Case Studies in Business Economics, Managerial Economics, Economics Case Study, MBA Case Studies
Ibs ® case development centre, asia-pacific's largest repository of management case studies, mba course case maps.
- Business Models
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Competition & Strategy ⁄ Competitive Strategies
- Core Competency & Competitive Advantage
- Corporate Strategy
- Corporate Transformation
- Diversification Strategies
- Going Global & Managing Global Businesses
- Growth Strategies
- Industry Analysis
- Managing In Troubled Times ⁄ Managing a Crisis ⁄ Product Recalls
- Market Entry Strategies
- Mergers, Acquisitions & Takeovers
- Product Recalls
- Restructuring / Turnaround Strategies
- Strategic Alliances, Collaboration & Joint Ventures
- Supply Chain Management
- Value Chain Analysis
- Vision, Mission & Goals
- Global Retailers
- Indian Retailing
- Brands & Branding and Private Labels
- Brand ⁄ Marketing Communication Strategies and Advertising & Promotional Strategies
- Consumer Behaviour
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Marketing Research
- Marketing Strategies ⁄ Strategic Marketing
- Positioning, Repositioning, Reverse Positioning Strategies
- Sales & Distribution
- Services Marketing
- Economic Crisis
- Fiscal Policy
- Government & Business Environment
- Macroeconomics
- Micro ⁄ Business ⁄ Managerial Economics
- Monetary Policy
- Public-Private Partnership
- Entrepreneurship
- Family Businesses
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Financial Management & Corporate Finance
- Investment & Banking
- Business Research Methods
- Operations & Project Management
- Operations Management
- Quantitative Methods
- Leadership,Organizational Change & CEOs
- Succession Planning
- Corporate Governance & Business Ethics
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- International Trade & Finance
- HRM ⁄ Organizational Behaviour
- Innovation & New Product Development
- Social Networking
- China-related Cases
- India-related Cases
- Women Executives ⁄ CEO's
- Effective Executive Interviews
- Video Interviews

Executive Brief
- Movie Based Case Studies
- Case Catalogues
- Case studies in Other Languages
- Multimedia Case Studies
- Textbook Adoptions
- Customized Categories
- Free Case Studies
- Faculty Zone
- Student Zone
Economics case studies
Covering micro as well as macro economics, some of IBSCDC's case studies require a prior understanding of certain economic concepts, while many case studies can be used to derive the underlying economic concepts. Topics like Demand and Supply Analysis, Market Structures (Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic, etc.), Cost Structures, etc., in micro economics and national income accounting, monetary and fiscal policies, exchange rate dynamics, etc., in macro economics can be discussed through these case studies.
Browse Economics Case Studies By
Sub-Categories
- Government and Business Environment
- Micro / Business / Managerial Economics
- Public Private Partnership
- Aircraft & Ship Building
- Automobiles
- Home Appliances & Personal Care Products
- Minerals, Metals & Mining
- Engineering, Electrical & Electronics
- Building Materials & Construction Equipment
- Food, Diary & Agriculture Products
- Oil & Natural Gas
- Office Equipment
- Banking, Insurance & Financial Services
- Telecommunications
- e-commerce & Internet
- Transportation
- Entertainment
- Advertising
- IT and ITES
- Leisure & Tourism
- Health Care
- Sports & Sports Related
- General Business
- Business Law, Corporate Governence & Ethics
- Conglomerates
Companies & Organizations
- China Aviation Oil Corp
- De Beers and Lev Leviev
- Goldman Sachs
- Gordon Brown
- Iliad Group, France Telecom
- Lehman Brothers
- Merrill Lynch
- Mittal Arcelor
- Morgan Stanley
- Northern Rock
- Temasek Holdings
- Wachovia Wells Fargo
- Dominican Republic
- Netherlands
- North America
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- South Korea
- United Kingdom
- United Arab Emirates
- United States
Recently Bought Case Studies
- Tata Consultancy Services: Managing Liquidity Risk
- SSS�s Experiment: Choosing an Appropriate Research Design
- Differentiating Services: Yatra.com�s �Click and Mortar�Model
- Wedding Services Business in India: Led by Entrepreneurs
- Shinsei Bank - A Turnaround
- Accenture�s Grand Vision: �Corporate America�s Superstar Maker�
- Tata Group�s Strategy: Ratan Tata�s Vision
- MindTree Consulting: Designing and Delivering its Mission and Vision
- Coca-Cola in India: Innovative Distribution Strategies with 'RED' Approach
- IndiGo�s Low-Cost Carrier Operating Model: Flying High in Turbulent Skies
- Evaluation of GMR Hyderabad International Airport Limited (GHIAL)
- Ambuja Cements: Weighted Average Cost of Capital
- Walmart-Bharti Retail Alliance in India: The Best Way Forward?
- Exploring Primary and Secondary Data: Lessons to Learn
- Global Inflationary Trends: Raising Pressure on Central Banks
- Performance Management System@TCS
- Violet Home Theater System: A Sound Innovation
- Consumer�s Perception on Inverters in India: A Factor Analysis Case
- Demand Forecasting of Magic Foods using Multiple Regression Analysis Technique
New Case Studies In Economics
- The Sri Lankan Economic Crisis � What Went Wrong?
- Crude Oil Market and the Law of Supply
- Understanding Crude Oil Demand
- The `C` Factor: Cement Industry in India � Unhealthy Oligopoly & Controls
- Venezuela`s Macroeconomic Crisis: An Enduring Ordeal of Worsening Economy with Alarming Inflation
- Guwahati Molestation Case: Professional Responsibility Vs Moral Ethics
- The Renaissance of the South Africa Music Industry
- EU BREAK-UP?
- The Cyprus Bailout - Is the European Zone Failing?
- Global Financial Crisis and ITS Impact on Real and Financial Sectors in India
Best Selling Case Studies In Economics
- Perfect Competition under eBay: A Fact or a Factoid?
- Mexican Telecom Industry: (Un)wanted Monopoly?
- Mobile Telephony in India: Would Cheaper Rates Bring More Profits?
- US Financial Crisis: The Fall of Lehman Brothers
- Executive Pay Package: A Study of Demand and Supply
- OPEC: The Economics of a Cartel (A)
- OPEC The Economics of a Cartel (B)
- OPEC: The Economics of a Cartel (C)
- Comparative Cost Advantage and the American Outsourcing Backlash
- Global Oil Prices: Demand Side vs Supply Side Factors
Video Inerviews
Case studies on.
- View all Casebooks »
Course Case Mapping For
- View All Course Casemaps »
- View all Video Interviews »
- Executive Briefs
- Executive Inerviews
- View all Executive Briefs »
Executive Interviews
- View All Executive Interviews »
Contact us: IBS Case Development Centre (IBSCDC), IFHE Campus, Donthanapally, Sankarapally Road, Hyderabad-501203, Telangana, INDIA. Mob: +91- 9640901313, E-mail: [email protected]

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Note that the Economics 103 Case Studies are meant to supplement the course material by giving you experience applying Economic concepts to real world examples. While they are beyond the level you will be tested on, they are useful for students who want a stronger grasp of the concepts and their applications.
Note that this case study is difficult if you do not print the diagrams, or reproduce them on graph paper. If you are unable to print, we recommend reviewing the solutions to ensure you understand the general lessons presented.

In 2016 rental vacancy rates dropped to as low as 0.6% in Greater Victoria. When compared to the national average of 3.3% it is clear why many media channels and individuals were calling it a ‘housing crisis’. Students were especially hit hard by these low vacancies, with some international students at Camoson college having to return home when they couldn’t find a place to stay. Using our competitive market model, let’s examine some of the factors that played into this crisis and policies that could be used to fix it.

Read more about the Victoria Housing crisis.
Below is a representation of the Victoria Housing Market.
1. Label Figure CS3 a. with the Equilibrium price and quantity, and label supply and demand curves as either renters or landlords.
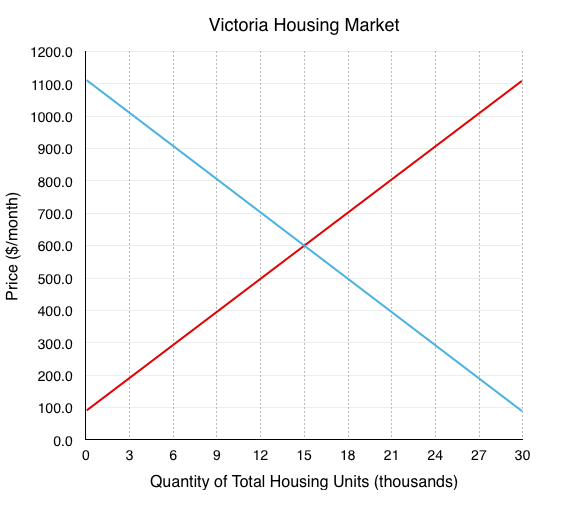
If supply is equal to demand there should be no vacancy, but we know that a 0% vacancy rate would be an extremely difficult market for renters.
2. Explain why a housing market at equilibrium could still have a vacancy rate of 4%.
One factor that has been blamed for the housing crisis is Airbnb. Airbnb describes itself as an online marketplace and hospitality service, enabling people to list or rent short-term lodging including vacation rentals, apartment rentals, homestays, hostel beds, or hotel rooms, with the cost of lodging set by the property owner. City councillors have targeted these short term rentals, saying that many landlords have opted to Airbnb their home, rather than rent out longer term. The growth of Airbnb in Vancouver has been shown below.
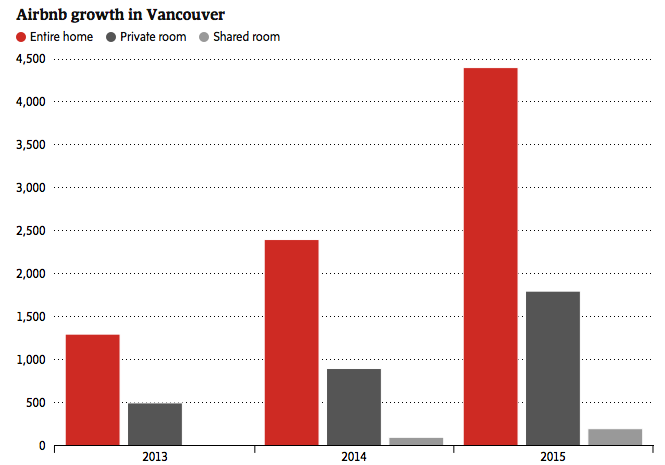
3. Assume 3000 landlords decide to switch from renting to Airbnb, show the impact of the changes on Figure CS3 b. Label the new equilibrium price and quantity.

Note that Airbnb has been adamant that short-term rentals have had a neglible impact on the housing market, citing that in Vancouver only 320 hosts rent out thier properties often enough to make more money that long term rentals. That represents only 0.11% of the total housing units. In Victoria, that would mean only 25 units are affected by short-term rentals.
Tom Davidoff , a University of B.C. business professor, said t he general public frequently looks at the fact that Airbnb is popular in expensive neighbourhoods and concludes that it is Airbnb that drives up rents there. But, he said, those neighbourhoods were expensive anyway and the impact of Airbnb taking a certain slice of the available stock is minimal.

Read more about Airbnb’s supposed impact on the market.
Another factor that has had an impact on the rental market is the inability of many young Canadians to buy homes. Not only have house prices skyrocketed, but more are burdened by student loans out of university. It is estimated that it takes 3 times longer (15 years) to save enough to have a 20% downpayment on a house than it did in 1976. This reduction in Canadians mortgaging a home has caused an increasing amount to enter the market.
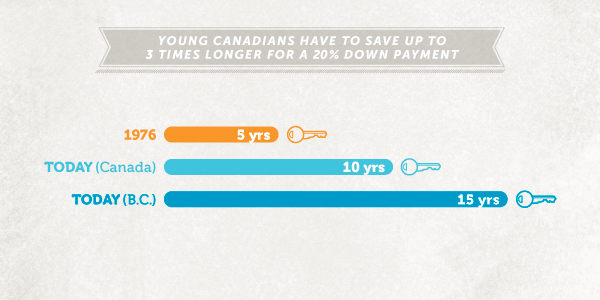
Read more about the increasing squeeze on millennials.
4. Assume 9000 new renters enter the market instead of mortgaging homes, show the impact of the changes on Figure CS3 b. Explain the impact of both the shock from Airbnb and the shock from less housing buyers on equilibrium price and quantity. Do the shocks work together or oppose one another?
In the housing market, prices are slow to adjust, landlords cannot simply raise prices immediately under the Residential Tenancy Act. Landlords can only raise prices when negotiating a new contract. This causes many unjustified evictions from landlords as they want to charge the new equilibrium price. In the short-term, prices stay relatively the same causing shortages or surplus.
5. Assume price remains at the original equilibrium , calculate the magnitude of the shortage or surplus of housing that results. Explain the impact this shortage will have the behaviour of landlords.
The British Columbia government unveiled a $500-million affordable-housing plan targeted at communities that have struggled with a shortage of low-cost housing. Premier Christy Clark announced her government’s commitment to fund 68 new projects to help address the crisis
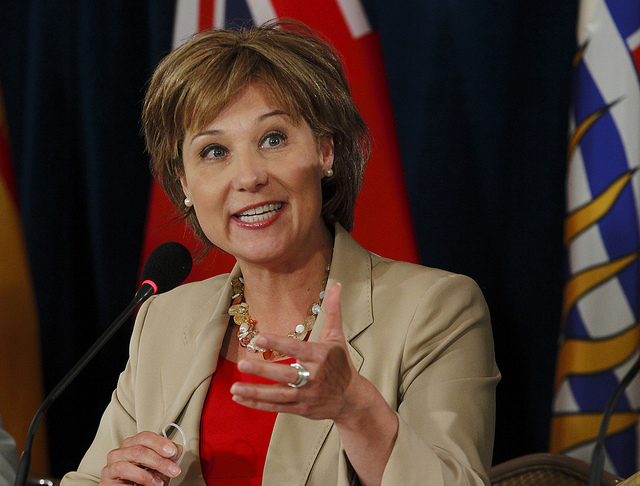

Read more about the governments response to the housing crisis.
6. Assume the government wants to bring price back to it’s original level, if it costs $50,000 to increase the number of rental units by one, how much will this cost the government?
Groups have criticized the government response, saying that they have ignored many other avenues that could more easily increase the supply of affordable housing.
7. Read the Executive Summary of the Alliance of BC Students White Paper on Student Housing.

What is the ABCS proposing that could help decrease price in the market? How would this affect supply and/or demand?

In this case study we have shown how microeconomic concepts of supply and demand can be used to understand current events in the news. Do you have a story you think would make a good case study? Contact [email protected] to propose your story.
Principles of Microeconomics Copyright © 2017 by University of Victoria is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Improving economics teaching and learning for over 20 years
Case Studies for Teaching Economics
This is an index of case studies in economics. Teaching case studies are on another part of the site.
Introductory
- Principles (General) (1)
- Principles of Macroeconomics (5)
- Principles of Microeconomics (4)
- Applied Economics (2)
- Statistics for Economists (1)
Intermediate
- Public-sector Economics and Public Choice Theory (1)
- International Economics (1)
- Managerial and Business Economics (3)
- Development Economics (2)
- European Economics (1)
- Law and Economics (1)
- Intermediate Macroeconomics (1)
- Intermediate Microeconomics (1)
- Advanced Applied Economics (1)
Latest Addition
The AEA provide this index to recent, accessible research summary articles from the Journal of Economic Perspectives , collected under the concept that each article illustrates. The resulting list gives alternatives to the standard examples for topics like asymmetrical information, externalities, or incentives.
- 100431 views
- Views on request

Library subject guides
- Key resources
- Books and e-books
- Statistics and country information
Case studies
Recommended databases: case studies, other databases: case studies, streaming videos: case studies.
- Company and industry information, financials
- Additional information
Case studies describe real world practical examples, including successes, issues and challenges. To find case studies using LibrarySearch or databases, add "case study" to your search terms.
- The case study handbook a student's guide This e-book provides tips on how to read, analyse and write about cases.
- Business source complete (EBSCO) Contains case studies from many sources. They can be found using advanced search and selecting "case study" as the Document Type.
- Harvard Business Review Journal of Harvard Business School that covers a wide range of business topics. Click “Search within this publication” and input search terms, then limit results by “Subject” to “Case studies”.
- Harvard Business Review Digital Articles Digital articles uploaded from the HBR.org site. Click “Search within this publication” and add “Case study” as a search term.
- Henry Stewart talks: The business and management collection A collection of video lectures, case studies and seminar-style talks. Subject areas include marketing & sale, global business management, organisation, commerce, technology, and operations.
- Emerald Insight An extensive business research database. Click on advanced search and then select the case studies checkbox.
- MarketLine Case Studies (Datamonitor) Explore business practices across a variety of industry sectors. Select "Analysis" from the menu bar and select Case studies. A selection of pre 2008/9 reports are also available from LibrarySearch; search for "Datamonitor Case Studies”.
- Factiva Use "case study" or "case studies" as terms when building your search. There is no option to limit to case studies as a resource type.
- SAGE Business cases Access to authoritative cases from over 100 countries. SAGE curates interdisciplinary cases on in-demand subjects such as marketing, entrepreneurship, accounting, healthcare management, leadership, social enterprise, and more.
- Arthur Andersen Case Studies in Business Ethics 90 case studies that highlight awareness of ethical issues in business.
- Business Case Studies Uses real information and issues from featured companies.
- Markkula Center for Applied Ethics - ethics case studies Find case studies and scenarios on a variety of fields in applied ethics.
- MIT LearningEdge Case Studies Some of the case studies featured on LearningEdge highlight the decision-making process in a business or management setting.
Case studies in video documentary format are available from these video streaming databases.
- ClickView A collection of educational videos, including professional development videos and case studies. To access you will need to use your RMIT student login. Streaming videos covering a variety of disciplines. Enter your search terms and then narrow using the “case study” Tag.
- Alexander Street A collection of documentaries, features, educational and informative videos (and audio), and archival material. Also includes industry specific textbooks, book chapters, corporate training videos, case studies and executive-oriented research reports. Enter your search terms and then filter your result by selecting “Case Study” as your Content Type.
- Kanopy Business Case Studies A selection of streaming videos examining companies, marketing strategies, and entrepreneurs. Browse the “Business” section and select “Business Case Studies”.
Finding case studies
The Library's Finding Case Studies guide explains different types of case studies and how to find them.

Writing a case study

See the Learning Lab tutorial on Writing a Case Study to find out how to read, analyse and respond to a case study.
- << Previous: Videos
- Next: Company and industry information, financials >>
- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 7:07 PM
- URL: https://rmit.libguides.com/economics
Browser does not support script.

Impact Case Studies

Impact case study: Improving the lives of the ultra-poor
Summary: Researchers at LSE provided robust evidence that large, one-off interventions can produce sustainable economic benefits for individuals, improving the lives of people in extreme poverty. Read the impact case study .
Professor Oriana Bandiera Professor of Economics | Sir Anthony Atkinson Chair in Economics
Professor Robin Burgess Professor of Economics | Director of IGC

Impact case study: State capacity: crafting effective development strategies Summary: LSE research has made a significant contribution to understanding state development and the causes of state fragility, shaping the work of multilateral development agencies. Read the impact case study .
Professor Sir Tim Besley School Professor of Economics and Political Science

Impact case study: Understanding and improving subjective wellbeing
Summary: LSE research has significantly contributed to promoting subjective wellbeing as a central objective of public policy, and provided new tools to support its measurement. Read the impact case study .
Professor Lord Richard Layard Emeritus Professor of Economics | Community Wellbeing Programme Co-Director
Professor Paul Dolan Professor of Behavioural Science

Impact case study: Supporting the development of a safer, more robust financial system for the eurozone
Summary: In response to the eurozone crisis, LSE economists co-developed an influential proposal for European Safe Bonds (ESBies), which would protect the financial system from future shocks. Read the impact case study .
Professor Ricardo Reis Arthur Williams Phillips Professor of Economics
Professor Dimitri Vayanos Professor of Finance | Director, Financial Markets Group

Impact case study: Improving productivity through better management practices
Summary: LSE research has demonstrated how management practices affect productivity, providing vital evidence for designing industrial strategies to tackle low productivity. Read the impact case study .
Professor John Van Reenen Ronald Coase Chair in Economics and School Professor
Professor Nicholas Bloom Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research
Professor Raffaella Sadun Harvard Business School

Knowledge Exchange and Impact (KEI) LSE's guidance for engaging non-academic audiences with research

Connect with Us
- Entertainment
- Gadgets Review
- Government Schemes
- Make Money Online
- Product Review
- Uncategorized
Solving Case Study in Economics: A Complete Guide

case study in economics
Case studies are invaluable in economics education, providing students with real-world scenarios to apply theoretical concepts and analytical skills. However, solving a case study in economics requires a structured approach that combines research, critical thinking, and a deep understanding of economic principles. This post presents a comprehensive guide on effectively solving a case study in economics , ensuring a thorough analysis and a grasp of practical implications.
Understanding the Case Study
Read carefully: .
Begin by reading the case study thoroughly. Pay attention to the details, context, and objectives presented. Identify the main issues, stakeholders, and the economic concepts at play.
Define the Problem:
Clearly define the economic problem or challenge presented in the case study. What are the fundamental problems that ought to be handled? Understanding the problem is crucial before proceeding with analysis.Identify the central economic problem or challenge that the case study presents. This could involve issues related to demand and supply, market structures, externalities, government interventions, or any other economic concept.
Gathering Relevant Information
Research: .
Conduct thorough research to gather additional information relevant to the case study. This may involve exploring economic theories, statistical data, and industry trends. Reliable sources such as academic journals, government reports, and reputable news outlets are valuable.
Identify Variables:
Identify the variables affecting the situation presented in the case study. These could include economic indicators, market conditions, government policies, etc.
Read also: How Trademark Registration Can Help in Business
Applying Economic Concepts
Use relevant theories: .
Apply relevant economic theories and concepts to analyze the case study. Consider concepts like supply and demand, elasticity, market structure, cost analysis, and utility theory, depending on the case context.
Quantitative Analysis:
If applicable, use quantitative methods such as calculations, graphs, and charts to illustrate your analysis. These tools can help visualize economic relationships and trends.
Data Interpretation
Cause and effect:.
Identify the cause-and-effect relationships driving the economic situation in the case study. Analyze how changes in one variable can impact others and lead to specific outcomes.
Consider Alternatives:
Explore solutions or strategies to address the issues presented. Consider the possible benefits and drawbacks of each option.
Making Recommendations
Informed decisions: .
Based on your analysis, make informed recommendations for addressing the challenges outlined in the case study in economics. Your recommendations should be rooted in economic theories and supported by your gathered data.
Justify Your Recommendations:
Clearly explain the rationale behind your recommendations. How will they positively impact the stakeholders involved? Justify your choices with economic logic.
Read also: Best Practices for Workday Financial Management Integration
Tips for Success
Practice: .
The more case studies you solve, the more comfortable you’ll become with the process. Practice hones your analytical skills and enables you to apply economic concepts effectively.
Collaborate:
Engage in discussions with peers or instructors. Collaborative analysis can offer diverse perspectives and deepen your understanding of the case.
Real-World Context:
Relate the case study to real-world economic scenarios. Understanding the practical implications of your analysis adds depth to your recommendations.
Stay Updated:
Case study in economics is a dynamic field. Stay updated with current economic trends, policy changes, and market developments to enhance the relevance of your analysis.
Read the Case Thoroughly
Begin by reading the case study attentively. Familiarize yourself with the context, characters, and economic issues presented. Take notes as you read to highlight key information and identify the main problems.
Apply Relevant Economic Concepts
Next, apply the economic concepts and theories you’ve learned in your coursework to the identified problem. Consider how concepts like elasticity, opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and cost-benefit analysis can be applied to the situation.
Collect Data and Information
Gather relevant data and information that can support your analysis. This may include statistical data, market trends, historical information, and other relevant sources that substantiate your arguments.
Analyze and Evaluate
Conduct a thorough analysis of the situation. Identify the factors contributing to the problem and evaluate their impact. Use graphs, charts, and diagrams to represent your analysis and provide clarity visually.
Explore Alternatives
Generate possible solutions or alternatives to address the identified problem. Consider the pros and cons of each solution, keeping in mind economic feasibility, ethical implications, and potential outcomes.
Apply Economic Theories
When formulating solutions, apply economic theories and principles that align with the situation. For instance, if you’re dealing with a market failure, explore how government intervention or corrective measures can be applied based on economic theories like externalities or public goods.
Quantitative Analysis
If applicable, perform quantitative analysis using relevant mathematical or statistical tools. This could involve calculating elasticity break-even points or analyzing cost structures to support your recommendations.
Justify Your Recommendations
Ensure that your solutions are well-justified and backed by solid economic reasoning. Explain how each solution addresses the problem and aligns with economic theories.
Consider Real-World Constraints
Acknowledge any real-world constraints that might affect the implementation of your recommendations. This could include budgetary limitations, political considerations, or social factors.
Solving an case study in economics writing is an enriching experience that bridges theory and practice. It requires a structured approach, from understanding the case to making well-informed recommendations. By thoroughly analyzing the economic concepts, interpreting data, and applying relevant theories, you can arrive at strategic solutions that align with economic principles.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related News

How to migrate from Wix to WordPress – Ultimate Guide

7 Best Team Collaboration Tools for Remote & In-Person
You may have missed.

How to Personalize Custom Boxes for Special Occasions?

How to Fix NVIDIA GeForce Experience Error Code 0x0003

Style Mastery: Essential Tips for Every Woman’s Occasion

Creating High-Performance Teams for Success

Health and Insurance Bridging the Gap of Technology

UBO Verification: Understand the Ultimate Beneficial Owners

The case method can be a powerful tool to teach economic concepts and frameworks. Topics in this section cover a wide range of real-life examples from around the world on a host of issues including infrastructure, trade, taxation, regulation and development.

Integrating Systems at Scale: Coordinating Health Care in Houston
Publication Date: November 8, 2023
This case concerns the Patient Care Intervention Center (PCIC) a values-based health technology social enterprise in Houston, Texas. This organization was founded to tackle fundamental problems in social and health services in the United...
A User-Centered Design Process for Data-Driven Policymaking
Publication Date: August 22, 2023
Well-conceived, user-friendly data visualizations have the potential to bring fresh perspectives derived from analyzing, visualizing, and presenting data to inform evidence-based policymaking. This case uses the Metroverse project from the...
Leadership and Negotiation: Ending the Western Hemisphere’s Longest Running Border Conflict
Publication Date: October 4, 2022
For centuries, Ecuador and Peru each claimed sovereignty over a historically significant, but sparsely inhabited tract of borderland in the Amazonian highlands. The heavily disputed area had led the two nations to war—or the brink of...
Pratham: The Challenge of Converting Schooling to Learning in India
Publication Date: November 18, 2020
This multimedia case brings video, text, and graphics together to offer a rare, immersive experience inside one of the developing world's most pressing challenges, low levels of learning. Pratham, counted among India's largest non-profits, has...
Video Series: Public Policy Applications of Microeconomic Concepts
Publication Date: September 24, 2019
MATERIALS FOR VIDEO CASEThe materials for this case are included in the teaching plan and are for registered instructors to use in class. If you do not have Educator Access, please register here (notification received within 2 business days). Abstract:...
Evaluating the Impact of Solar Lamps in Uganda
Publication Date: August 26, 2019
IDinsight, an evaluation company founded by graduates of the Harvard Kennedy School, designs and conducts evaluations that best suit the needs of clients across the developing world, offering timely and rigorous evidence to help decision making...

Untapped Potential: Renewable Energy in Argentina (Sequel)
Publication Date: October 6, 2020
In 2015, Mauricio Macri became President of Argentina and declared solving the energy crisis one of his top priorities. When Macri attempted to raise utility tariffs, however, he faced loud protests from citizens. In search of solutions to...

Untapped Potential: Renewable Energy in Argentina
Publication Date: August 23, 2019

Christine Lagarde (C): Managing the IMF
Publication Date: August 20, 2018
This case covers the career of Christine Lagarde from 2011 to 2018 as she takes the helm of troubled multilateral organization during a time of deepening economic turmoil. As the first female leader of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and...

Christine Lagarde (B): Being a Public Servant
This case covers the career of Christine Lagarde from 2005 to 2011 after she joins the French Government. After serving several grueling years as Finance Minister during the financial crises that started in 2007/2008, she is being considered as...
Christine Lagarde (A): A French Prime Minister Calls
This case covers formative events and influences in Christine Lagarde's childhood and her trajectory from studying political science and law to heading the world's largest law firm. As she prepares to transition back to practice in 2005, the new...
Christine Lagarde (Extended)
For a modular presentation of the same material, please see Christine Lagarde (A): A French Prime Minister Calls (2136.0), Christine Lagarde (B): Being a Public Servant (2137.0), and Christine Lagarde (C): Managing the IMF (2138.0). These...
Home > Case Studies
Case Studies
Discover all the ways our 2,000 customers succeed, thrive and grow with Oxford Economics. Read success stories from Oxford Economics' clients in sectors such as pensions, energy and Real Estate. Learn how they solved their business challenges, supported their businesses' growth and adapted to new markets using Oxford Economics market-leading consulting and subscription services.

Case Study | Multinational Drinks Company
Bespoke dashboards and agile on-demand economics support
Background Today’s turbulent macroeconomic and consumer environment makes strategy and planning particularly difficult for firms in the business-to-consumer sector. The pandemic, major global conflicts and geopolitical tensions have caused major supply-side disruptions. At the same time, the ever-changing consumer environment, recent unprecedented levels of inflation and the ensuing cost of living crisis have been a...

Case Study | Royal London
Exploring the implications of higher pension contributions
Many households fail to save adequately for retirement. Using in-house models, the study assesses the impact of higher pension contributions on both pension savings and UK economic growth.

Case Study | A global aggregate and building materials provider
Constructing Success by Capitalising on Long-Term Opportunities
Helping a strategy department identify its 10-year growth opportunities

Case Study | Semiconductor Industry Association
A unique policy-driven impact scenario for CHIPS Act
How Oxford Economics engaged the world’s largest chip manufacturers to develop an industry-wide impact assessment of the CHIPS and Sciences Act.

Case Study | Building material manufacturer
Benchmarking Success: Building a Global Market Demand Indicator
Creating a new demand measure to enable a building material manufacturer to gauge its performance.

Case Study | Multinational services company
Quantifying the impact of climate on customers
Leveraging industry-specific climate forecasts to future-proof revenue.

Case Study | Energy UK
Achieving net zero advocacy goals
Highlighting the economic opportunities the energy transition presents and the consequences of not grasping them.

Charting a course for global growth in the shipping industry
Empowering a leading shipping company to enhance its strategic planning and identify new routes for growth

Global macroeconomic and risk scenario tool
Enabling a major automotive manufacturer to anticipate and respond effectively to evolving market dynamics across its global operations.

Risk signal identification, prioritisation and monitoring evaluation model
Despite existing internal risk management processes, a major automotive manufacturer was unprepared for and failed to anticipate and mitigate significant risks and shocks that have significantly affected its operations in recent years, including its sales, supply chain and financing.

Bespoke automotive sector sales forecasting
Automotive companies face many challenges: regulations, emission controls, litigation, political uncertainty, complex and problematic supply chains and disruptive technology are perhaps among the most pressing.

Case Study | Australian Finance Industry Association
The economic impact of Buy Now Pay Later in Australia
Governments globally are realising the importance of payments and financial services efficiency to economic growth, financial wellbeing and social participation. The Australian Finance Industry Association (AFIA) recognises innovation, competition, market efficiency, economic growth and consumer protection are interrelated and, therefore, must be addressed collectively. An informed understanding of the Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) sector...

Case Study | City of Sydney

City of Sydney’s 2022 Business Needs Survey Report
The City of Sydney required an advisor with the capability to develop a high-impact, user-focused report to: The report had to be engaging and highly visual, containing a range of different devices to communicate economic insights to a range of readers. The solution Oxford Economics Australia developed a rich and compelling report to engage and...

Case Study | Leading Australian Law Firm
Expert Witness Report on property market influences and outlook
The repudiation of an existing development agreement resulted in Supreme Court proceedings whereby residential property market forecasts were required to demonstrate the outlook for the Darwin residential market at that time. Separate sale price and rent projections were needed (on an annual basis) for detached house and attached dwellings for the period of 2017-2030. Importantly,...

Case Study | QBE LMI
The Annual Housing Outlook 2022 – the Green Edition
The objective of this work was to reinforce QBE LMI’s position by providing an outlook of housing market performance and stimulate informed discussion about environmental sustainability within the housing market and a state by state performance analysis of housing market prices and rents. The solution The project was approached collaboratively with the QBE LMI project...

Case Study | Australia Energy Market
Forecasts and scenarios to inform the future of Australia’s energy market
Oxford Economics Australia was commissioned to produce macroeconomic and commodity scenario projections that could be used to generate long-term gas and electricity demand and supply projections across a range of energy transition scenarios. The solution We worked closely with the client’s team and their stakeholders to produce long-term (30-year) macroeconomic and commodity price forecasts, across...

Case Study | National Bureau of Statistics
Developing a leading statistical ecosystem to empower decision makers in government, the private sector and broader society
The National Bureau of Statistics asked Oxford Economics to redesign its existing statistical publications to make them more user-focused. This included: The solution Oxford Economics worked closely with the National Bureau of Statistics over a period of six months to develop 57 redesigned publication templates. The work was completed in two broad stages: The final...

Case Study | Schroders
Understanding climate-related implications on investment strategies
As global awareness of climate change continues to increase, investors are beginning to consider how climate risks and opportunities may affect long-term investment strategies and returns. Our client, Schroders, a large asset manager, is no exception, which is why they switched to our Global Climate Service as the economic foundation for their long-run asset class publication.

Case Study | Life insurance company
Improved research processes and forecasting accuracy
A leading life insurance company has used Oxford Economics' Global Economic Model to improve their global economic research processes and increase the accuracy of their own economic forecasts.

Case Study | Large global pension fund
Supporting investment strategy with long-term perspectives
Overview To make long-term investments, investors need long-term thinking. That’s why one of the largest pension funds globally subscribed to Oxford Economics’ Global Macro Service, Global Cities Service and Regional City Services. They currently use our macroeconomic forecasts as one of the references in reviewing market fundamentals for investment. The Challenge As long-term investors, our...
Find out how Oxford Economics can help you on your path to business growth

Sign up to our Resource Hub to download the latest and most popular reports.
Select to close video modal
Select to close video modal Play Video Select to play video
- Introduction
- Books and ebooks
- Business, economics and finance news
Case studies
- Company, industry and marketing information
- Data and statistics
- Journal articles
- Research methods and sources
- Referencing
- Locations and opening hours Find books, articles and more Use the library Accessibility and support Subject support Research support Special Collections Events About New University Library Contacts
A collection of business cases providing unlimited access to more than 5,500 authoritative cases from over 120 countries. SAGE curates interdisciplinary cases on in-demand subjects such as entrepreneurship, accounting, healthcare management, leadership, social enterprise, and more.
One of the most important scholarly business databases. Contains the full-text of over 1,800 journals within management and all related areas, plus over 2,000 magazine and trade publications. It includes full-text access to Harvard Business Review. Also includes selected company and marketing reports from Marketline and in-depth country profiles.
Cases studies of marketing excellence from all over the world, covering every marketing discipline. Selected Euromonitor company profiles in the following industries: Alcoholic drinks, Clothing and accessories, Financial services, Food, Leisure and entertainment, Healthcare, Retail, Soft drinks, Technology and electronics, Tobacco, Toiletries and cosmetics, Transport and tourism. Vast amount of data on global ad trends, advertising expenditure and media consumption.
- Open access case studies for economics, finance and management Full-text access to high quality business case studies from Stanford, MIT Sloan and others. less... Full-text access to high quality business case studies from Stanford, MIT Sloan and others.
Movies, documentaries, foreign films, classic cinema, independent films and educational videos.
Further help

Business Source Complete tutorial

- << Previous: Business, economics and finance news
- Next: Company, industry and marketing information >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 3:59 PM
- URL: https://bristol.libguides.com/economics

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Topic 7: Producer Theory

Some hate it and some love it, but regardless of how you feel oil is still a key part of our daily lives. The average Canadian uses about 20 barrels of oil each year, equivalent to about one and a half swimming pools. Since it is such a major part of our expenses, oil is a product where, when price changes, we really notice.
In 2008, China’s expansion sparked a long period of high prices. In this case study, we will analyze what has happened to these prices over time and the impact this has had on oil producers from the lens of producer theory.
To simplify our case study, let’s assume that the oil market is perfect competition.
1. Consider the following producer theory model for a single firm producing oil, and the aggregate supply and demand. What is the firm’s equilibrium price and quantity?

2. What is the firm’s profit at this level?
3. What will occur in the long-run for this market? Show this on the new graph below.

The period of high prices indeed incentivized private firms to search farther than ever before – in the Arctic, Brazil’s pre-salt fields, deep waters off Angola, and Canada’s oil sands to ever expand the supply of oil. Investors encouraged this activity, rewarding future growth as much as profitability.

Oil prices have been quite volatile. Recently, from mid 2014 to early 2016 oil prices plummeted from $110 a barrel to around $27. This sharp decline has been due to a number of causes. A key cause was when sanctions were lifted from Iran, a new producer entered the market with large quantities of oil. In addition, growing fears about action on climate change, coupled with the emergence of alternative-energy technologies, caused producers to pump as hard as they can, while they can.

Read more about the reasons for changing oil prices
3. Use the producer theory model from above to show the impact of Iran’s entry, assume this brings the market from long-run equilibrium to a price of $27.
4. What are the firms profits at this price?
In the industry at large, the incentive is to keep producing “as flat out as you can”, once investment costs have been sunk into the ground, says Simon Henry, Shell’s chief financial officer. He says it is sometimes more expensive to stop production than to keep pumping at low prices, because of the high cost of mothballing wells. He suggested that firms will not pack up so long as prices cover day-to-day costs, in some cases as low as $15 a barrel.
It may be uneconomic to drill new deepwater wells at prices under $60 a barrel, he says, but once they are built it may still make economic sense to keep them running at prices well below that. Such resilience is used by some to justify why they expect prices to remain “lower for longer”.

Read more about the impact of price changes on oil firms
6. What does this excerpt suggest about how firms will behave in the short run?
7. Based on the information given about this market, what do you think the time horizon will be for this industries ‘long run’? What will happen in the long run?
Notice that in our model when prices fall, even in the short run individual firms will decrease production. In reality, firms part of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) made a pact to keep production high, to try to retain market share and keep out competitors.
In his book “The Prize”, Daniel Yergin quotes an American academic writing as far back as 1926 about the “spectacle” of massive overproduction. “All saw the remedy but would not adopt it. The remedy was, of course, a reduction in the production.”
8. Comment on the effects of OPEC’s actions on the market.
In this case study we have shown how microeconomic concepts of monopoly and monopolistic competition can be used to understand current events in the news. Do you have a story you think would make a good case study? Contact [email protected] to propose your own case.
Principles of Microeconomics Copyright © 2017 by University of Victoria is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
- Business and society
- Business management
- Entrepreneurship
- Finance and investing
- Health and behavioral science

Algorithmic Nudges Don't Have to Be Unethical
- Mareike Möhlmann
- April 21, 2021
For a Codependent America and China, What Comes Next?
- Stephen Roach
- January 22, 2014
The Right Way to Restructure Conglomerates in Emerging Markets
- Tarun Khanna
- Krishna G. Palepu
- From the July–August 1999 Issue
Negotiation Strategies for a Downturn
- Mark Gordon and Danny Ertel
- April 08, 2008
America’s Lost Decade(s)
- Umair Haque
- August 20, 2010
How the Carl Icahns of the World Benefit Firms but Not Workers
- Walter Frick
- October 09, 2015

Even for Companies, the U.S. Is Split Between Haves and Have-Nots
- August 27, 2015

Enabling the Natural Act of Entrepreneurship
- Daniel Isenberg
- April 10, 2013

A Nigerian Model for Stakeholder Capitalism
- Ndubuisi Ekekwe
- May 19, 2021
It’s Manufacturing’s Turn for Special Treatment
- Gary P. Pisano
- March 05, 2012
4 Steps to Growth During a Recession
- Michael Roberto
How Open Innovation Can Help You Cope in Lean Times
- Henry W. Chesbrough
- Andrew R. Garman
- From the December 2009 Issue
The Economic Impact of the Japanese Disasters
- W. Carl Kester
- March 22, 2011
The Economy Hasn’t Changed Innovation
- Scott D. Anthony
- August 18, 2011
What the Insurance Industry Can Do to Fix Health Care
- Sukanya Soderland
- December 23, 2014

The UK Economic Crisis Might Not Be a One-Off
- John Van Reenen
- October 03, 2022
The Pope’s “War on Capitalism” and Why Rich Kids Stay Rich
- Kaisa Snellman
- December 03, 2013

Strategy in the Age of Superabundant Capital
- Michael Mankins
- Karen Harris
- David Harding
- From the March–April 2017 Issue

Adapting to Digital Disruption
- Julian Birkinshaw
- Thomas W. Malnight
- Pontus M.A. Siren
- Utsav Bhatt
- Jonathan Knee
- Alison Beard
- January 01, 2022

The Data Says Climate Change Could Cost Investors Trillions
- Andrew Winston
- April 14, 2016

The Panic of 2001 and Corporate Transparency, Accountability, and Trust (B)
- Robert F. Bruner
- September 21, 2017
Becton Dickinson: Ethics and Business Practices (A)
- Lynn Sharp Paine
- September 17, 1998
CNS Worldwide
- Robert J. Dolan
- Karthik Easwar
- May 26, 2017
Capital Controls in Chile in the 1990s (A)
- Laura Alfaro
- Rafael Di Tella
- Ingrid Vogel
- March 08, 2005
The Panic of 1837 and the Market Revolution in America (A) and (B) (Abridged)
- September 20, 2017
PAREXEL International Corp.: Scaling Up
- Regina E. Herzlinger
- Natalie Kindred
- September 26, 2013
Tata Steel Limited: Fighting Commoditization by Creating Innovative Services And Solutions
- D.V.R. Seshadri
- Devidutta Mohanty
- Raj Krishnan Shankar
- Rajesh Pandit
- March 31, 2023
Pro-invest: How to Launch a Private Equity Real Estate Fund
- Anne-Marie Carrick
- Bowen White
- Claudia Zeisberger
- August 26, 2016
Behavioural Insights Team (B)
- Michael Luca
- Patrick Rooney
- March 05, 2015
TATA MOTORS: BECOMING A GLOBAL CONTENDER
- Bala Chakravarthy
- Anna Moncef
- Sophie Coughlan
- December 09, 2008
The Panic of 2008 and Brexit: Regional Integration versus Nationalism
- October 09, 2017
Capital Controls in Chile in the 1990s (B)
- March 09, 2005
Grupo Garantia: Globalization, Industry Rivalry, and Conglomerate Diversification in Brazil (A)
- R. Jeffrey Ellis
- January 15, 2005
2016 Update: Argentina Turns the Page
- David E. Bell
- Forest L. Reinhardt
- May 11, 2016
Bridging the Digital Divide: HP's e-Inclusion (A)
- Daniel Traca
- January 01, 2004
The Curious Case of Dell (B)
- Marshall Sonenshine
- March 07, 2014
Taj Hotels: Leading Change, Driving Profitability (B)
- Anjali Raina
- Rachna Chawla
- September 18, 2017
Ti-Tech (A)
- Benson P. Shapiro
- John T. Gourville
- Craig E. Cline
- April 25, 2008
Financial Crisis and the Revolutions of 1848 (B)
- Scott Miller
- January 13, 2020
Welfare-to-Work Information and Statistics
- Rosabeth Moss Kanter
- Ellen Pruyne
- October 26, 1998

Gilead: Hepatitis-C Access Strategy (A) and (B), Teaching Plan
- V. Kasturi Rangan
- April 13, 2020
Popular Topics
Partner center.

Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies of 2021
Two cases about Hertz claimed top spots in 2021's Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies
Two cases on the uses of debt and equity at Hertz claimed top spots in the CRDT’s (Case Research and Development Team) 2021 top 40 review of cases.
Hertz (A) took the top spot. The case details the financial structure of the rental car company through the end of 2019. Hertz (B), which ranked third in CRDT’s list, describes the company’s struggles during the early part of the COVID pandemic and its eventual need to enter Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
The success of the Hertz cases was unprecedented for the top 40 list. Usually, cases take a number of years to gain popularity, but the Hertz cases claimed top spots in their first year of release. Hertz (A) also became the first ‘cooked’ case to top the annual review, as all of the other winners had been web-based ‘raw’ cases.
Besides introducing students to the complicated financing required to maintain an enormous fleet of cars, the Hertz cases also expanded the diversity of case protagonists. Kathyrn Marinello was the CEO of Hertz during this period and the CFO, Jamere Jackson is black.
Sandwiched between the two Hertz cases, Coffee 2016, a perennial best seller, finished second. “Glory, Glory, Man United!” a case about an English football team’s IPO made a surprise move to number four. Cases on search fund boards, the future of malls, Norway’s Sovereign Wealth fund, Prodigy Finance, the Mayo Clinic, and Cadbury rounded out the top ten.
Other year-end data for 2021 showed:
- Online “raw” case usage remained steady as compared to 2020 with over 35K users from 170 countries and all 50 U.S. states interacting with 196 cases.
- Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S..
- The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines.
- Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.
- A third of the cases feature a woman protagonist.
- Orders for Yale SOM case studies increased by almost 50% compared to 2020.
- The top 40 cases were supervised by 19 different Yale SOM faculty members, several supervising multiple cases.
CRDT compiled the Top 40 list by combining data from its case store, Google Analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption.
All of this year’s Top 40 cases are available for purchase from the Yale Management Media store .
And the Top 40 cases studies of 2021 are:
1. Hertz Global Holdings (A): Uses of Debt and Equity
2. Coffee 2016
3. Hertz Global Holdings (B): Uses of Debt and Equity 2020
4. Glory, Glory Man United!
5. Search Fund Company Boards: How CEOs Can Build Boards to Help Them Thrive
6. The Future of Malls: Was Decline Inevitable?
7. Strategy for Norway's Pension Fund Global
8. Prodigy Finance
9. Design at Mayo
10. Cadbury
11. City Hospital Emergency Room
13. Volkswagen
14. Marina Bay Sands
15. Shake Shack IPO
16. Mastercard
17. Netflix
18. Ant Financial
19. AXA: Creating the New CR Metrics
20. IBM Corporate Service Corps
21. Business Leadership in South Africa's 1994 Reforms
22. Alternative Meat Industry
23. Children's Premier
24. Khalil Tawil and Umi (A)
25. Palm Oil 2016
26. Teach For All: Designing a Global Network
27. What's Next? Search Fund Entrepreneurs Reflect on Life After Exit
28. Searching for a Search Fund Structure: A Student Takes a Tour of Various Options
30. Project Sammaan
31. Commonfund ESG
32. Polaroid
33. Connecticut Green Bank 2018: After the Raid
34. FieldFresh Foods
35. The Alibaba Group
36. 360 State Street: Real Options
37. Herman Miller
38. AgBiome
39. Nathan Cummings Foundation
40. Toyota 2010
1.1 What Is Economics, and Why Is It Important?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the importance of studying economics
- Explain the relationship between production and division of labor
- Evaluate the significance of scarcity
Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available. Resources, such as labor, tools, land, and raw materials are necessary to produce the goods and services we want but they exist in limited supply. Of course, the ultimate scarce resource is time- everyone, rich or poor, has just 24 expendable hours in the day to earn income to acquire goods and services, for leisure time, or for sleep. At any point in time, there is only a finite amount of resources available.
Think about it this way: In 2015 the labor force in the United States contained over 158 million workers, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The total land area was 3,794,101 square miles. While these are certainly large numbers, they are not infinite. Because these resources are limited, so are the numbers of goods and services we produce with them. Combine this with the fact that human wants seem to be virtually infinite, and you can see why scarcity is a problem.
Introduction to FRED
Data is very important in economics because it describes and measures the issues and problems that economics seek to understand. A variety of government agencies publish economic and social data. For this course, we will generally use data from the St. Louis Federal Reserve Bank's FRED database. FRED is very user friendly. It allows you to display data in tables or charts, and you can easily download it into spreadsheet form if you want to use the data for other purposes. The FRED website includes data on nearly 400,000 domestic and international variables over time, in the following broad categories:
- Money, Banking & Finance
- Population, Employment, & Labor Markets (including Income Distribution)
- National Accounts (Gross Domestic Product & its components), Flow of Funds, and International Accounts
- Production & Business Activity (including Business Cycles)
- Prices & Inflation (including the Consumer Price Index, the Producer Price Index, and the Employment Cost Index)
- International Data from other nations
- U.S. Regional Data
- Academic Data (including Penn World Tables & NBER Macrohistory database)
For more information about how to use FRED, see the variety of videos on YouTube starting with this introduction.
If you still do not believe that scarcity is a problem, consider the following: Does everyone require food to eat? Does everyone need a decent place to live? Does everyone have access to healthcare? In every country in the world, there are people who are hungry, homeless (for example, those who call park benches their beds, as Figure 1.2 shows), and in need of healthcare, just to focus on a few critical goods and services. Why is this the case? It is because of scarcity. Let’s delve into the concept of scarcity a little deeper, because it is crucial to understanding economics.
The Problem of Scarcity
Think about all the things you consume: food, shelter, clothing, transportation, healthcare, and entertainment. How do you acquire those items? You do not produce them yourself. You buy them. How do you afford the things you buy? You work for pay. If you do not, someone else does on your behalf. Yet most of us never have enough income to buy all the things we want. This is because of scarcity. So how do we solve it?
Visit this website to read about how the United States is dealing with scarcity in resources.
Every society, at every level, must make choices about how to use its resources. Families must decide whether to spend their money on a new car or a fancy vacation. Towns must choose whether to put more of the budget into police and fire protection or into the school system. Nations must decide whether to devote more funds to national defense or to protecting the environment. In most cases, there just isn’t enough money in the budget to do everything. How do we use our limited resources the best way possible, that is, to obtain the most goods and services we can? There are a couple of options. First, we could each produce everything we each consume. Alternatively, we could each produce some of what we want to consume, and “trade” for the rest of what we want. Let’s explore these options. Why do we not each just produce all of the things we consume? Think back to pioneer days, when individuals knew how to do so much more than we do today, from building their homes, to growing their crops, to hunting for food, to repairing their equipment. Most of us do not know how to do all—or any—of those things, but it is not because we could not learn. Rather, we do not have to. The reason why is something called the division and specialization of labor , a production innovation first put forth by Adam Smith ( Figure 1.3 ) in his book, The Wealth of Nations .
The Division of and Specialization of Labor
The formal study of economics began when Adam Smith (1723–1790) published his famous book The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Many authors had written on economics in the centuries before Smith, but he was the first to address the subject in a comprehensive way. In the first chapter, Smith introduces the concept of division of labor , which means that the way one produces a good or service is divided into a number of tasks that different workers perform, instead of all the tasks being done by the same person.
To illustrate division of labor, Smith counted how many tasks went into making a pin: drawing out a piece of wire, cutting it to the right length, straightening it, putting a head on one end and a point on the other, and packaging pins for sale, to name just a few. Smith counted 18 distinct tasks that different people performed—all for a pin, believe it or not!
Modern businesses divide tasks as well. Even a relatively simple business like a restaurant divides the task of serving meals into a range of jobs like top chef, sous chefs, less-skilled kitchen help, servers to wait on the tables, a greeter at the door, janitors to clean up, and a business manager to handle paychecks and bills—not to mention the economic connections a restaurant has with suppliers of food, furniture, kitchen equipment, and the building where it is located. A complex business like a large manufacturing factory, such as the shoe factory ( Figure 1.4 ), or a hospital can have hundreds of job classifications.
Why the Division of Labor Increases Production
When we divide and subdivide the tasks involved with producing a good or service, workers and businesses can produce a greater quantity of output. In his observations of pin factories, Smith noticed that one worker alone might make 20 pins in a day, but that a small business of 10 workers (some of whom would need to complete two or three of the 18 tasks involved with pin-making), could make 48,000 pins in a day. How can a group of workers, each specializing in certain tasks, produce so much more than the same number of workers who try to produce the entire good or service by themselves? Smith offered three reasons.
First, specialization in a particular small job allows workers to focus on the parts of the production process where they have an advantage. (In later chapters, we will develop this idea by discussing comparative advantage .) People have different skills, talents, and interests, so they will be better at some jobs than at others. The particular advantages may be based on educational choices, which are in turn shaped by interests and talents. Only those with medical degrees qualify to become doctors, for instance. For some goods, geography affects specialization. For example, it is easier to be a wheat farmer in North Dakota than in Florida, but easier to run a tourist hotel in Florida than in North Dakota. If you live in or near a big city, it is easier to attract enough customers to operate a successful dry cleaning business or movie theater than if you live in a sparsely populated rural area. Whatever the reason, if people specialize in the production of what they do best, they will be more effective than if they produce a combination of things, some of which they are good at and some of which they are not.
Second, workers who specialize in certain tasks often learn to produce more quickly and with higher quality. This pattern holds true for many workers, including assembly line laborers who build cars, stylists who cut hair, and doctors who perform heart surgery. In fact, specialized workers often know their jobs well enough to suggest innovative ways to do their work faster and better.
A similar pattern often operates within businesses. In many cases, a business that focuses on one or a few products (sometimes called its “ core competency ”) is more successful than firms that try to make a wide range of products.
Third, specialization allows businesses to take advantage of economies of scale , which means that for many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines. For example, if a factory produces only 100 cars per year, each car will be quite expensive to make on average. However, if a factory produces 50,000 cars each year, then it can set up an assembly line with huge machines and workers performing specialized tasks, and the average cost of production per car will be lower. The ultimate result of workers who can focus on their preferences and talents, learn to do their specialized jobs better, and work in larger organizations is that society as a whole can produce and consume far more than if each person tried to produce all of their own goods and services. The division and specialization of labor has been a force against the problem of scarcity.
Trade and Markets
Specialization only makes sense, though, if workers can use the pay they receive for doing their jobs to purchase the other goods and services that they need. In short, specialization requires trade.
You do not have to know anything about electronics or sound systems to play music—you just buy an iPod or MP3 player, download the music, and listen. You do not have to know anything about artificial fibers or the construction of sewing machines if you need a jacket—you just buy the jacket and wear it. You do not need to know anything about internal combustion engines to operate a car—you just get in and drive. Instead of trying to acquire all the knowledge and skills involved in producing all of the goods and services that you wish to consume, the market allows you to learn a specialized set of skills and then use the pay you receive to buy the goods and services you need or want. This is how our modern society has evolved into a strong economy.
Why Study Economics?
Now that you have an overview on what economics studies, let’s quickly discuss why you are right to study it. Economics is not primarily a collection of facts to memorize, although there are plenty of important concepts to learn. Instead, think of economics as a collection of questions to answer or puzzles to work. Most importantly, economics provides the tools to solve those puzzles.
Consider the complex and critical issue of education barriers on national and regional levels, which affect millions of people and result in widespread poverty and inequality. Governments, aid organizations, and wealthy individuals spend billions of dollars each year trying to address these issues. Nations announce the revitalization of their education programs; tech companies donate devices and infrastructure, and celebrities and charities build schools and sponsor students. Yet the problems remain, sometimes almost as pronounced as they were before the intervention. Why is that the case? In 2019, three economists—Esther Duflo, Abhijit Banerjee, and Michael Kremer—were awarded the Nobel Prize for their work to answer those questions. They worked diligently to break the widespread problems into smaller pieces, and experimented with small interventions to test success. The award citation credited their work with giving the world better tools and information to address poverty and improve education. Esther Duflo, who is the youngest person and second woman to win the Nobel Prize in Economics, said, "We believed that like the war on cancer, the war on poverty was not going to be won in one major battle, but in a series of small triumphs. . . . This work and the culture of learning that it fostered in governments has led to real improvement in the lives of hundreds of millions of poor people.”
As you can see, economics affects far more than business. For example:
- Virtually every major problem facing the world today, from global warming, to world poverty, to the conflicts in Syria, Afghanistan, and Somalia, has an economic dimension. If you are going to be part of solving those problems, you need to be able to understand them. Economics is crucial.
- It is hard to overstate the importance of economics to good citizenship. You need to be able to vote intelligently on budgets, regulations, and laws in general. When the U.S. government came close to a standstill at the end of 2012 due to the “fiscal cliff,” what were the issues? Did you know?
- A basic understanding of economics makes you a well-rounded thinker. When you read articles about economic issues, you will understand and be able to evaluate the writer’s argument. When you hear classmates, co-workers, or political candidates talking about economics, you will be able to distinguish between common sense and nonsense. You will find new ways of thinking about current events and about personal and business decisions, as well as current events and politics.
The study of economics does not dictate the answers, but it can illuminate the different choices.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro, Daniel MacDonald
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Economics 3e
- Publication date: Dec 14, 2022
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-1-what-is-economics-and-why-is-it-important
© Jan 23, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Help | Advanced Search
Economics > General Economics
Title: long-term forecasts of statewide travel demand patterns using large-scale mobile phone gps data: a case study of indiana.
Abstract: The growth in availability of large-scale GPS mobility data from mobile devices has the potential to aid traditional travel demand models (TDMs) such as the four-step planning model, but those processing methods are not commonly used in practice. In this study, we show the application of trip generation and trip distribution modeling using GPS data from smartphones in the state of Indiana. This involves extracting trip segments from the data and inferring the phone users' home locations, adjusting for data representativeness, and using a data-driven travel time-based cost function for the trip distribution model. The trip generation and interchange patterns in the state are modeled for 2025, 2035, and 2045. Employment sectors like industry and retail are observed to influence trip making behavior more than other sectors. The travel growth is predicted to be mostly concentrated in the suburban regions, with a small decline in the urban cores. Further, although the majority of the growth in trip flows over the years is expected to come from the corridors between the major urban centers of the state, relative interzonal trip flow growth will likely be uniformly spread throughout the state. We also validate our results with the forecasts of two travel demand models, finding a difference of 5-15% in overall trip counts. Our GPS data-based demand model will contribute towards augmenting the conventional statewide travel demand model developed by the state and regional planning agencies.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- Case Studies
- Online Courses
- Find an Expert
- Concepts & Biases
- Introduction to BE
- Sales & Conversions
- Product Design
- Customer Satisfaction
Case studies and examples of behavioral economics applications from marketing, sales, and other areas. Discover ground-breaking ideas and fascinating solutions.
List of 63 Articles

- Case study by Nir Eyal
Case Study: How Clever Product Design Turned Taking Medication into a Habit for Asthmatics

- Case study by Dectech
Case Study: An Insurance Company Reduced Fraud by 36% with Clever Messaging Rooted in Psychology

- Case study by MINDWORX Behavioral Consulting
Case Study: An Insurance Company Increased Email Conversions by 167% Using 3 Behavioral Principles

Case Study: How the Insurer Lemonade Built a Powerful Online Sales Process with Psychology at Its Core

- Case study by Patrick Fagan
Case Study: How a Health Club Created an Online Sales Process that Outperformed Face-to-face Sales

- Case study by MIDA
Case Study: How Porsche Impacted Sales by 28% by Confronting Sales Floor Biases

- Case study by Andrea Olson
Case Study: How an Insurance Company Used Behavioral Science to Get 30% More Customers to Use Certified Repair Shops

- Case study by Jez Groom
Case Study: An Ingenious Restaurant Menu Redesign that Increased Average Customer Spend
- Case study by Charlotte Blank
Case Study: An Eshop Increased CTR on Recommended Products by 40% by Being More Transparent
Subscribe to receive the most interesting case studies and articles biweekly.
This site uses cookies to provide services, personalise ads and to analyse traffic. You consent to our cookies if you continue to use our website. Read More .
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Microeconomics →

- 29 Nov 2022
- Research & Ideas
How Much More Would Holiday Shoppers Pay to Wear Something Rare?
Economic worries will make pricing strategy even more critical this holiday season. Research by Chiara Farronato reveals the value that hip consumers see in hard-to-find products. Are companies simply making too many goods?

- 07 Jan 2019
The Better Way to Forecast the Future
We can forecast hurricane paths with great certainty, yet many businesses can't predict a supply chain snafu just around the corner. Yael Grushka-Cockayne says crowdsourcing can help. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This study sheds light on the political pathology of fraudulent, illegal, and corrupt business practices. Features of the Chinese system—including regulatory gaps, a lack of formal means of property protection, and pervasive uncertainty—seem to facilitate the rise of mafia systems. 02 Feb 2021. Working Paper Summaries.
Covering micro as well as macro economics, some of IBSCDC's case studies require a prior understanding of certain economic concepts, while many case studies can be used to derive the underlying economic concepts. Topics like Demand and Supply Analysis, Market Structures (Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic, etc.), Cost Structures, etc., in micro economics and national income accounting ...
Below is a representation of the Victoria Housing Market. 1. Label Figure CS3 a. with the Equilibrium price and quantity, and label supply and demand curves as either renters or landlords. Figure CS3 a. If supply is equal to demand there should be no vacancy, but we know that a 0% vacancy rate would be an extremely difficult market for renters. 2.
Find case studies in economics by topic, level and source. Browse introductory, intermediate and advanced case studies from various journals and websites, or use the teaching case studies section for more resources.
Case studies. Case studies describe real world practical examples, including successes, issues and challenges. To find case studies using LibrarySearch or databases, add "case study" to your search terms. The case study handbook a student's guide. This e-book provides tips on how to read, analyse and write about cases.
A review article on the use of case studies in economics education, covering their origins, forms, benefits and research. The article provides suggestions on how to employ case studies in teaching economics and analyses the empirical evidence on their effectiveness.
Learn how LSE economists have made a difference in various fields of research, from poverty alleviation to financial stability. Explore the case studies of five professors and their collaborators, with links to their publications and impact.
Conclusion. Solving an case study in economics writing is an enriching experience that bridges theory and practice. It requires a structured approach, from understanding the case to making well-informed recommendations. By thoroughly analyzing the economic concepts, interpreting data, and applying relevant theories, you can arrive at strategic ...
Explore real-life examples of economic concepts and frameworks from around the world. Browse cases on topics such as health care, data visualization, border conflict, education, renewable energy, and IMF leadership.
Case Studies. Discover all the ways our 2,000 customers succeed, thrive and grow with Oxford Economics. Read success stories from Oxford Economics' clients in sectors such as pensions, energy and Real Estate. Learn how they solved their business challenges, supported their businesses' growth and adapted to new markets using Oxford Economics ...
Case studies. A collection of business cases providing unlimited access to more than 5,500 authoritative cases from over 120 countries. SAGE curates interdisciplinary cases on in-demand subjects such as entrepreneurship, accounting, healthcare management, leadership, social enterprise, and more. Includes full access to over 15,000 business case ...
In this case study, we will analyze what has happened to these prices over time and the impact this has had on oil producers from the lens of producer theory. To simplify our case study, let's assume that the oil market is perfect competition. 1. Consider the following producer theory model for a single firm producing oil, and the aggregate ...
W. Carl Kester. Human suffering is certainly our main concern in the immediate aftermath of Japan's 3/11 tragedy. But even as we focus on immediate human needs, we cannot avoid recognizing ...
criticize an argument, present a case study, extend a theory, evaluate an intellectual debate and so on. • Response Papers (1-2pp.). Response papers might involve summarizing the weekly readings or answering a specific question about the text. These will help get you thinking and stimulate class
Orders for Yale SOM case studies increased by almost 50% compared to 2020. The top 40 cases were supervised by 19 different Yale SOM faculty members, several supervising multiple cases. CRDT compiled the Top 40 list by combining data from its case store, Google Analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
The formal study of economics began when Adam Smith (1723-1790) published his famous book The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Many authors had written on economics in the centuries before Smith, but he was the first to address the subject in a comprehensive way.
The growth in availability of large-scale GPS mobility data from mobile devices has the potential to aid traditional travel demand models (TDMs) such as the four-step planning model, but those processing methods are not commonly used in practice. In this study, we show the application of trip generation and trip distribution modeling using GPS data from smartphones in the state of Indiana ...
1. Introduction. Online retailing is booming both globally and in emerging markets like Vietnam. Despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, the online retail sector saw a remarkable growth of 15% ($13.2 billion) in 2021 (VECOM, Citation 2020), with estimates projecting a growth rate of 29% from 2020 to 2025, resulting in a market size of $52 billion by 2025 (Anh, Citation 2021).
Case studies and examples of behavioral economics applications from marketing, sales and other business areas. Discover how top experts came up with ground-breaking ideas. ... It's packed full of business case studies, online courses, and how-to guides created by the world's top experts. InsideBE helps you apply behavioral insights to drive ...
We can forecast hurricane paths with great certainty, yet many businesses can't predict a supply chain snafu just around the corner. Yael Grushka-Cockayne says crowdsourcing can help. Open for comment; 1 Comment posted. Read Articles about Microeconomics- HBS Working Knowledge: The latest business management research and ideas from HBS faculty.