- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Free Math Lessons
Looking for free math tutorials online.
ChiliMath.com is a place for you to learn math at your own pace for FREE ! Allow me to help you solve math problems with a direct approach through the use of examples and diagrams.
New Lessons Added: March 10, 2024
Derivation of Pythagorean Theorem Formula
Absolute Value Equations Practice Problems with Answers
Literal Equations Practice Problems with Answers
LCM of Two Numbers Practice Problems with Answers
Quadratic Formula Practice Problems with Answers
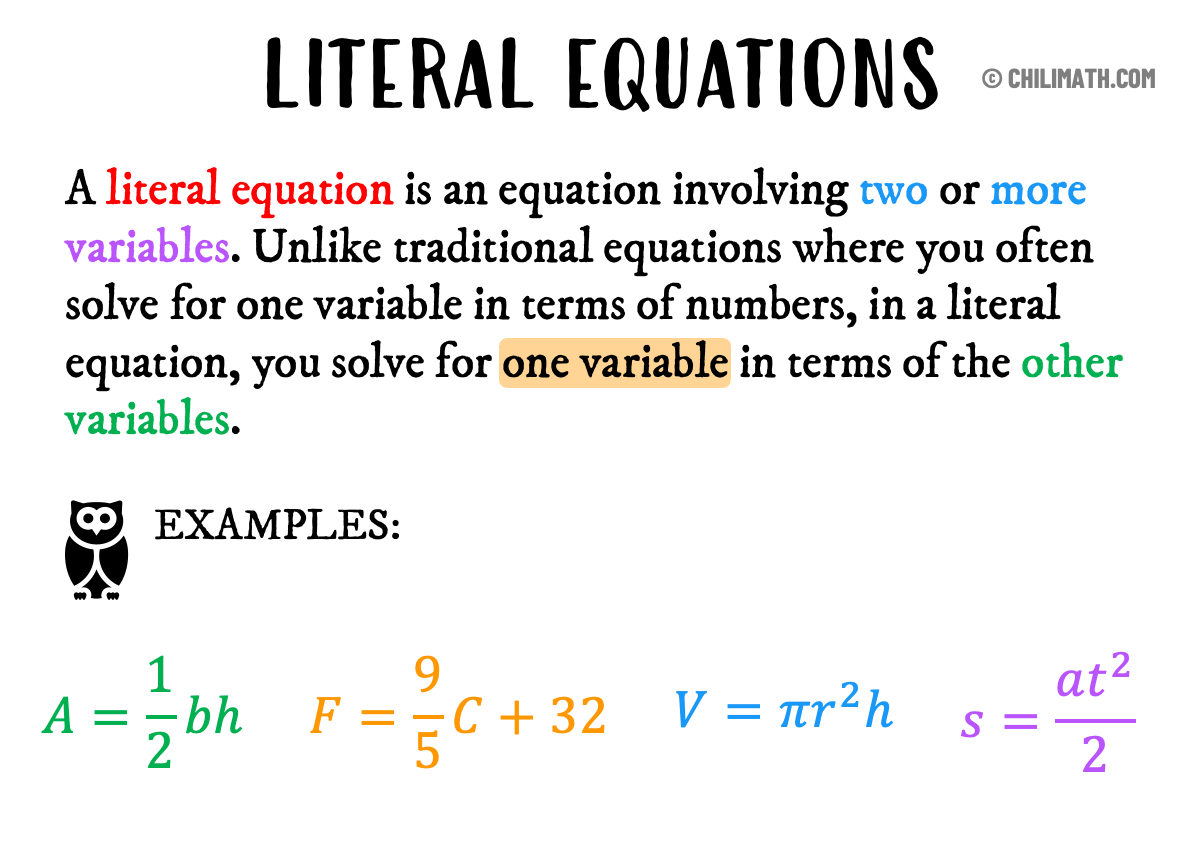
Whether you are a student studying algebra, a parent helping your kids with homework, or a teacher looking for additional learning resources then ChiliMath is the perfect free math help resource for you!
List of Algebra Lessons
Introductory Algebra
Intermediate Algebra
Advanced Algebra
Algebra Word Problems
Intro to Number Theory
Basic Math Proofs
Math can be challenging, but it is not difficult. As a math teacher, my goal is to encourage students just like you to solve as many problems as you can. With a lot of practice, you will build confidence, and in the process, develop your mathematical skills.
ChiliMath is a growing site created for students who need extra help in algebra/math. Since July 2011, I have added new topics on a regular basis with the goal of covering most lessons covered in an algebra class (Introductory Algebra, Intermediate Algebra, and Advanced Algebra).
I am also pleased to share that recently, I have started creating lessons for other math subjects as well such as Geometry, Number Theory, and Basic Math Proofs. Slowly but surely, and there’s more to come!
Please don’t forget to bookmark this page and reach out to me at contact(at)chilimath.com anytime if you found any typographical and/or content errors. I would greatly appreciate any support or help I can get to make this site better. Thank you very much for visiting my humble math website!

Math Practice
Geogebra math practice.
Math Practice is a tool for mastering algebraic notation. It supports students in their step-by-step math work, let's them explore different solution paths, and helps build confidence, fluency, and understanding.
Getting started as a teacher or student

Enhance your skills
Immerse yourself in the world of algebraic problems to fine-tune your mathematical abilities and elevate your skillset
Linear equations
Order of Operations
Algebraic Expressions
Polynomials
Unlocking the key elements
Use interactive notation to build comfort and fluency with algebraic transformations
Get adaptive hints and in-the-moment feedback to explore different solution paths
Get comprehensive help and guidance focused on improving understanding of basic concepts
Explore features
If you require any guidance on how to use GeoGebra Math Practice, explore the articles in our help center.
Guided tutorials
If you are new to using this tool, we offer easy-to-follow guided tutorials.

Unlimited AI-generated practice problems and answers
With Wolfram Problem Generator, each question is generated instantly, just for you.
Get integrated Step-by-step solutions with a subscription to Wolfram|Alpha Pro. Pro subscribers can also create printable worksheets for study sessions and quizzes.
The most amazing part of Wolfram Problem Generator is something you can't even see.
Instead of pulling problems out of a database, Wolfram Problem Generator makes them on the fly, so you can have new practice problems and worksheets each time. Each practice session provides new challenges.
Practice for all ages
Wolfram Problem Generator offers beginner, intermediate, and advanced difficulty levels for a number of topics including algebra, calculus, statistics, number theory, and more.
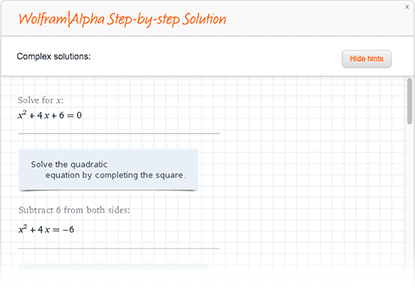
Work with Step-by-step Solutions!
Only Wolfram Problem Generator directly integrates the popular and powerful Step-by-step Solutions from Wolfram|Alpha. You can use a single hint to get unstuck, or explore the entire math problem from beginning to end.
Math Training
Math Training has practice problems on the most important skills for learning or preparing for algebra. To get started, click any of the subjects below.
Basic Arithmetic
Subtraction, multiplication, basic arithmetic review, multi-digit arithmetic, addition (2-digit), subtraction (2-digit), multiplication (2-digit by 1-digit), division (2-digit answer), multiplication (2-digit by 2-digit), multi-digit division, negative numbers, addition: negative numbers, subtraction: negative numbers, multiplication: negative numbers, division: negative numbers, order of operations, order of operations 1, basic equations, equations: fill in the blank 1, equations: fill in the blank 2, equations: fill in the blank 3 (order of operations), fractions of measurements, fractions of measurements 2, adding fractions, subtracting fractions, adding fractions: fill in the blank, multiplication: fractions 1, multiplication: fractions 2, division: fractions 1, division: fractions 2, division: fractions 3, addition (decimals), subtraction (decimals), multiplication 2 (example problem: 3.5*8), multiplication 3 (example problem: 0.3*80), division (decimals), division (decimals 2), percentages, percentages 1, percentages 2, chain reaction, balance arithmetic, number balance, basic balance 1, basic balance 2, basic balance 3, basic balance 4, basic balance 5, basic algebra, basic algebra 1, basic algebra 2, basic algebra 3, basic algebra 4, basic algebra 5, algebra: basic fractions 1, algebra: basic fractions 2, algebra: basic fractions 3, algebra: basic fractions 4, algebra: basic fractions 5.
Learn by doing
Guided interactive problem solving that’s effective and fun. master concepts in 15 minutes a day., data analysis, computer science, programming & ai, science & engineering, join over 10 million people learning on brilliant, over 50,000 5-star reviews on ios app store and google play.

Master concepts in 15 minutes a day
Whether you’re a complete beginner or ready to dive into machine learning and beyond, Brilliant makes it easy to level up fast with fun, bite-sized lessons.
Effective, hands-on learning
Visual, interactive lessons make concepts feel intuitive — so even complex ideas just click. Our real-time feedback and simple explanations make learning efficient.
Learn at your level
Students and professionals alike can hone dormant skills or learn new ones. Progress through lessons and challenges tailored to your level. Designed for ages 13 to 113.
Guided bite-sized lessons
We make it easy to stay on track, see your progress, and build your problem solving skills one concept at a time.
Stay motivated
Form a real learning habit with fun content that’s always well-paced, game-like progress tracking, and friendly reminders.
Guided courses for every journey
All of our courses are crafted by award-winning teachers, researchers, and professionals from MIT, Caltech, Duke, Microsoft, Google, and more.
- Foundational Math
- Software Development
- Foundational Logic
- Data Science
- High School Math
- Engineering
- Statistics and Finance
Courses in Foundational Math
- Solving Equations
- Measurement
- Mathematical Fundamentals
- Reasoning with Algebra
- Functions and Quadratics

10k+ Ratings

60k+ Ratings
We use cookies to improve your experience on Brilliant. Learn more about our cookie policy and settings .
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Ratio problem solving
Here you will learn about ratio problem solving, including how to set up and solve problems. You will also look at real life ratio word problems.
Students will first learn about ratio problem solving as part of ratio and proportion in 6 th grade and 7 th grade.
What is ratio problem solving?
Ratio problem solving is a collection of ratio and proportion word problems that link together aspects of ratio and proportion into more real life questions. This requires you to be able to take key information from a question and use your knowledge of ratios (and other areas of the curriculum) to solve the problem.
A ratio is a relationship between two or more quantities. They are usually written in the form a : b where a and b are two quantities. When problem solving with a ratio, the key facts that you need to know are:
- What is the ratio involved?
- What order are the quantities in the ratio?
- What is the total amount / what is the part of the total amount known?
- What are you trying to calculate ?
As with all problem solving, there is not one unique method to solve a problem. However, this does not mean that there aren’t similarities between different problems that you can use to help you find an answer.
The key to any problem solving is being able to draw from prior knowledge and use the correct piece of information to allow you to get to the next step and then the solution.
Let’s look at a couple of methods you can use when given certain pieces of information.
When solving ratio word problems, it is very important that you are able to use ratios. This includes being able to use ratio notation.
For example, Charlie and David share some sweets in the ratio of 3 : 5. This means that for every 3 sweets Charlie gets, David receives 5 sweets.
Charlie and David share 40 sweets, how many sweets do they each get?
You use the ratio to divide 40 sweets into 8 equal parts.
40 \div 8=5
Then you multiply each part of the ratio by 5.
3\times 5:5\times 5=15 : 25
This means that Charlie will get 15 sweets and David will get 25 sweets.
There can be ratio word problems involving different operations and types of numbers.
Here are some examples of different types of ratio word problems:
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6 th and 7 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Ratios and Proportional Relationships (6.RP.A.3) Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, for example, by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations.
- Grade 7 – Ratio and Proportional Relationships (7.RP.A.2) Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities.
How to do ratio problem solving
In order to solve problems including ratios:
Identify key information within the question.
Know what you are trying to calculate.
Use prior knowledge to structure a solution.
![practice problem solving maths [FREE] Ratio Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Ratio-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Ratio Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 and 7)
Use this quiz to check your 6th and 7th grade students’ understanding of ratios. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade ratio topics to identify areas of strength and support!
Ratio problem solving examples
Example 1: part:part ratio.
Within a school, the total number of students who have school lunches to packed lunches is 5 : 7. If 465 students have a school lunch, how many students have a packed lunch?
Within a school, the number of students who have school lunches to packed lunches is \textbf{5 : 7} . If \textbf{465} students have a school lunch, how many students have a packed lunch?
Here you can see that the ratio is 5 : 7, where the first part of the ratio represents school lunches (S) and the second part of the ratio represents packed lunches (P).
You could write this as:
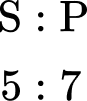
Where the letter above each part of the ratio links to the question.
You know that 465 students have school lunch.
2 Know what you are trying to calculate.
From the question, you need to calculate the number of students that have a packed lunch, so you can now write a ratio below the ratio 5 : 7 that shows that you have 465 students who have school lunches, and p students who have a packed lunch.
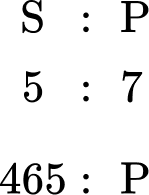
You need to find the value of p.
3 Use prior knowledge to structure a solution.
You are looking for an equivalent ratio to 5 : 7. So you need to calculate the multiplier.
You do this by dividing the known values on the same side of the ratio by each other.
465\div 5 = 93
This means to create an equivalent ratio, you can multiply both sides by 93.
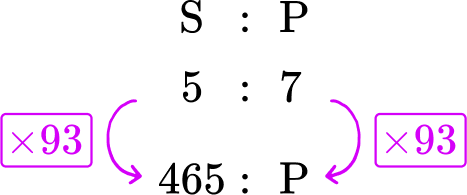
So the value of p is equal to 7 \times 93=651.
There are 651 students that have a packed lunch.
Example 2: unit conversions
The table below shows the currency conversions on one day.
Use the table above to convert £520 \; (GBP) to Euros € \; (EUR).
Use the table above to convert \bf{£520} \textbf{ (GBP)} to Euros \textbf{€ } \textbf{(EUR)}.
The two values in the table that are important are \text{GBP} and EUR. Writing this as a ratio, you can state,
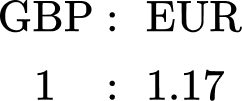
You know that you have £520.
You need to convert GBP to EUR and so you are looking for an equivalent ratio with GBP=£520 and EUR=E.

To get from 1 to 520, you multiply by 520 and so to calculate the number of Euros for £520, you need to multiply 1.17 by 520.
1.17 \times 520=608.4
So £520=€608.40.
Example 3: writing a ratio 1 : n
Liquid plant food is sold in concentrated bottles. The instructions on the bottle state that the 500 \, ml of concentrated plant food must be diluted into 2 \, l of water. Express the ratio of plant food to water, respectively, in the ratio 1 : n.
Liquid plant food is sold in concentrated bottles. The instructions on the bottle state that the \bf{500 \, ml} of concentrated plant food must be diluted into \bf{2 \, l} of water. Express the ratio of plant food to water respectively as a ratio in the form 1 : n.
Using the information in the question, you can now state the ratio of plant food to water as 500 \, ml : 2 \, l. As you can convert liters into milliliters, you could convert 2 \, l into milliliters by multiplying it by 1000.
2 \, l=2000 \, ml
So you can also express the ratio as 500 : 2000 which will help you in later steps.
You want to simplify the ratio 500 : 2000 into the form 1:n.
You need to find an equivalent ratio where the first part of the ratio is equal to 1. You can only do this by dividing both parts of the ratio by 500 (as 500 \div 500=1 ).
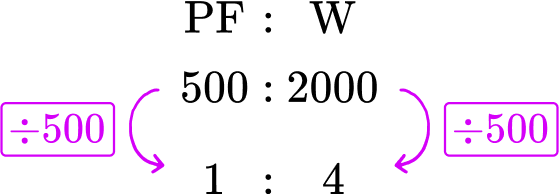
So the ratio of plant food to water in the form 1 : n is 1 : 4.
Example 4: forming and solving an equation
Three siblings, Josh, Kieran and Luke, receive an allowance each week proportional to their age. Kieran is 3 years older than Josh. Luke is twice Josh’s age. If Josh receives \$ 8 allowance, how much money do the three siblings receive in total?
Three siblings, Josh, Kieran and Luke, receive an allowance each week proportional to their ages. Kieran is \bf{3} years older than Josh. Luke is twice Josh’s age. If Luke receives \bf{\$ 8} allowance, how much money do the three siblings receive in total?
You can represent the ages of the three siblings as a ratio. Taking Josh as x years old, Kieran would therefore be x+3 years old, and Luke would be 2x years old. As a ratio, you have:
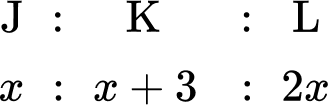
You also know that Luke receives \$ 8.
You want to calculate the total amount of allowance for the three siblings.
You need to find the value of x first. As Luke receives \$ 8, you can state the equation 2x=8 and so x=4.
Now you know the value of x, you can substitute this value into the other parts of the ratio to obtain how much money the siblings each receive.
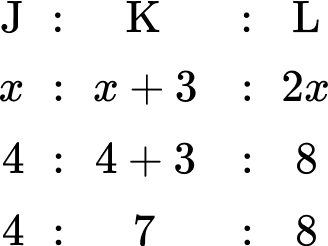
The total amount of allowance is therefore 4+7+8=\$ 19.
Example 5: simplifying ratios
Below is a bar chart showing the results for the colors of counters in a bag.
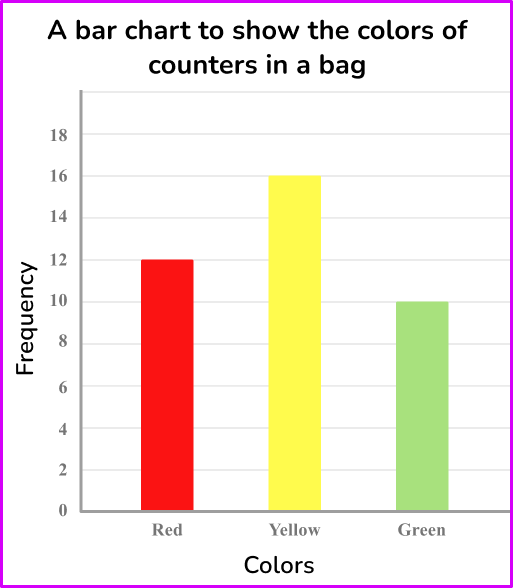
Express this data as a ratio in its simplest form.
From the bar chart, you can read the frequencies to create the ratio.

You need to simplify this ratio.
To simplify a ratio, you need to find the highest common factor of all the parts of the ratio. By listing the factors of each number, you can quickly see that the highest common factor is 2.
\begin{aligned} & 12 = 1, {\color{red}2}, 3, 4, 6, 12 \\\\ & 16 = 1, {\color{red}2}, 4, 8, 16 \\\\ & 10 = 1, {\color{red}2}, 5, 10 \end{aligned}
HCF(12,16,10) = 2
Dividing all the parts of the ratio by 2, you get
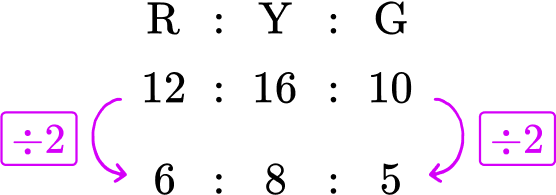
Our solution is 6 : 8 : 5.
Example 6: combining two ratios
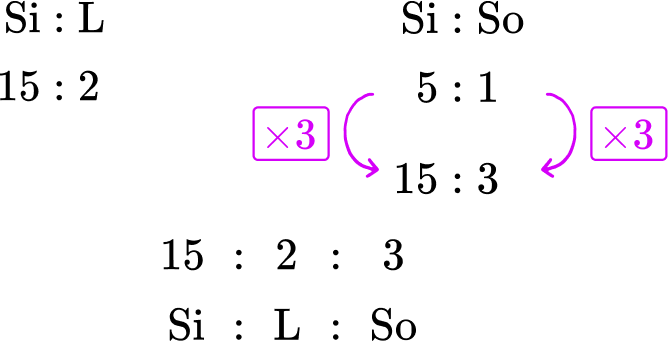
Glass is made from silica, lime and soda. The ratio of silica to lime is 15 : 2. The ratio of silica to soda is 5 : 1. State the ratio of silica:lime:soda.
Glass is made from silica, lime and soda. The ratio of silica to lime is \bf{15 : 2}. The ratio of silica to soda is \bf{5 : 1}. State the ratio of silica:lime:soda.
You know the two ratios

You are trying to find the ratio of all 3 components: silica, lime and soda.
Using equivalent ratios you can say that the ratio of Silica:Soda is equivalent to 15 : 3 by multiplying the ratio by 3.
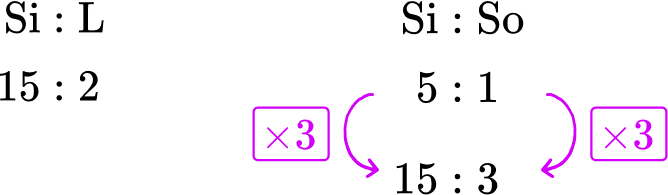
You now have the same amount of silica in both ratios and so you can now combine them to get the ratio 15 : 2 : 3.

Example 7: using bar modeling
India and Beau share some popcorn in the ratio of 5 : 2. If India has 75 \, g more popcorn than Beau, what was the original quantity?
India and Beau share some popcorn in the ratio of \bf{5 : 2} . If India has \bf{75 \, g} more popcorn than Beau, what was the original quantity?
You know that the initial ratio is 5 : 2 and that India has three more parts than Beau.
You want to find the original quantity.
Drawing a bar model of this problem, you have:
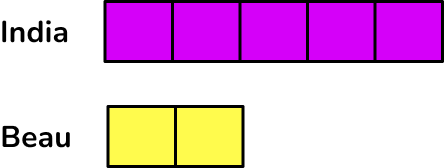
Where India has 5 equal shares, and Beau has 2 equal shares.
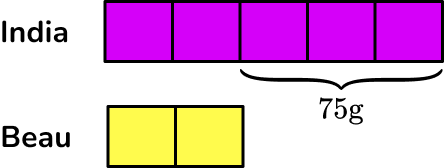
Each share is the same value and so if you can find out this value, you can then find the total quantity.
From the question, India’s share is 75 \, g more than Beau’s share so you can write this on the bar model.
You can find the value of one share by working out 75 \div 3=25 \, g.
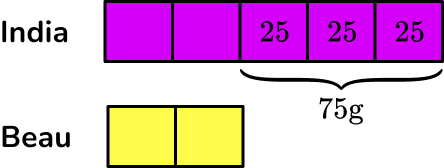
You can fill in each share to be 25 \, g.
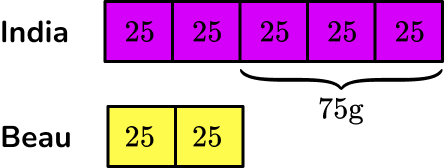
Adding up each share, you get
India=5 \times 25=125 \, g
Beau=2 \times 25=50 \, g
The total amount of popcorn was 125+50=175 \, g.
Teaching tips for ratio problem solving
- Continue to remind students that when solving ratio word problems, it’s important to identify the quantities being compared and express the ratio in its simplest form.
- Create practice problems for students using the information in your classroom. For example, ask students to find the ratio of boys to the ratio of girls using the total number of students in your classroom, then the school.
- To find more practice questions, utilize educational websites and apps instead of worksheets. Some of these may also provide tutorials for struggling students. These can also be helpful for test prep as they are more engaging for students.
- Use a variety of numbers in your ratio word problems – whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers – to give students a variety of practice.
- Provide students with a step-by-step process for problem solving, like the one shown above, that can be applied to every ratio word problem.
Easy mistakes to make
- Mixing units Make sure that all the units in the ratio are the same. For example, in example 6, all the units in the ratio were in milliliters. You did not mix ml and l in the ratio.
- Writing ratios in the wrong order For example, the number of dogs to cats is given as the ratio 12 : 13 but the solution is written as 13 : 12.
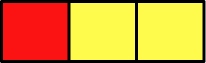
- Counting the number of parts in the ratio, not the total number of shares For example, the ratio 5 : 4 has 9 shares, and 2 parts. This is because the ratio contains 2 numbers but the sum of these parts (the number of shares) is 5+4=9. You need to find the value per share, so you need to use the 9 shares in your next line of working.
- Ratios of the form \bf{1 : \textbf{n}} The assumption can be incorrectly made that n must be greater than 1, but n can be any number, including a decimal.
Related ratio lessons
- Unit rate math
- Simplifying ratios
- Ratio to fraction
- How to calculate exchange rates
- Ratio to percent
- How to write a ratio
- Dividing ratios
- How to find the unit rate
- Ratio scale
- Constant of proportionality
Practice ratio problem solving questions
1. An online shop sells board games and computer games. The ratio of board games to the total number of games sold in one month is 3 : 8. What is the ratio of board games to computer games?

8-3=5 computer games sold for every 3 board games.
2. The ratio of prime numbers to non-prime numbers from 1-200 is 45 : 155. Express this as a ratio in the form 1 : n.
You need to simplify the ratio so that the first number is 1. That means you need to divide each number in the ratio by 45.
45 \div 45=1
155\div{45}=3\cfrac{4}{9}
3. During one month, the weather was recorded into 3 categories: sunshine, cloud and rain. The ratio of sunshine to cloud was 2 : 3 and the ratio of cloud to rain was 9 : 11. State the ratio that compares sunshine:cloud:rain for the month.
3 \times S : C=6 : 9
4. The angles in a triangle are written as the ratio x : 2x : 3x. Calculate the size of each angle.
You should know that the 3 angles in a triangle always equal 180^{\circ}.
\begin{aligned} & x+2 x+3 x=180 \\\\ & 6 x=180 \\\\ & x=30^{\circ} \\\\ & 2 x=60^{\circ} \\\\ & 3 x=90^{\circ} \end{aligned}
5. A clothing company has a sale on tops, dresses and shoes. \cfrac{1}{3} of sales were for tops, \cfrac{1}{5} of sales were for dresses, and the rest were for shoes. Write a ratio of tops to dresses to shoes sold in its simplest form.
\cfrac{1}{3}+\cfrac{1}{5}=\cfrac{5+3}{15}=\cfrac{8}{15}
1-\cfrac{8}{15}=\cfrac{7}{15}
6. The volume of gas is directly proportional to the temperature (in degrees Kelvin). A balloon contains 2.75 \, l of gas and has a temperature of 18^{\circ}K. What is the volume of gas if the temperature increases to 45^{\circ}K?
The given ratio in the word problem is 2. 75 \mathrm{~L}: 18^{\circ} \mathrm{K}
Divide 45 by 18 to see the relationship between the two temperatures.
45 \div 18=2.5
45 is 2.5 times greater than 18. So we multiply 2.75 by 2.5 to get the amount of gas.
2.75 \times 2.5=6.875 \mathrm{~l}
Ratio problem solving FAQs
A ratio is a comparison of two or more quantities. It shows how much one quantity is related to another.
A recipe calls for 2 cups of flour and 1 cup of sugar. What is the ratio of flour to sugar? (2 : 1)
In middle school ( 7 th grade and 8 th grade), students transition from understanding basic ratios to working with more complex and real-life applications of ratios and proportions. They gain a deeper understanding of how ratios relate to different mathematical concepts, making them more prepared for higher-level math topics in high school.
The next lessons are
- Converting fractions, decimals and percentages
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 8: Functions
About this unit.
A function is like a machine that takes an input and gives an output. Let's explore how we can graph, analyze, and create different types of functions.
Evaluating functions
- What is a function? (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: Evaluating functions from equation (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: Evaluating functions from graph (Opens a modal)
- Evaluating discrete functions (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: evaluating expressions with function notation (Opens a modal)
- Evaluate functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Evaluate functions from their graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Evaluate function expressions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Inputs and outputs of a function
- Worked example: matching an input to a function's output (equation) (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: matching an input to a function's output (graph) (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: two inputs with the same output (graph) (Opens a modal)
- Function inputs & outputs: equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Function inputs & outputs: graph Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Functions and equations
- Equations vs. functions (Opens a modal)
- Obtaining a function from an equation (Opens a modal)
- Function rules from equations Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Interpreting function notation
- Function notation word problem: bank (Opens a modal)
- Function notation word problem: beach (Opens a modal)
- Function notation word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Introduction to the domain and range of a function
- Intervals and interval notation (Opens a modal)
- What is the domain of a function? (Opens a modal)
- What is the range of a function? (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: domain and range from graph (Opens a modal)
- Domain and range from graph Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Determining the domain of a function
- Determining whether values are in domain of function (Opens a modal)
- Examples finding the domain of functions (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: determining domain word problem (real numbers) (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: determining domain word problem (positive integers) (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: determining domain word problem (all integers) (Opens a modal)
- Identifying values in the domain Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Determine the domain of functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Function domain word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Recognizing functions
- Recognizing functions from graph (Opens a modal)
- Does a vertical line represent a function? (Opens a modal)
- Recognizing functions from table (Opens a modal)
- Recognizing functions from verbal description (Opens a modal)
- Recognizing functions from verbal description word problem (Opens a modal)
- Recognize functions from graphs Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Recognize functions from tables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Maximum and minimum points
- Introduction to minimum and maximum points (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: absolute and relative extrema (Opens a modal)
- Relative maxima and minima Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Absolute maxima and minima Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Intervals where a function is positive, negative, increasing, or decreasing
- Increasing, decreasing, positive or negative intervals (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: positive & negative intervals (Opens a modal)
- Positive and negative intervals Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Increasing and decreasing intervals Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Interpreting features of graphs
- Graph interpretation word problem: temperature (Opens a modal)
- Graph interpretation word problem: basketball (Opens a modal)
- Creativity break: How can people get creative in algebra (Opens a modal)
- Graph interpretation word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Average rate of change
- Introduction to average rate of change (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: average rate of change from graph (Opens a modal)
- Worked example: average rate of change from table (Opens a modal)
- Average rate of change: graphs & tables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Average rate of change word problems
- Average rate of change word problem: table (Opens a modal)
- Average rate of change word problem: graph (Opens a modal)
- Average rate of change review (Opens a modal)
- Average rate of change word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Intro to inverse functions
- Intro to inverse functions (Opens a modal)
- Inputs & outputs of inverse functions (Opens a modal)
- Graphing the inverse of a linear function (Opens a modal)
- Finding inverse functions: linear (Opens a modal)
- Functions: FAQ (Opens a modal)
- Evaluate inverse functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Finding inverses of linear functions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Common Core State Standards Initiative
- Standards for Mathematical Practice
The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in their students. These practices rest on important “processes and proficiencies” with longstanding importance in mathematics education. The first of these are the NCTM process standards of problem solving, reasoning and proof, communication, representation, and connections. The second are the strands of mathematical proficiency specified in the National Research Council’s report Adding It Up : adaptive reasoning, strategic competence, conceptual understanding (comprehension of mathematical concepts, operations and relations), procedural fluency (skill in carrying out procedures flexibly, accurately, efficiently and appropriately), and productive disposition (habitual inclination to see mathematics as sensible, useful, and worthwhile, coupled with a belief in diligence and one’s own efficacy).
Standards in this domain:
Ccss.math.practice.mp1 make sense of problems and persevere in solving them..
Mathematically proficient students start by explaining to themselves the meaning of a problem and looking for entry points to its solution. They analyze givens, constraints, relationships, and goals. They make conjectures about the form and meaning of the solution and plan a solution pathway rather than simply jumping into a solution attempt. They consider analogous problems, and try special cases and simpler forms of the original problem in order to gain insight into its solution. They monitor and evaluate their progress and change course if necessary. Older students might, depending on the context of the problem, transform algebraic expressions or change the viewing window on their graphing calculator to get the information they need. Mathematically proficient students can explain correspondences between equations, verbal descriptions, tables, and graphs or draw diagrams of important features and relationships, graph data, and search for regularity or trends. Younger students might rely on using concrete objects or pictures to help conceptualize and solve a problem. Mathematically proficient students check their answers to problems using a different method, and they continually ask themselves, "Does this make sense?" They can understand the approaches of others to solving complex problems and identify correspondences between different approaches.
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
Mathematically proficient students make sense of quantities and their relationships in problem situations. They bring two complementary abilities to bear on problems involving quantitative relationships: the ability to decontextualize —to abstract a given situation and represent it symbolically and manipulate the representing symbols as if they have a life of their own, without necessarily attending to their referents—and the ability to contextualize , to pause as needed during the manipulation process in order to probe into the referents for the symbols involved. Quantitative reasoning entails habits of creating a coherent representation of the problem at hand; considering the units involved; attending to the meaning of quantities, not just how to compute them; and knowing and flexibly using different properties of operations and objects.
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.
Mathematically proficient students understand and use stated assumptions, definitions, and previously established results in constructing arguments. They make conjectures and build a logical progression of statements to explore the truth of their conjectures. They are able to analyze situations by breaking them into cases, and can recognize and use counterexamples. They justify their conclusions, communicate them to others, and respond to the arguments of others. They reason inductively about data, making plausible arguments that take into account the context from which the data arose. Mathematically proficient students are also able to compare the effectiveness of two plausible arguments, distinguish correct logic or reasoning from that which is flawed, and—if there is a flaw in an argument—explain what it is. Elementary students can construct arguments using concrete referents such as objects, drawings, diagrams, and actions. Such arguments can make sense and be correct, even though they are not generalized or made formal until later grades. Later, students learn to determine domains to which an argument applies. Students at all grades can listen or read the arguments of others, decide whether they make sense, and ask useful questions to clarify or improve the arguments.
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP4 Model with mathematics.
Mathematically proficient students can apply the mathematics they know to solve problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace. In early grades, this might be as simple as writing an addition equation to describe a situation. In middle grades, a student might apply proportional reasoning to plan a school event or analyze a problem in the community. By high school, a student might use geometry to solve a design problem or use a function to describe how one quantity of interest depends on another. Mathematically proficient students who can apply what they know are comfortable making assumptions and approximations to simplify a complicated situation, realizing that these may need revision later. They are able to identify important quantities in a practical situation and map their relationships using such tools as diagrams, two-way tables, graphs, flowcharts and formulas. They can analyze those relationships mathematically to draw conclusions. They routinely interpret their mathematical results in the context of the situation and reflect on whether the results make sense, possibly improving the model if it has not served its purpose.
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP5 Use appropriate tools strategically.
Mathematically proficient students consider the available tools when solving a mathematical problem. These tools might include pencil and paper, concrete models, a ruler, a protractor, a calculator, a spreadsheet, a computer algebra system, a statistical package, or dynamic geometry software. Proficient students are sufficiently familiar with tools appropriate for their grade or course to make sound decisions about when each of these tools might be helpful, recognizing both the insight to be gained and their limitations. For example, mathematically proficient high school students analyze graphs of functions and solutions generated using a graphing calculator. They detect possible errors by strategically using estimation and other mathematical knowledge. When making mathematical models, they know that technology can enable them to visualize the results of varying assumptions, explore consequences, and compare predictions with data. Mathematically proficient students at various grade levels are able to identify relevant external mathematical resources, such as digital content located on a website, and use them to pose or solve problems. They are able to use technological tools to explore and deepen their understanding of concepts.
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP6 Attend to precision.
Mathematically proficient students try to communicate precisely to others. They try to use clear definitions in discussion with others and in their own reasoning. They state the meaning of the symbols they choose, including using the equal sign consistently and appropriately. They are careful about specifying units of measure, and labeling axes to clarify the correspondence with quantities in a problem. They calculate accurately and efficiently, express numerical answers with a degree of precision appropriate for the problem context. In the elementary grades, students give carefully formulated explanations to each other. By the time they reach high school they have learned to examine claims and make explicit use of definitions.
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP7 Look for and make use of structure.
Mathematically proficient students look closely to discern a pattern or structure. Young students, for example, might notice that three and seven more is the same amount as seven and three more, or they may sort a collection of shapes according to how many sides the shapes have. Later, students will see 7 × 8 equals the well remembered 7 × 5 + 7 × 3, in preparation for learning about the distributive property. In the expression x 2 + 9 x + 14, older students can see the 14 as 2 × 7 and the 9 as 2 + 7. They recognize the significance of an existing line in a geometric figure and can use the strategy of drawing an auxiliary line for solving problems. They also can step back for an overview and shift perspective. They can see complicated things, such as some algebraic expressions, as single objects or as being composed of several objects. For example, they can see 5 - 3( x - y ) 2 as 5 minus a positive number times a square and use that to realize that its value cannot be more than 5 for any real numbers x and y .
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning.
Mathematically proficient students notice if calculations are repeated, and look both for general methods and for shortcuts. Upper elementary students might notice when dividing 25 by 11 that they are repeating the same calculations over and over again, and conclude they have a repeating decimal. By paying attention to the calculation of slope as they repeatedly check whether points are on the line through (1, 2) with slope 3, middle school students might abstract the equation ( y - 2)/( x - 1) = 3. Noticing the regularity in the way terms cancel when expanding ( x - 1)( x + 1), ( x - 1)( x 2 + x + 1), and ( x - 1)( x 3 + x 2 + x + 1) might lead them to the general formula for the sum of a geometric series. As they work to solve a problem, mathematically proficient students maintain oversight of the process, while attending to the details. They continually evaluate the reasonableness of their intermediate results.
Connecting the Standards for Mathematical Practice to the Standards for Mathematical Content
The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe ways in which developing student practitioners of the discipline of mathematics increasingly ought to engage with the subject matter as they grow in mathematical maturity and expertise throughout the elementary, middle and high school years. Designers of curricula, assessments, and professional development should all attend to the need to connect the mathematical practices to mathematical content in mathematics instruction.
The Standards for Mathematical Content are a balanced combination of procedure and understanding. Expectations that begin with the word "understand" are often especially good opportunities to connect the practices to the content. Students who lack understanding of a topic may rely on procedures too heavily. Without a flexible base from which to work, they may be less likely to consider analogous problems, represent problems coherently, justify conclusions, apply the mathematics to practical situations, use technology mindfully to work with the mathematics, explain the mathematics accurately to other students, step back for an overview, or deviate from a known procedure to find a shortcut. In short, a lack of understanding effectively prevents a student from engaging in the mathematical practices.
In this respect, those content standards which set an expectation of understanding are potential "points of intersection" between the Standards for Mathematical Content and the Standards for Mathematical Practice. These points of intersection are intended to be weighted toward central and generative concepts in the school mathematics curriculum that most merit the time, resources, innovative energies, and focus necessary to qualitatively improve the curriculum, instruction, assessment, professional development, and student achievement in mathematics.
- How to read the grade level standards
- Introduction
- Counting & Cardinality
- Operations & Algebraic Thinking
- Number & Operations in Base Ten
- Measurement & Data
- Number & Operations—Fractions¹
- Number & Operations in Base Ten¹
- Number & Operations—Fractions
- Ratios & Proportional Relationships
- The Number System
- Expressions & Equations
- Statistics & Probability
- The Real Number System
- Quantities*
- The Complex Number System
- Vector & Matrix Quantities
- Seeing Structure in Expressions
- Arithmetic with Polynomials & Rational Expressions
- Creating Equations*
- Reasoning with Equations & Inequalities
- Interpreting Functions
- Building Functions
- Linear, Quadratic, & Exponential Models*
- Trigonometric Functions
- High School: Modeling
- Similarity, Right Triangles, & Trigonometry
- Expressing Geometric Properties with Equations
- Geometric Measurement & Dimension
- Modeling with Geometry
- Interpreting Categorical & Quantitative Data
- Making Inferences & Justifying Conclusions
- Conditional Probability & the Rules of Probability
- Using Probability to Make Decisions
- Courses & Transitions
- Mathematics Glossary
- Mathematics Appendix A
3 Ways to Strengthen Math Instruction

- Share article
Students’ math scores have plummeted, national assessments show , and educators are working hard to turn math outcomes around.
But it’s a challenge, made harder by factors like math anxiety , students’ feelings of deep ambivalence about how math is taught, and learning gaps that were exacerbated by the pandemic’s disruption of schools.
This week, three educators offered solutions on how districts can turn around poor math scores in a conversation moderated by Peter DeWitt, an opinion blogger for Education Week.
Here are three takeaways from the discussion. For more, watch the recording on demand .
1. Intervention is key
Research shows that early math skills are a key predictor of later academic success.
“Children who know more do better, and math is cumulative—so if you don’t grasp some of the earlier concepts, math gets increasingly harder,” said Nancy Jordan, a professor of education at the University of Delaware.
For example, many students struggle with the concept of fractions, she said. Her research has found that by 6th grade, some students still don’t really understand what a fraction is, which makes it harder for them to master more advanced concepts, like adding or subtracting fractions with unlike denominators.
At that point, though, teachers don’t always have the time in class to re-teach those basic or fundamental concepts, she said, which is why targeted intervention is so important.

Still, Jordan’s research revealed that in some middle schools, intervention time is not a priority: “If there’s an assembly, or if there is a special event or whatever, it takes place during intervention time,” she said. “Or ... the children might sit on computers, and they’re not getting any really explicit instruction.”
2. ‘Gamify’ math class
Students today need new modes of instruction that meet them where they are, said Gerilyn Williams, a math teacher at Pinelands Regional Junior High School in Little Egg Harbor Township, N.J.
“Most of them learn through things like TikTok or YouTube videos,” she said. “They like to play games, they like to interact. So how can I bring those same attributes into my lesson?”
Part of her solution is gamifying instruction. Williams avoids worksheets. Instead, she provides opportunities for students to practice skills that incorporate elements of game design.
That includes digital tools, which provide students with the instant feedback they crave, she said.
But not all the games are digital. Williams’ students sometimes play “trashketball,” a game in which they work in teams to answer math questions. If they get the question right, they can crumble the piece of paper and throw it into a trash can from across the room.
“The kids love this,” she said.

Williams also incorporates game-based vocabulary into her instruction, drawing on terms from video games.
For example, “instead of calling them quizzes and tests, I call them boss battles,” she said. “It’s less frightening. It reduces that math anxiety, and it makes them more engaging.
“We normalize things like failure, because when they play video games, think about what they’re doing,” Williams continued. “They fail—they try again and again and again and again until they achieve success.”
3. Strengthen teacher expertise
To turn around math outcomes, districts need to invest in teacher professional development and curriculum support, said Chaunté Garrett, the CEO of ELLE Education, which partners with schools and districts to support student learning.
“You’re not going to be able to replace the value of a well-supported and well-equipped mathematics teacher,” she said. “We also want to make sure that that teacher has a math curriculum that’s grounded in the standards and conceptually based.”
Students will develop more critical thinking skills and better understand math concepts if teachers are able to relate instruction to real life, Garrett said—so that “kids have relationships that they can pull on, and math has some type of meaning and context to them outside of just numbers and procedures.”

It’s important for math curriculum to be both culturally responsive and relevant, she added. And teachers might need training on how to offer opportunities for students to analyze and solve real-world problems.
“So often, [in math problems], we want to go back to soccer and basketball and all of those things that we lived through, and it’s not that [current students] don’t enjoy those, but our students live social media—they literally live it,” Garrett said. “Those are the things that have to live out in classrooms right now, and if we’re not doing those things, we are doing a disservice.”
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
MathPapa Practice. MathPapa Practice has practice problems to help you learn algebra. Basic Arithmetic Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Basic Arithmetic Review Multi-Digit Arithmetic Addition (2-digit) Subtraction (2-digit) Multiplication (2-digit by 1-digit) ...
Algebra Lessons. Step-by-step lessons for learning to solve equations. Math practice puzzles and exercises to practice your math reasoning and arithmetic. A fun way to develop your math skills and build math confidence.
Timed addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems for basic math practice. Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond. Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly.
Wolfram for Education. Wolfram Demonstrations. Mathematica. MathWorld. Online practice problems with answers for students and teachers. Pick a topic and start practicing, or print a worksheet for study sessions or quizzes.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,100 Mastery points! There are lots of strategies we can use to solve equations. Let's explore some different ways to solve equations and inequalities. We'll also see what it takes for an equation to have no solution, or infinite solutions.
Regular Payments Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions - a collection of exam style questions for a wide range of topics. Perfect to use for revision, as homework or to target particular topics. Answers and video solutions are available for each.
Even simple math problems become easier to solve when broken down into steps. From basic additions to calculus, the process of problem solving usually takes a lot of practice before answers could come easily. As problems become more complex, it becomes even more important to understand the step-by-step process by which we solve them. At Cymath ...
Math Practice. Practice. Build your math skills, get used to solving different kind of problems. Practice thousands of problems, receive helpful hints. Quiz. Test yourself, drill down into any math topic or build a custom quiz. Check your progress, receive helpful tips.
ChiliMath.com is a place for you to learn math at your own pace for FREE! Allow me to help you solve math problems with a direct approach through the use of examples and diagrams. New Lessons Added:March 10, 2024. Derivation of Pythagorean Theorem Formula. Absolute Value Equations Practice Problems with Answers.
Math Practice is a tool for mastering algebraic notation. It supports students in their step-by-step math work, let's them explore different solution paths, and helps build confidence, fluency, and understanding. Enter your problem. Practice.
Only Wolfram Problem Generator directly integrates the popular and powerful Step-by-step Solutions from Wolfram|Alpha. You can use a single hint to get unstuck, or explore the entire math problem from beginning to end. Online practice problems for math, including arithmetic, algebra, calculus, linear algebra, number theory, and statistics.
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.
Basic Algebra 5. Algebra: Basic Fractions 1. Algebra: Basic Fractions 2. Algebra: Basic Fractions 3. Algebra: Basic Fractions 4. Algebra: Basic Fractions 5. Math practice problems to improve your math reasoning and arithmetic. A fun way to develop your math skills and build math confidence.
Brilliant - Build quantitative skills in math, science, and computer science with hands-on, interactive lessons.
40 \div 8=5 40 ÷ 8 = 5. Then you multiply each part of the ratio by 5. 5. 3\times 5:5\times 5=15 : 25 3 × 5: 5 × 5 = 15: 25. This means that Charlie will get 15 15 sweets and David will get 25 25 sweets. There can be ratio word problems involving different operations and types of numbers.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems. Try Math Solver. Type a math problem. Solve. Quadratic equation { x } ^ { 2 } - 4 x - 5 = 0. Trigonometry. 4 \sin \theta \cos \theta = 2 \sin \theta ... Practice, practice, practice. Search for additional learning materials, such as related worksheets and video tutorials.
Solving equations & inequalities. Unit 3. Working with units. Unit 4. Linear equations & graphs. ... Practice. Function inputs & outputs: equation Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! ... Average rate of change word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Intro to inverse functions. Learn. Intro to inverse functions
CCSS.Math.Practice.MP5 Use appropriate tools strategically. Mathematically proficient students consider the available tools when solving a mathematical problem. These tools might include pencil and paper, concrete models, a ruler, a protractor, a calculator, a spreadsheet, a computer algebra system, a statistical package, or dynamic geometry ...
2. 'Gamify' math class. Students today need new modes of instruction that meet them where they are, said Gerilyn Williams, a math teacher at Pinelands Regional Junior High School in Little Egg ...
In Padlet, the teacher can control the students, and in the online math solver, students can learn and practice. This study aimed to find the students' mathematical problem-solving ability after learning using the Padlet integrated by online math solver and compare this learning to conventional learning.