Dorothea Lange's Moving Photographs of The Depression Era
Editorial feature.
By Google Arts & Culture
Words by Rebecca Fulleylove
White Angel Breadline, San Francisco (1933) by Dorothea Lange San Francisco Museum of Modern Art (SFMOMA)
Meet the woman who showed America the consequences of the Great Depression
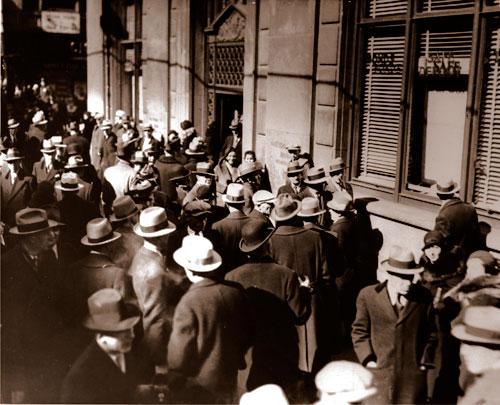
1. White Angel Breadline , San Francisco, 1933
White Angel Breadline, San Francisco by Dorothea Lange (From the collection of San Francisco Museum of Modern Art)
2. Migrant Mother , Nipomo, California, 1936
Migrant Mother, Nipoma, California (1936, printed 1976) by Dorothea Lange The Museum of Fine Arts, Houston
Migrant Mother by Dorothea Lange (From the collection of The Museum of Fine Arts, Houston)
3. Damaged Child, Shacktown , Elm Grove, Oklahoma, 1936
Damaged Child, Shacktown, Elm Grove, Oklahoma (1936) by Dorothea Lange George Eastman Museum
Damaged Child, Shacktown, Oklahoma by Dorothea Lange (From the collection of George Eastman Museum)
4. Ex-Slave With Long Memory , Alabama, 1937
Ex-Slave with Long Memory, Alabama (1937) by Dorothea Lange George Eastman Museum
Ex-Slave With Long Memory, Alabama by Dorothea Lange (From the collection of George Eastman Museum)
5. Six Tenant Farmers Without Farms , Hardeman County, Texas, 1937
Six Tenant Farmers without Farms, Hardeman County, Texas (May 1937, printed 1976) by Dorothea Lange The Museum of Fine Arts, Houston
Six Tenant Farmers Without Farms by Dorothea Lange (From the collection of The Museum of Fine Arts, Houston)
Explore more: – 7 Gordon Parks Images That Changed American Attitudes

The Usable Past: Reflections on American History 2000–2017
The museum of fine arts, houston, eastman: the inventor, george eastman museum, passion for perfection: the straus collection of renaissance art, cameras + fashion, space city: photographs from the museum of fine arts, houston, a renaissance couple, latino experience in the usa: works from the mfah collection, funny faces, #5womenartists, artistic genus: depictions of animals in the collections of the museum of fine arts, houston.
Great Depression Pictures
These 35 Photos Show the Economic Impact of the Great Depression
- Important Historical Figures
- U.S. Presidents
- Native American History
- American Revolution
- America Moves Westward
- The Gilded Age
- Crimes & Disasters
- The Most Important Inventions of the Industrial Revolution
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- Military History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Amadeo-Closeup-582619cd3df78c6f6acca4e6.jpg)
- M.B.A, MIT Sloan School of Management
- M.S.P, Social Planning, Boston College
- B.A., University of Rochester
The Farm Security Administration hired photographers to document the living conditions of the Great Depression . They are a landmark in the history of documentary photography. The photos show the adverse effects of the Great Depression and the Dust Bowl . Some of the most famous images portray people who were displaced from farms and migrated west or to industrial cities in search of work. These photos show better than charts and numbers the economic impact of the Great Depression.
Dust Attacks a Town
A dust storm rolled into Elkhart, Kansas, on May 21, 1937. The year before, the drought caused the hottest summer on record . In June, eight states experienced temperatures at 110 or greater. In July, the heat wave hit 12 more states : Iowa, Kansas (121 degrees), Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, North Dakota (121 degrees), Oklahoma (120 degrees), Pennsylvania, South Dakota (120 degrees), West Virginia, and Wisconsin. In August, Texas saw 120-degree record-breaking temperatures.
It was also the deadliest heat wave in U.S. history, killing 1,693 people. Another 3,500 people drowned while trying to cool off.
Causes of the Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl was caused by the worst drought in North America in 300 years. In 1930, weather patterns shifted over the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. The Pacific grew cooler than normal and the Atlantic became warmer. The combination weakened and changed the direction of the jet stream.
There were four waves of droughts: 1930-1931, 1934, 1936, and 1939-1940. The affected regions could not recover before the next one hit. By 1934, the drought covered 75% of the country, affecting 27 states. The worst-hit was the Oklahoma panhandle.
Once farmers settled the Midwest prairies, they plowed over 5.2 million acres of the tall, deep-rooted prairie grass. When the drought killed off the crops, high winds blew the topsoil away.
Effects of the Dust Bowl
Dust storms helped cause The Great Depression. Dust storms nearly covered buildings, making them useless. People became very ill from inhaling the dust.
These storms forced family farmers to lose their business, their livelihood, and their homes. By 1936, 21% of all rural families in the Great Plains received federal emergency relief. In some counties, it was as high as 90%.
Families migrated to California or cities to find work that often didn't exist by the time they got there. As farmers left in search of work, they became homeless. Almost 6,000 shanty towns, called Hoovervilles, sprang up in the 1930s.
Farming in 1935
This photo shows a team of two work horses hitched to a wagon with farm house visible in the background in Beltsville, Md., in 1935. It comes from the New York Public Library.
On April 15, 1934, the worst dust storm occurred. It was later named Black Sunday. Several weeks later, President Franklin D. Roosevelt passed the Soil Conservation Act. It taught farmers how to plant in a more sustainable way.
Farmers Who Survived the Dust Bowl
The photo shows a farmer cultivating corn with fertilizer on a horse drawn plow at the Wabash Farms, Loogootee, Indiana, June 1938. That year, the economy contracted 3.3% because FDR cut back on the New Deal. He was trying to balance the budget, but it was too soon. Prices dropped 2.8%, hurting the farmers who were left.
World's Greatest Standard of Living?
In March 1937, this billboard, sponsored by the National Association of Manufacturers, is displayed on Highway 99 in California during the Depression. It reads, "There's no way like the American way" and "world's highest standard of living." That year, the unemployment rate was 14.3%.
Men Were Desperate to Find Work
This photo shows two unemployed men walking towards Los Angeles, Calif., to find work.
On the Road to Find Work
The photo shows an impoverished family of nine on a New Mexico highway. The depression refugees left Iowa in 1932 due to their father's tuberculosis. He was an auto mechanic laborer and painter. The family had been on relief in Arizona.
Unemployment was 23.6%. The economy contracted 12.9%. People blamed President Herbert Hoover, who raised taxes that year to balance the budget. They voted for FDR, who promised a New Deal .
Come to California
The photo shows a roadside camp near Bakersfield, Calif., and the worldly possessions of refugees from Texas dust, drought, and depression. Many left their homes to find work in California. By the time they got there, the jobs were gone. This occurred in November 1935. Unemployment was 20.1%.
This Family Did Not Feel the Economy Improving
The photo shows a family of migrant workers fleeing from the drought in Oklahoma camp by the roadside in Blythe, Calif., on August 1, 1936. That month, Texas experienced 120 degrees, which was a record-breaking temperature.
By the end of the year, the heat wave had killed 1,693 people. Another 3,500 people drowned while trying to cool off.
The economy grew 12.9% that year. That was an incredible accomplishment, but too late to save this family's farm. Unemployment shrank to 16.9%. Prices rose 1.4%. The debt grew to $34 billion. To pay down the debt, President Roosevelt raised the top tax rate to 79%. But that proved to be a mistake. The economy wasn't strong enough to sustain higher taxes, and the Depression resumed.
Eating Along the Side of the Road
The photo shows the son of depression refugee from Oklahoma now in California taken in November 1936.
A Shanty Built of Refuse
This shanty was built of refuse near the Sunnyside slack pile in Herrin, Ill. Many residences in southern Illinois coal towns were built with money borrowed from building and loan associations, which almost all went bankrupt.
Migrant Workers in California
The photo shows a migrant worker, his young wife, and four children resting outside their temporary lodgings, situated on a migrant camp, Marysville, Calif., in 1935.
Living Out of a Car
This was the only home of a depression-routed family of nine from Iowa in August 1936.
Hooverville
Thousands of these farmers and other unemployed workers traveled to California to find work. Many ended up living as homeless “hobos” or in shantytowns called “Hoovervilles," named after then-President Herbert Hoover. Many people felt he caused the Depression by basically doing nothing to stop it. He was more concerned about balancing the budget, and felt the market would sort itself out.
Depression Family
The Great Depression displaced entire families, who became homeless. The children were most severely impacted. They often had to work to help make ends meet.
There were no social programs in the early part of the Depression. People lined up just to get a bowl of soup from a charity.
More Soup Lines
This photo shows another soup line during the Great Depression. Men this side of the sign are assured of a five-cent meal. The rest must wait for generous passersby. Buddy, can you spare a dime? The photo was taken between 1930 and 1940. There was no Social Security, welfare, or unemployment compensation until FDR and the New Deal.
Soup Kitchens Were Life Savers
Soup kitchens didn't offer much to eat, but it was better than nothing.
Even Gangsters Opened Soup Kitchens
A group of men line up outside a Chicago soup kitchen opened by Al Capone, sometime in the 1930s in this photo. In a bid to rebuild his reputation, Capone opened a soup kitchen amid the worsening economic conditions.
Soup Kitchens in 1930
Dolly Gann (L), sister of U.S. vice president Charles Curtis, helps serve meals to the hungry at a Salvation Army soup kitchen on December 27, 1930.
Effects of the Great Depression
This gentleman tried to remain well-dressed, but was forced to seek help from the Self Help Association. It was a dairy farm unit in California in 1936. Unemployment was 16.9%.
"He worked construction, but when the jobs disappeared he moved the family from Florida to his father's farm in North Georgia. On the farm, they grew a field of corn, many vegetables, apples and other fruit, and they had some livestock," according to a story from a reader.
The Faces of the Great Depression
This famous photo by Walker Evans is of Floyd Burroughs. He was from Hale County, Ala. The picture was taken in 1936.
"Fortune" magazine commissioned Walker Evans and staff writer James Agee to produce a feature on the plight of tenant farmers. They interviewed and photographed three families of cotton growers.
The magazine never published the article, but the two published " Now Let Us Praise Famous Men " in 1941.
Lucille Burroughs was Floyd's 10-year old daughter in " And Their Children After Them: The Legacy of 'Let Us Now Praise Famous Men. '" Dale Maharidge followed up on Lucille and others.
Lucille married when she was 15, and then divorced. She married again and had four children, but her husband died young.
Lucille had dreamed of becoming a teacher or a nurse. Instead, she picked cotton and waited tables. Sadly, she committed suicide in 1971. She was 45.
The Faces of the Great Depression - Migrant Mother
This woman is Florence Thompson, age 32, and the mother of five children. She was a peapicker in California. When this picture was taken by Dorothea Lange, Florence had just sold her family's home for money to buy food. The home was a tent.
In an interview available on YouTube , Florence revealed that her husband Cleo died in 1931. She picked 450 pounds of cotton a day. She moved to Modesto in 1945 and got a job in a hospital.
Children of Great Depression
The photo shows children of agricultural day laborers camped by the roadside near Spiro, Okla. There were no beds and no protection from the profusion of flies. It was taken by Russell Lee in June 1939
"For breakfast they would have cornmeal mush. For dinner, vegetables. For supper, cornbread. And they had milk at every meal. They worked hard and ate light, but they survived," a reader says.
Forced to Sell Apples
People with jobs would help out those without jobs by buying apples, pencils, or matches.
There Were No Jobs
Unemployed men are shown sitting outside waiting dinner at Robinson's soup kitchen located at 9th and Plum streets in Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1931. That year, the economy contracted 6.2%, and prices dropped 9.3%. Unemployment was 15.9%, but the worst was yet to come.
Stock Market Crash of 1929
The photo shows the floor of the New York Stock Exchange right after the stock market crash of 1929 . It was a scene of total panic as stockbrokers lost all.
Stock Market Crash Destroyed Confidence in Wall Street
After "Black Thursday" at the stock market of New York, the mounted police put the excited assemblage in motion. The photograph was taken on November 2, 1929.
Ticker Tapes Couldn't Keep Up With the Sales Volume
Brokers check the tape for daily prices in a scene from the film, 'The Wolf Of Wall Street,' which opened just months before the crash in 1929.
When the Great Depression Started
President Herbert Hoover and his wife, Lou Henry Hoover, are photographed in Chicago at the final game of the 1929 World Series between the Chicago Cubs and the Philadelphia Athletics, October 1929. The Great Depression had already begun in August of that year.
Hoover Replaced by Roosevelt
President Herbert Hoover (left) is photographed with his successor Franklin D. Roosevelt at his inauguration at the U.S. Capitol on March 4, 1933.
The New Deal Programs Employed Many
The photo shows part of a fashion parade at the largest WPA sewing shop in New York where 3,000 women produce clothing and linens to be distributed among the unemployed sometime in 1935. They work a six-day, thirty-hour week on two floors of the old Siegel Cooper Building.
Could the Great Depression Reoccur?
During the Great Depression, people lost their homes and lived in tents. Could that happen in the United States again? Probably not. Congress has demonstrated it would spend whatever is necessary, regardless of the damage to the debt.
Farm Security Administration. " About This Collection ,"
- The Story of the Great Depression in Photos
- A Short History of the Great Depression
- Top 5 Causes of the Great Depression
- Great Depression in Canada Pictures
- Hoovervilles: Homeless Camps of the Great Depression
- Top 10 New Deal Programs of the 1930s
- History of the Dust Bowl
- The Dust Bowl: The Worst Environmental Disaster in the United States
- Dorothea Lange
- What Caused the Great Depression?
- The Great Depression, World War II, and the 1930s
- Woody Guthrie, Legendary Songwriter and Folk Singer
- The 1930's Dust Bowl Drought
- How the Great Depression Altered US Foreign Policy
- Complete List of John Steinbeck's Books
- The U.S. Presidents and Their Era

THE DEPRESSION
Everyone was so shocked and panicky. No one knew what was ahead. — Dorothea Lange
THE DEPRESSION Topics

Discovering a Purpose: Early Documentary Work

The Dust Bowl

On the Road

In the Camps

In the Fields

Deep South: Picturing Race and Power

An American Exodus: A New Kind of Book

Migrant Mother: Birth of An Icon
Previous Section
EARLY WORK / PERSONAL WORK
Next Section
WORLD WAR II AT HOME
- The Great Depression
Curriculum for High School
- Lesson Plans for High School
- Crossword Puzzle
- Word Search
- Interview Videos
- Photos & Art
- Presentation Videos
More Teaching Resources
- Lessons for Grades 2-5
- Articles & Books
- Economics & History
- Movies & Newsreels
The Great Depression Photo Gallery
While the Great Depression was a time of tremendous poverty and suffering, it was also a period in which the arts flourished. Much of that art served to document the devastation of the Depression. The artists’ documentary spirit shines clearly through the photographs taken as part of the Historical Section of the Resettlement Administration and the Farm Security Administration.
The iconic photography used throughout the Great Depression Curriculum is available through the Library of Congress .
Tap a thumbnail image below.

Supplementary Photos & Art
- ThoughtCo: 20th Century History – Photographs of the Great Depression.
- Franklin Delano Roosevelt Library Photos – Copyright-free photos.
- Library of Congress: “America from the Great Depression to World War II: Photographs from the FSA – OWI, 1935-1945” – These are the famous photographs that you know (Dorothea Lange, etc.)
- Library of Congress: “Voices from the Dust Bowl” – Audio and photographs from the Library of Congress.
- Picturing the Century: The Great Depression and the New Deal – Online photos from a small collection at the National Archives and Records Administration.
- Works Progress Administration Posters at the Library of Congress
- FDR Cartoon Archive – Political cartoons from the presidency of Franklin Delano Roosevelt.
Stanford Humanities Today
Arcade: a digital salon.

Walker Evans' iconic photos of the Great Depression at Cantor Arts Center
In public programs, stanford scholars share their views on the groundbreaking artistic endeavors of photographer walker evans..
As he stares out from the darkness behind him, the defeated expression in the man's eyes pulls the viewer into a time of extreme hardship. Although this stark black-and-white photograph was taken nearly 80 years ago, the current recession has brought renewed meaning to this and the many other iconic Depression-era photographs of American photographer Walker Evans (1903-1975). From today until April 8, Stanford's Cantor Arts Center will showcase more than 125 of Evans' influential prints as well as an extensive selection of his original books and magazines.
This exhibition, entitled simply " Walker Evans ," will present his inspired visual documentation of the Great Depression along with a display of his collaboration with American author and journalist James Agee on the renowned book, Let Us Now Praise Famous Men. In 1936, Evans and Agee ventured to Alabama on a journalistic endeavor for Fortune magazine to document the lives of three tenant farmer families during the Depression. As the project progressed, it became evident that this was not going to be a traditional photo essay – rather, it was an experiment that was pushing the boundaries of photojournalism.
The resulting 400-plus-page opus chronicles the families with a combination of compelling photographs and descriptive text. Although the two disciplines work together to answer many questions about the reality of the time, the unique juxtaposition raises questions as well. To help readers work through these questions in Agee's dense and complex book, the "Walker Evans" exhibition will feature a free book discussion on Saturday, Feb. 25, with Stanford English Professor Gavin Jones . Jones, who examines Agee's and Evans' work through a literary lens in his book American Hungers: The Problem of Poverty in U.S. Literature, will lead attendees in a discussion.
Disjointed lives of the poor

The artists attempted to achieve this goal through a variety of investigational techniques. One of the most apparent was the decision to separate the photos from the narrative descriptions in the text. Evans' photographs are placed together at the beginning of the book with no titles, followed by Agee's lengthy written description of the pictured families.
Jones pointed out that this disjointed format highlights the beauty of Evans' minimalist photographs, but also makes it more difficult to follow the story of the families. "The important point is to recognize the reasons for the difficulty: to expose the problems and contradictions inherent in middle-class desires to understand and explain the poor," said Jones. "The style embodies rather than represents these dilemmas – it tries to make readers feel and experience them personally."

However, it is undeniable that this book would not have been as influential without the interplay of text and art. "Agee's text is an essential guide to Evans' photographs because Agee includes in his descriptions everything that Evans removes from his photographs," Jones said. Agee's words influence the way the audience views Evan' photographs, and vice versa. The tension that results from this interaction is where the social and political statements of the book truly stem from – statements that are still relevant today.
Interactive photo forum
The online " Walker Evans of the Week " program will be available for exhibition viewers who cannot attend the book discussion or who want to delve further into Evans' life and work. This project will highlight one piece of Evans' artwork from the exhibition each week on the Cantor Arts Center's Flickr page . Each of these entries will feature commentary from Annie Ronan, a Ph.D. candidate in Stanford's Art & Art History Department. This format will allow the audience to read Ronan's commentary and respond with questions or discussion points.
By Kelsey Geiser

Discovering Humanities Research at Stanford

Stanford Humanities Center
Advancing Research in the Humanities
Humanities Research for a Digital Future

The Humanities in the World
- Annual Reports
- Humanitrees
- Humanities Center Fellows
- Advisory Council
- Director's Alumni Cabinet
- Honorary Fellows
- Hume Honors Fellows
- International Visitors
- Workshop Coordinators
- Why Humanities Matter
- Fellowships for External Faculty
- Fellowships for Stanford Faculty
- Mellon Fellowship of Scholars in the Humanities
- Dissertation Fellowships FAQs
- Career Launch Fellowships
- Fellowships for Stanford Undergraduates
- International Visitors Program
- FAQ Mellon Fellowship
- Faculty Fellowships FAQ
- Events Archive
- Public Lectures
- Checklist for Event Coordinators
- Facilities Guidelines
- co-sponsorship from the Stanford Humanities Center
- Call for Proposals
- Manuscript Workshops
- Past Workshops
- Research Workshops
Featured Categories
Bourdain’s picks, photo essays.
West Virginia
A lost vision of West Virginia
During the Great Depression, the Farm Security Administration dispatched photographers across the United States to document poverty in America. The images they captured are some of the most iconic photos in history .
In West Virginia were two of the project’s most illustrious names: Marion Post Wolcott and Ben Shahn . Their best-known images of the state depict the hardscrabble life of coal miners there. These images have come to define West Virginia in the public eye, contributing to a persisting impression of a state full of hillbillies and hicks, a fact which Anthony Bourdain notes during his visit to McDowell County for “Parts Unknown.”
But those images dominate only because Wolcott’s and Shahn’s bosses wanted them to. Roy Stryker, the FSA photo editor in Washington, intended the photos to reinforce New Deal ideals and persuade Americans that the government needed their tax dollars to relieve the suffering of the poor.
But the West Virginia that Wolcott and Shahn witnessed was far deeper and more rounded than the selected images suggest. The photographers didn’t put their cameras down when poverty and suffering weren’t manifest. The two documented communities that brim with life, celebration, pride, and hard work.
The images rejected in Washington were, thankfully, never discarded. Tens of thousands of them survive, but for most of the 20th century it was necessary to travel to the Library of Congress to see them. In 2010 the library restarted the process of scanning the project’s 175,000 black-and-white negatives. The public can now browse the lion’s share of the collection with just a few mouse clicks. Here are a few of the many that speak to a different West Virginia from the one popularized by the FSA.
The newsletter you need Get more Bourdain in your inbox.
Thanks! You’re now subscribed to the newsletter.
More Stories
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Course: US history > Unit 7
- The presidency of Herbert Hoover
The Great Depression
- FDR and the Great Depression
- The New Deal
- The Great Depression was the worst economic downturn in US history. It began in 1929 and did not abate until the end of the 1930s.
- The stock market crash of October 1929 signaled the beginning of the Great Depression. By 1933, unemployment was at 25 percent and more than 5,000 banks had gone out of business.
- Although President Herbert Hoover attempted to spark growth in the economy through measures like the Reconstruction Finance Corporation, these measures did little to solve the crisis.
- Franklin Roosevelt was elected president in November 1932. Inaugurated as president in March 1933, Roosevelt’s New Deal offered a new approach to the Great Depression.
The stock market crash of 1929
Hoover's response to the crisis, what do you think.
- David M. Kennedy, Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929-1945 (New York: Oxford University Press, 1999), 37-41, 49-50.
- T.H. Watkins, The Hungry Years: A Narrative History of the Great Depression in America (New York: Henry Holt, 1999), 44-45; Kennedy, Freedom from Fear , 87.
- Louise Armstrong, We Too Are the People (Boston: Little, Brown & Co., 1938), 10.
- On bank failures, see Kennedy, Freedom from Fear , 65.
- See Kennedy, Freedom from Fear , 87, 208; Robert S. McElvaine, ed., Down and Out in the Great Depression: Letters from the “Forgotten Man” (Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1983), 81-94.
- John A. Garraty, The Great Depression: An Inquiry into the Causes, Course, and Consequences of the Worldwide Depression of the Nineteen-Thirties, as Seen by Contemporaries and in the Light of History (New York: Doubleday, 1987).
- Kennedy, Freedom from Fear , 83-85.
- On Hoovervilles and Hoover flags, Kennedy, Freedom from Fear , 91.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Pictures That Tell Stories: Photo Essay Examples

Like any other type of artist, a photographer’s job is to tell a story through their pictures. While some of the most creative among us can invoke emotion or convey a thought with one single photo, the rest of us will rely on a photo essay.
In the following article, we’ll go into detail about what a photo essay is and how to craft one while providing some detailed photo essay examples.
What is a Photo Essay?
A photo essay is a series of photographs that, when assembled in a particular order, tell a unique and compelling story. While some photographers choose only to use pictures in their presentations, others will incorporate captions, comments, or even full paragraphs of text to provide more exposition for the scene they are unfolding.
A photo essay is a well-established part of photojournalism and have been used for decades to present a variety of information to the reader. Some of the most famous photo essayists include Ansel Adams , W. Eugene Smith, and James Nachtwey. Of course, there are thousands of photo essay examples out there from which you can draw inspiration.
Why Consider Creating a Photo Essay?
As the old saying goes, “a picture is worth 1000 words.” This adage is, for many photographers, reason enough to hold a photo essay in particularly high regard.
For others, a photo essay allow them to take pictures that are already interesting and construct intricate, emotionally-charged tales out of them. For all photographers, it is yet another skill they can master to become better at their craft.
As you might expect, the photo essay have had a long history of being associated with photojournalism. From the Great Depression to Civil Rights Marches and beyond, many compelling stories have been told through a combination of images and text, or photos alone. A photo essay often evokes an intense reaction, whether artistic in nature or designed to prove a socio-political point.
Below, we’ll list some famous photo essay samples to further illustrate the subject.

Become the photographer you were born to be.
Join Cole’s Classroom

Famous Photo Essays
“The Great Depression” by Dorothea Lange – Shot and arranged in the 1930s, this famous photo essay still serves as a stark reminder of The Great Depression and Dust Bowl America . Beautifully photographed, the black and white images offer a bleak insight to one of the country’s most difficult times.
“The Vietnam War” by Philip Jones Griffiths – Many artists consider the Griffiths’ photo essay works to be some of the most important records of the war in Vietnam. His photographs and great photo essays are particularly well-remembered for going against public opinion and showing the suffering of the “other side,” a novel concept when it came to war photography.
Various American Natural Sites by Ansel Adams – Adams bought the beauty of nature home to millions, photographing the American Southwest and places like Yosemite National Park in a way that made the photos seem huge, imposing, and beautiful.
“Everyday” by Noah Kalina – Is a series of photographs arranged into a video. This photo essay features daily photographs of the artist himself, who began taking capturing the images when he was 19 and continued to do so for six years.
“Signed, X” by Kate Ryan – This is a powerful photo essay put together to show the long-term effects of sexual violence and assault. This photo essay is special in that it remains ongoing, with more subjects being added every year.
Common Types of Photo Essays
While a photo essay do not have to conform to any specific format or design, there are two “umbrella terms” under which almost all genres of photo essays tend to fall. A photo essay is thematic and narrative. In the following section, we’ll give some details about the differences between the two types, and then cover some common genres used by many artists.
⬥ Thematic
A thematic photo essay speak on a specific subject. For instance, numerous photo essays were put together in the 1930s to capture the ruin of The Great Depression. Though some of these presentations followed specific people or families, they mostly told the “story” of the entire event. There is much more freedom with a thematic photo essay, and you can utilize numerous locations and subjects. Text is less common with these types of presentations.
⬥ Narrative
A narrative photo essay is much more specific than thematic essays, and they tend to tell a much more direct story. For instance, rather than show a number of scenes from a Great Depression Era town, the photographer might show the daily life of a person living in Dust Bowl America. There are few rules about how broad or narrow the scope needs to be, so photographers have endless creative freedom. These types of works frequently utilize text.
Common Photo Essay Genres
Walk a City – This photo essay is when you schedule a time to walk around a city, neighborhood, or natural site with the sole goal of taking photos. Usually thematic in nature, this type of photo essay allows you to capture a specific place, it’s energy, and its moods and then pass them along to others.
The Relationship Photo Essay – The interaction between families and loved ones if often a fascinating topic for a photo essay. This photo essay genre, in particular, gives photographers an excellent opportunity to capture complex emotions like love and abstract concepts like friendship. When paired with introspective text, the results can be quite stunning.
The Timelapse Transformation Photo Essay – The goal of a transformation photo essay is to capture the way a subject changes over time. Some people take years or even decades putting together a transformation photo essay, with subjects ranging from people to buildings to trees to particular areas of a city.
Going Behind The Scenes Photo Essay – Many people are fascinated by what goes on behind the scenes of big events. Providing the photographer can get access; to an education photo essay can tell a very unique and compelling story to their viewers with this photo essay.
Photo Essay of a Special Event – There are always events and occasions going on that would make an interesting subject for a photo essay. Ideas for this photo essay include concerts, block parties, graduations, marches, and protests. Images from some of the latter were integral to the popularity of great photo essays.
The Daily Life Photo Essay – This type of photo essay often focus on a single subject and attempt to show “a day in the life” of that person or object through the photographs. This type of photo essay can be quite powerful depending on the subject matter and invoke many feelings in the people who view them.
Become the photographer of your dreams with Cole’s Classroom.
Start Free Trial
Photo Essay Ideas and Examples
One of the best ways to gain a better understanding of photo essays is to view some photo essay samples. If you take the time to study these executions in detail, you’ll see just how photo essays can make you a better photographer and offer you a better “voice” with which to speak to your audience.
Some of these photo essay ideas we’ve already touched on briefly, while others will be completely new to you.
Cover a Protest or March
Some of the best photo essay examples come from marches, protests, and other events associated with movements or socio-political statements. Such events allow you to take pictures of angry, happy, or otherwise empowered individuals in high-energy settings. The photo essay narrative can also be further enhanced by arriving early or staying long after the protest has ended to catch contrasting images.
Photograph a Local Event
Whether you know it or not, countless unique and interesting events are happening in and around your town this year. Such events provide photographers new opportunities to put together a compelling photo essay. From ethnic festivals to historical events to food and beverage celebrations, there are many different ways to capture and celebrate local life.
Visit an Abandoned Site or Building
Old homes and historical sites are rich with detail and can sometimes appear dilapidated, overgrown by weeds, or broken down by time. These qualities make them a dynamic and exciting subject. Many great photo essay works of abandoned homes use a mix of far-away shots, close-ups, weird angles, and unique lighting. Such techniques help set a mood that the audience can feel through the photographic essay.
Chronicle a Pregnancy
Few photo essay topics could be more personal than telling the story of a pregnancy. Though this photo essay example can require some preparation and will take a lot of time, the results of a photographic essay like this are usually extremely emotionally-charged and touching. In some cases, photographers will continue the photo essay project as the child grows as well.
Photograph Unique Lifestyles
People all over the world are embracing society’s changes in different ways. People live in vans or in “tiny houses,” living in the woods miles away from everyone else, and others are growing food on self-sustaining farms. Some of the best photo essay works have been born out of these new, inspiring movements.
Photograph Animals or Pets
If you have a favorite animal (or one that you know very little about), you might want to arrange a way to see it up close and tell its story through images. You can take photos like this in a zoo or the animal’s natural habitat, depending on the type of animal you choose. Pets are another great topic for a photo essay and are among the most popular subjects for many photographers.
Show Body Positive Themes
So much of modern photography is about showing the best looking, prettiest, or sexiest people at all times. Choosing a photo essay theme like body positivity, however, allows you to film a wide range of interesting-looking people from all walks of life.
Such a photo essay theme doesn’t just apply to women, as beauty can be found everywhere. As a photo essay photographer, it’s your job to find it!
Bring Social Issues to Life
Some of the most impactful social photo essay examples are those where the photographer focuses on social issues. From discrimination to domestic violence to the injustices of the prison system, there are many ways that a creative photographer can highlight what’s wrong with the world. This type of photo essay can be incredibly powerful when paired with compelling subjects and some basic text.
Photograph Style and Fashion
If you live in or know of a particularly stylish locale or area, you can put together an excellent thematic photo essay by capturing impromptu shots of well-dressed people as they pass by. As with culture, style is easily identifiable and is as unifying as it is divisive. Great photo essay examples include people who’ve covered fashion sub-genres from all over the world, like urban hip hop or Japanese Visual Kei.
Photograph Native Cultures and Traditions
If you’ve ever opened up a copy of National Geographic, you’ve probably seen photo essay photos that fit this category. To many, the traditions, dress, religious ceremonies, and celebrations of native peoples and foreign cultures can be utterly captivating. For travel photographers, this photo essay is considered one of the best ways to tell a story with or without text.
Capture Seasonal Or Time Changes In A Landmark Photo Essay
Time-lapse photography is very compelling to most viewers. What they do in a few hours, however, others are doing over months, years, and even decades. If you know of an exciting landscape or scene, you can try to capture the same image in Winter, Spring, Summer, and Fall, and put that all together into one landmark photo essay.
Alternatively, you can photograph something being lost or ravaged by time or weather. The subject of your landmark photo essay can be as simple as the wall of an old building or as complex as an old house in the woods being taken over by nature. As always, there are countless transformation-based landmark photo essay works from which you can draw inspiration.
Photograph Humanitarian Efforts or Charity
Humanitarian efforts by groups like Habitat for Humanity, the Red Cross, and Doctors Without Borders can invoke a powerful response through even the simplest of photos. While it can be hard to put yourself in a position to get the images, there are countless photo essay examples to serve as inspiration for your photo essay project.
How to Create a Photo Essay
There is no singular way to create a photo essay. As it is, ultimately, and artistic expression of the photographer, there is no right, wrong, good, or bad. However, like all stories, some tell them well and those who do not. Luckily, as with all things, practice does make perfect. Below, we’ve listed some basic steps outlining how to create a photo essay
Steps To Create A Photo Essay
Choose Your Topic – While some photo essayists will be able to “happen upon” a photo story and turn it into something compelling, most will want to choose their photo essay topics ahead of time. While the genres listed above should provide a great starting place, it’s essential to understand that photo essay topics can cover any event or occasion and any span of time
Do Some Research – The next step to creating a photo essay is to do some basic research. Examples could include learning the history of the area you’re shooting or the background of the person you photograph. If you’re photographing a new event, consider learning the story behind it. Doing so will give you ideas on what to look for when you’re shooting.
Make a Storyboard – Storyboards are incredibly useful tools when you’re still in the process of deciding what photo story you want to tell. By laying out your ideas shot by shot, or even doing rough illustrations of what you’re trying to capture, you can prepare your photo story before you head out to take your photos.
This process is especially important if you have little to no control over your chosen subject. People who are participating in a march or protest, for instance, aren’t going to wait for you to get in position before offering up the perfect shot. You need to know what you’re looking for and be prepared to get it.
Get the Right Images – If you have a shot list or storyboard, you’ll be well-prepared to take on your photo essay. Make sure you give yourself enough time (where applicable) and take plenty of photos, so you have a lot from which to choose. It would also be a good idea to explore the area, show up early, and stay late. You never know when an idea might strike you.
Assemble Your Story – Once you develop or organize your photos on your computer, you need to choose the pictures that tell the most compelling photo story or stories. You might also find some great images that don’t fit your photo story These can still find a place in your portfolio, however, or perhaps a completely different photo essay you create later.
Depending on the type of photographer you are, you might choose to crop or digitally edit some of your photos to enhance the emotions they invoke. Doing so is completely at your discretion, but worth considering if you feel you can improve upon the naked image.

Ready to take your photography to the next level?
Join Cole’s Classroom today! »
Best Photo Essays Tips And Tricks
Before you approach the art of photo essaying for the first time, you might want to consider with these photo essay examples some techniques, tips, and tricks that can make your session more fun and your final results more interesting. Below, we’ve compiled a list of some of the best advice we could find on the subject of photo essays.
⬥ Experiment All You Want
You can, and should, plan your topic and your theme with as much attention to detail as possible. That said, some of the best photo essay examples come to us from photographers that got caught up in the moment and decided to experiment in different ways. Ideas for experimentation include the following:
Angles – Citizen Kane is still revered today for the unique, dramatic angles used in the film. Though that was a motion picture and not photography, the same basic principles still apply. Don’t be afraid to photograph some different angles to see how they bring your subject to life in different ways.
Color – Some images have more gravitas in black in white or sepia tone. You can say the same for images that use color in an engaging, dynamic way. You always have room to experiment with color, both before and after the shoot.
Contrast – Dark and light, happy and sad, rich and poor – contrast is an instantly recognizable form of tension that you can easily include in your photo essay. In some cases, you can plan for dramatic contrasts. In other cases, you simply need to keep your eyes open.
Exposure Settings – You can play with light in terms of exposure as well, setting a number of different moods in the resulting photos. Some photographers even do random double exposures to create a photo essay that’s original.
Filters – There are endless post-production options available to photographers, particularly if they use digital cameras. Using different programs and apps, you can completely alter the look and feel of your image, changing it from warm to cool or altering dozens of different settings.
Want to never run out of natural & authentic poses? You need this ⬇️
Click here & get it today for a huge discount., ⬥ take more photos than you need .
If you’re using traditional film instead of a digital camera, you’re going to want to stock up. Getting the right shots for a photo essay usually involves taking hundreds of images that will end up in the rubbish bin. Taking extra pictures you won’t use is just the nature of the photography process. Luckily, there’s nothing better than coming home to realize that you managed to capture that one, perfect photograph.
⬥ Set the Scene
You’re not just telling a story to your audience – you’re writing it as well. If the scene you want to capture doesn’t have the look you want, don’t be afraid to move things around until it does. While this doesn’t often apply to photographing events that you have no control over, you shouldn’t be afraid to take a second to make an OK shot a great shot.
⬥ Capture Now, Edit Later
Editing, cropping, and digital effects can add a lot of drama and artistic flair to your photos. That said, you shouldn’t waste time on a shoot, thinking about how you can edit it later. Instead, make sure you’re capturing everything that you want and not missing out on any unique pictures. If you need to make changes later, you’ll have plenty of time!
⬥ Make It Fun
As photographers, we know that taking pictures is part art, part skill, and part performance. If you want to take the best photo essays, you need to loosen up and have fun. Again, you’ll want to plan for your topic as best as you can, but don’t be afraid to lose yourself in the experience. Once you let yourself relax, both the ideas and the opportunities will manifest.
⬥ It’s All in The Details
When someone puts out a photographic essay for an audience, that work usually gets analyzed with great attention to detail. You need to apply this same level of scrutiny to the shots you choose to include in your photo essay. If something is out of place or (in the case of historical work) out of time, you can bet the audience will notice.
⬥ Consider Adding Text
While it isn’t necessary, a photographic essay can be more powerful by the addition of text. This is especially true of images with an interesting background story that can’t be conveyed through the image alone. If you don’t feel up to the task of writing content, consider partnering with another artist and allowing them tor bring your work to life.
Final Thoughts
The world is waiting to tell us story after story. Through the best photo essays, we can capture the elements of those stories and create a photo essay that can invoke a variety of emotions in our audience.
No matter the type of cameras we choose, the techniques we embrace, or the topics we select, what really matters is that the photos say something about the people, objects, and events that make our world wonderful.
Dream of Being a Pro Photographer?
Join Cole’s Classroom today to make it a reality.
Similar Posts

5 Super Simple Tips for Capturing Water Reflections
Scenes so nice, you’ll see them twice! 5 Tips for Capturing Water Reflections (Plus two cheats!) If I had to pick a favorite type of landscape scene, it would probably involve a water reflection. There’s just something serene and peaceful about an image with water. If symmetry and mirror images are your creative jam, too,…

Easier Than You Think: How to Print Your Pictures on Metal
If you’re looking for a unique and head-turning way to display your photos or artwork, metal printing is one of the best options available. Metal prints are a relatively new printing method, and it offers plenty of advantages over traditional printing. This method allows you to display your metal photos or art with incredible clarity,…

Capturing Everyday Life: The Good, the Bad, the Beautiful
Many photographers that I know, myself included, got started with photography so that they could take pictures capturing everyday life. Not wanting to miss a moment or milestone. Sound familiar? If so, you probably started by aimlessly clicking the camera at your baby, your dog, your spouse or anything around you. Perhaps, you have some great…

What is Digital Photography?
Like it or not, we’re living in an electronic world, and digital photography is here to stay. When I got my first camera at age three, digital photography wasn’t a reality. To be honest, my camera wasn’t a reality either…it used a sponge to wet the “film,” so a picture appeared on my little plastic picture. …

Get your colors straight with Kelvin White Balance
Learn how and why to use Kelvin white balance to get perfect color in your images! Have you ever taken a photo in a high school gym? The colors are just…wonky. Skin tones look sickly, white uniforms look green. Or maybe you’ve shot in the shade only to find really blue-gray skin tones when you…
![the great depression photo essay [Updated 2019] What Is Chromatic Aberration And How Can You Avoid It?](https://colesclassroom.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Chromatic-Aberration-What-is-it-how-to-fix-it-768x512.jpg)
[Updated 2019] What Is Chromatic Aberration And How Can You Avoid It?
Struggling with Chromatic Aberration? Who doesn’t like crisp and lively photographs? Everyone wants to capture their life moments in a perfect photo. But if the picture does not depict the moment in the same way, it is quite disappointing. You go for a tropical vacation and the colors of your picture sometimes make the picture…
The leading authority in photography and camera gear.
Become a better photographer.
12.9 Million
Annual Readers
Newsletter Subscribers
Featured Photographers
Photography Guides & Gear Reviews

How to Create an Engaging Photo Essay (with Examples)
Photo essays tell a story in pictures. They're a great way to improve at photography and story-telling skills at once. Learn how to do create a great one.
Learn | Photography Guides | By Ana Mireles
Photography is a medium used to tell stories – sometimes they are told in one picture, sometimes you need a whole series. Those series can be photo essays.
If you’ve never done a photo essay before, or you’re simply struggling to find your next project, this article will be of help. I’ll be showing you what a photo essay is and how to go about doing one.
You’ll also find plenty of photo essay ideas and some famous photo essay examples from recent times that will serve you as inspiration.
If you’re ready to get started, let’s jump right in!
Table of Contents
What is a Photo Essay?
A photo essay is a series of images that share an overarching theme as well as a visual and technical coherence to tell a story. Some people refer to a photo essay as a photo series or a photo story – this often happens in photography competitions.
Photographic history is full of famous photo essays. Think about The Great Depression by Dorothea Lange, Like Brother Like Sister by Wolfgang Tillmans, Gandhi’s funeral by Henri Cartier Bresson, amongst others.
What are the types of photo essay?
Despite popular belief, the type of photo essay doesn’t depend on the type of photography that you do – in other words, journalism, documentary, fine art, or any other photographic genre is not a type of photo essay.
Instead, there are two main types of photo essays: narrative and thematic .
As you have probably already guessed, the thematic one presents images pulled together by a topic – for example, global warming. The images can be about animals and nature as well as natural disasters devastating cities. They can happen all over the world or in the same location, and they can be captured in different moments in time – there’s a lot of flexibility.
A narrative photo essa y, on the other hand, tells the story of a character (human or not), portraying a place or an event. For example, a narrative photo essay on coffee would document the process from the planting and harvesting – to the roasting and grinding until it reaches your morning cup.
What are some of the key elements of a photo essay?
- Tell a unique story – A unique story doesn’t mean that you have to photograph something that nobody has done before – that would be almost impossible! It means that you should consider what you’re bringing to the table on a particular topic.
- Put yourself into the work – One of the best ways to make a compelling photo essay is by adding your point of view, which can only be done with your life experiences and the way you see the world.
- Add depth to the concept – The best photo essays are the ones that go past the obvious and dig deeper in the story, going behind the scenes, or examining a day in the life of the subject matter – that’s what pulls in the spectator.
- Nail the technique – Even if the concept and the story are the most important part of a photo essay, it won’t have the same success if it’s poorly executed.
- Build a structure – A photo essay is about telling a thought-provoking story – so, think about it in a narrative way. Which images are going to introduce the topic? Which ones represent a climax? How is it going to end – how do you want the viewer to feel after seeing your photo series?
- Make strong choices – If you really want to convey an emotion and a unique point of view, you’re going to need to make some hard decisions. Which light are you using? Which lens? How many images will there be in the series? etc., and most importantly for a great photo essay is the why behind those choices.
9 Tips for Creating a Photo Essay

Credit: Laura James
1. Choose something you know
To make a good photo essay, you don’t need to travel to an exotic location or document a civil war – I mean, it’s great if you can, but you can start close to home.
Depending on the type of photography you do and the topic you’re looking for in your photographic essay, you can photograph a local event or visit an abandoned building outside your town.
It will be much easier for you to find a unique perspective and tell a better story if you’re already familiar with the subject. Also, consider that you might have to return a few times to the same location to get all the photos you need.
2. Follow your passion
Most photo essays take dedication and passion. If you choose a subject that might be easy, but you’re not really into it – the results won’t be as exciting. Taking photos will always be easier and more fun if you’re covering something you’re passionate about.
3. Take your time
A great photo essay is not done in a few hours. You need to put in the time to research it, conceptualizing it, editing, etc. That’s why I previously recommended following your passion because it takes a lot of dedication, and if you’re not passionate about it – it’s difficult to push through.
4. Write a summary or statement
Photo essays are always accompanied by some text. You can do this in the form of an introduction, write captions for each photo or write it as a conclusion. That’s up to you and how you want to present the work.
5. Learn from the masters
How Much Do You REALLY Know About Photography?! 🤔
Test your photography knowledge with this quick quiz!
See how much you really know about photography...

Your answer:
Correct answer:
SHARE YOUR RESULTS
Your Answers
Making a photographic essay takes a lot of practice and knowledge. A great way to become a better photographer and improve your storytelling skills is by studying the work of others. You can go to art shows, review books and magazines and look at the winners in photo contests – most of the time, there’s a category for photo series.
6. Get a wide variety of photos
Think about a story – a literary one. It usually tells you where the story is happening, who is the main character, and it gives you a few details to make you engage with it, right?
The same thing happens with a visual story in a photo essay – you can do some wide-angle shots to establish the scenes and some close-ups to show the details. Make a shot list to ensure you cover all the different angles.
Some of your pictures should guide the viewer in, while others are more climatic and regard the experience they are taking out of your photos.
7. Follow a consistent look
Both in style and aesthetics, all the images in your series need to be coherent. You can achieve this in different ways, from the choice of lighting, the mood, the post-processing, etc.
8. Be self-critical
Once you have all the photos, make sure you edit them with a good dose of self-criticism. Not all the pictures that you took belong in the photo essay. Choose only the best ones and make sure they tell the full story.
9. Ask for constructive feedback
Often, when we’re working on a photo essay project for a long time, everything makes perfect sense in our heads. However, someone outside the project might not be getting the idea. It’s important that you get honest and constructive criticism to improve your photography.
How to Create a Photo Essay in 5 Steps
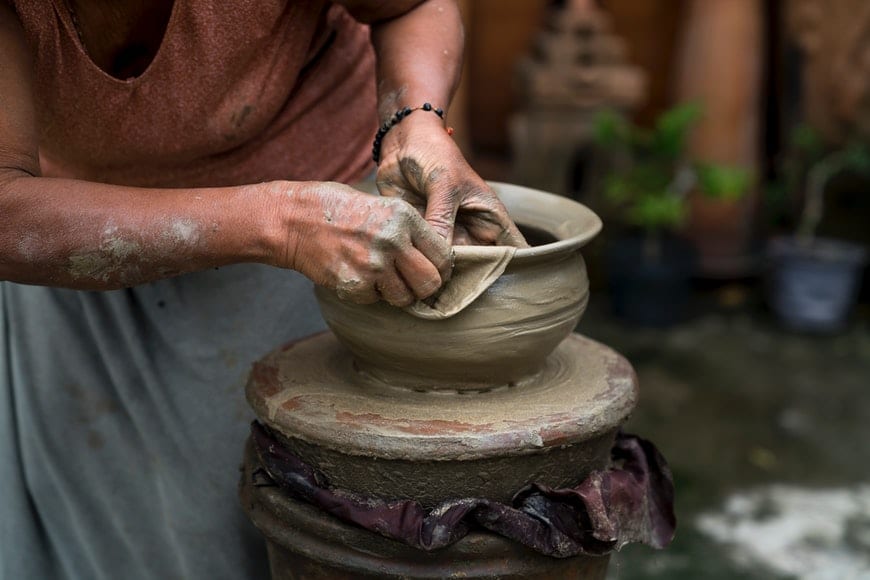

Credit: Quang Nguyen Vinh
1. Choose your topic
This is the first step that you need to take to decide if your photo essay is going to be narrative or thematic. Then, choose what is it going to be about?
Ideally, it should be something that you’re interested in, that you have something to say about it, and it can connect with other people.
2. Research your topic
To tell a good story about something, you need to be familiar with that something. This is especially true when you want to go deeper and make a compelling photo essay. Day in the life photo essays are a popular choice, since often, these can be performed with friends and family, whom you already should know well.
3. Plan your photoshoot
Depending on what you’re photographing, this step can be very different from one project to the next. For a fine art project, you might need to find a location, props, models, a shot list, etc., while a documentary photo essay is about planning the best time to do the photos, what gear to bring with you, finding a local guide, etc.
Every photo essay will need different planning, so before taking pictures, put in the required time to get things right.
4. Experiment
It’s one thing to plan your photo shoot and having a shot list that you have to get, or else the photo essay won’t be complete. It’s another thing to miss out on some amazing photo opportunities that you couldn’t foresee.
So, be prepared but also stay open-minded and experiment with different settings, different perspectives, etc.
5. Make a final selection
Editing your work can be one of the hardest parts of doing a photo essay. Sometimes we can be overly critical, and others, we get attached to bad photos because we put a lot of effort into them or we had a great time doing them.
Try to be as objective as possible, don’t be afraid to ask for opinions and make various revisions before settling down on a final cut.
7 Photo Essay Topics, Ideas & Examples
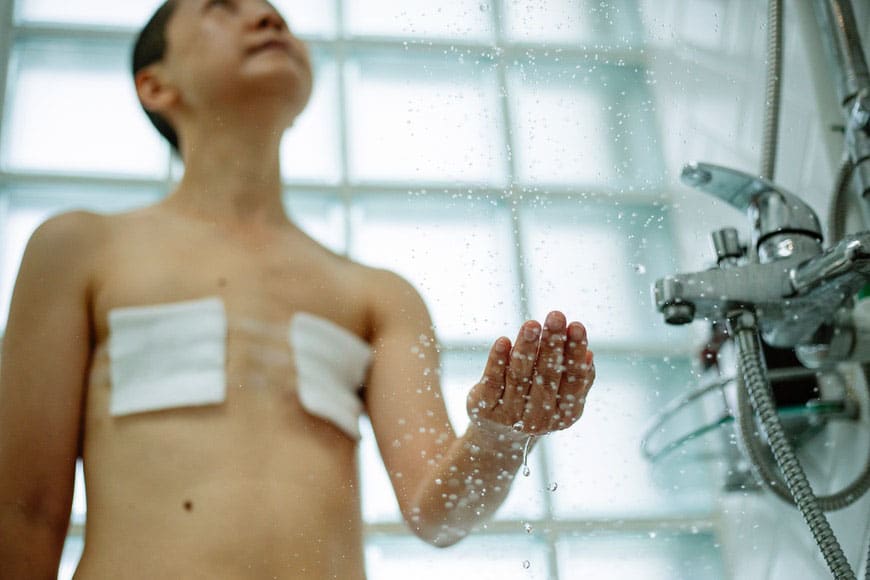

Credit: Michelle Leman
- Architectural photo essay
Using architecture as your main subject, there are tons of photo essay ideas that you can do. For some inspiration, you can check out the work of Francisco Marin – who was trained as an architect and then turned to photography to “explore a different way to perceive things”.
You can also lookup Luisa Lambri. Amongst her series, you’ll find many photo essay examples in which architecture is the subject she uses to explore the relationship between photography and space.
- Process and transformation photo essay
This is one of the best photo essay topics for beginners because the story tells itself. Pick something that has a beginning and an end, for example, pregnancy, the metamorphosis of a butterfly, the life-cycle of a plant, etc.
Keep in mind that these topics are linear and give you an easy way into the narrative flow – however, it might be difficult to find an interesting perspective and a unique point of view.
- A day in the life of ‘X’ photo essay
There are tons of interesting photo essay ideas in this category – you can follow around a celebrity, a worker, your child, etc. You don’t even have to do it about a human subject – think about doing a photo essay about a day in the life of a racing horse, for example – find something that’s interesting for you.
- Time passing by photo essay
It can be a natural site or a landmark photo essay – whatever is close to you will work best as you’ll need to come back multiple times to capture time passing by. For example, how this place changes throughout the seasons or maybe even over the years.
A fun option if you live with family is to document a birthday party each year, seeing how the subject changes over time. This can be combined with a transformation essay or sorts, documenting the changes in interpersonal relationships over time.
- Travel photo essay
Do you want to make the jump from tourist snapshots into a travel photo essay? Research the place you’re going to be travelling to. Then, choose a topic.
If you’re having trouble with how to do this, check out any travel magazine – National Geographic, for example. They won’t do a generic article about Texas – they do an article about the beach life on the Texas Gulf Coast and another one about the diverse flavors of Texas.
The more specific you get, the deeper you can go with the story.
- Socio-political issues photo essay
This is one of the most popular photo essay examples – it falls under the category of photojournalism or documental photography. They are usually thematic, although it’s also possible to do a narrative one.
Depending on your topic of interest, you can choose topics that involve nature – for example, document the effects of global warming. Another idea is to photograph protests or make an education photo essay.
It doesn’t have to be a big global issue; you can choose something specific to your community – are there too many stray dogs? Make a photo essay about a local animal shelter. The topics are endless.
- Behind the scenes photo essay
A behind-the-scenes always make for a good photo story – people are curious to know what happens and how everything comes together before a show.
Depending on your own interests, this can be a photo essay about a fashion show, a theatre play, a concert, and so on. You’ll probably need to get some permissions, though, not only to shoot but also to showcase or publish those images.
4 Best Photo Essays in Recent times
Now that you know all the techniques about it, it might be helpful to look at some photo essay examples to see how you can put the concept into practice. Here are some famous photo essays from recent times to give you some inspiration.
Habibi by Antonio Faccilongo
This photo essay wan the World Press Photo Story of the Year in 2021. Faccilongo explores a very big conflict from a very specific and intimate point of view – how the Israeli-Palestinian war affects the families.
He chose to use a square format because it allows him to give order to things and eliminate unnecessary elements in his pictures.
With this long-term photo essay, he wanted to highlight the sense of absence and melancholy women and families feel towards their husbands away at war.
The project then became a book edited by Sarah Leen and the graphics of Ramon Pez.

Picture This: New Orleans by Mary Ellen Mark
The last assignment before her passing, Mary Ellen Mark travelled to New Orleans to register the city after a decade after Hurricane Katrina.
The images of the project “bring to life the rebirth and resilience of the people at the heart of this tale”, – says CNNMoney, commissioner of the work.
Each survivor of the hurricane has a story, and Mary Ellen Mark was there to record it. Some of them have heartbreaking stories about everything they had to leave behind.
Others have a story of hope – like Sam and Ben, two eight-year-olds born from frozen embryos kept in a hospital that lost power supply during the hurricane, yet they managed to survive.
Selfie by Cindy Sherman
Cindy Sherman is an American photographer whose work is mainly done through self-portraits. With them, she explores the concept of identity, gender stereotypes, as well as visual and cultural codes.
One of her latest photo essays was a collaboration with W Magazine entitled Selfie. In it, the author explores the concept of planned candid photos (‘plandid’).
The work was made for Instagram, as the platform is well known for the conflict between the ‘real self’ and the one people present online. Sherman started using Facetune, Perfect365 and YouCam to alter her appearance on selfies – in Photoshop, you can modify everything, but these apps were designed specifically to “make things prettier”- she says, and that’s what she wants to explore in this photo essay.
Tokyo Compression by Michael Wolf
Michael Wolf has an interest in the broad-gauge topic Life in Cities. From there, many photo essays have been derived – amongst them – Tokyo Compression .
He was horrified by the way people in Tokyo are forced to move to the suburbs because of the high prices of the city. Therefore, they are required to make long commutes facing 1,5 hours of train to start their 8+ hour workday followed by another 1,5 hours to get back home.
To portray this way of life, he photographed the people inside the train pressed against the windows looking exhausted, angry or simply absent due to this way of life.
You can visit his website to see other photo essays that revolve around the topic of life in megacities.
Final Words
It’s not easy to make photo essays, so don’t expect to be great at it right from your first project.
Start off small by choosing a specific subject that’s interesting to you – that will come from an honest place, and it will be a great practice for some bigger projects along the line.
Whether you like to shoot still life or you’re a travel photographer, I hope these photo essay tips and photo essay examples can help you get started and grow in your photography.
Let us know which topics you are working on right now – we’ll love to hear from you!

Check out these 8 essential tools to help you succeed as a professional photographer.
Includes limited-time discounts.
You'll Also Like These:

Ana Mireles is a Mexican researcher that specializes in photography and communications for the arts and culture sector.
Penelope G. To Ana Mireles Such a well written and helpful article for an writer who wants to inclue photo essay in her memoir. Thank you. I will get to work on this new skill. Penelope G.
Herman Krieger Photo essays in black and white
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
👋 WELCOME TO SHOTKIT!

🔥 Popular NOW:

Unlock the EXACT blueprint to capture breathtaking iPhone photos!
Shotkit may earn a commission on affiliate links. Learn more.
- Great Depression Essays
The Great Depression Essay
The recession of the American economy led to the greatest depression that has never been experienced in the American economic history. The Great Depression, experienced between 1929 and 1932, was a period of extreme hardship in America as it forced Americans to experience an economic crisis which left many jobless and hopeless. It was the worst and longest difficult situation in the country’s economic history that threw many hardworking people into poverty. People lost their homes, farms as well as their businesses (Gunderson 4). The Great Depression led to economic stagnation and widespread unemployment and also the depression was experienced in virtually all in every major industrialized country (Hall and Ferguson 2). The impact of the Great Depression was devastating as many individuals lost their homes because they had no work and a steady income and as a result, most of them were forced to live in makeshift dwellings with poor condition and sanitation. Many children dropped out of school and married women were forced to carry a greater domestic burden. More so, the depression widened the gap between the rich and the poor (Freedman 14) because many poor individuals suffered the hardships during this period while the rich remained unaffected. This paper discusses the period of Great Depression and it covers the life during this time and how the city dwellers, farmers, children and minority groups were affected. The Great Depression started following the occurrence of the Wall Street crash and rapidly spread in different parts of the world; however, some have argued that it was triggered by mistakes in monetary policy and poor government policy (Evans 15). Different hardships and challenges were experience by individuals in different parts of the world with many people left with no work. More so, individuals especially farmers suffered from poverty and low profits, deflation and they had no opportunity for personal and economic growth. Notably, different people were affected differently, for instance, unemployment affected men and they were desperate for work while children were forced to leave school and search for something to do so as to earn money for their family. Farmers were greatly affected because this period led to decrease in price in the prices of their crops and livestock and they still worked hard to produce more so as to pay their debts, taxes and living expenses. The period before this economic crisis, farmers were already losing money due to industrialization in cities and so most of them were renting their land and machinery. When the depression started, prices on food produced by farmers deflated leaving them incapable of making profit and so they stopped selling their farm products and this in turn affected the city dwellers that were unable to produce their own food. Undoubtedly, after the stock market crash, many firms declined and many workers were forced out of their jobs because there were really no jobs. Moreover, many people had no money to purchase commodities and so the consumer demand for manufactured goods reduced significantly. Sadly, individuals had to learn to do without new clothing. The prices dropped significantly leaving farmers bankrupt and as a result most of them lost their farms. Some farmers were angry and desperate proposing that the government should intervene and ensure that farm families remain in their respective homes. But again, farmers were better off than city dwellers because they could produce much of their own food. Many farm families had large gardens with enough food crops and in some families, women made clothes from flour and feed sacks and generally, these farm families learned how to survive with what they have and little money.
Struggling with your HW?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease. Just fill in your HW requirements and you can count on us!
- Customer data protection
- 100% Plagiarism Free
Furthermore, the town and cities suffered too, for instance, as the factories were shutting down following the depression many industrial workers were left jobless. The life in the city was not easy as many individuals lived in overcrowded and unheated houses with poor sanitation. In addition, many firms closed and many individuals lost their jobs and had to deal with the reality of living in poverty. Town families were unable to produce their own food and so many city dwellers often went hungry during this period. During winter, they had hard times overcoming the cold because they had no money to buy coal to warm their houses. During the depression, the known role of women was homemaking because they had a difficult time finding jobs and so the only thing they were supposedly good at was preparing meals for their families and keeping their families together. Some women who managed to have jobs supported their families in overcoming this difficult time. Accordingly, many children were deprived their right to have access to quality education because many societies had to close down their schools due to lack of money. Some of them managed to be in schools but majority dropped out. More so, they suffered from malnutrition and those in rural areas were worse off because with the family’s low income, they were unable to purchase adequate nutritional food for all family members. Many children and even adults died from diseases and malnutrition (Gunderson 4). The minority groups in America especially the African American population who lived in rural areas working on the farms of white owners. Even though they lived in poverty, the Depression made the situation worse as their lived changed completely and remained extremely poor because the farmers they were working for had lost their land. All in all, many families struggled to leave on low incomes or no jobs with many children starving; lacked shelter and clothing as well as medical attention (Freedman 4).
In conclusion, the Great Depression was a tragic time in American history that left many people poor, unemployed or little pay, and children forced to work at a younger age. The Great Depression affected everyone from children to adults, farmers to city dwellers and so everyone’s lives changed drastically by the events experienced during this period. Many individuals were unemployed and remained desperate searching for better lives. In addition, children had no access to quality education as most of them left school and sadly they accompanied their mothers to look for work and search for a new life. However, some people particularly the employers and the wealthy were not affected during this period because they were protected from the depression with their position in the society.
Works Cited
Evans, Paul. “What Caused the Great Depression in the United States?” Managerial Finance 23.2 (1997): 15-24.
Used our essay samples for inspiration ?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Freedman, Russell. Children of the Great Depression. New York: Clarion Books, 2005. Print.
Gunderson, Cory G. The Great Depression. Edina, Minn: ABDO Pub, 2004. Internet resource.
Hall, Thomas E, and Ferguson J D. The Great Depression: An International Disaster of Perverse Economic Policies. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1998. Internet resource.
Related Essays
Find Free Essays
We provide you with original essay samples, perfect formatting and styling
Request must contain at least 2 characters
Popular Topics
Samples by Essay Type
Cite this page
About our services
Topic Great Depression
Level High School
This sample is NOT ORIGINAL. Get 100% unique essay written under your req
- Only $11 per page
- Free revisions included
Studyfy uses cookies to deliver the best experience possible. Read more.
Studyfy uses secured cookies. Read more.
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
Great Depression History
By: History.com Editors
Updated: October 20, 2023 | Original: October 29, 2009

The Great Depression was the worst economic crisis in modern history, lasting from 1929 until the beginning of World War II in 1939. The causes of the Great Depression included slowing consumer demand, mounting consumer debt, decreased industrial production and the rapid and reckless expansion of the U.S. stock market. When the stock market crashed in October 1929, it triggered a crisis in the international economy, which was linked via the gold standard. A rash of bank failures followed in 1930, and as the Dust Bowl increased the number of farm foreclosures, unemployment topped 20 percent by 1933. Presidents Herbert Hoover and Franklin D. Roosevelt tried to stimulate the economy with a range of incentives including Roosevelt’s New Deal programs, but ultimately it took the manufacturing production increases of World War II to end the Great Depression.
What Caused the Great Depression?
Throughout the 1920s, the U.S. economy expanded rapidly, and the nation’s total wealth more than doubled between 1920 and 1929, a period dubbed “ the Roaring Twenties .”
The stock market, centered at the New York Stock Exchange on Wall Street in New York City , was the scene of reckless speculation, where everyone from millionaire tycoons to cooks and janitors poured their savings into stocks. As a result, the stock market underwent rapid expansion, reaching its peak in August 1929.
By then, production had already declined and unemployment had risen, leaving stock prices much higher than their actual value. Additionally, wages at that time were low, consumer debt was proliferating, the agricultural sector of the economy was struggling due to drought and falling food prices and banks had an excess of large loans that could not be liquidated.
The American economy entered a mild recession during the summer of 1929, as consumer spending slowed and unsold goods began to pile up, which in turn slowed factory production. Nonetheless, stock prices continued to rise, and by the fall of that year had reached stratospheric levels that could not be justified by expected future earnings.
Stock Market Crash of 1929
On October 24, 1929, as nervous investors began selling overpriced shares en masse, the stock market crash that some had feared happened at last. A record 12.9 million shares were traded that day, known as “Black Thursday.”
Five days later, on October 29, or “Black Tuesday,” some 16 million shares were traded after another wave of panic swept Wall Street. Millions of shares ended up worthless, and those investors who had bought stocks “on margin” (with borrowed money) were wiped out completely.
As consumer confidence vanished in the wake of the stock market crash, the downturn in spending and investment led factories and other businesses to slow down production and begin firing their workers. For those who were lucky enough to remain employed, wages fell and buying power decreased.
Many Americans forced to buy on credit fell into debt, and the number of foreclosures and repossessions climbed steadily. The global adherence to the gold standard , which joined countries around the world in fixed currency exchange, helped spread economic woes from the United States throughout the world, especially in Europe.
Bank Runs and the Hoover Administration
Despite assurances from President Herbert Hoover and other leaders that the crisis would run its course, matters continued to get worse over the next three years. By 1930, 4 million Americans looking for work could not find it; that number had risen to 6 million in 1931.
Meanwhile, the country’s industrial production had dropped by half. Bread lines, soup kitchens and rising numbers of homeless people became more and more common in America’s towns and cities. Farmers couldn’t afford to harvest their crops and were forced to leave them rotting in the fields while people elsewhere starved. In 1930, severe droughts in the Southern Plains brought high winds and dust from Texas to Nebraska, killing people, livestock and crops. The “ Dust Bowl ” inspired a mass migration of people from farmland to cities in search of work.
In the fall of 1930, the first of four waves of banking panics began, as large numbers of investors lost confidence in the solvency of their banks and demanded deposits in cash, forcing banks to liquidate loans in order to supplement their insufficient cash reserves on hand.
Bank runs swept the United States again in the spring and fall of 1931 and the fall of 1932, and by early 1933 thousands of banks had closed their doors.
In the face of this dire situation, Hoover’s administration tried supporting failing banks and other institutions with government loans; the idea was that the banks in turn would loan to businesses, which would be able to hire back their employees.
FDR and the Great Depression
Hoover, a Republican who had formerly served as U.S. secretary of commerce, believed that government should not directly intervene in the economy and that it did not have the responsibility to create jobs or provide economic relief for its citizens.
In 1932, however, with the country mired in the depths of the Great Depression and some 15 million people unemployed, Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt won an overwhelming victory in the presidential election.
By Inauguration Day (March 4, 1933), every U.S. state had ordered all remaining banks to close at the end of the fourth wave of banking panics, and the U.S. Treasury didn’t have enough cash to pay all government workers. Nonetheless, FDR (as he was known) projected a calm energy and optimism, famously declaring "the only thing we have to fear is fear itself.”
Roosevelt took immediate action to address the country’s economic woes, first announcing a four-day “bank holiday” during which all banks would close so that Congress could pass reform legislation and reopen those banks determined to be sound. He also began addressing the public directly over the radio in a series of talks, and these so-called “ fireside chats ” went a long way toward restoring public confidence.
During Roosevelt’s first 100 days in office, his administration passed legislation that aimed to stabilize industrial and agricultural production, create jobs and stimulate recovery.
In addition, Roosevelt sought to reform the financial system, creating the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation ( FDIC ) to protect depositors’ accounts and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to regulate the stock market and prevent abuses of the kind that led to the 1929 crash.
The New Deal: A Road to Recovery
Among the programs and institutions of the New Deal that aided in recovery from the Great Depression was the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) , which built dams and hydroelectric projects to control flooding and provide electric power to the impoverished Tennessee Valley region, and the Works Progress Administration (WPA) , a permanent jobs program that employed 8.5 million people from 1935 to 1943.
When the Great Depression began, the United States was the only industrialized country in the world without some form of unemployment insurance or social security. In 1935, Congress passed the Social Security Act , which for the first time provided Americans with unemployment, disability and pensions for old age.
After showing early signs of recovery beginning in the spring of 1933, the economy continued to improve throughout the next three years, during which real GDP (adjusted for inflation) grew at an average rate of 9 percent per year.
A sharp recession hit in 1937, caused in part by the Federal Reserve’s decision to increase its requirements for money in reserve. Though the economy began improving again in 1938, this second severe contraction reversed many of the gains in production and employment and prolonged the effects of the Great Depression through the end of the decade.
Depression-era hardships fueled the rise of extremist political movements in various European countries, most notably that of Adolf Hitler’s Nazi regime in Germany. German aggression led war to break out in Europe in 1939, and the WPA turned its attention to strengthening the military infrastructure of the United States, even as the country maintained its neutrality.
African Americans in the Great Depression
One-fifth of all Americans receiving federal relief during the Great Depression were Black, most in the rural South. But farm and domestic work, two major sectors in which Black workers were employed, were not included in the 1935 Social Security Act, meaning there was no safety net in times of uncertainty. Rather than fire domestic help, private employers could simply pay them less without legal repercussions. And those relief programs for which African Americans were eligible on paper were rife with discrimination in practice since all relief programs were administered locally.
Despite these obstacles, Roosevelt’s “Black Cabinet,” led by Mary McLeod Bethune , ensured nearly every New Deal agency had a Black advisor. The number of African Americans working in government tripled .
Women in the Great Depression
There was one group of Americans who actually gained jobs during the Great Depression: Women. From 1930 to 1940, the number of employed women in the United States rose 24 percent from 10.5 million to 13 million Though they’d been steadily entering the workforce for decades, the financial pressures of the Great Depression drove women to seek employment in ever greater numbers as male breadwinners lost their jobs. The 22 percent decline in marriage rates between 1929 and 1939 also created an increase in single women in search of employment.
Women during the Great Depression had a strong advocate in First Lady Eleanor Roosevelt , who lobbied her husband for more women in office—like Secretary of Labor Frances Perkins , the first woman to ever hold a cabinet position.
Jobs available to women paid less but were more stable during the banking crisis: nursing, teaching and domestic work. They were supplanted by an increase in secretarial roles in FDR’s rapidly-expanding government. But there was a catch: over 25 percent of the National Recovery Administration’s wage codes set lower wages for women, and jobs created under the WPA confined women to fields like sewing and nursing that paid less than roles reserved for men.
Married women faced an additional hurdle: By 1940, 26 states had placed restrictions known as marriage bars on their employment, as working wives were perceived as taking away jobs from able-bodied men—even if, in practice, they were occupying jobs men would not want and doing them for far less pay.
Great Depression Ends and World War II Begins
With Roosevelt’s decision to support Britain and France in the struggle against Germany and the other Axis Powers, defense manufacturing geared up, producing more and more private-sector jobs.
The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941 led to America’s entry into World War II, and the nation’s factories went back into full production mode.
This expanding industrial production, as well as widespread conscription beginning in 1942, reduced the unemployment rate to below its pre-Depression level. The Great Depression had ended at last, and the United States turned its attention to the global conflict of World War II.
Photo Galleries

HISTORY Vault
Stream thousands of hours of acclaimed series, probing documentaries and captivating specials commercial-free in HISTORY Vault

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

The Great Depression
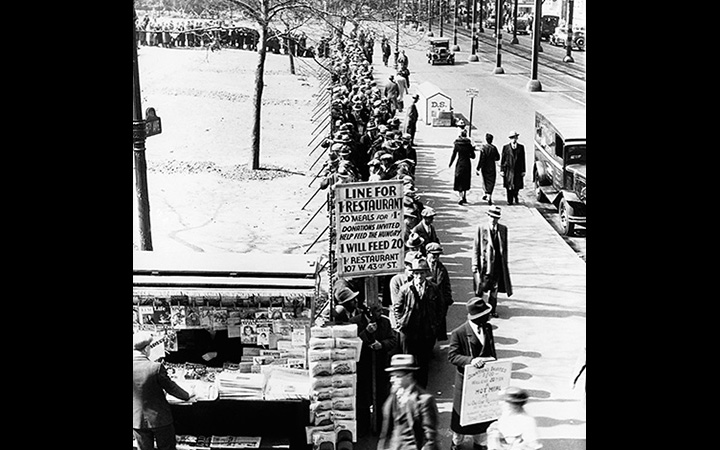

“Regarding the Great Depression, … we did it. We’re very sorry. … We won’t do it again.” —Ben Bernanke, November 8, 2002, in a speech given at “A Conference to Honor Milton Friedman … On the Occasion of His 90th Birthday.”
In 2002, Ben Bernanke , then a member of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, acknowledged publicly what economists have long believed. The Federal Reserve’s mistakes contributed to the “worst economic disaster in American history” (Bernanke 2002).
Bernanke, like other economic historians, characterized the Great Depression as a disaster because of its length, depth, and consequences. The Depression lasted a decade, beginning in 1929 and ending during World War II. Industrial production plummeted. Unemployment soared. Families suffered. Marriage rates fell. The contraction began in the United States and spread around the globe. The Depression was the longest and deepest downturn in the history of the United States and the modern industrial economy.
The Great Depression began in August 1929, when the economic expansion of the Roaring Twenties came to an end. A series of financial crises punctuated the contraction. These crises included a stock market crash in 1929 , a series of regional banking panics in 1930 and 1931 , and a series of national and international financial crises from 1931 through 1933 . The downturn hit bottom in March 1933, when the commercial banking system collapsed and President Roosevelt declared a national banking holiday . 1 Sweeping reforms of the financial system accompanied the economic recovery, which was interrupted by a double-dip recession in 1937 . Return to full output and employment occurred during the Second World War.
To understand Bernanke’s statement, one needs to know what he meant by “we,” “did it,” and “won’t do it again.”
By “we,” Bernanke meant the leaders of the Federal Reserve System. At the start of the Depression, the Federal Reserve’s decision-making structure was decentralized and often ineffective. Each district had a governor who set policies for his district, although some decisions required approval of the Federal Reserve Board in Washington, DC. The Board lacked the authority and tools to act on its own and struggled to coordinate policies across districts. The governors and the Board understood the need for coordination; frequently corresponded concerning important issues; and established procedures and programs, such as the Open Market Investment Committee, to institutionalize cooperation. When these efforts yielded consensus, monetary policy could be swift and effective. But when the governors disagreed, districts could and sometimes did pursue independent and occasionally contradictory courses of action.
The governors disagreed on many issues, because at the time and for decades thereafter, experts disagreed about the best course of action and even about the correct conceptual framework for determining optimal policy. Information about the economy became available with long and variable lags. Experts within the Federal Reserve, in the business community, and among policymakers in Washington, DC, had different perceptions of events and advocated different solutions to problems. Researchers debated these issues for decades. Consensus emerged gradually. The views in this essay reflect conclusions expressed in the writings of three recent chairmen, Paul Volcke r, Alan Greenspan , and Ben Bernanke .
By “did it,” Bernanke meant that the leaders of the Federal Reserve implemented policies that they thought were in the public interest. Unintentionally, some of their decisions hurt the economy. Other policies that would have helped were not adopted.
An example of the former is the Fed’s decision to raise interest rates in 1928 and 1929. The Fed did this in an attempt to limit speculation in securities markets. This action slowed economic activity in the United States. Because the international gold standard linked interest rates and monetary policies among participating nations, the Fed’s actions triggered recessions in nations around the globe. The Fed repeated this mistake when responding to the international financial crisis in the fall of 1931. This website explores these issues in greater depth in our entries on the stock market crash of 1929 and the financial crises of 1931 through 1933 .
An example of the latter is the Fed’s failure to act as a lender of last resort during the banking panics that began in the fall of 1930 and ended with the banking holiday in the winter of 1933. This website explores this issue in essays on the banking panics of 1930 to 1931 , the banking acts of 1932 , and the banking holiday of 1933 .
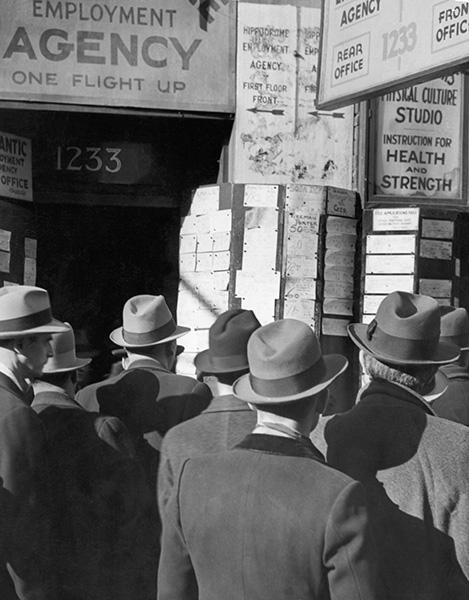

One reason that Congress created the Federal Reserve, of course, was to act as a lender of last resort. Why did the Federal Reserve fail in this fundamental task? The Federal Reserve’s leaders disagreed about the best response to banking crises. Some governors subscribed to a doctrine similar to Bagehot’s dictum, which says that during financial panics, central banks should loan funds to solvent financial institutions beset by runs. Other governors subscribed to a doctrine known as real bills. This doctrine indicated that central banks should supply more funds to commercial banks during economic expansions, when individuals and firms demanded additional credit to finance production and commerce, and less during economic contractions, when demand for credit contracted. The real bills doctrine did not definitively describe what to do during banking panics, but many of its adherents considered panics to be symptoms of contractions, when central bank lending should contract. A few governors subscribed to an extreme version of the real bills doctrine labeled “liquidationist.” This doctrine indicated that during financial panics, central banks should stand aside so that troubled financial institutions would fail. This pruning of weak institutions would accelerate the evolution of a healthier economic system. Herbert Hoover’s secretary of treasury, Andrew Mellon, who served on the Federal Reserve Board, advocated this approach. These intellectual tensions and the Federal Reserve’s ineffective decision-making structure made it difficult, and at times impossible, for the Fed’s leaders to take effective action.
Among leaders of the Federal Reserve, differences of opinion also existed about whether to help and how much assistance to extend to financial institutions that did not belong to the Federal Reserve. Some leaders thought aid should only be extended to commercial banks that were members of the Federal Reserve System. Others thought member banks should receive assistance substantial enough to enable them to help their customers, including financial institutions that did not belong to the Federal Reserve, but the advisability and legality of this pass-through assistance was the subject of debate. Only a handful of leaders thought the Federal Reserve (or federal government) should directly aid commercial banks (or other financial institutions) that did not belong to the Federal Reserve. One advocate of widespread direct assistance was Eugene Meyer , governor of the Federal Reserve Board, who was instrumental in the creation of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation .
These differences of opinion contributed to the Federal Reserve’s most serious sin of omission: failure to stem the decline in the supply of money. From the fall of 1930 through the winter of 1933, the money supply fell by nearly 30 percent. The declining supply of funds reduced average prices by an equivalent amount. This deflation increased debt burdens; distorted economic decision-making; reduced consumption; increased unemployment; and forced banks, firms, and individuals into bankruptcy. The deflation stemmed from the collapse of the banking system, as explained in the essay on the banking panics of 1930 and 1931 .
The Federal Reserve could have prevented deflation by preventing the collapse of the banking system or by counteracting the collapse with an expansion of the monetary base, but it failed to do so for several reasons. The economic collapse was unforeseen and unprecedented. Decision makers lacked effective mechanisms for determining what went wrong and lacked the authority to take actions sufficient to cure the economy. Some decision makers misinterpreted signals about the state of the economy, such as the nominal interest rate, because of their adherence to the real bills philosophy. Others deemed defending the gold standard by raising interests and reducing the supply of money and credit to be better for the economy than aiding ailing banks with the opposite actions.
On several occasions, the Federal Reserve did implement policies that modern monetary scholars believe could have stemmed the contraction. In the spring of 1931, the Federal Reserve began to expand the monetary base, but the expansion was insufficient to offset the deflationary effects of the banking crises. In the spring of 1932, after Congress provided the Federal Reserve with the necessary authority, the Federal Reserve expanded the monetary base aggressively. The policy appeared effective initially, but after a few months the Federal Reserve changed course. A series of political and international shocks hit the economy, and the contraction resumed. Overall, the Fed’s efforts to end the deflation and resuscitate the financial system, while well intentioned and based on the best available information, appear to have been too little and too late.
The flaws in the Federal Reserve’s structure became apparent during the initial years of the Great Depression. Congress responded by reforming the Federal Reserve and the entire financial system. Under the Hoover administration, congressional reforms culminated in the Reconstruction Finance Corporation Act and the Banking Act of 1932 . Under the Roosevelt administration, reforms culminated in the Emergency Banking Act of 1933 , the Banking Act of 1933 (commonly called Glass-Steagall) , the Gold Reserve Act of 1934 , and the Banking Act of 1935 . This legislation shifted some of the Federal Reserve’s responsibilities to the Treasury Department and to new federal agencies such as the Reconstruction Finance Corporation and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. These agencies dominated monetary and banking policy until the 1950s.
The reforms of the 1930s, ’40s, and ’50s turned the Federal Reserve into a modern central bank. The creation of the modern intellectual framework underlying economic policy took longer and continues today. The Fed’s combination of a well-designed central bank and an effective conceptual framework enabled Bernanke to state confidently that “we won’t do it again.”
- 1 These business cycle dates come from the National Bureau of Economic Research . Additional materials on the Federal Reserve can be found at the website of the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
Bibliography
Bernanke, Ben. Essays on the Great Depression . Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2000.
Bernanke, Ben, “ On Milton Friedman's Ninetieth Birthday ," Remarks by Governor Ben S. Bernanke at the Conference to Honor Milton Friedman, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, November 8, 2002.
Chandler, Lester V. American Monetary Policy, 1928 to 1941 . New York: Harper and Row, 1971.
Chandler, Lester V. American’s Greatest Depression, 1929-1941 . New York: Harper Collins, 1970.
Eichengreen, Barry. “The Origins and Nature of the Great Slump Revisited.” Economic History Review 45, no. 2 (May 1992): 213–239.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Schwartz. A Monetary History of the United States: 1867-1960 . Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1963.
Kindleberger, Charles P. The World in Depression, 1929-1939 : Revised and Enlarged Edition. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1986.
Meltzer, Allan. A History of the Federal Reserve: Volume 1, 1913 to 1951 . Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003.
Romer, Christina D. “The Nation in Depression.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 7, no. 2 (1993): 19-39.
Temin, Peter. Lessons from the Great Depression (Lionel Robbins Lectures) . Cambridge: MIT Press, 1989.
Written as of November 22, 2013. See disclaimer .
Essays in this Time Period
- Bank Holiday of 1933
- Banking Act of 1933 (Glass-Steagall)
- Banking Act of 1935
- Banking Acts of 1932
- Banking Panics of 1930-31
- Banking Panics of 1931-33
- Stock Market Crash of 1929
- Emergency Banking Act of 1933
- Gold Reserve Act of 1934
- Recession of 1937–38
- Roosevelt's Gold Program
Federal Reserve History


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This collection of pictures of the Great Depression offers a glimpse into the lives of Americans who suffered through it. Included in this collection are pictures of the dust storms that ruined crops, leaving many farmers unable to keep their land. Also included are pictures of migrant workers—people who had lost their jobs or their farms and ...
The department was set up to combat American rural poverty and Lange's work humanized the consequences of the Great Depression and influenced the development of documentary photography. Here we showcase the images that established Lange as one of the most influential photographers of the 20th century. 1. White Angel Breadline, San Francisco ...
Dorothea Lange's famous "Migrant Mother" photograph. Then in 1978, a woman named Florence Owens Thompson wrote a letter to the editor of the Modesto Bee newspaper. She was the mother in the famous ...
The pictures of the Great Depression show the terrible economic effects of that time. They have an emotional impact that statistics lack. ... Photo by Library Of Congress/Getty Images. A dust storm rolled into Elkhart, Kansas, on May 21, 1937. The year before, the drought caused the hottest summer on record. In June, eight states experienced ...
Beginning in the early 1930s, America suffered an economic crisis that lasted nearly a decade—the Great Depression. Until then, Dorothea Lange had been a successful portrait photographer. But the events of the time prompted her to leave the safety of her studio to create powerful images of people in crisis—Dust Bowl refugees, migrant workers, and the urban homeless. Through her photographs ...
The Great Depression Photo Gallery. While the Great Depression was a time of tremendous poverty and suffering, it was also a period in which the arts flourished. Much of that art served to document the devastation of the Depression. The artists' documentary spirit shines clearly through the photographs taken as part of the Historical Section ...
AA Photographic Essay. In April of 1939, a most remarkable display of photography. was held, the First International Photographic Exposition, at the Grand Central Palace in New York. This show. contained many camera images of the plight of Americans. during the Great Depression. When the U.S. Camera Annual of.
One photograph of Thompson, "Migrant Mother," became a defining symbol of the Great Depression. The pictures' publication incited an emergency food delivery to the pea picker's camp ...
The photo documentary projects of 1935-1942 were only part of a major commitment of the federal government to the cultural resources of the United States during the Great Depression. Photography was also part of the Historic American Buildings Survey, Historic American Engineering Record, and the Works Progress Administration's Federal Arts ...
In public programs, Stanford scholars share their views on the groundbreaking artistic endeavors of photographer Walker Evans. As he stares out from the darkness behind him, the defeated expression in the man's eyes pulls the viewer into a time of extreme hardship. Although this stark black-and-white photograph was taken nearly 80 years ago, the current recession has brought renewed meaning to ...
A Photo Essay on the Great Depression. Note: This page is very graphics heavy and will take several moments to load depending on the speed of your connection. ... In the summer of 1932, in the midst of the Great Depression, World War I veterans seeking early payment of a bonus scheduled for 1945 assembled in Washington to pressure Congress and ...
Great Depression. In one of the largest pea camps in. California. February, 1936. The photograph that has become known as "Migrant Mother" is one. of a series of photographs that Dorothea Lange made in February or. March of 1936 in Nipomo, California. Lange was concluding a month's.
Under the Farm Security Administration/Office of War Information, those photographers captured some of the most iconic images of the Great Depression and World War II, shaping much of the era's visual culture in the process. 170,000 of those crucial photos, which were kept and catalogued by the Library Congress, can now be seen in a massive ...
Step Three: Conclusion: What does the photo tell you about the Great Depression? Step Four: Creative Writing: From the perspective of a person in the photo, create a story (8-10 sentences in length) describing what your life would be like. Use the people, objects and activities in the
Photo by Marion Post Wolcott. Photo 1: A miner's wife on the porch of their home, an abandoned company store in Pursglove, 1938. Photo 2: Miners eating ice cream. Photos by Marion Post Wolcott. Residents of Jere eat at a Sunday school picnic brought to their town by neighboring parishes, September 1938.
Overview. The Great Depression was the worst economic downturn in US history. It began in 1929 and did not abate until the end of the 1930s. The stock market crash of October 1929 signaled the beginning of the Great Depression. By 1933, unemployment was at 25 percent and more than 5,000 banks had gone out of business.
Famous Photo Essays. "The Great Depression" by Dorothea Lange - Shot and arranged in the 1930s, this famous photo essay still serves as a stark reminder of The Great Depression and Dust Bowl America. Beautifully photographed, the black and white images offer a bleak insight to one of the country's most difficult times.
Some people refer to a photo essay as a photo series or a photo story - this often happens in photography competitions. Photographic history is full of famous photo essays. Think about The Great Depression by Dorothea Lange, Like Brother Like Sister by Wolfgang Tillmans, Gandhi's funeral by Henri Cartier Bresson, amongst others.
The Great Depression, experienced between 1929 and 1932, was a period of extreme hardship in America as it forced Americans to experience an economic crisis which left many jobless and hopeless. It was the worst and longest difficult situation in the country's economic history that threw many hardworking people into poverty.
493 Words2 Pages. The Great Depression was a time that stained the fabric of American history with dirt and mud and tears. Many did not understand, or care to understand the impact and consequences that came from the depression. In this particular photo, it utilizes emphasis and balance to get others, and more importantly, government agencies ...
The Great Depression was the worst economic downturn in the history of the industrialized world, lasting from 1929 to 1939. At its peak, the U.S. unemployment rate topped 20 percent.
This compilation of photos by multiple photographers during the horrid Great Depression era captures the unforeseen consequences of the New York Stock Exchange crash. It gives snapshots to a past inexperienced by today's youth. Hopefully, this photo essay can serve as a warning for future generations of the dangers that can lie in unhealthy ...
This website explores this issue in essays on the banking panics of 1930 to 1931, the banking acts of 1932, and the banking holiday of 1933. Men study the announcement of jobs at an employment agency during the Great Depression. (Photo: Bettmann/Bettmann/Getty Images)
The character of Atticus Finch is so beloved that when Richard Thomas walked on stage last night, he was met with applause for the opening night of "To Kill a Mockingbird" at the Walton Arts Center.