
20 Common Researcher Interview Questions and Answers
Common Researcher interview questions, how to answer them, and sample answers from a certified career coach.

You’ve been invited to interview for a research position—congratulations! You know you have the skills and experience, but now it’s time to prove it.
The key to success? Being prepared. To help make sure you shine in your upcoming interview, we’ve compiled some of the most common questions asked during research interviews. Read on, get familiar with them, and practice your answers so you can ace that job interview like a pro.
- What research methods do you use to collect data?
- How do you ensure the accuracy and validity of your research results?
- Describe a time when you had to analyze complex data sets and draw meaningful conclusions from them.
- Explain how you would go about designing an experiment or survey to answer a specific research question.
- Are you familiar with any statistical software programs? If so, which ones?
- What strategies do you use to stay organized while conducting research?
- How do you handle ethical considerations when conducting research?
- Have you ever encountered a situation where you had to adjust your research methodology due to unexpected circumstances?
- Describe a time when you had to present your research findings in a clear and concise manner.
- Do you have experience working with large datasets?
- What challenges have you faced when collecting primary data for a research project?
- How do you approach writing up a research paper or report?
- What techniques do you use to identify potential sources of bias in your research?
- How do you evaluate the quality of secondary sources used in your research?
- What strategies do you use to keep track of changes in the field of research you are studying?
- How do you decide which research questions to pursue?
- What is your experience with peer review processes?
- How do you manage competing demands on your time when conducting research?
- What strategies do you use to ensure that your research remains relevant and up-to-date?
- How do you ensure that your research meets the highest standards of academic integrity?
1. What research methods do you use to collect data?
Research methods are the core of any researcher’s job. You’ll need to be familiar with a variety of different methods, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and experiments, and be able to explain how you use each one in your work. This will help the interviewer understand your process and how you can contribute to their organization.
How to Answer:
You should be prepared to explain the research methods you have used in your past work. Talk about how you use surveys, interviews, focus groups, and experiments to collect data, as well as any other methods you may have experience with. If you’re just starting out, then talk through the steps you would take to select a method for each project. You can also mention any specialized methods or software that you are familiar with.
Example: “I use a variety of research methods to collect data, depending on the project. I often use surveys and interviews as primary sources of information, but I also have experience with focus groups, experiments, and software tools like Qualtrics for collecting quantitative data. I’m familiar with specialized methods such as content analysis and ethnography when appropriate. My goal is always to select the method that will provide the most accurate and reliable data for each project.”
2. How do you ensure the accuracy and validity of your research results?
Research requires a level of precision that goes beyond the normal workplace. Good researchers are able to identify what data is relevant and how to collect it in order to make reliable conclusions. Interviewers will want to know that you have the skills and knowledge to conduct research that is both accurate and valid. They’ll also want to know if you use any specific methods or tools to ensure accuracy and validity.
You should be prepared to explain what methods you use to ensure accuracy and validity of your research. This could include double-checking sources, using multiple data points, or triangulating information from different sources to verify results. You can also mention any specific tools or techniques you use, such as conducting surveys or interviews with experts in the field. Be sure to emphasize how important it is for you to make sure that your research is accurate and valid before drawing conclusions.
Example: “When I was working on a research project for ABC Corporation, I had to analyze the data from three different sources. My approach was to use statistical analysis techniques and software tools to cross-reference the data sets and identify any potential discrepancies or outliers. After analyzing the results, I identified a number of key trends that allowed us to draw meaningful conclusions about the company’s operations. The insights gained from this research ultimately led to improvements in the organization’s processes, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity.”
3. Describe a time when you had to analyze complex data sets and draw meaningful conclusions from them.
Research projects often involve a lot of data analysis and interpretation. Knowing how to take large amounts of data and make it into something meaningful is a valuable skill for any researcher. This question is a way for the interviewer to gauge your ability to work with data and draw meaningful conclusions from it.
You should be prepared to provide a specific example of when you had to analyze complex data sets and draw meaningful conclusions from them. Talk about the project, your approach to analyzing the data, and any insights or conclusions that you drew from it. Be sure to emphasize the impact of your findings on the project or organization as well.
Example: “I recently worked on a project for my previous employer in which I had to analyze a large and complex data set. My approach was to break down the data into smaller, more manageable chunks and then look for patterns or correlations between different variables. After doing this, I was able to identify a few key trends that were relevant to the project goals. This allowed us to make better decisions about how to allocate resources and focus our efforts, resulting in a successful outcome.”
4. Explain how you would go about designing an experiment or survey to answer a specific research question.
This question is designed to determine if you have the skills necessary to design and implement valid research experiments. The interviewer wants to know if you understand the fundamentals of research design, such as how to select a sample, how to develop a hypothesis, and how to determine the validity of a study. They also want to know if you can explain the process in a clear and concise manner.
Start by explaining the steps you would take to design an experiment or survey. You should include the following: defining the research question, selecting a sample, developing a hypothesis, creating a data collection plan, and determining how to analyze the results. Be sure to explain any specific techniques you might use in each step, such as random sampling or stratified sampling for your sample selection process. Finally, emphasize the importance of validating the results to ensure they are accurate and reliable.
Example: “When designing an experiment or survey, the first step is to define the research question. Once the research question has been identified, I would then select a sample that is representative of the population being studied. I would also develop a hypothesis based on my understanding of the research question and the available data. After that, I would create a data collection plan that outlines how the data will be collected, such as using surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Finally, I would determine the best method for analyzing the results in order to draw valid conclusions from the research. In all cases, it’s important to validate the results to ensure they are accurate and reliable.”
5. Are you familiar with any statistical software programs? If so, which ones?
Researchers often have to analyze data and present it in a meaningful way. This requires familiarity with statistical software programs like SPSS, SAS, or R. Knowing how to use these programs is a critical part of being a successful researcher, so this question is meant to gauge your level of expertise.
If you are familiar with any of the programs mentioned above, be sure to mention that and explain how you have used them in past research projects. If you are not familiar with these programs, it is still important to emphasize your ability to learn new software quickly. Explain how you approach learning new technologies and provide examples of times when you have successfully done so in the past.
Example: “I have used SPSS and SAS in my previous research projects. I am also comfortable with learning new statistical software programs, as I have done so on multiple occasions in the past. For example, when starting a new project at my last job, I was asked to learn R quickly in order to analyze data. Within two weeks, I had become proficient enough to use it for all of our research needs.”
6. What strategies do you use to stay organized while conducting research?
Research can be a long and complex process, with lots of data to sift through, organize, and analyze. It’s important to show the interviewer that you have a system in place to stay organized throughout the research process, from the initial research plan to the final report. This will demonstrate that you can effectively manage your time and resources, as well as prioritize tasks and remain focused on the task at hand.
You can answer this question by talking about the strategies you use to stay organized while conducting research. You could mention that you create detailed research plans, break down large tasks into smaller ones, and prioritize tasks based on importance and deadlines. Additionally, you could talk about how you utilize organizational tools such as spreadsheets and databases to store data, track progress, and easily access information when needed. Finally, you might also discuss how you take notes during your research process in order to keep track of important ideas or findings.
Example: “I use a variety of strategies to stay organized while conducting research. I always start by creating a detailed research plan that outlines the scope of my work and any deadlines associated with it. From there, I break down large tasks into smaller ones in order to tackle them more efficiently. Additionally, I prioritize tasks based on importance and deadlines in order to remain focused on the task at hand. To help store data, track progress, and access information quickly, I also utilize organizational tools such as spreadsheets and databases. Finally, I take notes during my research process in order to keep track of important ideas or findings.”
7. How do you handle ethical considerations when conducting research?
Research often involves collecting personal data, and it’s important that researchers understand how to approach these situations with respect and integrity. Interviewers want to know that you are aware of ethical considerations and that you are capable of adhering to them. This question is likely to be asked to all potential researchers, as it is an important part of the job.
Talk about the ethical considerations you take into account when conducting research. These can include obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring confidentiality and anonymity of data, respecting privacy laws, protecting vulnerable populations, and considering potential biases that may arise in your research. You should also mention any processes or protocols you have implemented to ensure ethical compliance with research projects. Finally, emphasize how important it is for researchers to adhere to ethical standards and how seriously you take them.
Example: “I understand the importance of adhering to ethical standards when conducting research, and I take this responsibility very seriously. In my current position as a researcher at ABC University, I follow a strict protocol for obtaining informed consent from participants and ensuring that data is kept confidential and anonymous. I also make sure to consider any potential biases in our research before collecting data and am familiar with applicable privacy laws. Lastly, I always strive to protect vulnerable populations, such as children or those with disabilities, when conducting research.”
8. Have you ever encountered a situation where you had to adjust your research methodology due to unexpected circumstances?
Research is a dynamic process and researchers must be prepared to adjust their methods as needed. This question is designed to assess the flexibility of potential candidates and their ability to think on their feet. It also provides insight into how well a candidate understands the research process, including how to identify and address potential problems.
To answer this question, provide an example of a situation where you had to adjust your research methodology due to unexpected circumstances. Explain how you identified the problem and how you adjusted your methods in order to successfully complete the project. Be sure to emphasize any creative solutions you implemented and the positive outcome that resulted from your adjustment.
Example: “I recently encountered a situation where I had to adjust my research methodology due to unexpected circumstances. I was conducting a survey to analyze consumer behavior in relation to a new product launch. After collecting the first round of data, I noticed a discrepancy in the results that could not be explained. After further investigation, I realized that the sample size I was using was not large enough to accurately capture the data. I quickly adjusted my methodology by increasing the sample size and collecting more data, which ultimately allowed me to identify the discrepancy and provide an accurate analysis of consumer behavior.”
9. Describe a time when you had to present your research findings in a clear and concise manner.
Researchers often have to communicate their findings to colleagues, stakeholders, and the public. The ability to communicate complex research findings in an understandable way is a key skill for someone in this role. This question allows the interviewer to gauge your ability to explain complex concepts in a clear and concise manner.
You should come prepared with an example of a time when you had to present your research findings. Talk about the project, what the goal was, and how you went about presenting it. If possible, provide specific details such as the type of presentation (oral, written, etc.), who you presented to, and the feedback you received. You should also explain the strategies that you used to make sure that the audience understood your message. This could include using visual aids, breaking down complex concepts into simpler terms, or providing examples to illustrate your points.
Example: “My most recent research project focused on the long-term effects of climate change on agricultural production. I knew that it was important to make sure that the findings were presented in a way that was easy to understand and digest. I created a PowerPoint presentation that included visuals and graphs to illustrate my points, as well as a written report that provided a detailed breakdown of the findings. I then presented my findings to a group of stakeholders and received positive feedback. They appreciated my ability to take complex concepts and explain them in a way that was easy to understand.”
10. Do you have experience working with large datasets?
Many research roles require the ability to work with large datasets and analyze the information within them. This question helps employers understand how comfortable you are with such tasks, and it also serves as a way to gauge your technical skills. To answer this question, talk about how you’ve used various tools and techniques to analyze data and how you’ve been able to draw meaningful insights from it.
Start by talking about the types of datasets you’ve worked with, such as structured or unstructured data, and explain how you’ve gone about analyzing them. Then, provide a few examples of projects you’ve completed that involved working with large datasets. Finally, discuss any tools or techniques you’ve used to work with the data, such as statistical software, data visualization tools, machine learning algorithms, etc. Be sure to emphasize your ability to draw meaningful insights from the data and how those insights have helped inform decisions.
Example: “I have experience working with large datasets in both structured and unstructured formats. I have utilized various tools and techniques to analyze the data, such as statistical software and data visualization tools. I’ve also employed machine learning algorithms to uncover patterns and trends from the data. For example, in my most recent project I utilized a variety of data sources to identify potential new markets for our company. Through analyzing the data, I was able to identify key demographic, geographic, and psychographic trends that we could use to target our new customers. This analysis provided valuable insights that informed our marketing strategy and ultimately led to increased sales.”
11. What challenges have you faced when collecting primary data for a research project?
Research often involves gathering primary data from sources such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations. It’s important to determine whether the candidate has the skills necessary to design and implement a research project in order to successfully collect data. This question helps the interviewer understand the candidate’s ability to handle the logistics and challenges of primary data collection.
When answering this question, it’s important to provide specific examples of challenges you have faced and how you overcame them. For example, you could talk about the challenge of finding participants for a survey or focus group, or the difficulty in scheduling interviews with busy professionals. You can also discuss any logistical issues that arose during data collection, such as having unreliable equipment or dealing with uncooperative participants. Be sure to emphasize your problem-solving skills and ability to think on your feet when facing unexpected obstacles.
Example: “I’ve encountered a few challenges when gathering primary data for research projects. For example, when I was working on a survey project for a university, it took me several weeks to find participants willing to answer the survey. I had to be creative in my approach and reach out to different groups, such as student organizations, to recruit participants. I also encountered a few logistical issues, such as having unreliable equipment or dealing with uncooperative participants. I was able to quickly come up with solutions to these issues, such as having backup equipment and developing strategies to engage the participants. Overall, I was able to successfully gather the data I needed and produce valuable research findings.”
12. How do you approach writing up a research paper or report?
Research is a process that requires both creativity and structure. As a researcher, you must be able to synthesize information from a variety of sources, develop strong arguments, and communicate those arguments clearly and concisely in written form. Being able to articulate your approach to researching and writing up a paper will demonstrate your ability to think critically and logically.
Your answer should include the steps you take when writing up a research paper or report. This could include outlining your topic, researching relevant sources, organizing and synthesizing data, developing an argument, drafting and revising the paper, and proofreading for accuracy. It is also important to emphasize how you use critical thinking skills to develop strong arguments and draw meaningful conclusions from your research. Finally, make sure to mention any specific techniques or strategies that you have used successfully in the past.
Example: “When writing up a research paper or report, I approach the task systematically. I begin by outlining my topic and any relevant research questions. I then conduct research to find relevant sources, both primary and secondary. I carefully review and analyze the information I find, and use it to develop my argument. After that, I draft and revise the paper, making sure to include evidence to support my points. Finally, I proofread for accuracy and clarity. Throughout the process, I strive to use critical thinking skills to ensure that my arguments are sound and my conclusions are meaningful.”
13. What techniques do you use to identify potential sources of bias in your research?
Researchers need to be able to identify potential sources of bias in their work, such as selection bias or confirmation bias, in order to ensure the accuracy of their data and the validity of their results. By asking this question, the interviewer is gauging your ability to identify potential sources of bias and how you handle them.
To answer this question, you should discuss the techniques you use to identify potential sources of bias in your research. This could include methods such as double-checking data for accuracy and completeness, using multiple sources of information, or conducting blind studies. Additionally, you can talk about how you handle any biases you may find, such as adjusting your research design or changing your methodology. Be sure to emphasize that accuracy and validity are important to you and that you take steps to ensure they remain a priority.
Example: “I understand the importance of accuracy and validity in research, so I always strive to identify and address any potential sources of bias. I use several techniques to identify bias, such as double-checking my data for accuracy and completeness, using multiple sources of information, and conducting blind studies. When I do identify a potential source of bias, I adjust my research design or change my methodology to address it. I also make sure to communicate any changes to my team and stakeholders to ensure that we’re all on the same page.”
14. How do you evaluate the quality of secondary sources used in your research?
One of the most important skills of a researcher is being able to evaluate the quality of sources used in research. This question allows the interviewer to get a better understanding of your research process and your ability to critically evaluate sources. It also allows them to gauge your level of experience in the field and your knowledge of the research landscape.
To answer this question, you should explain your process for evaluating secondary sources. You can talk about the criteria that you use to evaluate a source’s credibility such as its author or publisher, the date of publication, and any peer reviews that have been conducted on the source. Additionally, you can mention any methods you use to assess the accuracy of information in the source such as cross-referencing with other sources or conducting additional research on the topic. Finally, you should discuss how you use these evaluations to inform your own research.
Example: “When evaluating the quality of secondary sources I use in my research, I consider a few key factors. I always look at the author or publisher of the source, the date of publication, and any peer reviews that have been conducted. I also use a variety of methods to assess the accuracy of the information in the source, such as cross-referencing with other sources and conducting additional research. From there, I use my evaluations to inform my own research and determine how best to use the source. This helps me ensure that I’m using the most reliable and up-to-date sources in my research.”
15. What strategies do you use to keep track of changes in the field of research you are studying?
Research is an ever-evolving field and keeping up with changes in the field is essential to remain relevant and up to date. Interviewers want to know that you have the skills and strategies to stay on top of the latest research, trends, and developments in the field. They’ll be looking for evidence that you have the self-discipline and organizational skills to stay on top of your work and be able to provide timely, accurate research.
You should be prepared to discuss the strategies and tools you use to stay up-to-date on changes in your field. Talk about how you keep track of new research articles, publications, conferences, and other sources of information that are relevant to your work. You can also talk about how you use technology such as RSS feeds, social media, or email alerts to ensure that you’re aware of any news or updates related to your research. Additionally, mention any methods you have for organizing and cataloging the information you collect so it is easily accessible when needed.
Example: “To stay on top of changes in my field, I use a variety of strategies and tools. I subscribe to relevant RSS feeds and email alerts to ensure I’m aware of any new research articles or publications. I also use social media to follow industry leaders and experts in the field and get updates on their work. I also keep an organized library of research material that I have collected over the years. I use a combination of software tools and physical filing systems to keep track of all the information I need. This allows me to quickly access any information I need, when I need it.”
16. How do you decide which research questions to pursue?
Being a researcher requires the ability to prioritize and select the best questions to pursue in order to achieve the desired outcome. This question helps the interviewer get a sense of your process and how you approach problem solving. It also gives them an insight into your critical thinking skills, as well as your ability to analyze data and make meaningful conclusions.
The best way to answer this question is to provide a step-by-step approach of how you decide which research questions to pursue. Start by explaining the research process you go through, such as collecting data, analyzing it and forming hypotheses. Then explain how you prioritize certain questions based on their importance and relevance to the project at hand. Finally, discuss how you use your findings to make informed decisions about which questions are worth pursuing further.
Example: “When I’m deciding which research questions to pursue, I start by gathering all the available data related to the project. From there, I analyze the data to form hypotheses and then prioritize the questions based on their importance and relevance to the project. I also consider the impact each question could have on the overall outcome of the research. Once I have a list of the most important questions, I evaluate the data and use my findings to make informed decisions about which questions are worth pursuing further. Ultimately, my goal is to select the best questions that will yield the most meaningful results.”
17. What is your experience with peer review processes?
Peer review is a critical part of the research process. It requires that researchers review and critique each other’s work in order to ensure that the research is unbiased and credible. This question is a way for the interviewer to assess your knowledge of the research process and your ability to work with other researchers.
To answer this question, you should provide specific examples of your experience with peer review processes. Talk about how you have worked with other researchers to review and critique their work, as well as how you have incorporated feedback from peers into your own research. You can also discuss any challenges or successes you had during the process. Finally, emphasize your understanding of the importance of peer review in the research process and why it is necessary for producing high-quality results.
Example: “I have extensive experience with peer review processes, both as a reviewer and as an author. I have worked with other researchers to review their work and provide constructive feedback, as well as incorporating feedback from peers into my own research. I understand the importance of peer review in the research process and am committed to producing high-quality results. I have also had success in resolving disagreements between reviewers and authors when needed, and I have a strong track record of producing quality research that has been accepted for publication.”
18. How do you manage competing demands on your time when conducting research?
Research can be a demanding job, with a lot of deadlines, competing agendas, and complex data sets to analyze. The interviewer wants to make sure you can prioritize tasks, keep track of multiple projects, and adjust when needed. Your ability to manage competing demands on your time is a key indicator of how successful you will be at the job.
To answer this question, you should focus on how you prioritize tasks and manage deadlines. Talk about the strategies you use to stay organized, such as setting up a calendar or using task management tools. Also discuss any techniques you have for staying focused when there are multiple demands on your time. Finally, emphasize your ability to adjust your plans when needed, such as if an unexpected project comes in or a deadline needs to be moved up.
Example: “I have a few strategies for managing competing demands on my time when conducting research. I prioritize tasks by breaking them down into smaller, manageable chunks and then assigning deadlines to each one. I also use task management tools to keep track of what I need to do and stay organized. And I make sure to take regular breaks to stay focused and energized. When I need to adjust my plans due to unexpected events, I’m able to reassess and re-prioritize my tasks accordingly. I’m confident in my ability to manage competing demands on my time and stay organized when conducting research.”
19. What strategies do you use to ensure that your research remains relevant and up-to-date?
Research is a dynamic field, and the best researchers know that they need to stay informed of the latest developments and trends in order to remain relevant. This question allows your interviewer to assess your knowledge of the field and your commitment to keeping up with the latest research. It shows that you are aware of the need to stay ahead of the curve and that you have the skills to do so.
To answer this question, you should start by discussing the strategies that you use to stay informed. You can talk about how you read industry publications, attend conferences and seminars, or network with other researchers in your field. You should also mention any specific platforms or tools that you use to keep up-to-date on the latest research. Finally, you should explain why staying informed is important to you and how it helps you do better work.
Example: “I use a variety of strategies to ensure that my research remains relevant and up-to-date. I read industry publications, attend conferences and seminars, and network with other researchers to stay informed. I also use specific tools like Google Scholar and ResearchGate to keep track of new developments in my field. It’s important to me to stay ahead of the curve and make sure that my research is as current and relevant as possible. Doing so not only helps me do better work, but it also helps me to provide more value to my employer and contribute to the success of their projects.”
20. How do you ensure that your research meets the highest standards of academic integrity?
Research is the backbone of any organization, and it is crucial for a researcher to maintain the highest standards of academic integrity. Employers want to know that you understand the importance of being thorough and accurate, as well as ethical in your research. They may also want to know how you go about verifying the accuracy of your data and sources, and how you ensure that your research meets the standards expected in the field.
Start off by detailing the steps you take to ensure that your research meets academic integrity standards. For example, you can mention how you always double-check sources and data for accuracy and reliability, or how you use peer review processes to vet your work. Additionally, be sure to emphasize any specific techniques or methods you have used in the past to verify the validity of your findings. Finally, explain why it is important to you to maintain the highest level of academic integrity in your research.
Example: “I understand the importance of academic integrity and take it very seriously in my research. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy, I always double-check my sources and data, and use peer review processes to vet my work. Additionally, I frequently use replication studies to verify the validity of my findings. To me, it is essential to ensure that my research meets the highest standards of academic integrity, as it is the foundation of any successful research project.”
20 Interview Questions Every Data Center Engineer Must Be Able To Answer
20 help desk interview questions and answers, you may also be interested in..., 30 realtor interview questions and answers, 30 emergency room medical assistant interview questions and answers, 30 marketing manager interview questions and answers, 30 network support technician interview questions and answers.

Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional endeavors. They provide researchers with an opportunity to delve deep into the thoughts, experiences, and perspectives of an individual, thus enabling a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. It is important for researchers to design an effective and insightful method of data collection on a particular topic. A research interview is typically a two-person meeting conducted to collect information on a certain topic. It is a qualitative data collection method to gain primary information.
The three key features of a research interview are as follows:
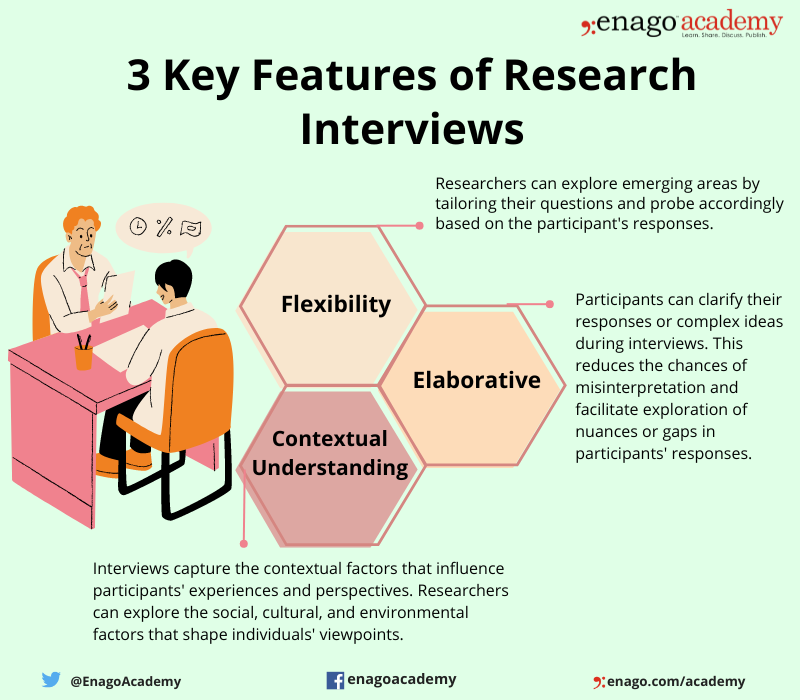
Table of Contents
The Significance of Research Interviews in Gathering Primary Data
The role of research interviews in gathering first-hand information is invaluable. Additionally, they allow researchers to interact directly with participants, enabling them to collect unfiltered primary data.
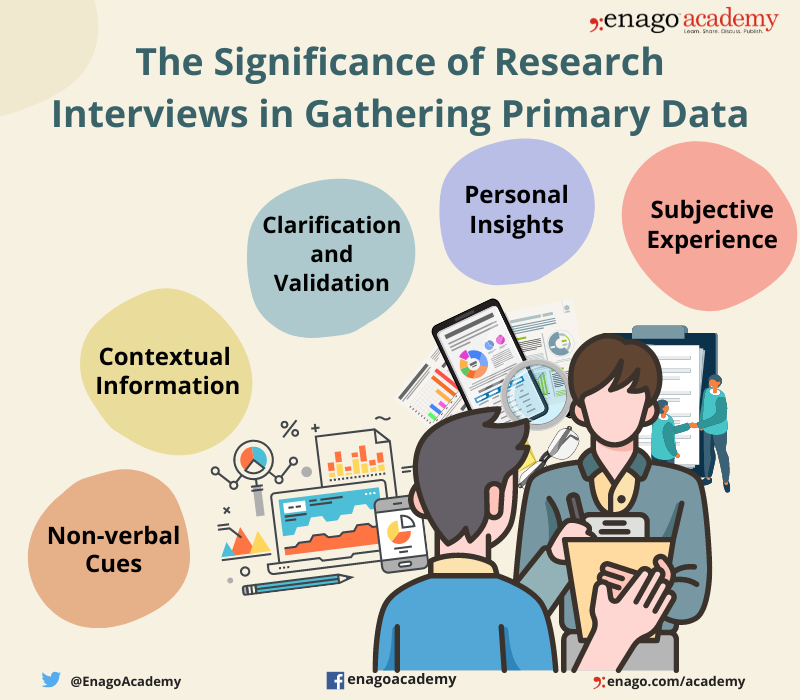
1. Subjective Experience
Research interviews facilitate in-depth exploration of a research topic. Thus, by engaging in one-to-one conversation with participants, researchers can delve into the nuances and complexities of their experiences, perspectives, and opinions. This allows comprehensive understanding of the research subject that may not be possible through other methods. Also, research interviews offer the unique advantage of capturing subjective experiences through personal narratives. Moreover, participants can express their thoughts, feelings, and beliefs, which add depth to the findings.
2. Personal Insights
Research interviews offer an opportunity for participants to share their views and opinions on the objective they are being interviewed for. Furthermore, participants can express their thoughts and experiences, providing rich qualitative data . Consequently, these personal narratives add a human element to the research, thus enhancing the understanding of the topic from the participants’ perspectives. Research interviews offer the opportunity to uncover unanticipated insights or emerging themes. Additionally, open-ended questions and active listening can help the researchers to identify new perspectives, ideas, or patterns that may not have been initially considered. As a result, these factors can lead to new avenues for exploration.
3. Clarification and Validation
Researchers can clarify participants’ responses and validate their understanding during an interview. This ensures accurate data collection and interpretation. Additionally, researchers can probe deeper into participants’ statements and seek clarification on any ambiguity in the information.
4. Contextual Information
Research interviews allow researchers to gather contextual information that offers a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Additionally, participants can provide insights into the social, cultural, or environmental factors that shape their experiences, behaviors, and beliefs. This contextual information helps researchers place the data in a broader context and facilitates a more nuanced analysis.
5. Non-verbal Cues
In addition to verbal responses, research interviews allow researchers to observe non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Additionally, non-verbal cues can convey information, such as emotions, attitudes, or levels of comfort. Furthermore, integrating non-verbal cues with verbal responses provides a more holistic understanding of participants’ experiences and enriches the data collection process.
Research interviews offer several advantages, making them a reliable tool for collecting information. However, choosing the right type of research interview is essential for collecting useful data.
Types of Research Interviews
There are several types of research interviews that researchers can use based on their research goals , the nature of their study, and the data they aim to collect. Here are some common types of research interviews:
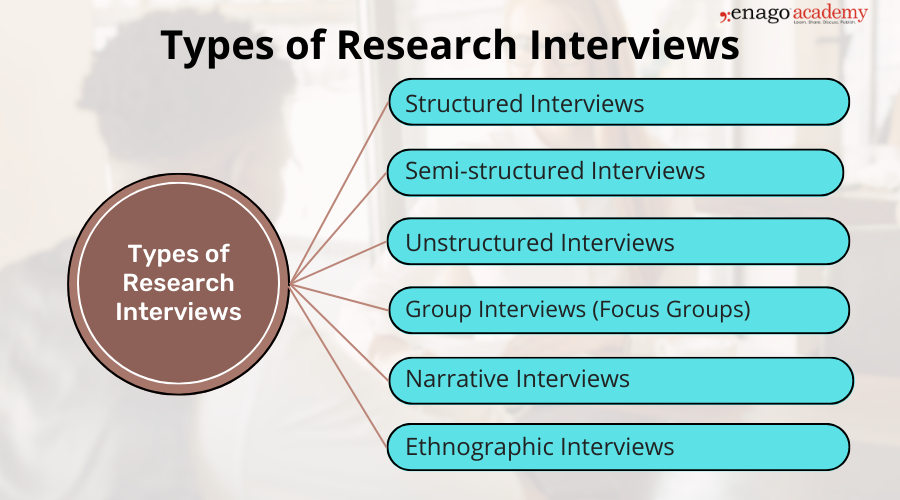
1. Structured Interviews
- Structured interviews are standardized and follow a fixed format.
- Therefore, these interviews have a pre-determined set of questions.
- All the participants are asked the same set of questions in the same order.
- Therefore, this type of interview facilitates standardization and allows easy comparison and quantitative analysis of responses.
- As a result, structured interviews are used in surveys or studies which aims for a high level of standardization and comparability.
2. Semi-structured Interviews
- Semi-structured interviews offer a flexible framework by combining pre-determined questions.
- So, this gives an opportunity for follow-up questions and open-ended discussions.
- Researchers have a list of core questions but can adapt the interview depending on the participant’s responses.
- Consequently, this allows for in-depth exploration while maintaining some level of consistency across interviews.
- As a result, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research, where content-rich data is desired.
3. Unstructured Interviews
- Unstructured interviews provide the greatest flexibility and freedom in the interview process.
- This type do not have a pre-determined set of questions.
- Thus, the conversation flows naturally based on the participant’s responses and the researcher’s interests.
- Moreover, this type of interview allows for open-ended exploration and encourages participants to share their experiences, thoughts, and perspectives freely.
- Unstructured interviews useful to explore new or complex research topics, with limited preconceived questions.
4. Group Interviews (Focus Groups)
- Group interviews involve multiple participants who engage in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic.
- This format allows the interaction and exchange of ideas among participants, generating a group dynamic.
- Therefore, group interviews are beneficial for capturing diverse perspectives, and generating collective insights.
- They are often used in market research, social sciences, or studies demanding shared experiences.
5. Narrative Interviews
- Narrative interviews focus on eliciting participants’ personal stories, views, experiences, and narratives. Researchers aim to look into the individual’s life journey.
- As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data.
- Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews.
6. Ethnographic Interviews
- Ethnographic interviews are conducted within the context of ethnographic research, where researchers immerse themselves in a specific social or cultural setting.
- These interviews aim to understand participants’ experiences, beliefs, and practices within their cultural context, thereby understanding diversity in different ethnic groups.
- Furthermore, ethnographic interviews involve building rapport, observing the participants’ daily lives, and engaging in conversations that capture the nuances of the culture under study.
It must be noted that these interview types are not mutually exclusive. Therefore, researchers often employ a combination of approaches to gather the most comprehensive data for their research. The choice of interview type depends on the research objectives and the nature of the research topic.
Steps of Conducting a Research Interview
Research interviews offer several benefits, and thus careful planning and execution of the entire process are important to gather in-depth information from the participants. While conducting an interview, it is essential to know the necessary steps to follow for ensuring success. The steps to conduct a research interview are as follows:
- Identify the objectives and understand the goals
- Select an appropriate interview format
- Organize the necessary materials for the interview
- Understand the questions to be addressed
- Analyze the demographics of interviewees
- Select the interviewees
- Design the interview questions to gather sufficient information
- Schedule the interview
- Explain the purpose of the interview
- Analyze the interviewee based on his/her responses
Considerations for Research Interviews
Since the flexible nature of research interviews makes them an invaluable tool for data collection, researchers must consider certain factors to make the process effective. They should avoid bias and preconceived notion against the participants. Furthermore, researchers must comply with ethical considerations and respect the cultural differences between them and the participants. Also, they should ensure careful tailoring of the questions to avoid making them offensive or derogatory. The interviewers must respect the privacy of the participants and ensure the confidentiality of their details.

By ensuring due diligence of these considerations associated with research interviews, researchers can maximize the validity and reliability of the collected data, leading to robust and meaningful research outcomes.
Have you ever conducted a research interview? What was your experience? What factors did you consider when conducting a research interview? Share it with researchers worldwide by submitting your thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform .
Frequently Asked Questions
• Identify the objectives of the interview • State and explain the purpose of the interview • Select an appropriate interview format • Organize the necessary materials for the Interview • Check the demographics of the participants • Select the Interviewees or the participants • Prepare the list of questions to gather maximum useful data from the participants • Schedule the Interview • Analyze the participant based on his/ her Responses
Interviews are important in research as it helps to gather elaborative first-hand information. It helps to draw conclusions from the non-verbal views and personal experiences. It reduces the ambiguity of data through detailed discussions.
The advantages of research interviews are: • It offers first-hand information • Offers detailed assessment which can result in elaborate conclusions • It is easy to conduct • Provides non-verbal cues The disadvantages of research interviews are: • There is a risk of personal bias • It can be time consuming • The outcomes might be unpredictable
The difference between structured and unstructured interview are: • Structured interviews have well-structured questions in a pre-determined order; while unstructured interviews are flexible and do not have a pre-planned set of questions. • Structured interview is more detailed; while unstructured interviews are exploratory in nature. • Structured interview is easier to replicate as compared to unstructured interview.
Focus groups is a group of multiple participants engaging in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic. This format allows for interaction and exchange of ideas among participants.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Personal tools
- Log in/Register Register

https://www.vitae.ac.uk/researcher-careers/pursuing-an-academic-career/applying-for-academic-jobs/commonly-asked-questions-in-academic-interviews
This page has been reproduced from the Vitae website (www.vitae.ac.uk). Vitae is dedicated to realising the potential of researchers through transforming their professional and career development.
- Vitae members' area
Commonly asked questions in academic interviews
Be prepared to answer the sort of questions in this list (which will be tailored to your research area) in addition to general interview questions. It is a good idea to prepare and even rehearse your answers. If you are confident in answering all of these you will be well-prepared.
About your research General research questions About you and your capabilities About your ability to gain funding About your proposed research About your role as supervisor/teacher About your ‘fit’ with the department
About your research
- What is innovative about your research ?
- How is your work distinct from your supervisor’s/principal investigator’s? How intellectually independent are you?
- What influences have you been exposed to? Do you think you have enough breadth of experience?
- Who has influenced you the most?
- What has been your role so far in developing research ideas and carrying them forward?
- What do you think are your most significant research accomplishments?
- What do you consider to be your best paper/work and why? What did it change about the way people approach the field?
- What are your most important publications?
- What has been the impact of your research?
- What papers do you have coming through in the next year?
- If we gave you the position what might go wrong? How will you manage the risks
General research questions
- What do you see yourself doing in ten years' time? What are your professional goals in the next five, and ten years?
- How will this job help you achieve your long term career plans?
- What would you do on the first day of the job?
- What are the big issues in your research area?
- Who are the key researchers in your area? How does your work compare with theirs?
- Who are your main competitors? What are they doing? How will you compete with them?
- Why would someone come to work for you and not for your competitors?
- How does your work align with contemporary trends or funding priorities?
- How would you bridge the gap from your research to research users?
- The university is keen to serve the wider community and economy. Does your planned research have any potential in these areas?
- How do you feel about translating your research into innovation or spin-outs? Can you give an example of when you have been enterprising?
- Describe in layman’s terms why your research project is interesting in two minutes.
About you and your capabilities
- How have you managed your research project?
- How do you balance your time? If several challenges came up at the same time (grant deadline, pastoral care for a student, teaching commitments) how would you prioritise?
- If you were starting your project again today, what would you do differently?
- Describe a research problem you have faced. What did you learn?
- What has been the most productive period in your research career and why?
- Why do you think you are ready for this position?
- If you get this position how will you run your research project?
- Why do you think you are the right person for this position?
About your ability to gain funding
- What experience do you have of attracting funding?
- Previously, you have only brought in small amounts of funding: how can you convince us you will be able to bring in larger amounts?
- Where will you apply for grants? If your funding applications are unsuccessful, what alternatives do you have in mind? (looking for knowledge of the funding infrastructure)
- How would you convince a funding body that they should fund your research rather than one of the other hundreds of proposals they receive?
- Who are you currently funded by, and why do you think they were interested in funding your project?
About your proposed research
- What will be your major focus as an independent researcher?
- In one sentence, what is the most important question you want to address?
- How does the work you propose follow on from what you are already doing?
- What will you focus on and what gives you a competitive edge in this area?
- What is the overall importance of this project? How do you see this work impacting the field?
- What will you do if your hypothesis is proved wrong? Can you see any of your research proposal failing?
- Why is the technique you have chosen more likely to succeed than other approaches?
- Have you already done anything to test the feasibility of your project?
- If you could only do one aspect of this project, which one do you think is key?
- If we gave you unlimited resources, what would you do with them?
- If we gave you X amount of money, what would you do with it?
- What resources will you need?
- How would you deal with the more limited resources or facilities compared to what you anticipate for the project?
- How do you plan to manage this project on a day-to-day level?
About your role as supervisor/ teacher
- Describe your teaching experience. How do you feel about teaching? What is your teaching philosophy?
- Do you have any experience in curriculum development?
- Have you supervised doctoral candidates, and how did you find this experience? How did you manage them?
- What advice would you give to a new researcher about supervising undergraduate or masters students?
- How would you go about interviewing a prospective postgraduate researcher?
- How would you induce a new doctoral candidate into their research project?
- How would you go about motivating a researcher who is going through a low point?
- How would you deal with a weak researcher?
- How would you deal with any conflict/disagreement within the research group? Do you have an example of when you have had to deal with a disagreement?
- Do you anticipate building a research group? How many people would you like for it to be optimal?

About your ‘fit’ with the department
- Why do you want to come here?
- What will you bring to the institution?
- We are keen to develop collaborations between departments. What opportunities for multi-disciplinary work does your research offer?
- How would you fit with the existing activities in the department? Who do would you expect to collaborate with in the institution? Why do you want to collaborate with them?
- What committee work have you done and what challenges has it presented?
- In what ways, other than research and teaching could you contribute to this department?
Bookmark & Share
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project
Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on October 19, 2023.
The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper , thesis or dissertation . It’s important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
The exact form of your question will depend on a few things, such as the length of your project, the type of research you’re conducting, the topic , and the research problem . However, all research questions should be focused, specific, and relevant to a timely social or scholarly issue.
Once you’ve read our guide on how to write a research question , you can use these examples to craft your own.
Note that the design of your research question can depend on what method you are pursuing. Here are a few options for qualitative, quantitative, and statistical research questions.
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, October 19). 10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-question-examples/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, evaluating sources | methods & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
IndianScribes
Research, Record, and Transcribe Better
Preparing Questions for a Qualitative Research Interview
Updated on: October 5, 2023

A qualitative research interview is an invaluable tool for researchers. Whether one’s studying social phenomena, exploring personal narratives, or investigating complex issues, interviews offer a means to gain unique insights.
“The quality of the data collected in a qualitative research interview is highly dependent on the quality and appropriateness of the questions asked.”
But how do you prepare the right questions to ensure your interviews yield rich data? In this guide, we’ll explore the types of qualitative research interviews and provide tips for crafting effective questions.
Table of Contents
Types of Qualitative Research Interviews
Before diving into question preparation, it’s important to select the type of qualitative research interview that’s best suited for the study at hand.
There are three types of qualitative research interviews:
Structured Interviews
Structured interviews involve asking the same set of pre-written questions to every participant. This approach ensures consistency, making it easier to compare data between participants or groups later.
When conducting structured interviews, keep these guidelines in mind:
- Pre-written Questions : All questions, including probes, should be meticulously written in advance.
- Detailed Questions : Questions should be detailed enough to be used verbatim during interviews.
- Consistent Sequence : The sequence of questions should be pre-decided and consistent across interviews.
Example of a Structured Interview Question
Question : Thinking back to your childhood days in Chelsea, can you remember what kind of local music was popular at the time?
- Why do you think it was so popular?
- Where was it played?
- Were there other popular genres?
Structured interviews are ideal when you need uniform data collection across all participants. They are common in large-scale studies or when comparing responses quantitatively.
Read more: Advantages & Disadvantages of Structured Interviews
Semi-structured Interviews
The second type of qualitative interviews are semi-structured interviews. In these interviews, the interview guide outlines the topics to be explored, but the actual questions are not pre-written.
This approach allows interviewers the freedom to phrase questions spontaneously and explore topics in more depth.
Example of a Semi-Structured Interview Question
Question : What problems did the participant face growing up in the community?
- Education-related.
- Related to their immediate family.
- Related to the community in general.
Semi-structured interviews strike a balance between flexibility and structure. They offer a framework within which interviewers can adapt questions to participants’ responses, making them suitable for in-depth exploration.
Unstructured Interviews
In unstructured interviews, often referred to as informal conversational interviews , are characterized by a lack of formal guidelines, predefined questions, or sequencing.
Questions emerge during the interview based on the conversation’s flow and the interviewee’s observations. Consequently, each unstructured interview is unique, and questions may evolve over time.
Unstructured interviews are highly exploratory and can lead to unexpected insights. They are particularly valuable when studying complex or novel phenomena where predefined questions may limit understanding.
Deciding What Information You Need
Once you’ve chosen the type of interview that suits your research study, the next step is to decide what information you need to collect.
Patton’s six types of questions offer a framework for shaping your inquiries:
- Behavior or Experience : Explore participants’ actions and experiences.
- Opinion or Belief : Probe participants’ beliefs, attitudes, and opinions.
- Feelings : Delve into the emotional aspects of participants’ experiences.
- Knowledge : Assess participants’ understanding and awareness of a topic.
- Sensory : Investigate how participants perceive and interact with their environment.
- Background or Demographic : Collect information about participants’ personal characteristics and histories.
Based on these categories, create a list of the specific information you aim to collect through the interview. This step ensures that your questions align with your research objectives.
Writing the Qualitative Research Interview Questions
After deciding the type of interview and nature of information you’d like to gather, the next step is to write the actual questions.
Using Open-Ended Questions
Open-ended questions are the backbone of qualitative research interviews. They encourage participants to share their experiences and thoughts in-depth, providing rich, detailed data.
Avoid ‘yes’ or ‘no’ questions, as they limit responses. Instead, use open-ended questions that grant participants the freedom to express themselves. Here are some examples –
Examples of Open-Ended Questions
How do you feel about working at ABC Corp. during your initial years there?
- Encourages participants to share their emotions and experiences.
Can you describe the attitudes and approach to work of the other people working with you at the time?
- Invites participants to reflect on their colleagues’ behaviors and attitudes.
Tell me more about your relationship with your peers.
- Encourages participants to provide narrative insights into their relationships.
Read More: 100 Open-Ended Qualitative Interview Questions
Going from Unstructured to Structured Questions
Unstructured Questions allow the interviewee to guide the conversation, letting them focus on what they think is most important.
These questions make the interview longer, but also provide richer and deeper insight.
Examples of Unstructured Questions
- Tell me about your experience working at [xxx].
- What did it feel like to live in that neighborhood?
- What stood out to you as the defining characteristic of that neighborhood?
Examples of Structured Questions
- What are some ways people dealt with the health issues caused by excessive chemical industries in the neighborhood?
- As an employee at ABC Corp. during the time, did you observe any specific actions taken by the employers to address the issue?
Probing Questions
Probing questions are used to get more information about an answer or clarify something. They help interviewers dig deeper, clarify responses, and gain a more comprehensive understanding.
Examples of Probing Questions
Tell me more about that.
- Encourages participants to elaborate on their previous response.
And how did you feel about that?
- Invites participants to share their emotional reactions.
What do you mean when you say [xxx]?
- Seeks clarification on ambiguous or complex statements.
Probing questions enhance the depth and clarity of the data collected, however they should be used judiciously to avoid overwhelming participants.
A General Last Question
As your interview approaches its conclusion, it’s beneficial to have a general last question that allows the interviewee to share any additional thoughts or opinions they feel are relevant.
For instance, you might ask:
Thank you for all that valuable information. Is there anything else you’d like to add before we end?
This open-ended question provides participants with a final opportunity to express themselves fully, ensuring that no critical insights are left unshared.
Preparing questions for qualitative research interviews requires a thoughtful approach that considers the interview type, desired information, and the balance between structured and unstructured questioning.
Here’s a great guide from the Harvard University on the subject.
6 Qualitative Research Methods
Read More »
Outsourcing Transcription of Research Interviews
- Choosing the Right Setting for a Qualitative Research Interview
- 5 Ways Researchers can Transcribe from Audio to Text
Reader Interactions
hlabishi says
April 8, 2015 at 12:37 pm
I found the information valuable. It will assist me a lot with my research work.
Harpinder says
June 8, 2015 at 10:40 pm
I am going for my pilot study. Above information is really valuable for me. Thank you.
September 28, 2015 at 10:21 am
thank you for Patton’s 6 types of questions related to: 1. Behavior or experience. 2. Opinion or belief. 3. Feelings. 4. Knowledge. 5. Sensory. 6. Background or demographic. Really helpful
IBRAHIM A. ALIYU says
October 7, 2015 at 6:04 pm
Very interesting and good guides, thanks a lot
Dumisani says
July 31, 2017 at 7:55 am
Very informative. Thank you
Yongama says
June 5, 2018 at 11:57 pm
this is a good information and it helped me
Joshua Nonwo says
June 3, 2019 at 11:02 pm
vital information that really help me to do my research. thank you so much.
June 12, 2019 at 7:36 pm
Thanks a lot. Example of structured interview broadens My mind in formulating my structured research question. Indeed very helpful.
mwiine says
November 29, 2019 at 6:31 am
thanx, a lot. the information will guide me in my research.
Kayayoo isaac says
November 29, 2019 at 7:54 am
Thanks for the information, it was very much helpful to me in the area of data collection.
leslie says
December 27, 2019 at 4:29 pm
very useful thanks.
louisevbanz says
January 20, 2020 at 3:19 pm
I’d like put the writers of this in my references. May I ask who the writers are and what year was this published? Thank you very much.
Daniel says
June 1, 2020 at 6:21 pm
Thank you very much. Helpful information in my preparations for structured interviews for my research .
abby kamwana says
December 8, 2020 at 9:03 am
This is the information i was looking for thank you so much!.
Cosmas W.K. Mereku (Prof.) says
June 15, 2021 at 8:59 am
I am teaching 42 MPhil and 6 PhD postgraduate music students research methods this academic year. Your guide to qualitative research interview questions has been very useful. Because the students are in different disciplines (music education, music composition, ethnomusicology and performance), all the types of questions discussed have been very useful. Thank you very much.
Gerald Ibrahim b. says
June 16, 2021 at 12:45 pm
One of my best article ever read..thanks alot this may help me in completing my research report…
Corazon T. Balulao says
March 1, 2022 at 7:47 am
Thank you so much for sharing with us it helps me a lot doing mt basic research
antoinette says
March 28, 2022 at 7:35 am
this was very helpful
พนันบอล เล่นยังไง says
November 21, 2023 at 5:55 am
Very good article! We are linking to this particularly great article on our website. Keep up the good writing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Transcription
- Qualitative Research
- Better Audio & Video
- Voice Recorders
- Focus Groups
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
Privacy Overview
15 Research Interviewer Interview Questions (With Example Answers)
It's important to prepare for an interview in order to improve your chances of getting the job. Researching questions beforehand can help you give better answers during the interview. Most interviews will include questions about your personality, qualifications, experience and how well you would fit the job. In this article, we review examples of various research interviewer interview questions and sample answers to some of the most common questions.

or download as PDF
Common Research Interviewer Interview Questions
How did you get interested in research, what are your current research projects, what are your future research goals, what motivates you to pursue research, what benefits have you found in conducting research, what difficulties have you encountered while conducting research, how do you design research projects, how do you select participants for your research studies, how do you collect data in your research studies, how do you analyze data in your research studies, how do you report results from your research studies, how do you use technology in your research, what ethical considerations do you take into account when conducting research, what impact do you hope your research will have, what advice would you give to someone who is considering a career in research.
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question. First, it can help the interviewer understand the research process and how the interviewee became involved in it. Second, it can help the interviewer assess the interviewee's commitment to research and their ability to communicate their interest in it. Finally, it can help the interviewer understand the interviewee's motivations for conducting research and whether they are likely to be able to continue doing so in the future.
Example: “ I have always been interested in finding out how things work and why they happen the way they do. This curiosity led me to pursue a degree in psychology, which gave me the opportunity to learn about research methods and design. After graduation, I worked as a research assistant on a number of projects, which allowed me to gain experience in conducting research. I enjoyed the process of collecting data and analyzing it to see what patterns emerged. This experience solidified my interest in research and made me want to pursue a career as a research interviewer. ”
The interviewer wants to know what the research interviewer is working on and how it is relevant to the research being conducted. This helps the interviewer determine if the research interviewer is knowledgeable about the topic and if they can contribute to the research.
Example: “ My current research projects include studying the effects of climate change on plant growth and development, as well as investigating the role of plants in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, I am also looking at how different land management practices can impact soil health and carbon sequestration. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask about your future research goals. First, they may be interested in knowing what direction your research is heading and whether your goals align with the mission of the organization. Second, they may want to know if you are planning on continuing your research career and, if so, whether you plan on staying with the organization. Finally, they may be interested in knowing what kinds of projects you are interested in pursuing in the future and whether you have the skills and experience to successfully complete them.
Example: “ My future research goals include continuing to work on understanding the mechanisms underlying disease development and progression, as well as identifying new therapeutic targets for treating disease. Additionally, I hope to continue to develop my skills in data analysis and modeling, in order to more effectively utilize large-scale data sets in my research. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question. First, they may be trying to gauge your interest in the research field and whether you are truly passionate about it. Second, they may be trying to assess your motivation for pursuing research in general. This is important because it can help them determine whether you are likely to stick with the research field and whether you are likely to be productive. Finally, they may be trying to get a sense of your goals and objectives for pursuing research. This is important because it can help them understand how your research interests align with the goals of the organization and whether you are a good fit for the position.
Example: “ There are many reasons that motivate me to pursue research. I am driven by the curiosity to understand how the world works and to discover new knowledge. I also enjoy the challenge of solving complex problems and the satisfaction that comes with finding new solutions. Additionally, I believe that research has the potential to make a positive impact on society, and I am passionate about using my skills and knowledge to improve the lives of others. Finally, I find the process of conducting research to be immensely rewarding, as it allows me to work collaboratively with others, learn new skills, and share my findings with the scientific community. ”
There are many benefits to conducting research, such as gaining new knowledge, understanding complex issues, and developing new solutions to problems. Conducting research can also help build credibility and improve decision-making.
Example: “ There are many benefits to conducting research, including gaining new knowledge and understanding of a topic, developing new skills and ways of thinking, and making new discoveries. Research can also lead to new insights and perspectives on familiar topics, and can help to solve problems and find solutions to challenges. Additionally, research can be a source of satisfaction and enjoyment, and can provide opportunities to work with others in a collaborative environment. ”
The interviewer is trying to gauge the interviewee's research experience and whether they are able to overcome difficulties. This is important because it shows whether the interviewee is able to persevere in the face of challenges and still produce quality work.
Example: “ The main difficulty I have encountered while conducting research is getting people to agree to be interviewed. Often times, people are either too busy or not interested in participating in research. In order to overcome this, I have had to get creative with my approaches and offer incentives for people to participate. Another difficulty I have encountered is when people do not want to answer certain questions truthfully. This can be frustrating because it can skew the results of the research. To combat this, I try to build rapport with the interviewee and create a comfortable environment where they feel they can be honest with me. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question to a research interviewer. First, the interviewer wants to know if the research interviewer is familiar with the process of designing research projects. This is important because the research interviewer will need to be able to design research projects that are both ethical and effective. Second, the interviewer wants to know if the research interviewer is familiar with the different types of research designs that are available. This is important because the research interviewer will need to be able to select the most appropriate design for each project. Finally, the interviewer wants to know if the research interviewer has a good understanding of the principles of research design. This is important because the research interviewer will need to be able to apply these principles to the design of each project.
Example: “ There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the design of research projects will vary depending on the specific topic being investigated and the goals of the researcher. However, there are some general principles that can be followed in order to ensure that research is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner. Firstly, it is important to clearly define the research question or problem that is being addressed. This will help to focus the research and ensure that all data collected is relevant to the question at hand. Once the research question has been defined, a literature review should be conducted in order to gain an understanding of previous work on the topic. This will allow the researcher to build on existing knowledge and identify any gaps in the literature that need to be addressed by the current study. After the literature review has been completed, a research design should be developed which outlines how data will be collected and analysed. This should be done in a way that will allow the researcher to answer the research question as effectively as possible. Once the research design has been finalised, ethical approval may need to be obtained before data collection can begin. Finally, once data has been collected, it should be analysed and interpreted in order to draw conclusions about the research question. ”
An interviewer might ask this question to get a sense of how the research interviewer goes about finding participants for their studies. It is important to know how research interviewers select participants because it can affect the validity and reliability of the data that is collected. If the selection process is not done carefully, it can introduce bias into the data.
Example: “ There are many ways to select participants for research studies. Some common methods include convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and quota sampling. Convenience sampling involves selecting participants who are easily accessible or available. Snowball sampling involves selecting participants through referrals from other participants. Quota sampling involves selecting a certain number of participants from each subgroup in a population. ”
There are a few reasons an interviewer might ask this question:
1. To gauge the research interviewer's methodology. It is important to collect data in a systematic and reliable way in order to produce valid results.
2. To see if the research interviewer is familiar with different data collection methods and can select the most appropriate one for the study at hand.
3. To assess the research interviewer's ability to plan and execute a study from start to finish.
4. To determine whether the research interviewer is able to troubleshoot and adapt if problems arise during data collection.
In general, it is important for the interviewer to have a clear understanding of the research process and be able to explain their methodology in detail. This question allows the interviewer to assess the interviewee's knowledge and skills in this area.
Example: “ There are a number of ways to collect data in research studies, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observation. The most appropriate method of data collection depends on the research question being asked and the type of data needed to answer that question. Surveys are a common method of data collection in social science research. Surveys can be administered in person, by phone, or online. When administering a survey, it is important to ensure that the questions are clear and concise, and that the response options are mutually exclusive and exhaustive. Interviews are another common method of data collection in social science research. Interviews can be conducted in person or over the phone, and can be structured or unstructured. When conducting an interview, it is important to establish rapport with the interviewee and to ask open-ended questions that allow the interviewee to elaborate on their answers. Focus groups are another common method of data collection in social science research. Focus groups typically involve a small group of people who are brought together to discuss a particular topic. The discussion is led by a moderator, and participants are encouraged to share their thoughts and opinions on the topic under discussion. Observation is another common method of data collection in social science research. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question:
1. To better understand the research process and how the interviewee uses data to inform their research studies.
2. To gauge the interviewee's level of experience and expertise in data analysis.
3. To assess the interviewee's ability to critically analyze and interpret data.
4. To determine if the interviewee is able to effectively communicate their findings to others.
5. To identify any areas where the interviewee might need improvement in their data analysis skills.
Overall, it is important for the interviewer to understand how the research interviewee analyzes data in their studies as this can give insights into the effectiveness of the research and the quality of the data. Additionally, this question can help to identify any areas where the interviewee could use additional training or development in order to improve their research skills.
Example: “ There are many ways to analyze data in research studies. Some common methods include statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, and comparative analysis. ”
The interviewer is trying to gauge the research interviewer's ability to communicate their findings. It is important for the research interviewer to be able to communicate their findings in a clear and concise manner.
Example: “ There are a few different ways to report results from research studies. One way is to publish the results in a scientific journal. This is often the most prestigious way to report results, as it allows other scientists to review and comment on the work. Another way to report results is to present them at a scientific conference. This allows scientists to discuss the work in person and can be a good way to get feedback from other researchers. Finally, some researchers choose to post their results on an online database, such as the National Institutes of Health's PubMed website. This allows anyone with an internet connection to access the results of the study. ”
The interviewer is trying to determine how the research interviewer uses technology in their work. This is important because it can help the interviewer understand how the research interviewer uses technology to collect and analyze data, as well as how they use technology to communicate with colleagues and clients.
Example: “ I use technology in my research in a few different ways. I use online databases to find sources, I use social media to connect with other researchers, and I use online tools to help me organize my research. I find that using online databases is a great way to find sources that I wouldn’t be able to find otherwise. I can search for specific keywords and narrow down my results to get exactly what I’m looking for. I also like being able to access sources from anywhere, so I can do my research from anywhere. I use social media to connect with other researchers and get ideas for my research. I follow experts in my field and see what they’re talking about. I also join online communities of researchers and participate in discussions. This helps me get new ideas and perspectives on my research. Finally, I use online tools to help me organize my research. I use a tool called Evernote to keep all my notes in one place, and I use a tool called Zotero to keep track of all the sources I’ve used. These tools help me stay organized and efficient in my research. ”
There are a few ethical considerations that an interviewer should take into account when conducting research. First, it is important to get informed consent from the participants. This means that the participants should be made aware of the nature of the research, what will be expected of them, and they should give their voluntary consent to participate. Second, the interviewer should protect the participants' confidentiality and anonymity. This means that the participants' names and other identifying information should not be shared without their consent. Third, the interviewer should ensure that the participants are not harmed in any way during the research. This means that the interviewer should take precautions to ensure the safety of the participants and avoid any potential physical or psychological harm.
Example: “ There are a number of ethical considerations that need to be taken into account when conducting research. These include: 1. Informed consent: This means that participants must be fully informed about the nature and purpose of the research before they can give their consent to take part. They should also be made aware of any risks or potential discomfort that could be associated with taking part. 2. Confidentiality: Participants must be assured that their identity will remain confidential and that any information they provide will not be used for any other purpose than the research itself. 3. anonymity: This means that participants must not be identifiable in any way from the data collected. This can sometimes be difficult to achieve, particularly if the research is being conducted online. 4. Respect for autonomy: This means that participants must be free to withdraw from the research at any time and without giving any reason. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question. First, they want to know if the research is important to the interviewee and if they are passionate about the topic. Second, they want to know if the interviewee has thought about how their research could make a difference in the world. This question allows the interviewer to gauge the interviewee's level of commitment to their research and its potential impact.
Example: “ I hope that my research will help to improve the understanding of the issue at hand and contribute to finding solutions that can improve the situation. ”
There are many reasons why an interviewer might ask this question to a research interviewer. It is important to remember that research is a very important part of any company or organization, and it is vital to the success of any project. Without good research, a company or organization can easily make bad decisions that can lead to failure.
One of the most important things to remember when considering a career in research is that it is important to be very patient. Research can be a very slow process, and it can take a long time to get results. It is also important to be very detail oriented, as even the smallest details can make a big difference in the outcome of a project.
Another important thing to keep in mind when considering a career in research is that it is important to be able to work well with others. Research is often done in teams, and it is important to be able to communicate effectively with other members of the team.
Overall, it is important to remember that a career in research can be very rewarding, but it is also important to be aware of the challenges that come along with it.
Example: “ There are a few things to keep in mind if you're considering a career in research. First, it's important to be aware of the different types of research careers available and to choose one that aligns with your interests and skills. Second, it's essential to have strong communication and writing skills, as well as the ability to effectively collaborate with others. Finally, it's important to be prepared for the long hours and dedication required to succeed in research. ”
Related Interview Questions
- Market Research Interviewer
- Telephone Interviewer
- Field Interviewer
- Research and Development Engineer
- Research Nurse
- Research Administrator

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
10 Common Job Interview Questions and How to Answer Them
- Vicky Oliver

Use this guide to stand out from the crowd and land the role you want.
Interviews can be high stress, anxiety-driving situations, especially if it’s your first interview. A little practice and preparation always pays off. While we can’t know exactly what an employer will ask, here are 10 common interview questions along with advice on how to answer them. The questions include:
- Could you tell me something about yourself and describe your background in brief? : Interviewers like to hear stories about candidates. Make sure your story has a great beginning, a riveting middle, and an end that makes the interviewer root for you to win the job.
- How do you deal with pressure or stressful situations? : Share an instance when you remained calm despite the turmoil. If it’s a skill you’re developing, acknowledge it and include the steps you’re taking to respond better to pressure in the future.
- What are your salary expectations? : Before you walk in for your first interview, you should already know what the salary is for the position you’re applying to. Check out websites such as Glassdoor, Fishbowl, or Vault.com for salary information. You could also ask people in the field by reaching out to your community on LinkedIn.
Where your work meets your life. See more from Ascend here .
Resignation numbers have remained abnormally high in the U.S. between July 2021 and October 2021, with millions of Americans quitting their jobs — which also means there are millions of new openings up for grabs. If you’re entering the market for the first time, or just looking to make a change, use this guide to prepare for your next interview.
- Vicky Oliver is a leading career development expert and the multi-best-selling author of five books, including 301 Smart Answers to Tough Interview Questions , named in the top 10 list of “Best Books for HR Interview Prep.” She’s a sought-after speaker and seminar presenter and a popular media source, having made over 900 appearances in broadcast, print, and online outlets.
Partner Center
Skip navigation
- Log in to UX Certification

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Planning research with generative ai.

April 5, 2024 2024-04-05
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
AI chatbots (like ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot) can support UX researchers of all experience levels in planning their research.
In This Article:
What is a research plan, using ai chatbots to write a research plan.
Good research always starts with a plan.
A research plan is a document that outlines the research objectives and how the research will be executed.
Research plans should include:
- The research goals or questions that the research is hoping to achieve or answer
- The method to be used and a description of how it will be carried out
- The tasks or questions that will be given to study participants
- The profile of the target participants
- The screener questionnaire used to recruit participants
Creating a research plan can be time-consuming. Even with a good template, a researcher must generate research questions, select the appropriate method(s), decide how to run sessions, and often create study collateral (like screeners and tasks) from scratch. The good news is that AI can help with many, if not all, of these tasks!
It can be tempting to just ask an AI tool to give you a research plan for a project. Don’t do that.
❌ Bad Prompt : Generate a research plan for a usability test of a food-delivery app.
This kind of request results in a generic, template-like response, partly because AI lacks the context to propose a complete research plan and partly because of how the model has been trained.
To construct a useful research plan, deconstruct the plan into parts and have the AI chatbot tackle each part individually. You can assemble responses in a final research plan.

Don’t expect the AI to ask you the right questions in order to get a comprehensive outcome. View the AI tool as a UX assistant , not as a UX mentor. You need to feed into the AI all the steps and details you want it to consider.
Follow the steps below for the best results.
Step 1: Provide Context
Imagine asking an experienced colleague for recommendations on what research study to run without giving them any context on what project you’re working on and what you’re trying to achieve. They would probably say, "It depends on what you’re trying to learn.” Conversing with AI presents no exception.
Start your conversation with enough context , especially if the AI tool does not already have this information stored about you or your current project. ( ChatGPT 4 allows users to store context for each new conversation.)
The contextual information you share should include who you work for, the scope of your project, and what you’re looking to achieve. Remember that some AI tools may use your conversations to train their models, so share only information you would be comfortable with being in the open domain.
Prompt Template: I work for [type or organization] . My company provides [what kind of product, service, or experience] . I need to run a user-research study to learn [something about users or a problem] .
Step 2: Generate Research Questions
After providing the AI tool with context, ask it to suggest specific research questions for the study. Here’s an example from a recent study on research repositories that I conducted for NN/g.
Prompt Example: I will run a research study and report on how UX practitioners across different organizations set up and use research repositories. Please generate 10 research questions that would be suitable for this sort of study.
It’s a good idea to ask generative AI tools for more options or ideas than you think you’ll need, because some will not be a good fit.
Microsoft Copilot responded to the prompt above with the 10 research questions below.
10 Research questions generated by Microsoft Copilot
Who are the primary users of the research repository within different organizations? What motivates users to engage with the research repository? How do different teams (design, product, sales, marketing) access and benefit from the research repository? What challenges do practitioners face when contributing to or retrieving information from the repository? What types of research artifacts (reports, raw data, templates) are most commonly stored in the repository? How do organizations structure their research repositories? What tools and templates are commonly used to facilitate research repository management? How do practitioners ensure the quality and accuracy of information in the repository? What impact does the research repository have on decision-making and project outcomes? What strategies can organizations implement to encourage widespread adoption and active participation in the research repository?
To broaden your pool of research questions, ask for further research questions or provide the same prompt in a new session. Repeat this process as many times as you need to generate a list that feels exhaustive of what you’d like to learn.
Some of the research questions Copilot generated for me were appropriate, and others were not. As a result, I had AI generate more research questions to choose from.

Unfortunately, most AI chatbots don’t offer an easy way to dismiss suggestions or combine specific responses and work from only these (a behavior called apple-picking ).
Pulling in generated research questions into an offline document (like a FigJam or Google Doc) allows you to easily group items, remove duplicates, or reword suggested research questions.

Begin a new chat session with your selected and refined set of research questions, so that the unwanted research questions are removed from the chat history.
Step 3: Request Methods
After sharing the context and your chosen research questions, ask the AI tool to identify suitable research methods.
Example Prompt : What study would you suggest to answer these research questions? Please be specific; cite which research questions would be answered by which research method if you suggest multiple methods.
Generative-AI advice is not always good advice. Often, these tools will suggest various methods and suggest you triangulate data from multiple sources. This approach is not always needed. Also, not all methods will be practical or the best fit for your study. Additionally, AI may suggest interviews and focus groups even for research questions better suited to a behavioral research method .
Ask AI chatbots to tell you which research methods would be suited to which research question and why. We also recommend doing some further reading on your own about any methods that are unfamiliar to you.
In response to the prompt above (and given my chosen research questions), ChatGPT recommended a survey, interviews with select UX practitioners, and case studies. These were all my chosen methods, so AI had done well here!
Step 4: Request Inclusion Criteria
AI can create inclusion criteria — a necessary component of your research plan. Do this step only after generating research questions and methods since these will inform who should participate in the research study.
Inclusion criteria (or recruitment criteria) are specific characteristics of the target population that need to be represented in your sample.
Start with inclusion criteria before asking the AI to help you write a screening questionnaire ; AI can only craft an appropriate screener after it “knows” who you’re looking to recruit.
Example Prompt: So that I recruit the right people for my interviews, help me create some inclusion criteria. What characteristics or behaviors should I recruit for?
Step 5: Request Help with Screeners, Interview Questions, and Tasks
Finally, ask the AI to put together:
- Interview questions or an interview guide (if conducting interviews)
- Tasks for a usability test
- Diary-study prompts (if relevant)
- Recruitment confirmation emails or other communication messages.
Unfortunately, there are a lot of bad examples of the above on the web. Conversational AI has been trained on all this data. Therefore, don’t be surprised if it produces poor study collateral on its first attempt! This is a major risk area for new researchers.
One way to mitigate this danger is to give the AI tool advice when crafting any of these outputs . Think of AI as a new research assistant who can learn extremely quickly.
Common mistakes that AI tools make include:
- Using words that appear in the interface in task instructions (priming)
- Creating task instructions that ask users to imagine they are someone that they are not
- Not including a goal or a call to action in the task instruction
- Not including distractor options in screening questionnaires
- Using overenthusiastic marketing language in recruitment materials
It’s not surprising that AI makes these mistakes since UX practitioners also make them!
To improve outputs, feed the AI essential tips, such as:
- When crafting tasks: Do not use the name of words or link labels in the task instruction. Find a natural-language equivalent to explain what the participant should do . (You can ask AI to “read” a website or an image.)
- When crafting recruitment materials: Use neutral and concise language in the recruitment email. Avoid using overly enthusiastic marketing language.
- When crafting a screener: Include multiple-choice questions and answer options that might disguise what the study is about and who I am looking to recruit.
Additionally, when possible, feed the AI with good examples of screener questionnaires, tasks, or interview questions, so it can follow their format or style.
Even with this advice, AI can still make mistakes. If you’re doubting its answers, check primary sources or speak with an experienced researcher for old-fashioned human guidance.
If you have ChatGPT’s Plus Plan, you can use our GPT for planning your research.
With the proper context, examples, and advice, AI tools, like ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot, can craft helpful research questions, tasks, interview questions, and other study collateral far more quickly than you could if you started from scratch.
Research leads and ResearchOps personnel can support junior researchers and PWDRs (People Who Do Research) by providing examples and advice that can be fed to AI agents. Experienced researchers can benefit from using AI to speed up their research-planning process and obtain further inspiration.
Free Downloads
Related courses, practical ai for ux professionals.
Leverage artificial intelligence tools to enhance your UX work and save valuable time
Interaction
ResearchOps: Scaling User Research
Orchestrate and optimize research to amplify its impact
Analytics and User Experience
Study your users’ real-life behaviors and make data-informed design decisions
Related Topics
- Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence
- Research Methods
Learn More:

AI on Intranets: 5 Valuable Features
Anna Kaley · 3 min

ELIZA Effect: Why We Fall in Love With AI
Caleb Sponheim · 3 min

Is Aggressive Marketing Influencing the UX of AI Agents?
Jakob Nielsen · 2 min
Related Articles:
Generative UI and Outcome-Oriented Design
Kate Moran and Sarah Gibbons · 6 min
AI Chat Is Not (Always) the Answer
Sarah Gibbons and Kate Moran · 5 min
The UX of AI: Lessons from Perplexity
Kate Moran · 5 min
Response Outlining with Generative-AI Chatbots
Tarun Mugunthan · 3 min
Sycophancy in Generative-AI Chatbots
Caleb Sponheim · 4 min
Prompt Structure in Conversations with Generative AI
Raluca Budiu, Feifei Liu, Amy Zhang, and Emma Cionca · 16 min
- Side Hustles
- Power Players
- Young Success
- Save and Invest
- Become Debt-Free
- Land the Job
- Closing the Gap
- Science of Success
- Pop Culture and Media
- Psychology and Relationships
- Health and Wellness
- Real Estate
- Most Popular
Related Stories
- Land the Job The No. 1 trait employers are looking for right now—and how to show you have it
- Land the Job The most common job-search mistake young workers make
- Land the Job The No. 1 reason people 'fail' job interviews, says ex-Amazon recruiter: 'It causes a lack of trust'
- Land the Job How to use ChatGPT to prep for a job interview, says ex-Disney recruiter
- Work Forgetting this job interview step is an 'easy strike' against you
The most important question to ask in a job interview, according to a LinkedIn expert

There are plenty of good questions to ask during a job interview to get to know your potential new employer.
While some of the best questions show you're interested in the future of the company (like, 'What's the expected growth of the team ?'), one question in particular can clue you in on how the company invests in the future of their employees.
"The most important question to ask before you accept a job is: What is your culture of learning?" says Aneesh Raman, a vice president and workforce expert at LinkedIn.
The workplace has changed tremendously in recent years among rapid tech advancements, shifts in where work gets done, and even an uncertain economic picture.
"We don't know so much of what's coming," Raman says, "but one thing we know is that organizations that build a culture of learning, and that have employees who lean into that culture of learning, are going to be able to adapt."
DON'T MISS: The ultimate guide to acing your interview and landing your dream job
It could also lead to a better employee experience: 7 in 10 people say learning improves their sense of connection to their organization, and 8 in 10 say it adds purpose to their work, according to LinkedIn .
What to listen for
Listen closely to how the hiring manager responds. More than likely, Raman says, they'll be able to tell you about the onboarding process, periodic training for cybersecurity and legal purposes, and maybe access to online courses like LinkedIn or Coursera.
These offerings are pretty typical but don't address the actual culture of learning, Raman says.
Instead, listen for evidence of the following six components of a culture of learning, according to LinkedIn expert Britt Andreatta :
- Learning opportunities aren't just limited to scheduled courses.
- Leaders encourage risk-taking, failure and learning from mistakes to innovate.
- Employees are empowered to find their own answers through on-demand resources.
- The organization provides both in-person and virtual, on-demand learning opportunities.
- Managers ask coaching questions — think: "How can I help you do your work?"
- Learning is part of the performance evaluation, and improvement is rewarded.
Junior workers may especially benefit from asking how managers promote a culture of learning, Raman says.
"Part of that culture of learning is learning how to work well with others," he says. Young professionals "need real coaching about corporate speak and corporate culture and things like what you're supposed to do in meetings."
He suggests asking about how a culture of learning extends to the day-to-day like through working with managers and other senior leaders to learn the ropes of the professional world.
Gauge the learning culture through other employees
Another good way to tell if employees are encouraged to learn and grow is to figure out who's actually doing it at the company.
For example, ask why the position you're interviewing for is vacant . Did the previous employee get promoted in the same line of work? Did they have the opportunity to train in a different department and move across the organization?
Take a look at some of the employees' LinkedIn profiles: Do people generally stay with the company for a long time? Do they often get promoted or gain access to stretch opportunities, like leading big projects or launching new initiatives?
You might also be able to speak with other members of the team about their experience over time.
It can also be a good idea to ask how learning and development is linked to the company's overall business goals, says Stephanie Conway, senior director of talent development at LinkedIn.
"Make sure to use the end of the interview to ask explicitly how learning plays into career growth and advancement at the company," she says.
A company that values training its employees should have a proven track record of employees growing within the organization.
Want to land your dream job in 2024? Take CNBC's new online course How to Ace Your Job Interview to learn what hiring managers are really looking for, body language techniques, what to say and not to say, and the best way to talk about pay.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
9. Describe a time when you had to present your research findings in a clear and concise manner. Researchers often have to communicate their findings to colleagues, stakeholders, and the public. The ability to communicate complex research findings in an understandable way is a key skill for someone in this role.
There are several types of interviews, often differentiated by their level of structure. Structured interviews have predetermined questions asked in a predetermined order. Unstructured interviews are more free-flowing. Semi-structured interviews fall in between. Interviews are commonly used in market research, social science, and ethnographic ...
In your answer, describe the extent of involvement for each individual. Example: "The participant is the individual who is involved in the research from the initial investigative stages to the findings and conclusions. Collaborators are the individuals who contribute to the final report writing and finalization of the research.
The first task is to figure out who to interview. Usually the research question specifies the participants. For example, a research question on the doctors' perception of their working conditions naturally suggests that doctors will make up the participant group. Following this example, doctors are the "population" this study is based on.
3. People's espoused theories differ from their theories-in-practice. Get them to tell a story. Ask "how" questions not "do". Use "tell me about" and "tell me more about that". Use open-ended questions. Approach your topic sideways. Don't take the first answer as a final answer. Ask for elaboration.
Here's a list of five qualitative research interview questions and some sample answers to consider when practicing for your interview: 1. Define market research and explain how it works. Interviewers may ask this question to evaluate your basic understanding of research and how to gather and understand it. Market research refers to another form ...
To help you prepare for the interview, here are five interview questions with sample answers to guide you in drafting your answers: 1. What is recursive abstraction? This question gives you the chance to elaborate on your research knowledge. It's important that you know and understand different data analysis methods to perform well in research ...
Do not expect interviewees to be able to directly address your research question. Instead, interviews should be structured around several focal questions designed to cover the main aspects of the research question o Questions should be designed to elicit an individual's experiences and understanding.
Researchers aim to look into the individual's life journey. As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data. Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews. 6.
Related: A guide to interview methods in research (With examples) 4. Please describe in your own words what coding means in qualitative research. This question looks to explore your fundamental understanding of an important aspect of qualitative research. It relates to qualitative data analysis.
Indeed Editorial Team. Updated August 11, 2022. A research interview is useful for researchers to gather information on a certain topic. You may interview a group of people, and you'll have a range of choices to ask specific questions. Research interviews allow an interviewee to elaborate on their responses to render a clear context to you.
Example: "There are many important skills for a researcher, but some of the most important include: -The ability to ask clear and concise research questions. -The ability to design effective research studies. -The ability to collect high-quality data. -The ability to analyze data effectively.
It is a good idea to prepare and even rehearse your answers. If you are confident in answering all of these you will be well-prepared. About your research. General research questions. About you and your capabilities. About your ability to gain funding. About your proposed research. About your role as supervisor/teacher.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Read more: Advantages & Disadvantages of Structured Interviews Semi-structured Interviews . The second type of qualitative interviews are semi-structured interviews. In these interviews, the interview guide outlines the topics to be explored, but the actual questions are not pre-written.. This approach allows interviewers the freedom to phrase questions spontaneously and explore topics in more ...
1. To gauge the research interviewer's methodology. It is important to collect data in a systematic and reliable way in order to produce valid results. 2. To see if the research interviewer is familiar with different data collection methods and can select the most appropriate one for the study at hand. 3.
In-depth research analyst interview questions Behavioral questions are common in interviews, where the employer may encourage you to cite specific examples of your workplace conduct or describe your likely response to hypothetical situations. Here are sample questions that can elicit an in-depth response: Tell me about a challenge you overcame ...
Vicky Oliver is a leading career development expert and the multi-best-selling author of five books, including 301 Smart Answers to Tough Interview Questions, named in the top 10 list of "Best ...
2. Explain the difference between deep learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning. This question tests your knowledge in the field. The interviewer may want to know that you can explain the subtle differences between each concept to ensure a strong grasp of foundational machine learning knowledge.
10 Research questions generated by Microsoft Copilot. ... With the proper context, examples, and advice, AI tools, like ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot, can craft helpful research questions, tasks, interview questions, and other study collateral far more quickly than you could if you started from scratch.
There are plenty of good questions to ask during a job interview to get to know your potential new employer. While some of the best questions show you're interested in the future of the company ...
When it's time to prepare for your interview, here are a few steps you can take to help ensure everything goes as smoothly as possible. 1. Do your research. Going into your interview, it's important to learn about the company you're applying to work for. Interviewers want to see that you're interested in their specific job opportunity ...