- Corpus ID: 61416846

Performance Analysis of Business Processes through Process Mining
- P. T. G. Hornix , Tm-Is A J M M Weijters , +2 authors Peter Hornix Stramproy
- Published 2007
- Business, Computer Science
Figures and Tables from this paper

71 Citations
Process mining : conformance and extension, process mining based on object-centric behavioral constraint (ocbc) models, stage-based business process mining, discovering colored petri nets from event logs, business process analysis in healthcare environments: a methodology based on process mining, discovering simulation models, discovering redo-activities and performers' involvements from xes-formatted workflow process enactment event logs, control metrics evaluation model for business processes using process mining, applying process mining to analyse business process performance in the physical asset management environment, event interval analysis: why do processes take time, 41 references, genetic process mining, discovering workflow performance models from timed logs, workflow mining: a survey of issues and approaches, multi-phase process mining : aggregating instance graphs into epcs and petri nets, multi-phase process mining: building instance graphs, the prom framework: a new era in process mining tool support, workflow mining: which processes can be rediscovered, conformance testing : measuring the alignment between event logs and process models, mining social networks: uncovering interaction patterns in business processes, a generic import framework for process event logs, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
- Help & FAQ
Multi-perspective process mining
- Process Analytics
Research output : Thesis › Phd Thesis 1 (Research TU/e / Graduation TU/e)
| Original language | English |
|---|---|
| Qualification | Doctor of Philosophy |
| Awarding Institution | |
| Supervisors/Advisors | , Promotor , Promotor , Copromotor |
| Award date | 7 Feb 2018 |
| Place of Publication | Eindhoven |
| Publisher | |
| Print ISBNs | 978-90-386-4438-7 |
| Publication status | Published - 7 Feb 2018 |
Bibliographical note
Promotion : time and place.
- 16:00, Auditorium, Senaatszaal
Access to Document
- 20180207_Mannhardt Final published version, 8.08 MB
Celonis - Thesis Award (PhD)
Mannhardt, F. (Recipient), 2019
Prize : Other › Career, activity or publication related prizes (lifetime, best paper, poster etc.) › Scientific
Process Mining Dissertation Award 2019
Mannhardt, F. (Recipient), Sept 2019
- Doctor of Philosophy 100%
T1 - Multi-perspective process mining
AU - Mannhardt, F.
N1 - Proefschrift
PY - 2018/2/7
Y1 - 2018/2/7
M3 - Phd Thesis 1 (Research TU/e / Graduation TU/e)
SN - 978-90-386-4438-7
T3 - SIKS dissertation series
PB - Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
CY - Eindhoven

- Contact/Imprint
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin - Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences - Process Management and Information Systems
Bachelor and master thesis.
General Information
Our team offers bachelor and master thesis topics as well as student projects to be written in English.
Student may apply for a thesis or a study project during within two application windows in a year, in which new topics are made available. The first window is open from February 1st until April 1st. The second window is open from July 1st until October 1st.
Here you can find the information on how to write a thesis with us. Slides are available here ( part I , part II ), and recordings here ( part I , part II ).
Furthermore, find below a summary of guidelines for working on your thesis with us.
Expression of Interest in a Topic (Thesis or Study Project)
If you are interested in one of the topics, please send an email expressing your interest to Dr. Saimir Bala (firstname[dot]lastname[at]hu-berlin.de). Please explain why this topic is interesting for you and how it fits your prior studies. Also explain what are your strengths in your studies and in which semester of your studies you are.
Process Overview
- There are two main time windows in which the team proposes new topics: Feb 1st – Apr 1st and Jul 1st – Oct 1st
- Within these windows students can apply for an open topic (see list of open topics below)
- Application is done by sending an email to Dr. Saimir Bala (firstname[dot]lastname[at]hu-berlin.de).
- We collect your applications and make a topic-student assignment in two rounds. First round on March, second round after the deadline. For the winter session, we have two rounds (Sep, Oct).
- Once a student has been matched to a supervisor, a kick-off meeting is scheduled to scope the topic.
- Then, students must submit a research proposal to the supervisor within a month.
- If the proposal is graded as passed, the supervision is officially registered
- Once the thesis work is concluded, the thesis defense is scheduled within a dedicated defense slot.
Important Dates
01.07.2024: New topics released. Students can express their interest.
02.09.2024: Topic assignment (1st round)
01.10.2024: Expression of interest deadline
02.10.2024: Topic assignment (2nd round)
Milestones :
- Kick-off: shortly after assignment round
- Research proposal submission deadline first round (1 month after official kick-off)
- Official start (if proposal sufficient)
- Thesis delivery
- Grading & Defence
Please consider the following hints and guidelines for working on your thesis:
- Templates for thesis and proposal: https://www.informatik.hu-berlin.de/de/studium/formulare/vorlagen
- Page limits are as follows
- page limit is for Bachelor Informatik 40 pages and for Kombibachelor Lehramt Informatik 30 pages
- page limit is for Master Informatik 80 pages and for Master Information Systems 60 pages
- The limits do not include cover, table of content, references, and appendices.
Prerequisites
The candidate is expected to be familiar with the general rules of writing a scientific paper. Some general references are helpful for framing any thesis, no matter which topic:
- Wil van der Aalst: How to Write Beautiful Process and Data Science Papers? Archive Report (2022).
- Jan Recker: Scientific Research in Information Systems: A Beginner's Guide . Springer, Heidelberg, Germany (2021).
- Jan Mendling, Benoit Depaire, Henrik Leopold: Methodology of Algorithm Engineering . Archive Report (2023).
- Claes Wohlin, Pär Runeson, Martin Höst, Magnus Ohlsson, Björn Regnell, Anders Wesslén Experimentation in software engineering . Springer Science & Business Media (2012).
- Ken Peffers, Tuure Tuunanen, Marcus A. Rothenberger, Samir Chatterjee: A Design Science Research Methodology for Information Systems Research . J of Management Information Systems 24(3): 45-77 (2008).
- Barbara Kitchenham, Rialette Pretorius, David Budgen, Pearl Brereton, Mark Turner, Mahmood Niazi, Stephen G. Linkman: Systematic literature reviews in software engineering - A tertiary study . Information & Software Technology 52(8): 792-805 (2010).
- Lagendijk, Ad. Survival Guide for Scientists: Writing, Presentation, Email . Amsterdam University Press (2008).
- Adam LeBrocq: Journal of the Association for Information Systems Style Guide. https://aisel.aisnet.org/cais/cais_style_guide.pdf
In agreement with the supervisor an individual list of expected readings should be studied by the student in preparation of the actual work on the thesis.
The grading of the thesis takes various criteria into account, relating both to the thesis as a product and the process of establishing its content. These include, but are not limited to:
- Correctness of spelling and grammar
- Aesthetic appeal of documents and figures
- Compliance with formal rules
- Appropriateness of thesis structure
- Coverage of relevant literature
- Appropriateness of research question and method
- Diligence of own research work
- Significance of research results
- Punctuality of work progress
- Proactiveness of handling research progress
Recent Topics
The following topics are available within the current application window.
Topic 1: Process prediction using object-centric event log (Bachelor/Master)
Business process prediction involves forecasting specific details, such as the next activity to be performed, the time remaining for the completion of a process instance, or key process indicators, for an ongoing process instance. Currently, the techniques rely on XES event logs as input data. However, the field of process mining is shifting towards utilizing object-centric event logs, which offer a comprehensive multidimensional view of the data. Despite this advancement, object-centric event logs have been underutilized as input for process prediction.
Research problem : The core research problem addressed is: How can process prediction benefit from an object-centric event log? The aim is to propose a method to process prediction using object-centric event log.
Requirements : The candidate must have previous knowledge of process mining and software development. Further desirable requirements are pro-activity and self-organization.
Initial references
- An Empirical Investigation of Different Classifiers, Encoding, and Ensemble Schemes for Next Event Prediction Using Business Process Event Logs. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 11(6): 68:1-68:34 (2020)
- Uncovering Object-Centric Data in Classical Event Logs for the Automated Transformation from XES to OCEL. BPM 2022: 379-396
- Benedikt Knopp, Wil M. P. van der Aalst:Order Management Object-centric Event Log in OCEL 2.0 Standard. Zenodo, 2023
Supervisor: Kate Revoredo
Topic 2: Causation discovery for process prediction (Bachelor/Master)
Business process prediction involves forecasting specific details, such as the next activity to be performed, the time remaining for the completion of a process instance, or key process indicators, for an ongoing process instance. Currently, most techniques rely on the order in which the events happened without considering the cause-effect relation among them.
Research problem: The core research problem addressed is: How can process prediction benefit from the cause-effect relation among the events? The aim is to propose a method to discover the cause relation among events and use this information for process prediction.
Requirements: The candidate must have previous knowledge of process mining, statistics, and software development. Further desirable requirements are pro-activity and self-organization.
- Jens Brunk, Matthias Stierle, Leon Papke, Kate Revoredo, Martin Matzner, Jörg Becker: Cause vs. effect in context-sensitive prediction of business process instances. Inf. Syst. 95: 101635 (2021)
- Pearl,J.(2011).Bayesiannetworks.
Topics 3: Uses of Models in Agile Software Development (Bachelor/Master)
Motivation & problem : Modeling is a key topic in software engineering. In software development projects, among other aspects, modeling supports the developer in understanding the design by providing an overview and a tool for communication with fellow developers and other stakeholders. The benefits of models for supporting system analysis and design activities have been highlighted regarding their cognitive effectiveness, often in the context of traditional methodologies. However, these benefits have also been discussed in the agile scene, but it is still not clear to what extent models are used in agile software development projects.
Objectives : conduct a systematic review of the literature, identify the uses of models in agile software development, categorize and prioritize them, and propose a framework to support agile software development based on these findings. The findings shall be evaluated according to the perspective of practitioners.
Prerequisites : (1) Basic knowledge of agile software development methodologies; (2) Intermediate knowledge of models used in software development; (3) Pro-activity, self-organization, attention to detail (desirable).
Initial References:
- Ambler, Scott W. The object primer: Agile model-driven development with UML 2.0. Cambridge University Press, 2004.
- Alfraihi, Hessa Abdulrahman A., and Kevin Charles Lano. "The integration of agile development and model driven development: A systematic literature review." The 5th International Confrence on Model-Driven Engineeing and Software Development (2017).
- Wagner, Stefan, Daniel Méndez Fernández, Michael Felderer, Antonio Vetrò, Marcos Kalinowski, Roel Wieringa, Dietmar Pfahl et al. "Status quo in requirements engineering: A theory and a global family of surveys." ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology (TOSEM) 28, no. 2 (2019): 1-48.
- Petre, Marian. "UML in practice." In 2013 35th international conference on software engineering (icse), pp. 722-731. IEEE, 2013.
Supervisor: Cielo González
Topic 4: Collaborative business-model-driven tool for agile software development projects (Bachelor/Master)
Motivation & problem: Agile software development methodologies and frameworks have changed the way software is created and are widely supported and used. However, this does not mean there are no challenges that jeopardize the principles of agile methodologies, increasing the failure rate of agile software development projects. This situation highlights the need for cohesive solutions. The use of business process models in the agile software development context emerges as a promising option due to their ability to facilitate communication and share knowledge.
Objectives : analyze, design, implement and evaluate a collaborative business-model-driven tool for agile software development projects. The objectives will be adapted to align with the student's study goals.
Prerequisites :(1) Knowledge of agile software development methodologies; (2) Knowledge of business process models; (3) Knowledge in frontend (e.g., JavaScript and TypeScript); (4) Knowledge in Java; (5) Knowledge in databases (e.g., PostgreSQL, mongoDB); (6) Pro-activity and self-organization.
Initial references:
- Moyano, Cielo González, et al. "Uses of business process modeling in agile software development projects." Information and Software Technology 152 (2022): 107028.
- Trkman, Marina, Jan Mendling, and Marjan Krisper. "Using business process models to better understand the dependencies among user stories." Information and software technology 71 (2016): 58-76.
Topic 5: Fair and Diverse Sampling of Event Logs (Bachelor and Master)
The sampling of large event logs, i.e. the selection of subsets of data, has been proposed as one possible solution to tackle the runtime requirements of process analysis tasks and to aid the understandability of data sets, that are too complex to analyze as a whole. In this context a diverse sample is one, which properly reflects the diversity or complexity of the event log, while a fair sample is one, which ensures, that each value is represented properly. For both quality criteria, approaches have been proposed, to solve these problems, for instance by optimizing subset selection functions or employing determinantal point processes.
In this thesis the student will:
* conduct research on existing approaches for diverse and fair sampling * implement selected approaches for the diverse and fair sampling for event logs * evaluate the implemented algorithms comparatively in terms of quality and efficiency
The student is expected to have existing knowledge in optimization or statistics or sampling.
Initial References
- Kabierski, M., van der Aa, H., and Weidlich, M. (2020). Sampling and approximation techniques for efficient process conformance checking. Information Systems. 104. 101666. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2020.101666
- Moumoulidou, Z., McGregor, A., and Meliou A.. Diverse Data Selection under Fairness Constraints. In 24th International Conference on Database Theory (ICDT 2021). Leibniz International Proceedings in Informatics (LIPIcs), Volume 186, pp. 13:1-13:25, Schloss Dagstuhl – Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik (2021), https://doi.org/10.4230/LIPIcs.ICDT.2021.13
- Celis, L., Vijay, K., Straszak, D., Deshpande, A., Kathuria, T., and Vishnoi, N. (2018). Fair and Diverse DPP-based Data Summarization. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.04023
Supervisor: Martin Kabierski
Topic 6: Estimating Saturation in Qualitative Studies (Master)
Grounded theory is a research methodology usually applied in qualitative analysis. It involves the collection of data (usually through interviews, surveys, ...), and the deduction of concepts, categories, and ultimately theories that emerge from the collected data. A central question to this iterative data collection-evaluation process is when one should stop collecting data, which ideally is at the point of saturation, i.e. when no new information is gained from new interviews. Determining when exactly this point has been reached is an ongoing topic of discussion and research. Species richness estimators, that estimate the completeness of samples, could be utilized to give saturation estimates that are data-driven and grounded in statistics.
In this thesis, the student will:
- assess the applicability of species richness estimation for determining saturation in qualitative studies - implement and apply the estimators to qualitative interview data - evaluate the feasibility of the approach and discuss potential limitations
The student is expected to have understanding of statistics and and optionally preliminary experience in the analysis of qualitative data. We note, that the student is not expected to collect data for the thesis, as this data will be provided by us.
- Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1994). Grounded theory methodology: An overview. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (pp. 273–285). Sage Publications, Inc. https://www.depts.ttu.edu/education/our-people/Faculty/additional_pages/duemer/epsy_5382_class_materials/Grounded-theory-methodology.pdf
- Saunders, Benjamin, et al. (2018). Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. In: Qual Quant 52 (pp. 1893-1907). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0574-8
- Gotelli, Nicholas & Chao, Anne. (2013). Measuring and Estimating Species Richness, Species Diversity, and Biotic Similarity from Sampling Data. 10.1016/B978-0-12-384719-5.00424-X. https://www.uvm.edu/~ngotelli/manuscriptpdfs/Gotelli_Chao_Encyclopedia_2013.pdf
Topic 7: Runtime Prediction of Alignment Construction Algorithms (Bachelor/Master)
Conformance Checking relates a process model to recorded instances of the execution of the process, typically stored in event logs, to determine where expected and actual behaviour deviate from each other. In this context alignment algorithms are regarded as the de facto standard method, due to their interpretability and accuracy in highlighting precise problem areas in the process. Yet, typically run times for alignment construction are prohibitively large, typically caused by a handful of traces in the log, for which the construction of an alignment is especially complex. One possible solution to this problem could lie in predicting the expected runtime of aligning a trace to the model, for instance using regression-based methods and then ignoring traces, that are expected to take long.
In this thesis, the student will: - assess the factors that influence the runtime of alignments - derive a methodology for predicting the runtime of alignment construction between event logs and process models - evaluate the accuracy of the predictor
The student is expected to have existing knowledge of process mining, conformance checking, and basic knowledge of regression analysis, or willingness to learn about these topics under guidance of the supervisor.
- Chapter 1, 2 and 7 in Carmona, J., van Dongen, B., Solti, A., & Weidlich, M. (2018). Conformance checking. Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99414-7
- Backhaus, K., Erichson, B., Weiber, R., Plinke, W. (2016). Regressionsanalyse. In: Multivariate Analysemethoden. Springer Gabler, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-08893-7_1
Topic 8: Event Log Privacy Auditing (Master)
Event Logs are often anonymized to ensure privacy. Most anonymization algorithms use formal privacy guarantees such as differential privacy. The issue with these techniques is that the algorithm or implementation could contain errors. Consequently, anonymized event logs might not have the targeted privacy guarantee and the individuals involved in the dataset might have a higher privacy loss than expected. Differential Privacy Auditing allows to check if an algorithm fulfils the differential privacy guarantee. The aim of this thesis is to adjust know Differential Privacy Auditing techniques to Event Log Anonymization and evaluate anonymization techniques from the process mining domain.
- Stephan A. Fahrenkrog-Petersen, Martin Kabierski, Han van der Aa, Matthias Weidlich: Semantics-aware mechanisms for control-flow anonymization in process mining. Inf. Syst.114: 102169 (2023)
- https://research.google/blog/dp-auditorium-a-flexible-library-for-auditing-differential-privacy/
Supervisor: Stephan Fahrenkrogh-Petersen
Topic 9: Analysis of theoretical explanations and scientific theories on transitioning from dashboards to decision making in organizational contexts (Bachelor)
This bachelor thesis seeks to analyze theoretical explanations and scientific theories concerning the transition from dashboards to decision-making processes. Dashboards are widely used tools in organizational contexts for decision-making. The study aims to examine the levels of management where dashboards are employed and how they contribute to the decision-making process within organizations. Literature :
- Burstein, F., & Holsapple, C. W. (2008). Handbook on Decision Support Systems 2. https://www.academia.edu/83497312/Handbook_on_Decision_Support_Systems_2
- Maynard, S., Burstein, F., & Arnott, D. (2001). A multi-faceted decision support system evaluation approach. Journal of Decision Systems, 10(3–4), 395–428. Mintzberg, H., Raisinghani, D., & Theoret, A. (1976). The Structure of “Unstructured”
- Decision Processes. Administrative Science Quarterly, 21(2), 246. https://doi.org/10.2307/2392045
Supervisor: Kristina Sahling
Topic 10: Visualizing Cyclic Time Arrangements in Process Graphs (Bachelor/Master)
Time is essential to understanding processes, yet most process mining approaches are limited to depicting time within a process graph as textual cues or color schemes. Adapting the visual appearance of process graphs to various time arrangements may enhance the accessibility for finding bottlenecks or delays. An example is aligning process graphs along a linear timeline [1]. In cases where processes involve repetitive patterns, such as in chronic health care or crop management, a cyclic arrangement may be useful. However, for the latter, an adequate solution in process mining is needed.
This thesis aims to develop and exemplify a design method for a visual solution in process mining that allows for exploring a cyclic time arrangement in a process graph. We will adapt the research objectives to align with the experience and study goals of the student.
Initial References :
- H. Kaur, J. Mendling, C. Rubensson, and T. Kampik, “Timeline-based Process Discovery,” CoRR, abs/2401.04114, 2024. Available: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2401.04114
- A. Yeshchenko and J. Mendling, “A Survey of Approaches for Event Sequence Analysis and Visualization using the ESeVis Framework.,” CoRR, abs/2202.07941, 2022. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.07941
- W. Aigner, S. Miksch, H. Schumann, and C. Tominski, Visualization of Time-Oriented Data. in Human-Computer Interaction Series. London: Springer London, 2011. Available: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-85729-079-3.
Supervisor: Christoffer Rubensson
Topic 11: Advanced Resource Analysis in Process Mining (Bachelor/Master)
In the last decade, process mining techniques have been developed to study human behavior in event data, such as the strength of collaboration between co-workers or even stress levels at a workplace. Since measuring human behavior is complex, this is a welcoming alternative to more labor-intensive methods like surveys. Still, most techniques are relatively simple but could be improved by applying theoretical frameworks from social science.
This thesis aims to develop a resource analysis approach (e.g., a metric, a concept, or a framework) in process mining grounded in an existing theory from social science. We will adapt the research objectives to align with the experience and study goals of the student.
- J. Nakatumba and W. M. P. van der Aalst, “Analyzing Resource Behavior Using Process Mining,” in Business Process Management Workshops. BPM 2009. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, S. Rinderle-Ma, S. Sadiq, and F. Leymann, Eds., Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2010. Available: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12186-9_8.
- A. Pika, M. Leyer, M. T. Wynn, C. J. Fidge, A. H. M. Ter Hofstede, and W. M. P. Van der Aalst, “Mining Resource Profiles from Event Logs,” in ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems, vol. 8, no. 1, 1:1-30, 2017. Available: https://doi.org/10.1145/3041218.
- Z. Huang, X. Lu, and H. Duan, “Resource behavior measure and application in business process management,” in Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 39, no. 7, 6458–6468, 2012. Available: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2011.12.061.
Topic 12: Anthropomorphic Perceptions of Large Language Models: what is the gender of ChatGPT and its Counterparts? (Bachelor/Master)
Description : In today's digital era, Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT are transforming the way we interact with technology, often blurring the boundaries between machine and human cognition. This thesis delves into the intriguing realm of anthropomorphism, the human tendency to attribute human-like qualities to non-human entities. Specifically, this research aims to uncover laypeople's underlying beliefs and implicit conceptions about ChatGPT and similar models concerning an implicit gender attribution. By designing and conducting a survey, the thesis will gain insights into individuals' perception of these cutting-edge technologies. The findings can potentially illuminate not only our relationship with LLMs but also the broader implications of human-machine interactions in an increasingly AI-driven world.
- Deshpande, A., Rajpurohit, T., Narasimhan, K., & Kalyan, A. (2023). Anthropomorphization of AI: Opportunities and Risks (arXiv:2305.14784). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.14784
- Farina, M., & Lavazza, A. (2023). ChatGPT in society: Emerging issues. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 6. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frai.2023.1130913
- Aşkın, G., Saltık, İ., Boz, T. E., & Urgen, B. A. (2023). Gendered Actions with a Genderless Robot: Gender Attribution to Humanoid Robots in Action. International Journal of Social Robotics, 15(11), 1915–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-022-00964-0
Supervisor: Jennifer Haase
HU on the internet
- Humboldt University on Facebook
- Die Humboldt-Universität bei BlueSky
- Humboldt University on Instagram
- Humboldt University on YouTube
- Humboldt University on LinkedIn
- RSS-Feeds of the Humboldt University
- Humboldt University on Twitter
- skip navigation
- Privacy Policy
- search search
- Campusplan Campus Map

- Thesis Projects
- ECTS Approval
Process Mining in Manufacturing: A Causal AI Approach
- Subject: Process Mining in Manufacturing: A Causal AI Approach
- Type: Master's thesis
- Date: Vergeben
Joshua Holstein
Background:
The landscape of modern manufacturing industries is witnessing an exponential increase in the volume of data generated by machinery. This data, albeit a rich resource, is underutilized when it comes to refining production processes. Traditional data analysis often zeroes in on singular features and, in the process, overlooks the complex relationships and correlations among these features. This oversight leads to missed opportunities for enhancing efficiency and more accurate defect detection. The introduction of sophisticated methodologies such as process mining and causal AI aims to decipher these hidden correlations and provide actionable insights.
Research Goal:
In association with Bayer AG, the objective of this thesis project is to utilize process mining techniques and causal AI for an in-depth analysis of machine-generated data in the manufacturing context. The aim is not merely to identify correlations between data features but to interpret and articulate these relationships in a way that is beneficial to domain experts. To achieve this, you will engage with industry professionals through interviews to understand their perspectives and needs concerning this kind of analysis. The insights gained will then be implemented in a Python environment for further evaluation and testing.
In the course of this thesis, you will:
- Apply your theoretical understanding to address real-world manufacturing problems
- Explore advanced techniques such as process mining and causal AI
- Collaborate closely with domain experts in the effort to enhance the efficiency and environmental sustainability of manufacturing processes
We invite applications from those who:
- Have a strong interest in machine learning and data analysis
- Are self-driven and goal-oriented, eager to address contemporary real-world problems, and motivated to contribute original ideas
- Are comfortable engaging with professionals, for instance, through interview studies
- Possess excellent English language skills, as the thesis will be written in English
Start: Immediately
Duration: 6 months
Location: Bayer AG, Remote or nearby Grenzach-Whylen
We promise a challenging research topic, attentive mentorship, and an environment that fosters both practical and theoretical skills. Interested candidates should send their CV, transcript of records, and a brief letter of motivation to [email protected].

Process Mining Conference 2024
6th International Conference on Process Mining, October 14-18, 2024
Call for Best Process Mining PhD Dissertation Award 2024
The IEEE Task Force for Process Mining is happy to announce the 2024 edition of the Best Process Mining PhD Dissertation Award .
The award will be delivered during the 6th International Conference on Process Mining (ICPM 2024).
Eligibility – updated criteria
Eligible candidates are those who officially obtained a PhD degree defended after January 1st, 2022, with a dissertation focused on process mining. Those who applied for the 2023 edition of the prize can also reapply for the 2024 edition.
We welcome theses that contributed to advancing the state of the art in the foundations, engineering, and on-field application of process mining techniques. In this context, the term “process mining” has to be understood in a broad sense: using event data produced during the execution of business, software, or system processes, in order to extract fact-based knowledge and insights on such processes and manage future processes in innovative ways.
For a thesis to be eligible, we also require that thesis-related results have been published in at least one flagship conference/journal for process mining, for example, ICPM, BPM, CAiSE, EDOC, Petri Nets, ICDM, Information Systems, IEEE TKDE, DKE, ACM TOSEM, IEEE TSC, IEEE TSE, ToPNoC, Decision Support Systems, and BISE. We remark that applications to other dissertation award initiatives are permitted.
The winner will receive the award at the ICPM 2024 Conference.
The award comes with a free registration to the ICPM 2024 conference, and with the option of publishing the thesis with Springer, in the LNBIP series.
Nomination and Submission
Candidates are nominated by their primary supervisor via a nomination letter. Each supervisor is only allowed to nominate one candidate. The candidate is responsible for submitting the application via Easychair ( https://easychair.org/conferences/?conf=icpm2024 ) selecting the “Best Process Mining PhD Dissertation Award” track.
The application consists of the following parts, which have all to be concatenated in a single PDF file (respecting the order):
- An extended abstract of the thesis, positioning the work in the state of the art and highlighting its main results, novelty, and (potential) impact [3-5 pages]
- A nomination letter by the supervisor [1-2 pages]
- The PhD evaluation report, including the reviews of the dissertation
- Full CV of the candidate, including the list of publications
- The dissertation itself
Questions and enquiries can be directed to the chair of the jury: Artem Polyvyanyy.
Selection Process
The selection process consists of two steps:
- Each thesis is individually reviewed by 2 or 3 jury members. All jury members process all reviews individually and submit a ranking of potential winners.
- During a plenary jury discussion, the winning candidate will be decided upon.
The selection is based on the following criteria:
- originality and depth of contribution;
- methodological soundness;
- form and quality of presentation;
- significance and potential impact for the research field;
implemented techniques and software availability in case of the algorithmic nature of the contribution.
Evaluation Panel (Tentative)
- Application submission deadline : July 12, 2024 July 26, 2024 (AOE)
- Wil van der Aalst , RWTH Aachen University, Germany
- Jochen De Weerdt , KU Leuven, Belgium
- Chiara Di Francescomarino , University of Trento, Italy
- Boudewijn van Dongen , Eindhoven University of Technology, Netherlands
- Hajo Reijers , Utrecht University, Netherlands
- Pnina Soffer , University of Haifa, Israel
- Arik Senderovich , York University, Canada
- Tijs Slaats , University of Copenhagen, Denmark
- Moe Wynn , Queensland University of Technology, Australia
- Utrecht University Student Theses Repository Home
- UU Theses Repository
Care Mining: An application of Process Mining in Value-Based Healthcare
Publication date
Collections.

Home > Statler College of Engineering and Mineral Resources > MININGENG > Mining Engineering Graduate Theses and Dissertations
Mining Engineering Graduate Theses and Dissertations
Theses/dissertations from 2024 2024.
CHARACTERIZATION AND EVALUATION OF VARIOUS BIOCHAR TYPES AS GREEN ADSORBENTS FOR RARE EARTH ELEMENT RECOVERY FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS , Oluwaseun Victor Famobuwa
Selective Recovery of Various Critical Metals from Acid Mine Drainage Sludge , Gorkem Gecimli
Theses/Dissertations from 2023 2023
Development of A Hydrometallurgical Process for the Extraction of Cobalt, Manganese, and Nickel from Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Byproduct , Alejandro Agudelo Mira
Selective Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Byproduct , Zeynep Cicek
Identification of Rockmass Deformation and Lithological Changes in Underground Mines by Using Slam-Based Lidar Technology , Francisco Eduardo Gil Hurtado
Analysis of the Brittle Failure Mechanism of Underground Stone Mine Pillars by Implementing Numerical Modeling in FLAC3D , Rosbel Jimenez
Analysis of the root causes of fatal injuries in the United States surface mines between 2008 and 2021. , Maria Fernanda Quintero
AUGMENTED REALITY AND MOBILE SYSTEMS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT OPERATORS IN SURFACE MINING , Juan David Valencia Quiceno
Theses/Dissertations from 2022 2022
Integrated Large Discontinuity Factor, Lamodel and Stability Mapping Approach for Stone Mine Pillar Stability , Mustafa Baris Ates
Noise Exposure Trends Among Violating Coal Mines, 2000 to 2021 , Hanna Grace Davis
Calcite depression in bastnaesite-calcite flotation system using organic acids , Emmy Muhoza
Investigation of Geomechanical Behavior of Laminated Rock Mass Through Experimental and Numerical Approach , Qingwen Shi
Static Liquefaction in Tailing Dams , Jose Raul Zela Concha
Experimental and Theoretical Investigation on the Initiation Mechanism of Low-Rank Coal's Self-Heating Process , Yinan Zhang
Development of an Entry-Scale Modeling Methodology to Provide Ground Reaction Curves for Longwall Gateroad Support Evaluation , Haochen Zhao
Size effect and anisotropy on the strength of shale under compressive stress conditions , Yun Zhao
Theses/Dissertations from 2021 2021
Evaluation of LIDAR systems for rock mass discontinuity identification in underground stone mines from 3D point cloud data , Mario Alejandro Bendezu de la Cruz
Implementing the Empirical Stone Mine Pillar Strength Equation into the Boundary Element Method Software LaModel , Samuel Escobar
Recovery of Phosphorus from Florida Phosphatic Waste Clay , Amir Eskanlou
Optimization of Operating Conditions and Design Parameters on Coal Ultra-Fine Grinding Through Kinetic Stirred Mill Tests and Numerical Modeling , Francisco Patino
The Effect of Natural Fractures on the Mechanical Behavior of Limestone Pillars: A Synthetic Rock Mass Approach Application , Mustafa Can Süner
Evaluation of Various Separation Techniques for the Removal of Actinides from A Rare Earth-Containing Solution Generated from Coarse Coal Refuse , Deniz Talan
Geology Oriented Loading Approach for Underground Coal Mines , Deniz Tuncay
Various Operational Aspects of the Extraction of Critical Minerals from Acid Mine Drainage and Its Treatment By-product , Zhongqing Xiao
Theses/Dissertations from 2020 2020
Adaptation of Coal Mine Floor Rating (CMFR) to Eastern U.S. Coal Mines , Sena Cicek
Upstream Tailings Dam - Liquefaction , Mladen Dragic
Development, Analysis and Case Studies of Impact Resistant Steel Sets for Underground Roof Fall Rehabilitation , Dakota D. Faulkner
The influence of spatial variance on rock strength and mechanism of failure , Danqing Gao
Fundamental Studies on the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Acid Mine Drainage , Xue Huang
Rational drilling control parameters to reduce respirable dust during roof bolting operations , Hua Jiang
Solutions to Some Mine Subsidence Research Challenges , Jian Yang
An Interactive Mobile Equipment Task-Training with Virtual Reality , Lazar Zujovic
Theses/Dissertations from 2019 2019
Fundamental Mechanism of Time Dependent Failure in Shale , Neel Gupta
A Critical Assessment on the Resources and Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Acid Mine Drainage , Christopher R. Vass
Time-dependent deformation and associated failure of roof in underground mines , Yuting Xue
Theses/Dissertations from 2018 2018
Parametric Study of Coal Liberation Behavior Using Silica Grinding Media , Adewale Wasiu Adeniji
Three-dimensional Numerical Modeling Encompassing the Stability of a Vertical Gas Well Subjected to Longwall Mining Operation - A Case Study , Bonaventura Alves Mangu Bali
Shale Characterization and Size-effect study using Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Diffraction , Debashis Das
Behaviour Of Laminated Roof Under High Horizontal Stress , Prasoon Garg
Theses/Dissertations from 2017 2017
Optimization of Mineral Processing Circuit Design under Uncertainty , Seyed Hassan Amini
Evaluation of Ultrasonic Velocity Tests to Characterize Extraterrestrial Rock Masses , Thomas W. Edge II
A Photogrammetry Program for Physical Modeling of Subsurface Subsidence Process , Yujia Lian
An Area-Based Calculation of the Analysis of Roof Bolt Systems (ARBS) , Aanand Nandula
Developing and implementing new algorithms into the LaModel program for numerical analysis of multiple seam interactions , Mehdi Rajaeebaygi
Adapting Roof Support Methods for Anchoring Satellites on Asteroids , Grant B. Speer
Simulation of Venturi Tube Design for Column Flotation Using Computational Fluid Dynamics , Wan Wang
Theses/Dissertations from 2016 2016
Critical Analysis of Longwall Ventilation Systems and Removal of Methane , Robert B. Krog
Implementing the Local Mine Stiffness Calculation in LaModel , Kaifang Li
Development of Emission Factors (EFs) Model for Coal Train Loading Operations , Bisleshana Brahma Prakash
Nondestructive Methods to Characterize Rock Mechanical Properties at Low-Temperature: Applications for Asteroid Capture Technologies , Kara A. Savage
Mineral Asset Valuation Under Economic Uncertainty: A Complex System for Operational Flexibility , Marcell B. B. Silveira
A Feasibility Study for the Automated Monitoring and Control of Mine Water Discharges , Christopher R. Vass
Spontaneous Combustion of South American Coal , Brunno C. C. Vieira
Calibrating LaModel for Subsidence , Jian Yang
Theses/Dissertations from 2015 2015
Coal Quality Management Model for a Dome Storage (DS-CQMM) , Manuel Alejandro Badani Prado
Design Programs for Highwall Mining Operations , Ming Fan
Development of Drilling Control Technology to Reduce Drilling Noise during Roof Bolting Operations , Mingming Li
The Online LaModel User's & Training Manual Development & Testing , Christopher R. Newman
How to mitigate coal mine bumps through understanding the violent failure of coal specimens , Gamal Rashed
Theses/Dissertations from 2014 2014
Effect of biaxial and triaxial stresses on coal mine shale rocks , Shrey Arora
Stability Analysis of Bleeder Entries in Underground Coal Mines Using the Displacement-Discontinuity and Finite-Difference Programs , Xu Tang
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Kinetics and Quality Parameters to Determine Spontaneous Combustion Propensity of U.S. Coals , Xinyang Wang
Bubble Size Effects in Coal Flotation and Phosphate Reverse Flotation using a Pico-nano Bubble Generator , Yu Xiong
Integrating the LaModel and ARMPS Programs (ARMPS-LAM) , Peng Zhang
Theses/Dissertations from 2013 2013
Column Flotation of Subbituminous Coal Using the Blend of Trimethyl Pentanediol Derivatives and Pico-Nano Bubbles , Jinxiang Chen
Applications of Surface and Subsurface Subsidence Theories to Solve Ground Control Problems , Biao Qiu
Calibrating the LaModel Program for Shallow Cover Multiple-Seam Mines , Morgan M. Sears
The Integration of a Coal Mine Emergency Communication Network into Pre-Mine Planning and Development , Mark F. Sindelar
Factors considered for increasing longwall panel width , Jack D. Trackemas
An experimental investigation of the creep behavior of an underground coalmine roof with shale formation , Priyesh Verma
Evaluation of Rope Shovel Operators in Surface Coal Mining Using a Multi-Attribute Decision-Making Model , Ivana M. Vukotic
Theses/Dissertations from 2012 2012
Calculating the Surface Seismic Signal from a Trapped Miner , Adeniyi A. Adebisi
Comprehensive and Integrated Model for Atmospheric Status in Sealed Underground Mine Areas , Jianwei Cheng
Production and Cost Assessment of a Potential Application of Surface Miners in Coal Mining in West Virginia , Timothy A. Nolan
The Integration of Geomorphic Design into West Virginia Surface Mine Reclamation , Alison E. Sears
Truck Cycle and Delay Automated Data Collection System (TCD-ADCS) for Surface Coal Mining , Patricio G. Terrazas Prado
New Abutment Angle Concept for Underground Coal Mining , Ihsan Berk Tulu
Theses/Dissertations from 2011 2011
Experimental analysis of the post-failure behavior of coal and rock under laboratory compression tests , Dachao Neil Nie
The influence of interface friction and w/h ratio on the violence of coal specimen failure , Simon H. Prassetyo
Theses/Dissertations from 2010 2010
A risk management approach to pillar extraction in the Central Appalachian coalfields , Patrick R. Bucks
The Impacts of Longwall Mining on Groundwater Systems -- A Case of Cumberland Mine Panels B5 and B6 , Xinzhi Du
Evaluation of ultrafine spiral concentrators for coal cleaning , Meng Yang
Theses/Dissertations from 2009 2009
Development of a coal reserve GIS model and estimation of the recoverability and extraction costs , Chandrakanth Reddy Apala
Application and evaluation of spiral separators for fine coal cleaning , Zhuping Che
Weak floor stability in the Illinois Basin underground coal mines , Murali M. Gadde
Design of reinforced concrete seals for underground coal mines , Rajagopala Reddy Kallu
Employing laboratory physical modeling to study the radio imaging method (RIM) , Jun Lu
Influence of cutting sequence and time effects on cutters and roof falls in underground coal mine -- numerical approach , Anil Kumar Ray
Implementing energy release rate calculations into the LaModel program , Morgan M. Sears
Modeling PDC cutter rock interaction , Ihsan Berk Tulu
Analytical determination of strain energy for the studies of coal mine bumps , Qiang Xu
Improvement of the mine fire simulation program MFIRE , Lihong Zhou
Theses/Dissertations from 2008 2008
Program-assisted analysis of the transverse pressure capacity of block stoppings for mine ventilation control , Timothy J. Batchler
Analysis of factors affecting wireless communication systems in underground coal mines , David P. McGraw
Analysis of underground coal mine refuge shelters , Mickey D. Mitchell
Theses/Dissertations from 2007 2007
Dolomite flotation of high magnesium phosphate ores using fatty acid soap collectors , Zhengxing Gu
Evaluation of longwall face support hydraulic supply systems , Ted M. Klemetti II
Experimental studies of electromagnetic signals to enhance radio imaging method (RIM) , William D. Monaghan
Analysis of water monitoring data for longwall panels , Joseph R. Zirkle
Theses/Dissertations from 2006 2006
Measurements of the electrical properties of coal measure rocks , Nikolay D. Boykov
- Collections
- Disciplines
- WVU Libraries
- WVU Research Office
- WVU Research Commons
- Open Access @ WVU
- Digital Publishing Institute
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS
Author Corner
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
KPMG Personalisation

Process Mining for Total Quality Management
This report talks about the transformational shift in traditional tqm that process mining can bring in today’s digital world.
- Share Share close
- 1000 Save this article to my library
- Go to bottom of page
- Home ›
- Insights ›
Process and task mining are transforming the way we look at processes today. They have the power to look at processes from a macro and micro view and provide deep insights. It is now possible to study highly complex processes in great detail and with much less human effort, for making them leaner and automated where possible, while also reducing process and user level variations, and improving the overall quality of the process.
TQM or Total Quality Management framework also recommends a systematic approach towards achieving organizational objectives effectively and efficiency. Process mining helps achieve process excellence through discovery, conformance and improvement. It is a major source of information while embarking on a simple operational efficiency and productivity drive or an overall business transformation.

Download the report (2.48 MB) ⤓
Key Contact
Access our latest insights on apple or android devices.
Diam dolor diam ipsum et tempor sit. Aliqu diam amet diam et eos labore. Clita erat ipsum et lorem et sit, sed stet no labore lorem sit clita duo justo eirmod magna dolore erat amet

Top 6 Benefits of Process Mining (new 2024 research)
Kazyna turdibayeva august 19, 2024 process intelligence.

Table of Contents
Process mining has emerged as a powerful tool for analyzing and improving business processes. In this article, we will explore the six key benefits of process mining as identified by a recent study by Deloitte and HFS Research.
What is process mining?
Process mining software helps you discover, analyze, and improve business processes using advanced data mining methods. This innovative technology helps you discover, analyze, and improve business processes using advanced data mining methods. Process mining is seen as an objective and data-driven way to evaluate the real state of processes and workflows in an organization. Process mining is the intersection of business process management and data science. In this way, process mining tools interact with business software systems to extract process information, typically in the form of event logs or business objects, for the purpose of process analysis and business process improvement. Process mining algorithms and dashboards give visibility to end-to-end processes, thus providing companies with valuable data that can be used to improve business operations and reach better company performance. In this way, it’s like an x-ray to the company workflows and processes.
Process Mining vs Task Mining
Task mining and process mining are two approaches that help organizations improve their operations through data analysis, but they serve different purposes. Process mining focuses on visualizing and analyzing entire business processes by extracting knowledge from event logs to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and variations in workflows. On the other hand, task mining delves into the specific actions of individual users, capturing their interactions with applications to uncover insights about how tasks are completed. While process mining provides a high-level overview of the process landscape, task mining offers granular insights into daily activities, enabling businesses to optimize both their processes and workflows effectively.
Six Key Benefits of Process Mining
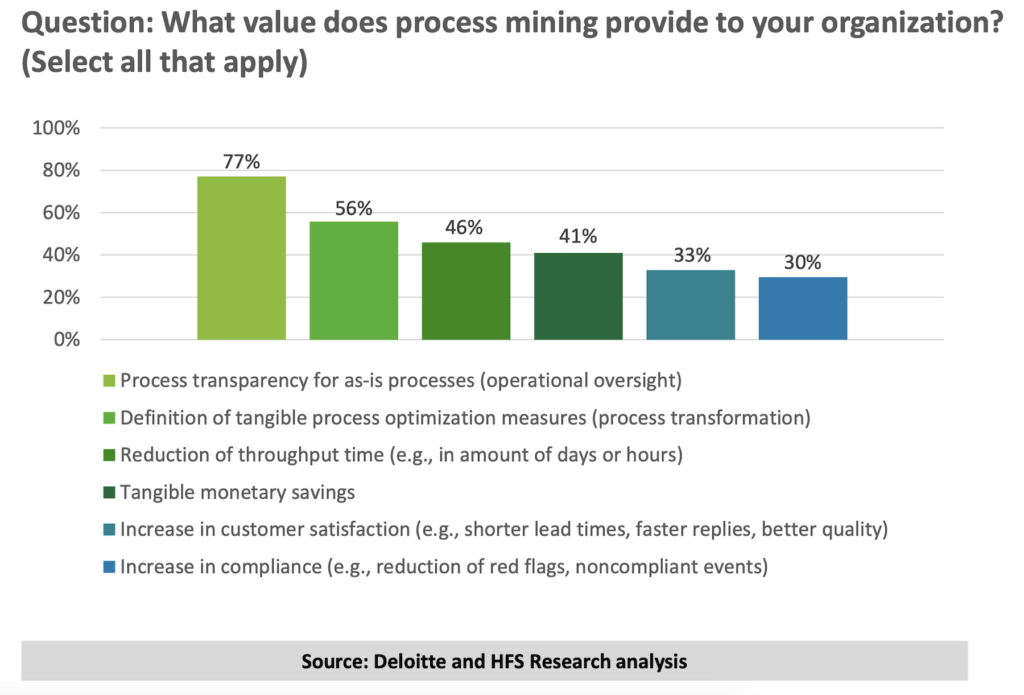
Source: Global Process Mining Survey, Deloitte, 2023
1. Process Transparency
Over 77% of enterprise leaders find process transparency to be the top value brought by process mining tools. You can think of this as being a detailed x-ray of the health of processes and workflows in an organization.
Understand As-Is Process
One of the most significant advantages of process mining is its ability to provide a clear, data-driven view of the current state of a business process. By analyzing event logs, process mining tools can automatically create visual process models, enabling organizations to see exactly how their processes are functioning. This transparency helps stakeholders understand the process flow, identify inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions.
Identify Inefficiencies
With process transparency, organizations can quickly spot inefficiencies and deviations from the intended process flow. This visibility allows businesses to identify the areas and root causes where resources are being wasted, tasks are being duplicated, or processes are not adhering to standard operating procedures. By addressing these issues, organizations can make significant improvements in process performance.
2. Process Transformation
The second key benefit of process mining to enterprise leaders is in support of process transformation. Process intelligence plays a crucial role in process transformation by leveraging data-driven insights to enhance automation initiatives. 56% of survey respondents felt process mining gives tangible process optimization insights and measures.

Optimize Process Models
Once the current state of a process has been analyzed, process mining tools can help organizations optimize their process models. By comparing the as-is process model to the happy path or intended process, organizations can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to transform their processes. This could involve redesigning process flows, automating manual tasks, or implementing new policies and procedures.
Continuous Improvement
Process mining facilitates a culture of continuous improvement within organizations. By regularly analyzing process data, businesses can monitor the impact of their process changes and ensure that improvements are sustained over time. This ongoing analysis enables organizations to stay agile and adapt quickly to changing market conditions, customer demands, and regulatory requirements.
3. Reduction in Throughput Time
The third key benefit of process mining is the ability to reduce throughput time . In other words, almost half of all respondents had seen process mining helping to streamline and speed up end-to-end processes.
Identify Bottlenecks
Process mining helps organizations identify bottlenecks in their processes, which can significantly impact throughput time. Bottlenecks occur when a process step has a limited capacity or resources, causing delays and inefficiencies in the overall process flow. By pinpointing these bottlenecks, organizations can prioritize improvement efforts and make targeted changes to their processes.
Streamline Processes
Reducing throughput time is often achieved by streamlining processes, which can involve eliminating unnecessary steps, automating manual tasks, or reallocating resources. Process mining provides the data and insights necessary to make informed decisions about how best to streamline processes, resulting in faster execution, reduced waiting times, and ultimately, improved efficiency.
4. Cost Savings
The fourth key benefit of process mining to enterprise leaders is tangible monetary savings. Over 40% of respondents to the Deloitte and HFS Research survey had found ways it reduced costs.
Reduce Manual Efforts
One of the most tangible benefits of process mining is its ability to identify opportunities for automation and the reduction of manual efforts. By pinpointing tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, or prone to human error, organizations can implement automation solutions that not only save time but also reduce labor costs.
Minimize Waste
Process mining can help organizations minimize waste by identifying inefficiencies, redundancies, and deviations from standard procedures. By addressing these issues, businesses can reduce resource consumption, avoid costly rework, and improve overall process efficiency, leading to significant cost savings.
5. Improved Customer Satisfaction
The fifth key benefit of process mining for enterprise leaders is improved customer satisfaction. Process mining is becoming increasingly popular in digitalized service businesses where the efficiency of processes can have a tangible impact on how quickly and accurately customers get service.
Faster Response Times
By reducing throughput time and streamlining processes, process mining can help organizations deliver products and services more quickly, resulting in faster response times for customers. This increase in speed can lead to higher customer satisfaction, as customers are more likely to have a positive experience when their needs are met promptly.
Enhance Customer Experience
Beyond just faster response times, process mining can also help organizations enhance the overall customer experience. By identifying inefficiencies and pain points within customer-facing processes, businesses can make targeted improvements that directly impact the customer journey. This could involve reducing the number of steps in a process, simplifying interactions, or implementing new communication channels.
6. Increased Compliance
If process mining wasn’t already hugely valuable, enterprise leaders also found that it has a proven benefit to workflow compliance.
Monitor Regulations
In today’s increasingly regulated business environment, ensuring compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards is essential. Process mining can help organizations monitor their adherence to these requirements by providing a transparent view of their processes and highlighting potential compliance risks.
Reduce Compliance Risks
By identifying and addressing deviations from standard procedures, process mining can help organizations reduce their exposure to compliance risks. This proactive approach to compliance management not only helps businesses avoid fines, penalties, and reputational damage but also fosters a culture of transparency and accountability.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, process mining offers numerous benefits to organizations seeking to optimize their business processes. By providing process transparency, facilitating transformation, reducing throughput time, cutting costs, improving customer satisfaction, and increasing compliance, process mining has become an indispensable tool for businesses looking to stay competitive and agile.
1. What is process mining?
Process mining is a technique that analyzes event logs to create visual process models, providing valuable insights into the current state of a business process and identifying areas for improvement. 2. How does process mining contribute to cost savings? Process mining helps organizations identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and deviations from standard procedures, enabling them to reduce resource consumption, avoid costly rework, and improve overall process efficiency, leading to significant cost savings. 3. How does process mining support compliance efforts? Process mining provides a transparent view of business processes, allowing organizations to monitor their adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards. By identifying and addressing deviations from standard procedures, businesses can reduce their exposure to compliance risks. 4. Can process mining improve customer satisfaction? Yes, by reducing throughput time and streamlining customer-facing processes, process mining can help organizations deliver products and services more quickly, resulting in faster response times and an enhanced customer experience. 5. Is process mining suitable for all industries? While process mining can be applied across various industries, it is particularly beneficial for businesses with complex processes and high volumes of data. These organizations can leverage process mining to gain valuable insights into their processes and drive significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.

Related Content
Process Intelligence
What is a Happy Path?
What is a happy path and how to achieve it? Read along and learn the tips and tricks that help you avoid process...
August 20, 2024
What are Event Logs in Process Mining?
Discover the power of event logs in process mining. Uncover hidden efficiencies, streamline operations, and improve business...
What is Process Intelligence?
Start your process excellence journey now! Learn about Process Intelligence in this comprehensive article....
August 16, 2024
Discover how leading organizations utilize ProcessMaker to streamline their operations through process automation.
Request a Demo
- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Partner Content
- Web Stories
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
SC verdict to hit mining firms; Tata Steel, JSW Steel to see lower profits
Tata steel, jsw steel, and other companies may see higher costs and reduced profitability from new state-imposed mining taxes, leading to inflation, following a supreme court decision.
)
The Supreme Court's decision permits states to impose taxes on mineral rights and mineral-bearing lands and to seek refunds of royalties from April 1, 2005, onwards
Listen to This Article
Supreme court ruling on mining taxes, more from this section.
)
Local manufacturing will offer 25K cr annual opportunity for vendors: ICRA
)
Festival season sees airfare surge of 10-25% for major domestic routes
)
Cement companies likely to continue raising prices until mid-Nov: Antique
)
Govt makes offshore mineral rules stricter but eases awarding process
)
Indian port workers to go on strike to demand better wages, benefits
)
SAIL, NMDC are down up to 9% in 1 month; is it time to buy steel stocks?
)
Tata Steel's Aashiyana expects to cross Rs 3,500 crore GMV in FY25
)
Tata Steel acquires about 1.16 bn equity shares in Singapore-based T Steel
)
Metal shares fall on adverse SC ruling; Tata Steel, Vedanta drop up to 6%
)
Cheap Chinese imports hurting domestic market: Tata Steel's T V Narendran
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Aug 20 2024 | 4:10 PM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Budget 2024 Olympics 2024 Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
Hazard analysis of flue gases generate by coal mining conveyor belt fires
- Published: 19 August 2024
Cite this article

- Furu Kang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9862-4687 1 , 2 ,
- Tiantian Zhang 1 ,
- Jun Deng 1 , 2 ,
- Shangkun Qing 3 ,
- Weifeng Wang 1 , 2 &
- Jiaxiang Zhang 1
To accurately grasp the non-thermal hazards such as smoke production performance and toxicity of smoke from coal mining conveyor belt fires, NBS smoke density test chamber, TG-DSC-FTIR, and Fourier transform infrared multi-component gas analyzer were utilized to investigate the light transmittance, thermal decomposition process, law of smoke generation, and toxicity evaluation of smoke generated by the coal mining polyvinyl chloride gum-elastic (PVG) conveyor belt fires. The study showed that the ignition time of coal mining PVG conveyor belt was 310 s and the light transmittance dropped to 0 in 60 s under the radiation intensity of 50 kW m −2 . During 243.29–358.20 °C, the mass loss ratio of PVG conveyor belt was over 60%, and large volumes of HCl, CO 2 , H 2 O generated. More specifically, the content of HCl began to increase rapidly at around 243.29 °C and the maximal content of HCl appeared at about 285.64 °C. Besides, the toxicity index (CIT c ) of HCl was more than 10 times that of the reference concentration, HCl and CO were the most significant toxic gases that caused death and injury in coal mining conveyor belt fires, followed by SO2, HCN, NO x , and CO2. The results had important guiding significance for the escape of people from coal mining conveyor belt fires and early monitoring and warning.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Explore related subjects
- Environmental Chemistry
Qu DR, Qiao TZ, Pang YS, Yang Y, Zhang HT. Research on ADCN method for damage detection of mining conveyor belt. Int J IEEE Sens. 2021;21(6):8662–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3048057 .
Article Google Scholar
Hou CC, Qiao TZ, Zhang HT, Pang YS, Xiong XY. Multispectral visual detection method for conveyor belt longitudinal tear. Measurement. 2019;143:246–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.05.010 .
Huang M. Study on system for monitoring mine belt conveyor fire. Int J Appl Mech Mater. 2012;226:734–9.
Wang K, Jiang SG, Ma XP, Wu ZY, Shao H, Zhang WQ, Cu CB. Numerical simulation and application study on a remote emergency rescue system during a belt fire in coal mines. Int J Nat Hazards. 2016;84:1463–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2538-z .
Zhu YF, Wang DM, Shao ZL, Xu CH, Zhu XL, Qi XY, Liu FM. A statistical analysis of coalmine fires and explosions in China. Int J Process Saf Environ Prot. 2019;121:357–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.11.013 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Yuan LM, Zhou LH, Smith AC. Modeling carbon monoxide spread in underground mine fires. Int J Appl Therm Eng. 2016;100:1319–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.03.007 .
Zhou G, Cheng WM, Zhang R, Shen BT, Nie W, Zhang L, Wang H. Numerical simulation and disaster prevention for catastrophic fire airflow of main air-intake belt roadway in coal mine-a case study. Int J Cent South Univ. 2015;22:2359–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2761-x .
Pulbere AM. Laboratory test results fire safety conveyor belts. Int J Mater Plast. 2017;54(2):281–5. https://doi.org/10.37358/MP.17.2.4833 .
Hansen R. Design fire scenarios involving non-fire resistant conveyor belts-numerical study. Int J Min Mater Met Eng. 2021;7(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.11159/ijmmme.2021.001 .
Lowndes IS, Silvester SA, Giddings D. The computational modelling of flame spread along a conveyor belt. Int J Fire Safety. 2007;42(1):51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2006.08.002 .
Yuan L, Mainiero RJ, Rowland JH, Thomas RA, Smith AC. Numerical and experimental study on flame spread over conveyor belts in a large-scale tunnel. J Loss Prev Process Ind. 2014;30:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2014.05.001 .
Perera IE, Litton CD. Impact of air velocity on the detection of fires in conveyor belt haulage-ways. Int J Fire Technol. 2012;48:405–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-011-0228-7 .
Haghighat A, Luxbacher K. Tenability analysis for improvement of firefighters’ performance in a methane fire event at a coal mine working face. J Fire Sci. 2018;36(3):256–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734904118767066 .
Pan RK, Gao RX, Chao JK, Jia HL. Thermal characteristics analysis of conveyor belt during ignition. Combust Sci Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00102202.2023.2258550 .
Li L, Si JH, Li ZX. Characteristics of the spatial and temporal evolution of the environmental parameters for belt fire in underground coal mine roadway. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2023;49:103346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2023.103346 .
Peng S, Huang Z, Dong DW. Numerical simulation study on fire hazard of a coal mine yransport roadway. Min Sci. 2022;29:33–52. https://doi.org/10.37190/msc222904 .
Barros-Daza MJ, Luxbacher KD, Lattimer BY, Hodges JL. Mine conveyor belt fire classification. J Fire Sci. 2022;40(1):44–69. https://doi.org/10.1177/07349041211056343 .
Tong R, Liu Y, Yang S, Yao Y. Numerical simulation for variation law of gas distribution during mine fire period. Int J Disaster Adv. 2013;6(s):131–8.
Google Scholar
Rowland I, Litton CD, Thomas RA. Evaluation of detection and response times of fire sensors using an atmospheric monitoring system. Int J Trans Soc Min Metall Explor Inc. 2016;340(1):104–12. https://doi.org/10.19150/trans.7334 .
Wang K, Jiang SG, Zhang WQ. A study on numerical of smoke flow regulation during remote emergency rescue of roadway fire disaster. Int J Disaster Adv. 2013;6:331–40.
CAS Google Scholar
Zhang C, Duan Q, Pan J, Li X. Research of fire hazard critical guidelines of mine use belt conveyor and automatic fighting fire system. InFifth World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (IEEE Cat. No. 04EX788) 2004 Jun 15 (Vol. 4, pp. 3742–3746). IEEE.
Szurgacz D, Zhirnkin S, Voth S, Pokrny J, Spearing AJS, Cehlar M, Stempniak M, Sobik L. Thermal imaging study to determine the operational condition of a conveyor belt drive system structure. Int J Energies. 2021;14(11):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14113258 .
Ray SK, Khan AM, Mohalik NK, Mishra D, Varma NK, Pandey JK, Singh PK. Methodology in early detection of conveyor belt fire in coal transportation. Int J Energ Source Part A. 2020;46:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1823527 .
Yuan LM, Smith AC. Numerical modeling of water spray suppression of conveyor belt fires in a large-scale tunnel. Int J Process Saf Environ Prot. 2015;95:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2015.02.018 .
Xiao Y, Chen LG, Zhang XY, Ren S, Li DJ. Controlling fire of belt conveyor and ventilation network calculation in underground coal mines. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci. 2018;189(4): 042028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/189/4/042028 .
Wang K, Jiang S, Ma X. Numerical simulation and application study on a remote emergency rescue system during a belt fire in coal mines. Nat Hazards. 2016;84:1463–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2538-z .
Wang K, Jiang SG, Ma XP, Wu ZY, Shao H, Zhang WQ, Cui CB. Information fusion of plume control and personnel escape during the emergency rescue of external-caused fire in a coal mine. Int J Process Saf Environ Prot. 2016;103:46–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.06.026 .
Zhang D, Liu MX, Wen H, Deng J, Wang WF, Shu CM. Use of coupled TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS to study combustion characteristics of conveyor belts in coal mines. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2023;148:4779–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11899-z .
Wang WF, Liu HF, Yang B, Zhang D, Lyu HF, Song XM, Shu CM. Pyrolysis characteristics and dynamics analysis of a coal mine roadway conveyor belt. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;148:4823–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11753-2 .
Wachowicz J. Heat release rate in evaluation of conveyor belts in full-scale fire tests. Int J Fire Mater. 1997;21:253–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1018(199711/12)21:63.0.CO;2-E .
Wachowicz J. Investigations of conveyor belts flammability comparison of flammability assessment using the large-scale gallery test and cone calorimeter. Int J Fire Mater. 1998;22:213–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1018(199809/10)22:5%3c213::AID-FAM657%3e3.0.CO;2-U .
Rowland JH III, Smith AC. Flammability of wider conveyor belts using large-scale fire tests. Int J Trans Soc Min Metal Explor. 2012;330:345–9.
Alvares N, Hasegawa H, Staggs K. Ignition, Heat release rate and suppression of elastomeric materials. Int J Fire Technol. 2016;52:1575–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-015-0483-0 .
Rickard H, Haukur I. Heat release rate measurements of burning mining vehicles in an underground mine. Int J Fire Saf. 2013;61:12–25.
Rowland JH, Verakis H, Hockenberry MA, Smith AC. Effect of air velocity on conveyor belt fire suppression systems. Int J Trans Soc Min Metall Explor. 2011;328:493–501.
Charles DL, Inoka EP. Evaluation of criteria for the detection of fires in underground conveyor belt haulage ways. Int J Fire Saf. 2012;51:110–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2012.04.004 .
Bilgin N, Balci C, Aslanbas A. Case studies leading to the management of tunnel fire risks during TBM drives in an old coalfield. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech. 2021;112: 103902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.103902 .
Chen P, Guo SL, Wang Y. Human evacuation affected by smoke movement in mine fires. Int J Int J Coal Sci Technol. 2016;1:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40789-015-0100-3 .
Litton CD, Perera IE, Harteis SP, Teacoach KA, DeRosa MI, Thomas RA, Smith AC. Some relevant parameters for assessing fire hazards of combustible mine materials using laboratory scale experiments. Int J Fuel. 2018;218(15):306–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.106 .
Wu L. Research progress on the damage rule of ventilation network caused by external fire in mine. Int J Clausius Scientific Press. 2019;3:1–4. https://doi.org/10.23977/erej.2019.31001 .
Krawiec P, Wargula L, Malozi D, Kaczmarzyk P, Dziechciarz A, Komorowska DC. The toxicological testing and thermal decomposition of drive and transport belts made of thermoplastic multilayer polymer materials. Int J Polymers. 2020;12:2232. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102232 .
Krawiec P, Wargula L, Komorowska DC, Janik P, Dziechciarz A, Kaczmarzyk P. Chemical compounds released by combustion of polymer composites fat belts. Int J Scientifc Reports. 2021;11:8269. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87634-9 .
Zuo QL, Wang YJ, Li JS. The field model construction and analysis of complex mine belt fire based on personnel evacuation theory. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2019;218: 012107. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/218/1/012107 .
Xiao Y, Chen L, Zhang X, Ren S, Li D. Controlling fire of belt conveyor and ventilation network calculation in underground coal mines. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. 2018;189: 042028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/189/4/042028 .
Michalik P, Zajac J. Use of thermovision for monitoring temperature conveyor belt of pipe conveyor. Int J Appl Mech Mater. 2014;68:238–42. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.683.238 .
Dobrota D, Petrescu V, Dimulescu CS, Oleksik M. Preparation and characterization of composites materials with rubber matrix and with polyvinyl chloride addition. Int J Polymers-basel. 2020;12(9):1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091978 .
Wang W, Liang YT, Zhao Q, Li P, Wang W. Study on mechanism of influence of microstructure on combustion characteristics of mine conveyor belt. Combust Sci Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00102202.2023.2203821 .
Wang WF, Huo YH, Kang FR, Han FL, Hao R, Bo Y, Cui ZL. Study on hazard of smoke generated by mining cable fires. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-023-12136-x .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by Key R&D Program of Xinjiang Autonomous Region (2022B03031-1); Science and technology supporting project of Guizhou Province (2023273); Key R&D Program of Shaanxi Province (2023-YBGY-479).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Safety Science and Engineering, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, 710054, Shaanxi, People’s Republic of China
Furu Kang, Tiantian Zhang, Jun Deng, Weifeng Wang & Jiaxiang Zhang
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Prevention and Control of Coal Fire, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 58, Yanta Mid. Rd, Xi’an, 710054, Shaanxi, People’s Republic of China
Furu Kang, Jun Deng & Weifeng Wang
Mining Safety Service and Security Center of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Urumqi, 830063, People’s Republic of China
Shangkun Qing
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Furu Kang .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kang, F., Zhang, T., Deng, J. et al. Hazard analysis of flue gases generate by coal mining conveyor belt fires. J Therm Anal Calorim (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13528-3
Download citation
Received : 04 May 2024
Accepted : 21 July 2024
Published : 19 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13528-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coal mining conveyor belt
- Smoke density
- Thermal decomposition
- Smoke toxicity
- Toxicity index
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Calls for privacy law overhaul after increasing number of workers forced to undergo blood tests
Topic: Work
The expectation for workers to provide blood samples, particularly in the mining and resources sectors, has raised concerns over privacy risks. ( AAP: Dan Peled )
A new report by the Australia Institute's Centre for Future Work has found that employers are requesting blood tests as part of the recruitment process without providing clear evidence as to why they are needed.
There is no guarantee employee records which would retain such medical information would be covered by the Privacy Act.
What's next?
The report has called for an overhaul to the Privacy Act to better protect the medical information of employees.
Nic Pipkin was asked to provide a blood sample as part of the recruitment process as a fly-in, fly-out electrical contractor.
He said he reluctantly consented to the test.
"It was a prerequisite for the job … you either get the blood test or you don't get the job."
His main concern was how his medical information would be used.
"I just want to ensure that my bloods are used for the sole purpose of employment … not going onto some privatised database or used in a malicious way," he said.
Mr Pipkin works in the mining and resource industry in Western Australia. He said it wasn't clear whether his medical results would be transferred if he changed companies or if they could potentially be "sold off".
"I've consented and accepted the fact that I needed (the test) to garner employment and I'm accepting of that, it's more where that goes moving forward.
"There should be stricter restrictions … because that's my DNA you know."
Workers in the mining and resources sectors say they feel obliged to undergo blood tests but are worried about how their medical information is being protected. ( ABC: Glyn Jones )
What are employers using blood tests for?
The expectation for workers to provide blood samples, particularly in the mining and resources sectors, has raised concerns over privacy risks.
A new report by the Australia Institute's Centre for Future Work, revealed that employers said they were using the tests to check for cardiovascular risks or to meet "legal obligations".
But there was no way of knowing the company’s true intention – nor was there any guarantee the employee records containing the medical information would be covered by the Privacy Act.
Senior Researcher Lisa Heap, who helped author the "No Blood No Job" report, said there was a growing expectation for potential employees to undergo tests without any clear indication of how the tests were connected to their job requirements.
Some jobs require employees to undergo medical testing for safety reasons but an increasing number of employers were not specifying why they needed medical information, according to the report. ( Pexels )
"Employers are requesting from employees sensitive information that they shouldn't have to provide as part of the recruitment process and that's becoming more of a routine practice," she said.
Dr Heap said some jobs legitimately required employees to undergo medical testing for safety reasons or to protect employees, in particular those working with biological hazards, but an increasing number of employers were not specifying why they needed medical information.
"Prospective employers shouldn't be able to ask for that information unless they can justify that there's a need.
"If organisations are pressed they're saying broad things like, 'for health and safety reasons' or 'because we have a legal obligation'."
Dr Heap said employers were not providing the appropriate level of detail needed to alleviate concern from prospective employees and the report found some workers were even asked to sign consent forms that placed no restrictions on the use of their information.
Dr Heap said an electrical trades worker in the construction sector revealed he was removed from the recruitment process when he declined a blood test. ( Diane Bain: ABC )
Can a worker refuse a blood test?
Dr Heap said people looking for work were particularly vulnerable and often not in a position to give informed consent.
"They're really not in a power position to be able to say, 'I'm really feeling uncomfortable about this'. So they're not in a position to be able to give informed consent."
She said an electrical trades worker in the construction sector revealed he was removed from the recruitment process when he declined a blood test.
"One of the workers who we interviewed did decline to have a blood test and they were immediately removed from the recruitment process … if they weren't prepared to give their blood they weren't even considered for the role.
"You're either in or you're out. If you don't give the blood you're out."
Senior Researcher Lisa Heap helped author the "No Blood No Job" report. ( Supplied )
How secure is an employee's medical information?
The Australia Institute report found that information provided to employers was covered under the Privacy Act, but employee records were not.
"We have argued in the report that the law needs to change," Dr Heap said.
"Either the privacy law needs to change or the workplace relations law (does).
"It's really alarming in this current environment where more and more information is being collected and we don't know how it's being used … it could be sold on to other parties, it could be used for purposes that workers did not understand it could be used for."
A spokesperson for the Attorney-General said the government had agreed in principle to enhance the privacy protections of employees as part of the review into the Privacy Act.
This included, "ensuring that employers only collect employee information that is reasonably necessary to administer the employment relationship, protecting employees' personal information from misuse, loss or unauthorised access and destroying it when no longer required, and notifying employees and the Information Commissioner of any data breach."
The Mineral Councils of Australia, an industry heavily referred to in the report, declined to comment.
The ABC also contacted the Recruitment, Consulting and Staffing Association – the peak body for recruitment – which was also unavailable for comment.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This thesis explores, develop and analyse process mining techniques that are able to handle streaming event data and identifies three main process mining types of analysis, i.e. process discovery, conformance checking and process enhancement. Modern information systems allow us to track, often in great detail, the execution of processes within companies. Consider for example luggage handling ...
The challenges from this thesis can also be compared to a set of challenges that are listed in the process mining manifesto [129]. Two of these challenges are drivers behind this thesis, being improving the usability and understandability of process mining for people without process mining experience.
Chapter 1 Introduction This thesis is the result of a graduation project carried out within Fluxicon1 and the Architecture of Infor- mation System (AIS) group2 of the Mathematics and Computer Science Department of TU/e. The goal of the project was the evaluation of commercial process mining systems based on a defined set of criteria.
lenges to the problem of process mining. Using the Design Science Research Methodology, this thesis introduces a new method to study, discover, and analyze cloud-based application processes using process mining tech-niques. It explores the applications and known challenges related to process mining in
This Master thesis is the result of 8 months of research on process mining, process performance, and the intriguing world where business and IT meet. I would not have been able to complete my master thesis project without the help and guidance of a lot of people, and therefore I would like to take the time to thank them (again).
Katri Tuunanen: Supporting implementation and use of process mining Master's Thesis Tampere University Master's Programme in Information and Knowledge Management November 2021 In competitive and continuously changing business environments, companies have a constant
Through process mining it is possible to (i) discover the process that better describes the user behavior, (ii) nd useful insights, (iii) discover and compare the processes of di erent behavi-oural clusters of users. Moreover, this thesis aims to make a second contribution by bridging the gap between process mining and recommender systems worlds.
This thesis follows the aim of analyzing data collection challenges in the healthcare sector and proposes an agile process mining framework, which enables a stepwise implementation of process mining techniques.
Abstract ii Abstract Context: Process mining is an approach that exploits event logs to discover real processes executed in organizations, enabling them to (re)design and improve process models. Goal modelling, on the other hand, is a requirements engineering (RE) approach mainly used to
Process Mining Dissertation Award The IEEE Task Force for Process Mining is happy to announce the 2020 edition of the Best Process Mining PhD Dissertation Award. The award will be delivered during the 2nd International Conference on Process Mining (ICPM2020), 5-8 October 2020.
This dissertation broadens the field of process mining to include the aspect of conformance and extension, and develops several Petri-net based approaches to measure conformance in these dimensions and describes five case studies in which these conformance checking techniques were successfully applied to real and artificial examples.
Abstract Currently, the process mining aims at an automatic extraction of process knowledge from the event logs recorded by information systems, and, therefore, by using these techniques, it becomes possible to grasp the complex nature of industrial processes. In fact, most of the industrial processes change over time, and through the process mining techniques, it is possible to analyse these ...
This thesis will introduce the most important process mining techniques and apply them to uses cases that are based on real life event data. Three process mining tools, ProM, Disco and Celonis, will be introduced and used to apply process mining techniques.
An outline of the practice of business process mining is given, along with an analysis of the main techniques developed by academia and commercial entities. This paper also acts as a primer for ...
In this thesis, we approach the eld of process mining from a machine-learning perspective. We shall develop a probabilistic process miner that, in contrast to the current state of the art, produces probability distributions over process models rather than producing actual models. Moreover, we shall develop model validation techniques for process mining.
Whereas data mining is a data-centric procedure, process mining focuses on a process-centric approach. Undoubtedly, process mining techniques can benefit from knowledges from the data mining methodologies and apply them to end-to-end processes.
Mannhardt, F. (2018). Multi-perspective process mining. [Phd Thesis 1 (Research TU/e / Graduation TU/e), Mathematics and Computer Science]. Technische Universiteit Eindhoven.
uni-stuttgart.de
This thesis aims to develop and exemplify a design method for a visual solution in process mining that allows for exploring a cyclic time arrangement in a process graph.
This oversight leads to missed opportunities for enhancing efficiency and more accurate defect detection. The introduction of sophisticated methodologies such as process mining and causal AI aims to decipher these hidden correlations and provide actionable insights. Research Goal: In association with Bayer AG, the objective of this thesis ...
The IEEE Task Force for Process Mining is happy to announce the 2024 edition of the Best Process Mining PhD Dissertation Award. The award will be delivered during the 6th International Conference on Process Mining (ICPM 2024). Eligibility - updated criteria Eligible candidates are those who officially obtained a PhD degree defended after January 1st, 2022, with a...
This thesis is an analysis of the care processes, with the following research question: "How can Process Mining strengthen Value-Based Health Care?" The costs in this thesis refer to performance times of care activities.
Theses/Dissertations from 2023. Development of A Hydrometallurgical Process for the Extraction of Cobalt, Manganese, and Nickel from Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Byproduct, Alejandro Agudelo Mira. Selective Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Acid Mine Drainage Treatment Byproduct, Zeynep Cicek. Identification of Rockmass Deformation and ...
Process mining helps achieve process excellence through discovery, conformance and improvement. It is a major source of information while embarking on a simple operational efficiency and productivity drive or an overall business transformation. Process Mining for Total Quality Management
Process mining examines the most recent data taken from information systems, but this does not necessarily provide a complete picture of how a company is doing right now. Offline analytics that are more "static" are produced by first extracting the data from event logs at a specific moment in time, cleaning it, and only then analyzing it. ...
3. How does process mining support compliance efforts? Process mining provides a transparent view of business processes, allowing organizations to monitor their adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards. By identifying and addressing deviations from standard procedures, businesses can reduce their exposure to compliance risks. 4.
Sensor and process control upgrades are often necessary to enable the deployment of AI. However, many organizations are not yet ready.
Mining royalty case: Tata Steel, JSW Steel, and other companies may see higher costs and reduced profitability from new state-imposed mining taxes, leading to inflation, following a Supreme Court decision ... Govt makes offshore mineral rules stricter but eases awarding process. Indian port workers to go on strike to demand better wages, benefits.
To accurately grasp the non-thermal hazards such as smoke production performance and toxicity of smoke from coal mining conveyor belt fires, NBS smoke density test chamber, TG-DSC-FTIR, and Fourier transform infrared multi-component gas analyzer were utilized to investigate the light transmittance, thermal decomposition process, law of smoke generation, and toxicity evaluation of smoke ...
Workers are being asked to undergo blood tests as part of the recruitment process, particularly in the mining and resources sectors, with no guarantee their health information is secure, a new ...