a topic that will be easier to research, which will give you a broader area of study.
Your instructor doesn’t restrict you on the sources you must use. Broaden your mind so that you don’t limit yourself to specific sources of information. Sometimes you will get helpful information from sources you slightest thought as good.
Write your central statement to base your position on the research. Make it coherent contentious, and let it be a summary of your arguments.
Create an outline that will guide you when arguing your points
- Start with the most vital points and smooth the flow.
- Pay attention to paragraph structure and let your arguments be clear.
- Finish with a compelling conclusion, and don’t forget to cite your sources.
A research paper requires extensive research methods to get solid points for supporting your stand. First, the sources you use must be verifiable by any other researcher. You must ensure your research work is original for your paper to be credible. Third, each point should be coherent with each paragraph. Finally, your research findings must be tagged on the research question and provide answers that apply to the current society.
Author’s Bio
Helen Birk is an online freelance writer who holds an outstanding record of helping numerous students do their academic assignments. She is an expert in essays and thesis writing, and students simply love her for her high-quality work. In addition, she enjoys cycling, doing pencil sketching, and listening to spiritual podcasts in her free time.
Tips for Writing Exam Essays
Writing essays for exams can feel like a huge challenge. You're under time pressure, feeling stressed, and expected to produce a well-organized, persuasive piece of writing. While some students may be tempted to seek out a top essay writing service for quick...
Write Your Successful Business Management Essay
Business Management Essay Writing: Step to Success A business essay is a short piece in which the author highlights some problems or business ideas and his achievements. Applicants, students and employees can write such an essay. Features of the business management...
How to Choose the Best Dissertation Writing Company
Guide on How to Choose the Best Dissertation Writing Company For many years the students have been ordering help with dissertations. Many such services have become extremely popular approximately 10 years ago and since then such websites only gain in popularity. For...
Guide on Where Can I Buy a Custom Essay Online?
Explore Where Can I Buy a Custom Essay Online? How to write an essay? Such a question is a main problem for schoolchildren and students because more and more often teachers offer to write a text in the essay genre. This type has become very popular, so we have...
Summer Office Wear For Men: A Style Guide For Teachers
As we dive into the scorching summer months, the struggle to maintain a professional appearance while staying cool and comfortable in the classroom becomes all too real. With global warming, expect harsh temperature changes with every seasonal transition. But don’t...
From Application to Offer: Navigating the Job Search Journey
Embarking on the job search journey can be an exhilarating yet daunting process. From crafting your application to the moment you receive that much-anticipated job offer, each step requires careful planning, preparation, and execution. This comprehensive guide aims to...
Mastering the Test: Strategies for Exam Success
The path to academic and professional certification is often paved with the challenge of passing rigorous exams. For many, the mere thought of an upcoming test can evoke a mix of anticipation and apprehension. However, success is not just a product of what you know...
How the Discovery Stage Contributes to the Success of a Business Project
A positive return on your investment in a business project is only possible when you enter the market with an offer demanded by consumers. They determine the success of the company through their purchases and give it a chance for further growth. That is why special...
Exploring Innovative Educational Leadership: A Comparative Analysis of Global Teaching Trends
If you pay attention to the educational sector, you'll notice a shift toward transformational leadership across all academic levels. It's an approach born out of the growing need to prepare students for a changing world where learners are no longer insulated from...
The Importance of STEM Education
In today's fast-paced world, STEM education, encompassing Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics, plays a pivotal role in shaping the future. It's not merely a set of subjects; it's a pathway to innovation, problem-solving, and economic growth. Fostering...
WANT MORE AMAZING CONTENT?
- Free GRE Practice Questions
- 100+ Personal Statement Templates
- 100+ Quotes to Kick Start Your Personal Statement
- 390 Adjectives to Use in a LOR

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?


Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
Product Development Use Cases
Risks with product development, what product development engineers do, what are product development strategies, is product development part of r&d, why product development is necessary, is product development agile, product development key skills, stages to product development.

What Are the 5 Characteristics of a Good Research Paper?
What are the 5 characteristics of a good research paper? Tune in to find out.
Top 5 Characteristics of a Good Research Paper
Good research is anchored on a sound research question.
A good research paper is one that gets you the best grade; it is one that makes a statement about the real world around you.
In essence, what makes it a good research paper is the way in which it answers the question that you wanted to answer.
The question is usually posed as a hypothesis. So, it needs to be answered in a way that shows proof of your observation about the world around you. A good research paper also needs to be interesting to read and support your point of view.
Good research follows a systematic, appropriate research methodology
A good research methodology is one that is systematic and scientific . First, it is one that follows a logical and coherent pattern of development.
It starts with an idea then moves on to design, data collection, analysis, and finally interpretation and presentation of results.
It also needs to be credible. Also, it does not make use of weak sources of information; it does not depend on hearsay for the core data.
In essence, a good research paper uses credible sources that have been vetted for accuracy and authenticity. They are also relevant to your topic and will support your argument.
Good research makes use of appropriate methods of data collection
The whole point of a research paper is to collect information from credible sources and analyze them in order to draw a conclusion.
This conclusion then becomes the thesis statement that you need to write about in the paper itself.
Good research papers use appropriate methods for collecting data. Whether it was through surveys, questionnaires, or interviews, or through analyzing existing data in the form of statistics, graphs, or charts.
Good research is guided by logic
A good research paper is one that you can logically support. The data that you collect needs to be analyzed and interpreted in a logical way.
The conclusion should be the one that logically follows from the research questions, the methodology, and the data.
Good research acknowledges its limitations and provides suggestions for future research
Finally, a good research paper is one that acknowledges any shortcomings or limitations in the research. It is one that recognizes the possibility of alternative conclusions and alternative interpretations of the data.
It is also one that makes suggestions for further research in the same area.
The Bottom Line
A good research paper follows a systematic, logical, and coherent pattern of development. It uses credible sources that have been verified for accuracy and authenticity.
It is guided by logic, it is systematic and it acknowledges its limitations.
What do you think are the top qualities of a good academic research paper? As always, we want to hear from you.
If you have any comments, questions, or concerns about this article, please leave them in the comments section below
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m3ijYqyWnog.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

More Stories
Is product development agile? If not, how can you make it agile? What are the steps you need to do? To find...
Product Development Factors
What are some of the most important product development factors that you need to know? How can these help you...
Why New Product Development Is Important
There are many reasons why new product development is important. These are the reasons why you need to do this process meticulously....
Product Development Qualifications
What are some of the product development qualifications that you need to have? How do you ensure you have these...
Product Development Lead
A product development lead is a person that has many responsibilities within the company he is working for. What are...
Product Development vs Market Development
Product development vs market development. What are the differences and similarities between these two? What is their purpose? To know...
Recent Post
Top category, vp research and development.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Latest science news, discoveries and analysis

Could a rare mutation that causes dwarfism also slow ageing?

Bird flu in US cows: is the milk supply safe?

Future of Humanity Institute shuts: what's next for ‘deep future’ research?

Judge dismisses superconductivity physicist’s lawsuit against university
Nih pay raise for postdocs and phd students could have us ripple effect, hello puffins, goodbye belugas: changing arctic fjord hints at our climate future, china's moon atlas is the most detailed ever made, ‘shut up and calculate’: how einstein lost the battle to explain quantum reality, ecologists: don’t lose touch with the joy of fieldwork chris mantegna.

Should the Maldives be creating new land?

Lethal AI weapons are here: how can we control them?

Algorithm ranks peer reviewers by reputation — but critics warn of bias

How gliding marsupials got their ‘wings’
Bird flu virus has been spreading in us cows for months, rna reveals, audio long read: why loneliness is bad for your health, nato is boosting ai and climate research as scientific diplomacy remains on ice, rat neurons repair mouse brains — and restore sense of smell.
Retractions are part of science, but misconduct isn’t — lessons from a superconductivity lab

Any plan to make smoking obsolete is the right step

Citizenship privilege harms science
European ruling linking climate change to human rights could be a game changer — here’s how charlotte e. blattner, will ai accelerate or delay the race to net-zero emissions, current issue.

The Maldives is racing to create new land. Why are so many people concerned?
Surprise hybrid origins of a butterfly species, stripped-envelope supernova light curves argue for central engine activity, optical clocks at sea, research analysis.

Ancient DNA traces family lines and political shifts in the Avar empire
A chemical method for selective labelling of the key amino acid tryptophan
Robust optical clocks promise stable timing in a portable package
Targeting RNA opens therapeutic avenues for Timothy syndrome
Bioengineered ‘mini-colons’ shed light on cancer progression, galaxy found napping in the primordial universe, tumours form without genetic mutations, marsupial genomes reveal how a skin membrane for gliding evolved.

Scientists urged to collect royalties from the ‘magic money tree’

Breaking ice, and helicopter drops: winning photos of working scientists

Shrouded in secrecy: how science is harmed by the bullying and harassment rumour mill
Want to make a difference try working at an environmental non-profit organization, how ground glass might save crops from drought on a caribbean island, books & culture.

How volcanoes shaped our planet — and why we need to be ready for the next big eruption

Dogwhistles, drilling and the roots of Western civilization: Books in brief

Cosmic rentals
Las borinqueñas remembers the forgotten puerto rican women who tested the first pill, dad always mows on summer saturday mornings, nature podcast.

Latest videos
Nature briefing.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: research on splicing image detection algorithms based on natural image statistical characteristics.
Abstract: With the development and widespread application of digital image processing technology, image splicing has become a common method of image manipulation, raising numerous security and legal issues. This paper introduces a new splicing image detection algorithm based on the statistical characteristics of natural images, aimed at improving the accuracy and efficiency of splicing image detection. By analyzing the limitations of traditional methods, we have developed a detection framework that integrates advanced statistical analysis techniques and machine learning methods. The algorithm has been validated using multiple public datasets, showing high accuracy in detecting spliced edges and locating tampered areas, as well as good robustness. Additionally, we explore the potential applications and challenges faced by the algorithm in real-world scenarios. This research not only provides an effective technological means for the field of image tampering detection but also offers new ideas and methods for future related research.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What the data says about crime in the U.S.
A growing share of Americans say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress to address this year. Around six-in-ten U.S. adults (58%) hold that view today, up from 47% at the beginning of Joe Biden’s presidency in 2021.
We conducted this analysis to learn more about U.S. crime patterns and how those patterns have changed over time.
The analysis relies on statistics published by the FBI, which we accessed through the Crime Data Explorer , and the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS), which we accessed through the National Crime Victimization Survey data analysis tool .
To measure public attitudes about crime in the U.S., we relied on survey data from Pew Research Center and Gallup.
Additional details about each data source, including survey methodologies, are available by following the links in the text of this analysis.
With the issue likely to come up in this year’s presidential election, here’s what we know about crime in the United States, based on the latest available data from the federal government and other sources.
How much crime is there in the U.S.?
It’s difficult to say for certain. The two primary sources of government crime statistics – the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS) – paint an incomplete picture.
The FBI publishes annual data on crimes that have been reported to law enforcement, but not crimes that haven’t been reported. Historically, the FBI has also only published statistics about a handful of specific violent and property crimes, but not many other types of crime, such as drug crime. And while the FBI’s data is based on information from thousands of federal, state, county, city and other police departments, not all law enforcement agencies participate every year. In 2022, the most recent full year with available statistics, the FBI received data from 83% of participating agencies .
BJS, for its part, tracks crime by fielding a large annual survey of Americans ages 12 and older and asking them whether they were the victim of certain types of crime in the past six months. One advantage of this approach is that it captures both reported and unreported crimes. But the BJS survey has limitations of its own. Like the FBI, it focuses mainly on a handful of violent and property crimes. And since the BJS data is based on after-the-fact interviews with crime victims, it cannot provide information about one especially high-profile type of offense: murder.
All those caveats aside, looking at the FBI and BJS statistics side-by-side does give researchers a good picture of U.S. violent and property crime rates and how they have changed over time. In addition, the FBI is transitioning to a new data collection system – known as the National Incident-Based Reporting System – that eventually will provide national information on a much larger set of crimes , as well as details such as the time and place they occur and the types of weapons involved, if applicable.
Which kinds of crime are most and least common?
Property crime in the U.S. is much more common than violent crime. In 2022, the FBI reported a total of 1,954.4 property crimes per 100,000 people, compared with 380.7 violent crimes per 100,000 people.
By far the most common form of property crime in 2022 was larceny/theft, followed by motor vehicle theft and burglary. Among violent crimes, aggravated assault was the most common offense, followed by robbery, rape, and murder/nonnegligent manslaughter.
BJS tracks a slightly different set of offenses from the FBI, but it finds the same overall patterns, with theft the most common form of property crime in 2022 and assault the most common form of violent crime.
How have crime rates in the U.S. changed over time?
Both the FBI and BJS data show dramatic declines in U.S. violent and property crime rates since the early 1990s, when crime spiked across much of the nation.
Using the FBI data, the violent crime rate fell 49% between 1993 and 2022, with large decreases in the rates of robbery (-74%), aggravated assault (-39%) and murder/nonnegligent manslaughter (-34%). It’s not possible to calculate the change in the rape rate during this period because the FBI revised its definition of the offense in 2013 .
The FBI data also shows a 59% reduction in the U.S. property crime rate between 1993 and 2022, with big declines in the rates of burglary (-75%), larceny/theft (-54%) and motor vehicle theft (-53%).
Using the BJS statistics, the declines in the violent and property crime rates are even steeper than those captured in the FBI data. Per BJS, the U.S. violent and property crime rates each fell 71% between 1993 and 2022.
While crime rates have fallen sharply over the long term, the decline hasn’t always been steady. There have been notable increases in certain kinds of crime in some years, including recently.
In 2020, for example, the U.S. murder rate saw its largest single-year increase on record – and by 2022, it remained considerably higher than before the coronavirus pandemic. Preliminary data for 2023, however, suggests that the murder rate fell substantially last year .
How do Americans perceive crime in their country?
Americans tend to believe crime is up, even when official data shows it is down.
In 23 of 27 Gallup surveys conducted since 1993 , at least 60% of U.S. adults have said there is more crime nationally than there was the year before, despite the downward trend in crime rates during most of that period.
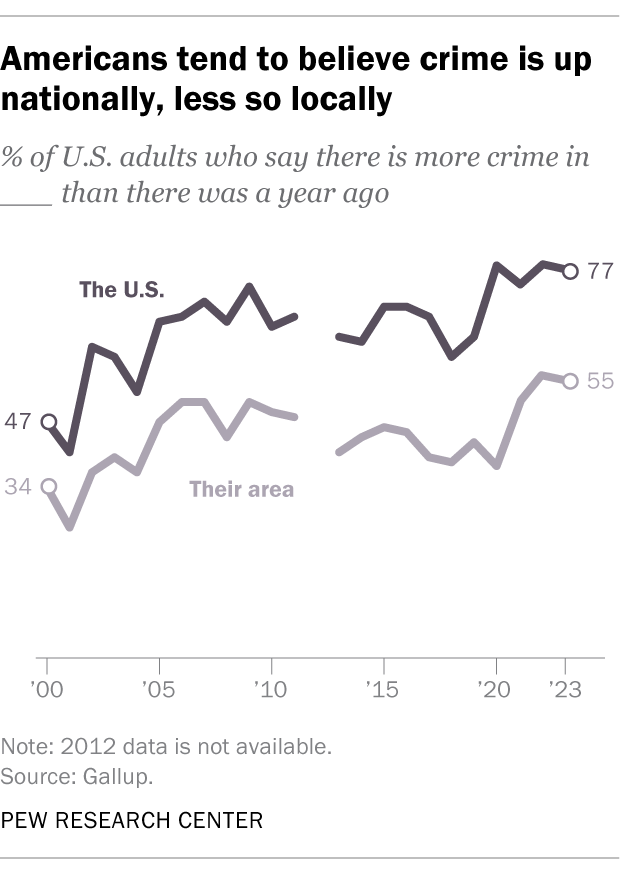
While perceptions of rising crime at the national level are common, fewer Americans believe crime is up in their own communities. In every Gallup crime survey since the 1990s, Americans have been much less likely to say crime is up in their area than to say the same about crime nationally.
Public attitudes about crime differ widely by Americans’ party affiliation, race and ethnicity, and other factors . For example, Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are much more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress this year (68% vs. 47%), according to a recent Pew Research Center survey.
How does crime in the U.S. differ by demographic characteristics?
Some groups of Americans are more likely than others to be victims of crime. In the 2022 BJS survey , for example, younger people and those with lower incomes were far more likely to report being the victim of a violent crime than older and higher-income people.
There were no major differences in violent crime victimization rates between male and female respondents or between those who identified as White, Black or Hispanic. But the victimization rate among Asian Americans (a category that includes Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders) was substantially lower than among other racial and ethnic groups.
The same BJS survey asks victims about the demographic characteristics of the offenders in the incidents they experienced.
In 2022, those who are male, younger people and those who are Black accounted for considerably larger shares of perceived offenders in violent incidents than their respective shares of the U.S. population. Men, for instance, accounted for 79% of perceived offenders in violent incidents, compared with 49% of the nation’s 12-and-older population that year. Black Americans accounted for 25% of perceived offenders in violent incidents, about twice their share of the 12-and-older population (12%).
As with all surveys, however, there are several potential sources of error, including the possibility that crime victims’ perceptions about offenders are incorrect.
How does crime in the U.S. differ geographically?
There are big geographic differences in violent and property crime rates.
For example, in 2022, there were more than 700 violent crimes per 100,000 residents in New Mexico and Alaska. That compares with fewer than 200 per 100,000 people in Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Hampshire and Maine, according to the FBI.
The FBI notes that various factors might influence an area’s crime rate, including its population density and economic conditions.
What percentage of crimes are reported to police? What percentage are solved?
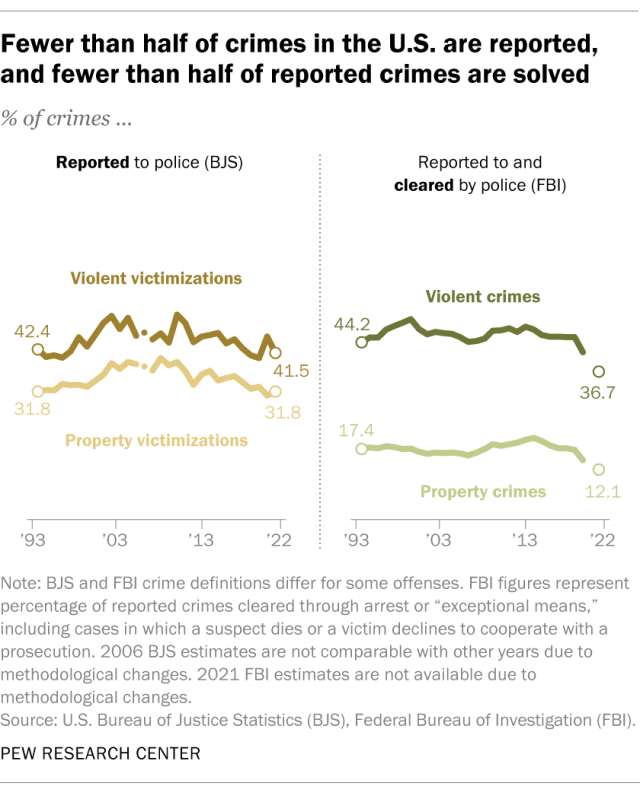
Most violent and property crimes in the U.S. are not reported to police, and most of the crimes that are reported are not solved.
In its annual survey, BJS asks crime victims whether they reported their crime to police. It found that in 2022, only 41.5% of violent crimes and 31.8% of household property crimes were reported to authorities. BJS notes that there are many reasons why crime might not be reported, including fear of reprisal or of “getting the offender in trouble,” a feeling that police “would not or could not do anything to help,” or a belief that the crime is “a personal issue or too trivial to report.”
Most of the crimes that are reported to police, meanwhile, are not solved , at least based on an FBI measure known as the clearance rate . That’s the share of cases each year that are closed, or “cleared,” through the arrest, charging and referral of a suspect for prosecution, or due to “exceptional” circumstances such as the death of a suspect or a victim’s refusal to cooperate with a prosecution. In 2022, police nationwide cleared 36.7% of violent crimes that were reported to them and 12.1% of the property crimes that came to their attention.
Which crimes are most likely to be reported to police? Which are most likely to be solved?
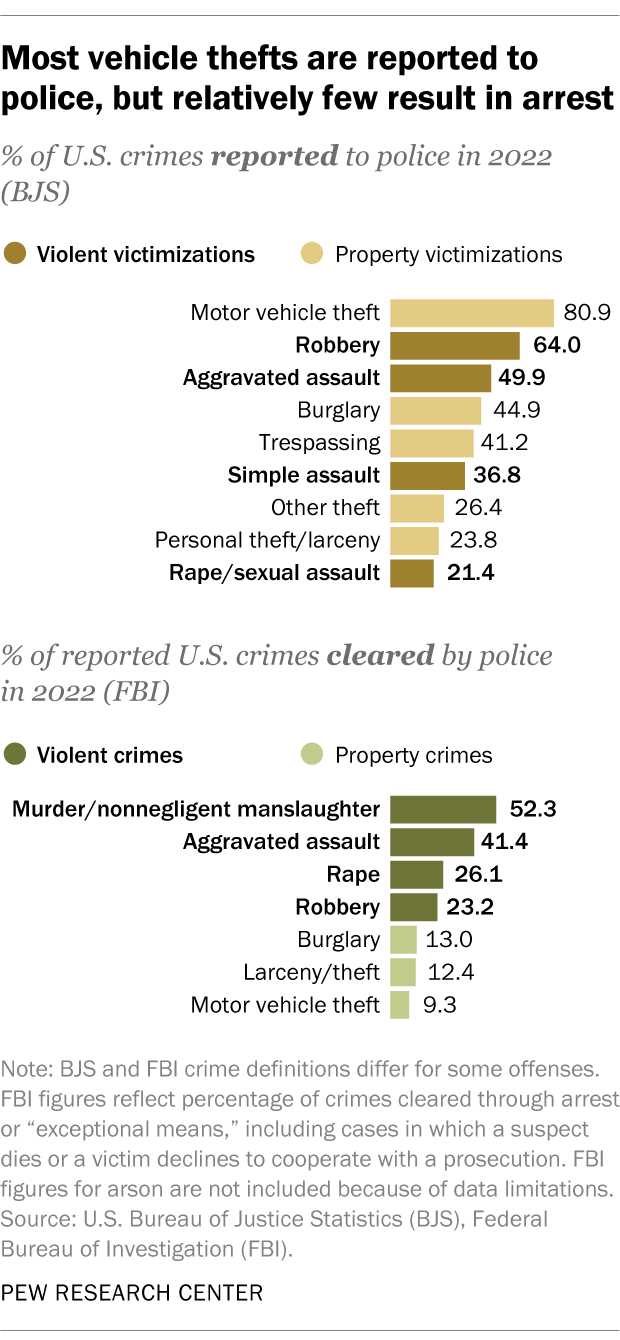
Around eight-in-ten motor vehicle thefts (80.9%) were reported to police in 2022, making them by far the most commonly reported property crime tracked by BJS. Household burglaries and trespassing offenses were reported to police at much lower rates (44.9% and 41.2%, respectively), while personal theft/larceny and other types of theft were only reported around a quarter of the time.
Among violent crimes – excluding homicide, which BJS doesn’t track – robbery was the most likely to be reported to law enforcement in 2022 (64.0%). It was followed by aggravated assault (49.9%), simple assault (36.8%) and rape/sexual assault (21.4%).
The list of crimes cleared by police in 2022 looks different from the list of crimes reported. Law enforcement officers were generally much more likely to solve violent crimes than property crimes, according to the FBI.
The most frequently solved violent crime tends to be homicide. Police cleared around half of murders and nonnegligent manslaughters (52.3%) in 2022. The clearance rates were lower for aggravated assault (41.4%), rape (26.1%) and robbery (23.2%).
When it comes to property crime, law enforcement agencies cleared 13.0% of burglaries, 12.4% of larcenies/thefts and 9.3% of motor vehicle thefts in 2022.
Are police solving more or fewer crimes than they used to?
Nationwide clearance rates for both violent and property crime are at their lowest levels since at least 1993, the FBI data shows.
Police cleared a little over a third (36.7%) of the violent crimes that came to their attention in 2022, down from nearly half (48.1%) as recently as 2013. During the same period, there were decreases for each of the four types of violent crime the FBI tracks:
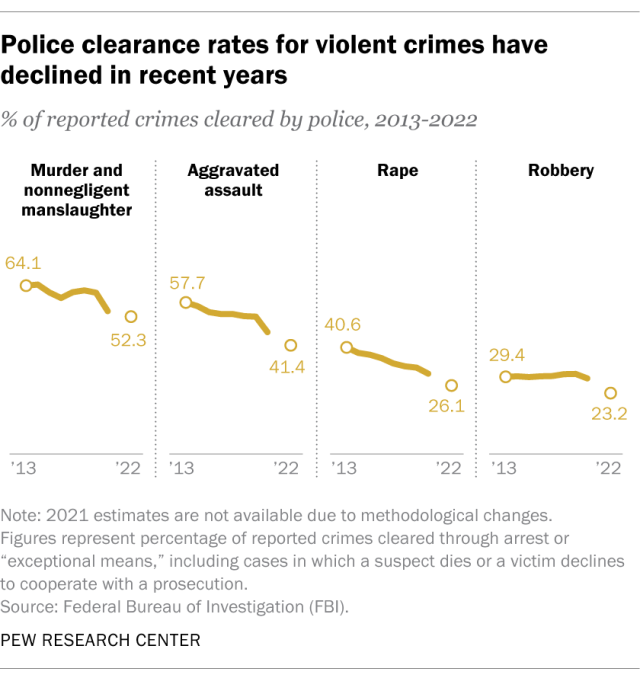
- Police cleared 52.3% of reported murders and nonnegligent homicides in 2022, down from 64.1% in 2013.
- They cleared 41.4% of aggravated assaults, down from 57.7%.
- They cleared 26.1% of rapes, down from 40.6%.
- They cleared 23.2% of robberies, down from 29.4%.
The pattern is less pronounced for property crime. Overall, law enforcement agencies cleared 12.1% of reported property crimes in 2022, down from 19.7% in 2013. The clearance rate for burglary didn’t change much, but it fell for larceny/theft (to 12.4% in 2022 from 22.4% in 2013) and motor vehicle theft (to 9.3% from 14.2%).
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on Nov. 20, 2020.
- Criminal Justice

John Gramlich is an associate director at Pew Research Center
8 facts about Black Lives Matter
#blacklivesmatter turns 10, support for the black lives matter movement has dropped considerably from its peak in 2020, fewer than 1% of federal criminal defendants were acquitted in 2022, before release of video showing tyre nichols’ beating, public views of police conduct had improved modestly, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The focus of this article is on whether the material that is included in a paper is suitable for a research paper, rather than whether it is well-written. Silverman's (2000) headings form an excellent basis for a discussion of what constitutes a good research paper: • Conceptualization and theoretical basis of the work.
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Qualities of Good Research 1. Good research is anchored on a sound research question. A sound research question is one of the most important characteristics of good research. In fact, formulating one is embedded in the curricula of research-heavy programs like engineering and physics degrees and careers.In 2010, Farrugia et al. proposed that developing a research question is the most important ...
The characteristic of a good research. A researcher should understand and have a clear understanding of the different. types of research design and select the type which apply best for the study ...
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow: 1. Context — your introduction. 2. Content — your results. 3. Conclusion — your discussion. Plan ...
Summary. The chapter indicates our reasons for publishing, the framework of a communication, how to introduce the topic and put forward a hypotheses before considering each of the conventional sections of a paper. It also emphasizes that the sequence in how a paper is compiled section by section will not be the order given here.
A good research involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. It entails feasible research methods based upon a research methodology that best suits the nature of your research question. It is built upon sufficient relevant data and is reproducible and replicable. It is based on a suitable rationale and can suggest ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Periodicals as Topic. Publishing / standards*. Writing / standards*. The quality of a research paper depends primarily on the quality of the research study it reports. However, there is also much that authors can do to maximise the clarity and usefulness of their papers. Journals' instructions for authors often focus on the format, style, and ...
A good research paper should be rigorous, controlled, Accurate, replicable, Clear, Concise, Valid, Verifiable, Sequential, etc. Cite. 2 Recommendations. Chinaza Godswill Awuchi. University of ...
Research Paper. A research paper is a product of seeking information, analysis, human thinking, and time. Basically, when scholars want to get answers to questions, they start to search for information to expand, use, approve, or deny findings. In simple words, research papers are results of processes by considering writing works and following ...
Characteristics of a good research paper Gives credit to previous research work on the topic. Writing a research paper aims to discover new knowledge, but the knowledge must have a base. Its base is the research done previously by other scholars. The student must acknowledge the previous research and avoid duplicating it in their writing process.
Qualities and Characteristics of a Good Scientific Research. Writing; Step-by-Step Approaches. Val Hyginus Udoka Eze 1, * Chidinma Esther Eze, Asiati Mbabazi, Ugwu. Chinyere N, Ugwu Okechukwu Paul ...
Shorten the text to make it more concise, while still remaining descriptive. Repeat this process until you have a title of fewer than 15 words. 2. A good title is easily searchable. Most readers ...
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Top 5 Characteristics of a Good Research Paper Good research is anchored on a sound research question. A good research paper is one that gets you the best grade; it is one that makes a statement about the real world around you. In essence, what makes it a good research paper is the way in which it answers the question that you wanted to answer.
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
Characteristics of Good Research. 1. The purpose of the research should be clearly defined (aims and. objectives). 2. The need and significance of the topic of research must be stated. 3. Research ...
With the development and widespread application of digital image processing technology, image splicing has become a common method of image manipulation, raising numerous security and legal issues. This paper introduces a new splicing image detection algorithm based on the statistical characteristics of natural images, aimed at improving the accuracy and efficiency of splicing image detection ...
For example, Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are much more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say reducing crime should be a top priority for the president and Congress this year (68% vs. 47%), according to a recent Pew Research Center survey. How does crime in the U.S. differ by demographic characteristics?