- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers


The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)

What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Hypothesis: How to Write it, Types, and Examples

Any research begins with a research question and a research hypothesis . A research question alone may not suffice to design the experiment(s) needed to answer it. A hypothesis is central to the scientific method. But what is a hypothesis ? A hypothesis is a testable statement that proposes a possible explanation to a phenomenon, and it may include a prediction. Next, you may ask what is a research hypothesis ? Simply put, a research hypothesis is a prediction or educated guess about the relationship between the variables that you want to investigate.
It is important to be thorough when developing your research hypothesis. Shortcomings in the framing of a hypothesis can affect the study design and the results. A better understanding of the research hypothesis definition and characteristics of a good hypothesis will make it easier for you to develop your own hypothesis for your research. Let’s dive in to know more about the types of research hypothesis , how to write a research hypothesis , and some research hypothesis examples .
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis ?
A hypothesis is based on the existing body of knowledge in a study area. Framed before the data are collected, a hypothesis states the tentative relationship between independent and dependent variables, along with a prediction of the outcome.
What is a research hypothesis ?
Young researchers starting out their journey are usually brimming with questions like “ What is a hypothesis ?” “ What is a research hypothesis ?” “How can I write a good research hypothesis ?”
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is testable, i.e., it can be supported or disproven through experimentation or observation.

Characteristics of a good hypothesis
Here are the characteristics of a good hypothesis :
- Clearly formulated and free of language errors and ambiguity
- Concise and not unnecessarily verbose
- Has clearly defined variables
- Testable and stated in a way that allows for it to be disproven
- Can be tested using a research design that is feasible, ethical, and practical
- Specific and relevant to the research problem
- Rooted in a thorough literature search
- Can generate new knowledge or understanding.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
A study begins with the formulation of a research question. A researcher then performs background research. This background information forms the basis for building a good research hypothesis . The researcher then performs experiments, collects, and analyzes the data, interprets the findings, and ultimately, determines if the findings support or negate the original hypothesis.
Let’s look at each step for creating an effective, testable, and good research hypothesis :
- Identify a research problem or question: Start by identifying a specific research problem.
- Review the literature: Conduct an in-depth review of the existing literature related to the research problem to grasp the current knowledge and gaps in the field.
- Formulate a clear and testable hypothesis : Based on the research question, use existing knowledge to form a clear and testable hypothesis . The hypothesis should state a predicted relationship between two or more variables that can be measured and manipulated. Improve the original draft till it is clear and meaningful.
- State the null hypothesis: The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between the variables you are studying.
- Define the population and sample: Clearly define the population you are studying and the sample you will be using for your research.
- Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis: Select appropriate research methods, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies, which will allow you to test your research hypothesis .
Remember that creating a research hypothesis is an iterative process, i.e., you might have to revise it based on the data you collect. You may need to test and reject several hypotheses before answering the research problem.
How to write a research hypothesis
When you start writing a research hypothesis , you use an “if–then” statement format, which states the predicted relationship between two or more variables. Clearly identify the independent variables (the variables being changed) and the dependent variables (the variables being measured), as well as the population you are studying. Review and revise your hypothesis as needed.
An example of a research hypothesis in this format is as follows:
“ If [athletes] follow [cold water showers daily], then their [endurance] increases.”
Population: athletes
Independent variable: daily cold water showers
Dependent variable: endurance
You may have understood the characteristics of a good hypothesis . But note that a research hypothesis is not always confirmed; a researcher should be prepared to accept or reject the hypothesis based on the study findings.

Research hypothesis checklist
Following from above, here is a 10-point checklist for a good research hypothesis :
- Testable: A research hypothesis should be able to be tested via experimentation or observation.
- Specific: A research hypothesis should clearly state the relationship between the variables being studied.
- Based on prior research: A research hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and previous research in the field.
- Falsifiable: A research hypothesis should be able to be disproven through testing.
- Clear and concise: A research hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner.
- Logical: A research hypothesis should be logical and consistent with current understanding of the subject.
- Relevant: A research hypothesis should be relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Feasible: A research hypothesis should be feasible to test within the scope of the study.
- Reflects the population: A research hypothesis should consider the population or sample being studied.
- Uncomplicated: A good research hypothesis is written in a way that is easy for the target audience to understand.
By following this research hypothesis checklist , you will be able to create a research hypothesis that is strong, well-constructed, and more likely to yield meaningful results.

Types of research hypothesis
Different types of research hypothesis are used in scientific research:
1. Null hypothesis:
A null hypothesis states that there is no change in the dependent variable due to changes to the independent variable. This means that the results are due to chance and are not significant. A null hypothesis is denoted as H0 and is stated as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is not zoonotic .”
2. Alternative hypothesis:
This states that there is a significant difference or relationship between the variables being studied. It is denoted as H1 or Ha and is usually accepted or rejected in favor of the null hypothesis.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is zoonotic .”
3. Directional hypothesis :
This specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables; therefore, it tends to use terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: “ The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment .”
4. Non-directional hypothesis:
While it does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables, a non-directional hypothesis states the existence of a relationship or difference between variables but not the direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship. A non-directional hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or when findings contradict previous research.
Example, “ Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express .”
5. Simple hypothesis :
A simple hypothesis only predicts the relationship between one independent and another independent variable.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging .”
6 . Complex hypothesis :
A complex hypothesis states the relationship or difference between two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging, reduces sun burn, and reduces the chances of skin cancer .” (Here, the three dependent variables are slowing skin aging, reducing sun burn, and reducing the chances of skin cancer.)
7. Associative hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis states that a change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables.
Example: “ There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health .”
8 . Causal hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect interaction between variables.
Example: “ Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage .”
Note that some of the types of research hypothesis mentioned above might overlap. The types of hypothesis chosen will depend on the research question and the objective of the study.

Research hypothesis examples
Here are some good research hypothesis examples :
“The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.”
“Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.”
“Plants that are exposed to certain types of music will grow taller than those that are not exposed to music.”
“The use of the plant growth regulator X will lead to an increase in the number of flowers produced by plants.”
Characteristics that make a research hypothesis weak are unclear variables, unoriginality, being too general or too vague, and being untestable. A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and improper methods.
Some bad research hypothesis examples (and the reasons why they are “bad”) are as follows:
“This study will show that treatment X is better than any other treatment . ” (This statement is not testable, too broad, and does not consider other treatments that may be effective.)
“This study will prove that this type of therapy is effective for all mental disorders . ” (This statement is too broad and not testable as mental disorders are complex and different disorders may respond differently to different types of therapy.)
“Plants can communicate with each other through telepathy . ” (This statement is not testable and lacks a scientific basis.)
Importance of testable hypothesis
If a research hypothesis is not testable, the results will not prove or disprove anything meaningful. The conclusions will be vague at best. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher focus on the study outcome and understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher make precise predictions based on prior research.
To be considered testable, there must be a way to prove that the hypothesis is true or false; further, the results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis
1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis ?
A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions. It helps a researcher identify what information to collect. A research hypothesis , however, is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Accordingly, it guides the study design and data analysis approach.
2. When to reject null hypothesis ?
A null hypothesis should be rejected when the evidence from a statistical test shows that it is unlikely to be true. This happens when the test statistic (e.g., p -value) is less than the defined significance level (e.g., 0.05). Rejecting the null hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true; it simply means that the evidence found is not compatible with the null hypothesis.
3. How can I be sure my hypothesis is testable?
A testable hypothesis should be specific and measurable, and it should state a clear relationship between variables that can be tested with data. To ensure that your hypothesis is testable, consider the following:
- Clearly define the key variables in your hypothesis. You should be able to measure and manipulate these variables in a way that allows you to test the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis should predict a specific outcome or relationship between variables that can be measured or quantified.
- You should be able to collect the necessary data within the constraints of your study.
- It should be possible for other researchers to replicate your study, using the same methods and variables.
- Your hypothesis should be testable by using appropriate statistical analysis techniques, so you can draw conclusions, and make inferences about the population from the sample data.
- The hypothesis should be able to be disproven or rejected through the collection of data.
4. How do I revise my research hypothesis if my data does not support it?
If your data does not support your research hypothesis , you will need to revise it or develop a new one. You should examine your data carefully and identify any patterns or anomalies, re-examine your research question, and/or revisit your theory to look for any alternative explanations for your results. Based on your review of the data, literature, and theories, modify your research hypothesis to better align it with the results you obtained. Use your revised hypothesis to guide your research design and data collection. It is important to remain objective throughout the process.
5. I am performing exploratory research. Do I need to formulate a research hypothesis?
As opposed to “confirmatory” research, where a researcher has some idea about the relationship between the variables under investigation, exploratory research (or hypothesis-generating research) looks into a completely new topic about which limited information is available. Therefore, the researcher will not have any prior hypotheses. In such cases, a researcher will need to develop a post-hoc hypothesis. A post-hoc research hypothesis is generated after these results are known.
6. How is a research hypothesis different from a research question?
A research question is an inquiry about a specific topic or phenomenon, typically expressed as a question. It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis.
7. Can a research hypothesis change during the research process?
Yes, research hypotheses can change during the research process. As researchers collect and analyze data, new insights and information may emerge that require modification or refinement of the initial hypotheses. This can be due to unexpected findings, limitations in the original hypotheses, or the need to explore additional dimensions of the research topic. Flexibility is crucial in research, allowing for adaptation and adjustment of hypotheses to align with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
8. How many hypotheses should be included in a research study?
The number of research hypotheses in a research study varies depending on the nature and scope of the research. It is not necessary to have multiple hypotheses in every study. Some studies may have only one primary hypothesis, while others may have several related hypotheses. The number of hypotheses should be determined based on the research objectives, research questions, and the complexity of the research topic. It is important to ensure that the hypotheses are focused, testable, and directly related to the research aims.
9. Can research hypotheses be used in qualitative research?
Yes, research hypotheses can be used in qualitative research, although they are more commonly associated with quantitative research. In qualitative research, hypotheses may be formulated as tentative or exploratory statements that guide the investigation. Instead of testing hypotheses through statistical analysis, qualitative researchers may use the hypotheses to guide data collection and analysis, seeking to uncover patterns, themes, or relationships within the qualitative data. The emphasis in qualitative research is often on generating insights and understanding rather than confirming or rejecting specific research hypotheses through statistical testing.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What is Thematic Analysis and How to Do It (with Examples)

What Skills are Required for Academic Writing
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
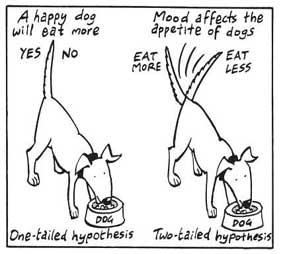
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes .
A hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research. If you want to test a relationship between two or more variables, you need to write hypotheses before you start your experiment or data collection.
Table of contents
What is a hypothesis, developing a hypothesis (with example), hypothesis examples, frequently asked questions about writing hypotheses.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess – it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
Variables in hypotheses
Hypotheses propose a relationship between two or more variables . An independent variable is something the researcher changes or controls. A dependent variable is something the researcher observes and measures.
In this example, the independent variable is exposure to the sun – the assumed cause . The dependent variable is the level of happiness – the assumed effect .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Step 1: ask a question.
Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research
Your initial answer to the question should be based on what is already known about the topic. Look for theories and previous studies to help you form educated assumptions about what your research will find.
At this stage, you might construct a conceptual framework to identify which variables you will study and what you think the relationships are between them. Sometimes, you’ll have to operationalise more complex constructs.
Step 3: Formulate your hypothesis
Now you should have some idea of what you expect to find. Write your initial answer to the question in a clear, concise sentence.
Step 4: Refine your hypothesis
You need to make sure your hypothesis is specific and testable. There are various ways of phrasing a hypothesis, but all the terms you use should have clear definitions, and the hypothesis should contain:
- The relevant variables
- The specific group being studied
- The predicted outcome of the experiment or analysis
Step 5: Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if … then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable.
In academic research, hypotheses are more commonly phrased in terms of correlations or effects, where you directly state the predicted relationship between variables.
If you are comparing two groups, the hypothesis can state what difference you expect to find between them.
Step 6. Write a null hypothesis
If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing , you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a .
| Research question | Hypothesis | Null hypothesis |
|---|---|---|
| What are the health benefits of eating an apple a day? | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will result in decreasing frequency of doctor’s visits. | Increasing apple consumption in over-60s will have no effect on frequency of doctor’s visits. |
| Which airlines have the most delays? | Low-cost airlines are more likely to have delays than premium airlines. | Low-cost and premium airlines are equally likely to have delays. |
| Can flexible work arrangements improve job satisfaction? | Employees who have flexible working hours will report greater job satisfaction than employees who work fixed hours. | There is no relationship between working hour flexibility and job satisfaction. |
| How effective is secondary school sex education at reducing teen pregnancies? | Teenagers who received sex education lessons throughout secondary school will have lower rates of unplanned pregnancy than teenagers who did not receive any sex education. | Secondary school sex education has no effect on teen pregnancy rates. |
| What effect does daily use of social media have on the attention span of under-16s? | There is a negative correlation between time spent on social media and attention span in under-16s. | There is no relationship between social media use and attention span in under-16s. |
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, May 06). How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/hypothesis-writing/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, operationalisation | a guide with examples, pros & cons, what is a conceptual framework | tips & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Research Hypothesis: What It Is, Types + How to Develop?

A research study starts with a question. Researchers worldwide ask questions and create research hypotheses. The effectiveness of research relies on developing a good research hypothesis. Examples of research hypotheses can guide researchers in writing effective ones.
In this blog, we’ll learn what a research hypothesis is, why it’s important in research, and the different types used in science. We’ll also guide you through creating your research hypothesis and discussing ways to test and evaluate it.
What is a Research Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is like a guess or idea that you suggest to check if it’s true. A research hypothesis is a statement that brings up a question and predicts what might happen.
It’s really important in the scientific method and is used in experiments to figure things out. Essentially, it’s an educated guess about how things are connected in the research.
A research hypothesis usually includes pointing out the independent variable (the thing they’re changing or studying) and the dependent variable (the result they’re measuring or watching). It helps plan how to gather and analyze data to see if there’s evidence to support or deny the expected connection between these variables.
Importance of Hypothesis in Research
Hypotheses are really important in research. They help design studies, allow for practical testing, and add to our scientific knowledge. Their main role is to organize research projects, making them purposeful, focused, and valuable to the scientific community. Let’s look at some key reasons why they matter:
- A research hypothesis helps test theories.
A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior.
- It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
It serves as a launching pad for investigation activities, which offers researchers a clear starting point. A research hypothesis can explore the relationship between exercise and stress reduction.
- Hypothesis guides the research work or study.
A well-formulated hypothesis guides the entire research process. It ensures that the study remains focused and purposeful. For instance, a hypothesis about the impact of social media on interpersonal relationships provides clear guidance for a study.
- Hypothesis sometimes suggests theories.
In some cases, a hypothesis can suggest new theories or modifications to existing ones. For example, a hypothesis testing the effectiveness of a new drug might prompt a reconsideration of current medical theories.
- It helps in knowing the data needs.
A hypothesis clarifies the data requirements for a study, ensuring that researchers collect the necessary information—a hypothesis guiding the collection of demographic data to analyze the influence of age on a particular phenomenon.
- The hypothesis explains social phenomena.
Hypotheses are instrumental in explaining complex social phenomena. For instance, a hypothesis might explore the relationship between economic factors and crime rates in a given community.
- Hypothesis provides a relationship between phenomena for empirical Testing.
Hypotheses establish clear relationships between phenomena, paving the way for empirical testing. An example could be a hypothesis exploring the correlation between sleep patterns and academic performance.
- It helps in knowing the most suitable analysis technique.
A hypothesis guides researchers in selecting the most appropriate analysis techniques for their data. For example, a hypothesis focusing on the effectiveness of a teaching method may lead to the choice of statistical analyses best suited for educational research.
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a specific idea that you can test in a study. It often comes from looking at past research and theories. A good hypothesis usually starts with a research question that you can explore through background research. For it to be effective, consider these key characteristics:
- Clear and Focused Language: A good hypothesis uses clear and focused language to avoid confusion and ensure everyone understands it.
- Related to the Research Topic: The hypothesis should directly relate to the research topic, acting as a bridge between the specific question and the broader study.
- Testable: An effective hypothesis can be tested, meaning its prediction can be checked with real data to support or challenge the proposed relationship.
- Potential for Exploration: A good hypothesis often comes from a research question that invites further exploration. Doing background research helps find gaps and potential areas to investigate.
- Includes Variables: The hypothesis should clearly state both the independent and dependent variables, specifying the factors being studied and the expected outcomes.
- Ethical Considerations: Check if variables can be manipulated without breaking ethical standards. It’s crucial to maintain ethical research practices.
- Predicts Outcomes: The hypothesis should predict the expected relationship and outcome, acting as a roadmap for the study and guiding data collection and analysis.
- Simple and Concise: A good hypothesis avoids unnecessary complexity and is simple and concise, expressing the essence of the proposed relationship clearly.
- Clear and Assumption-Free: The hypothesis should be clear and free from assumptions about the reader’s prior knowledge, ensuring universal understanding.
- Observable and Testable Results: A strong hypothesis implies research that produces observable and testable results, making sure the study’s outcomes can be effectively measured and analyzed.
When you use these characteristics as a checklist, it can help you create a good research hypothesis. It’ll guide improving and strengthening the hypothesis, identifying any weaknesses, and making necessary changes. Crafting a hypothesis with these features helps you conduct a thorough and insightful research study.
Types of Research Hypotheses
The research hypothesis comes in various types, each serving a specific purpose in guiding the scientific investigation. Knowing the differences will make it easier for you to create your own hypothesis. Here’s an overview of the common types:
01. Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states that there is no connection between two considered variables or that two groups are unrelated. As discussed earlier, a hypothesis is an unproven assumption lacking sufficient supporting data. It serves as the statement researchers aim to disprove. It is testable, verifiable, and can be rejected.
For example, if you’re studying the relationship between Project A and Project B, assuming both projects are of equal standard is your null hypothesis. It needs to be specific for your study.
02. Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is basically another option to the null hypothesis. It involves looking for a significant change or alternative that could lead you to reject the null hypothesis. It’s a different idea compared to the null hypothesis.
When you create a null hypothesis, you’re making an educated guess about whether something is true or if there’s a connection between that thing and another variable. If the null view suggests something is correct, the alternative hypothesis says it’s incorrect.
For instance, if your null hypothesis is “I’m going to be $1000 richer,” the alternative hypothesis would be “I’m not going to get $1000 or be richer.”
03. Directional Hypothesis
The directional hypothesis predicts the direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They specify whether the effect will be positive or negative.
If you increase your study hours, you will experience a positive association with your exam scores. This hypothesis suggests that as you increase the independent variable (study hours), there will also be an increase in the dependent variable (exam scores).
04. Non-directional Hypothesis
The non-directional hypothesis predicts the existence of a relationship between variables but does not specify the direction of the effect. It suggests that there will be a significant difference or relationship, but it does not predict the nature of that difference.
For example, you will find no notable difference in test scores between students who receive the educational intervention and those who do not. However, once you compare the test scores of the two groups, you will notice an important difference.
05. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis predicts a relationship between one dependent variable and one independent variable without specifying the nature of that relationship. It’s simple and usually used when we don’t know much about how the two things are connected.
For example, if you adopt effective study habits, you will achieve higher exam scores than those with poor study habits.
06. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is an idea that specifies a relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. It is a more detailed idea than a simple hypothesis.
While a simple view suggests a straightforward cause-and-effect relationship between two things, a complex hypothesis involves many factors and how they’re connected to each other.
For example, when you increase your study time, you tend to achieve higher exam scores. The connection between your study time and exam performance is affected by various factors, including the quality of your sleep, your motivation levels, and the effectiveness of your study techniques.
If you sleep well, stay highly motivated, and use effective study strategies, you may observe a more robust positive correlation between the time you spend studying and your exam scores, unlike those who may lack these factors.
07. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis proposes a connection between two things without saying that one causes the other. Basically, it suggests that when one thing changes, the other changes too, but it doesn’t claim that one thing is causing the change in the other.
For example, you will likely notice higher exam scores when you increase your study time. You can recognize an association between your study time and exam scores in this scenario.
Your hypothesis acknowledges a relationship between the two variables—your study time and exam scores—without asserting that increased study time directly causes higher exam scores. You need to consider that other factors, like motivation or learning style, could affect the observed association.
08. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables. It suggests that changes in one variable directly cause changes in another variable.
For example, when you increase your study time, you experience higher exam scores. This hypothesis suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship, indicating that the more time you spend studying, the higher your exam scores. It assumes that changes in your study time directly influence changes in your exam performance.
09. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement based on things we can see and measure. It comes from direct observation or experiments and can be tested with real-world evidence. If an experiment proves a theory, it supports the idea and shows it’s not just a guess. This makes the statement more reliable than a wild guess.
For example, if you increase the dosage of a certain medication, you might observe a quicker recovery time for patients. Imagine you’re in charge of a clinical trial. In this trial, patients are given varying dosages of the medication, and you measure and compare their recovery times. This allows you to directly see the effects of different dosages on how fast patients recover.
This way, you can create a research hypothesis: “Increasing the dosage of a certain medication will lead to a faster recovery time for patients.”
10. Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement or assumption about a population parameter that is the subject of an investigation. It serves as the basis for statistical analysis and testing. It is often tested using statistical methods to draw inferences about the larger population.
In a hypothesis test, statistical evidence is collected to either reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis due to insufficient evidence.
For example, let’s say you’re testing a new medicine. Your hypothesis could be that the medicine doesn’t really help patients get better. So, you collect data and use statistics to see if your guess is right or if the medicine actually makes a difference.
If the data strongly shows that the medicine does help, you say your guess was wrong, and the medicine does make a difference. But if the proof isn’t strong enough, you can stick with your original guess because you didn’t get enough evidence to change your mind.
How to Develop a Research Hypotheses?
Step 1: identify your research problem or topic..
Define the area of interest or the problem you want to investigate. Make sure it’s clear and well-defined.
Start by asking a question about your chosen topic. Consider the limitations of your research and create a straightforward problem related to your topic. Once you’ve done that, you can develop and test a hypothesis with evidence.
Step 2: Conduct a literature review
Review existing literature related to your research problem. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge in the field, identify gaps, and build a foundation for your hypothesis. Consider the following questions:
- What existing research has been conducted on your chosen topic?
- Are there any gaps or unanswered questions in the current literature?
- How will the existing literature contribute to the foundation of your research?
Step 3: Formulate your research question
Based on your literature review, create a specific and concise research question that addresses your identified problem. Your research question should be clear, focused, and relevant to your field of study.
Step 4: Identify variables
Determine the key variables involved in your research question. Variables are the factors or phenomena that you will study and manipulate to test your hypothesis.
- Independent Variable: The variable you manipulate or control.
- Dependent Variable: The variable you measure to observe the effect of the independent variable.
Step 5: State the Null hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no significant difference or effect. It serves as a baseline for comparison with the alternative hypothesis.
Step 6: Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis
Choose research methods that align with your study objectives, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies. The selected methods enable you to test your research hypothesis effectively.
Creating a research hypothesis usually takes more than one try. Expect to make changes as you collect data. It’s normal to test and say no to a few hypotheses before you find the right answer to your research question.
Testing and Evaluating Hypotheses
Testing hypotheses is a really important part of research. It’s like the practical side of things. Here, real-world evidence will help you determine how different things are connected. Let’s explore the main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis.
Before testing, clearly articulate your research hypothesis. This involves framing both a null hypothesis, suggesting no significant effect or relationship, and an alternative hypothesis, proposing the expected outcome.
- Collect data strategically.
Plan how you will gather information in a way that fits your study. Make sure your data collection method matches the things you’re studying.
Whether through surveys, observations, or experiments, this step demands precision and adherence to the established methodology. The quality of data collected directly influences the credibility of study outcomes.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test.
Choose a statistical test that aligns with the nature of your data and the hypotheses being tested. Whether it’s a t-test, chi-square test, ANOVA, or regression analysis, selecting the right statistical tool is paramount for accurate and reliable results.
- Decide if your idea was right or wrong.
Following the statistical analysis, evaluate the results in the context of your null hypothesis. You need to decide if you should reject your null hypothesis or not.
- Share what you found.
When discussing what you found in your research, be clear and organized. Say whether your idea was supported or not, and talk about what your results mean. Also, mention any limits to your study and suggest ideas for future research.
The Role of QuestionPro to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
QuestionPro is a survey and research platform that provides tools for creating, distributing, and analyzing surveys. It plays a crucial role in the research process, especially when you’re in the initial stages of hypothesis development. Here’s how QuestionPro can help you to develop a good research hypothesis:
- Survey design and data collection: You can use the platform to create targeted questions that help you gather relevant data.
- Exploratory research: Through surveys and feedback mechanisms on QuestionPro, you can conduct exploratory research to understand the landscape of a particular subject.
- Literature review and background research: QuestionPro surveys can collect sample population opinions, experiences, and preferences. This data and a thorough literature evaluation can help you generate a well-grounded hypothesis by improving your research knowledge.
- Identifying variables: Using targeted survey questions, you can identify relevant variables related to their research topic.
- Testing assumptions: You can use surveys to informally test certain assumptions or hypotheses before formalizing a research hypothesis.
- Data analysis tools: QuestionPro provides tools for analyzing survey data. You can use these tools to identify the collected data’s patterns, correlations, or trends.
- Refining your hypotheses: As you collect data through QuestionPro, you can adjust your hypotheses based on the real-world responses you receive.
A research hypothesis is like a guide for researchers in science. It’s a well-thought-out idea that has been thoroughly tested. This idea is crucial as researchers can explore different fields, such as medicine, social sciences, and natural sciences. The research hypothesis links theories to real-world evidence and gives researchers a clear path to explore and make discoveries.
QuestionPro Research Suite is a helpful tool for researchers. It makes creating surveys, collecting data, and analyzing information easily. It supports all kinds of research, from exploring new ideas to forming hypotheses. With a focus on using data, it helps researchers do their best work.
Are you interested in learning more about QuestionPro Research Suite? Take advantage of QuestionPro’s free trial to get an initial look at its capabilities and realize the full potential of your research efforts.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Qualtrics vs Google Forms: Which is the Best Platform?
Jul 24, 2024
TypeForm vs. SurveyMonkey: Which is Better in 2024?
SurveyMonkey vs Google Forms: A Detailed Comparison
Jul 23, 2024
Jotform vs Typeform: Which is the Best Option? Comparison (2024)
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
How to Write a Research Hypothesis
- Research Process
- Peer Review
Since grade school, we've all been familiar with hypotheses. The hypothesis is an essential step of the scientific method. But what makes an effective research hypothesis, how do you create one, and what types of hypotheses are there? We answer these questions and more.
Updated on April 27, 2022

What is a research hypothesis?
General hypothesis.
Since grade school, we've all been familiar with the term “hypothesis.” A hypothesis is a fact-based guess or prediction that has not been proven. It is an essential step of the scientific method. The hypothesis of a study is a drive for experimentation to either prove the hypothesis or dispute it.
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is more specific than a general hypothesis. It is an educated, expected prediction of the outcome of a study that is testable.
What makes an effective research hypothesis?
A good research hypothesis is a clear statement of the relationship between a dependent variable(s) and independent variable(s) relevant to the study that can be disproven.
Research hypothesis checklist
Once you've written a possible hypothesis, make sure it checks the following boxes:
- It must be testable: You need a means to prove your hypothesis. If you can't test it, it's not a hypothesis.
- It must include a dependent and independent variable: At least one independent variable ( cause ) and one dependent variable ( effect ) must be included.
- The language must be easy to understand: Be as clear and concise as possible. Nothing should be left to interpretation.
- It must be relevant to your research topic: You probably shouldn't be talking about cats and dogs if your research topic is outer space. Stay relevant to your topic.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
Pose it as a question first.
Start your research hypothesis from a journalistic approach. Ask one of the five W's: Who, what, when, where, or why.
A possible initial question could be: Why is the sky blue?
Do the preliminary research
Once you have a question in mind, read research around your topic. Collect research from academic journals.
If you're looking for information about the sky and why it is blue, research information about the atmosphere, weather, space, the sun, etc.
Write a draft hypothesis
Once you're comfortable with your subject and have preliminary knowledge, create a working hypothesis. Don't stress much over this. Your first hypothesis is not permanent. Look at it as a draft.
Your first draft of a hypothesis could be: Certain molecules in the Earth's atmosphere are responsive to the sky being the color blue.
Make your working draft perfect
Take your working hypothesis and make it perfect. Narrow it down to include only the information listed in the “Research hypothesis checklist” above.
Now that you've written your working hypothesis, narrow it down. Your new hypothesis could be: Light from the sun hitting oxygen molecules in the sky makes the color of the sky appear blue.
Write a null hypothesis
Your null hypothesis should be the opposite of your research hypothesis. It should be able to be disproven by your research.
In this example, your null hypothesis would be: Light from the sun hitting oxygen molecules in the sky does not make the color of the sky appear blue.
Why is it important to have a clear, testable hypothesis?
One of the main reasons a manuscript can be rejected from a journal is because of a weak hypothesis. “Poor hypothesis, study design, methodology, and improper use of statistics are other reasons for rejection of a manuscript,” says Dr. Ish Kumar Dhammi and Dr. Rehan-Ul-Haq in Indian Journal of Orthopaedics.
According to Dr. James M. Provenzale in American Journal of Roentgenology , “The clear declaration of a research question (or hypothesis) in the Introduction is critical for reviewers to understand the intent of the research study. It is best to clearly state the study goal in plain language (for example, “We set out to determine whether condition x produces condition y.”) An insufficient problem statement is one of the more common reasons for manuscript rejection.”
Characteristics that make a hypothesis weak include:
- Unclear variables
- Unoriginality
- Too general
- Too specific
A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and methods . The goal of a paper is to prove or disprove a hypothesis - or to prove or disprove a null hypothesis. If the hypothesis is not a dependent variable of what is being studied, the paper's methods should come into question.
A strong hypothesis is essential to the scientific method. A hypothesis states an assumed relationship between at least two variables and the experiment then proves or disproves that relationship with statistical significance. Without a proven and reproducible relationship, the paper feeds into the reproducibility crisis. Learn more about writing for reproducibility .
In a study published in The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India by Dr. Suvarna Satish Khadilkar, she reviewed 400 rejected manuscripts to see why they were rejected. Her studies revealed that poor methodology was a top reason for the submission having a final disposition of rejection.
Aside from publication chances, Dr. Gareth Dyke believes a clear hypothesis helps efficiency.
“Developing a clear and testable hypothesis for your research project means that you will not waste time, energy, and money with your work,” said Dyke. “Refining a hypothesis that is both meaningful, interesting, attainable, and testable is the goal of all effective research.”
Types of research hypotheses
There can be overlap in these types of hypotheses.
Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a hypothesis at its most basic form. It shows the relationship of one independent and one independent variable.
Example: Drinking soda (independent variable) every day leads to obesity (dependent variable).
Complex hypothesis
A complex hypothesis shows the relationship of two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: Drinking soda (independent variable) every day leads to obesity (dependent variable) and heart disease (dependent variable).
Directional hypothesis
A directional hypothesis guesses which way the results of an experiment will go. It uses words like increase, decrease, higher, lower, positive, negative, more, or less. It is also frequently used in statistics.
Example: Humans exposed to radiation have a higher risk of cancer than humans not exposed to radiation.
Non-directional hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis says there will be an effect on the dependent variable, but it does not say which direction.
Associative hypothesis
An associative hypothesis says that when one variable changes, so does the other variable.
Alternative hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis states that the variables have a relationship.
- The opposite of a null hypothesis
Example: An apple a day keeps the doctor away.
Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis states that there is no relationship between the two variables. It is posed as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Researchers use a null hypothesis to work to be able to reject it. A null hypothesis:
- Can never be proven
- Can only be rejected
- Is the opposite of an alternative hypothesis
Example: An apple a day does not keep the doctor away.
Logical hypothesis
A logical hypothesis is a suggested explanation while using limited evidence.
Example: Bats can navigate in the dark better than tigers.
In this hypothesis, the researcher knows that tigers cannot see in the dark, and bats mostly live in darkness.
Empirical hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is also called a “working hypothesis.” It uses the trial and error method and changes around the independent variables.
- An apple a day keeps the doctor away.
- Two apples a day keep the doctor away.
- Three apples a day keep the doctor away.
In this case, the research changes the hypothesis as the researcher learns more about his/her research.
Statistical hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a look of a part of a population or statistical model. This type of hypothesis is especially useful if you are making a statement about a large population. Instead of having to test the entire population of Illinois, you could just use a smaller sample of people who live there.
Example: 70% of people who live in Illinois are iron deficient.
Causal hypothesis
A causal hypothesis states that the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable.
Example: Using tobacco products causes cancer.
Final thoughts
Make sure your research is error-free before you send it to your preferred journal . Check our our English Editing services to avoid your chances of desk rejection.

Jonny Rhein, BA
See our "Privacy Policy"
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- 4 minute read
- 341.7K views
Table of Contents
One of the most important aspects of conducting research is constructing a strong hypothesis. But what makes a hypothesis in research effective? In this article, we’ll look at the difference between a hypothesis and a research question, as well as the elements of a good hypothesis in research. We’ll also include some examples of effective hypotheses, and what pitfalls to avoid.
What is a Hypothesis in Research?
Simply put, a hypothesis is a research question that also includes the predicted or expected result of the research. Without a hypothesis, there can be no basis for a scientific or research experiment. As such, it is critical that you carefully construct your hypothesis by being deliberate and thorough, even before you set pen to paper. Unless your hypothesis is clearly and carefully constructed, any flaw can have an adverse, and even grave, effect on the quality of your experiment and its subsequent results.
Research Question vs Hypothesis
It’s easy to confuse research questions with hypotheses, and vice versa. While they’re both critical to the Scientific Method, they have very specific differences. Primarily, a research question, just like a hypothesis, is focused and concise. But a hypothesis includes a prediction based on the proposed research, and is designed to forecast the relationship of and between two (or more) variables. Research questions are open-ended, and invite debate and discussion, while hypotheses are closed, e.g. “The relationship between A and B will be C.”
A hypothesis is generally used if your research topic is fairly well established, and you are relatively certain about the relationship between the variables that will be presented in your research. Since a hypothesis is ideally suited for experimental studies, it will, by its very existence, affect the design of your experiment. The research question is typically used for new topics that have not yet been researched extensively. Here, the relationship between different variables is less known. There is no prediction made, but there may be variables explored. The research question can be casual in nature, simply trying to understand if a relationship even exists, descriptive or comparative.
How to Write Hypothesis in Research
Writing an effective hypothesis starts before you even begin to type. Like any task, preparation is key, so you start first by conducting research yourself, and reading all you can about the topic that you plan to research. From there, you’ll gain the knowledge you need to understand where your focus within the topic will lie.
Remember that a hypothesis is a prediction of the relationship that exists between two or more variables. Your job is to write a hypothesis, and design the research, to “prove” whether or not your prediction is correct. A common pitfall is to use judgments that are subjective and inappropriate for the construction of a hypothesis. It’s important to keep the focus and language of your hypothesis objective.
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions.
Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis:
- Predicts the relationship and outcome
- Simple and concise – avoid wordiness
- Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Observable and testable results
- Relevant and specific to the research question or problem
Research Hypothesis Example
Perhaps the best way to evaluate whether or not your hypothesis is effective is to compare it to those of your colleagues in the field. There is no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a powerful research hypothesis. As you’re reading and preparing your hypothesis, you’ll also read other hypotheses. These can help guide you on what works, and what doesn’t, when it comes to writing a strong research hypothesis.
Here are a few generic examples to get you started.
Eating an apple each day, after the age of 60, will result in a reduction of frequency of physician visits.
Budget airlines are more likely to receive more customer complaints. A budget airline is defined as an airline that offers lower fares and fewer amenities than a traditional full-service airline. (Note that the term “budget airline” is included in the hypothesis.
Workplaces that offer flexible working hours report higher levels of employee job satisfaction than workplaces with fixed hours.
Each of the above examples are specific, observable and measurable, and the statement of prediction can be verified or shown to be false by utilizing standard experimental practices. It should be noted, however, that often your hypothesis will change as your research progresses.
Language Editing Plus
Elsevier’s Language Editing Plus service can help ensure that your research hypothesis is well-designed, and articulates your research and conclusions. Our most comprehensive editing package, you can count on a thorough language review by native-English speakers who are PhDs or PhD candidates. We’ll check for effective logic and flow of your manuscript, as well as document formatting for your chosen journal, reference checks, and much more.

Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?

How to Write an Effective Problem Statement for Your Research Paper
You may also like.

Submission 101: What format should be used for academic papers?

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- How it works

How to Write a Hypothesis – Steps & Tips
Published by Alaxendra Bets at August 14th, 2021 , Revised On October 26, 2023
What is a Research Hypothesis?
You can test a research statement with the help of experimental or theoretical research, known as a hypothesis.
If you want to find out the similarities, differences, and relationships between variables, you must write a testable hypothesis before compiling the data, performing analysis, and generating results to complete.
The data analysis and findings will help you test the hypothesis and see whether it is true or false. Here is all you need to know about how to write a hypothesis for a dissertation .
Research Hypothesis Definition
Not sure what the meaning of the research hypothesis is?
A research hypothesis predicts an answer to the research question based on existing theoretical knowledge or experimental data.
Some studies may have multiple hypothesis statements depending on the research question(s). A research hypothesis must be based on formulas, facts, and theories. It should be testable by data analysis, observations, experiments, or other scientific methodologies that can refute or support the statement.
Variables in Hypothesis
Developing a hypothesis is easy. Most research studies have two or more variables in the hypothesis, particularly studies involving correlational and experimental research. The researcher can control or change the independent variable(s) while measuring and observing the independent variable(s).
“How long a student sleeps affects test scores.”
In the above statement, the dependent variable is the test score, while the independent variable is the length of time spent in sleep. Developing a hypothesis will be easy if you know your research’s dependent and independent variables.
Once you have developed a thesis statement, questions such as how to write a hypothesis for the dissertation and how to test a research hypothesis become pretty straightforward.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Step-by-Step Guide on How to Write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps involved in how to write a hypothesis for a dissertation.
Step 1: Start with a Research Question
- Begin by asking a specific question about a topic of interest.
- This question should be clear, concise, and researchable.
Example: Does exposure to sunlight affect plant growth?
Step 2: Do Preliminary Research
- Before formulating a hypothesis, conduct background research to understand existing knowledge on the topic.
- Familiarise yourself with prior studies, theories, or observations related to the research question.
Step 3: Define Variables
- Independent Variable (IV): The factor that you change or manipulate in an experiment.
- Dependent Variable (DV): The factor that you measure.
Example: IV: Amount of sunlight exposure (e.g., 2 hours/day, 4 hours/day, 8 hours/day) DV: Plant growth (e.g., height in centimetres)
Step 4: Formulate the Hypothesis
- A hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables.
- It is often written as an “if-then” statement.
Example: If plants receive more sunlight, then they will grow taller.
Step 5: Ensure it is Testable
A good hypothesis is empirically testable. This means you should be able to design an experiment or observation to test its validity.
Example: You can set up an experiment where plants are exposed to varying amounts of sunlight and then measure their growth over a period of time.
Step 6: Consider Potential Confounding Variables
- Confounding variables are factors other than the independent variable that might affect the outcome.
- It is important to identify these to ensure that they do not skew your results.
Example: Soil quality, water frequency, or type of plant can all affect growth. Consider keeping these constant in your experiment.
Step 7: Write the Null Hypothesis
- The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no effect or no relationship between the variables.
- It is what you aim to disprove or reject through your research.
Example: There is no difference in plant growth regardless of the amount of sunlight exposure.
Step 8: Test your Hypothesis
Design an experiment or conduct observations to test your hypothesis.
Example: Grow three sets of plants: one set exposed to 2 hours of sunlight daily, another exposed to 4 hours, and a third exposed to 8 hours. Measure and compare their growth after a set period.
Step 9: Analyse the Results
After testing, review your data to determine if it supports your hypothesis.
Step 10: Draw Conclusions
- Based on your findings, determine whether you can accept or reject the hypothesis.
- Remember, even if you reject your hypothesis, it’s a valuable result. It can guide future research and refine questions.
Three Ways to Phrase a Hypothesis
Try to use “if”… and “then”… to identify the variables. The independent variable should be present in the first part of the hypothesis, while the dependent variable will form the second part of the statement. Consider understanding the below research hypothesis example to create a specific, clear, and concise research hypothesis;
If an obese lady starts attending Zomba fitness classes, her health will improve.
In academic research, you can write the predicted variable relationship directly because most research studies correlate terms.
The number of Zomba fitness classes attended by the obese lady has a positive effect on health.
If your research compares two groups, then you can develop a hypothesis statement on their differences.
An obese lady who attended most Zumba fitness classes will have better health than those who attended a few.
How to Write a Null Hypothesis
If a statistical analysis is involved in your research, then you must create a null hypothesis. If you find any relationship between the variables, then the null hypothesis will be the default position that there is no relationship between them. H0 is the symbol for the null hypothesis, while the hypothesis is represented as H1. The null hypothesis will also answer your question, “How to test the research hypothesis in the dissertation.”
H0: The number of Zumba fitness classes attended by the obese lady does not affect her health.
H1: The number of Zumba fitness classes attended by obese lady positively affects health.
Also see: Your Dissertation in Education
Hypothesis Examples
Research Question: Does the amount of sunlight a plant receives affect its growth? Hypothesis: Plants that receive more sunlight will grow taller than plants that receive less sunlight.
Research Question: Do students who eat breakfast perform better in school exams than those who don’t? Hypothesis: Students who eat a morning breakfast will score higher on school exams compared to students who skip breakfast.
Research Question: Does listening to music while studying impact a student’s ability to retain information? Hypothesis 1 (Directional): Students who listen to music while studying will retain less information than those who study in silence. Hypothesis 2 (Non-directional): There will be a difference in information retention between students who listen to music while studying and those who study in silence.
How can ResearchProspect Help?
If you are unsure about how to rest a research hypothesis in a dissertation or simply unsure about how to develop a hypothesis for your research, then you can take advantage of our dissertation services which cover every tiny aspect of a dissertation project you might need help with including but not limited to setting up a hypothesis and research questions, help with individual chapters , full dissertation writing , statistical analysis , and much more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 rules for writing a good hypothesis.
- Clear Statement: State a clear relationship between variables.
- Testable: Ensure it can be investigated and measured.
- Specific: Avoid vague terms, be precise in predictions.
- Falsifiable: Design to allow potential disproof.
- Relevant: Address research question and align with existing knowledge.
What is a hypothesis in simple words?
A hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction about something that can be tested. It is a statement that suggests a possible explanation for an event or phenomenon based on prior knowledge or observation. Scientists use hypotheses as a starting point for experiments to discover if they are true or false.
What is the hypothesis and examples?
A hypothesis is a testable prediction or explanation for an observation or phenomenon. For example, if plants are given sunlight, then they will grow. In this case, the hypothesis suggests that sunlight has a positive effect on plant growth. It can be tested by experimenting with plants in varying light conditions.
What is the hypothesis in research definition?
A hypothesis in research is a clear, testable statement predicting the possible outcome of a study based on prior knowledge and observation. It serves as the foundation for conducting experiments or investigations. Researchers test the validity of the hypothesis to draw conclusions and advance knowledge in a particular field.
Why is it called a hypothesis?
The term “hypothesis” originates from the Greek word “hypothesis,” which means “base” or “foundation.” It’s used to describe a foundational statement or proposition that can be tested. In scientific contexts, it denotes a tentative explanation for a phenomenon, serving as a starting point for investigation or experimentation.
You May Also Like
Penning your dissertation proposal can be a rather daunting task. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation proposal.
To help students organise their dissertation proposal paper correctly, we have put together detailed guidelines on how to structure a dissertation proposal.
Here we explore what is research problem in dissertation with research problem examples to help you understand how and when to write a research problem.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
| Quantitative research questions | Quantitative research hypotheses |
|---|---|
| Descriptive research questions | Simple hypothesis |
| Comparative research questions | Complex hypothesis |
| Relationship research questions | Directional hypothesis |
| Non-directional hypothesis | |
| Associative hypothesis | |
| Causal hypothesis | |
| Null hypothesis | |
| Alternative hypothesis | |
| Working hypothesis | |
| Statistical hypothesis | |
| Logical hypothesis | |
| Hypothesis-testing | |
| Qualitative research questions | Qualitative research hypotheses |
| Contextual research questions | Hypothesis-generating |
| Descriptive research questions | |
| Evaluation research questions | |
| Explanatory research questions | |
| Exploratory research questions | |
| Generative research questions | |
| Ideological research questions | |
| Ethnographic research questions | |
| Phenomenological research questions | |
| Grounded theory questions | |
| Qualitative case study questions |
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
| Quantitative research questions | |
|---|---|
| Descriptive research question | |
| - Measures responses of subjects to variables | |
| - Presents variables to measure, analyze, or assess | |
| What is the proportion of resident doctors in the hospital who have mastered ultrasonography (response of subjects to a variable) as a diagnostic technique in their clinical training? | |
| Comparative research question | |
| - Clarifies difference between one group with outcome variable and another group without outcome variable | |
| Is there a difference in the reduction of lung metastasis in osteosarcoma patients who received the vitamin D adjunctive therapy (group with outcome variable) compared with osteosarcoma patients who did not receive the vitamin D adjunctive therapy (group without outcome variable)? | |
| - Compares the effects of variables | |
| How does the vitamin D analogue 22-Oxacalcitriol (variable 1) mimic the antiproliferative activity of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D (variable 2) in osteosarcoma cells? | |
| Relationship research question | |
| - Defines trends, association, relationships, or interactions between dependent variable and independent variable | |
| Is there a relationship between the number of medical student suicide (dependent variable) and the level of medical student stress (independent variable) in Japan during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic? | |
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
| Quantitative research hypotheses | |
|---|---|
| Simple hypothesis | |
| - Predicts relationship between single dependent variable and single independent variable | |
| If the dose of the new medication (single independent variable) is high, blood pressure (single dependent variable) is lowered. | |
| Complex hypothesis | |
| - Foretells relationship between two or more independent and dependent variables | |
| The higher the use of anticancer drugs, radiation therapy, and adjunctive agents (3 independent variables), the higher would be the survival rate (1 dependent variable). | |
| Directional hypothesis | |
| - Identifies study direction based on theory towards particular outcome to clarify relationship between variables | |
| Privately funded research projects will have a larger international scope (study direction) than publicly funded research projects. | |
| Non-directional hypothesis | |
| - Nature of relationship between two variables or exact study direction is not identified | |
| - Does not involve a theory | |
| Women and men are different in terms of helpfulness. (Exact study direction is not identified) | |
| Associative hypothesis | |
| - Describes variable interdependency | |
| - Change in one variable causes change in another variable | |
| A larger number of people vaccinated against COVID-19 in the region (change in independent variable) will reduce the region’s incidence of COVID-19 infection (change in dependent variable). | |
| Causal hypothesis | |
| - An effect on dependent variable is predicted from manipulation of independent variable | |
| A change into a high-fiber diet (independent variable) will reduce the blood sugar level (dependent variable) of the patient. | |
| Null hypothesis | |
| - A negative statement indicating no relationship or difference between 2 variables | |
| There is no significant difference in the severity of pulmonary metastases between the new drug (variable 1) and the current drug (variable 2). | |
| Alternative hypothesis | |
| - Following a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis predicts a relationship between 2 study variables | |
| The new drug (variable 1) is better on average in reducing the level of pain from pulmonary metastasis than the current drug (variable 2). | |
| Working hypothesis | |
| - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory | |
| Dairy cows fed with concentrates of different formulations will produce different amounts of milk. | |
| Statistical hypothesis | |
| - Assumption about the value of population parameter or relationship among several population characteristics | |
| - Validity tested by a statistical experiment or analysis | |
| The mean recovery rate from COVID-19 infection (value of population parameter) is not significantly different between population 1 and population 2. | |
| There is a positive correlation between the level of stress at the workplace and the number of suicides (population characteristics) among working people in Japan. | |
| Logical hypothesis | |
| - Offers or proposes an explanation with limited or no extensive evidence | |
| If healthcare workers provide more educational programs about contraception methods, the number of adolescent pregnancies will be less. | |
| Hypothesis-testing (Quantitative hypothesis-testing research) | |
| - Quantitative research uses deductive reasoning. | |
| - This involves the formation of a hypothesis, collection of data in the investigation of the problem, analysis and use of the data from the investigation, and drawing of conclusions to validate or nullify the hypotheses. | |
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
| Qualitative research questions | |
|---|---|
| Contextual research question | |
| - Ask the nature of what already exists | |
| - Individuals or groups function to further clarify and understand the natural context of real-world problems | |
| What are the experiences of nurses working night shifts in healthcare during the COVID-19 pandemic? (natural context of real-world problems) | |
| Descriptive research question | |
| - Aims to describe a phenomenon | |
| What are the different forms of disrespect and abuse (phenomenon) experienced by Tanzanian women when giving birth in healthcare facilities? | |
| Evaluation research question | |
| - Examines the effectiveness of existing practice or accepted frameworks | |
| How effective are decision aids (effectiveness of existing practice) in helping decide whether to give birth at home or in a healthcare facility? | |
| Explanatory research question | |
| - Clarifies a previously studied phenomenon and explains why it occurs | |
| Why is there an increase in teenage pregnancy (phenomenon) in Tanzania? | |
| Exploratory research question | |
| - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated to have a deeper understanding of the research problem | |
| What factors affect the mental health of medical students (areas that have not yet been fully investigated) during the COVID-19 pandemic? | |
| Generative research question | |
| - Develops an in-depth understanding of people’s behavior by asking ‘how would’ or ‘what if’ to identify problems and find solutions | |
| How would the extensive research experience of the behavior of new staff impact the success of the novel drug initiative? | |
| Ideological research question | |
| - Aims to advance specific ideas or ideologies of a position | |
| Are Japanese nurses who volunteer in remote African hospitals able to promote humanized care of patients (specific ideas or ideologies) in the areas of safe patient environment, respect of patient privacy, and provision of accurate information related to health and care? | |
| Ethnographic research question | |
| - Clarifies peoples’ nature, activities, their interactions, and the outcomes of their actions in specific settings | |
| What are the demographic characteristics, rehabilitative treatments, community interactions, and disease outcomes (nature, activities, their interactions, and the outcomes) of people in China who are suffering from pneumoconiosis? | |
| Phenomenological research question | |
| - Knows more about the phenomena that have impacted an individual | |
| What are the lived experiences of parents who have been living with and caring for children with a diagnosis of autism? (phenomena that have impacted an individual) | |
| Grounded theory question | |
| - Focuses on social processes asking about what happens and how people interact, or uncovering social relationships and behaviors of groups | |
| What are the problems that pregnant adolescents face in terms of social and cultural norms (social processes), and how can these be addressed? | |
| Qualitative case study question | |
| - Assesses a phenomenon using different sources of data to answer “why” and “how” questions | |
| - Considers how the phenomenon is influenced by its contextual situation. | |
| How does quitting work and assuming the role of a full-time mother (phenomenon assessed) change the lives of women in Japan? | |
| Qualitative research hypotheses | |
|---|---|
| Hypothesis-generating (Qualitative hypothesis-generating research) | |
| - Qualitative research uses inductive reasoning. | |
| - This involves data collection from study participants or the literature regarding a phenomenon of interest, using the collected data to develop a formal hypothesis, and using the formal hypothesis as a framework for testing the hypothesis. | |
| - Qualitative exploratory studies explore areas deeper, clarifying subjective experience and allowing formulation of a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach. | |
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
| Variables | Unclear and weak statement (Statement 1) | Clear and good statement (Statement 2) | Points to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research question | Which is more effective between smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion? | “Moreover, regarding smoke moxibustion versus smokeless moxibustion, it remains unclear which is more effective, safe, and acceptable to pregnant women, and whether there is any difference in the amount of heat generated.” | 1) Vague and unfocused questions |
| 2) Closed questions simply answerable by yes or no | |||
| 3) Questions requiring a simple choice | |||
| Hypothesis | The smoke moxibustion group will have higher cephalic presentation. | “Hypothesis 1. The smoke moxibustion stick group (SM group) and smokeless moxibustion stick group (-SLM group) will have higher rates of cephalic presentation after treatment than the control group. | 1) Unverifiable hypotheses |
| Hypothesis 2. The SM group and SLM group will have higher rates of cephalic presentation at birth than the control group. | 2) Incompletely stated groups of comparison | ||
| Hypothesis 3. There will be no significant differences in the well-being of the mother and child among the three groups in terms of the following outcomes: premature birth, premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at < 37 weeks, Apgar score < 7 at 5 min, umbilical cord blood pH < 7.1, admission to neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and intrauterine fetal death.” | 3) Insufficiently described variables or outcomes | ||
| Research objective | To determine which is more effective between smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion. | “The specific aims of this pilot study were (a) to compare the effects of smoke moxibustion and smokeless moxibustion treatments with the control group as a possible supplement to ECV for converting breech presentation to cephalic presentation and increasing adherence to the newly obtained cephalic position, and (b) to assess the effects of these treatments on the well-being of the mother and child.” | 1) Poor understanding of the research question and hypotheses |
| 2) Insufficient description of population, variables, or study outcomes |
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
| Variables | Unclear and weak statement (Statement 1) | Clear and good statement (Statement 2) | Points to avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research question | Does disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur in childbirth in Tanzania? | How does disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur and what are the types of physical and psychological abuses observed in midwives’ actual care during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania? | 1) Ambiguous or oversimplistic questions |
| 2) Questions unverifiable by data collection and analysis | |||
| Hypothesis | Disrespect and abuse (D&A) occur in childbirth in Tanzania. | Hypothesis 1: Several types of physical and psychological abuse by midwives in actual care occur during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. | 1) Statements simply expressing facts |
| Hypothesis 2: Weak nursing and midwifery management contribute to the D&A of women during facility-based childbirth in urban Tanzania. | 2) Insufficiently described concepts or variables | ||
| Research objective | To describe disrespect and abuse (D&A) in childbirth in Tanzania. | “This study aimed to describe from actual observations the respectful and disrespectful care received by women from midwives during their labor period in two hospitals in urban Tanzania.” | 1) Statements unrelated to the research question and hypotheses |
| 2) Unattainable or unexplorable objectives |
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
How to write a research hypothesis
Last updated
19 January 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Start with a broad subject matter that excites you, so your curiosity will motivate your work. Conduct a literature search to determine the range of questions already addressed and spot any holes in the existing research.
Narrow the topics that interest you and determine your research question. Rather than focusing on a hole in the research, you might choose to challenge an existing assumption, a process called problematization. You may also find yourself with a short list of questions or related topics.
Use the FINER method to determine the single problem you'll address with your research. FINER stands for:
I nteresting
You need a feasible research question, meaning that there is a way to address the question. You should find it interesting, but so should a larger audience. Rather than repeating research that others have already conducted, your research hypothesis should test something novel or unique.
The research must fall into accepted ethical parameters as defined by the government of your country and your university or college if you're an academic. You'll also need to come up with a relevant question since your research should provide a contribution to the existing research area.
This process typically narrows your shortlist down to a single problem you'd like to study and the variable you want to test. You're ready to write your hypothesis statements.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- Types of research hypotheses
It is important to narrow your topic down to one idea before trying to write your research hypothesis. You'll only test one problem at a time. To do this, you'll write two hypotheses – a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha).
You'll come across many terms related to developing a research hypothesis or referring to a specific type of hypothesis. Let's take a quick look at these terms.
Null hypothesis
The term null hypothesis refers to a research hypothesis type that assumes no statistically significant relationship exists within a set of observations or data. It represents a claim that assumes that any observed relationship is due to chance. Represented as H0, the null represents the conjecture of the research.
Alternative hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis accompanies the null hypothesis. It states that the situation presented in the null hypothesis is false or untrue, and claims an observed effect in your test. This is typically denoted by Ha or H(n), where “n” stands for the number of alternative hypotheses. You can have more than one alternative hypothesis.
Simple hypothesis
The term simple hypothesis refers to a hypothesis or theory that predicts the relationship between two variables - the independent (predictor) and the dependent (predicted).
Complex hypothesis
The term complex hypothesis refers to a model – either quantitative (mathematical) or qualitative . A complex hypothesis states the surmised relationship between two or more potentially related variables.
Directional hypothesis
When creating a statistical hypothesis, the directional hypothesis (the null hypothesis) states an assumption regarding one parameter of a population. Some academics call this the “one-sided” hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis indicates whether the researcher tests for a positive or negative effect by including either the greater than (">") or less than ("<") sign.
Non-directional hypothesis
We refer to the alternative hypothesis in a statistical research question as a non-directional hypothesis. It includes the not equal ("≠") sign to show that the research tests whether or not an effect exists without specifying the effect's direction (positive or negative).
Associative hypothesis
The term associative hypothesis assumes a link between two variables but stops short of stating that one variable impacts the other. Academic statistical literature asserts in this sense that correlation does not imply causation. So, although the hypothesis notes the correlation between two variables – the independent and dependent - it does not predict how the two interact.
Logical hypothesis
Typically used in philosophy rather than science, researchers can't test a logical hypothesis because the technology or data set doesn't yet exist. A logical hypothesis uses logic as the basis of its assumptions.
In some cases, a logical hypothesis can become an empirical hypothesis once technology provides an opportunity for testing. Until that time, the question remains too expensive or complex to address. Note that a logical hypothesis is not a statistical hypothesis.
Empirical hypothesis
When we consider the opposite of a logical hypothesis, we call this an empirical or working hypothesis. This type of hypothesis considers a scientifically measurable question. A researcher can consider and test an empirical hypothesis through replicable tests, observations, and measurements.
Statistical hypothesis
The term statistical hypothesis refers to a test of a theory that uses representative statistical models to test relationships between variables to draw conclusions regarding a large population. This requires an existing large data set, commonly referred to as big data, or implementing a survey to obtain original statistical information to form a data set for the study.
Testing this type of hypothesis requires the use of random samples. Note that the null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing.
Causal hypothesis
The term causal hypothesis refers to a research hypothesis that tests a cause-and-effect relationship. A causal hypothesis is utilized when conducting experimental or quasi-experimental research.
Descriptive hypothesis
The term descriptive hypothesis refers to a research hypothesis used in non-experimental research, specifying an influence in the relationship between two variables.
- What makes an effective research hypothesis?
An effective research hypothesis offers a clearly defined, specific statement, using simple wording that contains no assumptions or generalizations, and that you can test. A well-written hypothesis should predict the tested relationship and its outcome. It contains zero ambiguity and offers results you can observe and test.
The research hypothesis should address a question relevant to a research area. Overall, your research hypothesis needs the following essentials:
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
- How to develop a good research hypothesis
In developing your hypothesis statements, you must pre-plan some of your statistical analysis. Once you decide on your problem to examine, determine three aspects:
the parameter you'll test
the test's direction (left-tailed, right-tailed, or non-directional)
the hypothesized parameter value
Any quantitative research includes a hypothesized parameter value of a mean, a proportion, or the difference between two proportions. Here's how to note each parameter:
Single mean (μ)
Paired means (μd)
Single proportion (p)
Difference between two independent means (μ1−μ2)
Difference between two proportions (p1−p2)
Simple linear regression slope (β)
Correlation (ρ)
Defining these parameters and determining whether you want to test the mean, proportion, or differences helps you determine the statistical tests you'll conduct to analyze your data. When writing your hypothesis, you only need to decide which parameter to test and in what overarching way.
The null research hypothesis must include everyday language, in a single sentence, stating the problem you want to solve. Write it as an if-then statement with defined variables. Write an alternative research hypothesis that states the opposite.
- What is the correct format for writing a hypothesis?
The following example shows the proper format and textual content of a hypothesis. It follows commonly accepted academic standards.
Null hypothesis (H0): High school students who participate in varsity sports as opposed to those who do not, fail to score higher on leadership tests than students who do not participate.
Alternative hypothesis (H1): High school students who play a varsity sport as opposed to those who do not participate in team athletics will score higher on leadership tests than students who do not participate in athletics.
The research question tests the correlation between varsity sports participation and leadership qualities expressed as a score on leadership tests. It compares the population of athletes to non-athletes.
- What are the five steps of a hypothesis?
Once you decide on the specific problem or question you want to address, you can write your research hypothesis. Use this five-step system to hone your null hypothesis and generate your alternative hypothesis.
Step 1 : Create your research question. This topic should interest and excite you; answering it provides relevant information to an industry or academic area.
Step 2 : Conduct a literature review to gather essential existing research.
Step 3 : Write a clear, strong, simply worded sentence that explains your test parameter, test direction, and hypothesized parameter.
Step 4 : Read it a few times. Have others read it and ask them what they think it means. Refine your statement accordingly until it becomes understandable to everyone. While not everyone can or will comprehend every research study conducted, any person from the general population should be able to read your hypothesis and alternative hypothesis and understand the essential question you want to answer.
Step 5 : Re-write your null hypothesis until it reads simply and understandably. Write your alternative hypothesis.
What is the Red Queen hypothesis?
Some hypotheses are well-known, such as the Red Queen hypothesis. Choose your wording carefully, since you could become like the famed scientist Dr. Leigh Van Valen. In 1973, Dr. Van Valen proposed the Red Queen hypothesis to describe coevolutionary activity, specifically reciprocal evolutionary effects between species to explain extinction rates in the fossil record.
Essentially, Van Valen theorized that to survive, each species remains in a constant state of adaptation, evolution, and proliferation, and constantly competes for survival alongside other species doing the same. Only by doing this can a species avoid extinction. Van Valen took the hypothesis title from the Lewis Carroll book, "Through the Looking Glass," which contains a key character named the Red Queen who explains to Alice that for all of her running, she's merely running in place.
- Getting started with your research
In conclusion, once you write your null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha), you’ve essentially authored the elevator pitch of your research. These two one-sentence statements describe your topic in simple, understandable terms that both professionals and laymen can understand. They provide the starting point of your research project.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
What Is a Hypothesis and How Do I Write One?
General Education

Think about something strange and unexplainable in your life. Maybe you get a headache right before it rains, or maybe you think your favorite sports team wins when you wear a certain color. If you wanted to see whether these are just coincidences or scientific fact, you would form a hypothesis, then create an experiment to see whether that hypothesis is true or not.
But what is a hypothesis, anyway? If you’re not sure about what a hypothesis is--or how to test for one!--you’re in the right place. This article will teach you everything you need to know about hypotheses, including:
- Defining the term “hypothesis”
- Providing hypothesis examples
- Giving you tips for how to write your own hypothesis
So let’s get started!

What Is a Hypothesis?
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as “an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.” In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess . Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it’s true or not. Keep in mind that in science, a hypothesis should be testable. You have to be able to design an experiment that tests your hypothesis in order for it to be valid.
As you could assume from that statement, it’s easy to make a bad hypothesis. But when you’re holding an experiment, it’s even more important that your guesses be good...after all, you’re spending time (and maybe money!) to figure out more about your observation. That’s why we refer to a hypothesis as an educated guess--good hypotheses are based on existing data and research to make them as sound as possible.
Hypotheses are one part of what’s called the scientific method . Every (good) experiment or study is based in the scientific method. The scientific method gives order and structure to experiments and ensures that interference from scientists or outside influences does not skew the results. It’s important that you understand the concepts of the scientific method before holding your own experiment. Though it may vary among scientists, the scientific method is generally made up of six steps (in order):
- Observation
- Asking questions
- Forming a hypothesis
- Analyze the data
- Communicate your results
You’ll notice that the hypothesis comes pretty early on when conducting an experiment. That’s because experiments work best when they’re trying to answer one specific question. And you can’t conduct an experiment until you know what you’re trying to prove!
Independent and Dependent Variables
After doing your research, you’re ready for another important step in forming your hypothesis: identifying variables. Variables are basically any factor that could influence the outcome of your experiment . Variables have to be measurable and related to the topic being studied.
There are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables. I ndependent variables remain constant . For example, age is an independent variable; it will stay the same, and researchers can look at different ages to see if it has an effect on the dependent variable.
Speaking of dependent variables... dependent variables are subject to the influence of the independent variable , meaning that they are not constant. Let’s say you want to test whether a person’s age affects how much sleep they need. In that case, the independent variable is age (like we mentioned above), and the dependent variable is how much sleep a person gets.
Variables will be crucial in writing your hypothesis. You need to be able to identify which variable is which, as both the independent and dependent variables will be written into your hypothesis. For instance, in a study about exercise, the independent variable might be the speed at which the respondents walk for thirty minutes, and the dependent variable would be their heart rate. In your study and in your hypothesis, you’re trying to understand the relationship between the two variables.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
The best hypotheses start by asking the right questions . For instance, if you’ve observed that the grass is greener when it rains twice a week, you could ask what kind of grass it is, what elevation it’s at, and if the grass across the street responds to rain in the same way. Any of these questions could become the backbone of experiments to test why the grass gets greener when it rains fairly frequently.
As you’re asking more questions about your first observation, make sure you’re also making more observations . If it doesn’t rain for two weeks and the grass still looks green, that’s an important observation that could influence your hypothesis. You'll continue observing all throughout your experiment, but until the hypothesis is finalized, every observation should be noted.
Finally, you should consult secondary research before writing your hypothesis . Secondary research is comprised of results found and published by other people. You can usually find this information online or at your library. Additionally, m ake sure the research you find is credible and related to your topic. If you’re studying the correlation between rain and grass growth, it would help you to research rain patterns over the past twenty years for your county, published by a local agricultural association. You should also research the types of grass common in your area, the type of grass in your lawn, and whether anyone else has conducted experiments about your hypothesis. Also be sure you’re checking the quality of your research . Research done by a middle school student about what minerals can be found in rainwater would be less useful than an article published by a local university.

Writing Your Hypothesis
Once you’ve considered all of the factors above, you’re ready to start writing your hypothesis. Hypotheses usually take a certain form when they’re written out in a research report.
When you boil down your hypothesis statement, you are writing down your best guess and not the question at hand . This means that your statement should be written as if it is fact already, even though you are simply testing it.
The reason for this is that, after you have completed your study, you'll either accept or reject your if-then or your null hypothesis. All hypothesis testing examples should be measurable and able to be confirmed or denied. You cannot confirm a question, only a statement!
In fact, you come up with hypothesis examples all the time! For instance, when you guess on the outcome of a basketball game, you don’t say, “Will the Miami Heat beat the Boston Celtics?” but instead, “I think the Miami Heat will beat the Boston Celtics.” You state it as if it is already true, even if it turns out you’re wrong. You do the same thing when writing your hypothesis.
Additionally, keep in mind that hypotheses can range from very specific to very broad. These hypotheses can be specific, but if your hypothesis testing examples involve a broad range of causes and effects, your hypothesis can also be broad.

The Two Types of Hypotheses
Now that you understand what goes into a hypothesis, it’s time to look more closely at the two most common types of hypothesis: the if-then hypothesis and the null hypothesis.
#1: If-Then Hypotheses
First of all, if-then hypotheses typically follow this formula:
If ____ happens, then ____ will happen.
The goal of this type of hypothesis is to test the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variable. It’s fairly simple, and each hypothesis can vary in how detailed it can be. We create if-then hypotheses all the time with our daily predictions. Here are some examples of hypotheses that use an if-then structure from daily life:
- If I get enough sleep, I’ll be able to get more work done tomorrow.
- If the bus is on time, I can make it to my friend’s birthday party.
- If I study every night this week, I’ll get a better grade on my exam.
In each of these situations, you’re making a guess on how an independent variable (sleep, time, or studying) will affect a dependent variable (the amount of work you can do, making it to a party on time, or getting better grades).
You may still be asking, “What is an example of a hypothesis used in scientific research?” Take one of the hypothesis examples from a real-world study on whether using technology before bed affects children’s sleep patterns. The hypothesis read s:
“We hypothesized that increased hours of tablet- and phone-based screen time at bedtime would be inversely correlated with sleep quality and child attention.”
It might not look like it, but this is an if-then statement. The researchers basically said, “If children have more screen usage at bedtime, then their quality of sleep and attention will be worse.” The sleep quality and attention are the dependent variables and the screen usage is the independent variable. (Usually, the independent variable comes after the “if” and the dependent variable comes after the “then,” as it is the independent variable that affects the dependent variable.) This is an excellent example of how flexible hypothesis statements can be, as long as the general idea of “if-then” and the independent and dependent variables are present.
#2: Null Hypotheses
Your if-then hypothesis is not the only one needed to complete a successful experiment, however. You also need a null hypothesis to test it against. In its most basic form, the null hypothesis is the opposite of your if-then hypothesis . When you write your null hypothesis, you are writing a hypothesis that suggests that your guess is not true, and that the independent and dependent variables have no relationship .
One null hypothesis for the cell phone and sleep study from the last section might say:
“If children have more screen usage at bedtime, their quality of sleep and attention will not be worse.”
In this case, this is a null hypothesis because it’s asking the opposite of the original thesis!
Conversely, if your if-then hypothesis suggests that your two variables have no relationship, then your null hypothesis would suggest that there is one. So, pretend that there is a study that is asking the question, “Does the amount of followers on Instagram influence how long people spend on the app?” The independent variable is the amount of followers, and the dependent variable is the time spent. But if you, as the researcher, don’t think there is a relationship between the number of followers and time spent, you might write an if-then hypothesis that reads:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will not spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
In this case, the if-then suggests there isn’t a relationship between the variables. In that case, one of the null hypothesis examples might say:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
You then test both the if-then and the null hypothesis to gauge if there is a relationship between the variables, and if so, how much of a relationship.

4 Tips to Write the Best Hypothesis
If you’re going to take the time to hold an experiment, whether in school or by yourself, you’re also going to want to take the time to make sure your hypothesis is a good one. The best hypotheses have four major elements in common: plausibility, defined concepts, observability, and general explanation.
#1: Plausibility
At first glance, this quality of a hypothesis might seem obvious. When your hypothesis is plausible, that means it’s possible given what we know about science and general common sense. However, improbable hypotheses are more common than you might think.
Imagine you’re studying weight gain and television watching habits. If you hypothesize that people who watch more than twenty hours of television a week will gain two hundred pounds or more over the course of a year, this might be improbable (though it’s potentially possible). Consequently, c ommon sense can tell us the results of the study before the study even begins.
Improbable hypotheses generally go against science, as well. Take this hypothesis example:
“If a person smokes one cigarette a day, then they will have lungs just as healthy as the average person’s.”
This hypothesis is obviously untrue, as studies have shown again and again that cigarettes negatively affect lung health. You must be careful that your hypotheses do not reflect your own personal opinion more than they do scientifically-supported findings. This plausibility points to the necessity of research before the hypothesis is written to make sure that your hypothesis has not already been disproven.
#2: Defined Concepts
The more advanced you are in your studies, the more likely that the terms you’re using in your hypothesis are specific to a limited set of knowledge. One of the hypothesis testing examples might include the readability of printed text in newspapers, where you might use words like “kerning” and “x-height.” Unless your readers have a background in graphic design, it’s likely that they won’t know what you mean by these terms. Thus, it’s important to either write what they mean in the hypothesis itself or in the report before the hypothesis.
Here’s what we mean. Which of the following sentences makes more sense to the common person?
If the kerning is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
If the space between letters is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
For people reading your report that are not experts in typography, simply adding a few more words will be helpful in clarifying exactly what the experiment is all about. It’s always a good idea to make your research and findings as accessible as possible.

Good hypotheses ensure that you can observe the results.
#3: Observability
In order to measure the truth or falsity of your hypothesis, you must be able to see your variables and the way they interact. For instance, if your hypothesis is that the flight patterns of satellites affect the strength of certain television signals, yet you don’t have a telescope to view the satellites or a television to monitor the signal strength, you cannot properly observe your hypothesis and thus cannot continue your study.
Some variables may seem easy to observe, but if you do not have a system of measurement in place, you cannot observe your hypothesis properly. Here’s an example: if you’re experimenting on the effect of healthy food on overall happiness, but you don’t have a way to monitor and measure what “overall happiness” means, your results will not reflect the truth. Monitoring how often someone smiles for a whole day is not reasonably observable, but having the participants state how happy they feel on a scale of one to ten is more observable.
In writing your hypothesis, always keep in mind how you'll execute the experiment.
#4: Generalizability
Perhaps you’d like to study what color your best friend wears the most often by observing and documenting the colors she wears each day of the week. This might be fun information for her and you to know, but beyond you two, there aren’t many people who could benefit from this experiment. When you start an experiment, you should note how generalizable your findings may be if they are confirmed. Generalizability is basically how common a particular phenomenon is to other people’s everyday life.
Let’s say you’re asking a question about the health benefits of eating an apple for one day only, you need to realize that the experiment may be too specific to be helpful. It does not help to explain a phenomenon that many people experience. If you find yourself with too specific of a hypothesis, go back to asking the big question: what is it that you want to know, and what do you think will happen between your two variables?

Hypothesis Testing Examples
We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you’ve seen some good hypothesis examples. We’ve included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses.
Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
You are a student at PrepScholar University. When you walk around campus, you notice that, when the temperature is above 60 degrees, more students study in the quad. You want to know when your fellow students are more likely to study outside. With this information, how do you make the best hypothesis possible?
You must remember to make additional observations and do secondary research before writing your hypothesis. In doing so, you notice that no one studies outside when it’s 75 degrees and raining, so this should be included in your experiment. Also, studies done on the topic beforehand suggested that students are more likely to study in temperatures less than 85 degrees. With this in mind, you feel confident that you can identify your variables and write your hypotheses:
If-then: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, significantly fewer students will study outside.”
Null: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, the same number of students will study outside as when it is more than 60 degrees.”
These hypotheses are plausible, as the temperatures are reasonably within the bounds of what is possible. The number of people in the quad is also easily observable. It is also not a phenomenon specific to only one person or at one time, but instead can explain a phenomenon for a broader group of people.
To complete this experiment, you pick the month of October to observe the quad. Every day (except on the days where it’s raining)from 3 to 4 PM, when most classes have released for the day, you observe how many people are on the quad. You measure how many people come and how many leave. You also write down the temperature on the hour.
After writing down all of your observations and putting them on a graph, you find that the most students study on the quad when it is 70 degrees outside, and that the number of students drops a lot once the temperature reaches 60 degrees or below. In this case, your research report would state that you accept or “failed to reject” your first hypothesis with your findings.
Experiment #2: The Cupcake Store (Forming a Simple Experiment)
Let’s say that you work at a bakery. You specialize in cupcakes, and you make only two colors of frosting: yellow and purple. You want to know what kind of customers are more likely to buy what kind of cupcake, so you set up an experiment. Your independent variable is the customer’s gender, and the dependent variable is the color of the frosting. What is an example of a hypothesis that might answer the question of this study?
Here’s what your hypotheses might look like:
If-then: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will buy more yellow cupcakes than purple cupcakes.”
Null: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will be just as likely to buy purple cupcakes as yellow cupcakes.”
This is a pretty simple experiment! It passes the test of plausibility (there could easily be a difference), defined concepts (there’s nothing complicated about cupcakes!), observability (both color and gender can be easily observed), and general explanation ( this would potentially help you make better business decisions ).

Experiment #3: Backyard Bird Feeders (Integrating Multiple Variables and Rejecting the If-Then Hypothesis)
While watching your backyard bird feeder, you realized that different birds come on the days when you change the types of seeds. You decide that you want to see more cardinals in your backyard, so you decide to see what type of food they like the best and set up an experiment.
However, one morning, you notice that, while some cardinals are present, blue jays are eating out of your backyard feeder filled with millet. You decide that, of all of the other birds, you would like to see the blue jays the least. This means you'll have more than one variable in your hypothesis. Your new hypotheses might look like this:
If-then: “If sunflower seeds are placed in the bird feeders, then more cardinals will come than blue jays. If millet is placed in the bird feeders, then more blue jays will come than cardinals.”
Null: “If either sunflower seeds or millet are placed in the bird, equal numbers of cardinals and blue jays will come.”
Through simple observation, you actually find that cardinals come as often as blue jays when sunflower seeds or millet is in the bird feeder. In this case, you would reject your “if-then” hypothesis and “fail to reject” your null hypothesis . You cannot accept your first hypothesis, because it’s clearly not true. Instead you found that there was actually no relation between your different variables. Consequently, you would need to run more experiments with different variables to see if the new variables impact the results.

Experiment #4: In-Class Survey (Including an Alternative Hypothesis)
You’re about to give a speech in one of your classes about the importance of paying attention. You want to take this opportunity to test a hypothesis you’ve had for a while:
If-then: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will listen better than students who do not.
Null: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will not listen better or worse than students who do not.
You give your speech and then ask your teacher if you can hand out a short survey to the class. On the survey, you’ve included questions about some of the topics you talked about. When you get back the results, you’re surprised to see that not only do the students in the first two rows not pay better attention, but they also scored worse than students in other parts of the classroom! Here, both your if-then and your null hypotheses are not representative of your findings. What do you do?
This is when you reject both your if-then and null hypotheses and instead create an alternative hypothesis . This type of hypothesis is used in the rare circumstance that neither of your hypotheses is able to capture your findings . Now you can use what you’ve learned to draft new hypotheses and test again!
Key Takeaways: Hypothesis Writing
The more comfortable you become with writing hypotheses, the better they will become. The structure of hypotheses is flexible and may need to be changed depending on what topic you are studying. The most important thing to remember is the purpose of your hypothesis and the difference between the if-then and the null . From there, in forming your hypothesis, you should constantly be asking questions, making observations, doing secondary research, and considering your variables. After you have written your hypothesis, be sure to edit it so that it is plausible, clearly defined, observable, and helpful in explaining a general phenomenon.
Writing a hypothesis is something that everyone, from elementary school children competing in a science fair to professional scientists in a lab, needs to know how to do. Hypotheses are vital in experiments and in properly executing the scientific method . When done correctly, hypotheses will set up your studies for success and help you to understand the world a little better, one experiment at a time.

What’s Next?
If you’re studying for the science portion of the ACT, there’s definitely a lot you need to know. We’ve got the tools to help, though! Start by checking out our ultimate study guide for the ACT Science subject test. Once you read through that, be sure to download our recommended ACT Science practice tests , since they’re one of the most foolproof ways to improve your score. (And don’t forget to check out our expert guide book , too.)
If you love science and want to major in a scientific field, you should start preparing in high school . Here are the science classes you should take to set yourself up for success.
If you’re trying to think of science experiments you can do for class (or for a science fair!), here’s a list of 37 awesome science experiments you can do at home
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!

What is Research Hypothesis: Definition, Types, and How to Develop
Read the blog to learn how a research hypothesis provides a clear and focused direction for a study and helps formulate research questions.
June 28, 2024

In this Article
A research hypothesis provides a clear, testable statement that guides the direction and focus of a study.
The benefit is that the hypothesis makes selecting appropriate research methods or statistical means possible, making the analysis more effective and achieving a result. Above all, the idea selected for the research also makes the study more focused, and the hypothesis does that best of all. Finally, when researchers propose and test a hypothesis, they can confirm, enhance, reconsider, or reject any theories.
In this blog, we'll explore the concept of a research hypothesis, its significance in research, and the various types utilized in scientific studies. Additionally, we'll provide a step-by-step guide on formulating your research hypothesis and methods for testing and evaluating it.
What is a Research Hypothesis?
A research hypothesis is a foundational element in both qualitative and quantitative research . It is a precise, testable statement that predicts a possible relationship between two or more variables. This hypothesis is developed based on existing theories, observations, or previous research and aims to provide a direction for further investigation.
A research hypothesis starts with a question a researcher is trying to answer. It implies its effect or outcome and provides a basic ground to construct investigations, surveys, or other methods. It explains what a researcher can expect to find. Once the expectations are clearly stated, a researcher will build the methodology by choosing methods and tools for data collection and analysis.
Examples of Research Hypothesis
Here are some examples of research hypotheses across various fields:
- Hypothesis: Individuals who practice mindfulness meditation daily will report lower levels of stress compared to those who do not practice mindfulness.
- Independent Variable: Mindfulness meditation practice.
- Dependent Variable: Levels of stress.
- Hypothesis: Students who receive personalized tutoring in math will perform better on standardized tests than those who do not.
- Independent Variable: Personalized tutoring in math.
- Dependent Variable: Performance on standardized tests.
- Hypothesis: Consumers exposed to advertisements with emotional appeals will have a higher purchase intention than those with rational appeals.
- Independent Variable: Type of advertisement appeal (emotional vs. rational).
- Dependent Variable: Purchase intent .
- Hypothesis: Increasing the minimum wage will decrease employee turnover rates in the retail sector.
- Independent Variable: Minimum wage increase.
- Dependent Variable: Employee turnover rates in the retail sector.
Technology:
- Hypothesis: Users who receive personalized recommendations on a streaming platform will spend more time watching content than users who do not receive personalized recommendations.
- Independent Variable: Personalized recommendations.
- Dependent Variable: Time spent watching content.
[ Note : Here, Independent Variable is the factor manipulated or controlled in an experiment to observe its effect.
Dependent Variable is the factor that is measured or observed in an experiment to assess the impact of the independent variable.]
What is the Importance of Hypothesis in Research?

The importance of a hypothesis in research cannot be overstated, as it serves several crucial functions in the scientific inquiry process.
Here are the key reasons why hypotheses are fundamental to research:
1. Guides the Research Process
A hypothesis gives a study a clear direction as it outlines what you intend to study and establishes the relationship you are trying to find between variables. It is precise and to the point, which helps formulate your research questions and plan your methods. Using a hypothesis helps organize the testing process from the beginning to the end of the study.
2. Defines the Variables
A well-formulated hypothesis specifies the independent and dependent variables. It defines the object of manipulation and measurement. According to the definition, the hypothesis is an assumption about the relationship between the objects of study. Since statistics is a field of research, the hypothesis is a predictive statement that can be tested empirically.
3. Facilitates Testability and Empirical Investigation
A well-defined hypothesis indicates a clear relationship between the studied variables, thus providing a foundation for designing experiments and observations. In some cases, a null hypothesis is stated to subsequently apply the appropriate statistical test to either validate an already formulated and appropriate hypothesis or reject it.
4. Enhances Objectivity
A hypothesis helps minimize researcher bias by proposing a specific prediction. It forces the researcher to rely on empirical data rather than subjective opinions or beliefs. This objectivity is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the scientific process and ensuring that the findings are credible and reliable.
5. Promotes Critical Thinking and Theoretical Frameworks
Creating a reasonable and viable hypothesis starts with deeply understanding the problem and the field. With a clear sense of the scope of existing evidence and knowledge, there would be a way to go beyond what other researchers have already done. By thoroughly reviewing the literature, researchers are in a position to critically evaluate it and identify problems or questions that remain unresolved.
6. Enables Structured Analysis and Interpretation
A hypothesis is a tentative assumption that provides a context for data analysis and interpretation. It allows for determining specific statistical tests to run and understanding how to interpret them. If the results support the hypothesis, then there is sufficient evidence to claim and infer that the chosen variables are related in a particular way to each other.
If the hypothesis does not match the outcomes, it raises the question of the theoretical assumptions supporting it and additional testing that may be indicated.
7. Drives Scientific Progress
Testing hypotheses continually allows researchers to enrich knowledge beyond merely investigating a particular aspect. The data supporting both hypotheses, the data refuting them, may give rise to new theories, which may serve as the foundation for new research. Such a loop significantly benefits researchers who need to extend their understanding of a particular aspect of the outer world.
{{cta-button}}
What Are The Types of Research Hypotheses?
Research hypotheses can broadly be categorized into several types, each serving different purposes in scientific inquiry.
Here are the main types of research hypotheses:
1. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis posits a relationship between two variables. It suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship without specifying the direction of the effect. For example:
"Increased exercise leads to improved cardiovascular health."
2. Complex Hypothesis
Complex hypotheses involve relationships between multiple variables. These hypotheses may propose how several factors interact to produce a particular outcome. For example:
"The interaction between genetic predisposition, diet, and exercise influences longevity."
3. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis suggests that there is a relationship between two variables, but it does not imply causation. It states that changes in one variable are associated with changes in another. For example:
"There is a correlation between income level and access to healthcare services."
4. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis asserts that changes in one variable directly cause changes in another. It implies a cause-and-effect relationship that can be tested through experimentation or controlled observation. For example:
"Increased consumption of sugary drinks causes an increase in body weight."
5. Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. It specifies whether one variable will increase or decrease in response to changes in another variable. For example:
"Higher levels of education lead to higher income levels."
6. Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis does not predict the direction of the relationship between variables. It simply suggests that there is a relationship without specifying whether one variable will increase or decrease in response to changes in another variable. For example:
"There is a relationship between social media use and levels of anxiety."
7. Null Hypothesis (H₀)
The null hypothesis states no significant relationship exists between the variables being studied. It proposes that any observed differences or effects are due to random chance or sampling error. It is often used to test against the alternative hypothesis (H₁), which proposes the existence of a relationship or effect. For example:
"There is no significant difference in test scores between students who study with music and students who study in silence."
How to Develop a Research Hypothesis?

Developing a research hypothesis involves a systematic process to ensure clarity, testability, and relevance to the research question. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to develop a research hypothesis:
Step 1: Identify the Research Problem or Question
Start by clearly defining the research problem or question you want to investigate. This could be based on gaps in existing literature, observations, theories, or practical issues.
Step 2: Review Existing Literature
Conduct a thorough review of relevant literature to understand what is already known about the topic. Identify theories, findings, and gaps in knowledge that can help inform the development of your hypothesis.
Step 3: Specify Variables
Identify the variables involved in your study. Variables are measurable traits, conditions, or characteristics that can change or vary.
Specifically, determine:
Independent Variable: The factor you manipulate or study in your research.
Dependent Variable: The outcome or response you are measuring or observing about the independent variable.
Step 4: Formulate a Hypothesis
Formulate a clear and specific hypothesis based on your research problem, literature review, and identified variables. A good hypothesis should:
State the expected relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
Be testable through empirical research methods (e.g., experiments, surveys, observations).
Be concise and specific, avoiding ambiguity.
Simple hypothesis: "Increased exposure to sunlight leads to higher levels of vitamin D in humans."
Directional hypothesis: "Children who participate in regular physical activity will have lower levels of obesity than children who do not."
Non-directional hypothesis: "There is a relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover."
Step 5: Consider Alternative Hypotheses
While formulating your hypothesis, consider alternative explanations or hypotheses that could also explain the relationship between your variables. This helps in ensuring that your hypothesis is well-grounded and comprehensive.
Step 6: Ensure Testability
Ensure that your hypothesis is testable using appropriate research methods and techniques. Define how to measure or manipulate the variables to gather empirical evidence supporting or refuting your hypothesis.
Step 7: Write and Refine
Write down your hypothesis in a clear and concise statement. Revise and refine it as needed to improve clarity and specificity. Ensure that it aligns with the objectives of your study and effectively addresses the research question.
Step 8: Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your hypothesis, seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or peers in your field. Their input can help identify potential weaknesses or ambiguities in your hypothesis and suggest improvements.
Step 9: Finalize Your Hypothesis
Once you have refined your hypothesis based on feedback and considerations, finalize it as the guiding statement for your research study.
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
A good research hypothesis possesses several key characteristics that make it effective and suitable for investigation:
1. Clear and Specific
The hypothesis should be precise in its wording and focus. It should clearly state what the researcher intends to investigate or test.
2. Testable
A hypothesis must be capable of being empirically tested and verified or falsified through observation or experimentation. This means there should be a way to gather data that supports or refutes the hypothesis.
3. Falsifiable
There must be a possibility of proving the hypothesis false. A hypothesis that cannot be proven false typically falls outside scientific inquiry. This criterion ensures that research remains objective and open to revision based on evidence.
4. Grounded in Theory
A good hypothesis is usually based on existing theories or literature. It should be informed by a solid understanding of the topic and build upon previous research findings or established principles.
5. Rationale
It should provide a logical rationale or explanation for the expected outcome. This rationale is often derived from the literature review or preliminary observations.
6. Empirical Relevance
The hypothesis should address a question relevant to the field of study and contribute to existing knowledge. It should propose a relationship or difference between variables that is worth investigating.
While the hypothesis should be clear and specific, it should also be concise and to the point. It typically consists of a statement or a few sentences summarizing the expected relationship between variables.
8. Variables
A hypothesis should identify the variables involved and specify how they are expected to relate. This includes independent variables (the factors that are manipulated or controlled) and dependent variables (the outcomes or effects being measured).
9. Observable and Measurable
The variables in the hypothesis should be observable and measurable, allowing for data collection that can be analyzed statistically.
10. Revisable
A hypothesis is not a conclusion but a tentative assumption or prediction that guides the research process. It should be open to revision based on the study's findings.
The Role of Decode in Testing Research Hypotheses

Decode is a powerful survey and consumer research platform powered by Insights AI, that can be instrumental in testing research hypotheses.
Here's how Decode can support you in this process:
- Survey Design and Data Collection: Craft targeted questions using Decode's intuitive interface to gather relevant data for your research.
- Exploratory Research: Conduct exploratory research to understand the landscape of your topic—Leverage Decode's functionalities for surveys and feedback mechanisms to gain valuable insights from your target audience.
- Literature Review and Background Research: Supplement your literature review by collecting data on sample populations' opinions, experiences, and preferences through Decode surveys . This combined data and a thorough literature evaluation can help you build a well-grounded hypothesis with a strong foundation in real-world knowledge.
- Identifying Variables: Design targeted survey questions within Decode to pinpoint relevant variables crucial to your research topic.
- Testing Assumptions: Before solidifying your research hypothesis, informally test your assumptions using surveys created on Decode. This allows for early feedback and potential refinement.
- Data Analysis Tools: Decode provides built-in data analysis tools. Utilize these tools to uncover patterns, correlations, and trends within the data you collect through your surveys.
- Refining Your Hypotheses: As you gather data through Decode surveys, you can continuously adjust and refine your hypotheses based on the real-world responses you receive. This iterative process ensures your hypothesis stays aligned with the insights you uncover.
Final Words
A research hypothesis serves as a guide for scientists. It is a tested idea that applies across different fields, including medicine, social sciences, and natural sciences. Integrating theories with hands-on information assists researchers in exploring and discovering new information.
Decode is a valuable tool for researchers. It simplifies creating surveys, gathering data, and analyzing information. It supports all types of research, from forming hypotheses to testing them. Start a free trial to explore its features and maximize your research potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a research hypothesis example.
A research hypothesis example is: "Students who receive daily math tutoring will have higher test scores than students who do not."
What do you write in a research hypothesis?
In a research hypothesis, you write a clear and testable statement predicting the relationship between two or more variables. It should specify the variables and the expected outcome.
What is the purpose of a research hypothesis?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus, mi quis viverra ornare, eros dolor interdum nulla, ut commodo diam libero vitae erat. Aenean faucibus nibh et justo cursus id rutrum lorem imperdiet. Nunc ut sem vitae risus tristique posuere.
With lots of unique blocks, you can easily build a page without coding.
Click on Study templates
Start from scratch
Add blocks to the content
Saving the Template
Publish the Template
A research hypothesis provides a focused direction for research. It guides the study design, data collection, and analysis by predicting a specific outcome that can be tested.
What are the three major types of hypotheses?
The three major types of hypotheses are:
- Null Hypothesis (H₀): States that there is no effect or relationship between variables.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H₁): Suggests that there is an effect or relationship between variables.
- Directional Hypothesis: Specifies the expected direction of the relationship between variables (e.g., positive or negative).
Soham is a true Manchester United fan who finds joy in more than just football. Whether navigating the open road, scoring virtual goals in FIFA, reading novels, or enjoying quality time with friends, Soham embraces a life full of diverse passions.
Product Marketing Specialist
Related Articles

TAM SAM SOM: What It Means and How to Calculate It?
Understanding TAM, SAM, SOM helps businesses gauge market potential. Learn their definitions and how to calculate them for better business decisions and strategy.

Understanding Likert Scales: Advantages, Limitations, and Questions
Using Likert scales can help you understand how your customers view and rate your product. Here's how you can use them to get the feedback you need.

Mastering the 80/20 Rule to Transform User Research
Find out how the Pareto Principle can optimize your user research processes and lead to more impactful results with the help of AI.

Understanding Consumer Psychology: The Science Behind What Makes Us Buy
Gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer psychology and learn how to apply these insights to inform your research and strategies.

A Guide to Website Footers: Best Design Practices & Examples
Explore the importance of website footers, design best practices, and how to optimize them using UX research for enhanced user engagement and navigation.

Customer Effort Score: Definition, Examples, Tips
A great customer score can lead to dedicated, engaged customers who can end up being loyal advocates of your brand. Here's what you need to know about it.

How to Detect and Address User Pain Points for Better Engagement
Understanding user pain points can help you provide a seamless user experiences that makes your users come back for more. Here's what you need to know about it.

What is Quota Sampling? Definition, Types, Examples, and How to Use It?
Discover Quota Sampling: Learn its process, types, and benefits for accurate consumer insights and informed marketing decisions. Perfect for researchers and brand marketers!

What Is Accessibility Testing? A Comprehensive Guide
Ensure inclusivity and compliance with accessibility standards through thorough testing. Improve user experience and mitigate legal risks. Learn more.

Maximizing Your Research Efficiency with AI Transcriptions
Explore how AI transcription can transform your market research by delivering precise and rapid insights from audio and video recordings.

Understanding the False Consensus Effect: How to Manage it
The false consensus effect can cause incorrect assumptions and ultimately, the wrong conclusions. Here's how you can overcome it.

5 Banking Customer Experience Trends to Watch Out for in 2024
Discover the top 5 banking customer experience trends to watch out for in 2024. Stay ahead in the evolving financial landscape.

The Ultimate Guide to Regression Analysis: Definition, Types, Usage & Advantages
Master Regression Analysis: Learn types, uses & benefits in consumer research for precise insights & strategic decisions.

EyeQuant Alternative
Meet Qatalyst, your best eyequant alternative to improve user experience and an AI-powered solution for all your user research needs.

EyeSee Alternative
Embrace the Insights AI revolution: Meet Decode, your innovative solution for consumer insights, offering a compelling alternative to EyeSee.

Skeuomorphism in UX Design: Is It Dead?
Skeuomorphism in UX design creates intuitive interfaces using familiar real-world visuals to help users easily understand digital products. Do you know how?

Top 6 Wireframe Tools and Ways to Test Your Designs
Wireframe tools assist designers in planning and visualizing the layout of their websites. Look through this list of wireframing tools to find the one that suits you best.

Revolutionizing Customer Interaction: The Power of Conversational AI
Conversational AI enhances customer service across various industries, offering intelligent, context-aware interactions that drive efficiency and satisfaction. Here's how.

User Story Mapping: A Powerful Tool for User-Centered Product Development
Learn about user story mapping and how it can be used for successful product development with this blog.

Understanding Customer Retention: How to Keep Your Customers Coming Back
Understanding customer retention is key to building a successful brand that has repeat, loyal customers. Here's what you need to know about it.

Demographic Segmentation: How Brands Can Use it to Improve Marketing Strategies
Read this blog to learn what demographic segmentation means, its importance, and how it can be used by brands.

Mastering Product Positioning: A UX Researcher's Guide
Read this blog to understand why brands should have a well-defined product positioning and how it affects the overall business.

Discrete Vs. Continuous Data: Everything You Need To Know
Explore the differences between discrete and continuous data and their impact on business decisions and customer insights.

50+ Employee Engagement Survey Questions
Understand how an employee engagement survey provides insights into employee satisfaction and motivation, directly impacting productivity and retention.

What is Experimental Research: Definition, Types & Examples
Understand how experimental research enables researchers to confidently identify causal relationships between variables and validate findings, enhancing credibility.

A Guide to Interaction Design
Interaction design can help you create engaging and intuitive user experiences, improving usability and satisfaction through effective design principles. Here's how.

Exploring the Benefits of Stratified Sampling
Understanding stratified sampling can improve research accuracy by ensuring diverse representation across key subgroups. Here's how.

A Guide to Voice Recognition in Enhancing UX Research
Learn the importance of using voice recognition technology in user research for enhanced user feedback and insights.

The Ultimate Figma Design Handbook: Design Creation and Testing
The Ultimate Figma Design Handbook covers setting up Figma, creating designs, advanced features, prototyping, and testing designs with real users.

The Power of Organization: Mastering Information Architectures
Understanding the art of information architectures can enhance user experiences by organizing and structuring digital content effectively, making information easy to find and navigate. Here's how.

Convenience Sampling: Examples, Benefits, and When To Use It
Read the blog to understand how convenience sampling allows for quick and easy data collection with minimal cost and effort.

What is Critical Thinking, and How Can it be Used in Consumer Research?
Learn how critical thinking enhances consumer research and discover how Decode's AI-driven platform revolutionizes data analysis and insights.

How Business Intelligence Tools Transform User Research & Product Management
This blog explains how Business Intelligence (BI) tools can transform user research and product management by providing data-driven insights for better decision-making.

What is Face Validity? Definition, Guide and Examples
Read this blog to explore face validity, its importance, and the advantages of using it in market research.

What is Customer Lifetime Value, and How To Calculate It?
Read this blog to understand how Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) can help your business optimize marketing efforts, improve customer retention, and increase profitability.

Systematic Sampling: Definition, Examples, and Types
Explore how systematic sampling helps researchers by providing a structured method to select representative samples from larger populations, ensuring efficiency and reducing bias.

Understanding Selection Bias: A Guide
Selection bias can affect the type of respondents you choose for the study and ultimately the quality of responses you receive. Here’s all you need to know about it.

A Guide to Designing an Effective Product Strategy
Read this blog to explore why a well-defined product strategy is required for brands while developing or refining a product.

A Guide to Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in UX: Definition, Strategies, and Examples
Discover what an MVP is, why it's crucial in UX, strategies for creating one, and real-world examples from top companies like Dropbox and Airbnb.

Asking Close Ended Questions: A Guide
Asking the right close ended questions is they key to getting quantitiative data from your users. Her's how you should do it.

Creating Website Mockups: Your Ultimate Guide to Effective Design
Read this blog to learn website mockups- tools, examples and how to create an impactful website design.

Understanding Your Target Market And Its Importance In Consumer Research
Read this blog to learn about the importance of creating products and services to suit the needs of your target audience.

What Is a Go-To-Market Strategy And How to Create One?
Check out this blog to learn how a go-to-market strategy helps businesses enter markets smoothly, attract more customers, and stand out from competitors.

What is Confirmation Bias in Consumer Research?
Learn how confirmation bias affects consumer research, its types, impacts, and practical tips to avoid it for more accurate and reliable insights.

Market Penetration: The Key to Business Success
Understanding market penetration is key to cracking the code to sustained business growth and competitive advantage in any industry. Here's all you need to know about it.

How to Create an Effective User Interface
Having a simple, clear user interface helps your users find what they really want, improving the user experience. Here's how you can achieve it.

Product Differentiation and What It Means for Your Business
Discover how product differentiation helps businesses stand out with unique features, innovative designs, and exceptional customer experiences.

What is Ethnographic Research? Definition, Types & Examples
Read this blog to understand Ethnographic research, its relevance in today’s business landscape and how you can leverage it for your business.

Product Roadmap: The 2024 Guide [with Examples]
Read this blog to understand how a product roadmap can align stakeholders by providing a clear product development and delivery plan.

Product Market Fit: Making Your Products Stand Out in a Crowded Market
Delve into the concept of product-market fit, explore its significance, and equip yourself with practical insights to achieve it effectively.

Consumer Behavior in Online Shopping: A Comprehensive Guide
Ever wondered how online shopping behavior can influence successful business decisions? Read on to learn more.

How to Conduct a First Click Test?
Why are users leaving your site so fast? Learn how First Click Testing can help. Discover quick fixes for frustration and boost engagement.

What is Market Intelligence? Methods, Types, and Examples
Read the blog to understand how marketing intelligence helps you understand consumer behavior and market trends to inform strategic decision-making.

What is a Longitudinal Study? Definition, Types, and Examples
Is your long-term research strategy unclear? Learn how longitudinal studies decode complexity. Read on for insights.

What Is the Impact of Customer Churn on Your Business?
Understanding and reducing customer churn is the key to building a healthy business that keeps customers satisfied. Here's all you need to know about it.

The Ultimate Design Thinking Guide
Discover the power of design thinking in UX design for your business. Learn the process and key principles in our comprehensive guide.

100+ Yes Or No Survey Questions Examples
Yes or no survey questions simplify responses, aiding efficiency, clarity, standardization, quantifiability, and binary decision-making. Read some examples!

What is Customer Segmentation? The ULTIMATE Guide
Explore how customer segmentation targets diverse consumer groups by tailoring products, marketing, and experiences to their preferred needs.

Crafting User-Centric Websites Through Responsive Web Design
Find yourself reaching for your phone instead of a laptop for regular web browsing? Read on to find out what that means & how you can leverage it for business.

How Does Product Placement Work? Examples and Benefits
Read the blog to understand how product placement helps advertisers seek subtle and integrated ways to promote their products within entertainment content.

The Importance of Reputation Management, and How it Can Make or Break Your Brand
A good reputation management strategy is crucial for any brand that wants to keep its customers loyal. Here's how brands can focus on it.

A Comprehensive Guide to Human-Centered Design
Are you putting the human element at the center of your design process? Read this blog to understand why brands must do so.

How to Leverage Customer Insights to Grow Your Business
Genuine insights are becoming increasingly difficult to collect. Read on to understand the challenges and what the future holds for customer insights.

The Complete Guide to Behavioral Segmentation
Struggling to reach your target audience effectively? Discover how behavioral segmentation can transform your marketing approach. Read more in our blog!

Creating a Unique Brand Identity: How to Make Your Brand Stand Out
Creating a great brand identity goes beyond creating a memorable logo - it's all about creating a consistent and unique brand experience for your cosnumers. Here's everything you need to know about building one.

Understanding the Product Life Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the product life cycle, or the stages a product goes through from its launch to its sunset can help you understand how to market it at every stage to create the most optimal marketing strategies.

Empathy vs. Sympathy in UX Research
Are you conducting UX research and seeking guidance on conducting user interviews with empathy or sympathy? Keep reading to discover the best approach.

What is Exploratory Research, and How To Conduct It?
Read this blog to understand how exploratory research can help you uncover new insights, patterns, and hypotheses in a subject area.

First Impressions & Why They Matter in User Research
Ever wonder if first impressions matter in user research? The answer might surprise you. Read on to learn more!

Cluster Sampling: Definition, Types & Examples
Read this blog to understand how cluster sampling tackles the challenge of efficiently collecting data from large, spread-out populations.

Top Six Market Research Trends in 2024
Curious about where market research is headed? Read on to learn about the changes surrounding this field in 2024 and beyond.

Lyssna Alternative
Meet Qatalyst, your best lyssna alternative to usability testing, to create a solution for all your user research needs.

What is Feedback Loop? Definition, Importance, Types, and Best Practices
Struggling to connect with your customers? Read the blog to learn how feedback loops can solve your problem!

UI vs. UX Design: What’s The Difference?
Learn how UI solves the problem of creating an intuitive and visually appealing interface and how UX addresses broader issues related to user satisfaction and overall experience with the product or service.

The Impact of Conversion Rate Optimization on Your Business
Understanding conversion rate optimization can help you boost your online business. Read more to learn all about it.

Insurance Questionnaire: Tips, Questions and Significance
Leverage this pre-built customizable questionnaire template for insurance to get deep insights from your audience.

UX Research Plan Template
Read on to understand why you need a UX Research Plan and how you can use a fully customizable template to get deep insights from your users!

Brand Experience: What it Means & Why It Matters
Have you ever wondered how users navigate the travel industry for your research insights? Read on to understand user experience in the travel sector.

Validity in Research: Definitions, Types, Significance, and Its Relationship with Reliability
Is validity ensured in your research process? Read more to explore the importance and types of validity in research.

The Role of UI Designers in Creating Delightful User Interfaces
UI designers help to create aesthetic and functional experiences for users. Here's all you need to know about them.

Top Usability Testing Tools to Try in 2024
Using usability testing tools can help you understand user preferences and behaviors and ultimately, build a better digital product. Here are the top tools you should be aware of.

Understanding User Experience in Travel Market Research
Ever wondered how users navigate the travel industry for your research insights? Read on to understand user experience in the travel sector.

Top 10 Customer Feedback Tools You’d Want to Try
Explore the top 10 customer feedback tools for analyzing feedback, empowering businesses to enhance customer experience.

10 Best UX Communities on LinkedIn & Slack for Networking & Collaboration
Discover the significance of online communities in UX, the benefits of joining communities on LinkedIn and Slack, and insights into UX career advancement.

The Role of Customer Experience Manager in Consumer Research
This blog explores the role of Customer Experience Managers, their skills, their comparison with CRMs, their key metrics, and why they should use a consumer research platform.

Product Review Template
Learn how to conduct a product review and get insights with this template on the Qatalyst platform.

What Is the Role of a Product Designer in UX?
Product designers help to create user-centric digital experiences that cater to users' needs and preferences. Here's what you need to know about them.

Top 10 Customer Journey Mapping Tools For Market Research in 2024
Explore the top 10 tools in 2024 to understand customer journeys while conducting market research.

Generative AI and its Use in Consumer Research
Ever wondered how Generative AI fits in within the research space? Read on to find its potential in the consumer research industry.

All You Need to Know About Interval Data: Examples, Variables, & Analysis
Understand how interval data provides precise numerical measurements, enabling quantitative analysis and statistical comparison in research.

How to Use Narrative Analysis in Research
Find the advantages of using narrative analysis and how this method can help you enrich your research insights.
A Guide to Asking the Right Focus Group Questions
Moderated discussions with multiple participants to gather diverse opinions on a topic.

From Idea to Impact: Demystifying the Process of New Product Development
What are the stages to be undertaken during a new product development? Read all about it here.

How to Conduct Agile UX Research?
Navigating the Agile landscape: A comprehensive guide to conducting Agile UX Research with AI-powered research platforms

How Chief Product Officers Leverage User Research for Business Success
Understand the changing role of Chief Product Officers and how they should respond to evolving customer needs with user research.

Top 10 Tree Testing Tools in 2024
This blog will help you pick the best tree testing tool for you that can be utilized to identify usability issues in the website or app navigation.

Top 10 UX Design Trends in 2024
What are some of the top UX design trends that will be at the forefront in 2024? Read on to find out.

From Vision to Execution: The Essential Role of Brand Strategists in Building Strong Brands
Brand strategists help to shape the identity, perception, and market positioning of a brand. Here’s everything you need to know about them.

Conducting a Descriptive Research Design for Consumer Research
Discover the advantages of descriptive market research and why you should implement it to create an impact within your industry domain.
Maximize Your Research Potential
Experience why teams worldwide trust our Consumer & User Research solutions.
Book a Demo

Definition of a Hypothesis
What it is and how it's used in sociology
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Recommended Reading
- Archaeology
A hypothesis is a prediction of what will be found at the outcome of a research project and is typically focused on the relationship between two different variables studied in the research. It is usually based on both theoretical expectations about how things work and already existing scientific evidence.
Within social science, a hypothesis can take two forms. It can predict that there is no relationship between two variables, in which case it is a null hypothesis . Or, it can predict the existence of a relationship between variables, which is known as an alternative hypothesis.
In either case, the variable that is thought to either affect or not affect the outcome is known as the independent variable, and the variable that is thought to either be affected or not is the dependent variable.
Researchers seek to determine whether or not their hypothesis, or hypotheses if they have more than one, will prove true. Sometimes they do, and sometimes they do not. Either way, the research is considered successful if one can conclude whether or not a hypothesis is true.
Null Hypothesis
A researcher has a null hypothesis when she or he believes, based on theory and existing scientific evidence, that there will not be a relationship between two variables. For example, when examining what factors influence a person's highest level of education within the U.S., a researcher might expect that place of birth, number of siblings, and religion would not have an impact on the level of education. This would mean the researcher has stated three null hypotheses.
Alternative Hypothesis
Taking the same example, a researcher might expect that the economic class and educational attainment of one's parents, and the race of the person in question are likely to have an effect on one's educational attainment. Existing evidence and social theories that recognize the connections between wealth and cultural resources , and how race affects access to rights and resources in the U.S. , would suggest that both economic class and educational attainment of the one's parents would have a positive effect on educational attainment. In this case, economic class and educational attainment of one's parents are independent variables, and one's educational attainment is the dependent variable—it is hypothesized to be dependent on the other two.
Conversely, an informed researcher would expect that being a race other than white in the U.S. is likely to have a negative impact on a person's educational attainment. This would be characterized as a negative relationship, wherein being a person of color has a negative effect on one's educational attainment. In reality, this hypothesis proves true, with the exception of Asian Americans , who go to college at a higher rate than whites do. However, Blacks and Hispanics and Latinos are far less likely than whites and Asian Americans to go to college.
Formulating a Hypothesis
Formulating a hypothesis can take place at the very beginning of a research project , or after a bit of research has already been done. Sometimes a researcher knows right from the start which variables she is interested in studying, and she may already have a hunch about their relationships. Other times, a researcher may have an interest in a particular topic, trend, or phenomenon, but he may not know enough about it to identify variables or formulate a hypothesis.
Whenever a hypothesis is formulated, the most important thing is to be precise about what one's variables are, what the nature of the relationship between them might be, and how one can go about conducting a study of them.
Updated by Nicki Lisa Cole, Ph.D
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- What It Means When a Variable Is Spurious
- Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
- Difference Between Independent and Dependent Variables
- The Difference Between Control Group and Experimental Group
- Lambda and Gamma as Defined in Sociology
- What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
- Understanding Path Analysis
- Visualizing Social Stratification in the U.S.
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Deductive Versus Inductive Reasoning
- Example of a Chi-Square Goodness of Fit Test
- What Level of Alpha Determines Statistical Significance?
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- How Intervening Variables Work in Sociology
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Understanding Science
How science REALLY works...
- Understanding Science 101
- Misconceptions
- Testing ideas with evidence is at the heart of the process of science.
- Scientific testing involves figuring out what we would expect to observe if an idea were correct and comparing that expectation to what we actually observe.
Misconception: Science proves ideas.
Misconception: Science can only disprove ideas.
Correction: Science neither proves nor disproves. It accepts or rejects ideas based on supporting and refuting evidence, but may revise those conclusions if warranted by new evidence or perspectives. Read more about it.
Testing scientific ideas
Testing ideas about childbed fever.
As a simple example of how scientific testing works, consider the case of Ignaz Semmelweis, who worked as a doctor on a maternity ward in the 1800s. In his ward, an unusually high percentage of new mothers died of what was then called childbed fever. Semmelweis considered many possible explanations for this high death rate. Two of the many ideas that he considered were (1) that the fever was caused by mothers giving birth lying on their backs (as opposed to on their sides) and (2) that the fever was caused by doctors’ unclean hands (the doctors often performed autopsies immediately before examining women in labor). He tested these ideas by considering what expectations each idea generated. If it were true that childbed fever were caused by giving birth on one’s back, then changing procedures so that women labored on their sides should lead to lower rates of childbed fever. Semmelweis tried changing the position of labor, but the incidence of fever did not decrease; the actual observations did not match the expected results. If, however, childbed fever were caused by doctors’ unclean hands, having doctors wash their hands thoroughly with a strong disinfecting agent before attending to women in labor should lead to lower rates of childbed fever. When Semmelweis tried this, rates of fever plummeted; the actual observations matched the expected results, supporting the second explanation.
Testing in the tropics
Let’s take a look at another, very different, example of scientific testing: investigating the origins of coral atolls in the tropics. Consider the atoll Eniwetok (Anewetak) in the Marshall Islands — an oceanic ring of exposed coral surrounding a central lagoon. From the 1800s up until today, scientists have been trying to learn what supports atoll structures beneath the water’s surface and exactly how atolls form. Coral only grows near the surface of the ocean where light penetrates, so Eniwetok could have formed in several ways:
Hypothesis 2: The coral that makes up Eniwetok might have grown in a ring atop an underwater mountain already near the surface. The key to this hypothesis is the idea that underwater mountains don’t sink; instead the remains of dead sea animals (shells, etc.) accumulate on underwater mountains, potentially assisted by tectonic uplifting. Eventually, the top of the mountain/debris pile would reach the depth at which coral grow, and the atoll would form.
Which is a better explanation for Eniwetok? Did the atoll grow atop a sinking volcano, forming an underwater coral tower, or was the mountain instead built up until it neared the surface where coral were eventually able to grow? Which of these explanations is best supported by the evidence? We can’t perform an experiment to find out. Instead, we must figure out what expectations each hypothesis generates, and then collect data from the world to see whether our observations are a better match with one of the two ideas.
If Eniwetok grew atop an underwater mountain, then we would expect the atoll to be made up of a relatively thin layer of coral on top of limestone or basalt. But if it grew upwards around a subsiding island, then we would expect the atoll to be made up of many hundreds of feet of coral on top of volcanic rock. When geologists drilled into Eniwetok in 1951 as part of a survey preparing for nuclear weapons tests, the drill bored through more than 4000 feet (1219 meters) of coral before hitting volcanic basalt! The actual observation contradicted the underwater mountain explanation and matched the subsiding island explanation, supporting that idea. Of course, many other lines of evidence also shed light on the origins of coral atolls, but the surprising depth of coral on Eniwetok was particularly convincing to many geologists.
- Take a sidetrip
Visit the NOAA website to see an animation of coral atoll formation according to Hypothesis 1.
- Teaching resources
Scientists test hypotheses and theories. They are both scientific explanations for what we observe in the natural world, but theories deal with a much wider range of phenomena than do hypotheses. To learn more about the differences between hypotheses and theories, jump ahead to Science at multiple levels .
- Use our web interactive to help students document and reflect on the process of science.
- Learn strategies for building lessons and activities around the Science Flowchart: Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-12 Grades 13-16
- Find lesson plans for introducing the Science Flowchart to your students in: Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-16
- Get graphics and pdfs of the Science Flowchart to use in your classroom. Translations are available in Spanish, French, Japanese, and Swahili.
Observation beyond our eyes
The logic of scientific arguments
Subscribe to our newsletter
- The science flowchart
- Science stories
- Grade-level teaching guides
- Teaching resource database
- Journaling tool

Science Hypothesis
Ai generator.
Hypothesis are the bedrock of scientific investigation, guiding researchers toward understanding the unknown. Crafting effective science hypotheses involves precise formulation and prediction. This hypothesis statement guide delves into the intricacies of constructing science hypothesis statements, offering practical examples and valuable tips to ensure your hypothesis stand strong against the rigors of experimentation and analysis.
What is Science Hypothesis? – Definition
A science hypothesis is a proposed explanation or educated guess that can be tested through experimentation or observation. It serves as a preliminary assumption or prediction about a phenomenon, often derived from existing knowledge or theories. Science hypotheses are essential for guiding research and helping scientists investigate the validity of their predictions.
What is an example of a hypothesis statement in science?
Example of a hypothesis statement in science: “If the temperature of water increases, then the rate of plant growth will also increase.” This hypothesis predicts a cause-and-effect relationship between water temperature and plant growth, which can be tested through controlled experiments.
100 Science Hypothesis Statement Examples

Size: 223 KB
Science hypotheses lay the foundation for empirical exploration. These Thesis statements predict outcomes based on existing knowledge and guide research. Explore a variety of science hypothesis examples across different disciplines, showcasing the diverse ways scientists propose, test, and validate their assumptions. From physics to biology, chemistry to astronomy, delve into these examples that highlight the essence of scientific inquiry and discovery.
- Physics : If the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull on another object will also increase.
- Biology : If plants are exposed to different light wavelengths, then the one exposed to red light will exhibit the highest growth rate.
- Chemistry : If the concentration of a reactant increases, then the rate of the chemical reaction will also increase.
- Astronomy : If the distance between two galaxies decreases, then their gravitational attraction will intensify.
- Geology : If the temperature of a rock sample increases, then its density will decrease due to expansion.
- Psychology : If individuals are exposed to positive affirmations, then their self-esteem scores will improve.
- Sociology : If economic inequality increases, then crime rates within a community will also rise.
- Environmental Science : If pollution levels decrease in a river, then the diversity of aquatic species will increase.
- Computer Science : If the processing speed of a computer chip increases, then the execution time of a software program will decrease.
- Meteorology : If atmospheric pressure drops significantly, then the likelihood of stormy weather conditions will rise.
- Neuroscience : If individuals engage in regular meditation, then their brain’s gray matter volume in regions associated with mindfulness will increase.
- Economics : If interest rates decrease, then consumer spending will rise due to increased borrowing.
- Anthropology : If a society’s cultural diversity increases, then its acceptance of differing norms and values will also grow.
- Zoology : If predators are introduced to an ecosystem, then the population of prey species will decline.
- Medical Research : If a new drug is administered, then patients with a specific medical condition will experience a reduction in symptoms.
- Nutrition Science : If individuals consume a diet high in antioxidants, then their risk of developing certain chronic diseases will decrease.
- Materials Science : If the temperature of a metal is lowered, then its electrical conductivity will decrease due to reduced kinetic energy.
- Political Science : If voter education initiatives increase, then voter turnout rates in elections will also rise.
- Geography : If urbanization expands in a region, then the average local temperature will increase due to the heat island effect.
- Ecology : If a keystone species is removed from an ecosystem, then the overall biodiversity of that ecosystem will be negatively impacted.
- Medieval History : If trade routes between two civilizations strengthen, then cultural exchange and technological advancements will flourish.
- Microbiology : If a specific bacterium is introduced to a microbial community, then it will outcompete other species for resources.
- Oceanography : If ocean temperatures rise, then coral reefs will experience bleaching due to the loss of symbiotic algae.
- Education : If class sizes are reduced, then student engagement and learning outcomes will improve.
- Genetics : If individuals inherit two recessive alleles for a particular trait, then they will exhibit the trait phenotypically.
- Criminology : If community policing initiatives are implemented, then the crime rate in neighborhoods will decrease due to improved trust between law enforcement and residents.
- Botany : If plants are exposed to varying levels of nutrients, then their growth rate and overall health will be affected accordingly.
- Epidemiology : If individuals are vaccinated against a specific virus, then the incidence of that virus in the population will decline.
- Architecture : If buildings are designed with energy-efficient features, then their energy consumption and environmental impact will be reduced.
- Literary Studies : If readers are exposed to diverse genres of literature, then their vocabulary and literary comprehension will expand.
- Mechanical Engineering : If the surface area of a heat exchanger is increased, then its efficiency in transferring thermal energy will improve.
- Artificial Intelligence : If a machine learning algorithm is trained on a larger dataset, then its accuracy in making predictions will increase.
- Sports Science : If athletes incorporate specific pre-game rituals, then their performance and focus during competitions will improve.
- Archaeology : If a new excavation site is discovered, then artifacts and evidence of past civilizations will be uncovered.
- Film Studies : If films use non-linear storytelling techniques, then audience engagement and interpretation will become more complex.
- Fashion Design : If clothing materials with better breathability are used, then wearers’ comfort levels in hot weather will increase.
- Music Psychology : If listeners are exposed to music with a fast tempo, then their heart rate and energy levels will be positively affected.
- Environmental Engineering : If a wastewater treatment system is upgraded, then the water quality of nearby rivers and streams will improve.
- Philosophy : If ethical dilemmas are discussed openly, then individuals’ moral reasoning and decision-making skills will become more refined.
- Cognitive Science : If individuals practice mindfulness meditation, then their attention span and cognitive control will enhance.
- Political Economy : If trade barriers between two countries are lifted, then their economic interdependence and cooperation will strengthen.
- Agricultural Science : If certain crops are rotated in a field, then soil fertility and nutrient content will be better maintained.
- Cultural Anthropology : If cultural norms change to value gender equality, then the division of labor and social roles will evolve accordingly.
- Linguistics : If a language’s phonetic structure is altered, then the perception and articulation of speech sounds will be affected.
- Religious Studies : If religious festivals are celebrated widely, then social cohesion and a sense of community among participants will increase.
- Urban Planning : If public transportation infrastructure is improved, then the use of private vehicles and traffic congestion will decrease.
- Renewable Energy : If solar panel efficiency increases, then the cost-effectiveness of solar energy as a power source will improve.
- Sustainable Agriculture : If organic farming practices are adopted, then soil health and biodiversity in agricultural fields will be enhanced.
- Human Genetics : If a specific gene mutation is present, then the likelihood of developing a hereditary disease will be higher.
- Space Exploration : If a spacecraft is sent to a distant planet, then the data collected will provide insights into its composition and environment.
- Cultural Studies : If a society values inclusivity in its media representations, then stereotypes and biases will be challenged.
- Quantum Physics : If two entangled particles are measured, then the measurement of one particle will instantaneously affect the state of the other particle, regardless of distance.
- Social Work : If support systems are established for individuals facing addiction, then their likelihood of successful recovery will increase.
- Civil Engineering : If a bridge is constructed using specific materials and design principles, then its load-bearing capacity and structural integrity will be maximized.
- Educational Technology : If interactive learning platforms are integrated into classrooms, then students’ engagement and retention of concepts will rise.
- Animal Behavior : If a specific stimulus is introduced to an animal’s environment, then its behavioral response will indicate whether the stimulus is perceived as positive or negative.
- Public Health : If a vaccination campaign targets a high percentage of the population, then the spread of a contagious disease will be curbed.
- Forensic Science : If DNA evidence is analyzed from a crime scene, then it can be matched to potential suspects or used to exonerate individuals.
- Game Design : If a game incorporates branching storylines, then players’ choices will lead to multiple possible outcomes and endings.
- Gender Studies : If gender stereotypes are challenged in educational settings, then students’ understanding of gender roles and identities will evolve.
- Particle Physics : If a new particle is discovered in particle accelerator experiments, then it may contribute to our understanding of fundamental forces.
- Culinary Science : If cooking techniques are adjusted, then the texture and flavor of a dish will be enhanced.
- Developmental Psychology : If children are exposed to early childhood education programs, then their cognitive and social development will be positively influenced.
- Journalism : If journalists provide unbiased coverage of events, then the public’s perception and understanding of news stories will be more accurate.
- Business Management : If a company implements remote work policies, then employees’ job satisfaction and productivity will be impacted.
- Astronomy : If a telescope observes a distant celestial object, then its light spectrum can reveal information about its composition and distance.
- Climate Science : If greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise, then global temperatures will increase, leading to more frequent and severe climate events.
- Molecular Biology : If a specific gene is mutated, then the protein it codes for may lose its function, leading to a genetic disorder.
- Urban Sociology : If urban planning focuses on mixed-use development, then neighborhoods will become more walkable and vibrant.
- Environmental Science : If deforestation continues in a particular region, then biodiversity loss and habitat destruction will result.
- Educational Psychology : If students receive constructive feedback, then their academic performance and self-esteem will improve.
- Sports Nutrition : If athletes consume a balanced diet, then their energy levels and physical performance will be optimized.
- Industrial Engineering : If a manufacturing process is streamlined, then production efficiency and cost-effectiveness will increase.
- Climate Change Mitigation : If renewable energy sources replace fossil fuels, then carbon emissions and air pollution will decrease.
- Criminal Justice : If restorative justice programs are implemented, then recidivism rates among offenders will decrease.
- Cognitive Neuroscience : If brain imaging techniques are used, then neural activity patterns associated with memory retrieval can be identified.
- Environmental Policy : If conservation policies are enforced, then endangered species populations will have a chance to recover.
- Tourism Management : If sustainable tourism practices are adopted, then the negative impact of tourism on local ecosystems will be minimized.
- Public Opinion Research : If surveys are conducted on political preferences, then insights into voter behavior and attitudes can be gained.
- Sociolinguistics : If language use changes over time, then linguistic patterns and dialects in a community may evolve.
- Consumer Behavior : If marketing strategies incorporate social media influencers, then consumer purchasing decisions will be influenced.
- Digital Communication : If online privacy measures are strengthened, then users’ data security and trust in digital platforms will increase.
- Cancer Research : If a specific genetic mutation is identified, then targeted therapies can be developed to treat the cancer associated with that mutation.
- Human Rights Advocacy : If educational campaigns raise awareness about human rights violations, then public pressure on governments to address these issues will rise.
- Educational Assessment : If standardized tests are redesigned to focus on critical thinking skills, then students’ analytical abilities will be better evaluated.
- Epidemiology : If a specific virus spreads within a community, then the rate of infection and transmission can be studied to develop effective containment strategies.
- Cognitive Psychology : If memory recall is examined under different conditions, then the factors influencing memory retrieval can be identified.
- Financial Economics : If interest rates are lowered by the central bank, then borrowing costs for businesses and individuals will decrease.
- Marine Biology : If ocean temperatures rise due to climate change, then coral bleaching events will become more frequent, leading to coral reef degradation.
- Political Science : If voter turnout is influenced by campaign advertising, then the correlation between media exposure and voting behavior can be analyzed.
- Clinical Psychology : If cognitive-behavioral therapy is administered to individuals with anxiety disorders, then their symptoms will show a reduction.
- Public Policy : If a government enforces stricter regulations on smoking in public spaces, then the prevalence of smoking-related health issues will decline.
- Material Science : If a new material is developed with specific properties, then its potential applications in various industries can be explored.
- Language Acquisition : If children are exposed to multiple languages in their early years, then their linguistic skills may develop differently compared to monolingual children.
- Tourism Economics : If travel restrictions are lifted, then the recovery of the tourism industry and its contribution to the local economy can be assessed.
- Behavioral Economics : If individuals are given incentives to make environmentally friendly choices, then the impact of economic incentives on behavior can be studied.
- Educational Technology : If online learning platforms are used in classrooms, then their effect on student engagement and academic performance can be evaluated.
- Health Policy : If universal healthcare coverage is implemented, then access to medical services and health outcomes for the population can be improved.
- Agricultural Economics : If crop yields are compared between traditional farming methods and modern agricultural practices, then the efficiency of different approaches can be determined.
- Literary Analysis : If a specific theme is analyzed across different literary works, then the ways in which authors address and convey that theme can be explored.
Science Hypothesis Statement Examples for Psychology
These psychology hypothesis pertain to human behaviors, emotions, or cognitive processes. They are tailored to the field of psychology, which studies the human mind and behavior. For instance, “Effects of Sleep on Memory” posits a connection between sleep duration and memory performance.
- Effects of Sleep on Memory : People who sleep 8 hours per night will perform better on memory tests compared to those who sleep only 4 hours.
- Role of Colors in Mood Regulation : Exposure to blue light will decrease feelings of sadness in depressed individuals.
- Childhood Attachment and Adult Relationships : Individuals with secure childhood attachments will have more stable romantic relationships in adulthood.
- Influence of Music on Productivity : Listening to classical music while working increases task completion rates among office workers.
- Gaming and Reaction Time : Regular gamers will have quicker reaction times than non-gamers in response to unexpected stimuli.
- Effects of Meditation on Stress : Individuals who practice daily meditation will report lower stress levels compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Social Media Usage and Loneliness : High usage of social media correlates with increased feelings of loneliness in teenagers.
- Class Size and Student Performance : Students in smaller class sizes will score higher on standardized tests than students in larger class sizes.
- Scent and Memory Recall : People exposed to a specific scent during learning will recall information better when the same scent is present during retrieval.
- Financial Incentives and Motivation : Providing financial incentives will increase motivation for completing mundane tasks.
Simple Science Hypothesis Statement Examples
These are basic and straightforward scientific hypotheses that cover various fields, such as biology or physics. They’re easy to understand even for people without much scientific background. For instance, the simple hypothesis tatement about “Plant Growth” directly relates the use of fertilizer to plant height.
- Plant Growth : Adding fertilizer will make plants grow taller.
- Solar Energy : Increasing sunlight exposure will increase the voltage output of a solar cell.
- Density : Objects made of metal will sink in water.
- Digestion : Enzyme supplements will increase the speed of food digestion.
- Osmosis : Potatoes placed in salt water will shrink due to loss of water.
- Evaporation : Water will evaporate faster on a hot day compared to a cold day.
- Nutrition : Plants given sugar water will develop yellow leaves.
- Magnetism : Increasing the temperature of a magnet will decrease its magnetic strength.
- Conduction : Metals will conduct electricity better than plastics.
- Reflection : Shiny surfaces reflect more light than dull surfaces.
Strong Science Hypothesis Statement Examples
These are more detailed and specific hypotheses, often relating to a well-defined scientific question. They may also suggest a precise outcome or relationship. For example, “Vaccination and Immunity” indicates a specific result (production of specific antibodies) in response to a defined action (vaccinating mice).
- Environmental Toxins and Cell Growth : Exposure to specific environmental toxins will inhibit the division of cells in an organism.
- Nutrition and Cognitive Performance : Diets rich in omega-3 fatty acids will significantly enhance cognitive performance in adults over 60.
- Genetic Mutations and Disease Resistance : Specific genetic mutations in fruit flies will confer resistance to a particular pesticide.
- Neurotransmitters and Behavior : An increase in serotonin levels in the brain will lead to a decrease in aggressive behaviors in rats.
- Plant Pathogens and Resistance : Tomato plants genetically modified to express the XYZ gene will resist infection from the ABC pathogen more effectively than non-modified plants.
- Vaccination and Immunity : Vaccinating mice with a particular strain of virus will lead to the production of specific antibodies that prevent future infections.
- Hormonal Levels and Bone Density : Post-menopausal women with decreased estrogen levels will have a significant reduction in bone density compared to pre-menopausal women.
- Enzyme Concentration and Reaction Rate : Doubling the concentration of an enzyme in a solution will double the rate of the substrate’s conversion to the product.
- Climate Change and Coral Bleaching : An increase in sea surface temperature by 2°C will lead to a 50% increase in coral bleaching events.
- Pesticides and Pollinator Health : Exposure to the pesticide DEF will reduce the foraging ability of honeybees by at least 30%.
Scientific Hypothesis Statement Examples
These are broader scientific hypothesis applicable to different scientific disciplines. They’re structured to make clear, testable predictions about the relationship between variables. “Bacterial Growth,” for instance, predicts the outcome of bacteria exposed to UV light.
- Bacterial Growth : Bacteria exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light will have a reduced growth rate compared to those not exposed to UV light.
- Antibiotic Resistance : Overuse of antibiotics in livestock will lead to an increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria in humans.
- Evolutionary Adaptation : Birds with longer beaks will have an advantage in accessing food after a drastic environmental change.
- Photosynthesis Rate : Plants grown under red light will have a lower rate of photosynthesis compared to those grown under blue light.
- Stem Cell Differentiation : The presence of growth factor X will guide stem cells to differentiate into nerve cells more frequently than muscle cells.
- Ozone Layer and UV Radiation : Depletion of the ozone layer will result in increased UV radiation levels on Earth’s surface.
- Protein Folding : Mutation at position 123 in protein Z will lead to a misfolded protein structure.
- Water Quality and Fish Health : Rivers with high levels of industrial pollutants will have a reduced fish population due to compromised gill functionality.
- Seismic Activity and Plate Tectonics : Regions located at the boundaries of tectonic plates will experience more frequent and stronger earthquakes.
- Drug Efficacy : Patients treated with drug Y will recover from infection twice as fast as those treated with a placebo.
Alternative Hypothesis Statement Examples for Science
The alternative hypothesis states that there is a statistically significant relationship between two variables. It’s what you might want to prove or demonstrate. For example, the hypothesis about “Green Tea and Metabolism” suggests that drinking green tea can have a positive effect on metabolic rates.
- Dietary Supplements and Energy Levels : Consuming a daily vitamin B12 supplement will increase energy levels in vegans.
- Soil Type and Crop Yield : Sandy soil will produce a lower maize yield than loamy soil.
- Air Pollution and Respiratory Diseases : Living in areas with higher particulate matter (PM2.5) levels will increase the incidence of respiratory diseases.
- Green Tea and Metabolism : Drinking green tea daily will increase metabolic rates in adults.
- Exercise and Brain Health : Engaging in regular aerobic exercise will increase cognitive function in older adults.
- Artificial Sweeteners and Appetite : Consuming artificial sweeteners will increase appetite in individuals.
- Forest Density and Wildlife Diversity : Forests with higher tree density will support a more diverse range of wildlife.
- Hydration and Skin Health : Drinking at least 2 liters of water daily will improve skin elasticity.
- Biofuels and Engine Performance : Engines running on biofuel will have a higher fuel efficiency than those running on traditional petroleum fuels.
- Artificial Light and Plant Growth : Plants grown under LED lights will have a faster growth rate than those grown under fluorescent lights.
Null Hypothesis Statement Examples for Science
The null hypothesis posits that there is no relationship between two variables. It’s the statement you want to test against. Scientists often set out to reject the null hypothesis to demonstrate there’s a relationship. For instance, “Diet and Weight Loss” asserts there’s no difference in weight loss outcomes between two diet types.
- Diet and Weight Loss : There is no difference in weight loss between individuals on a low-carb diet and those on a low-fat diet.
- Antibacterial Soap and Hand Hygiene : Using antibacterial soap does not decrease the number of bacteria on hands compared to using regular soap.
- Meditation and Blood Pressure : There is no difference in blood pressure levels between individuals who meditate daily and those who don’t.
- Organic Foods and Nutrient Content : Organic fruits and vegetables have the same nutrient content as non-organic fruits and vegetables.
- Pain Relievers and Pain Reduction : Over-the-counter pain reliever X does not reduce pain more effectively than a placebo.
- Educational Method and Learning : There is no difference in learning outcomes between students taught using method A and those taught using method B.
- Herbal Treatment and Sleep Duration : Herbal treatment Y does not increase sleep duration compared to a placebo.
- Sunscreen and Sunburn : There is no difference in sunburn incidence between individuals using sunscreen with SPF 30 and those using sunscreen with SPF 50.
- Caffeine and Alertness : Consuming caffeine does not increase alertness levels compared to not consuming caffeine.
- Probiotics and Gut Health : Taking daily probiotics does not increase the diversity of gut bacteria compared to not taking probiotics.
What is a good hypothesis for a science project?
A good hypothesis is a fundamental cornerstone for any scientific project. It provides direction for your research, helping you to focus your investigations and understand the potential outcomes. Here’s what characterizes a good hypothesis:
- Testable : A good hypothesis must be something that can be supported or refuted through experimentation, observation, or analysis.
- Clear and Concise : It should be straightforward and to the point, making it easier for you or others to test.
- Logical : It should make logical sense, building upon existing knowledge and literature.
- Specific : The hypothesis should clearly identify the variables and the relationship between them.
- Relevant : It should be pertinent to the subject matter and not diverge into unrelated areas.
- Predictive : It should make a clear prediction about what you expect to happen in your study.
How do you write a scientific hypothesis statement? – A Step by Step Guide
- Identify Your Research Question : Before you can draft a hypothesis, you need to determine what you’re trying to answer. For example, “Does the type of soil affect plant growth?”
- Perform Preliminary Research : Understand existing literature on the topic. This will help ensure that your hypothesis is original and rooted in current understanding.
- Independent Variable (what you change): e.g., type of soil.
- Dependent Variable (what you measure): e.g., plant growth.
- Make a Prediction : Based on your research, predict the relationship between your variables.
- If : Describes the change or treatment (independent variable).
- Then : Predicts the outcome (dependent variable).
- Because : Provides a rationale based on your background research. E.g., “If a plant is grown in sandy soil, then it will grow slower than in loamy soil, because sandy soil retains less water.”
- Keep it Simple : Avoid complex sentences or jargon. Your hypothesis should be understandable even to someone not in your field.
- Review and Revise : Once drafted, revisit your hypothesis. Ensure it aligns with your research question and that it remains clear and testable.
Tips for Writing Science Hypothesis
- Start with Curiosity : Your initial question should stem from genuine curiosity. It might begin as a broad query which you then refine.
- Use Open-Ended Questions : Start your question with words like “How,” “What,” or “Why.” These types of questions don’t presuppose an answer and lead to more in-depth investigation.
- One Variable at a Time : Especially for beginner projects, limit your hypothesis to one independent variable to keep your study focused and manageable.
- Avoid Biased Language : Your hypothesis should not show any personal biases. Instead of “I believe” or “I think,” use neutral terms.
- Stay Relevant to Available Tools and Resources : Ensure that you can test your hypothesis with the tools, time, and resources available to you.
- Peer Review : Before finalizing your question and hypothesis, have a peer or mentor review it. They might catch ambiguities or complexities you missed.
- Be Ready to Accept Any Outcome : A common mistake is becoming too attached to proving your hypothesis right. Remember, disproving a hypothesis can be just as valuable as proving it.
By carefully crafting your research question and hypothesis, you’ll set a solid foundation for your science project. Whether your results support or challenge your initial predictions, you’ll contribute to the vast and ever-growing body of scientific knowledge.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Back to blog home
Hypothesis testing explained in 4 parts, yuzheng sun, phd.
As data scientists, Hypothesis Testing is expected to be well understood, but often not in reality. It is mainly because our textbooks blend two schools of thought – p-value and significance testing vs. hypothesis testing – inconsistently.
For example, some questions are not obvious unless you have thought through them before:
Are power or beta dependent on the null hypothesis?
Can we accept the null hypothesis? Why?
How does MDE change with alpha holding beta constant?
Why do we use standard error in Hypothesis Testing but not the standard deviation?
Why can’t we be specific about the alternative hypothesis so we can properly model it?
Why is the fundamental tradeoff of the Hypothesis Testing about mistake vs. discovery, not about alpha vs. beta?
Addressing this problem is not easy. The topic of Hypothesis Testing is convoluted. In this article, there are 10 concepts that we will introduce incrementally, aid you with visualizations, and include intuitive explanations. After this article, you will have clear answers to the questions above that you truly understand on a first-principle level and explain these concepts well to your stakeholders.
We break this article into four parts.
Set up the question properly using core statistical concepts, and connect them to Hypothesis Testing, while striking a balance between technically correct and simplicity. Specifically,
We emphasize a clear distinction between the standard deviation and the standard error, and why the latter is used in Hypothesis Testing
We explain fully when can you “accept” a hypothesis, when shall you say “failing to reject” instead of “accept”, and why
Introduce alpha, type I error, and the critical value with the null hypothesis
Introduce beta, type II error, and power with the alternative hypothesis
Introduce minimum detectable effects and the relationship between the factors with power calculations , with a high-level summary and practical recommendations
Part 1 - Hypothesis Testing, the central limit theorem, population, sample, standard deviation, and standard error
In Hypothesis Testing, we begin with a null hypothesis , which generally asserts that there is no effect between our treatment and control groups. Commonly, this is expressed as the difference in means between the treatment and control groups being zero.
The central limit theorem suggests an important property of this difference in means — given a sufficiently large sample size, the underlying distribution of this difference in means will approximate a normal distribution, regardless of the population's original distribution. There are two notes:
1. The distribution of the population for the treatment and control groups can vary, but the observed means (when you observe many samples and calculate many means) are always normally distributed with a large enough sample. Below is a chart, where the n=10 and n=30 correspond to the underlying distribution of the sample means.
2. Pay attention to “the underlying distribution”. Standard deviation vs. standard error is a potentially confusing concept. Let’s clarify.
Standard deviation vs. Standard error
Let’s declare our null hypothesis as having no treatment effect. Then, to simplify, let’s propose the following normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 as the range of possible outcomes with probabilities associated with this null hypothesis.
The language around population, sample, group, and estimators can get confusing. Again, to simplify, let’s forget that the null hypothesis is about the mean estimator, and declare that we can either observe the mean hypothesis once or many times. When we observe it many times, it forms a sample*, and our goal is to make decisions based on this sample.
* For technical folks, the observation is actually about a single sample, many samples are a group, and the difference in groups is the distribution we are talking about as the mean hypothesis. The red curve represents the distribution of the estimator of this difference, and then we can have another sample consisting of many observations of this estimator. In my simplified language, the red curve is the distribution of the estimator, and the blue curve with sample size is the repeated observations of it. If you have a better way to express these concepts without causing confusiongs, please suggest.
This probability density function means if there is one realization from this distribution, the realitization can be anywhere on the x-axis, with the relative likelihood on the y-axis.
If we draw multiple observations , they form a sample . Each observation in this sample follows the property of this underlying distribution – more likely to be close to 0, and equally likely to be on either side, which makes the odds of positive and negative cancel each other out, so the mean of this sample is even more centered around 0.
We use the standard error to represent the error of our “sample mean” .
The standard error = the standard deviation of the observed sample / sqrt (sample size).
For a sample size of 30, the standard error is roughly 0.18. Compared with the underlying distribution, the distribution of the sample mean is much narrower.
In Hypothesis Testing, we try to draw some conclusions – is there a treatment effect or not? – based on a sample. So when we talk about alpha and beta, which are the probabilities of type I and type II errors , we are talking about the probabilities based on the plot of sample means and standard error .
Part 2, The null hypothesis: alpha and the critical value
From Part 1, we stated that a null hypothesis is commonly expressed as the difference in means between the treatment and control groups being zero.
Without loss of generality*, let’s assume the underlying distribution of our null hypothesis is mean 0 and standard deviation 1
Then the sample mean of the null hypothesis is 0 and the standard error of 1/√ n, where n is the sample size.
When the sample size is 30, this distribution has a standard error of ≈0.18 looks like the below.
*: A note for the technical readers: The null hypothesis is about the difference in means, but here, without complicating things, we made the subtle change to just draw the distribution of this “estimator of this difference in means”. Everything below speaks to this “estimator”.
The reason we have the null hypothesis is that we want to make judgments, particularly whether a treatment effect exists. But in the world of probabilities, any observation, and any sample mean can happen, with different probabilities. So we need a decision rule to help us quantify our risk of making mistakes.
The decision rule is, let’s set a threshold. When the sample mean is above the threshold, we reject the null hypothesis; when the sample mean is below the threshold, we accept the null hypothesis.
Accepting a hypothesis vs. failing to reject a hypothesis
It’s worth noting that you may have heard of “we never accept a hypothesis, we just fail to reject a hypothesis” and be subconsciously confused by it. The deep reason is that modern textbooks do an inconsistent blend of Fisher’s significance testing and Neyman-Pearson’s Hypothesis Testing definitions and ignore important caveats ( ref ). To clarify:
First of all, we can never “prove” a particular hypothesis given any observations, because there are infinitely many true hypotheses (with different probabilities) given an observation. We will visualize it in Part 3.
Second, “accepting” a hypothesis does not mean that you believe in it, but only that you act as if it were true. So technically, there is no problem with “accepting” a hypothesis.
But, third, when we talk about p-values and confidence intervals, “accepting” the null hypothesis is at best confusing. The reason is that “the p-value above the threshold” just means we failed to reject the null hypothesis. In the strict Fisher’s p-value framework, there is no alternative hypothesis. While we have a clear criterion for rejecting the null hypothesis (p < alpha), we don't have a similar clear-cut criterion for "accepting" the null hypothesis based on beta.
So the dangers in calling “accepting a hypothesis” in the p-value setting are:
Many people misinterpret “accepting” the null hypothesis as “proving” the null hypothesis, which is wrong;
“Accepting the null hypothesis” is not rigorously defined, and doesn’t speak to the purpose of the test, which is about whether or not we reject the null hypothesis.
In this article, we will stay consistent within the Neyman-Pearson framework , where “accepting” a hypothesis is legal and necessary. Otherwise, we cannot draw any distributions without acting as if some hypothesis was true.
You don’t need to know the name Neyman-Pearson to understand anything, but pay attention to our language, as we choose our words very carefully to avoid mistakes and confusion.
So far, we have constructed a simple world of one hypothesis as the only truth, and a decision rule with two potential outcomes – one of the outcomes is “reject the null hypothesis when it is true” and the other outcome is “accept the null hypothesis when it is true”. The likelihoods of both outcomes come from the distribution where the null hypothesis is true.
Later, when we introduce the alternative hypothesis and MDE, we will gradually walk into the world of infinitely many alternative hypotheses and visualize why we cannot “prove” a hypothesis.
We save the distinction between the p-value/significance framework vs. Hypothesis Testing in another article where you will have the full picture.
Type I error, alpha, and the critical value
We’re able to construct a distribution of the sample mean for this null hypothesis using the standard error. Since we only have the null hypothesis as the truth of our universe, we can only make one type of mistake – falsely rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. This is the type I error , and the probability is called alpha . Suppose we want alpha to be 5%. We can calculate the threshold required to make it happen. This threshold is called the critical value . Below is the chart we further constructed with our sample of 30.
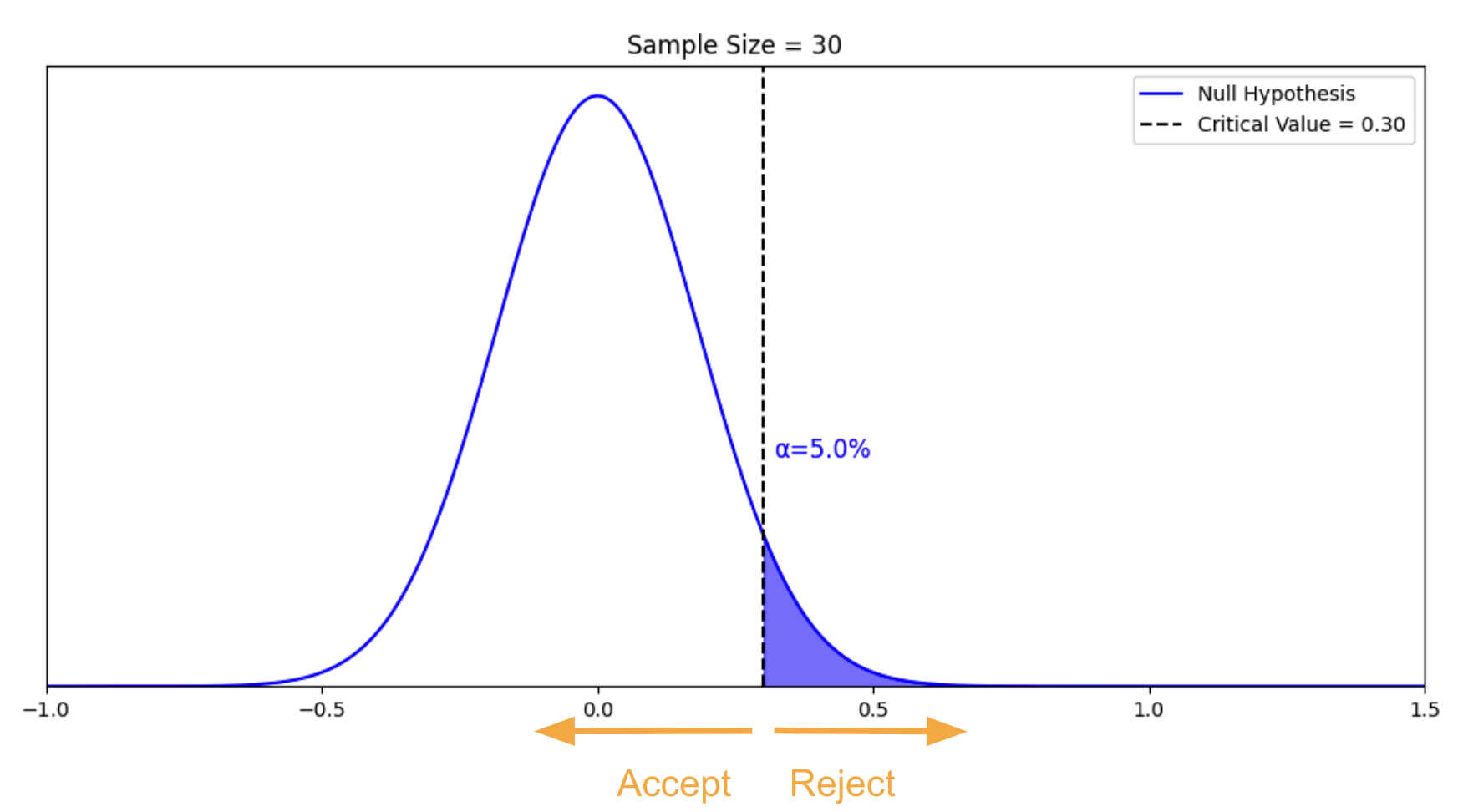
In this chart, alpha is the blue area under the curve. The critical value is 0.3. If our sample mean is above 0.3, we reject the null hypothesis. We have a 5% chance of making the type I error.
Type I error: Falsely rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true
Alpha: The probability of making a Type I error
Critical value: The threshold to determine whether the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not
Part 3, The alternative hypothesis: beta and power
You may have noticed in part 2 that we only spoke to Type I error – rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. What about the Type II error – falsely accepting the null hypothesis when it is not true?
But it is weird to call “accepting” false unless we know the truth. So we need an alternative hypothesis which serves as the alternative truth.
Alternative hypotheses are theoretical constructs
There is an important concept that most textbooks fail to emphasize – that is, you can have infinitely many alternative hypotheses for a given null hypothesis, we just choose one. None of them are more special or “real” than the others.
Let’s visualize it with an example. Suppose we observed a sample mean of 0.51, what is the true alternative hypothesis?
With this visualization, you can see why we have “infinitely many alternative hypotheses” because, given the observation, there is an infinite number of alternative hypotheses (plus the null hypothesis) that can be true, each with different probabilities. Some are more likely than others, but all are possible.
Remember, alternative hypotheses are a theoretical construct. We choose one particular alternative hypothesis to calculate certain probabilities. By now, we should have more understanding of why we cannot “accept” the null hypothesis given an observation. We can’t prove that the null hypothesis is true, we just fail to accept it given the observation and our pre-determined decision rule.
We will fully reconcile this idea of picking one alternative hypothesis out of the world of infinite possibilities when we talk about MDE. The idea of “accept” vs. “fail to reject” is deeper, and we won’t cover it fully in this article. We will do so when we have an article about the p-value and the confidence interval.
Type II error and Beta
For the sake of simplicity and easy comparison, let’s choose an alternative hypothesis with a mean of 0.5, and a standard deviation of
1. Again, with a sample size of 30, the standard error ≈0.18. There are now two potential “truths” in our simple universe.
Remember from the null hypothesis, we want alpha to be 5% so the corresponding critical value is 0.30. We modify our rule as follows:
If the observation is above 0.30, we reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis ;
If the observation is below 0.30, we accept the null hypothesis and reject the alternative hypothesis .
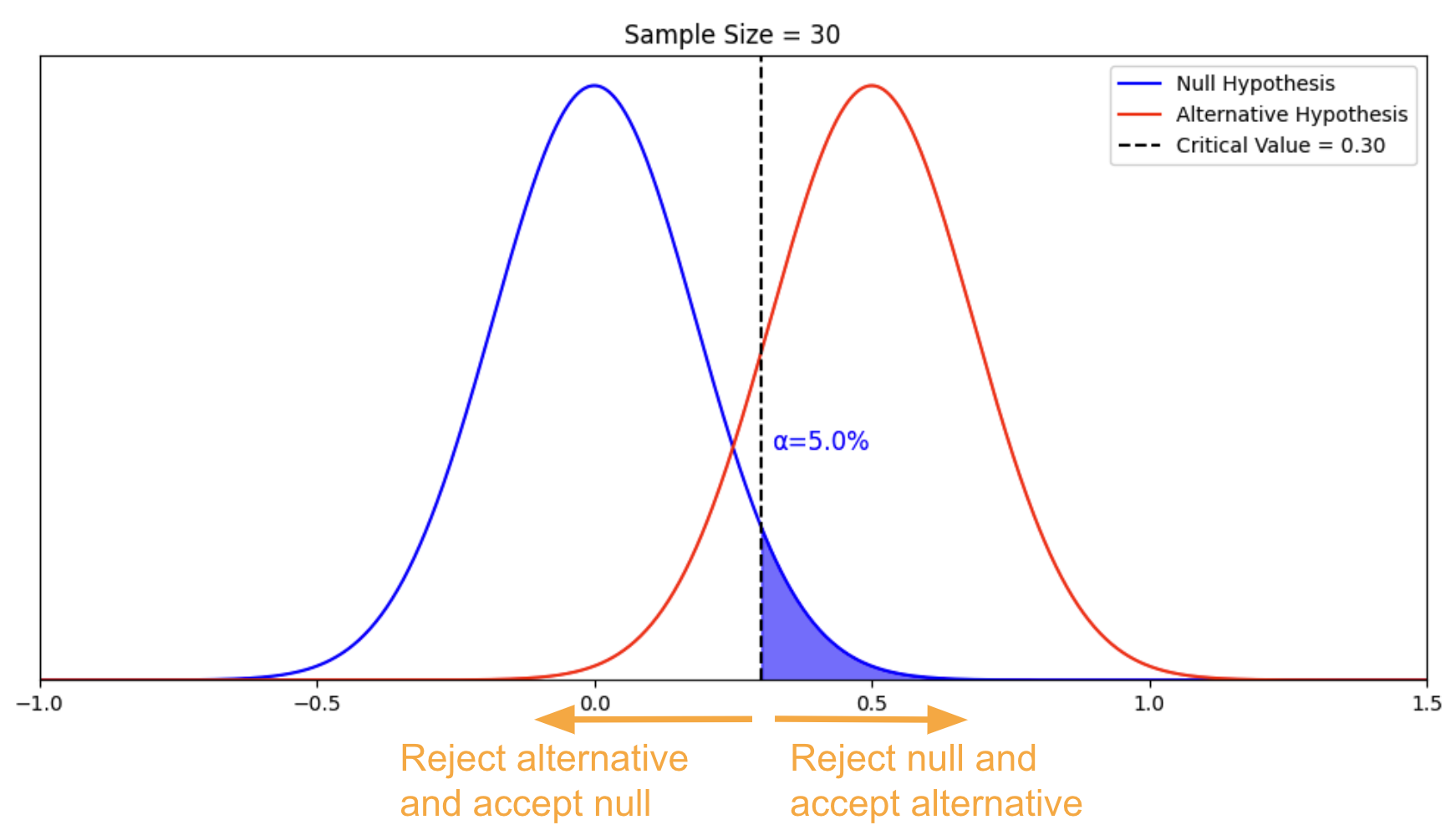
With the introduction of the alternative hypothesis, the alternative “(hypothesized) truth”, we can call “accepting the null hypothesis and rejecting the alternative hypothesis” a mistake – the Type II error. We can also calculate the probability of this mistake. This is called beta, which is illustrated by the red area below.
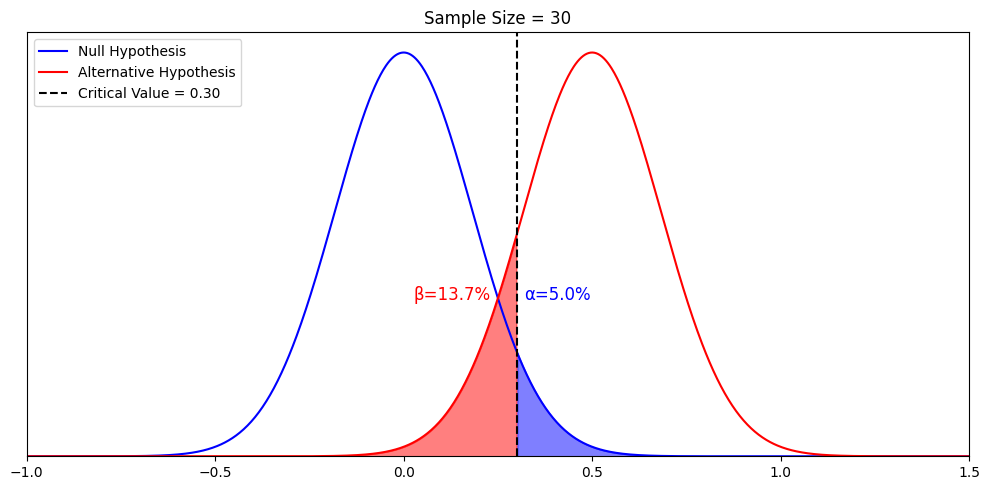
From the visualization, we can see that beta is conditional on the alternative hypothesis and the critical value. Let’s elaborate on these two relationships one by one, very explicitly, as both of them are important.
First, Let’s visualize how beta changes with the mean of the alternative hypothesis by setting another alternative hypothesis where mean = 1 instead of 0.5
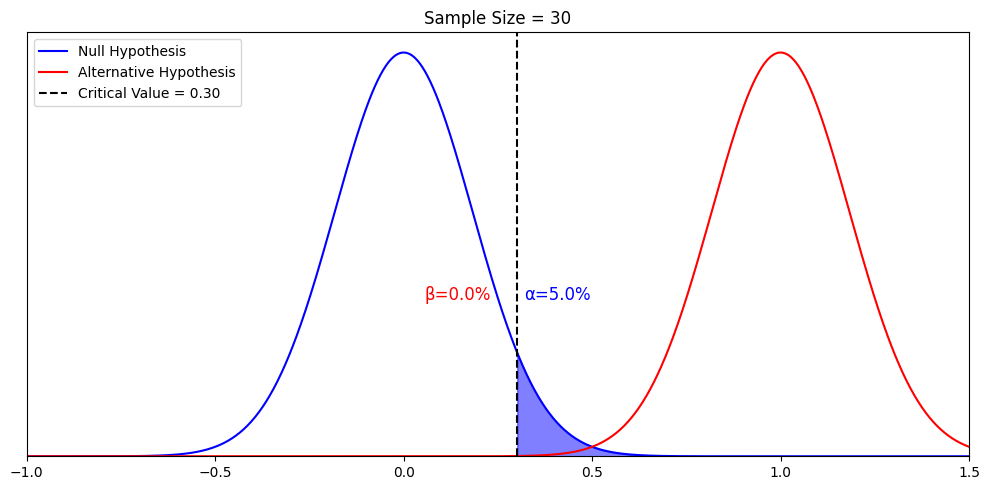
Beta change from 13.7% to 0.0%. Namely, beta is the probability of falsely rejecting a particular alternative hypothesis when we assume it is true. When we assume a different alternative hypothesis is true, we get a different beta. So strictly speaking, beta only speaks to the probability of falsely rejecting a particular alternative hypothesis when it is true . Nothing else. It’s only under other conditions, that “rejecting the alternative hypothesis” implies “accepting” the null hypothesis or “failing to accept the null hypothesis”. We will further elaborate when we talk about p-value and confidence interval in another article. But what we talked about so far is true and enough for understanding power.
Second, there is a relationship between alpha and beta. Namely, given the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis, alpha would determine the critical value, and the critical value determines beta. This speaks to the tradeoff between mistake and discovery.
If we tolerate more alpha, we will have a smaller critical value, and for the same beta, we can detect a smaller alternative hypothesis
If we tolerate more beta, we can also detect a smaller alternative hypothesis.
In short, if we tolerate more mistakes (either Type I or Type II), we can detect a smaller true effect. Mistake vs. discovery is the fundamental tradeoff of Hypothesis Testing.
So tolerating more mistakes leads to more chance of discovery. This is the concept of MDE that we will elaborate on in part 4.
Finally, we’re ready to define power. Power is an important and fundamental topic in statistical testing, and we’ll explain the concept in three different ways.
Three ways to understand power
First, the technical definition of power is 1−β. It represents that given an alternative hypothesis and given our null, sample size, and decision rule (alpha = 0.05), the probability is that we accept this particular hypothesis. We visualize the yellow area below.
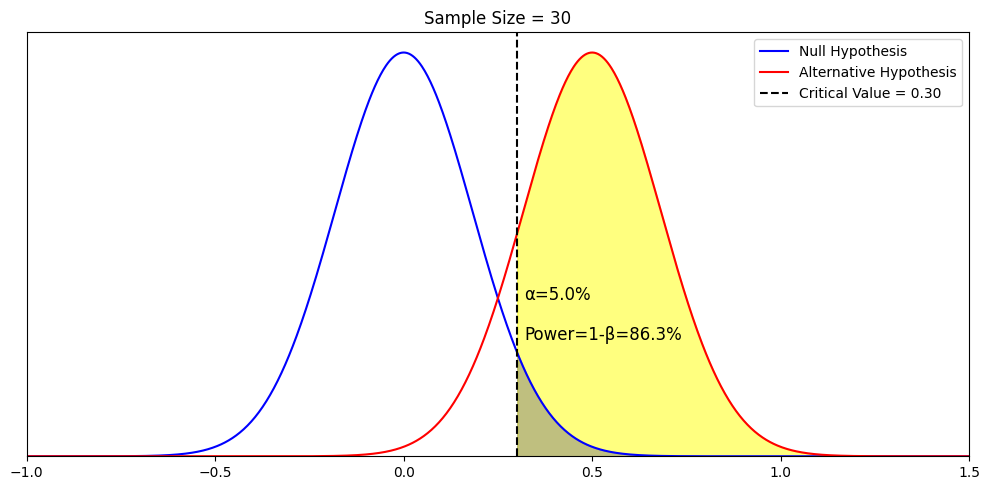
Second, power is really intuitive in its definition. A real-world example is trying to determine the most popular car manufacturer in the world. If I observe one car and see one brand, my observation is not very powerful. But if I observe a million cars, my observation is very powerful. Powerful tests mean that I have a high chance of detecting a true effect.
Third, to illustrate the two concepts concisely, let’s run a visualization by just changing the sample size from 30 to 100 and see how power increases from 86.3% to almost 100%.
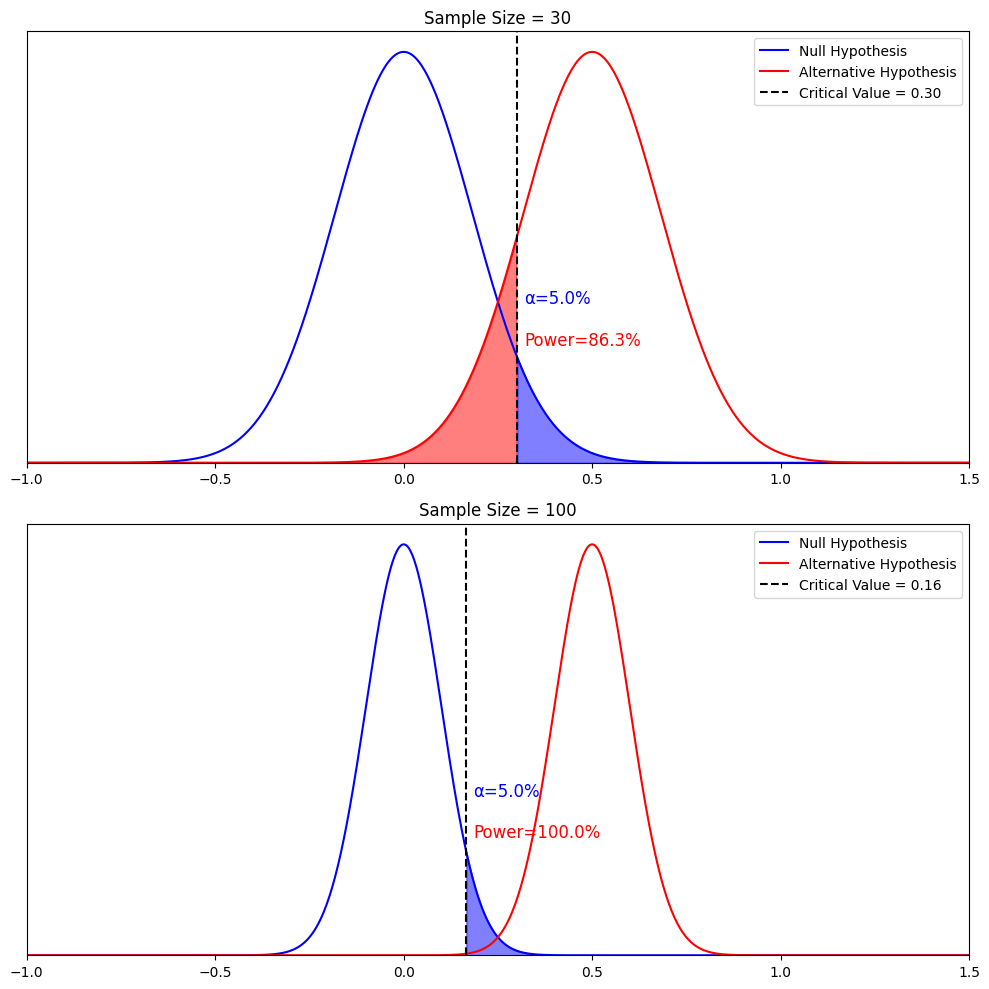
As the graph shows, we can easily see that power increases with sample size . The reason is that the distribution of both the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis became narrower as their sample means got more accurate. We are less likely to make either a type I error (which reduces the critical value) or a type II error.
Type II error: Failing to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true
Beta: The probability of making a type II error
Power: The ability of the test to detect a true effect when it’s there
Part 4, Power calculation: MDE
The relationship between mde, alternative hypothesis, and power.
Now, we are ready to tackle the most nuanced definition of them all: Minimum detectable effect (MDE). First, let’s make the sample mean of the alternative hypothesis explicit on the graph with a red dotted line.
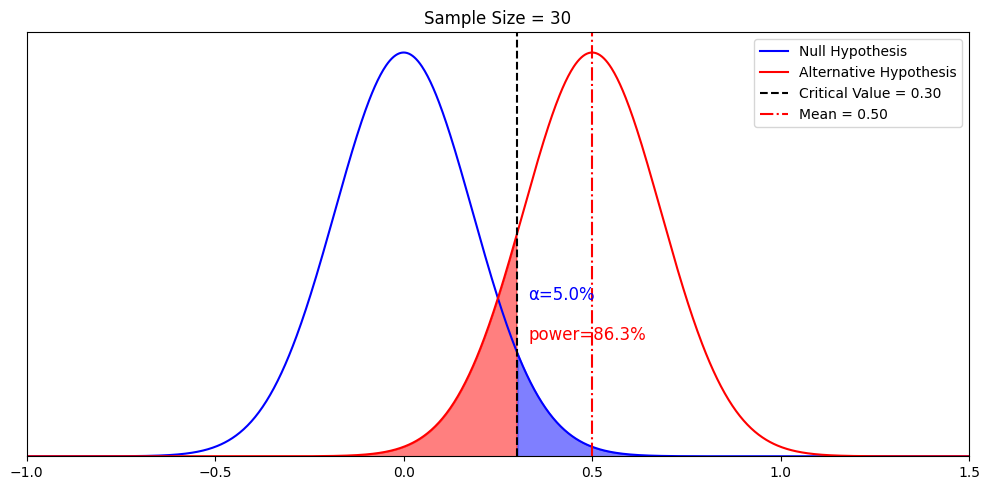
What if we keep the same sample size, but want power to be 80%? This is when we recall the previous chapter that “alternative hypotheses are theoretical constructs”. We can have a different alternative that corresponds to 80% power. After some calculations, we discovered that when it’s the alternative hypothesis with mean = 0.45 (if we keep the standard deviation to be 1).
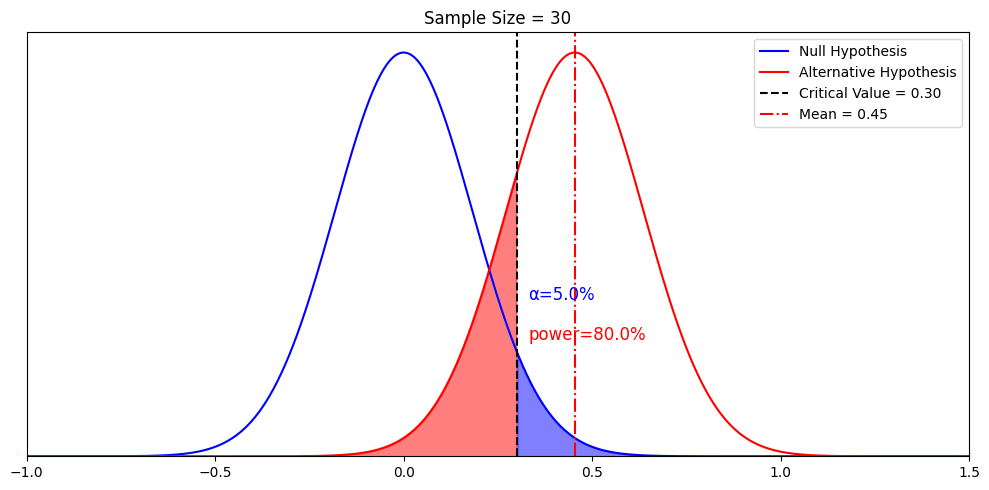
This is where we reconcile the concept of “infinitely many alternative hypotheses” with the concept of minimum detectable delta. Remember that in statistical testing, we want more power. The “ minimum ” in the “ minimum detectable effect”, is the minimum value of the mean of the alternative hypothesis that would give us 80% power. Any alternative hypothesis with a mean to the right of MDE gives us sufficient power.
In other words, there are indeed infinitely many alternative hypotheses to the right of this mean 0.45. The particular alternative hypothesis with a mean of 0.45 gives us the minimum value where power is sufficient. We call it the minimum detectable effect, or MDE.
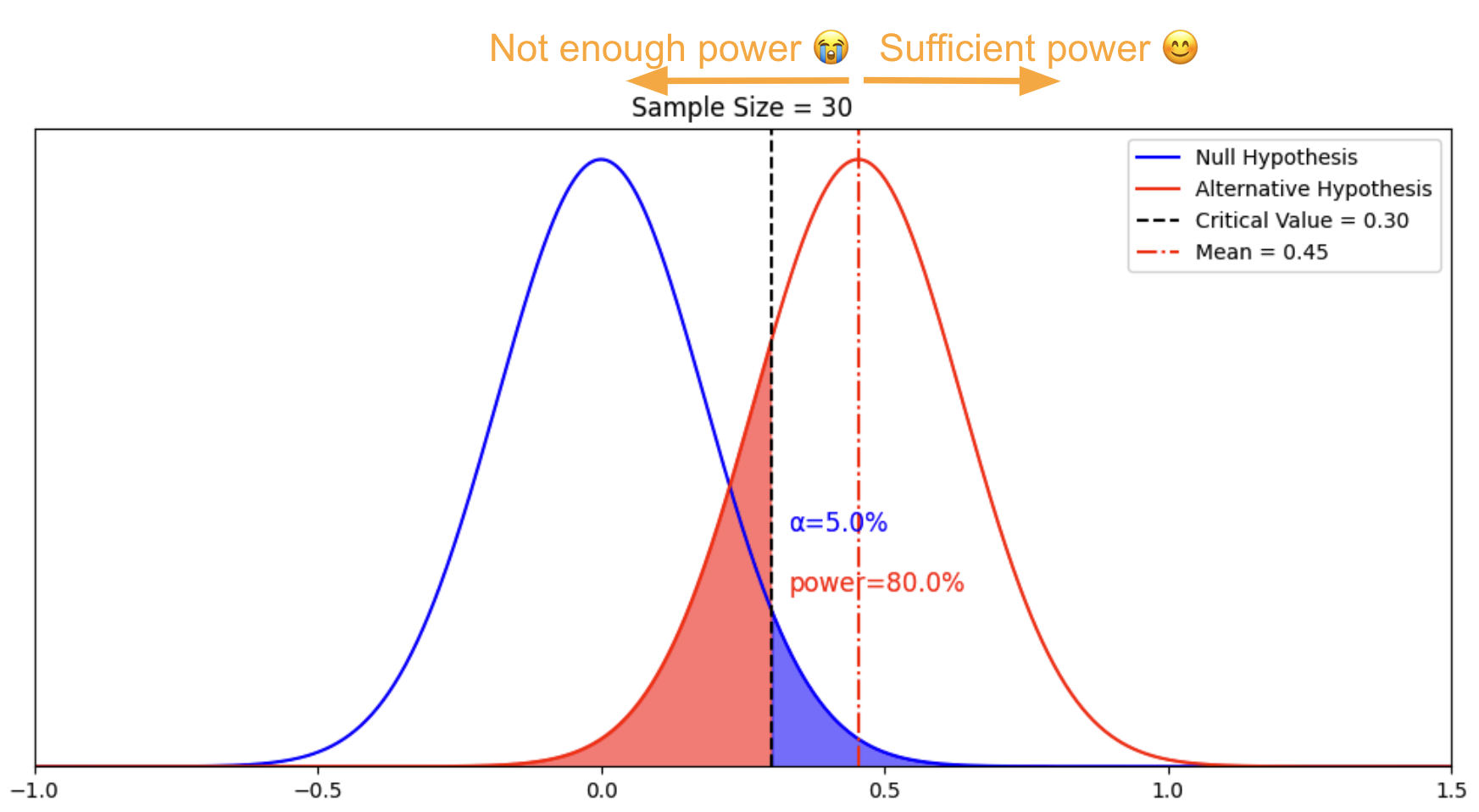
The complete definition of MDE from scratch
Let’s go through how we derived MDE from the beginning:
We fixed the distribution of sample means of the null hypothesis, and fixed sample size, so we can draw the blue distribution
For our decision rule, we require alpha to be 5%. We derived that the critical value shall be 0.30 to make 5% alpha happen
We fixed the alternative hypothesis to be normally distributed with a standard deviation of 1 so the standard error is 0.18, the mean can be anywhere as there are infinitely many alternative hypotheses
For our decision rule, we require beta to be 20% or less, so our power is 80% or more.
We derived that the minimum value of the observed mean of the alternative hypothesis that we can detect with our decision rule is 0.45. Any value above 0.45 would give us sufficient power.
How MDE changes with sample size
Now, let’s tie everything together by increasing the sample size, holding alpha and beta constant, and see how MDE changes.
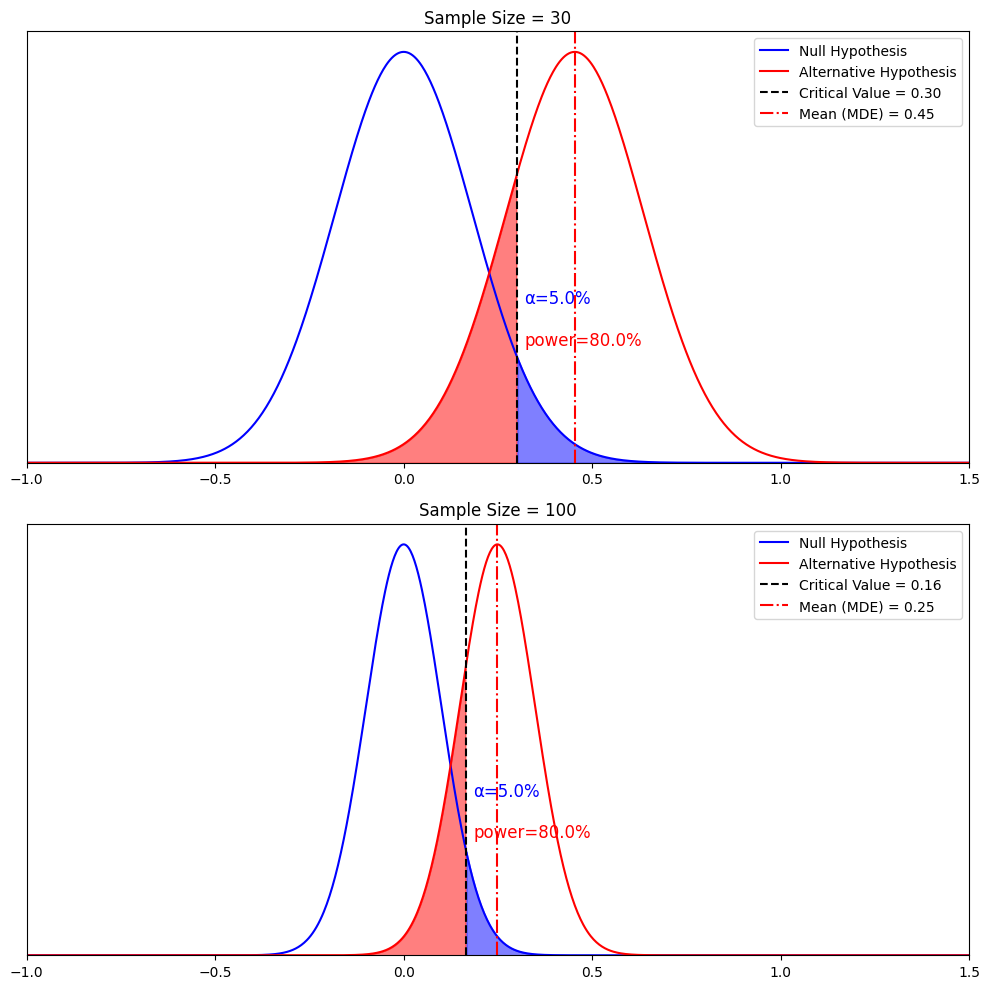
Narrower distribution of the sample mean + holding alpha constant -> smaller critical value from 0.3 to 0.16
+ holding beta constant -> MDE decreases from 0.45 to 0.25
This is the other key takeaway: The larger the sample size, the smaller of an effect we can detect, and the smaller the MDE.
This is a critical takeaway for statistical testing. It suggests that even for companies not with large sample sizes if their treatment effects are large, AB testing can reliably detect it.
Summary of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s review all the concepts together.
Assuming the null hypothesis is correct:
Alpha: When the null hypothesis is true, the probability of rejecting it
Critical value: The threshold to determine rejecting vs. accepting the null hypothesis
Assuming an alternative hypothesis is correct:
Beta: When the alternative hypothesis is true, the probability of rejecting it
Power: The chance that a real effect will produce significant results
Power calculation:
Minimum detectable effect (MDE): Given sample sizes and distributions, the minimum mean of alternative distribution that would give us the desired alpha and sufficient power (usually alpha = 0.05 and power >= 0.8)
Relationship among the factors, all else equal: Larger sample, more power; Larger sample, smaller MDE
Everything we talk about is under the Neyman-Pearson framework. There is no need to mention the p-value and significance under this framework. Blending the two frameworks is the inconsistency brought by our textbooks. Clarifying the inconsistency and correctly blending them are topics for another day.
Practical recommendations
That’s it. But it’s only the beginning. In practice, there are many crafts in using power well, for example:
Why peeking introduces a behavior bias, and how to use sequential testing to correct it
Why having multiple comparisons affects alpha, and how to use Bonferroni correction
The relationship between sample size, duration of the experiment, and allocation of the experiment?
Treat your allocation as a resource for experimentation, understand when interaction effects are okay, and when they are not okay, and how to use layers to manage
Practical considerations for setting an MDE
Also, in the above examples, we fixed the distribution, but in reality, the variance of the distribution plays an important role. There are different ways of calculating the variance and different ways to reduce variance, such as CUPED, or stratified sampling.
Related resources:
How to calculate power with an uneven split of sample size: https://blog.statsig.com/calculating-sample-sizes-for-a-b-tests-7854d56c2646
Real-life applications: https://blog.statsig.com/you-dont-need-large-sample-sizes-to-run-a-b-tests-6044823e9992
Create a free account
2m events per month, free forever..
Sign up for Statsig and launch your first experiment in minutes.
Build fast?
Try statsig today.
Recent Posts
Top 8 common experimentation mistakes and how to fix them.
I discussed 8 A/B testing mistakes with Allon Korem (Bell Statistics) and Tyler VanHaren (Statsig). Learn fixes to improve accuracy and drive better business outcomes.
Introducing Differential Impact Detection
Introducing Differential Impact Detection: Identify how different user groups respond to treatments and gain useful insights from varied experiment results.
Identifying and experimenting with Power Users using Statsig
Identify power users to drive growth and engagement. Learn to pinpoint and leverage these key players with targeted experiments for maximum impact.
How to Ingest Data Into Statsig
Simplify data pipelines with Statsig. Use SDKs, third-party integrations, and Data Warehouse Native Solution for effortless data ingestion at any stage.
A/B Testing performance wins on NestJS API servers
Learn how we use Statsig to enhance our NestJS API servers, reducing request processing time and CPU usage through performance experiments.
An overview of making early decisions on experiments
Learn the risks vs. rewards of making early decisions in experiments and Statsig's techniques to reduce experimentation times and deliver trustworthy results.
Free Al Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
- Practical Skills
How to Write a Hypothesis? [Tips with Examples]
Click here if you have ever found yourself in the position of having to wrestle with the development of a hypothesis for your research paper. As an expert writer, I have seen that this is where most students begin to sweat. It is a potpourri of theory and practice, hence rather intimidating. But not to worry because I have got your back. This guide is a pool of tips and tricks for writing a hypothesis to set the stage for compelling research.
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a tentative statement, usually in the form of an educated guess, that provides a probable explanation for something either a phenomenon or a relationship between variables. This will, therefore, form a basis for conducting experiments and research studies, hence laying down the course of your investigation and mainly laying the ground for your conclusion.
A good hypothesis should be:
Specific and clear
Testable and falsifiable
Based upon existing knowledge
Logically consistent
Types of Hypothesis
There are different kinds of hypotheses used in research, all of which serve different purposes depending on the nature of the study. Here are eight common types:
1. The null hypothesis (H0): asserts that there is no effect or relationship between variables. This forms a baseline for comparison. Example: "There is no difference in test scores for students who study music and for those who do not."
2. Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The hypothesis that postulates some effect or relationship between variables; it is, therefore, the opposite of the null hypothesis. For instance, "Students who study with music have different test scores than those who study in silence."
3. Simple Hypothesis: The hypothesis that states a relationship between two variables: one independent and one dependent. For example, "More sunlight increases plant growth."
4. Complex Hypothesis: This hypothesis involves the relationship of more than one variable. For example, "More sunlight and water increase plant growth."
5. Directional Hypothesis: The hypothesis which specifies the direction of the effect between variables. For instance, "Students who study with music will have higher test scores than students who study in silence."
6. Non-Directional Hypothesis: This is a hypothesis used where the relationship is indicated, but the direction is not specified. For example, "There is a difference in test scores between students who study with music and those who study in silence."
7. Associative Hypothesis: This hypothesis merely states that the change in one variable is associated with a change in another. It does not indicate cause and effect. For example: "There is a relationship between study habits and academic performance."
8. Causal Hypothesis: This hypothesis states that one variable causes a change in another. For example: "Increased study time results in higher test scores."
Understanding such types of hypotheses will help in the selection of the correct hypothesis for your research and in making your analysis clear and effective.
5 Steps to Write a Good Hypothesis [With Examples]
An excellent hypothesis provides a backbone to any scientific research. Leave some help behind in writing one? Follow this easy guide:
Step 1: Ask a Question
First, you must understand what your research question is. Suppose you want to carry out an experiment on plant growth. Your question can be, "How does sunlight affect plant growth?"
Use WPS AI to help when you get stuck. Feed it a topic, and it will come up with related questions to ask.
Step 2: Do Preliminary Research
Do some research to see what's already known about your topic. That way, you can build upon existing knowledge.
Research information in journals, books and credible websites. Then summarize what you read. This will help you formulate your hypothesis.
Step 3: Define Variables
Identify your variables:
Independent Variable: What you manipulate. For example, the amount of sun.
Dependent Variable: What you measure. For example, plant growth rate.
Clearly defining these makes your hypothesis specific and testable.
Step 4: State Your Hypothesis
State your question in the form of a hypothesis. Here are some examples:
If then: "If plants receive more sunlight, then they will grow faster."
Comparative statements: "Plants receiving more sunlight grow faster than plants receiving less."
Correlation statements: "There is positive correlation between sunlight and plant growth." This kind of pattern makes your hypothesis easy to test.
Step 5: Refine Your Hypothesis
Revise your hypothesis to be clear and specific, and elicit feedback to improve it.
You will also need a null hypothesis, which says that there is no effect or relationship between variables. An example would be, "Sunlight has no effect on the growth of plants."
With these steps, you are now bound to come up with a testable hypothesis. WPS AI can help you in this process more efficiently.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
A good hypothesis is seen as the backbone of doing effective research. Following are some key characteristics that define a good hypothesis:
A good hypothesis has to be testable either by experimentation or observation. The hypothesis should clearly predict what can be measured or observed. For example, "If it receives more sunlight, the plant will grow taller" is a testable hypothesis since it states what can be measured.
Falsifiable
A hypothesis has to be falsifiable: it should be able to prove it wrong. This feature is important because it accommodates testing in science. For example, the statement "All swans are white" is falsifiable since it just takes one black swan to disprove the claim.
A good hypothesis should be grounded in current knowledge and should be properly reasoned. It should be broad or reasonable within existing knowledge. For example, "Increasing the amount of sunlight will boost plant growth" makes sense, in that it tallies with generally known facts about photosynthesis.
Specific and Clear
What is needed is clarity and specificity. A hypothesis has to be brief, yet free from ambiguity. For instance, "Increased sunlight leads to taller plants" is clear and specific whereas "Sunlight affects plants" is too vague.
Built upon Prior Knowledge
A good hypothesis is informed by prior research and existing theories. The available knowledge enlightens it to build on what is known to find new relationships or effects. For example, "Given photosynthesis requires sunlight, increasing sunlight will enhance plant growth" is informed by available scientific understanding.
Ethical Considerations
Finally, a good hypothesis needs to consider the ethics involved. The research should not bring damage to participants or the environment. For instance, "How the new drug will affect a human when tested without testing it on animals" may present an ethical concern.
Checklist for Reviewing Your Hypothesis
To be certain that your hypothesis has the following characteristics, use this checklist to review your hypothesis:
1. Is the hypothesis testable through experimentation or observation?
2. Can the hypothesis be proven false?
3. Is the hypothesis logically deduced from known facts?
4. Is your hypothesis clear and specific?
5. Does your hypothesis relate to previous research or theories?
6. Will there be any ethical issues with the proposed research?
7. Are your independent and dependent variables well defined?
8. Is your hypothesis concise and ambiguity free?
9. Did you get feedback to help in refining your hypothesis?
10. Does your hypothesis contain a null hypothesis for comparison?
By making sure that your hypothesis has these qualities, you are much more likely to set yourself on the course of higher-quality research and larger impacts. WPS AI can help fine-tune a hypothesis to ensure it is well-structured and clear.
Using WPS to Perfect your Hypothesis
Drafting a good hypothesis is the real inception of any research project. WPS AI, with its advanced language functions, can very strongly improve this stage of your study. Here's how WPS AI can help you perfect your hypothesis:
Check Grammar and Syntax
Grammar and punctuation errors can make your hypothesis weak. WPS AI checks and corrects this with the assurance that your hypothesis is as clear as possible and professional in its presentation. For example, when your hypothesis is written, "If the temperature increases then plant growth will increases", WPS AI can correct it to "If the temperature increases, then plant growth will increase."
Rewrite Your Hypothesis for Clarity
There needs to be a clear hypothesis. WPS AI can suggest ways to reword your hypothesis so that it makes sense. If your original hypothesis is, "More sunlight will result in more significant plant growth due to photosynthesis," WPS AI can suggest, "Increased sunlight will lead to greater plant growth through enhanced photosynthesis."
Automatic Content Expansion
Sometimes, your hypothesis or the related paragraphs may require more detail. WPS AI's [Continue Writing] feature can help enlarge the content. For example, after having written, "This study will examine the effects of sunlight on plant growth", using [Continue Writing] it can enlarge it to, "This research paper is going to study how sunlight affects the growth of plants by measuring their height and their health under different amounts of sunlight over a period of six weeks."
WPS AI is a great tool that can help you in drafting a good hypothesis for your research. It will help you check grammar, syntax, clarity, and completeness. Using WPS AI , you will be assured that the results of your hypothesis will be well-written and clear to understand.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
The hypothesis is one single testable prediction regarding some phenomenon. The theory is an explanation for some part of the natural world which is well-substantiated by a body of evidence, together with multiple hypotheses.
What do I do if my hypothesis isn't supported by my data?
If your results turn out not to support your hypothesis, analyze the data again to see why your result rejects your hypothesis. Do not manipulate the observations or experiment so that it leads to your hypothesis.
Can there be more than one hypothesis in a research study?
Yes, there may be more than one hypothesis, especially when one research study is examining several interrelated phenomena or variables. Each hypothesis has to be separately and clearly stated and tested.
Correct formulation of a strong, testable hypothesis is one of the most critical steps in the application of the scientific method and within academic research. The steps provided in this article will help you write a hypothesis that is clear, specific, and based on available knowledge. Give the tools and tips a try to elevate your academic writing and kick your research up a notch.
- 1. How to Write a Bibliography [Tips with Examples]
- 2. How to Write a Cover Letter [Tips with Examples]
- 3. How to Write a Call to Action - Steps with Examples
- 4. How to Write a Proposal [ Steps & Examples]
- 5. How to Write a Book Review [Tips with Examples]
- 6. How to Write a Cover Letter for Teaching Positions [Tips with Examples]
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a or H 1 ) : There’s an effect in the population.
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, similarities and differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”:
- The null hypothesis ( H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.”
- The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample. It’s critical for your research to write strong hypotheses .
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept . Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect,” “no difference,” or “no relationship.” When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
You can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population. Some percentage of the time, your inference about the population will be incorrect. When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error . When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s a type II error.
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
| ( ) | ||
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person does not differ between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in the textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has on exam scores. | : There is no relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β = 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression.* | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is greater than or equal to the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; ≥ . |
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect,” “a difference,” or “a relationship.” When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
| Does tooth flossing affect the number of cavities? | Tooth flossing has an on the number of cavities. | test: The mean number of cavities per person differs between the flossing group (µ ) and the non-flossing group (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| Does the amount of text highlighted in a textbook affect exam scores? | The amount of text highlighted in the textbook has an on exam scores. | : There is a relationship between the amount of text highlighted and exam scores in the population; β ≠ 0. |
| Does daily meditation decrease the incidence of depression? | Daily meditation the incidence of depression. | test: The proportion of people with depression in the daily-meditation group ( ) is less than the no-meditation group ( ) in the population; < . |
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question.
- They both make claims about the population.
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
| A claim that there is in the population. | A claim that there is in the population. | |
|
| ||
| Equality symbol (=, ≥, or ≤) | Inequality symbol (≠, <, or >) | |
| Rejected | Supported | |
| Failed to reject | Not supported |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
General template sentences
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable.
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a ): Independent variable affects dependent variable.
Test-specific template sentences
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
| ( ) | ||
| test
with two groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable differs between group 1 (µ ) and group 2 (µ ) in the population; µ ≠ µ . |
| with three groups | The mean dependent variable does not differ between group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) in the population; µ = µ = µ . | The mean dependent variable of group 1 (µ ), group 2 (µ ), and group 3 (µ ) are not all equal in the population. |
| There is no correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ = 0. | There is a correlation between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; ρ ≠ 0. | |
| There is no relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β = 0. | There is a relationship between independent variable and dependent variable in the population; β ≠ 0. | |
| Two-proportions test | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion does not differ between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; = . | The dependent variable expressed as a proportion differs between group 1 ( ) and group 2 ( ) in the population; ≠ . |
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, June 22). Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, inferential statistics | an easy introduction & examples, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations, what is your plagiarism score.

What We Know About After-Death Communication Experiences
Is death really the end of everything research offers clues..
Updated July 23, 2024 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
- Understanding Grief
- Take our Depression Test
- Find a therapist to heal from grief
- Having experiences that feel as if one is interacting with a deceased person are common.
- These experiences tend to be positive and may even be experienced as therapeutic.
- Research finds that after-death communication experiences can occur outside of grief.

Co-authored with Imants Barušs, Ph.D.
After-death communications (ADCs) refer to the apparent communication of the deceased with the living, which are sensory experiences in nature. Experiences range significantly but can include full-body visualizations, dreams , hearing footsteps, electronic devices flickering on or off, feeling a hug, or conversations with the deceased. 1 Noted psychologist Carl Jung had dreams of his father after his father’s death, which made him think more about life after death.
ADCs are surprisingly common; studies conducted on various populations have found prevalence rates ranging from 31 to 82 percent. 2 These numbers sometimes include those who were previously doubtful of the validity of such experiences—including, in one case, a skeptic who was rattled by the apparently spontaneous playing of a broken radio during his wedding. 3 Even people who identify as atheists can report these experiences, according to empirical survey data across diverse populations. 4
A robust amount of scholarly literature around ADC experiences has emerged in recent times, which explicitly describes ADCs as helpful, reassuring, transformative, and positive in some capacity for most experiencers. This is supported by many clinical experts in thanatology, psychology, end-of-life care, and medicine, who have discussed ADCs as non-pathological experiences that are often supportive, meaningful, and affirming for the bereaved. 5
Continuing Bonds Theory
Continuing bonds theory, which is observable in cross-cultural traditions across the world, demonstrates how having an authentic sense of connection to the deceased tends to be therapeutic rather than harmful. 6 This framework for understanding grief, based partially on attachment theory and cultural studies, outlines how individuals, families, or communities who are grieving do not need to disconnect from the deceased.
Continuing bonds affirms that grief doesn’t subscribe to a rigid timeline, and that people can live their lives freely without needing to repress or sever their relationship with the deceased. 7 By continuing an ongoing relationship with the deceased, people can grapple with the deeper meaning of loss over time in a way that is personally meaningful. Thus, continuing bonds theory normalizes after-death communication experiences.
Traditional continuing bonds theorists frequently emphasize symbolic, emotional, or active participation in memorial activities, which emphasizes the mental representation of the deceased within people who are bereaved. 8 As a result, some continuing bonds scholars simply convey that the "dead are dead." These theorists are correct in acknowledging a person has physically died, and thereby an observable change in a relationship has occurred.
However, after-death communication experiences challenge the notion of what death even means. The entire ADC research literature demonstrates how continuing bonds may not be merely a mental representation; there is some possibility that an interactive connection could potentially occur between the living and the deceased.
After-Death Communications Occur Outside of Grief
Research finds that some people experience anomalous experiences in which the deceased person is clearly a separate entity, and many people report that it is the deceased who "initiates" these experiences spontaneously. 4
Elsaesser et al. (2021) discovered that 27 percent of research participants who had ADC experiences identified as not being in a state of grieving or mourning; some people had never even known the deceased person they believed they were connecting with, and thus never grieved. This demonstrates how some people have after-death communication experiences outside the context of grief and bereavement . In other words, this suggests that ADCs are not merely an extension of the grieving process, and that something else may be happening here.
The Survival Hypothesis
In the eyes of some, after-death communication experiences support the survival hypothesis, which suggests that consciousness continues after physical death. Experiences like these make us question the notion that there is only oblivion upon death. It is possible that interactions with the deceased mean that memories, perceptions, and individual experiences do not stop with physical death.

In the West, most of us were educated and socially conditioned to believe these sorts of things aren’t supposed to happen, but they do. Personally, we encourage readers to keep an open mind around after-death communication experiences and to follow the evidence where it leads. Science is an empirical investigation of whatever one wishes, which does not have to be defined by societal norms or follow dogmatic beliefs about materialism . 9
ADC experiences provide us with rich opportunities to explore the nature of consciousness. The question of whether we continue to exist in some form after death has serious consequences for the way we live.

This post was co-authored with Imants Barušs, Ph.D., a Professor in the Department of Psychology at King's University College at Western University. He is the author of 8 books, over 50 academic papers, and over 100 presentations at conferences and universities around the world.
Readers who are interested in learning more can read Death As An Altered State of Consciousness and Transcendent Mind: Rethinking the Science of Consciousness.
1. Barušs, I. (2023). Death as an altered state of consciousness: A scientific approach . American Psychological Association.
2. Kamp, K. S., Steffen, E. M., Alderson-Day, B., Allen, P., Austad, A., Hayes, J., Larøi, F., Ratcliffe, M., & Sabucedo, P. (2020). Sensory and quasi-sensory experiences of the deceased in bereavement: An interdisciplinary and integrative review. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 46 (6), 1367–1381.
3. Shermer, M. (2014). Infrequencies. Scientific American , 311(4).
4. Elsaesser, E., Roe, C. A., Cooper, C. E., & Lorimer, D. (2021). The phenomenology and impact of hallucinations concerning the deceased. BJPsych Open , 7 (5), Article e148.
5. Penberthy, J. K., Pehlivanova, M., Kalelioglu, T., Roe, C. A., Cooper, C. E., Lorimer, D., & Elsaesser, E. (2023). Factors moderating the impact of after death communications on beliefs and spirituality. OMEGA - Journal of Death and Dying , 87 (3), 884–901.
6. Klass D., & Steffen E. (2018). Introduction: Continuing bonds—20 years on. In D. Klass, & E. Steffen (Eds.), Continuing bonds in bereavement: New directions for research and practice (pp. 1–14). Routledge.
7. Shelvock, M., Kinsella, E. A., & Harris, D. (2022). Beyond the corporatization of death systems: Towards green death practices. Illness, Crisis, and Loss , 30 (4), 640-658.
8. Jahn, D. R., & Spencer-Thomas, S. (2018). A qualitative examination of continuing bonds through spiritual experiences in individuals bereaved by suicide. Religions , 9 (8), 248-.
9. Barušs, I., & Mossbridge, J. (2017). Transcendent mind: Rethinking the science of consciousness . American Psychological Association.

Mark Shelvock, MACP, is a licensed psychotherapist in Canada and a Certified Thanatologist with the Association for Death Education and Counselling. He also teaches in the Grief Education Program at OISE, University of Toronto.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
share this!
July 25, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Bat evolution study supports gliding-to-flying hypothesis

In new research published in PeerJ , researchers from the University of Washington, University of Texas at Austin and Oregon Institute of Technology, led by undergraduate student Abby Burtner, have advanced our understanding of the evolutionary origins of flight in bats.
The study, titled "Gliding toward an Understanding of the Origin of Flight in Bats," employs phylogenetic comparative methods to explore the evolutionary transition from gliding to powered flight in these unique mammals.
Bats are the only mammals capable of powered flight, a feat enabled by their highly specialized limb morphology. However, the evolutionary pathway that led to this capability has remained elusive due to an incomplete fossil record. The team's research provides significant insights by testing the hypothesis that bats evolved from gliding ancestors.
The research team analyzed a comprehensive dataset of limb bone measurements that included four extinct bats and 231 extant mammals with various locomotor modes. Their findings reveal that gliders exhibit relatively elongate forelimb and narrower hindlimb bones that are intermediate between those of bats and non-gliding arboreal mammals. Evolutionary modeling of these data offers support for the hypothesis that selection may be strong on certain forelimb traits, pulling them from a glider towards a flyer adaptive zone in bats.
"We propose an adaptive landscape of limb bone traits across locomotor modes based on the results from our modeling analyses," said Dr. Santana. "Our results, combined with previous research on bat wing development and aerodynamics, support a hypothetical evolutionary pathway wherein a glider-like forelimb morphology preceded the evolution of specialized bat wings."
This study not only supports the gliding-to-flying hypothesis but also challenges the traditional view of bat and glider limb evolution. The researchers emphasize the need for future studies to test the biomechanical implications of these bone morphologies and to consider the complex genetic and ecological factors that influenced the evolution of bat-powered flight.
"Our findings contribute to the hypothesis that bats evolved from gliding ancestors and lay a morphological foundation in our understanding of bat flight," Dr. Law added. "However, we stress that additional fossils are necessary to truly unravel the mysteries of this remarkable evolutionary transition."
Journal information: PeerJ
Provided by PeerJ
Explore further
Feedback to editors

New study disputes Hunga Tonga volcano's role in 2023–24 global warm-up
10 hours ago

New self-powered electrostatic tweezer enhances object manipulation and microfluidics

Climate is most important factor in where mammals choose to live, study finds
11 hours ago

Team develops novel hybrid scheme for compressible flow computations

Twisted carbon nanotubes could achieve significantly better energy storage than advanced lithium-ion batteries
3D models show dolphins already used narrow-band sound waves for orientation 5 million years ago
Raman spectroscopy offers new insights into ionic liquid acidity
12 hours ago

New clam species discovered in South Africa's kelp forest

Communicating numbers boosts trust in climate change science, research suggests

New interaction network in endocytosis process discovered
Relevant physicsforums posts, the predictive brain (stimulus-specific error prediction neurons).
Jul 21, 2024
Contradictory statements made by two different professors
The cass report (uk).
Jul 19, 2024
Understanding COVID Quarantine Guidance
Innovative ideas and technologies to help folks with disabilities.
Jul 18, 2024
New and Interesting Publications Relevant to the Origin of Life
Jul 15, 2024
More from Biology and Medical
Related Stories

Scientists expand understanding of limb evolution in earliest birds
Jun 5, 2023

Giving drones wrap-and-grip wings to allow them to land on poles and tree limbs
Jul 16, 2024

How gliding animals fine-tuned the rules of evolution
Feb 18, 2020

A key gene helps explain how the ability to glide has emerged over-and-over during marsupial evolution
Apr 24, 2024

High-flying morpho butterflies evolved into efficient gliders
Nov 29, 2021

Sep 23, 2019
Recommended for you

New understanding of fly behavior has potential application in robotics, public safety
13 hours ago

Increased demand for metals and minerals needed for clean energy transition puts 4,000+ species at risk, finds study

Invasive, blood-sucking fish 'may hold the key to understanding where we came from,' say biologists
15 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

COMMENTS
Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
6. Write a null hypothesis. If your research involves statistical hypothesis testing, you will also have to write a null hypothesis. The null hypothesis is the default position that there is no association between the variables. The null hypothesis is written as H 0, while the alternative hypothesis is H 1 or H a.
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation ('x affects y because …'). A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses.
A research hypothesis helps test theories. A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior. It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
Research hypothesis checklist. Once you've written a possible hypothesis, make sure it checks the following boxes: It must be testable: You need a means to prove your hypothesis. If you can't test it, it's not a hypothesis. It must include a dependent and independent variable: At least one independent variable ( cause) and one dependent ...
An effective hypothesis in research is clearly and concisely written, and any terms or definitions clarified and defined. Specific language must also be used to avoid any generalities or assumptions. Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis: Predicts the relationship and outcome.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing: State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ). Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis. Perform an appropriate statistical test. Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Present the findings in your results ...
A research hypothesis predicts an answer to the research question based on existing theoretical knowledge or experimental data. Some studies may have multiple hypothesis statements depending on the research question(s). A research hypothesis must be based on formulas, facts, and theories. It should be testable by data analysis, observations ...
Learning how to write a hypothesis comes down to knowledge and strategy. So where do you start? Learn how to make your hypothesis strong step-by-step here.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question. A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on ...
A research hypothesis defines the theory or problem your research intends to test. It is the "educated guess" of what the final results of your research or experiment will be. Before you can write the research hypothesis and its alternative, you must focus and define your research problem.
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as "an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.". In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess. Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it's true or not.
A research hypothesis provides a clear, testable statement that guides the direction and focus of a study. The benefit is that the hypothesis makes selecting appropriate research methods or statistical means possible, making the analysis more effective and achieving a result. Above all, the idea selected for the research also makes the study ...
A hypothesis is a prediction of what will be found at the outcome of a research project and is typically focused on the relationship between two different variables studied in the research. It is usually based on both theoretical expectations about how things work and already existing scientific evidence. Within social science, a hypothesis can ...
A hypothesis is a specific prediction, based on previous research that can be tested in an experiment. A hypothesis is often called an "educated guess," but this is an oversimplification.
Hypothesis 2: The coral that makes up Eniwetok might have grown in a ring atop an underwater mountain already near the surface. The key to this hypothesis is the idea that underwater mountains don't sink; instead the remains of dead sea animals (shells, etc.) accumulate on underwater mountains, potentially assisted by tectonic uplifting.
Science hypotheses lay the foundation for empirical exploration. These Thesis statements predict outcomes based on existing knowledge and guide research. Explore a variety of science hypothesis examples across different disciplines, showcasing the diverse ways scientists propose, test, and validate their assumptions.
Mistake vs. discovery is the fundamental tradeoff of Hypothesis Testing. So tolerating more mistakes leads to more chance of discovery. This is the concept of MDE that we will elaborate on in part 4. Finally, we're ready to define power. Power is an important and fundamental topic in statistical testing, and we'll explain the concept in ...
A good hypothesis is seen as the backbone of doing effective research. Following are some key characteristics that define a good hypothesis: Testable. A good hypothesis has to be testable either by experimentation or observation. The hypothesis should clearly predict what can be measured or observed.
The alternative hypothesis (H a) is the other answer to your research question. It claims that there's an effect in the population. Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it's the claim that you expect or hope will be true. The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis.
Research finds that some people experience anomalous experiences in which the deceased person is clearly a separate entity, and many people report that it is the deceased who "initiates" these ...
1 Throughout this paper, G is a finite group and p is a prime number. For the positive integers a and b, ap and gcd(a,b) denote the p-part of a and the greatest common divisor of a and b, respectiv...
The study, titled "Gliding toward an Understanding of the Origin of Flight in Bats," employs phylogenetic comparative methods to explore the evolutionary transition from gliding to powered flight ...
Congratulations to Dr. Stephen Nadeau on the publication of "Opioids: Analgesia, Euphoria, Dysphoria, and Oblivion: Observations and a Hypothesis," which appears in the July issue of Medical Research Archives. Abstract Introduction: In a previous paper, we inquired into the root causes of the two opioid crises our nation is facing, one evolved from the effects of…