Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech
Methods of speech delivery, learning objectives.
Identify the four types of speech delivery methods and when to use them.
There are four basic methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous. We’ll look at each method and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each.

A manuscript page from President George W. Bush’s address to the nation on the day of the 9/11 attacks in 2001.
A manuscript speech is when the speaker writes down every word they will speak during the speech. When they deliver the speech, they have each word planned and in front of them on the page, much like a newscaster who reads from a teleprompter.
The advantage of using a manuscript is that the speaker has access to every word they’ve prepared in advance. There is no guesswork or memorization needed. This method comforts some speakers’ nerves as they don’t have to worry about that moment where they might freeze and forget what they’ve planned to say. They also are able to make exact quotes from their source material.
When the exact wording of an idea is crucial, speakers often read from a manuscript, for instance in communicating public statements from a company.
However, the disadvantage with a manuscript is that the speakers have MANY words in front of them on the page. This prohibits one of the most important aspects of delivery, eye contact. When many words are on the page, the speakers will find themselves looking down at those words more frequently because they will need the help. If they do look up at the audience, they often cannot find their place when the eye returns to the page. Also, when nerves come into play, speakers with manuscripts often default to reading from the page and forget that they are not making eye contact or engaging their audience. Therefore, manuscript is a very difficult delivery method and not ideal. Above all, the speakers should remember to rehearse with the script so that they practice looking up often.

Public Speaking in History
The fall of the Berlin Wall on November 9, 1989, owed in large part to a momentary error made by an East German government spokesperson. At a live press conference, Günter Schabowski tried to explain new rules relaxing East Germany’s severe travel restrictions. A reporter asked, “when do these new rules go into effect?” Visibly flustered, Schabowski said, “As far as I know, it takes effect immediately, without delay.” In fact, the new visa application procedure was supposed to begin the following day, and with a lot of bureaucracy and red tape. Instead, thousands of East Berliners arrived within minutes at the border crossings, demanding to pass through immediately. The rest is history.
The outcome of this particular public-relations blunder was welcomed by the vast majority of East and West German citizens, and hastened the collapse of communism in Eastern and Central Europe. It’s probably good, then, that Schabowski ran this particular press conference extemporaneously, rather than reading from a manuscript.
You can view the transcript for “The mistake that toppled the Berlin Wall” here (opens in new window) .
A memorized speech is also fully prepared in advance and one in which the speaker does not use any notes. In the case of an occasion speech like a quick toast, a brief dedication, or a short eulogy, word-for-word memorization might make sense. Usually, though, it doesn’t involve committing each and every word to memory, Memorizing a speech isn’t like memorizing a poem where you need to remember every word exactly as written. Don’t memorize a manuscript! Work with your outline instead. Practice with the outline until you can recall the content and order of your main points without effort. Then it’s just a matter of practicing until you’re able to elaborate on your key points in a natural and seamless manner. Ideally, a memorized speech will sound like an off-the-cuff statement by someone who is a really eloquent speaker and an exceptionally organized thinker!
The advantage of a memorized speech is that the speaker can fully face their audience and make lots of eye contact. The problem with a memorized speech is that speakers may get nervous and forget the parts they’ve memorized. Without any notes to lean on, the speaker may hesitate and leave lots of dead air in the room while trying to recall what was planned. Sometimes, the speaker can’t remember or find his or her place in the speech and are forced to go get the notes or go back to the PowerPoint in some capacity to try to trigger his or her memory. This can be an embarrassing and uncomfortable moment for the speaker and the audience, and is a moment which could be easily avoided by using a different speaking method.
How to: memorize a speech
There are lots of tips out there about how to memorize speeches. Here’s one that loosely follows an ancient memorization strategy called the method of loci or “memory palace,” which uses visualizations of familiar spatial environments in order to enhance the recall of information.
You can view the transcript for “How to Memorize a Speech” here (opens in new window) .
An impromptu speech is one for which there is little to no preparation. There is often not a warning even that the person may be asked to speak. For example, your speech teacher may ask you to deliver a speech on your worst pet peeve. You may or may not be given a few minutes to organize your thoughts. What should you do? DO NOT PANIC. Even under pressure, you can create a basic speech that follows the formula of an introduction, body, and conclusion. If you have a few minutes, jot down some notes that fit into each part of the speech. (In fact, the phrase “speaking off the cuff,” which means speaking without preparation, probably refers to the idea that one would jot a few notes on one’s shirt cuff before speaking impromptu.) [1] ) An introduction should include an attention getter, introduction of the topic, speaker credibility, and forecasting of main points. The body should have two or three main points. The conclusion should have a summary, call to action, and final thought. If you can organize your thoughts into those three parts, you will sound like a polished speaker. Even if you only hit two of them, it will still help you to think about the speech in those parts. For example, if a speech is being given on a pet peeve of chewed gum being left under desks in classrooms, it might be organized like this.
- Introduction : Speaker chews gum loudly and then puts it under a desk (attention getter, demonstration). Speaker introduces themselves and the topic and why they’re qualified to speak on it (topic introduction and credibility). “I’m Katie Smith and I’ve been a student at this school for three years and witnessed this gum problem the entire time.”
- Body : Speaker states three main points of why we shouldn’t leave gum on desks: it’s rude, it makes custodians have to work harder, it affects the next student who gets nastiness on their seat (forecast of order). Speaker then discusses those three points
- Conclusion : Speaker summarizes those three points (summary, part 1 of conclusion), calls on the audience to pledge to never do this again (call to action), and gives a quote from Michael Jordan about respecting property (final thought).
While an impromptu speech can be challenging, the advantage is that it can also be thrilling as the speaker thinks off the cuff and says what they’re most passionate about in the moment. A speaker should not be afraid to use notes during an impromptu speech if they were given any time to organize their thoughts.
The disadvantage is that there is no time for preparation, so finding research to support claims such as quotes or facts cannot be included. The lack of preparation makes some speakers more nervous and they may struggle to engage the audience due to their nerves.
Extemporaneous
The last method of delivery we’ll look at is extemporaneous. When speaking extemporaneously, speakers prepare some notes in advance that help trigger their memory of what they planned to say. These notes are often placed on notecards. A 4”x6” notecard or 5”x7” size card works well. This size of notecards can be purchased at any office supply store. Speakers should determine what needs to go on each card by reading through their speech notes and giving themselves phrases to say out loud. These notes are not full sentences, but help the speakers, who turn them into a full sentence when spoken aloud. Note that if a quote is being used, listing that quote verbatim is fine.
The advantage of extemporaneous speaking is that the speakers are able to speak in a more conversational tone by letting the cards guide them, but not dictate every word they say. This method allows for the speakers to make more eye contact with the audience. The shorter note forms also prevent speakers from getting lost in their words. Numbering these cards also helps if one gets out of order. Also, these notes are not ones the teacher sees or collects. While you may be required to turn in your speech outline, your extemporaneous notecards are not seen by anyone but you. Therefore, you can also write yourself notes to speak up, slow down, emphasize a point, go to the next slide, etc.
The disadvantage to extemporaneous is the speakers may forget what else was planned to say or find a card to be out of order. This problem can be avoided through rehearsal and double-checking the note order before speaking.
Many speakers consider the extemporaneous method to be the ideal speaking method because it allows them to be prepared, keeps the audience engaged, and makes the speakers more natural in their delivery. In your public speaking class, most of your speeches will probably be delivered extemporaneously.
- As per the Oxford English Dictionary' s entry for "Off the Cuff." See an extensive discussion at Mark Liberman's Language Log here: https://languagelog.ldc.upenn.edu/nll/?p=4130 ↵
- Method of loci definition. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Method_of_loci . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- The mistake that toppled the Berlin Wall. Provided by : Vox. Located at : https://youtu.be/Mn4VDwaV-oo . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- How to Memorize a Speech. Authored by : Memorize Academy. Located at : https://youtu.be/rvBw__VNrsc . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Address to the Nation. Provided by : U.S. National Archives. Located at : https://prologue.blogs.archives.gov/2011/09/06/911-an-address-to-the-nation/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Methods of Speech Delivery. Authored by : Misti Wills with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

10 Tips for Improving Your Public Speaking Skills
Few are immune to the fear of public speaking. Marjorie North offers 10 tips for speakers to calm the nerves and deliverable memorable orations.
Marjorie North
Snakes? Fine. Flying? No problem. Public speaking? Yikes! Just thinking about public speaking — routinely described as one of the greatest (and most common) fears — can make your palms sweat. But there are many ways to tackle this anxiety and learn to deliver a memorable speech.
In part one of this series, Mastering the Basics of Communication , I shared strategies to improve how you communicate. In part two, How to Communicate More Effectively in the Workplace , I examined how to apply these techniques as you interact with colleagues and supervisors in the workplace. For the third and final part of this series, I’m providing you with public speaking tips that will help reduce your anxiety, dispel myths, and improve your performance.
Here Are My 10 Tips for Public Speaking:
1. nervousness is normal. practice and prepare.
All people feel some physiological reactions like pounding hearts and trembling hands. Do not associate these feelings with the sense that you will perform poorly or make a fool of yourself. Some nerves are good. The adrenaline rush that makes you sweat also makes you more alert and ready to give your best performance.
The best way to overcome anxiety is to prepare, prepare, and prepare some more. Take the time to go over your notes several times. Once you have become comfortable with the material, practice — a lot. Videotape yourself, or get a friend to critique your performance.
Communication Strategies: Presenting with Impact
Search all Communication programs.
2. Know Your Audience. Your Speech Is About Them, Not You.
Before you begin to craft your message, consider who the message is intended for. Learn as much about your listeners as you can. This will help you determine your choice of words, level of information, organization pattern, and motivational statement.
3. Organize Your Material in the Most Effective Manner to Attain Your Purpose.
Create the framework for your speech. Write down the topic, general purpose, specific purpose, central idea, and main points. Make sure to grab the audience’s attention in the first 30 seconds.
4. Watch for Feedback and Adapt to It.
Keep the focus on the audience. Gauge their reactions, adjust your message, and stay flexible. Delivering a canned speech will guarantee that you lose the attention of or confuse even the most devoted listeners.
5. Let Your Personality Come Through.
Be yourself, don’t become a talking head — in any type of communication. You will establish better credibility if your personality shines through, and your audience will trust what you have to say if they can see you as a real person.
6. Use Humor, Tell Stories, and Use Effective Language.
Inject a funny anecdote in your presentation, and you will certainly grab your audience’s attention. Audiences generally like a personal touch in a speech. A story can provide that.
7. Don’t Read Unless You Have to. Work from an Outline.
Reading from a script or slide fractures the interpersonal connection. By maintaining eye contact with the audience, you keep the focus on yourself and your message. A brief outline can serve to jog your memory and keep you on task.
8. Use Your Voice and Hands Effectively. Omit Nervous Gestures.
Nonverbal communication carries most of the message. Good delivery does not call attention to itself, but instead conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly and without distraction.
9. Grab Attention at the Beginning, and Close with a Dynamic End.
Do you enjoy hearing a speech start with “Today I’m going to talk to you about X”? Most people don’t. Instead, use a startling statistic, an interesting anecdote, or concise quotation. Conclude your speech with a summary and a strong statement that your audience is sure to remember.
10. Use Audiovisual Aids Wisely.
Too many can break the direct connection to the audience, so use them sparingly. They should enhance or clarify your content, or capture and maintain your audience’s attention.
Practice Does Not Make Perfect
Good communication is never perfect, and nobody expects you to be perfect. However, putting in the requisite time to prepare will help you deliver a better speech. You may not be able to shake your nerves entirely, but you can learn to minimize them.
Find related Communication programs.
Browse all Professional & Executive Development programs.
About the Author
North is a consultant for political candidates, physicians, and lawyers, and runs a private practice specializing in public speaking, and executive communication skills. Previously, she was the clinical director in the department of speech and language pathology and audiology at Northeastern University.
Why Gender Equity in the Workplace is Good for Business
Research indicates a correlation between gender equity and organizational success, yet it also points to obstacles for women in leadership.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.1 Four Methods of Delivery
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the four methods of speech delivery.
- Understand when to use each of the four methods of speech delivery.
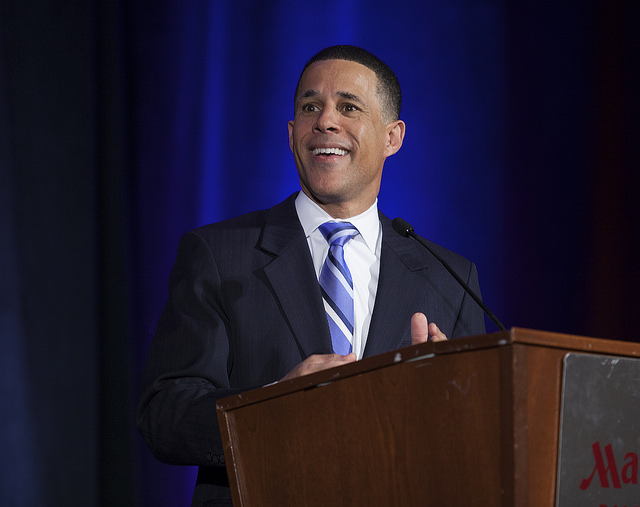

Maryland GovPics – House of Ruth Luncheon – CC BY 2.0.
The easiest approach to speech delivery is not always the best. Substantial work goes into the careful preparation of an interesting and ethical message, so it is understandable that students may have the impulse to avoid “messing it up” by simply reading it word for word. But students who do this miss out on one of the major reasons for studying public speaking: to learn ways to “connect” with one’s audience and to increase one’s confidence in doing so. You already know how to read, and you already know how to talk. But public speaking is neither reading nor talking.
Speaking in public has more formality than talking. During a speech, you should present yourself professionally. This doesn’t mean you must wear a suit or “dress up” (unless your instructor asks you to), but it does mean making yourself presentable by being well groomed and wearing clean, appropriate clothes. It also means being prepared to use language correctly and appropriately for the audience and the topic, to make eye contact with your audience, and to look like you know your topic very well.
While speaking has more formality than talking, it has less formality than reading. Speaking allows for meaningful pauses, eye contact, small changes in word order, and vocal emphasis. Reading is a more or less exact replication of words on paper without the use of any nonverbal interpretation. Speaking, as you will realize if you think about excellent speakers you have seen and heard, provides a more animated message.
The next sections introduce four methods of delivery that can help you balance between too much and too little formality when giving a public speech.
Impromptu Speaking
Impromptu speaking is the presentation of a short message without advance preparation. Impromptu speeches often occur when someone is asked to “say a few words” or give a toast on a special occasion. You have probably done impromptu speaking many times in informal, conversational settings. Self-introductions in group settings are examples of impromptu speaking: “Hi, my name is Steve, and I’m a volunteer with the Homes for the Brave program.” Another example of impromptu speaking occurs when you answer a question such as, “What did you think of the documentary?”
The advantage of this kind of speaking is that it’s spontaneous and responsive in an animated group context. The disadvantage is that the speaker is given little or no time to contemplate the central theme of his or her message. As a result, the message may be disorganized and difficult for listeners to follow.
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you are called upon to give an impromptu speech in public.
- Take a moment to collect your thoughts and plan the main point you want to make.
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak.
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace your listeners can follow.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking.
As you can see, impromptu speeches are generally most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
Extemporaneous Speaking
Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes. By using notes rather than a full manuscript, the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses. The opportunity to assess is also an opportunity to restate more clearly any idea or concept that the audience seems to have trouble grasping.
For instance, suppose you are speaking about workplace safety and you use the term “sleep deprivation.” If you notice your audience’s eyes glazing over, this might not be a result of their own sleep deprivation, but rather an indication of their uncertainty about what you mean. If this happens, you can add a short explanation; for example, “sleep deprivation is sleep loss serious enough to threaten one’s cognition, hand-to-eye coordination, judgment, and emotional health.” You might also (or instead) provide a concrete example to illustrate the idea. Then you can resume your message, having clarified an important concept.
Speaking extemporaneously has some advantages. It promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible. In addition, your audience is likely to pay better attention to the message because it is engaging both verbally and nonverbally. The disadvantage of extemporaneous speaking is that it requires a great deal of preparation for both the verbal and the nonverbal components of the speech. Adequate preparation cannot be achieved the day before you’re scheduled to speak.
Because extemporaneous speaking is the style used in the great majority of public speaking situations, most of the information in this chapter is targeted to this kind of speaking.
Speaking from a Manuscript
Manuscript speaking is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains his or her attention on the printed page except when using visual aids.
The advantage to reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. As we mentioned at the beginning of this chapter, in some circumstances this can be extremely important. For example, reading a statement about your organization’s legal responsibilities to customers may require that the original words be exact. In reading one word at a time, in order, the only errors would typically be mispronunciation of a word or stumbling over complex sentence structure.
However, there are costs involved in manuscript speaking. First, it’s typically an uninteresting way to present. Unless the speaker has rehearsed the reading as a complete performance animated with vocal expression and gestures (as poets do in a poetry slam and actors do in a reader’s theater), the presentation tends to be dull. Keeping one’s eyes glued to the script precludes eye contact with the audience. For this kind of “straight” manuscript speech to hold audience attention, the audience must be already interested in the message before the delivery begins.
It is worth noting that professional speakers, actors, news reporters, and politicians often read from an autocue device, such as a TelePrompTer, especially when appearing on television, where eye contact with the camera is crucial. With practice, a speaker can achieve a conversational tone and give the impression of speaking extemporaneously while using an autocue device. However, success in this medium depends on two factors: (1) the speaker is already an accomplished public speaker who has learned to use a conversational tone while delivering a prepared script, and (2) the speech is written in a style that sounds conversational.
Speaking from Memory
Memorized speaking is the rote recitation of a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script in a stage play, television program, or movie scene. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage to memorization is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. Being free of notes means that you can move freely around the stage and use your hands to make gestures. If your speech uses visual aids, this freedom is even more of an advantage. However, there are some real and potential costs. First, unless you also plan and memorize every vocal cue (the subtle but meaningful variations in speech delivery, which can include the use of pitch, tone, volume, and pace), gesture, and facial expression, your presentation will be flat and uninteresting, and even the most fascinating topic will suffer. You might end up speaking in a monotone or a sing-song repetitive delivery pattern. You might also present your speech in a rapid “machine-gun” style that fails to emphasize the most important points. Second, if you lose your place and start trying to ad lib, the contrast in your style of delivery will alert your audience that something is wrong. More frighteningly, if you go completely blank during the presentation, it will be extremely difficult to find your place and keep going.
Key Takeaways
- There are four main kinds of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized.
- Impromptu speaking involves delivering a message on the spur of the moment, as when someone is asked to “say a few words.”
- Extemporaneous speaking consists of delivering a speech in a conversational fashion using notes. This is the style most speeches call for.
- Manuscript speaking consists of reading a fully scripted speech. It is useful when a message needs to be delivered in precise words.
- Memorized speaking consists of reciting a scripted speech from memory. Memorization allows the speaker to be free of notes.
- Find a short newspaper story. Read it out loud to a classroom partner. Then, using only one notecard, tell the classroom partner in your own words what the story said. Listen to your partner’s observations about the differences in your delivery.
- In a group of four or five students, ask each student to give a one-minute impromptu speech answering the question, “What is the most important personal quality for academic success?”
- Watch the evening news. Observe the differences between news anchors using a TelePrompTer and interviewees who are using no notes of any kind. What differences do you observe?
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Speak Like a Pro: The Ultimate Guide to Flawless Speech Delivery Techniques Revealed!
Eloquence Everly

As an affiliate, we may earn a commission from qualifying purchases. We get commissions for purchases made through links on this website from Amazon and other third parties.
Implementing effective speech delivery techniques is essential to captivate and engage your audience. By following these techniques, you can improve your public speaking skills and deliver persuasive and engaging presentations.
Key Takeaways:
- Thoroughly prepare and practice your speech before delivering it.
- Create a distraction-free presentation environment with proper lighting and visibility.
- Pay attention to your personal appearance and maintain good body language during the speech.
- Focus on vocal delivery strategies such as clear enunciation , appropriate loudness and speed , and variations in speed and force .
- Utilize effective body language by maintaining eye contact , using gestures and movement naturally, and avoiding distracting mannerisms.
Preparation for Speech Delivery
Before delivering a speech, thorough preparation is essential. By taking the time to prepare, you can ensure a smooth and confident delivery that captivates your audience . Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Create a Well-Organized Set of Notes: To guide you during your presentation, create a clear and concise set of notes. This will help you stay on track and ensure you cover all your key points. Structure your notes in a logical manner, using headings and bullet points for easy reference.
- Engage in Ample Practice: Practice makes perfect, so dedicate time to rehearse your speech. Familiarize yourself with the content, flow, and timing of your presentation. Practice in front of a mirror, friends, or colleagues to receive feedback and make necessary improvements.
- Prepare the Presentation Environment : The environment in which you deliver your speech can greatly impact its effectiveness. Consider factors such as lighting, visibility, and distractions. Ensure that the room is well-lit and that your audience can see and hear you clearly. Eliminate any distractions or potential interruptions.
- Test and Have a Backup Plan for Audiovisual Equipment : If you will be using audiovisual equipment , such as a microphone or projector, it is crucial to test them beforehand. Check for any technical issues and have a backup plan in case of equipment failure. This will help you avoid any disruptions and allow for a seamless delivery.
By adequately preparing your speech, notes, and the presentation environment , you can set yourself up for success and deliver a confident and impactful presentation to your audience.
Personal Appearance and Body Language
When delivering a speech, your personal appearance and body language significantly impact the impression you make on your audience. Here are some key tips to ensure you project confidence and professionalism:
Dress Appropriately
Choose attire that is suitable for the occasion and reflects your respect for the audience and the topic. Ensure your outfit is clean, well-fitted, and comfortable. Avoid wearing hats or caps that can obstruct your face and hinder your nonverbal communication.
Maintain Good Posture
Stand or sit up straight, with your shoulders back and chin parallel to the ground. This posture exudes confidence and engages your audience . Remember to distribute your weight evenly and avoid excessive shifting or fidgeting.
Eye Contact
Maintaining eye contact is crucial for establishing connection and credibility with your audience. Look directly at individuals while speaking, making an effort to engage different parts of the room. Avoid constantly referring to notes or reading from a script, as this can diminish the impact of your message.
Avoid Distracting Mannerisms
Be mindful of your body language throughout your speech. Minimize excessive hand movements, pacing, or other distracting mannerisms that can detract from your message. Focus on conveying confidence and clarity through calm and composed gestures .
By paying attention to your personal appearance and body language, you can enhance your speech delivery and effectively engage your audience .
Vocal Delivery Strategies
Your vocal delivery plays a crucial role in how your speech is received by the audience. By implementing effective vocal techniques, you can enhance the impact of your message and maintain audience attention. Let’s explore some strategies to improve your vocal delivery :
Enunciation and Clarity
Clear enunciation is vital for effective communication. Ensure that you pronounce your words distinctly and avoid mumbling or garbling. By articulating each word clearly, you enhance the audience’s understanding and engagement with your speech.
Appropriate Loudness and Speed
Adjusting your volume and speed based on the audience, venue, and topic is crucial for effective vocal delivery. Speak loudly enough to be heard, but avoid being overly loud or shouting. Similarly, vary your speed to maintain audience interest and emphasize key points, but avoid speaking too quickly or too slowly.
Variations in Speed, Inflections, and Force
Utilizing variations in speed, inflections, and force adds depth and meaning to your speech. By emphasizing certain words or phrases, you can convey the significance and emotion behind them. Adjusting the pace of your speech can create anticipation or highlight important information. Use this technique strategically to enhance your message and keep your audience engaged.
Minimize Filler Words
Filler words such as “um,” “uh,” and “like” can detract from the impact and clarity of your delivery. Minimize their use to ensure a smooth and impactful presentation. Pausing briefly instead of using filler words can also add emphasis and facilitate better understanding.
“Clear and confident vocal delivery is essential for engaging your audience. Enunciate your words with clarity, speak at an appropriate loudness and speed , utilize variations in speed and force , and minimize the use of filler words. These strategies will help you captivate your audience and effectively convey your message.”
Now that you have learned about effective vocal delivery strategies, let’s move on to exploring the importance of body language in speech delivery.
Effective Use of Body Language
When delivering a speech, your body language can greatly impact how your message is received by the audience. By mastering the art of body language , you can effectively communicate your ideas and captivate your listeners.
Maintaining Eye Contact
One of the most important aspects of body language is maintaining eye contact with your audience. This establishes a connection between you and your listeners, making them feel engaged and involved in your speech. Avoid excessively reading from notes, as this can hinder eye contact and create a barrier between you and your audience. Instead, glance at your notes discreetly when necessary and focus on making eye contact with individuals throughout the room.
Using Gestures and Movement
“Gestures, in my opinion, are the most powerful tool we have in becoming an effective communicator.” – Andrea Foy
Gestures and movement can add depth and emphasis to your speech. Use them naturally to illustrate concepts, reinforce transitions between ideas, and highlight key points. However, it’s important to be mindful of using gestures in a controlled and purposeful manner. Avoid excessive or distracting movements that can draw attention away from your message. Instead, use gestures and movement to enhance your delivery and engage your audience.
Show Enthusiasm and Commitment
When delivering a speech, it’s vital to demonstrate interest and passion in your topic. Show enthusiasm through your body language, such as by smiling, using facial expressions that reflect your emotions, and maintaining an open and confident posture. This not only captures the audience’s attention but also conveys your commitment to the subject matter, making your speech more compelling and memorable.
Avoiding Distracting Mannerisms
While gestures and movement are important, it’s crucial to avoid distracting or aimless mannerisms that can detract from your message. Be aware of any nervous habits, such as fidgeting, excessive hand movements, or aimless shifting of weight. These mannerisms can undermine your credibility and divert the audience’s attention from your speech. Practice self-awareness and aim for body language that is purposeful, controlled, and complementary to your message.
Improving Verbal Delivery
When delivering a speech, your verbal delivery plays a crucial role in engaging your audience. To ensure your message reaches every corner of the room, focus on the following aspects:
- Projection : Speak with enough volume to reach people in the back of the room. This will ensure clear communication and prevent your words from getting lost in the space.
- Comfortable Rate : Speak at a pace that allows your audience to comprehend and absorb your message. Pausing occasionally not only helps you catch your breath but also gives the listeners time to process the information.
- Clear Articulation : Enunciate your words clearly to facilitate understanding. Avoid mumbling or rushing through your sentences, as this can make it difficult for your audience to follow along.
- Vocal Habits : Pay attention to any vocal habits that may distract your listeners. Eliminate vocalized pauses like “um” or “uh” and work on maintaining a steady volume throughout your speech. Avoid speaking more softly at the end of sentences, as it can diminish the impact of your message.
Sample Table: Comparing Verbal Delivery Techniques
By focusing on projection , comfortable rate , clear articulation , and eliminating distracting vocal habits , you can deliver a speech that captivates your audience and ensures effective communication.
Enhancing Nonverbal Delivery
Nonverbal delivery plays a crucial role in enhancing your overall speech delivery and making a lasting impact on your audience. By utilizing effective eye contact, movement , gestures, and an unobtrusive use of notes , you can captivate and engage your listeners. These nonverbal elements add depth and authenticity to your speech, helping to convey your message effectively.
Eye Contact: Making eye contact with individuals in your audience establishes a connection and shows that you are genuinely interested in their presence. Avoid excessive reading from notes, as it can break the eye contact and lessen your impact. Instead, actively engage with your audience, scanning the room and making meaningful eye contact with different individuals throughout your speech.
Movement: Movement on stage or in front of your audience can help you control nervousness and create visual interest. Utilize the space around you, taking purposeful steps and making slight changes in position to capture the attention of your listeners. Movement should be natural and deliberate, enhancing your message rather than distracting from it.
Gestures: Gestures and arm movements can add emphasis and clarify your spoken words. Use them to reinforce key points, illustrate concepts, and enhance the overall impact of your speech. Effective gestures appear natural and are synchronized with the rhythm and flow of your speech, engaging your audience on a visual level and reinforcing the meaning of your words.
Unobtrusive Use of Notes: While it is common to use notes during a speech to stay on track and remember important points, it is essential to use them unobtrusively. Ensure that your notes are legible and well-organized, allowing you to find the information you need without causing distractions. Place your notes discreetly or use a small podium or lectern to hold them, allowing for seamless transitions and maintaining the focus on your delivery.
Avoid any distracting mannerisms or gestures that detract from your communication. Practice incorporating these nonverbal elements into your delivery to create a powerful and engaging speech that leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Managing Nervousness and Overcoming Challenges
Nervousness is a common experience when delivering a speech. However, it’s important to remember that you are not alone in feeling this way. Chances are, many members of your audience are also experiencing nerves. The good news is that most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience, so you can stay calm and composed even if you’re feeling a bit jittery.
Embrace nervousness as it can actually be a valuable tool in enhancing your speech delivery. It can make you more alert, animated, and enthusiastic about your topic. Instead of trying to suppress it, harness that nervous energy and channel it into your presentation. When you embrace your nerves, you can turn them into a positive force that adds authenticity and passion to your speech.
Handling mistakes is another important aspect of managing nervousness . It’s natural to feel flustered if you make a mistake or lose your place during your speech. However, it’s crucial to remember that these slip-ups happen to everyone at some point. Instead of panicking, take a moment to collect yourself, take a deep breath, and calmly continue from where you left off. Most importantly, don’t dwell on the mistake or draw attention to it. Keep your focus on delivering your message effectively.
By embracing and managing nervousness , you can transform it from a potential obstacle into a catalyst for a powerful and engaging presentation. Embrace the nerves, handle mistakes gracefully, and let your genuine enthusiasm shine through.
Mastering effective speech delivery techniques is essential for becoming a confident and persuasive speaker. By implementing these techniques, such as thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, and effective vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, you can captivate your audience and deliver impactful presentations.
Preparing well before your speech, organizing your notes, and creating a suitable environment are all crucial steps in ensuring an effective delivery. Your personal appearance and body language contribute greatly to the overall impression you make on your audience. Maintaining eye contact, using gestures and movement, and speaking with clear articulation and appropriate variations in speed and force all enhance your communication.
While it is natural to feel nervous before delivering a speech, embracing this nervousness can actually help enhance your delivery. Remember, you are not alone in experiencing nerves, and most signs of nervousness are invisible to the audience. Embrace the energy that nerves bring and use it to your advantage, channeling it into a more animated and enthusiastic performance.
By following these effective speech delivery techniques, you can confidently communicate your ideas and engage your audience in a persuasive and impactful manner. Remember to always strive for clear and effective communication, and never hesitate to seek further opportunities for growth and improvement in your public speaking skills .
What are some effective speech delivery techniques?
Implementing effective speech delivery techniques involves thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, and managing nervousness .
How important is speech preparation for effective delivery?
Speech preparation is crucial for effective delivery. Creating well-organized notes, practicing, and preparing the presentation environment and audiovisual equipment are essential steps.
How does personal appearance and body language impact speech delivery?
Personal appearance, such as appropriate dressing and tidy hair, and positive body language help to engage the audience. Standing or sitting up straight, making eye contact, and avoiding distracting mannerisms are key aspects.
What are some vocal delivery strategies for effective speech delivery?
Enunciating clearly, speaking with appropriate loudness and speed, using variations in speed and inflections, and minimizing filler words are important strategies for vocal delivery.
How can body language enhance speech delivery?
Maintaining eye contact, using gestures and movement naturally, and displaying enthusiasm through body language can enhance the impact of your speech.
What are some tips for improving verbal delivery in a speech?
Projecting your voice, speaking at a comfortable rate, articulating words clearly, and eliminating vocal habits are key tips to improve verbal delivery.
How can nonverbal delivery support speech delivery?
Making eye contact with the audience, using movement and gestures, and using notes unobtrusively can make your speech more engaging and effective.
How can one manage nervousness during speech delivery?
Managing nervousness can be achieved by realizing that it’s common, remaining calm and composed, using nervous energy to enhance your delivery, and embracing mistakes as learning opportunities.
What are the key takeaways for effective speech delivery?
By implementing effective speech delivery techniques , one can become a confident and persuasive speaker. Thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, and managing nervousness are key components.
About the author
Latest Posts

Dive Into The World of Human and Animal Communication Dynamics
Human-animal communication is a fascinating field that delves into the interactions and connections between humans and animals. It examines how these two different species can communicate and understand each other on various levels. From verbal language to nonverbal cues, humans […]

The Ultimate Showdown: Is Human and Animal Communication Different?
Humans and animals have distinct differences in their communication methods and abilities. While animals rely on signals and limited vocalizations, humans have the unique capability of using organized language to express complex ideas. This article will explore the key characteristics […]

Unlocking the Secrets of Animal Communication with Humans
Animal communication has long captivated human curiosity. Throughout history, humans have marveled at the diverse ways in which animals convey their messages, through vocalizations, body language, and even telepathy. While telepathic communication between animals and humans may seem like a […]

Press ESC to close

Mastering Effective Speech Delivery: From Practice to Performance

Start this journey! Dive into the amazing world of effective speech delivery. Find out the secrets of how to engage an audience. Transform practice into incredible performances!
Connect with the audience from the start. Get their attention with interesting opening lines and stories. This sets the stage for a remarkable speech.
Understand body language and vocal projection. Use facial expressions, gestures, and tone to emphasize your message. Show confidence and be authoritative.
Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a shining example of great communication. King inspired millions with his passion and words. It’s proof of the potential of effective speech.
To be a masterful speaker, practice storytelling, connecting with an audience, and using body language. Draw inspiration from great orators. Embrace your inner orator! Make a lasting impact with your words.
Importance of Effective Speech Delivery
Delivering a speech effectively is essential for capturing the audience’s attention and getting your message across. Here are 4 key reasons why:
- Engagement: Deliver your speech in an engaging way and your listeners will stay hooked until the end. This ensures that your message resonates with them.
- Clarity: Delivery makes your speech clearer. This helps people understand your words and the main points of your message.
- Persuasion: Good delivery has a persuasive effect. Use the right tone, gestures, and body language to establish a connection with the audience and sway them towards your viewpoint.
- Rapport-building: Effective delivery builds a rapport between you and the audience. Your confident demeanor builds trust and engagement.
It is also important to remember that delivery requires practice and preparation. Pay attention to vocal variety, pacing, enunciation, body posture, and gestures.
Take Tony Robbins as an example – he once gave an inspiring speech that changed the lives of many. His passion filled every word and the crowd was entranced. By delivering the speech with such passion and conviction, Tony Robbins inspired and empowered the audience, leaving a lasting impact on their lives.
Preparing for Speech Delivery
Maximize potential as a speaker and successfully convey your message with this 6-step guide on prepared speech delivery . Follow these steps:
- Determine the purpose and select the topic .
- Research for relevant information and supportive evidence .
- Create an outline, using headings and subheadings .
- Craft an attention-grabbing intro and clearly state the purpose .
- Follow with a coherent presentation of main points and examples .
- Incorporate visuals like slides or props to enhance understanding .
- Lastly, practice delivery techniques like pacing, modulation, body language, and eye contact . Get feedback from others to refine further.
Don’t forget to refine language for the target audience. Look to Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech for inspiration – a powerful, passionate, and compelling speech that captivated the audience and started a movement.
Practicing Speech Delivery
Learn the art of speech delivery with this 6-step guide !
- Prep : Research & gather info. Organize thoughts and make an outline.
- Warm-up : Do vocal exercises like breathing, tongue twisters & scales.
- Memorize : Get key points down. Practice without notes or prompts.
- Body Language : Check your facial expressions, gestures & posture in a mirror.
- Rehearse : Keep increasing the speed & emphasize important words.
- Feedback : Get constructive criticism from trusted people. Join a club to practice.
Remember, each individual has a unique style. Embrace it & stay open to learning opportunities.
True History: Winston Churchill was a master of speech delivery . His powerful speeches during WWII motivated & inspired the UK. He was meticulous in his prep & used rhetorical devices to great effect. His speech delivery had a major impact on history.
Techniques for Effective Speech Delivery
Speech delivery is key to captivating your audience and getting your message across. To master the skill, here are three techniques to enhance it:
- Body Language: Move and gesture purposefully to engage the audience. Use hand and facial expressions to emphasize points and convey emotions. Stand tall and keep an open posture.
- Vocal Range and Tone: Vary your pitch, volume, and tone. Pause for emphasis and modulate your voice for a dynamic flow.
- Eye Contact: Establish eye contact with your audience to build trust. Look at individuals or small groups. Make your speech personal and persuasive.
Remember, successful speech delivery goes beyond words. To perfect it, rehearse in front of a mirror or record yourself. Practice makes perfect!
Also Read: Find Your Passion: A Path to Self-Discovery and Fulfillment
Overcoming Nervousness
Nerves can trip up even the most eloquent speakers, but with a few effective strategies, you can conquer them. Preparing is key. Invest time in practicing your speech and knowing it backwards and forwards. This will build confidence and reduce nervousness.
Visualize success too. Imagine you’re delivering an awesome speech to a captivated audience. This exercise helps create positive thoughts and boosts your assurance.
Controlled breathing is invaluable for fighting nerves. Slow, deep breaths can soothe the mind and relax the body. Taking care of yourself – like getting enough sleep, eating well and exercising – also helps reduce anxiety.
Let me share an inspiring story. A young executive was set to give a presentation to lots of industry experts. Despite feeling jittery beforehand, she practiced and rehearsed her speech. On the day, she focused on visualizing success and took deep breaths for inner calmness. As she spoke confidently and connected with the audience, her nerves vanished. By using these strategies, she conquered her nerves and gave an outstanding performance.
As this tale shows, conquering nervousness isn’t impossible. With dedication, visualization exercises, controlled breathing and self-care – anyone can beat their anxiety and speak confidently. Remember everyone gets nervous sometimes – how we manage it makes us stand out as confident speakers.
Tips for Captivating the Audience
To captivate your listeners , you need effective speech delivery! Here are some tips to try:
- Be personal: Relate to the audience with anecdotes or experiences.
- Use body language: Use gestures, facial expressions, and posture to make your message more impactful.
- Tell stories: Storytelling adds emotion and helps the audience understand your message better.
- Use visual aids: Slides or props can add visual interest and comprehension to your speech.
- Pause for emphasis: Pauses give time to reflect, create suspense, and highlight important points.
Adapt your speech to meet the needs of your listeners. And don’t forget the power of humor! Incorporate tasteful humor at appropriate moments to keep engagement high.
Did you know? Visuals can increase information retention in the audience by a whopping 400%!
Also Read: Top 100 Commonly Used A to Z Phrasal Verbs for English Fluency
For great speech delivery, it’s important to practice and plan. Engage the audience with body language, vocal variation, and clear pronunciation . Incorporate visuals and tech to boost the impact of the speech. Adapt to the audience’s needs and interests to keep their attention. Remember that practice makes perfect!
To make it unique, include storytelling techniques to engage the audience emotionally. Use rhetorical devices like similes and metaphors . Also, adjust pacing and rhythm for emphasis.
We recall an inspiring incident involving Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. His “I Have a Dream” speech in 1963, inspired millions. His voice and powerful message advocating for racial equality captivated the audience. His ability to connect emotionally, through vivid language and imagery, showcases the power of effective speech delivery. Know More – The Fluent Life
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What are some tips for effective speech delivery? A: Some tips for effective speech delivery include practicing beforehand, using body language and gestures, speaking clearly and confidently, and engaging the audience through eye contact.
Q2: How can I improve my speaking voice for better speech delivery? A: To improve your speaking voice, you can try exercises like breathing techniques, vocal warm-ups, and speaking with proper posture. It is also helpful to listen to and mimic good speakers to develop your own style.
Q3: How do I overcome nervousness when delivering a speech?| A: To overcome nervousness when delivering a speech , you can prepare well in advance, practice in front of a mirror or with a supportive audience, focus on your message rather than your fear, and use relaxation techniques such as deep breathing.
Q4: What are some common mistakes to avoid during speech delivery? A: Some common mistakes to avoid during speech delivery include speaking too fast or too slow, using excessive filler words like um or uh, reading directly from notes instead of engaging with the audience, and lacking enthusiasm or energy in delivery.
Q5: How can I keep the audience engaged during my speech? A: To keep the audience engaged during your speech, you can use storytelling, humor, visual aids, rhetorical questions, and interactive elements like asking for volunteers or involving the audience in small activities. It is also important to maintain a confident and enthusiastic delivery.
Q6: What are effective ways to conclude a speech for a strong impact?
A: Effective ways to conclude a speech for a strong impact include summarizing key points, providing a memorable closing statement or call-to-action, using inspirational quotes or stories, and leaving the audience with a thought-provoking question or idea to ponder upon.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Share Article:
You might also like

Public Speaking for Social Impact: A Strong Tool

Public Speaking in Digital Age: Webinars and Online Conferences

Public Speaking Ethics: Principles of Responsible Communication
Other stories, building confidence in public speaking: be successful speaker, effective audience engagement techniques: keep them interested.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Delivering a Speech
Introduction
9.1 Managing Public Speaking Anxiety
Sources of speaking anxiety.
Aside from the self-reported data in national surveys that rank the fear of public speaking high for Americans, decades of research conducted by communication scholars shows that communication apprehension is common among college students (Priem & Solomon, 2009). Communication apprehension (CA) is fear or anxiety experienced by a person due to real or perceived communication with another person or persons. CA is a more general term that includes multiple forms of communication, not just public speaking. Seventy percent of college students experience some CA, which means that addressing communication anxiety in a class like the one you are taking now stands to benefit the majority of students (Priem & Solomon, 2009). Think about the jitters you get before a first date, a job interview, or the first day of school. The novelty or uncertainty of some situations is a common trigger for communication anxiety, and public speaking is a situation that is novel and uncertain for many.
Public speaking anxiety is a type of CA that produces physiological, cognitive, and behavioral reactions in people when faced with a real or imagined presentation (Bodie, 2010). Physiological responses to public speaking anxiety include increased heart rate, flushing of the skin or face, and sweaty palms, among other things. These reactions are the result of natural chemical processes in the human body. The fight or flight instinct helped early humans survive threatening situations. When faced with a ferocious saber-toothed tiger, for example, the body released adrenaline, cortisol, and other hormones that increased heart rate and blood pressure to get more energy to the brain, organs, and muscles in order to respond to the threat. We can be thankful for this evolutionary advantage, but our physiology has not caught up with our new ways of life. Our body does not distinguish between the causes of stressful situations, so facing down an audience releases the same hormones as facing down a wild beast.
Cognitive reactions to public speaking anxiety often include intrusive thoughts that can increase anxiety: “People are judging me,” “I’m not going to do well,” and “I’m going to forget what to say.” These thoughts are reactions to the physiological changes in the body but also bring in the social/public aspect of public speaking in which speakers fear being negatively judged or evaluated because of their anxiety. The physiological and cognitive responses to anxiety lead to behavioral changes. All these thoughts may lead someone to stop their speech and return to their seat or leave the classroom. Anticipating these reactions can also lead to avoidance behavior where people intentionally avoid situations where they will have to speak in public.
Addressing Public Speaking Anxiety

While we cannot stop the innate physiological reactions related to anxiety from occurring, we do have some control over how we cognitively process them and the behaviors that result. Research on public speaking anxiety has focused on three key ways to address this common issue: systematic desensitization, cognitive restructuring, and skills training (Bodie,2010).
Although systematic desensitization may sound like something done to you while strapped down in the basement of a scary hospital, it actually refers to the fact that we become less anxious about something when we are exposed to it more often (Bodie, 2010). As was mentioned earlier, the novelty and uncertainty of public speaking is a source for many people’s anxiety. So becoming more familiar with public speaking by speaking more often can logically reduce the novelty and uncertainty of it.
Systematic desensitization can result from imagined or real exposure to anxiety-inducing scenarios. In some cases, an instructor leads a person through a series of relaxation techniques. Once relaxed, the person is asked to imagine a series of scenarios including speech preparation and speech delivery. This is something you could also try to do on your own before giving a speech. Imagine yourself going through the process of preparing and practicing a speech, then delivering the speech, then returning to your seat, which concludes the scenario. Aside from this imagined exposure to speaking situations, taking a communication course like this one is a great way to engage directly in systematic desensitization. Almost all students report that they have less speaking anxiety at the end of a semester than when they started, which is at least partially due to the fact they engaged with speaking more than they would have done if they were not taking the class.
Cognitive Restructuring
Cognitive restructuring entails changing the way we think about something. A first step in restructuring how we deal with public speaking anxiety is to cognitively process through our fears to realize that many of the thoughts associated with public speaking anxiety are irrational (Allen, Hunter & Donohue, 2009). For example, people report a fear of public speaking over a fear of snakes, heights, financial ruin, or even death. It’s irrational to think that the consequences of giving a speech in public are more dire than getting bit by a rattlesnake, falling off a building, or dying. People also fear being embarrassed because they mess up. Well, you cannot literally die from embarrassment, and in reality, audiences are very forgiving and overlook or do not even notice many errors that we, as speakers, may dwell on. Once we realize that the potential negative consequences of giving a speech are not as dire as we think they are, we can move on to other cognitive restructuring strategies.
Communication-orientation modification therapy (COM therapy) is a type of cognitive restructuring that encourages people to think of public speaking as a conversation rather than a performance (Motley, 2009). Many people have a performance-based view of public speaking. This can easily be seen in the language that some students use to discuss public speaking. They say that they “rehearse” their speech, deal with “stage fright,” then “perform” their speech on a “stage.” There is no stage at the front of the classroom; it is a normal floor. To get away from a performance orientation, we can reword the previous statements to say that they “practice” their speech, deal with “public speaking anxiety,” then “deliver” their speech from the front of the room. Viewing public speaking as a conversation also helps with confidence. After all, you obviously have some conversation skills, or you would not have made it to college. We engage in conversations every day. We do not have to write everything we are going to say out on a note card, we do not usually get nervous or anxious in regular conversations, and we are usually successful when we try. Even though we do not engage in public speaking as much, we speak to others in public all the time. Thinking of public speaking as a type of conversation helps you realize that you already have accumulated experiences and skills that you can draw from, so you are not starting from scratch.
Last, positive visualization is another way to engage in cognitive restructuring. Speaking anxiety often leads people to view public speaking negatively. They are more likely to judge a speech they gave negatively, even if it was good. They are also likely to set up negative self-fulfilling prophecies that will hinder their performance in future speeches. To use positive visualization, it is best to engage first in some relaxation exercises such as deep breathing or stretching, and then play through vivid images in your mind of giving a successful speech. Do this a few times before giving the actual speech. Students sometimes question the power of positive visualization, thinking that it sounds corny. Ask an Olympic diver what his or her coach says to do before jumping off the diving board and the answer will probably be “Coach says to image completing a perfect 10 dive.” Likewise a Marine sharpshooter would likely say his commanding officer says to imagine hitting the target before pulling the trigger. In both instances, positive visualization is being used in high-stakes situations. If it is good enough for Olympic athletes and snipers, it is good enough for public speakers.
Skills training is a strategy for managing public speaking anxiety that focuses on learning skills that will improve specific speaking behaviors. These skills may relate to any part of the speech-making process, including topic selection, research and organization, delivery, and self-evaluation. Skills training, like systematic desensitization, makes the public speaking process more familiar for a speaker, which lessens uncertainty. In addition, targeting specific areas and then improving on them builds more confidence, which can in turn lead to more improvement. Feedback is important to initiate and maintain this positive cycle of improvement. You can use the constructive criticism that you get from your instructor and peers in this class to target specific areas of improvement.
Self-evaluation is also an important part of skills training. Make sure to evaluate yourself within the context of your assignment or job and the expectations for the speech. Do not get sidetracked by a small delivery error if the expectations for content far outweigh the expectations for delivery. Combine your self-evaluation with the feedback from your instructor, boss, and/or peers to set specific and measurable goals and then assess whether or not you meet them in subsequent speeches. Once you achieve a goal, mark it off your list and use it as a confidence booster. If you do not achieve a goal, figure out why and adjust your strategies to try to meet it in the future.
Physical Relaxation Exercises
Suggestions for managing speaking anxiety typically address its cognitive and behavioral components, while the physical components are left unattended. While we cannot block these natural and instinctual responses, we can engage in physical relaxation exercises to counteract the general physical signs of anxiety caused by cortisol and adrenaline release, which include increased heart rate, trembling, flushing, high blood pressure, and speech disfluency.
Some breathing and stretching exercises release endorphins, which are your body’s natural antidote to stress hormones. Deep breathing is a proven way to release endorphins. It also provides a general sense of relaxation and can be done discretely, even while waiting to speak. In order to get the benefits of deep breathing, you must breathe into your diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle below your lungs that helps you breathe and stand up straight, which makes it a good muscle for a speaker to exercise. To start, breathe in slowly through your nose, filling the bottom parts of your lungs up with air. While doing this, your belly should pooch out. Hold the breath for three to five full seconds and then let it out slowly through your mouth. After doing this only a few times, many students report that they can actually feel a flooding of endorphins, which creates a brief “light-headed” feeling. Once you practice and are comfortable with the technique, you can do this before you start your speech, and no one sitting around you will even notice. You might also want to try this technique during other stressful situations. Deep breathing before dealing with an angry customer or loved one, or before taking a test, can help you relax and focus.
Stretching is another way to release endorphins. Very old exercise traditions like yoga, tai chi, and Pilates teach the idea that stretching is a key component of having a healthy mind and spirit. Exercise in general is a good stress reliever, but many of us do not have the time or willpower to do it. However, we can take time to do some stretching. Obviously, it would be distracting for the surrounding audience if a speaker broke into some planking or Pilates just before his or her speech. Simple and discrete stretches can help get the body’s energy moving around, which can make a speaker feel more balanced and relaxed. Our blood and our energy/ stress have a tendency to pool in our legs, especially when we are sitting.
Vocal Warm-Up Exercises

Vocal warm-up exercises are a good way to warm up your face and mouth muscles, which can help prevent some of the fluency issues that occur when speaking. Newscasters, singers, and other professional speakers use vocal warm-ups. I lead my students in vocal exercises before speeches, which also helps lighten the mood. We all stand in a circle and look at each other while we go through our warm-up list. For the first warm-up, we all make a motorboat sound, which makes everybody laugh. The full list of warm-ups follows and contains specific words and exercises designed to warm up different muscles and different aspects of your voice. After going through just a few, you should be able to feel the blood circulating in your face muscles more. It is a surprisingly good workout!
Top Ten Ways to Reduce Speaking Anxiety
Many factors contribute to speaking anxiety. There are also many ways to address it. The following is a list of the top ten ways to reduce speaking anxiety that I developed with my colleagues, which helps review what we have learned.
- Remember, you are not alone. Public speaking anxiety is common, so do not ignore it—confront it.
- Remember, you cannot literally “die of embarrassment.” Audiences are forgiving and understanding.
- Remember, it always feels worse than it looks.
- Take deep breaths. It releases endorphins, which naturally fight the adrenaline that causes anxiety.
- Look the part. Dress professionally to enhance confidence.
- Channel your nervousness into positive energy and motivation.
- Start your outline and research early. Better information = higher confidence.
- Practice and get feedback from a trusted source. (Do not just practice for your cat.)
- Visualize success through positive thinking.
- Prepare, prepare, prepare! Practice is a speaker’s best friend.
9.2 Delivery Methods and Practice Sessions
There are many decisions to make during the speech-making process. Making informed decisions about delivery can help boost your confidence and manage speaking anxiety. In this section, we will learn about the strengths and weaknesses of various delivery methods. We will also learn how to make the most of your practice sessions.
Delivery Methods
Different speaking occasions call for different delivery methods. While it may be acceptable to speak from memory in some situations, lengthy notes may be required in others. The four most common delivery methods are impromptu, manuscript, memorized, and extemporaneous.
Impromptu Delivery
When using impromptu delivery , a speaker has little to no time to prepare for a speech (LibreTexts, 2021). This means there is little time for research, audience analysis, organizing, and practice. For this reason, impromptu speaking often evokes higher degrees of speaking anxiety than other delivery types. Although impromptu speaking arouses anxiety, it is also a good way to build public speaking skills. Using some of the exercises for managing speaking anxiety discussed earlier in this chapter can help a speaker manage the challenges of impromptu speaking (LibreTexts, 2021). Only skilled public speakers with much experience are usually able to “pull off” an impromptu delivery without looking unprepared. Otherwise, a speaker who is very familiar with the subject matter can sometimes be a competent impromptu speaker, because their expertise can compensate for the lack of research and organizing time.
When Mark Twain famously said, “It usually takes me more than three weeks to prepare a good impromptu speech,” he was jokingly pointing out the difficulties of giving a good impromptu speech, essentially saying that there is no such thing as a good impromptu speech, as good speeches take time to prepare. We do not always have the luxury of preparation, though. So when speaking impromptu, be brief, stick to what you know, and avoid rambling. Quickly organize your thoughts into an introduction, body, and conclusion. Try to determine three key ideas that will serve as the basis of your main points.
When would impromptu speaking be used? Since we have already started thinking of the similarities between public speaking and conversations, we can clearly see that most of our day-to-day interactions involve impromptu speaking. When your roommate asks you what your plans for the weekend are, you do not pull a few note cards out of your back pocket to prompt your response. This type of conversational impromptu speaking is not anxiety inducing because we are talking about our lives, experiences, or something with which we are familiar. This is also usually the case when we are asked to speak publicly with little to no advance warning.
For example, if you are at a meeting for work and you are representing the public relations department, a colleague may ask you to say a few words about a recent news story involving a public relations misstep of a competing company. In this case, you are being asked to speak on the spot because of your expertise. A competent communicator should anticipate instances like this when they might be asked to speak. Of course, being caught completely off guard or being asked to comment on something unfamiliar to you creates more anxiety. In such cases, do not pretend to know something you do not, as that may come back to hurt you later. You can usually mention that you do not have the necessary background information at that time but will follow up later with your comments.
Manuscript Delivery
Speaking from a written or printed document that contains the entirety of a speech is known as manuscript delivery . Manuscript delivery can be the best choice when a speech has complicated information and/or the contents of the speech are going to be quoted or published (LibreTexts, 2021). Despite the fact that most novice speakers are not going to find themselves in that situation, many are drawn to this delivery method because of the security they feel with having everything they are going to say in front of them. Unfortunately, the security of having every word you want to say at your disposal translates to a poorly delivered and unengaging speech (LibreTexts, 2021). Even with every word written out, speakers can still have fluency hiccups and verbal fillers as they lose their place in the manuscript or trip over their words. The alternative, of course, is that a speaker reads the manuscript the whole time, effectively cutting himself or herself off from the audience. One way to make a manuscript delivery more engaging is to use a teleprompter. Almost all politicians who give televised addresses use them.
To make the delivery seem more natural, print the speech out in a larger-than-typical font, triple-space between lines so you can easily find your place, use heavier-than-normal paper so it is easy to pick up and turn the pages as needed, and use a portfolio so you can carry the manuscript securely.
Memorized Delivery
Completely memorizing a speech and delivering it without notes is known as memorized delivery (LibreTexts, 2021). Some students attempt to memorize their speech because they think it will make them feel more confident if they do not have to look at their notes; however, when their anxiety level spikes at the beginning of their speech and their mind goes blank for a minute, many admit they should have chosen a different delivery method. When using any of the other delivery methods, speakers still need to rely on their memory. An impromptu speaker must recall facts or experiences related to their topic, and speakers using a manuscript want to have some of their content memorized so they do not read their entire speech to their audience. The problem with memorized delivery overall is that it puts too much responsibility on our memory, which we all know from experience is fallible (LibreTexts, 2021).
Even with much practice, our memories can fail. If you do opt to use memorized delivery, make sure you have several “entry points” determined, so you can pick up at spots other than the very beginning of a speech if you lose your place and have to start again. Memorized delivery is very useful for speakers who are going to be moving around during a speech when carrying notes would be burdensome. I only recommend memorized delivery in cases where the speech is short (only one to two minutes), the speech is personal (like a brief toast), or the speech will be repeated numerous times (like a tour guide’s story), and even in these cases, it may be perfectly fine to have notes. Many students think that their anxiety and/or delivery challenges will vanish if they just memorize their speech only to find that they are more anxious and have more problems.
Extemporaneous Delivery
Extemporaneous delivery entails memorizing the overall structure and main points of a speech and then speaking from keyword/key-phrase notes (LibreTexts, 2021). This delivery mode brings together many of the strengths of the previous three methods. Since you only internalize and memorize the main structure of a speech, you do not have to worry as much about the content and delivery seeming stale. Extemporaneous delivery brings in some of the spontaneity of impromptu delivery but still allows a speaker to carefully plan the overall structure of a speech and incorporate supporting materials that include key facts, quotations, and paraphrased information (LibreTexts, 2021). You can also more freely adapt your speech to fit various audiences and occasions, since not every word and sentence is predetermined. This can be especially beneficial when you deliver a speech multiple times.
When preparing a speech that you will deliver extemporaneously, you will want to start practicing your speech early and then continue to practice as you revise your content. Investing quality time and effort into the speech-outlining process helps with extemporaneous delivery. As you put together your outline, you are already doing the work of internalizing the key structure of your speech. Read parts of your outline aloud as you draft them to help ensure they are written in a way that makes sense and is easy for you to deliver.
By the time you complete the formal, full-sentence outline, you should have already internalized much of the key information in your speech. Now, you can begin practicing with the full outline. As you become more comfortable with the content of your full outline, start to convert it into your speaking outline. Take out information that you know well and replace it with a keyword or key phrase that prompts your memory. You will probably want to leave key quotes, facts, and other paraphrased information, including your verbal source citation information, on your delivery outline so you make sure to include it in your speech. Once you’ve converted your full outline into your speaking outline, practice it a few more times, making sure to take some time between each practice session so you don’t inadvertently start to memorize the speech word for word. The final product should be a confident delivery of a well-organized and structured speech that is conversational and adaptable to various audiences and occasions.
Practicing Your Speech

Practicing a speech is essential, and practice sessions can be more or less useful depending on how you approach them (Dlugan, 2008). There are three primary phases to the practice process. In the first phase, you practice as you are working through your ideas and drafting your outline. In the second, you practice for someone and get feedback (Dlugan, 2008). In the third, you put the final changes on the speech.
Start practicing your speech early, as you are working through your ideas, by reading sections aloud as you draft them into your working outline. This will help ensure your speech is fluent and sounds good for the audience. Start to envision the audience while you practice and continue to think about them throughout the practicing process. This will help minimize anxiety when you actually have them sitting in front of you. Once you have completed your research and finished a draft of your outline, you will have already practiced your speech several times, as you were putting it together. Now, you can get feedback on the speech as a whole.
You begin to solicit feedback from a trusted source in the second phase of practicing your speech (Dlugan, 2008). This is the most important phase of practicing, and the one that most speakers do not complete. Beginning speakers may be nervous to practice in front of someone. That is normal. However, review the strategies for managing anxiety discussed earlier in this chapter and try to face that anxiety. After all, you will have to face a full audience when you deliver the speech, so getting used to speaking in front of someone can only help you at this point. Choose someone who will give you constructive feedback on your speech. Before you practice for them, explain the assignment or purpose of the speech. When practicing for a classroom speech, you may even want to give the person the assignment guidelines or a feedback sheet that has some key things for them to look for. Ask them for feedback on content and delivery. Almost anyone is good at evaluating delivery, but it is more difficult to evaluate content. In addition, in most cases, the content of your speech will be account for more of your grade. Also, begin to time your speech at this point, so you can determine if it meets any time limits that you have.
In addition to practicing for a trusted source for feedback, you may want to audio or video record your speech (Dlugan, 2008). This can be useful because it provides an objective record that you can then compare with the feedback you got from your friend and to your own evaluation of your speech. The most important part of this phase is incorporating the feedback you receive into your speech. If you practice for someone, get feedback, and then do not do anything with the feedback, then you have wasted your time and theirs. Use the feedback to assess whether or not you met your speaking goals. Was your thesis supported? Was your specific purpose met? Did your speech conform to any time limits that were set? Based on your answers to these questions, you may need to make some changes to your content or delivery, so do not put this part of practicing off to the last minute. Once the content has been revised as needed, draft your speaking outline and move on to the next phase of practice.
During the third and final phase of practice, you are putting the final changes on your speech. You should be familiar with the content based on your early practice sessions. You have also gotten feedback and incorporated that feedback into the speech. Your practice sessions at this point should pre-create, as much as possible, the conditions in which you will be giving your speech. You should have your speaking outline completed so you can practice with it. It is important to be familiar with the content on your note cards or speaking outline so you will not need to rely on it so much during the actual delivery. You may also want to practice in the type of clothing you will be wearing on speech day. This can be useful if you are wearing something you do not typically wear—a suit for example—so you can see how it might affect your posture, gestures, and overall comfort level.
If possible, at least one practice session in the place you will be giving the speech can be very helpful; especially if it is a room you are not familiar with. Make sure you are practicing with any visual aids or technology you will use so you can be familiar with it and it does not affect your speech fluency. (Dlugan, 2008).Continue to time each practice round. If you are too short or too long, you will need to go back and adjust your content some more. Always adjust your content to fit the time limit; do not try to adjust your delivery. Trying to speed talk or stretch things out to make a speech faster or longer is a mistake that will ultimately hurt your delivery, which will hurt your credibility. The overall purpose of this phase of practicing is to minimize surprises that might throw you off on speech day.
Vocal Delivery
Vocal delivery includes components of speech delivery that relate to your voice. These include rate, volume, pitch, articulation, pronunciation, and fluency. Our voice is important to consider when delivering our speech for two main reasons. First, vocal delivery can help us engage and interest the audience. Second, vocal delivery helps ensure we communicate our ideas clearly.
Speaking for Engagement
We have all had the displeasure of listening to an unengaging speaker. Even though the person may care about his or her topic, an unengaging delivery that does not communicate enthusiasm will translate into a lack of interest for most audience members (Davis, 2021). Although a speaker can be visually engaging by incorporating movement and gestures, a flat or monotone vocal delivery can be sedating or even annoying. Incorporating vocal variety in terms of rate, volume, and pitch is key to being a successful speaker.
Rate of speaking refers to how fast or slow you speak (Barnard, 2018). If you speak too fast, your audience will not be able to absorb the information you present. If you speak too slowly, the audience may lose interest. The key is to vary your rate of speaking in a middle range, staying away from either extreme, in order to keep your audience engaged. In general, a higher rate of speaking signals that a speaker is enthusiastic about his or her topic. Speaking slowly may lead the audience to infer that the speaker is uninterested, uninformed, or unprepared to present his or her own topic. These negative assumptions, whether they are true or not, are likely to hurt the credibility of the speaker (Barnard, 2018). The goal is to speak at a rate that will interest the audience and will effectively convey your information. Speaking at a slow rate throughout a speech would likely bore an audience, but that is not a common occurrence.
Volume refers to how loud or soft your voice is. As with speaking rate, you want to avoid the extremes of being too loud or too soft, but still vary your volume within an acceptable middle range (Packard, 2020). When speaking in a typically sized classroom or office setting that seats about twenty-five people, using a volume a few steps above a typical conversational volume is usually sufficient. When speaking in larger rooms, you will need to project your voice. You may want to look for nonverbal cues from people in the back rows or corners, like leaning forward or straining to hear, to see if you need to adjust your volume more. Obviously, in some settings, a microphone will be necessary so the entire audience can hear you. Like rate, audiences use volume to make a variety of judgments about a speaker. Sometimes, softer speakers are judged as meek (Packard, 2020). This may lead to lowered expectations for the speech or less perceived credibility. Loud speakers may be seen as overbearing or annoying, which can lead audience members to disengage from the speaker and message. Be aware of the volume of your voice and, when in doubt, increase your volume a notch, since beginning speakers are more likely to have an issue of speaking too softly rather than too loudly.
Pitch refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is. As with other vocal qualities, there are natural variations among people’s vocal pitch. Unlike rate and volume, we have less control over pitch. For example, males generally have lower pitched voices than females. Despite these limitations, each person still has the capability to change their pitch across a range large enough to engage an audience. Changing pitch is a good way to communicate enthusiasm and indicate emphasis or closure (Scotti, 2015). In general, our pitch goes up when we are discussing something exciting. Our pitch goes down slightly when we emphasize a serious or important point. Lowering pitch is also an effective way to signal transitions between sections of your speech or the end of your speech, which cues your audience to applaud and avoids an awkward ending.
Of the vocal components of delivery discussed so far, pitch seems to give beginning speakers the most difficulty. It is as if giving a speech temporarily numbs their ability to vary their pitch. Record yourself practicing your speech to help determine if the amount of pitch variety and enthusiasm you think you convey while speaking actually comes through. Speakers often assume that their pitch is more varied and their delivery more enthusiastic than the audience actually perceives it to be (Scotti, 2015). Many students note this on the self-evaluations they write after viewing their recorded speech.
Vocal Variety
Overall, the lesson to take away from this section on vocal delivery is that variety is key. Vocal variety includes changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that can make you look more prepared, seem more credible, and be able to engage your audience better (Moore, 2015). Employing vocal variety is not something that takes natural ability or advanced skills training. It is something that beginning speakers can start working on immediately and everyone can accomplish. The key is to become aware of how you use your voice when you speak, and the best way to do this is to record yourself (Moore, 2015). We all use vocal variety naturally without thinking about it during our regular conversations, and many of us think that this tendency will translate over to our speaking voices. This is definitely not the case for most beginning speakers. Unlike in your regular conversations, it will take some awareness and practice to use vocal variety in speeches. I encourage students to make this a delivery priority early on. Since it is something anyone can do, improving in this area will add to your speaking confidence, which usually translates into better speeches and better grades further on.
Speaking for Clarity
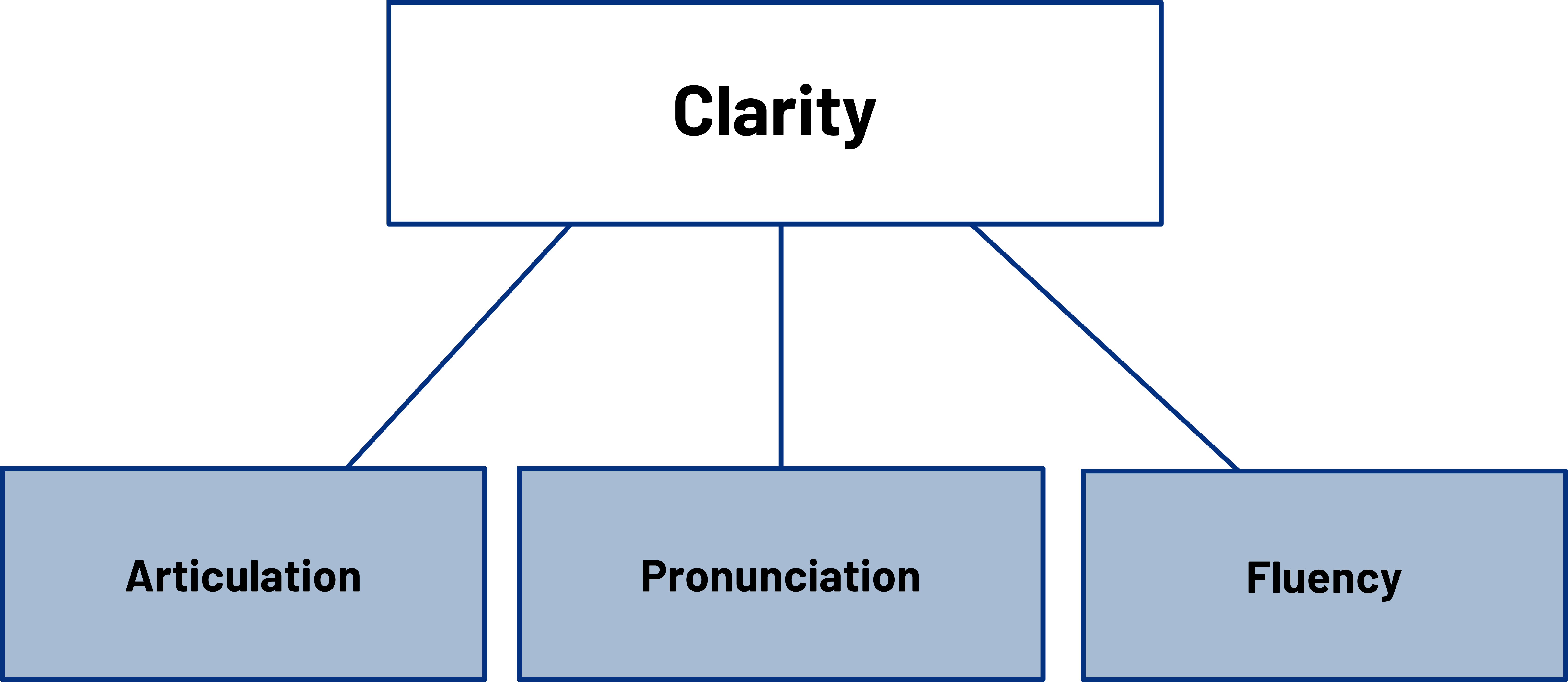
In order to be an effective speaker, your audience should be able to understand your message and digest the information you present (Rampton, 2021). Audience members will make assumptions about our competence and credibility based on how we speak. As with other aspects of speech delivery, many people are not aware that they have habits of speech that interfere with their message clarity. Since most of our conversations are informal and take place with people we know, many people do not make a concerted effort to articulate every word clearly and pronounce every word correctly (Rampton, 2021). Most of the people we talk to either do not notice our errors or do not correct us if they do notice. Since public speaking is generally more formal than our conversations, we should be more concerned with the clarity of our speech.
Articulation
Articulation refers to the clarity of sounds and words we produce. If someone is articulate, they speak words clearly, and speakers should strive to speak clearly. Poor articulation results when speakers do not speak clearly (Ward, 2020). For example, a person may say dinnt instead of didn’t , gonna instead of going to , wanna instead of want to , or hunnerd instead of hundred . Unawareness and laziness are two common challenges to articulation. As with other aspects of our voice, many people are unaware that they regularly have errors in articulation. Recording yourself speak and then becoming a higher self-monitor are effective ways to improve your articulation. Laziness, on the other hand, requires a little more motivation to address. Some people just get in the habit of not articulating their words well. Both mumbling and slurring are examples of poor articulation. In informal settings, this type of speaking may be acceptable, but in formal settings, it will be evaluated negatively. It will hurt a speaker’s credibility. Perhaps the promise of being judged more favorably is enough to motivate a mumbler to speak more clearly.
When combined with a low volume, poor articulation becomes an even greater problem. Doing vocal warm-ups like the ones listed in Section 10.1 “Managing Public Speaking Anxiety” or tongue twisters can help prime your mouth, lips, and tongue to articulate words more clearly. When you notice that you have trouble articulating a particular word, you can either choose a different word to include in your speech or you can repeat it a few times in a row in the days leading up to your speech to get used to saying it.
Pronunciation
Unlike articulation, which focuses on the clarity of words, pronunciation refers to speaking words correctly, including the proper sounds of the letters and the proper emphasis (Shtern, 2017). Mispronouncing words can damage a speaker’s credibility, especially when the correct pronunciation of a word is commonly known. We all commonly run into words that we are unfamiliar with and therefore may not know how to pronounce. Here are three suggestions when faced with this problem. First, look the word up in an online dictionary. Many dictionaries have a speaker icon with their definitions, and when you click on it, you can hear the correct pronunciation of a word. Some words have more than one pronunciation—for example, Caribbean —so choosing either of the accepted pronunciations is fine. Just remember to use consistently that pronunciation to avoid confusing your audience. If a word does not include an audio pronunciation, you can usually find the phonetic spelling of a word, which is the word spelled out the way it sounds.
Second, there will occasionally be words that you cannot locate in a dictionary. These are typically proper nouns or foreign words. In this case, use the “phone-a-friend” strategy. Call up the people you know who have large vocabularies or are generally smart when it comes to words, and ask them if they know how to pronounce it. If they do, and you find them credible, you are probably safe to take their suggestion.
Third, “fake it ‘til you make it” should only be used as a last resort. If you cannot find the word in a dictionary and your smart friends do not know how to pronounce it, it is likely that your audience will also be unfamiliar with the word. In that case, using your knowledge of how things are typically pronounced, decide on a pronunciation that makes sense and confidently use it during your speech. Most people will not question it. In the event that someone does correct you on your pronunciation, thank him or her for correcting you and adjust your pronunciation.
Fluency refers to the flow of your speaking. To speak with fluency means that your speech flows well and that there are not many interruptions to that flow. Two main disfluencies or problems affect the flow of a speech. Fluency hiccups are unintended pauses in a speech that usually result from forgetting what you were saying, being distracted, or losing your place in your speaking notes. Fluency hiccups are not the same as intended pauses, which are useful for adding emphasis or transitioning between parts of a speech. While speakers should try to minimize fluency hiccups, even experienced speakers need to take an unintended pause sometimes to get their bearings or to recover from an unexpected distraction. Fluency hiccups become a problem when they happen regularly enough to detract from the speaker’s message.
Verbal fillers are words that speakers use to fill in a gap between what they were saying and what they are saying next (Hennessy, 2019). Common verbal fillers include um , uh , ah , er , you know , and like . The best way to minimize verbal fillers is to become a higher self-monitor and realize that you use them. Many students are surprised when they watch the video of their first speech and realize they said “um” thirty times in three minutes. Gaining that awareness is the first step in eliminating verbal fillers, and students make noticeable progress with this between their first and second speeches (Hennessy, 2019). If you do lose your train of thought, having a brief fluency hiccup is better than injecting a verbal filler, because the audience may not even notice the pause or may think it was intentional.
9.3 Physical Delivery
Physical delivery.
Many speakers are more nervous about physical delivery than vocal delivery. Putting our bodies on the line in front of an audience often makes us feel more vulnerable than putting our voice out there. Yet most audiences are not as fixated on our physical delivery as we think they are. Knowing this can help relieve some anxiety, but it does not give us a free pass when it comes to physical delivery. We should still practice for physical delivery that enhances our verbal message. Physical delivery of a speech involves nonverbal communication through the face and eyes, gestures, and body movements.
Physical Delivery and the Face
We tend to look at a person’s face when we are listening to them (Hoffler, 2016). Again, this often makes people feel uncomfortable and contributes to their overall speaking anxiety. Many speakers do not like the feeling of having “all eyes” on them, even though having a room full of people avoiding making eye contact with you would be much more awkward. Remember, it is a good thing for audience members to look at you, because it means they are paying attention and interested. Audiences look toward the face of the speaker for cues about the tone and content of the speech.

Facial Expressions

Facial expressions can help bring a speech to life when used by a speaker to communicate emotions and demonstrate enthusiasm for the speech (Hoffler, 2016). As with vocal variety, we tend to use facial expressions naturally and without conscious effort when engaging in day-to-day conversations. Yet many speakers’ expressive faces turn “deadpan” when they stand in front of an audience. Some people naturally have more expressive faces than others do have—think about the actor Jim Carey’s ability to contort his face as an example. However, we can also consciously control and improve on our facial expressions to be speakers that are more effective. As with other components of speech delivery, becoming a higher self-monitor and increasing your awareness of your typical delivery habits can help you understand, control, and improve your delivery. Although you should not only practice your speech in front of a mirror, doing so can help you get an idea of how expressive or unexpressive your face is while delivering your speech.
Facial expressions help set the emotional tone for a speech, and it is important that your facial expressions stay consistent with your message (Hoffler, 2016). In order to set a positive tone before you start speaking, briefly look at the audience and smile. A smile is a simple but powerful facial expression that can communicate friendliness, openness, and confidence. Facial expressions communicate a range of emotions and are associated with various moods or personality traits.
For example, combinations of facial expressions can communicate that a speaker is tired, excited, angry, confused, frustrated, sad, confident, smug, shy, or bored, among other things. Even if you are not bored, for example, a slack face with little animation may lead an audience to think that you are bored with your own speech, which is not likely to motivate them to be interested. So make sure your facial expressions are communicating an emotion, mood, or personality trait that you think your audience will view favorably. Also, make sure your facial expressions match with the content of your speech. When delivering something lighthearted or humorous, a smile, bright eyes, and slightly raised eyebrows will nonverbally enhance your verbal message. When delivering something serious or somber, a furrowed brow, a tighter mouth, and even a slight head nod can enhance that message. If your facial expressions and speech content are not consistent, your audience could become confused by the conflicting messages, which could lead them to question your honesty and credibility.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is an important element of nonverbal communication in all communication settings. Eye contact can also be used to establish credibility and hold your audience’s attention (Barnard, 2017). We often interpret a lack of eye contact to mean that someone is not credible or not competent, and as a public speaker, you do not want your audience thinking either of those things. Eye contact holds attention because an audience member who knows the speaker is making regular eye contact will want to reciprocate that eye contact to show that they are paying attention. This will also help your audience remember the content of your speech better, because acting as if we are paying attention actually leads us to pay attention and better retain information.
Norms for eye contact vary among cultures (Barnard, 2017). Therefore, it may be difficult for speakers from countries that have higher power distances or are more collectivistic to get used to the idea of making direct and sustained eye contact during a speech. In these cases, it is important for the speaker to challenge himself or herself to integrate some of the host culture’s expectations and for the audience to be accommodating and understanding of the cultural differences.
Physical Delivery and the Body
Have you ever gotten dizzy as an audience member because the speaker paced back and forth? Anxiety can lead us to do some strange things with our bodies, like pacing, that we do not normally do, so it is important to consider the important role that your body plays during your speech. We call extra movements caused by anxiety nonverbal adaptors . Most of them manifest as distracting movements or gestures. These nonverbal adaptors, like tapping a foot, wringing hands, playing with a paper clip, twirling hair, jingling change in a pocket, scratching, and many more, can definitely detract from a speaker’s message and credibility. Conversely, a confident posture and purposeful gestures and movement can enhance both.
Posture is the position we assume with our bodies, either intentionally or out of habit. Although people, especially young women, used to be trained in posture, often by having them walk around with books stacked on their heads, you should use a posture that is appropriate for the occasion while still positioning yourself in a way that feels natural. In a formal speaking situation, it is important to have an erect posture that communicates professionalism and credibility (Clayton, 2018). However, a military posture of standing at attention may feel and look unnatural in a typical school or business speech. In informal settings, it may be appropriate to lean on a table or lectern, or even sit among your audience members (Clayton, 2018). Head position is also part of posture. In most speaking situations, it is best to keep your head up, facing your audience. A droopy head does not communicate confidence. Consider the occasion important, as an inappropriate posture can hurt your credibility.
Gestures include arm and hand movements. We all go through a process of internalizing our native culture from childhood. An obvious part of this process is becoming fluent in a language. Perhaps less obvious is the fact that we also become fluent in nonverbal communication, gestures in particular. We all use hand gestures while we speak, but we didn’t ever take a class in matching verbal communication with the appropriate gestures; we just internalized these norms over time based on observation and put them into practice. By this point in your life, you have a whole vocabulary of hand movements and gestures that spontaneously come out while you are speaking. Some of these gestures are emphatic and some are descriptive (Koch, 2007).
Emphatic gestures are the most common hand gestures we use, and they function to emphasize our verbal communication and often relate to the emotions we verbally communicate (Toastmasters International, 2011). Pointing with one finger or all the fingers straight out is an emphatic gesture. We can even bounce that gesture up and down to provide more emphasis. Moving the hand in a circular motion in front of our chest with the fingers spread apart is a common emphatic gesture that shows excitement and often accompanies an increased rate of verbal speaking. We make this gesture more emphatic by using both hands. Descriptive gestures function to illustrate or refer to objects rather than emotions (Toastmasters International, 2011). We use descriptive gestures to indicate the number of something by counting with our fingers or the size, shape, or speed of something. Our hands and arms are often the most reliable and easy-to-use visual aids a speaker can have.
While the best beginning strategy is to gesture naturally, you also want to remain a high self-monitor and take note of your typical patterns of gesturing. If you notice that you naturally gravitate toward one particular gesture, make an effort to vary your gestures more. You also want your gestures to be purposeful, not limp or lifeless.

Sometimes movement of the whole body, instead of just gesturing with hands, is appropriate in a speech. When students are given the freedom to move around, it often ends up becoming floating or pacing, which are both movements that comfort a speaker by expending nervous energy but only serve to distract the audience (Toastmasters International, 2011). Floating refers to speakers who wander aimlessly around, and pacing refers to speakers who walk back and forth in the same path. To prevent floating or pacing, make sure that your movements are purposeful. Many speakers employ the triangle method of body movement where they start in the middle, take a couple steps forward and to the right, then take a couple steps to the left, then return to the center. Obviously, you do not need to do this multiple times in a five- to ten-minute speech, as doing so, just like floating or pacing, tends to make an audience dizzy.
To make your movements appear more natural, time them to coincide with a key point you want to emphasize or a transition between key points. Minimize other movements from the waist down when you are not purposefully moving for emphasis. Speakers sometimes tap or shuffle their feet, rock, or shift their weight back and forth from one leg to the other. Keeping both feet flat on the floor, and still, will help avoid these distracting movements (Toastmasters International, 2011).
Credibility and Physical Delivery
Audience members primarily take in information through visual and auditory channels. Just as the information you present verbally in your speech can add to or subtract from your credibility, nonverbal communication that accompanies your verbal messages affects your credibility.
Professional Dress and Appearance
No matter what professional field you go into, you will need to consider the importance of personal appearance (Caffrey, 2020). Although it may seem petty or shallow to put so much emphasis on dress and appearance, impressions matter, and people make judgments about our personality, competence, and credibility based on how we look. In some cases, you may work somewhere with a clearly laid out policy for personal dress and appearance. In many cases, the suggestion is to follow guidelines for “business casual.”
Despite the increasing popularity of this notion over the past twenty years, people’s understanding of what business casual means is not consistent (Caffrey, 2020). The formal dress codes of the mid-1900s, which required employees to wear suits and dresses, gave way to the trend of business casual dress, which seeks to allow employees to work comfortably while still appearing professional. While most people still dress more formally for job interviews or high-stakes presentations, the day-to-day dress of working professionals varies.
Visual Aids and Delivery
Visual aids play an important role in conveying supporting material to your audience. They also tie to delivery, since using visual aids during a speech usually requires some physical movements. It is important not to let your use of visual aids detract from your credibility (Beqiri, 2018). Many good speeches are derailed by posters that fall over, videos with no sound, and uncooperative PowerPoint presentations.
Figure 9.1: Systematic desensitization can include giving more public speeches, taking communication courses, or imagining public speaking scenarios. William Moreland. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/GkWP64truqg
Figure 9.2: Vocal warm-up exercises. Andrea Piacquadio. 2020. Pexels license . https://www.pexels.com/photo/man-in-red-polo-shirt-3779453/
Figure 9.3: Primary phases to the practice process. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 9.4: Three facets of speaking for clarity. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0 .
Figure 9.5: Facial expressions set the tone for a speech, and should be consistent with your message. Afif Kusuma. 2021. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/F3dFVKj6q8I
Figure 9.6: To make your movements appear natural, time them to coincide with a key point. Product School. 2019. Unsplash license . https://unsplash.com/photos/S3hhrqLrgYM
Section 9.1
Allen, M., Hunter, J. E., & Donohue, W. A. (1989). Meta-analysis of self-report data on the effectiveness of public speaking anxiety treatment techniques. Communication Education, 38 (1), 54–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634528909378740
Bodie, G. D. (2010). A racing heart, rattling knees, and ruminative thoughts: Defining, explaining, and treating public speaking anxiety. Communication Education, 59 (1), 70–105. https://doi.org/10.1080/03634520903443849
Motley, M. T. (2009). COM therapy. In J. A. Daly, J. C. McCroskey, J. Ayres, T. Hopf, and D. M. Ayers Sonandré (Eds.), Avoiding communication: Shyness, reticence, and communication apprehension (pp. 379-400) (3rd ed.). Hampton Press.
Priem, J. S., & Haunani Solomon, D. (2009). Comforting apprehensive communicators: The effects of reappraisal and distraction on cortisol levels among students in a public speaking class. Communication Quarterly, 57 (3), 259-281.
Section 9.2
Barnard, D. (2018, January 20). Average speaking rate and words per minute . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/average-speaking-rate-words-per-minute
Davis, B. (2021, June 1). Why is audience engagement important? https://www.mvorganizing.org/why-is-audience-engagement-important/
Hennessy, C. (2019, March 27). Verbal filler: How to slow the flow . https://www.throughlinegroup.com/2019/03/27/verbal-filler-how-to-slow-the-flow/
LibreTexts. (2021, February 20). Methods of speech delivery . https://socialsci.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Communication/Public_Speaking/Exploring_Public_Speaking_(Barton_and_Tucker)/11%3A_Delivery/11.02%3A_Methods_of_Speech_Delivery
Moore, K. (2015, January 13). Public speaking tips: Use vocal variety like a pro! https://coachkiomi.com/best-public-speaking-tips-use-vocal-variety/
Packard, D. (2020, July 13). Speaking up: How to increase the volume of your voice . https://packardcommunications.com/speaking-up-how-to-increase-the-volume-of-your-voice/
Rampton, J. (2021, July 27). Learning to speak with clarity . https://www.calendar.com/blog/learning-to-speak-with-clarity/
Scotti, S. (2015, December 1). Vocal delivery: Take command of your voice . https://professionallyspeaking.net/vocal-delivery-take-command-of-your-voice-part-one/
Shtern, A. (2017, April 17). The importance of good pronunciation . https://shaneschools.com/en/the-importance-of-good-pronunciation/
Section 9.3
Barnard, D. (2017, October 24). The importance of eye contact during a presentation . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/importance-of-eye-contact-during-a-presentation
Beqiri, G. (2018, June 21). Using visual aids during a presentation or training session . https://virtualspeech.com/blog/visual-aids-presentation
Caffrey, A. (2020, February 25). The importance of personal appearance . http://www.publicspeakingexpert.co.uk/importanceofpersonalappearance.html
Clayton, D. (2018, October 31). The importance of good posture in public speaking . https://simplyamazingtraining.co.uk/blog/good-posture-public-speaking
Hoffler, A. (2016, June 7). Why facial expressions are important in public speaking . https://www.millswyck.com/2016/06/07/the-importance-of-facial-expression/
Koch, A. (2007). Speaking with a purpose (7th ed.). Pearson, 2007.
Toastmasters International. (2011). Gestures: Your body speaks . https://web.mst.edu/~toast/docs/Gestures.pdf
Fear or anxiety experience by a person due to real or perceived communication with another person or persons. This is a fear or anxiety that involves several types of communication not limited to public speaking.
Type of communication apprehension that produces physiological, cognitive, and behavioral reactions in people when faced with a real or imagined presentation
A type of cognitive restructuring that encourages people to think of public speaking as conversation rather than a performance
When a speaker has little or no time to prepare a speech
Speaking from a well written or printed document that contains the entirety of a speech
Completely memorizing a speech and delivering it without notes
Memorizing the overall structure and main points of a speech and then speaking from keyword/key-phrase notes
Refers to how fast or slow you speak
Refers to how loud or soft you speak
Refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is
Changes in your rate, volume, and pitch that make you sound more prepared and credible
Refers to the clarity of sounds and words you pronounce
Whether you say the words correctly
Refers to the flow of your speaking
Unintended pauses in a speech that usually result from forgetting what you were saying, being distracted, or losing your place in speaking
The umms, uhhs, and other linguistic pauses of conversation
The feelings expressed on a person’s face
The act of looking directly into one another’s eyes
Extra movements caused by anxiety (i.e., tapping your foot, wringing your hands, playing with a paperclip, twirling hair, or scratching)
The position in which someone holds their body when standing or sitting
A movement of part of the body, especially a hand or the head, to express an idea or meaning
Communication in the Real World Copyright © by Faculty members in the School of Communication Studies, James Madison University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Aesthetics and Delivery
Learning Objectives
- Define verbal delivery
- Understand the benefits of effective vocal delivery
- Explore techniques for evoking senses through language
- Utilize specific techniques to enhance vocal delivery
Humans are communicators. We rely on processes of communication to make sense of our world and we rely on others’ communicating with us to create shared meaning. Through symbols, we use and adapt language with one another and our communities.
The same is true for speeches, but what symbols you select and how you portray them—what we’ll call verbal delivery — are central to your audience and how they experience or comprehend what you say.
For example, consider your favorite podcaster or podcast series. We love crime podcasts! Despite being reliant on vocal delivery only, the presenters’ voices paint an aesthetic picture as they walk us through stories around crime, murder, and betrayal. So, how do they do it? What keeps millions of people listening to podcasts and returning to their favorite verbal-only speakers? Is it how they say it? Is it the language they choose? All of these are important parts of effective vocal delivery.
Below, we begin discussing vocal delivery—language choices, projection, vocal enunciation, and more.
Language and Aesthetics
It was 5 p.m. As she looked out the smudged window over the Kansas pasture, the wind quickly died down and the rolling clouds turned a slight gray-green. Without warning, a siren blared through the quiet plains as she pulled her hands up to cover her ears. Gasping for breath, she turned toward the basement and flew down the stairs as the swirling clouds charged quickly toward the farm house.
What’s happening in this story? What are you picturing? A treacherous tornado? A devastating storm rumbling onto a small Kansas farm? If so, the language in the story was successful.
Like this example demonstrates, the language that you use can assist audiences in creating a mental picture or image – creating a visualization is a powerful tool as a speaker.
Aesthetics is, certainly, based on how you deliver or embody your speech. But aesthetics also incorporates language choices and storytelling – techniques that craft a meaningful picture and encompass how you deliver the information or idea to your audience. In this section, we will extend our conversation from Chapter 5 about language to explore vivid language, implementing rhetorical techniques, and storytelling as an aesthetic tool to create resonance with your audience.
Vivid Language
Vivid language evokes the senses and is language that arouses the sensations of smelling, tasting, seeing, hearing, and feeling. Think of the word “ripe.” What is “ripe?” Do ripe fruits feel a certain way? Smell a certain way? Taste a certain way? Ripe is a sensory word. Most words just appeal to one sense, like vision. Think of color. How can you make the word “blue” more sensory? How can you make the word “loud” more sensory? How would you describe the current state of your bedroom or dorm room to leave a sensory impression? How would you describe your favorite meal to leave a sensory impression?
In the opening Kansas storm example above, the author may want the audience to sense danger or a certain intensity around the approaching tornado. To create that audience experience, you must craft language that emphasizes these elements.
When using vivid language, you’re trying to bring those sensations to life in a way that can create a vivid experience for your audience. “How can I best represent this idea?” you might ask or “how can I best create a scenario where the audience feels like they’re a part of the scene?”
Viivd language can take time to craft. As you work through your speech, determine where you’d like the audience to experience a particular sensation, and focus on integrating vivid language.
Remember that pathos is a persuasive appeal that is at your disposal, and using vivid language can assist in creating an emotional experience and sensation for the audience.
Rhetorical Techniques
There are several traditional techniques that have been used to engage audiences and make ideas more attention-getting and memorable. These are called rhetorical techniques. Although “rhetorical” is associated with persuasive speech, these techniques are also effective with other types of speeches. We suggest using alliteration, parallelism, and rhetorical tropes.
Alliteration is the repetition of initial consonant sounds in a sentence or passage. In his “I Have a Dream Speech,” Dr. Martin Luther King said, “I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.” Do you notice how the consonant of “C” resounds throughout?
Parallelism is the repetition of sentence structures. It can be useful for stating your main ideas. Which one of these sounds better?
“Give me liberty or I’d rather die.”
“Give me liberty or give me death.”
The second one uses parallelism. Quoting again from JFK’s inaugural address: “Let every nation know, whether it wishes us well or ill, that we shall pay any price, bear any burden, meet any hardship, support any friend, oppose any foe to assure the survival and the success of liberty.” The repetition of the three-word phrases in this sentence (including the word “any” in each) is an example of parallelism.
Tropes are a turning of the text where the literal meaning is changed or altered to provide new insight (Brummett, 2019). This is often referred to as figurative language, or using comparisons with objects, animals, activities, roles, or historical or literary figures. A literal statement would say, “The truck is fast.” Figurative says, “The truck is as fast as…“ or “The truck runs like…”
You are likely most familiar with the metaphor – one type of trope. Metaphors are direct comparisons, such as “When he gets behind the wheel of that truck, he is Kyle Busch at Daytona.” Here are some more examples of metaphors:
Love is a battlefield.
Upon hearing the charges, the accused clammed up and refused to speak without a lawyer.
Every year a new crop of activists is born.
Similes are closely related to metaphors, and use “like” or “as” when crafting a comparison. “The truck runs like,” is the beginning of a simile.
Tropes are useful because they assist the audience in seeing an idea in a new way or a new light. This can be particularly helpful if you’re struggling to create a vivid experience but have been unsuccessful at evoking the senses. A metaphor can assist by comparing your argument with an idea that the audience is familiar with. If you’re trying to evoke a particular felt sense, make sure the compared idea can conjure up that particular feeling.
Whatever trope you use, the goal is to craft an interesting comparison or turn the text in a unique way that leads to great comprehension for the audience.
Storytelling
Stories and storytelling, in the form of anecdotes and narrative illustrations, are a powerful tool as a public speaker. For better or worse, audiences are likely to remember anecdotes and narratives long after a speech’s statistics are forgotten. Human beings love stories and will often will walk away from a speech moved by or remembering a powerful story or example.
So, what makes a good story?
As an art form, storytelling may include:
- Attention to sequence, or the order of the story;
- Embedding a dramatic quality (or using pathos);
- The use of imagery (or figurative language).
While there is no “one-model-fits-all” view of storytelling, we often know a good story when we hear one, and they are a helpful way to expand your argument and place it in a context.
If you have personal experience with an argument or advocacy that you select, it may be helpful to provide a short story for the audience that provides insight into what you know. Remember that anecdotes are a form of evidence, and we can feel more connected with an idea if the story is related to something a speaker has been through. For example, if you selected police brutality as a speech advocacy, embedding a story about police violence may support your thesis statement and allow your audience to visualize what that might be like. It may draw them in to see a perspective that they hadn’t considered.
Similarly, consider the placement of your story. While your speech may rely on a longer narrative form as an organizational pattern, it’s more likely that you’ll integrate a short story within your speech. We most commonly recommend stories as:
- The attention getter
- Evidence within a main point
- A way to wrap up the speech and leave the audience with something meaningful to consider.
Stories, rhetorical techniques, and vivid language are important mechanisms to evoke language with aesthetics. In addition to what you say, verbal delivery also includes how you say it, including: vocal projection, verbal enunciation and punctuation, and vocal rate.
You may have experienced a situation where an audience notified a speaker that they couldn’t be heard. “Louder!” Here, the audience is letting the speaker know to increase their volume , or the relative softness or loudness of one’s voice. In this example, the speaker needed to more fully project their vocals to fit the speaking-event space by increasing their volume. In a more formal setting, however, an audience may be skeptical to give such candid feedback, so it is your job to prepare.
Projection is a strategy to vocally fill the space ; thus, the space dictates which vocal elements need to be adapted because every person in the room should comfortably experience your vocal range. If you speak too softly (too little volume or not projecting), your audience will struggle to hear and understand and may give up trying to listen. If you speak with too much volume, your audience may feel that you are yelling at them, or at least feel uncomfortable with you shouting. The volume you use should fit the size of the audience and the room.
Vocal Enunciation and Punctuation
Vocal enunciation is often reduced to pronouncing words correctly, but enunciation also describes the expression of words and language.
Have you ever spoken to a friend who replied, “Stop that! You’re mumbling.” If so, they’re signaling to you that they aren’t able to understand your message. You may have pronounced the words correctly but had indistinct enunciation of the words, leading to reduced comprehension.
One technique to increase enunciation occurs during speech rehearsal, and it’s known as the “dash” strategy: e-nun-ci-ate e- ve – ry syll – a – bal in your pre- sen -ta- tion .
The dashes signify distinct vocal enunciation to create emphasis and expression. However, don’t go overboard! The dash strategy is an exaggerated exercise, but it can lead to a choppy vocal delivery.
Instead, use the dash strategy to find areas where difficult and longer words need more punctuated emphasis and, through rehearsal, organically integrate those areas of emphasis into your presentational persona.
Verbal punctuation is the process of imagining the words as they’re written to insert purposeful, punctuated pauses to conclude key thoughts. Your speech is not a run-on sentence. Verbal punctuation allows decisiveness and avoids audiences wondering, “is this still the same sentence?”
Verbal punctuation is a strategy to minimize vocalized fillers , including common fillers of “like, and, so, uh.” Rather than use a filler to fill a vocal void in the speech, punctuate the end of the sentence through a decisive pause (like a period in writing!).
We know what you’re thinking: “there’s no way that reducing fillers is this easy.” You’re partially right. We all use vocalized fillers, particularly in informal conversation, but the more you rehearse purposeful punctuation and decisive endings to your well-crafted thoughts and arguments, the fewer filler words you will use.
It is also helpful to ask for input and feedback from friends, colleagues, or teachers. “What are my filler words?” We have listed common fillers, but you may unconsciously rely on different words. One author, for example, was never aware that they used “kind of” until a colleague pointed the filler out. Once you’re aware of your filler words, work to carefully, consciously, and meticulously try to catch yourself when you say it. “Consciously” is key here, because you need to bring an awareness about your fillers to the forefront of your brain.
Pace and Rate
How quickly or slowly you say the words of your speech is the rate . A slower rate may communicate to the audience that you do not fully know the speech. “Where is this going?” they may wonder. It might also be slightly boring if the audience is processing information faster than it’s being presented.
By contrast, speaking too fast can be overly taxing on an audience’s ability to keep up with and digest what you are saying. It sometimes helps to imagine that your speech is a jog that you and your friends (the audience) are taking together. You (as the speaker) are setting the pace based on how quickly you speak. If you start sprinting, it may be too difficult for your audience to keep up and they may give up halfway through. Most people who speak very quickly know they speak quickly, and if that applies to you, just be sure to practice slowing down and writing yourself delivery cues in your notes to maintain a more comfortable rate.
You will want to maintain a good, deliberate rate at the beginning of your speech because your audience will be getting used to your voice. We have all called a business where the person answering the phone mumbles the name of the business in a rushed way. We aren’t sure if we called the right number. Since the introduction is designed to get the audience’s attention and interest in your speech, you will want to focus on clear vocal rate here.
You might also consider varying the rate depending on the type of information being communicated. While you’ll want to be careful going too slow consistently, slowing your rate for a difficult piece of supporting material may be helpful. Similarly, quickening your rate in certainly segments can communicate an urgency.
And although awkward, watching yourself give a speech via recording (or web cam) is a great way to gauge your natural rate and pace.
Vocal Pauses
The common misconception for public speaking students is that pausing during your speech is bad, but pausing (similar to and closely aligned with punctuation) can increase both the tone and comprehension of your argument. This is especially true if you are making a particularly important point or wanting a statement to have powerful impact: you will want to give the audience a moment to digest what you have said. You may also be providing new or technical information to an audience that needs additional time to absorb what you’re saying.
For example, consider the following statement: “Because of issues like pollution and overpopulation, in 50 years the earth’s natural resources will be so depleted that it will become difficult for most people to obtain enough food to survive.” Following a statement like this, you want to give your audience a brief moment to fully consider what you are saying. Remember that your speech is often ephemeral : meaning the audience only experiences the speech once and in real time (unlike reading where an audience can go back).
Use audience nonverbal cues and feedback (and provide them as an audience member) to determine if additional pauses may be necessary for audience comprehension. Audiences are generally reactive and will use facial expressions and body language to communicate if they are listening, if they are confused, angry, or supportive.
Of course, there is such a thing as pausing too much, both in terms of frequency and length. Someone who pauses too often may appear unprepared. Someone who pauses too long (more than a few seconds) runs the risk of the audience feeling uncomfortable or, even worse, becoming distracted or letting their attention wander.
Pauses should be controlled to maintain attention of the audience and to create additional areas of emphasis.
In this chapter, we introduced verbal delivery as a core component of your speech aesthetics. Verbal delivery includes language – including vivid language, tropes, and storytelling. In addition, projection, rate, punctuation, enunciation, and pausing all work to deliver an effective presentation. The “rehearsal” chapter will assist as you consider the verbal dynamics of your speech and begin to strategize best practices for deliver as you prepare to present.
In Chapter 9, we’ll continue discussing aesthetics by integrating nonverbal delivery.
Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy Copyright © 2019 by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- Speech delivery
What is delivery in speech?
The 2 basic principles of effective speech delivery and how to excel in both of them.
By: Susan Dugdale
Speech delivery is not WHAT you say, but HOW you say it. It's a catch-all term covering all the elements that make up giving a speech.
These include:
- the style or method you select to use to give your speech
- vocal aspects: how you use your voice
- personal presentation aspects: how you dress for the occasion, how you move and gesture, how you make eye contact, and how you use visual aids
Use the index below to find out more about how to deliver a good speech.
What's on this page
2 basic principles of effective speech delivery
The two basic principles underlying effective speech delivery are simple.
- that the speaker uses the most appropriate delivery style or method for the speech content, its purpose and its audience
- that audience engagement is highest when a speaker has thoroughly prepared and practiced
A speech is successful when the speaker fulfills both of them.
Return to top
Speech delivery for different situations
There are four basic styles or methods of speech delivery: manuscript, memorized, extemporaneous, and impromptu.
Each has its place. Which one you choose to use depends on the type of information you have to deliver, your speech purpose, the context or setting for it, your audience's expectations and needs, the time you have available to prepare the speech, and your own capabilities as a speaker.
Manuscript speeches
A manuscript speech is one that has been completely scripted: word for word, sentence by sentence, from beginning to end. It is read by the speaker, either from notes on paper or from a teleprompter.
Manuscript speeches are used by anybody whose words are going to be closely scrutinized and need to be 100% accurate, for example: newscasters, government and public service officials.
And they're also used by people who don't have the time available to thoroughly practice giving their speech any other way, and those who are speaking at an emotional occasion (for example a wedding or funeral) and don't want to run the risk of finding themselves overcome and literally at a loss for words.
Memorized speeches
A memorized speech is entirely committed to memory and delivered verbatim - word for word as written. To be successful you must have plenty of time to do the work required. Knowing a speech so thoroughly that you don't need to think about what comes next gives a speaker complete freedom to specifically tailor the delivery for the audience. That's a great experience!
Extemporaneous speeches
An extemporaneous speech is one combining the use of speaking notes (an outline or cue cards ) with key words and phrases for reference, and unscripted speech. It is the most common delivery style.
Although it may appear impromptu, it is not. To be effective the speaker will have rehearsed the speech carefully, particularly the transitions or links between points.
Impromptu speeches
An impromptu speech is one that is 'made up on the spot', generally without planning. These are mostly short and although they are often social speeches: for example, a welcome to an event, a toast, or a few words of thanks, they are also asked for in our workplaces. Examples are being requested at a meeting to quickly summarize current team issues, to give an overview of the state of the latest project etc.
For more information about each style please see: 4 modes of speech delivery .
Tools for effective speech delivery
Use the links to find out more about the techniques and tools needed for developing good speech delivery.
The 9 vocal aspects of speech delivery This is a very long page covering the impact of voice quality on our lives, ( how what we sound like in the ears of others affects what happens in our lives), the nine vocal aspects of speech delivery, (pitch, tone, articulation, pronunciation, volume, rate, fluency, pausing, and breath), and how to work with each of them. (Plus scholarly references.)
Specific vocal aspects of delivery with exercises
Voice image : how the quality of our voices is a major influence on what happens in our lives and the character traits we attribute to a person because of how their voice sounds. With links to scholarly research articles.
Vocal variety : pitch (how high or low our voice is and its range), tone (the emotional content conveyed by how the words are spoken eg. lovingly, angrily, shyly ...) and volume (how loud or soft our voice is).
Speech rate : how speech rate (talking too fast or too slowly) affects listeners, how to develop a flexible speaking rate to fit the needs of your content and those listening to you, six exercises.
How to calculate your own habitual speech rate : two ways to find out how fast you speak, speech rate guidelines, plus a standard test passage printable.
How many words per minute in a speech : a quick reference guide for the number of words needed for 1 - 10 minute speeches delivered at a slow, medium or fast speech rate.
Diction exercises : 35 articulation drills using tongue twisters, with audio examples.
Mrs Tongue Does Her Housework : a sequence of tongue stretches for improving agility and accuracy set to a simple story. An evergreen exercise that's been used by speech therapists and drama teachers for years!
Proper pronunciation : an overview of the possible consequences of mispronouncing common words and phrases. With links to truly excellent resources to assist with pronunciation issues.
How to use silence effectively : harnessing the power of the pause - the benefits of using pauses for both the speaker and the audience. An easily learned 'counting' method for working where pauses should be used, and how long to make them. With audio examples.
Voice health : how to look after your voice and keep it healthy. Very important for teachers, salespeople, call center workers - anybody who uses their voice in order to work.
The physical aspects of speech delivery
Breath : to deliver a speech well we need to breathe well which in turn will also help to control nervousness or anxiety about speaking in front of others. These exercises are easy to do and very effective.
Body language : how stance, gesture, facial expressions, eye contact, movement around the stage etc., influences how an audience responds to a speaker.
Eye contact : 5 exercises for teaching and practicing eye contact, the importance and meaning of eye contact, cultural differences - plus references.
Characterization for storytelling : an introduction to taking on physical and vocal characteristics to enhance telling a story as part of a speech.
Personal grooming : a checklist for speakers because how you present yourself matters.
How to practice a speech : step by step guidelines on how to thoroughly rehearse a speech. Preparing what you are going to say is the first half of the task. Presenting it is the second, and to do that well, you need to practice.
How to practice public speaking : 9 key ways to effectively prepare for a presentation. (This page is an excellent supplement to what's covered in how to practice a speech .)
Managing public speaking anxiety
Feeling nervous prior to giving a speech is absolutely normal. Most people feel like that and then, as they get into their presentation, the anxiety disappears. But sometimes it sticks around and it takes a little more effort to send it on its way.
These pages will help.
- 14 ways to calm public speaking fear
- Breathing exercises (especially recommended!)
- Letting go of public speaking fear - a free 7 part e-course
- How to manage public speaking anxiety using self-hypnosis
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.3: Delivery Techniques
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4136
What you’ll learn to do: Describe delivery techniques for use during a public speech
As alluded to in the prior section, a live speech is, in effect, a performance. In addition to what you say, audience members will be reacting—both consciously and unconsciously—to how you say it. In this section, we’ll discuss fundamental considerations, including how to open your speech, how to use gestures and body language to punctuate your message, and what types of language to avoid.
learning outcomes
- Discuss effective ways to begin your speech
- Discuss strategies to effectively use body language and gestures to emphasize your message
- Discuss strategies to effectively use vocal variety to emphasize your message
- Identify types of language to avoid in your speech
Starting Your Speech
Your opening comments, like the lead sentences of an article, can make or break a speech. As William Zinsser phrases it in On Writing Well , “The most important sentence in any article is the first one. If it doesn’t induce the reader to proceed to the second sentence, your article is dead.” [1] In a chapter on speaking, Management Communication author James O’Rourke tells the story of a plant controller who was asked to make a five-minute presentation about his value to the company. In an attempt to tap into the imagination of the audience of eighteen senior executives, the controller opened with a race car metaphor. After four sentences, he was cut off and asked to leave the room. In another instance, a speaker’s opening joke, drawn from a book of speaking tips, fell flat. After the fact, the speaker reflected that a joke wasn’t the best fit for a rather serious audience and noted that “when you lose something in the first two minutes of a talk, you just can’t get it back.”
With this type of pressure, what’s a speaker to do? Often, the best option is to forget the introduction until you know what it’s introducing—until you have completed a full draft of your whole speech. That is, don’t force an introduction and don’t become too invested in your first idea. Write a draft or “working” opening and allow additional options to emerge as you work through the research (including audience research) and content development process. The dual objectives are to capture your audience’s attention and to set the stage for your speech. That is, your opening should reflect your stated intent and be an accurate indication of what will follow—the main substance of your speech.
In an article for YPO , an association for chief executives under the age of 45, communication strategist Matt Eventoll summarizes effective ways to open a speech and throws in one classic—and oddly common—fail. First, the effective options:
- Quote. Use a relevant quote to set the tone for the speech.
- “What if?” or, similarly, “Imagine.” Asking a “what if” or “imagine” question immediately engages your audience and invites them to be a part of the creative process.
- Question. Posing a question engages the brain and prompts an instinctive answer, whether internal or verbalized.
- Silence. A strategic silence of two to ten seconds creates an additional level of attention and expectation. The caveat: you had better be able to deliver!
- Statistic. A powerful, relevant statistic can convey a key idea with impact and evoke emotion.
- Statement. An emphatic phrase or statement can be used to create a sense of drama and anticipation.
The epic fail, generally followed by a collective disconnect on the part of the audience, is opening with some variation of “thank you for inviting me” or “today I’m going to be talking about.” If your audience isn’t invested from the beginning, it’s likely the point of your speech will never really be heard.
practice question
As with many things in life, getting started—in our case, writing the start to a speech—is often the hardest part. Which of the following is an effective way of opening a speech:
- Using a joke you found online.
Asking a "what if" question.
- Thanking the audience for the invitation.
Body Language and Gestures
One of the essential rules, and success factors, for public speaking is authenticity. This is as true for your non-verbal language as it is of the words you say and the ideas you express. Body language and gestures are a form of expression and can be either meaningful or distracting.

Toastmasters International, the global non-profit dedicated to teaching public speaking skills, believes that “gestures are probably the most evocative form of nonverbal communication a speaker can employ.” [2] In their Gestures: Your Body Speaks publication, they identify the following seven benefits of incorporating gestures into your speech: [3]
Clarify and support your words Dramatize your ideas Lend emphasis and vitality to the spoken word Help dissipate nervous tension Function as visual aids Stimulate audience participation Are highly visible
The improper use of gestures can have just as powerful an effect but will likely be detrimental. To avoid this, record yourself presenting and make sure your gestures are consistent with your words. When the two are telling different stories, you create confusion and lose credibility and rapport with the audience.
Body language—how you dress as well as your mannerisms—is another powerful communication element. For perspective on this point, and a powerful speaking and life hack, watch social psychologist Amy Cuddy’s “ Your Body Language May Shape Who You Are ” TED Talk. The core idea is that we make judgments based on body language, and those judgments can predict meaningful life outcomes. In one example cited, social scientist Alex Todorov found that one-second judgments of political candidates’ faces predict 70 percent of U.S. Senate and gubernatorial race outcomes. What is perhaps more important, however, is that our body language reflects how we judge, think, and feel about ourselves. The key takeaway from this is that our bodies change our minds. That is, we can change not only how we are perceived but how we perceive ourselves by managing our body language. As a speaker, you must be conscious of, and cultivate, the presence you bring to your speech.
To quote Toastmasters International, “When you present a speech, you send two kinds of messages to your audience. While your voice is transmitting a verbal message, a vast amount of information is being visually conveyed by your appearance, your manner, and your physical behavior.” [4]
Your use of gestures and body movement should reflect not only your personal communication style but should also match the audience and the environment. A good practice is to “preview” the attendees or venue by sitting in on a prior event, watching a video, or scanning the event’s social feeds. This will give you a sense for audience dynamics and the size of the room. Certainly ask the event organizers in advance about the setup of the room in which you will speak. Consider adjusting your gestures to fit the audience, room size, and acoustics. For example, you may may want to tone down your gestures in a smaller space and put more emphasis on vocal rather than physical delivery. This doesn’t mean that you should put your personality on “mute” if you’re a naturally ebullient or expressive person. The key is to manage your mannerisms so they don’t overpower either your audience or your words. If the room is a large auditorium filled with enthusiastic fans, you may want to increase your physical presence with gestures to better “fill” the space. Rehearse new elements so they become fluid and reinforce rather than detract from your message. Remember that gestures and body language are most effective when they’re used as “visual punctuation.”
You are rehearsing a forthcoming speech to an alumni association gathering. One of your friends—a “go big or go home” type—recommends you turn up the volume on your body language. You decide to video your presentation and review yourself. What effect should you strive for?
- Gestures that mask your nervous energy.
- Maximum drama--a powerful presence.
Gestures that clarify and support your message.
Vocal Variety
Just as gestures and body language affect how you are perceived, vocal variety effects how you are heard. As presentation skills training consultant Gavin Meikle notes, “A carefully crafted speech can be ruined by a dull vocal delivery.” [5] In a series of posts on vocal variety, Meikle identifies six key elements, common errors, and good practices to develop greater vocal impact. [6]
- Volume. Develop your range and vary your volume. To help put this in perspective, consider the saying, “A good speech needs light and shade.”
- Pitch and Resonance. Research suggests a general preference for lower vocal pitch, with participants ascribing more positive personality traits to lower pitched voices. For example, Margaret Thatcher was considered to have a voice of leadership.
- Pace and Pause. Be aware of and manage your speaking speed and practice your pauses. It’s been found that people who slow down their pace when speaking to groups are thought to have greater gravitas, credibility, and authority.
- Ending a spoken sentence with a rising tone indicates a question or suggestion.
- Ending a spoken sentence with a descending tone is generally interpreted as an order.
- A flat intonation is used to indicate a statement.
As legendary advertising creative director William Bernbach noted, “It’s not just what you say that stirs people. It’s the way that you say it.”
Each member of your work group is required to role-play a 5 minute employee coaching session in front of the management team. As one of the younger members of the group, your focus is on projecting a tone of confidence and command. Which of the following vocal techniques will make your vocal delivery more powerful when used judiciously?
End key sentences with a descending tone.
- End key sentences with a rising tone.
- Use a flat intonation throughout.
Language Choices
Whether we speak to inform, persuade, or inspire, the common denominator is a desire to communicate and to arrive at a shared understanding of an idea or situation. To quote author and TED Conference curator Chris Anderson, “Your number one task as a speaker is to transfer into your listeners’ minds an extraordinary gift—a strange and beautiful object that we call an idea.” [7] And yet, the very expertise that makes us the right person to deliver a speech on a particular topic can make us incapable of achieving that objective. An in-depth understanding can lead us to oversimplify or over complicate the explanation of a concept foreign to our audience.
One of the most common barriers to communication is jargon, or the terminology associated with a particular profession. As the French philosopher Étienne Bonnot de Condillac observed, “Every science requires a special language because every science has its own ideas.” For perspective on this challenge, and how to overcome it, watch Communications teacher Melissa Marshall’s “ Talk Nerdy to Me ” TED Talk. Directed at scientists, but with broad applicability to communicators, Marshall describes her “Alice in Wonderland” experience teaching communication skills to engineering students. Extrapolating on her point, if we don’t know about or don’t understand the work of those who are trying to solve the grand challenges of our times, then we can’t support it. Marshall notes that jargon in particular, is a barrier to communication. For example, “you can say ‘spatial and temporal,’ but why not just say “space and time,” which is so much more accessible to us?” [8] A few specific recommendations:
- Because you’re giving a speech, rather than a business presentation as discussed in Module 6: Reports and Module 8: Developing and Delivering Business Presentations, you shouldn’t need bullet points to keep you or your audience on track.
- Use stories and analogies to scaffold your important points
- Display images and diagrams to illustrate what’s being described.
A related point, covered in detail in Module 13: Social Diversity in the Workplace, is to be sensitive to socio-cultural variations in language and interpretation. As the French proverb notes, “The spoken word belongs half to him who speaks and half to him who listens.”
You're tasked with presenting the overarching rollout of a new IT system that will change workflow for your whole company. You will be presenting to the entire division in a large auditorium. Your speech will be followed up by smaller, how-to oriented presentations for individual teams. Your primary objective should be to:
- Use jargon to establish credibility and confidence in successful project completion.
- Convey the complexity of the project, using appropriate technical terminology.
Communicate the project process and benefits using common technology and/or visuals
The following video is a great talk about the mistakes and cornerstones of speech, which help you encourage your audience to listen and care about your points:

https://youtu.be/eIho2S0ZahI
- http://training.npr.org/digital/lead...te-a-good-one/ ↵
- Toastmasters International. Gestures: Your Body Speaks , p. 8 . 2011. Web. 26 Jun 2018. ↵
- Ibid. ↵
- Meikle, Gavin. " Six Elements of Vocal Variety and How to Master Them. " Inter-Activ . 18 Jun 2017. Web. 25 Jun 2018. ↵
- Anderson, Chris. " TED's secret to great public speaking ." TED . Mar 2016. Web. 25 Jun 2018 ↵
- Marshall, Melissa. " Talk Nerdy to Me ." TED . Jun 2012. Web. 25 Jun 2018 ↵
Quick links
Controlling speech anxiety, vocal variety, body language, practicing and preparation, general delivery tips.
As we know, words communicate meaning. But the way we say words also communicates meaning . This is why effective speakers devote time to improving their delivery.
So what exactly is delivery? Delivery is the speaker’s physical (vocal and bodily) actions during a speech. The main purpose of delivery is to enhance, not distract from, the message. In order to help you avoid distracting from your message, we’ve created a document about what not to do while delivering a speech.
We consider several aspects of delivery: controlling speech anxiety , vocal variety , body language , and practice .
It’s important to thoughtfully consider both the organization and oral style of the speech before discussing the principles of delivery. It doesn’t matter how great your delivery is if the speech is disorganized and hard to understand.
If you’re confident about organization and oral style , it’s time to work on delivery!
To control your speech anxiety the first step is simple: practice. The better you know your speech, the more comfortable you’ll feel. Comfort generally helps reduce anxiety.
In addition, it would be incredibly helpful to practice in the same room you’ll be giving the speech or to practice in front of other people. Both of these situations will simulate the speaking experience, and make the actual speaking experience feel less foreign, and less anxiety provoking.
You’ll be most anxious in the first minute of the speech. After the first minute (or so) anxiety levels tend to stabilize and decrease. Since the first minute can be the most challenging, it may be wise to memorize your opening.
For additional methods to deal with speech anxiety, this article will prove useful. If you’re in a rush, here are a few quick tips summarized:
- Visualize your success.
- Find a friendly face.
- Take a few calming breaths.
Even the best orators still get nervous when speaking; it’s normal, so don’t worry about it.
Please contact the Center for Counseling and Wellness if your anxiety is daily and inhibiting.
Vocal variety is essential to a captivating delivery. In oral rhetoric classes, you’ll learn about effective vocal variety. You may have an excellently written speech, but if delivered without vocal variety, it will be boring and dry. However, not every speech assignment at Calvin is for an oral rhetoric class. So what is vocal variety and how does one use it?
Vocal variety includes elements such as pitch, tone, volume, and rate .
How do I speak with vocal variety?
To learn about pitch, tone, volume, and rate variation, watch this video by Florida International University's Comm Art Studio from 1:10 to 6:09.
Additional tips related to vocal variety:
- Practice in everyday conversation to make vocal changes second nature.
- If you’re using a notecard, use slash marks or asterisks to mark cardinal places to vary pitch or slow down.
- Pause or slow down to emphasize important words or concepts.
- Speed up to solicit excitement or energy.
- Use a lower pitch to create an authoritative tone.
Many extraordinary speakers rely heavily on vocal variation. Listen to Meghan Markle, now the Duchess of Sussex, in her 2015 address to the United Nations. Markle frequently changes pitch and rate--pitch to make the speech interesting and rate to emphasize different points. (At 5:20-6:05 she slows down to emphasize her message; this is an effective rate change.)
Sometimes our voices sound scratchy when we speak. This may be vocal fry.
What is vocal fry and how to avoid it?
Vocal fry is the lowest voice register of the human voice. It sounds muffled and unclear. Speaking professionals recommend you avoid it during public speaking. If you think vocal fry may be a problem for you, watch this short video .
If you need help or someone to listen, come to the Rhetoric Center!
Many speakers use notecards for guidance through speech delivery. Notecards aren’t the same as the outline . Normally, the outline is turned in to the teacher and consists of complete sentences. The notecards would be the reverse: they are guideposts for the speaker, normally written as single words, phrases, or bullet points that are easy to glance read during a speech.
Note cards can also be used for notes about the delivery. Many speakers use slash marks to signal places where a pause would help. If you sound monotone or struggle with vocal variety, note places where vocal variation would be appropriate.
For a deeper look on how to use notecards, check out this resource from Oral Communication Center, Hamilton College.
Some people recommend using only one or two notecards. Typically, we at the Rhetoric Center don’t recommend that it’s better to have more cards to make sure you don’t get lost.
While you’re using notecards, it’s tempting to forget to make eye contact with the audience; remember, eye contact will communicate confidence.
For an example, look at this notecard for a speech about the Orlando shooting.
For further direction, check out Hamilton College or visit the Rhetoric Center.
Body language communicates meaning just like your words and how you say them. Consider what your body language says about you and your message while you’re speaking. For instance, your body language can affect your tone, your audience’s attention, and your audience perception of you.
Body language and movement affects the tone of your speech or presentation. For instance, how much moving should take place during a eulogy? Probably none. In a eulogy you want to be more composed. However, in a more energetic environment, such as an informative speech, it would be more acceptable to use movement. For example, Michelle Obama, in her campaign speech for Hillary Clinton , uses energetic body language to excite voters about voting for her preferred candidate.
Body language can either gain or lose the attention of your audience over the course of a speech. If used conservatively and properly, it can make your speech more interesting and engaging. If used excessively and carelessly, it can distract your audience from your message.
Confidence or insecurity
Body language communicates confidence or insecurity. If your back is turned to the audience, you’re pacing back and forth, or your hands are in your pockets, you’ll probably come off as insecure. On the other hand, walking with confidence and using hand gestures meaningfully will communicate confidence.
Now that you’re aware of how body language can affect your speeches, let’s consider how to use our body language while speaking.
What do I move and how?
Need some options for body movement? Watch from (6:52-9:55) for fundamental body movement concepts during a speech. Pay attention, but also put it to practice!
A few suggestions on body movement:
- Face the audience and don’t turn your back to them.
- Be in the center of room and don’t walk to near to the edges.
- Don’t put your hands in your pockets or on your hips; this creates emotional barriers.
Practicing is critical to the performance and success of the speech. When practicing, it’s normal to touch up and fix slight wording issues, but at this point in the writing process the speech should be pretty much finished. If you still have more to write, we recommend the speech writing and organization pages.
How do you practice for a speech?
Keep practicing and don’t always start at the beginning; change where you start practicing.
If you always start with the beginning, then you’ll know the beginning best, and the rest will get progressively harder. You should know every part of the speech equally well if you keep changing your starting location. However, memorizing the first few lines isn’t a bad idea because the first few lines will be the hardest to recite when confronted by speech anxiety.
This resource from University of Hawai'i Maui Community College Speech Department will prove helpful when practicing speeches. Read the “Do’s” and “Don'ts” carefully.
It’s also beneficial to imitate the environment of the speech. This can be done by practicing in front of people and in the real space you’ll be giving the speech in. It’ll be easier to deliver if it’s not your first time seeing the space.
Watch two examples related to preparation: one bad and one good .
- Avoid filler words. Filler words, such as “umm” and “like,” take away from your credibility as a speaker, affecting how the audience receives your message.
- Maintain eye contact; it demonstrates confidence!
- If you slip up, don’t apologize. Apologizing makes you appear insecure and affects your credibility as a speaker.
- Pauses help. They can make a speech somber and serious. President Obama used pauses for effective emotional measures in his speech following the shooting at Sandy Hook elementary school , particularly in his introduction.
- Slow down; you deliver the speech faster than your practiced it. Even if your practice trials were perfectly timed, it’s common for speakers to speed up the actual delivery.
For additional tips, check out this resource on general guidelines for speech delivery (The Writing Resources Center, Swem Library, College of William & Mary).
If you have any questions or would like a Rhetoric Center consultant to listen to your speech, schedule an appointment.
In this presentation, business tycoon Elon Musk appears extremely nervous and unprepared. This probably results from the fact that Musk doesn't practice his speeches . To see how fragmented and clustered the speech is watch the first 1:30. In addition to being fragmented and clustered, Musk uses filler words, such as “um” and “eh,” like air. This makes him appear insecure. Ironically, this is an important speech updating the world on a possible mission to Mars, delivered by an important man who needs no introduction, yet the beginning of the speech sounds amateur because of his lack of preparation. Further practice would’ve made him seem more natural and effective, and therefore would’ve reduced his anxiety.
Practice helps, even for Elon Musk.
On the other hand, practice puts the most nervous speakers at peace during their presentations.
Winston Churchill, on June 18 1940, delivered one of the most enduring speeches in English history: “Their Finest Hour.” This World War II speech was given via broadcast to the British people and just after France had accepted the German armistice.
It was only a month into Churchill’s ministership, and he was terrified of public speaking because of his speech impediment. However, according to Carmine Gallo from Forbes , Churchill’s practice helped him overcome his anxiety. If you listen to 26:55-30:02 of Churchill’s speech, you can clearly identify his rhythm and diction; this would be impossible to achieve without considerable preparation and knowledge of his own speech.
This note card was used for a speech commemorating the victims of the Pulse shooting in Orlando, Florida.
For starters, the notecard is legible and uses slash marks as possible places to pause when reading. These pauses, a form of vocal variety, place emphasis on each name being read, which would trigger an emotional response. However, more information could probably be fit on the bottom of the card. Perhaps something to prompt the next sentence.
It’s important that the notecard doesn’t use full sentences; rather, use trigger words and phrases. Compare the notecard to the outline version of the first sentence: “Today, I wanted to individually remember those lost on June 12, 2016.” The word “individually” is nowhere near as important as “remember.” So “individually” gets put on the card and not “remember.”
Furthermore, things that must be exact need to be written on the cards. This includes dates, names, and quotes. You don’t want to say (or pronounce) any of these incorrectly as it could reduce your credibility.
Michael Bay, the famous film director, didn’t prepare sufficiently for this speech. This embarrassing mess resulted from a miscommunication between Bay and the teleprompt person. However, this could’ve been prevented with preparation. For starters, Bay should have had a backup, hard copy version of the speech. This may not have been ideal, but it would’ve prevented the disaster.
Make sure you have a backup plan .
Bay’s problems didn’t end with his miscommunication; he also didn’t know when to begin the speech. He started before his introducer asked him the first question. If prepared, he would’ve known how to start. In addition, the final question about his movies was a simple throw away by the interviewer in attempt to save Bay. Bay said he couldn’t read the teleprompter, apologized, and left. He didn’t need the teleprompter to answer this question about his movies (that he has spend hundreds or thousands of hours working on). This demonstrates unpreparedness; If he knew the speech, rather than just relying on the teleprompter, he would’ve been able to answer the last question.
On the other hand, careful preparation can make for a great speech. For Monica Lewinsky's Ted Talk on “The Price of Shame” she had no teleprompter, so she used paper notes, which can be seen on the small podium in front of her. Even though she used paper notes, her speech was well practiced. This is evident in her consistent eye-contact, lack of mistakes, and how she carried the room with evidently prepared diction and vocal variety.
- Faculty & Staff
- Admitted Students
- Administration
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Vision 2030
- Sustainability
- Media Center
- Campus & Location
- Consumer Information
- Safer Spaces
- Majors & Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Online Programs »
- First-Year Opportunities
- Academic Calendar
- Course Offerings
- The Calvin Core
- Calvin Academy for Lifelong Learning
- Off-Campus Programs
- Student Services
- Centers & Institutes
- Global Campus
- Hekman Library »
- Request Information
- Facts & Standards
- Cost & Aid »
- Internationals
- Military & Veterans »
- Residence Life
- Faith & Worship
- Student Involvement & Activities
- Life in Grand Rapids
- Careers & Outcomes
- Multicultural & International Students
- Wellness & Safety
- Service Learning
- Arts Collective
- Box Office »
- Get Involved
- CalvinKnights.com
- Outdoor Recreation
- Intramurals
- Group Fitness
- Sports Camps
- Delivery Techniques →
Mastering Public Speaking Techniques: Tips and Strategies for Success

One of the greatest feelings of dread and anxiety can come from stepping up in front of a crowd and giving a speech. Public speaking can feel like the biggest high-stakes test of your composure, but it doesn’t have to be. By utilizing the tried-and-true methods shared in this post, you’ll be able to crush any fears you have about being in front of a crowd and take control of your public speaking experience. With thorough preparation, careful practice, and a little bit of extra preparation, you’ll find that your fear of public speaking will start to disappear. So, buckle up, get your nerves under control, and keep reading for some of the best tips out there for conquering your fear of public speaking with proven techniques!
Techniques Preparing for Public Speaking
Preparing for Public Speaking—the most important step for overcoming fear of speaking in front of an audience—should begin well before the event. The most effective way to ensure success is to create a detailed plan that covers all aspects of the speech ahead of time, including what you will say and how you will say it. A few practical steps to prepare include: • Research the subject thoroughly to make sure you have a sound understanding of all relevant content. Make sure to cover any opposing views when reporting on research as this allows you to better understand your topic and be more prepared if someone challenges one of your facts. • Craft an outline of the entire speech , with bullet points that provide an overview. • Rehearse your speech out loud several times, especially the introduction and conclusion , to ensure it flows well and sounds natural when speaking in front of people. It can also help to record yourself speaking so you can listen back for any adjustments you want to make. • Become familiar with any tools or technology you are using during the presentation as you don’t want that to add additional stress. While thorough preparation is essential for minimizing fear, some argue that too much planning can backfire as it doesn’t allow enough flexibility for moments when things don’t go according to plan. However, having a framework in place is still beneficial since it provides direction and structure, while still allowing some room for improvisation or unexpected content additions along the way.
Preparing Your Content
Preparing your content is essential to accomplishing a successful speech. Knowing the ins and outs of the topic and having specific points in mind will provide peace of mind when speaking in front of an audience. As part of that preparation, it could be beneficial to debate both sides of any argument contained within the presentation. This not only helps prove the speaker has proficient knowledge on the subject, but also keeps listeners engaged by presenting different perspectives. Once any underlying debate is addressed, it’s important for those giving the presentation to focus on what’s truly important about the topic – its key points and structure . Outlining exactly how each slide or section should flow is incredibly beneficial. When anxiety peaks up just before or during a speech, remembering this “road map” can make a huge difference by bringing confidence back into both presentation and listener’s attention. Finally, practice plays a major role in any success. Whether practicing in private or in front of others, repeating material until comfort in confident is built up is a necessary step for effective communication when public speaking. Now that we know how one can best prepare content for their presentation, let’s move onto the next step; preparing our nerves to conquer our fear of public speaking.
Preparing Your Nerves
Preparing your nerves for public speaking is a critical step to take in order to boost your confidence and ensure you deliver an outstanding presentation. While preparing your nerves may feel like an intimidating task, there are many proven techniques to help you tame any anxieties and leave the stage feeling triumphant. One of the most effective ways to prepare your nerves is to practice beforehand. A lot of speakers consider this method as obvious, yet it is the best way to gain a seamless flow throughout the presentation. Leverage the moments right before you start speaking to review your content, vocalize key points, swiftly shift between slides , or get yourself into a positive mindset. The more prepared you feel, the easier it will be to remain calm while standing in front of an audience. Visualization techniques can also be extremely beneficial when it comes to preparing your nerves. Studies have indicated that athletes who visualize themselves performing well are more likely to achieve success during actual events. This same concept can be applied in public speaking by visualizing how you would deliver an impeccable speech with stellar body language and confident presence. Taking deep breaths is another key way of preparing your nerves for public speaking. Taking continuous deep breaths helps remind us that we are still alive and demands that we focus on our breath instead of other anxious thoughts which may penetrate through our mind. This technique not only release tension but also induces feelings of calmness within us which can make big difference when facing an audience full of eyes staring at us. Though these techniques are extremely effective, one should be mindful when using them. Sometimes over-practicing can fuel our anxiety rather than calming us down, whilst over-visualising can hinder our motivational capacity if things don’t go as expected during the speech. By preparing your nerves through deliberate practice and thoughtful visualization, you’re setting yourself up for a successful performance. The key is knowing when too much is too much and finding ways to relax your body and mind before taking the stage. Now that you know how to ease those pesky nerves, let’s explore delivery techniques for nailing your next public speaking performance.
Public Speaking Delivery Techniques
Delivery techniques is an important part of public speaking success. Delivery should be natural and easy to listen to, yet clear and authoritative. To effectively command the attention of an audience and engage them with your content, it’s important to understand how to use words effectively in your delivery. When delivering a speech, be sure to speak slowly and clearly , emphasizing important ideas. Pacing yourself with pauses is also important; brief pauses can help emphasize key points in the speech and keep the attention of your audience. It’s essential to enunciate, so people don’t miss vital information or drift off during the presentation. Additionally, using verbal cues such as rising of voice and physical gestures can help bring energy into the presentation. Using verbal variety when speaking is just as important as maintaining the pace. This means keeping up a diversity between loud and soft, fast and slow, and long and short utterances that follows the flow of the message itself. While delivery shouldn’t be overly dramatic (unless for comedic affect), varying the volume and speed of your delivery can add an interesting inflection that will better convey a point than just monotone talking would. Lastly, maintaining eye contact with audience members helps build trust between speaker and listener. These effective delivery techniques have been proven to keep audience members engaged and take a speaker’s performance level up a notch—but they are pointless if there’s no one looking back at you! Keeping eye contact throughout your presentation is essential; this is what will join together both speaker and listener in a mutual understanding of each other’s perspective. In our next section we’ll discuss techniques for maintaining eye contact which can really boost public-speaking confidence !
Keeping Eye Contact
Eye contact is one of the most effective ways to make a strong connection with your audience and get your point across. It boosts credibility, shows confidence and demonstrates authority. However, it can also be intimidating to many public speakers. To help conquer the fear of maintaining eye contact during a speech or presentation, consider the following tips: • Take Your Time: Don’t rush into making eye contact too soon. Take the time to introduce yourself before you begin speaking and engage the audience in conversation. You will have an easier time making eye contact when you feel comfortable and relaxed. • Practice Makes Perfect: The best way to become more comfortable with maintaining eye contact is to practice making it during your rehearsals. Make sure to observe yourself in the mirror or on video to identify any areas where you can improve. • Connect With Individuals: Making brief eye contact with a few members of your audience can be more effective than staring at a crowd for an extended period of time without addressing individual members. Don’t forget about body language – breaking eye contact naturally and periodically will prevent your audience from feeling threatened or uncomfortable. • Stay Focused: If eye contact becomes too overwhelming, try looking at specific points around the room that are non-threatening spaces like artwork or mantelpieces rather than individuals’ faces. This will give you something to focus on while still allowing you to appear as though you’re making eye contact with everyone in the room. Making eye contact when giving a speech can be daunting, but by following these tips, public speakers can develop the confidence needed to make their message more powerful and impactful. By utilizing volume, pauses and expressions, speakers can further enhance their presentations in order to make a lasting impact on their audience.
Using Volume, Pauses and Expressions
Using volume, pauses and expressions can be very important tools for those facing public speaking anxiety. As strange as it may seem, the many view public speaking as the victim of the situation – after all, when you become scared, your body reacts in a way that makes your speech nearly inaudible. To combat this natural reaction, practitioners need to pay attention to their vocal projection and ensure that they are making themselves heard. Additionally, they should make sure that they speak loudly enough to fill the room with their voice . The use of pauses and expressional tones also plays an important role in effective public speaking techniques. Pauses can help build suspense and draw out the importance of certain points or ideas while expressing keeps audiences engaged and interested in what is being said. Expressions are key because they bring unique nuances to each speaker’s presentation and can add flavor to topics that may be mundane otherwise. So whether someone is only lightly smiling or emphasizing a point by using their hands and body language, having a set of expressions helps demonstrate how passionate one is about what he or she is saying. In conclusion, mastering the art of volume, pauses and expressions is essential for any successful public speaker. Used jointly, these techniques offer audiences insight into how passionate one is about his or her topic, as well as generates interest between the audience and speaker. In the following section we will discuss how vital rehearsing can be for those hoping to successfully overcome their fear of public speaking.
Techniques for Rehearsing Public Speaking
Rehearsing for public speaking is an essential first step in conquering the fear of presenting in front of an audience. After preparing and researching your material, it’s highly recommended that you practice your speech or presentation in private before going out in public. Doing this will help build your confidence so that you are ready to tackle any unexpected questions or issues that may arise while talking in public. The best way to prepare is by allowing yourself plenty of practice time. This could range from a few days to several months, depending on the complexity of your presentation or speech. While rehearsing alone, focus on using visual aids, handouts or other tools that can help grab the attention of your audience and help keep them engaged until you have finished speaking. During practice, also pay close attention to your vocal projection and pacing as well as emphasizing key points with proper body language. Sometimes watching recordings of yourself can be helpful as well. It’s often easier to recognize and work on areas where you need improvement while viewing a recording as opposed to just listening to yourself speak since little mistakes are easier to spot visually. Additionally, recording yourself also makes it easier to see how others perceive you. Having someone else observe you during rehearsals can be beneficial too. Designate someone who knows what they’re doing when it comes to public speaking, such as a speech instructor or professional speaker , to give some honest feedback about how prepared you are for the actual performance. Not only will this allow you to refine any weak points in your speech but can also provide invaluable insights from experienced professionals that can give your performance an edge over the competition. Although rehearsing is key for overcoming fears associated with public speaking, it’s important not to become too reliant on memorization which could hinder your ability to think on the fly if something does not go according to plan during the actual performance. Instead, focus more on becoming thoroughly familiar with the basic outlines and main topics of the speech so that if necessary, you will be able to naturally transition into different ideas or answer spontaneous questions without having an entire script memorized word-for-word. By fully mastering strategies like these during rehearsals, presentations and speeches become less intimidating and put you one step closer toward conquering your fear of speaking in public settings. After all this hard work, it’s time reward yourself with a little bit of fun by introducing lighthearted elements into your presentations while keeping your audience entertained – our next section will explore how you can get fun involved with public speaking!
Getting Fun in your Speech
One of the more enjoyable ways to ease into conquering one’s fear of public speaking is to get a little bit playful with your speech. Introducing fun elements into a presentation can keep the audience engaged and energized while also helping break the ice between you and the crowd. There are several ways to add some joy to your presentation, from using props, or humorous stories, or adding multimedia elements like video clips and music. When considering whether or not to inject fun elements into your speech, there is an argument for both sides. On the one hand having prop or story might be exactly what is needed to create an emotional connection with the listeners and lighten up the situation. On the other hand, something that was meant to be lighthearted could be taken too far and distract from the point of the message. Ultimately, it will depend on you as a speaker to decide if incorporating humor makes sense for your presentation and how far to go in doing so. It’s important to recognize that although getting a little fun in your speech can serve to help further connect with an audience , it shouldn’t become the main focus of your presentation and should be used sparingly. To maintain audience focus, it’s wise to move on or cut a joke or amusing anecdote that isn’t working out – even if it means skipping over an entire section of material. Ready to take things up a notch? The next section will discuss using Visual Aids in your speech.
Crucial Summary Points
Incorporating fun elements into public speech can help a speaker build a connection with the audience, but it should be done sparingly and should not become the focus of the presentation. Visual aids can be used to take a speech up a notch and should be discussed in the next section.
Visual Aids Techniques
Many speakers incorporate visual aids into their public speaking engagements to help illustrate their points and ideas. Visual aids can be powerful tools for successfully making a point or idea stick with the audience. Although visual aids are advantageous in public speaking, there can also be drawbacks to using them as well. One advantage of using visual aids is that they can break up the monotony of an overly long talk by giving the audience something to look at and engage with other than the speaker. It can also give the audience something more tangible to pay attention to and remember if the presentation includes complex information or lengthy facts. Additionally, with technology at the level it is today, high-quality visuals with sound effects create a stimulating and memorable experience for those attending the presentation. On the flip side, visual aids may lead to distraction from the actual message or topic the speaker is trying to convey. This can occur if the presenter becomes too showy with the visuals and neglects to explain them in detail. Additionally, visual aids can overload an audience with too much information if used incorrectly, which tends to have opposite of intended effect of having an audience remember key details more easily. Visual aids also require extra prep time when setting up a presentation and need to fit with any existing décor. Regardless of whether one chooses to use visual aids or not, it is important they recognize potential benefits and risks that come along with integrating visuals into any presentation. With thoughtful positioning and execution, incorporating proper visuals into presentation can greatly enhance communication quality in an effective way. With that said, it is important for presenters to manage any nervousness they may be feeling before presenting in order to effectively communicate their points.
Handling Nervousness Techniques
Nervousness is a common reaction to public speaking, and it can be hard to combat. With the right preparation and mindset, however, people can work through their fear and flourish in any speaking situation. Starting with the basics of positive self-talk is essential. It’s important to remember that everyone gets a little nervous while speaking in public, but acknowledging the presence of nerves is an opportunity to take advantage of an adrenaline boost. Positive messages such as “I’ll do great” and “I have something valuable to add” will help turn any anxious energy into a productive tool for success. Another tip to handle nervousness during public speaking is to practice visualization techniques throughout the day leading up your speech. Picture yourself feeling confident and relaxed as you deliver your presentation. This acts as a mental “warm up” before going on stage or behind the podium. Also, taking deep breaths and stretching beforehand can literally change your body chemistry; creating the relaxed state you want. Finally, it’s important to recognize when to slow down. It’s normal to be excited while presenting, but attempting to rush through a presentation can create unneeded stress which will likely create more pressure and anxiety. Practicing mindfulness during delivery will minimize any unnecessary tension; intentionally pausing between sentences and visually connecting with each audience member are good habits to take note of. The anticipation of public speaking can often seem overwhelming. Though persistency may be challenging, results found with such prospective methods will cause a far more comfortable experience when it’s time for the big speech. CONCLUSION AND OVERALL TECHNIQUES: With proper preparation and techniques that combat nervousness, anyone can ace public speaking for their desired outcome. The following section will discuss conclusion and overall techniques for conquering fear in public speaking scenarios.
Conclusion and Overall Public Speaking Techniques
Public speaking can be a daunting task, but it doesn’t have to be. By utilizing various techniques before, during and after your speech or presentation, you can overcome any fear or anxiety you have before stepping on stage. The first step is understanding yourself as a speaker in order to discover what techniques work best for you. If possible, practice with an audience prior to the main event. This could involve an informal workshop or getting constructive feedback from friends and family members over Skype or Zoom , for example. Additionally, use visualization techniques during the days leading up to your speech and rehearse frequently beforehand. Arm yourself with knowledge about the topic so that you can answer difficult questions confidently. During your presentation, remind yourself of your purpose and focus on delivering authentic content. Don’t forget to take deep breaths and pause when needed in order to stay calm under pressure. It is also beneficial to connect with the audience by making eye contact and speaking naturally in order to create an engaging atmosphere. Afterwards, reflect on the experience. Ask colleagues, mentors or friends to critique your performance so that you know what areas need improvement. Celebrate successful parts of the presentation before making any changes to future presentations or speeches in order to keep morale high. Overall, public speaking is an invaluable skill that requires practice and repetition in order for it become easier and more comfortable over time. Every person is different, but with dedication and research into these proven techniques, anyone can improve their ability to communicate clearly even when faced with daunting crowds.
Most Common Questions
What tips should beginners know about public speaking.
Beginners should start by getting comfortable with their material. Know the subject matter inside and out—not just the facts but also how to communicate it effectively. Make sure to practice speaking in front of a mirror or someone else so you can get feedback and reduce any nervousness.It is also important to structure your speech properly, use stories and anecdotes to give your talk more depth , and keep it interesting for the audience. Additionally, be sure to prepare for anything unexpected since there will likely be questions and sporadic situations that arise during a speech. Finally, make sure to leave time to practice breathing exercises beforehand to steady nerves and help calm down pre-speech jitters.
What strategies can help someone overcome stage fright when speaking in public?
One of the most effective strategies for overcoming stage fright when speaking in public is to practice your speech beforehand. Knowing your content and being confident in your material can help you feel more relaxed and help take some of the stress away from the actual presentation. Additionally, it’s important to try and connect with your audience. Speak in real, relatable terms and make an effort to look people in the eyes when talking. Doing this will not only build confidence but also a connection between you and your audience, making it easier to talk without fear. Another important strategy is to focus on your breathing. By taking deep breaths, you can gain control over both your mind and body while speaking in front of an audience. Moreover, visualizing yourself giving a successful performance can be helpful too: picture yourself speaking clearly and confidently; being calm and well-prepared; dealing effectively with questions; and leaving the room feeling proud. Lastly, don’t be afraid to use humor – it can lighten up the atmosphere, build rapport with your audience, and reduce tension.
What are the common pitfalls to avoid when giving a public speech?
Common pitfalls to avoid when giving a public speech include: 1. Not knowing your material—it is important to be well prepared and have a clear understanding of the topics you will be discussing during your speech, as it will help you remain confident and in control of the conversation. 2. Taking on too much—a common mistake is trying to cover too much material within a single speech, leaving the audience overwhelmed and unable to follow along with what you’re saying. Instead, focus on the main points you wish to make and don’t move too quickly through each topic. 3. Speaking too fast—many people become nervous when speaking publicly and can end up talking too quickly, making it difficult for their audience to understand them. Make sure to practice your delivery in advance, pausing often and speaking slowly and clearly during the actual presentation. 4. Avoiding eye contact—looking at your audience is an essential part of public speaking, as it helps build confidence and demonstrate that you’re engaged with your listeners. Don’t just focus on one person or group in the crowd; instead, look around often throughout the presentation. 5. Being overly rehearsed—while it’s important to have prepared notes and an outline for your speech , try not to be too rigidly rehearsed. Your presentation should feel like a natural conversation between you and your audience, so allow yourself enough flexibility to adapt as needed throughout your talk.
Speech delivery practice
A speech is not an assignment that can be done the night before; practice is essential. Practicing a speech will boost your confidence as a speaker and ease potential anxiety.
Podium/lectern practice
Using or not using a podium does not make or break a speech. If using a podium, it should not be used to hide from the audience.
- Stand tall—do not hold or lean on the podium
- Makes an impact especially at the conclusion of the speech
- Allows audience to see you as a person, not just a face behind the podium
- Be sure gestures can be seen
- It is easy with a podium to look down especially if you have notes or outlines
- Maintain eye contact with the audience
Notes can be helpful. Know your instructor’s preference as some allow notes and some don’t.
- Make sure to look at the audience
- Know your notes well enough to find what you need
- Know at what point(s) in your speech you may need to look down at your notes
- Notes should be simple enough to keep the speech on track
A gesture is the movement of your hands to express an idea. When practicing your speech, do not practice gestures, let them occur naturally.
- Use natural gestures. Gestures should be relaxed and enhance your speech
- If the topic is exciting, then be excited
- Make gestures visible, even if using a podium/lectern
- Use gestures sparingly. Gestures should not be what the audience remembers about your speech
Vocal delivery
Your voice should be loud enough to be heard and have variation (not monotone). This occurs naturally in conversation with friends—so your speech should sound the same.
Try practicing the following to work on vocal variations and delivery.
- Tongue twisters
- Funny voices
These will help you transition to a natural variation in volume and tone.
Adapt to length of the speech
In extemporaneous speaking, there are no ties to a manuscript, so there is flexibility in structure.
- Move to conclusion of the speech
- The audience doesn’t know what was planned—they just experience the speech as it is delivered
- Understands your topic
- Remembers your thesis and key points
Be direct in speaking
For clarity and time constraints, watch for places where phrases can be more concise. Practicing your speech will allow you to hear where phrases can be shortened and made more concise. For example, instead of “due to the fact” say “because”.
Beebe, S. A., & Beebe, S. J. (2012). A concise public speaking handbook . Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Lucas, S. (2012). The art of public speaking . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Sprague, J. & Stuart, D. (2013). The speaker's compact handbook, 4th ed . Portland: Ringgold, Inc.
Vrooman, S. S. (2013). The zombie guide to public speaking: Why most presentations fail, and what you can do to avoid joining the horde . Place of publication not identified: CreateSpace.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.3: Techniques for Effective Delivery
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 82764
Use of Your Body
As you stand before an audience, be confident and be yourself. Remember, you planned for this speech, you prepared well, and you practiced so that you know the material you will present. You are probably the expert in the room on this subject. If not, why are you the one making the presentation?
You need to consider not only what you say, but also how your body will support you and your words. When your actions are wedded to your words, the impact of your speech will be strengthened. If your platform behavior includes mannerisms unrelated to your spoken message, those actions will call attention to themselves and away from your speech.
Here are five areas on which to focus as you plan, practice, and present:
- Gripping or leaning on the lectern
- Finger tapping
- Lip biting or licking
- Toying with a pen or jewelry
- Adjusting hair or clothing
- Chewing gum
- Head wagging
These all have two things in common: They are physical manifestations of simple nervousness and they are performed unconsciously. When you make a verbal mistake, you can easily correct it, because you can hear your own words. However, you cannot see yourself, so most distracting mannerisms go uncorrected. You cannot eliminate distractions unless you know they exist.
The first step in self-improvement is to learn what you want to change. In speech preparation, nothing is as revealing as a video of your self. The first step in eliminating any superfluous behavior is to obtain an accurate picture of your body’s image while speaking. This should include:
- Body movement
- Facial expressions
- Eye contact
The next step is to free yourself of physical behaviors that do not add to your speech. This can be accomplished by simply becoming aware of your problem areas. After you have viewed a video of yourself speaking, review the video several times and make a list of all the distracting mannerisms you notice. Once you have completed these reviews, go over the list of all the distracting mannerisms you saw and heard. The next time you are having a conversation with someone you know well, try to notice whether you use any of these distracting mannerisms even in casual circumstances. Tackle each of your negative points one at a time.
Many people say, “I’m okay in a small group, but when I get in front of a larger group I freeze. ” The only difference between speaking to a small informal group and to a sizable audience is the number of listeners. To compensate for this, you need only to amplify your natural behavior. Be authentically yourself, but amplify your movements and expressions just enough so that the audience can see them.
By involving yourself in your message, you will be natural and spontaneous without having to consciously think about what you are doing or saying. For many of us, this is not as easy as it sounds because it requires us to drop the mask that shields the “real self ” in public.
To become an effective speaker, it is essential that you get rid of your mask and share your true feelings with your audience. Your audience wants to know how you feel about your subject. If you want to convince others, you must convey your convictions. Speak from the heart and to the soul.
How many of us have ever experienced a situation in which we had not prepared well for a presentation? How did we come across? On the other hand, think of those presentations that did go well. These are the ones for which we were properly prepared.
Record your presentation and review it using the four steps described above.
Since you are talking about yourself, you do not need to research the topic; however, you do need to prepare what you are going to say and how you are going to say it. Plan everything including your gestures and walking patterns.
Facial Expressions
Leave that deadpan expression to poker players. A speaker realizes that appropriate facial expressions are an important part of effective communication. In fact, facial expressions are often the key determinant of the meaning behind the message. People watch a speaker’s face during a presentation. When you speak, your face -more clearly than any other part of your body -communicates to others your attitudes, feelings, and emotions.
Remove expressions that do not belong on your face. Inappropriate expressions include distracting mannerisms or unconscious expressions not rooted in your feelings, attitudes, and emotions. In much the same way that some speakers perform random, distracting gestures and body movements, nervous speakers often release excess energy and tension by unconsciously moving their facial muscles (e.g., licking lips, tightening the jaw).
One type of unconscious facial movement which is less apt to be read clearly by an audience is involuntary frowning. This type of frowning occurs when a speaker attempts to deliver a memorized speech. There are no rules governing the use of specific expressions. If you relax your inhibitions and allow yourself to respond naturally to your thoughts, attitudes, and emotions, your facial expressions will be appropriate and will project sincerity, conviction, and credibility.
Eye Contact
Eye contact is the cement that binds together speakers and their audiences. When you speak, your eyes involve your listeners in your presentation. Jan Costagnaro says, “When you maintain eye contact, you present an air of confidence in yourself and what you are communicating. People who are listening to what you are saying will take you more seriously, and will take what you say as important. If you lose eye contact or focus on everything else but the person(s) you are speaking to, you may not be taken seriously and the truth in your points may be lost. ” There is no surer way to break a communication bond between you and the audience than by failing to look at your listeners. No matter how large your audience may be, each listener wants to feel that you are speaking directly to him/her.
The adage, “The eyes are the mirror of the soul, ” underlines the need for you to convince people with your eyes, as well as your words. Only by looking at your listeners as individuals can you convince them that you are sincere and are interested in them and that you care whether they accept your message. When you speak, your eyes also function as a control device you can use to ensure the audience’s attentiveness and concentration.
Eye contact can also help to overcome nervousness by making your audience a known quantity. Effective eye contact is an important feedback device that makes the speaking situation a two-way communication process. By looking at your audience, you can determine how they are reacting.
When you develop the ability to gauge the audience’s reactions and adjust your presentation accordingly, you will be a much more effective speaker. The following supporting tips will help you be more confident and improve your ability to make eye contact:
Know your material. Know the material so well that you do not have to devote your mental energy to the task of remembering the sequence of ideas and words.
Prepare well and rehearse enough so that you do not have to depend too heavily on notes. Many speakers, no matter how well prepared, need at least a few notes to deliver their message. If you can speak effectively without notes, by all means do so. But if you choose to use notes, they should be only a delivery outline, using key words. Notes are not a substitute for preparation and practice.
Establish a personal bond with listeners. Begin by selecting one person and talking to him/ her personally. Maintain eye contact with that person long enough to establish a visual bond (about five to ten seconds). This is usually the equivalent of a sentence or a thought. Then shift your gaze to another person. In a small group, this is relatively easy to do. But, if you are addressing hundreds or thousands of people, it is impossible. What you can do is pick out one or two individuals in each section of the room and establish personal bonds. Then, each listener will get the impression you are talking directly to him/her.
Monitor visual feedback. While you are talking, your listeners are responding with their own nonverbal messages. Use your eyes to actively seek out this valuable feedback. If individuals aren’t looking at you, they may not be listening either. Make sure they can hear you. Then work to actively engage them.
Your Appearance Matters
Multiple studies have has shown that appearance influences everything from employment to social status. Whether we like to admit it or not, ours is a culture obsessed with appearance. Attractive people are more likely to get the job, get the promotion, and get the girl (or guy). Bonnie Berry’s 2008 research on physical appearance also shows that communicator attractiveness influences how an audience perceives the credibility of the speaker. Overall, more attractive speakers were thought to be more credible (51).
So what does that mean for you as you prepare for a speech? Bottom line: Make an effort. If your listeners will have on suits and dresses, wear your best suit or dress -the outfit that brings you the most compliments. Make sure that every item of clothing is clean and well tailored. Certainly a speaker who appears unkempt gives the impression to the audience that s/he doesn’t really care, and that’s not the first impression that you want to send to your listeners.
- Provided by : Florida State College at Jacksonville. License : CC BY: Attribution

- Choosing Good Topics
- Controversial
- Demonstration
- Extemporaneous
- Informative
- School/College
- Special Occasion
- Public Speaking Help
- Writing a Speech
- Free Sample Speeches
- Share Your Speech
- Speech Delivery Tips

Effective speech delivery is an important part of public speaking. No matter how inspiring, informative or persuasive the speech you have written, poor delivery will leave your audience feeling flat, and your presentation will be less than memorable.
There are some (lucky!) people that seem to be born to speak in public. The rest of us, however, may need a little coaching and prodding to deliver our speeches more eloquently.
Whilst it might take some work to feel like a polished pro, using the following practical speech delivery tips will certainly help to get you on your way to being a more effective, dynamic speaker.
Body Language
The way you present yourself, physically , begins speaking for you before you say your first word.
When you get up to speak before an audience, make sure that your body language does not betray you. Practice good posture, but avoid being stiff.
Even at a formal business event, you do not want to appear wooden in your physical appearance. Avoid fidgeting and keep your head high.
Little signs of nervousness can damage your presentation, so try to keep these kinds of nervous tics at bay. If you're struggling, try holding a tiny object such as a paper-clip. Some people find that unobtrusively playing with such an item helps them appear otherwise calm and relaxed!
Once you feel that you are projecting a calm, relaxed and confident aura, then it's time to think about how to deliver your words as effectively as possible.
You have to project your voice . Some people get nervous and mumble while giving public speeches.
Improving your speech delivery is all about getting your message across, so make sure that everyone can hear you. If you have a microphone available, by all means use it. If not, simply concentrate on the person at the back of the room and imagine that you are speaking to them directly. This will ensure you pitch your voice at just the right level.
Try to avoid speaking in a monotone fashion. In an effort to be clear and concise, people often become monotone... and that equals bored listeners!
While you don't want to go overboard and have too much emotion in your voice, you should be animated enough to let your listeners know that you are a human speaker and not an animatronic robot.
Nothing causes listeners to drift off faster than a monotone speaker, so avoid this habit at all costs.
Don't be a ditherer!
A final tip for delivering your speech is to avoid the nervous little words, like "um", "ah", and "mmm" . Many people don't realize it, but they use these little space fillers constantly in their every day speaking.
Don't let them creep into YOUR public speaking. Nothing indicates a speaker who is nervous or unprepared faster than these habitual, little sounds.
Record yourself giving your speech before the actual event. If you notice them popping up in your speech, take measures to cut them out when you give your speech in front of an audience.

Public speaking can cause a lot of anxiety for people who are not used to doing it. Even the seasoned pros and naturals get nervous sometimes.
Keep these tips in mind and practice the art of good speech delivery prior to your speaking engagement, to give a talk that will wow your audience.
Free email delivery
MASTER INFORMATIVE SPEAKING WITH OUR FREE CHECKLIST!
We are offering you a FREE SpeakFlight Informative Speaking Preparation Checklist. This valuable resource is packed with step-by-step guidance to help you create compelling, memorable, and effective informative speeches.
Share this page
You might like these.

Practice Public Speaking at Home
How to practice public speaking at home

Public Speaking Exercises You Can Do at Home
Public speaking exercises you can do at home. Discover some simple exercises to help you prepare for your next public speaking presentation.

Public Speaking Made Easy
Public speaking made easy! Giving a speech doesn't have to be as scary as it sounds. With some tried and true tips you can become a better public speaker!
Related speech delivery tips and guides
- Guide to Speech Writing
- The Importance of Public Speaking
- Public Speaking for Kids
- Public Speaking Jokes
Writing Tips...
- Effective Speech Writing - How to Keep Your Audience Hooked!
- How to Come Up with Topic Ideas
- Speech Titles
- Speech Introductions
Speech Delivery Tips...
- Build Your Confidence
- Effective Public Speaking
- How to Hypnotize Your Audience
- Public Speaking Exercises
- Tips for Using a Microphone
- Using Visual Aids
- Best Speech Topics

Easily search your speech type
Just check out the sitemap for best-speech-topics.com , which lists all the pages on the site, or use the search box below:
Return to the Top of the Page
Get to Know Us
- Privacy Policy
Attention Grabbers
- Positive Quotes for Kids
- Quotes for Graduation Speeches
- Poems & Quotes on Death
- Quotes on Retirement
Most Popular Pages
- Free Samples
- Good Speech Topics
- Hypnotize Your Audience
- Welcome Speech
Select a Speech Topic
- Argumentative
- Commemorative
- Inspirational
- Interesting
- Other Topics
Let Us Help You
- How To Write a Speech
- Demonstration Outline
- Informative Outline
- Introductions
- Using a Microphone
- Speech Help
- Speeches Made Easy
19.7 Spotlight on … Delivery/Public Speaking
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Implement various technologies effectively to address an audience, matching the capacities of each to the rhetorical situation.
- Apply conventions of speech delivery, such as voice control, gestures, and posture.
- Identify and show awareness of cultural considerations.
Think of a speech you have seen or heard, either in person, on television, or online. Was the speech delivered well, or was it poorly executed? What aspects of the performance make you say that? Both good and poor delivery of a speech can affect the audience’s opinion of the speaker and the topic. Poor delivery may be so distracting that even the message of a well-organized script with strong information is lost to the audience.
Speaking Genres: Spoken Word, Pulpit, YouTube, Podcast, Social Media
The world today offers many new (and old) delivery methods for script writing. While the traditional presidential address or commencement speech on a stage in front of a crowd of people is unlikely to disappear, newer script delivery methods are now available, including many that involve technology. From YouTube , which allows anyone to upload videos, to podcasts, which provide a platform for anyone, celebrities and noncelebrities alike, to produce a radio-like program, it seems that people are finding new ways to use technology to enhance communication. Free resources such as YouTube Studio and the extension TubeBuddy can be a good starting place to learn to create these types of media.
Voice Control
Whether the method is old or new, delivering communication in the speaking genre relies not only on words but also on the way those words are delivered. Remember that voice and tone are important in establishing a bond with your audience, helping them feel connected to your message, creating engagement, and facilitating comprehension. Vocal delivery includes these aspects of speech:
- Rate of speech refers to how fast or slow you speak. You must speak slowly enough to be understood but not so slowly that you sound unnatural and bore your audience. In addition, you can vary your rate, speeding up or slowing down to increase tension, emphasize a point, or create a dramatic effect.
- Volume refers to how loudly or softly you speak. As with rate, you do not want to be too loud or too soft. Too soft, and your speech will be difficult or impossible to hear, even with amplification; too loud, and it will be distracting or even painful for the audience. Ideally, you should project your voice, speaking from the diaphragm, according to the size and location of the audience and the acoustics of the room. You can also use volume for effect; you might use a softer voice to describe a tender moment between mother and child or a louder voice to emphatically discuss an injustice.
- Pitch refers to how high or low a speaker’s voice is to listeners. A person’s vocal pitch is unique to that person, and unlike the control a speaker has over rate and volume, some physical limitations exist on the extent to which individuals can vary pitch. Although men generally have lower-pitched voices than women, speakers can vary their pitch for emphasis. For example, you probably raise your pitch naturally at the end of a question. Changing pitch can also communicate enthusiasm or indicate transition or closure.
- Articulation refers to how clearly a person produces sounds. Clarity of voice is important in speech; it determines how well your audience understands what you are saying. Poor articulation can hamper the effect of your script and even cause your audience to feel disconnected from both you and your message. In general, articulation during a presentation before an audience tends to be more pronounced and dramatic than everyday communication with individuals or small groups. When presenting a script, avoid slurring and mumbling. While these may be acceptable in informal communication, in presented speech they can obscure your message.
- Fluency refers to the flow of speech. Speaking with fluency is similar to reading with fluency. It’s not about how fast you can speak, but how fluid and meaningful your speech is. While inserting pauses for dramatic effect is perfectly acceptable, these are noticeably different from awkward pauses that result from forgetting a point, losing your place, or becoming distracted. Practicing your speech can greatly reduce fluency issues. A word on verbal fillers , those pesky words or sounds used to fill a gap or fluency glitch: utterances such as um , ah , and like detract from the fluency of your speech, distract the audience from your point, and can even reduce your credibility. Again, practice can help reduce their occurrence, and self-awareness can help you speak with more fluency.
Gestures and Expressions
Beyond vocal delivery, consider also physical delivery variables such as gestures and facial expressions . While not all speech affords audiences the ability to see the speaker, in-person, online, and other forms of speech do. Gestures and facial expressions can both add to and detract from effective script delivery, as they can help demonstrate emotion and enthusiasm for the topic. Both have the ability to emphasize points, enhance tone, and engage audiences.
Eye contact is another form of nonverbal, physical communication that builds community, communicates comfort, and establishes credibility. Eye contact also can help hold an audience’s attention during a speech. It is advisable to begin your speech by establishing eye contact with the audience. One idea is to memorize your opening and closing statements to allow you to maintain consistent eye contact during these important sections of the script and strengthen your connection with the audience.
Although natural engagement through gestures, facial expressions, and eye contact can help an audience relate to a presenter and even help establish community and trust, these actions also can distract audiences from the content of the script if not used purposefully. In general, as with most delivery elements, variation and a happy medium between “too much” and “too little” are key to an effective presentation. Some presenters naturally have more expressive faces, but all people can learn to control and use facial expressions and gestures consciously to become more effective speakers. Practicing your speech in front of a mirror will allow you to monitor, plan, and practice these aspects of physical delivery.
Posture and Movement
Other physical delivery considerations include posture and movement. Posture is the position of the body. If you have ever been pestered to “stand up straight,” you were being instructed on your posture. The most important consideration for posture during a speech is that you look relaxed and natural. You don’t want to be slumped over and leaning on the podium or lectern, but you also don’t want a stiff, unnatural posture that makes you look stilted or uncomfortable. In many speeches, the speaker’s posture is upright as they stand behind a podium or at a microphone, but this is not always the case. Less formal occasions and audiences may call for movement of the whole body. If this informality fits your speech, you will need to balance movement with the other delivery variables. This kind of balance can be challenging. You won’t want to wander aimlessly around the stage or pace back and forth on the same path. Nor will you want to shuffle your feet, rock, or shift your weight back and forth. Instead, as with every other aspect of delivery, you will want your movements to be purposeful, with the intention of connecting with or influencing your audience. Time your movements to occur at key points or transitions in the script.
Cultural Considerations
Don’t forget to reflect on cultural considerations that relate to your topic and/or audience. Cultural awareness is important in any aspect of writing, but it can have an immediate impact on a speech, as the audience will react to your words, gestures, vocal techniques, and topic in real time. Elements that speakers don’t always think about—including gestures, glances, and changes in tone and inflection—can vary in effectiveness and even politeness in many cultures. Consideration for cultural cues may include the following:
- Paralanguage : voiced cultural considerations, including tone, language, and even accent.
- Kinesics : body movements and gestures that may include facial expressions. Often part of a person’s subconscious, kinesics can be interpreted in various ways by members of different cultures. Body language can include posture, facial expressions (smiling or frowning), and even displays of affection.
- Proxemics : interpersonal space that regulates intimacy. Proxemics might indicate how close to an audience a speaker is located, whether the speaker moves around, and even how the speaker greets the audience.
- Chronemics : use of time. Chronemics refers to the duration of a script.
- Appearance : clothing and physical appearance. The presentation of appearance is a subtle form of communication that can indicate the speaker’s identity and can be specific to cultures.
Stage Directions
You can think proactively about ways to enhance the delivery of your script, including vocal techniques, body awareness, and cultural considerations. Within the draft of your script, create stage directions . An integral part of performances such as plays and films, stage directions can be as simple as writing in a pause for dramatic effect or as complicated as describing where and how to walk, what facial expressions to make, or how to react to audience feedback.
Look at this example from the beginning of the student sample. Stage directions are enclosed in parentheses and bolded.
student sample text Several years ago, I sat in the waiting area of a major airport, trying to ignore the constant yapping of a small dog cuddled on the lap of a fellow passenger. An airline rep approached the woman and asked the only two questions allowed by law. (high-pitched voice with a formal tone) “Is that a service animal? (pause) What service does it provide for you?” end student sample text
student sample text (bold, defiant, self-righteous tone) “Yes. It keeps me from having panic attacks,” the woman said defiantly, and the airline employee retreated. (move two steps to the left for emphasis) end student sample text
student sample text Shortly after that, another passenger arrived at the gate. (spoken with authority) She gripped the high, stiff handle on the harness of a Labrador retriever that wore a vest emblazoned with the words “The Seeing Eye.” (speed up speech and dynamic of voice for dramatic effect) Without warning, the smaller dog launched itself from its owner’s lap, snarling and snapping at the guide dog. (move two steps back to indicate transition) end student sample text
Now it’s your turn. Using the principle illustrated above, create stage directions for your script. Then, practice using them by presenting your script to a peer reviewer, such as a friend, family member, or classmate. Also consider recording yourself practicing your script. Listen to the recording to evaluate it for delivery, fluency, and vocal fillers. Remember that writing is recursive: you can make changes based on what works and what doesn’t after you implement your stage directions. You can even ask your audience for feedback to improve your delivery.
Podcast Publication
If possible, work with your instructor and classmates to put together a single podcast or a series of podcasts according to the subject areas of the presentations. The purpose of these podcasts should be to invite and encourage other students to get involved in important causes. Work with relevant student organizations on campus to produce and publicize the podcasts for maximum impact. There are many free resources for creating podcasts, including Apple’s GarageBand and Audacity .
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/19-7-spotlight-on-delivery-public-speaking
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5: Presenting Your Speech Module
Body and Voice During Delivery
The interplay between the verbal and nonverbal components of your speech can either bring the message vividly to life or confuse or bore the audience. Therefore, it is best that you neither overdramatize your speech delivery behaviors nor downplay them. This is a balance achieved through rehearsal, trial and error, and experience. One way to think of this is in terms of the Goldilocks paradigm: you don’t want to overdo the delivery because you might distract your audience by looking hyper or overly ani- mated. Conversely, someone whose delivery is too understated (meaning they don’t move their hands or feet at all) looks unnatural and uncomfortable, which can also distract. Just like Goldilocks, you want a delivery that is “just right.” This middle ground between too much and too little is a much more natural approach to public speaking delivery. This natural approach will be covered in more detail in the following sections where we discuss specific aspects of your delivery and what you need to think about while actually giving your speech.
Almost everyone who gives a speech in public gets scared or nervous to some extent. Even professionals who do this for a living feel that way, but they have learned how to combat those nerves through experience and practice. When we get scared or nervous, our bodies emit adrenaline into our systems so we can deal with whatever problem is causing us to feel that way. Unfortunately, you will need to be standing relatively still for the next 5-7 minutes, so that burst of adrenaline is going to try to work its way out of your body and manifest itself somehow. One of the main ways is through your hands.
It may sound funny, but we have seen more than one student unknowingly incorporate “jazz hands” (shaking your hands at your sides with fingers opened wide) at various points in their speech. While certainly an extreme example, this and behaviors like it can easily becoming distracting. At the other end of the scale, people who don’t know what to do with their hands or use them “too little” sometimes hold their arms stiffly at their sides, behind their backs, or in their pockets, all of which can also look unnatural and distracting.
The key for knowing what to do with your hands is to use them naturally as you would in normal conversation. If you were standing around talking to your friends and wanted to list three reasons why you should all take
a road trip this weekend, you would probably hold up your fingers as you counted off the reasons (“First, we hardly ever get this opportunity. Second, we can…”). Try to pay attention to what you do with your hands in regular conversations and incorporate that into your delivery.
However, with all that said, if you have nothing else to do with your hands, such as meaningful gestures, the default position for them is to be resting gently on the sides of the lectern (see Figure 11.2). You don’t want to grip the lectern tightly, but resting them on the edges keeps them in position to move your notes on if you need to or use them to gesture. As stated above, you want to practice this way beforehand so you are used to speaking this way when you come to class.
Just like your hands, a lot of nervous energy is going to try to work its way out of your body through your feet. On the “too much” end, this is most common when people start “dancing” behind the lectern Another variation is twisting feet around each other or the lower leg. On the other end are those who put their feet together, lock their knees, and never move from that position. Both of these options look unnatural, and therefore will prove to be distracting to your audience. Locking your knees can also lead to loss of oxygen in your brain, not a good state to be in, because it can cause you to faint.
The default position for your feet, then, is to have them shoulder-width apart with your knees slightly bent (see Figure 11.3). Again, you want to look and feel natural, so it is fine to adjust your weight or move out from behind the lectern, but constant motion (or perpetual stillness) will not lead to good overall delivery.
These two sections on hands and feet mention “energy.” Public speakers need to look energetic—not hyperactive, but engaged and upbeat about communicating their message. The energy is part of the muscle memory we saw in Chapter 1. Slumping, low and unvarying pitch and rate, and lack of gestures telegraph “I don’t care” to an audience.
There is a very simple rule when it comes to what you should bring with you to the lectern when you give your speech: Only bring to the lectern what you absolutely need to give the speech. Anything else you have with you will only serve as a distraction for both you and the audience. For the purposes of this class, the only objects you should need to give your speech are whatever materials you are speaking from, and possibly a visual aid if you are using one. Beyond that, don’t bring pens, laptops, phones, lucky charms, or notebooks with you to the lectern. These extra items can ultimately become a distraction themselves when they fall off the lectern or get in your way. Some students like to bring their electronic tablet, lap- top computer, or cell phone with them, but there are some obvious disadvantages to these items, especially if you don’t turn the ringer on your cell phone off. Cell phones are not usually large enough to serve as presentation notes; we’ve seen students squint and hold the phone up to their faces.
Not only do you need to be aware of what you bring with you, but you should also be aware of what you have on your person as well. Sometimes, in the course of dressing for a speech, we can overlook simple issues that can cause problems while speaking. Some of these can include:
• Jewelry that ‘jingles’ when you move, such as heavy bracelets;
• Uncomfortable shoes or shoes that you are not used to (don’t make speech day the first time you try wearing high heels);
• Anything with fringe, zippers, or things hanging off it. They might become irresistible to play with while speaking;
• For those with longer hair, remember that you will be looking down at your notes and then looking back up. Don’t be forced to “fix” your hair or tuck it behind your ear every time you look up. Use a barrette, hairband, or some other method to keep your hair totally out of your face so that the audience can see your eyes and you won’t have to ad- just your hair constantly. It can be very distracting to an audience to watch a speaker pull hair from his face after every sentence.
The Lectern and Posture
We have already discussed the lectern, but it is worth mentioning again briefly here. The lectern is a tool for you to use that should ultimately make your speech easier to give, and you need to use it that way. On the “too much” end, some people want to trick their audience into thinking
they are not nervous by leaning on the podium in a relaxed manner, some- time going so far as to actually begin tipping the podium forward. Your lectern is NOT part of your skeletal system, to prop you up, so don’t do this. On the “too little” end are those who are afraid to touch it, worried that they will use it incorrectly or somehow knock it over (you won’t!).
As always, you want the “Goldilocks” middle ground. As stated above, rest your notes and hands on it, but don’t lean on the lectern or “hug” it. Practicing with a lectern (or something similar to a lectern) will eliminate most of your fears about using it.
The lectern use is related to posture. Most of us let gravity pull us down. One of the muscle memory tricks of public speaking is to roll your shoulders back. Along with making your shoulder muscles feel better, doing so with feet apart and knees bent, rolling your shoulders back will lead to a more credible physical presence—you’ll look taller and more energetic. You’ll also feel better, and you’ll have larger lung capacity for breathing to support your tone and volume.
Eye Contact
As we’ve said consistently throughout this book, your audience is the single biggest factor that influences every aspect of your speech. And since eye contact is how you establish and maintain a rapport with your audience during your speech, it is an extremely important element of your delivery. Your professor may or may not indicate a standard for how much eye contact you need during the speech, such as 50%, but he or she will absolutely want to see you making an effort to engage your audience through looking directly at them.
What is important to note here is that you want to establish genuine eye contact with your audience, and not “fake” eye contact. There have been a lot of techniques generated for “faking” eye contact, and none of them look natural. For example, these are not good ideas:
• Three points on the back wall – You may have heard that instead of making eye contact, you can just pick three points on the back wall and look at those. What ends up happening, though, is you look like you are staring off into space and your audience will spend the majority of your speech trying to figure out what you are looking at. To avoid this, look around the entire room, including the front, back, left, and right sides of the space.
• The swimming method – This happens when someone is reading his or her speech and looks up quickly and briefly to try to make it seem like they are making eye contact, not unlike a swimmer who pops his head out of the water for a breath before going back under. Eye contact is more than just physically moving your head; it is about looking at your audience and establishing a connection. In general, your eye contact should last at least five seconds at a time and should be with individuals throughout the room.
• The stare down – Since you will, to some degree, be graded on your eye contact, some students think (either consciously or not), that the best way to ensure they get credit for establishing eye contact is to always and exclusively look directly at their professor. While we certainly appreciate the attention, we want to see that you are establishing eye contact with your entire audience, not just one person. Also, this behavior is uncomfortable for the instructor.
Volume refers to the relative softness or loudness of your voice. Like most of the other issues we’ve discussed in this section, the proper volume for a given speaking engagement usually falls on the scale in Figure 11.4. If you speak too softly (“too little” volume), your audience will struggle to hear and understand you and may give up trying to listen. If you speak with “too much” volume, your audience may feel that you are yelling at them, or at least feel uncomfortable with you shouting. The volume you use should fit the size of the audience and the room.
Fortunately, for the purposes of this class, your normal speaking voice will probably work just fine since you are in a relatively small space with around twenty people. However, if you know that you are naturally a soft-spoken person, you will need to work on breathing to get more air into your lungs, and on projecting your voice to the people in the last row, not just those in the front. Of course, if you are naturally a very loud talker, you may want to make other adjustments when giving your speech. Obviously this will all change if you are asked to speak in a larger venue or given a microphone to use.
Public speaking relies on the voice for interest, credibility, audibility, and clarity. The British Prime Minister of the 19th century was quoted saying, “There is no greater index of character so sure as the voice.” While that seems exaggerated today, a public speaker at any level cannot ignore the energy, loudness, and clarity in their voice. There are four steps to voice production: breathing (produced by the lungs, which are largely responsible for the vocal characteristic of volume); phonation (the production of the sound in the vocal folds, which close and vibrate to produce sound for speaking as the air is exhaled over them; phonation creates pitch); resonation (a type of amplification of the sound in the larynx, oral cavity, and nasal cavity, which creates the characteristic of quality); and articulation, which produces the sounds of language others can understand and is responsible for rate and for being understood.
The visual in Figure 11.5 shows a cutaway of these parts of the anatomy. Your instructor may give you more directions on maximizing the power of your voice to achieve more variety and power. In section 11.6 we include a vocal exercise for doing so. We have all listened to a low-energy, monotone, monorate speaker and know how hard it is, so you should pay attention to your recording, perhaps by closing your eyes and just listening, to see if your voice is flat and lifeless.
Pitch is the relative highness or lowness of your voice, and like everything, you can have too much or too little (with regard to variation of it). Too much pitch variation occurs when people “sing” their speeches, and their voices oscillate between very high pitched and very low pitched. While un- common, this is sometimes attributed to nerves. More common is too little variation in pitch, which is known as being monotone .
Delivering a speech in a monotone manner is usually caused by reading too much; generally the speaker’s focus is on saying the words correctly (because they have not practiced). They forget to speak normally to show their interest in the topic, as we would in everyday conversation. For most people, pitch isn’t a major issue, but if you think it might be for you, ask the people in your practice audience what they think. Generally, if we are interested in and passionate about communicating our thoughts, we are not likely to be monotone. We are rarely monotone when talking to friends and family about matters of importance to us, so pick topics you care about.
How quickly or slowly you say the words of your speech is the rate . Too little rate (i.e. speaking too slowly) will make it sound like you may not fully know your speech or what you are talking about, and will ultimately cost you some credibility with your audience. It may also result in the audience being bored and lose focus on what you are saying. Rate is one reason you should try to record yourself, even if just audio on your phone, beforehand and be mindful of time when you practice. Your voice’s rate will affect the time it takes to give the speech.
By contrast, too much rate (i.e. speaking too fast) can be overly taxing on an audience’s ability to keep up with and digest what you are saying. It sometimes helps to imagine that your speech is a jog or run that you and your friends (the audience) are taking together. You (as the speaker) are setting the pace based on how quickly you speak. If you start sprinting, it may be too difficult for your audience to keep up and they may give up halfway through. If you know you speak quickly, especially when nervous, be sure to practice slowing down and writing yourself delivery cues in your notes (see Chapter 6) to maintain a more comfortable rate. As always, re- cording and timing your speech during practice helps.
You especially will want to maintain a good, deliberate rate at the beginning of your speech because your audience will be getting used to your voice. We have all called a business where the person answering the phone mumbles the name of the business in a rushed way. We aren’t sure if we called the right number. Since the introduction is designed to get the audience’s attention and interest in your speech, you will want to focus on clear delivery there. Regulating rate is another reason why video-recording yourself can be so helpful because we often to not realize how fast we speak.
The common misconception for public speaking students is that pausing during your speech is bad, but that isn’t necessarily true. You pause in nor- mal conversations, so you shouldn’t be afraid of pausing while speaking.
This is especially true if you are making a particularly important point or want for a statement to have a more powerful impact: you will want to give the audience a moment to digest what you have said.
For example, consider the following statement: “Because of issues like pollution and overpopulation, in 50 years the earth’s natural resources will be so depleted that it will become difficult for most people to obtain enough food to survive.” Following a statement like this, you want to give your audience just a brief moment to fully consider what you are saying. Hopefully they will think something along the lines of What if I’m still alive then? or What will my children do? and become more interested in hearing what you have to say.
Of course, there is such a thing as pausing too much, both in terms of frequency and length. Someone who pauses too often (after each sentence) may come off seeming like they don’t know their speech very well. Some- one who pauses too long (more than a few seconds), runs the risk of the audience feeling uncomfortable or, even worse becoming distracted or letting their attention wander. We are capable of processing words more quickly than anyone can speak clearly, which is one of the reasons listening is difficult. Pauses should be controlled to maintain attention of the audience.
Vocalized pauses
At various points during your speech, you may find yourself in need of a brief moment to collect your thoughts or prepare for the next section of your speech. At those moments, you will be pausing, but we don’t always like to let people know that we’re pausing. So what many of us do in an attempt to “trick” the audience is fill in those pauses with sounds so that it appears that we haven’t actually paused. These are known as vocalized pauses , or sometimes “fillers.” Another term for them is “nonfluencies.”
Everyone uses vocalized pauses to some degree, but not everyone’s are problematic. This obviously becomes an issue when the vocalized pauses become distracting due to their overuse. We have little doubt that you can remember a time when you were speaking to someone who said the word “like” after every three words and you became focused on it. One of your authors remembers attending a wedding and (inadvertently) began counting the number of times the best man said “like” during his toast (22 was the final count). The most common vocalized pause is “uh,” but then there are others. Can you think of any?
The bad news here is that there is no quick fix for getting rid of your vocalized pauses. They are so ingrained into all of our speech patterns that getting rid of them is a challenge. However, there is a two-step process you can employ to begin eliminating them. First, you need to identify what your particular vocalized pause is. Do you say “um,” “well,” or “now” be- fore each sentence? Do you finish each thought with, “you know?” Do you use “like” before every adjective (as in “he was like so unhappy”)?
After figuring out what your vocalized pause is, the second step is to care- fully and meticulously try to catch yourself when you say it. If you hear yourself saying “uh,” remind yourself, I need to try to not say that . Catching yourself and being aware of how often you use vocalized pauses will help you begin the process of reducing your dependence on them and hopefully get rid of them completely.
One of the authors uses a game in her class that she adopted from a couple of disc jockeys she used to hear. It is called the “uh game.” The callers had to name six things in a named category (items in a refrigerator, pro-football teams, makes of cars, etc.) in twenty seconds without saying a vocalized pause word or phrase. It sounds easy, but it isn’t, especially on the spot with a radio audience. It is a good way to practice focusing on the content and not saying a vocalized pause.
The ten items listed above represent the major delivery issues you will want to be aware of when giving a speech, but it is by no means an exhaustive list. There is however, one final piece of delivery advice we would like to offer. We know that no matter how hard you practice and how diligent you are in preparing for your speech, you are most likely going to mess up some aspect of your speech when you give it in class, at least a little. That’s normal. Everyone does it. The key is to not make a big deal about it or let the audience know you messed up. Odds are that they will never even realize your mistake if you don’t tell them there was a mistake. Saying something like “I can’t believe I messed that up” or “Can I start over?” just telegraphs to the audience your mistake. In fact, you have most likely never heard a perfect speech delivered in your life. It is likely that you just didn’t realize that the speaker missed a line or briefly forgot what they wanted to say.
As has been the driving maxim of this chapter, this means that you need to
Practice your speech beforehand, at home or elsewhere, the way you will give it in class.
Since you know you are likely going to make some sort of mistake in class, use your practice time at home to work on how you will deal with those mistakes. If you say a word incorrectly or start reading the wrong sentence, don’t go back and begin that section anew. That’s not what you would do in class, so just correct yourself and move on. If you practice dealing with your mistakes at home, you will be better prepared for the inevitable errors that will find their way into your speech in class.
A final thought on practice. We have all heard, “Practice makes perfect.” That is not always true. Practice makes permanent; the actions become habitual. If you practice incorrectly, your performance will be incorrect. Be sure your practice is correct.
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Pomaka English
Supporting English language learners and educators

Three tips for improving your speech delivery
Having problems with people undersanding your speaking?
While things like fluency and vocabulary are important, your delivery (how you speak) is also very important. In fact, if your delivery is unclear, your fluency and vocabulary can be almost meaningless. Varying delivery can also help keep the listener interested.
Delivery is not only about pronunciation, but also, and just as importantly, about your prosody . Prosody is related to your intonation, stress, and pausing. It helps to create the timing and rhythm of speech that listeners will be expecting. It is also an important part of communicating meaning. It is used in all types of speaking from conversations to presentations.
Continued below
Having taught oral presentation classes for a number of years, I’ve always been surprised how quickly student delivery improved after addressing basic problems with prosody . From this experience, and having taught a range of other speaking and pronunciation classes, below three tips I’ve found useful for improving speech delivery.
Pause in the right places It’s difficult to understand a speaker who pauses in the wrong places. It makes speech seem unnatural and disjointed. It’s even more difficult to understand a speaker who doesn’t pause at all.
When speaking, try to take short pauses between grammatical phrases eg. where you would usually use a comma or period. For example, “Because of the rain today (pause) we’re going to have the lunch indoors (pause)” The phrases between these pauses are called thought groups and are important to helping listeners understand you. They also help you control your speed and give you a chance to catch your breath! Thought groups are especially important when you have to speak for a long period, for example, telling a story or doing a presentation.
Know which words to stress The thought group s mentioned above usually have one word that has a little more stress than the other words in the same group. This is called the focus word . Focus words help to create a natural rhythm to your speech. Usually the focus word will be the last content word (non-grammatical word eg. noun, verb) in the thought group . For example “I haven’t checked my MAIL yet.” When stressing the focus word , be careful to stress the correct part of the word, or its primary stress (see Fig.1). For example, “The teacher wants us to reCORD it.”

Fig.1
Usually focus words come near the end of each thought group, but it is also possible to stress other words in the group. This might be to compare things, for example, “I have some GOOD news and some BAD news.” Or, this might be to give new or correct information, for example “Actually, I’m coming at ONE thirty, not two thirty.”
Use basic intonation Changing intonation at the end of thought groups further contributes to the overall rhythm. It also communicates meaning to the listener. Falling intonation at the end can tell the listener you have finished communicating your idea or sentence. However, importantly, slightly falling (or even slightly rising) intonation at the end can tell the listener you want to continue speaking about that idea.
You can also use intonation changes to convey other meaning to the listener, especially in conversation. For example, rising intonation usually tells the listener that you are unsure about the information, are surprised, or you would like check the information. For example “You’re going whERE tomorrow?” (surprise), “You’re going to New YORK?” (check)
Want to try some thought group practice? Listen to the MP3 file of the business presentation below (see Fig.2). Listen carefully for the pauses, stress ( focus words ) and intonation. Then practice reading it aloud to yourself. Try and copy the thought group patterns.

Audio file
Related links:
Recommened free pronunciation sites (and apps)
Do people speak too quickly for you?
Privacy Overview
© Copyright 2023 Pomaka - All rights reserved

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the four types of speech delivery methods (manuscript, memorized, impromptu, and extemporaneous) and their advantages and disadvantages. Find out how to use each method with tips and examples from history and public speaking.
Nonverbal communication carries most of the message. Good delivery does not call attention to itself, but instead conveys the speaker's ideas clearly and without distraction. 9. Grab Attention at the Beginning, and Close with a Dynamic End. Do you enjoy hearing a speech start with "Today I'm going to talk to you about X"? Most people ...
Learn how to improve your speech delivery skills with tips on conversational style, eye contact, vocalics, physical manipulation, and variety. This chapter explains the importance of nonverbal communication and speech delivery elements for effective public speaking.
Learn the advantages and disadvantages of four methods of speech delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized. Find out how to prepare, present, and connect with your audience using different techniques and strategies.
Mastering effective speech delivery techniques is essential for becoming a confident and persuasive speaker. By implementing these techniques, such as thorough preparation, proper personal appearance, and effective vocal and nonverbal delivery strategies, you can captivate your audience and deliver impactful presentations.
These are called the delivery modes, or simply, ways of delivering speeches. The three modes are impromptu delivery, manuscript delivery, and extemporaneous delivery. Each of these involves a different relationship between a speech text, on the one hand, and the spoken word, on the other. These are described in detail below.
Here are 4 key reasons why: Engagement: Deliver your speech in an engaging way and your listeners will stay hooked until the end. This ensures that your message resonates with them. Clarity: Delivery makes your speech clearer. This helps people understand your words and the main points of your message.
4. Take Deep Breaths: Before and during the speech, take a few deep breaths as this will help calm nerves and make sure your breathing is regulated throughout the duration of your presentation. 5. Speak Slowly: It is common to feel anxious while giving a speech and try to rush through it too quickly.
In some cases, an instructor leads a person through a series of relaxation techniques. Once relaxed, the person is asked to imagine a series of scenarios including speech preparation and speech delivery. ... As with other components of speech delivery, becoming a higher self-monitor and increasing your awareness of your typical delivery habits ...
Techniques for Effective Delivery Whenever you speak in public, it is really a multimedia experience for the audience. Not only does the audience listen to the speech, but they also get to see you in action. And, if the speaker uses visual aids, such as demonstration objects, charts, or PowerPoint slides, the audience receives other visual ...
Conclusion. In this chapter, we introduced verbal delivery as a core component of your speech aesthetics. Verbal delivery includes language - including vivid language, tropes, and storytelling. In addition, projection, rate, punctuation, enunciation, and pausing all work to deliver an effective presentation.
Here are some techniques to follow: 1. Fit the Message to the Audience. Guidelines for effective public speaking often include tips that apply to any situation. But sometimes, it pays to tailor your delivery based on your audience. Matching subject matter and delivery style helps you make the best possible impression.
Use the links to find out more about the techniques and tools needed for developing good speech delivery. The 9 vocal aspects of speech delivery This is a very long page covering the impact of voice quality on our lives, (how what we sound like in the ears of others affects what happens in our lives), the nine vocal aspects of speech delivery, (pitch, tone, articulation, pronunciation, volume ...
What you'll learn to do: Describe delivery techniques for use during a public speech. As alluded to in the prior section, a live speech is, in effect, a performance. In addition to what you say, audience members will be reacting—both consciously and unconsciously—to how you say it. In this section, we'll discuss fundamental ...
Slow down; you deliver the speech faster than your practiced it. Even if your practice trials were perfectly timed, it's common for speakers to speed up the actual delivery. For additional tips, check out this resource on general guidelines for speech delivery (The Writing Resources Center, Swem Library, College of William & Mary).
Connect speech delivery to the three artistic proofs: ethos, pathos and logos. Understand the ethical issues in speech delivery. CHAPTER OUTLINE ... relaxation techniques for such situations include deep breathing and visualizing a successful speech (Behnke & Sawyer, 2004). Shallow breathing limits your oxygen intake and adds
Delivery techniques is an important part of public speaking success. Delivery should be natural and easy to listen to, yet clear and authoritative. To effectively command the attention of an audience and engage them with your content, it's important to understand how to use words effectively in your delivery.
Place of publication not identified: CreateSpace. 1664 N. Virginia Street, Reno, NV 89557. William N. Pennington Student Achievement Center, Mailstop: 0213. (775) 784-6030. Nervous about giving a speech? Get tips for polishing your delivery and what to practice so your speech is professional.
2. Build Self-Confidence by Being Yourself: The most important rule for making your body communicate effectively is to be yourself. The emphasis should be on the sharing of ideas, not on the performance. Strive to be as genuine and natural as you are when you speak to family members and friends.
Practice good posture, but avoid being stiff. Even at a formal business event, you do not want to appear wooden in your physical appearance. Avoid fidgeting and keep your head high. Little signs of nervousness can damage your presentation, so try to keep these kinds of nervous tics at bay.
Apply conventions of speech delivery, such as voice control, gestures, and posture. ... vocal techniques, and topic in real time. Elements that speakers don't always think about—including gestures, glances, and changes in tone and inflection—can vary in effectiveness and even politeness in many cultures. Consideration for cultural cues ...
Body and Voice During Delivery. The interplay between the verbal and nonverbal components of your speech can either bring the message vividly to life or confuse or bore the audience. Therefore, it is best that you neither overdramatize your speech delivery behaviors nor downplay them. This is a balance achieved through rehearsal, trial and ...
Listen carefully for the pauses, stress ( focus words) and intonation. Then practice reading it aloud to yourself. Try and copy the thought group patterns. Fig.2. Audio file. Extra tip! Record yourself speaking : Try writing a short 2min speech about yourself. Mark your thought groups, focus words and intonation.