- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution


Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- News & Views
- Critical thinking in...
Critical thinking in healthcare and education
- Related content
- Peer review
- Jonathan M Sharples , professor 1 ,
- Andrew D Oxman , research director 2 ,
- Kamal R Mahtani , clinical lecturer 3 ,
- Iain Chalmers , coordinator 4 ,
- Sandy Oliver , professor 1 ,
- Kevan Collins , chief executive 5 ,
- Astrid Austvoll-Dahlgren , senior researcher 2 ,
- Tammy Hoffmann , professor 6
- 1 EPPI-Centre, UCL Department of Social Science, London, UK
- 2 Global Health Unit, Norwegian Institute of Public Health, Oslo, Norway
- 3 Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford University, Oxford, UK
- 4 James Lind Initiative, Oxford, UK
- 5 Education Endowment Foundation, London, UK
- 6 Centre for Research in Evidence-Based Practice, Bond University, Gold Coast, Australia
- Correspondence to: J M Sharples Jonathan.Sharples{at}eefoundation.org.uk
Critical thinking is just one skill crucial to evidence based practice in healthcare and education, write Jonathan Sharples and colleagues , who see exciting opportunities for cross sector collaboration
Imagine you are a primary care doctor. A patient comes into your office with acute, atypical chest pain. Immediately you consider the patient’s sex and age, and you begin to think about what questions to ask and what diagnoses and diagnostic tests to consider. You will also need to think about what treatments to consider and how to communicate with the patient and potentially with the patient’s family and other healthcare providers. Some of what you do will be done reflexively, with little explicit thought, but caring for most patients also requires you to think critically about what you are going to do.
Critical thinking, the ability to think clearly and rationally about what to do or what to believe, is essential for the practice of medicine. Few doctors are likely to argue with this. Yet, until recently, the UK regulator the General Medical Council and similar bodies in North America did not mention “critical thinking” anywhere in their standards for licensing and accreditation, 1 and critical thinking is not explicitly taught or assessed in most education programmes for health professionals. 2
Moreover, although more than 2800 articles indexed by PubMed have “critical thinking” in the title or abstract, most are about nursing. We argue that it is important for clinicians and patients to learn to think critically and that the teaching and learning of these skills should be considered explicitly. Given the shared interest in critical thinking with broader education, we also highlight why healthcare and education professionals and researchers need to work together to enable people to think critically about the health choices they make throughout life.
Essential skills for doctors and patients
Critical thinking is not a new concept in education: at the beginning of the last century the US educational reformer John Dewey identified the need to help students “to think well.” 3 Critical thinking encompasses a broad set of skills and dispositions, including cognitive skills (such as analysis, inference, and self regulation); approaches to specific questions or problems (orderliness, diligence, and reasonableness); and approaches to life in general (inquisitiveness, concern with being well informed, and open mindedness). 4
An increasing body of evidence highlights that developing critical thinking skills can benefit academic outcomes as well as wider reasoning and problem solving capabilities. 5 For example, the Thinking, Doing, Talking Science programme trains teachers in a repertoire of strategies that encourage pupils to use critical thinking skills in primary school science lessons. An independently conducted randomised trial of this approach found that it had a positive impact on pupils’ science attainment, with signs that it was particularly beneficial for pupils from poorer families. 6
In medicine, increasing attention has been paid to “critical appraisal” in the past 40 years. Critical appraisal is a subset of critical thinking that focuses on how to use research evidence to inform health decisions. 7 8 9 The need for critical appraisal in medicine was recognised at least 75 years ago, 10 and critical appraisal has been recognised for some decades as an essential competency for healthcare professionals. 11 The General Medical Council’s Good Medical Practice guidance includes the need for doctors to be able to “provide effective treatments based on the best available evidence.” 12
If patients and the public are to make well informed health choices, they must also be able to assess the reliability of health claims and information. This is something that most people struggle to do, and it is becoming increasingly important because patients are taking on a bigger role in managing their health and making healthcare decisions, 13 while needing to cope with more and more health information, much of which is not reliable. 14 15 16 17
Teaching critical thinking
Although critical thinking skills are given limited explicit attention in standards for medical education, they are included as a key competency in most frameworks for national curriculums for primary and secondary schools in many countries. 18 Nonetheless, much health and science education, and education generally, still tends towards rote learning rather than the promotion of critical thinking. 19 20 This matters because the ability to think critically is an essential life skill relevant to decision making in many circumstances. The capacity to think critically is, like a lot of learning, developed in school and the home: parental influence creates advantage for pupils who live in homes where they are encouraged to think and talk about what they are doing. This, importantly, goes beyond simply completing tasks to creating deeper understanding of learning processes. As such, the “critical thinking gap” between children from disadvantaged communities and their more advantaged peers requires attention as early as possible.
Although it is possible to teach critical thinking to adults, it is likely to be more productive if the grounds for this have been laid down in an educational environment early in life, starting in primary school. Erroneous beliefs, attitudes, and behaviours developed during childhood may be difficult to change later. 21 22 This also applies to medical education and to health professionals. It becomes increasingly difficult to teach these skills without a foundation to build on and adequate time to learn them.
Strategies for teaching students to think critically have been evaluated in health and medical education; in science, technology, engineering, and maths; and in other subjects. 23 These studies suggest that critical thinking skills can be taught and that in the absence of explicit teaching of critical thinking, important deficiencies emerge in the abilities of students to make sound judgments. In healthcare studies, many medical students score poorly on tests that measure the ability to think critically , and the ability to think critically is correlated with academic success. 24 25
Evaluations of strategies for teaching critical thinking in medicine have focused primarily on critical appraisal skills as part of evidence based healthcare. An overview of systematic reviews of these studies suggests that improving evidence based healthcare competencies is likely to require multifaceted, clinically integrated approaches that include assessment. 26
Cross sector collaboration
Informed Health Choices, an international project aiming to improve decision making, shows the opportunities and benefits of cross sector collaboration between education and health. 27 This project has brought together people working in education and healthcare to develop a curriculum and learning resources for critical thinking about any action that is claimed to improve health. It aims to develop, identify, and promote the use of effective learning resources, beginning at primary school, to help people to make well informed choices as patients and health professionals, and well informed decisions as citizens and policy makers.
The project has drawn on several approaches used in education, including the development of a “spiral curriculum,” measurement tools, and the design of learning resources. A spiral curriculum begins with determining what people should know and be able to do, and outlines where they should begin and how they should progress to reach these goals. The basic ideas are revisited repeatedly, building on them until the student has grasped a deep understanding of the concepts. 28 29 The project has also drawn on educational research and methods to develop reliable and valid tools for measuring the extent to which those goals have been achieved. 30 31 32 The development of learning resources to teach these skills has been informed by educational research, including educational psychology, motivational psychology, and research and methods for developing learning games. 33 34 35 It has also built on the traditions of clinical epidemiology and evidence based medicine to identify the key concepts required to assess health claims. 29
It is difficult to teach critical thinking abstractly, so focusing on health may have advantages beyond the public health benefits of increasing health literacy. 36 Nearly everyone is interested in health, including children, making it easy to engage learners. It is also immediately relevant to students. As reported by one 10 year old in a school that piloted primary school resources, this is about “things we might actually use instead of things we might use when we are all grown up and by then we’ll forget.” Although the current evaluation of the project is focusing on outcomes relating to appraisal of treatment claims, if the intervention shows promise the next step could be to explore how these skills translate to wider educational contexts and outcomes.
Beyond critical thinking
Exciting opportunities for cross sector collaboration are emerging between healthcare and education. Although critical thinking is a useful example of this, other themes cross the education and healthcare domains, including nutrition, exercise, educational neuroscience, learning disabilities and special education needs, and mental health.
In addition to shared topics, several common methodological and conceptual issues also provide opportunities for sharing ideas and innovations and learning from mistakes and successes. For example, the Education Endowment Foundation is the UK government’s What Works Centre for education, aiming to improve evidence based decision making. Discussions hosted by the foundation are exploring how methods to develop guidelines in healthcare can be adapted and applied in education and other sectors.
Similarly, the foundation’s universal use of independent evaluation for teaching and learning interventions is an approach that should be explored, adapted, and applied in healthcare. Since the development and evaluation of educational interventions are separated, evaluators have no vested interested in the results of the assessment, all results are published, and bias and spin in how results are analysed and presented are reduced. By contrast, industry sponsorship of drug and device studies consistently produces results that favour the manufacturer. 37
Another example of joint working between educators and health is the Best Evidence Medical Education Collaboration, an international collaboration focused on improving education of health professionals. 38 And in the UK, the Centre for Evidence Based Medicine coordinates Evidence in School Teaching (Einstein), a project that supports introducing evidence based medicine as part of wider science activities in schools. 39 It aims to engage students, teachers, and the public in evidence based medicine and develop critical thinking to assess health claims and make better choices.
Collaboration has also been important in the development of the Critical Thinking and Appraisal Resource Library (CARL), 40 a set of resources designed to help people understand fair comparisons of treatments. An important aim of CARL is to promote evaluation of these critical thinking resources and interventions, some of which are currently under way at the Education Endowment Foundation. On 22 May 2017, the foundation is also cohosting an event with the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health that will focus on their shared interest in critical thinking and appraisal skills.
Education and healthcare have overlapping interests. Doctors, teachers, researchers, patients, learners, and the public can all benefit from working together to help people to think critically about the choices they make. Events such as the global evidence summit in September 2017 ( https://globalevidencesummit.org ) can help bring people together and build on current international experience.
Contributors and sources: This article reflects conclusions from discussions during 2016 among education and health service researchers exploring opportunities for cross sector collaboration and learning. This group includes people with a longstanding interest in evidence informed policy and practice, with expertise in evaluation design, reviewing methodology, knowledge mobilisation, and critical thinking and appraisal.
Competing interests: We have read and understood BMJ policy on declaration of interests and declare that we have no competing interests.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
- ↵ Krupat E, Sprague JM, Wolpaw D, Haidet P, Hatem D, O’Brien B. Thinking critically about critical thinking: ability, disposition or both? Med Educ 2011 ; 357 : 625 - 35 . doi:10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03910.x pmid:21564200 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Huang GC, Newman LR, Schwartzstein RM. Critical thinking in health professions education: summary and consensus statements of the millennium conference 2011. Teach Learn Med 2014 ; 357 : 95 - 102 . doi:10.1080/10401334.2013.857335 pmid:24405353 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Dewey J. How we think. D C Heath, 1910 . https://archive.org/details/howwethink000838mbp doi:10.1037/10903-000 .
- ↵ Facione PA. Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations. American Philosophical Association, 1990 , http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED315423.pdf .
- ↵ Higgins S, Katsipataki M, Coleman R, et al. The Sutton Trust-Education Endowment Foundation Teaching and Learning Toolkit. Education Endowment Foundation, 2015 .
- ↵ Hanley P, Slavin RE, Elliot L. Thinking, doing, talking science. Evaluation report and executive summary. Education Endowment Foundation, 2015 , https://v1.educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/uploads/pdf/Oxford_Science.pdf .
- ↵ Sackett DL. How to read clinical journals: I. why to read them and how to start reading them critically . Can Med Assoc J 1981 ; 357 : 555 - 8 . pmid:7471000 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Guyatt G, Cairns J, Churchill D, et al. Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. Evidence-based medicine. A new approach to teaching the practice of medicine . JAMA 1992 ; 357 : 2420 - 5 . doi:10.1001/jama.1992.03490170092032 pmid:1404801 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Oxman AD, Sackett DL, Guyatt GH. The Evidence-Based Medicine Working Group. Users’ guides to the medical literature. I. How to get started . JAMA 1993 ; 357 : 2093 - 5 . doi:10.1001/jama.1993.03510170083036 pmid:8411577 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Rynearson EH. Endocrinology: a critical appraisal . Cal West Med 1940 ; 357 : 257 - 9 . pmid:18745588 . OpenUrl
- ↵ General Medical Council. Tomorrow's doctors. General Medical Council, 1993. http://www.gmc-uk.org/10a_annex_a.pdf_25398162.pdf
- ↵ General Medical Council. Good medical practice. General Medical Council, 2013. http://www.gmc-uk.org/static/documents/content/GMP_.pdf
- ↵ Edwards A, Elwyn G. Shared decision-making in health care: achieving evidence-based patient choice. 2nd ed . Oxford University Press, 2009 .
- ↵ Sumner P, Vivian-Griffiths S, Boivin J, et al. Exaggerations and caveats in press releases and health-related science news. PLoS One 2016 ; 357 : e0168217 . doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0168217 pmid:27978540 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Schwartz LM, Woloshin S, Andrews A, Stukel TA. Influence of medical journal press releases on the quality of associated newspaper coverage: retrospective cohort study. BMJ 2012 ; 357 : d8164 . doi:10.1136/bmj.d8164 . pmid:22286507 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Glenton C, Paulsen EJ, Oxman AD. Portals to Wonderland: health portals lead to confusing information about the effects of health care. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2005 ; 357 : 7 . doi:10.1186/1472-6947-5-7 pmid:15769291 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Moynihan R, Bero L, Ross-Degnan D, et al. Coverage by the news media of the benefits and risks of medications . N Engl J Med 2000 ; 357 : 1645 - 50 . doi:10.1056/NEJM200006013422206 pmid:10833211 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Voogt J, Roblin NP. A comparative analysis of international frameworks for 21st century competences: implications for national curriculum policies. J Curric Stud 2012 ; 357 : 299 - 321 doi:10.1080/00220272.2012.668938 . OpenUrl
- ↵ National Research Council. Taking science to school: learning and teaching science in grades K-8. National Academies Press, 2007 .
- ↵ Nordheim L, Pettersen KS, Flottorp S, Hjälmhult E. Critical appraisal of health claims: science teachers’ perceptions and practices . Health Educ J 2016 ; 357 : 449 - 66 doi:10.1108/HE-04-2015-0016 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Committee on Science Learning. Kindergarten through eighth grade. How children learn science. In: Duschl RA, Schweingruber A, Shouse AW, eds. Taking science to school: learning and teaching science in grades K-8. National Academies Press, 2007 .
- ↵ Vosniadou S. International handbook of research on conceptual change. 2nd ed . Routledge, 2013 .
- ↵ Abrami PC, Bernard RM, Borokhovski E, Waddington DI, Wade CA, Persson T. Strategies for teaching students to think critically a meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 2015 ; 357 : 275 - 314 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Ross D, Schipper S, Westbury C, et al. Examining critical thinking skills in family medicine residents . Fam Med 2016 ; 357 : 121 - 6 . pmid:26950783 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Ross D, Loeffler K, Schipper S, Vandermeer B, Allan GM. Do scores on three commonly used measures of critical thinking correlate with academic success of health professions trainees? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad Med 2013 ; 357 : 724 - 34 . doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e31828b0823 pmid:23524925 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Young T, Rohwer A, Volmink J, Clarke M. What are the effects of teaching evidence-based health care (EBHC)? Overview of systematic reviews. PLoS One 2014 ; 357 : e86706 . doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086706 pmid:24489771 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Informed Health Choices Group. Informed health choices. www.informedhealthchoices.org
- ↵ Harden RM, Stamper N. What is a spiral curriculum? Med Teach 1999 ; 357 : 141 - 3 . doi:10.1080/01421599979752 pmid:21275727 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Austvoll-Dahlgren A, Oxman AD, Chalmers I, et al. Key concepts that people need to understand to assess claims about treatment effects. J Evid Based Med 2015 ; 357 : 112 - 25 . doi:10.1111/jebm.12160 pmid:26107552 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Austvoll-Dahlgren A, Nsangi A, Semakula D. Interventions and assessment tools addressing key concepts people need to know to appraise claims about treatment effects: a systematic mapping review. Syst Rev 2016 ; 357 : 215 . doi:10.1186/s13643-016-0389-z pmid:28034307 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Austvoll-Dahlgren A, Semakula D, Nsangi A, et al. The development of the “claim evaluation tools”: assessing critical thinking about effects. BMJ Open forthcoming .
- ↵ Austvoll-Dahlgren A, Guttersrud Ø, Semakula D, Nsangi A, Oxman AD. Measuring ability to assess claims about treatment effects: a latent trait analysis of the claim evaluation tools using Rasch modelling. BMJ Open [ forthcoming ].
- ↵ Sandoval WA, Sodian B, Koerber S, Wong J. Developing children’s early competencies to engage with science . Educ Psychol 2014 ; 357 : 139 - 52 doi:10.1080/00461520.2014.917589 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Pintrich PR. A motivational science perspective on the role of student motivation in learning and teaching contexts . J Educ Psychol 2003 ; 357 : 667 - 86 doi:10.1037/0022-0663.95.4.667 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Clark DB, Tanner-Smith EE, Killingsworth SS. Digital games, design, and learning: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Rev Educ Res 2016 ; 357 : 79 - 122 . doi:10.3102/0034654315582065 pmid:26937054 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Berkman ND, Sheridan SL, Donahue KE, Halpern DJ, Crotty K. Low health literacy and health outcomes: an updated systematic review . Ann Intern Med 2011 ; 357 : 97 - 107 . doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-00005 pmid:21768583 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Lundh A, Sismondo S, Lexchin J, Busuioc OA, Bero L. Industry sponsorship and research outcome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012 ; 357 : MR000033 . pmid:23235689 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Thistlethwaite J, Hammick M, The Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) Collaboration: into the next decade. Med Teach 2010 ; 357 : 880 - 2 . doi:10.3109/0142159X.2010.519068 pmid:21039096 . OpenUrl
- ↵ Centre for Evidence Based Medicine. Einstein—taking EBM to schools. http://www.cebm.net/taking-ebm-schools
- ↵ Castle JC, Chalmers I, Atkinson P, et al. Establishing a library of resources to help people understand key concepts in assessing treatment claims—the Critical Thinking and Appraisal Resource Library (CARL). PLoS One forthcoming .
You are using an outdated browser
Unfortunately Ausmed.com does not support your browser. Please upgrade your browser to continue.
Cultivating Critical Thinking in Healthcare
Published: 06 January 2019

Critical thinking skills have been linked to improved patient outcomes, better quality patient care and improved safety outcomes in healthcare (Jacob et al. 2017).
Given this, it's necessary for educators in healthcare to stimulate and lead further dialogue about how these skills are taught , assessed and integrated into the design and development of staff and nurse education and training programs (Papp et al. 2014).
So, what exactly is critical thinking and how can healthcare educators cultivate it amongst their staff?
What is Critical Thinking?
In general terms, ‘ critical thinking ’ is often used, and perhaps confused, with problem-solving and clinical decision-making skills .
In practice, however, problem-solving tends to focus on the identification and resolution of a problem, whilst critical thinking goes beyond this to incorporate asking skilled questions and critiquing solutions .
Several formal definitions of critical thinking can be found in literature, but in the view of Kahlke and Eva (2018), most of these definitions have limitations. That said, Papp et al. (2014) offer a useful starting point, suggesting that critical thinking is:
‘The ability to apply higher order cognitive skills and the disposition to be deliberate about thinking that leads to action that is logical and appropriate.’
The Foundation for Critical Thinking (2017) expands on this and suggests that:
‘Critical thinking is that mode of thinking, about any subject, content, or problem, in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully analysing, assessing, and reconstructing it.’
They go on to suggest that critical thinking is:
- Self-directed
- Self-disciplined
- Self-monitored
- Self-corrective.

Key Qualities and Characteristics of a Critical Thinker
Given that critical thinking is a process that encompasses conceptualisation , application , analysis , synthesis , evaluation and reflection , what qualities should be expected from a critical thinker?
In answering this question, Fortepiani (2018) suggests that critical thinkers should be able to:
- Formulate clear and precise questions
- Gather, assess and interpret relevant information
- Reach relevant well-reasoned conclusions and solutions
- Think open-mindedly, recognising their own assumptions
- Communicate effectively with others on solutions to complex problems.
All of these qualities are important, however, good communication skills are generally considered to be the bedrock of critical thinking. Why? Because they help to create a dialogue that invites questions, reflections and an open-minded approach, as well as generating a positive learning environment needed to support all forms of communication.
Lippincott Solutions (2018) outlines a broad spectrum of characteristics attributed to strong critical thinkers. They include:
- Inquisitiveness with regard to a wide range of issues
- A concern to become and remain well-informed
- Alertness to opportunities to use critical thinking
- Self-confidence in one’s own abilities to reason
- Open mindedness regarding divergent world views
- Flexibility in considering alternatives and opinions
- Understanding the opinions of other people
- Fair-mindedness in appraising reasoning
- Honesty in facing one’s own biases, prejudices, stereotypes or egocentric tendencies
- A willingness to reconsider and revise views where honest reflection suggests that change is warranted.
Papp et al. (2014) also helpfully suggest that the following five milestones can be used as a guide to help develop competency in critical thinking:
Stage 1: Unreflective Thinker
At this stage, the unreflective thinker can’t examine their own actions and cognitive processes and is unaware of different approaches to thinking.
Stage 2: Beginning Critical Thinker
Here, the learner begins to think critically and starts to recognise cognitive differences in other people. However, external motivation is needed to sustain reflection on the learners’ own thought processes.
Stage 3: Practicing Critical Thinker
By now, the learner is familiar with their own thinking processes and makes a conscious effort to practice critical thinking.
Stage 4: Advanced Critical Thinker
As an advanced critical thinker, the learner is able to identify different cognitive processes and consciously uses critical thinking skills.
Stage 5: Accomplished Critical Thinker
At this stage, the skilled critical thinker can take charge of their thinking and habitually monitors, revises and rethinks approaches for continual improvement of their cognitive strategies.
Facilitating Critical Thinking in Healthcare
A common challenge for many educators and facilitators in healthcare is encouraging students to move away from passive learning towards active learning situations that require critical thinking skills.
Just as there are similarities among the definitions of critical thinking across subject areas and levels, there are also several generally recognised hallmarks of teaching for critical thinking . These include:
- Promoting interaction among students as they learn
- Asking open ended questions that do not assume one right answer
- Allowing sufficient time to reflect on the questions asked or problems posed
- Teaching for transfer - helping learners to see how a newly acquired skill can apply to other situations and experiences.
(Lippincott Solutions 2018)
Snyder and Snyder (2008) also make the point that it’s helpful for educators and facilitators to be aware of any initial resistance that learners may have and try to guide them through the process. They should aim to create a learning environment where learners can feel comfortable thinking through an answer rather than simply having an answer given to them.
Examples include using peer coaching techniques , mentoring or preceptorship to engage students in active learning and critical thinking skills, or integrating project-based learning activities that require students to apply their knowledge in a realistic healthcare environment.
Carvalhoa et al. (2017) also advocate problem-based learning as a widely used and successful way of stimulating critical thinking skills in the learner. This view is echoed by Tsui-Mei (2015), who notes that critical thinking, systematic analysis and curiosity significantly improve after practice-based learning .
Integrating Critical Thinking Skills Into Curriculum Design
Most educators agree that critical thinking can’t easily be developed if the program curriculum is not designed to support it. This means that a deep understanding of the nature and value of critical thinking skills needs to be present from the outset of the curriculum design process , and not just bolted on as an afterthought.
In the view of Fortepiani (2018), critical thinking skills can be summarised by the statement that 'thinking is driven by questions', which means that teaching materials need to be designed in such a way as to encourage students to expand their learning by asking questions that generate further questions and stimulate the thinking process. Ideal questions are those that:
- Embrace complexity
- Challenge assumptions and points of view
- Question the source of information
- Explore variable interpretations and potential implications of information.
To put it another way, asking questions with limiting, thought-stopping answers inhibits the development of critical thinking. This means that educators must ideally be critical thinkers themselves .
Drawing these threads together, The Foundation for Critical Thinking (2017) offers us a simple reminder that even though it’s human nature to be ‘thinking’ most of the time, most thoughts, if not guided and structured, tend to be biased, distorted, partial, uninformed or even prejudiced.
They also note that the quality of work depends precisely on the quality of the practitioners’ thought processes. Given that practitioners are being asked to meet the challenge of ever more complex care, the importance of cultivating critical thinking skills, alongside advanced problem-solving skills , seems to be taking on new importance.
Additional Resources
- The Emotionally Intelligent Nurse | Ausmed Article
- Refining Competency-Based Assessment | Ausmed Article
- Socratic Questioning in Healthcare | Ausmed Article
- Carvalhoa, D P S R P et al. 2017, 'Strategies Used for the Promotion of Critical Thinking in Nursing Undergraduate Education: A Systematic Review', Nurse Education Today , vol. 57, pp. 103-10, viewed 7 December 2018, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0260691717301715
- Fortepiani, L A 2017, 'Critical Thinking or Traditional Teaching For Health Professionals', PECOP Blog , 16 January, viewed 7 December 2018, https://blog.lifescitrc.org/pecop/2017/01/16/critical-thinking-or-traditional-teaching-for-health-professions/
- Jacob, E, Duffield, C & Jacob, D 2017, 'A Protocol For the Development of a Critical Thinking Assessment Tool for Nurses Using a Delphi Technique', Journal of Advanced Nursing, vol. 73, no. 8, pp. 1982-1988, viewed 7 December 2018, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jan.13306
- Kahlke, R & Eva, K 2018, 'Constructing Critical Thinking in Health Professional Education', Perspectives on Medical Education , vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 156-165, viewed 7 December 2018, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40037-018-0415-z
- Lippincott Solutions 2018, 'Turning New Nurses Into Critical Thinkers', Lippincott Solutions , viewed 10 December 2018, https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/expert-insights/turning-new-nurses-into-critical-thinkers
- Papp, K K 2014, 'Milestones of Critical Thinking: A Developmental Model for Medicine and Nursing', Academic Medicine , vol. 89, no. 5, pp. 715-720, https://journals.lww.com/academicmedicine/Fulltext/2014/05000/Milestones_of_Critical_Thinking___A_Developmental.14.aspx
- Snyder, L G & Snyder, M J 2008, 'Teaching Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills', The Delta Pi Epsilon Journal , vol. L, no. 2, pp. 90-99, viewed 7 December 2018, https://dme.childrenshospital.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Optional-_Teaching-Critical-Thinking-and-Problem-Solving-Skills.pdf
- The Foundation for Critical Thinking 2017, Defining Critical Thinking , The Foundation for Critical Thinking, viewed 7 December 2018, https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/our-conception-of-critical-thinking/411
- Tsui-Mei, H, Lee-Chun, H & Chen-Ju MSN, K 2015, 'How Mental Health Nurses Improve Their Critical Thinking Through Problem-Based Learning', Journal for Nurses in Professional Development , vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 170-175, viewed 7 December 2018, https://journals.lww.com/jnsdonline/Abstract/2015/05000/How_Mental_Health_Nurses_Improve_Their_Critical.8.aspx
Anne Watkins View profile
Help and feedback, publications.
Ausmed Education is a Trusted Information Partner of Healthdirect Australia. Verify here .
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Editor's Choice
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- About The British Journal of Social Work
- About the British Association of Social Workers
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Dispatch Dates
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
- < Previous
A Beginner's Guide to Critical Thinking and Writing in Health and Social Care, 2nd edn
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Malcolm Payne, A Beginner's Guide to Critical Thinking and Writing in Health and Social Care, 2nd edn, The British Journal of Social Work , Volume 45, Issue 7, October 2015, Pages 2229–2231, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcv066
- Permissions Icon Permissions
I want to start with a paragraph of warning, especially to students. Although it has its merits, this book is written by and for nurses. You would have thought that, if the authors (or perhaps it was their publishers) were going to add ‘and social care’ to the title, they would have taken their own advice and, at least as a precaution against the kind of review this is going to be, carried out a simple computer-based literature search using the terms ‘critical’ and ‘social work’. They would then, perhaps, have felt the need to refer to critical social science, including work by Habermas and his predecessors in the Frankfurt School, and feminism. Informal, but according to this book uncritical, research techniques such as asking around or looking in a bookshop would have revealed to the authors the internet journal Critical Social Work and texts by writers such as Jan Fook, Mel Gay, Stephen Webb and many others interpreting that social science in social work and building the concept of critical reflection, since it is a major stream of writing in our profession. A social work student will fail an assignment on critical practice if they fail to deal adequately with this material, and this book will not help them.
Email alerts
Citing articles via.
- Recommend to your Library
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1468-263X
- Print ISSN 0045-3102
- Copyright © 2024 British Association of Social Workers
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Find My Rep
You are here
Sage online ordering services will be unavailable due to system maintenance on April 13th between 2:00 am and 8:00 am UK time If you need assistance, please contact Sage at [email protected] . Thank you for your patience and we apologise for the inconvenience.
Critical Thinking in Health and Social Care
- Stella Jones-Devitt - York St John University, UK
- Liz Smith - University of Hull, UK
- Description
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace.
The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in practice using case studies, problem-solving scenarios and workplace examples. The practical tools which form the core of the book are contextualised by an exploration of what constitutes knowledge and evidence and the types of assumptions which are commonly held and which have a bearing on practice.
This is an essential text for advanced post-graduate health and social care students, and for those who are moving into more senior and strategic roles. Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care provides an array of tools which can be used to challenge and change existing practice and to solve problems.
Some students experience difficulty in understanding what is required when they are asked to be critical. Such students are directed to this book.
Excellent for supporting study skills workshop - I also recommend it in other units
Excellent core text , have used it as a core text to support undergraduate dissertation students and also as essentail reading for the MSC postgraduate students.
Preview this book
For instructors, select a purchasing option, order from:.
- VitalSource
- Amazon Kindle
- Google Play
Related Products

SAGE Knowledge is the premier social sciences platform for SAGE and CQ Press book, reference and video content.
The platform allows researchers to cross-search and seamlessly access a wide breadth of must-have SAGE book and reference content from one source.
You are here
Critical Thinking in Health and Social Care
- Stella Jones-Devitt - York St John University, UK
- Liz Smith - University of Hull, UK
- Description
The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in practice using case studies, problem-solving scenarios and workplace examples. The practical tools which form the core of the book are contextualised by an exploration of what constitutes knowledge and evidence and the types of assumptions which are commonly held and which have a bearing on practice.
This is an essential text for advanced graduate health and social care students, and for those who are moving into more senior and strategic roles. Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care provides an array of tools which can be used to challenge and change existing practice and to solve problems.
Stella Jones-Devitt is Head of Subject for Health Studies and Community Engagement at York St John University, U.K. Liz Smith is Programme Leader for Health Professional Studies, Faculty of Health and Social Care, University of Hull, U.K.
Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
We hope you'll consider this SAGE text. Email us at [email protected] , or click here to find your SAGE rep .
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
Some students experience difficulty in understanding what is required when they are asked to be critical. Such students are directed to this book.
Excellent for supporting study skills workshop - I also recommend it in other units
Excellent core text , have used it as a core text to support undergraduate dissertation students and also as essentail reading for the MSC postgraduate students.
Preview this book
Select a purchasing option, related products.

This title is also available on SAGE Knowledge , the ultimate social sciences online library. If your library doesn’t have access, ask your librarian to start a trial .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Lippincott Open Access

Reflective practice in health care and how to reflect effectively
Kiron koshy.
a Brighton and Sussex University Hospital
Christopher Limb
b Western Sussex University Hospitals, Worthing
Buket Gundogan
c UCL Medical School, University College London, London
Katharine Whitehurst
d Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital, UK
Daniyal J. Jafree
Reflective practice is a paper requirement of your career progression in health care. However, if done properly, it can greatly improve your skills as a health care provider. This article provides some structure to reflective practice to allow a health care provider to engage more with reflective practice and get more out of the experience.
Introduction
Reflective practice is something most people first formally encounter at university. This may be reflecting on a patient case, or an elective, or other experience. However, what you may not have considered is that you have been subconsciously reflecting your whole life: thinking about and learning from past experiences to avoid things that did not work and to repeat things that did. For example after tasting a food you do not like, you remember that experience, think about it, and when you next see that same food you know to avoid it. In medicine it is one of the best approaches to convert theoretical knowledge into practice.
As you progress through medical school and into foundation years as a doctor it becomes even more common. It is now expected to provide evidence of your reflections through your training on the ePortfolio and then throughout the rest of your professional life in revalidation. Hence, it is a good idea to get it right from the beginning.
First and foremost the biggest mistake you can make when reflecting is to treat it as a tick box exercise and a waste of time. With a bit of thought reflections can be a very useful tool in learning. Would you remember a generic case from a book? Would hanging all of those facts on a patient you have met make it more memorable? It allows you to recognize your own strengths and weakness, and use this to guide on-going learning. By reflection you will develop your skills in self-directed learning, improve motivation, and improve the quality of care you are able to provide.
What to reflect on
This can be anything.
Most reflections are on things that go wrong. These situations stay in one’s head and force us to begin to think about whether they could have done anything differently. For example:
- Postoperative complications
- Missed diagnosis
- A dissatisfied patient
- Failed procedure
However, reflecting on things that went well can often be more rewarding and be just as useful. It can build confidence and help you to repeat it again on another occasion. For example:
- A well-managed cardiac arrest
- An interesting seminar or conference
- A patient thank you letter
- A difficult but well performed procedure
Stages of reflecting
There are numerous models for reflections, but it is important to understand why you are asking each question and how that will help you to reflect 1 . This an integration of many concepts but the broad process is similar in all models: what happened, why does this matter and what are the next steps? 2
What, where, and who—the situation
Think about the situation in detail: What happened exactly and in what order, where were you at the time and who else was involved? What part did you have to play? What was the final outcome?
How did it make you feel—your emotional state
What was running through your head and how did you feel about it? Be honest with yourself: were you afraid, confused, angry or scared? If you can understand how you were feeling at the time it will help you put together why things happened as they did, and help you to recognize similar situations in the future.
Why did it happen—making sense of the situation
Now you have thought about the situation in greater detail, and probably recognized things that would have otherwise gone unnoticed, think about why things happened as they did. How did the situation, yourself, and others interact at the time. Did the situation go well or was there room for improvement?
Could you have done anything differently—critical review and development of insight
With the help of hindsight how would you have managed the situation differently? Think about what factors you could have influenced: is there anything you could have tried that may have improved the situation, or is there anything you did that was particularly important in the situation? It is easy to remember the things that you did not do and it is often the things that you did well that are forgotten.
What will you do differently in the future—how will this change your practice
This is arguably the most important stage in reflecting. You need to pull together everything you have thought of before to learn, change your own practice, and improve 3 . Do not only think about what you would do differently in that specific situation, but think whether you have thought of any transferable knowledge or skills you can utilize elsewhere. For example: if you reflect on a postprocedural complication do not only think of how you would manage this again but also how you would prevent it happening if you performed the procedure yourself! If you are a part of a well-led cardiac arrest do not think only of what you would do next to help, but also how you would lead an arrest in the future, or even how you would lead a team in any other situation!
Re-enforcement—what happens when you put this into practice
Test your reflections: When comparable situations happen again, do things change as you would expect them to? This is a chance to repeat the reflective cycle to refine and develop your understanding.
How to make the best use of reflective practice
As mentioned previously most people see reflective practice as a tick box exercise, but it does not have to be.
Over the next day take note of any interesting situations that arise. Later in the day try mentally reflecting, following this framework, and if you think any will be particularly useful to you write them down. If you try this for a week you will begin to see similar situations arising and how your reflective practice is positively affecting you.
Remember: you do not always have to learn only from your own experience; learn from others’ mistakes as well. Reflect on situations that you have witnessed to work out why things happened as they did, and how this can influence you.
It can be useful to take these reflections for peer or senior review: others may be able to draw light on things you have not noticed. This can allow you to recognize points for improvement and work on them. This can also be a useful learning opportunity for the other involved!
An example to put this into practice
I was involved in a patient confrontation; the patient was unhappy with her hospital stay and wanted to be discharged home. Unfortunately she required a package of care and so could not be discharged. I explained this and she returned to her bed. I was happy I had explained everything to her and continued with my other jobs.
Who, what, and why
I was involved in a patient confrontation; an elderly patient was unhappy with hospital stay and wanted to be discharged home. She was under our general surgical team for a head injury and observation after a normal CT head. She had been seen on our ward round and told that she was medically fit for discharge but still awaiting social services: her house had been reviewed and deemed unsafe so she was waiting for banisters to be installed. The issue was raised with me by chance as I was doing other things on the ward. I explained this to her and although she remained annoyed I was able to make her understand what the delay was and she returned to her bedside. She did not seek further clarification that day.
How did it make you feel
At the time I felt rushed and frustrated. I had a lot of other work to be done and this was distracting from that. She had already been told she was waiting for social services in the morning. I understood why this was difficult for her but did not think I would be able to do anything to help.
Why did it happen
The morning ward round was quite rushed and so our explanation was limited to telling her we were waiting for social services. I can understand from her point of view this may have meant very little, and so my explanation of what exactly we were doing may have relieved some frustration. Having been waiting up to this point, it is no surprise she continued to be angry but may have been accepting of this plan.

Could you have done anything differently
I think my explanation was very good, and the patient seemed happy with this, although I did not give a rough idea of how long this would take. It may have been useful to have spoken to the sister in charge to ask for what progress had been made to feed back to the patient. Also I did not ask her whether she was happy with this explanation: I may have been able to satisfy her frustration further by answering a few more questions or even recognize any other issues at home that may need addressing before discharge. Although the information given in the ward round was correct, it was not understandable to the patient. If this had all been quickly clarified in the morning, the patient would have been happy throughout the day and not caused a problem later on.
What will you do differently in the future
I think that the route problem in this situation was our explanation on the morning ward round. Furthermore, I am not sure how long such issues take to be addressed. To avoid a similar situation in the future I will speak to the other health care professionals on the ward to get a round idea of how long occupational interventions such as this and other community interventions take to start. This means when future patients are medically fit I can spend a moment in the morning informing them of what needs to be done and how long it may take. Hopefully this will allow me to address patient concerns early to avoid them becoming an issue when it is too late.
Re-enforcement
I will reflect on how future situations similar to this develop, looking for an improvement in the quality of my patient care.
Following a structure helps to focus a reflection: I am sure you will agree the learning points are much clearer from a good reflection!
Conclusions
To summarize, the benefits of reflecting are clear: it may be difficult to do initially, but through practice you will develop your own skills and become a better learner. Many structures are available so choose one what works for you. Reflective practice is an important part of your career progression on paper, but if done well, can greatly improve your skills as a health care provider.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest with regard to the content of this report.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Published online 15 June 2017

A Crash Course in Critical Thinking
What you need to know—and read—about one of the essential skills needed today..
Posted April 8, 2024 | Reviewed by Michelle Quirk
- In research for "A More Beautiful Question," I did a deep dive into the current crisis in critical thinking.
- Many people may think of themselves as critical thinkers, but they actually are not.
- Here is a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you are thinking critically.
Conspiracy theories. Inability to distinguish facts from falsehoods. Widespread confusion about who and what to believe.
These are some of the hallmarks of the current crisis in critical thinking—which just might be the issue of our times. Because if people aren’t willing or able to think critically as they choose potential leaders, they’re apt to choose bad ones. And if they can’t judge whether the information they’re receiving is sound, they may follow faulty advice while ignoring recommendations that are science-based and solid (and perhaps life-saving).
Moreover, as a society, if we can’t think critically about the many serious challenges we face, it becomes more difficult to agree on what those challenges are—much less solve them.
On a personal level, critical thinking can enable you to make better everyday decisions. It can help you make sense of an increasingly complex and confusing world.
In the new expanded edition of my book A More Beautiful Question ( AMBQ ), I took a deep dive into critical thinking. Here are a few key things I learned.
First off, before you can get better at critical thinking, you should understand what it is. It’s not just about being a skeptic. When thinking critically, we are thoughtfully reasoning, evaluating, and making decisions based on evidence and logic. And—perhaps most important—while doing this, a critical thinker always strives to be open-minded and fair-minded . That’s not easy: It demands that you constantly question your assumptions and biases and that you always remain open to considering opposing views.
In today’s polarized environment, many people think of themselves as critical thinkers simply because they ask skeptical questions—often directed at, say, certain government policies or ideas espoused by those on the “other side” of the political divide. The problem is, they may not be asking these questions with an open mind or a willingness to fairly consider opposing views.
When people do this, they’re engaging in “weak-sense critical thinking”—a term popularized by the late Richard Paul, a co-founder of The Foundation for Critical Thinking . “Weak-sense critical thinking” means applying the tools and practices of critical thinking—questioning, investigating, evaluating—but with the sole purpose of confirming one’s own bias or serving an agenda.
In AMBQ , I lay out a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you’re thinking critically. Here are some of the questions to consider:
- Why do I believe what I believe?
- Are my views based on evidence?
- Have I fairly and thoughtfully considered differing viewpoints?
- Am I truly open to changing my mind?
Of course, becoming a better critical thinker is not as simple as just asking yourself a few questions. Critical thinking is a habit of mind that must be developed and strengthened over time. In effect, you must train yourself to think in a manner that is more effortful, aware, grounded, and balanced.
For those interested in giving themselves a crash course in critical thinking—something I did myself, as I was working on my book—I thought it might be helpful to share a list of some of the books that have shaped my own thinking on this subject. As a self-interested author, I naturally would suggest that you start with the new 10th-anniversary edition of A More Beautiful Question , but beyond that, here are the top eight critical-thinking books I’d recommend.
The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark , by Carl Sagan
This book simply must top the list, because the late scientist and author Carl Sagan continues to be such a bright shining light in the critical thinking universe. Chapter 12 includes the details on Sagan’s famous “baloney detection kit,” a collection of lessons and tips on how to deal with bogus arguments and logical fallacies.

Clear Thinking: Turning Ordinary Moments Into Extraordinary Results , by Shane Parrish
The creator of the Farnham Street website and host of the “Knowledge Project” podcast explains how to contend with biases and unconscious reactions so you can make better everyday decisions. It contains insights from many of the brilliant thinkers Shane has studied.
Good Thinking: Why Flawed Logic Puts Us All at Risk and How Critical Thinking Can Save the World , by David Robert Grimes
A brilliant, comprehensive 2021 book on critical thinking that, to my mind, hasn’t received nearly enough attention . The scientist Grimes dissects bad thinking, shows why it persists, and offers the tools to defeat it.
Think Again: The Power of Knowing What You Don't Know , by Adam Grant
Intellectual humility—being willing to admit that you might be wrong—is what this book is primarily about. But Adam, the renowned Wharton psychology professor and bestselling author, takes the reader on a mind-opening journey with colorful stories and characters.
Think Like a Detective: A Kid's Guide to Critical Thinking , by David Pakman
The popular YouTuber and podcast host Pakman—normally known for talking politics —has written a terrific primer on critical thinking for children. The illustrated book presents critical thinking as a “superpower” that enables kids to unlock mysteries and dig for truth. (I also recommend Pakman’s second kids’ book called Think Like a Scientist .)
Rationality: What It Is, Why It Seems Scarce, Why It Matters , by Steven Pinker
The Harvard psychology professor Pinker tackles conspiracy theories head-on but also explores concepts involving risk/reward, probability and randomness, and correlation/causation. And if that strikes you as daunting, be assured that Pinker makes it lively and accessible.
How Minds Change: The Surprising Science of Belief, Opinion and Persuasion , by David McRaney
David is a science writer who hosts the popular podcast “You Are Not So Smart” (and his ideas are featured in A More Beautiful Question ). His well-written book looks at ways you can actually get through to people who see the world very differently than you (hint: bludgeoning them with facts definitely won’t work).
A Healthy Democracy's Best Hope: Building the Critical Thinking Habit , by M Neil Browne and Chelsea Kulhanek
Neil Browne, author of the seminal Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking, has been a pioneer in presenting critical thinking as a question-based approach to making sense of the world around us. His newest book, co-authored with Chelsea Kulhanek, breaks down critical thinking into “11 explosive questions”—including the “priors question” (which challenges us to question assumptions), the “evidence question” (focusing on how to evaluate and weigh evidence), and the “humility question” (which reminds us that a critical thinker must be humble enough to consider the possibility of being wrong).

Warren Berger is a longtime journalist and author of A More Beautiful Question .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Support Group
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Critical thinking refers to deliberately scrutinizing and evaluating theories, concepts, or ideas using reasoned reflection and analysis. The act of thinking critically implies moving beyond simply understanding information, but questioning its source, its production, and its presentation in order to expose potential bias or researcher subjectivity [i.e., being influenced by personal opinions and feelings rather than by external determinants ] . Applying critical thinking to investigating a research problem involves actively challenging assumptions and questioning the choices and potential motives underpinning how the author designed the study, conducted the research, and arrived at particular conclusions or recommended courses of action.
Mintz, Steven. "How the Word "Critical" Came to Signify the Leading Edge of Cultural Analysis." Higher Ed Gamma Blog , Inside Higher Ed, February 13, 2024; Van Merriënboer, Jeroen JG and Paul A. Kirschner. Ten Steps to Complex Learning: A Systematic Approach to Four-component Instructional Design . New York: Routledge, 2017.
Thinking Critically
Applying Critical Thinking to Research and Writing
Professors like to use the term critical thinking; in fact, the idea of being critical permeates much of higher education writ large. In the classroom, the idea of thinking critically is often mentioned by professors when students ask how they should approach a research and writing assignment [other approaches your professor might mention include interdisciplinarity, comparative, gendered, global, etc.]. However, critical thinking is more than just an approach to research and writing. It is an acquired skill used in becoming a complex learner capable of discerning important relationships among the elements of, as well as integrating multiple ways of understanding applied to, the research problem. Critical thinking is a lens through which you holistically interrogate a topic.
Given this, thinking critically encompasses a variety of inter-related connotations applied to college-level research and writing * :
- Integrated and Multi-Dimensional . Critical thinking is not focused on any one element of research, but rather, is applied holistically throughout the process of identifying the research problem, reviewing of literature, applying methods of analysis, describing the results, discussing their implications, and, if appropriate, offering recommendations for further research. The act of thinking critically is also non-linear [i.e., applies to going back and changing prior thoughts when new evidence emerges]; it permeates the entire research endeavor from contemplating what to write to proofreading the final product.
- Humanize Research . Thinking critically can help humanize the research problem by extending the scope of your analysis beyond the boundaries of traditional approaches to studying the topic. Traditional approaches can include, for example, sampling homogeneous populations, considering only certain factors related to investigating a phenomenon, or limiting the way you frame or represent the context of your study. Critical thinking can help reveal opportunities to incorporate the experiences of others into the research, creating a more representative examination of the research problem.
- Normative . This refers to the idea that critical thinking can be used to challenge prior assumptions in ways that advocate for social justice, equity, and inclusion and which can lead to research having a more transformative and expansive impact. In this respect, critical thinking can be a method for breaking away from dominant culture norms so as to produce research outcomes that illuminate previously hidden aspects of exploitation and injustice.
- Power Dynamics . Research in the social and behavioral sciences often includes examining aspects of power and influence that shape social relations, organizations, institutions, and the production and maintenance of knowledge. This approach encompasses studying how power operates, how it can be acquired, and how power and influence can be maintained. Critical thinking can reveal how societal structures perpetuate power and influence in ways that marginalizes and oppresses certain groups or communities within the contexts of history , politics, economics, culture, and other factors.
- Reflection . A key aspect of critical thinking is practicing reflexivity; the act of turning ideas and concepts back onto yourself in order to reveal and clarify your own beliefs, assumptions, and perspectives. Being critically reflexive is important because it can reveal hidden biases you may have that could unintentionally influence how you interpret and validate information. The more reflexive you are, the better able and more comfortable you are about opening yourself up to new modes of understanding.
- Rigorous Questioning . Thinking critically is guided by asking questions that lead to addressing complex concepts, principles, theories, or problems more effectively and to help distinguish what is known from from what is not known [or that may be hidden]. In this way, critical thinking involves deliberately framing inquiries not just as research questions, but as a way to focus on systematic, disciplined, in-depth questioning concerning the research problem and your positionality as a researcher.
- Social Change . An overarching goal of critical thinking applied to research and writing is to seek to identify and challenge sources of inequality, exploitation, oppression, and marinalization that contributes to maintaining the status quo within institutions of society. This can include entities, such as, schools, courts, businesses, government agencies, religious centers, that have been created and maintained through certain ways of thinking within the dominant culture.
In writing a research paper, the act of critical thinking applies most directly to the literature review and discussion sections of your paper . In reviewing the literature, it is important to reflect upon specific aspects of a study, such as, determining if the research design effectively establishes cause and effect relationships or provides insight into explaining why certain phenomena do or do not occur, assessing whether the method of gathering data or information supports the objectives of the study, and evaluating if the assumptions used t o arrive at a specific conclusion are evidence-based and relevant to addressing the research problem. An assessment of whether a source is helpful to investigating the research problem also involves critically analyzing how the research challenges conventional approaches to investigations that perpetuate inequalities or hides the voices of others.
Critical thinking also applies to the discussion section of your paper because this is where you interpret the findings of your study and explain its significance. This involves more than summarizing findings and describing outcomes. It includes reflecting on their importance and providing reasoned explanations why the research study is important in filling a gap in the literature or expanding knowledge and understanding about the topic in ways that inform practice. Critical reflection helps you think introspectively about your own beliefs concerning the significance of the findings but in ways that avoid biased judgment and decision making.
* Mintz, Steven. "How the Word "Critical" Came to Signify the Leading Edge of Cultural Analysis." Higher Ed Gamma Blog , Inside Higher Ed, February 13, 2024; Suter, W. Newton. Introduction to Educational Research: A Critical Thinking Approach. 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2012
Behar-Horenstein, Linda S., and Lian Niu. “Teaching Critical Thinking Skills in Higher Education: A Review of the Literature.” Journal of College Teaching and Learning 8 (February 2011): 25-41; Bayou, Yemeserach and Tamene Kitila. "Exploring Instructors’ Beliefs about and Practices in Promoting Students’ Critical Thinking Skills in Writing Classes." GIST–Education and Learning Research Journal 26 (2023): 123-154; Butcher, Charity. "Using In-class Writing to Promote Critical Thinking and Application of Course Concepts." Journal of Political Science Education 18 (2022): 3-21; Loseke, Donileen R. Methodological Thinking: Basic Principles of Social Research Design. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2012; Hart, Claire et al. “Exploring Higher Education Students’ Critical Thinking Skills through Content Analysis.” Thinking Skills and Creativity 41 (September 2021): 100877; Sabrina, R., Emilda Sulasmi, and Mandra Saragih. "Student Critical Thinking Skills and Student Writing Ability: The Role of Teachers' Intellectual Skills and Student Learning." Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences 17 (2022): 2493-2510.Van Merriënboer, Jeroen JG and Paul A. Kirschner. Ten Steps to Complex Learning: A Systematic Approach to Four-component Instructional Design. New York: Routledge, 2017; Yeh, Hui-Chin, Shih-hsien Yang, Jo Shan Fu, and Yen-Chen Shih. "Developing College Students’ Critical Thinking through Reflective Writing." Higher Education Research & Development 42 (2023): 244-259.
- << Previous: Academic Writing Style
- Next: Choosing a Title >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Open access
- Published: 10 April 2024
The burden of anxiety, depression, and stress, along with the prevalence of symptoms of PTSD, and perceptions of the drivers of psychological harms, as perceived by doctors and nurses working in ICUs in Nepal during the COVID-19 pandemic; a mixed method evaluation
- Shirish KC 1 ,
- Tiffany E. Gooden 2 ,
- Diptesh Aryal 1 ,
- Kanchan Koirala 1 ,
- Subekshya Luitel 1 ,
- Rashan Haniffa 3 , 4 ,
- Abi Beane 3 , 4 on behalf of
Collaboration for Research, Implementation, and Training in Critical Care in Asia and Africa (CCAA)
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 450 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
20 Accesses
4 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in significant physical and psychological impacts for survivors, and for the healthcare professionals caring for patients. Nurses and doctors in critical care faced longer working hours, increased burden of patients, and limited resources, all in the context of personal social isolation and uncertainties regarding cross-infection. We evaluated the burden of anxiety, depression, stress, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and alcohol dependence among doctors and nurses working in intensive care units (ICUs) in Nepal and explored the individual and social drivers for these impacts.
We conducted a mixed-methods study in Nepal, using an online survey to assess psychological well-being and semi-structured interviews to explore perceptions as to the drivers of anxiety, stress, and depression. Participants were recruited from existing national critical care professional organisations in Nepal and using a snowball technique. The online survey comprised of validated assessment tools for anxiety, depression, stress, PTSD, and alcohol dependence; all tools were analysed using published guidelines. Interviews were analysed using rapid appraisal techniques, and themes regarding the drivers for psychological distress were explored.
134 respondents (113 nurses, 21 doctors) completed the online survey. Twenty-eight (21%) participants experienced moderate to severe symptoms of depression; 67 (50%) experienced moderate or severe symptoms of anxiety; 114 (85%) had scores indicative of moderate to high levels of stress; 46 out of 100 reported symptoms of PTSD. Compared to doctors, nurses experienced more severe symptoms of depression, anxiety, and PTSD, whereas doctors experienced higher levels of stress than nurses. Most (95%) participants had scores indicative of low risk of alcohol dependence. Twenty participants were followed up in interviews. Social stigmatism, physical and emotional safety, enforced role change and the absence of organisational support were perceived drivers for poor psychological well-being.
Nurses and doctors working in ICU during the COVID-19 pandemic sustained psychological impacts, manifesting as stress, anxiety, and for some, symptoms of PTSD. Nurses were more vulnerable. Individual characteristics and professional inequalities in healthcare may be potential modifiable factors for policy makers seeking to mitigate risks for healthcare providers.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Between January 2020 and December 2021, the COVID-19 pandemic led to an estimated 18.2 million deaths [ 1 ]. Globally, healthcare systems were overwhelmed during the pandemic, with intensive care units (ICUs) receiving an unprecedented burden of patients [ 2 ]. In Nepal, the government first declared a lockdown on March 24, 2020, that lasted until July 21, 2020, and the second lockdown was announced on April 29, 2021, which was fully lifted on September 1, 2021 [ 3 ]. The first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic reached a peak of over 5000 cases a day in October 2020, and the second wave reached a peak of more than 9000 cases a day in May 2021, which was almost double [ 4 ]. Prior to the pandemic, Nepal reported a capacity of 1595 ICU beds across 194 hospitals and around 840 ventilators, equating to 2.8 ventilator-equipped ICU beds per 100,000 people [ 5 ]. To cope with the influx of COVID-19 patients, several existing postoperative wards and other high-dependency units of the hospitals were converted into improvised critical care units [ 6 ]. Globally, healthcare professionals (HCPs) and specifically those working in ICU and critical care services, arguably were at the frontline of the healthcare response. These HCPs faced the uncertainty of managing this new condition, extended working hours, limited personal protective equipment (PPE), and an increased risk of infection as they provide essential lifesaving interventions, including intubation and non-invasive respiratory management [ 7 , 8 ].
The impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health and well-being of HCPs who worked during and after this global emergency are slowly becoming apparent. Research emerging from China, the USA, and Europe [ 9 ] describes a significant burden of psychological distress and symptoms synonymous with mental health conditions in HCPs. This is also evident from the limited studies that have been conducted in Nepal. For instance, one study conducted among 150 HCPs from outpatient clinics and inpatient wards caring for COVID-19 patients in Nepal reported that 38% of participants suffered from anxiety and/or depression [ 10 ]. Another Nepali study revealed that the prevalence of anxiety and depression among HCPs, including health assistants and support staff was 47% and 41%, respectively [ 11 ]. A larger online survey of 475 HCPs including pharmacists, paramedics and public health practitioners reported similar findings (42% had anxiety) and noted that nurses had a higher proportion of symptoms compared to other HCPs [ 12 ].. Whilst these studies, in conjunction with a meta-analysis, indicate that depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic disorder (PTSD) are highly prevalent among HCPs during the pandemic [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ], fewer studies have explored the disparities between professionals’ roles, specifically among ICU workers, a group exposed to more advanced cases of COVID-19. Indeed a small study in Nepal comprising 96 nurses revealed that nurses who worked directly with COVID-19 patients experienced more severe symptoms of depression and anxiety [ 13 ]. The nature and characteristics of mental health symptoms appear to vary geographically, the HCPs’ role, their individual characteristics (age, gender) along with health system’s pre-existing resource capacity and ability to respond to increasing demand placed by events such as a pandemic. Understanding the mental health impact of ICU workers, any disparities between professional roles and drivers behind poor mental health in Nepal will help to identify what support is needed for ICU workers for pandemic preparedness; thus, providing important directions for investment in health systems strengthening.
We aimed to investigate the burden of anxiety, depression, stress, PTSD, and alcohol dependence among doctors and nurses in Nepal that worked in the ICU during the COVID-19 pandemic. We further sought to identify the factors driving the self-reported burden of psychological distress by exploring the lived experiences of these two different professional groups, and how these experiences impacted their psychological health and well-being.
Study design
We undertook a mixed-methods cross-sectional study [ 14 ] in Nepal with ICU doctors and nurses, combining an online questionnaire consisting of validated self-assessment tools combined with semi-structured interviews. The following self-reporting psychological assessment tools were used, given they have been used in previous studies in other settings and their widely validated in a variety of settings: Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) [ 15 ], Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) [ 16 ], Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) [ 17 ], PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5 (PCL-5) [ 18 ] and Alcohol Use Disorder identification Tool (AUDIT) [ 19 ]. BDI, BAI, and AUDIT have been validated in Nepal [ 20 , 21 , 22 ] and the PSS has been tested for reliability and correlation in Nepal [ 23 ]. Whilst the PCL-5 has not been validated in a Nepali setting, it was piloted (along with all other assessment tools used) with 20 people before the study commenced. Participants were given the flexibility to complete the questionnaire in either Nepali or English language. Despite this option, all participants opted to respond in English.
Ethics approval
was granted from the Nepal Health Research Council (approval number: 176/2021 P). All participants provided informed consent electronically before completing the online questionnaire. Participants from the qualitative component provided further informed verbal consent before the interview commenced.
In 2020, Nepal reported a capacity of 1595 ICU beds across 194 hospitals and around 840 ventilators, equating to 2.8 ventilator-equipped ICU beds per 100,000 people [ 5 ]. A year later, Nepal was under a state of health emergency, with patients being turned down due to a lack of ICU beds, oxygen, and ventilators [ 24 ].
Participants and recruitment
Doctors and nurses with experience in caring for COVID-19 patients in Nepalese ICUs were eligible for participation. Initially doctors registered with the Nepalese Society of Critical Care Medicine (NSCCM) [ 25 ] and nurses registered with the Critical Care Nurses Association of Nepal (CCNAN) [ 26 ] were contacted and invited to participate. Both organisations consist of voluntary memberships and represent the doctors and nurses working in a critical care setting in Nepal. At the time of recruitment, there were 187 doctors and 104 nurses registered at these organisations. This initial purposive sampling was augmented by snowballing techniques, whereby respondents were invited to forward the questionnaire link to other doctors or nurses working in ICUs [ 27 ]. Following completion of the questionnaire, respondents were invited to participate in a virtual interview. A convenience sample of 20 participants (a number which, based on the literature, was likely to provide saturation of findings [ 28 ]) was subsequently scheduled for an interview.
Study materials and data collection
The questionnaire was developed using an online survey platform (Google Forms) [ 29 ]. The questionnaire was piloted for readability and responder reliability with twenty HCPs based in Nepal, prior to roll out, who did not participate in the final analysis. Questionnaire content included socio-demographic information; age, sex, professional role and experience, degree of schooling, and home living arrangements; factors which had been identified as being important in the burden of psychological distress and impact on family life in similar research conducted during the previous SARS pandemic as well as the current COVID-19 event [ 30 ]. Participants could opt out of the study at any time. Participants could only complete the questionnaire once, and all survey responses were anonymous. Participants were signposted to healthcare services available to them should they be suffering from any distressing, mild, moderate or severe mental health symptoms. Invitations to participate in the questionnaire were sent out from 20th May 2021, and the questionnaire was closed to responses on 2nd October 2021.
The semi-structured interview topic guide was co-developed between doctors and nurses working in ICUs in Kathmandu. Co-design was used to ensure the sensitivity and appropriateness of the questions. None of the doctors and nurses involved in the codesign of the topic guide participated in the study proper. The qualitative component was aimed to augment the quantitative findings by providing an understanding of what social, organisational, and environmental factors were related to HCPs’ mental health. Topic guide questions focused on HCPs’ perceptions of their experiences of working during the pandemic and explored social, organisational, and environmental factors that may have influenced their self-reported burden and symptoms of psychological distress. These factors were selected from a review of the findings of the previously published meta-analysis and other studies conducted in Nepal [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. The interview questions were piloted with five HCPs for interpretability and interviewer consistency. All interviews were conducted via video conferencing (Zoom) [ 31 ] between September 2021 and March 2022. Five ICU nurses with experience in conducting interviews and mixed methods research led the data collection following training on the topic guide. To ensure there was no prior relationship between the interviewer and the participant, interviewers were assigned to participants that worked in different ICUs than themselves and were not known to the interviewee. No one other than the interviewer and the participant was present for each interview, and interviews were conducted at the time chosen by the interviewee. Rapid assessment procedure (RAP) sheets were used for note-taking during the interviews [ 32 ]. Commonly used in rapid evaluations - designed to improve the rapidity and replicability of research during public health emergencies - RAP sheets help reduce the need for long-form transcription and encourage reflexivity for both interviewers and researchers, reduce interviewer bias, and enable validation of internal consistency with coding [ 33 ]. The RAP sheet contained the summary of questions from the topic guide, and the interviewers took notes of what the participants said regarding each question during the interview.
Data analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to describe participants’ demographics and professional profiles. Psychological health and well-being assessment tools from the questionnaire were analysed using published guidelines. For the BDI, each of the 21 items corresponding to a symptom of depression was summed for each participant to give a single total score [ 16 ]. With each item ranging from 0 to 3 points, a total score of 13 or less was considered minimal to no depression, 14 to 19 as mild depression, 20 to 28 as moderate depression, and 29 to 63 as severe depression [ 16 ]. Data is also presented separately for suicidality (question 9 from the BDI) whereby anyone that said they have thoughts about or plans to kill themselves is said to have experienced suicidality. The BAI scores reported included the 21 symptoms of anxiety that ranged between 0 and 63 points [ 15 ]. The values for each symptom were summed, and a total score of 0 to 7 was interpreted as a minimal level of anxiety, 8 to 15 as mild, 16 to 25 as moderate, and 26 to 63 as severe anxiety [ 15 ]. Scores on the PSS ranged from 0 to 40, with higher scores indicating higher perceptions of stress [ 17 ]: scores ranging from 0 to 13 were considered low descriptors of stress; 14 to 26 moderate; and 27 to 40 were considered higher levels of perceived stress. For alcohol use disorder reported using AUDIT [ 19 ], a score of 0 indicated no previous or current alcohol use; a score of 1 to 7 suggested low-risk consumption; 8 to 14 hazardous or harmful alcohol consumption; 15 or higher indicated the likelihood of alcohol dependence (moderate to severe alcohol use disorder). The PCL-5 included 20 items with a score range of 0 to 80 and a score of 33 or higher, indicating the presence of PTSD [ 18 ]. A sensitivity analysis was conducted for the BDI, BAI and AUDIT scores based on local validation studies whereby a score of 15 or lower from the BDI indicated no depression [ 20 ], 12 or lower from the BAI indicated no anxiety [ 21 ], and a score of 11 or above from the AUDIT indicated discriminate dependent drinkers [ 22 ].
RAP sheets, along with interviewer notes, were reviewed by the research team before analysis to ensure information was complete. SK, KK and AB used a constant comparative method, coding data following each round of interviews and then reflecting back on the summary of the codes together with the interviewers to promote the accuracy of findings and reduce recall and interviewer bias. In addition, emerging themes identified following each round of coding were used to guide subsequent interviews [ 34 ]. The broader research team met following each coding round to review the findings and reflexivity [ 35 ]. Categories and the subsequent themes (‘drivers’) were developed through the iterative process of interviewing, coding, analysing, and reviewing.
We invited 120 doctors and 341 nurses to participate. A total of 21 doctors and 113 nurses responded, all of which completed the BDI, BAI, PSS, and AUDIT questions; 100 completed the PCL-5 (16 doctors and 84 nurses). Nearly all nurses were female (99%, n = 112), whereas most doctors were male (81%, n = 17). The characteristics of respondents are described in Table 1 .
50% ( n = 67) of respondents reported experiencing symptoms associated with moderate to severe anxiety, and a further 27% ( n = 36) scored for mild anxiety as a result of working in the ICU during the COVID-19 pandemic (Table 2 ). Anxiety levels (and associated symptoms) were more pronounced in nurses than doctors, with 55% ( n = 62) of the former scoring moderate to severe on the anxiety scale, compared to 24% ( n = 6) of the latter. 21% ( n = 28) of respondents described symptoms associated with moderate to severe depression, with a near-even split between nurses and doctors. Three-quarters of respondents ( n = 114; 85%) had scores indicative of moderate to high levels of stress; this proportion was higher among doctors ( n = 19; 91%) compared to nurses ( n = 95; 84%). Of the 100 individuals that completed the PCL-5 assessment (16 doctors and 84 nurses), 45% ( n = 46) reported a constellation of symptoms closely associated with PTSD, with a higher prevalence among nurses ( n = 40; 47%) compared to doctors ( n = 6; 38%).
Using cut-off scores from Nepali validation studies, 45 (34%) participants were experiencing mild, moderate or severe depressive symptoms, 80 (60%) were experiencing mild, moderate or severe anxiety symptoms, and 3 (2%) were considered discriminate dependent drinkers. These results are in line with our main analysis, including that a greater proportion of nurses were still found to suffer from depression and anxiety symptoms (supplementary Table 1 ).
Forty-six respondents to the online questionnaire volunteered to participate in the subsequent semi-structured interviews. Twenty participants were approached and consented to an interview: 16 were nurses (all female), and 4 were doctors (1 female, 3 male). On average, each interview resulted in 45 to 60 min of qualitative data. Saturation was met within the first 15 interviews, and findings were consistent between the coders and the research team. Analysis and synthesis of the interviews revealed nine themes, which, when codified, can be described as three key drivers of the psychological symptoms and impacts on mental well-being experienced by the interviewees: social stigmatism, physical and emotional safety, and organisational support. (Fig. 1 ). During the interviews, HCPs further described some of the coping strategies that they found helpful in mitigating the impacts experienced and may provide insights for future pandemic preparedness. These three themes, the drivers, and coping strategies, are explored below, along with quotes from the respondents.
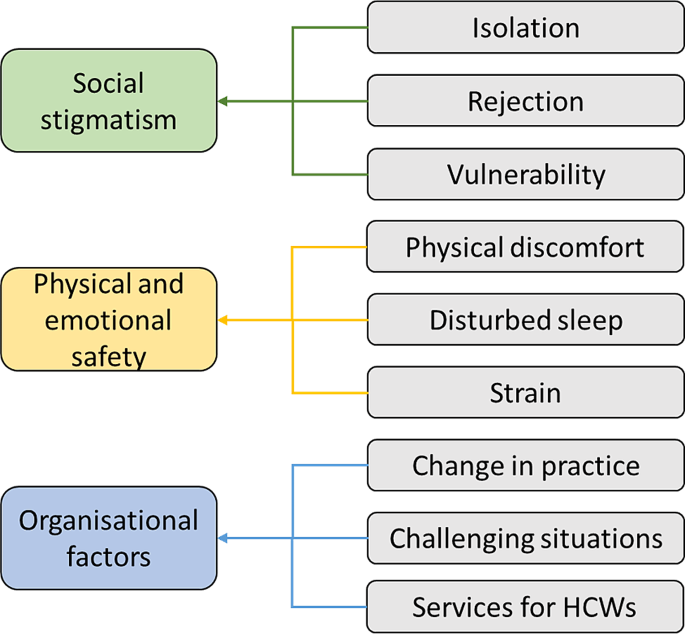
Coding tree for the four main drivers for psychological distress
Social stigmatism
Interviewees described experiencing feelings of social stigmatisation as a result of interactions with their families, peers, as well as from the wider public. Examples of stigmatism experienced included physical avoidance from neighbours and community members when the HCP travelled to and from and around their home, especially when dwellings were in shared buildings and common areas.
“My house owner avoided talking and meeting me because I worked with COVID patients.” [N]. “I have an elderly family member, and I was afraid and worried [for them] when I came back from duty.” [N].
Interviewees described how rumours would spread within the community, notably related to concerns of risk of co-infection or cross-infection, either directly from parent to child or indirectly via friends and extended family. Some HCPs were asked or elected to stay away from their home so as to reduce the stigma to them and their family and in an attempt to reduce the risk of co-infection, particularly when they had vulnerable family members. Interviewees described how this self-selected or enforced separation and isolation resulted in feelings of rejection, physically and emotionally heightened feelings of stress and anxiety, alongside the threat to physical and emotional safety.
Physical and emotional safety
Increased workload and an enforced change in working pattern/ shift structures were experienced by all the HCPs interviewed. These longer overall working hours, increased duration of shift patterns, and enforced working rotas were perceived as resulting in a loss of physical and emotional safety by the interviewees. Feelings of loss of control, insomnia, or disruption to sleep patterns, alongside physical discomfort through sustained working in personal protective equipment, often in hot and humid temperatures. This physical and mental endurance contributed to feelings of emotional stress and anxiety.
“Shift frequency was increased, and I only got one night off in a week. Sometimes I had to work extra hours, which was very stressful.” [N]. “My sleep pattern had changed, I felt restless and was afraid about COVID” [D].
The change in shift structure and in working patterns meant for some HCPs enforced separation from family and friends whereby HCPs sought accommodation away from family or in temporary lodgings. This again resulted in isolation and additional strain on other family members so as to provide care for HCP’s dependents.
“I had to involve other family members to arrange for the medication and care of my grandmother” [N].
Increased working hours and changes in working patterns further had physical impacts; participants described skipping meals or having limited time to eat. The need to wear personal protective equipment (PPE), and indeed the risks to safety when PPE was not available, associated risks of non-availability of equipment, brought with it a risk to physical and emotional safety. HCPs interviewed reported skin lacerations, irritation, and discomfort whilst wearing equipment in hot, humid working environments.
“We had to frequently change the PPE and masks, which has caused skin problems that still exist.” [N].
Organisational support
Interviewees found the COVID-19 pandemic brought new and often enforced work responsibilities, some of which were associated with high levels of professional anxiety, stress, and uncertainty. A professionally challenging situation, even for those with many years of ICU working experience. HCPs faced emotionally challenging tasks such as dealing with end-of-life situations (particularly without relatives of the patient present) and having to comfort relatives over the phone, of which they received limited to no training or support on handling such situations.
“I went through an emotional breakdown while dealing with the end of the life situation of patients without the presence of family members in the COVID ICU… I felt sad when a young patient lost their lives” [D]. “Accommodation or isolation facilities should be provided by the hospital” [D]. “If incentives were provided in time and staff were provided with health insurance it would motivate us” [N].
Ever-changing role and responsibilities created anxiety for HCPs as to what care to deliver, and the rapidity and uncertainty of care were associated with feelings of vulnerability. Interviewees expressed how they wished there was a need for greater organisational support to better cope with the frequent updates and changes to practice. Furthermore, HCPs expressed concerns regarding a shortage of staff and the lack of mental health counselling and support, accommodation on-site at the hospital, and transportation to and from work.
“Mental health support or counselling facilities were not provided. It should be there… seniors and hospital staff should also talk to the staff to know the situation.” [N]. “Safety of healthcare workers should be the priority and nurse-patient ratio should be maintained to provide quality care to the patients… hospital should have recruited more staff.” [N].
Coping strategies
Participants described various ways in which they coped with the emotional, physical, social, and professional impacts of working through the pandemic. This included speaking with family and friends about the pressures they were under, taking up activities in their off time, such as gardening and reading, and using media entertainment such as music, movies, and shows. A few participants also mentioned that comparing the situation in Nepal to other countries (i.e., keeping up-to-date with the news) also helped them cope. Others mentioned that detachment from social media and more self-awareness through meditation helped.
“I ventilated my feelings with friends and family. Listening to soothing music also helped me cope with the stress.” [N]. “I coped by gardening with my sister in my home.” [N]. “I… watched the news that compared the death rates, which was low compared to others.” [D].
The COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on healthcare services and population health internationally is unprecedented in recent times. As healthcare professionals, policymakers, and researchers work to strengthen services in preparation for future pandemics now and mitigate the long-term impacts on individual and population health, understanding the impact on and perspectives of doctors and nurses at the frontline of care can provide important learning regarding the individuals characteristics and professional, social and economic drivers which may increase the risk of psychological impacts.
Mandated and enforced changes in role, specifically in working hours and shift patterns, were a key driver of psychological anxiety and distress. Within hospitals in Nepal, many departments were closed, and stay-at-home orders meant that outpatient or clinical services all but ceased. This resulted in an increased role and scope for critical care trained staff, and in contrast to other health systems (such as the UK) where healthcare staff were redeployed to ICU, there was a separation for ICU staff even from their professional peers working in other specialties. The increased scope and uncertainty of the HCP’s role, along with limited choice in redeployment in the ICU was another driver of poor mental health- and dominated nursing participants’ experiences. Interviewees described how these changes impacted not only themselves but the multigenerational families for whom many cared for. This enforcement of role change, and the related descriptions of the drivers for these impacts as experienced by participants in this study point not only to the differences in roles between nurses and doctors; but also highlights disparities in autonomy, advocacy for role change during international emergencies, and the implications of work on home and family life [ 36 ].
Giving staff choice to select shift patterns and ensuring the opportunity to have periods of rest to reconnect with family and have self-care is needed. Consultation and shared decision-making, even in times of restricted choice, are associated with improved perceptions of work from staff and may result in reducing psychological distress and promoting emotional safety, which is, in turn, associated with better outcomes for patients [ 37 , 38 ]. However, nurses in Nepal, as with many health systems, may have less opportunity for strategic and organisational decision making in response to public health emergencies. The impact of ongoing disparities between professionals and their agency to advocate for wellbeing and safety warrants further research.
Nurses were disproportionately burdened by both occurrence and severity of symptoms of anxiety and depression as a result of their work during the pandemic when compared to doctors.
Nearly half of all respondents had symptoms of anxiety and PTSD (again more prevalent in nurses), and the burden of anxiety symptoms was higher than the reported 22–33% from a recent umbrella review [ 39 ]. The burden of stress we report was also higher than a smaller study conducted in Nepal during the pandemic, which reported stress among 53.2% of healthcare professionals working in hospitals, primary health centres, pharmacies, and health posts in Nepal [ 40 ]; it was also higher than a meta-analysis of published studies exploring the incidence of both stress (57%) and PTSD (22%) among all cadres of healthcare workers [ 41 ]. One reason for the higher reported symptoms in our study may be the focus on ICU workers and their role in the management of end-of-life care. Indeed, our results for depression and anxiety are comparable to a study involving nurses working directly with COVID-19 in Nepal [ 13 ]. Studies conducted elsewhere in Asia have highlighted this positive relationship between ICU experiences and poor mental health [ 42 ].
Nurses in Nepal, as with many other countries, are more likely to be female, younger in age, and have less opportunity for graduate study; and have lower earning potential than physician colleagues [ 43 ]; all characteristics associated with increased risk of poorer mental health outcomes [ 44 ]. Exploration into the disparities of the psychological and health impacts of COVID-19 on different cadres of healthcare workers is emerging. A systematic review conducted in 2020, identified 27 studies which sought to explore the disparity in impacts of the pandemic on HCP’s psychological well-being. The findings from the review are in line with ours, indicating that the burden of symptoms for anxiety, depression, and PTSD is higher in nurses compared to doctors [ 45 ]. Notably only a few of these studies used validated tools for assessment of specific symptoms of anxiety, depression, or substance misuse [ 45 ]. Our study serves to strengthen the evidence of the vulnerability of nurses.
Nepal, like many other lower and middle-income countries in South and Southeast Asia, enforced large-scale lockdowns and restrictions of movement for all but essential healthcare and municipal staff [ 46 ]. As such, social stigmatism, physical and emotional safety, and organisational support were key drivers behind the elevated symptoms of psychological distress in ICU HCPs and may be a key determinant of differences between health systems internationally. Furthermore, the family responsibilities and social circumstances for nurses, contributed to their experiences of isolation, rejection, vulnerability, physical discomfort, and strain. These drivers mirrored those reported from Europe; and may reflect differences experienced by nurses as a result of their gender, and role norms of primary family carers within society [ 44 ].
Interviewees from both professional groups expressed concern at the absence of preparedness and support they felt from their employing institutions. This is notable given the ongoing investment in pandemic preparedness and the potential to make changes now to prepare for the next pandemic or public health emergency. Interventions such as resilience training, scenario-based simulation training, and group exercises based on psychoeducation and cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) principles have proved effective in reducing anxiety, depression, stress, and PTSD among doctors and nurses while simultaneously improving their ability to work in unprecedented situations in other sectors [ 47 ]. Similar provisions may be valuable for ICU-based healthcare professionals and are deliverable online, making rollout potentially more feasible.
Strengths and limitations
A strength of this study is the exploration of participants’ perspectives on the drivers behind the burden of poor mental health described in ICU HCPs. This mixed methods approach offers insights into doctors’ and nurses’ unique individual, social and professional characteristics that may be associated with increased risk of distress. These differences and their potential for disparity in impacts on health and wellbeing should be of interest to policymakers and healthcare facility managers involved in future pandemic preparedness. However, the study has some limitations to acknowledge. Given the use of the snowball technique, we were able to ensure a high number of respondents, but as a consequence, we were unable to track the number of respondents that came from using this technique compared to those initially invited from the NSCCM and CCNAN. Therefore, a response rate and, subsequently, a non-response rate could not be reported. We did not collect information on the level of training in critical care that participants received; trained health professionals are likely to have additional skills in how to handle the potential stressful environment in critical care settings. Also, due to the lack of validation of the PCL-5 in Nepal, the results of this assessment tool should be interpreted with caution. The survey tools used for this study have not been validated in an online format. However, given these tools were self-reporting, and were piloted and administered in English, the online format is thought to have minimal impact on the results. Additionally, participants for the qualitative component were recruited based on convenience sampling; therefore, the diversity of the sample may not be optimised. We acknowledge that recall bias may be present in the participants during the interview, given they were recalling their experiences throughout the pandemic for up to 24 months prior to the interview; however, we hope the piloting of the interviews, the use of multiple researchers to code the data, and the constant comparative nature of the evaluation will mitigate this potential.
The COVID-19 pandemic negatively impacted the mental health of HCPs worldwide. This study strengthens existing evidence that nurses were (and may remain) at increased risk of both cross infection and may also be more vulnerable to psychological impacts including anxiety, depression and PTSD than their professional colleagues. In addition, critical care staff may be at even greater risk, due to the uniqueness of their role which includes prolonged periods of time with infected patients, frontline role in managing end of life care, and as described here, limited ability to advocate for changing role and working patterns during an emergency. Professional hierarchies, and social-economic and gender profiles unique to nurses, may be potential drivers for these disparities, and warrants further research. Learning from the ICU HCPs’ experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic may inform future preparedness strategies e to mitigate short and long-term mental illness among ICU HCPs in future pandemics.
Data availability
The interview guide is available in the Figshare repository,
https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24247384.v1 .
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the Figshare repository, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.23999790.v1 .
Abbreviations
Coronavirus disease 2019
Intensive care unit
Healthcare professional
Personal protective equipment
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Nepalese Society of Critical Care Medicine
Critical Care Nurses Association of Nepal
Beck Anxiety Inventory
Beck Depression Inventory
Perceived Stress Scale
PTSD Checklist for Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5
Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Tool
Rapid assessment procedure
Cognitive behavioural therapy
Wang H, Paulson KR, Pease SA, et al. Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020–21. Lancet. 2022;399(10334):1513–36.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Greco M, De Corte T, Ercole A et al. Clinical and organizational factors associated with mortality during the peak of first COVID-19 wave: the global UNITE-COVID study. Intensive Care Med. 2022:1–16.
All Covid restrictions lifted in Valley [Internet]. kathmandupost.com. [Accessed 7 Feb 2024]. Available from: https://kathmandupost.com/valley/2022/03/05/all-covid-restrictions-lifted-in-valley .
Kharel P. Nepal’s fight against the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic. repositoryunescaporg [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Feb 7]; Available from: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12870/5102 .
Neupane HC, Gauli B, Adhikari S, et al. Contextualizing critical care medicine in the face of COVID-19 pandemic. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2020;58(226):447.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Shrestha GS, Lamsal R, Tiwari P, Acharya SP. Anesthesiology and critical care response to COVID-19 in Resource-Limited settings. Anesthesiol Clin. 2021;39(2):285–92.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hölscher AH. Patient, surgeon, and health care worker safety during the COVID-19 pandemic. Ann Surg. 2021;274(5):681.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gholami M, Fawad I, Shadan S, et al. COVID-19 and healthcare workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;104:335–46.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ghahramani S, Kasraei H, Hayati R et al. Health care workers’ mental health in the face of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract. 2022:1–10.
Gupta AK, Mehra A, Niraula A, et al. Prevalence of anxiety and depression among the healthcare workers in Nepal during the COVID-19 pandemic. Asian J Psychiatr. 2020;54:102260.
Adhikari SP, Rawal N, Shrestha DB et al. Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and perceived stigma in healthcare workers in Nepal during later phase of first wave of covid-19 pandemic: a web-based cross-sectional survey. Cureus. 2021, 13(6).
Khanal P, Devkota N, Dahal M, et al. Mental health impacts among health workers during COVID-19 in a low resource setting: a cross-sectional survey from Nepal. Global Health. 2020;16(1):1–12.
Google Scholar
Tamrakar P, Pant SB, Acharya SP. Anxiety and depression among nurses in COVID and non-COVID intensive care units. Nurs Crit Care. 2021 Sep 28.
Fitzpatrick R, Boulton M. Qualitative methods for assessing health care. Qual Health Care. 1994;3(2):107.
Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, et al. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1988;56(6):893.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Richter P, Werner J, Heerlein A, et al. On the validity of the Beck Depression Inventory. Psychopathology. 1998;31(3):160–8.
Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. Perceived stress scale. Measuring Stress: Guide Health Social Scientists. 1994;10(2):1–2.
Blevins CA, Weathers FW, Davis MT, et al. The posttraumatic stress disorder checklist for DSM-5 (PCL‐5): development and initial psychometric evaluation. J Trauma Stress. 2015;28(6):489–98.
Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, et al. Development of the alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): WHO collaborative project on early detection of persons with harmful alcohol consumption-II. Addiction. 1993;88(6):791–804.
Kohrt B, Kunz RD, Koirala NR, Sharma VD, Nepal, Mahendra. Validation of a Nepali version of the Beck Depression Inventory. Nepal J Psychiatry. 2002;2:123–30.
Kohrt B, Kunz R, Koirala N, Campus M, Nepal. Validation of the Nepali version of beck anxiety inventory. Journal of Institute of Medicine [Internet]. 2007 Jan 21 [cited 2024 Feb 7]; Available from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Validation-of-the-Nepali-version-of-beck-anxiety-Kohrt-Kunz/148d 01852884f54d28967e105d57c177a3f0be36.
Pradhan B, Chappuis F, Baral D, Karki P, Rijal S, Hadengue A et al. The alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): validation of a Nepali version for the detection of alcohol use disorders and hazardous drinking in medical settings. Substance Abuse Treatment, Prevention, and Policy [Internet]. 2012;7(1). Available from: https://substanceabusepolicy.biomedcentral.com/articles/ https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-597X-7-42 .
Sharma P, Devkota G. Mental health screening questionnaire: a study on reliability and correlation with perceived stress score. J Psychiatrists’ Association Nepal. 2019;8(2):4–8.
Article Google Scholar
Pandey BD, Morita K, Costello A. Twin crises in Nepal: covid-19 and climate change. 2022, 377.
Nepalese Society of Critical Care Medicine. NSCCM. 2022. [Accessed 16 August 2023]. Available from http://www.nsccm.org.np/ .
Critical Care Nurses Association of Nepal. Critical Care Nurses Association of Nepal. 2022. [Accessed 16 August 2023]. Available from https://ccnan.org.np/ .
Etikan I, Alkassim R, Abubakar S. Comparision of snowball sampling and sequential sampling technique. Biom Biostat Int J. 2016;3(1):55.
Saunders B, Sim J, Kingstone T, et al. Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Qual Quant. 2018;52(4):1893–907.
Google Inc. Google Forms. 2022. [Accessed 16 August 2023]. Available from https://www.google.co.uk/forms/about/ .
Zerbini G, Ebigbo A, Reicherts P et al. Psychosocial burden of healthcare professionals in times of COVID-19–a survey conducted at the University Hospital Augsburg. Ger Med Sci. 2020, 18.
Zoom Z. One platform to connect. 2022. [Accessed 16 August 2023]. Available from https://zoom.us/ .
Vindrola-Padros C, Chisnall G, Cooper S, et al. Carrying out rapid qualitative research during a pandemic: emerging lessons from COVID-19. Qual Health Res. 2020;30(14):2192–204.
Beebe J. Basic concepts and techniques of rapid appraisal. Hum Organ. 1995;54(1):42–51.
Althubaiti A. Information bias in health research: definition, pitfalls, and adjustment methods. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2016:211–7.
Macbeth D. On reflexivity in qualitative research: two readings, and a third. Qual Inq. 2001;7(1):35–68.
Jackson D, Anders R, Padula WV, et al. Vulnerability of nurse and physicians with COVID-19: monitoring and surveillance needed. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(19–20):3584.
Bae SH. Intensive care nurse staffing and nurse outcomes: a systematic review. Nurs Crit Care. 2021;26(6):457–66.
Ejebu O-Z, Dall’Ora C, Griffiths P. Nurses’ experiences and preferences around shift patterns: a scoping review. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(8):e0256300.
Fernandez R, Sikhosana N, Green H, et al. Anxiety and depression among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic umbrella review of the global evidence. BMJ Open. 2021;11(9):e054528.
Kafle K, Shrestha DB, Baniya A, et al. Psychological distress among health service providers during COVID-19 pandemic in Nepal. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(2):e0246784.
Marvaldi M, Mallet J, Dubertret C, et al. Anxiety, depression, trauma-related, and sleep disorders among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;126:252–64.
Thatrimontrichai A, Weber DJ, Apisarnthanarak A. Mental health among healthcare personnel during COVID-19 in Asia: a systematic review. J Formos Med Assoc. 2021;120(6):1296–304.
Prakash S, Yadav P, Yadav K. Perspectives of developing nursing education in Nepal. Nurs Care Open Access J. 2018;5(4):214–20.
Tiete J, Guatteri M, Lachaux A, et al. Mental health outcomes in healthcare workers in COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 care units: a cross-sectional survey in Belgium. Front Psychol. 2021;11:612241.
Kunz M, Strasser M, Hasan A. Impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on healthcare workers: systematic comparison between nurses and medical doctors. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2021;34(4):413.
Adhikari NK, Beane A, Devaprasad D et al. Impact of COVID-19 on non-COVID intensive care unit service utilization, case mix and outcomes: a registry-based analysis from India. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 6.
Zaçe D, Hoxhaj I, Orfino A, et al. Interventions to address mental health issues in healthcare workers during infectious disease outbreaks: a systematic review. J Psychiatr Res. 2021;136:319–33.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the volunteers who took the time to interview the participants: Radhika Maharjan, Dipika Khadka, Anita Bashyal, Samina Amatya, and Roshani Kafle. We also want to thank Dr. Rohini Nepal and Jugmaya Chaudhary of Rhythm Neuropsychiatry Hospital and Research Centre for their contribution to advising and reviewing the self-reporting psychological assessment tools used in the questionnaire. We would also like to thank Transcultural Psychosocial Organisation (TPO) Nepal and Dr. Nabaraj Koirala for the permission to use the Nepali-validated version of BDI I and BAI for the study. We additionally thank Nilu Dullewe, who helped in coding the qualitative data. For the ongoing mutual support for improvements in ICU care, we would also like to acknowledge and thank members of the CCAA.
CCAA members
Diptesh Aryal, Shirish KC, Kanchan Koirala, Subekshya Luitel, Rohini Nepal, Sushil Khanal, Hem R Paneru, Subha K Shreshta, Sanjay Lakhey, Samina Amatya, Kaveri Thapa, Radhika Maharjan, Roshani Kafle, Anita Bashyal, Reema Shrestha, Dipika Khadka and Nilu Dullewe.
This study was funded by a Wellcome Innovations Flagship Programme grant (Wellcome grant number: 215522/Z/19/Z). They had no role in the design, analysis, or reporting of this protocol.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nepal Intensive Care Research Foundation, Kathmandu, Nepal
Shirish KC, Diptesh Aryal, Kanchan Koirala & Subekshya Luitel
Institute of Applied Health Research, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK
Tiffany E. Gooden
Centre for Inflammation Research, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Rashan Haniffa & Abi Beane
Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Bangkok, Thailand
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
- Diptesh Aryal
- , Shirish KC
- , Kanchan Koirala
- , Subekshya Luitel
- , Rohini Nepal
- , Sushil Khanal
- , Hem R Paneru
- , Subha K Shreshta
- , Sanjay Lakhey
- , Samina Amatya
- , Kaveri Thapa
- , Radhika Maharjan
- , Roshani Kafle
- , Anita Bashyal
- , Reema Shrestha
- , Dipika Khadka
- & Nilu Dullewe
Contributions
All authors conceptualised this study. SK, DA, AB, RH, and SL developed the protocol, study methods, and materials. KK and SL facilitated the data collection, supervised by SK and DA. Data were analysed by SK, AB, KK, and TEG. SK and TEG wrote the drafts of the manuscript, and all authors reviewed the manuscript and consented to it being submitted. AB is the senior author.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Diptesh Aryal .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethics approval was granted from the Nepal Health Research Council (approval number: 176/2021 P). All participants provided informed consent electronically before completing the online questionnaire. Participants from the qualitative component provided further informed verbal consent before the interview commenced.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Members of the CCAA are listed in the acknowledgments
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
KC, S., Gooden, T.E., Aryal, D. et al. The burden of anxiety, depression, and stress, along with the prevalence of symptoms of PTSD, and perceptions of the drivers of psychological harms, as perceived by doctors and nurses working in ICUs in Nepal during the COVID-19 pandemic; a mixed method evaluation. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 450 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10724-7
Download citation
Received : 05 September 2023
Accepted : 14 February 2024
Published : 10 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-10724-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Pandemic preparedness, psychological distress
- Healthcare professionals
- Critical care
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Find My Rep
You are here
Critical Thinking in Health and Social Care
- Stella Jones-Devitt - York St John University, UK
- Liz Smith - University of Hull, UK
- Description
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace.
The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in practice using case studies, problem-solving scenarios and workplace examples. The practical tools which form the core of the book are contextualised by an exploration of what constitutes knowledge and evidence and the types of assumptions which are commonly held and which have a bearing on practice.
This is an essential text for advanced post-graduate health and social care students, and for those who are moving into more senior and strategic roles. Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care provides an array of tools which can be used to challenge and change existing practice and to solve problems.
Some students experience difficulty in understanding what is required when they are asked to be critical. Such students are directed to this book.
Excellent for supporting study skills workshop - I also recommend it in other units
Excellent core text , have used it as a core text to support undergraduate dissertation students and also as essentail reading for the MSC postgraduate students.
Preview this book
For instructors, purchasing options.
Please select a format:
Order from:
- VitalSource
- Amazon Kindle
- Google Play
Related Products

SAGE Knowledge is the ultimate social sciences digital library for students, researchers, and faculty. Hosting more than 4,400 titles, it includes an expansive range of SAGE eBook and eReference content, including scholarly monographs, reference works, handbooks, series, professional development titles, and more.
The platform allows researchers to cross-search and seamlessly access a wide breadth of must-have SAGE book and reference content from one source.
SAGE Knowledge brings together high-quality content from across our imprints, including CQ Press and Corwin titles.
The Good Side: Doulas and Maternal Health Care
WASHINGTON (Gray DC) - Black Maternal Health week is April 11 – 17. Black mothers in America are three times more likely to die during pregnancy or delivery than moms of any other race. Experts say there’s several reasons, including healthcare disparities, underlying conditions and structural racism. Debra Alfarone introduces us to a mom and a doula, dedicating her life to advocate for mothers of all races before, during and after childbirth.
Copyright 2024 Gray DC. All rights reserved.

Officials can’t give condition of man who fell into Susquehanna River

OJ Simpson has died, family says on social media platform X

FBI now involved in investigation into death of Aliza Spencer

Deputies: Man tried setting person on fire, also tried fire station burglary

Man arrested after robberies in Binghamton, Endicott
Latest news.

Here’s how you can participate in the new Chenango County hiking challenge

State Senator Webb hosts roundtable discussion for minority business owners

Chenango County man arrested on child sex crime

Vehicle crashes into Endicott home


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is just one skill crucial to evidence based practice in healthcare and education, write Jonathan Sharples and colleagues , who see exciting opportunities for cross sector collaboration Imagine you are a primary care doctor. A patient comes into your office with acute, atypical chest pain. Immediately you consider the patient's sex and age, and you begin to think about what ...
Multiple conceptions of critical thinking likely offer educators the ability to express diverse beliefs about what 'good thinking' means in variable contexts. The findings suggest that any single definition of critical thinking in the health professions will be inherently contentious and, we argue, should be.
Critical thinking skills have been linked to improved patient outcomes, better quality patient care and improved safety outcomes in healthcare (Jacob et al. 2017).. Given this, it's necessary for educators in healthcare to stimulate and lead further dialogue about how these skills are taught, assessed and integrated into the design and development of staff and nurse education and training ...
Critical thinking about the evidence of the social work literature would give the lie to the assumption that untranslated health care thinking routinely applies to it. Since this book has reached a second edition and tells us that the first edition was highly commended in the BMA Medical Books Award a few years ago, there is of course useful ...
Without critical thinking, physicians, and particularly residents, are prone to cognitive errors, which can lead to diagnostic errors, especially in a high-stakes environment such as the intensive care unit. Although challenging, critical thinking skills can be taught.
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace. The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in ...
Critical Thinking in Health and Social Care. S. Jones-Devitt, Liz Smith. Published 25 October 2007. Philosophy, Medicine, Sociology. TLDR. This chapter discusses critical thinking in the context of health and social care practice and discusses the role of evidence, evidence-based decision-making, and the implications for practice. Expand.
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace. The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in ...
"In my estimation this is the definitive beginner's guide to critical thinking and writing in health and social care. After reading this book any student should understand why and how critical thinking underpins professional practice and the highest endeavours in academic work and research."
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace. The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in ...
Helen Aveyard is Senior Lecturer at Oxford Brookes University, UK and author of the bestselling book Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care, 2nd edition and A Beginner's Guide to Evidence Based Practice, both published by the Open University Press.. Pam Sharp is Senior Lecturer at Oxford Brookes University, UK.
Effective critical thinking and reasoning supports effective practice. This module helps qualified practitioners in health and social care to evolve their professional practice in ways that remain focused on solutions and constructive outcomes for the people who use their service. It explores how practitioners think, make judgements and reach ...
Influencing the `critical thinking' culture of your workplace ; In summary ; Key points ; 6 Shaping the future: what is the role of critical thinking in the development of health and social care services? Why is critical thinking important for developing a broader perspective in your personal, professional and academic life?
This beginner's guide introduces the skills of critical thinking, critical writing and critical appraisal in health and social care, and talks you through every stage of becoming a critical thinker. Each chapter tackles a different aspect of the process and shows you how it's done using examples and simple language.
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace. The book presents a range ...
Health care professional curricula need to facilitate the development of critical-thinking skills in students. This systematic review shows that there are mixed results with respect to the acquisition of critical-thinking skills in health care professional students as measured by the CCTST and the WGCTA. There are a limited number of moderate ...
"In my estimation this is the definitive beginner's guide to critical thinking and writing in health and social care. After reading this book any student should understand why and how critical thinking underpins professional practice and the highest endeavours in academic work and research." ... "Health and social care professionals navigate ...
Liz Rockingham, Adult Field Lead / Teaching Fellow, University of Surrey, UK "In my estimation this is the definitive beginner's guide to critical thinking and writing in health and social care. After reading this book any student should understand why and how critical thinking underpins professional practice and the highest endeavours in ...
Introduction. Reflective practice is something most people first formally encounter at university. This may be reflecting on a patient case, or an elective, or other experience. However, what you may not have considered is that you have been subconsciously reflecting your whole life: thinking about and learning from past experiences to avoid ...
According to the University of the People in California, having critical thinking skills is important because they are [ 1 ]: Universal. Crucial for the economy. Essential for improving language and presentation skills. Very helpful in promoting creativity. Important for self-reflection.
Neil Browne, author of the seminal Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking, has been a pioneer in presenting critical thinking as a question-based approach to making sense of the ...
Critical thinking refers to deliberately scrutinizing and evaluating theories, concepts, or ideas using reasoned reflection and analysis. The act of thinking critically implies moving beyond simply understanding information, but questioning its source, its production, and its presentation in order to expose potential bias or researcher subjectivity [i.e., being influenced by personal opinions ...
Critical Thinking for Nursing, Health and Social Care. Rena Frohman, Karen Lupton. Bloomsbury Publishing, Apr 2, 2020 - Study Aids - 190 pages. This practical book will equip students with the critical thinking, reading and writing skills required to succeed both on their course and in their professional placements.
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in significant physical and psychological impacts for survivors, and for the healthcare professionals caring for patients. Nurses and doctors in critical care faced longer working hours, increased burden of patients, and limited resources, all in the context of personal social isolation and uncertainties regarding cross-infection.
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace. The book presents a range of different approaches, which have particular relevance in the context of health and social care. Each approach is explained and grounded in ...
As conversations and thinking concerning changing the field that calls itself "global health" have proliferated over the past three years, a key predicament has emerged. While almost all in the field agree that something must change, for the vast majority a world without this complex, massive project and apparatus is still unimaginable and undesirable.
Strengthen the health and care workforce: Invest in the education, employment, and retention of health workers, including by addressing existing shortages, and ensure decent pay and working conditions to ensure they are equipped to deliver high-quality health care.5. Institutionalize social participation in decision-making: Ensure the inclusion ...
At Gray, our journalists report, write, edit and produce the news content that informs the communities we serve. Click here to learn more about our approach to artificial intelligence.
Critical Thinking in Health & Social Care is designed to equip practitioners with the knowledge and tools they need to critically examine practice in their own workplace. The book presents a range of different approaches, each of which is explained and grounded in practice using case studies, problem-solving scenarios and workplace examples.
Adult social care is considered a priority because of the difficulty in attracting enough workers to fill vacancies as the population ages, with around one in 10 jobs available.