How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.

Elements of a fantastic thesis introduction
Open with a (personal) story, begin with a problem, define a clear research gap, describe the scientific relevance of the thesis, describe the societal relevance of the thesis, write down the thesis’ core claim in 1-2 sentences, support your argument with sufficient evidence, consider possible objections, address the empirical research context, give a taste of the thesis’ empirical analysis, hint at the practical implications of the research, provide a reading guide, briefly summarise all chapters to come, design a figure illustrating the thesis structure.
An introductory chapter plays an integral part in every thesis. The first chapter has to include quite a lot of information to contextualise the research. At the same time, a good thesis introduction is not too long, but clear and to the point.
A powerful thesis introduction does the following:
- It captures the reader’s attention.
- It presents a clear research gap and emphasises the thesis’ relevance.
- It provides a compelling argument.
- It previews the research findings.
- It explains the structure of the thesis.
In addition, a powerful thesis introduction is well-written, logically structured, and free of grammar and spelling errors. Reputable thesis editors can elevate the quality of your introduction to the next level. If you are in search of a trustworthy thesis or dissertation editor who upholds high-quality standards and offers efficient turnaround times, I recommend the professional thesis and dissertation editing service provided by Editage .
This list can feel quite overwhelming. However, with some easy tips and tricks, you can accomplish all these goals in your thesis introduction. (And if you struggle with finding the right wording, have a look at academic key phrases for introductions .)
Ways to capture the reader’s attention
A powerful thesis introduction should spark the reader’s interest on the first pages. A reader should be enticed to continue reading! There are three common ways to capture the reader’s attention.
An established way to capture the reader’s attention in a thesis introduction is by starting with a story. Regardless of how abstract and ‘scientific’ the actual thesis content is, it can be useful to ease the reader into the topic with a short story.
This story can be, for instance, based on one of your study participants. It can also be a very personal account of one of your own experiences, which drew you to study the thesis topic in the first place.
Start by providing data or statistics
Data and statistics are another established way to immediately draw in your reader. Especially surprising or shocking numbers can highlight the importance of a thesis topic in the first few sentences!
So if your thesis topic lends itself to being kick-started with data or statistics, you are in for a quick and easy way to write a memorable thesis introduction.
The third established way to capture the reader’s attention is by starting with the problem that underlies your thesis. It is advisable to keep the problem simple. A few sentences at the start of the chapter should suffice.
Usually, at a later stage in the introductory chapter, it is common to go more in-depth, describing the research problem (and its scientific and societal relevance) in more detail.
You may also like: Minimalist writing for a better thesis
Emphasising the thesis’ relevance
A good thesis is a relevant thesis. No one wants to read about a concept that has already been explored hundreds of times, or that no one cares about.
Of course, a thesis heavily relies on the work of other scholars. However, each thesis is – and should be – unique. If you want to write a fantastic thesis introduction, your job is to point out this uniqueness!
In academic research, a research gap signifies a research area or research question that has not been explored yet, that has been insufficiently explored, or whose insights and findings are outdated.
Every thesis needs a crystal-clear research gap. Spell it out instead of letting your reader figure out why your thesis is relevant.
* This example has been taken from an actual academic paper on toxic behaviour in online games: Liu, J. and Agur, C. (2022). “After All, They Don’t Know Me” Exploring the Psychological Mechanisms of Toxic Behavior in Online Games. Games and Culture 1–24, DOI: 10.1177/15554120221115397
The scientific relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your work in terms of advancing theoretical insights on a topic. You can think of this part as your contribution to the (international) academic literature.
Scientific relevance comes in different forms. For instance, you can critically assess a prominent theory explaining a specific phenomenon. Maybe something is missing? Or you can develop a novel framework that combines different frameworks used by other scholars. Or you can draw attention to the context-specific nature of a phenomenon that is discussed in the international literature.
The societal relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your research in more practical terms. You can think of this part as your contribution beyond theoretical insights and academic publications.
Why are your insights useful? Who can benefit from your insights? How can your insights improve existing practices?

Formulating a compelling argument
Arguments are sets of reasons supporting an idea, which – in academia – often integrate theoretical and empirical insights. Think of an argument as an umbrella statement, or core claim. It should be no longer than one or two sentences.
Including an argument in the introduction of your thesis may seem counterintuitive. After all, the reader will be introduced to your core claim before reading all the chapters of your thesis that led you to this claim in the first place.
But rest assured: A clear argument at the start of your thesis introduction is a sign of a good thesis. It works like a movie teaser to generate interest. And it helps the reader to follow your subsequent line of argumentation.
The core claim of your thesis should be accompanied by sufficient evidence. This does not mean that you have to write 10 pages about your results at this point.
However, you do need to show the reader that your claim is credible and legitimate because of the work you have done.
A good argument already anticipates possible objections. Not everyone will agree with your core claim. Therefore, it is smart to think ahead. What criticism can you expect?
Think about reasons or opposing positions that people can come up with to disagree with your claim. Then, try to address them head-on.
Providing a captivating preview of findings
Similar to presenting a compelling argument, a fantastic thesis introduction also previews some of the findings. When reading an introduction, the reader wants to learn a bit more about the research context. Furthermore, a reader should get a taste of the type of analysis that will be conducted. And lastly, a hint at the practical implications of the findings encourages the reader to read until the end.
If you focus on a specific empirical context, make sure to provide some information about it. The empirical context could be, for instance, a country, an island, a school or city. Make sure the reader understands why you chose this context for your research, and why it fits to your research objective.
If you did all your research in a lab, this section is obviously irrelevant. However, in that case you should explain the setup of your experiment, etcetera.
The empirical part of your thesis centers around the collection and analysis of information. What information, and what evidence, did you generate? And what are some of the key findings?
For instance, you can provide a short summary of the different research methods that you used to collect data. Followed by a short overview of how you analysed this data, and some of the key findings. The reader needs to understand why your empirical analysis is worth reading.
You already highlighted the practical relevance of your thesis in the introductory chapter. However, you should also provide a preview of some of the practical implications that you will develop in your thesis based on your findings.
Presenting a crystal clear thesis structure
A fantastic thesis introduction helps the reader to understand the structure and logic of your whole thesis. This is probably the easiest part to write in a thesis introduction. However, this part can be best written at the very end, once everything else is ready.
A reading guide is an essential part in a thesis introduction! Usually, the reading guide can be found toward the end of the introductory chapter.
The reading guide basically tells the reader what to expect in the chapters to come.
In a longer thesis, such as a PhD thesis, it can be smart to provide a summary of each chapter to come. Think of a paragraph for each chapter, almost in the form of an abstract.
For shorter theses, which also have a shorter introduction, this step is not necessary.
Especially for longer theses, it tends to be a good idea to design a simple figure that illustrates the structure of your thesis. It helps the reader to better grasp the logic of your thesis.
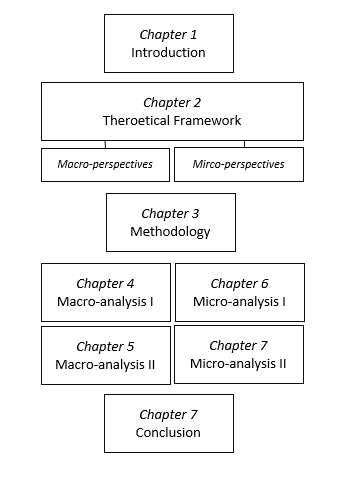
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The most useful academic social networking sites for PhD students
10 reasons not to do a master's degree, related articles.

Dealing with conflicting feedback from different supervisors

How to deal with procrastination productively during thesis writing

The importance of sleep for efficient thesis writing

Theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: Simple definitions and an overview of key differences

How To Write A Thesis Introduction Chapter
Crafting the introductory chapter of a thesis can be confusing. If you are feeling the same, you are the at right place.
This post will explore how you can write a thesis introduction chapter, by outlining the essential components of a thesis introduction. We will look at the process, one section at a time, and explain them to help you get a hang of how to craft your thesis introduction.
How To Write A Good Thesis Introduction?
The opening section of a thesis introduction sets the stage for what’s to come, acting as a crucial hook to capture the reader’s attention.
Unlike the broader strokes found in the table of contents, this initial foray into your research is where you must distill the essence of your thesis into a potent, digestible form.
A skillful introduction begins with a concise preview of the chapter’s terrain, delineating the structure of the thesis with a clarity that avoids overwhelming the reader.
This is not the stage for exhaustive details; rather, it’s where you prime the reader with a snapshot of the intellectual journey ahead.
In crafting this segment, insiders advise adhering to a quartet of foundational sentences that offer an academic handshake to the reader.
First Section: I ntroduces the broad field of research, such as the significance of organisational skills development in business growth.
Second Section: Narrows the focus, pinpointing a specific research problem or gap — perhaps the debate on managing skill development in fast-paced industries like web development.
Third Section: Clearly state the research aims and objectives, guiding the reader to the ‘why’ behind your study. Finally, a sentence should outline the roadmap of the introduction chapter itself, forecasting the background context, research questions, significance, and limitations that will follow.
Such a calibrated approach ensures that every element from the research objective to the hypothesis is presented with precision.
This method, a well-guarded secret amongst seasoned researchers, transforms a mundane introduction into a compelling entrée into your dissertation or thesis.
Background To The Study
This section sets the tone for the research journey ahead. The goal here is to capture the reader’s attention by threading relevant background information into a coherent narrative that aligns with the research objectives of the thesis.
To write a good thesis introduction, one must carefully describe the background to highlight the context in which the research is grounded.
This involves not just a literature review but a strategic presentation of the current state of research, pinpointing where your work will wedge itself into the existing body of knowledge.
For instance, if the research project focuses on qualitative changes in urban planning, the introduction should spotlight key developmental milestones and policy shifts that foreground the study’s aims and objectives.
When writing this section, articulate the focus and scope of the research, ensuring the reader grasps the importance of the research questions and hypothesis.
This section must not only be informative but also engaging. By the end of the introductory chapter, the reader should be compelled to continue reading, having grasped a clear and easy-to-understand summary of each chapter that will follow.
It’s a good idea to address frequently asked questions and to clearly state any industry-specific terminology, assuming no prior expertise on the reader’s part.
This approach establishes a solid foundation for the rest of the thesis or dissertation, ensuring the reader is well-prepared to dive into the nuances of your research project.
Research Problem
Crafting the nucleus of your thesis or dissertation hinges on pinpointing a compelling research problem. This step is crucial; it is the keystone of a good thesis introduction chapter, drawing the reader’s attention and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.

A well-defined research problem addresses a gap in the existing literature, underscored by a qualitative or quantitative body of research that lacks consensus or is outdated, especially in rapidly evolving fields.
Consider the dynamic sphere of organizational skills development. Established research might agree on strategies for industries where skills change at a snail’s pace.
However, if the landscape shifts more quickly—take web development for example, where new languages and platforms emerge incessantly—the literature gap becomes evident.
Herein lies the research problem: existing strategies may not suffice in industries characterized by a swift knowledge turnover.
When writing your introduction, your goal is to clearly state this gap. A great thesis introduction delineates what is known, what remains unknown, and why bridging this chasm is significant.
It should illuminate the research objectives and questions, laying out a roadmap for the reader in a language that’s clear and easy to understand, regardless of their familiarity with the topic.
You’ll be able to capture and maintain the reader’s interest by effectively communicating why your research matters—setting the scene for your hypothesis and subsequent investigation.
Remember, a good thesis introduction should not only provide background information but also articulate the focus and scope of the study, offering a preview of the structure of your thesis.
Research Aims, Objectives And Questions
This pivotal section lays out the foundation by providing relevant background information, but it is the articulation of research aims, objectives, and questions that clarifies the focus and scope of your study.
The research aim is the lighthouse of your thesis, illuminating the overarching purpose of your investigation.
For instance, a thesis exploring skills development in fast-paced industries might present an aim to evaluate the effectiveness of various strategies within UK web development companies. This broad goal sets the direction for more detailed planning.
Research objectives drill down into specifics, acting as stepping stones toward achieving your aim. They are the tangible checkpoints of your research project, often action-oriented, outlining what you will do.
Examples might include identifying common skills development strategies or evaluating their effectiveness. These objectives segment the monumental task into manageable portions, offering a clear and easy way to write a structured pathway for the research.

Equally critical are the research questions, which translate your objectives into inquiries that your thesis will answer. They narrow the focus even further, dictating the structure of the thesis.
For instance:
- “What are the prevalent skills development strategies employed by UK web development firms?”
- “How effective are these strategies?”
Such questions demand concrete responses and guide the reader through the rest of the thesis.
Significance Of The Study
The “Significance of the Study” section within the introduction chapter of your thesis or dissertation holds considerable weight in laying out the importance of your research.

This segment answers the pivotal question: “Why does this research matter?” It is strategically placed after the background information and literature review to underscore the contribution your study makes to the existing body of research.
In writing this section, you’ll be able to capture the reader’s attention by clearly stating the impact and added value your research project offers.
Whether it’s a qualitative or quantitative study, the significance must be articulated in terms of:
- Theoretical
- Academic, and
- Societal contributions.
For instance, it may fill gaps identified in the literature review, propose innovative solutions to pressing problems, or advance our understanding in a certain field.
A good thesis introduction will succinctly convey three main things: the research objective, the hypothesis or research questions, and the importance of your research.
It’s a good idea to provide your reader with a roadmap, foreshadowing the structure of the thesis and offering a summary of each chapter, thus enticing the reader to continue reading.
When you write the introduction section, it should also serve as a concise synopsis of the focus and scope of your research.
It’s often beneficial to include examples of introductions that clearly state the research objectives and questions, offering a snapshot of the whole thesis, and setting the stage for the rest of your thesis.
Limitations Of The Study
A thorough thesis introduction lays out specific research objectives and questions, yet it also sheds light on the study’s inherent boundaries. This is the purpose of the Limitation of The Study section.
The limitations section is not a confession of failure; instead, it’s a good idea to see it as demonstrating academic maturity.
Here, you clearly state the parameters within which the research was conducted.
For instance, a qualitative study might face scrutiny for subjectivity, or a quantitative one for potentially oversimplifying complexities. Other common constraints include the scope—perhaps focusing on a narrow aspect without considering variable interplay—resources, and generalizability.
For example, a study concentrated on a specific industry in Florida may not hold water in a different context, for example in Tokyo, Japan.
It’s essential to write this section with transparency. A good thesis introduction doesn’t shy away from limitations. Instead, it captures the reader’s attention by laying them out systematically, often in a dedicated paragraph for each chapter.
This honesty allows the reader to understand the research’s focus and scope while providing a clear and easy-to-follow structure of the thesis.
This approach also serves to manage the reader’s expectations. By preempting frequently asked questions about the scope of your research, the introductory chapter establishes a trust that encourages the reader to continue reading, aware of the contours shaping the body of research.
Thus, a well-articulated limitations section is not just part of the thesis; it is an integral piece of a responsibly woven research narrative.
Structural Outline Of Thesis, Thesis Statement
Within the thesis or dissertation, the structural outline section is akin to a compass, orienting the reader’s journey through the academic landscape laid out within the pages.
Crafting this section is a strategic exercise, one that requires an understanding of the work’s skeleton.
In essence, it’s the blueprint for the construction of a scholarly argument, and writing a good thesis necessitates a clear and easy-to-follow outline.
When you write a thesis outline, it’s not only about catching the reader’s attention; it’s also about holding it throughout the rest of the thesis.
This is where the structural outline comes into play, often beginning with an introduction chapter that presents the thesis statement, research objectives, and the importance of your research.
Following the introduction, a typical outline might proceed with Chapter 2, offering a literature review to acquaint the reader with existing literature and how this piece of research fits within it.
Subsequent chapters, each with a paragraph in the outline, detail the methodological approach—whether it’s qualitative or quantitative—and the research’s focus and scope.
A well-thought-out outline should also preview the structure of the thesis, succinctly:
- Summarizing the main aim and objectives of each chapter, and
- Indicating the type of data and analysis that will be presented.
This roadmap reassures the reader that the dissertation or thesis will cover the necessary ground in a logical progression, continuing from where the introduction first captivated their interest.
The structural outline is not only part of the thesis—it’s a strategic framework that informs the reader what to expect in each subsequent chapter.
Done correctly, this section allows the reader to understand the whole thesis in a nutshell and can often serve as a checklist for both the reader and the writer.
This ensures that the key stages of the research project are clearly stated and that the reader is provided with a roadmap to guide them through the detailed landscape of your scholarly work.
Write An Introduction Chapter With Ease
Mastering the thesis introduction chapter is a critical step towards a successful dissertation. It’s about striking a balance between engagement and information, presenting a snapshot of your research with clarity and intrigue.
Remember to start with a hook, establish the context, clarify your aims, and highlight the significance, all while being mindful of the study’s scope and limitations.
By adhering to these principles, your introduction will not only guide but also inspire your readers, laying a strong foundation for the in-depth exploration that follows in your thesis or dissertation.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- Leeds University Business School
- Research and innovation
- Research and innovation blog
How to write an introduction chapter for a thesis
Louisa Hill is a Senior Teaching Fellow and delivers workshops for Postgraduate Researchers who want to teach.

When writing a thesis, you will need to write an introductory chapter. This chapter is critical as it is the first thing that the examiner will read and it is therefore important to make a good first impression.
A good introduction chapter should incite the reader to read the rest of the thesis by establishing the context of your topic, the motivation for undertaking your work and the importance of your research.
As a lecturer and supervisor, I have read many introductory chapters for research projects such as theses. Here is my advice to those undertaking a research project and writing a thesis.
Capture the reader’s interest
Initially you need to capture the reader’s attention with a discussion of a broader theme relating to your research. To add impact draw on research, data and quotations from international or national professional bodies, governmental organisations or key authors on the topic of study.
Give an overview of your research topic
Your discussion should then begin by detailing the broader aspects of the topic more, before focussing on the specific topic of your research. It is a good idea when you do this to assume that the reader knows nothing about your topic. Therefore definitions, drawing on key research, need to be clarified and explained. Alternatively, if having read key literature for the literature review chapter, you are not satisfied with existing definitions, then draw on these, to devise your own (but make it clear you have done this).
Detail how your research is going to make a contribution
You must then sell your idea for undertaking the research topic, demonstrating the main reasons why the research will make a significant contribution to the current body of research. This can be achieved by demonstrating a gap or limitation with existing research, then showing how your research will resolve this. There are different types of contribution (see Constructing Research Questions: Doing Interesting Research ).
Explain what your interest is in the topic
Next you need to demonstrate your personal reasons for choosing the topic. These could relate to your previous research, work or experiences.
List your research objectives
You need to include your three or four overarching research objectives. Also include corresponding research questions if it is a qualitative piece of research or hypotheses if it is quantitative-based. The former are usually derivatives of the research objectives. Note though that these objectives and questions or hypotheses are fluid in nature and can be tweaked as you undertake the research.
Give a forthcoming chapter overview
The final part of the introduction is an overview of the rest of the chapters in the thesis. The other sections can go in any order, providing it is a logical sequence.
Learn from others
Look at other theses for example from White Rose etheses or your university library’s website. The majority of journal articles that you will read in the content of your topic will also provide useful insights.
Speak with your supervisor
Remember to always speak with your supervisor and have regular catch-ups. They will be able to offer guidance and encouragement, and steer you in the right direction.
Related content
- Writing a research PhD proposal
- Presenting with impact
- The benefits of undertaking a placement alongside your PhD
If you would like to get in touch regarding any of these blog entries, or are interested in contributing to the blog, please contact:
Email: [email protected] Phone: +44 (0)113 343 8754
Click here to view our privacy statement. You can repost this blog article, following the terms listed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International licence .
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and may not reflect the views of Leeds University Business School or the University of Leeds.
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
How to Write a Thesis Introduction
What types of information should you include in your introduction .
In the introduction of your thesis, you’ll be trying to do three main things, which are called Moves :
- Move 1 establish your territory (say what the topic is about)
- Move 2 establish a niche (show why there needs to be further research on your topic)
- Move 3 introduce the current research (make hypotheses; state the research questions)
Each Move has a number of stages. Depending on what you need to say in your introduction, you might use one or more stages. Table 1 provides you with a list of the most commonly occurring stages of introductions in Honours theses (colour-coded to show the Moves ). You will also find examples of Introductions, divided into stages with sample sentence extracts. Once you’ve looked at Examples 1 and 2, try the exercise that follows.
Most thesis introductions include SOME (but not all) of the stages listed below. There are variations between different Schools and between different theses, depending on the purpose of the thesis.
Stages in a thesis introduction
- state the general topic and give some background
- provide a review of the literature related to the topic
- define the terms and scope of the topic
- outline the current situation
- evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap
- identify the importance of the proposed research
- state the research problem/ questions
- state the research aims and/or research objectives
- state the hypotheses
- outline the order of information in the thesis
- outline the methodology
Example 1: Evaluation of Boron Solid Source Diffusion for High-Efficiency Silicon Solar Cells (School of Photovoltaic and Renewable Energy Engineering)
Example 2: Methods for Measuring Hepatitis C Viral Complexity (School of Biotechnology and Biological Sciences)
Note: this introduction includes the literature review.
Now that you have read example 1 and 2, what are the differences?
Example 3: The IMO Severe-Weather Criterion Applied to High-Speed Monohulls (School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering)
Example 4: The Steiner Tree Problem (School of Computer Science and Engineering)
Introduction exercise
Example 5.1 (extract 1): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.2 (extract 2): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.3
Example 5.4 (extract 4): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.5 (extract 5): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.6 (extract 6): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Well, firstly, there are many choices that you can make. You will notice that there are variations not only between the different Schools in your faculty, but also between individual theses, depending on the type of information that is being communicated. However, there are a few elements that a good Introduction should include, at the very minimum:
- Either Statement of general topic Or Background information about the topic;
- Either Identification of disadvantages of current situation Or Identification of the gap in current research;
- Identification of importance of proposed research
- Either Statement of aims Or Statement of objectives
- An Outline of the order of information in the thesis
Engineering & science
- Report writing
- Technical writing
- Writing lab reports
- Introductions
- Literature review
- Writing up results
- Discussions
- Conclusions
- Writing tools
- Case study report in (engineering)
- ^ More support
Scholarly Resources 4 Students | scite.ai 21 May 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a good thesis introduction

1. Identify your readership
2. hook the reader and grab their attention, 3. provide relevant background, 4. give the reader a sense of what the paper is about, 5. preview key points and lead into your thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a good thesis introduction, related articles.
Many people struggle to write a thesis introduction. Much of your research prep should be done and you should be ready to start your introduction. But often, it’s not clear what needs to be included in a thesis introduction. If you feel stuck at this point not knowing how to start, this guide can help.
Tip: If you’re really struggling to write your thesis intro, consider putting in a placeholder until you write more of the body of your thesis. Then, come back to your intro once you have a stronger sense of the overall content of your thesis.
A good introduction draws readers in while providing the setup for the entire project. There is no single way to write an introduction that will always work for every topic , but the points below can act as a guide. These points can help you write a good thesis introduction.
Before even starting with your first sentence, consider who your readers are. Most likely, your readers will be the professors who are advising you on your thesis.
You should also consider readers of your thesis who are not specialists in your field. Writing with them in your mind will help you to be as clear as possible; this will make your thesis more understandable and enjoyable overall.
Tip: Always strive to be clear, correct, concrete, and concise in your writing.
The first sentence of the thesis is crucial. Looking back at your own research, think about how other writers may have hooked you.
It is common to start with a question or quotation, but these types of hooks are often overused. The best way to start your introduction is with a sentence that is broad and interesting and that seamlessly transitions into your argument.
Once again, consider your audience and how much background information they need to understand your approach. You can start by making a list of what is interesting about your topic:
- Are there any current events or controversies associated with your topic that might be interesting for your introduction?
- What kinds of background information might be useful for a reader to understand right away?
- Are there historical anecdotes or other situations that uniquely illustrate an important aspect of your argument?
A good introduction also needs to contain enough background information to allow the reader to understand the thesis statement and arguments. The amount of background information required will depend on the topic .
There should be enough background information so you don't have to spend too much time with it in the body of the thesis, but not so much that it becomes uninteresting.
Tip: Strike a balance between background information that is too broad or too specific.
Let the reader know what the purpose of the study is. Make sure to include the following points:
- Briefly describe the motivation behind your research.
- Describe the topic and scope of your research.
- Explain the practical relevance of your research.
- Explain the scholarly consensus related to your topic: briefly explain the most important articles and how they are related to your research.
At the end of your introduction, you should lead into your thesis statement by briefly bringing up a few of your main supporting details and by previewing what will be covered in the main part of the thesis. You’ll want to highlight the overall structure of your thesis so that readers will have a sense of what they will encounter as they read.
A good introduction draws readers in while providing the setup for the entire project. There is no single way to write an introduction that will always work for every topic, but these tips will help you write a great introduction:
- Identify your readership.
- Grab the reader's attention.
- Provide relevant background.
- Preview key points and lead into the thesis statement.
A good introduction needs to contain enough background information, and let the reader know what the purpose of the study is. Make sure to include the following points:
- Briefly describe the motivation for your research.
The length of the introduction will depend on the length of the whole thesis. Usually, an introduction makes up roughly 10 per cent of the total word count.
The best way to start your introduction is with a sentence that is broad and interesting and that seamlessly transitions into your argument. Consider the audience, then think of something that would grab their attention.
In Open Access: Theses and Dissertations you can find thousands of recent works. Take a look at any of the theses or dissertations for real-life examples of introductions that were already approved.


How to Write Thesis Introduction Chapter: An Ultimate Guide
If you’ve landed here, you might be in the early challenging phase of penning down the dissertation introduction chapter. Well, we all know that it’s not an easy feat.
In this post, we will learn and review all the essential ingredients necessary for writing a strong dissertation and the details on which you should focus in this section.
Let’s get started by finding out what a thesis introduction is!
What Is Thesis Introduction?
The introduction is the first chapter of your dissertation that is placed right after the table of content. Your introduction should be intriguing and informative enough to draw your readers’ attention and set up the ground for your research with clarity, direction, and purpose on a relevant topic.
Your dissertation introduction should include;
- Topic Introduction And Subject Background: This initial part serves as an introduction, providing a broad overview of your research and the necessary context for your project, explaining the factors surrounding it.
- Research problem: This section highlights the gap or deficiency in current research that your study aims to address.
- Focus And scope: Clearly articulate the specific achievements and inquiries your research intends to accomplish.
- Relevance And importance: Justify the worth and value of your research, explaining why it is important to undertake and the contributions it will make.
- Questions And objectives: Outline the specific research questions or objectives that this dissertation will address and achieve.
- Limitations: Acknowledge and address the potential limitations inherent in your project and approach.
- Structure Overview: Briefly outline the organisation and framework of your dissertation or thesis, helping the reader navigate its contents.
How To Start Writing The Dissertation Introduction
While the dissertation introduction traditionally serves as the opening section, it is not mandatory to write it first. In fact, it is often one of the final components to be written, usually preceding the abstract.
But we suggest you write a rough draft of your dissertation introduction before starting the research to guide you throughout the writing process. However, revise the introduction from time to time to ensure that it matches the content of all sections.
1. Topic Introduction And Subject Background
Start by introducing your dissertation subject and providing essential contextual details. Define the significance of your research to educate your readers and grab their interest. It’s better to demonstrate the timeliness or importance of your topic, potentially by referring to a pertinent news article, ongoing academic discussion, or practical issue.
2. Focus And scope
After providing a concise introduction to the broader field of study, it is essential to narrow your research focus and clearly delineate your investigation’s specific boundaries and objectives.
There are several ways through which you can narrow down your research focus, including:
- Time period
- Demographics
- Geographical area
- Topics, themes, and aspects
3. Research Problem
Once you have provided your readers with an overview of your research area, it becomes essential to delve into the specifics of the research problem that your dissertation or thesis will address. While the background section may have hinted at potential research problems, this section aims to narrow down the focus and emphasise the specific research problem you will concentrate on.
Now, you might wonder, what exactly constitutes a research problem?
A research problem arises when there is a need to address a question or set of questions, but there exists a gap in the current literature, or the existing research presents conflicting or inconsistent findings.
To present your research problem effectively, it is crucial to clarify what is missing in the current literature and why it poses a problem. It is generally advisable to structure this discussion into three sections, namely:
- The Current State Of Research: This entails highlighting what is already well-established in the existing literature.
- The Literature Gap: Here, you identify the aspects or areas that are missing or inadequately addressed in the literature.
- The Significance Of The Problem: This section elucidates why filling this gap in the literature is important and emphasises the implications and potential contributions of addressing the research problem.
By structuring your discussion in this manner, you can effectively convey the specific research problem and its importance within the existing academic landscape.
4. Relevance And importance
To establish a strong foundation for your research, it is crucial to articulate your motivation behind undertaking this study and highlight its connection to existing scholarship. It is also important to outline the anticipated contributions and novel insights your research aims to offer.
Begin by providing a concise overview of the current state of research, including relevant literature citations. While it is important to acknowledge key sources, keep in mind that a more comprehensive survey of relevant literature will be conducted in the literature review section, thus avoiding excessive detail in the introduction.
Ultimately, your dissertation introduction should
- Contributes to resolving the theoretical or practical problem.
- Fills a gap in the existing literature.
- Expands and builds upon previous research.
- Introduces a new understanding of the topic.
5. Questions And Objectives
Formulating research questions and objectives is critical to any introduction, as it establishes the framework for the subsequent thesis or dissertation. How you craft these questions and objectives will vary based on your field of study, subject matter, and specific focus.
Moreover, if your objective in conducting research is to evaluate hypotheses, you can express them in this section. Additionally, your introduction provides an opportune space to present a conceptual framework that proposes associations among variables.
6. The limitations
After successfully defining your dissertation’s subject area and objectives, it is important to address the potential limitations of your research in a brief discussion.
Scope: It is crucial to acknowledge any narrow focus in your research that may overlook the interaction between certain variables.
Research Methodology: Critiques may arise regarding the subjectivity of qualitative methodologies or the oversimplification associated with quantitative methodologies.
Resources: It is important to consider limitations such as time constraints, financial constraints, equipment availability, and personal research experience.
Generalisability Of Findings: Keep in mind that findings obtained from studying a specific industry or country may not be readily applicable or generalised to other industries or countries.
7. Structure Overview
The structural outline is the last component after effectively conveying the research topic, significance, and limitations. Its purpose is to give the reader a clear idea of the dissertation or thesis structure.
In this section, a concise summary of each chapter, including the introduction chapter, is necessary. A sentence or two that outlines the purpose and contents of each chapter will suffice to guide the reader. It’s important to avoid excessive detail as this section serves as an outline, not a comprehensive research summary.
Introduction Checklist
☐ I have captivated the reader with an interesting introduction to my research subject.
☐ I have presented essential background information to aid the reader’s comprehension of the topic.
☐ I have precisely indicated the main focus of my research.
☐ I have demonstrated the significance and relevance of the dissertation topic.
☐ I have clearly defined the problem or question my research aims to tackle.
☐ I have outlined the specific goals and objectives of the research.
☐ I have given a brief overview of the structure of the dissertation.
Wrapping Up!
By incorporating these elements into your dissertation introduction chapter, you will create a compelling opening that establishes a strong framework for the rest of your dissertation. It’s important to note that your university might have specific requirements or additional components for the introduction, so make sure to review your project guidelines thoroughly.
Recent Posts
- Dealing with Academic Rejection: Coping Strategies for Overcoming Setbacks
- Time Management Strategies: Balancing Research, Writing, Teaching Responsibilities, and Personal Life
- Innovative Research Methodologies: Navigating the Future of Academic Inquiry
- Top UK Law Thesis Writing Services: A Must Read for Students
- Excelling in Nursing Thesis: Best Writing Service in UK
Your Dissertation Proposal Is Completely Secured And Never Reused For Another Client.
Work Done On Order Specifications With 0% Plagiarism And 100% Ordinally

Our Customer Support Agents Are Available Round The Clock To Answer Your Queries

Have Any Confusions Regarding Your Essay? Consult Our Experts For Better Guidance

How to Write a Compelling Thesis Introduction

The introduction to your thesis is like a first impression: you want it to be great. It is the first chapter and appears before the literature review and after the table of contents. You want the introduction to set the stage for your reader: tell them what you’re writing about, why, and what comes next. So how can you write a compelling thesis introduction?
Structure and elements of a thesis introduction
Before you write a compelling thesis introduction, you need to know what elements belong in this section and how it should be structured. A typical thesis introduction includes:
- A clear thesis statement
- An explanation of the context (brief background) for the study
- The focus and scope of the paper
- An explanation of the relevance and importance of your research
- A description of the objectives of your research and how your methodology achieves them
- A guide to the structure of the rest of the thesis (roadmap)
A thesis introduction is typically about 10% of the total length of your paper. If your introduction includes diagrams or figures, the length may be longer. It is critical to include all of the points above when writing a clear and compelling introduction. You may include additional elements if you feel they are essential in introducing your topic to the audience.
Thesis introduction: Getting started
If you do decide to write your introduction first, you can draw on the information in your thesis/dissertation proposal to help construct your draft.
How should you draft your thesis introduction, and when should you do it?
Despite the fact that your introduction comes first in the structure of your thesis, there is absolutely no need to write it first. Starting your thesis is often difficult and overwhelming, and many writers suffer from blank page syndrome —the paralysis of not knowing where to start. For this reason, some people advocate writing a kind of placeholder introduction when you begin, just to get something written down. You are free to write the introduction section at the beginning, middle, or end of the thesis drafting process . I personally find it preferable to write the introduction to a paper after I have already drafted a significant portion of the remainder of the paper. This is because I can draw on what I have written already to make sure that I cover all of the important points above.
However, if you do decide to write your introduction first, you can draw on the information in your thesis/dissertation proposal to help construct your draft. Just keep in mind that you will need to revisit your introduction after you have written the rest of your thesis to make sure it still provides an accurate roadmap and summary of the paper for your readers.
Topic and background information
When you introduce your topic, you want to draw your reader in.
Your thesis introduction should begin by informing the reader what your topic is and providing them with some relevant background information. The amount of background information you provide in this step will actually depend on what type of thesis/dissertation you are writing.
If you are writing a paper in the natural sciences or some social sciences, then it will have a separate background section after the introduction. Not a lot of background information is needed here. You can just state the larger context of the research. However, if your paper is structured such that there is no separate background chapter, then this portion of your thesis will be a bit longer and that is okay.
When you introduce your topic, you want to draw your reader in. Provide them with the reasons your research is interesting and important so that they will want to keep reading. Don’t be afraid to offer up some surprising facts or an interesting anecdote. You don’t need to be sensationalist, but your writing does not have to be dry and boring also! It is encouraged that you try to connect to your reader by offering them a relevant fact or story about your topic.
Example (topic) Weaknesses in financial regulatory systems in the United States
Example (context): Highlight some news stories about banks allowing money laundering on a massive scale, which financed gangs and led to more street drugs in major American cities. You could include a story about someone personally impacted by drugs in their neighborhood and then connect the presence of drugs to the gangs who were allowed to launder their money through big banks.
Focus and scope of your thesis
Once you have introduced your reader to the broader topic and provided some background information, you might want to explain the specific focus and scope of your thesis.
Once you have introduced your reader to the broader topic and provided some background information, you might want to explain the specific focus and scope of your thesis. What aspect of your topic will you research in particular? Why? What will your research not cover, and why? While this second part is optional, it is often helpful to be very specific about the aims of your research.
Example : Regulatory capture in the Federal Reserve and how it contributes to lax enforcement of anti-money laundering regulations.
You might write about this by explaining that your study focuses on regulatory capture in the Federal Reserve because they are one of the primary regulatory bodies monitoring the financial institutions, which were caught allowing money laundering. You could further specify that you will be focusing specifically on the role the Federal Reserve plays in monitoring banks for compliance with anti-money laundering laws; however, you will not be talking about the role they play in monitoring for compliance in other areas such as loans or mergers. This prepares your reader for what they are going to read and sets their expectations for what will come next.
Explaining the relevance and importance of your research
You must explain to the reader why your research matters, and by implication, why your reader should continue reading!
This is one of the most critical parts of your introduction. You must explain to the reader why your research matters, and by implication, why your reader should continue reading! Your research does not have to be completely revolutionary or groundbreaking to have value. You don’t need to inflate the importance of the thesis/dissertation you are writing when explaining why the research you have done is worthwhile.
Example: Corruption is an increasingly important issue in the maintenance and promotion of democratic norms and good governance. Without the ability to enforce effective penalties against institutions that turn a blind eye to money laundering, democratic governments like the United States will be threatened by the increasing power of bad actors flouting regulations. With the dollar being the global reserve currency, the US must enforce anti-money laundering legislation at home to have any hopes of shutting down global networks of corrupt operators that rely on its financial institutions. Identifying the presence of regulatory capture in the Federal Reserve sounds the alarm bell for lawmakers and regulators and suggests important interventions for policymakers are needed.
The above example clearly explains the wider impact of the issue without making overly broad statements such as “this research will revolutionize financial regulation in the United States as we know it” or “this research provides a roadmap for ending corrupt financial flows.” Just focus on what made the issue important and interesting to you and clearly state it within the broader context you provided earlier on.
Giving your reader a roadmap
At the end of your thesis introduction, you will want to provide your reader with a roadmap to the rest of the thesis.
At the end of your thesis introduction, you will want to provide your reader with a roadmap to the rest of the thesis. This differs from your table of contents in that it provides more context and details for how and why you have structured your thesis the way you have. The format of “first, next, finally” is a clear and easy way to structure this section of your introduction.
Example: First , this study reviews the existing literature on regulatory capture and how it impacts enforcement actions, with a specific focus on financial institutions and the history of the Federal Reserve. Next , it discusses the materials used for this research and how analysis was performed. Finally , it explains the results of the data analysis and investigates what the results mean and implications for future policymaking.
Now your reader knows exactly what to expect and how this fits into your overall aims and objectives. They are primed with the knowledge of your topic, its background, its relevance, and your specific focus in this study.
One common problem people have when writing an introduction to a thesis is actually writing too much . Many students and young researchers fear they won’t have enough to say and then will find themselves with a super long introduction that they somehow need to cut in half. You don’t have to give too much detail in the introduction of your thesis! Remember, the substance of your paper is located in the chapters that follow. If you are struggling with how to cut down (or add to) your introduction, you might benefit from the help of a professional editor who can see your paper with fresh eyes and quickly help you revise it. The introduction is the first part of your thesis/dissertation that people will read, so use these tips to make sure you write a great one! Check out our site for more tips on how to write a good thesis/dissertation, where to find the best thesis editing services , and more about thesis editing and proofreading services .
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Checklist: Tips for writing a compelling thesis introduction
Remember the below points when you are writing a thesis introduction:
Know your audience
Refer to your thesis/dissertation proposal or notes
Make sure you clearly state your topic, aims, and objectives
Explain why your research matters
Try to offer interesting facts or statistics that may surprise your reader and draw their interest
Draw a roadmap of what your paper will discuss
Don’t try to write too much detail about your topic
Remember to revise your introduction as you revise other sections of your thesis
What are the typical elements in an introduction section? +
The typical elements in an introduction section are as follows:
- Thesis statement
- Brief background of the study
- The focus and scope of the article
- The relevance and importance of your research
Do I have to write my introduction first? +
You can write your introduction section whenever you feel ready. Many writers save the introduction section for last to make sure they provide a clear summary and roadmap of the content of the rest of the paper.
How long should my introduction be? +
Most introductions are about 10% of the total paper, but can be longer if they include figures or diagrams.
- How it works
How to Write the Thesis Or Dissertation Introduction – Guide
Published by Carmen Troy at August 31st, 2021 , Revised On January 24, 2024
Introducing your Dissertation Topic
What would you tell someone if they asked you to introduce yourself? You’d probably start with your name, what you do for a living…etc., etc., etc. Think of your dissertation. How would you go about it if you had to introduce it to the world for the first time?
Keep this forefront in your mind for the remainder of this guide: you are introducing your research to the world that doesn’t even know it exists. Every word, phrase and line you write in your introduction will stand for the strength of your dissertation’s character.
This is not very different from how, in real life, if someone fails to introduce themselves properly (such as leaving out what they do for a living, where they live, etc.) to a stranger, it leaves a lasting impression on the stranger.
Don’t leave your dissertation a stranger among other strangers. Let’s review the little, basic concepts we already have at the back of our minds, perhaps, to piece them together in one body: an introduction.
What Goes Inside an Introduction
The exact ingredients of a dissertation or thesis introduction chapter vary depending on your chosen research topic, your university’s guidelines, and your academic subject – but they are generally mixed in one sequence or another to introduce an academic argument.
The critical elements of an excellent dissertation introduction include a definition of the selected research topic , a reference to previous studies on the subject, a statement of the value of the subject for academic and scientific communities, a clear aim/purpose of the study, a list of your objectives, a reference to viewpoints of other researchers and a justification for the research.
Topic Discussion versus Topic Introduction
Discussing and introducing a topic are two highly different aspects of dissertation introduction writing. You might find it easy to discuss a topic, but introducing it is much trickier.
The introduction is the first thing a reader reads; thus, it must be to the point, informative, engaging, and enjoyable. Even if one of these elements is missing, the reader will not be motivated to continue reading the paper and will move on to something different.
So, it’s critical to fully understand how to write the introduction of a dissertation before starting the actual write-up.
When writing a dissertation introduction, one has to explain the title, discuss the topic and present a background so that readers understand what your research is about and what results you expect to achieve at the end of the research work.
As a standard practice, you might work on your dissertation introduction chapter several times. Once when you’re working on your proposal and the second time when writing your actual dissertation.
“ Want to keep up with the progress of the work done by your writer? ResearchProspect can deliver your dissertation order in three parts; outline, first half, and final dissertation delivery. Here is the link to our online order form .
Many academics argue that the Introduction chapter should be the last section of the dissertation paper you should complete, but by no means is it the last part you would think of because this is where your research starts from.
Write the draft introduction as early as possible. You should write it at the same time as the proposal submission, although you must revise and edit it many times before it takes the final shape.
Considering its importance, many students remain unsure of how to write the introduction of a dissertation. Here are some of the essential elements of how to write the introduction of a dissertation that’ll provide much-needed dissertation introduction writing help.
Below are some guidelines for you to learn to write a flawless first-class dissertation paper.
Steps of Writing a Dissertation Introduction
1. research background – writing a dissertation introduction.
This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
Your research background should include significant concepts related to your dissertation topic. This will give your supervisor and markers an idea that you’ve investigated the research problem thoroughly and know the various aspects of your topic.
The introduction to a dissertation shouldn’t talk only about other research work in the same area, as this will be discussed in the literature review section. Moreover, this section should not include the research design and data collection method(s) .
All about research strategy should be covered in the methodology chapter . Research background only helps to build up your research in general.
For instance, if your research is based on job satisfaction measures of a specific country, the content of the introduction chapter will generally be about job satisfaction and its impact.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in academic style
- Plagiarism free
- Never resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements

2. Significance of the Research
As a researcher, you must demonstrate how your research will provide value to the scientific and academic communities. If your dissertation is based on a specific company or industry, you need to explain why that industry and company were chosen.
If you’re comparing, explain why you’re doing so and what this research will yield. Regardless of your chosen research topic, explain thoroughly in this section why this research is being conducted and what benefits it will serve.
The idea here is to convince your supervisor and readers that the concept should be researched to find a solution to a problem.
3. Research Problem
Once you’ve described the main research problem and the importance of your research, the next step would be to present your problem statement , i.e., why this research is being conducted and its purpose.
This is one of the essential aspects of writing a dissertation’s introduction. Doing so will help your readers understand what you intend to do in this research and what they should expect from this study.
Presenting the research problem competently is crucial in persuading your readers to read other parts of the dissertation paper . This research problem is the crux of your dissertation, i.e., it gives a direction as to why this research is being carried out, and what issues the study will consider.
For example, if your dissertation is based on measuring the job satisfaction of a specific organisation, your research problem should talk about the problem the company is facing and how your research will help the company to solve that.
If your dissertation is not based on any specific organisation, you can explain the common issues that companies face when they do not consider job satisfaction as a pillar of business growth and elaborate on how your research will help them realise its importance.
Citing too many references in the introduction chapter isn’t recommended because here, you must explain why you chose to study a specific area and what your research will accomplish. Any citations only set the context, and you should leave the bulk of the literature for a later section.
4. Research Question(s)
The central part of your introduction is the research question , which should be based on your research problem and the dissertation title. Combining these two aspects will help you formulate an exciting yet manageable research question.
Your research question is what your research aims to answer and around which your dissertation will revolve. The research question should be specific and concise.
It should be a one- or two-line question you’ve set out to answer through your dissertation. For the job satisfaction example, a sample research question could be, how does job satisfaction positively impact employee performance?
Look up dissertation introduction examples online or ask your friends to get an idea of how an ideal research question is formed. Or you can review our dissertation introduction example here and research question examples here .
Once you’ve formed your research question, pick out vital elements from it, based on which you will then prepare your theoretical framework and literature review. You will come back to your research question again when concluding your dissertation .
Sometimes, you might have to formulate a hypothesis in place of a research question. The hypothesis is a simple statement you prove with your results , discussion and analysis .
A sample hypothesis could be job satisfaction is positively linked to employee job performance . The results of your dissertation could be in favour of this dissertation or against it.
Tip: Read up about what alternative, null, one-tailed and two-tailed hypotheses are so you can better formulate the hypothesis for your dissertation. Following are the definitions for each term, as retrieved from Trochim et al.’s Research Methods: The Essential Knowledge Base (2016):
- Alternative hypothesis (H 1 ): “A specific statement of prediction that usually states what you expect will happen in your study.”
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): “The hypothesis that describes the possible outcomes other than the alternative hypothesis. Usually, the null hypothesis predicts there will be no effect of a program or treatment you are studying.”
- One-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that specifies a direction; for example, when your hypothesis predicts that your program will increase the outcome.”
- Two-tailed hypothesis: “A hypothesis that does not specify a direction. For example, if you hypothesise that your program or intervention will affect an outcome, but you are unwilling to specify whether that effect will be positive or negative, you are using a two-tailed hypothesis.”
Get Help with Any Part of Your Dissertation!
UK’s best academic support services. How would you know until you try?
Interesting read: 10 ways to write a practical introduction fast .
Get Help With Any Part of Your Dissertation!
Uk’s best academic support services. how would you know until you try, 5. research aims and objectives.
Next, the research aims and objectives. Aims and objectives are broad statements of desired results of your dissertation . They reflect the expectations of the topic and research and address the long-term project outcomes.
These statements should use the concepts accurately, must be focused, should be able to convey your research intentions and serve as steps that communicate how your research question will be answered.
You should formulate your aims and objectives based on your topic, research question, or hypothesis. These are simple statements and are an extension of your research question.
Through the aims and objectives, you communicate to your readers what aspects of research you’ve considered and how you intend to answer your research question.
Usually, these statements initiate with words like ‘to explore’, ‘to study’, ‘to assess’, ‘to critically assess’, ‘to understand’, ‘to evaluate’ etc.
You could ask your supervisor to provide some thesis introduction examples to help you understand better how aims and objectives are formulated. More examples are here .
Your aims and objectives should be interrelated and connect to your research question and problem. If they do not, they’ll be considered vague and too broad in scope.
Always ensure your research aims and objectives are concise, brief, and relevant.
Once you conclude your dissertation , you will have to revert back to address whether your research aims and objectives have been met.
You will have to reflect on how your dissertation’s findings , analysis, and discussion related to your aims and objectives and how your research has helped in achieving them.
6. Research Limitations
This section is sometimes a part of the dissertation methodology section ; however, it is usually included in the introduction of a dissertation.
Every research has some limitations. Thus, it is normal for you to experience certain limitations when conducting your study.
You could experience research design limitations, data limitations or even financial limitations. Regardless of which type of limitation you may experience, your dissertation would be impacted. Thus, it would be best if you mentioned them without any hesitation.
When including this section in the introduction, make sure that you clearly state the type of constraint you experienced. This will help your supervisor understand what problems you went through while working on your dissertation.
However, one aspect that you should take care of is that your results, in no way, should be influenced by these restrictions. The results should not be compromised, or your dissertation will not be deemed authentic and reliable.
After you’ve mentioned your research limitations, discuss how you overcame them to produce a perfect dissertation .
Also, mention that your limitations do not adversely impact your results and that you’ve produced research with accurate results the academic community can rely on.
Also read: How to Write Dissertation Methodology .
7. Outline of the Dissertation
Even though this isn’t a mandatory sub-section of the introduction chapter, good introductory chapters in dissertations outline what’s to follow in the preceding chapters.
It is also usual to set out an outline of the rest of the dissertation . Depending on your university and academic subject, you might also be asked to include it in your research proposal .
Because your tutor might want to glance over it to see how you plan your dissertation and what sections you’d include; based on what sections you include and how you intend to research and cover them, they’d provide feedback for you to improve.
Usually, this section discusses what sections you plan to include and what concepts and aspects each section entails. A standard dissertation consists of five sections : chapters, introduction, literature review , methodology , results and discussion , and conclusion .
Some dissertation assignments do not use the same chapter for results and discussion. Instead, they split it into two different chapters, making six chapters. Check with your supervisor regarding which format you should follow.
When discussing the outline of your dissertation , remember that you’d have to mention what each section involves. Discuss all the significant aspects of each section to give a brief overview of what your dissertation contains, and this is precisely what our dissertation outline service provides.
Writing a dissertation introduction might seem complicated, but it is not if you understand what is expected of you. To understand the required elements and make sure that you focus on all of them.
Include all the aspects to ensure your supervisor and other readers can easily understand how you intend to undertake your research.
“If you find yourself stuck at any stage of your dissertation introduction, get introduction writing help from our writers! At ResearchProspect, we offer a dissertation writing service , and our qualified team of writers will also assist you in conducting in-depth research for your dissertation.
Dissertation Introduction Samples & Examples
Check out some basic samples of dissertation introduction chapters to get started.
FAQs about Dissertation Introduction
What is the purpose of an introduction chapter.
It’s used to introduce key constructs, ideas, models and/or theories etc. relating to the topic; things that you will be basing the remainder of your dissertation on.
How do you start an introduction in a dissertation?
There is more than one way of starting a dissertation’s introductory chapter. You can begin by stating a problem in your area of interest, review relevant literature, identify the gap, and introduce your topic. Or, you can go the opposite way, too. It’s all entirely up to your discretion. However, be consistent in the format you choose to write in.

How long can an introduction get?
It can range from 1000 to 2000 words for a master’s dissertation , but for a higher-level dissertation, it mostly ranges from 8,000 to 10,000 words ’ introduction chapter. In the end, though, it depends on the guidelines provided to you by your department.
Steps to Writing a Dissertation Introduction
You may also like.
Not sure how to write dissertation title page? All dissertations must have a dissertation title page where necessary information should be clearly presented
Not sure how to start your dissertation and get it right the first time? Here are some tips and guidelines for you to kick start your dissertation project.
Dissertation conclusion is perhaps the most underrated part of a dissertation or thesis paper. Learn how to write a dissertation conclusion.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
We use cookies on this site to enhance your experience
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.
A link to reset your password has been sent to your email.
Back to login
We need additional information from you. Please complete your profile first before placing your order.
Thank you. payment completed., you will receive an email from us to confirm your registration, please click the link in the email to activate your account., there was error during payment, orcid profile found in public registry, download history, phd writing 3: how to write the introduction chapter of a thesis.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 11 November, 2021
If you find it tricky to write the introduction chapter of a PhD thesis, rest assured that you’re not alone. The introduction can be one of the hardest sections to write for any piece of research writing. However, the introduction is also one of the most important sections as it lays the groundwork for the following chapters and offers a first impression of the rest of the research that you are about to share. This article discusses some of the key things to consider as you write your introduction.
Write your introduction last
It is very common practice for most researchers to write the introduction chapter last. You might be wondering why that is, since it is the first chapter of the thesis. However, think of it in this way: you cannot introduce something until you know exactly what you are introducing .
You will have a complete overview and understanding of the entire project only when you have largely completed it and written all the other constituent parts. By writing the introduction at the end of your project, you’ll be able to look back over your initial research questions , the way you conducted the research, the results you generated and the conclusions you formed. You will then be in a better position to present and introduce the research as a whole, coherent piece of work.
Provide an overview
The introduction should offer the reader an overview of the research that you have conducted. You are setting the scene for your reader and giving them a broad idea of what they can expect throughout the rest of the thesis. As such, you don’t need to go into too much depth at this stage – the details can come later in the following chapters. In particular, you need to talk about what you are studying and why.
What are you studying?
The introduction is the best place to outline your working hypothesis and/or research questions . After all, this is what the rest of your thesis will entail.
Make it very clear for your reader exactly what you are setting out to investigate.
What are you trying to find out? What are you testing? What answers or results are you hoping to obtain by doing this study?
You might find it easier and clearer to outline your research questions as distinct bullet points . Then, you can follow this list with a more detailed discussion of each of the questions or hypotheses – for example, why you are asking each question, what you hope to find out from each question and what methods you will use to answer those questions.
Why are you doing this research?
Apart from giving your reader an idea of what your thesis is about, it is important to explain in the introduction why you are doing this research. Start by highlighting exactly what issue(s) you are addressing in this research, then outline why this research is important and why there is a need for this study to be conducted.
Although you shouldn’t give everything away and reveal all your findings and conclusions at the beginning of the thesis, you can begin to hint at the potential impact and implications that such a study could create, either for your specific field, or for society more generally. This will again emphasise the significance and relevance of this research.
Offer some background
In order to effectively set the scene, you can also begin to introduce some of the most prominent work that has already been done on the subject. This chapter is a good place to contextualise your research within the broader, existing body of work. Again, you don’t need to go into great detail – that will be covered in the literature review – but it can be helpful to briefly mention some of the existing relevant work that has informed and motivated your unique study.
For example, perhaps your research responds directly to a recent scientific discovery. You can use the introduction to refer to this previous study and explain how you are addressing the limitations and problems of that study or exploring the effects of using an alternative method.
How are you conducting this research?
When you’ve introduced the reasons informing your study and explained what you will be investigating, you will then want to offer a brief explanation of how you have designed and conducted this research. Again, as you are only giving an overview at this stage, you don’t need to go into too much detail – further explanations will come later in your methods /methodology chapter.
Remember that you want to offer your reader a broad idea of what the overall research project entails. Naturally, this includes some discussion of the main approaches and directions you took in your research to adequately answer the questions that you set out to investigate.
Offer a clear chapter outline
It is a good idea to include a section within your introduction that clearly outlines what each of the proceeding chapters will include. As you write these chapter outlines, think of them as small summaries, or mini abstracts, of each chapter .
Your reader will then have a much firmer and focused idea of what is to come next, and how each chapter will connect with and links to each other. Think of the chapter outline as something like a recipe or a roadmap laying out the steps that the reader will follow.
In conclusion
Although it can feel a bit overwhelming to have to summarise all your research into a single introductory chapter, it might help to place yourself in the position of your ideal reader or examiner .
What would you like them to know as they start reading your thesis? What important pieces of information would they need here in order to fully appreciate and understand the rest of your paper?
Think about what you would like to see and what details you appreciate when you read introductory chapters, and try to recreate that same clarity for your reader.
Read next (final) in series: PhD Writing 4: How to write the conclusion chapter of your thesis
Read previous in series: PhD Writing 2: How to improve your writing skills in preparation for writing your thesis
Charlesworth Author Services , a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Visit our new Researcher Education Portal that offers articles and webinars covering all aspects of your research to publication journey! And sign up for our newsletter on the Portal to stay updated on all essential researcher knowledge and information!
Register now: Researcher Education Portal
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Share with your colleagues
Related articles.

Tips for designing your Research Question
Charlesworth Author Services 01/08/2017 00:00:00

The best way to write the Study Background
Charlesworth Author Services 25/10/2021 00:00:00

PhD Writing 1: Things you should do in preparation for writing your thesis
Charlesworth Author Services 28/10/2021 00:00:00
Related webinars

Bitesize Webinar: Effective paper writing for early career researchers: Module 1: Writing an effective PhD thesis
Charlesworth Author Services 02/03/2021 00:00:00

Bitesize webinar: Effective paper writing for early career researchers: Module 2: Writing an effective masters' dissertation

Bitesize webinar: Effective paper writing for early career researchers: Module 3: The right mindset for academic paper writing

Bitesize Webinar: Effective paper writing for early career researchers: Module 4: How to sell yourself as a researcher

How to start writing from Day One of your PhD
Charlesworth Author Services 15/01/2020 00:00:00

A simple guide to begin Publishing during Your PhD
Charlesworth Author Services 03/01/2020 00:00:00

How can I reach the level of academic writing needed for a PhD?
Charlesworth Author Services 22/04/2021 00:00:00
Thesis Writing
Writing A Thesis Introduction
Thesis Introduction: A Step-by-Step Guide With Examples
11 min read

People also read
Thesis Writing - An Ultimate Writing Guide With Tips & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Proposal - Sample Proposals and Tips!
Interesting Thesis Topics & Ideas To Get Started
Thesis Format Essentials: Structure, Tips, and Templates
You're staring at a blinking cursor, trying to figure out where to start your introduction for your thesis writing.
It's hard to know where to start, and even harder to keep your introduction engaging and on-topic.
We've written this guide that will take you step-by-step through the process of writing an amazing introduction. You'll also find examples of introductions for different types of papers.
So let's get started!
- 1. What is a Thesis Introduction?
- 2. Components of Thesis Introduction
- 3. Thesis Introduction Outline
- 4. How to Start a Thesis Introduction?
- 5. How to Write a Thesis Introduction?
- 6. Thesis Introduction Examples
- 7. Thesis Introduction Writing Tips
- 8. Introduction Writing Checklist
What is a Thesis Introduction?
A thesis introduction is the opening section of a research paper or thesis writing that serves as a roadmap for the entire study.
It provides context and background information for the research topic. The introduction outlines the study's purpose, problem statement, and methodology.
It engages readers, captures their interest, and sets expectations for the rest of the paper.
Importance of Writing a Good Thesis Introduction
Let’s see why a good introduction is important in thesis writing:
- First Impressions: The introduction is your first opportunity to make a positive impression on readers. It's crucial in piquing their interest.
- Contextual Understanding: It offers the necessary background information, ensuring that readers comprehend the research's significance and relevance.
- Problem Statement: The introduction presents the research problem, outlining what the study aims to address, and emphasizing its importance.
- Clarity: A well-structured introduction enhances the clarity of your work, making it easier for readers to follow your thesis.
- Guidance: It serves as a guide for the reader, providing a clear path of what to expect throughout the research, including the methodology and expected outcomes.
How Long is a Thesis Introduction?
The introduction of your thesis paper makes up roughly 10% of your total word count. Therefore, a PhD thesis paper introduction would be 8000 - 10000 words. However, a Master's thesis would be 1500 - 2000 words long.
Although the thesis introduction length can be increased if the writer includes images, diagrams, and descriptions.
Components of Thesis Introduction
The thesis introduction format comprises several essential components that collectively set the stage for your research. These components include:
- Hook or Attention-Grabber
- Background Information
- Problem Statement
- Purpose of the Study
- Significance of the Research
- Overview of the Methodology
Thesis Introduction Outline
A thesis introduction chapter structure contains the following sections:
Thesis Introduction Outline Sample

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How to Start a Thesis Introduction?
Starting a thesis introduction can be overwhelming, but there are some steps you can follow to make it easier:
- Choose a Topic Select a topic that you are passionate about and that aligns with your research interests. Your topic should also be relevant to your field of study and have enough existing research to support your thesis. You can also choose unique ideas from our compiled list of thesis topics .
- Research the Content Conduct thorough research on your topic by reviewing the literature, collecting data, and analyzing existing research in your field. This will help you identify gaps in the literature that your thesis will address.
- Organize the Ideas Organize and compile the main arguments, ideas, and claims in the next step. These thoughts will be helpful to describe and present the thesis statement . Logically organizing your thoughts is crucial for developing an effective and coherent paper. You can create a clear story from the start of your paper to the end. Also, include a table of contents at the beginning of your thesis. It serves as a mind map to discuss the layout of your research proposal .
- Define the Subject and Relevant Themes Define the subject and the relevant themes before starting your thesis introduction. The subject of a thesis is the central topic or idea that it addresses. It should be specific enough to be covered by the scope of the thesis, yet broad enough to allow for meaningful discussion. Relevant themes are those ideas that are most applicable to the subject of the thesis. These themes often come from other fields and add depth to the argument being made in the thesis. This way it would be easier for the reader to skim and get a good idea by going through it.
- Define Your Thesis Statement Once you have conducted your research, define your thesis statement. Your thesis statement should clearly articulate the main argument or point you will be making in your thesis.
Check out this video to learn more about writing a good introduction for your thesis!
How to Write a Thesis Introduction?
Once you are done with the prewriting steps discussed above, you are now ready to dive into actual writing. Here is a step-by-step guide for you to follow while writing a thesis introduction.

A detailed description of the steps to write an introduction is given below.
Step 1: Hook the Reader’s Interest
A writer should begin writing the introduction with a hook statement to draw the reader’s interest. It can be a question, quotation, or interesting transitions into your arguments. Also, make a list of interesting, current events or controversies related to your topic. It will help in creating a strong introduction and thesis statement.
Step 2: Mention the Research Gap
Review and evaluate the existing literature critically. It will help the researcher in finding and addressing the research gap.
Step 3: State the Background Information
A good introduction to the thesis always states the historical background of the chosen topic. It is usually cited in the first paragraph and shows the current position of the subject.
Step 4: Back Your Topic with Relevant Literature
The introduction is a mix of previous research and a literature review. Thus, the topic should be backed with relevant resources. It is also used to explain the context and significance of previous studies. Moreover, it further acknowledges credible sources of information to solidify your claim.
When choosing relevant literature, there are a few things to consider.
- Firstly, the literature should be from reputable sources such as scholarly journals or books.
- Secondly, it should be related to your topic and provide evidence for your claims.
- Lastly, it should be up-to-date and accurate.
By taking these factors into account, you can ensure that your work is well-informed and credible.
Step 5: Mention the Hypothesis
Formulate a hypothesis for your research work. It will discuss what you aim to achieve along with the possibilities.
A valid hypothesis must be testable, measurable, and based on evidence from existing literature or theoretical frameworks.
The hypothesis should also provide a logical explanation for the relationship between the variables in question.
Step 6: Provide Significance of Your Research
The gap will help to evaluate the situation and explain the significance of the current research. Thus, add the purpose of your paper explaining why the research is done. It will also demonstrate the possible contributions of the research work in the future.
Step 7: Outline the Research Questions
The next step is to outline your research questions. These should be relevant to the purpose of your study. Moreover, it will also help you discuss the problems that you seek to address.
Step 8: State Research Objectives
State the research aims and objectives to define the primary purpose of the work. It should give a direction to the research by providing an overview of what it aims to achieve.
Step 9: Discuss the Research Methodology
The next step is to define the terms and methodology you are going to apply in your research. It is a good technique to make your study authentic, credible, and useful.
Step 10: Finalize your Introduction
Ask yourself the following questions after finishing writing the introduction.
- Does your introduction discuss the problem your thesis is addressing?
- Does this section address the contribution the research work is making?
- Does it provide a detailed overview of your thesis?
- Does it end by briefly discussing the content of each chapter?
- Does it make a case for the research?
- Does it outline research questions, problems, and hypotheses clearly?
Thesis Introduction Examples
Below are sample thesis introductions to help you compose perfect introductions.
Ph.D. thesis introduction
Master thesis introduction example
Bachelor thesis introduction example
Thesis introduction sample for criminology
Thesis Introduction Writing Tips
The following are some writing tips to help you draft perfect thesis introductions.
- Highlight the importance of your research early on to engage the reader's interest.
- Introduce the key aspects of the topic to provide context and understanding.
- Craft a dissertation introduction that clearly sets the stage for your research.
- Offer a concise overview of the structure to help the reader navigate your thesis effectively.
- It must follow a coherent thesis format by providing concise information.
- Do not use technical language as it will leave the reader confused.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Introduction Writing Checklist
Use the below checklist to assess your introduction and identify what information is missing. This should help you ensure that your intro has all of the necessary components for a successful outcome.
In conclusion, crafting a strong thesis introduction is a crucial element of any academic paper. It sets the tone for your entire essay and provides a roadmap for your reader to follow. By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you can create a well-structured introduction for your thesis.
However, if you are still struggling to write a compelling thesis introduction, don't worry. MyPerfectWords.com is here to help. With qualified writing experts, we provide the best thesis writing service at student-friendly costs.
So, contact us today to discuss your thesis paper, and let us help you achieve your academic goals. By placing a write an essay for me request, you'll get a perfectly crafted thesis!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

- Directories
Chapter introductions
Your overall thesis objectives or questions can be distinguished from specific objectives of each chapter, however, it should be broad enough to embody the latter. So whenever you have difficulty deciding what information to include in the thesis introduction and what to include in the introductory sections of individual chapters, remember it's primarily a matter of scale (see the table below).
Introductions
- ANU Library Academic Skills
- +61 2 6125 2972
How to write an introduction chapter
This blog post looks at how to write an introduction chapter for an academic research report such as an undergraduate final year project, an MSc dissertation or a PhD thesis.
Steven Firth
What is the point of an introduction chapter? Why is it needed? For me, the job of the introduction chapter is to set up the Research Questions for the report. Research Questions are powerful tools and, once fully formed, create a foundation for writing the rest of the report.
Research Questions are typically a list of three questions that the report is studying. This is important as this is a research report, and the key task is to demonstrate the research which is taking place.
All other questions about the content of the report then simply refer back to the research questions. What should be in the Background section of the Introduction chapter? Well, anything that the reader needs to know in order to understand the Research Questions. What should be discussed in the Literature Review? Further background, explanation and previous research on anything covered by the Research Questions. How should the Results chapter be structured? How about three subsections, one for each of the Research Questions.
The basic structure of most Introduction chapters looks like this:
Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1. Background (2 to 3 pages) 1.2. Research Problem (1 page) 1.3. Research Questions (3 questions, each question is a paragraph of text) 1.4. Aims and Objectives (one aim, 5-6 objectives, each objective is a paragraph of text) 1.5. Outputs of this Research (0.5 to 1 page) 1.6. Structure of this Report (1 page)
Tips for clarity
Always put yourself in the mind of a person who is reading your report for the first time. Help them to quickly work out what is going on and how the different things fit together.
For example:
- Use numbered lists for Research Questions and Objectives etc.
- Introduce Research Questions and Objectives with a simple sentence such as ‘The three research questions studied in this work are: …’
- Give a sentence to explain every new term when it is first used in the text.
- Make sure the first sentence of each section explains what is going on in this section.
- Try to make it so the first sentences of each paragraph could be read by themselves and the reader could still follow the outline of the story.
Tips for depth
Creating depth in writing uses skills such as critical thinking and reflection.
Here are some tips:
When writing a Research Question or Objective, do two things. First state the Research Question or Objective itself in a single sentence (perhaps in bold text). Second write a paragraph directly below the Research Question or Objective which answers questions such as:
- why is this Research Question or Objective important?
- what do the various terms mean?
- what are some examples of how this might be done?
In the Background and Research Problem sections, try starting sentences with the following:
- “The challenges in this field of study are…”
- “The limitation of the previous work are…”
- “One explanation for this is…”
- “It is clear that…”
- “The strengths of such an approach are…”
- “This is important because…”
Simple mistakes to avoid
Here are some simple mistakes which should be avoided:
- The Background section contains text which has nothing to do with the research questions. Always ask yourself if the content you are writing is relevant to the Research Questions. If not, then take it out.
- The Title contains terms which aren’t explained in the background section. If the Title contains a term such as ‘Thermal Comfort’ or ‘Overheating’ then it’s important to give a definition of these terms.
- The Research Questions are stated as a single sentence with no further explanation. Instead provide a paragraph for explanation for each Research Question.
- Several ‘aims’ are introduced throughout the chapter - make sure only one Aim is given.
- The Aim introduces new terms or concepts which haven’t been previously introduced in the Title or the Research Questions. Instead make sure the Aim is simply rephrasing the information already provided.
The Introduction chapter is one of the most important chapters in a report as it sets the scene and the tone for the reader. Keep it well structured, easy to follow and full of explanations, and try to provide the reader with the answer to the questions “what’s going on here?” and “why is this important?”.
Sign up for more like this.
- About LiveInnovation.org
- Prof. Dr. Francisco Tigre Moura
- Academic Research
- Live AM: Artist Monitor
- Live FM: Fan Monitor
- Books and e-Books
- Media/Events
- Consumer Behavior
- Marketing Research
- Statistics Support
- Thesis Writing

- Research Support
How to Write an INTRODUCTION Chapter (of a Thesis)
So it seems like you’ve read my previous article on how to develop a fantastic marketing or management thesis idea , right?
That is great. But perhaps now you have a clear idea of what to do for your research project but you don’t know exactly how to start your bachelor or masters thesis?
No worries! We’ve got your back. Here are some (hopefully) useful tips to do a great job and impress your supervisor and reviewers!
First of all: There is NO specific correct way to structure the Introduction chapter. But I suggest you cover the following structure:
***********************************************************
- Introduction
1.1 Personal Motivation
1.2 Research Aims and Objectives
1.2.1 Aim
1.2.2 Objectives
1.3 Structure of the Thesis
Let’s discuss each topic in detail so that you don’t miss anything and can look impressively smart!
Imagine that your grandma is going to read your thesis and it is entitled “Applying Machine to Machine Interaction to Improve Sustainability Practices in Music Festivals”.
Would she know what “Machine to Machine Interaction” is? (Maybe she does and even more than us two put together!). But let’s assume she has no clue!
Would she know which sustainability practices are applied in music festivals? (Well, maybe she went to Woodstock in 1969, had an affair with Jimmy Hendrix and helped them reduce water consumption!). But let’s assume she has no clue of what it is!
This is exactly the point of an introduction! The reader (whoever he/she may be!) has to be able to read your introduction and have an OVERALL idea and be FAMILIARIZED with the CONTEXT of your study.
And how do you achieve it? SIMPLE. Do the following:
- What is it? When did it start?
- Which are they? What are examples of practices applied to music festivals?
- What is the trend within the industry sector/product type/service type you are discussing? In the last decade, has it increased? Decreased? How large is the global/regional market size? What are sales volumes of key players?
- Use RELIABLE sources for your data: renowned institutions and organizations, research groups, scientific publications.
- Make sure to REFERENCE all your data.
Video Support: Introduction Chapter
In case you are enjoying the article, do not forget to watch the video with further support on how to write the introduction chapter of your thesis.
Here is the section of the thesis where you describe your motivation for conducting a study on this topic.
In other words: Explain why you are writing about “Applying Machine to Machine Interaction to Improve Sustainability Practices in Music Festivals” and not about any other random topic such as: “If there is life on other planets, aliens would also be fans of The Beatles”.
To explain your motivation and why you chose this topic you should ideally be very personal and even write this section in the first person ( other academics might disagree with me on this, but it’s ok ).
And keep this section SHORT. Two GOOD paragraphs should be enough.
Here it is VERY SIMPLE. You have read the recommendations on LiveInnovation.org on “ How to Develop a Research Project (or Thesis) Idea ”, right? NO? (Oh man, it’s not easy being your supervisor. Honestly!). So go check the site for it!
If you have, (Good on you, I’m proud!), then simply describe your aim in a sub-section 1.2.1 and 1.2.2 your objectives.
The objectives in 1.2.2 can even be stated in bullet points.
And here it is absolutely easy!
Even if you have a headache, you team has lost, you ran out of Oreo Ice cream Sandwich in the fridge and your 6 year old neighbor is learning to play the violin, you can still write this section.
It will only take you one or two paragraphs to describe in GENERAL terms what will be discussed in the following chapters.
ONE SUGGESTION: Leave this for last and only write it once you have finished the entire thesis.
So basically you should have done the following in this chapter:
- First you have familiarized your reader with the context of your study, regardless of who is reading (Your former hippie grandma or Michael Jordan).
- You have familiarized the reader with YOU, by explaining WHY you are writing about this topic.
- You have explained what the thesis will be about.
- Finally you have anticipated the reader with what he/she/it will face on the coming chapters until the end of the thesis.
So now you are DONE with Chapter one and can focus on the rest of the thesis!
(In case you want to thank me later: I truly enjoy beer, Port wine and Whiskey).
Download the Recommendations
Did you like this article? Would like to have these recommendations with you while studying?
GREAT! Simply download the file here with all details: LiveInnovation.org - Introduction Chapter of a Thesis.pdf
In case you would like to have more research suggestions, check our research resources section .

RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

SOUNDS LIKE A THESIS is now available on Spotify!

Download Our e-Book: “Sounds Like A Thesis”

SPSS Tutorial Series on YouTube: Learn Quickly and Easily
Privacy overview.
This is an necessary category.
This is an non-necessary category.
How To Write The Methodology Chapter
The what, why & how explained simply (with examples).
By: Jenna Crossley (PhD) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | September 2021 (Updated April 2023)
So, you’ve pinned down your research topic and undertaken a review of the literature – now it’s time to write up the methodology section of your dissertation, thesis or research paper . But what exactly is the methodology chapter all about – and how do you go about writing one? In this post, we’ll unpack the topic, step by step .
Overview: The Methodology Chapter
- The purpose of the methodology chapter
- Why you need to craft this chapter (really) well
- How to write and structure the chapter
- Methodology chapter example
- Essential takeaways
What (exactly) is the methodology chapter?
The methodology chapter is where you outline the philosophical underpinnings of your research and outline the specific methodological choices you’ve made. The point of the methodology chapter is to tell the reader exactly how you designed your study and, just as importantly, why you did it this way.
Importantly, this chapter should comprehensively describe and justify all the methodological choices you made in your study. For example, the approach you took to your research (i.e., qualitative, quantitative or mixed), who you collected data from (i.e., your sampling strategy), how you collected your data and, of course, how you analysed it. If that sounds a little intimidating, don’t worry – we’ll explain all these methodological choices in this post .

Why is the methodology chapter important?
The methodology chapter plays two important roles in your dissertation or thesis:
Firstly, it demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks. A flawed research design or methodology would mean flawed results. So, this chapter is vital as it allows you to show the marker that you know what you’re doing and that your results are credible .
Secondly, the methodology chapter is what helps to make your study replicable. In other words, it allows other researchers to undertake your study using the same methodological approach, and compare their findings to yours. This is very important within academic research, as each study builds on previous studies.
The methodology chapter is also important in that it allows you to identify and discuss any methodological issues or problems you encountered (i.e., research limitations ), and to explain how you mitigated the impacts of these. Every research project has its limitations , so it’s important to acknowledge these openly and highlight your study’s value despite its limitations . Doing so demonstrates your understanding of research design, which will earn you marks. We’ll discuss limitations in a bit more detail later in this post, so stay tuned!
Need a helping hand?
How to write up the methodology chapter
First off, it’s worth noting that the exact structure and contents of the methodology chapter will vary depending on the field of research (e.g., humanities, chemistry or engineering) as well as the university . So, be sure to always check the guidelines provided by your institution for clarity and, if possible, review past dissertations from your university. Here we’re going to discuss a generic structure for a methodology chapter typically found in the sciences.
Before you start writing, it’s always a good idea to draw up a rough outline to guide your writing. Don’t just start writing without knowing what you’ll discuss where. If you do, you’ll likely end up with a disjointed, ill-flowing narrative . You’ll then waste a lot of time rewriting in an attempt to try to stitch all the pieces together. Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind .
Section 1 – Introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims . As we’ve discussed many times on the blog, your methodology needs to align with your research aims, objectives and research questions. Therefore, it’s useful to frontload this component to remind the reader (and yourself!) what you’re trying to achieve.
In this section, you can also briefly mention how you’ll structure the chapter. This will help orient the reader and provide a bit of a roadmap so that they know what to expect. You don’t need a lot of detail here – just a brief outline will do.
Section 2 – The Methodology
The next section of your chapter is where you’ll present the actual methodology. In this section, you need to detail and justify the key methodological choices you’ve made in a logical, intuitive fashion. Importantly, this is the heart of your methodology chapter, so you need to get specific – don’t hold back on the details here. This is not one of those “less is more” situations.
Let’s take a look at the most common components you’ll likely need to cover.
Methodological Choice #1 – Research Philosophy
Research philosophy refers to the underlying beliefs (i.e., the worldview) regarding how data about a phenomenon should be gathered , analysed and used . The research philosophy will serve as the core of your study and underpin all of the other research design choices, so it’s critically important that you understand which philosophy you’ll adopt and why you made that choice. If you’re not clear on this, take the time to get clarity before you make any further methodological choices.
While several research philosophies exist, two commonly adopted ones are positivism and interpretivism . These two sit roughly on opposite sides of the research philosophy spectrum.
Positivism states that the researcher can observe reality objectively and that there is only one reality, which exists independently of the observer. As a consequence, it is quite commonly the underlying research philosophy in quantitative studies and is oftentimes the assumed philosophy in the physical sciences.
Contrasted with this, interpretivism , which is often the underlying research philosophy in qualitative studies, assumes that the researcher performs a role in observing the world around them and that reality is unique to each observer . In other words, reality is observed subjectively .
These are just two philosophies (there are many more), but they demonstrate significantly different approaches to research and have a significant impact on all the methodological choices. Therefore, it’s vital that you clearly outline and justify your research philosophy at the beginning of your methodology chapter, as it sets the scene for everything that follows.

Methodological Choice #2 – Research Type
The next thing you would typically discuss in your methodology section is the research type. The starting point for this is to indicate whether the research you conducted is inductive or deductive .
Inductive research takes a bottom-up approach , where the researcher begins with specific observations or data and then draws general conclusions or theories from those observations. Therefore these studies tend to be exploratory in terms of approach.
Conversely , d eductive research takes a top-down approach , where the researcher starts with a theory or hypothesis and then tests it using specific observations or data. Therefore these studies tend to be confirmatory in approach.
Related to this, you’ll need to indicate whether your study adopts a qualitative, quantitative or mixed approach. As we’ve mentioned, there’s a strong link between this choice and your research philosophy, so make sure that your choices are tightly aligned . When you write this section up, remember to clearly justify your choices, as they form the foundation of your study.
Methodological Choice #3 – Research Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your research strategy (also referred to as a research design ). This methodological choice refers to the broader strategy in terms of how you’ll conduct your research, based on the aims of your study.
Several research strategies exist, including experimental , case studies , ethnography , grounded theory, action research , and phenomenology . Let’s take a look at two of these, experimental and ethnographic, to see how they contrast.
Experimental research makes use of the scientific method , where one group is the control group (in which no variables are manipulated ) and another is the experimental group (in which a specific variable is manipulated). This type of research is undertaken under strict conditions in a controlled, artificial environment (e.g., a laboratory). By having firm control over the environment, experimental research typically allows the researcher to establish causation between variables. Therefore, it can be a good choice if you have research aims that involve identifying causal relationships.
Ethnographic research , on the other hand, involves observing and capturing the experiences and perceptions of participants in their natural environment (for example, at home or in the office). In other words, in an uncontrolled environment. Naturally, this means that this research strategy would be far less suitable if your research aims involve identifying causation, but it would be very valuable if you’re looking to explore and examine a group culture, for example.
As you can see, the right research strategy will depend largely on your research aims and research questions – in other words, what you’re trying to figure out. Therefore, as with every other methodological choice, it’s essential to justify why you chose the research strategy you did.
Methodological Choice #4 – Time Horizon
The next thing you’ll need to detail in your methodology chapter is the time horizon. There are two options here: cross-sectional and longitudinal . In other words, whether the data for your study were all collected at one point in time (cross-sectional) or at multiple points in time (longitudinal).
The choice you make here depends again on your research aims, objectives and research questions. If, for example, you aim to assess how a specific group of people’s perspectives regarding a topic change over time , you’d likely adopt a longitudinal time horizon.
Another important factor to consider is simply whether you have the time necessary to adopt a longitudinal approach (which could involve collecting data over multiple months or even years). Oftentimes, the time pressures of your degree program will force your hand into adopting a cross-sectional time horizon, so keep this in mind.
Methodological Choice #5 – Sampling Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your sampling strategy . There are two main categories of sampling, probability and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling involves a random (and therefore representative) selection of participants from a population, whereas non-probability sampling entails selecting participants in a non-random (and therefore non-representative) manner. For example, selecting participants based on ease of access (this is called a convenience sample).
The right sampling approach depends largely on what you’re trying to achieve in your study. Specifically, whether you trying to develop findings that are generalisable to a population or not. Practicalities and resource constraints also play a large role here, as it can oftentimes be challenging to gain access to a truly random sample. In the video below, we explore some of the most common sampling strategies.
Methodological Choice #6 – Data Collection Method
Next up, you’ll need to explain how you’ll go about collecting the necessary data for your study. Your data collection method (or methods) will depend on the type of data that you plan to collect – in other words, qualitative or quantitative data.
Typically, quantitative research relies on surveys , data generated by lab equipment, analytics software or existing datasets. Qualitative research, on the other hand, often makes use of collection methods such as interviews , focus groups , participant observations, and ethnography.
So, as you can see, there is a tight link between this section and the design choices you outlined in earlier sections. Strong alignment between these sections, as well as your research aims and questions is therefore very important.
Methodological Choice #7 – Data Analysis Methods/Techniques
The final major methodological choice that you need to address is that of analysis techniques . In other words, how you’ll go about analysing your date once you’ve collected it. Here it’s important to be very specific about your analysis methods and/or techniques – don’t leave any room for interpretation. Also, as with all choices in this chapter, you need to justify each choice you make.
What exactly you discuss here will depend largely on the type of study you’re conducting (i.e., qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods). For qualitative studies, common analysis methods include content analysis , thematic analysis and discourse analysis . In the video below, we explain each of these in plain language.
For quantitative studies, you’ll almost always make use of descriptive statistics , and in many cases, you’ll also use inferential statistical techniques (e.g., correlation and regression analysis). In the video below, we unpack some of the core concepts involved in descriptive and inferential statistics.
In this section of your methodology chapter, it’s also important to discuss how you prepared your data for analysis, and what software you used (if any). For example, quantitative data will often require some initial preparation such as removing duplicates or incomplete responses . Similarly, qualitative data will often require transcription and perhaps even translation. As always, remember to state both what you did and why you did it.
Section 3 – The Methodological Limitations
With the key methodological choices outlined and justified, the next step is to discuss the limitations of your design. No research methodology is perfect – there will always be trade-offs between the “ideal” methodology and what’s practical and viable, given your constraints. Therefore, this section of your methodology chapter is where you’ll discuss the trade-offs you had to make, and why these were justified given the context.
Methodological limitations can vary greatly from study to study, ranging from common issues such as time and budget constraints to issues of sample or selection bias . For example, you may find that you didn’t manage to draw in enough respondents to achieve the desired sample size (and therefore, statistically significant results), or your sample may be skewed heavily towards a certain demographic, thereby negatively impacting representativeness .
In this section, it’s important to be critical of the shortcomings of your study. There’s no use trying to hide them (your marker will be aware of them regardless). By being critical, you’ll demonstrate to your marker that you have a strong understanding of research theory, so don’t be shy here. At the same time, don’t beat your study to death . State the limitations, why these were justified, how you mitigated their impacts to the best degree possible, and how your study still provides value despite these limitations .
Section 4 – Concluding Summary
Finally, it’s time to wrap up the methodology chapter with a brief concluding summary. In this section, you’ll want to concisely summarise what you’ve presented in the chapter. Here, it can be a good idea to use a figure to summarise the key decisions, especially if your university recommends using a specific model (for example, Saunders’ Research Onion ).
Importantly, this section needs to be brief – a paragraph or two maximum (it’s a summary, after all). Also, make sure that when you write up your concluding summary, you include only what you’ve already discussed in your chapter; don’t add any new information.

Methodology Chapter Example
In the video below, we walk you through an example of a high-quality research methodology chapter from a dissertation. We also unpack our free methodology chapter template so that you can see how best to structure your chapter.
Wrapping Up
And there you have it – the methodology chapter in a nutshell. As we’ve mentioned, the exact contents and structure of this chapter can vary between universities , so be sure to check in with your institution before you start writing. If possible, try to find dissertations or theses from former students of your specific degree program – this will give you a strong indication of the expectations and norms when it comes to the methodology chapter (and all the other chapters!).
Also, remember the golden rule of the methodology chapter – justify every choice ! Make sure that you clearly explain the “why” for every “what”, and reference credible methodology textbooks or academic sources to back up your justifications.
If you need a helping hand with your research methodology (or any other component of your research), be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through every step of the research journey. Until next time, good luck!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

51 Comments
highly appreciated.
This was very helpful!
This was helpful
Thanks ,it is a very useful idea.
Thanks ,it is very useful idea.
Thank you so much, this information is very useful.
Thank you very much. I must say the information presented was succinct, coherent and invaluable. It is well put together and easy to comprehend. I have a great guide to create the research methodology for my dissertation.
Highly clear and useful.
I understand a bit on the explanation above. I want to have some coach but I’m still student and don’t have any budget to hire one. A lot of question I want to ask.
Thank you so much. This concluded my day plan. Thank you so much.
Thanks it was helpful
Great information. It would be great though if you could show us practical examples.
Thanks so much for this information. God bless and be with you
Thank you so so much. Indeed it was helpful
This is EXCELLENT!
I was totally confused by other explanations. Thank you so much!.
justdoing my research now , thanks for the guidance.
Thank uuuu! These contents are really valued for me!
This is powerful …I really like it
Highly useful and clear, thank you so much.
Highly appreciated. Good guide
That was helpful. Thanks
This is very useful.Thank you
Very helpful information. Thank you
This is exactly what I was looking for. The explanation is so detailed and easy to comprehend. Well done and thank you.
Great job. You just summarised everything in the easiest and most comprehensible way possible. Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much for the ideas you have given this will really help me a lot. Thank you and God Bless.
Such great effort …….very grateful thank you
Please accept my sincere gratitude. I have to say that the information that was delivered was congruent, concise, and quite helpful. It is clear and straightforward, making it simple to understand. I am in possession of an excellent manual that will assist me in developing the research methods for my dissertation.
Thank you for your great explanation. It really helped me construct my methodology paper.
thank you for simplifieng the methodoly, It was realy helpful
Very helpful!
Thank you for your great explanation.
The explanation I have been looking for. So clear Thank you
Thank you very much .this was more enlightening.
helped me create the in depth and thorough methodology for my dissertation
Thank you for the great explaination.please construct one methodology for me
I appreciate you for the explanation of methodology. Please construct one methodology on the topic: The effects influencing students dropout among schools for my thesis
This helped me complete my methods section of my dissertation with ease. I have managed to write a thorough and concise methodology!
its so good in deed
wow …what an easy to follow presentation. very invaluable content shared. utmost important.
Peace be upon you, I am Dr. Ahmed Khedr, a former part-time professor at Al-Azhar University in Cairo, Egypt. I am currently teaching research methods, and I have been dealing with your esteemed site for several years, and I found that despite my long experience with research methods sites, it is one of the smoothest sites for evaluating the material for students, For this reason, I relied on it a lot in teaching and translated most of what was written into Arabic and published it on my own page on Facebook. Thank you all… Everything I posted on my page is provided with the names of the writers of Grad coach, the title of the article, and the site. My best regards.
A remarkably simple and useful guide, thank you kindly.
I real appriciate your short and remarkable chapter summary
Bravo! Very helpful guide.
Only true experts could provide such helpful, fantastic, and inspiring knowledge about Methodology. Thank you very much! God be with you and us all!
highly appreciate your effort.
This is a very well thought out post. Very informative and a great read.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR SHARING YOUR NICE IDEA
I love you Emma, you are simply amazing with clear explanations with complete information. GradCoach really helped me to do my assignment here in Auckland. Mostly, Emma make it so simple and enjoyable
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
HOW TO WRITE CHAPTER 1 OF A DISSERTATION OR THESIS

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough. Note.
Limitations Of The Study. - Outlines study boundaries. - Addresses constraints. - Manages reader expectations. - Establishes trust with transparency. Structural Outline Of Thesis. - Acts as a blueprint for the thesis. - Outlines each chapter succinctly. - Ensures logical progression of research work.
This template covers all the core components required in the introduction chapter/section of a typical dissertation or thesis, including: The opening section. Background of the research topic. Statement of the problem. Rationale (including the research aims, objectives, and questions) Scope of the study. Significance of the study.
Give a forthcoming chapter overview. The final part of the introduction is an overview of the rest of the chapters in the thesis. The other sections can go in any order, providing it is a logical sequence. Learn from others. Look at other theses for example from White Rose etheses or your university library's website. The majority of journal ...
Stages in a thesis introduction. state the general topic and give some background. provide a review of the literature related to the topic. define the terms and scope of the topic. outline the current situation. evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap. identify the importance of the proposed research.
2. Hook the reader and grab their attention. 3. Provide relevant background. 4. Give the reader a sense of what the paper is about. 5. Preview key points and lead into your thesis statement. Frequently Asked Questions about writing a good thesis introduction.
Its purpose is to give the reader a clear idea of the dissertation or thesis structure. In this section, a concise summary of each chapter, including the introduction chapter, is necessary. A sentence or two that outlines the purpose and contents of each chapter will suffice to guide the reader.
Before you write a compelling thesis introduction, you need to know what elements belong in this section and how it should be structured. A typical thesis introduction includes: A clear thesis statement. An explanation of the context (brief background) for the study. The focus and scope of the paper.
1. Research Background - Writing a Dissertation Introduction. This is the very first section of your introduction. Building a background of your chosen topic will help you understand more about the topic and help readers know why the general research area is problematic, interesting, central, important, etc.
Knowing how to write a thesis introduction chapter well is your key to impressing your examiner from the get-go and ensuring they're super keen to read the rest of your masters or PhD thesis. ... Clearly define the terms you'll be using and establish boundaries to delineate the scope of your thesis. For example, if your research focuses on ...
The introduction should offer the reader an overview of the research that you have conducted. You are setting the scene for your reader and giving them a broad idea of what they can expect throughout the rest of the thesis. As such, you don't need to go into too much depth at this stage - the details can come later in the following chapters.
Step 1: Hook the Reader's Interest. A writer should begin writing the introduction with a hook statement to draw the reader's interest. It can be a question, quotation, or interesting transitions into your arguments. Also, make a list of interesting, current events or controversies related to your topic.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first chapter of your dissertation or thesis is the introduction. It comes right after the table of contents, and its main goal is to explain the background of your research topic, your focus and scope, the importance of your research, your questions and goals, and a brief summary of your structure. Your introduction chapter gets the reader ...
Chapter introductions. The purpose of the thesis introduction is to orient the reader to the research presented in the body of your thesis. The introduction should include all information necessary to prepare the reader, to put the reader in the picture in terms of the specifics of your research project: what the thesis focuses on; the context ...
The basic structure of most Introduction chapters looks like this: Chapter 1: Introduction. 1.1. Background (2 to 3 pages) 1.2. Research Problem (1 page) 1.3. Research Questions (3 questions, each question is a paragraph of text) 1.4.
This chapter is your opportunity to leave a strong impression on the reader (assessors) about the strength and relevance of your research, and your skills as a researcher. Importantly, the conclusion chapter must link with your introduction chapter to complete the framing of the thesis and demonstrate that you have achieved what you set out to do.
Example: IS-AV construction Chapter 1 presents an introduction to the problem and Chapter 2 discusses the relevant literature. Example 3: The "I" construction. Another option is to use the "I" construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style). However, depending on your field of study, this ...
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION. 1. The purpose of this qualitative grounded theory study was to identify what motivates. women to stay in or return to science, technology, engineering, and math professions. (STEM), leading to a motivation model. As illustrated in the literature review, research has. abbreviations. introduce introduce you can use Once ...
SIMPLE. Do the following: Introduce and explain BASIC concepts of your thesis to your reader for the first time in a simple way (leave the detailed descriptions for your Theoretical background/Literature Review). In the example above, you would explain: "Machine to Machine Interaction". For example:
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
1. Understand the elements and objectives of chapter 1 In a dissertation or thesis, the introduction always appears as chapter 1 right after the table of contents. To write an effective chapter 1, you first need to grasp the key elements that build up the introductory chapter and the main purposes of an introduction. Writing this chapter entails painting a clear picture to your readers of what ...