- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
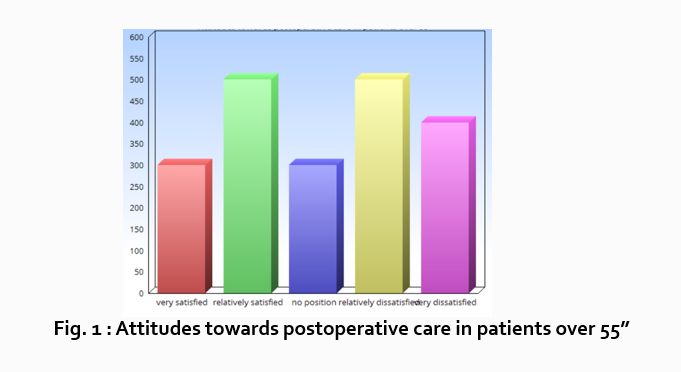
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
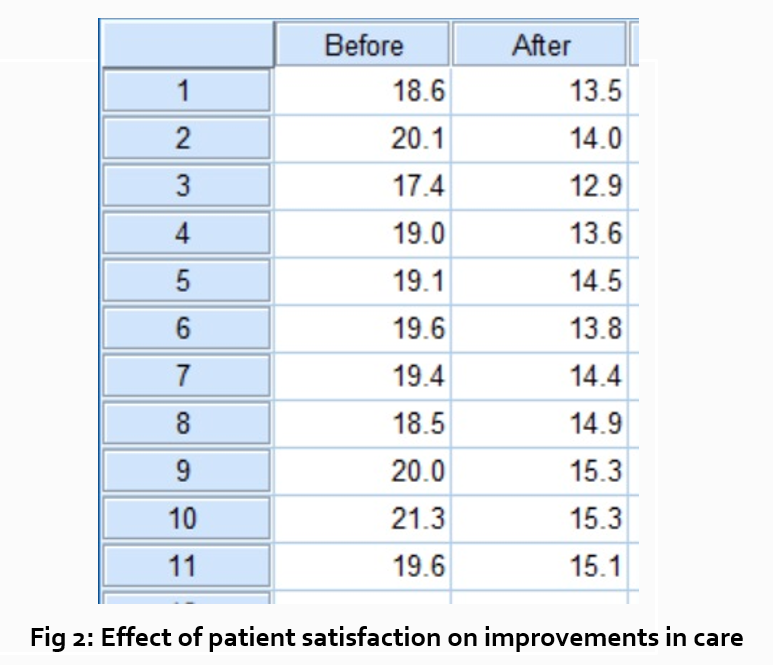
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
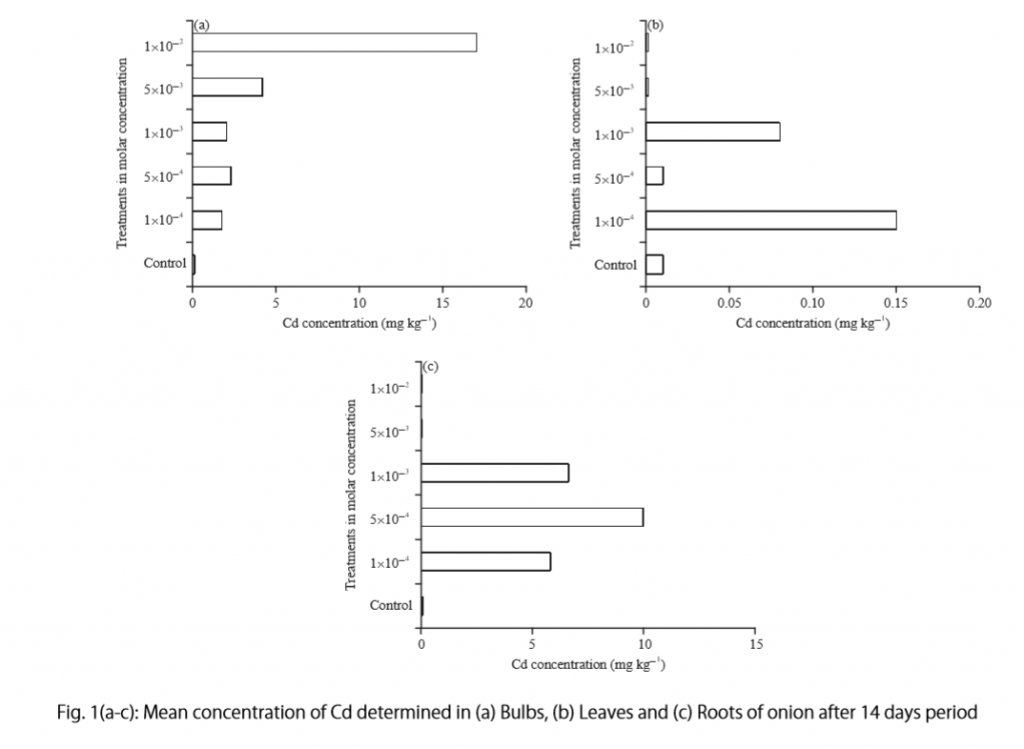
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers
- Discoveries
- Right Journal
- Journal Metrics
- Journal Fit
- Abbreviation
- In-Text Citations
- Bibliographies
- Writing an Article
- Peer Review Types
- Acknowledgements
- Withdrawing a Paper
- Form Letter
- ISO, ANSI, CFR
- Google Scholar
- Journal Manuscript Editing
- Research Manuscript Editing
Book Editing
- Manuscript Editing Services
Medical Editing
- Bioscience Editing
- Physical Science Editing
- PhD Thesis Editing Services
- PhD Editing
- Master’s Proofreading
- Bachelor’s Editing
- Dissertation Proofreading Services
- Best Dissertation Proofreaders
- Masters Dissertation Proofreading
- PhD Proofreaders
- Proofreading PhD Thesis Price
- Journal Article Editing
- Book Editing Service
- Editing and Proofreading Services
- Research Paper Editing
- Medical Manuscript Editing
- Academic Editing
- Social Sciences Editing
- Academic Proofreading
- PhD Theses Editing
- Dissertation Proofreading
- Proofreading Rates UK
- Medical Proofreading
- PhD Proofreading Services UK
- Academic Proofreading Services UK
Medical Editing Services
- Life Science Editing
- Biomedical Editing
- Environmental Science Editing
- Pharmaceutical Science Editing
- Economics Editing
- Psychology Editing
- Sociology Editing
- Archaeology Editing
- History Paper Editing
- Anthropology Editing
- Law Paper Editing
- Engineering Paper Editing
- Technical Paper Editing
- Philosophy Editing
- PhD Dissertation Proofreading
- Lektorat Englisch
- Akademisches Lektorat
- Lektorat Englisch Preise
- Wissenschaftliches Lektorat
- Lektorat Doktorarbeit
PhD Thesis Editing
- Thesis Proofreading Services
- PhD Thesis Proofreading
- Proofreading Thesis Cost
- Proofreading Thesis
- Thesis Editing Services
- Professional Thesis Editing
- Thesis Editing Cost
- Proofreading Dissertation
- Dissertation Proofreading Cost
- Dissertation Proofreader
- Correção de Artigos Científicos
- Correção de Trabalhos Academicos
- Serviços de Correção de Inglês
- Correção de Dissertação
- Correção de Textos Precos
- 定額 ネイティブチェック
- Copy Editing
- FREE Courses
- Revision en Ingles
- Revision de Textos en Ingles
- Revision de Tesis
- Revision Medica en Ingles
- Revision de Tesis Precio
- Revisão de Artigos Científicos
- Revisão de Trabalhos Academicos
- Serviços de Revisão de Inglês
- Revisão de Dissertação
- Revisão de Textos Precos
- Corrección de Textos en Ingles
- Corrección de Tesis
- Corrección de Tesis Precio
- Corrección Medica en Ingles
- Corrector ingles
Select Page
How To Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper
Posted by Rene Tetzner | Sep 2, 2021 | Paper Writing Advice | 0 |

How To Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper Each research project is unique, so it is natural for one researcher to make use of somewhat different strategies than another when it comes to designing and writing the section of a research paper dedicated to findings. The academic or scientific discipline of the research, the field of specialisation, the particular author or authors, the targeted journal or other publisher and the editor making the decisions about publication can all have a significant impact. The practical steps outlined below can be effectively applied to writing about the findings of most advanced research, however, and will prove especially helpful for early-career scholars who are preparing a research paper for a first publication.

Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the targeted journal (or other publisher) provides for authors and read research papers it has already published, particularly ones similar in topic, methods or results to your own. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches. Watch particularly for length limitations and restrictions on content. Interpretation, for instance, is usually reserved for a later discussion section, though not always – qualitative research papers often combine findings and interpretation. Background information and descriptions of methods, on the other hand, almost always appear in earlier sections of a research paper. In most cases it is appropriate in a findings section to offer basic comparisons between the results of your study and those of other studies, but knowing exactly what the journal wants in the report of research findings is essential. Learning as much as you can about the journal’s aims and scope as well as the interests of its readers is invaluable as well.

Step 2 : Reflect at some length on your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements while planning the findings section of your paper. Choose for particular focus experimental results and other research discoveries that are particularly relevant to your research questions and objectives, and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses. Streamline and clarify your report, especially if it is long and complex, by using subheadings that will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Consider appendices for raw data that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers. The opening paragraph of a findings section often restates research questions or aims to refocus the reader’s attention, and it is always wise to summarise key findings at the end of the section, providing a smooth intellectual transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows in most research papers. There are many effective ways in which to organise research findings. The structure of your findings section might be determined by your research questions and hypotheses or match the arrangement of your methods section. A chronological order or hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. It may be best to present all the relevant findings and then explain them and your analysis of them, or explaining the results of each trial or test immediately after reporting it may render the material clearer and more comprehensible for your readers. Keep your audience, your most important evidence and your research goals in mind.

Step 3 : Design effective visual presentations of your research results to enhance the textual report of your findings. Tables of various styles and figures of all kinds such as graphs, maps and photos are used in reporting research findings, but do check the journal guidelines for instructions on the number of visual aids allowed, any required design elements and the preferred formats for numbering, labelling and placement in the manuscript. As a general rule, tables and figures should be numbered according to first mention in the main text of the paper, and each one should be clearly introduced and explained at least briefly in that text so that readers know what is presented and what they are expected to see in a particular visual element. Tables and figures should also be self-explanatory, however, so their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for a reader to understand the findings you intend to show without returning to your text. If you construct your tables and figures before drafting your findings section, they can serve as focal points to help you tell a clear and informative story about your findings and avoid unnecessary repetition. Some authors will even work on tables and figures before organising the findings section (Step 2), which can be an extremely effective approach, but it is important to remember that the textual report of findings remains primary. Visual aids can clarify and enrich the text, but they cannot take its place.
Step 4 : Write your findings section in a factual and objective manner. The goal is to communicate information – in some cases a great deal of complex information – as clearly, accurately and precisely as possible, so well-constructed sentences that maintain a simple structure will be far more effective than convoluted phrasing and expressions. The active voice is often recommended by publishers and the authors of writing manuals, and the past tense is appropriate because the research has already been done. Make sure your grammar, spelling and punctuation are correct and effective so that you are conveying the meaning you intend. Statements that are vague, imprecise or ambiguous will often confuse and mislead readers, and a verbose style will add little more than padding while wasting valuable words that might be put to far better use in clear and logical explanations. Some specialised terminology may be required when reporting findings, but anything potentially unclear or confusing that has not already been defined earlier in the paper should be clarified for readers, and the same principle applies to unusual or nonstandard abbreviations. Your readers will want to understand what you are reporting about your results, not waste time looking up terms simply to understand what you are saying. A logical approach to organising your findings section (Step 2) will help you tell a logical story about your research results as you explain, highlight, offer analysis and summarise the information necessary for readers to understand the discussion section that follows.
Step 5 : Review the draft of your findings section and edit and revise until it reports your key findings exactly as you would have them presented to your readers. Check for accuracy and consistency in data across the section as a whole and all its visual elements. Read your prose aloud to catch language errors, awkward phrases and abrupt transitions. Ensure that the order in which you have presented results is the best order for focussing readers on your research objectives and preparing them for the interpretations, speculations, recommendations and other elements of the discussion that you are planning. This will involve looking back over the paper’s introductory and background material as well as anticipating the discussion and conclusion sections, and this is precisely the right point in the process for reviewing and reflecting. Your research results have taken considerable time to obtain and analyse, so a little more time to stand back and take in the wider view from the research door you have opened is a wise investment. The opinions of any additional readers you can recruit, whether they are professional mentors and colleagues or family and friends, will often prove invaluable as well.
You might be interested in Services offered by Proof-Reading-Service.com
Journal editing.
Journal article editing services
PhD thesis editing services
Scientific Editing
Manuscript editing.
Manuscript editing services
Expert Editing
Expert editing for all papers
Research Editing
Research paper editing services
Professional book editing services
How To Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper These five steps will help you write a clear & interesting findings section for a research paper
Related Posts

How To Write a Journal Article
September 6, 2021

Tips on How To Write a Journal Article
August 30, 2021

How To Write Highlights for an Academic or Scientific Paper
September 7, 2021

Tips on How To Write an Effective Figure Legend
August 27, 2021
Our Recent Posts

Our review ratings
- Examples of Research Paper Topics in Different Study Areas Score: 98%
- Dealing with Language Problems – Journal Editor’s Feedback Score: 95%
- Making Good Use of a Professional Proofreader Score: 92%
- How To Format Your Journal Paper Using Published Articles Score: 95%
- Journal Rejection as Inspiration for a New Perspective Score: 95%
Explore our Categories
- Abbreviation in Academic Writing (4)
- Career Advice for Academics (5)
- Dealing with Paper Rejection (11)
- Grammar in Academic Writing (5)
- Help with Peer Review (7)
- How To Get Published (146)
- Paper Writing Advice (17)
- Referencing & Bibliographies (16)

- Manuscript Preparation
How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
- 54.9K views
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

- Research Process
Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

studioprogetto.net
helping you conduct any research project easily
Tips & Sample to Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper
The section allows you to present the data that founded the basis of your investigations. The findings section of research paper also helps to justify your thoughts and affirm a position. It reveals whether your original idea was confirmed by the data you collected.
The best advice on how to write the findings section of a research paper is to look back at where it all began. You went into the research to investigate a principle. It is time to tell your reader what you found. The data you present will then be used to justify a position.
The findings section of a research paper also combines the revelations from your Literature Review, though faintly. It will require the use of descriptions and discussions of the results obtained during data analysis.
Expert tips on how to present research findings
- Revisit your thesis statement and research questions
Research questions and the thesis statement are the anchors of this chapter. Your entire data collection escapade was about proving your statement. For this reason, revising or reminding the reader acts as the wake-up call. It shows the genesis of your quest to find data.
The research questions also help you to choose tools and data analysis techniques. Each question will result in particular data and findings. By revisiting, you help the reader to connect your methods and the findings you get.
- Identify a story in your data
What is the data telling you about your hypothesis? Research findings definition point at a revelation. That revelation is done as you read through the data from one section to the other. Each data entry reveals something you were investigating. The reader is interested in understanding this story. It explains why the section is always descriptive. Your idea is to help the reader to understand the revelation made by the data you have collected.
- Find focus in your data
Data can be read in so many ways. However, you must direct the reader on how he will understand and interpret your data. From the sample of summary of findings in research, you will discover that the researcher shines a spotlight on a particular element of the data. The aspect of the data that receives attention helps him to answer the research questions.
- Give the lessons
This is where you acknowledge that your methods were right but still missed some of the points. It is a time to affirm your assertions while also admitting the points that were missed in the course of data collection. A research findings example will help you to accurately capture this aspect.
- Draw a conclusion
You have the Discussion chapter to draw your conclusions but you still must guide the reader on what to see in your data presentation. The sentences are usually very short. In fact, each paragraph or finding is only three sentences long. The conclusions affirm or disapprove of the question that you were investigating.
Here is a presentation of findings in research paper example to guide you when writing your own:
Rate of weight gain
The findings indicated that people gain more weight towards the end of the year compared to the beginning
Uptake of exercises and gym activity
Data reveals that most people enroll in the gym and take on exercise at the beginning of the year.
Opinion on weight loss
Most people believe that they can lose weight by exercising, going to the gym, and dieting.
Place of dieting in weight loss
While people appreciate diet as a source of weight loss, most of them are not willing to take the option.
Weight lost groups
Most of those interviewed said that exercise groups kept them motivated to lose weight.
Exercising at home
While it is convenient, most people feel better going to the gym
Online exercise routines
Most respondents cited online routines as effective at the beginning but cause them to lose morale.
Improvising around the house
Most respondents have improvised exercise tools around the house but they still prefer gym equipment
Exercising with partners
Those who exercised with their partners achieved the results faster and were satisfied
Exercise and age
People turn to exercises in their late thirties onwards.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How To Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper
How To Write the Findings Section of a Research Paper Each research project is unique, so it is natural for one researcher to make use of somewhat different strategies than another when it comes to designing and writing the section of a research paper dedicated to findings. The academic or scientific discipline of the research, the field of specialisation, the particular author or authors, the targeted journal or other publisher and the editor making the decisions about publication can all have a significant impact. The practical steps outlined below can be effectively applied to writing about the findings of most advanced research, however, and will prove especially helpful for early-career scholars who are preparing a research paper for a first publication. Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the targeted journal (or other publisher) provides for authors and read research papers it has already published, particularly ones similar in topic, methods or results to your own. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches. Watch particularly for length limitations and restrictions on content. Interpretation, for instance, is usually reserved for a later discussion section, though not always – qualitative research papers often combine findings and interpretation. Background information and descriptions of methods, on the other hand, almost always appear in earlier sections of a research paper. In most cases it is appropriate in a findings section to offer basic comparisons between the results of your study and those of other studies, but knowing exactly what the journal wants in the report of research findings is essential. Learning as much as you can about the journal’s aims and scope as well as the interests of its readers is invaluable as well. PhD Thesis Editing Services Step 2 : Reflect at some length on your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements while planning the findings section of your paper. Choose for particular focus experimental results and other research discoveries that are particularly relevant to your research questions and objectives, and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses. Streamline and clarify your report, especially if it is long and complex, by using subheadings that will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Consider appendices for raw data that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers. The opening paragraph of a findings section often restates research questions or aims to refocus the reader’s attention, and it is always wise to summarise key findings at the end of the section, providing a smooth intellectual transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows in most research papers. There are many effective ways in which to organise research findings. The structure of your findings section might be determined by your research questions and hypotheses or match the arrangement of your methods section. A chronological order or hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. It may be best to present all the relevant findings and then explain them and your analysis of them, or explaining the results of each trial or test immediately after reporting it may render the material clearer and more comprehensible for your readers. Keep your audience, your most important evidence and your research goals in mind. Step 3 : Design effective visual presentations of your research results to enhance the textual report of your findings. Tables of various styles and figures of all kinds such as graphs, maps and photos are used in reporting research findings, but do check the journal guidelines for instructions on the number of visual aids allowed, any required design elements and the preferred formats for numbering, labelling and placement in the manuscript. As a general rule, tables and figures should be numbered according to first mention in the main text of the paper, and each one should be clearly introduced and explained at least briefly in that text so that readers know what is presented and what they are expected to see in a particular visual element. Tables and figures should also be self-explanatory, however, so their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for a reader to understand the findings you intend to show without returning to your text. If you construct your tables and figures before drafting your findings section, they can serve as focal points to help you tell a clear and informative story about your findings and avoid unnecessary repetition. Some authors will even work on tables and figures before organising the findings section (Step 2), which can be an extremely effective approach, but it is important to remember that the textual report of findings remains primary. Visual aids can clarify and enrich the text, but they cannot take its place. Step 4 : Write your findings section in a factual and objective manner. The goal is to communicate information – in some cases a great deal of complex information – as clearly, accurately and precisely as possible, so well-constructed sentences that maintain a simple structure will be far more effective than convoluted phrasing and expressions. The active voice is often recommended by publishers and the authors of writing manuals, and the past tense is appropriate because the research has already been done. Make sure your grammar, spelling and punctuation are correct and effective so that you are conveying the meaning you intend. Statements that are vague, imprecise or ambiguous will often confuse and mislead readers, and a verbose style will add little more than padding while wasting valuable words that might be put to far better use in clear and logical explanations. Some specialised terminology may be required when reporting findings, but anything potentially unclear or confusing that has not already been defined earlier in the paper should be clarified for readers, and the same principle applies to unusual or nonstandard abbreviations. Your readers will want to understand what you are reporting about your results, not waste time looking up terms simply to understand what you are saying. A logical approach to organising your findings section (Step 2) will help you tell a logical story about your research results as you explain, highlight, offer analysis and summarise the information necessary for readers to understand the discussion section that follows. PhD Thesis Editing Services Step 5 : Review the draft of your findings section and edit and revise until it reports your key findings exactly as you would have them presented to your readers. Check for accuracy and consistency in data across the section as a whole and all its visual elements. Read your prose aloud to catch language errors, awkward phrases and abrupt transitions. Ensure that the order in which you have presented results is the best order for focussing readers on your research objectives and preparing them for the interpretations, speculations, recommendations and other elements of the discussion that you are planning. This will involve looking back over the paper’s introductory and background material as well as anticipating the discussion and conclusion sections, and this is precisely the right point in the process for reviewing and reflecting. Your research results have taken considerable time to obtain and analyse, so a little more time to stand back and take in the wider view from the research door you have opened is a wise investment. The opinions of any additional readers you can recruit, whether they are professional mentors and colleagues or family and friends, will often prove invaluable as well.
Why Our Editing and Proofreading Services? At Proof-Reading-Service.com we offer the highest quality journal article editing , phd thesis editing and proofreading services via our large and extremely dedicated team of academic and scientific professionals. All of our proofreaders are native speakers of English who have earned their own postgraduate degrees, and their areas of specialisation cover such a wide range of disciplines that we are able to help our international clientele with research editing to improve and perfect all kinds of academic manuscripts for successful publication. Many of the carefully trained members of our expert editing and proofreading team work predominantly on articles intended for publication in scholarly journals, applying painstaking journal editing standards to ensure that the references and formatting used in each paper are in conformity with the journal’s instructions for authors and to correct any grammar, spelling, punctuation or simple typing errors. In this way, we enable our clients to report their research in the clear and accurate ways required to impress acquisitions proofreaders and achieve publication.
Our scientific proofreading services for the authors of a wide variety of scientific journal papers are especially popular, but we also offer manuscript proofreading services and have the experience and expertise to proofread and edit manuscripts in all scholarly disciplines, as well as beyond them. We have team members who specialise in medical proofreading services , and some of our experts dedicate their time exclusively to PhD proofreading and master’s proofreading , offering research students the opportunity to improve their use of formatting and language through the most exacting PhD thesis editing and dissertation proofreading practices. Whether you are preparing a conference paper for presentation, polishing a progress report to share with colleagues, or facing the daunting task of editing and perfecting any kind of scholarly document for publication, a qualified member of our professional team can provide invaluable assistance and give you greater confidence in your written work.
If you are in the process of preparing an article for an academic or scientific journal, or planning one for the near future, you may well be interested in a new book, Guide to Journal Publication , which is available on our Tips and Advice on Publishing Research in Journals website.
Guide to Academic and Scientific Publication
How to get your writing published in scholarly journals.
It provides practical advice on planning, preparing and submitting articles for publication in scholarly journals.
PhD Success
How to write a doctoral thesis.
If you are in the process of preparing a PhD thesis for submission, or planning one for the near future, you may well be interested in the book, How to Write a Doctoral Thesis , which is available on our thesis proofreading website.
PhD Success: How to Write a Doctoral Thesis provides guidance for students familiar with English and the procedures of English universities, but it also acknowledges that many theses in the English language are now written by candidates whose first language is not English, so it carefully explains the scholarly styles, conventions and standards expected of a successful doctoral thesis in the English language.
Why Is Proofreading Important?
To improve the quality of papers.
Effective proofreading is absolutely vital to the production of high-quality scholarly and professional documents. When done carefully, correctly and thoroughly, proofreading can make the difference between writing that communicates successfully with its intended readers and writing that does not. No author creates a perfect text without reviewing, reflecting on and revising what he or she has written, and proofreading is an extremely important part of this process.

- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Research Summary

It’s a common perception that writing a research summary is a quick and easy task. After all, how hard can jotting down 300 words be? But when you consider the weight those 300 words carry, writing a research summary as a part of your dissertation, essay or compelling draft for your paper instantly becomes daunting task.
A research summary requires you to synthesize a complex research paper into an informative, self-explanatory snapshot. It needs to portray what your article contains. Thus, writing it often comes at the end of the task list.
Regardless of when you’re planning to write, it is no less of a challenge, particularly if you’re doing it for the first time. This blog will take you through everything you need to know about research summary so that you have an easier time with it.
What is a Research Summary?
A research summary is the part of your research paper that describes its findings to the audience in a brief yet concise manner. A well-curated research summary represents you and your knowledge about the information written in the research paper.
While writing a quality research summary, you need to discover and identify the significant points in the research and condense it in a more straightforward form. A research summary is like a doorway that provides access to the structure of a research paper's sections.
Since the purpose of a summary is to give an overview of the topic, methodology, and conclusions employed in a paper, it requires an objective approach. No analysis or criticism.
Research summary or Abstract. What’s the Difference?
They’re both brief, concise, and give an overview of an aspect of the research paper. So, it’s easy to understand why many new researchers get the two confused. However, a research summary and abstract are two very different things with individual purpose. To start with, a research summary is written at the end while the abstract comes at the beginning of a research paper.
A research summary captures the essence of the paper at the end of your document. It focuses on your topic, methods, and findings. More like a TL;DR, if you will. An abstract, on the other hand, is a description of what your research paper is about. It tells your reader what your topic or hypothesis is, and sets a context around why you have embarked on your research.
Getting Started with a Research Summary
Before you start writing, you need to get insights into your research’s content, style, and organization. There are three fundamental areas of a research summary that you should focus on.
- While deciding the contents of your research summary, you must include a section on its importance as a whole, the techniques, and the tools that were used to formulate the conclusion. Additionally, there needs to be a short but thorough explanation of how the findings of the research paper have a significance.
- To keep the summary well-organized, try to cover the various sections of the research paper in separate paragraphs. Besides, how the idea of particular factual research came up first must be explained in a separate paragraph.
- As a general practice worldwide, research summaries are restricted to 300-400 words. However, if you have chosen a lengthy research paper, try not to exceed the word limit of 10% of the entire research paper.
How to Structure Your Research Summary
The research summary is nothing but a concise form of the entire research paper. Therefore, the structure of a summary stays the same as the paper. So, include all the section titles and write a little about them. The structural elements that a research summary must consist of are:
It represents the topic of the research. Try to phrase it so that it includes the key findings or conclusion of the task.
The abstract gives a context of the research paper. Unlike the abstract at the beginning of a paper, the abstract here, should be very short since you’ll be working with a limited word count.
Introduction
This is the most crucial section of a research summary as it helps readers get familiarized with the topic. You should include the definition of your topic, the current state of the investigation, and practical relevance in this part. Additionally, you should present the problem statement, investigative measures, and any hypothesis in this section.
Methodology
This section provides details about the methodology and the methods adopted to conduct the study. You should write a brief description of the surveys, sampling, type of experiments, statistical analysis, and the rationality behind choosing those particular methods.
Create a list of evidence obtained from the various experiments with a primary analysis, conclusions, and interpretations made upon that. In the paper research paper, you will find the results section as the most detailed and lengthy part. Therefore, you must pick up the key elements and wisely decide which elements are worth including and which are worth skipping.
This is where you present the interpretation of results in the context of their application. Discussion usually covers results, inferences, and theoretical models explaining the obtained values, key strengths, and limitations. All of these are vital elements that you must include in the summary.
Most research papers merge conclusion with discussions. However, depending upon the instructions, you may have to prepare this as a separate section in your research summary. Usually, conclusion revisits the hypothesis and provides the details about the validation or denial about the arguments made in the research paper, based upon how convincing the results were obtained.
The structure of a research summary closely resembles the anatomy of a scholarly article . Additionally, you should keep your research and references limited to authentic and scholarly sources only.
Tips for Writing a Research Summary
The core concept behind undertaking a research summary is to present a simple and clear understanding of your research paper to the reader. The biggest hurdle while doing that is the number of words you have at your disposal. So, follow the steps below to write a research summary that sticks.
1. Read the parent paper thoroughly
You should go through the research paper thoroughly multiple times to ensure that you have a complete understanding of its contents. A 3-stage reading process helps.
a. Scan: In the first read, go through it to get an understanding of its basic concept and methodologies.
b. Read: For the second step, read the article attentively by going through each section, highlighting the key elements, and subsequently listing the topics that you will include in your research summary.
c. Skim: Flip through the article a few more times to study the interpretation of various experimental results, statistical analysis, and application in different contexts.
Sincerely go through different headings and subheadings as it will allow you to understand the underlying concept of each section. You can try reading the introduction and conclusion simultaneously to understand the motive of the task and how obtained results stay fit to the expected outcome.
2. Identify the key elements in different sections
While exploring different sections of an article, you can try finding answers to simple what, why, and how. Below are a few pointers to give you an idea:
- What is the research question and how is it addressed?
- Is there a hypothesis in the introductory part?
- What type of methods are being adopted?
- What is the sample size for data collection and how is it being analyzed?
- What are the most vital findings?
- Do the results support the hypothesis?
Discussion/Conclusion
- What is the final solution to the problem statement?
- What is the explanation for the obtained results?
- What is the drawn inference?
- What are the various limitations of the study?
3. Prepare the first draft
Now that you’ve listed the key points that the paper tries to demonstrate, you can start writing the summary following the standard structure of a research summary. Just make sure you’re not writing statements from the parent research paper verbatim.
Instead, try writing down each section in your own words. This will not only help in avoiding plagiarism but will also show your complete understanding of the subject. Alternatively, you can use a summarizing tool (AI-based summary generators) to shorten the content or summarize the content without disrupting the actual meaning of the article.
SciSpace Copilot is one such helpful feature! You can easily upload your research paper and ask Copilot to summarize it. You will get an AI-generated, condensed research summary. SciSpace Copilot also enables you to highlight text, clip math and tables, and ask any question relevant to the research paper; it will give you instant answers with deeper context of the article..
4. Include visuals
One of the best ways to summarize and consolidate a research paper is to provide visuals like graphs, charts, pie diagrams, etc.. Visuals make getting across the facts, the past trends, and the probabilistic figures around a concept much more engaging.
5. Double check for plagiarism
It can be very tempting to copy-paste a few statements or the entire paragraphs depending upon the clarity of those sections. But it’s best to stay away from the practice. Even paraphrasing should be done with utmost care and attention.
Also: QuillBot vs SciSpace: Choose the best AI-paraphrasing tool
6. Religiously follow the word count limit
You need to have strict control while writing different sections of a research summary. In many cases, it has been observed that the research summary and the parent research paper become the same length. If that happens, it can lead to discrediting of your efforts and research summary itself. Whatever the standard word limit has been imposed, you must observe that carefully.
7. Proofread your research summary multiple times
The process of writing the research summary can be exhausting and tiring. However, you shouldn’t allow this to become a reason to skip checking your academic writing several times for mistakes like misspellings, grammar, wordiness, and formatting issues. Proofread and edit until you think your research summary can stand out from the others, provided it is drafted perfectly on both technicality and comprehension parameters. You can also seek assistance from editing and proofreading services , and other free tools that help you keep these annoying grammatical errors at bay.

8. Watch while you write
Keep a keen observation of your writing style. You should use the words very precisely, and in any situation, it should not represent your personal opinions on the topic. You should write the entire research summary in utmost impersonal, precise, factually correct, and evidence-based writing.
9. Ask a friend/colleague to help
Once you are done with the final copy of your research summary, you must ask a friend or colleague to read it. You must test whether your friend or colleague could grasp everything without referring to the parent paper. This will help you in ensuring the clarity of the article.
Once you become familiar with the research paper summary concept and understand how to apply the tips discussed above in your current task, summarizing a research summary won’t be that challenging. While traversing the different stages of your academic career, you will face different scenarios where you may have to create several research summaries.
In such cases, you just need to look for answers to simple questions like “Why this study is necessary,” “what were the methods,” “who were the participants,” “what conclusions were drawn from the research,” and “how it is relevant to the wider world.” Once you find out the answers to these questions, you can easily create a good research summary following the standard structure and a precise writing style.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

Plasma Processing of Materials: Scientific Opportunities and Technological Challenges (1991)
Chapter: 1 summary, findings, conclusions, and recommendations, 1 summary, findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
This study focuses on the plasma processing of materials, a technology that impacts and is of vital importance to several of the largest manufacturing industries in the world. Foremost among these industries is the electronics industry, in which plasma-based processes are indispensable for the manufacture of very large-scale integrated (VLSI) microelectronic circuits (or chips). Plasma processing of materials is also a critical technology in the aerospace, automotive, steel, biomedical, and toxic waste management industries. Because plasma processing is an integral part of the infrastructure of so many American industries, it is important for both the economy and the national security that America maintain a strong leadership role in this technology.
A plasma is a partially or fully ionized gas containing electrons, ions, and neutral atoms or molecules. In Chapter 2 , the panel categorizes different kinds of plasmas and focuses on properties of man-made low-energy, highly collisional plasmas that are particularly useful in materials processing applications. The outstanding properties of most plasmas applied to processing of materials are associated with nonequilibrium conditions. These properties present a challenge to the plasma scientist and an opportunity to the technologist. The opportunities for materials processing stem from the ability of a plasma to provide a highly excited medium that has no chemical or physical counterpart in a natural, equilibrium environment. Plasmas alter the normal pathways through which chemical systems evolve from one stable state to another, thus providing the potential to produce materials with properties that are not attainable by any other means.
Applications of plasma-based systems used to process materials are diverse because of the broad range of plasma conditions, geometries, and excitation methods that may be used. The scientific underpinnings of plasma applications are multidisciplinary and include elements of electrodynamics, atomic science, surface science, computer science, and industrial process control. Because of the diversity of applications and the multidisciplinary nature of the science, scientific understanding lags technology. This report highlights this critical issue.
A summary of the many industrial applications of plasma-based systems for processing materials is included in Chapter 2 . Electronics and aerospace are the two major industries that are served by plasma processing technologies, although the automotive industry is likely to become a significant user of plasma-processed materials like those now in widespread use in the aerospace industry. The critical role of plasma processing technology in industry is illustrated in Chapter 2 .
For the electronics industry more than for any other considered by the panel, the impact of—and the critical and urgent need for—plasma-based materials processing is overwhelming. Thus Chapter 3 further elucidates plasma processing of electronic materials and, in particular, the use of plasmas in fabricating microelectronic components. The plasma equipment industry is an integral part of the electronics industry and has experienced dramatic growth in recent years because of the increasing use of plasma processes to meet the demands of fabricating devices with continually shrinking dimensions. In this country, the plasma equipment industry
is composed of many small companies loosely connected to integrated circuit manufacturers. In Japan, on the other hand, equipment vendors and device manufacturers are tightly linked and are often parts of the same company.
Plasma processes used today in fabricating microelectronic devices have been developed largely by time-consuming, costly, empirical exploration. The chemical and physical complexity of plasma-surface interactions has so far eluded the accurate numerical simulation that would enable process design. Similarly, plasma reactors have also been developed by trial and error. This is due, in part, to the fact that reactor design is intimately intertwined with the materials process for which it will be used. Nonetheless, fundamental studies of surface processes and plasma phenomena—both experimental and numerical—have contributed to process development by providing key insights that enable limitation of the broad process-variable operating space. The state of the science that underpins plasma processing technology in the United States is outlined in Chapter 4 . Although an impressive arsenal of both experimental and numerical tools has been developed, significant gaps in understanding and lack of instrumentation limit progress.
The broad interdisciplinary nature of plasma processing is highlighted in the discussion of education issues outlined in Chapter 5 , which addresses the challenges and opportunities associated with providing a science education in the area of plasma processing. For example, graduate programs specifically focused on plasma processing are rare because of insufficient funding of university research programs in this field. By contrast, both Japan and France have national initiatives that support education and research in plasma processing.
FINDINGS, CONCLUSIONS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Finding and Conclusion : In recent years, the number of applications requiring plasmas in the processing of materials has increased dramatically. Plasma processing is now indispensable to the fabrication of electronic components and is widely used in the aerospace industry and other industries. However, the United States is seeing a serious decline in plasma reactor development that is critical to plasma processing steps in the manufacture of VLSI microelectronic circuits. In the interest of the U.S. economy and national defense, renewed support for low-energy plasma science is imperative.
Finding and Conclusion : The demand for technology development is outstripping scientific understanding of many low-energy plasma processes. The central scientific problem underlying plasma processing concerns the interaction of low-energy collisional plasmas with solid surfaces. Understanding this problem requires knowledge and expertise drawn from plasma physics, atomic physics, condensed matter physics, chemistry, chemical engineering, electrical engineering, materials science, computer science, and computer engineering. In the absence of a coordinated approach, the diversity of the applications and of the science tends to diffuse the focus of both.
Finding : Technically, U.S. laboratories have made many excellent contributions to plasma processing research—making fundamental discoveries, developing numerical algorithms, and inventing new diagnostic techniques. However, poor coordination and inefficient transfer of insights gained from this research have inhibited its use in the design of new plasma reactors and processes.
Finding : The Panel on Plasma Processing of Materials finds that plasma processing of materials is a critical technology that is necessary to implement key recommendations contained in the National Research Council report Materials Science and Engineering for the 1990s (National Academy Press, Washington, D.C., 1989) and to enhance the health of technologies as identified in Report of the National Critical Technologies Panel (U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1991). Specifically, plasma processing is an essential element in the synthesis and processing arsenal for manufacturing electronic, photonic, ceramic, composite, high-performance metal, and alloy materials.
Accordingly, the panel recommends:
Plasma processing should be identified as a component program of the Federal Initiative on advanced materials synthesis and processing that currently is being developed by the Office of Science and Technology Policy.
Through such a Plasma Processing Program, federal funds should be allocated specifically to stimulate focused research in plasma processing, both basic and applied, consistent with the long-term economic and defense goals of the nation.
The Plasma Processing Program should not only provide focus on common goals and promote coordination of the research performed by the national laboratories, universities, and industrial laboratories, but also integrate plasma equipment suppliers into the program.
Finding and Conclusion : Currently, computer-based modeling and plasma simulation are inadequate for developing plasma reactors. As a result, the detailed descriptions required to guide the transfer of processes from one reactor to another or to scale processes from a small to a large reactor are not available. Until we understand how geometry, electromagnetic design, and plasma-surface interactions affect material properties, the choice of plasma reactor for a given process will not be obvious, and costly trial-and-error methods will continue to be used. Yet there is no fundamental obstacle to improved modeling and simulation nor to the eventual creation of computer-aided design (CAD) tools for designing plasma reactors. The key missing ingredients are the following:
A reliable and extensive plasma data base against which the accuracy of simulations of plasmas can be compared . Plasma measurement technologies are sophisticated, but at present experiments are performed on a large variety of different reactors under widely varying conditions. A coordinated effort to diagnose simple, reference reactors is necessary to generate the necessary data base for evaluation of simulation results and to test new and old experimental methodology.
A reliable and extensive input data base for calculating plasma generation, transport, and surface interaction . The dearth of basic data needed for simulation of plasma generation, transport, and surface reaction processes results directly from insufficient generation of data, insufficient data compilation, insufficient distribution of data, and insufficient funding of these activities. The critical basic data needed for simulations and experiments have not been prioritized. For plasma-surface interactions, in particular, lack of data has precluded the formation of mechanistic models on which simulation tools are based. Further experimental studies are needed to elucidate these mechanisms.
Efficient numerical algorithms and supercomputers for simulating magnetized plasmas in three dimensions . The advent of unprecedented supercomputer capability in the next 5 to 10 years will have a major impact in this area, provided that current simulation methods are expanded to account for multidimensional effects in magnetized plasmas.
The Plasma Processing Program should include a thrust toward development of computer-aided design tools for developing and designing new plasma reactors.
The Plasma Processing Program should emphasize a coordinated approach toward generating the diagnostic and basic data needed for improved plasma and plasma-surface simulation capability.
A program to extend current algorithms for plasma reactor simulation should be included among the activities funded under the umbrella of the federal High
Performance Computing and Communications program 1 developed by the Office of Science and Technology Policy and started in FY92.
Finding and Conclusion : In the coming decade, custom-designed and custom-manufactured chips, i.e ., application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), will gain an increasing fraction of the world market in microelectronic components. This market, in turn, will belong to the flexible manufacturer who uses a common set of processes and equipment to fabricate many different circuit designs. Such flexibility in processing will result only from real understanding of processes and reactors. On the other hand, plasma processes in use today have been developed using a combination of intuition, empiricism, and statistical optimization. Although it is unlikely that detailed, quantitative, first-principles-based simulation tools will be available for process design in the near future, design aids such as expert systems, which can be used to guide engineers in selecting initial conditions from which the final process is derived, could be developed if gaps in our fundamental understanding of plasma chemistry were filled.
Finding and Conclusion : Three areas are recognized by the panel as needing concerted, coordinated experimental and theoretical research: surface processes, plasma generation and transport, and plasma-surface interactions. For surface processes, studies using well-controlled reactive beams impinging on well-characterized surfaces are essential for enhancing our understanding and developing mechanistic models. For plasma generation and transport, chemical kinetic data and diagnostic data are needed to augment the basic plasma reactor CAD tool. For studying plasma-surface interactions, there is an urgent need for in situ analytical tools that provide information on surface composition, electronic structure, and material properties.
Finding and Conclusion : Breakthroughs in understanding the science will be paced by development of tools for the characterization of the systems. To meet the coming demands for flexible device manufacturing, plasma processes will have to be actively and precisely controlled. But today no diagnostic techniques exist that can be used unambiguously to determine material properties related to device yield. Moreover, the parametric models needed to relate diagnostic data to process variables are also lacking.
According, the panel recommends:
The Plasma Processing Program should be dedicated in part to the development of plasma process expert systems.
A coordinated program should be supported to generate basic data and simulation of surface processes, plasma generation and transport, and plasma-surface interactions.
A program should be supported that focuses on development of new instrumentation for real-time, in situ monitoring for control and analysis.
Finding : Research resources in low-energy plasma science in the United States are eroding at an alarming rate. U.S. scientists trained in this area in the 1950s and early 1960s are retiring or are moving to other areas of science for which support is more forthcoming. When compared to those in Japan and France, the U.S. educational infrastructure in plasma processing lacks focus, coordination, and funding. As a result, the United States will not be prepared to maintain its leading market position in plasma processing, let alone capture more market share as the plasma process industry grows into the 21st century.
Finding : Graduate programs are not offering adequate educational opportunities in the science of weakly ionized, highly collisional plasmas. An informal survey by the panel indicated that only a few U.S. universities offer formal course work in this science and that there are
insufficient texts on collisional plasmas and plasma processing. These deficiencies are a direct result of low-level funding for graduate research in plasma processing and low-energy plasmas.
Finding and Conclusion : The most serious need in undergraduate education is adequate, modern teaching laboratories. Due to the largely empirical nature of many aspects of plasma processing, proper training in the traditional scientific method, as provided in laboratory classes, is a necessary component of undergraduate education. The Instrumentation and Laboratory Improvement Program sponsored by the National Science Foundation has been partly successful in fulfilling these needs, but it is not sufficient.
Finding and Conclusion : Research experiences for undergraduates made available through industrial cooperative programs or internships are essential for high-quality technical education. But teachers and professors themselves must first be educated in low-energy plasma science and plasma processing before they can be expected to educate students. Industrial-university links can also help to impart a much needed, longer-term view to industrial research efforts.
As part of the Plasma Processing Program, government and industry together should support cooperative programs specific to plasma processing with universities and national laboratories.
A program should be established to provide industrial internships for teachers and professors in the area of plasma processing.
Plasma processing of materials is a critical technology to several of the largest manufacturing industries in the world—electronics, aerospace, automotive, steel, biomedical, and toxic waste management. This book describes the relationship between plasma processes and the many industrial applications, examines in detail plasma processing in the electronics industry, highlights the scientific foundation underlying this technology, and discusses education issues in this multidisciplinary field.
The committee recommends a coordinated, focused, and well-funded research program in this area that involves the university, federal laboratory, and industrial sectors of the community. It also points out that because plasma processing is an integral part of the infrastructure of so many American industries, it is important for both the economy and the national security that America maintain a strong leadership role in this technology.
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
“Something Works” in U.S. Jails: Misconduct and Recidivism Effects of the IGNITE Program
A longstanding and influential view in U.S. correctional policy is that “nothing works” when it comes to rehabilitating incarcerated individuals. We revisit this hypothesis by studying an innovative law-enforcement-led program launched in the county jail of Flint, Michigan: Inmate Growth Naturally and Intentionally Through Education (IGNITE). We develop an instrumental variable approach to estimate the effects of IGNITE exposure, which leverages quasi-random court delays that cause individuals to spend more time in jail both before and after the program’s launch. Holding time in jail fixed, we find that one additional month of IGNITE exposure reduces within-jail misconduct by 49% and reduces three-month recidivism by 18%, with the recidivism effects growing over time. Surveys of staff and community members, along with administrative test score records and within-jail text messages, suggest that cultural change and improved literacy and numeracy scores are key contributing mechanisms.
We thank Mauricio Cáceres Bravo, Jennifer Doleac, Sara Heller, Adriana Lleras-Muney, Matthew Mizel, Michael Mueller-Smith, Matthew Pecenco, Evan Rose, Nico Rotundo, Yotam Shem-Tov, and seminar participants at Harvard University, Opportunity Insights, the University of Connecticut, the University of Michigan, the NBER Economics of Crime Working Group, and the University of California Los Angeles for helpful comments. We are grateful to Meghan Beal at the National Sheriffs’ Association, Superintendent Mickie Kujat and Principal Brad Basista of Mt. Morris Consolidated Schools, and to the administration and incarcerated individuals of Genesee County and Saginaw County Jails—especially Deputy Annie Bueche, Undersheriff Mike Gomez, Major Jason Gould, Lieutenant Ebony Rasco, and Sheriff Christopher Swanson. We gratefully acknowledge funding from Arnold Ventures. Xingyou Ye, Miguel Purroy, Meera Mody, Anne Fogarty, Jeongmook Lim, and Michelle Wu provided expert research assistance. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
Working Groups
Conferences, more from nber.
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Exploring the factors that influence continued use of sharing economic platforms: Insights from idle fish
- Author & abstract
- Related works & more
Corrections
- Shengxiang She
- Yaoping Liu
- Daranee Pimchangthong
- Pharath Run
- Khoirul Anwar
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 27 March 2024
Tweeting your research paper boosts engagement but not citations
- Bianca Nogrady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Even before complaints about X’s declining quality, posting a paper on the social-media platform did not lead to a boost in citations. Credit: Matt Cardy/Getty
Posting about a research paper on social-media platform X (formerly known as Twitter) doesn’t translate into a bump in citations, according to a study that looked at 550 papers.
The finding comes as scientists are moving away from the platform in the wake of changes after its 2022 purchase by entrepreneur Elon Musk.
An international group of 11 researchers, who by the end of the experiment had between them nearly 230,000 followers on X, examined whether there was evidence that posting about a paper would increase its citation rate.
“There certainly is a correlation, and that’s been found in a lot of papers. But very few people have ever looked to see whether there’s any experimental causation,” says Trevor Branch, a marine ecologist at the University of Washington in Seattle and lead author on the paper, published in PLoS ONE last week 1 .
Every month for ten months, each researcher was allocated a randomly selected primary research article or review from a journal of their choice to post about on their personal account. Four randomly chosen articles from the same edition of the journal served as controls, which the researchers did not post about. They conducted the experiment in the period before Elon Musk took ownership of what was then known as Twitter and complaints of its declining quality increased.
‘Nail in the coffin’
Three years after the initial posts, the team compared the citation rates for the 110 posted articles with those of the 440 control articles, and found no significant difference. The researchers did acknowledge that their followers might not have been numerous enough to detect a statistically significant effect on citations.
The rate of daily downloads for the posted papers was nearly fourfold higher on the day that they were shared, compared with controls. Shared papers also had significantly higher accumulated Altmetric scores both 30 days and three years after the initial post. Calculated by London-based technology company Digital Science, an Altmetric score, says Branch, is a measure of how many people have looked at a paper and are talking about it, but it’s not a reliable indicator of a paper’s scientific worth. “It’s thoroughly biased by how many people with large followings tweet about it,” he says.
The findings echo those of information scientist Stefanie Haustein at the University of Ottawa, whose 2013 study 2 found a low correlation between posts and citations.
Haustein says the problem with using posts as a metric is that, even a decade ago, there was a lot of noise in the signal.
“We actually showed that a lot of the counts on Twitter you would get were bots, it wasn’t even humans,” says Haustein, who wasn’t involved in the new study.
She says the more recent departure of scientists from the platform has been the final nail in the coffin of the idea that posting could increase citations.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00922-y
Branch, T. A. et al. PLoS ONE 19 , e0292201 (2024).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Haustein, S., Peters, I., Sugimoto, C. R., Thelwall, M. & Larivière, V. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 65, 656–669 (2014).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

- Communication
- Scientific community

Divas, captains, ghosts, ants and bumble-bees: collaborator attitudes explained
Career Column 15 MAR 24

Three actions PhD-holders should take to land their next job
Career Column 13 MAR 24

This geologist communicates science from the ski slopes
Career Q&A 11 MAR 24

The corpse of an exploded star and more — March’s best science images
News 28 MAR 24

How OpenAI’s text-to-video tool Sora could change science – and society
News 12 MAR 24

Giant plume of plasma on the Sun’s surface and more — February’s best science images
News 01 MAR 24

The EU’s ominous emphasis on ‘open strategic autonomy’ in research
Editorial 03 APR 24
Time to sound the alarm about the hidden epidemic of kidney disease
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
Correspondence 02 APR 24
Faculty Positions, Aging and Neurodegeneration, Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine
Applicants with expertise in aging and neurodegeneration and related areas are particularly encouraged to apply.
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine (WLLSB)
Faculty Positions in Chemical Biology, Westlake University
We are seeking outstanding scientists to lead vigorous independent research programs focusing on all aspects of chemical biology including...
School of Life Sciences, Westlake University
Faculty Positions in Neurobiology, Westlake University
We seek exceptional candidates to lead vigorous independent research programs working in any area of neurobiology.
Seeking Global Talents, the International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University
Welcome to apply for all levels of professors based at the International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University.
Yiwu, Zhejiang, China
International School of Medicine, Zhejiang University
Nanjing Forestry University is globally seeking Metasequoia Scholars and Metasequoia Talents
Located next to Purple Mountain and Xuanwu Lake, Nanjing Forestry University (NJFU) is a key provincial university jointly built by Jiangsu Province
Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Nanjing Forestry University (NFU)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative Findings. Qualitative research is an exploratory research method used to understand the complexities of human behavior and experiences. Qualitative findings are non-numerical and descriptive data that describe the meaning and interpretation of the data collected. Examples of qualitative findings include quotes from participants ...
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to ...
Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples. Published on December 21, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on January 17, 2024. The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses.. The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields ...
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
Research Results. Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Don't make the reader do the analytic work for you. Now, on to some specific ways to structure your findings section. 1). Tables. Tables can be used to give an overview of what you're about to present in your findings, including the themes, some supporting evidence, and the meaning/explanation of the theme.
Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarizing your major findings. To speed up the process you can use a summarizer to quickly get an overview of all important findings. Don't just repeat all the data you have already reported—aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research ...
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
The Results (also sometimes called Findings) section in an empirical research paper describes what the researcher(s) found when they analyzed their data. Its primary purpose is to use the data collected to answer the research question(s) posed in the introduction, even if the findings challenge the hypothesis.
Step 4: Write your findings section in a factual and objective manner. The goal is to communicate information - in some cases a great deal of complex information - as clearly, accurately and precisely as possible, so well-constructed sentences that maintain a simple structure will be far more effective than convoluted phrasing and expressions.
The discussion section is one of the final parts of a research paper, in which an author describes, analyzes, and interprets their findings. They explain the significance of those results and tie everything back to the research question(s). In this handout, you will find a description of what a discussion section does, explanations of how to ...
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper. Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions. The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is ...
Expert tips on how to present research findings. Revisit your thesis statement and research questions. Research questions and the thesis statement are the anchors of this chapter. Your entire data collection escapade was about proving your statement. For this reason, revising or reminding the reader acts as the wake-up call.
Step 2: Reflect at some length on your research results in relation to the journal's requirements while planning the findings section of your paper. Choose for particular focus experimental results and other research discoveries that are particularly relevant to your research questions and objectives, and include them even if they are ...
However, a research summary and abstract are two very different things with individual purpose. To start with, a research summary is written at the end while the abstract comes at the beginning of a research paper. A research summary captures the essence of the paper at the end of your document. It focuses on your topic, methods, and findings ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
The conclusions are as stated below: i. Students' use of language in the oral sessions depicted their beliefs and values. based on their intentions. The oral sessions prompted the students to be ...
Performance Computing and Communications program 1 developed by the Office of Science and Technology Policy and started in FY92.. Finding and Conclusion: In the coming decade, custom-designed and custom-manufactured chips, i.e., application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), will gain an increasing fraction of the world market in microelectronic components.
In addition to working papers, the NBER disseminates affiliates' latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter, the NBER Digest, the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability, the Bulletin on Health, and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports, video lectures, and interviews.
Here we report high-precision chemical abundances for a homogeneous sample of ninety-one co-natal pairs of stars with a well defined selection function and identify at least seven instances of ...
Findings suggest trade-offs faced by health policymakers seeking to achieve multiple health objectives. Acknowledgements and Disclosures Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute on Mental Health of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number 1R01MH132552 (PI: Johanna Catherine Maclean).
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
The presented findings contribute to our understanding of attention mechanisms and highlight the promising clinical applications of TMS in addressing attention-related disorders. This synthesis of theoretical and practical insights aims to propel further advancements in attention research and its therapeutic applications.
Making the shift from global to territorial food systems is critical for sustainability and demands transformative, coherent, and integrated land and food policies. However, how policy integration may be achieved or hindered remains unclear, particularly in the case of coexisting agri-food models. The coexistence of conflicting models, such as specialization versus diversification and agro ...
In addition to working papers, the NBER disseminates affiliates' latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter, the NBER Digest, the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability, the Bulletin on Health, and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports, video lectures, and interviews.
The paper accomplishes this by discussing the practical suggestions of the research findings for the platforms of the sharing economy. ... utilizing a digital questionnaire disseminated via Credamo, which yielded 400 valid responses. The sample pool on this platform is of exceptional quality. Prior to accessing the questionnaire, the ...
Posting about a research paper on social-media platform X (formerly known as Twitter) doesn't translate into a bump in citations, according to a study that looked at 550 papers. The finding ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.