Project Management Plan: Samples, Examples & Free Template
Learn how to create a project management plan that actually works and ensures you get your project over the line on time and on budget, with samples and examples

Table of Contents
What is a project management plan, what is a project management plan used for, what are the main elements of a project plan, how to write a project management plan, sample project management plan outline, using our project management plan template to build your project plan, project management plan: faq's.
A project management plan is a comprehensive document that outlines how a project will be executed, monitored, controlled and closed. For project managers and their teams, it's the ultimate toolkit for achieving their objectives while managing day-to-day pressures such as time, cost, scope, resourcing and risk. This guide outlines what a project management plan is used for, why it's important , and offers a step-by-step guide on how to make one that actually works.
Your project plan document is where you go deep on the ins, outs, overs, and unders of your project. It's where you break this vision down into the day-to-day execution of your project, covering everything you need to do to reach your project goals.
A detailed project plan will plot out everything from timelines to budget, resourcing to deliverables, and more, giving you a blueprint of what needs to be done (and when) that you can use to guide — and assess — your project.
The key components of a project management plan are:
Project Objectives
Scope Statement
Schedule Management
Cost Management
Resource Management
Communication Plan
Stakeholder Management
Procurement Management
Closure Criteria
Project Organization
Ready to get down to business? Here are 5 key things you need to do when writing a project plan.
1. Identify the baselines for your project
Before you begin writing a project plan, you need to make sure you have the basics down. Start by identifying the baselines for the project’s scope, schedule and cost, as the rest of your project planning will need to fit in around those constraints.
As mentioned above, these baselines should already be roughly outlined in your project charter — but here’s where you really start to map them out and create accurate estimates. And the more detailed, the better, because these are what you’ll be using for comparison to measure how your project performs.
2. Identify your project dependencies
Or in other words, ask yourself: what needs to happen before this other thing can happen? Identifying your project dependencies at the outset of your project means you can plan your timelines more efficiently, spot potential blockers, and ensure that you avoid unnecessary delays.
3. Identify project stakeholders
You’ll already have done the groundwork for this in your stakeholder analysis, but as you flesh out your project management plan and think through the phases of your project in more detail, you’ll likely start to find more project stakeholders at each phase.
Now is also a good time to go deeper on which stakeholders need to be informed and involved at which stages, for a more comprehensive stakeholder management plan you can use at each phase of your project.
4. Identify project milestones
What are the key markers of your project’s progress? It can be a concrete deliverable, the end of a phase in a stage-gate process — whatever milestones make sense to you, breaking your project down into manageable chunks, each with a defined goal, helps to keep the team motivated, allows you to celebrate each achievement, and signposts how the overall progress is coming along. Learn more about using Milestones here .

5. Identify who’s responsible for what
Once you start to get a big-picture understanding of the work that’s needed and the resources you have to complete it, you can start deciding who should do what. Giving each item an owner is essential to getting things done. No more “oh, was I supposed to do that?” — once you identify who’s responsible for what, you can ensure accountability and transparency.

The 5 Stages of Team Development
All teams develop according to some natural patterns and using that knowledge, you can offer some guidance to build the kind of team that communicates well and finds better ways to collaborate and achieve the goals you’ve established. Here’s what you need to know.
Now let's go through a sample project plan. In the below example, we highlight the main sections of the plan and what needs to be included in each one to set your project up for success.
Section 1: Executive summary
The executive summary offers a concise overview of the entire project. It includes key highlights such as the project's purpose, objectives, scope, timeline, budget, and major stakeholders. It's often the first section stakeholders read to get a high-level understanding of the project.
Section 2: Project introduction
This section sets the stage by providing context and background information about the project. It explains why the project is being undertaken and introduces the main objectives and scope of the project.
Section 3: Project objectives
Here, the project's specific goals and objectives are outlined in detail. Objectives should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) to provide clarity and guidance.
Section 4: Project scope
The scope section defines what is included and excluded from the project. It helps prevent scope creep by establishing clear boundaries and also mentions any assumptions and constraints that may affect the project.
Section 5: Schedule management
This section details the project's timeline, including milestones and deadlines. It breaks down the project into tasks and identifies task dependencies. Often, visual representations like Gantt charts are used for clarity.
Section 6: Cost management
Here, the project budget is presented, including cost estimates for various project components. It may also outline cost control measures to ensure the project stays within budget.
Section 7: Quality management
This section focuses on the quality standards and objectives for the project. It describes quality control and assurance processes, as well as any inspection and testing procedures that will be implemented.
Project management template
Save time on setup without sacrificing attention to detail. With our project management template, you can quickly create project management plans that help you complete your project on time and on budget.
Section 8: Resource management
In this section, the project team is introduced, and roles and responsibilities are defined. It addresses resource allocation, scheduling, and, if applicable, procurement needs.
Section 9: Risk management
The risk management section identifies potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the project. It discusses risk assessment, prioritization, and mitigation strategies to reduce the impact of these risks.
Section 10: Communication plan
The communication plan outlines how project information will be shared with stakeholders and team members. It specifies communication methods, frequency, and reporting channels to ensure effective communication throughout the project.
Section 11: Stakeholder management
This section lists project stakeholders and analyzes their interests, influence, and expectations. It also outlines strategies for engaging and managing these stakeholders to ensure their needs are addressed.
Section 12: Procurement management
If procurement of goods or services is involved, this section explains the procurement strategy, vendor selection criteria, and how contracts will be managed.
Section 13: Change management
Change management procedures are detailed here, including how changes to the project scope, schedule, or other aspects will be requested, evaluated, approved, and communicated.
Section 14: Closure criteria
Criteria for determining when the project is complete and ready for closure are specified in this section. It may also include plans for project handover and post-project evaluation.
Section 15: Project organization
This section describes the project team's structure, roles, and responsibilities, ensuring everyone understands their positions and reporting lines. It may also mention external stakeholders and their roles if applicable.
Once you’ve documented your project management plan, bring it to life with a project management tool that will help you to stay on track, keep your team accountable, and promote transparency.
Here are 3 ways you can use Teamwork.com to supercharge your project management plan.
Add your supporting documentation to Teamwork Spaces
Use the Teamwork.com and Teamwork Spaces integration to link a project in Teamwork.com with a space in Teamwork Spaces, so your important project documents are only ever a click away.
Some documents you might want to add in addition to your project charter and project management plan include:
Scoping documents
Risk assessments
Change management plans
SOPs for important project processes
List of stakeholders and their roles
Outline of approval processes
Communications management plan
Any other best practices documentation or supporting info as necessary
You can even embed task lists into your pages and mark tasks as complete right from Teamwork Spaces, so you can keep work flowing without even needing to switch tabs.
Start adding your Milestones
Break down your work into Milestones and task lists that are going to help you reach them. With Teamwork.com, you can assign an owner to each Milestone, map out your Milestone due dates and see them represented in the project calendar, and even get a full change history for milestones so you can track any edits.
Visualize your task dependencies with a Gantt chart
Gantt chart-style views are a useful way to get a visual representation of your tasks and their dependencies, allowing for better scheduling and resourcing. In Teamwork.com, you can drag and drop to quickly rearrange your project schedule , without throwing everything out of order or straying off-plan.
Remember: software should support the way you work, not dictate it. So regardless of methodology or team type, create a project plan that works for you and your team — and find a tool that helps you put it into action.
Use our project plan template
Now that you know how to create a project management plan that actually works, you’re ready to implement using our team management software . To help you get up and running quickly, we’ve created a ready to use project plan template . Our project template will help you quickly create project plans that ensure all of your projects are completed on time and on budget
What is a project management plan template?
A project management plan template is a pre-designed framework that provides a structured format for creating a project management plan. It serves as a starting point for project managers and teams to develop their specific project plans, saving time and ensuring that key project management components are properly addressed.
How can a template help you build a great project management plan?
A template can help you build a great project management plan by saving time, ensuring comprehensive coverage of project management aspects, and incorporating industry best practices and visual aids for clarity. They also support collaboration, version control, and customization to fit the unique needs of each project, making them a valuable tool for project managers in achieving successful project outcomes.
What is the main purpose of a project management plan?
The main purpose of a project management plan is to provide a comprehensive and structured roadmap for successfully executing, monitoring, controlling, and closing a project. It serves as a central document that outlines project objectives, scope, schedule, budget, quality standards, resource allocation, risk management strategies, and communication approaches.
What tools do I need to help manage a project plan?
To effectively manage a project plan, you'll need a set of tools and software that cover various aspects of project management. These include project management software, communication and collaboration platforms, file and document management solutions, time and task tracking apps, and budgeting and financial management tools.
What steps are involved in the project planning process?
The steps involved in the project planning process include defining specific project objectives and scope, identifying deliverables and key milestones, budgets, risk assessment and quality control measures. It should also include a communication plan and stakeholder engagement strategies.
You may also like...

Get started with Teamwork.com
Start working together beautifully. See how Teamwork.com can help your team with our 30-day free trial.
- Atlassian Guard
- Jira Service Management
- Continuous Delivery
- IT Service Management
- Inside Atlassian
- Project Management
- Work Management
- Company News

How to write an effective project plan in 6 simple steps

Contributing writer
If you’re a Type A personality, project planning might sound like music to your ears. Setting deadlines, organizing tasks, and creating order out of chaos — what’s not to love?
The reality is that project planning isn’t for everyone. In one survey by Association for Project Management, 76% of project professionals said their main project was a source of stress . Poor planning, unclear responsibilities, and overallocation are often the culprits behind the stress.
An effective project plan helps teams stay within budget, scope, and schedule, while delivering quality work. In short, it gets you to the finish line without the stress.
What is a project plan?
A project plan, also known as a work plan, is a blueprint of your project lifecycle. It’s like a roadmap — it clearly outlines how to get from where you are now (the beginning of the project) to where you want to go (the successful completion of the project).
“A project plan is an action plan outlining how…[to] accomplish project goals,” says Jami Yazdani , certified Project Management Professional (PMP), project coach, project management consultant, and founder of Yazdani Consulting and Facilitation .
A comprehensive project plan includes the project schedule, project scope, due dates, and deliverables. Writing a good project plan is key for any new, complex project in the pipeline.
Why Are Project Plans Important?
Project plans allow you to visualize your entire project, from beginning to end—and develop a clear strategy to get from point A to point B. Project plans steer stakeholders in the right direction and keep team members accountable with a common baseline.
Project plans help you stay agile
Projects are bound by what is traditionally called the “iron triangle” of project management . It means that project managers have to work within the three constraints of scope, resources (project budget and teams), and schedule. You cannot make changes to one without impacting the other two.
Modern-day project management has shifted to a more agile approach, with a focus on quality. This means that resources and schedules remain unchanged but a fixed number of iterations (flexible scope) helps teams deliver better quality and more value.
A project plan puts this “agile triangle” in place by mapping out resources, schedules, and the number of iterations — sprints if you’re using a Scrum framework and work in progress (WIP) limits if you’re using the Kanban methodology .
As Yazdani points out, “Project plans help us strategize a path to project success, allowing us to consider the factors that will impact our project, from stakeholders to budget to schedule delays, and plan how to maximize or mitigate these factors.”
Project plans provide complete visibility
A project plan, when created with a comprehensive project management software , gives you 360-degree visibility throughout the project lifecycle.
As a project manager, you need a single source of truth on team members and their project tasks, project scope, project objectives, and project timelines. A detailed project plan gives you this visibility and helps teams stay on track.

Project plans also help to get everyone involved on the same page, setting clear expectations around what needs to be accomplished, when, and by who.
“Project plans create a framework for measuring project progress and success,” says Yazdani. “Project plans set clear expectations for…stakeholders by outlining exactly what…will [be accomplished] and when it will be delivered.”
Project plans boost engagement and productivity
A well-written project plan clarifies how each individual team member’s contributions play into the larger scope of the project and align with company goals. When employees see how their work directly impacts organizational growth, it generates buy-in and drives engagement , which is critical to a project’s success.
“Project plans provide…teams with purpose and direction,” says Yazdani. “Transparent project plans show team members how their individual tasks and responsibilities contribute to the overall success of the project, encouraging engagement and collaboration.”
How To Write A Project Plan in 6 Steps
Writing a project plan requires, well, planning. Ideally, the seeds for a project plan need to be sowed before internal project sign-off begins. Before that sign-off, conduct capacity planning to estimate the resources you will need and if they’re available for the duration of the project. After all, you want to set your teams up for success with realistic end dates, buffer time to recharge or catch up in case of unexpected delays, and deliver quality work without experiencing burnout .
Based on organizational capacity, you can lay down project timelines and map out scope as well as success metrics, outline tasks, and build a feedback loop into your project plan. Follow these project planning steps to create a winning plan:
1. Establish Project Scope And Metrics
Defining your project scope is essential to protecting your iron, or agile, triangle from crumbling. Too often, projects are hit with scope creep , causing delays, budget overruns, and anxiety.
“Clearly define your project’s scope or overall purpose,” says Yazdani. “Confirm any project parameters or constraints, like budget, resource availability, and timeline,” says Yazdani.
A project purpose statement is a high-level brief that defines the what, who, and why of the project along with how and when the goal will be accomplished. But just as important as defining your project scope and purpose is defining what metrics you’re going to use to track progress.
“Establish how you will measure success,” says Yazdani. “Are there metrics, performance criteria, or quality standards you need to meet?”
Clearly defining what your project is, the project’s overall purpose, and how you’re going to measure success lays the foundation for the rest of your project plan—so make sure you take the time to define each of these elements from the get-go.
2. Identify Key Project Stakeholders
Get clarity on the team members you need to bring the project to life. In other words, identify the key stakeholders of the project.
“List individuals or groups who will be impacted by the project,” says Yazdani.
In addition to identifying who needs to be involved in the project, think about how they’ll need to be involved—and at what level. Use a tool like Confluence to run a virtual session to clarify roles and responsibilities, and find gaps that need to be filled.
Let’s say you’re managing a cross-functional project to launch a new marketing campaign that includes team members from your marketing, design, and sales departments.
When identifying your key stakeholders, you might create different lists based on the responsibility or level of involvement with the project:
- Decision-makers (who will need to provide input at each step of the project)
- Managers (who will be overseeing employees within their department)
- Creative talent (who will be actually creating the project deliverables for the campaign) from each department.
Give your project plan an edge by using a Confluence template like the one below to outline roles and responsibilities.

Define roles, discuss responsibilities, and clarify which tasks fall under each teammate’s purview using this Confluence template.
Getting clarity on who needs to be involved in the project—and how they’re going to be involved—will help guide the rest of the project plan writing process (particularly when it comes to creating and assigning tasks).
3. Outline Deliverables
Now is the time to get granular.
Each project milestone comprises a series of smaller, tangible tasks that your teams need to produce. While a big-picture view keeps teams aligned, you need signposts along the way to guide them on a day-to-day or weekly basis. Create a list of deliverables that will help you achieve the greater vision of the project.
“What will you create, build, design, produce, accomplish or deliver?” says Yazdani. “Clearly outline your project’s concrete and tangible deliverables or outcomes.” Centralize these deliverables in a Trello board with designated cards for each one, like in the example below, so you keep work moving forward.

Each card on a board represents tasks and ideas and you can move cards across lists to show progress.
Defining the concrete items you need your project to deliver will help you reverse-engineer the things that need to happen to bring those items to life—which is a must before moving on to the next step.
4. Develop Actionable Tasks
Task management is an important component of any project plan because they help employees see what exactly they need to accomplish. Drill down those deliverables into actionable tasks to assign to your team.
You can use either Confluence or Jira for different task management needs. If you want to track tasks alongside your work, like action items from a meeting or small team projects, it’s best to use Confluence. But if a project has multiple teams and you need insight into workflows, task history, and reporting, Jira makes it easy.
“Let your deliverables guide the work of the project,” says Yazdani. “Break down each deliverable into smaller and smaller components until you get to an actionable task.” If a major deliverable is a set of content pieces, the smaller actionable tasks would be to create topic ideas, conduct research, and create outlines for each topic.
Once you’ve broken down all of your deliverables into manageable, assignable subtasks, analyze how each of those tasks interacts with each other. That way, you can plan, prioritize, assign, and add deadlines accordingly.
“Highlight any dependencies between tasks, such as tasks that can’t be started until another task is complete,” says Yazdani. “List any resources you will need to accomplish these tasks.”
When a task has multiple assignees, you need to streamline the workflow in your project plan. Say the content pieces you outlined need to be edited or peer-reviewed. A couple of articles may need an interview with a subject matter expert. Lay down a stage-by-stage process of each piece of content and pinpoint when each team member comes into play so you prevent bottlenecks and adjust timeframes.
5. Assign Tasks And Deadlines
Assign tasks to your team and collaborate with employees to set deadlines for each task. When you involve employees in setting workloads and deadlines , you increase ownership and boost the chances of delivering quality work on time.
After all, you want to move projects forward at a steady pace, but you also want to make sure your teams stay motivated and engaged. So, when writing your project plan, make sure to “set realistic and achievable deadlines for completing tasks and deliverables,” says Yazdani. “Highlight dates that are inflexible and factor in task dependencies. Add in milestones or checkpoints to monitor progress and celebrate successes .”

Use Jira and Confluence to create tasks that live alongside your project plan or meeting agendas.
Once you map out all of your tasks and deadlines, you should have a clear picture of how and when your project is going to come together—and the initial writing process is just about finished.
But that doesn’t mean your project plan is complete! There’s one more key step to the process.
6. Share, Gather Feedback, And Adjust The Project Plan As Necessary
While steps 1 through 5 may make up your initial writing process, if you want your project plan to be as strong and complete as it can be, it’s important to share it with your team—and get their input on how they think it can be improved.
“Share the plan with your project team and key stakeholders, gathering feedback to make adjustments and improvements,” says Yazdani.
A tool like Confluence helps knowledge flow freely within teams and departments, leading to better teamwork, higher collaboration, and a shared understanding of priorities. Coworkers can use comments, mentions, notifications, and co-editing capabilities to provide and discuss feedback.
After you gather your team’s feedback —and make any necessary adjustments based on that feedback—you can consider your project plan complete. Hooray!
But as your project progresses, things may change or evolve—so it’s important to stay flexible and make changes and adjustments as needed.
“Expect to update your plan as you gather more information, encounter changing requirements and delays, and learn from feedback and mistakes,” says Yazdani. “By using your project plan to guide your activities and measure progress, you’ll be able to refine and improve your plan as you move through the project, tweaking tasks and deadlines as deliverables are developed.”
Download a template to create your project plan and customize it based on your needs.
Example of a simple project plan
A project plan doesn’t have to be a complicated spreadsheet with multiple tabs and drop-down menus. It’s best to use a project planning tool like Confluence — or at least a project plan template — to make sure you cover every aspect of the project. A simple project plan includes these elements:
- Project name, brief summary, and objective.
- Project players or team members who will drive the project, along with their roles and responsibilities.
- Key outcomes and due dates.
- Project elements, ideally divided into must-have, nice-to-have and not-in-scope categories.
- Milestones, milestone owners, and a project end date.
- Reference material relevant to the project.

Best Practices For Writing Effective Project Plans
A project planning process can quickly turn into a mishmash of goals and tasks that end up in chaos but these best practices can give you a framework to create a project plan that leads to success.
Use Other Project Plans For Inspiration
There’s no need to reinvent the wheel for every new project! Instead, look to other successful project plans for inspiration—and use them as a guide when writing the plan for your project.
“Review templates and plans for similar projects, or for other projects within your organization or industry, to get ideas for structuring and drafting your own plan,” says Yazdani.
To get started, use a Trello project management template and customize it for your project plan by creating unique lists and adding cards under each list.

Build your team’s ideal workflow and mark each stage of the project plan as a list, with cards for each task.
Get Your Team Involved In The Process
You may be in charge of spearheading the project. But that doesn’t mean that you have to—or even that you should—write the project plan alone.
“Collaborate with your project team and key stakeholders on crafting a project plan,” says Yazdani. “Input into the project plan supports buy-in to project goals and encourages continued engagement throughout the project.”
With Confluence , you can organize project details in a centralized space and build a project plan collaboratively.
Don’t Let Perfect Be The Enemy Of The Good
You may be tempted to write (and rewrite) your project plan until you’ve got every detail mapped out perfectly. But spending too much time trying to get everything “perfect” can actually hold up the project. So don’t let perfect be the enemy of the good—and instead of getting caught up in getting everything perfect from the get-go, stay willing and flexible to adjust your project plan as you move forward.
“Focus on outcomes, not plan perfection,” says Yazdani. “While it would be awesome for the first draft of our plan to require no changes while also inspiring our team and ensuring project success, our goal shouldn’t be a perfect plan. Our goal is a plan that allows us to successfully deliver on project goals. Responsiveness to changing needs and a shifting environment is more important than plan perfection.”
Use the right tools to succeed with your project plan
Writing a project plan, especially if you’re new to the process, can feel overwhelming. But now that you know the exact steps to write one, make sure you have the tools you need to create a strong, cohesive plan from the ground up—and watch your project thrive as a result.
Atlassian Together can help with project planning and management with a powerful combination of tools that make work flow across teams.
Guide your team to project success with Atlassian Together’s suite of products.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing What is a Project Management Plan and How to Create One
What is a Project Management Plan and How to Create One
Written by: Midori Nediger Dec 11, 2023

Have you ever been part of a project that didn’t go as planned?
It doesn’t feel good.
Wasted time, wasted resources. It’s pretty frustrating for everyone involved.
That’s why it’s so important to create a comprehensive project management plan before your project gets off the ground.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to create and design a successful project management plan.
We’ll also showcase easy-to-customize project plan templates you can create today with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor. Let’s get started!
Click to jump ahead:
What is a project management plan?
5 things you need to know before creating a project management plan, what should a project management plan include, how do you write a project plan, project plan best practices, project management plan templates and examples, common mistakes to avoid when creating a project management plan.
A project management plan is a formal document that defines how a project is going to be carried out by outlining the scope, goals, budget, timeline and deliverables of a project. Its crucial role lies in ensuring the project stays on course.
You write a project plan during the project planning stage of the project life cycle , and it must be approved by stakeholders before a project can move on the execution stage.
If some of these terms are new to you, you can get up to speed with this post on project management terms .
This means your project plan must be engaging, organized, and thorough enough to gain the support of your stakeholders.

Further Reading : New to project management? Read our blog post on the 4 stages of the project life cycle .
The importance of a project management plan
A well-developed project management plan sets the foundation for a successful project by providing a roadmap that guides the project team toward successful project completion. A good project management plan can ensure that:
- Project objectives and goals are clearly defined and understood
- Project scope is effectively managed
- Resources are allocated efficiently to maximize productivity and minimize waste
- Risks are identified, assessed and mitigated
- Project tasks and activities are well-organized and executed in a timely manner.
- Communication among team members , stakeholders and project sponsors is effective and transparent
- Changes to the project are properly evaluated, approved and implemented
- Lessons learned and best practices are documented for future reference and improvement
- Stakeholders are engaged and satisfied with the project outcomes
- The project is delivered within the specified timeline, budget and quality standards
Before diving into creating a project management plan, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the project objectives and the expectations of stakeholders involved.
Without a firm grasp of these fundamental elements, your project may face significant challenges or fail to deliver the desired outcomes.
Here are key points to consider when creating a project management plan:
- Project Objectives: Clearly understand the project objectives and what you want to achieve. Identify the desired outcomes, deliverables and the purpose of the project.
- Scope of the Project: Determine the boundaries and extent of the project. Define what is included and excluded to ensure clarity and prevent scope creep .
- Stakeholders: Identify all stakeholders who will be impacted by or have an interest in the project. Understand their needs, expectations and level of involvement.
- Resources: Assess the resources required to execute the project successfully. This includes human resources, budget, equipment and materials. Determine their availability and allocation.
- Risks and Constraints: Identify potential risks, uncertainties and constraints that may affect the project. Understand the challenges, limitations and potential obstacles that need to be addressed.
Now that you have these key areas identified, let’s get started with creating your project plan.
Before you start assembling your own plan, you should be familiar with the main components of a typical project plan .
A project management plan should include the following sections:
- Executive summary: A short description of the contents of the report
- Project scope & deliverables: An outline of the boundaries of the project, and a description of how the project will be broken down into measurable deliverables
- Project schedule: A high-level view of project tasks and milestones ( Gantt charts are handy for this)
- Project resources: The budget, personnel, and other resources required to meet project goals
- Risk and issue management plan: A list of factors that could derail the project and a plan for how issues will be identified, addressed, and controlled
- Communication management plan: A plan for how team and stakeholder communication will be handled over the course of the project
- Cost and quality management plan: This section encompasses the project’s budget, cost estimation,and cost control mechanisms. It also includes quality assurance testing and control measures as well as any testing or verification activities to be performed.
Basically, a project plan should tell stakeholders what needs to get done, how it will get done, and when it will get done.
That said, one size doesn’t fit all. Every project management plan must be tailored to the specific industry and circumstances of the project. You can use a project management app for smoother project planning.
For example, this marketing plan looks client facing. It is tailored to sell the client on the agency:

Whereas this commercial development plan focuses on specific objectives and a detailed timeline:

With those basics out of the way, let’s get into how to write a project management plan that’s as engaging as it is professional.
Further Reading : If you’re looking to create a proposal, read our in-depth business proposal guide. Then try our job proposal templates or business proposal templates .
To write a successful project plan, follow these 5 steps below to create an effective project plan that serves as a valuable tool for project management:
1. Highlight the key elements of your project plan in an executive summary
An executive summary is a brief description of the key contents of a project plan .
I t’s usually the first thing stakeholders will read, and it should act like a Cliff’s-notes version of the whole plan.
It might touch on a project’s value proposition, goals, deliverables, and important milestones, but it has to be concise (it is a summary, after all). First, make sure you develop a proof of concept .
In this example, an executive summary can be broken into columns to contrast the existing problem with the project solution:

The two-column format with clear headers helps break up the information, making it extremely easy to read at a glance.
Here’s another example of a project management plan executive summary. This one visually highlights key takeaways with big fonts and helpful icons:

In this case, the highlighted facts and figures are particularly easy to scan (which is sure to make your stakeholders happy).
But your executive summary won’t always be so simple.
For larger projects, your executive summary will be longer and more detailed.
This project management plan template has a text-heavy executive summary, though the bold headers and different background colors keep it from looking overwhelming:

It’s also a good idea to divide it up into sections, with a dedicated header for each section:

Regardless of how you organize your executive summary, it should give your stakeholders a preview of what’s to come in the rest of the project management plan.
2. Plot your project schedule visually with a Gantt chart
A carefully planned project schedule is key to the success of any project. Without one, your project will likely crumble into a mess of missed deadlines, poor team management, and scope creep.
Luckily, project planning tools like Gantt charts and project timelines make creating your project schedule easy. You can visually plot each project task, add major milestones, then look for any dependencies or conflicts that you haven’t accounted for.
For example, this Gantt chart template outlines high-level project activities over the course of an entire quarter, with tasks color-coded by team:

A high-level roadmap like the one above is probably sufficient for your project management plan. Every team will be able to refer back to this timeline throughout the project to make sure they’re on track.
But before project kickoff, you’ll need to dig in and break down project responsibilities by individual team member, like in this Gantt chart example:
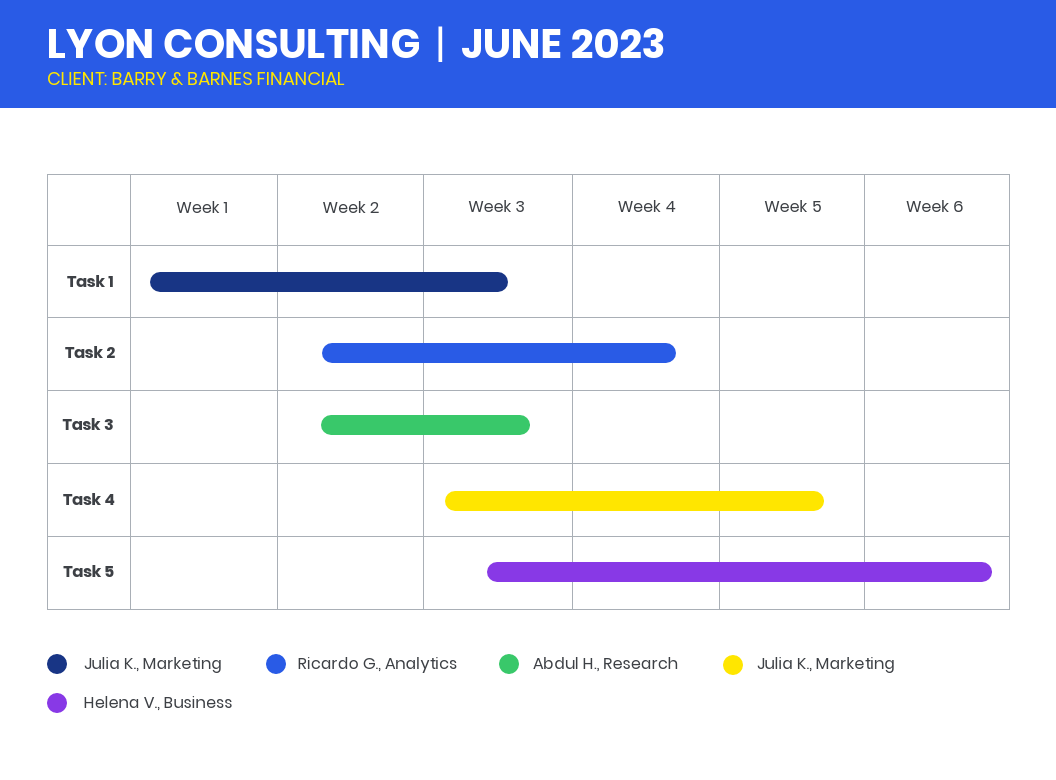
In the later execution and monitoring phases of the project, you’ll thank yourself for creating a detailed visual roadmap that you can track and adjust as things change.
You can also use a project management tool to keep your team organized.
Further Reading: Our post featuring Gantt chart examples and more tips on how to use them for project management.
3. Clarify the structure of your project team with a team org chart
One of the hardest aspects of project planning is assembling a team and aligning them to the project vision.
And aligning your team is all about communication–communicating the project goals, communicating stakeholder requests, communicating the rationale behind big decisions…the list goes on.
This is where good project documentation is crucial! You need to create documents that your team and your stakeholders can access when they have questions or need guidance.
One easy thing to document visually is the structure of your team, with an organizational chart like this one:

In an organizational chart you should include some basic information like team hierarchy and team member contact information. That way your stakeholders have all of the information they need at their fingertips.
But in addition to that, you can indicate the high-level responsibilities of each team member and the channels of communication within the team (so your team knows exactly what they’re accountable for).
Here’s another simple organizational structure template that you can use as a starting point:

Create an organizational chart with our organizational chart maker .
4. Organize project risk factors in a risk breakdown structure
A big part of project planning is identifying the factors that are likely to derail your project, and coming up with plans and process to deal with those factors. This is generally referred to as risk management .
The first step in coming up with a risk management plan is to list all of the factors at play, which is where a risk breakdown structure comes in handy. A risk breakdown structure is a hierarchical representation of project risks, organized by category.
This risk breakdown structure template, for example, shows project risk broken down into technical risk, management risk, and external risk:

Once you’ve constructed your risk breakdown structure, you’ll be ready to do a deep dive into each risk (to assess and plan for any triggers and outcomes).
Streamline your workflow with business process management software .
5. Plan ahead: create project status reports to communicate progress to stakeholders
As I mentioned earlier, communication is fundamental in any project.
But even so, something that’s often overlooked by project managers is a communication management plan–a plan for how the project team is going to communicate with project stakeholders . Too often, project communication defaults to ad-hoc emails or last-minute meetings.
You can avoid this by planning ahead. Start with a project kickoff meeting and include a project status report template as part of your communication plan.
Here’s an example of a simple project status report that you might send to stakeholders on a weekly basis:
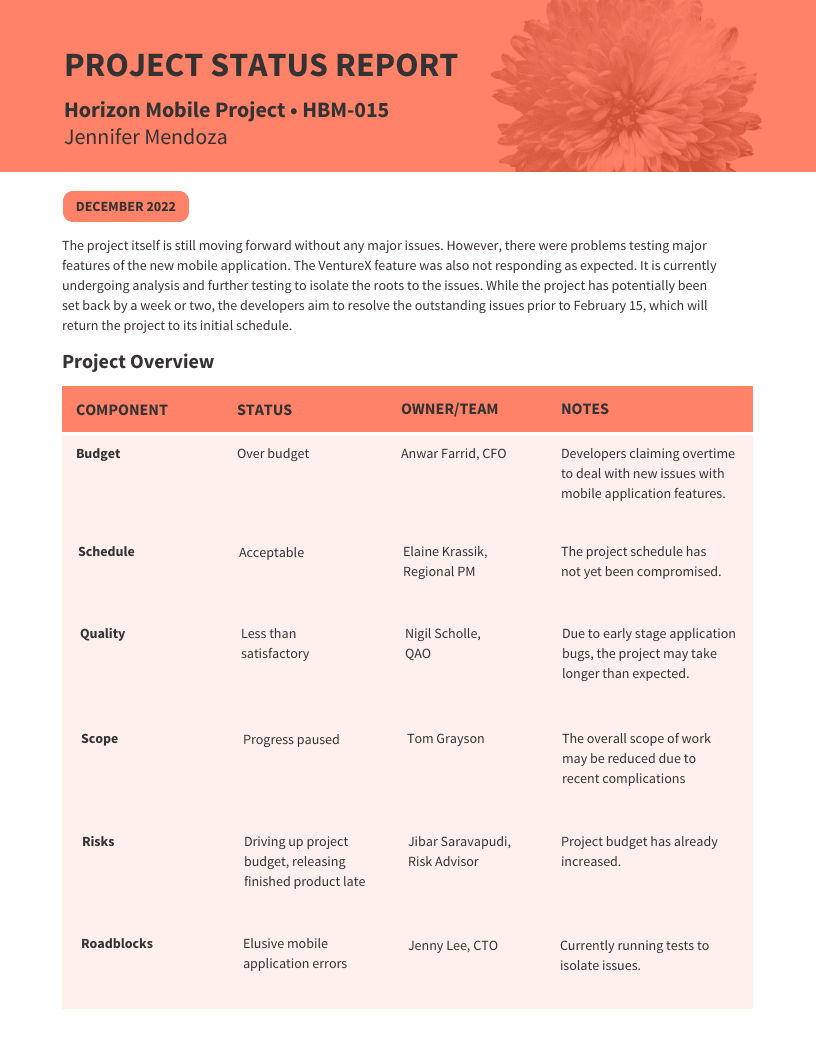
This type of report is invaluable for communicating updates on project progress. It shows what you’ve accomplished in a clear, consistent format, which can help flag issues before they arise, build trust with your stakeholders , and makes it easy to reflect on project performance once you’ve reached your goals.
You might also want to include a broader status report for bigger updates on a monthly or quarterly basis, like this one:

The above template allows you to inform stakeholders of more major updates like new budget requirements, revised completion dates, and project performance ratings.
You can even include visualization of up-to-date project milestones, like this example below:

Want more tips on creating visuals to enhance your communications? Read our visual communication guide for businesses .
Before you dive in, remember: a clear and adaptable plan is crucial for project success. Here are some best practices to keep your project plan on track:
- Use headers, columns and highlights to make your executive summary easy to read
- Plot your project schedule with a Gantt chart (with tasks color-coded by department or team member)
- Use visuals like organizational charts and risk breakdown structures to communicate across your team and with stakeholders
- Pick a flexible template that you can update to align with stakeholder requests
A project management plan is probably the most important deliverable your stakeholders will receive from you (besides the project itself).
It holds all of the information that stakeholders will use to determine whether your project moves forward or gets kicked to the curb.
That’s why it’s a good idea to start with a project management plan template. Using a template can help you organize your information logically and ensure it’s engaging enough to hold your stakeholders’ attention.
Construction project management plan template
Time is money, especially with construction projects. Having a construction plan template brings order to the chaos.
Instead of staring at a messy pile of construction stuff, you’ve got a plan that breaks everything down into bite-sized pieces.
And let’s not forget the paperwork. Construction projects have rules and regulations to follow. Your project plan helps you stay on the right side of the law with all the necessary documentation and compliance measures.
Start with a meticulous project overview, like in the second page of this template:

Though you may think this project will be similar to others you’ve done in the past, it’s important to nail the details.
This will also help you understand the scope of work so you can estimate costs properly and arrive at a quote that’s neither too high or low. Ontario Construction News has great advice on this process.
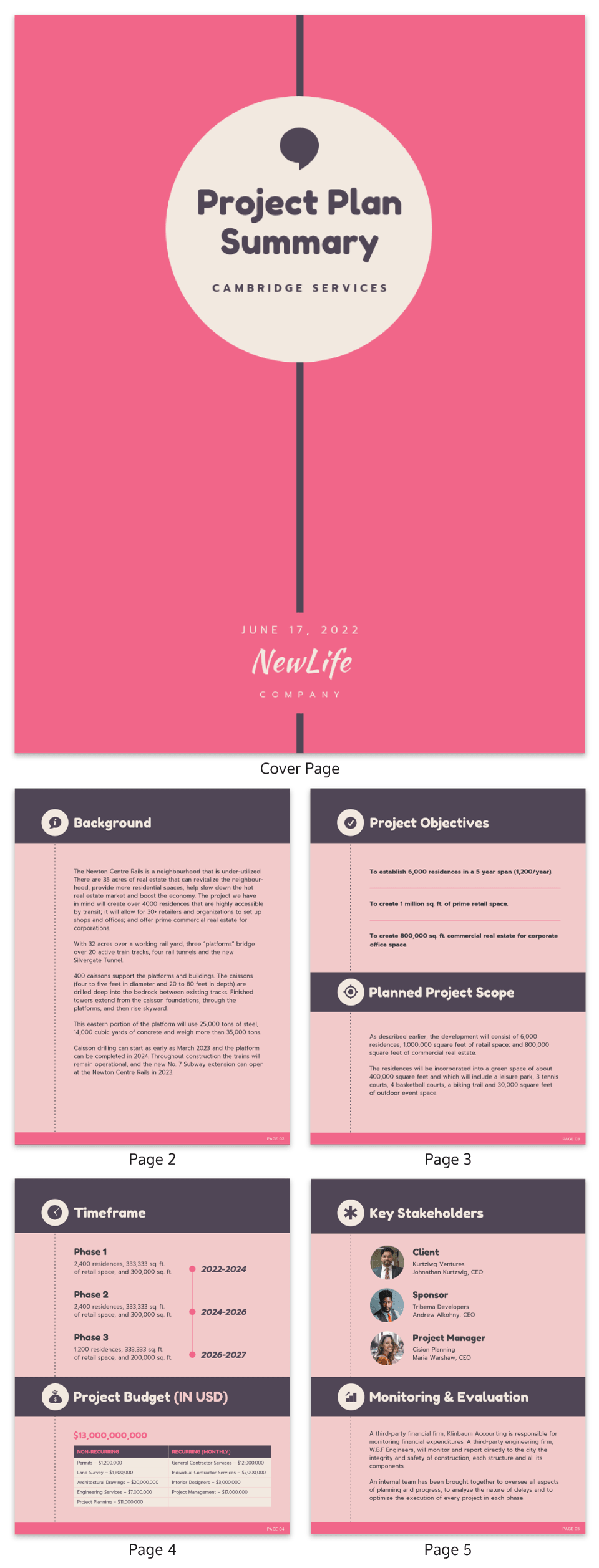
Simple project management plan template
This simple project management plan template that clearly lays out all of the information your stakeholders will need:
Simple project management communication plan template
A key part of project management is making sure everyone’s in the loop. A project communication plan ensures everyone knows how, where, who and when the team will communicate during the course of the project. Also construction scheduling is a critical aspect of the project management plan as it helps to ensure that all necessary tasks are completed within the allocated time frame and budget.
The key is to figure out what kind of communications is valuable to stakeholders and what is simply overwhelming and won’t lead to better decisions.
This template clearly outlines all of these factors to help manage expectations and eliminate confusion about what will get communicated and when:

Commercial development project plan template
The below project management plan template is simple and minimal, but still uses a unique layout and simple visuals to create an easy-to-read, scannable project overview.
This template is perfect for building or construction management , or any technical projects:

When picking a project plan template, look for one that’s flexible enough to accommodate any changes your stakeholders might request before they’ll approve the project. You never know what might change in the early planning stages of the project! You can also use project management tools to help you with your planning !
Creating a solid project management plan is crucial for setting your project up for success. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Lack of clear goals: Don’t just have a vague idea of what you want to achieve. Define clear, SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-bound) for your project. That way, everyone will be on the same page and it’ll be easier to measure progress effectively.
- Unrealistic timelines: Be optimistic, but also realistic. Don’t underestimate the time required for tasks. Factor in potential delays and buffer time when creating your project schedule.
- Scope creep: New requirements mid-project can affect deadlines and budgets. Plan the project clearly upfront, and take into consideration any changes that might come up.
- Poor communication: Communication is key throughout the project lifecycle. Regularly update stakeholders, team members and clients on progress, roadblocks and changes.
- Ignoring risks: Things don’t always go according to plan. Identify potential risks upfront and have a mitigation strategy in place for each one.
- Not involving stakeholders: Get key stakeholders involved early on. This helps manage everyone’s expectations and that you have the buy-in you need for success.
- Neglecting resource constraints: Don’t overload your team or underestimate the resources needed. Carefully consider the skills, time and budget available when planning your project.
- Micromanaging: Trust your team! Delegate tasks effectively and give them the autonomy they need to do their jobs.
- Failing to document: Keep good records. Document project decisions, plans and communication. This helps maintain transparency and ensures everyone has access to the latest information.
- Not adapting to change: Be prepared to adapt your plan as needed. Projects are rarely static, so be flexible and willing to adjust your approach based on new information or developments.
So, that’s the scoop on project management plans! I hope this piece will help you to avoid confusion, keep expectations in check and be ready to tackle any bumps for your upcoming projects.
If you ever need a revision, just follow the steps we talked about, use those best practices and you’ll have a plan that sets your project up for a win. Just remember, even the best plans need some tweaking sometimes. Be flexible and adjust as needed and you’re good to go!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
9 raci chart examples for project management.
September 7, 2023
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
Not having project roles and responsibilities set in place leads to a myriad of project management-related issues—schedule delays, scaling costs, and lower performance, just to name a few.
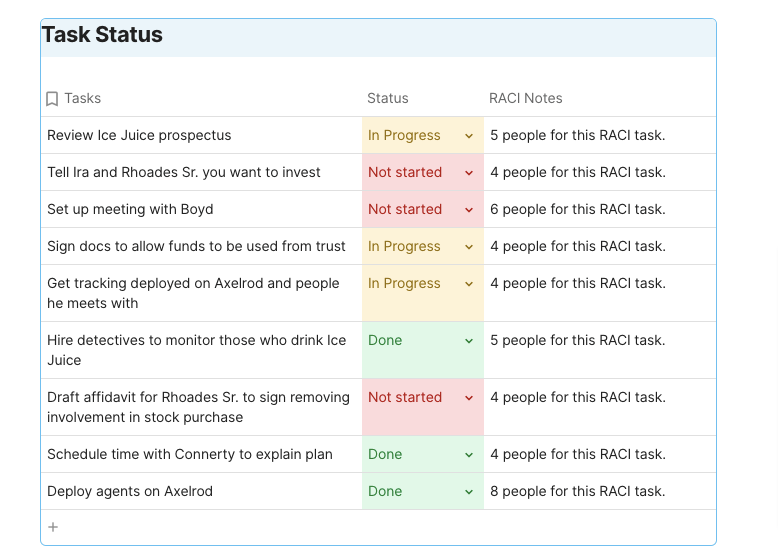
That’s when the RACI matrix, also known as the RACI diagram or responsibility assignment matrix, comes into the picture. 🖼️
The RACI model helps with mapping all of the stakeholders’ roles and responsibilities, bringing structure and clarity, and engaging everyone from the team in the successful project delivery so that miscalculations are out of the question.
Here’s why many people from the corporate world across various industries, from healthcare to construction, swear by RACI charts . 🙏
What is a RACI Matrix Chart?
Advantages of the raci chart model, when to use the raci chart model, how to create a raci chart model, clickup examples, miro examples.
- Coda Examples
Who Benefits From Using a RACI Chart?
Raci is the way to go.
RACI matrix is a simple approach to defining project roles and responsibilities that help produce desired outcomes.
This term is an acronym that stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. RACI essentially describes the different roles assigned to team members involved in the project and details who does what.
Responsible : As you can already suggest, this person is responsible for taking action and ensuring that tasks on the project are being worked on.
Typically, this is a team member or a project manager that reports to an A. You can have more Rs in a RACI, and some of them can also be involved in the decision-making process .
However, it is highly advisable not to blow things up out of proportion and over-assign the number of Responsibles in your responsibility assignment matrix.
Accountable : That’s someone who ensures all the responsibilities are assigned properly, approves or rejects work or decisions (basically, this person is a decision maker), and ensures that everything is successfully and timely delivered. According to the RACI matrix, there should be only one A.
Consulted : This is the person the team consults about various topics and actions, an expert. This person, or multiple persons, provides feedback and evaluates so tasks can be performed.
Informed : Someone who should be updated on progress once everything is done and dusted but isn’t directly involved in the process. This person doesn’t contribute to making decisions or delivering tasks nor is consulted on any matter.
We know project management teams love abbreviations : PMP, KPI, SOW, and SME. The list goes on and on, but the RACI matrix chart makes it a breeze to scheme out key decisions, tasks, milestones , and roles.
When it comes to large project management teams, where team members are distributed across multiple departments and reliant on other teams, it is kind of natural to suffer from role confusion.
In a situation like this, it’s up to a project manager or the leading project team to step up and make sure that every member of every team is well aware of what’s expected from them. Things can get even more challenging if the work is remotely managed and done. However, that’s when the RACI matrix comes to the rescue! 🚀
The RACI chart model provides a myriad of benefits in this regard :
- It eliminates role confusion and confusion about who makes decisions (it could be that the Accountable or Responsible party is the decision-maker, so it should be made clear from the beginning)
- It encourages teamwork and communication between everyone involved in the project, which leads to setting expectations straight
- It prevents over and under-allocation of resources of a team member and ensures a smooth reallocation of resources when needed
- It can guarantee that even in case of resource reallocation, no task is overlooked
- By using it, you’ll streamline communications, eliminate conflict resolution, instill trust and ensure a high level of engagement
- Ultimately, it improves project efficiency and saves time
It’s worth mentioning that the RACI chart can ensure that every relationship is managed appropriately, whether it be with customers, sponsors, VIP clients, internal users, suppliers, investors, executives, analysts, or government regulators.
That’s why this model ticks all of the boxes for both B2B and B2C businesses. ✅
RACI matrix can be used for all-things-project-management, from clarifying team member roles and tasks to eliminating any sort of confusion and stalled processes.
The great thing is that it is unbelievably flexible, and you can use it no matter which industry you are in. 🤩
Here are some of the examples of when the RACI chart model can be helpful :
- Role confusion typically gets in the way of progress and bogs down the approval process or when decisions are made seemingly arbitrarily, again, because of the lack of transparency around the roles
- When authority, responsibilities, roles, and tasks are not clearly defined
- When there is no clarity on who should be performing tasks, which either results in multiple people working on the same task or none of them working on the project tasks they should be working on
As an example, any project manager or product owner is somehow (wrongfully) seen as responsible for every little detail and the success of a project team in general.
The RACI chart takes the burden of these roles. It allows developers and designers to be responsible for their scope of work .
However, note that RACI is not the one-size-fits-all solution.
It works wonders with larger, complex projects that involve multiple stakeholders. On the other hand, it simply doesn’t cut the mustard for smaller project management teams and fast-moving projects since it can only slow down the decision-making process and the project as a whole.
Before you actually start creating a RACI chart, take these factors into account :
- Ideally, one person should have only one type of responsibility
- The Accountable person should have the authority and be able to provide guidance and help with completing tasks
- Assign a single Accountable party per deliverable
- Every task should be associated with Responsible and Accountable roles while it is not mandatory to ask for outside input if the task is not overly complex
- Stakeholders should be informed even about minor changes and updates on the project
Now, here’s how to create a RACI chart:
1. define deliverables.
Define and list the main project tasks that need to be completed and list them all on the left side of the RACI chart, one under another.
Do not include all of the project deliverables in the chart, or else you’ll go too granular and make it too complex to use and understand.
2. Identify project roles
Identify members of the project team and their roles (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed ) and add them to the top of the chart, one next to another.
For instance, you can go for something like this: project executive, project manager, business analyst, technical architect , and application developer.
Alternatively, you can specify roles by name. This is particularly useful since it clarifies who does what and if multiple stakeholders are assigned similar roles.
3. Connect the dots
Now is the time to connect tasks and roles. ♻️
Assigning Responsible and Accountable per task is a must, while you should also think carefully about who needs to be Consulted and who is Informed about the deliverables.
4. Resolve any conflicts if they occur
Ideally, one team member should be assigned to only a few responsibilities (two to three maxi).
If there are many empty cells, try reallocating resources (change Responsible to Consulted).
Also, if there are too many Accountable roles, this could slow down the decision-making process, so aim to have just one Accountable person per task.
Too many Cs can also cause delays for project managers since some under the consultant role can often be switched to Informed. Having no C and I roles usually points to a lack of communication within the team.
RACI Matrix Examples and Use Cases
For our first batch examples, we’ll be using our beloved tool, ClickUp . You can customize every part of the platform, making it easier than ever to create your ideal RACI matrix. When you need inspiration or guidance, take advantage of the ready-to-use and editable RACI Planning Template in ClickUp to help get you started.
Let’s see how much flexibility we can have when creating RACI charts in ClickUp.
Simple RACI Chart in Doc View
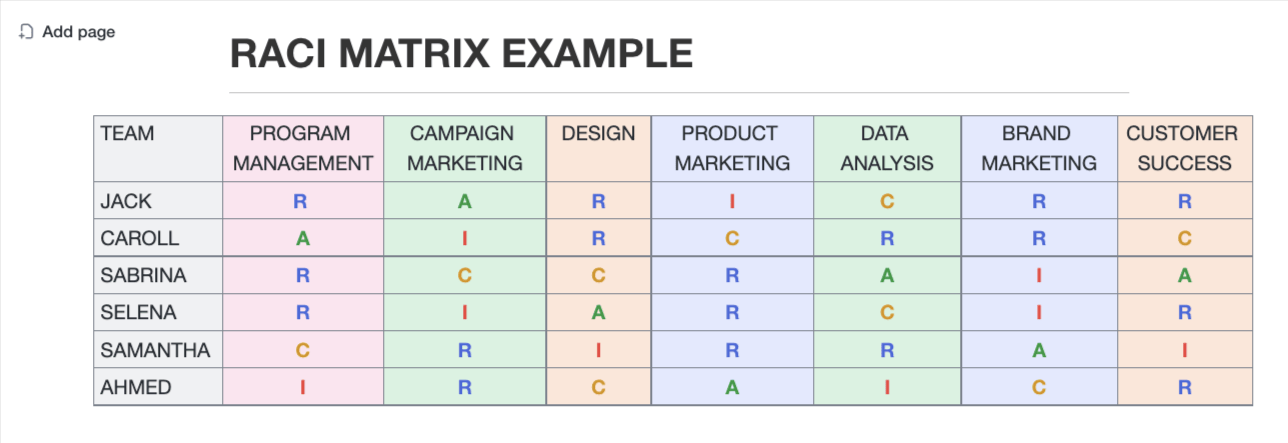
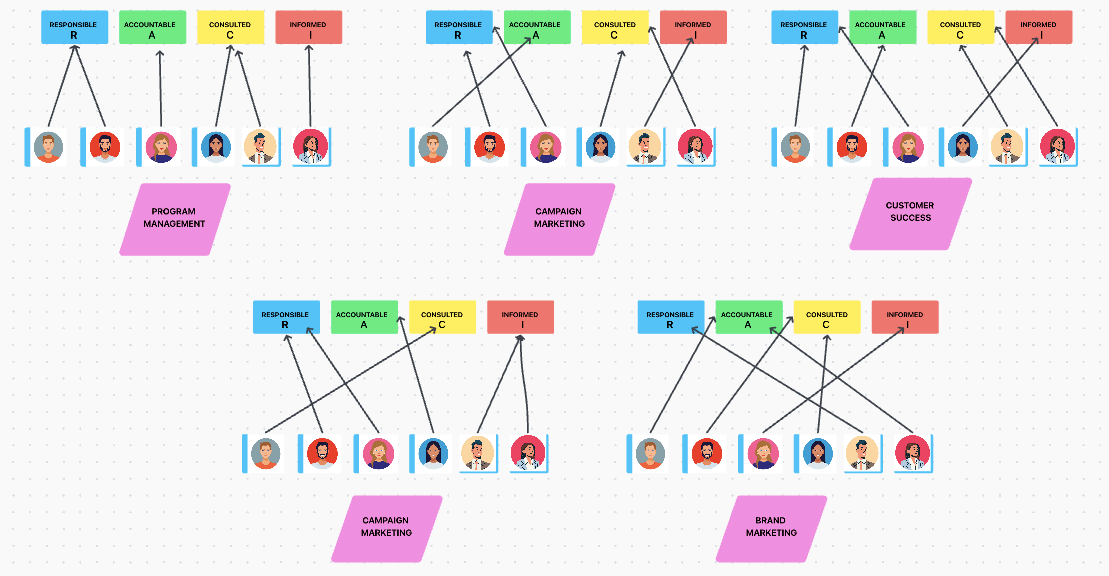
Here’s a perfect example of what we’ve explained above. ClickUp’s Doc view can be used for making a RACI chart without overcomplicating things.
Stakeholders to the left, roles to the top and right. Jack, Sabrina, and Selena are Responsible for program management , Caroll is Accountable, Samatha is Consulted, and Ahmed is Informed.
It’s a great thing that there’s only one responsible person who holds the role of Accountable when it comes to program management. That’s the thing with campaign marketing , design, product marketing , data analysis, brand marketing, and customer success, too!
It’s also easy to spot that no resources are over-allocated. Jack is the Responsible person for program management, brand marketing, and customer success while he is Accountable for campaign marketing, Informed for product marketing , and Consulted for Data Analysis.
Color-Coded RACI Matrix in List View
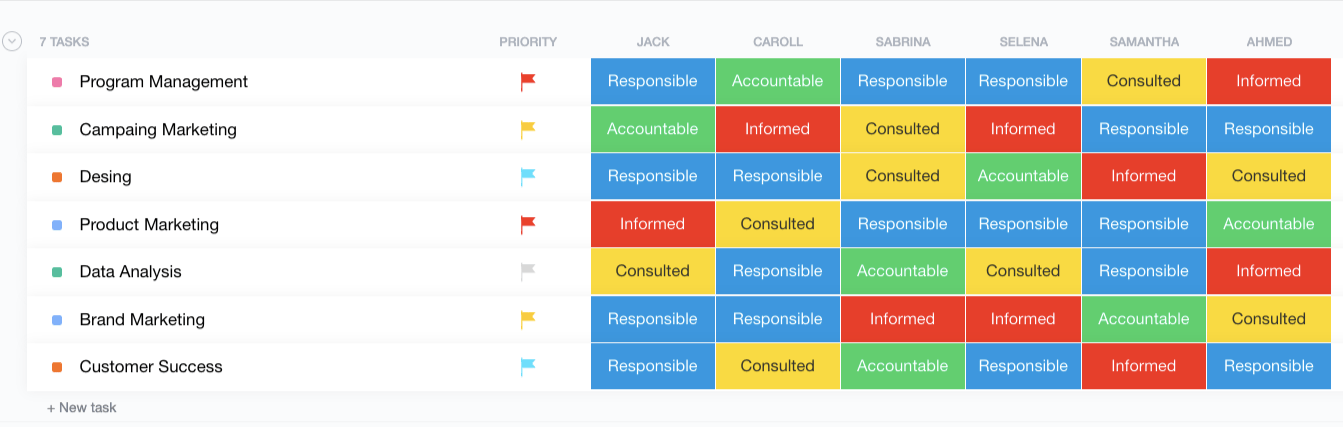
ClickUp’s List view lets us go more into detail with the RACI chart. It also allows you to bring a pop of color to the whole concept to make sometimes dull project management more refreshing. 🌈
You can actually choose between various role colors. We used blue for Responsible, green for Accountable, and so on. It’s totally up to you to customize the table and roles to your liking.
Here, we also have slightly different positioning of roles and tasks. Project tasks are listed on the left, one under another, while names and responsibilities are located on the top and to the right (if you prefer this kind of visualization, that’s totally cool).
You can also see priority flags that can give everyone direction and point out tasks that need to be taken care of ASAP and the ones that can wait a little bit. 🚩
RACI Model in Table View
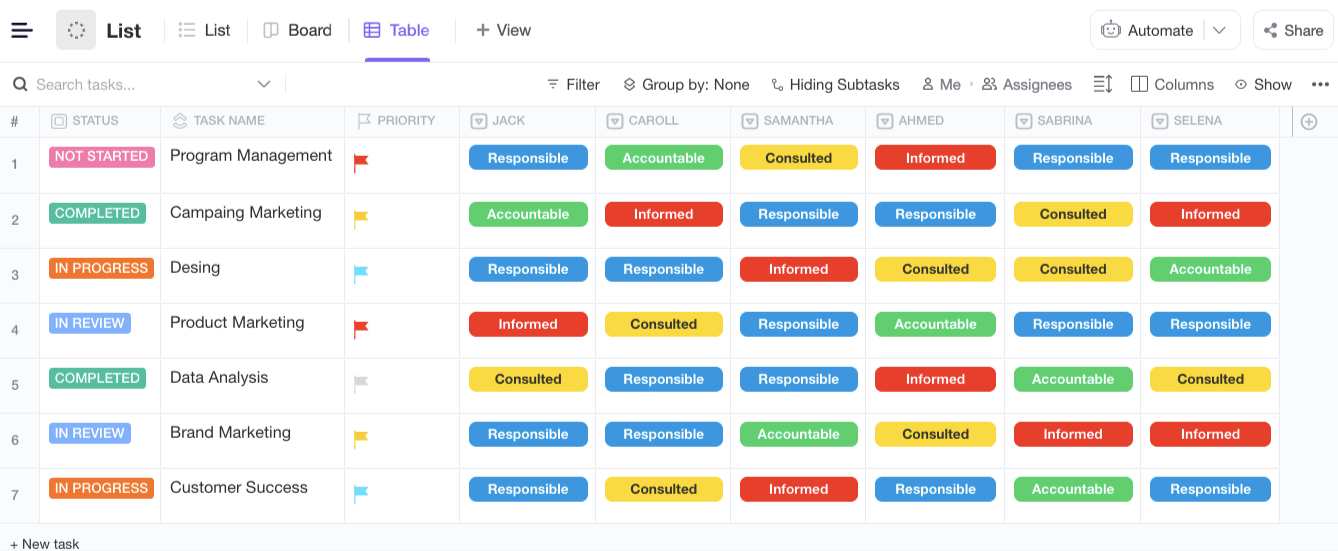
The Table view allows getting more nitty-gritty with your RACI chart. Aside from seeing roles, tasks, and priorities, you can also track the status of each task from the chart. Statuses are fully customizable; this is just an example of how you can name and color each.
RACI Chart Example Grouped by Status
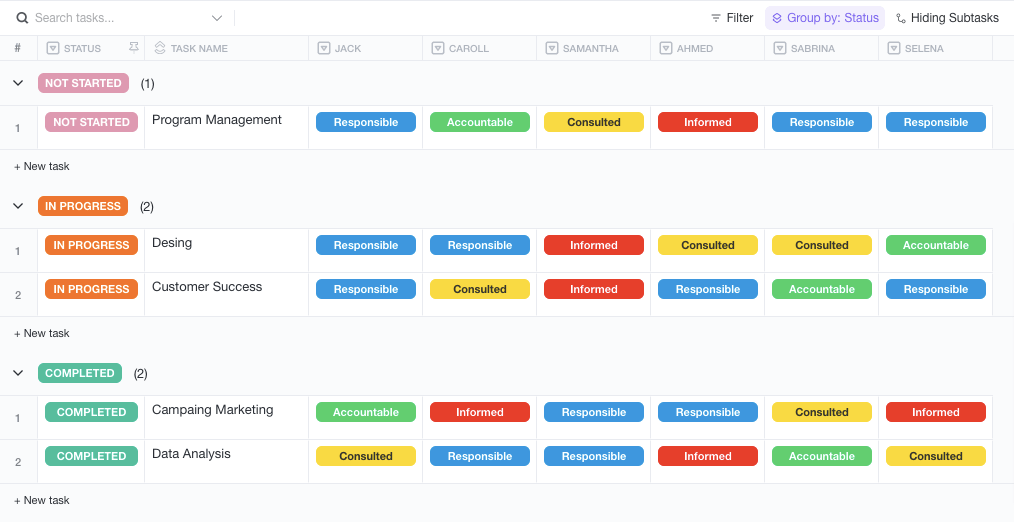
Within the Table view, ClickUp also lets you filter and group tasks by name, role, status, priority, etc. This allows you to get more into the nitty-gritty details of your RACI chart and see which tasks are in progress, which ones are yet to be worked on, and which ones are completed.
Finally, as already known, ClickUp views , and the Whiteboard is among our favorites! 😍
RACI Roles in Whiteboard View
The ClickUp Whiteboard makes it easy to visualize tasks, roles, and roles separately, all with a touch of color. It ensures that everyone works as a team. This leaves practically no room for conflicts or low morale.
Next up is the infamous mind mapping tool, Miro . Let’s see what kind of RACI magic we can come up with.
RACI Stakeholder Map
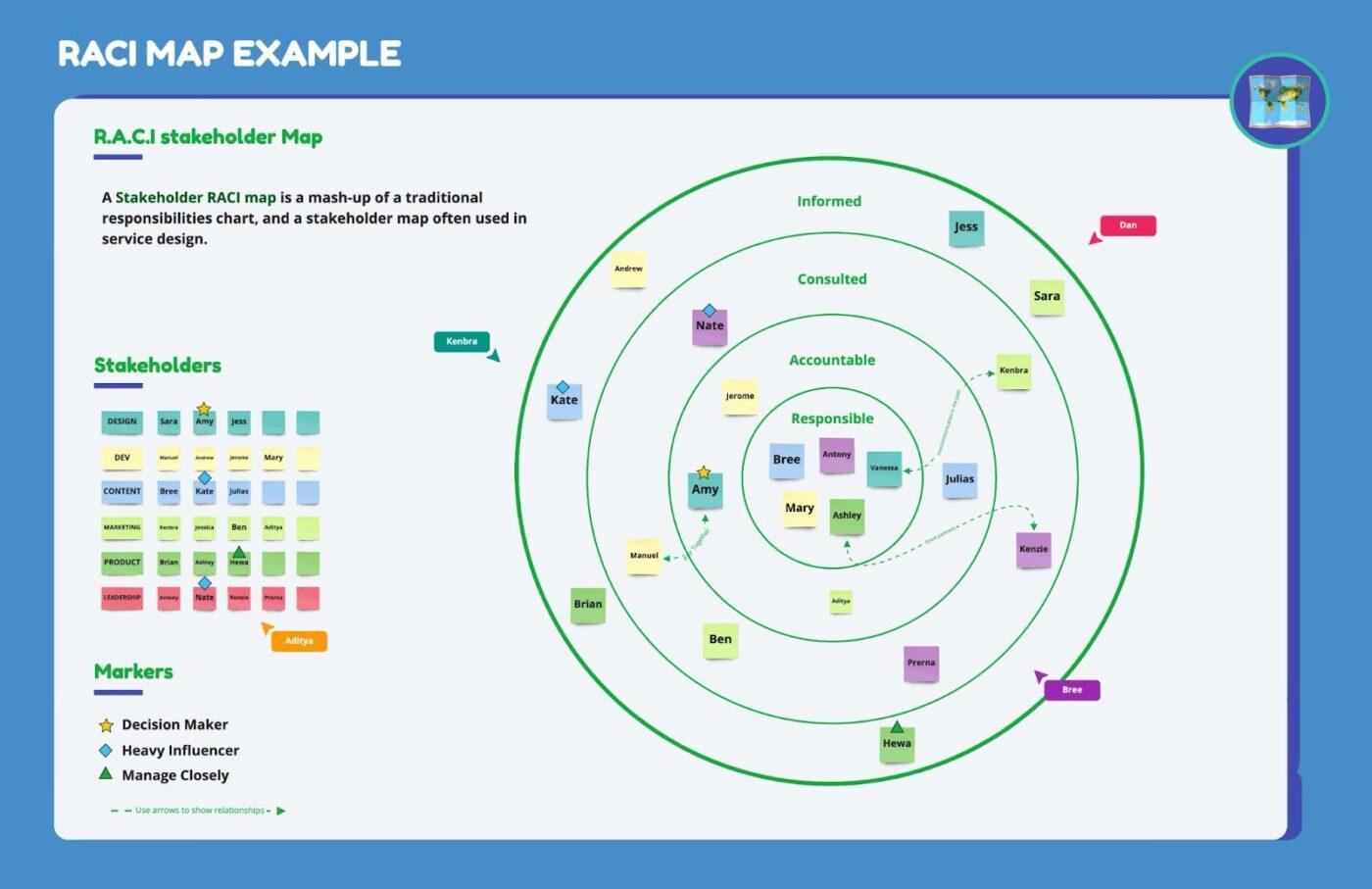
Miro is another excellent tool you can use for assigning roles, responsibilities, and tasks. In this particular example, Miro shows you can easily create a RACI stakeholders matrix for service design teams.
Can you tell that there’s something different here? 🤔
Exactly! Instead of sticking with the regular RACI chart, Miro decided to take a new approach and have everything from roles and responsibilities to tasks neatly organized using the Map view. 🗺️
You can see the stakeholders and tasks on the left, their roles (decision maker, heavy influencers, manage closely) visualized below, and all of them together within a circular-shaped map.
You can see that roles are layered in circles, going from the ones with, let’s say, less responsibility (e.g., Informed) to Responsible.
I don’t know about you, but we love digital sticky notes! The names of everyone on the team are written on these sticky notes, while their roles are indicated by using emojis.
Bonus: Stakeholder Mapping Templates
RACI Marketing Team Model
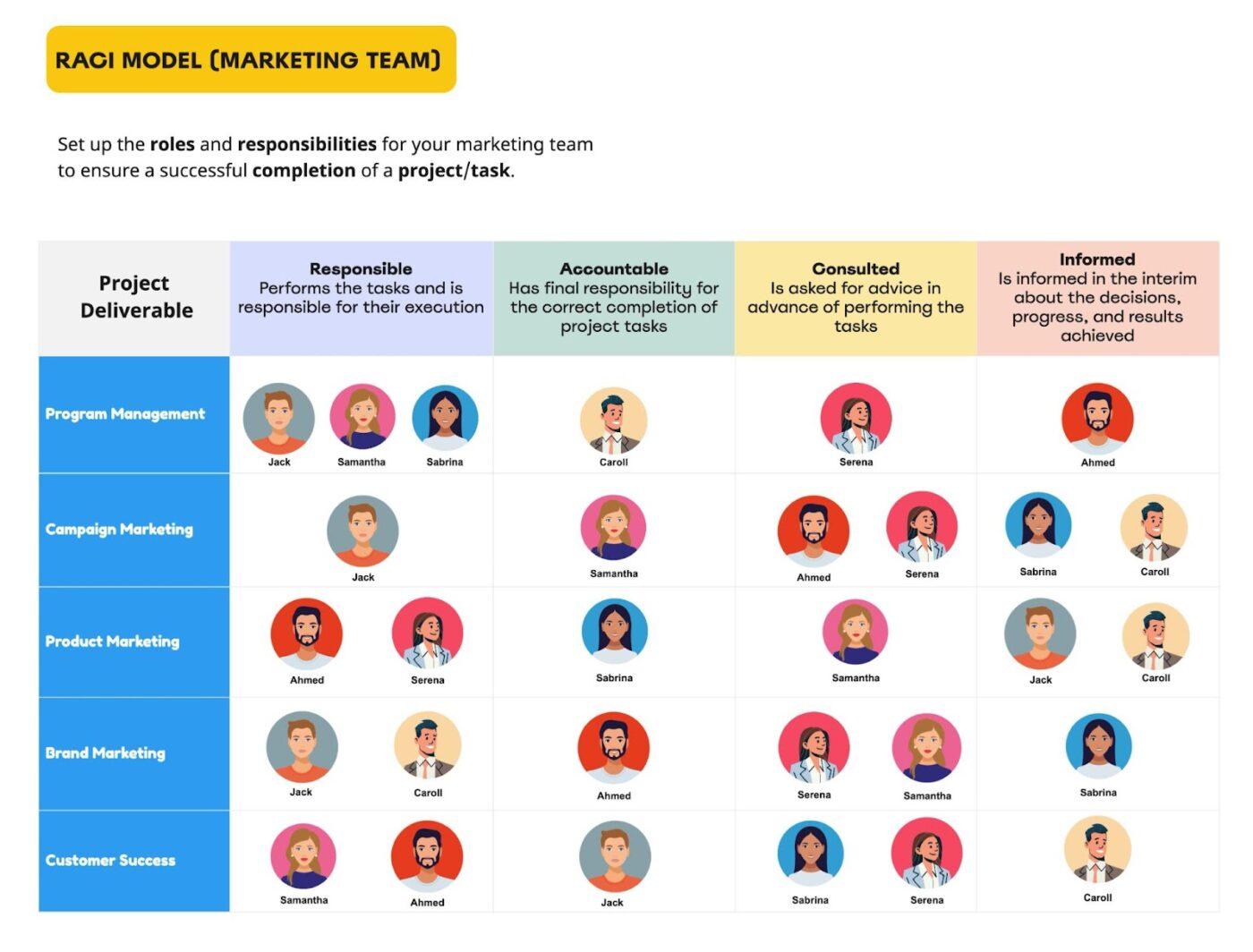
This RACI chart is specifically built for the needs of marketing teams. Project management, campaign, product, and brand marketing, as well as customer success, a.k.a deliverables, are positioned on the left.
Responsibilities and roles are clearly defined per task, while team members are grouped and arranged accordingly, so everyone knows what they are doing, and what everyone else is doing.
There’s a single Accountable person for each task, while the number of Responsible persons is relatively balanced.
Coda Example s
Last but not least in the tools lineup, we have the new kid in the project management block, Coda . Let’s see how it stacks up against our previous RACI templates.
Bonus: Perceptual map templates !
RACI Matrix Example by Task Breakdown
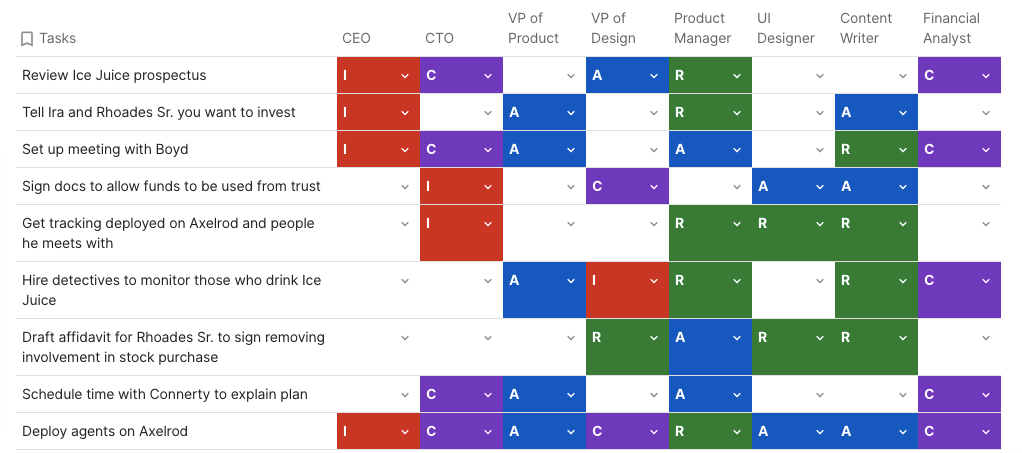
Coda gives a practical example of what it looks like to create and use a RACI chart, even if you are not necessarily working on an overly complex project.
All of the tasks are clearly defined, as well as all of the roles (CEO, CTO, VP of product, product manager, UI designer, content writer, and financial analyst) and responsibilities that are displayed in vivid colors. This allows for better visibility and differentiation, and we can also integrate it with third-party software to schedule consultancies or even track the progress of each project.
RACI Chart Example by Task Status
Coda also lets you track the status of each task (not started, in progress, done) on the RACI chart, color-code each status, and add notes to clarify who is working on which task and how many resources are available.
Instead of starting from scratch, you can choose among several other absolutely rocking RACI chart templates that will save you valuable time and set your team up to speed from the very first second!
Bonus: Matrix Templates & Matrix Organizational Structure Examples
Project Managers: A RACI chart is a useful tool for project managers who need to track the various tasks and roles associated with a project. By tracking these roles, it helps to ensure that everyone involved in the project is held accountable for their individual tasks.
- Project Management RACI Chart
- Project Deliverables RACI Chart
- Construction Project RACI Chart
- Agile Projects RACI Chart
Business Leaders: A RACI chart is also useful for business leaders who need to clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member. This chart can also be used to identify gaps in roles and responsibilities and help develop an effective plan for allocating resources accordingly.
- Executives RACI Chart
- Change Management RACI Chart
- Stakeholders RACI Chart
RACI is not a project plan but rather a document used for defining roles and responsibilities—it provides more than a clear outline, so your job is to ensure that work and responsibilities are fairly allocated. It also describes the project tasks that need to be completed in advance to eliminate confusion and bottlenecks.
Now that you know more about the RACI Matrix, it’s your turn to try it for yourself! Load one of the templates like the ClickUp RACI template , for example, customize it to your liking, and start delegate tasks and responsibilities more effectively.
Good luck! 😊
Guest writer :

Alladdine Djaidani is a digital marketer and the founder of HustlerEthos.com .
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
How to Create a Realistic Project Plan with Templates & Examples
As a project manager, a huge part of your role is to write project plans that help you keep projects on track. But that’s not all a project plan should do.
A project plan is arguably the most important document you’ll create for a project. At its core, a plan should communicate your project approach and the process your team will use to manage the project according to scope.
Let’s take a closer look at how you can develop a rock-solid planning process that guides your team and projects to success.
What is a project plan?
Project plan example: what to include, why you should always write a project plan, 5 steps to an effective project planning process, how to create a project plan in teamgantt, free project plan templates.
A project plan is a document that maps out the tasks, effort, timing, and resources needed to meet project goals within a predefined scope. It’s often presented in the form of a gantt chart because it’s easy to visualize the project timeline and ensure work stays on track.
Any solid project management plan should answer the following questions:
- What are the major deliverables?
- How will we get to those deliverables and the deadline?
- Who’s on the project team, and what role will they play in those deliverables?
- Which stakeholders need to provide feedback on deliverables, and when?
- When will the team meet milestones?
A project plan communicates this information in a simple, straightforward way so everyone clearly understands the objectives and how they contribute to project success. It may also be accompanied by other planning documents, such as a project charter , risk assessment , or communication plan .
While no two project plans are alike, they all share the same common building blocks. Be sure to include the following components in any project plan you create:
- Project tasks : A detailed list of work to be done organized by project phase, process step, or work group
- Project schedule : A visual timeline of task start dates, durations, and deadlines, with clear progress indicators
- Key milestones : Major events, dates, decisions, and deliverables used for tracking forward progress
- Dependencies : A line connecting tasks that need to happen in a certain order
- Resources : Assignments that indicate the person or team responsible for completing a task
Here’s a simple example of what a project plan looks like with these basic elements highlighted:

Some people don’t understand the power of a good project plan. If you feel pressured to skip the plan and jump right into the work, remind your team and stakeholders that having a plan benefits everyone by making it easier to:
- Build consensus before work begins : A detailed project plan ensures everyone has a clear understanding of—and agrees on—the overall process, scope, staffing, and even communications from the outset. That goes a long way in keeping project confusion and pop-up requests from gumming up the works.
- Avoid scheduling conflicts : Project plans enable you to organize tasks so it’s clear who's responsible for what and when. If your team is juggling multiple projects, you can cross-reference other plans to see who’s available to take on new work before committing to a timeline.
- Monitor project goals and scope : When new tasks creep in, it’s easy to lose sight of the original objectives. Spelling out the work you need to complete in a time-based plan keeps project goals front and center so you can ensure project scope stays intact.
- Hold your team and stakeholders accountable : A good project plan sets expectations around the process and pacing you'll follow each step of the way. When plans are shared with teams and stakeholders, it keeps folks honest about what is—or isn’t—happening and forces you to resolve issues in a timely way.
Easy drag and drop features with templates for faster scheduling. Plan a project in minutes, collaborate easily as a team, and switch to calendar and list views in a single click.

Poor planning can lead to some pretty ugly consequences—from missed deadlines and budget overages to team burnout and client frustration. That’s why it’s important to establish a solid process you can use to plan any project.
Planning a project doesn’t have to be difficult. These basic project planning steps can help you write a plan that’s both realistic and on target.

- Start with project discovery & definition
- Draft a rough outline of your plan
- Formalize your project management plan
- Present & confirm your plan
- Execute your plan & adjust as needed
Step 1: Start with project discovery and definition
A project plan is more than a dry document with dates. It’s the story of your project, and you don’t want it to be a tall tale! So make sure you know all the facts before you start creating a project plan.
Understand the project scope and value
Understanding the ins and outs of the project will help you determine the best process and identify any snags that might get in the way of success. Conduct your own research to dig deeper on:
- Project goals and outcomes
- Partnerships and outlying dependencies
- Potential issues and risks
Review the scope of work , and dive into any documents or communications relevant to the project (maybe an RFP or notes from sales calls or client meetings). Be thorough in your research to uncover critical project details, and ask thoughtful questions before you commit to anything.
Interview key stakeholders
If you want to dazzle stakeholders with a stellar project delivery, you’ve got to know how they work and what they expect. Schedule time with your main project contact, and ask them some tough questions about process, organizational politics, and general risks before creating a project plan.
This will give project stakeholders confidence that your team has the experience to handle any difficult personality or situation. It also shows you care about the success of the project from the start.
Be sure to discuss these things with your stakeholders:
- Product ownership and the decision-making process
- Stakeholder interest/involvement levels
- Key outages, meetings, deadlines, and driving factors
- Related or similar projects, goals, and outcomes
- The best way to communicate with partners and stakeholders
See a list of sample interview questions to ask stakeholders so you can develop better project plans.
Get to know your team
The last step in the research phase is to take time to learn more about the people who’ll be responsible for the work. Sit down with your team and get to know their:
- Collaboration and communication styles
- Availability and workload
Understanding these basics about your team will help you craft a thoughtful plan that takes their work styles and bandwidth into consideration. After all, a happy team delivers better projects.
Step 2: Draft a rough outline of your plan
Now that you’ve gathered the basic project details, the next step is to knock out a rough draft of your plan. Take some time to think about the discussions you had in the pre-planning phase and the approach your team might take to meet the project goals.
Sketch out the main components of your project plan
Sit down with a pen and paper (or a whiteboard), and outline how the project should work at a high level. Be sure you have a calendar close by to check dates.
If you’re at a loss for where to begin, start with the who, what, when, and how of the project. A first outline can be very rough and might look something like a work breakdown structure . Make sure your project outline includes the following components:
- Deliverables and the tasks required to create them
- Your client’s approval process
- Timeframes associated with tasks/deliverables
- Ideas on resources needed for tasks/deliverables
- A list of the assumptions you’re making in the plan
- A list of absolutes as they relate to the project budget and/or deadlines
Considering these elements will help you avoid surprises—or at least minimize them. And remember, you’re doing this as a draft so you can use it as a conversation-starter for your team. It’s not final yet!
Get input from your team on process, effort, and timing
You don’t want to put yourself or your team in an awkward position by not coming to a consensus on the approach before presenting it to your client. That's why a project manager can’t be the only one writing a project plan.
Once you’ve created a basic project outline, take those rough ideas and considerations to your team. This enables you to invite discussion about what might work rather than simply dictating a process. After all, every project must begin with clear communication of the project goals and the effort required to meet them.
Be sure to get input from your team on how they can complete the tasks at hand without killing the budget and the team’s morale. As a project manager, you can decide on Agile vs. Waterfall approaches , but when it comes down to it, you need to know that the team can realistically execute the plan.
You can also use this review time to question your own thinking and push the team to take a new approach to the work. For example, if you’re working on a digital product, could designers start creating visual concepts while the wireframes are being developed? Or can you have two resources working on the same task at once?
Running ideas by the team and having an open dialogue about the approach not only helps you build a more accurate project plan. It gets everyone thinking about the project in the same terms. This type of buy-in and communication builds trust and gets people excited about working together to solve a goal. It can work wonders for the greater good of your team and project.
Step 3: Formalize your project management plan
You should feel comfortable enough at this point to put together a rock-solid project schedule using whatever tool works for you.
Build out a detailed project schedule that’s easy to read
Any good online project planning tool will help you formalize your thoughts and lay them out in a consistent, visual format that’s easy to follow and track. (Ahem, TeamGantt works nicely for a lot of happy customers. )
Make sure tasks have clear start and end dates so there’s no question when work needs to happen to hit project deadlines. Organize work into phases, and use labels and/or color-coding to improve scannability. The easier your project plan is to understand at a glance, the better!
See how to create a project plan in TeamGantt
Consider how your team likes to work
Be as flexible as possible when it comes to how your project plan is presented. There's no absolute when it comes to how to format your plan as long as you and your team understand what goes into one.
Remember, people absorb information differently. While you might be partial to a gantt chart, others might prefer to view tasks in a list, calendar, or even a kanban board. You can make all of those variations work if you’ve taken the steps to create a solid plan.
For example, here’s an Agile project plan we built that lists each sprint as its own task group with milestones for sprint planning and deployment.

And here’s what that same project plan looks like if you turn it into a kanban board in TeamGantt. Simply click the Board tab and set up your columns so your team can manage their daily workflows more easily.

If your team currently prefers spreadsheets and isn’t quite ready to use TeamGantt yet, try our free Excel gantt chart template .
Step 4: Present and confirm your plan
You’re almost finished! Now it’s time to do your due diligence. It’s easy to throw stuff in a plan, but you have to make sure you get it right.
Run your final plan by your internal team
Your team needs to know the reality of your plan as it stands after you’ve built it out in TeamGantt. And you want to be sure they’re comfortable committing to the details. If they don’t, things will quickly fall apart!
Always review your final plan with your team before delivering it to stakeholders. Why? Because things like dates and tasks—and even assignments—will shift as you formalize the rough sketch of your plan.
Here are a few things you’ll want to discuss with your team as you review the final plan together:
- Review times
- Team work times
- Dependencies
- Time off, meetings, and milestones
- The final deadline
- Any assumptions you’ve made
- Major changes since your last talk
There’s nothing more embarrassing than delivering a plan with an error or a promise you can’t keep. Taking a few minutes to get buy-in from your team will give everyone peace of mind about your plan.
Review your project plan with stakeholders
Once you’ve confirmed the plan with your team and have their full sign-off, you’re ready to share your project plan with stakeholders .
When delivering your project plan, make sure you provide an executive summary. This might come in the form of a project brief . A short recap of the overall methodology, resources, assumptions, deadlines, and related review times will help you convey what the plan means to the project and everyone involved.
Project plans can be daunting, so schedule time to present your project plan to stakeholders at a high level. Here are some things you’ll want to point out about your plan during this review:
- Overall process and pacing
- Major deliverables and timing
- The time they’ll have to review deliverables
- Overall timing for task groups or phases
- How far off you are from the deadline
- Wiggle room on the final deadline
If a stakeholder is interested in the day-to-day details, feel free to walk them through the plan line by line. Otherwise, start by explaining overall sections or phases, and be sure to come back to your plan at intervals throughout the project to remind them of tasks, next steps, and overall progress.
Step 5: Execute your plan and adjust as needed
Some projects are smooth and easy to manage, and others are a complete nightmare that wake you up at 3 a.m. every other night. Thankfully, having a solid project plan is your best defense against project chaos once work gets underway.
Keep in mind that project plans are living documents. Projects change constantly, and someone has to stay on top of—and document—that change. Remember to:
- Update your plan regularly as work progresses and things change
- Communicate changes to your team, partners, and stakeholders
- Monitor and communicate risks as your project evolves
Ready to plan your project in TeamGantt? Follow these easy steps to build a plan that’s structured well and includes the elements you need for project success.
1. Enter your basic project details.
To create a new project plan in TeamGantt, click the New Project button in the upper right corner of the My Projects screen. Then enter your project name and start date, and select the days of the week you want to include in your plan. Click Create New Project to move on to the next step.

2. List out your project tasks and milestones.
Now the real planning fun begins! Enter all the different tasks it will take to get the job done. If there are any key meetings, deliverable deadlines, or approvals, add those as milestones in your project plan.

3. Organize tasks into subgroups.
Scrolling through one long list of tasks can be mind-numbing, even to the best of us. Break tasks down into phases or sections to ensure your project plan is easy to read and understand.
4. Add task durations and milestone dates to the project timeline.
A visual project plan makes it easy to see exactly what needs to get done by when. Make sure every task has a start and end date so nothing falls through the cracks. TeamGantt’s drag and drop feature makes this planning step quick and easy.

5. Connect related tasks with dependencies.
Adding dependencies between tasks ensures work gets done in the right order and also helps you plan for delay risks. If your plan shifts and you need to move tasks around, dependencies speed up the process.

6. Assign responsible team members to tasks.
That way there’s no confusion about who’s doing what, and your team can update and manage their daily tasks . Don’t forget to check team availability along the way to avoid overloading anyone with too much work.

7. Use the RACI chart to define task roles more clearly.
This feature takes accountability one step further by letting you assign more specific roles to each task: Responsible , Accountable , Consulted , and Informed . Learn how RACI charts work and what each role means.

8. Add hourly estimates and/or points to each task.
This makes it easy to see the lift each task involves at a glance. Including hourly estimates in your project plan also enables you to manage workloads and track overages more accurately.

9. Color-code tasks for better scannability.
You can use colors to categorize tasks by project phase, priority, department, or team member—whatever makes visual sense to you and your team.

10. Add notes to clarify tasks or spell out important details.
There’s no such thing as too much information if it means your team has what they need to deliver quality work on time. Use the Notes section of your Discussion tab to enter any pertinent details your team will find helpful.

11. Upload important documents to the project.
This ensures project files are accessible to everyone in a centralized hub. For example, you might attach your creative brief to the project so your content and design teams have clear direction for completing their deliverables.
If you’re planning a project for the first time or taking on a totally new type of project, you might be struggling to get your plan off the ground. We created a simple project management plan template to help you get started.
TeamGantt gives you the ability to quickly and easily build and adjust your plan using drag and drop scheduling. Plus, it comes with customizable views to fit every team member’s work style.
Try our basic project plan template for free!

Looking for more specific project plan examples to jumpstart your process? Use these project planning templates to generate ideas and save time building out your plan:
- Construction project plan template
- Event planning template
- Strategic marketing plan template
- Tactical marketing plan template
- Software development plan template
- Video production schedule template
- Website project plan template
Plan your next project in minutes
Discover just how easy project planning can be with TeamGantt. Create your first gantt chart for free!

- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Project Proposal (Examples & Template Included)

Table of Contents
Types of project proposals, project proposal vs. project charter, project proposal vs. business case, project proposal vs. project plan, project proposal outline, how to write a project proposal, project proposal example, project proposal tips, what is a project proposal.
A project proposal is a project management document that’s used to define the objectives and requirements of a project. It helps organizations and external project stakeholders agree on an initial project planning framework.
The main purpose of a project proposal is to get buy-in from decision-makers. That’s why a project proposal outlines your project’s core value proposition; it sells value to both internal and external project stakeholders. The intent of the proposal is to grab the attention of stakeholders and project sponsors. Then, the next step is getting them excited about the project summary.
Getting into the heads of the audience for which you’re writing the project proposal is vital: you need to think like the project’s stakeholders to deliver a proposal that meets their needs.
We’ve created a free project proposal template for Word to help structure documents, so you don’t have to remember the process each time.

Get your free
Project Proposal Template
Use this free Project Proposal Template for Word to manage your projects better.
In terms of types of project proposals, you can have one that’s formally solicited, informally solicited or a combination. There can also be renewal and supplemental proposals. Here’s a brief description of each of them.
- Solicited project proposal: This is sent as a response to a request for proposal (RFP) . Here, you’ll need to adhere to the RFP guidelines of the project owner.
- Unsolicited project proposal: You can send project proposals without having received a request for a proposal. This can happen in open bids for construction projects , where a project owner receives unsolicited project proposals from many contractors.
- Informal project proposal: This type of project proposal is created when a client asks for an informal proposal without an RFP.
- Renewal project proposal: You can use a renewal project proposal when you’re reaching out to past customers. The advantage is that you can highlight past positive results and future benefits.
- Continuation project proposal: A continuation project proposal is sent to investors and stakeholders to communicate project progress.
- Supplemental project proposal: This proposal is sent to investors to ask for additional resources during the project execution phase.
All the elements in the above project proposal outline are present in our template. This free project proposal template for Word will provide you with everything you need to write an excellent project proposal. It will help you with the executive summary, project process, deliverables, costs—even terms and conditions. Download your free template today.
A project proposal is a detailed project document that’s used to convince the project sponsor that the project being proposed is worth the time, money and effort to deliver it. This is done by showing how the project will address a business problem or opportunity. It also outlines the work that will be done and how it will be done.
A project charter can seem like the same thing as a project proposal as it also defines the project in a document. It identifies the project objectives, scope, goals, stakeholders and team. But it’s done after the project has been agreed upon by all stakeholders and the project has been accepted. The project charter authorizes the project and documents its requirements to meet stakeholders’ needs.

A business case is used to explain why the proposed project is justified. It shows that the project is worth the investment of time and money. It’s more commonly used in larger companies in the decision-making process when prioritizing one project over another.
The business case answers the questions: what is the project, why should it be taken up, who will be involved and how much will it cost? It’s therefore related to a project proposal, but the project proposal comes before the business case and is usually part of the larger proposal.
Again, the project proposal and the project plan in this case are very similar documents. It’s understandable that there would be some confusion between these two project terms. They both show how the project will be run and what the results will be. However, they’re not the same.
The project proposal is a document that aims to get a project approved and funded. It’s used to convince stakeholders of the viability of the project and their investment. The project plan, on the other hand, is made during the planning phase of the project, once it’s been approved. It’s a detailed outline of how the project will be implemented, including schedule, budget, resources and more.

There are several key operational and strategic questions to consider, including:
- Executive summary: This is the elevator pitch that outlines the project being proposed and why it makes business sense. While it also touches on the information that’ll follow in the project proposal, the executive summary should be brief and to the point.
- Project background: This is another short part of the proposal, usually only one page, which explains the problem you’ll solve or the opportunity you’re taking advantage of with the proposed project. Also, provide a short history of the business to put the company in context to the project and why it’s a good fit.
- Project vision & success criteria: State the goal of the project and how it aligns with the goals of the company. Be specific. Also, note the metrics used to measure the success of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: There are always risks. Detail them here and what strategies you’ll employ to mitigate any negative impact as well as take advantage of any positive risk.
- Project scope & deliverables: Define the project scope, which is all the work that has to be done and how it will be done. Also, detail the various deliverables that the project will have.
- Set SMART goals: When setting goals, be SMART. That’s an acronym for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. All your goals would be defined by those five things.
- Project approach: Define the approach you’ll use for the contract. There are several different types of contracts used in construction , for example, such as lump sum, cost plus, time and materials, etc. This is also a good place to describe the delivery method you’ll use.
- Expected benefits: Outline the benefits that will come from the successful completion of the project.
- Project resource requirements: List the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., that you’ll need to execute the project if approved.
- Project costs & budget: Detail all the costs, including resources, that’ll be required to complete the project and set up a budget to show how those costs will be spent over the course of the project.
- Project timeline: Lay out the project timeline , which shows the project from start to finish, including the duration of each phase and the tasks within it, milestones, etc.
In addition to these elements, it’s advisable to use a cover letter, which is a one-page document that helps you introduce your project proposal and grab the attention of potential clients and stakeholders.
To make the best proposal possible, you’ll want to be thorough and hit on all the points we’ve listed above. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a persuasive priority proposal.
1. Write an Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the main elements of your project proposal, such as your project background, project objectives and project deliverables, among other things. The goal is to capture the attention of your audience and get them excited about the project you’re proposing. It’s essentially the “elevator pitch” for the project life cycle. It should be short and to the point.
The executive summary should be descriptive and paint a picture of what project success looks like for the client. Most importantly, it should motivate the project client; after all, the goal is getting them to sign on the dotted line to get the project moving!
2. Provide a Project Background
The project background is a one-page section of your project proposal that explains the problem that your project will solve. You should explain when this issue started, its current state and how your project will be the ideal solution.
- Historic data: The history section outlines previously successful projects and those that could have run more smoothly. By doing so, this section establishes precedents and how the next project can be more effective using information from previous projects.
- Solution: The solution section addresses how your project will solve the client’s problem. Accordingly, this section includes any project management techniques , skills and procedures your team will use to work efficiently.
3. Establish a Project Vision & Success Criteria
You’ll need to define your project vision. This is best done with a vision statement, which acts as the north star for your project. It’s not specific as much as it’s a way to describe the impact your company plans to make with the project.
It’s also important to set up success criteria to show that the project is in fact doing what it’s proposed to do. Three obvious project success criteria are the triple constraint of cost, scope and time. But you’ll need to set up a way to measure these metrics and respond to them if they’re not meeting your plan.
4. Identify Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
To reduce the impact of risk in your project, you need to identify what those risks might be and develop a plan to mitigate them . List all the risks, prioritize them, describe what you’ll do to mitigate or take advantage of them and who on the team is responsible for keeping an eye out for them and resolving them.
5. Define Your Project Scope and Project Deliverables
The project scope refers to all the work that’ll be executed. It defines the work items, work packages and deliverables that’ll be delivered during the execution phase of your project life cycle. It’s important to use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to define your tasks and subtasks and prioritize them.
6. Set SMART Goals for Your Project Proposal
The best mindset when developing goals and objectives for your project proposal is to use the SMART system :
- Specific – Make sure your goals and objectives are clear, concise and specific to the task at hand.
- Measurable – Ensure your goals and objectives are measurable so it’s obvious to see when things are on track and going well, and conversely, when things are off track and issues need to be addressed. Measurable goals make it easy to develop the milestones you’ll use to track the progress of the project and identify a reasonable date for completion and/or closure.
- Attainable – It’s important every project has a “reach” goal. Hitting this goal would mean an outstanding project that extends above and beyond expectations. However, it’s important that the project’s core goal is attainable, so morale stays high and the job gets done with time and resources to spare.
- Relevant – Make sure all of your goals are directly relevant to the project and address the scope within which you’re working.
- Time-Based – Timelines and specific dates should be at the core of all goals and objectives. This helps keep the project on track and ensures all project team members can manage the work that’s ahead of them.
7. Explain What’s Your Project Approach
Your project approach defines the project management methodology , tools and governance for your project. In simple terms, it allows project managers to explain to stakeholders how the project will be planned, executed and controlled successfully.
8. Outline The Expected Benefits of Your Project Proposal
If you want to convince internal stakeholders and external investors, you’ll need to show them the financial benefits that your project could bring to their organization. You can use cost-benefit analysis and projected financial statements to demonstrate why your project is profitable.
9. Identify Project Resource Requirements
Project resources are critical for the execution of your project. The project proposal briefly describes what resources are needed and how they’ll be used. Later, during the planning phase, you’ll need to create a resource management plan that’ll be an important element of your project plan. Project requirements are the items, materials and resources needed for the project. This section should cover both internal and external needs.
10. Estimate Project Costs and Project Budget
All the resources that you’ll need for your project have a price tag. That’s why you need to estimate those costs and create a project budget . The project budget needs to cover all your project expenses, and as a project manager, you’ll need to make sure that you adhere to the budget.
11. Define a Project Timeline
Once you’ve defined your project scope, you’ll need to estimate the duration of each task to create a project timeline. Later during the project planning phase , you’ll need to create a schedule baseline, which estimates the total length of your project. Once the project starts, you’ll compare your actual project schedule to the schedule baseline to monitor progress.
Now let’s explore some project proposal examples to get a better understanding of how a project proposal would work in the real world. For this example, let’s imagine a city that’s about to build a rapid transit system. The city government has the funds to invest but lacks the technical expertise and resources that are needed to build it, so it issues a request for proposal (RFP) document and sends it to potential builders.
Then, the construction companies that are interested in executing this rapid transit project will prepare a project proposal for the city government. Here are some of the key elements they should include.
- Project background: The construction firm will provide an explanation of the challenges that the project presents from a technical perspective, along with historical data from similar projects that have been completed successfully by the company.
- Project vision & success criteria: Write a vision statement and explain how you’ll track the triple constraint to ensure the successful delivery of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: List all risks and how they’ll be mitigated, and be sure to prioritize them.
- Project scope & deliverables: The work that’ll be done is outlined in the scope, including all the deliverables that’ll be completed over the life cycle of the project.
- Set SMART goals: Use the SMART technique to define your project goals by whether they’re specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
- Project approach: Define the methodology that the project manager will employ to manage the project. Also, figure out what type of contract will be used to define the project.
- Expected benefits: Show how the project will deliver advantages to the company and define what these benefits are in a quantifiable way.
- Project resource requirements: List all the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., needed to execute the project.
- Project costs & budget: Estimate the cost of the project and lay that out in a project budget that covers everything from start to finish.
- Project timeline: Outline the project schedule, including phases, milestones and task duration on a visual timeline.
Whatever project proposal you’re working on, there are a few tips that apply as best practices for all. While above we suggested a project proposal template that would have a table of contents, meaning it would be many pages long, the best-case scenario is keeping the proposal to one or two pages max. Remember, you’re trying to win over stakeholders, not bore them.
Speaking of project stakeholders , do the research. You want to address the right ones. There’s no point in doing all the work necessary to write a great proposal only to have it directed to the wrong target audience. Whoever is going to read it, though, should be able to comprehend the proposal. Keep the language simple and direct.
When it comes to writing, get a professional. Even a business document like a project proposal, business case or executive summary will suffer if it’s poorly constructed or has typos. If you don’t want to hire a professional business writer, make sure you get someone on your project team to copy, edit and proof the document. The more eyes on it, the less likely mistakes will make it to the final edition.
While you want to keep the proposal short and sweet, it helps to sweeten the pot by adding customer testimonials to the attachments. Nothing sells a project plan better than a customer base looking for your product or service.
ProjectManager & Project Proposals
ProjectManager allows you to plan proposals within our software. You can update tasks for the project proposal to signify where things stand and what’s left to be done. The columns allow you to organize your proposal by section, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) of sorts.
When building a project proposal, it’s vital to remember your target audience. Your audience includes those who are excited about the project, and see completion as a gain for their organization. Conversely, others in your audience will see the project as a pain and something to which they aren’t looking forward. To keep both parties satisfied, it’s essential to keep language factual and concise.
Our online kanban boards help you think through that language and collaborate on it effectively with other team members, if necessary. Each card shows the percentage completed so everyone in the project management team is aware of the work done and what’s left to be done.
As you can see from the kanban board above, work has begun on tasks such as product documentation and design. Tasks regarding stakeholder feedback, ideation, market research and more have been completed, and there’s a good start on the engineering drawings, 3D rendering, supply chain sourcing and translation services.
A PDF is then attached to the card, and everyone added to the task receives an email notifying them of the change. This same process can be used throughout the life-cycle of the project to keep the team updated, collaborating, and producing a first-class project proposal. In addition to kanban boards, you can also use other project management tools such as Gantt charts , project dashboards, task lists and project calendars to plan, schedule and track your projects.
Project proposals are just the first step in the project planning process. Once your project is approved, you’ll have to solidify the plan, allocate and manage resources, monitor the project, and finally hand in your deliverables. This process requires a flexible, dynamic and robust project management software package. ProjectManager is online project management software that helps all your team members collaborate and manage this process in real-time. Try our award-winning software with this free 30-day trial .


Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
Get inspired: 4 great project management examples
We’re all familiar with is project management example. The moment when (eek!), your boss says, “Could you just…[insert incomprehensible but seemingly important task]?”
There is quite a wide range of project management tasks out there, all demanding that you complete the project on time and within budget. An example of an IT project could be creating a system to manage issues tracking, while one for operations could be creating a roster of employee dietary needs against package deliveries from start to finish.
No matter how simple or complex the project, we have it on good authority—and so do groups like the Project Management Institute — that starting with a sample project methodology is a great way to start.
In this article, we’ll cover that, identify the four key factors common to successful project examples, and share some top project management examples you can draw inspiration from.
Why do the best project management examples start with a methodology?
Identifying a methodology during the project planning phase is both good project management practice, and common sense.
Organizations that invest in good project management practices, waste 21 times less money than those without an effective project management approach.
Methodologies set you up for success by providing the big picture perspective on each part of the project schedule and how the project is going to run.
There are traditionally 2 methodologies used for managing projects and they both have pros and cons:
This example of a project management methodology is a linear, step-by-step approach where each new project phase follows the end of the previous one.
With this methodology, having a robust project plan is vital and lots of work needs to be done upfront to get really clear on the project goal. Examples of project teams who may use this method are those with fixed timelines and budgets, such as aerospace or defense teams.

The Agile project management method in contrast is a more iterative approach where the project team members and business stakeholders work together to refine the project outcome through feedback and review.
Project activities are delivered through short “sprints” or iterations and a list of what needs to be done next — usually called the “backlog” — is prioritized according to feedback. Project activities are delivered through short “sprints” or iterations and a list of what needs to be done next — usually called the “backlog” — is prioritized according to feedback. IT projects are examples where Agile might be used.

Whichever methodology you choose, there are a number of things you can do to increase your chance of a successful project and start earning kudos from your boss.
What are the critical success factors?
The Association for Project Management (APM) says there are 12 conditions for project success. It came as no surprise to us here at monday.com that proven methods and tools were one of the 12. After all, that’s what we’re in the business of. Read on for a list that could make you rethink how you craft project management project ideas.
These 12 conditions fall into 4 main factors:
- Visibility . From the outset, the project’s goals need to be clear to all stakeholders. During the life cycle of the project, it’s important to understand who is working on what and when. A well-defined project management plan reduces confusion and makes sure the workload is evenly spread across the project team.
- Efficiency . To maximize the project’s value you need to minimize waste during the project lifecycle. Whether that’s wasted time, effort, or money, these things need to be monitored and well-controlled to determine project progress.
- Communication . Communication between members of the project team and the wider business is key for successful implementation. Effectively communicating the benefits of the project can improve the chance of its outcome lasting longer than ice cream on a hot day.
- Collaboration . Few projects run independently. Most success in project examples is attributed to collaboration across teams, and with internal or external stakeholders for creating a project and getting the job done.
How can tools help?
Ok, you’ve picked a methodology and you’re ready to get started. So why exactly does the APM think tools are so important for project success in any business project example?
Well first of all, you need a place to organize all of your information and to craft a smooth and automated workflow. Check out what one user had to say about monday.com as their project management tool .
monday.com is excellent at planning. Personally, we think it’s the best. What might surprise you is how intuitive it is to use. And how it integrates with all your other favorite tools. And inspires you more than a gantt chart . Which might be just what’s needed after that stakeholder meeting on a dreary November afternoon. Don’t miss more quality content! hbspt.forms.create({ portalId: "5945317", css: "", formId: "dbfb5b7f-21a2-4092-a3fb-0b6365ad349c", target: '#subscribe-cta-banner-form-0', formInstanceId: 'hs-from-instance-0', });

monday.com makes it easy to monitor the project through its lifecycle, keeping a keen eye out for scope creep with intuitive and customizable templates. Our project management software can also help you out with resource management , time tracking, and managing project risk.
And, what about a more Agile approach? Well, good visibility and communication are key.
Using a project management tool, such as a Kanban board , to help you track what’s been done, is being done, and needs to be completed is important for managing the backlog.

Using a sprint retrospective tool allows you to review the sprint and collect the feedback necessary to decide on the next steps. Without an ability to gather and track this feedback it’s likely that effort will be spent doing the wrong things, decreasing the project’s overall value.
Don’t miss more quality content!
4 great project management examples.
To get an inside look at how monday.com is the perfect platform to get your optimized project management workflow up and running, here are four examples from real monday.com customers.
1. The National Hockey League (NHL)
- Challenge: Increase visibility
After first loading NHL game stats onto the web over 25 years ago, NHL developers have managed 100s of requests for custom applications. In-house developers now share the workload with a team in Belarus.
Relying on email and text to collaborate over different time zones was causing several challenges including unclear prioritization and ineffective workload management.
- Solution: Development roadmap and sprint planning
Using the monday.com platform has brought transparency across the development cycle. Now, at any moment, everyone on the team can see who is working on what, and when.
Using the bar graph view, the business can easily track which units have commissioned the most development cycles across the year. The team also uses the Calendar and Chart app to organize and track fan engagement programs.

While initially focused on improving their sprint planning , the NHL has also begun to exploit other capabilities of the monday.com Work OS. Building workflow apps within the platform has reduced the need for custom development, reducing the development time by 4+ weeks per cycle.
For more on how the NHL increased their visibility and saved 4 weeks per development cycle, check out their case study .
- Challenge: Improve efficiency while scaling globally
Zippo compiled their product catalog on paper-based worksheets before transferring them to a digital version. The process took around 2 weeks for 20–30 active projects and became outdated almost as soon as it was completed. Zippo knew if they wanted to scale their business their processes needed to become more efficient.
- Solution: In integrated Work OS capable of managing internal workflows and external suppliers
Initially signing on 10–15 users with a monday.com Pro account, Zippo now has around 125 users on an Enterprise solution. Building the product catalog has become a collaborative effort with users able to drag-and-drop projects into the catalog and shift things around in real time as priorities change.
Through the dashboard views, stakeholders can track progress across all the projects and monitor the overall workload of the team. This means people can be matched to resource gaps speeding up delivery.
Zippo also set up an automated system for workflow approval. A reminder is sent to the task owner if there is an outstanding request. This makes the approval process faster and increases efficiency.
These changes mean that, over the last 8 months, Zippo could focus on global expansion, acquiring new businesses, and entering new markets.
For more on how Zippo improved their efficiency and saved £82k/year while expanding into new markets, check out their case study .
- Challenge: Enable global collaboration while keeping the ‘local hero’ approach
The music streaming service, Deezer has a team of editors worldwide who understand local music tastes and market towards them. Coordinating this dispersed team from the European HQ was challenging and campaign management was siloed within countries.
Business development was also managed regionally. With no centralized system, it was hard to prioritize support requests to other departments such as finance and legal. This meant new deals took a long time to reach the market.
- Solution: An integrated, intuitive workspace that brings multinational collaboration
Deezer used monday.com to build a centralized pipeline of all business development projects which meant work could be analyzed and prioritized globally. This streamlined the work required from the support departments improving time to market speed.
There were also benefits for the customer engagement team. With the monday.com Work OS, campaign planning , management, and evaluation are now visible to teams in all countries.
For more on how Deezer improved global collaboration and increased their customer engagement by 483%, check out their case study .
4. Israeli Government
- Challenge: Ensure effective communication during a global pandemic
As the number of cases grew, Israel set up a National COVID-19 Control Center. The Control Center brought together civilian and military agencies, for the first time, to manage the crisis and support front-line workers. Each agency had its own processes and way of working but a coordinated response was needed immediately if the situation wasn’t to grow out of control.

( Image Source )
It was proving incredibly challenging to get accurate testing information from labs and hospitals meaning it was impossible to create a “big picture” perspective of the situation. Essential equipment and suppliers were sourced in an ad-hoc manner and there was no central communication channel to monitor or follow up leads on potential suppliers.
- Solution: A centralized, flexible platform with customizable permissions
Communication around procurement is now seamless, with multiple connected workflow apps integrating information on requirements, suppliers, approvals, and financing. These have customized permissions so the right people approve each step at the right time.
It’s also easier for hospitals and labs to communicate with the Control Center. The team worked with monday.com to create web and mobile forms to collect up to date information. These can be submitted at any time and entered into the centralized system immediately.
For more on how monday.com is continuing to support the Israeli government with their COVID-19 response check out their case study .
Be your own project management example
At monday.com we provide you with the features and solutions to help you feel more confident in tackling your next project with more ease and efficiency. What do you want to manage better?
Send this article to someone who’d like it.
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
3 elements every project charter needs

Getting started on a new project or initiative can be an exciting feeling. But what about the step right before that, when you need to get your project approved?
The project pitching and approval process can feel like a black box if you’ve never done it before. From gathering the right information to presenting it in a way that works for your project stakeholders, you want to make sure you have the materials you need to succeed. One way to do that is with a project charter.
What is a project charter?
A project charter is an elevator pitch of your project objectives, project scope, and project responsibilities in order to get approval from key project stakeholders. In the charter, you should provide a short, succinct explanation of the main elements of your project before you get started. By creating a project charter before getting started on other, more in-depth project planning documents, you can get approval or course-correct if necessary.
A project charter is one of many project planning materials you can create. Here’s how it compares to other project planning elements:
Project charters vs. project plans
A project charter should only include three elements: your project objectives, scope, and responsibilities. Once your charter has been approved, you should then create a project plan. Your project plan builds on your project charter to provide a more in-depth blueprint of the key elements of your project.
There are seven key elements in a project plan:
Success metrics
Stakeholders and roles
Scope and budget
Milestones and deliverables
Timeline and schedule
Project charters vs. project briefs
A project brief is a short document that you should create after your project has been officially approved. The brief is a condensed version of your project plan that your project team and stakeholders can refer back to frequently. Your brief, like the charter, provides context about why this project is a good idea, in addition to what you’ll be doing during the project.
A project brief has four parts:
Background information
Project objectives and success criteria
Project timeline
Target audience
Project charter vs. business case
A project charter and business case have the same fundamentals: these are both tools to pitch a project to the appropriate stakeholders. The main difference between a project charter and a business case is scope.
A business case is a formal document that explains the benefits and risks of a significant business investment. For example, if you’re pitching a large-scale investment with an external agency, a significant increase in current business practices, or a new product line or service, you’d want to create a business case. Alternatively, if your project needs approval but it’s smaller in scope—for example, a campaign that’s similar to past campaigns or a product launch that fits within your current go-to-market strategy—create a project charter instead.
Do you need a project charter?
There are a variety of project planning tools, and a project charter isn’t always the best one for the job. Here’s when to create one—and when you might be better off creating something else.
Create a project charter to pitch and get approval for a project. A project charter gives stakeholders a clear sense of your project objectives, scope, and responsibilities. Key stakeholders can use the project charter to approve a project or suggest changes.
Create a business case if your project represents a significant business investment. A business case includes additional information and documentation, including the project’s return on investment and any relevant project risks .
Create a project plan if your project has been approved. A project plan will build on your project charter to provide additional information, like the project timeline or key project milestones .
Create a project brief if you want to create a document that summarizes the key high-level details of your project plan.
Create an executive summary if you want to provide a summary of your document to executive stakeholders.
Create a project roadmap if you want to view a high-level timeline of your project in a Gantt chart .
How to create a project charter
In a project charter, you’ll share project details with key stakeholders in order to get approval to kick off your project. There are three main project charter elements:
To begin your project charter, share your project objectives and project purpose. In this section, you should outline why this project is important and what the key objectives are for the end of the project. Make sure your project purpose clearly explains why it’s important to work on this project and how this project will support your company goals.
In addition to your project purpose, you should also clarify your project objectives. These are the things you plan to achieve by the end of the project, like deliverables or assets. To create good project objectives, follow the SMART method . Make sure your objectives are:
The second key element in your project charter is the project scope. Your project scope statement defines exactly what is and isn’t part of the project. When you draft a project scope, you’re setting boundaries and, more importantly, outlining what you won’t do during the project timeline.
As you create your project charter, the most important part of explaining scope is outlining the ideal project budget. Remember, you will use your project charter document to pitch this project to stakeholders—so you need to clearly show what the budget is and where that money will go.
In the final section of your project charter, you should explain who will be working on the project. This includes any key project stakeholders, executive stakeholders, project sponsors , and the general project team. If you haven’t already, draft up a brief resource management plan to illustrate how various resources will be allocated during the project.
Project charter examples
![example of project assignment [Product UI] Marketing campaign project charter (Project Brief)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/627803c4-1f04-422b-b318-f384187cec59/inline-project-planning-project-charter-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Project charter template
When you’re ready to get started, follow this easy-to-use template to create your next project charter.
Project name
Name your project. Make sure this is descriptive enough that most people will understand what you’re working on.
Project manager
Who is the point of contact for this project?
Last revision date
Your project charter is a living document. Including the last revision date can be helpful for team members who are frequently checking back on the charter.
Project purpose
Why are you working on this project?
Project objectives
What deliverables and assets do you plan to achieve by the end of the project?
Project scope
What are the boundaries of your project deliverables? Which initiatives are not included in the project?
Project team and resources
Who is working on this project? Which resources (e.g. people, tools, and budget) are available for this work.
Stakeholders and approvers
Who are the project stakeholders? Who needs to approve the project charter or any project deliverables?
From project charter to project success
Once your project charter has been approved, you can move forward with project planning. As you create additional project planning documents and get started with project management, make sure you are storing all of your project details in a centralized tool that everyone can access.
Naturally, we think Asana is the best tool for the job. With Asana, you can manage team projects and tasks to stay in sync and hit your deadlines. Learn more about the benefits of project management .
Related resources

Provider onboarding software: Simplify your hiring process

15 creative elevator pitch examples for every scenario

Timesheet templates: How to track team progress

Scaling clinical trial management software with PM solutions

- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Pinterest
- Share through Email
6 Steps To Create A Project Charter (+ Examples & A Template)

Sarah is a project manager and strategy consultant with 15 years of experience leading cross-functional teams to execute complex multi-million dollar projects. She excels at diagnosing, prioritizing, and solving organizational challenges and cultivating strong relationships to improve how teams do business. Sarah is passionate about productivity, leadership, building community, and her home state of New Jersey.
Expert Evidence
Galen is a digital project manager with over 10 years of experience shaping and delivering human-centered digital transformation initiatives in government, healthcare, transit, and retail. He is a digital project management nerd, a cultivator of highly collaborative teams, and an impulsive sharer of knowledge. He's also the co-founder of The Digital Project Manager and host of The DPM Podcast.
Project charters are important documents that describe the scope and objectives of a project. Find out how to get our template to speed up the process of creating one, and get the deets on what to include and best practices from the experts.

Project Can't Start Without A Charter: Projects can't officially start without a charter, and skipping this step leads to misalignment and an increased risk of project failure.
Charters Secure Alignment & Buy-In: A project charter outlines the scope and business case, so all stakeholders are aligned on project purpose and deliverables before the project actually kicks off.
Blueprint for Project Success: A project charter defines roles, responsibilities, and project objectives, and empowers the project manager to execute project work and spend the project budget.
Keep It Simple & Big Picture: Your charter should provide a high-level overview, avoid unnecessary details, and keep things simple so that anyone involved in the project can understand what's going on.
Use a Template: Instead of creating a charter from scratch for each new project, use a template (such as ours!) to save you time.
Project charters outline the scope and objectives of your project. If you’re looking to kick off your new project on the right foot, a comprehensive charter is the way to start, and it saves you time down the line.
Without one, your project can't actually officially start, and there's no guarantee that all your stakeholders will be aligned on the project purpose and deliverables. This sets you up for scope creep, miscommunications, and ultimately, project failure.
I’ll describe what a project charter is and how a well-crafted one keeps us on track throughout the project management life cycle. You’ll also find project charter samples, a project charter template, and a list of software tools to help you develop and manage your charter.
What is a Project Charter?
A project charter is a formal document that outlines the shared understanding of a project’s scope , development, and project objectives , while also defining the roles and responsibilities of each party involved. It’s generally a fairly short document.
Project charters give the green light for a project to begin. Similar to the legal definition of the word “charter,” a charter in project management authorizes a project to exist and empowers the project manager to execute the work and spend the project budget. If the charter is approved, the project moves into the planning phase.
You might also see a project charter referred to as a brief or project initiation document (PID) .
Here's a quick recap:

When Should I Create the Project Charter?
The project manager should create the project charter during the project initiation phase . Documenting the purpose of the project, what activities will be part of execution, and who is responsible for performing which activities is critical for aligning key stakeholders before the project kickoff.
Project Charter Template & Sample
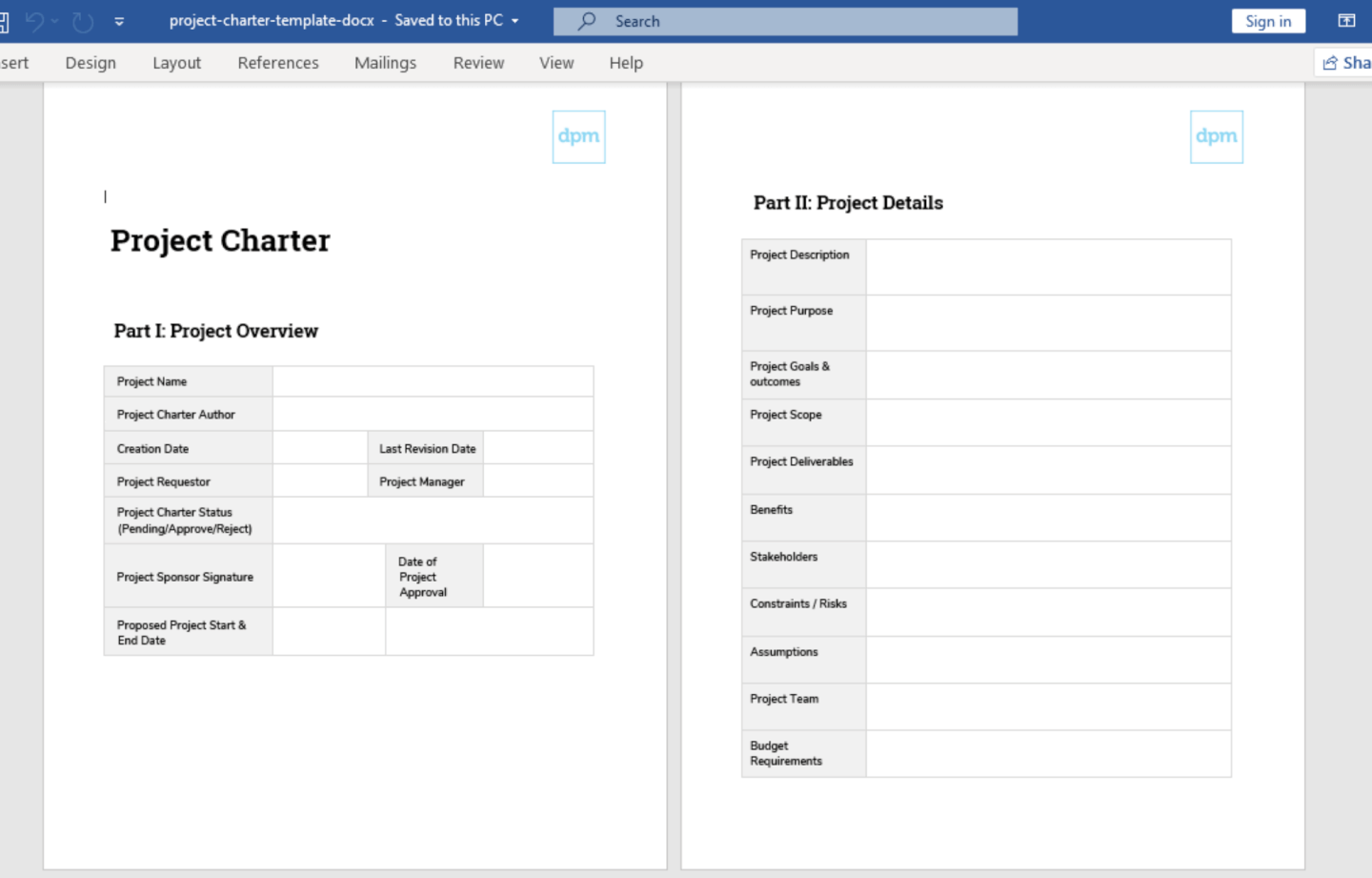
Download your template here and use this guide as you are completing it—the insights in this article will help you create a rock-solid project charter. We’ve also included a filled-in sample to give you an idea of what yours should look like.
Project Charter vs. Statement of Work (SoW) and Project Plan
It’s easy to confuse a project charter with a SoW or a project management plan (also known as a project plan), as these documents are closely related. In this section, I’ll define each document and explain when and how you’d use it.

Statement Of Work
A SoW addresses the business need for a project, states what is included or not included as part of a project, and describes specific project deliverables. A SoW also typically summarizes project assumptions and proposed acceptance criteria.
A SoW is a crucial point of reference for project stakeholders, and it’s absolutely essential for PMs to know how to create a SoW . While a well-written SOW can save you a world of trouble, on the flip side, even a tiny mistake can have massive repercussions down the line.
You can think of the SoW as a precursor to and key source of input for the formal project charter.

Sign up to get weekly insights, tips, and other helpful content from digital project management experts.
- Your email *
- Yes, I want to sign up to receive regular emails filled with tips, expert insights, and more to build my PM practice.
- By submitting you agree to receive occasional emails and acknowledge our Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time. Protected by reCAPTCHA; Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Project Plan
Whereas the project charter explains the “what” and “why” of a project, the project plan describes the “how.” Similar to how the project charter builds on the SoW, the project plan builds on the project charter.
A project plan explains how you will manage the various aspects of a project, including potential risks, the project schedule , communications, etc.
Why is the Project Charter Important?
The project charter document is important because it gets your stakeholders to agree on why you’re doing the project, what’s in scope (at a high level), and who’s doing what. Some organizations require a signed project charter before allocating resources , including funding, to your project.
Let’s consider the benefits more in-depth, from the perspectives of each party involved.
Benefits for Project Managers & Teams
- Articulates project value proposition : helps you determine if it’s worthwhile to carry out the project
- Saves time down the road : the time you take to clarify objectives at the beginning of a project is time you won’t need to spend troubleshooting and negotiating later in the project life cycle
- Clarifies the budget : ensures that funding is available and will be released on time. Settling your spending authority and budgets saves time prior to starting the project.
- Sets clear guidelines for your project team : defining success criteria is invaluable for guiding the team as you begin to brief out the project
- Boosts team morale : a team working under a sloppy charter will repeatedly find themselves confused, with their hard work wasted or headed in the wrong direction. A well-written charter gives metrics for a successful project that your team can feel motivated and confident to work toward.
Benefits for Clients & Other Stakeholders
- Creates a shared understanding : stakeholders know what to expect and what constraints the project faces
- Serves as a marketing tool : the project charter can function as a sales document to justify new or existing investments.
What to Include in a Project Charter
Here's what to include in your project charter:

- Introduction : explains the purpose of the charter and provides the project name
- Business case and scope statement : explains the purpose of the project (including business drivers and any related projects), defines high-level activities that are part of the scope of the project (this will help avoid scope creep later), and covers the expected return on investment
- Success criteria : defines what success looks like and how the team will measure success
- Major requirements or deliverables : summarizes high-level requirements and/or key deliverables
- Budget : estimates project costs, ideally by project phase, and defines sources of project funding
- Milestone schedule : estimates project duration and summarizes each major part of the project and all milestones
- Assumptions and constraints : identifies known and unknown parameters upon project initiation
- Project risks : summarizes major known threats or opportunities that may affect project success
- Team and organization : defines project roles and responsibilities
- Approvals : includes a space for stakeholders to record their approval (or disapproval) of the charter.
In addition to these project charter sections, you may also include an appendix with documents such as:
- List of deliverables : if deliverables are already defined, this list contains details about each deliverable—what it is and the associated acceptance criteria
- Scheduling documents : project timeline, calendar, or other documents that sequence project activities and include details about each project milestone or phase
- Communication plan : this includes details about how each person involved will be kept informed about progress, scope changes , etc.
The Project Management Institute’s Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) is a good reference for more information about each of these key elements.
How to Create a Project Charter
There’s no single right way to create a project management charter, but here is a basic process you could consider:
1. Discuss With Stakeholders & Team
Gather information about the project by meeting with key stakeholders, including the project manager, sponsors, clients, and representative project team members.
Don’t forget that stakeholders may also include other teams that provide specialized support, such as network capacity and security experts.
2. Take & Organize Notes
In your discussions, ask questions and take notes that help you to fill out each of the sections of your charter. Use your time wisely to collect the most salient information; you can always fill in the supporting details later on.
3. Use A Template
Take advantage of the myriad project charter templates available online to create the format that best serves your project needs.
DPM Members can use our pre-made charter template, along with a bunch of other time-saving resources. Alternatively, you could use one of the sample project charters in this post as a starting point.
Or, if you want to build your own charter from scratch, you can work through this detailed guide from the Treasury Board of Canada , line-by-line.
4. Include Specific Information
Let’s start with a bad example. For a banking client, a project manager writes the project goal statement in the charter as “improve communication channels.” Yes, good communication is a worthy goal, but the way this is written leaves a lot to the imagination:
- Whose communication channels will be improved? Customers? Internal staff?
- How many users’ needs are we trying to address?
- Will we be updating an existing system or building a completely new system?
- When will it be completed?
- Does the scope extend to training on the new communication tool ?
- Will the contract include any ongoing support for the system?
A complete charter would provide clear, specific information on these questions so that the reader can understand the project purpose . Here’s a better example of a project scope statement (a key part of your charter):
“Create a new communication system to replace ABC system by December 2024, so that customers can chat with their product managers via XYZ bank’s proprietary mobile apps. Train 400 employees to maintain and support the system in-house.”
Of course, this is only the goal statement, not the entire charter. Yet, this example showcases the difference between a sloppily written and a thoughtfully written charter.
Apply similar logic to craft other sections of the charter. The goal of this exercise is for the project sponsor to have sufficient information to be able to approve the project.
5. Review With Team Representatives
After drafting a project charter but before reviewing it with a client, set aside time to review the charter with key members of your team to assess accuracy and completeness.
6. Present For Approval
Notice that this step is not “send for approval.” The project charter is the key to getting approval to undertake the project, and it’s important that it’s presented properly. Avoid simply attaching your charter as a PDF in an email, only to be ignored or dismissed out of hand.
Instead, present your charter to your sponsors, stakeholders, or clients—do this in a meeting or through a slide presentation that includes supporting media. Make sure you leave sufficient time for questions and answers.
Project Charter Examples
Here are three different examples of project charters to consider:
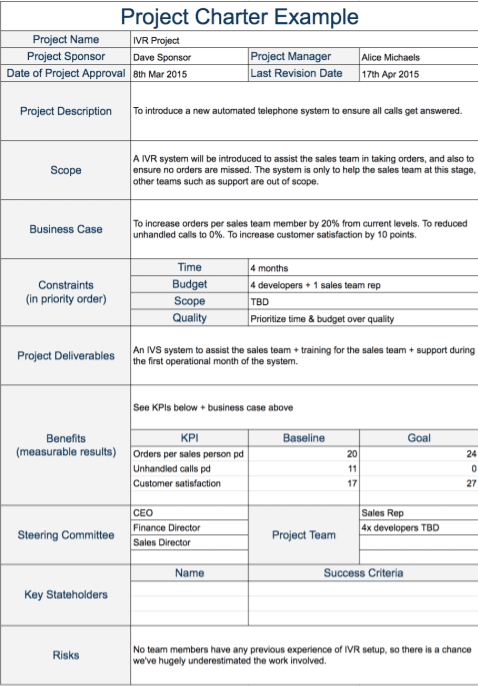
In this example project charter for an interactive voice response system, the project manager has included some notes on the business case, in addition to a project description and the scope.
They've also listed the constraints in priority order, which is useful for providing quick context to whoever is reading this document.
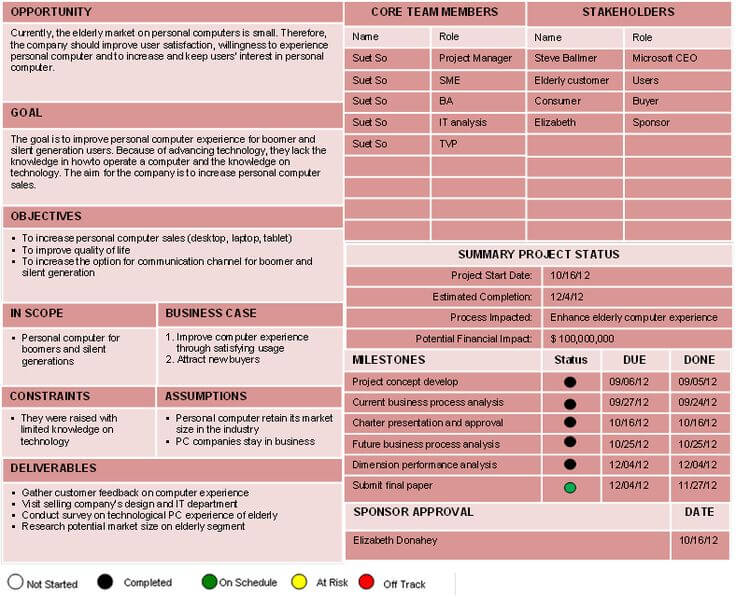
This project charter example clearly lists the project objectives, as well as the milestones and an accompanying timeline.
While you don't necessarily need a complete timeline yet (this will be defined in the project plan), this is a good item to include and then update for project status reports , as the team is completing the work in the execution phase.
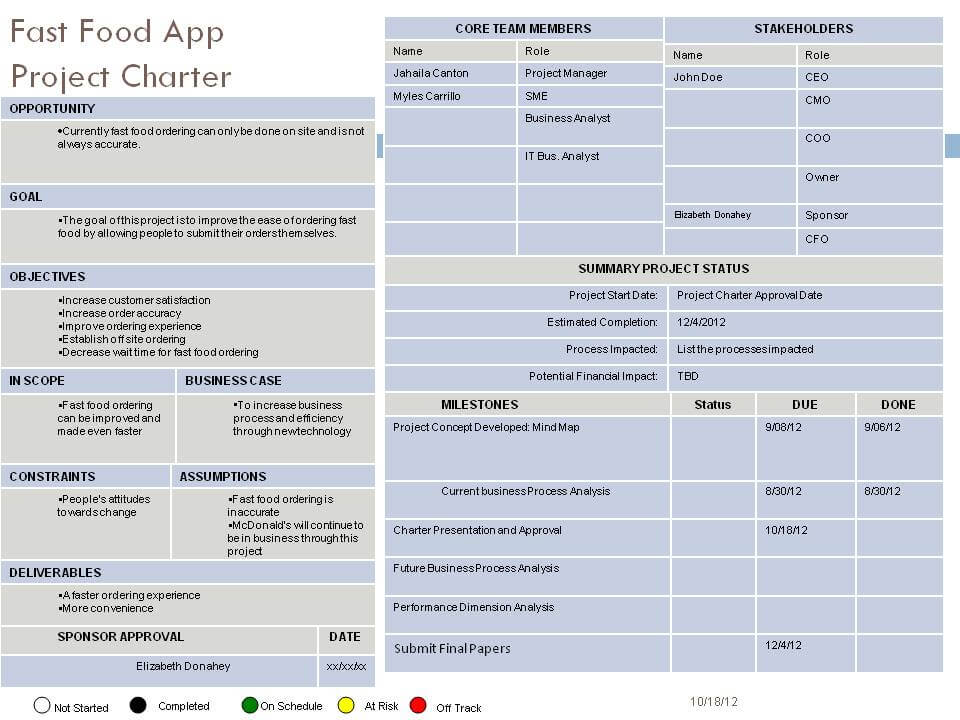
This one is similar to the above example in that it includes milestones and a timeline.
It has also clearly laid out the objectives and what's in scope, and includes some notes on the processes that the project will impact, which is useful as this relates to the constraint of attitude towards change (which is listed in the constraints section).
Expert Tips for Creating a Project Charter
When creating a project charter, keep in mind these tips and best practices:
- Keep it simple . Your project charter should leave no room for interpretation. A layperson with no knowledge of the project or your organization should be able to pick up the document and understand what’s going on.
- Big picture over details . Provide a high level overview of the project purpose and outcomes, and avoid getting bogged down in unnecessary details that hinder alignment or create accountability problems later on.
- Create consensus . You could draft the most eloquent project charter on the planet, but it serves no purpose if stakeholders aren’t willing to agree to it. Remember that the project charter is a tool that supports stakeholder alignment. If your charter doesn’t bring stakeholders together, there’s no point in writing one.
Project Management Tools For Developing & Managing Charters
Software tools offer a simple way to develop and store your project charter in an accessible place where all stakeholders and team members can access it as needed.
Types of project management software tools that can be useful include:
- Project management software : You can enter the details about objectives and scope from your project charter and then measure how you're tracking against them throughout the project.
- Mind mapping software : This software is useful for brainstorming and organizing information about the project before you start creating a charter.
- Gantt chart maker : Use this software for plotting milestones and timelines, which will come in handy after your charter is approved.
What's Next?
Have more questions about RACI charts? Become a DPM member and join the conversation in Slack with 100s of other digital project managers! You’ll also get access to 100+ templates, samples, and examples of project documents, which will save you time and increase your chances of project success.
How to Handle Scope Changes in Project Management
5 project management software evaluation criteria 2024, 11 tips for managing projects & resource library for beginners.

- How-to Guides
Tips for Students: Writing Project Management Assignments
by MyMG Team · Published March 23, 2020 · Updated July 4, 2024

Is it confusing for you to kickstart the writing process for your project management assignment? Does all that jargon like sustainability strategies, project feasibility, or risk mitigation make you feel stressed?
What is the best way to highlight your challenging project management topic acceptably?
‘Phew, what a challenging paper! How can I find a professional writer to deal with these boring assignments?”
Ok, we hear you. You can do it online in a matter of minutes. In fact, assignment writing help services can take all your project management paper worries away and deliver you a custom essay or even a 5-star dissertation without any hassle for you.
Sounds fantastic? That’s exactly what they do.
“Ok, cool. Is this a reliable way to deal with my papers?” Sure. Unless you are super lazy and want to turn them in without any modifications.
“What do you mean?” If you want to avoid any troubles in your college or university and have no time/desire to write your assignment on your own, you can look for expert help online.
However, once you get a well-written paper on your topic from the expert writer in that subject area, you need to rewrite it and modify it to some extent.
If you do this, nobody will ever accuse you of cheating or plagiarism, and you’ll save tons of time instead of completing your assignment from scratch.
Now, let’s explore the top tips for writing your project management assignments.
Get Enough Time for Writing
Essay writing is an essential academic skill. To create amazing papers, it’s crucial to have a great essay writing competence. How do you get it? Through practice. Write often. Write a lot.
One of the golden rules of writing any kind of essay is to make sure you get enough time in your schedule for research and writing.
Understand that you need some time to complete the work without being in a rush. Rarely, you can come up with an exceptional essay overnight. For this, you need to be really motivated, inspired and loaded with facts, arguments, and brilliant ideas.
Of course, there needs to be adequate time for choosing a topic, doing the research, reading all the materials and taking notes, gathering the notes into a logical order to form an outline, and writing the essay. Without doing all these things, you won’t be able to submit a top-grade paper on time.
Once you finish writing your paper, you still need to put in some work. What does it mean? Your essay needs to be proofread, edited, and polished up.
Every student works at a different pace, so discovering how much time is needed is an individual thing, and the first most crucial essay writing skill.
Choosing a topic
This step is central to a knockout essay. That’s because the topic can make or break the article. Choose it carefully if you have such an opportunity. If the instructor has assigned a topic, then it is up to you to find a perfect angle on the topic to base your essay on.
Photo by Dollar Gill on Unsplash
Research and taking notes
The research phase is where the student dives into what others have written about the general topic. This step could be done before step 2 if the student needs help narrowing down the topic or the angle on the topic.
Jotting down notes during the reading and referencing the source for the notes will save tons of time later on in writing.
Forming the Outline and Writing the Essay
The notes are organized into groups that logically fit together. A description for each set is like a subheading. These can be arranged in chronological order or organized in a fashion that flows well from one idea to the next. This is the outline of the body of the essay.
Writing the essay consists of filling in the details for each of the sections in the outline. It includes writing a captivating opening paragraph and a memorable summary at the end.
Proofreading and editing
Unfortunately, this important step is often missed. Even the best essays will fail without detailed proofreading and in-depth editing.
It is best if this step is done by another person, as it is easy for a writer to overlook their own mistakes in assignment writing.
The proofreader and editor should be someone who is really good at writing, not just a neighbour or friend because they are available and free.
So now you know all the basic steps that you need to take to be able to submit a winning project management assignment on time. Don’t just sleep on these tips. Put them into work and you will see the results.
Alternatively, you may always choose a service for you to assist.
Tags: project manager student tasks writing
We are a small group of professionals specializing in project management. We wish you success in your career, business, studies, or whatever else you think is worth your time and effort—we are pleased to know that our advice is helpful.
- Next story How do HR personnel change workplace culture? Five Tips to change it today too
- Previous story How to Stay Organized: Five Ways for Project Managers
You may also like...

The Relationship Between Project Management And Risk Management
August 21, 2020
by Jordan MacAvoy · Published August 21, 2020 · Last modified June 26, 2023

Top 5 Characteristics of a Good Project Manager
August 6, 2012
by Daniel Linman · Published August 6, 2012 · Last modified June 26, 2023
Content Writing Guide for Small Businesses in 2019
April 15, 2019
by Robert Everett, a guest post writer · Published April 15, 2019 · Last modified June 26, 2023
Worth Reading

11 Essential Time Management Hacks for Road Warriors
August 16, 2015

Project Facilitation – Definition, Role and Skills
September 13, 2012

7 warning signs your project is going to fall down
November 21, 2019

The Summer of Freedom: Why the Next Few Months of 2021 Pose a Unique Challenge to Project Managers
June 4, 2021
#ezw_tco-3 .ez-toc-title{ font-size: 120%; ; ; } #ezw_tco-3 .ez-toc-widget-container ul.ez-toc-list li.active{ background-color: #ededed; } Table of Contents Toggle
Career & Lifestyle / Teamwork & Leadership
Tracking Employee Productivity at Workplace: 5 Proven Tactics for Growth-Oriented Managers

Website Project Planning: Six Steps to Success

Project initiation stage – Project Initiation Document (PID). Duties of project owner and project team

Organizing Procurement and Purchasing Activities in a Project

Two Common Mistakes in Project Procurement Contracts

Project Sponsor – The Role and Responsibilities
- Google Meet
- Mobile Dialer

Resent Search

Academic Counselling Sessions

Academic Counselling and Sample Service

Professional Proofreading Services

Technical Assistance

Counseling Sample & Proofreading
How to make an Assignment for Project Management
A project is the sequence of actions that is planned so that the goal is able to be accomplished. A project could last between a couple of days to several months, or even years based on the quantity that is required. Management principles for projects help in ensuring that the task is executed efficiently. It assists in analyzing the situation , and then plan and manage tasks that are relevant to the project so that it's possible to ensure the effective execution of the plan.
The courses in project management are taught using a mix of written university assignments on project management and case studies for projects. proposals for writing project scopes, scenarios, and also sample project management samples based on actual projects and management reports. Students often find it difficult to comprehend project management essays since this course takes place in an interconnected mixture of finance, accounting management, business, and IT computer systems. If they do not have a comprehensive understanding of all these areas, students frequently fail in their project management assignments as well as the scope of their work can result in poor marks. It is difficult to gain a comprehensive understanding of these areas with extremely short deadlines and rigid timetables for study is not possible.
The professionals in the Project Management at Assignment Work will assist you in delivering the most effective work in the field of Project Management. The report will be so complete and precise that you'll never think that it's being performed by an outsider. The professionals who offer assistance with your Project Management Assignment online are experts certified and are part of the business sector exclusively. Before we get into our options for assignment assistance, we'd like to provide a short overview of assistance with project management assignments and the importance of it.
What is Project Management?
Project management is the application the knowledge, skills, and experience using a an official set of tools and techniques to a vast array of activities in order to fulfill the needs that the task. Project management requires specialized understanding and expertise. It's achieved by several procedures, including starting, planning, executing the project, coordinating, and closing projects. They are executed by the project manager and his team. Teams of project managers oversee the activities of the project, which includes different demands on costs, scope, time as well as risk and high-quality stakeholders who have different needs.
To provide an error-free project management plan and a project management assignment assistance report AHECounselling guarantees that you receive the top report written by PMP certified (project management plan) experts around the globe. Because the experts are part of the field, you can be assured of high-quality and a fault-free report on project management. The plan is based on the timeline, resources for activities and other pertinent details. We guarantee that you will provide the correct project management plans according to the guidelines provided by your college or university.
There are many methods that are used for various purposes in obtaining results using Project Management Plan.
* Critical Chain Project Management
* Agile Scheduling
* Waterfall
* Critical Path Method
Our academic experts will provide the highest quality of your project management task and provide an analysis that makes utilization of an extensive array of applications within the fields of integration cost and quality, human resource procurement, scope, time communication, risk management and management of stakeholder.
Project management consists of five major processes, as described below.
The processes that initiate the project determine the nature and the scope that the undertaking will take. If this step is not executed properly, the project won't effective in meeting demands of the company. The team members require knowledge of business requirements and must make sure that all the necessary controls are included in their project.
The initial stage must include the following steps: analyze the business requirements and review of the operations currently in operation along with financial analysis of costs and benefits , including budget analysis for stakeholder analysis, user analysis, and the support staff for the project, which includes cost as well as deliverables, tasks and the timetable
Design and planning
Following the beginning phase, the project will be scheduled to the right degree of specifics. The goal is to establish the duration as well as resources, costs and time to determine the amount of work required and effectively reduce risk in the course of project execution.
Planning for projects generally involves the determination of how to plan a specific project, defining an outline of the plan, choosing the planning team, selecting deliverables and developing an outline of the structure for work choosing the necessary activities to finish those deliverables and connecting the tasks by estimating the required resources for the project as well as estimating the time and cost to develop the schedule, risk management getting formal approval before you start work.
Executing refers to the procedures that are used to finish the work which is outlined in the plan of the project to meet the requirements of the project. Execution requires coordination of personnel and resources, and taking care of the integration and execution of the project according to the project management plan. The deliverables are outcomes of the processes that are performed according to the specifications of the plan for managing projects.
Monitoring and Controlling
Monitoring and controlling is the procedures used to watch the execution of projects so that problems that could arise can be identified quickly and corrective actions can be initiated immediately, as needed and to ensure the proper execution for the undertaking. The primary advantage is that the performance of the project is monitored and evaluated regularly to detect deviations from the plan of management for the project.
Closing is an official acceptance of project as well as the end of the project. Administrative tasks include the archiving of the documents and files.
The different types of Management Methodologies and Examples
Waterfall is a good choice for is perfect for companies in industry particularly in design and development of products and construction.
PRINCE2 The project management approach is based upon the product, therefore its methods focus on getting concrete results , not on the scheduling of actions.
AGILE Methodology for Project Management: It assures flexibility and allows for the modification of the product at any time during the duration of the project. In the process of progressively completing all phases to produce the final product achieved. This is founded on of whatever is effective. It is suitable for the IT sector.
Scrum An approach for short-term planning that is suitable for the development of software. There isn't a project manager in this scenario; everything will be managed through an individual, the Scrum master, the person who starts and oversees the work that is done.
Kanban Kanban: This KANBAN system is a flexible method of managing projects that is rooted in JIT manufacturing processes. It uses labels and cards to determine the requirements. It is based on the traditional approach.
PMBOK PMBOK outlines several aspects of a plan in a linear fashion in which the problem/need as well as the scope and plan are established during the beginning phases. It is not a suitable method to use alongside other more flexible and agile methodologies. It is based on the traditional method.
LEAN It was used by Toyota in the 70's, it's ideal for industrial settings that is designed to ensure efficient production. The management determines what products to produce, so that teams can begin to work toward those goals.
Hire Now Best Online Project Management Assignment Help Service
In the end, if you're exhausted of looking for the most reliable and trustworthy project management experts who can ensure you get the best marks in your degree in project management or to receive academic assistance with managing construction projects then AHECounselling is the right choice for you. AHECounselling has a staff of more than 100experts in project management that can assist you immediately with your project management course by giving you authentic and timely advice on the best methods of project management and tools for managing projects you require. We also have hundreds of project management sample projects and project plan templates which will assist you in all of your project management classes, whether it's writing a thorough project scope essay or a model of the life cycle within every project plan. All you have to do is contact us with the AHECounselling Project Management requirements and connect via telephone, email or live chat service 24x7 to receive the best support for managing projects.

Top 10 Best Universities Ranking list in India 2022

Generic Conventions: Assignment Help Services

Research Paper Topics For Medical

Top 5 Resources for Writing Excellent Academic Assignments

How to Write a Literature Review for Academic Purposes

Tips for Writing a killer introduction to your assignment

How To Write A Compelling Conclusion For Your University Assignment

Research Papers Topics For Social Science

Best 150 New Research Paper Ideas For Students

7 Best Plagiarism Checkers for Students And Teachers in 2024
Enquiry form.
All Formats
Project Templates
8+ sample project assignment templates.
Project assignment template provides for the detailed list of work assigned to fulfill the process of a project. It takes into consideration the restriction of time period assigned for each duty, roles and responsibilities of each team member etc which is key to the success of the Project Implementation Template.

Project Daily Assignments
Project Weekly Assignments

Project Monthly Assignments
Project School Assignments

New Project Assignment Template

Writing Project Assignment Template

Integrative Assignment Project Template

Project Creative Essay Assignment

> Advantages of Using Project Assignment Templates
- You can create a timesheet schedule that you can follow every day to keep your work on time.
- You can create your own checklist where you are keep a check on the task you have completed and the tasks that are pending.
- You can manage time and budget by cutting down unnecessary strategies and unnecessary expenses.
- You can create a summary and an objective list so that you do not deviate from the very core subject by adding unnecessary information.
- You can save a lot of time energy and money by using the digital technology for making notes for your project.
> What are the Steps to be Followed to Make Project Assignment Templates?
> to conclude the statements mentioned above we state, more in project templates.
100+ Ultimate Agreement Template Bundle
Marketing content approval agreement template, digital marketing agency ugc influencer collaboration agreement template, project status report template, construction project agreement template, project agreement template, project portfolio dashboard template, subcontractor confidentiality agreement template, project team agreement template, project finance agreement template.
- 38+ Project Report Templates – Word, PDF, Google Docs
- 29+ Sample Project Documentation Templates
- 13+ Project Documentation Templates
- FREE 8+ Project Scope Templates in PDF, Word
- FREE 11+ Project Case Study Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Project Proposal Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Project Proposal Outline in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | Editable PDF | InDesign | Photoshop | Publisher | PDF
- 3+ Charity Project Budget Templates in PDF | DOC
- 8+ Sample Project Overview Templates
- 10+ Internship Project Proposal Templates in PDF | DOC
- 13+ Internship Project Report Templates in DOC | PDF
- 6+ Project SWOT Analysis Template
- 12+ Hospital Project Report Templates in PDF
- 15+ Project Schedule Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | Numbers | XLS | PDF
- 13+ Project Action Plan Templates
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
- Digital Offerings
- Biochemistry
- College Success
- Communication
- Electrical Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Mathematics
- Nutrition and Health
- Philosophy and Religion
- Our Mission
- Our Leadership
- Accessibility
- Diversity, Equity, Inclusion
- Learning Science
- Sustainability
- Affordable Solutions
- Curriculum Solutions
- Inclusive Access
- Lab Solutions
- LMS Integration
- Instructor Resources
- iClicker and Your Content
- Badging and Credidation
- Press Release
- Learning Stories Blog
- Discussions
- The Discussion Board
- Webinars on Demand
- Digital Community
- Macmillan Learning Peer Consultants
- Macmillan Learning Digital Blog
- Learning Science Research
- Macmillan Learning Peer Consultant Forum
- The Institute at Macmillan Learning
- Professional Development Blog
- Teaching With Generative AI: A Course for Educators (Start date May 13th, 2024)
- Teaching With Generative AI: A Course for Educators (Start date July 8, 2024)
- Teaching with Generative AI: Course Alumni
- English Community
- Achieve Adopters Forum
- Hub Adopters Group
- Psychology Community
- Psychology Blog
- Talk Psych Blog
- History Community
- History Blog
- Communication Community
- Communication Blog
- College Success Community
- College Success Blog
- Economics Community
- Economics Blog
- Institutional Solutions Community
- Institutional Solutions Blog
- Handbook for iClicker Administrators
- Nutrition Community
- Nutrition Blog
- Lab Solutions Community
- Lab Solutions Blog
- STEM Community
- STEM Achieve Adopters Forum
- Contact Us & FAQs
- Find Your Rep
- Training & Demos
- First Day of Class
- For Booksellers
- International Translation Rights
- Permissions
- Report Piracy
Digital Products
Instructor catalog, our solutions.
- Macmillan Community
A Short Proposal Assignment Idea

- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
- Composition
- Developmental English
- assignments: english
- professional communication
- technical writing
- workplace writing
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
- Bedford New Scholars 50
- Composition 565
- Corequisite Composition 58
- Developmental English 38
- Events and Conferences 6
- Instructor Resources 9
- Literature 55
- Professional Resources 4
- Virtual Learning Resources 48

Say My Name Transcription Project: Resource Guide
- Assignment Examples
- Transcription Guidelines
- What's Getting Transcribed
- Say My Name Transcription Project: Pre-Assessment Survey Please have your students fill out this survey before they are presented with information about White Hall and how to transcribe historical documents.
- Say My Name Transcription Project: Post Assessment Survey After your students have completed their transcription project, please have them fill out this survey.
- Deciphering Cursive Handwriting from UNC-Wilmington Library Resources on cursive handwriting from the University of North Carolina Wilmington Library include: a video tutorial, common abbreviation, cursive handwriting quizzes, and more.
Coming Soon!
- From the Page
- Sample Letter
Archives Instruction
The Research Center for Special Collections & Archives (RC-SCA) is happy to provide your class with introductory information on White Hall and the Say My Name Transcription Project. Please fill out the form linked below if you would like us to meet with your class.
- Instruction Request Form
Example 1 (In-Class)
This assignment is courtesy of Heather Fox
Archival Investigation: Transcribing White Hall Documents
- Read and study the "Transcription Guidelines" .
- Peruse documents that require transcription. Choose TWO documents that require transcription and work together to complete the transcription. When choosing, find a document that has writing on a full page (versus a line or two on a page). If in doubt, please ask me first. Also, while transcribing, be sure to save your work often.
- Share your findings and experiences with the class.
Absences Only: If absent, complete a Transcribe Archival Investigation Report , which should be submitted in PDF form to Blackboard and must contain the following items for full credit:
- The title of the document
- The link to the document that enables me to access it
- Your group’s screen print photograph of your completed transcription of the document
- A 2-3 sentence summary of the document that you transcribed, which includes the amount of time that it took the group to transcribe the document
- One paragraph that describes your “meta” observations about this archival research experience, in terms of the scope and purpose of the project as part of our course’s theme and objectives
Notes from Heather
- I tend to provide less instruction up front and work alongside students as they work through questions/considerations.
- Have students work in pairs. Pair cursive readers with non-cursive readers.
- Since some documents are more difficult to read than others, suggest that students look for easier to read documents, instead of picking the nearest option when they open the site.
- Comparing letter formations and reading in context within the same document can help with deciphering text.
- If a group does not finish a full transcription, "Save" without pressing "Done".
- Leave time for students to complete the post assessment during class.
Example 2 (Outside Class plus In-Class)
This assignment is courtesy of Ginny Whitehouse
Transcribing Historical Documents
Outside Class Assignment
- Using your EKU email account, sign up for “From the Page” so that you can be assigned transcriptions in the next class.
- Watch the video from the UNC-Wilmington Library on “Reading Cursive Handwriting” then take two of the cursive handwriting quizzes at the bottom of the page. Retake until you get 100%.
- Read the “Transcription Guidelines" .
- Use those guidelines to transcribe the "Sample Letter" provided from EKU Archives.
- Take the End of Class Quiz by Noon Wednesday.
In-Class Assignment (Thursday class)
- Transcribe the historical document assigned to you.
Notes from Ginny
- The "End of Class Quiz" was just a matter of them copying and pasting the "Sample Letter" transcription. I gave them full credit for making a solid effort.
- At the Thursday class, we talked about the prep work they did.
- My class said the Wilmington video, particularly, and the "Transcription Guidelines" were helpful.
- The Wilmington quizzes helped them gain confidence but they didn’t learn anything new.
- Doing the "Sample Letter" exercise was really important for most of the students.
- We reviewed in class the "Sample Letter" and discussed some mistakes/inconsistencies that they had, such as not including the header information on the letter and not returning after each line. For those who struggle with detail work, this level of “step by step” instruction was good.
Example 3 (Outside Class)
- Peruse documents that require transcription. Choose ONE document that requires transcription review and work together to complete the transcription. When choosing, find a document that has writing on a full page (versus a line or two on a page). If in doubt, please ask me first. Also, while transcribing, be sure to save your work often.
- Once you have completed your transcription review, take a screen shot photo of your work.
- Your group’s Transcribe Archival Investigation Report should be submitted in PDF form to Blackboard and must contain the following items for full credit:
- << Previous: About
- Next: Transcription Guidelines >>
- Last Updated: Aug 14, 2024 11:25 PM
- URL: https://libguides.eku.edu/c.php?g=1416637
EO/AA Statement | Privacy Statement | 521 Lancaster Avenue, Library 126, Richmond, KY 40475 | (859) 622-1792 ©

Title Page Setup
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student title page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
Title page setup is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.3 and the Concise Guide Section 1.6
Related handouts
- Student Title Page Guide (PDF, 263KB)
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names | Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Cecily J. Sinclair and Adam Gonzaga |
| Author affiliation | For a student paper, the affiliation is the institution where the student attends school. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author name(s). | Department of Psychology, University of Georgia |
| Course number and name | Provide the course number as shown on instructional materials, followed by a colon and the course name. Center the course number and name on the next double-spaced line after the author affiliation. | PSY 201: Introduction to Psychology |
| Instructor name | Provide the name of the instructor for the course using the format shown on instructional materials. Center the instructor name on the next double-spaced line after the course number and name. | Dr. Rowan J. Estes |
| Assignment due date | Provide the due date for the assignment. Center the due date on the next double-spaced line after the instructor name. Use the date format commonly used in your country. | October 18, 2020 |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Professional title page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names
| Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Francesca Humboldt |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals after author names to connect the names to the appropriate affiliation(s). If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). | Tracy Reuter , Arielle Borovsky , and Casey Lew-Williams | |
| Author affiliation
| For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center each affiliation on its own line.
| Department of Nursing, Morrigan University |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals before affiliations to connect the affiliations to the appropriate author(s). Do not use superscript numerals if all authors share the same affiliations (see Section 2.3 of the for more). | Department of Psychology, Princeton University | |
| Author note | Place the author note in the bottom half of the title page. Center and bold the label “Author Note.” Align the paragraphs of the author note to the left. For further information on the contents of the author note, see Section 2.7 of the . | n/a |
|
| The running head appears in all-capital letters in the page header of all pages, including the title page. Align the running head to the left margin. Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head. | Prediction errors support children’s word learning |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Reflection assignment
Embedding a block?

Reflection assignments are used to encourage students to think about their learning experiences and the knowledge and skills they have obtained. Students are actively being involved in a process of self-assessment which helps them to develop a more profound understanding of the course materials and their own learning process.
Reflection assignments offer various advantages for both teaching staff members and students.
- This type of assignment stimulates students to consciously reflect on what they’ve learned, which topics they found difficult and how they can improve their knowledge and skills. This stimulates metacognition and self-regulation.
- Through reflection assignments, you gain insight on the students’ progress and understanding, which provides valuable information for your lesson preparation and guidance.
There are various ways to use reflection assignments in your class.
- One possible way is to ask students to write a one-minute-paper , in which they describe a concept or theory in their own words in a few sentences. This assignment forces students to reflect on what they’ve learned and helps them to express their understanding.
- Another version is the muddiest point technique, where the students are asked to describe the most difficult part of the class or exercises. Here, they are challenged to specifically reflect on the parts of the course materials they haven’t fully mastered yet. This can be useful when dealing with certain complex topics or when identifying the learning parts that require extra focus.
- Additionally, you can let students reflect on statements by asking them why a certain statement is true or not. This improves critical thinking and the information evaluation process.
Reflection assignments are rarely assessed formatively. It can, however, be useful to give feedback on the reflections of students or to let them give feedback to each other. This helps students gain insight in their strengths and points for improvement and encourages them to further reflection and growth.
Click through to the tools you can use in the teaching activity 'reflection assignment' in an online context:
Click through to training initiatives and self-study modules involving the teaching activity 'reflection assignment':
Inspiring examples
Be inspired by colleagues who have integrated the educational activity 'reflection assignment' into their teaching practice or project:
How can I revise my assignments to deter student use of AI?
As generative AI becomes more advanced and accessible, it’s helpful to revise assignments in ways that deter unauthorized use while promoting genuine learning. Here are detailed strategies for creating assignments that are less susceptible to misuse by AI and encourage authentic student engagement:
Oral presentations and defenses
Incorporating presentations and defenses into assignments encourages students to articulate their ideas and demonstrate their understanding without relying on AI-generated content. By requiring students to present their work and engage in question-and-answer sessions, instructors promote effective communication skills and critical thinking abilities. These assignments provide valuable opportunities for students to showcase their knowledge, receive immediate feedback, and engage in meaningful dialogue with peers and instructors
- Presentations: Require students to present their findings to the class or in a one-on-one session with the instructor.
- Q&A sessions: Follow presentations with a question-and-answer session to assess the student’s comprehension and ability to discuss their work.
- Recorded videos: Have students submit video presentations where they explain their project and process.
Example prompts
- Prepare a 10-minute presentation on your term paper, followed by a 5-minute Q&A session where you answer questions about your research and conclusions.
- Prepare a 15-minute presentation on your final project, followed by a 10-minute Q&A session where you will answer questions from your classmates and the instructor about your methodology and findings.
- Record a video presentation explaining the key points of your research paper. In your video, address potential counterarguments and provide a detailed justification for your conclusions.
In-class writing and assessments
In-class writing and assessments offer students the opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge and skills in real-time, deterring unauthorized use of AI. By conducting writing assignments and assessments during class time, instructors ensure that students must rely on their own understanding and abilities without the aid of AI. These assignments promote active learning, critical thinking, and effective time management skills, leading to more authentic assessment outcomes.
- Timed essays: Schedule in-class essay writing sessions where students respond to prompts within a set time.
- One-minute papers: Have students write a quick, one-minute paper at the end of class to summarize key concepts or respond to a prompt.
- Short-answer questions: Use short-answer questions in exams that require critical thinking and synthesis of course material.
- Concept maps: Have students create concept maps in class to visually organize and represent their understanding of a topic.
- Writing workshops: Organize workshops where students work on writing tasks and receive immediate feedback.
- During our next class, you will write an in-class essay on one of the key topics we have covered. Bring any notes or materials you need, but all writing must be done in class.
- Create a concept map that outlines the major theories we covered this week. Include key concepts, their relationships, and examples.
- Complete a short-answer quiz in class that requires you to synthesize information from multiple lectures and readings, demonstrating your understanding of key concepts.
Unique assignments
Unique assignments challenge students to think creatively and independently, making it difficult for them to rely on AI-generated content. By incorporating creative activities, multi-modal projects, interdisciplinary tasks, and original research assignments, instructors encourage students to explore new ideas and approaches to learning. These assignments foster innovation, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills, preparing students to adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing world.
- Creative projects: Design assignments that involve creative output, such as creating a multimedia presentation, designing an experiment, or developing a prototype.
- Original research: Encourage students to conduct primary research, such as interviews, surveys, or experiments that require data collection and analysis.
- Interdisciplinary tasks: Develop assignments that require integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines, promoting complex problem-solving and critical thinking.
- Develop a multimedia presentation on a local issue of your choice. Conduct interviews with community members, gather data, and present your findings along with proposed solutions.
- Create a podcast episode on a topic related to our course. Conduct interviews, gather data, and present your findings in a compelling audio format.
- Design a prototype or model that illustrates a key concept from the course. Prepare a detailed report and presentation explaining how your prototype works and its applications.
Instructor- student conferences
Instructor conferences provide personalized feedback and support to students, deterring unauthorized use of AI by fostering direct interaction and accountability. By scheduling one-on-one or small group conferences, instructors create opportunities for in-depth discussions, clarification of concepts, and guidance on assignments. Conferences promote student engagement, confidence, and academic integrity, leading to deeper learning and greater success in the course.
- Progress check-ins: Schedule regular conferences to discuss the student’s progress on long-term assignments.
- Draft reviews: Review drafts with students during the conference, offering feedback and asking questions to gauge their understanding.
- Personalized feedback: Use the conference to give personalized advice and address any concerns or challenges the student might have.
- Schedule a 15-minute conference with me to discuss your research paper draft. Be prepared to explain your research process, your main arguments, and the feedback you have received so far.
- Schedule a conference to discuss your progress on the midterm project. Be prepared to present your research question, preliminary findings, and any challenges you are facing.
- Meet with me to review your annotated bibliography. We will discuss your sources, how they relate to your research question, and any gaps in your literature review.
Scaffolded assignments
Scaffolded assignments break down complex tasks into manageable steps, discouraging reliance on AI while promoting active learning and skill development. By providing clear instructions, interim deadlines, and targeted feedback, instructors support students’ progress and success throughout the assignment process. Scaffolded assignments foster independence, resilience, and mastery of course content, enhancing students’ ability to tackle challenges and achieve their academic goals.
- Task segmentation: Divide the assignment into distinct stages, such as topic selection, research proposal, annotated bibliography, draft submission, and final paper.
- Interim deadlines: Set deadlines for each stage to ensure steady progress and timely feedback.
- Skill development: Use each stage to develop specific skills, such as research methods, critical analysis, and academic writing.
- Submit a topic proposal with a research question by Week 3.
- Submit an annotated bibliography of at least 10 sources by Week 5.
- Submit a detailed outline by Week 7.
- Submit a complete first draft by Week 9.
- Submit the final paper by Week 12.
- Research question and hypothesis by Week 2.
- Literature review by Week 4.
- Methodology section by Week 6.
- Preliminary data analysis by Week 8.
- Complete draft by Week 10.
- Final submission by Week 12.
Metacognitive reflection on the writing process
Metacognitive reflection on the writing process empowers students to develop a deeper understanding of their own thinking and learning strategies, deterring the use of AI by promoting self-awareness and authenticity. By prompting students to analyze their writing process, identify strengths and areas for improvement, and reflect on their decision-making, instructors foster critical thinking and independent problem-solving skills. Reflective components encourage students to take ownership of their learning journey, leading to greater engagement, confidence, and academic growth.
- Process analysis: Ask students to write a process analysis detailing how they approached the writing assignment, including planning, research, drafting, and revising.
- Reflective questions: Provide prompts that guide students to reflect on their cognitive strategies, such as “How did you decide which sources to use?” or “What challenges did you face during the drafting process?”
- Self-assessment: Have students assess their own work using a rubric before submission, reflecting on their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Write a process analysis of your research paper. Discuss how you selected your topic, conducted your research, organized your ideas, and revised your drafts. Reflect on the strategies that were most effective and the challenges you encountered.
- Write a reflective essay analyzing your writing process for this assignment. Discuss how you organized your research, drafted your paper, and revised it. What strategies worked well, and what would you change in the future?
- Submit a self-assessment of your final paper using the provided rubric. Reflect on your strengths and areas for improvement, and describe the steps you took to address feedback from peers and the instructor.
By revising assignments to include personalized, process-oriented, and reflective components, instructors can deter unauthorized use of AI while fostering a deeper engagement with the material. These strategies not only uphold academic integrity but also enhance the learning experience, encouraging students to develop critical thinking, creativity, and independent problem-solving skills.
This content was developed with the assistance of Open AI’s ChatGPT.
Media Releases
- Dean’s Office
- Texas Geosciences
- Science Y’all
- In the News
- Scientist Profiles
- 2023 Newsletter
- 2022 Newsletter
- 2021 Newsletter
- 2020 Newsleter
- 2019 Newsletter
- 2018 Newsletter
- 2017 Newsletter
- 2016 Newsletter
- 2015 Newsletter
- 2014 Newsletter
- PDF Archive
- The Geoscientist
- Advancing Excellence
- Media Contacts
TERMINUS Blog: Robot Meets Glacier
August 15, 2024

|
|
Ancient snow-capped peaks guard the entrance to the glacial valley. There’s less than half a mile of seawater between us and the glacier, with its river-like trail that weaves a jagged path to the mountains beyond.
I’m aboard the research vessel Celtic Explorer and I’m watching the robot submersible Nereid Under Ice (NUI) maneuvering just off the starboard bow, its bright orange and red bay doors peeping above the surface.
It’s 2 pm on day three of my assignment with the TERMINUS Greenland research expedition. In a few moments, NUI’s vertical thrusters will burst into life and carry it down to the murky deep.

The NUI team including its pilot (and his repurposed X Box controller) are topside in the Celtic Explorer’s science operations room. Their attention is fixed on the instrument panels in front of them, keeping an eye on the submersible’s position and making sure it’s in good shape. In water this cloudy, navigation is by sonar and echolocation, and thus, done very carefully.
NUI is the centerpiece of the TERMINUS Greenland project, a scientific underwater exploration of Greenland’s glaciers that’s led by Ginny Catania, professor at the Jackson School of Geosciences and the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics. The submersible is both a remotely operated vehicle, tethered to the ship by a slender fiber optic cable through which it is piloted, and an autonomous drone, able to follow a predetermined survey route before finding its way home.
“I see NUI as the star of this expedition,” Catania said. “The science we’ve done with NUI has been incredible. Just seeing it in action and the organization behind it has been a career highlight.”
NUI’s dives so far have revealed deep channels, overhangs and ice caverns along the glacial wall.
|
|
|
NUI expedition leader, Molly Curran of Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, which developed and operates the submersible, later explained to me why NUI is so uniquely suited to this kind of environment.
The vehicle’s fiber optic cable allows it to be directly controlled from distances up to 8 km away and reach depths of at least 4 km. That’s ideal for navigating the jagged underwater face of a glacier from a safe distance. Conventional ROVs are unable to stray further than a few dozen meters while autonomous vehicles would almost certainly get lost in the glacier’s underwater ice caves.
“Only a hybrid vehicle allows us to get to these hard-to-reach places,” she said.

Two hours into the dive, NUI encounters just such a cavern and, for a while at least, the pilot allows it to drift into the icy chasm.
“Oh my god what is that?” says Catania. The video feed shows only turbid water, but the cavern’s walls are clear in the vehicle’s sonar. The other scientists crowding round the NUI team gasp in disbelief.
Over the course of the next hour and a half, NUI carefully makes its way along the length of the glacier, mapping it from top to bottom with a multibeam sonar. Multibeam sonar is typically used to create bathymetries of the seafloor but at the UT scientists’ request, the NUI team have jury-rigged the instrument to NUI’s side and pointed it at the glacier’s face.
By 5:30pm the multibeam survey is complete and the team have made history using it to map the face of a glacier.
Its primary mission complete, the NUI team direct the vehicle to its next objective. Catania and her team have selected four locations just meters from the glacier, where NUI will run its ocean sensors vertically from surface to seafloor. At the bottom NUI will use its robotic arm to push clear plastic tubes into the seafloor and retrieve foot-long sediment cores for later study.
At the first site, a wide-eyed tiny shrimp peers into NUI’s high-resolution camera as the pilot maneuvers a sediment core into place. There are no curious visitors at the second site, where sediment rivers pouring out from the glacier bring visibility to zero. The pilot works quickly before NUI’s instrument bay fill with sand.
Shortly after 7 pm, while on its way to the third site, NUI’s fiber optic tether breaks. The video feed cuts out and the pilot’s control is severed. The team quickly program a secondary science route and transmit it acoustically through the water. Without direct pilot control NUI is unable to gather more sediment cores but it’s still able to complete the rest of its science mission autonomously, before returning to the Celtic Explorer some three hours later.
Curran explains that breaking the fiber optic tether was always a risk in the fjord, where the movement of the glacier has left parts of the seafloor scattered with moraines. It’s likely that the cable caught on one of these shallow drifts and snapped. Catania and Curran have no complaints; the dive was an unmitigated success.

With NUI safely back on deck, the team will spend the following day servicing the vehicle, replacing the fiber optic tether, and prepping it for its next dive.
Catania still has her eye on returning to Kangerlussuup Sermia, the expedition’s first glacier. That glacier is much larger and more erratic than the current one and thus scientifically more important. NUI has already mapped that glacier’s seafloor and moraines. But they’ve yet to map it’s face with multibeam or take vertical measurements of the water column.
Both of those will be much harder at the larger glacier but the NUI team and the scientists of the TERMINUS expedition are eager to take on the task.
Departments & Units
- Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences
- Bureau of Economic Geology
- Institute for Geophysics
Administration & Offices
- College Leadership
- Career Services
- Business Services
- Development and Alumni Relations
- Office of Communications
- Information Technology Office
Helpful Links
- Emergency Information
- JSG Directory
- JSG Profiles

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A project management plan template is a pre-designed framework that provides a structured format for creating a project management plan. It serves as a starting point for project managers and teams to develop their specific project plans, saving time and ensuring that key project management components are properly addressed.
How To Write A Project Plan in 6 Steps Writing a project plan requires, well, planning. Ideally, the seeds for a project plan need to be sowed before internal project sign-off begins. Before that sign-off, conduct capacity planning to estimate the resources you will need and if they're available for the duration of the project. After all, you want to set your teams up for success with ...
Ready to take on a new project? Here are five real-life project management examples along with templates to help you get started faster.
Learn the phases of project management with our 6 project management examples. Use these templates to create a plan for your own projects.
This easy-to-follow guide will show you how to write an effective and comprehensive project management plan, with examples and templates.
The assignment is to complete, at the end of the course, a project that covers all, or at least most, of the concepts covered in the course. In addition to a formal written analysis, students are expected to present their lessons learned to the class. Several lectures were allotted to cover this. The grade on the project can be weighted between the written analysis and the class presentation.
Learn all about the RACI Matrix and explore examples and templates to help you get started.
Learn what a project plan is and why it's so important in project management. Plus, get templates and examples you can use to guide your own planning process.
The project management case studies listed below place the students in the position of the project manager, sponsor, and other stakeholders. Students develop problem solving skills by critically analyzing the various scenarios. The case studies are broken down to allow for easy integration with the various lecture topics of PM-1.
Project planning is the second step in the project process, when you create your project plan. Learn what to include and see examples to get you started.
Learn how to a stellar project proposal. See the bets format, typical sections, best practices and even get a free template.
Learn more about key project success factors and be inspired by 4 real life project management examples to optimize your workflow!
This report will present an appropriate project organisation structure to the board of KFH along with a project plan, cost and time schedule, project evaluation and role of project players.
Create a project charter to pitch a project and get it approved. Give project stakeholders a clear sense of your main objectives and scope. Learn how.
Overall purpose of this assignment is to present a project management process. The main outcome of the project is to refurbish the QA Higher Education building in London including classrooms and lobbies. The project will be developed by PRINCE2 program which is passionately used in many organisations.
A project charter is a formal document that details project scope, objectives, and the roles of people involved. Here's how to create it & a template to get started.
Professional assignment writing help services take all your project management paper worries away and deliver a 5-star essay or dissertation with no hassle.
Upon completing this series, you will be able to (1) write a narrative charter statement, (2) create a work breakdown structure, (3) sequence project activities, (4) build a project schedule, (5) create a project budget, (6) create a responsibility assignment matrix, (7) identify project risks and (8) define responses for those risks.
The courses in project management are taught using a mix of written university assignments on project management and case studies for projects. proposals for writing project scopes, scenarios, and also sample project management samples based on actual projects and management reports. Students often find it difficult to comprehend project management essays since this course takes place in an ...
8+ Sample Project Assignment Templates Project assignment template provides for the detailed list of work assigned to fulfill the process of a project. It takes into consideration the restriction of time period assigned for each duty, roles and responsibilities of each team member etc which is key to the success of the Project Implementation Template.
This study explores the project assignment process of organizations in high-velocity industries, in particular those that implement new product and software development projects in multiple-project environments. It focuses on the process of assigning projects to project managers, especially those who lead multiple, simultaneous projects.
This post explains a short assignment one teacher uses to have students write a short, memo-based project proposal.
A guide for faculty who are having their classes transcribe historical documents for "Say My Name: Identifying the African Americans Enslaved at White Hall"
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
Reflection assignments are used to encourage students to think about their learning experiences and the knowledge and skills they have obtained. Students are actively being involved in a process of self-assessment which helps them to develop a more profound understanding of the course materials and their own learning process.
Learn how to design assignments to make it more difficult for students to use generative AI when AI use is not desired.
NUI is the centerpiece of the TERMINUS Greenland project, a scientific underwater exploration of Greenland's glaciers that's led by Ginny Catania, professor at the Jackson School of Geosciences and the University of Texas Institute for Geophysics.