- Government Exam Articles

Web Browser
Web Browser is a common term which is frequently used by people while discussing the Internet. However, the exact definition of a web browser is known by few only.
Web Browser Definition: A software application used to access information on the World Wide Web is called a Web Browser. When a user requests some information, the web browser fetches the data from a web server and then displays the webpage on the user’s screen.
It is also important to know in detail about what a web browser is for candidates preparing for Government exams. This is because Computer Knowledge is a common topic for many competitive exams and questions based on web browsers may be asked.
In this article, we shall discuss in detail the different types of web browsers and their development over the years. Also, web browser functions have been given along with some sample questions from the competitive exam perspective.
To learn more about the other Computer Awareness related topics, candidates can check the links given below:
History of Web Browser
Today web browsers are easily accessible and can be used on devices like computer, laptops, mobile phones, etc. but this evolution of making browsers available for easy use took many years.
Given below are some salient points which one must know with regard to the history of web browsers:
- “WorldWideWeb” was the first web browser created by Tim Berners Lee in 1990. This is completely different from the World Wide Web we use today
- In 1993, the “Mosaic” web browser was released. It had the feature of adding images and an innovative graphical interface. It was the “the world’s first popular browser”
- After this, in 1994, Marc Andreessen (leader of Mosaic Team) started working on a new web browser, which was released and was named “Netscape Navigator”
- In 1995, “Internet Explorer” was launched by Microsoft. It soon overtook as the most popular web browser
- In 2002, “Mozilla Firefox” was introduced which was equally as competent as Internet Explorer
- Apple too launched a web browser in the year 2003 and named it “Safari” . This browser is commonly used in Apple devices only and not popular with other devices
- Finally, in the year 2008, Google released “Chrome” and within a time span of 3 years it took over all the other existing browsers and is one of the most commonly used web browsers across the world
For those who are willing to know more about the Internet , can visit the linked article.
Functions of Web Browser
Our dependency on the Internet has massively increased. Stated below are functions of web browsers and how are they useful:
- The main function is to retrieve information from the World Wide Web and making it available for users
- Visiting any website can be done using a web browser. When a URL is entered in a browser, the web server takes us to that website
- To run Java applets and flash content, plugins are available on the web browser
- It makes Internet surfing easy as once we reach a website we can easily check the hyperlinks and get more and more useful data online
- Browsers user internal cache which gets stored and the user can open the same webpage time and again without losing extra data
- Multiple webpages can be opened at the same time on a web browser
- Options like back, forward, reload, stop reload, home, etc. are available on these web browsers, which make using them easy and convenient
Given below are a few difference between articles for candidates to learn more about the different computer features:
Types of Web Browser
The functions of all web browsers are the same. Thus, more than the different types there are different web browsers which have been used over the years.
Discussed below are different web browser examples and their specific features:
1. WorldWideWeb
- The first web browser ever
- Launched in 1990
- It was later named “Nexus” to avoid any confusion with the World Wide Web
- Had the very basic features and less interactive in terms of graphical interface
- Did not have the feature of bookmark
- It was launched in 1993
- The second web browser which was launched
- Had a better graphical interface. Images, text and graphics could all be integrated
- It was developed at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications
- The team which was responsible for creating Mosaic was lead by Marc Andreessen
- It was named “the world’s first popular browser”
3. Netscape Navigator
- It was released in 1994
- In the 1990s, it was the dominant browser in terms of usage share
- More versions of this browser were launched by Netscape
- It had an advanced licensing scheme and allowed free usage for non-commercial purposes
4. Internet Explorer
- It was launched in 1995 by Microsoft
- By 2003, it has attained almost 95% of usage share and had become the most popular browsers of all
- Close to 10 versions of Internet Explorer were released by Microsoft and were updated gradually
- It was included in the Microsoft Windows operating system
- In 2015, it was replaced with “Microsoft Edge”, as it became the default browser on Windows 10
- It was introduced in 2002 and was developed by Mozilla Foundation
- Firefox overtook the usage share from Internet Explorer and became the dominant browser during 2003-04
- Location-aware browsing was made available with Firefox
- This browser was also made available for mobile phones, tablets, etc.
6. Google Chrome
- It was launched in 2008 by Google
- It is a cross-platform web browser
- Multiple features from old browsers were amalgamated to form better and newer features
- To save computers from malware, Google developed the ad-blocking feature to keep the user data safe and secure
- Incognito mode is provided where private searching is available where no cookies or history is saved
- Till date, it has the best user interface
Apart from these, Opera Mini web browser was introduced in 2005 which was specially designed for mobile users. Before the mobile version, the computer version “Opera” was also released in 1995. It supported a decent user interface and was developed by Opera Software.
As for Government aspirants, apart from Computer Knowledge, various other subjects are included in the exam syllabus. The links for the same are given below:
Sample Questions on Web Browsers
For most competitive exams, questions in the form of MCQ (multiple choice questions) are asked. Thus, given below are web browser example questions for the reference of candidates.
Q 1. ______ rendering engine is used by Mozilla Firefox
Answer: (3) Gecko
Q 2. Which of these web browsers is also known as Nexus?
- Internet Explorer
- WorldWideWeb
Answer: (5) WorldWideWeb
Q 3. Which of the following is considered as “the world’s first popular browser”?
- Netscape Navigator
- MSIE (Microsoft Internet Explorer)
Answer: (2) Mosaic
Q 4. In which year was the first web browser created?
Answer: (3) 1990
Q 5. Which among the following web browsers was the first to introduce graphical interface?
Answer: (4) Netscape
The questions above will help candidates apprehend the type or pattern in which questions may be asked in the final exam from this topic. To get the Preparation Strategy for Competitive Exams , visit the linked article.
Get more questions from the various subjects to excel in the upcoming Government exams, aspirants can also refer to the following links:
For any further information for the upcoming exams or study material and preparation tips, turn to BYJU’S for assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions on Web Browser
Q 1. what is the definition of a web browser, q 2. what is the difference between a web browser and a search engine, q 3. what the best web browser examples.
Ans. Given below are the examples of the most commonly used web browsers:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
There were web browsers like Netscape Navigator and WorldWideWeb, which were used before the above-mentioned browsers.
Q 4. When was the first web browser released?

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Connect with us for Free Preparation
Get access to free crash courses & video lectures for all government exams..
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Firefox is no longer supported on Windows 8.1 and below.
Please download Firefox ESR (Extended Support Release) to use Firefox.
Download Firefox ESR 64-bit
Download Firefox ESR 32-bit
Firefox is no longer supported on macOS 10.14 and below.
What is a web browser?
A web browser takes you anywhere on the internet, letting you see text, images and video from anywhere in the world.
The web is a vast and powerful tool. Over the course of a few decades, the internet has changed the way we work, the way we play and the way we interact with one another. Depending on how it’s used, it bridges nations, drives commerce, nurtures relationships, drives the innovation engine of the future and is responsible for more memes than we know what to do with.
It’s important that everyone has access to the web, but it’s also vital that we all understand the tools we use to access it. We use web browsers like Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge and Apple Safari every day, but do we understand what they are and how they work? In a short period of time we’ve gone from being amazed by the ability to send an email to someone around the world, to a change in how we think of information. It’s not a question of how much you know anymore, but simply a question of what browser or app can get you to that information fastest.
In a short period of time, we’ve gone from being amazed by the ability to send an email to someone around the world, to a change in how we think about information.
How does a web browser work?
A web browser takes you anywhere on the internet. It retrieves information from other parts of the web and displays it on your desktop or mobile device. The information is transferred using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which defines how text, images and video are transmitted on the web. This information needs to be shared and displayed in a consistent format so that people using any browser, anywhere in the world can see the information.
Sadly, not all browser makers choose to interpret the format in the same way. For users, this means that a website can look and function differently. Creating consistency between browsers, so that any user can enjoy the internet, regardless of the browser they choose, is called web standards .
When the web browser fetches data from an internet connected server, it uses a piece of software called a rendering engine to translate that data into text and images. This data is written in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) and web browsers read this code to create what we see, hear and experience on the internet.
Hyperlinks allow users to follow a path to other pages or sites on the web. Every webpage, image and video has its own unique Uniform Resource Locator (URL), which is also known as a web address. When a browser visits a server for data, the web address tells the browser where to look for each item that is described in the html, which then tells the browser where it goes on the web page.
Cookies (not the yummy kind)
Websites save information about you in files called cookies . They are saved on your computer for the next time you visit that site. Upon your return, the website code will read that file to see that it’s you. For example, when you go to a website, the page remembers your username and password – that’s made possible by a cookie.
There are also cookies that remember more detailed information about you. Perhaps your interests, your web browsing patterns, etc. This means that a site can provide you more targeted content – often in the form of ads. There are types of cookies, called third-party cookies, that come from sites you’re not even visiting at the time and can track you from site to site to gather information about you, which is sometimes sold to other companies. Sometimes you can block these kinds of cookies, though not all browsers allow you to.
When you go to a website and the page remembers your username and password – that’s made possible by a cookie.
Understanding privacy
Nearly all major browsers have a private browsing setting. These exist to hide the browsing history from other users on the same computer. Many people think that private browsing or incognito mode will hide both their identity and browsing history from internet service providers, governments and advertisers. They don’t. These settings just clear the history on your system, which is helpful if you’re dealing with sensitive personal information on a shared or public computer. Firefox goes beyond that.
Firefox helps you be more private online by letting you block trackers from following you around the web.
Making your web browser work for you
Most major web browsers let users modify their experience through extensions or add-ons. Extensions are bits of software that you can add to your browser to customize it or add functionality. Extensions can do all kinds of fun and practical things like enabling new features, foreign language dictionaries, or visual appearances and themes.
All browser makers develop their products to display images and video as quickly and smoothly as possible, making it easy for you to make the most of the web. They all work hard to make sure users have a browser that is fast, powerful and easy to use. Where they differ is why. It’s important to choose the right browser for you. Mozilla builds Firefox to ensure that users have control over their online lives and to ensure that the internet is a global, public resource, accessible to all.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Internet Basics - Using a Web Browser
Internet basics -, using a web browser, internet basics using a web browser.

Internet Basics: Using a Web Browser
Lesson 5: using a web browser.
/en/internetbasics/understanding-the-cloud/content/
Using a web browser
A web browser is a type of software that allows you to find and view websites on the Internet. Even if you didn't know it, you're using a web browser right now to read this page! There are many different web browsers, but some of the most common ones include Google Chrome , Safari , and Mozilla Firefox .
No matter which web browser you use, you'll want to learn the basics of browsing the Web. In this lesson, we'll talk about navigating to different websites, using tabbed browsing , creating bookmarks , and more.
Watch the video below to learn the basics of using a web browser.
We'll be using the Google Chrome web browser throughout this lesson, but you can use any browser you want. Keep in mind that your browser may look and act a bit differently, but all web browsers work in basically the same way.
URLs and the address bar
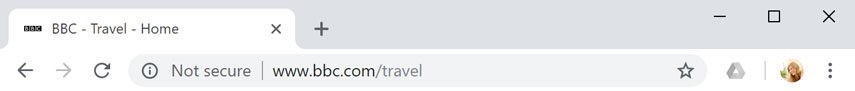
Each website has a unique address, called a URL (short for Uniform Resource Locator ). It's like a street address that tells your browser where to go on the Internet. When you type a URL into the browser's address bar and press Enter on your keyboard, the browser will load the page associated with that URL.
In the example below, we've typed www.bbc.com/travel into the address bar.
Whenever you see a word or phrase on a website that's blue or underlined in blue , it's probably a hyperlink , or link for short. You might already know how links work, even if you've never thought about them much before. For example, try clicking the link below.
Hey, I'm a link! Click me!
Links are used to navigate the Web . When you click a link, it will usually take you to a different webpage. You may also notice that your cursor changes into a hand icon whenever you hover over a link.
If you see this icon, it means you've found a link. You'll find other types of links this way too. For example, many websites actually use images as links, so you can just click the image to navigate to another page.
Review our lesson on Understanding Hyperlinks to learn more.
Navigation buttons
The Back and Forward buttons allow you to move through websites you've recently viewed . You can also click and hold either button to see your recent history.

The Refresh button will reload the current page. If a website stops working, try using the Refresh button.

Tabbed browsing
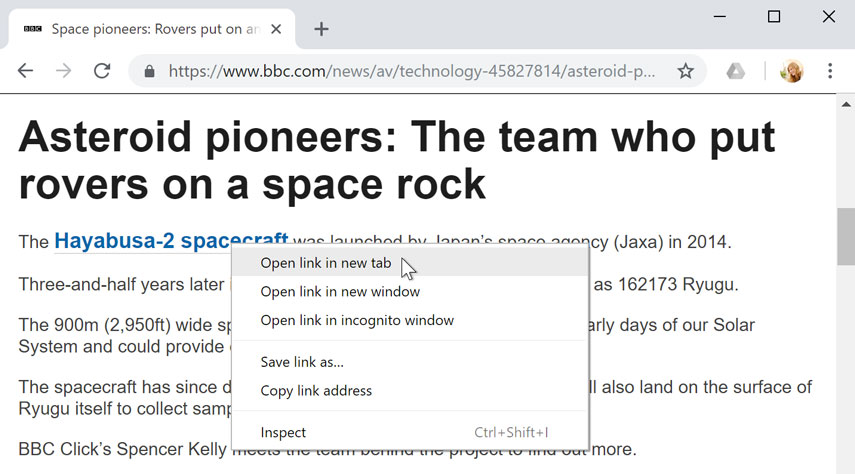
Many browsers allow you to open links in a new tab . You can open as many links as you want, and they'll stay in the same browser window instead of cluttering your screen with multiple windows.
To open a link in a new tab, right-click the link and select Open link in new tab (the exact wording may vary from browser to browser).
To close a tab, click the X .

To create a new blank tab , click the button to the right of any open tabs.

Bookmarks and history
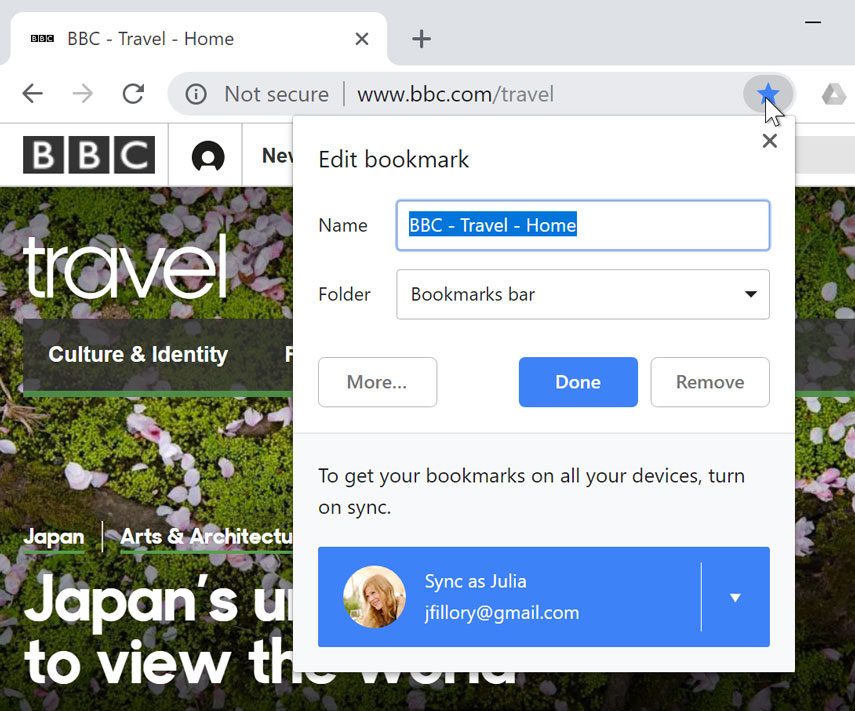
If you find a website you want to view later, it can be hard to memorize the exact web address. Bookmarks , also known as favorites , are a great way to save and organize specific websites so you can revisit them again and again. Simply locate and select the Star icon to bookmark the current website.
Your browser will also keep a history of every site you visit. This is another good way to find a site you visited previously. To view your history, open your browser settings—usually by clicking the icon in the upper-right corner—and select History .
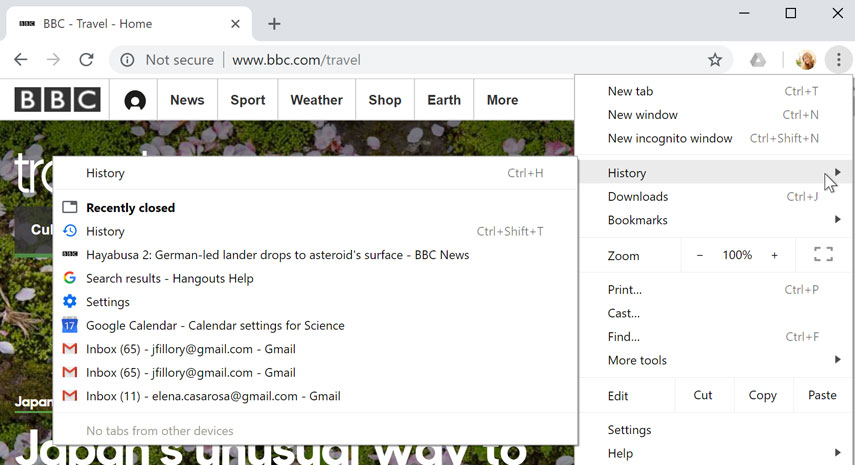
Downloading files
Links don't always go to another website. In some cases, they point to a file that can be downloaded , or saved, to your computer.
If you click a link to a file, it may download automatically, but sometimes it just opens within your browser instead of downloading. To prevent it from opening in the browser, you can right-click the link and select Save link as (different browsers may use slightly different wording, like Save target as ).
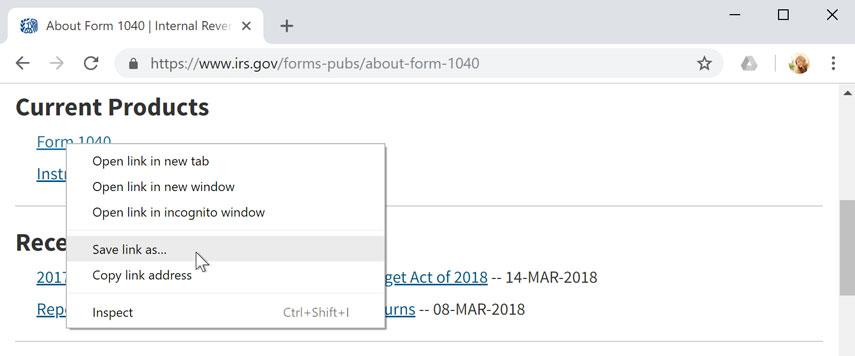
Review our lesson on Downloading and Uploading to learn more.
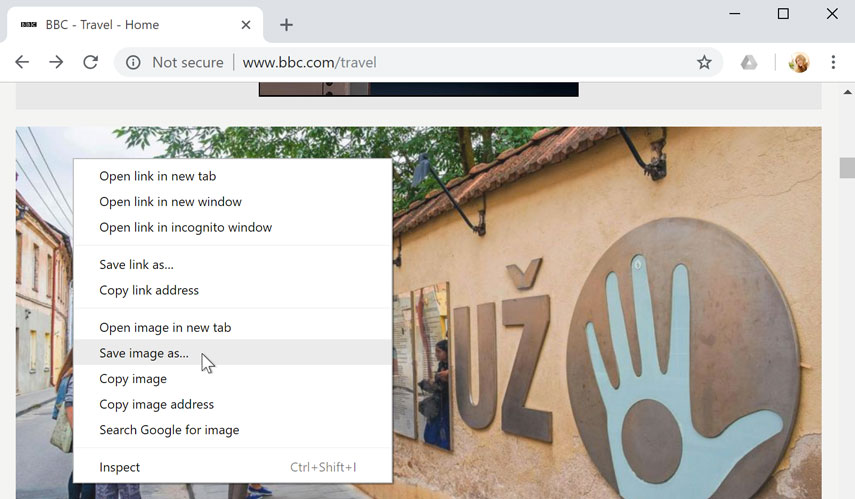
Saving images
Sometimes you may want to save an image from a website to your computer. To do this, right-click the image and select Save image as (or Save picture as ).
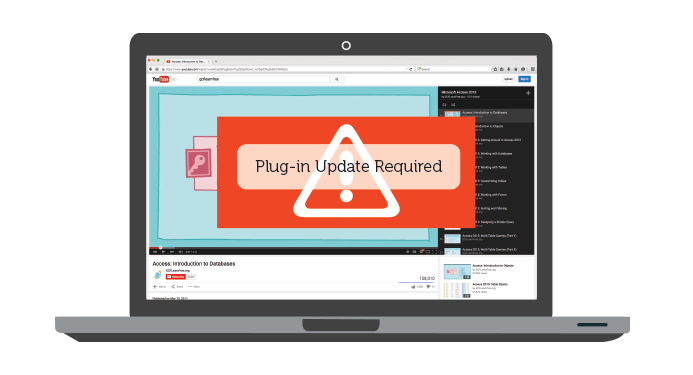
Plug-ins are small applications that allow you to view certain types of content within your web browser. For example, Adobe Flash and Microsoft Silverlight are sometimes used to play videos, while Adobe Reader is used to view PDF files.
If you don't have the correct plug-in for a website, your browser will usually provide a link to download it. There may also be times when you need to update your plug-ins. Review our lesson on Installing and Updating Plug-ins to learn more.
/en/internetbasics/understanding-hyperlinks/content/
Privacy and Security Comparison of Web Browsers: A Review
- Conference paper
- First Online: 31 March 2022
- Cite this conference paper

- R. Madhusudhan 12 &
- Saurabh V. Surashe 12
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems ((LNNS,volume 451))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications
1232 Accesses
1 Citations
In today’s digital world, mobile phones, computers, laptops and other digital devices are the most important things. The global pandemic like, Covid-19 has drastically changed the whole world, and in the post Covid world, most of the businesses are switching to online business, online marketing, online customer service, etc. Due to this, the usage of web browsers has increased exponentially. So, when we are using the internet to a very much great extent then, there are also chances of getting tracked, hacked, or cyber-bullying, etc. Hence, there comes the need for privacy protection while internet surfing in web browsers. In this paper, we have surveyed different research papers. This paper focuses on the popular desktop browsers on Windows such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari, Brave, Tor, etc. This work studies the different parameters considered for privacy leakage; different methods used for evaluation both in normal browsing mode and in private browsing mode. The work proposed that the documentation given for the private mode for popular browsers is not complete, and also that users’ privacy, can be leaked.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Tsalis, N., Mylonas, A., Nisioti, A., Gritzalis, D., Katos, V.: Exploring the protection of private browsing in desktop browsers. Comput. Secur. 67 , 181–197 (2017)
Article Google Scholar
Virvilis, N., Mylonas, A., Tsalis, N., Gritzalis, D.: Security busters: web browser security vs. rogue sites. Comput. Secur. 52 , 90–105 (2015)
Bouguettaya, A., Rezgui, A., Eltoweissy, M.: Privacy on the web: facts, challenges, and solutions. IEEE Secur. Priv. 1 (6), 40–49 (2003)
Mimecast: What is web security? (2021). https://www.mimecast.com/content/web-security/
Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (2021). https://www.cert-in.org.in/s2cMainServlet?pageid=PUBANULREPRT
The Hindu: More than 6.07 lakh cyber security incidents observed till June 2021: Government (2021). https://www.thehindu.com/business/cert-in-observed-more-than-607-lakh.-cyber-security-incidents-till-june-2021-government/article35726974.ece
Horsman, G., et al.: A forensic examination of web browser privacy-modes. Forensic Sci. Int. Rep. 1 , 100036 (2019)
Google Scholar
Korniotakis, J., Papadopoulos, P., Markatos, E.P.: Beyond black and white: combining the benefits of regular and incognito browsing modes. In: ICETE, pp. 192–200 (2020)
Private browsing (2018). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_browsing
CodeDocs: Private browsing (2021). https://codedocs.org/what-is/private-browsing
Kerschbaumer, C., Crouch, L., Ritter, T., Vyas, T.: Can we build a privacy-preserving web browser we all deserve? XRDS: crossroads. ACM Mag. Stud. 24 (4), 40–44 (2018)
Cookie Script: All you need to know about third-party cookies (2021). https://cookie-script.com/all-you-need-to-know-about-third-party-cookies.html
The end of third-party cookies and what to focus on now (2021). https://www.mightyroar.com/blog/third-party-cookies
Leith, D.J.: Web browser privacy: what do browsers say when they phone home? IEEE Access 9 , 41615–41627 (2021)
Jadoon, A.K., Iqbal, W., Amjad, M.F., Afzal, H., Bangash, Y.A.: Forensic analysis of Tor browser: a case study for privacy and anonymity on the web. Comput. Secur. 299 , 59–73 (2019)
Gabet, R.M., Seigfried-Spellar, K.C., Rogers, M.K.: A comparative forensic analysis of privacy enhanced web browsers and private browsing modes of common web browsers. Int. J. Electron. Secur. Digit. Forensics 10 (4), 356–371 (2018)
Cozza, F., et al.: Hybrid and lightweight detection of third party tracking: design, implementation, and evaluation. Comput. Netw. 167 , 106993 (2020)
Wu, Q., Liu, Q., Zhang, Y., Wen, G.: TrackerDetector: a system to detect third-party trackers through machine learning. Comput. Netw. 91 , 164–173 (2015)
Google safe browsing (2021). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google_Safe_Browsing
Kim, H., Kim, I.S., Kim, K.: AIBFT: artificial intelligence browser forensic toolkit. Forensic Sci. Int. Digit. Invest. 36 , 301091 (2021)
StatCounter GlobalStats: Desktop browser market share worldwide (2021). https://gs.statcounter.com/browser-market-share/desktop/worldwide
Brave (web browser) (2022). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brave_(web_browser)
Cookie policy - Arad Group (2021). https://arad.co.il/app/uploads/Cookie-policy.pdf
Malandrino, D., Scarano, V.: Privacy leakage on the web: diffusion and countermeasures. Comput. Secur. 57 (14), 2833–2855 (2013)
Mazel, J., Garnier, R., Fukuda, K.: A comparison of web privacy protection techniques. Comput. Commun. 144 , 162–174 (2019)
CookiePro: What’s the difference between first and third-party cookies? (2021). https://www.cookiepro.com/knowledge/whats-the-difference-between-first-and.-third-party-cookies/
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mathematical and Computational Sciences, NIT - K Surathkal, Karnataka, India
R. Madhusudhan & Saurabh V. Surashe
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Corresponding author
Correspondence to R. Madhusudhan .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Information and Communication Engineering, Fukuoka Institute of Technology, Fukuoka, Japan
Leonard Barolli
University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Farookh Hussain
Faculty of Bussiness Administration, Rissho University, Tokyo, Japan
Tomoya Enokido
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Madhusudhan, R., Surashe, S.V. (2022). Privacy and Security Comparison of Web Browsers: A Review. In: Barolli, L., Hussain, F., Enokido, T. (eds) Advanced Information Networking and Applications. AINA 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 451. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99619-2_44
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99619-2_44
Published : 31 March 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-99618-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-99619-2
eBook Packages : Intelligent Technologies and Robotics Intelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Cryptography and Security
Title: sok: on the analysis of web browser security.
Abstract: Web browsers are integral parts of everyone's daily life. They are commonly used for security-critical and privacy sensitive tasks, like banking transactions and checking medical records. Unfortunately, modern web browsers are too complex to be bug free (e.g., 25 million lines of code in Chrome), and their role as an interface to the cyberspace makes them an attractive target for attacks. Accordingly, web browsers naturally become an arena for demonstrating advanced exploitation techniques by attackers and state-of-the-art defenses by browser vendors. Web browsers, arguably, are the most exciting place to learn the latest security issues and techniques, but remain as a black art to most security researchers because of their fast-changing characteristics and complex code bases. To bridge this gap, this paper attempts to systematize the security landscape of modern web browsers by studying the popular classes of security bugs, their exploitation techniques, and deployed defenses. More specifically, we first introduce a unified architecture that faithfully represents the security design of four major web browsers. Second, we share insights from a 10-year longitudinal study on browser bugs. Third, we present a timeline and context of mitigation schemes and their effectiveness. Fourth, we share our lessons from a full-chain exploit used in 2020 Pwn2Own competition. and the implication of bug bounty programs to web browser security. We believe that the key takeaways from this systematization can shed light on how to advance the status quo of modern web browsers, and, importantly, how to create secure yet complex software in the future.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
DBLP - CS Bibliography
Bibtex formatted citation.
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- Case Study Example
Web Browser Case Studies Samples For Students
14 samples of this type
During studying in college, you will surely have to compose a bunch of Case Studies on Web Browser. Lucky you if linking words together and organizing them into relevant text comes easy to you; if it's not the case, you can save the day by finding an already written Web Browser Case Study example and using it as a model to follow.
This is when you will certainly find WowEssays' free samples directory extremely helpful as it includes numerous skillfully written works on most various Web Browser Case Studies topics. Ideally, you should be able to find a piece that meets your requirements and use it as a template to build your own Case Study. Alternatively, our competent essay writers can deliver you a unique Web Browser Case Study model written from scratch according to your individual instructions.
The Conclusion Section On Web Browser Research Case Study Example
Server-side scripting languages case study example.
There are many reasons why programmers want to use server-side scripting in their projects. Accessibility where users can reach the web content using any browser, any device and anywhere, the manageability where codes can be changed easily, security since the source code is not exposed and the web-based 3-tier architecture that enables scalability are some of the reasons that programmers choose server-side scripting.
Below is an evaluation of the three server-side scripting languages
- JSP/Servlets - ASP/ASP.net - Python
JSP/Servlet
Lab2 answers case study example.
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your case study done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page
Variables Used Case Study
.University
Free Case Study On Google Today And In The Future
Q1 four main products of google, example of case study on online threats, institutional, sales force cloud computing case study.
Cloud computing involves delivery of computer software or hardware through internet. The end users of software or the hardware receive this application via a web browser. Cloud computing enables a firm to reduce the cost associated with the infrastructure. The firm is relieved the cost of developing of the infrastructure. As a result, the firm will be in a position to concentrate on other factors that affect the success of a business, to remain competitive in business, Salesforce.com has embraced cloud computing. The firm leases its software as opposed to other firm, which sell their software and hardware.
Case Study On Social Networking
Social networking timeline, free basic concept of dithering case study sample, image dithering, case study on gyour name, web application security, example of case study on new payroll application architecture.
(Study Program)
Case Study On Nsecurity, Firewalls, And VPN Solutions
The mobile commerce explosion case studies example, introduction, free case study on computer security.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic search engines
1. Google Scholar
4. science.gov, 5. semantic scholar, 6. baidu scholar, get the most out of academic search engines, frequently asked questions about academic search engines, related articles.
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
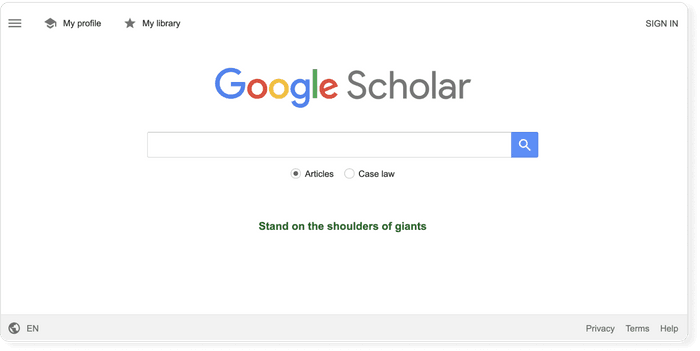
Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles
- Abstracts: only a snippet of the abstract is available
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, Vancouver, RIS, BibTeX
BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany. That is also where its name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles (contains duplicates)
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open-access research papers. For each search result, a link to the full-text PDF or full-text web page is provided.
- Coverage: approx. 136 million articles
- Links to full text: ✔ (all articles in CORE are open access)
- Export formats: BibTeX
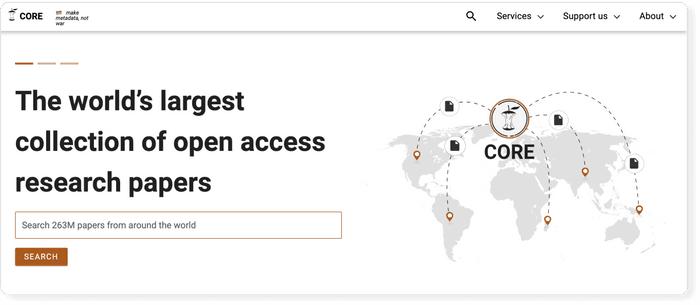
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need anymore to query all those resources separately!
- Coverage: approx. 200 million articles and reports
- Links to full text: ✔ (available for some databases)
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX (available for some databases)
Semantic Scholar is the new kid on the block. Its mission is to provide more relevant and impactful search results using AI-powered algorithms that find hidden connections and links between research topics.
- Coverage: approx. 40 million articles
- Export formats: APA, MLA, Chicago, BibTeX

Although Baidu Scholar's interface is in Chinese, its index contains research papers in English as well as Chinese.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 100 million articles
- Abstracts: only snippets of the abstract are available
- Export formats: APA, MLA, RIS, BibTeX

RefSeek searches more than one billion documents from academic and organizational websites. Its clean interface makes it especially easy to use for students and new researchers.
- Coverage: no detailed statistics available, approx. 1 billion documents
- Abstracts: only snippets of the article are available
- Export formats: not available
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Google Scholar is an academic search engine, and it is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only let's you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free, but also often provides links to full text PDF file.
Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature developed at the Allen Institute for AI. Sematic Scholar was publicly released in 2015 and uses advances in natural language processing to provide summaries for scholarly papers.
BASE , as its name suggest is an academic search engine. It is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that's where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
CORE is an academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers. For each search result a link to the full text PDF or full text web page is provided.
Science.gov is a fantastic resource as it bundles and offers free access to search results from more than 15 U.S. federal agencies. There is no need any more to query all those resources separately!
Live Trainings - Join one of our free training sessions to get the most out of Papers
Browser Extension
Enjoy 1-click importing of references and PDFs across the web - wherever you are discovering new literature - with our browser-based importer.
Install ReadCube’s Browser Extension via Chrome Store , Firefox , Safari , and Edge .
Search for papers as you normally would on PubMed, Google Scholar, Dimensions, and journal websites. Click on "Add to Library" button to sync articles to your Papers Library. You can even select the collections you'd like to file it in. What's more, you will instantly see if that article is already saved in your library with a direct link to view that copy!
Unlike other bookmarklets and extensions, our Browser Extension offers 1-click downloads of open access articles PLUS full-text access via your organization's subscriptions. For ReadCube customers , our extensions also support access via our on-demand document delivery service.


- 1-888-302-2840
- 1-888-422-8036
- Web Browsers
- Your research paper is written by certified writers
- Your requirements and targets are always met
- You are able to control the progress of your writing assignment
- You get a chance to become an excellent student!

Essay Details:
Essay text:
This keeps the file size to a minimum and it means that Firefox will run well on older computers without using up numerous system resources. In addition, Firefox is also more opposed to crashing. The last Web browser I will cover is Netscape. Firefox can be linked to Netscape. Internet Explorer has many security concerns, and it does not have the built in Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed reader, but it should be included in the beta version. In addition, Internet Explorer is offering their next version only to people running Windows XP SP2. Mozilla Firefox is rapidly taking over. This open-source browser includes tabbed browsing and RSS feeds...

Calculate a fair price for your order
Do you need an essay?
A professional team of writers is able to craft custom essays from scratch according to your instructions. We are ready to satisfy writing needs of every demanding customer.

Do you need many essays?
The product provided is intended to be used for research or study purposes. Get instant access to over 200,000 papers.
Common topics in this essay:
- Never Heard, Never Forgot
- Browser Wars
- I Heard The Owl Call My Name
- I Heard the Owl Call my Name
- The Wonderful State of Memory
- Kurds - A People Without a State
- The Wonderful War On Drugs
- analysis Thomas Hobbes's claim "a state of nature is, or would be, a state of war of everyone against everyone."
- hobbes leviathan state government social order state of war
- Mozilla Help
- Using Firefox
- XML ? Attributes, Parsers, and Browser Compatibility
Feedback of people who used our services.
My experience with ManyEssays.com is extremely satisfying! I was amazed on your user-friendly website which is very helpful. I have also happy on how your customer service experts ...
I would like to say thank you for the level of excellence on providing written works. My University required us a very difficult paper using a very specific writing format and ...
I am happy with the results your company gives. ManyEssays.com is the best place for essays!
I was given by my professor a very difficult essay assignment and I really don’t know what to do. I needed help and ManyEssays.com came at the right time. I quickly availed your ...
I am very happy on the excellent job your writers did on my thesis. It was beautiful in every way, it was a literary masterpiece! Everything was done according to instructions and ...
A top-notch organization all the way and a model in excellent service, your company is. The level of expertise in your field is exceptional as you have in your employment the best ...
Your writing service is so amazing! I was skeptic at first on how your company provides result, but my skepticism gradually vanished immediately after you had finished one task in ...
Your services were an important factor for my academic advance during my college years. I really thank you that you were there when I needed help in my term paper. Your company ...
Similar Essays:
- Free Samples >
- Type of Paper >
Web Browser Essays Samples That Help You Write Better, Faster & with Gusto
Crafting Essays is quite a tough task on its own. Crafting outstanding Essays is an even more exhausting exercise. Crafting a first-rate Web Browser Essay is, well, something supernatural. Yet, with the WePapers.com free database of expertly written Web Browser Essay examples, the job is perfectly viable. Look through our catalog, find a piece that satisfies your key requirements and use it as a source of content presentation and structuring ideas in order to develop your own original Essay on Web Browser.
In case you lack time or energy for inspecting plenty of examples in search of inspiration or writing ideas, you can simply order a unique Web Browser Essay sample custom-written specifically for you to be utilized as a foundation for an entirely original academic work.
We use cookies to improve your experience with our site. Please accept before continuing or read our cookie policy here .
Wait, have you seen our prices?
- Meta Quest 4
- Google Pixel 9
- Google Pixel 8a
- Apple Vision Pro 2
- Nintendo Switch 2
- Samsung Galaxy Ring
- Yellowstone Season 6
- Recall an Email in Outlook
- Stranger Things Season 5
5 web browsers you should use instead of Google Chrome or Edge
Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge dominate the world of web browsers, but they’re not for everyone. Whether you want a browser that better respects your privacy or need an app that does things a little bit differently, you don’t have to stick to the usual suspects.
There’s a world of alternative web browsers out there if you want to give something new a try. Here, we’ve put together five excellent options, with each one bringing fresh new ideas to the table. So, if you’re sick of Chrome and Edge, take one of these browsers for a spin.
Arc does things differently in almost every way you can think of. It’s full of little innovations that add up to an all-new way of browsing. Yet it’s familiar enough that the learning curve is minimal, meaning you don’t need to put in countless hours just to come to grips with it.
- 5 laptops you should buy instead of the M2 MacBook Air
- Google’s Incognito Mode is in trouble
- 5 GPUs you should buy instead of the RTX 4070
Look around and you’ll quickly see its interesting new ideas. You can cycle through your open tabs in the same way you Alt-Tab/Command-Tab through desktop apps. There’s a built-in command bar that lets you perform tasks just by typing (just like Spotlight in macOS). And there’s even a miniature Arc browser for when you want to quickly fetch information without clogging up your main window.
One my favorite Arc features is the Easel. Here, you can store web page snippets — including live ones that update in real time — on a single large canvas. This is perfect for planning a holiday or a home makeover, and functions like your own in-app Pinterest board.
There are so many clever features like this that Arc has quickly become one of the best Chrome and Edge alternatives there is. Give it a go and you’ll quickly see why.
I’m a real Firefox loyalist, having used it for well over 15 years now . But I haven’t stuck around because of inertia: This app is genuinely one of the best browsers you can use for a host of great reasons.
It’s built by a nonprofit that puts privacy rights at the heart of the way it works, so you know there’s no funny business of the sort you might expect from Google or Microsoft. It’s not just a philosophical stance, either — Firefox comes bundled with a bunch of privacy-preserving features. It prevents user fingerprinting (meaning it stops trackers from building a profile of your activities), blocks ad trackers from the word go, protects you from cross-site cookies, and comes with a free password manager . It all contributes to a better browsing experience.
But there’s much more to Firefox than just privacy. I love how I can quickly send tabs from one device to another using its cross-platform syncing. It also has a large and thriving community of extension developers, so you’re spoiled for choice if you need to add some extra functionality to your browser. That makes it a leading contender to replace Chrome and Edge on your computer.
If you’re a gamer, you’ll have a set of requirements that will help you get more from your computer. You don’t want other apps hogging system resources that should be going toward your game, for example, and you might want to have services like Twitch and Discord within easy reach.
The Opera GX browser is tailor-made for gamers, and it gives you these capabilities along with a whole lot more. For example, you can set limits on your CPU, memory, and network consumption to ensure optimal gaming performance. Or you can use its included artificial intelligence assistant to quickly perform tasks that would otherwise slow you down.
It also has a ton of built-in connections to other apps, from Twitch and Discord to Spotify and WhatsApp. So instead of having to fire up these apps or navigate to these websites while you’re busy gaming, you can get right into your favorite services with just a click or two.
If privacy is your top priority, DuckDuckGo is the browser for you. Everything it does is designed to protect you online and keep your private data out of the hands of trackers and data brokers looking to sell it for profit.
Take DuckDuckGo’s custom search engine , for instance. This never saves any personal data that could link you to your searches, meaning your IP address and unique identifiers are never logged. Unlike Google, there’s nothing for advertisers to gather up and sell.
The DuckDuckGo browser also blocks cross-site cookies following you around the web and removes trackers from your incoming emails. And yet it does all this without sacrificing quality: Its search results are excellent, and it’s packed with other useful features that elevate your browsing experience. It shows that safeguarding your privacy doesn’t have to be difficult.
Over time, even the best browsers can become bloated with feature creep, going from sleek and speedy to slow and sluggish. If you’re sick of this kind of drag, give Min a try. It doesn’t get simpler than this one.
As its name suggests, Min is all about minimalism. It pares back the unnecessary cruft from your browsing experience, leaving you with an app that gets out of the way and lets you surf the web in peace.
Most of the time, the only interface element you’ll see is the tab bar, enabling the webpage you’re on to expand and fill your screen. Tabs and browsing sessions can be grouped by task to help you stay organized, and Min uses DuckDuckGo’s private search and blocks ads and trackers by default. It’s a different way to browse, but one a lot of people will appreciate.
Editors' Recommendations
- 5 headsets you should buy instead of the Vision Pro
- This secret Microsoft Edge feature changed the way I work
- 5 image-editing apps you should use instead of Adobe Photoshop
- 5 calendar apps you should use instead of Google Calendar
- 5 email apps you should use instead of Gmail or Outlook
- Google Chrome

There's no laptop quite like the MacBook Pro right now. No alternatives on the Windows side can match the power, efficiency, and battery life in a laptop of this size -- and that's not even mentioning the Pro's premium features and design.
There are, however, a few laptops that come close, while undercutting it significantly in price. So, if you're looking for a proper Windows alternative to the more powerful configurations of the MacBook Pro, or even just a cheaper laptop that can replicate some of what the MacBook Pro can do, here are a few solid options to consider before shelling out the cash on a MacBook Pro. HP Envy 16
Google is now fleshing out its newly unified Gemini AI system in its browser with its first attempt at implementing Chat with Gemini into the Chrome Omnibox.
This latest effort will update Google Chrome with a Chat with Gemini shortcut in the Chrome Omnibox, allowing users to access the AI chatbot feature without having to go to the Gemini website, according to WindowsReport. The Omnibox serves as an address bar and search bar, and it adds multiple other tasks to a browser. Now with a simple @ prompt, you can also access Google's AI chatbot to answer questions, create images, and generate summaries, among other tasks.
Google has agreed to settle a $5 billion lawsuit brought by claimants who accused the web giant of privacy invasion by tracking their online activities despite being in “incognito mode” when using the company’s Chrome browser.
After lawyers announced on Thursday that they’d reached a preliminary agreement, U.S. District Judge Yvonne Gonzalez Rogers put a scheduled trial for the case in California on hold, Reuters reported.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A web browser is a computer program application for reading pages of the World Wide Web.Since the late 1990s, most personal computers and mobile phones and other mobile devices have a browser.. Web browsers are used by people to find and look at websites on the Internet.The first web browser was created in 1990. Many web browsers are available for free.
Web Browser Definition: A software application used to access information on the World Wide Web is called a Web Browser. When a user requests some information, the web browser fetches the data from a web server and then displays the webpage on the user's screen. It is also important to know in detail about what a web browser is for candidates ...
A web browser takes you anywhere on the internet. It retrieves information from other parts of the web and displays it on your desktop or mobile device. The information is transferred using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, which defines how text, images and video are transmitted on the web. This information needs to be shared and displayed in a ...
Using a web browser. A web browser is a type of software that allows you to find and view websites on the Internet. Even if you didn't know it, you're using a web browser right now to read this page! There are many different web browsers, but some of the most common ones include Google Chrome, Safari, and Mozilla Firefox.
A web browser displaying a web pageA web browser is an application for accessing websites.When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people have used a ...
In this paper, we have done a survey of different research papers related to web browser privacy and security and found that all the web browsers make use of safe browsing services to protect the user from phishing attacks. But this method has few privacy concerns. Similarly, for chrome update extension, it also contacts chrome update API every ...
The History Of Web Browsers Information Technology Essay. What started with just one web browser known as Mosaic, which was established in 1993, nowadays there are a wide selection of different types of web browsers available. Each different web browser fulfills different requirements but each have the same purpose, to connect us to the World ...
Essay, Pages 4 (882 words) Views. 925. Web browsers, the portal to the cyber realm, work as the gateway for users to access the vast expanse of the Internet. These applications are a necessity for any computer user seeking to explore web pages, connect to the Internet, or navigate local area networks like the ones found in homes, offices, or ...
Web browsers play an integral role in the modern, Internet-connected lifestyle. We rely on web browsers to pay mortgages, schedule vaccines, and connect to people worldwide. In other words, web browsers become the gatekeeper to cyberspace, and their insecurity is a critical threat to the safety, fairness and privacy of our society.
The major web browsers are Google Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, and Safari History. In 1991, the first web browser was released by Sir Tim Berners-Lee. It was named WorldWideWeb and was later renamed to Nexus to avoid confusion with www system. It was the first graphical web browser and WYSIWTG HTML editor.
Google Chrome is a freeware web browser developed by Google that uses the WebKit layout engine. It was released as a beta version for Microsoft Windows on September 2, 2008, and as a stable public release on December 11, 2008. As of September 2012, according to StatCounter, Google Chrome had 34% worldwide usage share of web browsers making it ...
SOK: On the Analysis of Web Browser Security. Web browsers are integral parts of everyone's daily life. They are commonly used for security-critical and privacy sensitive tasks, like banking transactions and checking medical records. Unfortunately, modern web browsers are too complex to be bug free (e.g., 25 million lines of code in Chrome ...
Internet explorer, Google chrome, and Mozilla Firefox are among top browsers that take the lead in technology and market. One may not know exactly which one to indulge with since some of them release 72 new versions every week. (Kern & Phetteplace, 2012, p. 213). Conversely, Internet explorer has been restructured to be finger-friendly hence ...
Accessible how-to guides full of examples that help you write a flawless essay, proposal, or dissertation. Chrome extension. Cite any page or article with a single click right from your browser. Templates. Time-saving templates that you can download and edit in Word or Google Docs.
14 samples of this type. During studying in college, you will surely have to compose a bunch of Case Studies on Web Browser. Lucky you if linking words together and organizing them into relevant text comes easy to you; if it's not the case, you can save the day by finding an already written Web Browser Case Study example and using it as a model ...
A browser which does not support multiple languages is text like gibberish. Best browsers support multiple languages for users. Internet Explorer. One of the most powerful web browsers, internet explorer had the 95% usage market share in 2003. This web browser was developed by Microsoft and including by default in Microsoft windows operating ...
Web Browser. Web Browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content. [1] Hyperlinks present in resources enable users to easily ...
Academic search engines have become the number one resource to turn to in order to find research papers and other scholarly sources. While classic academic databases like Web of Science and Scopus are locked behind paywalls, Google Scholar and others can be accessed free of charge. In order to help you get your research done fast, we have compiled the top list of free academic search engines.
Browser Extension. Enjoy 1-click importing of references and PDFs across the web - wherever you are discovering new literature - with our browser-based importer. Install ReadCube's Browser Extension via Chrome Store, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Search for papers as you normally would on PubMed, Google Scholar, Dimensions, and journal websites.
Essay text: This keeps the file size to a minimum and it means that Firefox will run well on older computers without using up numerous system resources. In addition, Firefox is also more opposed to crashing. The last Web browser I will cover is Netscape. Firefox can be linked to Netscape.
Crafting Essays is quite a tough task on its own. Crafting outstanding Essays is an even more exhausting exercise. Crafting a first-rate Web Browser Essay is, well, something supernatural. Yet, with the WePapers.com free database of expertly written Web Browser Essay examples, the job is perfectly viable.
There's a world of alternative web browsers out there if you want to give something new a try. Here, we've put together five excellent options, with each one bringing fresh new ideas to the table.