Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech

The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
Unlimited Academic AI-Proofreading
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences , such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes , these are the building blocks of grammar.
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , the label part of speech has generally been discarded in favor of the term word class or syntactic category . These terms make words easier to qualify objectively based on word construction rather than context. Within word classes, there is the lexical or open class and the function or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below and get started practicing identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence. They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Examples: softly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, softly, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spacial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet, with.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples: articles: a, an, the ; determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- The attributive noun [or converted adjective] work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a command to an understood "you".
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- Sentence Parts and Sentence Structures
- 100 Key Terms Used in the Study of Grammar
- Prepositional Phrases in English Grammar
- The Top 25 Grammatical Terms
- Foundations of Grammar in Italian
- Pronoun Definition and Examples
- What Is an Adverb in English Grammar?
- What Are the Parts of a Prepositional Phrase?
- Definition and Examples of Adjectives
- Definition and Examples of Function Words in English
- Lesson Plan: Label Sentences with Parts of Speech
- Sentence Patterns
- Nominal: Definition and Examples in Grammar
- Constituent: Definition and Examples in Grammar
- Adding Adjectives and Adverbs to the Basic Sentence Unit
- The Difference Between Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
part of speech
noun phrase
Definition of part of speech, examples of part of speech in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'part of speech.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1517, in the meaning defined above
Articles Related to part of speech

A Comprehensive Guide to Forming...
A Comprehensive Guide to Forming Compounds
Everything you need to know

The Adverb: A Most Fascinating POS
'POS' means "part of speech," obviously
Dictionary Entries Near part of speech
partnership life insurance
part of the package
Cite this Entry
“Part of speech.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/part%20of%20speech. Accessed 12 Apr. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of part of speech, more from merriam-webster on part of speech.
Nglish: Translation of part of speech for Spanish Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about part of speech
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 12, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Definition & Examples
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyse how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, ‘laugh’ can be a noun (e.g., ‘I like your laugh’) or a verb (e.g., ‘don’t laugh’).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, other parts of speech, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., ‘jump’), occurrence (e.g., ‘become’), or state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., past simple ), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding’-ed’ to the end of the word (or ‘-d’ if the word already ends in ‘e’). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
‘I’ve already checked twice’.
‘I heard that you used to sing ‘.
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., ‘a red hat’), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like ‘to be’ (e.g., ‘the hat is red ‘).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding ‘-ly’ to the end of an adjective (e.g., ‘slow’ becomes ‘slowly’), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., ‘at’) or phrase (e.g., ‘on top of’) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., ‘the door’, ‘the energy’, ‘the mountains’).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., ‘a poster’, ‘an engine’).
There’s a concert this weekend.
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., ‘a dog’, ‘an island’).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., ‘ in the field’)
- Noun (e.g., ‘I have an in with that company’)
- Adjective (e.g., ‘Tim is part of the in crowd’)
- Adverb (e.g., ‘Will you be in this evening?’)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., ‘a cup and plate’), or two adjectives (e.g., ‘strong and smart’). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use 'The', 'A' or 'An'
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of part of speech in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- What part of speech is it?
- In this dictionary , parts of speech are printed in italic , after pronunciations .
- appositively
- attributively
- indirect object
- post-modifier
- postposition
- postpositional
- postpositive
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
part of speech | American Dictionary
Examples of part of speech, translations of part of speech.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
singing or playing notes that are at the right pitch (= level) or that agree with others being sung or played

Alike and analogous (Talking about similarities, Part 1)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add part of speech to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, understanding the 8 parts of speech: definitions and examples.
General Education
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives, the top issue related to adverbs.
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of part of speech noun from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
- part of speech
- alphabetical
- pronunciation
Take your English to the next level
The Oxford Learner’s Thesaurus explains the difference between groups of similar words. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app

Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
Are you trying to master the grammatical rules of English? If so, understanding the 8 parts of speech is crucial. But what exactly are the parts of speech? How many are there? And how do you know which words fall into each category? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the definitions and examples of the 8 parts of speech, making it easier for you to navigate the intricacies of the English language.
English can be a challenging language to learn, but by understanding the parts of speech, you’ll gain a solid foundation for constructing sentences with clarity and precision. Whether you’re a student, a writer, or simply someone looking to improve your language skills, this article will provide you with a clear understanding of each part of speech. So, let’s immerse and explore the definitions and examples of the 8 parts of speech, empowering you to communicate effectively and confidently in English.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the 8 parts of speech is crucial for mastering English grammar.
- The 8 parts of speech are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
- Nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas.
- Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition.
- Verbs describe actions or states of being.
- Adjectives provide additional details about nouns.
- Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
- Prepositions show relationships between words in a sentence.
- Conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses together.
- Interjections express strong emotions or surprise.
What Are Parts of Speech?
When it comes to understanding the intricacies of English grammar, learning the different parts of speech is crucial. But what exactly are parts of speech? How many are there? And how do you determine which words belong to each part of speech? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide clear definitions and examples for each part of speech, helping you navigate the complexities of the English language.
Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They can be common or proper, singular or plural. Examples of nouns include “dog,” “New York City,” and “love.”
Pronouns are words used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. They can refer to individuals or groups. Examples of pronouns include “he,” “she,” “it,” and “they.”
Verbs are action words that describe what a subject does or the state of being. They can be in different tenses and forms. Examples of verbs include “run,” “jump,” and “is.”
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns, giving more details or information about them. They can describe qualities, size, shape, color, and more. Examples of adjectives include “beautiful,” “large,” and “blue.”
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing information on how, when, where, or to what extent. They often end in “-ly.” Examples of adverbs include “quickly,” “happily,” and “very.”
Prepositions
Prepositions show a relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They indicate position, direction, time, or manner. Examples of prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” and “from.”
Conjunctions
Conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses together. They can be coordinating or subordinating. Examples of conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” and “because.”
Interjections
Interjections are short exclamations used to express emotions or surprise. They are often followed by exclamation marks. Examples of interjections include “Wow,” “Yay,” and “Ouch!”
Parts of Speech
Understanding the different parts of speech is crucial for building a strong foundation in English grammar. Each part of speech plays a unique role in the construction of sentences, providing clarity and meaning to our language. In this section, we will explore the definitions and examples of the eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. It can refer to both concrete objects, such as “book” or “dog,” and abstract concepts, such as “love” or “happiness.” Nouns are often referred to as “persons, places, or things,” but it is essential to recognize that they encompass much more than that. Here are some examples of nouns used in sentences:
- The cat is sleeping on the couch.
- I love to read a good book .
- She has a beautiful voice .
Pronouns are words that are used to replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetitive use of nouns and add fluency to our language. Personal pronouns, such as “he,” “she,” or “they,” refer to specific individuals or groups of people. Here are some examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- She is going to the store.
- We had an amazing time at the party.
- Please give me the book.
Verbs are action words that express an action, occurrence, or state of being. They are the backbone of a sentence and provide information about what is happening. Verbs can be either transitive or intransitive, depending on whether they require an object to complete their meaning. Here are some examples of verbs used in sentences:
- The dog ran in the park.
- I love to swim in the ocean.
- They are studying for the exam.
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns. They provide additional information about the nouns they accompany, such as their size, color, or quality. Adjectives help make our language more vivid and expressive. Here are some examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- She has a beautiful smile.
- The blue sky is clear today.
- He is a talented musician.
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is performed. Adverbs enhance the meaning of a sentence and add precision to our language. Here are some examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- He quickly finished his assignments.
- She sings beautifully .
- They went outside to play.
Preposition
Prepositions are words that indicate the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They often express location, direction, time, or manner. Prepositions are essential for understanding spatial and temporal relationships. Here are some examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The cat is under the table.
- We walked through the park.
- The book is on the shelf.
Conjunction
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence. They help establish relationships between different parts of a sentence, coordinating or subordinating their meaning. Conjunctions are essential for creating complex sentences. Here are some examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- I will go to the store, but I need to buy milk.
- Because it was raining, we stayed indoors.
- He likes both chocolate and vanilla ice cream.
Interjection
Interjections are words or phrases used to convey strong emotions or reactions. They are often standalone expressions and can add emphasis or express surprise, joy, or frustration. Interjections bring life and emotion to our language. Here are some examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow , that’s an impressive performance!
- Ouch , that hurt!
- Alas , I lost my wallet.
Understanding and mastering the eight parts of speech will greatly enhance your language skills and enable you to effectively communicate in English. From nouns that identify people and things to verbs that express actions, each part of speech contributes to the overall structure and meaning of a sentence. Keep practicing and exploring the various functions of these parts of speech to become a confident English speaker and writer.
Examples of Each Part of Speech
Nouns play a crucial role in sentence construction as they represent people, places, things, or ideas. Here are some examples of nouns:
Pronouns, on the other hand, replace nouns to avoid repetition. Here are a few examples for better understanding:
- If you leave now, only James and I will remain behind.
- Their feet ached more than ours .
Verbs express actions, feelings, or states of being. Check out these verb examples:
- We sang songs , danced all night , and by the morning had fallen in love .
- Can you bring me something from the kitchen?
Adjectives add descriptions to nouns. Here are a few examples:
- The tall building stood out in the city skyline.
Adverbs add meaning to verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Take a look at these examples:
- The car drove quickly down the street.
- She performed very well in the competition.
Prepositions express the relationship between nouns, pronouns, and other words. Here are some examples:
- The book is on the table.
- The cat jumped over the fence.
Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence. Check out these examples:
- He likes tea and coffee.
- She is tired, but she is determined to finish the project.
Interjections convey strong emotions or sudden reactions. Here are a few examples:
- Wow , what a beautiful sunset!
- Oh no , I forgot to bring my umbrella.
Remember, understanding the different parts of speech and their functions is crucial in constructing meaningful sentences. Keep practicing and exploring the various examples to strengthen your language skills.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the eight parts of speech in English grammar, you are equipped with the knowledge to construct sentences with precision and clarity. By mastering the definitions and examples of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections, you can effectively communicate in English.
Each part of speech serves a unique purpose in sentence construction, providing meaning and structure to our language. Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas, while pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. Verbs express actions or states of being, while adjectives and adverbs provide descriptions and modify other words. Prepositions indicate relationships between words, conjunctions connect words or phrases, and interjections express strong emotions.
By practicing and exploring the functions of these parts of speech, you will become a confident English speaker and writer. Remember to apply this knowledge in your daily conversations and written communication to enhance your language skills.
Continue to refine your understanding and usage of the eight parts of speech, and watch as your language abilities flourish.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech - Definition, 8 Types and Examples
In the English language , every word is called a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
Table of Contents
Parts of speech definition, different parts of speech with examples.
- Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
A Small Exercise to Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech, what is a part of speech.
Parts of speech are among the first grammar topics we learn when we are in school or when we start our English language learning process. Parts of speech can be defined as words that perform different roles in a sentence. Some parts of speech can perform the functions of other parts of speech too.
- The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines parts of speech as “one of the classes into which words are divided according to their grammar, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc.”
- The Cambridge Dictionary also gives a similar definition – “One of the grammatical groups into which words are divided, such as noun, verb, and adjective”.
Parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.

8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns . Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- She bought a pair of shoes . (thing)
- I have a pet. (animal)
- Is this your book ? (object)
- Many people have a fear of darkness . (ideas/abstract nouns)
- He is my brother . (person)
- This is my school . (place)
Also, explore Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns .
2. Pronouns are words that are used to substitute a noun in a sentence. There are different types of pronouns. Some of them are reflexive pronouns, possessive pronouns , relative pronouns and indefinite pronouns . I, he, she, it, them, his, yours, anyone, nobody, who, etc., are some of the pronouns.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- I reached home at six in the evening. (1st person singular pronoun)
- Did someone see a red bag on the counter? (Indefinite pronoun)
- Is this the boy who won the first prize? (Relative pronoun)
- That is my mom. (Possessive pronoun)
- I hurt myself yesterday when we were playing cricket. (Reflexive pronoun)
3. Verbs are words that denote an action that is being performed by the noun or the subject in a sentence. They are also called action words. Some examples of verbs are read, sit, run, pick, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- She plays cricket every day.
- Darshana and Arul are going to the movies.
- My friends visited me last week.
- Did you have your breakfast?
- My name is Meenakshi Kishore.
4. Adverbs are words that are used to provide more information about verbs, adjectives and other adverbs used in a sentence. There are five main types of adverbs namely, adverbs of manner , adverbs of degree , adverbs of frequency , adverbs of time and adverbs of place . Some examples of adverbs are today, quickly, randomly, early, 10 a.m. etc.
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy an umbrella? (Adverb of place)
- I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick. (Adverb of time)
- Savio reads the newspaper everyday . (Adverb of frequency)
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner)
- Tony was so sleepy that he could hardly keep his eyes open during the meeting. (Adverb of degree)
5. Adjectives are words that are used to describe or provide more information about the noun or the subject in a sentence. Some examples of adjectives include good, ugly, quick, beautiful, late, etc.
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- The place we visited yesterday was serene .
- Did you see how big that dog was?
- The weather is pleasant today.
- The red dress you wore on your birthday was lovely.
- My brother had only one chapati for breakfast.
6. Prepositions are words that are used to link one part of the sentence to another. Prepositions show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Some examples of prepositions are in, out, besides, in front of, below, opposite, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The teacher asked the students to draw lines on the paper so that they could write in straight lines.
- The child hid his birthday presents under his bed.
- Mom asked me to go to the store near my school.
- The thieves jumped over the wall and escaped before we could reach home.
7. Conjunctions are a part of speech that is used to connect two different parts of a sentence, phrases and clauses . Some examples of conjunctions are and, or, for, yet, although, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- Meera and Jasmine had come to my birthday party.
- Jane did not go to work as she was sick.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot score good marks.
- I have not finished my project, yet I went out with my friends.
8. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong emotions or feelings. Some examples of interjections are oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc. It is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow ! What a wonderful work of art.
- Alas ! That is really sad.
- Yippee ! We won the match.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun – Tom lives in New York .
- Pronoun – Did she find the book she was looking for?
- Verb – I reached home.
- Adverb – The tea is too hot.
- Adjective – The movie was amazing .
- Preposition – The candle was kept under the table.
- Conjunction – I was at home all day, but I am feeling very tired.
- Interjection – Oh ! I forgot to turn off the stove.
Let us find out if you have understood the different parts of speech and their functions. Try identifying which part of speech the highlighted words belong to.
- My brother came home late .
- I am a good girl.
- This is the book I was looking for.
- Whoa ! This is amazing .
- The climate in Kodaikanal is very pleasant.
- Can you please pick up Dan and me on your way home?
Now, let us see if you got it right. Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun
What are parts of speech?
The term ‘parts of speech’ refers to words that perform different functions in a sentence in order to give the sentence a proper meaning and structure.
How many parts of speech are there?
There are 8 parts of speech in total.
What are the 8 parts of speech?
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections are the 8 parts of speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Understanding Parts of Speech (9 Types With Examples)

What are parts of speech? In the American English language, parts-of-speech is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. They exist under the verb , noun, pronoun, interjection , adjective , conjunction, adverb, and preposition forms.
Learn more about parts of the speech in this comprehensive worksheet…
What are parts of speech?
“Parts of speech” refers to the essential words used in sentence formation in the English language.
Every word used in a sentence structure plays an important role in defining the sentence’s meaning. These words use and placement give proper intentions in sentence structures.
Parts of speech are the basic grammar lessons taught during the primary phases of learning English.
Any word used in sentence formation falls into one of these categories for proper sentence structure.
Some of those words can be a part of one or more parts of speech. This topic further explores the essential parts of speech used in the English language.
Watch this as a video lesson
In total, there are nine categories of parts of speech
These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns , Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs , Pronouns, Prepositions , Conjunctions, and Interjections.
Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e. , Articles, a subprogram of determiners.
To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential to clearly understand the various parts of speech and select the right parts of speech form at the appropriate place in the sentence.
What are the 9 parts of speech with their functions?
Here are the nine parts of speech and how they impact the English language.
‘Verbs’ are the words used in a sentence to define the action/state of action being performed. Most of the sentences in sentence formation require the inclusion of verbs.
Some examples of verbs used in the English language are Love, Break, Fall , and Cry . These are the basic forms of verbs and are known as infinitives .
Most of the verbs used have two other major forms called participles . The use of these participles is for the formation of various verb-tense combinations.
These participles define the forms of verbs concerning the time of action/performance. These verb-tense combinations can be used in two types: Active voice and passive voice .
A ‘noun’ are words used in a sentence to give recognition or the name of an object, individual, or animal.
Nouns can be sub-classified into two major categories: Common nouns , which give generic descriptor names to things, and common items, such as a bat, a bicycle , etc. The other category of nouns is Proper nouns , which have specific descriptor names to refer to a specialized object, place, or individual, such as Charley, The Empire State Building, The Telegraph , etc.
Additionally, nouns can be classified as singular nouns and plural nouns based on the number of individuals/objects.
Singular Nouns
The definition of a Singular Noun is the same as that of a noun when used commonly. It carries the same definition as the noun: “A word referring towards an individual/object/event/material/place.”
Plural Nouns
The word plural relates to “more than one in certain languages or more than two in certain languages.”
Thus singular nouns can be converted to their plural noun format when there is an implication of more than one or two objects/individuals/places.
A general Singular/Common Noun can be turned into the appropriate form of a Plural Noun by adding a ‘s’/’es’/’ ies’/’ves.’ It is also initiated by changing ‘us’ to ‘i’, ‘is’ to ‘es’ , or ‘on’ to ‘a’ .
Some common nouns do not change when interchanged between their singular and plural noun forms. Some other common nouns do not fall under plural nouns and are called irregular nouns, which are made plural by changing the spelling or adding a suffix to the word.
‘Adjectives’ are words that give a description or modify the scope of nouns/pronouns by being specific. For example, adjectives used to define a noun can be red, small, hot, common, etc.
An adjective is usually placed before a noun or after the verb that it modifies. Three forms of adjectives are used to compare similar characteristics of different individuals/objects. These three degrees of comparison are:
- Positive/Absolute form
This comparison of adjectives defines the original form of the adjective as stated in English. For example, “this candy is tasty .” This degree of comparison states that no relative subject is available for comparison.
- Comparative form
This form of the adjective gives a relative comparison between two objects performing similar actions with identical characteristics. For example, “the candy we had today is tastier than the one we received yesterday.”
- Superlative form
This form of the adjective gives the superiority declaration of one object over similar objects possessing similar characteristics. For example, “this candy is the tastiest I have ever had in the last two years .”
Adjectives can be sub-classified based on their function in sentence formation. This sub-classification is:
- Possessive Adjectives
These adjectives show/represent the possessiveness of an object. For example, mine, my, his/her, their, its, etc.
- Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives modify the noun/pronoun by interrogation. Only a select few adjectives are available in this form. For example, whose, which, what, and where.
- Demonstrative Adjectives
These adjectives describe the current state/position of the noun/pronoun concerning space/time. For example, this, these, those, that.
- Compound Adjectives
These adjectives are a result of the combination of two or more adjectives. The resulting adjective modifies the subject in the sentence. For example, hand-dried, heavy-weighted, spike-haired, etc.
‘Determiners’ are the words placed before a noun/pronoun group terms to refer to a single/multiple things. Some commonly used determiners in English are ‘a’, ‘the’, ‘some’, ‘any’, and ‘this.’ Determiners are generally placed before descriptive adjectives . It tells the reader more about the description of the noun being referred to.
Determiners are classified into sub-categories, articles, and demonstratives.
An ‘Article’ can be either definite or indefinite. An article modifies a noun/pronoun without specifying any description of the object. In English, an example of a ‘definite article’ is the , whereas examples of two ‘indefinite articles’ are a and an .
Here, the refers to specific things or things that are identified beforehand. A or a refer to non-specific things that have not been identified beforehand.
Demonstratives
A ‘Demonstrative’ is defined as a demonstrative adjective/pronoun based on its usage in the sentence. Some examples of demonstratives are ‘this’, ‘that’, and ‘those’ .
A determiner has the same rules of use as in the case of adjectives in sentence formation. Thus, confusion takes place when carefully choosing the type of parts of speech to assign when given a choice of either a determiner or adjective.
An ‘Adverb’ defines essential information about the verb, similar to what an adjective is to a noun. It provides a descriptor for a verb used in a sentence and some cases, can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Some adverbs used in sentences with verbs are ‘slowly’, ‘hastily’, ‘unfortunately’, and ‘angrily’.
Adverbs are further sub-classified into various types based on their application in a sentence.
- Adverbs of Time (to inform about the occurrence of a verb), For example, ‘now’, ‘tomorrow’, and ‘soon’.
- Adverbs of Manner (to describe the action of a verb), For example, ‘hastily’, ‘slowly’, and ‘minutely’.
- Adverbs of Place (to indicate the place of action of the verb),
- Adverbs of Frequency (to describe the frequency of a verb action),
- Adverbs of Degree (to describe the intensity of an action),
- Conjunctive Adverbs (are used to link/act as a conjunction to two sentences).
A ‘Pronoun’ is a word used in specifically providing an alternate name for a non/noun phrase. They are alternate words for referring to an object/individual when the requirement of a noun is unnecessary, as the noun has been mentioned previously in some parts of the sentence.
Some examples of pronouns are ‘it’, ‘he/she’, and ‘himself/herself’.
Pronouns are sub-classified into different categories based on their use in the sentence.
Some of these sub-categories are:
- Relative Pronouns (to relate a part of a sentence with the other)
- Possessive Pronouns (to show possessiveness)
- Reflexive Pronouns (to refer back to the subject of discussion)
- Demonstrative Pronouns (to refer to specific objects/individuals)
- Interrogative Pronouns (to ask questions)
- Indefinite Pronouns (to avoid reference to any specific object/individual/place)
- Personal Pronouns (to use as substitutes for proper names)
- Subject Pronouns (to assign acting on an object)
- Object Pronouns (to assign receiving action towards an object)
- Reciprocal Pronouns (to express two-way/mutual relationship)
- Preposition
A ‘Preposition’ is a word used as a connective between a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun with another word.
Prepositions are used in sentence formations to convey these meanings:
- To show the direction towards/of something/someone
- To refer to the period of an action taking place
- To specify the location/position of an object
- To present the space and time relationship between objects
Based on their use and function, prepositions are classified into four subtypes:
- Prepositions of Time (to indicate the happening of an action/event)
- Preposition of Place (to indicate the location of an object)
- Preposition of Direction (to indicate the direction/orientation of an object)
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationship (to indicate an object moving away/towards a source)
- Conjunction
A ‘Conjunction’ is a word that combines two/more objects and behaves as connectives in a sentence. These can appear in the beginning/middle/end of the sentence following the location of the objects.
There are three types of conjunctions used in sentence formation:
- Coordinate conjunction (to combine two independent clauses )
- Subordinate conjunction (to combine an independent with a dependent clause)
- Correlation conjunction (to combine two phrases having equal weightage)
Interjection
An ‘Interjection’ is a word to convey the expression of a variety of emotions/feelings. As such, there is no specific rule for the use of interjection and where it is to be placed.
However, in most cases, it is placed at the beginning of the sentence. For example, some of the most commonly used interjections are ‘ouch’, ‘phew’, and ‘well’.
Parts of speech examples
Here are some examples of the parts of speech used in sentences. Note the placement and its relation with other parts of speech present in the sentence format.
- John is cutting a pipe.
- John intends to come to the office this Monday .
- Jogging regularly is good for health.
- Drinking and driving put other motorists in danger.
- Would you want to wear a suit?
- I love to sing in between classes.
See another example in the image below.
- Juno ran towards the classroom.
- The janitor requested the students to clear their lockers.
- The monkey was caged after being sedated.
- I gifted my brother a phone .
- Why did you purchase the book ?
- I misplaced the manuscript .
- Do you want to eat some ice cream ?
- Mum loved my new car .
- Daniel gifted his brother a Porsche.

- I purchased a blue suit for the reception.
- Mary purchased two oranges from the fruit seller.
- The curry is tasty .
- Juno’s brother is arrogant .
- The documentary that premiered on television was fascinating .
- Giovanni Giorgio is a great music composer.
- My house is currently under lease.
- This novel is lengthy.
- I purchased some fruits and vegetables.
- She sent me an expensive watch.
- Velma loved the dress gifted by her parents.
- Joyce and Jill watched a movie together.
- Grandma gave us materials to prepare the dessert.

- Typically , we visit Mom on Mondays.
- Don’t you taste the coffee to be too bitter?
- Do not be nervous. You will eventually get the hang of it.
- The movie I watched was very scientific.
- It is scorching hot inside the workshop.
- Can I visit the office today ?
- His aunt will be staying at the apartment for a while .
- He is the man I was referring to.
- I found my missing luggage outside the airport.

- I won’t be coming to the office in the afternoon.
- He arranged the cutlery on the table.
- Bhaskar made the dog hide under its bed.
- I enjoy strolling by the lake in the mornings.
- James and I trekked to the hilltop today.
- I stayed back home because I felt uneasy.
- He did not enjoy the yogurt , yet he finished it.

- Interjection
- Hurray! We got the funding.
- Ouch! That wound looks severe.
- Wow! You look great in the wedding gown.
- Oh my God ! I hope he is safe.
See an example in the image below.
Words with more than one job
Many parts of speech can have more than one function/job in the sentence. This improves the versatility of the words being used and makes the use more situational in its placement and conveyance of meaning.
- Myers can shift for herself (Preposition)
- Give prayers to the Almighty; for He is the one above all (Conjunction)
- We require more women to have the same vigor. (Adjective)
- More of the women died in the operating room than in the cabin. (Pronoun)
- Agatha needs to shut the gossiping and work more (Adverb)
To see how all the objects work together, see the table below.
Here is a chart showing the parts of speech:
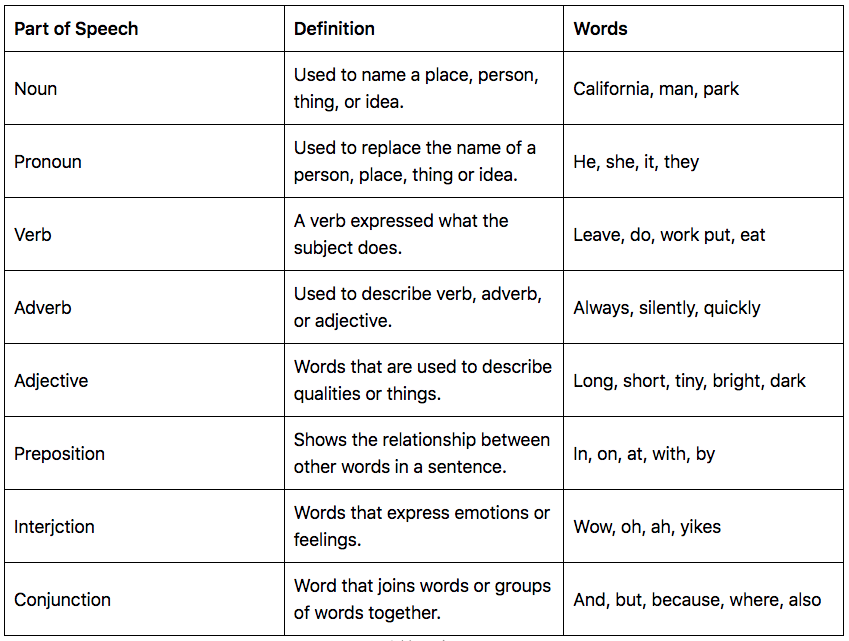
How to identify parts of speech
In sentence formation, it often becomes difficult to ascertain the parts of speech represented by each word. To help out and to make the process of identification easier, follow these steps:
- Identify any word which names an object/individual/place in a generalized form as a noun .
- To identify a specific noun, use pronouns .
- Any words which describe/identify actions/performance are verbs .
- Any word that modifies or gives a greater definition to nouns is an adjective.
- Any word that modifies or gives meaning to the actions of verbs, are adverbs.
- It is easy to pick out prepositions as they describe relationships between a noun/pronoun with other nouns/pronouns.
- Any joiner used to join two clauses is a conjunction .
- Exclamations generally follow any interjections in the text.

- Parts of speech
More parts of speech:
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
- Possessive nouns
- Irregular plural nouns
- Proper nouns
- Concrete nouns
- Collective nouns
- Possessive and plural nouns
- Verbs: The Definitive Guide
- Nouns | Explore Definition, Examples & Types with Examples
- What Are Pronouns? Definitions and Examples
- What Are Adverbs? (with Examples)
- Interjections – Explore Meaning, Definition, Usage and Examples
- What Is A Conjunction? Types & Examples
- The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- What Is a Determiner?
- The 8 Parts of Speech: Examples and Rules
- Adverbs – What is It? Explore the Meaning, Definition, Types, Usage and Examples
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
Home » 8 Parts of Speech | 8 Types, Definition and Examples
8 Parts of Speech | 8 Types, Definition and Examples

Are you curious to Speak or Learn the English Language? well, Every word in the English language is referred to as a component of speech. A word’s function in a sentence indicates the portion of speech to which it belongs. The “8 Parts of Speech,” which have distinct roles in sentence formation, are some of these building elements. To assist you in understanding the fundamentals of grammar, we will go over the various parts of speech in this tutorial, along with their definitions, types, and instances. This article explains the various parts of speech and provides examples and a definition.
The parts of speech are the conventional grammatical categories to which words are assigned based on their syntactic roles, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, and so forth. Stated differently, they talk about the varied roles that words might play in a sentence and the connections that words have to one another as defined by syntax and grammar.
Every single English word can be classified into one of the eight components of speech. A word’s part of speech is the purpose it fulfills in a sentence. These jobs were also designed to work as a team, much like any workplace or ensemble cast television series.
Table of Contents
What Is a Part of Speech?
Before delving into the specifics, let’s clarify what we mean by a “Part of speech.” In grammar, a part of speech is a category of words with similar grammatical properties. These categories help us understand how words function within sentences.
8 Parts of Speech:
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
Let us now dissect each of the 8 parts of speech:
Noun: the foundation of sentences.
- Types: Common nouns, proper nouns, abstract nouns, concrete nouns. See more…
- Definition: A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea.
- Example: cat , London , happiness , desk
Pronoun: Substitutes for Nouns
- Types: Personal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns.
- Definition: A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition.
- Example: he , she , it , they
Verb: The Action Words
- Types: Action verbs, linking verbs, helping verbs.
- Definition: A verb expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being.
- Example: She runs every morning. The flowers smell delightful.
Adjective: Describing Words
- Types: Descriptive adjectives, limiting adjectives.
- Definition: An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun.
- Example: The blue sky, tall trees, delicious food.
Adverb: Modifiers of Verbs
- Types: Adverbs of manner, place, time, degree.
- Definition: An adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb
- Example: He ran quickly , She sings beautifully .
Preposition: Indicators of Position or Relationship
- Types: Simple prepositions, compound prepositions.
- Definition: A preposition shows the relationship between its object and another word in the sentence.
- Example: The book is on the table. She walked across the bridge.
Conjunction: Joining Words
- Types: Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions.
- Definition: A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses.
- Example: She likes tea and coffee. He went to the store because he needed groceries.
Interjection: Expressions of Emotion
- Types: Expressive interjections, introductory interjections.
- Definition: An interjection expresses strong emotions or sudden bursts of feeling.
- Example: Wow! That was amazing! Ouch! That hurt.
You may also like

Example Sentences of Present Continuous Tense

Present indefinite Tense Examples Sentences in English

Abstract Nouns List A to Z in English | 500+ Abstract...

Proper Nouns List A to Z | 500+ Proper Nouns

Common Nouns List A to Z | 500+ Common Nouns

Singular Plural Words List From A to Z | 500+ Singular...
About the author.
mrmrsenglish.com
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Parts of Speech in English, Definition, Types, Examples, Rules
Parts of speech in english grammar, parts of speech definition, parts of speech chart, list of parts of speech, examples of parts of speech.
Table of Contents
When you speak or write a sentence in the English language, all the words in that sentence fall into one of the following categories. There are generally Eight such parts in the English language. These parts or categories are commonly known as “parts of speech”. Some of the words also fall into more than one of these categories. Here in this article, we have explained all the 8 parts of speech in detail. For easy understanding, we have also provided the necessary examples regarding different parts of speech in English Grammar .
Now as you have understood the basic concept behind the “Parts of Speech”. Let us proceed to the details of various parts of the speech.
The simplest definition for the term parts of speech is as follows:
“Parts of speech is a term used to describe the traditional class of words in the English language that varies according to the function performed or the idea denoted by those words in a sentence. There are 8 parts of speech in English, namely Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections.
Parts of Speech chart is a great tool to memorize all the parts of speech in English Grammar with its examples and definitions. Go through the parts of the speech chart below for a better understanding of parts of speech. Even if you understand the parts of speech well, this chart will help you to quickly revise all the parts of speech.
There are mainly 8 parts of speech . The different parts of speech have their importance and rules of usage. After reading this you will be able to easily use the parts of speech in a sentence. There are a lot of books and websites that even mention that there are 9 parts of speech but the 8 parts of speech detailed below are the most important and the most commonly used ones.
- Noun - Noun is the name of a person, place, or thing. A noun is often used with an article, but it's not mandatory to use an article before a noun. A noun can be a subject as well as an object.
- Pronoun - Pronouns are those words that replace the nouns in a paragraph so that the passage sounds grammatically correct. Pronouns help avoid the repetition of the nouns again and again.
- Verbs- Verbs are commonly known as action words. They express being or action in a sentence. Verbs are of two types, the main verbs or the helping verbs. Verbs play an important role in determining tenses.
- Adjectives - Adjectives are mostly used to modify nouns or even pronouns. Adjectives help describe nouns or pronouns. The articles are also considered as a part of adjectives. But here we have defined articles separately as another part of speech.
- Adverb - Adverbs are those words that add something to the meaning of a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb usually answers the questions of when, where, how, why, under what conditions, or to what degree. Adverbs often end with “-ly”. An adverb is not used with nouns. Using an Adverb with nouns is a blunder.
- Prepositions - As the name suggests, prepositions are positioned before a noun or pronoun in a sentence. It helps form a phrase that usually helps replace numerous words in a sentence. For example, “Ask around” a phrasal preposition means inviting someone for a purpose.
- Conjunctions- Conjunctions are the joining words that help combine separate sentences or words into a single sentence. Conjunctions help us to write and speak with fewer words or phrases at a time.
- Interjections- Interjections are stand-alone expressions for various emotions that can also be used without a sentence. They help convey strong feelings or reactions to a situation.
Above we have already explained the various parts of speech but with a few examples of parts of speech, you will be able to remember the various parts of speech easily. Let's have a look at the Parts of Speech Examples.
- That cat is black
- He lost his socks
- The monkey is eating bananas
- Raj has not completed his tasks yet
- She is angry.
- They have already left
- Those puppies are so cute.
- Ram is playing
- Shyam is eating
- He is riding a bicycle.
- She looks sad
4) Adjective
- She is a cruel sister
- He looks charming.
- The lady looks pretty in a saree.
- That was a huge bungalow.
- Rita arrived early today
- She drives slowly
- She speaks softly
- Only Rohit was late at the party
6) Prepositions
- I am standing over the bridge
- They all spoke against the watchman
- She lives across the street.
- Sorry for the delay.
7) Conjunctions
- Shreya and Riya are friends.
- She is pretty but not smart.
- She loves momos with mayonnaise.
- The students were not keeping quiet so the teacher left.
8) Interjections
- Oops! I forget her birthday.
- Ouch! I am hurt.
- Alas! A bad day.
- Ahh! What a lovely pair of shoes.
In some books and websites Articles in English are considered as one of the parts of speech. The Articles (A, An, and The) are discussed below:
Articles- There are only three articles in the English language. A, An, and The are the only articles that are used before the nouns to clearly define numbers.
A - It is used to determine one or a single object before consonants
An - An also represents one but only before vowels
The - The is used before universal truths.
Q. What are the parts of speech?
Q. How many parts of speech are there in English Grammar?
Q. Is article a part of speech?
Important Links

Parts of Speech Definition (8)Types and Examples

Parts of Speech in English refer to words that are into eight categories according to their use and function in sentences. Explore Parts of Speech: Definition, (8)Types, Examples, and Explanation to get a clear idea.
Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech are words used in sentences to make different functions and meanings. Without parts of speech, a sentence can not be expressed.
Parts of Speech Definition
Words are divided into different kinds or classes according to the purpose that they are used for. The different kinds of words are called Parts of Speech. – J.C. Nesfield
Different Parts of Speech with Examples
Parts of Speech can be divided into eight classes the function they perform in sentences.
1. Noun: The Taj Mahal is one of the seven wonders.
2. Pronoun: He can make it easier.
3. Adjective: She is as beautiful as a rose.
4. Verb: Mother cooks food.
5. Adverb: Barking dog seldom bites.
6. Preposition: The book is on the table.
7. Conjunction: Do or die
8. Interjection: Hurrah! we have won the match.
(8)Types of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. noun: .
A noun is a word that names a thing, person, or place.
(a) Ram is a good boy .
(b) India is our motherland .
(c) Oil floats on water .
(d) kindness is a great quality .
(e) The committee has approved the decision.
All the above italic words in sentences are nouns .
2. Pronoun:
A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun.
(a) Vinod is studying. He has a test tomorrow.
(b) It is going to rain. I don’t have an umbrella.
(c) My parents and I are in Munnar. We like this place.
(d) That is a nice sari! you look very pretty in it .
(e) Nilima is a good girl. She reads in a college.
3. Adjective:
An adjective is a word that adds something to the meaning of a Noun or Pronoun.
(a) This is a pretty house.
(b) The small boy is crying.
(c) He seems angry .
(d) There are four candles on the table.
(e) Many men were present.
All the above italic words in sentences are Adjectives .
4. Verb:
A verb is doing a word. It is used to express an action or state about people, animals, or things.
(a) I am angry.
(b) Mr ram drives a motorcycle.
(c) They push the suitcase under the cot.
(d) The Rose smells sweet.
(e) Iron and copper are useful metals.
All the above italic words in sentences are Verbs .
5. Adverb:
An adverb is a word that tells us more about verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.
a) He walks fast .
(b) He is very clever.
(c) She pronounced the word quite correctly .
(d) Some people spell badly .
(e) They asked me to wait here .
All the above italic words in sentences are Adverbs .
6. Preposition:
A preposition is a word placed before a Noun or a noun-equivalent or a pronoun to show its relation to some other word in the sentence.
(a) The book is on the table.
(b) He came to me.
(c) She is in the garden.
(d) The girl is fond of music.
(e) The little girl sat under a tree.
All the above italic words in sentences are Prepositions .
7. Conjunction:
A conjunction is a word that is used to join words, phrases, clauses, and sentences.
(a) It is very hot, and everybody is sweating.
(b) We can go to a film or we can go to the beach.
(c) He sat behind you, but in front of me.
(d) As he was ill, he did not go to his school.
(e) Ram as well as Karim went there.
All the above italic words in sentences are Conjunctions .
8. Interjection :
An interjection is a word that is used to show a strong or sudden feeling of happiness, sadness, surprise, or hurt.
(a) Hurrah! I did very well in maths.
(b) Alas! we lost the battle.
(c) Oh dear! how did they catch the thief?
(d) Ouch! you stepped on my toe.
(e) Goodness! He should not have said that.
All the above italic words in sentences are Interjections .
Some Examples of Parts of Speech in Sentences
1. The sun shines bright. ( Noun )
2. He is a brave boy. ( Pronoun )
3. She is absent because she is ill. ( Pronoun )
4. The girl wrote a letter to her father. ( Verb )
5. Kolkata is a big city. ( Adjective )
6. He worked the sum quickly . ( Adverb )
7. This flower is very beautiful. ( Adverb )
8. There is a cow in the garden. ( Preposition )
9. Rama and Hari are cousins. ( Conjunction )
10. Two and two make four. ( Conjunction )
11. Alas! He is dead. ( Interjection )
12. I can run fast, but miss the train. ( Conjunction )
13. Iron and copper are useful metals. ( Adjective )
14. His courage won him honour. ( Noun )
15. She pronounced the word quiet correctly. ( Adverb )
16. The girl is fond of music. ( Preposition )
Same Word used as different Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech.
Q1 What are parts of speech? Ans: Parts of Speech are words used in a sentence. Those words make a sentence meaningful.
Q2 How many parts of speech are there? Ans: There are 8 parts of speech according to function and meaning in sentences..
Q3 W hat are the 8 parts of speech grammar?
Ans: Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections are the 8 parts of speech Grammar.
Related posts:


Start Watching Part 2 of the RHOP Season 8 Reunion
Mia Thornton clarifies why she and Gordon separated: "A girl's gotta do what a girl's gotta do." Start watching Reunion Part 2 now!
Season 8 Episode 20 - Videos

Trending on Bravo

Plates Aplenty

Ariana Madix Discloses Her House Counter Offer: "I'm Including All Furniture"

Tom Sandoval Asks Tom Schwartz to Be His Roommate

Tom Schwartz Gives an Update on His Friendship With Jo Wenberg

Lala Kent Claps Back at Katie Maloney Questioning Her Loyalty

The Cast Reacts to Tom Schwartz's Platinum Blonde Hair: "Bless His Heart"

Your Tasty First Look at Last Chance Kitchen Season 21

The Big Stink

Lala Kent Wants to "Take the Science Jargon Out" of Her Baby Journey: "You Were Brought Here Out of So Much Love"

The 16th Chef

Your First Look at the Vanderpump Rules Season 11 After Show

Brock Davies Wishes He Had Been More Supportive of Scheana Shay

James Kennedy Claims Tom Schwartz Was "Leading Jo Wenberg On"

Was Katie Maloney Intentionally "Cockblocking" Tom Schwartz?
Still to Come on Summer House Season 8!

What Is the Status of Tom Schwartz’s Situationship With Jo Wenberg?

Kyle Cooke Breaks Down Over a Recent Discovery in Amanda Batula's Phone

Amanda Batula Is Ready to Move Out of New York City: "A Part of Me Wants Chickens and Goats"
Meet the children winning thousands playing Pokémon– and the parents coaching them
Whether they battle with trading cards or a Nintendo Switch, the dedication required goes far beyond the realms of a ‘children’s game’

For most children, the idea of spending two hours of an afternoon tinkering with a spreadsheet is the sort of nightmare they hope to avoid until adulthood. But for 11-year-old Drake Zhu, a high-ranking player of the Pokémon Trading Card Game (TCG) from New Zealand, it’s his daily routine.
As part of a strict, self-imposed regime, Drake spends two hours every evening battling opponents via an online simulator. In between games, he meticulously updates his spreadsheet, noting how his chosen deck of cards performs against other players.
With one eye on ExCel, Drake continuously makes adjustments – removing cards and adding others from a pool of hundreds, before firing up the simulator again. He estimates he plays hundreds of games in a single sitting. “But I’m strict with myself,” he says. “I have to do my homework first and eat dinner with the family.”
This level of dedication might seem somewhat intense for a children’s card game, but the world of the Pokémon TCG is a potentially lucrative one. Cash prizes can reach up to £20,000 for over 16s, and Drake is preparing for the largest in-person Pokémon tournament ever.
For the uninitiated, Pokémon cards function similarly to Top Trumps. Players “battle” their chosen Pokémon against their opponents, and the ones with higher attack values win.
Though designed for children to pick up and play, the game masks a surprisingly deep level of strategy. Players must build a deck of monsters which synergise with one another and supplement them with “item” and “trainer” cards to gain an advantage. An aptitude for maths is essential , and Drake is top of his class.
In times gone by, such stereotypically “nerdy” pursuits might have been quite lonely, but Drake also attends in-person tournaments at local hobby shops and plays with friends at school. Much of the time he spends online is social too, in communication with friends across the globe, many of whom he has met at tournaments abroad.
It is at one such tournament that I meet Drake and his father, Joe, 41, a software developer. The pair have travelled to London’s ExCel Centre for the Pokémon European International Championships, on two back-to-back 12-hour flights from Auckland, via Shanghai.
The cavernous hallway is a Pokémon lover’s paradise: Above the thousands of fans and players dressed head-to-toe in merchandise hangs a gigantic inflatable Pikachu – the franchise’s mascot – while speakers blast music from the games over the excited chatter of competitors and spectators.

It has been an intense weekend for father and son. The day before, they were here from 9am to 7pm as Drake competed in preliminary rounds, sustaining themselves with muesli bars and bananas to keep their energy levels up .
For his part, Joe sees little difference between his son’s hobby and his own childhood, save for the fact Pokémon has facilitated a few family holidays. This year’s World Championships, for which Drake has already qualified, are being held in Honolulu, Hawaii – suggesting the hours with the spreadsheet have paid off.
“The Pokémon experience is similar to any of the hobbies I had when I was young,” says Joe. “I didn’t play card games as a kid – I played volleyball and football. But those sports didn’t offer me the chance to go abroad.”
The family limits how much time Drake spends looking at screens and encourages him to take up sports too, he adds. “But if he’s on a screen we’re fine with it so long as he’s practising and not just watching YouTube or whatever.”
Official Pokémon tournaments are separated into three divisions. Drake competes in the junior division, for those aged 12 and under, while players aged 13-15 compete in the senior division, and everyone aged 16 and over competes in the master division, where the top cash prize is $25,000 (£20,000).
Sadly for Drake, he is eliminated before reaching the final. On a spotlit stage at the back of the arena, the top two junior players are preparing to face off for the chance to win $7,000 (£5,300) in cash and 216 packs of trading cards.
One of them is 10-year-old Peter Shapkin from Hampshire. A live audience of hundreds is watching, plus a few thousand on a live stream, as he anxiously shuffles his deck of cards. Above Peter, giant screens display a live feed of the table dividing him and his opponent, while commentators discuss the players’ chosen decks with all the solemnity of Premier League pundits – it is a broadcast-level production, and the atmosphere is tense.
Peter’s moment in the spotlight does not last long, however. Though he and his opponent wear noise-cancelling headphones throughout the match, the overhead camera can see the players’ hands – and the pundits waste no time in informing the audience that Peter’s chances are slim. It is not long before he is defeated.

His father Konstantin, 47, is watching on from the sidelines, dressed in a Pokémon T-shirt resembling a football jersey – giving him the air of a coach. The championships have been a family weekend holiday of sorts for him and his two sons: all three have competed in separate age brackets, but only Peter made the final rounds.
“I only got into the card game for them – my wife has no clue,” says Konstantin. “One day they brought some cards home from school and tried to create their own rules, so I helped them learn the real game by buying some simple pre-made decks.”
Konstantin says Peter was only five when the family began learning the game and credits the cards with developing his son’s reading and maths skills. “Ultimately, it’s nice to have something in common with your kids,” he adds.
Peter began playing in small competitions at a local game shop in Aldershot, Hampshire, and quickly proved a prodigy at the TCG. Despite his loss in London, he has already qualified for this year’s World Championships. His prize money pot is largely spent getting to and from the next tournament, with only the very top players handed “travel awards” by The Pokémon Company International (TPCI).
As for the rest of the cash, Konstantin says it has allowed Peter to understand the value of money at an early age. “He has a phone that he paid for himself. I would have bought him one anyway, but he feels like it’s his phone because he won the money to buy it,” he says. “Other kids get their phones for free, but he earned it.”
None of this has come at the expense of a social life, either, Konstantin argues. “Peter is only 10 but has already visited Brazil, the USA, Australia, Japan and many European countries. He now has friends from all over the world,” he says. “As a child, I never had such opportunities.”
But the tournaments are undeniably taxing on the children striving for the top. A few hours after his match, Peter is still visibly upset and exhausted. Though the 10-year-old still walks away with a second-place $5,000 cash prize and a free trip to Hawaii, losing at the last minute clearly stings.

“There’s so much stress on you,” he says. “You can’t make mistakes and it’s just really tiring. I was really tired yesterday and I’m tired now – you use your brain for a solid 50 minutes for each round.”
Not in the mood to say much more, Peter heads home to Hampshire with his father. Does seeing his son so devastated not bother Konstantin?
“This was the first time Peter was on the big stage and the live stream,” he says. “He was understandably tired and overwhelmed by the whole situation. However, he was absolutely delighted to have reached the finals.”
In fact, Konstantin says the experience is character-building. “Learning to deal with winning and losing is part of the journey,” he explains. “When Peter was younger he got very emotional every time he lost. Since then he has matured and learned to accept defeat gracefully.
“As a parent, I think this is an invaluable experience for him as later in life he will have enough resilience to deal with adversities and frustration.”

The TCG matches wrap up, signalling the start of the Video Game Championship (VGC) finals. These games are played on the Nintendo Switch, and cash prizes range between $1,000 and $5,000.
Up first is 12-year-old Kevin Han, from Pennsylvania, who is unbothered by the crowd and commentators. In mere minutes, he wins, two games to zero. After gamely hugging his opponent, a beaming Kevin thanks his family for their support before explaining in detail his strategy, peppering his speech with percentage calculations and in-game jargon.
Backstage, he gives a flavour of the mental maths required. “For example, my Flutter Mane holds the Choice Specs item, so its Moonblast attack will do 70 per cent to an Incineroar’s health bar, but if the Incineroar is a ‘bulky’ variant the attack will only do 50 per cent,” he explains. This is one of dozens of calculations Kevin has committed to memory, typically with the help of fan-made calculators.

Kevin’s attitude to practice is far less regimented than Drake’s, and he is less obviously overwhelmed by the occasion than Peter seemed to be. But it wasn’t always that way.
“Kevin had his fair share of disappointments and bitter experiences, where as a parent I questioned whether or not he should even continue his Pokémon tournaments,” says his mother, Anita. “My husband and I take our kids to these tournaments primarily to spend time with them and to have fun. When you see your child experience a competition where it can crush your child’s love for the game, you start to ask if continuing in this journey is truly worth it.”
Ultimately Anita left it up to Kevin, who decided to continue. Like Konstantin, Anita believes that learning to cope with defeat is an important part of growing up . “People talk about children needing to develop ‘grit’ now,” she continues. “I realised that through an activity like competitive Pokémon, children can develop grit through the process of losing, going back to the drawing board, and competing again.”
Kevin now has a rule for himself: if it stops being fun, he stops playing. “Before tournaments, I sometimes have no sleep at all because of the nerves,” he says. “But I don’t like to practise every day, because if I force myself to play when I don’t want to then I’ll lose my love for Pokémon.”
Recommended
Five ways to make your children more resilient
- Facebook Icon
- WhatsApp Icon

Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives
Search form, you are here, final rule: definition of “engaged in the business” as a dealer in firearms.

On April 10 , 2024, the Attorney General signed ATF’s final rule, Definition of “Engaged in the Business” as a Dealer in Firearms, amending ATF’s regulations in title 27, Code of Federal Regulations (“CFR”), part 478. The final rule implements the provisions of the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act (“BSCA,” effective June 25, 2022), which broadened the definition of when a person is considered “engaged in the business” as a dealer in firearms (other than a gunsmith or pawnbroker). The Final Rule clarifies that definition. It will be published in the Federal Register and will be effective 30-days from publication.
This final rule incorporates BSCA’s definitions of “predominantly earn a profit” and “terrorism,” and amends the regulatory definitions of “engaged in the business as a dealer other than a gunsmith or pawnbroker” and “principal objective of livelihood and profit” to ensure each conforms with the BSCA’s statutory changes and can be relied upon by the public.
The final rule clarifies when a person is “engaged in the business” as a dealer in firearms at wholesale or retail by:
- clarifying the definition of “dealer,” and defining the terms “purchase,” “sale,” and “something of value” as they apply to dealers;
- adding definitions for the term “personal collection (or personal collection of firearms, or personal firearms collection),” and for “responsible person”;
- setting forth conduct that is presumed to constitute “engaging in the business” of dealing in firearms, and presumed to demonstrate the intent to “predominantly earn a profit” from the sale or disposition of firearms, absent reliable evidence to the contrary, in civil and administrative proceedings;
- clarifying that the intent to “predominantly earn a profit” does not require the person to have received pecuniary gain, and that intent does not have to be shown when a person purchases or sells a firearm for criminal or terrorism purposes;
- clarifying the circumstances when a person would not be presumed to engaged in the business of dealing in firearms, including as an auctioneer, or when purchasing firearms for, and selling firearms from, a personal collection;
- addressing the procedures former licensees, and responsible persons acting on behalf of such licensees, must follow when they liquidate business inventory upon revocation or other termination of their license; and
- clarifying that licensees must follow the verification and recordkeeping procedures in 27 CFR 478.94 and Subpart H , rather than using an ATF Form 4473 when firearms are transferred to other licensees, including transfers by a licensed sole proprietor to that person’s personal collection.
Please note that this is the text of the final rule as signed by the Attorney General, but the official version of the final rule will be as it is published in the Federal Register. The rule will go into effect once it is published in the Federal Register.
Read a copy of the rule.
Related Resources
- Overview of Final Rule 2022R-17F Definition of “Engaged in the Business” as a Dealer in Firearms (coming soon)
- Final Rule 2022R-17F – Questions & Answers
- Notice of Proposed Rulemaking – Definition of “Engaged in the Business”
- Notice of Proposed Rule Making – Comments
- Press Release: Justice Department Publishes New Rule To Update Definition of "Engaged in the Business" as a Firearms Dealer
- Director Dettelbach’s Remarks on the “Engaged in the Business” Final Rule
Background Information
- Bipartisan Safer Communities Act, Public Law 117-159 (June 25, 2022)
- Gun Control Act of 1968
- National Firearms Act
- Rules and Regulation
- Regulations.atf.gov
Contact Information
- For questions regarding the application of the final rule , email the Firearms Industry Programs Branch .
- For media inquiries, email ATF Public Affairs or call 202-648-8500 .
- For congressional inquiries, email ATF Legislative Affairs or call 202-648-8510 .
- For questions regarding the rulemaking process, email the Office of Regulatory Affairs .
- Action/Adventure
- Children's/Family
- Documentary/Reality
- Amazon Prime Video

More From Decider

'The Golden Bachelor' Stars Gerry Turner And Theresa Nist Divorcing Three...

'The View' Reacts To O.J. Simpson's Death: "The Tragedy Was The...

'The View' Forced To Evacuate Their Studio Before Wednesday's Show After...

'X-Men '97' Gives Gambit a Hero Moment You'll Never Forget

Holly Madison Says She “Tried” Exotic Dancing But Doesn’t Have...

'Captain America: The Winter Soldier' at 10: The Movie That Made (and...

Joy Behar Says She Was "Dragged Into" Controversy Over Beyoncé's 'Jolene'...

Guy Fieri Calls Drew Barrymore "Gangster" For Talking With Her "Mouth Full...
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to copy URL
Jax Taylor Suggests Son’s Speech Delay Is The Result Of Vaccines — Despite Studies Proving Their Safety
Where to stream:.

‘Vanderpump Rules’ Alum Faith Stowers Sues Bravo For Discrimination And Retaliation, Claims She Was Forced To “Get Intimate” With Lala Kent
‘the valley’ star brittany cartwright has heard about scheana shay’s alleged hookup with john mayer “for years”: “she’s got the receipts” , lisa vanderpump jokes about what she’d do differently on ‘vanderpump villa’: “i’d have another house completely full of staff waiting to replace them” [exclusive], ‘vanderpump villa’ star hannah fouch “loves” that she and marciano brunette are getting compared to stassi schroeder and jax taylor: “stassi is an icon”.
Jax Taylor and Brittany Cartwright candidly opened up about their three-year-old son’s speech struggles on the most recent episode of The Valley . Following the episode, Taylor seemed to suggest in a social media comment that Cruz’s delay was linked to vaccinations he had received.
“My son crawled early, walked early and even spoke early,” Taylor wrote in the controversial comment. “Then we got him vaccinated and it all stopped. I am not saying vaccines are the cause but what else could it be, how can [a] kid be talking fully, walking fully then stop two weeks after vaccinations?”
It should be noted that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC ) says vaccines are “very safe.” The CDC’s official site states, “The United States’ long-standing vaccine safety system ensures that vaccines are as safe as possible. Currently, the United States has the safest vaccine supply in its history. Millions of children safely receive vaccines each year.”
Despite his remarks, it appears Taylor has been vaccinated in the past himself. He posted on X in 2021, “This second vaccine shot is kicking my ass!!” likely referring to the COVID-19 vaccine.
Taylor and Cartwright, who welcomed Cruz in April 2021, revealed on the most recent episode of The Valley that they had hired a speech therapist to help their son.
“Cruz has done everything on time when it comes to crawling, walking, sitting up,” Cartwright said in the episode. “He was saying dada, mama, doggy, things like that. And then he just seemed to regress one day. He stopped talking almost altogether. And now we are going to put him in speech therapy just to make sure that he has all the help that he needs.”
Taylor referred to Cruz as a “smart kid,” telling his now-estranged wife, “I feel like I’ve been researching everything and I feel like I’m doing everything I’m supposed to be doing.”
The Jax’s Studio City owner admitted that he often “[compares] my child to other kids and that’s pretty much Parenting 101, you should not do that.” Meanwhile, Cartwright said that she was concerned for her son.
“It can make you really, really sad sometimes because you just want your kid to be so perfect and whenever things go a little bit different than you planned it can be a lot of pressure for a mom,” she said in her confessional interview. “I don’t ever want to see him struggle with anything.”
Cartwright and Taylor announced their separation ahead of The Valley’s premiere, but they have each maintained that their son is their main priority.
While speaking with DECIDER earlier this month, Cartwright confirmed that she was excited to share her son with the world on the new reality show. “It can be a little scary because people judge you like crazy, but he’s the best thing in my entire life and he’s my whole world. Having him be a part of all this is really exciting,” she said.
The Valley airs on Tuesday at 9 p.m. ET on Bravo. New episodes are available to stream the next day on Peacock .

Does 'Yellowstone' Return Tonight? Everything To Know About 'Yellowstone's Season 5, Part 2 Premiere Date

Dwayne Johnson Gets Into Verbal Altercation With WWE Fan: "Watch Your F**king Mouth"

'The View' Reacts To O.J. Simpson's Death: "The Tragedy Was The Injustice"

Where To Watch 'When Calls The Heart' Season 11: Start Time, Streaming Info

Is Woody Allen's 'Coup de Chance' Streaming on Netflix or HBO Max?

R.I.P. Cole Brings Plenty: '1923' Actor Found Dead At 27 After Going Missing
Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Announces Student Debt Relief for Millions in Swing-State Pitch
During an appearance in Wisconsin, President Biden said 10 million borrowers could see debt relief of at least $5,000. The plan could help rally support among young voters.
- Share full article
Biden Announces New Plan for Student Debt Relief
President biden announced a large-scale effort to help pay off federal student loans for more than 20 million borrowers..
Today, I’m proud to announce five major actions to continue to relieve student debt for more than 30 million Americans since I started my administration. And starting this fall, we plan to deliver up to $20,000 in interest relief to over 20 million borrowers and full forgiveness for millions more. [applause] I will never stop to deliver student debt relief and hardworking Americans. And it’s only in the interest of America that we do it. And again, it’s for the good of our economy that’s growing stronger and stronger, and it is, by freeing millions of Americans from this crushing debt of student debt. It means they can finally get on with their lives instead of being put — their lives being put on hold.

By Michael D. Shear
Reporting from Madison, Wis.
President Biden on Monday announced a large-scale effort to help pay off federal student loans for tens of millions of American borrowers, seeking an election-year boost by returning to a 2020 campaign promise that was blocked by the Supreme Court last year.
Mr. Biden’s new plan would reduce the amount that 25 million borrowers still owe on their undergraduate and graduate loans. It would wipe away the entire amount for more than four million Americans. Altogether, White House officials said, 10 million borrowers would see debt relief of $5,000 or more.
“While a college degree still is a ticket to the middle class, that ticket is becoming much too expensive,” Mr. Biden said during a speech to a small but enthusiastic audience filled with supporters. “Today, too many Americans, especially young people, are saddled with too much debt.”
Mr. Biden announced the plan in Madison, Wis., the capital of a critical swing state and a college town that symbolizes the president’s promise to make higher-education affordability a cornerstone of his economic agenda.
But it is a promise he has so far failed to achieve, largely because of legal challenges from Republicans and other critics. They accuse Mr. Biden of unlawfully using his executive authority to enact a costly transfer of wealth from taxpayers who have not taken out federal student loans to those who have.
Officials did not say how much the new plan would cost in coming years, but critics have said it could increase inflation and add to the federal debt by billions of dollars.
Mr. Biden said his new effort would help the economy by removing the drag of enormous debt from people who would otherwise not be able to buy a home or pursue a more economically sound future.
“We’re giving people a chance to make it,” Mr. Biden said. “Not a guarantee. Just a chance to make it.”
Mr. Biden’s announcement was a presidential do-over. In the summer of 2022, he put in motion a plan to wipe out $400 billion in student debt for about 43 million borrowers. That was blocked by the Supreme Court , which said he exceeded his authority. In the months since, Mr. Biden has waived small amounts of debt using existing programs. But now he is attempting a larger effort closer to the scale of his first try.
The original plan relied on a law called the HEROES Act, which the administration argued allowed the government to waive student debt during a national emergency like the Covid pandemic. The justices disagreed after Republican attorneys general and others challenged the debt waiver plan.
The new approach is different.
For months, Mr. Biden’s Education Department has been developing regulations using a long process authorized by the Higher Education Act. Instead of an across-the-board waiver of debt, the new approach targets five groups of borrowers: those whose loans have ballooned because of interest; borrowers who have been paying for decades; those who have economic hardship; people who qualify for existing debt relief programs but have not applied; and people whose loans come from schools that have since been denied certification or have lost eligibility for federal student aid programs.
Administration officials said because the new approach is based on a different law, it is more likely to survive the expected challenges. They said lawyers for the White House and the Education Department have studied the Supreme Court ruling and have designed the new program to make sure it does not violate the principles laid out by the justices.
But lawyers for those who oppose the approach are likely to argue that waiving the debt is unfair to those who already paid back their loans or never took out college loans in the first place. That argument helped sway the justices in the last case.
Neal McCluskey, the director of the Center for Educational Freedom at the Cato Institute, called the new plan “dangerous policy” that is unfair to taxpayers and would cause colleges and universities to raise their prices.
“The Constitution gives Congress, not the president, the authority to enact law, and the Supreme Court has already struck down a unilateral, mass student debt cancellation scheme by the Biden administration,” he said. “It would stick taxpayers with bills for debts other people chose for their own financial advancement.”
The legal challenges will likely take months to resolve, and that could leave the debt relief plan in limbo as voters go to the polls in November to choose between Mr. Biden and former President Donald J. Trump.
Members of Mr. Biden’s administration fanned out across the country on Monday to talk about the new plan, betting that it will rally support among voters who were disappointed that the court blocked the first one, which would have eliminated up to $20,000 in debt for tens of millions of borrowers. Vice President Kamala Harris held a round-table discussion with a teacher, a nurse and a social worker in Philadelphia. Miguel A. Cardona, the education secretary, spoke in New York City.
“We need you to stay in these jobs doing this work,” Ms. Harris said in the library of an elementary school. “And you shouldn’t have to make a decision about whether you serve or are able to pay your bills.”
But beyond the threat of legal action, the president faces steep obstacles just because of the calendar. The new plan has not yet been published in the Federal Register, which will kick off a required, monthslong public comment period before it can take effect. Officials said on Sunday only that they hoped some of the provisions would begin going into effect in “early fall” of this year.
Administration officials hope that the president’s supporters will give him credit for trying, even if many of the borrowers do not end up seeing any relief before they go to the ballot box. Andrew O’Neill, the legislative director for Indivisible, a liberal advocacy organization, praised Mr. Biden’s announcement.
“Progressives have led the fight for student debt cancellation, and Joe Biden has responded,” he said in a statement. “More than 30 million folks will now get relief from Biden’s programs. That’s a huge deal.”
White House officials have been scrambling for months to respond to the anger about student loans among the president’s base. In one poll released last month, more than 70 percent of young people said the issue of student loan forgiveness was “important” or “very important” to them as they make their decision in the 2024 election campaign.
Officials said the five groups of people targeted in the new plan will address most of the egregious issues that some borrowers have with their student loans.
People whose loans have grown beyond the amount they originally borrowed because of interest would have up to $20,000 of that interest wiped away, leaving them to repay only the amount they originally borrowed. People making less than $120,000 a year, or couples making less than $240,000, would qualify to have all of their interest forgiven.
Officials said that 23 million people would most likely have all of their interest-related balances waived from that provision.
About two million borrowers who already qualify to have their student loans waived under existing programs have not applied for relief. Under the new rules, the Education Department would be authorized to cancel the debt for those people without their having to apply.
People who took out federal student loans for undergraduate degrees and began repaying them more than 20 years ago would automatically have the debt canceled under the new plan. Graduate students who borrowed money and began repaying 25 years ago would have their debt canceled.
Officials said that about 2.5 million people would qualify under that rule.
People who borrowed money to attend colleges that have since lost their certification or their eligibility to participate in the federal student aid program would have their debt canceled. Officials did not say how many people that would affect. And people who are especially burdened with other expenses — such as high medical debt or child care — could apply to have their student loans forgiven.
Officials did not estimate how many people might qualify for what they called the “hardship” programs.
Nicholas Nehamas contributed reporting from Philadelphia.
Michael D. Shear is a White House correspondent for The New York Times, covering President Biden and his administration. He has reported on politics for more than 30 years. More about Michael D. Shear
Our Coverage of the 2024 Election
Presidential Race
The democratic party is unifying around a blunt message on abortion, solely blaming Donald Trump for the country’s shift, ahead of Kamala Harris’s trip to Arizona, where Democrats hope to keep Republicans reeling.
Trump and Mike Johnson, the G.O.P. speaker, at odds over many issues, are making a common cause on “election integrity,” ahead of Johnson’s trip to Mar-a-Lago.
Price pressures aren’t easing fast enough to guarantee the interest-rate cuts President Biden had hoped to see , so his message is evolving as he casts Trump and Republicans as uninterested in the actual policy work of fighting inflation and as barriers to his own proposals.
The political prediction markets — which allow traders to place bets on the outcome of the November election — show that the presidential race is tight, giving Trump an even chance of winning the election . So far, it appears the market doesn't care either way.
Trump’s penchant for bending the truth has been well documented, but a close study of how he does so reveals a kind of technique to his dishonesty .
Primaries in three Mid-Atlantic House districts will test whether the battle cry of “save democracy” will be enough even for Democratic voters who have many other concerns.
In Arizona’s crucial Senate race, Ruben Gallego, who has long embraced his progressive background, is striking a moderate tone .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much set in stone.
part of speech: [noun phrase] a traditional class of words (such as adjectives, adverbs, nouns, and verbs) distinguished according to the kind of idea denoted and the function performed in a sentence.
PART OF SPEECH meaning: 1. one of the grammatical groups, such as noun, verb, and adjective, into which words are divided…. Learn more.
noun. part of speech, lexical category to which a word is assigned based on its function in a sentence. There are eight parts of speech in traditional English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, and interjection. In linguistics, parts of speech are more typically called word classes.
For instance, the verb "eats" is a present-tense verb, and its past form is "ate.". 4. Adjective. Another part of speech is the adjective, which modifies or describes a noun or a pronoun. It typically answers the questions "what kind," "which one," or "how much.". For example: Blue.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles. Many words can function as different parts of ...
Part of speech. In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech ( abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class [1] or grammatical category [2]) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic ...
PART OF SPEECH definition: 1. one of the grammatical groups, such as noun, verb, and adjective, into which words are divided…. Learn more.
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here's a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words .
The parts of speech refer to categories to which a word belongs. In English, there are eight of them : verbs , nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Many English words fall into more than one part of speech category. Take the word light as an example.
The 9 parts of speech are adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, determiners, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. (These are also known as "word classes.") A Formal Definition. A "part of speech" is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English, the main parts of speech are noun ...
Definition of part of speech noun in Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
Part of speech definition: any of the classes into which words in some languages, as Latin and English, have traditionally been divided on the basis of their meaning, form, or syntactic function, as, in English, noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. See examples of PART OF SPEECH used in a sentence.
Each part of speech plays a unique role in the construction of sentences, providing clarity and meaning to our language. In this section, we will explore the definitions and examples of the eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples: 1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns. Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs, Pronouns, Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections. Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e., Articles, a subprogram of determiners. To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential to ...
The "8 Parts of Speech," which have distinct roles in sentence formation, are some of these building elements. ... types, and instances. This article explains the various parts of speech and provides examples and a definition. The parts of speech are the conventional grammatical categories to which words are assigned based on their ...
The simplest definition for the term parts of speech is as follows: "Parts of speech is a term used to describe the traditional class of words in the English language that varies according to the function performed or the idea denoted by those words in a sentence. There are 8 parts of speech in English, namely Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs ...
Parts of Speech. Parts of Speech are words used in sentences to make different functions and meanings. Without parts of speech, a sentence can not be expressed. Parts of Speech Definition. Words are divided into different kinds or classes according to the purpose that they are used for. The different kinds of words are called Parts of Speech.
Some parts of Mayhew's body were found on Tuesday, April 2, in Rowdown Fields, a public park in New Addington, Croydon, after police were called to the scene.
As talks over the post-Brexit border deal with Spain resume, long standing plans to make its airport into a point of access for travellers to southern Spain - becoming part of the EU's ...
A total solar eclipse passed over North America on Monday, putting on a dramatic show that was visible to millions of people.
The image displays the logo of Bravo, consisting of a gradient from blue to purple speech bubble with the word "bravo" in white lowercase letters.
For his part, Joe sees little difference between his son's hobby and his own childhood, save for the fact Pokémon has facilitated a few family holidays. ... peppering his speech with percentage ...
On April 10, 2024, the Attorney General signed ATF's final rule, Definition of "Engaged in the Business" as a Dealer in Firearms, amending ATF's regulations in title 27, Code of Federal Regulations ("CFR"), part 478. The final rule implements the provisions of the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act ("BSCA," effective June 25, 2022), which broadened the definition of when a
In a decision published on March 21, 2024, the German Federal Administrative Court (Bundesverwaltungsgericht, BVerwG) held that a parent must assume at least 60% of the care of the child to be considered a "single parent" within the meaning of the Child Support Advancements Act (Unterhaltsvorschussgesetz, UhVorschG).Advance child support is paid to single parents if the other parent never ...
Jax Taylor and Brittany Cartwright candidly opened up about their three-year-old son's speech struggles on the most recent episode of The Valley. Following the episode, Taylor seemed to suggest ...
transcript. Biden Announces New Plan for Student Debt Relief President Biden announced a large-scale effort to help pay off federal student loans for more than 20 million borrowers.
With her third national championship win, Dawn Staley has firmly established herself in the pantheon of the greatest NCAA women's basketball coaches in history.