We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business

How to Write a Project Proposal (with Examples & Templates)
By Jennifer Gaskin , Dec 11, 2023

For businesses that rely on clients and partnerships to generate sales and revenue, project proposals are must-haves. A polished, professional project proposal is one of the best ways to present the capabilities your team has and put your goods and services in the best possible light.
But creating a good project proposal is more than just a timeline and a budget. Adding visual flourishes like charts, graphs and other imagery can help elevate a boring proposal to the top of the pile. Learn how you can create a successful project proposal and take a look at several project proposal templates you can fully customize using Venngage.
Click to jump ahead:
- What is a project proposal and how to use it
How to write a project proposal in 9 steps
4 project proposal examples with templates.
- What are the 6 types of project proposals?
What are the contents of a project proposal?
What is a project proposal & how to use it.
A project proposal is a formal document that outlines the details, objectives and scope of a proposed project. The purpose of a project proposal is to describe the parameters of a potential project or initiative.
Depending on the industry and type of project proposal (more on that in a moment), these documents can include things like scope of work, timelines, staffing, budget, capability statement and more.
Companies that receive project proposals from other firms or individuals use these documents to narrow down their options and make an informed decision about the best partner for them. And companies that create project proposals use them to make their pitch for the project.
Here’s an example of a project proposal to propose a new partnership:

It’s important to note that project proposals are not the same as business proposals , though there are some similarities. One of the biggest differences is that business proposals tend to be more general and expansive. Learn more about writing a great business proposal.
Writing a great project proposal can be a challenge. That’s because you need to craft the message specifically for the company or individual you’re sending the proposal to.
But don’t worry if you don’t know where to start, here’s how you write an effective project proposal:
Step 1: Review the RFP (if you have one)
If there is no formal RFP, you’ll still need to start out researching as much as you can about your potential client. That means finding out not only about the problem you’re hoping to solve but the history of the client, their industry, their competitors and more. Getting to know them better will help you understand how to portray yourself or your company in the best light.
Step 2: Create a project proposal outline
Whether you use the sections we listed above in that order, add or remove ones or shift things around, jot down a quick outline of sections to keep in mind as you work.
Step 3: Define the problem and present your solution
Kick things off by clearly nailing down the problem or need your project is tackling. Back it up with some hard evidence and data to show why this issue is a big deal. Break it down for your audience, explaining how your project is going to make their lives better.
Step 4: Highlight elements that may set your proposal apart
For example, if you know that your company will be able to complete the task more quickly than any competitors, make that the focus of your solution or scope of work section. Compare your proposed timeline with what your competitors are likely to propose to the client.
You should also make notes of any elements that you might be able to visualize through a graph, chart or other design element — visuals can help not only make your project proposal easier on the eyes, but they can make it more memorable and illustrate to the client that you are able to think creatively.
Here’s an example of how it can look in your project proposal:

Step 5: Define project deliverables and goals
A rock-solid project hinges on clarity, and that starts with laying out precisely what your project will deliver. Whether it’s reports, shiny new products, or top-notch services, make it crystal clear from the get-go.
Next, set the bar with measurable goals and objectives that scream success. Break them down so everyone’s on the same page. And because time is money, map out a timeline that’s not just a bunch of dates but a roadmap with key pit stops.
These milestones and deadlines are the heartbeat of your project, guiding you through each phase and making sure you hit the finish line with style. It’s all about setting the stage for success and making sure everyone’s got their eyes on the prize.
Step 6: State your plan or approach
Now, we’ve made it to the meat of your project proposal. In this section, walk your readers through the nitty-gritty of your project management approach.
Break down the essentials when it comes to resources—think people, equipment, and budget. And, while you’re at it, clue them in on your game plan for handling potential challenges through your risk management strategy. Additionally, consider your approach to project management, for example agile project management prioritizes flexibility and adaptability in order to effectively respond to changes and deliver successful outcomes.
Step 7: Outline your project schedule and budget
Crafting a successful project hinges on meticulous planning, starting with the creation of a detailed project schedule.
Break down the project into specific tasks and assign realistic timelines to each one. This step-by-step schedule, like a roadmap, not only helps in visualizing the project’s progression but also aids in resource allocation and risk management.
Simultaneously, developing a comprehensive budget is paramount. Dive deep into identifying and estimating all project costs, including personnel, materials equipment, and any potential contingencies. The budget acts as the financial backbone, ensuring that resources are allocated judiciously.
But here’s the deal – keep it real. Your schedule and budget need to be doable, considering the real-world factors at play. It’s all about laying the groundwork for success and keeping everyone in the loop from start to finish.
Step 8: Write the executive summary
The executive summary serves as the project’s sneak peek, condensing the entire proposal into a punchy snapshot. This opening act isn’t just a formality; it’s your chance to grab the reader’s attention from the get-go.
Picture it like the movie trailer – it needs to be compelling, leaving the audience eager for the full feature. In this compact summary, shine a spotlight on the critical elements of your proposal.
Outline the problem you’re tackling, showcase your ingenious solution, spell out the perks and benefits and throw in a quick glance at the budget for good measure. It’s your project’s elevator pitch, setting the stage for what’s to come and making sure your audience is hooked right from the first line.
Step 9: Proofread and edit
Before sending your proposal out into the world, give it a thorough once-over. Take the time to meticulously proofread every nook and cranny, hunting down grammar slip-ups, punctuation quirks and sneaky spelling errors.
A second perspective can catch things you might have overlooked. And let’s talk presentation – ensure your proposal isn’t just a content champ but looks the part too. Format it like a pro, making sure it’s visually appealing and easy on the eyes.
After all, a polished proposal not only communicates your ideas effectively but also leaves a lasting impression. Browse Venngage’s selection of project proposal templates to get a head start today!
Additional tips:
Avoid overly salesy language.
It can be tempting, particularly if you’re sending unsolicited project proposals, to use some of the same language in your proposal as you might in an ad, but you should keep such wording to a minimum.
Let the proposal speak for itself; if you or your firm truly are the best one for the job, it should be evident in your proposal. Being straightforward can also signal to the hiring party that you don’t want to waste their time with flowery language. It’s better to deal in facts rather than opinions for project proposals.
Establish a single point of contact
Some project proposals will include lists or even short bios of your staff members who will be involved in the project. But it’s a good idea to ensure that your project proposal makes it clear whom the client should contact to move the project forward or submit any questions. Include this person’s information at the beginning and the end of your document.
Write with one voice
While it’s common for large RFPs to be completed by many people on the team, ensure that whoever is responsible for bringing it all together has a chance to make the document feel cohesive. It should read as if one person put the entire thing together.
Now that we’ve explored some of the background and purpose of project proposals, let’s take a look at some templates you can customize using Venngage for your own project.
Construction project proposal examples
The construction industry is a complex one, and project proposals are critical for landing business and keeping projects on track. But there are many approaches a construction project proposal can take.
Taking the complicated and making it simple is a challenge, particularly in this field, but as this project proposal example shows, it can be done. By using simple, clear language and well-placed visual emphasis, this free project proposal template stands out for its simplicity.

Many hiring companies simply skim project proposals for things like budget and timeframe, and while you still need to craft an engaging proposal, it’s a good idea to put those types of elements front and center, as this construction project proposal does.

Remember that regardless of whether your firm is hired for the job at hand, every document you send to another business is a chance to establish your company’s brand identity. Use a template like the one below, update it with your logo and brand colors and fonts to keep it aligned with your messaging.

As you can see from the example below, a few color changes can make a huge difference:

To easily apply your brand colors and logos, simply have them automatically extracted from your website using Autobrand:
And apply them to your design in one click with My Brand Kit :
Design project proposal examples
You might think it would be a no-brainer for a designer to create a well-designed project proposal, but it’s common for creative people to have difficulty when it comes to analytical thinking. That’s why having a couple of great project proposals in your back pocket is perfect for a designer.
Project proposals in creative fields tend to be a bit less buttoned-up than those in other industries, so use your proposal as an opportunity to make a bold design statement. The template below, for example, uses a striking color palette and minimalist imagery on the cover to make the proposal stand out, and those touches are reinforced throughout the document.

This example, similarly, uses creative color combinations to strike a design-forward tone. But as both of these templates illustrate, the bones of the project proposal must be sound, and all the information required should still be covered.

Work project proposal examples
Not every industry requires a unique approach to project proposals, and, in fact, for most applications, a general work proposal template will suffice, provided that you do your due diligence in following any requirements set forward by the hiring party.
This template created for a consulting firm illustrates a straightforward approach to project proposals that you can easily adapt for your needs. Add or remove pages, insert charts and graphs or new icons and craft a compelling narrative.

This project proposal template is an excellent example of how companies can use established templates to create a unique proposal. Note how they’ve used the sections that apply to them and put them together in a way to appeal to their potential client.

Marketing project proposal examples
Marketers and marketing agencies are regularly asked to submit RFPs, whether for individual projects or long-term engagements, so the average marketing agency will need to have several project proposals on hand that they can modify when new requests come in.
This social media marketing project proposal template is ideal for a single campaign rather than a multi-year engagement. In that situation, it’s crucial to make sure all dates and milestones in the campaign are clearly stated.

Ideally, a marketing agency or marketer will get a chance to pitch for long-term work. In that case, this project proposal template is ideal for outlining all aspects of the project proposal, including a timeline that extends to a full year.

A critical aspect of modern marketing success is doing a great deal of research on keywords, competitors and traffic, and many marketers include such metrics in their project proposals, along the lines of this example. Note how high-impact charts and graphs are used to help the audience absorb the data and make an informed decision. There are various marketing proposal examples that you can look at to inspire your next proposal design and help catch the attention of your clients.

What are the 6 types of project proposal s?
Because every project is unique, there are many types of project proposals, but these are the most common ones:
Solicited through RFP
RFP stands for Request for Proposal (they may also be called Request for Quotation, or RFQ).
These types of project proposals typically come with the most stringent requirements and obligations. The hiring company will usually list out the elements that must be included in the RFP as well as any limitations or conditions that apply.
From the vendor’s standpoint, being asked to submit an RFP is generally a good sign because it means that your firm (or yourself, if you’re an individual) has made it through the initial round of research by the hiring party.
I nformally solicited
Informally solicited project proposals are similar to RFPs or formally solicited proposals in that they may have just as many requirements, but because they’re outside of the formal RFP process, the requirements often aren’t stated up front. That could mean the vendor needs to do more research and ask more questions of the hiring party, or it could mean there actually aren’t as many requirements.
Another benefit of submitting an informally solicited project proposal is that the absence of a formal process likely means the vendor will be up against less competition.
Unsolicited
Also called spec (speculative) proposals, unsolicited project proposals come from the vendor’s side rather than the hiring party.
These proposals are particularly difficult because the hiring party, well, may not be hiring at all. With a spec or unsolicited project proposal, the vendor believes there’s a need for their services and must not only convince the hiring party that the need exists, but that the vendor is the best one to fill that need.
Pre-proposals
Pre-proposals can be considered mini versions of RFPs. They are often sought by a hiring party that wants to avoid a lengthy proposal process — or simply doesn’t want to read a long pitch. These types of proposals are brief, usually a few pages at most, and depending on the results, the hiring party may make an offer or make a full RFP request.
Non-competing/continuation proposals
Continuation proposals are common in multi-year projects or ones in which both parties may have agreed to certain conditions governing how the project proceeds.
With a continuation proposal, the goal isn’t to pitch your services but rather to keep the client up to date on the project, inform them of any metrics they need to know or that may be part of the scope of work and get their formal approval to continue with the project.
Competing/renewal proposals
Renewal proposals are similar to continuation proposals, but instead of being created in the middle of a project, a renewal project proposal is generated once a project or contract has ended. They’re also called competing proposals because the vendor will need to make their case as to why the project or contract should be renewed.
It may be wise to approach these types of proposals as you might an unsolicited one, but the benefit to the vendor is that (if the project has been a success), they will have past results with that specific client to showcase in their new proposal.
The content of project proposals will vary depending on the industry and the type of proposal. For example, while solicited, unsolicited and pre-proposals will typically include a budget that is negotiable, a continuation proposal’s budget has likely already been set. That said, here are the typical contents of a project proposal:
- Summary : An executive summary or project background is typically the first section of a project proposal. Most vendors use this as an opportunity to thank the hiring company for the opportunity, as well as summarizing what the client is about to see through the remainder of the proposal.
This template shows a complete executive summary for a product launch, which can be longer than a typical executive brief or project background in your proposal — something to keep in mind:

- Objective : An explanation of what needs to be done or what problem can be solved if the hiring party accepts the proposal.

- Solution : An explanation of what the vendor would do to solve the problem or how they would approach completing the needed task.

- Scope of work : A detailed description of what exactly would be done, when and how much it would cost. This section may also need to include legal information, though in most cases, contracts are separate from project proposals.
Here’s an example of how you can write down the scope of work for your proposed project:

Call to action : The final section of your project proposal (assuming there are no appendices) should let the hiring party know what to do next. Include a place for them to sign the document to show their acceptance, as well as contact information in case they have further questions. To make the proposal legally binding, you can send it to your client via a free eSignature software such as Papersign and collect their signature in a compliant manner.

- Appendix : Appendices in project proposals could include information that didn’t fit within the client’s requirements or that helps to further explain information in the main part of the document. This section is optional.
Project proposal FAQs
What is the difference between project proposals and project charters.
The difference between both is that project proposals serve to present a project’s goals and approach for approval. On the contrary, project charters officially authorize the project, defining roles, responsibilities and initial objectives.
What is the difference between project proposals and business cases?
Project proposals focus on securing approval by presenting a project idea and its feasibility. On the other hand, a business case provides a more comprehensive analysis, including financial aspects and long-term strategic impact, aiding stakeholders in making informed decisions.
What is the difference between project proposals and project plans?
Project proposals aim to gain approval by detailing the project’s purpose and scope, whereas project plans are comprehensive documents specifying tasks, timelines and resources necessary for successful project execution.
Highlight your products effectively with Venngage’s professional project proposal templates
Letting a potential customer know what you’re capable of is a critical tool in many fields, and project proposals can highlight your company in a way few other documents can.
Start with one of these templates or create your project proposal from scratch. Whether your company has just gotten an RFP or you want to land that big fish in your industry, Venngage makes it simple to create an effective project proposal without becoming overwhelmed. It’s free to get started.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
How to Write a Project Proposal (Examples & Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a project proposal, types of project proposals, project proposal vs. project charter, project proposal vs. business case, project proposal vs. project plan, project proposal outline, how to write a project proposal, project proposal example, project proposal tips.
- ProjectManager & Project Proposals
A project proposal is a project management document that’s used to define the objectives and requirements of a project. It helps organizations and external project stakeholders agree on an initial project planning framework.
The main purpose of a project proposal is to get buy-in from decision-makers. That’s why a project proposal outlines your project’s core value proposition; it sells value to both internal and external project stakeholders. The intent of the proposal is to grab the attention of stakeholders and project sponsors. Then, the next step is getting them excited about the project summary.
Getting into the heads of the audience for which you’re writing the project proposal is vital: you need to think like the project’s stakeholders to deliver a proposal that meets their needs.
We’ve created a free project proposal template for Word to help structure documents, so you don’t have to remember the process each time.

Get your free
Project Proposal Template
Use this free Project Proposal Template for Word to manage your projects better.
In terms of types of project proposals, you can have one that’s formally solicited, informally solicited or a combination. There can also be renewal and supplemental proposals. Here’s a brief description of each of them.
- Solicited project proposal: This is sent as a response to a request for proposal (RFP) . Here, you’ll need to adhere to the RFP guidelines of the project owner.
- Unsolicited project proposal: You can send project proposals without having received a request for a proposal. This can happen in open bids for construction projects , where a project owner receives unsolicited project proposals from many contractors.
- Informal project proposal: This type of project proposal is created when a client asks for an informal proposal without an RFP.
- Renewal project proposal: You can use a renewal project proposal when you’re reaching out to past customers. The advantage is that you can highlight past positive results and future benefits.
- Continuation project proposal: A continuation project proposal is sent to investors and stakeholders to communicate project progress.
- Supplemental project proposal: This proposal is sent to investors to ask for additional resources during the project execution phase.
A project proposal is a detailed project document that’s used to convince the project sponsor that the project being proposed is worth the time, money and effort to deliver it. This is done by showing how the project will address a business problem or opportunity. It also outlines the work that will be done and how it will be done.
A project charter can seem like the same thing as a project proposal as it also defines the project in a document. It identifies the project objectives, scope, goals, stakeholders and team. But it’s done after the project has been agreed upon by all stakeholders and the project has been accepted. The project charter authorizes the project and documents its requirements to meet stakeholders’ needs.
A business case is used to explain why the proposed project is justified. It shows that the project is worth the investment of time and money. It’s more commonly used in larger companies in the decision-making process when prioritizing one project over another.
The business case answers the questions: what is the project, why should it be taken up, who will be involved and how much will it cost? It’s therefore related to a project proposal, but the project proposal comes before the business case and is usually part of the larger proposal.
Again, the project proposal and the project plan in this case are very similar documents. It’s understandable that there would be some confusion between these two project terms. They both show how the project will be run and what the results will be. However, they’re not the same.
The project proposal is a document that aims to get a project approved and funded. It’s used to convince stakeholders of the viability of the project and their investment. The project plan, on the other hand, is made during the planning phase of the project, once it’s been approved. It’s a detailed outline of how the project will be implemented, including schedule, budget, resources and more.
All the elements in the above project proposal outline are present in our template. This free project proposal template for Word will provide you with everything you need to write an excellent project proposal. It will help you with the executive summary, project process, deliverables, costs—even terms and conditions. Download your free template today.
There are several key operational and strategic questions to consider, including:
- Executive summary: This is the elevator pitch that outlines the project being proposed and why it makes business sense. While it also touches on the information that’ll follow in the project proposal, the executive summary should be brief and to the point.
- Project background: This is another short part of the proposal, usually only one page, which explains the problem you’ll solve or the opportunity you’re taking advantage of with the proposed project. Also, provide a short history of the business to put the company in context to the project and why it’s a good fit.
- Project vision & success criteria: State the goal of the project and how it aligns with the goals of the company. Be specific. Also, note the metrics used to measure the success of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: There are always risks. Detail them here and what strategies you’ll employ to mitigate any negative impact as well as take advantage of any positive risk.
- Project scope & deliverables: Define the project scope, which is all the work that has to be done and how it will be done. Also, detail the various deliverables that the project will have.
- Set SMART goals: When setting goals, be SMART. That’s an acronym for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. All your goals would be defined by those five things.
- Project approach: Define the approach you’ll use for the contract. There are several different types of contracts used in construction , for example, such as lump sum, cost plus, time and materials, etc. This is also a good place to describe the delivery method you’ll use.
- Expected benefits: Outline the benefits that will come from the successful completion of the project.
- Project resource requirements: List the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., that you’ll need to execute the project if approved.
- Project costs & budget: Detail all the costs, including resources, that’ll be required to complete the project and set up a budget to show how those costs will be spent over the course of the project.
- Project timeline: Lay out the project timeline , which shows the project from start to finish, including the duration of each phase and the tasks within it, milestones, etc.
In addition to these elements, it’s advisable to use a cover letter, which is a one-page document that helps you introduce your project proposal and grab the attention of potential clients and stakeholders.
To make the best proposal possible, you’ll want to be thorough and hit on all the points we’ve listed above. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a persuasive priority proposal.
1. Write an Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the main elements of your project proposal, such as your project background, project objectives and project deliverables, among other things. The goal is to capture the attention of your audience and get them excited about the project you’re proposing. It’s essentially the “elevator pitch” for the project life cycle. It should be short and to the point.
The executive summary should be descriptive and paint a picture of what project success looks like for the client. Most importantly, it should motivate the project client; after all, the goal is getting them to sign on the dotted line to get the project moving!
2. Provide a Project Background
The project background is a one-page section of your project proposal that explains the problem that your project will solve. You should explain when this issue started, its current state and how your project will be the ideal solution.
- Historic data: The history section outlines previously successful projects and those that could have run more smoothly. By doing so, this section establishes precedents and how the next project can be more effective using information from previous projects.
- Solution: The solution section addresses how your project will solve the client’s problem. Accordingly, this section includes any project management techniques , skills and procedures your team will use to work efficiently.
3. Establish a Project Vision & Success Criteria
You’ll need to define your project vision. This is best done with a vision statement, which acts as the north star for your project. It’s not specific as much as it’s a way to describe the impact your company plans to make with the project.
It’s also important to set up success criteria to show that the project is in fact doing what it’s proposed to do. Three obvious project success criteria are the triple constraint of cost, scope and time. But you’ll need to set up a way to measure these metrics and respond to them if they’re not meeting your plan.
4. Identify Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
To reduce the impact of risk in your project, you need to identify what those risks might be and develop a plan to mitigate them . List all the risks, prioritize them, describe what you’ll do to mitigate or take advantage of them and who on the team is responsible for keeping an eye out for them and resolving them.
5. Define Your Project Scope and Project Deliverables
The project scope refers to all the work that’ll be executed. It defines the work items, work packages and deliverables that’ll be delivered during the execution phase of your project life cycle. It’s important to use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to define your tasks and subtasks and prioritize them.
6. Set SMART Goals for Your Project Proposal
The best mindset when developing goals and objectives for your project proposal is to use the SMART system :
- Specific – Make sure your goals and objectives are clear, concise and specific to the task at hand.
- Measurable – Ensure your goals and objectives are measurable so it’s obvious to see when things are on track and going well, and conversely, when things are off track and issues need to be addressed. Measurable goals make it easy to develop the milestones you’ll use to track the progress of the project and identify a reasonable date for completion and/or closure.
- Attainable – It’s important every project has a “reach” goal. Hitting this goal would mean an outstanding project that extends above and beyond expectations. However, it’s important that the project’s core goal is attainable, so morale stays high and the job gets done with time and resources to spare.
- Relevant – Make sure all of your goals are directly relevant to the project and address the scope within which you’re working.
- Time-Based – Timelines and specific dates should be at the core of all goals and objectives. This helps keep the project on track and ensures all project team members can manage the work that’s ahead of them.
7. Explain What’s Your Project Approach
Your project approach defines the project management methodology , tools and governance for your project. In simple terms, it allows project managers to explain to stakeholders how the project will be planned, executed and controlled successfully.
8. Outline The Expected Benefits of Your Project Proposal
If you want to convince internal stakeholders and external investors, you’ll need to show them the financial benefits that your project could bring to their organization. You can use cost-benefit analysis and projected financial statements to demonstrate why your project is profitable.
9. Identify Project Resource Requirements
Project resources are critical for the execution of your project. The project proposal briefly describes what resources are needed and how they’ll be used. Later, during the planning phase, you’ll need to create a resource management plan that’ll be an important element of your project plan. Project requirements are the items, materials and resources needed for the project. This section should cover both internal and external needs.
10. Estimate Project Costs and Project Budget
All the resources that you’ll need for your project have a price tag. That’s why you need to estimate those costs and create a project budget . The project budget needs to cover all your project expenses, and as a project manager, you’ll need to make sure that you adhere to the budget.
11. Define a Project Timeline
Once you’ve defined your project scope, you’ll need to estimate the duration of each task to create a project timeline. Later during the project planning phase , you’ll need to create a schedule baseline, which estimates the total length of your project. Once the project starts, you’ll compare your actual project schedule to the schedule baseline to monitor progress.
Now let’s explore some project proposal examples to get a better understanding of how a project proposal would work in the real world. For this example, let’s imagine a city that’s about to build a rapid transit system. The city government has the funds to invest but lacks the technical expertise and resources that are needed to build it, so it issues a request for proposal (RFP) document and sends it to potential builders.
Then, the construction companies that are interested in executing this rapid transit project will prepare a project proposal for the city government. Here are some of the key elements they should include.
- Project background: The construction firm will provide an explanation of the challenges that the project presents from a technical perspective, along with historical data from similar projects that have been completed successfully by the company.
- Project vision & success criteria: Write a vision statement and explain how you’ll track the triple constraint to ensure the successful delivery of the project.
- Potential risks and mitigation strategies: List all risks and how they’ll be mitigated, and be sure to prioritize them.
- Project scope & deliverables: The work that’ll be done is outlined in the scope, including all the deliverables that’ll be completed over the life cycle of the project.
- Set SMART goals: Use the SMART technique to define your project goals by whether they’re specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound.
- Project approach: Define the methodology that the project manager will employ to manage the project. Also, figure out what type of contract will be used to define the project.
- Expected benefits: Show how the project will deliver advantages to the company and define what these benefits are in a quantifiable way.
- Project resource requirements: List all the resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, etc., needed to execute the project.
- Project costs & budget: Estimate the cost of the project and lay that out in a project budget that covers everything from start to finish.
- Project timeline: Outline the project schedule, including phases, milestones and task duration on a visual timeline.
Whatever project proposal you’re working on, there are a few tips that apply as best practices for all. While above we suggested a project proposal template that would have a table of contents, meaning it would be many pages long, the best-case scenario is keeping the proposal to one or two pages max. Remember, you’re trying to win over stakeholders, not bore them.
Speaking of project stakeholders , do the research. You want to address the right ones. There’s no point in doing all the work necessary to write a great proposal only to have it directed to the wrong target audience. Whoever is going to read it, though, should be able to comprehend the proposal. Keep the language simple and direct.
When it comes to writing, get a professional. Even a business document like a project proposal, business case or executive summary will suffer if it’s poorly constructed or has typos. If you don’t want to hire a professional business writer, make sure you get someone on your project team to copy, edit and proof the document. The more eyes on it, the less likely mistakes will make it to the final edition.
While you want to keep the proposal short and sweet, it helps to sweeten the pot by adding customer testimonials to the attachments. Nothing sells a project plan better than a customer base looking for your product or service.
ProjectManager & Project Proposals
ProjectManager allows you to plan proposals within our software. You can update tasks for the project proposal to signify where things stand and what’s left to be done. The columns allow you to organize your proposal by section, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) of sorts.
When building a project proposal, it’s vital to remember your target audience. Your audience includes those who are excited about the project, and see completion as a gain for their organization. Conversely, others in your audience will see the project as a pain and something to which they aren’t looking forward. To keep both parties satisfied, it’s essential to keep language factual and concise.
Our online kanban boards help you think through that language and collaborate on it effectively with other team members, if necessary. Each card shows the percentage completed so everyone in the project management team is aware of the work done and what’s left to be done.
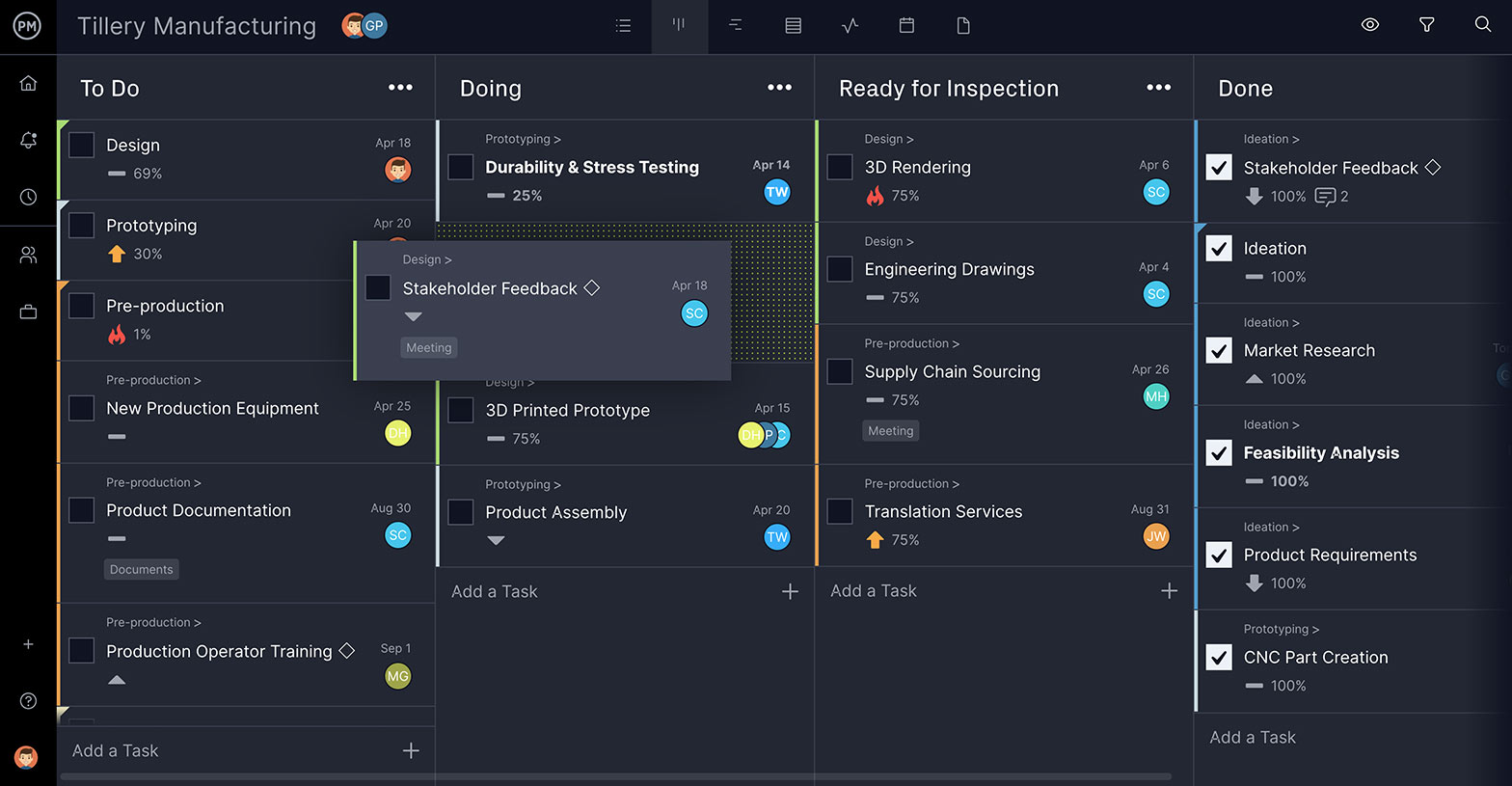
As you can see from the kanban board above, work has begun on tasks such as product documentation and design. Tasks regarding stakeholder feedback, ideation, market research and more have been completed, and there’s a good start on the engineering drawings, 3D rendering, supply chain sourcing and translation services.
A PDF is then attached to the card, and everyone added to the task receives an email notifying them of the change. This same process can be used throughout the life-cycle of the project to keep the team updated, collaborating, and producing a first-class project proposal. In addition to kanban boards, you can also use other project management tools such as Gantt charts , project dashboards, task lists and project calendars to plan, schedule and track your projects.
Project proposals are just the first step in the project planning process. Once your project is approved, you’ll have to solidify the plan, allocate and manage resources, monitor the project, and finally hand in your deliverables. This process requires a flexible, dynamic and robust project management software package. ProjectManager is online project management software that helps all your team members collaborate and manage this process in real-time. Try our award-winning software with this free 30-day trial .

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- 6 steps for writing a persuasive projec ...
6 steps for writing a persuasive project proposal

A project proposal is a written document outlining everything stakeholders should know about a project, including the timeline, budget, objectives, and goals. Your project proposal should summarize your project details and sell your idea so stakeholders buy in to the initiative. In this guide, we’ll teach you how to write a project proposal so you can win approval and succeed at work.
All projects have creation stories, but they don’t start with someone declaring, “Let there be resources!” To move forward with a project, teams must submit a proposal to decision-makers within their organization or to external stakeholders.
What is a project proposal?
A project proposal is a written document outlining everything stakeholders should know about a project, including the timeline, budget, objectives , and goals. Your project proposal should summarize your project details and sell your idea so stakeholders feel inclined to get involved in the initiative.
![creative writing project proposal [inline illustration] What is a project proposal? (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/c2b04f48-8d95-4e09-aa12-e7d5e0b8c89c/inline-project-planning-how-to-write-a-proposal-for-a-project-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
The goal of your project proposal is to:
Secure external funding
Allocate company resources to your project
Gain stakeholder buy-in
Build momentum and excitement
Project proposals vs. project charters vs. business cases
Project proposals and project charters serve different purposes in the project creation process, and it’s important to understand the difference between the two. While a project proposal takes place in the initiation phase of the project, the project charter takes place in the planning phase.
As mentioned above, a project proposal is a persuasive document meant to convince stakeholders why the project should be carried out. A project charter is a reference document that defines project objectives, and it can’t be created until the project proposal is approved.
People also confuse the business case with the project proposal, but the business case also comes after the proposal. Once the project is approved through a proposal, a business case may be used to secure additional funding for the project.
Types of project proposals
There are six types of proposals you may encounter as a project manager, and understanding the different formats can be useful as you write yours. Each type has a different goal.
![creative writing project proposal [inline illustration] Types of project proposals (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/b89609ec-25cf-4fa6-a4af-0688f71a4ed6/inline-project-planning-how-to-write-a-proposal-for-a-project-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Solicited: You’ll send solicited proposals in response to a Request for Proposal (RFP). An RFP announces a project in detail and asks for bids from qualified teams. Because you’re competing against other companies for this type of proposal, you must do thorough research and write persuasively.
Unsolicited: You’ll send unsolicited proposals without an RFP, meaning no one asked for your proposal. In this case, you won’t be up against other companies or teams, but you’ll still need to be persuasive because you have no knowledge of whether the stakeholder you’re pitching to needs you.
Informal: You may have a client send you an informal request for a project proposal, in which case you can respond with your project pitch. Because this isn’t an official RFP, the rules are less concrete.
Renewal: You’ll send renewals to existing clients in hopes that they’ll extend their services with your organization. In this type of project proposal, the goal is to emphasize past results your team has produced for the client and persuade them you can produce future results.
Continuation: You’ll send continuations as a reminder to a stakeholder letting them know the project is beginning. In this project proposal, you’ll simply provide information about the project instead of persuading the stakeholder.
Supplemental: Similar to a continuation proposal, you’ll send a supplemental proposal to a stakeholder already involved in your project. In this type of proposal, you’re letting the stakeholder know the project is beginning, while also asking for additional resources. You should persuade the stakeholder to contribute more to the project in this proposal.
The tone of voice and content of your project proposal will differ based on the type of proposal you’re sending. When you know your project goals, you can write your proposal accordingly.
How to write a project proposal
These step-by-step instructions apply to most project proposals, regardless of type. You’ll need to customize your proposal for the intended audience, but this project proposal outline can serve as a reference to ensure you’re including the key components in your document.
![creative writing project proposal [inline illustration] How to write a project proposal (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ddf5a670-2fa4-4216-ac08-affdd7201741/inline-project-planning-how-to-write-a-proposal-for-a-project-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Write an executive summary
The executive summary serves as the introduction to your project proposal. Similar to a report abstract or an essay introduction, this section should summarize what’s coming and persuade the stakeholder to continue reading. Depending on the complexity of your project, your executive summary may be one paragraph or a few paragraphs.
Your executive summary should include:
The problem your project plans to solve
The solution your project provides for that problem
The impact your project will have
You should only address these items briefly in your executive summary because you’ll discuss these topics in more detail later in your proposal.
2. Explain the project background
In this section, you’ll go into the background of the project. Use references and statistics to convince your reader that the problem you’re addressing is worthwhile.
Some questions to include are:
What is the problem your project addresses?
What is already known about this problem?
Who has addressed this problem before/what research is there?
Why is past research insufficient at addressing this problem?
You can also use this section to explain how the problem you hope to solve directly relates to your organization.
3. Present a solution
You just presented a problem in the project background section, so the next logical step in proposal writing is to present a solution. This section is your opportunity to outline your project approach in greater detail.
Some items to include are:
Your vision statement for the project
Your project schedule , including important milestones
Project team roles and responsibilities
A risk register showing how you’ll mitigate risk
The project deliverables
Reporting tools you’ll use throughout the project
You may not have all these items in your proposal format, but you can decide what to include based on the project scope . This section will likely be the longest and most detailed section of your proposal, as you’ll discuss everything involved in achieving your proposed solution.
4. Define project deliverables and goals
Defining your project deliverables is a crucial step in writing your project proposal. Stakeholders want to know what you’re going to produce at the end of your project, whether that’s a product, a program, an upgrade in technology, or something else. As the stakeholder reads through your vision, this will be the section where they say, “Aha, this is what they’ll use my resources for.”
When defining your deliverables, you should include:
The end product or final objective of your project
A project timeline for when deliverables will be ready
SMART goals that align with the deliverables you’re producing
While it’s important to show the problem and solution to your project, it’s often easier for stakeholders to visualize the project when you can define the deliverables.
5. List what resources you need
Now that you’ve outlined your problem, approach, solution, and deliverables, you can go into detail about what resources you need to accomplish your initiative.
In this section, you’ll include:
Project budget : The project budget involves everything from the supplies you’ll need to create a product to ad pricing and team salaries. You should include any budget items you need to deliver the project here.
Breakdown of costs: This section should include research on why you need specific resources for your project; that way, stakeholders can understand what their buy-in is being used for. This breakdown can also help you mitigate unexpected costs.
Resource allocation plan : You should include an overview of your resource allocation plan outlining where you plan to use the specific resources you need. For example, if you determine you need $50,000 to complete the project, do you plan to allocate this money to salaries, technology, materials, etc.
Hopefully, by this point in the proposal, you’ve convinced the stakeholders to get on board with your proposed project, which is why saving the required resources for the end of the document is a smart strategic move.
6. State your conclusion
Finally, wrap up your project proposal with a persuasive and confident conclusion. Like the executive summary, the conclusion should briefly summarize the problem your project addresses and your solution for solving that problem. You can emphasize the impact of your project in the conclusion but keep this section relevant, just like you would in a traditional essay.
Tips for writing an effective project proposal
Following the steps listed above will ensure your project proposal has all the right elements. But if you want to impress your readers and win their approval, your writing must shine. In addition to the above, a project proposal includes:
Know your audience
As you write your proposal, keep your audience (i.e. the stakeholders) in mind at all times. Remember that the goal of the proposal is to win your audience over, not just to present your project details. For example, if you’re creating a new editing tool for a children’s publishing house, can you determine whether your stakeholders are parents and appeal to their emotional side when persuading them to buy in to your product?
Be persuasive
Persuasion is important in a project proposal because you’re hoping your audience will read your proposal and do something for you in return. If your reader isn’t intrigued by your project, they won’t feel inclined to help you. If you describe your editing tool but don’t mention the many features it will offer, how it will benefit clients, and its positive impact in the industry, your audience will wonder, “Why should I care about this project?”
Keep it simple
While you should go into detail on your problem, approach, and solution, you shouldn’t make your project proposal overly complex. This means you can discuss the project plan for your proposed editing tool without discussing what codes the engineers will use to make each feature work.
Do your research
A successful project proposal includes thorough research. Be prepared to back up your problem—and solution—with reputable sources, case studies, statistics, or charts so you don’t leave your audience with questions. When writing your proposal, put yourself in the reader’s shoes and ask:
Why is this a problem?
How is this a solution to the problem?
Has anyone addressed this problem before?
What are the project costs?
If you can answer these questions, then you’ve likely done enough research to support your proposed initiative.
Use project management tools to strengthen your project proposal
Good project proposals require team collaboration . With the right management tools, your team can communicate, share information, and work together on one shared document.
When you store all your project information in one place, it’s easy to access that data when you need it. Project proposals stem from well-organized and properly planned projects, which is why project management software is a key resource to effectively write a project proposal. Ready to get started? Try Asana .
Related resources

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
How to Write a Proposal for a Project (With Examples)
An excellent project proposal should address the client’s main concerns and goals, sell your unique approach, and clarify the project process.
If the project is crystal clear to both you and your client, you can reduce confusion, scope creep , and complaints.
In this guide to writing proposals for projects, we dive into what this type of proposal must include and how to write one. Plus, we showcase excellent examples to copy and data-driven best practices to follow.
What’s in this guide:
What is a project proposal?
What to include in a project proposal, how to write a project proposal.
Examples of project proposals
Tips for writing a project proposal
Looking for proposal templates, automated follow-ups, and closing insights? Get a custom Proposify demo .

12 min. read
A project proposal is sent by a design, consulting, or other type of firm to a potential client in order to present important project details like deliverables, timelines, expected outcomes, and costs. When the terms of service are included, a signed project proposal can double as a contract for the legal protection of both parties.
A project proposal is not to be confused with a request for proposal (RFP), which is sent by a corporation or government agency to multiple consulting firms in order to receive the maximum amount of proposals and pricing options for a project that they’ve already defined internally.
A project proposal, on the other hand, is created as part of a consultative selling process and can benefit a client even if they don’t move forward with the work because of the helpful project breakdown.
Types of project proposals
There are many different types of project proposals, from different lengths to fee structures.
Project length:
Short, one-time project
Longer, phased project
Retainer or ongoing project
Paid discovery or audit project
Payment type:
Hourly with estimated hours
Hourly with min and max hour range
Hybrid flat rate and hourly (common in interior design, event planning, and other fields with hard costs and hourly costs)
Industries:
Website design
Graphic design
Architecture and engineering
Construction and property services
Commercial leasing
Interior design
Event planning
Software subscriptions
Administrative management
Payroll and HR management
Market research and analysis
Software development
Product development
Solicitation types:
Solicited proposals sent in response to an RFPs
Unsolicited proposals sent without a prior RFP
A successful project proposal will include all or most of these important sections. You can mix and match them with your own templates or AI writing tools to craft the perfect project proposal outline.
The cover page is the easiest page to write.
It typically includes:
Your company’s name
The client’s name or project name
A photograph or graphic design
You might also choose to include your contact information on the cover page, but this is usually reserved for the About Us page or a dedicated contact page.
Executive summary or letter
The executive summary is where you offer an overview of your methodology and the proposed project. Consider it elevator pitch. Shoot to write approximately 75 - 200 words.
Use this free AI-enabled character counter to help both get through writer's block as well as make sure your executive summary is the right length.
Many other parts of the proposal will be written as bullet points or very short phrases, so use this section to really paint the full picture of the project with language that is on-brand.

Goals or objectives
You can include the project goals and objectives of the client in the executive summary, in the project summary, or in a section dedicated just for this purpose.
You might write 75 - 150 words describing the goals, or utilize a bulleted list of 3-8 goals.
The approach section can go by a lot of different names, such as “solution” or “methodology.” In this section, you’re describing the strategy behind your approach. It sets the stage for the project details and budget to follow.
This is particularly important when winning over new clients who aren’t familiar with what sets your business apart from the competition.
A catering company might use this proposal page to talk about the sort of experience or quality of food they provide.
Meanwhile, a marketing company might include its brand ethos or core beliefs here.
Project summary and deliverables
While the previous section is about the strategy, this section is all about the specifics. Spell out exactly what you’ll do for the client.
Here’s what you might include in the project summary:
A quick description of the project
A list of project deliverables
A description of project phases with their own deliverables
A project timeline or roadmap
Your project management process
The collaboration or communication software you plan to use
Measurable or specific milestones in the project
A description of the project team and the talent included

About the company
You can write an About Us page, an Our Team page, or both. An About Us page should include a description of what your company does, your target audience, and the results you provide. An Our Team page will feature bios of important people on your team.

You need to spell out the project costs. Depending on the nature of your business, you might show a flat rate project total, your hourly rate alongside the number of estimated hours , or a variety of package options for the client to choose from.
Terms and conditions
Next up: terms and conditions. When using a proposal management software with e-signatures , your proposal can work as a binding contract. Include your master service agreement and allow the project summary to serve as the statement of work.
Social proof and samples
Prospective clients will need some reassurance to help them trust your business.
Consider including:
Testimonials
Star rating averages
Portfolio pieces
Work samples
Mini case studies

Ready to pitch a new project? Here’s a step-by-step process to create a winning project proposal.
1. Discover the client’s needs
The first step is to understand the client’s current challenges and goals. As part of your discovery process, you might conduct a single sales call, or several.
Some companies actually charge for a longer discovery or audit process, and use a proposal to sell that introductory service. They will then later upsell that client on a project based on their findings with a custom proposal. However, most firms conduct the discovery process for free and then make project recommendations in their first proposal.
2. Define their core problem and goals
Next, you’ll want to distill everything the client has shared with you. You might take some time to gather your notes, talk it through with a colleague, and then determine the most important objectives. These project objectives will guide all further decisions.
3. Determine the best approach to serve them
Now it’s time to decide which method or approach will lead to project success. If you have a templatized project process and always serve similar clients, you can offer your usual solution.
But if you offer custom work unique to each client, then you’ll need to decide on the approach. For example, an event planner might decide to offer event marketing, registration, setup, and breakdown services if a client doesn’t have any in-house resources, but they might only offer setup and breakdown if the client has in-house marketing and ticketing specialists.
4. Breakdown the project into deliverables, timelines, etc.
Now that you’ve done your research and decided what to pitch to the client, it’s time to break the project down.
Determine the project costs or pricing options, break up work into phases, and clarify deliverables. You can jot this down on a piece of paper or work directly inside of a proposal template .
5. Add all necessary sections and details to your proposal
Write out your proposal and make sure that you’ve covered all of the bases. It’s worth noting that longer isn’t necessarily better. Through our analysis of 1 million proposals, we found that winning proposals have 7 sections and 11 pages on average .
The most common proposal structure is:
Executive summary
Approach or solution
Deliverables
Keep in mind that you can alter and rename these sections to match your services and unique brand voice. Leverage an AI writing generator to help brainstorm content while you work on the sections of your proposal.
6. Send the proposal to the client (with e-signatures)
Now it’s time to send the proposal. You can save time and reduce your software needs by using one software for both proposals and contracts. Just make sure that you’ve included your terms and conditions.
Proposals with e-signatures assigned to both the sender and recipient have a 426% higher closing rate. And if you sign the proposal first (before the client opens it), you’ll increase your chances of closing by a further 36.8%.
7. Handle change requests promptly
Be on hand to make changes per client requests, whether they want to change the project scope or adjust contractual language because of their picky legal team.
Being asked to revise a proposal isn’t necessarily a bad thing. In fact, proposals that are revised a couple of times are more likely to close.

5 examples of proposals for a project
Need some inspiration? These project proposals offer examples of exactly what to include in your next pitch.
1. Printing project with optional items
This printing proposal offers an excellent example of how to clearly communicate your pricing and offer interactive options. When we analyzed 1 million proposals sent with our platform, we found that proposals with fee tables have a 35.8% higher closing rate than those without and that proposals with editable quantities have an 18.5% higher closing rate.

You can use this proposal template with your free trial of Proposify and easily customize it for your unique business offerings.
This example project proposal template includes these sections:
Our Services
Sample Work
Your Investment
2. Marketing proposal with project timeline
A project timeline is an important part of any project proposal. This marketing proposal template offers a great example of how to share this timeline in a simple format.

Break your project down into distinct steps so the client knows exactly what to expect.
This example proposal template includes the following sections:
Overview & Goals
Scope of Services
3. Accounting project with goals and batches of work
Our next example is an accounting proposal .
This proposal stands out because it includes the client’s goals in the Project Summary section. See those short and sweet bullet points? They serve as a smart way to let the client know that you understand their goals and will be able to satisfy them.

This proposal also includes a breakdown of work that is categorized into four different batches, or chunks: QuickBooks Startup, Data Migration, QuickBooks Data Build, Overall (throughout the project). You can use this example when breaking down a project into different stages or services.

Access this accounting proposal template with a paid subscription or a free trial of Proposify.
The template includes the following sections:
Project Summary
Work Proposal
4. Construction project with project summary and exclusions
Do you need to include exclusions in your proposals? If the type of work you offer is contingent on other service providers or lends itself to complications, then you might want to start adding exclusions. This can help protect your business from the many risks associated with project scope confusion or misaligned expectations.
This construction proposal template , available inside of Proposify, offers a perfect example of an exclusion section, which follows what is included in the project.

The project proposal template includes the following sections:
Cover Letter
Meet Our Team
Previous Projects
Project Schedule
5. Event management project with hourly work estimates
Event planning is complicated—that’s exactly why the event industry serves as a great example of how to charge for both hourly work and fixed costs at the same time.
You can access this event planning proposal template with your Proposify account (check it out with a free trial ).
In the Budget section, the proposal kicks things off with a fee table including all of the hourly costs .

This project proposal also has a second fee table to estimate the hard costs , such as catering and photography, and the hourly costs and hard costs are then added up for the full project total.

This template includes the following sections:
Introduction
Our Understanding of Your Needs
Writing a great proposal is a lot of work.
Here are some project proposal best practices that will help you save time and get better results:
Create templates for different services, projects, or clients. The faster you send a proposal, the more likely it is to close. Try creating a few different templates to make it easy to generate a new proposal based on the clients’ unique needs. And of course, you can always speed up the process by beginning with one of our templates .
Get the client’s opinion on your plan before you turn it into a proposal. Try pitching your project idea to the client at the end of the sales call. Check to see their reaction. If they love what you’ve suggested, turn that into your proposal. If not, ask what they have in mind. This way, you’ll create a proposal that is more likely to close.
Ask the client what they want the proposal to include. If your client has given you a detailed RFP , you’ll know exactly what to include in your proposal. If not, don’t be afraid to ask. Especially when working with large corporations and government agencies, your main point of contact should be able to share what all stakeholders will expect to see in the project plan.
Offer dynamic pricing options. Proposals with both optional rows and editable quantities have a 20.2% higher close rate. Consider add-ons and options that will cater to decision-makers while customizing and perfecting the project scope. Clients should be able to select the options directly in the business proposal to create an accurate project total in real-time and then sign off on it.
Include multimedia content in your proposal. Proposal content shouldn’t just be in a written format. Accompany your writing with mages and videos to help them visualize the project. Proposals with images are 72% more likely to close and proposals with videos are 41% more likely to close. Try including pictures of your team and your previous work and illustrations of your process or typical ROI.
Write and automate follow-up emails. Proposals with just one automated follow-up email are 35% more likely to close. If you use Proposify, you can easily turn on automated follow-ups for every proposal. You can use our follow-up email templates, or create your own templates for different types of clients or projects.
Next steps: write your own project proposal
An excellent project proposal should include the project roadmap, milestones, budget, and any supplemental information that will help the client really understand the value of the project and secure buy-in.
To make any proposal more likely to close, make sure you include multimedia content, pricing options, and e-signatures.
Proposify’s proposal templates , automated follow-ups, and viewing analytics can take your proposal closing game to a whole new level. Book a demo today.

Winning Proposal Structure Tips (What The Research Says)
June 21, 2022

4 Tips That Will Make Any Proposal More Likely to Close
July 12, 2022


It’s about more than just proposals—it’s about world domination.
Get a demo and start your team's total takeover.
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
How to write a project proposal (examples & templates).
Senior Content Marketing Manager
July 13, 2023
Have you ever left a doctor’s appointment feeling uncertain about the treatment plan? It stinks—no one likes being left in limbo when it comes to things that matter to them.
Clients feel the same type of frustration when they receive unclear project details from agencies. Reassure your customers with a strong project proposal—a statement that clarifies what your agency will do to help the client meet their goals.
This proposal is basically a “diagnosis” and a “treatment plan.” It shows the client you understand their situation and outlines what project deliverables your agency will create to help the customer meet their objective.
Boost clients’ confidence in your projects with this guide. It’s packed with proposal writing best practices, project proposal examples, and more to help you strengthen your pitches.
What is a Project Proposal?
Types of project proposals, step 1: research your prospective client’s product and industry, step 2: brainstorm with your internal team, step 3: define deliverables and determine the required resources, step 4: write the project proposal, step 5: add design elements to the project proposal, step 6: present it to your prospective client, step 7: follow up with the prospective client.

A project proposal is a document that outlines what deliverables your agency will create and the objectives you plan to meet through the work. It should describe your diagnostic and prescriptive approach to getting them where they want to be.
Project Proposal Example Outline
A good project proposal should include the Who, What, Where, When, and How of the solution you provide. Specifically, your project proposal needs to include:
- Table of Contents : An index of what’s to come in the project proposal and page numbers
- Executive Summary : A statement that describes the project background and gives a brief overview of what’s to come in the proposal
- Goals : The long-term outcome the client wants to achieve
- Problem Statement : A summary of the obstacles standing in the way of the client’s goals
- Value Statement : A summary statement of how your agency’s services and expertise will solve the problem statement and benefit the client
- Strategy : The high-level proposed solution for how you will reach the client’s goals
- Project Scope : The services that will be included in your agency’s project approach
- Project Deliverables : Individual tasks within the services you provide that contribute to the project objective(s)
- Measures of Success : Metrics that will be used to measure project success (KPIs)
- Timelines : A roadmap of when the client can expect project deliverables and key milestones along the way
- Case Studies : Success stories and testimonials from clients you’ve worked with on similar projects
- Budget : The monetary resources required to complete the project proposal . Include more than one package with a range of pricing to fit different project budgets and goals).
- Project Summary : A concrete takeaway that summarizes the key details of the project proposal.
- Next Steps : Don’t forget your call to action! Tell the client how to get started working with you.!
Not sure how to tie all of this together? Don’t worry; we’ll cover that later!
There are a few different situations where you would submit a project proposal to a client:
- Solicited project proposal : A prospective client approaches you with a Request For Proposal (RFP) , and you submit a proposal in response.
- Unsolicited project proposal : You identify a prospect in your CRM that fits your ideal customer profile (ICP) and submit an unsolicited project proposal to start a contracting conversation without the prospect reaching out first.
- Informal project proposal : A more conversational approach to a proposal or one that wasn’t specifically requested.
- Renewal project proposal : An existing client is up for renewal. You send this proposal as a prerequisite to resigning so you can reevaluate your current relationship and set new goals.
- Continuation project proposal : Remind or convince current clients to continue the project or provide details about any outstanding or new tasks that might be needed to complete the project.
- Supplemental project proposal : You identify the need to expand an existing project’s scope of work and redefine the client relationship.
Related: Business Proposal Templates
The benefits of writing proposals for projects
A well-written project proposal is a powerful tool for showing clients why hiring your agency is their best chance for success.
Specifically, project proposals have a few key benefits:
- Credibility: Provides you a platform to establish your expertise with the prospect
- Differentiation: Give the prospect something concrete to take to internal stakeholders to compare and contrast your services with others competing for the project and get buy-in from their decision-makers.
- Alignment: Aligns internal and external teams on what the goals and vision are for the project proposal from the very beginning.
How to Write a Project Proposal in 7 Steps
A project proposal can either be a big selling point or a missed opportunity; the difference comes down to your process for developing one. Before you begin writing a project proposal, centralize your team communication . Then you can establish a clear planning process so nothing falls through the cracks.
Bonus: Project Planning Tools
Your prospective client doesn’t want an impersonal project proposal. They want a statement that shows you understand their history, branding, industry, and customers. Show the client you get them and what matters to them by conducting research for your project proposal.
While conducting your research, consider the following:
- What are your customer’s objectives that are driving this project?
- What gaps in industry knowledge does your agency have that you need to explore during market research ?
- How long will you have to conduct your research?
- What form of data collection will you use?
- Will you conduct a competitor audit, client surveys, or an organizational gap analysis?
- Once you collect the data, how will you analyze it?
- Are there limitations to your research that need to be considered during your planning?
- Do any themes rise to the top as you conduct your research?
- What resources did you use in developing your research?
- Are the sources credible?
- Are the sources diverse enough to accurately represent the industry?
Don’t forget to document all of your findings in ClickUp’s User Research Plan Template so you can easily reference your analysis in the following steps of your project proposal!
Armed with your research, rally the troops! It’s time to collaborate with your internal team on how you can solve the client’s needs before you put it on paper.
Brainstorm together using the mind mapping methodology— a visual diagram of ideas connected by a central concept. It’s an easy way for your teams to brain-dump ideas and talk through each of their unique perspectives on the project – ultimately coming up with the best ideas.
For example, developing concepts for a marketing campaign requires inputs from multiple teams in your agency. Using ClickUp’s Mind Map will help subject matter experts from across the agency weigh in on the best approach while keeping the client’s goal as the central concept.
Corral all that genius in one room with ClickUp’s template for project mapping ! With this resource, you can easily brainstorm and organize ideas visually to identify connections between them quickly.
Once your team has identified the best approach to the project, it’s time to outline the specifics of the solution in a project plan . This includes identifying phases of the project, defining deliverables, and filling in the details of each task.
Using a project management tool, work with your team to assign the timeline, project budget , and task owners for each deliverable to determine the project’s overall scope. Here are a few ClickUp project management tools that will help you communicate each of these details:
- Custom Fields: ClickUp’s custom fields enable you to assign unique values to tasks like budgets, task owners, due dates, and so much more.
- Gantt Chart: It’s easy to define timelines when you look at tasks in ClickUp’s Gantt chart view , where you can define dependencies between tasks and layout project deliverables in sequential order.
- Checklists: Sometimes, you just need a simple to-do list to make sure you’ve assigned each piece of the project; that’s where checklists are super handy! Easily tag in task owners, set due dates, and notify the project team of completion with a single click.
Now that you have all the project’s internal details, it’s time to organize them into a concise, personalized proposal statement. Collaborating on all of the ideas in a project proposal whiteboard makes it easy to define your proposal as you go.
Once you have outlined the key concepts on ClickUp’s Whiteboard , it’s time to tag in your copywriting team to round out those ideas and write a cohesive proposal Doc. The copywriting team should reference the Whiteboard, project map, and research document as they write to make sure it’s as personalized to the client as possible.
The copy needs to be definitive, concise, and measurable as possible. Once the copywriters are done, give your internal project team a chance to review and surface any revisions needed before sending the project proposal on to the next step.
Make sure you clearly define the project budget as well. The last thing a client wants is to see various costs from initial conversations.
Now for the fun part! Tag your creative team to translate that project background document into a beautifully designed project proposal (a.k.a. make it pretty!). If you don’t have an internal design team, there are several drag-and-drop design templates from services like Pitch and Canva .
Consider standardizing your proposal in a template regardless of whether you have an internal design team or are using one of these services. Your team can simply adapt ClickUp’s Project Proposal Whiteboard Template for each new client to maintain brand consistency and save time.

You did it!
The day has finally come—you get to wow your client with your genius. Whether you meet in person or via zoom, send a meeting agenda and a copy of your project proposal via email to your client prior to the proposal presentation.
Providing the proposed project and meeting cadence beforehand will give the client time to consider the proposal, form any questions, and potentially add notes to the meeting agenda.
CLICKUP PRO TIP Make this step quick, easy, and consistent across teams by developing a standardized email template in ClickUp .
During the meeting, keep detailed meeting notes and assign follow-up tasks immediately so nothing falls through the cracks post-meeting. Easily take notes and assign action items in real-time with the ClickUp Meeting Minutes Template to create the best project proposal.
Make sure to keep your proposal presentation to the point and as brief as possible. You don’t want to bore your audience before they get to the end.
At the end of the presentation, reiterate the next steps you’ve outlined in the proposal and note how much lead time your team will need if the client chooses to sign on. After presenting the project proposal, answer as many questions as possible, and follow up via email with any answers you don’t immediately have.
We’ve all been there. One minute an agency is promising you the world, and the next, they’re ghosting you for the next best client. Don’t let prospects slip through the cracks.
Keep track of every stage of your project proposals so you know who is responsible for reaching out to the prospect, and when your team last contacted them.
Tracking the client lifecycle in real-time is easy in ClickUp with custom fields. You can define the stages of your project proposals through custom fields, assigning roles, setting due dates for routine follow-ups, and tagging team members. You can also send client emails and comments right from the task window, giving you a clear audit trail of each customer communication.
Related Project Proposal Resources:
- Project Proposal Templates
- Professional Services Template
- Creative Project Plan Template
- Creative Agency Proposal Planning Template
- Consulting Project Plan Template
- Grant Proposal Template
- Consulting Templates
- RFQ Templates
Use ClickUp for Your Next Project Proposal
At the core of successful project proposals, there’s a team that collaborates effectively. And that’s exactly what ClickUp enables your agency to do.
We bring all of your tools, documents, teams, dashboards, budgets, and workflows into one project management software. This is all in an effort to put an end to context-switching and siloed workflows from working within multiple tools.
What’s better?
We have over 1,000 app integrations and a full library of free templates built by project management experts that make workflow building easy. You no longer have to spend your precious time creating every process and procedure from the ground up.
It’s already here, just waiting for you in ClickUp. Get started today— completely for free —and see why so many agencies are switching to ClickUp.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
How to Write a Business Project Proposal that Gets Approved
Updated on: 5 January 2023
Writing a business project proposal definitely takes time and careful consideration, but it will pay off when you have managed to impress your investors.
Your project getting approved or funded may depend on how effective your project proposal is, so investing that extra effort into perfecting it is essential.
There are steps that you can follow to make sure that your business proposal makes a great impact on your company’s decision-makers , and in this post, we will walk you through them, explaining how to write a project proposal step-by-step. Also provided are templates that you can use to write a winning project proposal.
What is a Project Proposal
Let’s start with the basics.
What is a project proposal? It’s a document that lists down all aspects of a project ; its background, vision, goals, tasks, requirements, owners, associated risks, etc. So it basically explains what your project is, what you want to achieve with it, and how you plan to execute it.
It’s one of the many crucial parts of the planning phase of the project. It lays out each and every step of the project, allowing everyone to understand what is required of them, their priorities, and the common goal they are supposed to work towards.
The purpose of the project proposal is to communicate the value of your project to all stakeholders; clients, employers, investors, and convince them of the value of the project.
Benefits of a well-structured project proposal
- Clarifies the expectations of the project – project requirements and the action plan
- Helps increase the viability of the project
- Offers a large overview of the project allowing you to identify issues easily
- Simplifies project implementation
Different types of project proposals include
- Formally solicited – a proposal that is made in response to an official Request for Proposal (RFP). The RFP document usually outlines the stakeholder requirements and even sometimes spells out the instructions to prepare the proposal.
- Informally solicited – this type of proposal does not require an RFP, which means there is no official document outlining the demands of the customer or the stakeholder, therefore doesn’t consist of the specific details a formal one usually has.
- Unsolicited – this type of proposal is thought of by the person creating them and not expected or requested by anyone, yet they can be of a lot of value to the stakeholder .
- Continuation – this basically requires you to update an ongoing or already approved proposal or remind the stakeholders of it. You are required to check-in with the stakeholders and discuss progress.
- Renewal – this is written in support of renewing a project that has been terminated or outlived its usefulness.
- Supplemental – when you need more resources than what was originally allocated to a project, you can write a supplemental project proposal . Its purpose is to justify the need for extra resources and re-estimate the project scope and timeline.
How to Write a Project Proposal
Once you have identified the type of project proposal that suits your requirement, you can start writing your business project proposal.
Before you actually begin to write down the project proposal, there are a few preliminary steps that you need to take. These are:
- Identify who your stakeholders are. While you should aim to win the attention and interest of your stakeholders with your proposal, the best way to do that is to think like them. Understand who they are, what they already know of, and what they prefer in terms of your idea. Based on who they are, you can alter the information you include, and the language you use.
- Gather information about the problem the project is aiming to solve, especially in terms of how it’s affecting your stakeholders and their interests.
- Conduct research into the current state of the issue and the potential solutions that have already been discovered by those who are outside of your company or by your own team. This will help you adjust your own solution to generate a more solid argument or determine whether it’s worth pursuing (especially if the solutions found by others have already been tested and failed).
- Determine the impact of the project on your company’s success or how it will benefit your stakeholders. Layout the success metrics for the proposal and showcase the results, and if you find any risks involved, don’t be afraid to bring them to light as well; in any case, knowing them will allow you to alter your action plan to withstand them.
- Specify a timeline and the resources needed to complete the project. Check if the teams, equipment, and material needed to carry out the project tasks are available and the objectives can be achieved in a timely manner. Take into account the other projects your team will be working on, the equipment or material that’s currently unavailable, and any extra costs on resources you will have to bear in order to carry out the proposed project.
- Create an outline of your project proposal based on the information you have gathered. Write down the core elements; more or less the basic elements should include an introduction, problem, solution, the action plan, timeline and resources, and a conclusion.
Completing the initial steps above provides you a good head start to writing your business project proposal. Your next step is to organize your research into a coherent document – an actual proposal. Here’s how to write a proposal for a project from scratch;
1. Write the executive summary
The executive summary offers a quick overview of the proposal that is to follow. It’s not only the first thing the reader will see, but sometimes it’s the only thing a stakeholder will read before making a decision about the proposed idea. Therefore, the executive summary should make sense to someone who hasn’t read it; for this purpose, it should consist of a synopsis of all the sections in the document.
- An analysis of the problem
- The conclusions you have arrived at
- The recommended action plan
Aim to keep the summary intriguing and convincing; make use of notable statistics in the first two sentences to pique the interest of the reader.
2. Define the problem
Give a brief description of the problem your project aims to solve.
Referring to the research you have done earlier, you can explain the current situation of the problem in terms of what’s being done about it both within and outside of your organization, and why your stakeholders should be concerned about it.
While you need to be straightforward with your explanation, remember to use the language and concepts your stakeholders resonate with the most.
03. Introduce your solution
Now that the stakeholders know what the problem is, it’s time to explain how your project or your solution comes into play. This section is usually the most detailed out part of the project proposal, and to retain the attention of your reader, you can play around with the use of visuals.
This section should explain your solution along with how you plan to execute it. It should reinforce the fact that your decision is backed by proper and thorough research. Clarify,
- The project approach ; how the team will be put together, the tools and equipment that will be used, and how you will be handling the changes during execution.
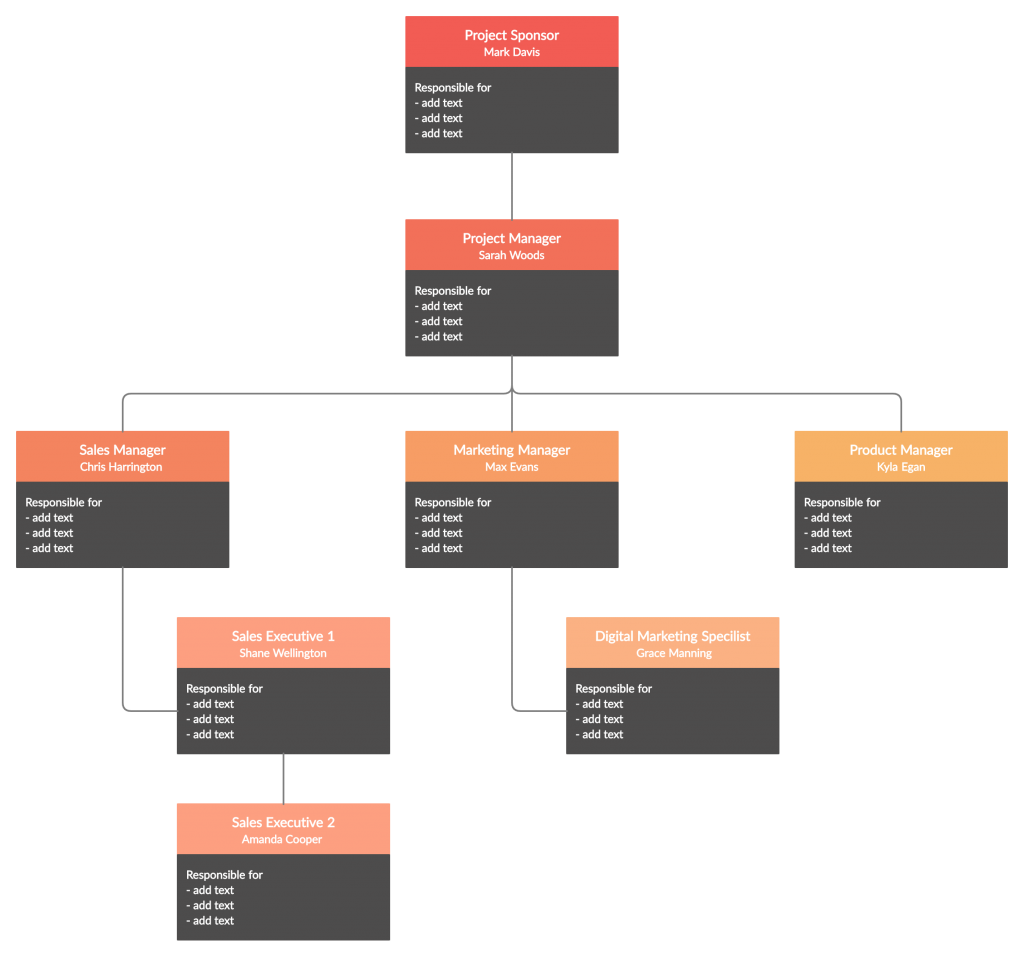
- Project schedule ; list the project tasks along with time estimations for each of them. The task breakdown will enable you to allocate your team properly, and you can use a Gantt chart in this section to clearly outline the resources, tasks, and timeline.
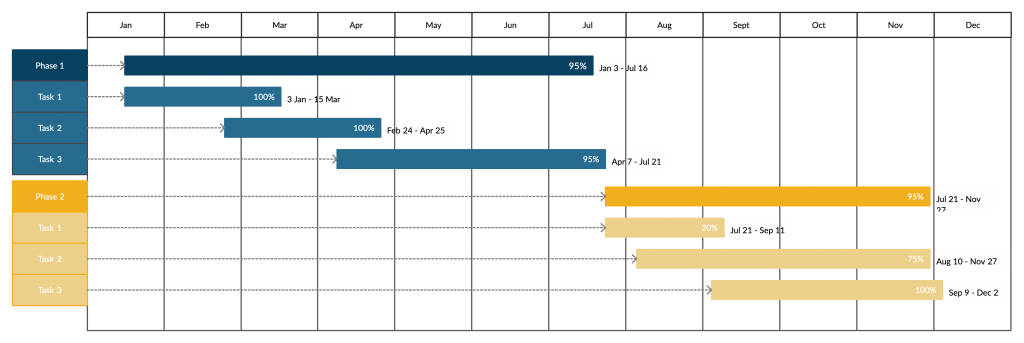
- Project deliverables ; deliverables are the outcomes of a completed project (i.e. product, service or a detailed report). Mention your project deliverables along with delivery dates. Use a work breakdown structure here to help the stakeholders get a clearer picture.
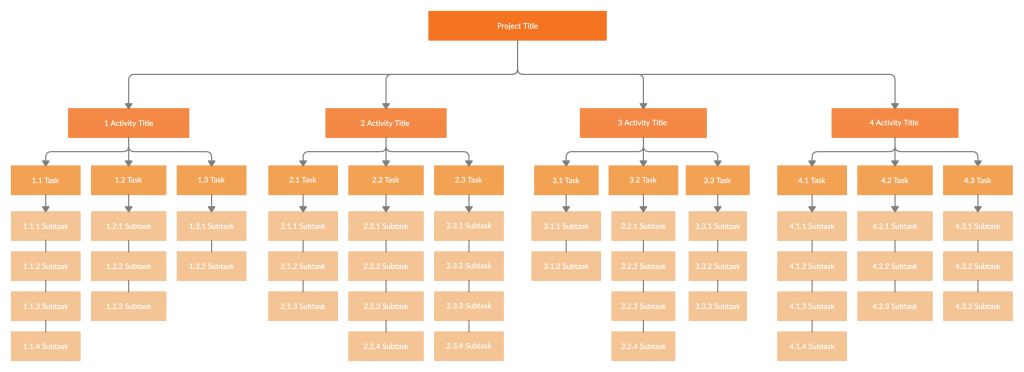
As required you can also include additional information such as the anticipated risks and steps you would take to overcome them, a communications plan , and milestones to help track progress.
In order to make this section more reader-friendly, you can present all this information using an action plan .
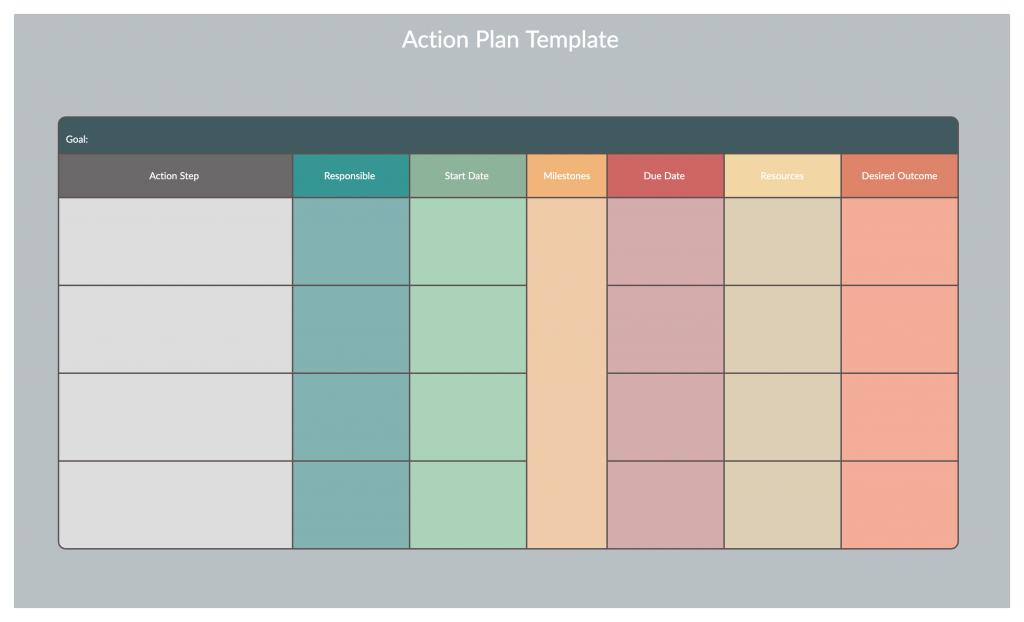
04. Outline the project costs
This section focuses on the estimated cost of the proposed project. It should include an itemized budget for the project.
The purpose of this section is to help the investors get an idea as to whether the project costs can fit into their own budgets, therefore make sure that the calculations are as accurate as possible.
05. Conclude your proposal
Provide a brief review of all the key points discussed throughout the proposal. As this is the last section, it’s also the last chance you have to convince your stakeholders; therefore reinforce your solution and why your stakeholders should care about it while ensuring that your proposed method is in the best interest of the organization.
06. Add an appendix
This section is reserved for the reference documents, charts , graphs, etc. that were referred to when writing the project proposal.
07. Revise and refine
In order to substantiate your professionalism and win over your stakeholders, you must present an error-free project proposal.
Proofread your proposal to check for any spelling mistakes and grammatical errors. Often a fresh pair of eyes helps detect mistakes easily; either get a colleague to review the document or wait 1-2 days and review it anew yourself.
Project Proposal Templates
A detailed, well-structured project proposal will help you stay focused and stay on track by offering you the necessary instructions throughout the project, which is certainly better than picking things out from your memory or conversations you had with your team during that meeting a few weeks back.
To make it easy for everyone, you can have a standard project proposal template that they can refer to when documenting their project idea.
Following are a few project proposal templates that you can share with the team.
One Page Business Project Proposal
You can edit this template online and share the link with your team or the stakeholders online so they can collaborate on it too. Connect with them via Creately in-app video conferencing and walk them through each section of the proposal. Alternatively, using in-line commenting, they can also leave their feedback on the proposal.

Project Proposal Template
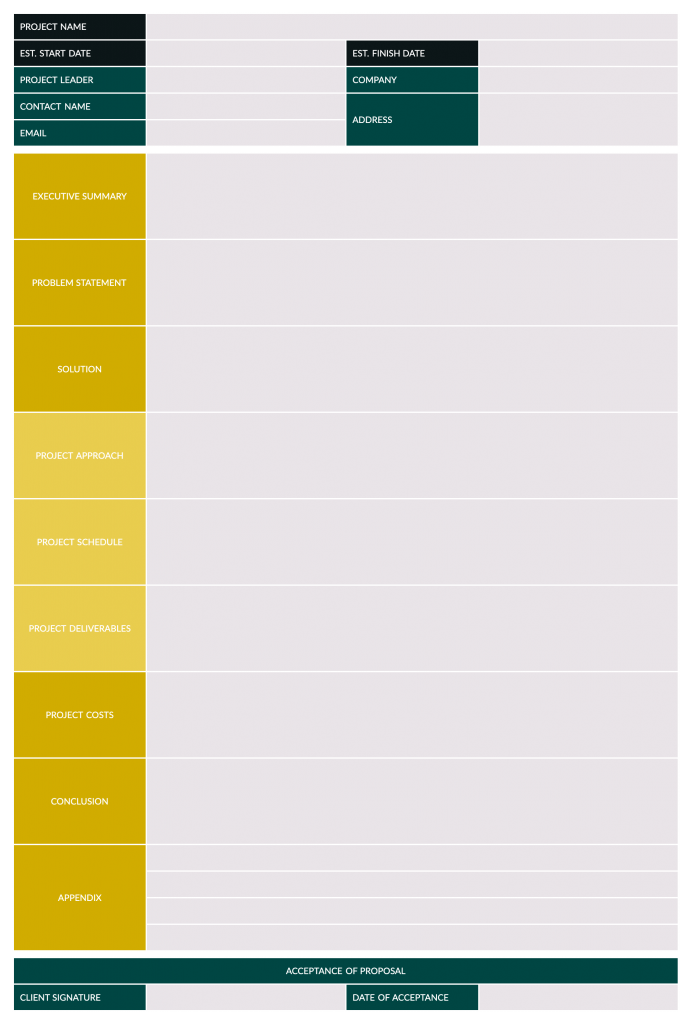
What’s Your Process for Writing a Business Project Proposal?
Creating a project proposal can sometimes be a mini project in itself. Using a proper process checklist or a standard template can help you accelerate things. Before writing your project proposal, follow the preliminary steps mentioned above first. Keep your target stakeholders in mind and make a compelling case for your proposal.
Want to share your thoughts on how to write a proposal for a project ? Let us know in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

More Related Articles
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please enter an answer in digits: four + 16 =
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning.
- Jira Software
- Jira Work Management
- Jira Service Management
- Atlassian Access
- Company News
- Continuous Delivery
- Inside Atlassian
- IT Service Management
- Work Management
- Project Management

How to write a project proposal that’s persuasive and precise
Project proposals are a great way to kick off an initiative. They show a clear path of execution and make stakeholders aware of costs and benefits. They can convince a team or manager to make a change. Or they can show a client what services and solutions you can provide. You can write a project proposal for just about anything: to build a new tool, for a process to improve team workflows, or to create a new website. Here’s how to write a project proposal that’s professional, informative, and persuasive.
What’s included in a project proposal?
A well-written project proposal includes the following:
- Goals (What problem are you trying to solve? And how?)
- Timeline of the project (Including milestones along the way)
- Budget (What’s it going to cost? And what’s the expected return?)
- Objectives (How will you measure if the goal has been achieved?)
Target your project proposal for your audience
You might not think you work in marketing, but if you want to convince someone to accept your project, then think again! Know your target audience segment and adjust your message accordingly. Think carefully about who you’re talking to—your client? your boss?—and what they care about. Consider their goals, such as driving more leads, or increasing employee productivity. What factors are important to them? And how are they balanced and prioritized?
Think about how they prefer to receive information. Are they looking at the big picture? Or the small details? Would they prefer chart and graph visualizations? Or a short list of bullet points? Or maybe they want to hear a story?
Use all of this information to customize the proposal for your specific audience. If it’s more relatable, they’ll be most likely to grasp the information and respond positively.
Organize your ideas before you write
Choose the right tools to help keep your ideas and your research organized. Create your proposal on a Trello board to sort related documents, ideas, and important information for each section of the project proposal.
Stay on the board and use it to track progress and activities to reach your objective. With Timeline View , you can monitor the steps to help you reach your goal. Viewing Trello cards in a timeline to see overlaps in work, or identify potential bottlenecks down the road.
Dashboards help quantify and sort the work on your project. For example, when you assign cards to your teammates, you’re able to sort by person to see who might be overloaded with work all at once. Dashboard gives you a quick visual overview for reference.
Of course, you can start your project proposal Trello board from scratch, but you’ll save time if you copy and customize this project proposal template at the start.

You can also use a slide deck or a text document to kick off your thinking, but only Trello will keep your ideas organized and help you track your progress in real time.
Back up your content with data
Your proposal will be stronger if you have hard facts to back it up. Use statistics that are relevant, such as successful campaigns at similar companies or metric improvements associated with the project. If you can’t find any within your organization, research your project subject matter and look for stats and data that relate to your project.
For example, if you’re writing a proposal to optimize a client’s website, it’s powerful to mention that 25% of visitors abandon a website if it takes more than four seconds to load.
Call out the costs and risks
Highlight the positive outcomes that will come from doing the project. But your project proposal will be even more convincing if you also acknowledge the pitfalls and costs. Show the full scope of the project to build trust and transparency with your reader. If risks are known ahead of time, your project will be ready to confront them.
Cost analysis
Provide a total estimated cost for the project, but also list each line item. Get granular to show thoughtful detail, and to show potential points of adjustment. Justify the reason for each cost. Explain why they’re necessary and what you expect to gain.
Although it’s not always possible, it’s best if you can associate a dollar amount of benefit behind each cost. Calculate the return on investment (ROI) to show why it’s worth it to spend the money.
Keep in mind that costs are more than just dollars. Resources such as software or raw materials or employee time are a cost. Account for it so there are no surprises later.
Risk analysis
Every project has risk. It could waste time and money. Or it could have more serious legal ramifications or an impact on brand loyalty.
Explain how you plan to mitigate those risks and prevent them. Be realistic. Also indicate how likely those risks are to occur, and what you could do to fix them.
Set SMART goals and outcomes
A persuasive project proposal includes a definition of success with a plan for how to reach it. Create a SMART goal for your project that clearly defines what a successful outcome looks like. Your goal should be:
- S pecific (clearly defined)
- M easurable (quantifiable, and include a way to “check off” its completion)
- A chievable (it’s okay to be a stretch, but don’t make it impossible)
- R elevant (a positive impact for the stakeholders)
- T ime-bound (include a clear timeframe or deadline for success)
Once you’ve set your target goal, create outcomes and milestones to help measure progress on the journey. Define metrics that show if you’re on track to reach your goal, or if you need to make adjustments to the plan.
If it’s hard to predict exactly what outcomes and metrics to expect, show best-, mid-, and worst-case scenarios. Your best case should show a very optimistic goal of what you think you can achieve if everything goes according to plan. Your mid-case goal should allow for a few hiccups along the way. Your worst-case scenario includes the minimum of what you think is possible, even if many things go wrong.
Here’s what it might look like to create a project proposal for a new ad campaign:
Write the project proposal
Your project proposal will likely be read by multiple people, each with a different level of investment in the project. Include these sections in your pitch to make it digestible and accessible for every stakeholder.
Begin with an executive summary
Summarize the key points of your proposal, such as the estimated goal and outcomes with costs. Identify the key stakeholders and the resources to make it happen. Quickly share the best and worst-case scenarios, so the range of expected outcomes are clear. Keep this short and easy to read: Just a few bullet points or a single paragraph.
Keep the project proposal simple
Add detail and data to your executive summary, but don’t feel pressured to write a book. More words do not mean better quality. Write to get your point across, then review it to make it more clear and concise.
Add an appendix for all of the details
For lengthy studies, analyses, and reports that will help support your project, lean on your appendix. Keep the project proposal tight; not every reader will want to see every detail. Instead, reference the appendix in your proposal and send readers there for all of the details and nitty-gritty.
Practice your pitch
If you plan to present the proposal on a call or in person, practice your talking points and presentation. Do not simply read the project proposal to your audience, as their attention may wander.
Include your personality and passion, as this will help you sell the project. Be sure to show your enthusiasm. Share why you care about the initiative personally and what motivates you to make the project happen.
Your drive and your passion—and the right tools—will help position your project proposal for success.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.
See why the world’s best creative teams run on Workamajig
How to create impossibly good project proposals.

- Understand your readers and mirror their preferences
- Address the root cause of proposal rejection
- Justify the project’s existence by tying a dollar value to the problem
- Apply project management best practices to project proposals
- Use a conventional project proposal outline
- Use persuasive copy
- Reframe your content based on proposal-type
Browse more blogs
It all starts with the project proposal. From million-dollar ad campaigns to thousand-dollar one-pagers, so much of your agency’s success depends on sending persuasive proposals. This guide will show you how to create more compelling project proposal outlines.
Of all the documents you’ll create while running a project, few are more important than the project proposal .
This tiny document is the seed that gives birth to million-dollar projects. You’ll use it to win new clients, persuade sponsors to increase funding and convince existing clients to renew their contracts.
A great project proposal is at once informative and persuasive. It may revolve around data, but it doesn’t shy from using marketing copy. It is, at heart, the distillation of several skills - project management , data analysis, copywriting, etc.
Given this expansive brief, writing a convincing project proposal can be a challenge even for agency veterans.
In this guide, I’ll share 7 tips you must follow to create more convincing project proposals.
1. Understand your readers and mirror their preferences
The project proposal isn't just a project management document. It is also a marketing document.
And as with any marketing document, you have to keep your audience in mind when creating it.
In practical terms, this means using the same language, tone, style, and level of complexity as your audience.
If your audience is a veteran CTO, feel free to pepper in jargon. If it's a small business owner who has never touched a computer before, dumb things down.
Doing this means that you have to research your audience thoroughly. LinkedIn is your best friend here. Dig through their profile and approximate the following:
- Experience with your proposed solution or technology, based on past employment & education history. For example, you don't have to explain " CRM " to a former Salesforce exec.
- Interests are based on public group affiliations and recent shares. If a target is a part of a LinkedIn group on AI and has shared articles on AI/ML in the past, you can assume that he would understand AI terms.
- Busyness based on seniority and other commitments.
Publicly shared interests and group memberships show what your target audience is interested in.
Use this information to create a rough sketch of the target, such as this:
This will tell you how much detail you should include in a proposal. A veteran CTO, for instance, might want to know the technical details of your proposed solution. A small business owner might be more interested in the impact on his bottom line.
2. Address the root cause of proposal rejection
A client might reject your proposal for any number of reasons. Perhaps he isn't sure of your ability to deliver results. Or perhaps he has a better price than a competitor.
But as Francis McNamara points out , most proposals are rejected because of a failure of persuasion, not a failure of process.
It is very seldom that sponsors discard proposals because they don't have enough data. Rather, it is because you failed to make the data compelling enough.
Addressing this root cause of the proposal requires two things:
Within the context of a project proposal, persuasion means two things:
- Emphasizing results that will have the biggest impact on the decision maker, i.e. its target audience.
- Countering the target audience's rejections (with storytelling, data, and past results).
A mistake you can make is to assume that the motivations of the business and the decision-maker are the same. While there is certainly a big overlap, decision-makers also have independent goals and ambitions - to get a promotion, to improve their department's performance, etc.
Your goal should be to highlight the project results that will benefit the decision-makers the most.
For example, your project might have two key benefits - improving website performance by 20% and increasing online sales by 5%.
- Pitching to the VP of engineering: Highlight performance improvements and technical underpinnings of the solution.
- Pitching to the VP of sales: Highlight the impact on sales and total revenue.
Persuasion defines what you say in the project proposal. Clarity defines how you say it.
In practical terms, clarity is a function of the proposal's formatting, tone, and copy. Your target shouldn't have to read through two pages before understanding the project's key benefit. Nor should he have to trawl through paragraph after paragraph of jargon.
To be clear, then, is to:
- Present the key benefit(s) of the project quickly and succinctly.
- Structure the proposal in a way to emphasize its biggest benefits upfront.
- Only include information necessary to make a decision and omit the rest.
- Use copy that aligns with the target's interests, knowledge, and busyness.
3. Justify the project’s existence by tying a dollar value to the problem
In a 2009 PMI conference paper , Eddie Merla, says that one of the chief causes of project failure is “weak justification”.
“Sometimes the concept may be properly stated but the justification for the project is weak… the lack of justification indicated a lack of commitment on the part of the team to build a compelling business case.”
This is a frequent problem on technical and creative projects. The technical or creative problem might seem substantial enough on its own. But if you can’t connect it to a business issue, you’ll struggle to justify the project’s existence.
One way to do this is to tie a dollar figure to the problem. Focus on what the business stands to lose if it doesn’t solve the problem. Since people are more likely to avoid a loss than to seek a gain (i.e. loss aversion theory ), emphasizing the loss can sell the urgency and impact of the project.
For example, in a project to improve website speed, focus on how slow websites lead to abandoned carts and thus, a loss in revenue.
Try using ROI analysis to figure out the project’s impact on the business. Don’t focus on the exactness of your financial metrics. Rather, focus on their completeness.
At the very least, your proposal should highlight the following:
- The current state of the problem and its negative impact on the business
- The estimated positive impact of the project on the business
- The approximate cost of the resources required to deliver the project
A project with a “strong” justification would have a large difference between the project impact and project cost. The more “complete” you can be with this data, the easier it will be to justify the project’s existence.
4. Apply project management best practices to project proposals
A project proposal is a significantly exhaustive undertaking. You need to research stakeholders, map the relationships between them, identify risks, etc.
How can you make sure that get every detail right and still meet your deadlines?
Easy: treat the project proposal as a mini, self-contained project.
The more complex the proposal, the more you'll want to adopt PM best practices while creating it.
For example, a complex project proposal might go through several stakeholders before it is approved. All these stakeholders will have their own concerns, goals, and preferences.
By creating a stakeholder management plan, you can address all these concerns.
Here are a few things you can do to manage the proposal creation process better:
- Assign tasks (stakeholder research, data gathering, etc.) to different team members.
- Map the relationships between stakeholders and create plans for managing them.
- Create a Gantt chart to map the proposal creation-approval process.
- Create a communication plan for each stakeholder addressed in the proposal.
- Create a risk management plan for risks identified in the proposal.
I don't recommend doing this for every project, but if the project is large and lucrative enough, it is better to be over-prepared than under-prepared.
The best part is that you can use a lot of this data later once you actually win the project.
5. Use a conventional project proposal outline
When it comes to proposal formatting, it’s better to follow traditions than to think outside the box. Sponsors are used to seeing key information structured in a specific way. Tinkering with it will just cause confusion.
So what exactly is this “traditional” proposal format?
Use this image as a reference:
Each section in this project proposal outline serves a specific purpose:
- Executive summary gives a quick, punchy summary of the problem, your solution, and its net impact. Sponsors will often decide to read further based on this summary. Make sure that it is succinct but also sells the project.
- Project background includes a section on the history of the problem in the context of the business, a brief overview of your requirements, and a few details about your proposed solution.
- Project proposal should focus on the project’s goals and vision, key deliverables, timeframe, and ownership. Other details you can include are key risks and issues, success criteria, and reporting.
- Project financials should include details on the estimated budget and approximate financial impact post-completion.
- Project authorization should include a list of everyone who has authorization throughout the project.
- Appendix is where you can attach additional documents supporting your case.
You don’t have to use these exact headings, but I do recommend following the same core structure – summarize the problem, frame the project in context, emphasize the solution, and list the project’s financials and authorization.
6. Use persuasive copy
The purpose of a proposal is to sell the project. You can’t really expect to do that if your copy reads like it was lifted from an academic journal.
You don’t have to turn it into a sales page, but you should use at least a few persuasive writing tactics, such as:
- Use a punchy statistic, testimonial, or case study result at the start of the proposal to grab the reader’s attention.
- Avoid jargon – unless your audience is well-versed in it and expects it.
- Write at grade 5-8 reading level. Use simpler words and shorter sentences whenever possible. Use Hemingway App to check the reading level as you write.
- Use social proof in the form of testimonials, case studies, and quotes from similar projects.
- Use the inverse pyramid writing style where you highlight the most important information at the top and push the minor details to the bottom.
- Use the 1-2-3-4 copywriting formula – identify what you’re pitching, its benefits, why you’re the right person to do it, and what the sponsor needs to do next.
- Highlight your experience, qualifications, and past results. This is a form of persuasion through authority.
Don’t be afraid to use superlatives and sales-focused “power” words (“amazing”, “incredible”, etc.) in your copy. Your objective, after all, is to sell the project.
7. Reframe your content based on proposal-type
Not every proposal has the same objective. A proposal sent in response to a RFP has a different goal from one sent to renew a contract with an existing client.
In the case of the former, you need to emphasize your value and experience. In the latter’s case, you’re already a known quantity to the client.
Most agencies will send the following six types of proposals:
- Solicited: These are sent in response to a Request for a Proposal. You’ll be competing against several other vendors for the client’s business. Your proposal, therefore, needs to be exhaustively researched and persuasive. It also needs to adhere to the guidelines in the RFP.
- Unsolicited: These are “cold” proposals sent to prospective clients. Since the client did not ask for the proposal, you must do a lot of homework to get noticed. Bring anything but your A-game here and you’ll land straight in the trash can.
- Informal: These proposals are sent in response to an informal request from the client. While they must be sufficiently detailed, you don’t have to follow any specific guidelines (as in an RFP).
- Renewal: This proposal is sent to pitch the renewal of an existing contract. Since you’ve already worked with the client, you don’t have to focus much on your work. Rather, your goal should be to emphasize your past results and how you can exceed them in the future.
- Continuation & Supplemental: These two proposal types are largely similar. The former – continuation proposal – is sent to remind the sponsor that you’re working on a project, and to update them on its latest status. The latter – the supplemental proposal – is sent to remind the sponsor about the project and request additional resources.
How much effort you put into each proposal should depend on which category it falls into. Unsolicited proposals require a lot of effort, but you can normally cut that short if you nurture leads upfront.
Similarly, proposals sent in response to an RFP must be comprehensive enough to fight off competitors.
Renewal, continuation, and supplemental proposals, on the other hand, should be shorter since they’ve already been approved in part.
Over to you
Crafting a compelling project proposal is an art. You have to inform and persuade, all within the confines of a few pages. A strong proposal justifies the existence of the project while also making a case for your agency.
Use these tips to help you create better project proposals.
Related Posts

The Project Intake Process Explained

How To Write a Project Proposal with Examples & Free Templates

How to Create the Most Compelling Project Dashboard
Run better projects sign up for our free project management resources..
Get all our templates, tips, and fresh content so you can run effective, profitable, low-stress projects in your agency or team.
Department of English and Related Literature
PhD in English with Creative Writing
Join a thriving community of researchers to develop a substantial research project alongside an original piece of creative writing.
Join a passionate and intellectual research community to explore literature across all periods and genres.
Your research
Our PhD in English with Creative Writing encourages distinctive approaches to practice-based literary research. This route allows you to develop a substantial research project, which incorporates an original work of creative writing (in prose, poetry, or other forms). As part of a thriving community of postgraduate researchers and writers, you'll be supported by world-leading experts with a wide range of global and historical specialisms, and given access to unique resources including our letterpress printing studio and Writer in Residence.
Under the guidance of your supervisor, you will complete a critical research component of 30-40,000 words and a creative component written to its natural length (eg a book-length work of poetry, fiction, or creative nonfiction). A typical semester will involve a great deal of independent research, punctuated by meetings with your supervisor who will be able to suggest direction and address concerns throughout the writing process. You will be encouraged to undertake periods of research at archives and potentially internationally, depending on your research.
Throughout your degree, you will have the opportunity to attend a wide range of research training sessions in order to learn archival and research skills, as well as a range of research and creative seminars organised by the research schools and our distinguished Writers at York series. This brings speakers from around the world for research talks, author conversations, and networking.
Applicants for the PhD in English with Creative Writing should submit a research proposal for their overall research project, along with samples of creative and critical writing, demonstrating a suitable ability in each, as part of the application. Proposals should include plans for a critical research component of 30-40,000 words and a creative component written to its natural length (eg a book-length work of poetry, fiction or creative nonfiction), while demonstrating a clear relationship between the two.
Students embarking on a PhD programme are initially enrolled provisionally for this qualification until they pass their progression review at the end of their first full year of study.
[email protected] +44 (0) 1904 323366
Related links
- How to apply
- Research degree funding
- Accommodation
- International students
- Life at York
You also have the option of enrolling in a PhD in English with Creative Writing by distance learning, where you will have the flexibility to work from anywhere in the world. You will attend the Research Training Programme online in your first year and have supervision and progression meetings online.
You must attend a five-day induction programme in York at the beginning of your first year. You will also visit York in your second and third years (every other year for part-time students).
Apply for PhD in English with Creative Writing (distance learning)
World-leading research
We're a top ten research department according to the Times Higher Education’s ranking of the latest REF results (2021).
35th in the world
for English Language and Literature in the QS World University Rankings by Subject, 2023.
Committed to equality
We're proud to hold an Athena Swan Bronze award in recognition of the work we do to support gender equality in English.
Writers at York series
We host a series of hugely successful seminars, open to everyone, where a stellar cast of world-famous contemporary writers deliver readings and workshops.

Explore funding for postgraduate researchers in the Department of English and Related Literature.

Supervision
Explore the expertise of our staff and identify a potential supervisor.
Research student training
You'll receive training in research methods and skills appropriate to the stage you've reached and the nature of your work. In addition to regular supervisory meetings to discuss planning, researching and writing the thesis, we offer sessions on bibliographic and archival resources (digital, print and manuscript). You'll receive guidance in applying to and presenting at professional conferences, preparing and submitting material for publication and applying for jobs. We meet other training needs in handling research data, various modern languages, palaeography and bibliography. Classical and medieval Latin are also available.
We offer training in teaching skills if you wish to pursue teaching posts following your degree. This includes sessions on the delivery and content of seminars and workshops to undergraduates, a structured shadowing programme, teaching inductions and comprehensive guidance and resources for our graduate teaching assistants. Our teacher training is directed by a dedicated member of staff.
You'll also benefit from the rich array of research and training sessions at the Humanities Research Centre .
Course location
This course is run by the Department of English and Related Literature.
You'll be based on Campus West , though your research may take you further afield.
We also have a distance learning option available for this course.
Entry requirements
For doctoral research, you should hold or be predicted to achieve a first-class or high upper second-class undergraduate degree with honours (or equivalent international qualification) and a Masters degree with distinction.
The undergraduate and Masters degrees should be in literature and/or creative writing, or in a related subject that is related to the proposed research project.
Other relevant experience and expertise may also be considered:
- Evidence of training in research techniques may be an advantage.
- It would be expected that postgraduate applicants would be familiar with the recent published work of their proposed supervisor.
- Publications are not required and the Department of English and Related Literature does not expect applicants to have been published before they start their research degrees.
Supervisors interview you to ensure a good supervisory match and to help with funding applications.
The core deciding factor for admission is the quality of the research proposal, though your whole academic profile will be taken into account. We are committed to ensuring that no prospective or existing student is treated less favourably. See our admissions policy for more information.
Apply for the PhD in English with Creative Writing
Have a look at the supporting documents you may need for your application.
Before applying, we advise you to identify potential supervisors in the department. Preliminary enquiries are welcomed and should be made as early as possible. However, a scattershot approach – emailing all staff members regardless of the relationship between their research interests and yours – is unlikely to produce positive results.
If it's not clear which member of staff is appropriate, you should email the Graduate Chair .
Students embarking on a PhD programme are initially enrolled provisionally for that qualification. Confirmation of PhD registration is dependent upon the submission of a satisfactory proposal that meets the standards required for the degree, usually in the second year of study.
Find out more about how to apply .
English language requirements
You'll need to provide evidence of your proficiency in English if it's not your first language.
Check your English language requirements
Research proposal
In order to apply for a PhD, we ask that you submit a research proposal as part of your application.
When making your application, you're advised to make your research proposals as specific and clear as possible. Please indicate the member(s) of staff that you'd wish to work with
You’ll need to provide a summary of between 250 and 350 words in length of your research proposal and a longer version of around 800 words (limit of 1000). The proposal for the MA in English (by research) should be 400–500 words.
Your research proposal should:
- Identify the precise topic of your topic and communicate the main aim of your research.
- Provide a rigorous and thorough description of your proposed research, including the contributions you will make to current scholarly conversations and debates. Creative Writing proposals should include plans for a critical research and a creative component.
- Describe any previous work you have done in this area, with reference to relevant literature you have read so far.
- Communicate the central sources that the project will address and engage.
- Offer an outline of the argument’s main claims and contributions. Give a clear indication of the authors and texts that your project will address.
- Include the academic factors, such as university facilities, libraries resources, centres, other resources, and / or staff, which have specifically led you to apply to York.
What we look for:
- How you place your topic in conversation with the scholarly landscape: what has been accomplished and what you plan to achieve. This is your chance to show that you have a good understanding of the relevant work on your topic and that you have identified a new way or research question to approach the topic.
- Your voice as a scholar and critical thinker. In clean, clear prose, show those who will assess your application how your proposal demonstrates your original thinking and the potential of your research.
- Your fit with York, including the reasons for working with your supervisor and relevant research schools and centres.
- Above all, remember that there isn’t one uniform way to structure and arrange your research proposal, and that your approach will necessarily reflect your chosen topic.
Careers and skills
- You'll receive support in applying to and presenting at professional conferences, preparing and submitting material for publication and applying for jobs.
- You'll benefit from training in handling research data, various modern languages, palaeography and bibliography. Classical and medieval Latin are also available. The Humanities Research Centre also offers a rich array of valuable training sessions.
- We also offer training in teaching skills if you wish to pursue a teaching post following your degree. This includes sessions on the delivery and content of seminars and workshops to undergraduates, a structured shadowing programme, teaching inductions and comprehensive guidance and resources for our graduate teaching assistants.
- You'll have the opportunity to further your training by taking courses accredited by Advance HE: York Learning and Teaching Award (YLTA) and the York Professional and Academic Development scheme (YPAD) .
Find out more about careers

Discover York

We offer a range of campus accommodation to suit you and your budget, from economy to deluxe.

Discover more about our researchers, facilities and why York is the perfect choice for your research degree.

Graduate Research School
Connect with researchers across all disciplines to get the most out of your research project.
Find a supervisor
Explore our staff expertise
Find out all you need to know about applying to York
Find funding to support your studies

College of Arts & Sciences
Creative Writing Honors Thesis Proposal
Application guidelines.
Students interested in pursuing a senior thesis project in creative writing should create a proposal according to the guidelines below. They must also show evidence of substantial and successful course work in the specific genre in which they wish to pursue a project (i.e. if the student is interested in a poetry project, they should have already taken at least one poetry writing class, received an outstanding grade in that class, and have plans to take more classes or tutorials in poetry writing and/or to take full advantage of other poetry offerings sponsored by the University, including those sponsored by the Lannan Center). Students who wish to pursue a hybrid critical/creative project should include elements of both application guidelines in their applications, including their writing samples.
The proposal should include the following:
- A project description that explains the scope, focus, goals, and intent of the project (3 pages, double-spaced)
- A brief artist’s statement (2–3 pages, double-spaced) that does the following:
- Provides a narrative account of how the student came to be interested in this particular project (course work, readings, unofficial creative and intellectual explorations);
- Demonstrates the student’s proficiency in the project’s genre, and delineates the course work, tutorials, readings, and extracurricular activities that have prepared them for this project;
- Situates the project, providing an analysis of how it engages with other contemporary works in the same genre and/or its historical precedents;
- Outlines how this project will engage with and contribute to timely aesthetic, intellectual, and creative conversations.
- Faculty of Arts
- School of Culture and Communication
- Current students
Creative Writing research proposals
Some guidelines to assist you in developing a proposal for a research higher degree in Creative Writing at the University of Melbourne (MA or PhD).
The creative PhD at the University of Melbourne is developed and marked as a single thesis, with two major elements: a dissertation and a creative work.
Each part usually contributes 50% to the overall word count. It is possible to increase the dissertation above 50%, but the creative work cannot be more than 50%.
One way to understand the unity of the creative PhD thesis is to consider that there is one overarching research question or hypothesis, which is approached within the thesis in two different manners, a scholarly one and a creative one.
The dissertation is not an exegesis. The dissertation does not offer a commentary on the creative processes or the intentions of the writer. The dissertation is intended to stand independently as a scholarly work making an original contribution to its field or discipline. In creative writing, this field is often interdisciplinary, but it can be characterised as a discipline interested in writerly questions, that is questions that take into account creativity, creative processes, the decision-making that goes into a creative text, cultural and technological influences on writing, questions of genre boundaries (including emerging genres, hybrid genres), and questions that address issues in conceiving of writing as a craft. This is a broad description and it is not exhaustive, but it does indicate that most dissertations are investigating aspects of the act of writing.
In your proposal you should make it clear what your research question is, and how this question fits with or responds to an ongoing critical discourse. You should identify the fields or disciplines you will draw upon, what models of analysis you will adopt, and what critical and creative texts you wish to discuss in your dissertation.
The creative work will need to be articulated in your proposal with some detail, understanding that as with all creative works there will be room for re-considerations and re-drafting. You should show how your creative work addresses or arises from your research question.
Your proposal should include an indicative list of the texts you will consult.
For more information please see the Doctor of Philosophy (Arts) web page.
Writing a Project Proposal
Main navigation, a good proposal describes....
- what you hope to accomplish
- why those objectives are important to your academic or artistic field
- how you intend to achieve your objectives
Your original project proposal is the core of your grant application.
Detailed Proposal Requirements
- General guidelines for all grant proposals
- Additional specific guidelines for Research, Arts/Design, and Senior Synthesis project proposals -- please follow carefully!
- Ways to turn your good proposal into a great one
- Sample Project Proposals : Check out exemplars of past student project proposals.
Connect with Faculty Mentors and UADs
- Faculty Mentors should meet required eligibility criteria .
- Students should schedule a meeting with their Undergraduate Advising Director (UAD) as they write their proposal. UADs are well-versed with all VPUE Undergraduate Research Grants!
Watch a 3-minute overview of the VPUE Student Grant application process.
Watch a 2-minute video on how to write the critical dialogue section of a creative arts project proposal.
Samara has spent seven admissions cycles helping students best represent themselves as both individuals and applicants in the elite college admissions process. As an alumna of Cornell University and child of 2 Harvard alumni interviewers, Samara is familiar with the Ivy League's rigorous academics and application process. Using her academic foundation in communication and Fortune 100 PR and brand management experience, Samara collaborates with her clients to craft narratives that best represent themselves to admissions committees. The wit, candor, and strategy Samara brings to collaborating with clients has been highly effective. Her clients have gained admission to Columbia, The University of Pennsylvania, Cornell, UC Berkley, NYU, and Boston University, among others. She looks forward to adding your student’s successful admission to this impressive list!
Samara helped students get into:
Samara helps with…, next available sessions, describe yourself in five words, best piece of advice, favorite book, favorite subject in school, favorite after-school activities, favorite artist, favorite tv show, favorite food, di | additional hour, 5 hour package, 10 hour package, advising hours, college admissions advising.
Set a focus for each session or get help with any aspect of the admissions process.
Essay review
Full review, description.
A comprehensive review of your essay draft. Recommended if you have a rough or strong draft.
Samara’s most recent videos

Live Review Session with Samara

How Admissions Officers Evaluate Your Application
Recent reviews.
“This is what I had been looking for."
“Thanks for the input and direction. Very helpful."
“Thanks for great edits and very valuable suggestions."
Join a quick meeting
Tips for success, 1. prepare for your first session.
- Book Category Tool
- Gadgets and Gizmos
- All About Me
The 60 Best Fantasy Writing Prompts for Your Book
- by Sam Howard
In this article, I will provide an in-depth look at fantasy writing prompts that you can use to spark ideas for your own fantasy stories. Whether you want to write an epic fantasy novel, a short fantasy story, or something in between, these prompts will help unleash your creativity.
You’ll learn about the key elements that quality fantasy fiction has in common, what goes into a compelling fantasy story, different subgenres of fantasy to explore, and a whopping 60 fantasy prompts to ignite your imagination. My goal is to give you plenty of inspiration to start writing your own fantasy tales.
In this article, you will learn:
- Common features of fantasy stories
- Criteria for good fantasy writing
- An overview of major fantasy subgenres
- 60 unique fantasy ideas to use as starting points
Commonalities in Fantasy Fiction
While fantasy stories can vary widely, from high fantasy epics to paranormal romance, most quality fantasy fiction contains certain core elements. Understanding these common building blocks can help you craft a compelling fantasy tale within any subgenre.
Nearly all fantasy stories contain some form of magic or supernatural phenomena. This magic system doesn’t have to be elaborate, but it generally establishes what’s possible in the fictional world. The mechanics and limits around magic guide what characters can plausibly think and do.
Additionally, fantasy novels typically take place in worlds very unlike our own modern-day reality. While urban fantasy and magical realism bend this rule, most fantasy realms feature invented geographies, histories, cultures and politics – creating an immersive setting.
Fantasy protagonists also tend to go on an epic hero’s journey, facing increasingly difficult external conflicts on quests with high stakes. Internal conflicts often run parallel, with characters battling their own flaws and demons even as bigger foes materialize.
And although tropes aren’t mandatory, incorporating classic fantasy elements like magical swords, wands, spells and mythical creatures can help signal to readers that fantastical adventures lie ahead.
What Makes a Fantasy Good?
Like any fiction, compelling fantasy writing usually shares certain basics like dimensional characters, solid pacing, an interesting plot and engaging themes. Still, I’ve noticed some particular qualities that help set great fantasy tales apart:
- Unique magic system – The magic may not be explained in granular detail initially, but original fantasy worlds feature systems governing supernatural forces that feel fresh rather than derivative.
- Rich worldbuilding – Vivid descriptions breathe life into new environments, their histories, inhabitants and cultures. This convinces readers the setting is worthy of emotionally investing in.
- Relatable characters – Whether human or otherwise, protagonists and central figures invite understanding through authentic characterization and motivations. Their beliefs and inner lives reflect the fantastic world.
- Clever dialogue – Conversation often crackles with personality even amid strange circumstances. Witty repartee between characters fuels charged dynamics.
- Riveting action – Suspense escalates through mounting confrontations, accelerating pacing, higher-stakes drama and new magical discoveries that propel the plot.
Of course personal taste plays a major role too. Composing fantasy with complex themes or injecting humor also attracts loyal audiences. But master the story essentials above while delivering the magical escapism fantasy embodies, and readers will surely come.
Types of Fantasy
Fantasy fiction encompasses a spectrum of subgenres, each with distinctive traits. Having an overview can help you orient your ideas within the style of fantasy you’re most excited to write:
- High/Epic Fantasy – Stories told on a grand scale, often in entirely fictional secondary worlds with sprawling geography and elaborate histories. Densely-plotted heroic quests to defeat supreme evil drive intense action. Prominent examples include Lord of the Rings and George R. R. Martin’s A Song of Ice and Fire .
- Sword & Sorcery – Quest-driven tales focused on mighty warriors, wizards and assorted fighters navigating peril with steel and magic. Generally lower stakes than epic fantasy. Often feature wanderers exploring rich lands from Robert E. Howard’s Conan the Barbarian stories to Kull the Conqueror .
- Dark Fantasy – Fantasy with horror elements and grim undercurrents. Prevalent atmosphere of darkness or dread surrounds macabre magic, death and destruction. Case in point, the harrowing worlds of The Chronicles of Thomas Covenant or the graphic novel series Berserk .
- Urban Fantasy – Supernatural stories unfolding in contemporary real-world settings, typically cities. Magic and magical beings exist in hiding, unknown to the mainstream. Series like Harry Potter as well as The Dresden Files falls under this category.
- Magical Realism – Fiction where fantastical elements subtly intrude on otherwise-normal environments. Often Literary fiction exploring cultural hybridity through a touch of the extraordinary. Gabriel Garcia Marquez’s One Hundred Years of Solitude epitomizes the style.
- Mythic Fantasy – Fantasy tales drawing on the themes, symbols and elements of ancient myths, legends, folklore or fairy tales. Modern examples include the web novel Lore Olympus , a retelling of Greek mythic romances, or Catherynne M. Valente’s Deathless , which reimagines a Russian folk tale.
- Portal Fantasy – Involves characters entering unfamiliar, magical fantasy worlds through portals connecting them to our primary Earth reality. C.S Lewis’ beloved The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe helped codify conventions of the genre.
Of course additional hybrid subgenres abound too like comic fantasy, supernatural fantasy, science fantasy and more. As you explore ideas, having touchpoints like these can unfold helpful context.
60 Unique Fantasy Prompts
Now you have a solid grounding on key aspects of fantasy and its major categories. Harness all this knowledge along with the expansive 60 fantasy prompts below to kickstart your next writing project within the genre you love.
I’ve grouped prompts into handy subsections matching different facets of fantasy. Feel free to tweak or combine prompts as you see fit to develop your own tale etched with original magic.
Portal Fantasy Story Starters
- A child discovers an enchanted mirror in an abandoned house that serves as a portal to another world.
- Siblings find their late grandmother’s ornate wooden wardrobe transports them to the magical land she often told stories about.
- Every year on their birthday, a person dreams the same dream – of a glowing cave beckoning them to enter. On their 18th birthday they discover the actual glowing cave while hiking nearby.
- A young witch-in-training finds a portal inside a tree hollow that leads her to the future domain of her powerful future self.
- An archaeologist excavates a temple from an ancient civilization with a magical portal at its center, still active after all this time. Where might it lead?
- A video game enthusiast discovers that the VR world of their new game engine is an actual alternate reality.
- A photographer takes a tumble while shooting urban architecture, only to enter a portal into a bustling epic fantasy city through a clever trompe l’oeil mural.
- Every house on a block contains a hidden portal to a different fantasy world – except the cranky old man protagonist’s home. When he discovers a young girl trapped and unable to activate her house’s portal, they set off on an odd couple adventure.
- At a magical lake, people enter the water beneath a full moon to briefly visit whoever they’ve lost that they miss most in vision-like dreams.
- A fairy ring of mushrooms in the forest actually serves as a portal between worlds. A mother and daughter each independently take shelter among the mushrooms from rain, ushering an unlikely reunion in the magical realm the portal leads to.
Urban Fantasy Story Ideas
- A busy lawyer discovers their high-powered wardrobe contains enchanted clothing that allows them to manifest their words and soothe frayed nerves around them.
- Gargoyles mysteriously appear on buildings throughout a city. When people walk beneath them after sundown, their greatest ambitions manifest unconsciously.
- A blogger finds handwritten fairytale poems fluttering in the streets. They discover the poet they memorialize died years earlier, yet their ghost continues creating through magic ink that materializes their verses.
- A jaded bureaucract discovers a secret pocket realm accessible through filing cabinets in their office where unwanted documents and office supplies become enchanted.
- A vigilante hacker develops a computer virus that deploys magical rather than technological effects, serving surreptitious justice on corrupt officials undermined through inexplicable luck.
- A chocolatier uses enchanted confections to help customers relive their most cherished memories while enjoying inventive sweets, until the magic goes awry.
- A developer converts dilapidated warehouses into wildly successful commercial properties by making droves inexplicably view their imperfections as quaint through an enchantment. However, without keeping the spell in check the glamour produces catastrophes.
- A painter creates impossible combinations of real realms from dreams by mixing enchanted ink into their watercolors. Trouble arises when people leap physically into the worlds on canvas without the magician’s permission.
- A grandmother runs a magical greenhouse passed down generations where every flower’s scent imbues a unique imagining gift when inhaled. As surrounding neighbourhoods destabilize, enticing buyers threaten the family legacy and community peace the greenhouse protects.
- A chic fashion designer sews impossible dresses that render wearers unnoticed in public spaces, allowing celebrities reprieve and young female interns escape from harassment. However when a customer wants to adapt her stealth designs to commit crimes, she must fight back.
Dark Fantasy Story Ideas
- In a realm where necromancers are priests, graveyards become animate with the rattling bones and shambling corpses of those mourners fail to appease through proper funereal tributes.
- An amoral wizard-artificer breeds terrifying beast-machine hybrids by infusing strange pulsating relics into flesh, bone and iron during unholy experiments, slowly losing their humanity in the process.
- A cursed charm from ages past compels its possessors to transfer the Hello through murder alone so they might live. The chain of possessed “inheritors” spans centuries leaving macabre legends, like an archeologistInheritor driven to study and ultimately pocket the ancient artifact that possesses them next despite all warnings.
- Every year villages offer up people chosen by lottery to a towering labyrinthine prison as tithes appeasing its monstrous warden – except this year, chance selects the beloved daughter of a grieving mother who vows to topple the entire tithe system and destroy the warden who keeps it in place no matter the cost.
- Poisonous purple clouds spread from a crater where a mysterious obsidian meteor struck, their lethal miasma driving people to madness before painful death sweeps them away. Desperate holdouts too poor to flee struggle to survive while negotiating fragile alliances.
- A ruthless band of treasure hunters seeking mythic riches slaughter their way through an old-growth forest but encounter wrathful plant spirits and sentient trees that manipulate nature itself to violently expel the invaders.
- An innocent child is born with emerald eyes that involuntarily turn those who behold them into lifeless onyx statues over time. They must find a way to hide their curse from superstitious townspeople who would condemn them for witchcraft.
- Harrowed parents in in an isolated village cut off from outside aid can only watch their loved ones fall prey to a contagious werewolf curse transforming helpless victims monthly beneath the full moon. A lone misunderstood wizard may be able to help before it’s too late.
- Shadowy nightmare beings thrive on human fear and take monstrous shape from an individual’s personal phobias before entering bedrooms unseen to feast. A young girl fights sleeplessness as she desperately learns how to lucid dream so that she may turn these creatures of darkness into her own guardians against harm.
- A violent clan of nomadic raiders invades a suspected witch’s well-hidden sanctuary domicile seeking to capture and torture her for nefarious purposes. But they soon discover her cabin in the dark forest contains uncanny horrors guarding far greater secrets within which promise terrifying power should they seize it as their own.
High Fantasy Story Starters
- In a land where dragon riders defend humanity against otherworldly threats, an orphan stable hand discovers an abandoned dragon egg and faces backlash as they raise the hatchling in secret, forging an unbreakable bond.
- An exiled knight errant and mage masquerading as a common sellsword venture deep into forgotten valleys chasing legends of a fallen kingdom’s lost treasure, but release an ancient guardian entity in the perilous ruins below.
- A womdering ronin samurai and mystic swordsman with a cursed blade joins forces with rebel guerillas and a young rural farm boy working to end a tyrannical warlord’s conquests. During a pivotal confrontation at the despot’s stronghold, it’s revealed the protagonists all hail from the same ninja shinobi clan.
- A soldier spared from death during a decisive battle gradually transforms into an undead revenant beholden to sinister forces because of the necromantic axe that saved his life. Seeking a cure, he returns to his home village but learns even greater dangers haunt his once idyllic community.
- A plucky thieves guild urchin who narrowly escapes captivity and her orphan friends accidentally unleash an imprisoned magical creature while hiding in castle ruins. Its freedom could spell salvation or doom for the kingdom.
- A gifted apothecarist monastery acolyte mistakes a crucial ingredient during an accelerated plague remedy trial, inadvertently creating a ravenous undead epidemic infecting the abbey’s medicinal garden instead of the life-saving panacea everyone hoped for.
- After an ambitious noble house launches a coup against the crown, the deposed queen entrusts her newborn heir to loyalist allies who disguise themselves as common laborers as they ferry the scion to safety through contested territory. The babe bears a unique birthmark signifying they are the rightful future ruler.
- The sole surviving member of a legendary guardian order embarks on a dangerous quest to convene compatriots in a desperate attempt to combat the malevolent god recently freed from its aeons-long imprisonment now threatening civilization anew.
- A court jester hailed as the cleverest in the land is actually a powerful mageSaboteur patiently dismantling the empire subjugating the mages through subtle magical pranks embarrass leading officials. However, when the king brings in an estranged childhood friend as an inquisitor who sees through the deception, the fight turns serious.
- After frightened woodcutters report a phoenix roosting in a shadowed glen once struck by lightning during a dry storm, druids debate whether its glorious immolation ritual signals ruin or rebirth while opportunistic trappers encroach against all advice.
Magic Discovery Story Prompts
- While salvaging equipment from an alchemical workshop, a tinkerer haphazardly activates an experimental transmutation engine revealing new metals and gemstones but can’t control what it conjures, attracting greedy opportunists and magical investigators alike.
- An obsessive aristocrat commissions explorers to chart rumored ley lines crisscrossing her lands hoping to harness ambient magical energy flowing through them. But breaching these channels of power has unintended effects even the mysterious ley walkers they consult against better judgement couldn’t predict.
- In a magic academy where rival factions vie for prestige and sway using illegally-obtained relics stolen from crypts, museums and private collections, a principled teacher tries limiting growing corruption as repercussions from meddling with dangerous artifacts shake the arcane institution’s foundations.
- An antiques appraiser routinely consults mystics whenever they encounter particularly beguiling magical objects of inscrutable origin, but after they help a powerful benefactor procure a set of seven rings believed crucial for a secret unity ritual, reality itself seems to glitch and blur around them.
- A tribal shaman hunting fungi components to restock their village’s medicinal stores realizes the magical mycelium network binding specific flora grants personalized visions of possible futures after accidental overexposure. Sharing this revelation could enable defensive premonitions yet invites outside exploitation.
- Academics excavating a newly uncovered tomb complex note its strange hieroglyphs glow whenever workers disturbed lost relics and scrolls strewn about the premises. Exact deciphering proves difficult but points to catalogues of profound magical knowledge awaiting proper translation back at the university.
- Over multiple generations spanning centuries, successive guardians of an enigmatic lighthouse ensure its beacon fire continues burning to luminously outline treacherous shallows and navigate ships away from rocky disaster. But the latest caretaker worries their diminishing eyesight risks losing track of a delivery shipment carrying the secret flame’s fuel – luminous nighthawk eggs harvested only under a blue moon’s sight.
- Far from colonial authorities in balmy tropics, secreted among volcanic peaks and plunging ravines, autonomous villages still prosper by distilling elusive absinthe liquor through unique botanicals granting imbibers reality-warping and time-bending qualities when sipped sparingly. An exiled occultistdecrypts production secrets in order to barter access home.
- When hostile treasure hunters probing a seam of glowstone in the abyssal depths of an ancient dwarven mine complex inadvertently unearth a towering titan imprisoned for instigating the legendary War of Fire Giants, their screaming vanguard flees for the surface to spread warning while veteran champions steel themselves to make a heroic last stand against the fiery colossus they’ve unleashed until reinforcements hopefully still versed in binding runes and shielding wards arrive in time.
Mythic Creatures Story Ideas
- An amateur cryptozoologist receives photos depicting an unknown serpentine beast spied coiling amongst legendary loch waters, prompting a dangerous pursuit to confirm rumours suggesting this mystical lake entity survives against all odds using chameleonic camouflage mechanisms to avoid modern detection.
- While surveying prospective marshland real estate, curious scouts discover timid willowy beings with leafy hair resembling botanical dryads shyly withdrawing amidst the isolated bog.their disturbance risks permanently scattering these rare sylvan spirits before conservation efforts establish protected areas.
- Daring divers conducting submarine surveys along a remote archipelago document an elegant tribe of humanoids swimming through crystal waters with bioluminescent skin, membranes between elongated digits, and gently swirling spines running from nape down backs evoking mythical merfolk. Attempts to discretely monitor them raise urgent preservation questions once footage leaks publicly.
- Supposed extinct miniature stallions with pearlescent spiral horns projecting from their foreheads turn up mystifying wildlife experts seeking to verify their validity as alicorns and pinpoint origins of the diminutive equines inexplicably spotted in various surprising locations worldwide given lack of previous sightings. Where did they emerge from and how did they proliferate globally?
- While researching folk beliefs associated with a puzzling root vegetable grown by rural cultivators, an ethnobotanist finally pieces together why superstitious farmers harvest these specific tuberous plants according to lunar cycles. It seems consuming them under moonlight alters people’s perceptions towards seeing capricious pookah fae shapeshifting through forms.
- Baffled pet owners across several cities surreptitiously consult veterinarians after hours concerning their animals’ unusual behavior patterns, but the consensus suggests certain elemental sprites remarkably reactive to pollution and habitat disruptions have begun intervening through willing animal vessels letting them convey crucial environmental restoration messages.
- A celebrated chimera in antiquity renown for its oracular sight and wisdom unexpectedly resurfaces after centuries dormant to reluctantly help a perilously fractured kingdom, but its sphinx-like proclamations prove so cryptic that divine decipherers must convene to properly unravel prophetic statements encoded within imagery-rich verse.
- exploring a tidal cave network reveals crude bioluminescent cave paintings depicting now extinct mega faunas living amongst early humans, yet one hitherto unidentified sauropod they spot outlined multiple times near vital freshwater outlets suggests maybe a special phoenix-like regeneration is involved accounting for why this particular colossal species still roams secluded sites according to rare sightings.
- After inheriting an eccentric relative’s overgrown estate, the new groundskeeper gradually befriends gargantuan guardian statues prowling the property each night that their ancestor had long ago awakened from stone hibernation using ancient runic synergies. Now fully sentient yet still bound by geas-fueled oaths to defend sacred boundary wards against trespassers in perpetuity.
- Investigating terrifying instances of dangerous predators found mysteriously slaughtered throughout remote mountain hiking trails points to the legendary involvement of a massive fur-covered humanoid people come down seasonally from hidden villages nestled amongst cloud-piercing peaks to harvest resources, leaving occasional violent calling cards warning human settlers away.
- Clearing out a backyard garden plot, homeowners unearthed strange skull fragments alongside unusual claw and vertebrae remains resembling no catalogued regional wildlife. However, after unexpectedly animated beings self-assembling from these unknown animal bones and sinew subsequently carry their whining dog away towards the forested foothills, frantic owners contact monster hunting occultists and sabermetric scientists to identify what may have emerged and strategize safe retrievals.
These 150 fantasy writing prompts offer a treasure trove of story ideas you can explore within magical realms of your own imagining, whether building out entire worlds or just enhancing life’s hidden wonders. From portals leading across dimensions to mythical beasts and magical objects with cryptic purposes, let these prompts stir your creativity.
Remember the key ingredients that make fantasy tales resonate. Bake in rich worldbuilding, dimensional characters, suspenseful pacing and themes that connect with readers. Study classics of the genre you wish to emulate while putting your own distinct spin on tropes. Keep magic and supernatural forces integral without overshadowing interpersonal relationships, inner turmoil and relatable conflicts that bring fantasy down to earth even amidst the extraordinary.
Most importantly, believe fervently in the realms you envision and pour passion into each enchanted word set to page. If you thoroughly enjoy building new worlds and want readers to find the same wonder escaping routine reality, then fantasy fiction offers endless gateways forescape. Now step through the portal of your imagination – let these prompts guide your journey into fantastical storytelling!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 9: Proofread and edit. Before sending your proposal out into the world, give it a thorough once-over. Take the time to meticulously proofread every nook and cranny, hunting down grammar slip-ups, punctuation quirks and sneaky spelling errors. A second perspective can catch things you might have overlooked.
Step 1: Write the Executive Summary. Coming up with an executive summary is the first step to take when writing a project proposal. It's a relatively shorter section designed to give investors and stakeholders a brief overview of the most important information about the project.
This free project proposal template for Word will provide you with everything you need to write an excellent project proposal. It will help you with the executive summary, project process, deliverables, costs—even terms and conditions. Download your free template today. ProjectManager's project proposal template.
With our project proposal generator, you can make a project proposal with ease. Start from scratch, or kickstart your writing process by browsing our templates library for project proposal ideas. Choose a layout that fits your needs and start writing right away on the Canva Docs editor. Easily format your document with our drag-and-drop tools.
Your project proposal should summarize your project details and sell your idea so stakeholders feel inclined to get involved in the initiative. The goal of your project proposal is to: Secure external funding. Allocate company resources to your project. Gain stakeholder buy-in. Build momentum and excitement.
1. Discover the client's needs. The first step is to understand the client's current challenges and goals. As part of your discovery process, you might conduct a single sales call, or several. Some companies actually charge for a longer discovery or audit process, and use a proposal to sell that introductory service.
Edit/proofread your proposal. After writing your project proposal, make the necessary edits to ensure it's clear, helpful, and persuasive. Ensure the proposal is attractive, organized, and visually appealing. Check the tone and language too, and don't forget to proofread for grammar, punctuation, and spelling mistakes.
Step 4: Write the project proposal. Now that you have all the project's internal details, it's time to organize them into a concise, personalized proposal statement. Collaborating on all of the ideas in a project proposal whiteboard makes it easy to define your proposal as you go. Once you have outlined the key concepts on ClickUp's ...
Create an outline of your project proposal based on the information you have gathered. Write down the core elements; more or less the basic elements should include an introduction, problem, solution, the action plan, timeline and resources, and a conclusion. Completing the initial steps above provides you a good head start to writing your ...
A persuasive project proposal includes a definition of success with a plan for how to reach it. Create a SMART goal for your project that clearly defines what a successful outcome looks like. Your goal should be: S pecific (clearly defined) M easurable (quantifiable, and include a way to "check off" its completion)
Section 1: Executive summary. Write an introductory section, called the executive summary, to summarize your project. Just like the introduction of an essay, this section should aim to catch your recipient's attention and encourage them to read on. Your executive summary should include details about the following:
Given this expansive brief, writing a convincing project proposal can be a challenge even for agency veterans. In this guide, I'll share 7 tips you must follow to create more convincing project proposals. ... This is a frequent problem on technical and creative projects. The technical or creative problem might seem substantial enough on its ...
Steps to writing your own project proposal. Step 1: Define the problem; Step 2: Present your solution; Step 3: Define your deliverables and success criteria; Step 4: State your plan or approach;
Writing a Practice Based PhD Proposal - Creative Writing York Centre for Writing: School of Humanities ... creative and critical questions that your project will discuss. • Start with your creative proposal and give the foundations of form, genre, length, etc. ... • What does my creative writing seek to assess - this might be about a ...
MA Thesis Proposal. For my creative project, I intend to write four retellings of fairy tales. As I will discuss in. the essay on craft, the concept of the fairy tale has gone through many permutations in western. society, from oral tales to the collections of the Brothers Grimm to much more recent retellings,
Applicants for the PhD in English with Creative Writing should submit a research proposal for their overall research project, along with samples of creative and critical writing, demonstrating a suitable ability in each, as part of the application. Proposals should include plans for a critical research component of 30-40,000 words and a ...
Application Guidelines. Students interested in pursuing a senior thesis project in creative writing should create a proposal according to the guidelines below. They must also show evidence of substantial and successful course work in the specific genre in which they wish to pursue a project (i.e. if the student is interested in a poetry project ...
Creative Writing research proposals. Some guidelines to assist you in developing a proposal for a research higher degree in Creative Writing at the University of Melbourne (MA or PhD). The creative PhD at the University of Melbourne is developed and marked as a single thesis, with two major elements: a dissertation and a creative work. ...
Detailed Proposal Guidelines. VPUE Project Proposal Writing Guide. (link is external) : Read this document carefully and follow the guidelines based on the project you envision to pursue. In this guide, you will find: General guidelines for all grant proposals. Additional specific guidelines for Research, Arts/Design, and Senior Synthesis ...
From Professional Development to Critical and Creative Practice. Victoria, BC: University of Victoria. This work is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. Download this book for free at https://onlineacademiccommunity.uvic.ca/comarts/ References to internet URLs were accurate at the time of writing.
Creativity has an innate ability to transcend boundaries, enabling it to reach across cultures, languages, and backgrounds. By tapping into human emotions, imagination, and empathy, creative ...
You can use this time as you see fit for project planning, school list strategy, creative writing ideation, offline edits, mock interviews, and more. $ ... creative writing ideation, offline edits, mock interviews, and more. $1,500 ($150/hr) Save 19%. Book package. Advising hours. College admissions advising. $185.00 / 60 min. Set a focus for ...
Prominent examples include Lord of the Rings and George R. R. Martin's A Song of Ice and Fire. Sword & Sorcery - Quest-driven tales focused on mighty warriors, wizards and assorted fighters navigating peril with steel and magic. Generally lower stakes than epic fantasy.