Recommended

About us | Advertise with us | Contact us

Quality Assurance / Pharmaceutical Quality Systems in manufacturing medicinal products
Posted: 12 September 2018 | Anastasia Petropoulu | 1 comment
Quality Assurance (QA) covers all aspects that could have an impact on the quality of prescribed pharmaceutical products. This article focuses on some of the Pharmaceutical Quality Systems in relation to QA of manufactured medicines.

Quality Assurance (QA) is a wide concept and covers all aspects that could have an impact on the quality of prescribed pharmaceutical products. The objectives of QA are: to ensure that the prescribed medicine competently provides the desired effect to the person taking it; to protect patients from accidentally being administered an incorrect or contaminated medication; and to ensure medicines comply with the regulation.
Pharmaceutical Quality Systems (PQS) consist of eight pillars, which are designed to provide high quality finished pharmaceutical products, with QA and PQS working together in synergy (Figure 1). Pharmaceutical companies strive to provide high quality products to enable them to enhance their reputation, maximise profit and to provide high quality drugs to humans and animals. To meet these targets, they rely on well-designed PQS, which involve the coordination of quality through processes, with the aim of producing finished products of the highest quality. 1
It is worth noting that the European Medicines Agency (EMA) defines PQS as: “The degree of excellence processed by an item” and “Meeting the requirements of specific customers’ needs”. 6
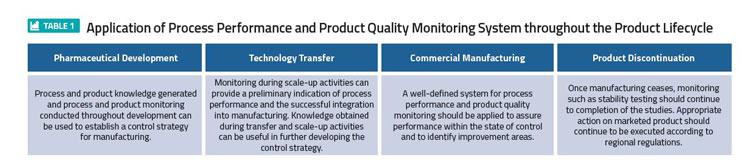
The general model of controlling quality involves standards. Those include: checking the value or degree of the set standards, checking the product for conformity and feeding this back into the initial system and checking stages. 2 The control of quality is an essential process and should be applied at all manufacturing stages; starting with the design, through to assembly of raw materials, in-process, post process and finally the finished products including stability testing. This explains why Quality Control is often described as being the most appropriate Total Quality Control (TQC) concept (Table 1). 4,3
This article will focus on some of the Pharmaceutical Quality Systems in relation to QA of manufactured medicines. As mentioned previously, the eight pillars of PQS constitute a good foundation for discussion (Figure 1). 7

Figure 1: Eight Quality Systems contribute to the high quality of the finished pharmaceutical product
The application of a process performance and product quality monitoring system throughout the product lifecycle is shown in Table 1. This illustrates the most effective monitoring system that provides assurance of the continued capability of processes and controls to produce a product of desired quality and to identify areas for continual improvement, according to PQS Q10. 5
Nevertheless, it is not possible to mention high quality finished pharmaceuticals without mentioning Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and Validation. 5 It is well known that all manufacturing stages need quality assurance actions to ensure successful results; but how can they be achieved, and which is the most important action during all the manufacturing stages?
The answers can be found by applying GMP in each step of the manufacturing process. 3 GMP is part of Quality Management that ensures products are consistently produced and controlled to the quality standards appropriate to their intended use and as required by the marketing authorisation or product specification. 3 Furthermore, it ensures the manufactured products meet the end-user’s needs in terms of safety, quality and efficacy. GMP involves monitoring of processes, equipment, personnel and the environment in pharmaceutical companies. 4
GMP is essential in all cases from initial drug trials to commercial launch. To obtain the best product, a manufacturer needs a system in place to ensure regular formulation, processing and composition. 4 Without regulation of a manufacturing process, the consequences cause confusion that might escape notice in the first instance but at some later point will invalidate the safety of the product. This means someone will get harmed or it will cost the manufacturer money. However, the importance of patient safety is what drives companies to improve quality and prevent unnecessary expenditure on manufacturing. 4
GMP applies to all types of pharmaceuticals. For example, a ‘standard product’ is one in which the unit operation and risk assessment of the end product suggests simple equipment ambient conditions; however, this doesn’t mean that the system can be abused. GMP should be applied, and the product manufactured, according to highly-regimented and regulated procedures. 4 On the other hand, sterile medicines require different processes and equipment. 4,2 These types of manufacturing processes often include biotechnology derivatives; where the consistency and potency of bio-preparation, that needs validation and constant monitoring, is often highly variable but may also be associated with issues such as purity. 2 Sterile manufacture tends to be more vigorous in terms of equipment and specialised clean rooms. These specialised conditions and the nature of the drug itself often require additional staff training and a stronger reliance on the Qualified Person (QP) to sign-off. 4
Figure 2 shows how Quality by Design embraces an integrated science and risk-based approach with continuous improvement for the entire product lifecycle. 8 Process validation is needed to underpin confidence in the compatibility and coherence of each individual stage in a process of manufacture of pharmaceuticals. 4
Figure 2: Challenges in Implementing Quality by Design: An Industry Perspective
This represents the biggest part of the validation process in pharmaceutical products. However, cleaning and analytical validation are equally as important in manufacturing validation as in-process, or on-process, control. The aim is to ensure end-product suitability by fragmenting the process into modules with an appropriate consideration of risk and non-compliance to established standards. 4 As such, the essential considerations of any validation of manufacturing should include:
- The importance of following and establishing an environment of GMP
- The site / building / equipment limitations, aspects associated with packaging / storage / handling of the product
- The complexity of routine production, provision of a suitable audit trail in terms of detailed reports and records. 3,4
Additional aspects of higher-end quality in a manufacturing validation include: the probability for consistency of manufacturing and the consequences of inconsistency. Another parameter in the validation process is the use of a pilot trial to identify the point of ‘weakness’ in a particular stage of a manufacturing process where particular attention is required. 4 Pharmaceutical companies should have a system for implementing corrective and preventive actions arising from the investigation of complaints, product rejections, non-conformances, recalls, deviations, audits, regulatory inspections and findings, trends from process performance and product quality monitoring. A structured approach to the investigation process should be used, with the objective of determining the root cause. 3,4
A Quality Risk Management system (Figure 3) involves monitoring and assessing the system’s or procedure’s effectiveness. This mainly involves investigating deviations that have occurred during any step of the manufacturing process, or identifying other factors such as damaged or faulty raw materials, devices or equipment.
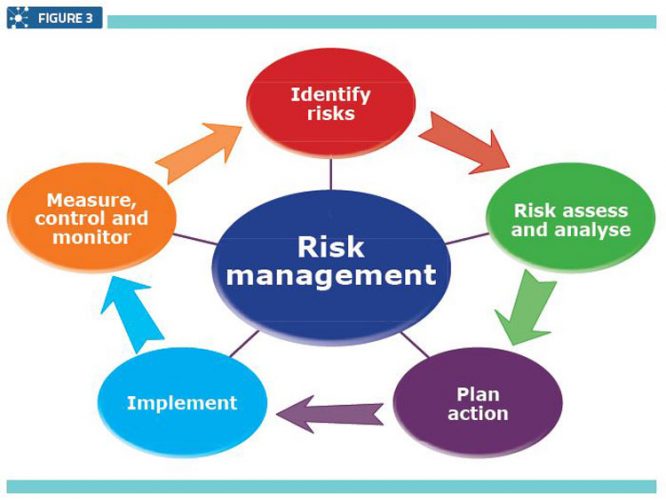
Quality risk management
The root cause analysis is identified and documented and finally an evaluation is undertaken to confirm quality objectives were achieved and the quality of the product was not affected. 2 In other words, this system was built to ensure the quality of products by solving various issues or identifying risks and preventing the same happening again.
Risk management principles are used in many areas of business, including pharmaceuticals. The manufacturing and use of medicinal products, including its components, involves some degree of risk, whereas the risk to its quality is just one part of the overall risk. 4 A robust quality risk management programme can ensure the high quality of pharmaceuticals by providing a proactive means of identifying and controlling potential quality issues during development and manufacturing. Effective quality risk management can provide regulators with greater assurance of a company’s ability to deal with possible risks and can positively affect the level of direct regulatory oversight. 4,6
Efficient quality management results from the correct interfacing of quality control, quality assurance and quality improvement initiatives. It is achieved through acting on feedback from the people involved in the product supply chain. A quality cycle is a group of experts who meet with the aim of improving the quality of manufacturing processes, the environment, health and safety etc. Effective communication between the investors in the group can result in an improvement over and above those routine improvements. 4,6
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, QA is the parameter used to ensure prescribed medicine effectively produces the desired effect on the person taking it. The PQS, part of QA system, was designed to help manufacturers achieve the target for high quality finished pharmaceutical products; leading to the required level of drug regulations and providing efficacy and safety for patients. 4 The parameters for approaching these targets include:
- The pharmaceutical product is designed to meet the need and performance requirements
- The process is designed to consistently meet product critical quality attributes 8
- Processes, equipment, personnel and deviations are identified and controlled in an appropriate manner
- The whole manufacturing process is constantly monitored and updated to enable consistency in quality over time.
The application of Pharmaceutical Quality Systems in pharmaceutical products can extend to pharmaceutical development, which should facilitate innovation and continual improvement of prescribed medication. 2,6 It is the tool with which to achieve product realisation by designing, planning, implementing, maintaining and continuously improving a system, to allow the consistent delivery of pharmaceuticals with appropriate quality attributes. 4,6
- Article: Viper. 2015. Quality In Pharmaceutical Industry Management, UK essays
- Book: Beaney AM. 2006. Quality Assurance of Aseptic Preparation Services, fourth edition, published by pharmaceutical press
- Book: MHRA. 2017. Rules and Guidance for Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Distributors, London Pharmaceutical Press, Chapter 2 EU Guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice
- Book: Sarker DK. 2008. Quality Systems and Control for Pharmaceuticals, School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences University of Brighton, UK
- Article: ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. 2008. Pharmaceutical Quality Systems, Q10, step 4 version
- Article: EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY, science medicines health. 2015. EMA/CHMP/ICH/24235/2006, ICH guideline Q9 on Quality risk management, step 5
- Image: Morley L, CEO, EUSA, Pharma. 2016. Total Quality Service Management, Regulis, UK
- Image: Torres L. 2015. Challenges in Implementing Quality By Design: An Industry Perspective, BioProcess International
- Image: Quality Risk Manager for Manufacturing Systems; a Contamination Control Perspective, T. PDA Technical Report No 54-5 (TR 54-5)
Anastasia Petropoulu is a Radiopharmacy Technician / Clinical Scientist in the Radiopharmacy Department of University Hospital Bristol NHS Foundation Trust, Anastasia obtained a certificate in Health and Science followed by a BSc Hons degree in Pharmaceutical Science at the University of the West of England. She has gained experience in Quality Assurance / Quality Systems (QA / QS) by completing work in both pharmacy and the food industry. Anastasia has worked in Greece in the food industry as a Quality Assurance technician and in the UK pharmaceutical industry at Norbrook Laboratories Ltd in Northern Ireland and gained experience in testing raw materials as a Quality Control Analyst. She has also worked at NHSBT Bristol and the University Hospital Bristol NHS Foundation Trust, where she assisted in the production of parenteral nutrition and cytotoxic medicines. She currently works in Radiopharmacy as a Radiopharmacy Technician / Clinical Scientist where she applies PQS in the manufacturing process of radiopharmaceuticals.
The rest of this content is restricted - login or subscribe free to access

Why subscribe? Join our growing community of thousands of industry professionals and gain access to:
- bi-monthly issues in print and/or digital format
- case studies, whitepapers, webinars and industry-leading content
- breaking news and features
- our extensive online archive of thousands of articles and years of past issues
- ...And it's all free!
Click here to Subscribe today Login here
Issue 4 2018
Related topics
Aseptic Processing , Industry Insight , Manufacturing , QA/QC
Related organisations
European Medicines Agency.

Next-Generation Rapid mRNA Vaccine CQA Analytics

Novel medicine could address short stature in children
By Catherine Eckford (European Pharmaceutical Review)

CRISPR technologies fuelling haematological innovations
EFPIA reaction to European Parliament plenary vote

New partnership to advance European oligonucleotide manufacturing
One response to “quality assurance / pharmaceutical quality systems in manufacturing medicinal products”.
Very well defined about the role of quality and most of the companies should remember that quality should be built inside the system.
Thanks for such a great post Anastasia Petropoulu.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
© Russell Publishing Limited , 2010-2024. All rights reserved.
Website development by e-Motive Media Limited .

Cookie Settings
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorised as ”Necessary” are stored on your browser as they are as essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. For our other types of cookies “Advertising & Targeting”, “Analytics” and “Performance”, these help us analyse and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these different types of cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience. You can adjust the available sliders to ‘Enabled’ or ‘Disabled’, then click ‘Save and Accept’. View our Cookie Policy page.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.

Modern Aspects of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance pp 1–7 Cite as
Introduction: Quality Assurance from Perspective of Pharmaceutical Industry
- Minal Ghante 4 ,
- Shrikant Dargude 4 ,
- Arpana Patil 5 &
- Vidhya Bhusari 4
- First Online: 12 March 2024
36 Accesses
Pharmaceutical development requires product quality, design, and operational efficiency. Pharmaceutical development is a multifarious process that encompasses various facets, including product quality, design, and operational efficiency. Operational excellence helps improve pharmaceutical product quality by optimizing manufacturing processes, reducing waste, and enhancing productivity augmenting operational efficiency and effectiveness. Quality assurance is essential to ensure that pharmaceutical products are safe, effective, and meet quality standards. The integration of operational excellence and quality management systems can help achieve pharmaceutical product quality and operational excellence goals. This chapter elaborates upon the intricate concept of quality assurance in the pharmaceutical industry, with a meticulous focus on the manifold perspectives that undergird its implementation. It underscores the paramount importance of quality assurance in ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products and expounds upon the regulatory frameworks that have been instituted to ensure compliance. This chapter also scrutinizes the multifarious challenges that the pharmaceutical industry faces in implementing quality assurance, including the exigency of a robust quality management system, the salience of risk management, and the pivotal role of technology in ensuring quality. In sum, this chapter provides a comprehensive, all-encompassing overview of quality assurance in the pharmaceutical industry and its indispensability in guaranteeing the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Levi L, Walker GC, Pugsley LI. Quality control of pharmaceuticals. Can Med Assoc J. 1964;91(15):781–5.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fellows M, Friedli T, Li Y, et al. Benchmarking the quality practices of global pharmaceutical manufacturing to advance supply chain resilience. AAPS J. 2022;24 https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-022-00761-7 .
International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use pharmaceutical quality system Q10
Google Scholar
Kieffer RG. The changing role of quality assurance in the pharmaceutical industry. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2014;68:313–9.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
VanDuyse SA, Fulford MJ, Bartlett MG. ICH Q10 pharmaceutical quality system guidance: understanding its impact on pharmaceutical quality. AAPS J. 2021;23 https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-021-00657-y .
Haleem RM, Salem MY, Fatahallah FA, Abdelfattah LE. Quality in the pharmaceutical industry – a literature review. Saudi Pharm J. 2015;23:463–9.
Lebrun P, Giacoletti K, Scherder T, et al. A quality by design approach for longitudinal quality attributes. J Biopharm Stat. 2015;25(2):247–59.
Suleman S, Belew S, Kebebe D, et al. Quality-by-design principles applied to the establishment of a pharmaceutical quality control laboratory in a resource-limited setting: the lab water. Int J Anal Chem. 2022;2022 https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2062406 .
Korakianiti E, Rekkas D. Statistical thinking and knowledge management for quality-driven design and manufacturing in pharmaceuticals. Pharm Res. 2011;28:1465–79.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Friedli T, Basu P, Bellm D, Werani J. Leading pharmaceutical operational excellence outstanding practices and cases. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer; 2013.
Book Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance, Sinhgad Technical Education Society’s, Smt. Kashibai Navale College of Pharmacy (Kondhwa), Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, India
Minal Ghante, Shrikant Dargude & Vidhya Bhusari
Department of Pharmaceutics, Sinhgad Technical Education Society’s Smt. Kashibai Navale College of Pharmacy (Kondhwa), Pune, India
Arpana Patil
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Minal Ghante .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance, Smt. Kashibai Navale College of Pharmacy, Pune, Maharashtra, India
Minal Ghante
Manohar Potdar
Vidhya Bhusari
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Ghante, M., Dargude, S., Patil, A., Bhusari, V. (2024). Introduction: Quality Assurance from Perspective of Pharmaceutical Industry. In: Ghante, M., Potdar, M., Bhusari, V. (eds) Modern Aspects of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9271-3_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-9271-3_1
Published : 12 March 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-9270-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-9271-3
eBook Packages : Chemistry and Materials Science Chemistry and Material Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- July 25, 2022
The importance of quality in the pharmaceutical industry
A viewpoint by June Sum , Consultant.
Quality is one of the most important management principles for any organization regardless of industry. This is particularly true for the pharmaceutical sector: maintaining quality product standards is essential for the prevention and treatment of numerous medical disorders.
Although the pharmaceutical industry has been around for centuries, in recent years we have experienced an increase in the number of drugs being launched in the market. As a result of this increase, the need for quality assurance and quality control measures has risen. For instance, drug manufacturers must follow strict guidelines to get their drugs approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the United States. Such guidelines include requirements for testing, manufacturing, labelling, packaging, storing and distributing pharmaceuticals.
Quality Management
Quality management is a crucial component of any successful organization as it ensures that products and services are produced and distributed consistently and effectively.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) is the element of quality management that ensures goods are produced and controlled according to the quality standards of their intended use and that they meet the requirements specified by the marketing authorization or product specification. Additionally, it ensures that manufactured goods are safe, of high quality, and effective. For pharmaceutical companies, GMP entails the monitoring of procedures, apparatuses, employees, and environments.
Quality planning, quality control, and quality assurance are all important aspects of quality management too. We’ll look at what quality management is, why it’s important, and the main components and principles of quality management in this article.
Quality planning
Quality planning refers to the process of defining the quality requirements and standards of a product or service and identifying the resources needed to meet such requirements and standards. The planning phase is the first stage in establishing a good quality management system. It is in this phase that companies define their baseline quality objectives. Once goals have been set, organizations must determine what is required to achieve these objectives and what procedures should be implemented to ensure their success. During this stage of the quality management process, it is important to keep in mind the following considerations:
- The organization’s definition of success
- How often procedures and processes will be evaluated for improvement
- If the stakeholders have any quality-related priorities, goals, or ambitions
- If there are any legal procedures or standards that must be followed in order to achieve the desired quality level
Quality Control
Quality control is the next step in the quality management process. At this stage, companies assess through physical inspection and testing whether their plan is achievable. They must verify that all requirements are being met and identify any issues that may need to be corrected. It is therefore important to pay close attention to all product elements, that is, every component of the product and all manufacturing procedures.
The data collected should be presented in a way that makes it simple to examine. Document management software enables teams to create and easily share histograms, run charts and cause-and-effect diagrams.
Quality control involves ensuring standards and procedures are being met. This may include conformance testing as well as feeding information back into the initial system and examination phases. It is important to apply quality management throughout the entire manufacturing process.
Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance (QA) is a broad concept that encompasses all factors that could potentially affect the quality of prescribed pharmaceutical products. The goal of quality assurance is to verify that prescribed medications provide the desired effect to its consumers; safeguarding patients from receiving defective or contaminated prescriptions by accident; and ensuring that medications comply with regulations.
Pharmaceutical Quality Systems (PQS) consist of eight pillars that help companies oversee quality management methods with ease: allowing the consistent delivery of pharmaceutical products of the highest quality.
The eight pillars of PQS:
- Quality risk management
- Quality management system consultancy & design
- Good distribution practice & good manufacturing practice compliance
- Standard operating procedures development
- Qualified person & responsible person provision
- Inspection preparation & support
Quality Improvement
Once the quality management process is complete, reviewing the results and developing an action plan for improvement is key. Continuously performing the quality control management process, re-evaluating both the procedure and the product while keeping compliance in mind, will result in a better final product, happier customers and more profit.
At Amaris Consulting, we offer a wide spectrum of services to pharmaceutical, medical device, and biotechnology companies. Our quality experts assist businesses in meeting and exceeding customer expectations while supporting you throughout the entire drug development life cycle.
Share Post:
Amaris Consulting is your stepping stone to cross rivers of change, meet challenges, and achieve all your projects with success.
- Life Sciences
- IS & Digital
- Engineering
©2024 Amaris Consulting
Get in touch
Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry Essay
Several controversies have been hitting the pharmaceutical industry in the last few years. The larger percentage of the controversies ranges from Medicare fraud to high-priced medications that are marketed by these firms. From the researcher’s point of view, big pharmaceutical corporations are putting huge profits on top of patients, spiraling shammed public relations campaigns and more. Before the recent changes, Medicare CEOs and these companies had been reported to have involved in frauds worth billions of shillings.
The indications are that the costs of the drugs are rising more rapidly than any other thing a patient can pay for. It has been found that medications are the most rapidly increasing part of the patient health care bill. It is argued that most of the patient’s expenditure on drugs has also risen.
The reason is that the quantities of drugs that are being prescribed have increased. Moreover, the practitioners are prescribing new ineffective drugs that are more expensive than the old effective less costly drugs.
More appalling is the fact that the prices of these consistently prescribed drugs are in a great deal jacked up, in most cases a number of times a year. The discounts as well as other incentives the medical practitioners such as the oncologists are receiving are used as a reason for hiking the prices. The government as well as other researchers has found that these benefits are unwarranted.
The most shocking thing about these drug price controversies is that the trusted health care providers have an ulterior motive behind these prescriptions. Researchers found out that there is a correlation between the methods through which cancer doctors are being paid to the choice of drugs they use in a particular treatment of cancer such as chemotherapy (Abelson par.9).
Once the oncologists have decided on the type of treatment, the mode of payment influences the type of drug prescription. As opposed to the expectations those who are fairly paid are likely to prescribe more expensive drugs.
Reports indicate that most of the pharmaceutical firms’ representatives provide hand-outs to influence medical practitioners to recommend the drugs they represent. Going by analytic reviews of the articles on the diabetes drugs Avandia, it is true that drug manufacturers are paying medical experts to make positive conclusions about their drugs safety and effectiveness. In fact, Avandia case is one out of many (Bakalar par.1).
There are several cases where the medical expert opinions are influenced by the financial handouts. It is agreed among the medical professionals that the interaction between the pharmaceutical companies and the health providers are not in the best interest of the patient. Moreover, most of the doctors agree that solicitation of drugs directly from these companies compromises the ethical standards and impractical, most can be influenced by free gifts and hand outs from these companies.
Some sections of the medical profession argue that their treatment decisions are for the best interest of the patients (Abelson par.7). The argument is that doctors only prescribe drugs that are clinically recommended. Moreover, quality health care must be more costly. However, in the case of cancer therapy, there is no any evidence that one type of chemotherapy drugs are working better than the others.
In this case, the medical practitioners have the wide array of manufacturers or the pharmaceutical agents to choose from. Therefore, regardless of their persistence that their therapy decisions are based on what they feel is best for the patient; medical practitioners are influenced by other factors such as payment policies as well as other financial influences coming from the drug manufacturers.
Works Cited
Abelson, Reed. Pay Method Said to Sway Drug Choices of Oncologists . 2006. Web.
Bakalar, Nicholas. Study Sees a Slant in Articles on Drug . 2010. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 6). Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry. https://ivypanda.com/essays/practices-in-the-pharmaceutical-industry-essay/
"Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry." IvyPanda , 6 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/practices-in-the-pharmaceutical-industry-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry'. 6 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry." January 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/practices-in-the-pharmaceutical-industry-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry." January 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/practices-in-the-pharmaceutical-industry-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Practices in the Pharmaceutical Industry." January 6, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/practices-in-the-pharmaceutical-industry-essay/.
- The Plight of the Community Oncology Medicare Patient
- Ethical Issues in GlaxoSmithKline
- Practice of Qualitative Research Report
- Breaking Bad News by Medical Practitioners
- Medical Marijuana Legalization by National Football League
- Ambulance Service with Inappropriate Call Outs Burden
- A De-Emphasis Technique for Delivering Bad News
- Stock-Outs and Their Impact on the Company’s Progress
- Thyroid Cancer Chemotherapy
- The Presentation Delivery: Training Package
- Baseline Pharmaceutical Engineering Guides
- Use of Psychotropic Medications in the Treatment of Drug Abuse
- Problem of Hydrocodone Addiction in US
- Action of Nandrolone on the Cardiovascular, Renal, Blood and Respiratory Systems
- Use of Methadone, Methadone clinics, and Needle Exchange Programs
- RECRUITMENT

Technical Writing Tips for Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Students
October 8, 2019

One aspect of pharmaceutical quality assurance that is very important, and that anyone working in the industry should be aware of, is technical writing. Technical writing is different from other kinds of writing, because it is focused first and foremost on clarity. Long sentences and descriptions might work well in an article or book, but not for a piece of technical writing.
Whether you find yourself working with Standard Operation Procedures (SOPs), Master Batch Records (MBRs), or other pieces of writing, clarity and accuracy will be essential. With a few helpful hints, you’ll be on track to writing these documents in a manner that everyone can understand and easily follow.

Working in quality assurance means working on different documents
Continue reading to learn more about technical writing and find out how you can build your own skills!
What to Think About Before Getting Started
Strong technical writing skill is essential for quality assurance in pharmaceutical operations that require different documents.
Before you get started with a piece of technical writing, you should be sure to make a plan.
- Before you even commit to writing your first sentence, think about what your objective is.
- Consider who you are writing for and what information you must communicate.
- In some cases, it is a good idea to make a preliminary writing document such as an outline or a graphic organizer before you start writing.
When planning your document, consider ways that you can enhance brevity. In fact, you should never use two words when one will do. Your writing should get to the point. In technical writing, there is no room for descriptive language. Write what needs to be said in a way that it can be well understood, and keep sentences short and easy to follow so that no misunderstandings occur.

Writing should be clear and easy to understand
Word Choice for Clarity in Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Writing
Regardless of whether you’re writing SOPs, MBRs, or another document during your career in pharmaceutical quality assurance , there are a few guidelines or rules of technical writing that can be applied across all situations. Word choice and clarity are a couple of things you’ll want to keep in mind, to be sure your point gets across.
- Word Choice – This is a matter of making your writing easy to understand. When you are deciding which words to use to say something, choose the word that will cause the least amount of confusion, and which can be processed with the most ease.
- Clarity – Make sure that what is clear to you is also clear for the person that might read your work. Your choice of words will help you to do this, as well as clarification when necessary. For example, if you use an acronym, make sure that the reader knows what that acronym means in order to ensure that your writing is as clear as possible.

If you can, have someone re-read your work to make sure it’s clear
Are you interested in earning a Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance diploma ?
Contact AAPS today to learn more about our programs!
Categories: Pharmaceutical Quality Control & Assurance
Tags: pharmaceutical quality assurance , pharmaceutical quality assurance diploma , Quality assurance in pharmaceutical
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013

Interested in AAPS? Contact us directly or provide your information for a call back.
Toronto campus, hours of operation.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Health Sci (Qassim)
- v.7(3); 2013 Nov
Pharmaceuticals Safety Practices-A Comparative Pilot Study
Introduction.
The safety of medicine is essential for the safety of patients. Inappropriate drug storage, expiration dates, sharing prescription drugs, self medication habits and misuse of some drugs are contributing factors affecting medication safety. One or more of these factors may lead to serious health complications and even death.
The purpose of this study was to highlight the common errors and pharmaceutical malpractices that people usually engage in on a daily basis and to correlate these to culture, gender and educational levels. This may spread awareness in an easy and understandable manner and provide certain guidelines to drug consumers ensuring that pharmaceutical preparations are used correctly and safely.
Two hundred questionnaires were randomly distributed in two countries; Saudi Arabia and India. The collected data were statistically analyzed.
Outcomes and conclusion
Results showed that alarming percentages of various participants were using pharmaceuticals inappropriately due to carelessness, unawareness or intentional mistakes. Therefore, active participation by health care professionals is essential for the prevention of drug misuse. Increasing population awareness about self medication, products expiration, pharmaceuticals labels and optimum storage conditions would minimize the adverse effects and may even be life saving.
Medication and patient safety measures are indispensable in any health care system. Medication safety is the design of medication administration strategy to ensure the five rights; right patient, right medication, right dose, right route and right time. ( 1 ) While patient safety refers to the sustained, proactive process of identifying, avoiding and rapidly resolving errors, omissions, mishaps and miscommunications that could affect a patient’s healing, health or well-being at any point, at any time, in any care setting. ( 1 )
Adverse drug events are common, costly and serious problems. These include adverse drug reactions and medication errors. ( 2 ) The latter means any preventable actions that may lead to patient harm. These errors may include sharing prescription drugs, self medication habits, medication misuse, administration of drugs after expiration date, carelessness of reading the labels and misplacement of the products.
Whether it is prescription or Over-the-Counter (OTC), no medicine is without risk. ( 3 ) Up to half of people who use medicines, do not use them as prescribed. ( 4 ) Home medicine chests, which are often kept in inappropriate locations and containers, promote opportunities for irrational consumption, exchanging of medicines, irresponsible self-medication, unintentional toxic exposure and intentional intoxication (drug misuse among the adolescents). ( 5 ) Proper methods of storage and preservation of drugs are of great importance for maintenance of their potency. ( 6 ) Depending on the product’s composition, it may expire long before its expiration date if it has not been stored and handled properly. ( 7 ) Some of the environmental factors such as air, chemicals, insects and bacterial and fungal growth increase the risk of contamination. ( 8 , 9 ) Others like moisture, light and temperature variations may adversely affect the different dosage forms of drugs and may lower their original potency. ( 8 , 9 ) Summer heat can potentially degrade the drug which is often unnoticed especially in hot countries. ( 4 ) Reading the label before purchasing any sort of cosmetic product or medicine is less practiced by the consumers. ( 6 ) Most people find it difficult to understand the terminology and instructions given in the leaflet due to lack of its simple explanation especially for those with low literacy level. ( 10 ) A high incidence of inappropriate medication use has been documented in the older non-institutionalized population ( 11 – 13 ) and in long-term care. ( 14 ) Therefore, the risk of medication errors may be high in older home healthcare patients. Such patients are frequent medication users, and advanced age and frailty may increase their susceptibility to adverse medication effects. ( 15 )
This goes not only for medicines but also for cosmetics as well. Many people use makeup on a daily basis which is a major factor of concern since a considerable amount of cosmetics can actually be absorbed into the skin or breathed into the lungs. ( 16 )
Global drug safety depends on strong national systems that monitor the development and quality of medicines, report their harmful effects, and provide accurate information for their safe use. ( 3 , 7 ) Saudi Food and Drug Authority (SFDA) and Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) are the two regional regulatory authorities that assure the safety, quality and efficacy of medications in Saudi Arabia (SA) and India (IN), respectively. ( 17 , 18 ) Research has shown that medical errors and the associated injuries are a significant problem as these errors occur frequently and have significant clinical and financial consequences. ( 19 , 20 ) Hence, preventing medication errors is a blueprint for change in medication safety. ( 21 ) Recent research reports have raised concern about the protocols of administration of various pharmaceuticals that are used in health care systems and their effects on medication and patient safety in order to minimize the index of errors to the lowest. ( 22 – 26 )
Literature data from survey studies on the prevalence of common medication errors at home is lacking. Medication-related safety incidents are a source of concern not only to patients but also to policy makers and clinicians. ( 22 ) To promote adherence to medication and patient safety measures there is an urgent need to highlight the common errors that individuals make during their daily life when using pharmaceutical preparations either due to unawareness or carelessness. Comparing such practices between people of different genders, education levels or from different communities would help in determining their predisposing factors. Therefore, this snapshot study was carried out to determine how individuals use pharmaceuticals and highlight their daily home malpractices in order to focus on ways to minimize the index of errors and improve the patients’ health, recovery and well-being.
Materials and Methods
- Individuals from Saudi Arabia and India.
- Questionnaire made of 23 questions.

Inclusion Criteria
- Individuals of both genders
- Individuals aged above 18 years
Exclusion Criteria
- Uneducated people who could not read or write
- Individuals aged less than 18 years
This research design was cross sectional and used a questionnaire survey distributed randomly among selected populations in Saudi Arabia and India. The questionnaire had multiple questions pertaining to pharmaceutical preparations used and kept at home and self medication habits. Some of these questions were about the placement of drugs stored at home whether they are prescription or OTC, keeping the leftover drugs for future use (standby drugs), checking the labels and expiration dates of pharmaceuticals, understanding instructions given, sharing medications and completion of the recommended dose.
A questionnaire comprising of 38 questions was designed after referring to previous studies and interviews with five senior pharmacists who had over ten years of experience in the academic field. ( 27 ) Pretesting was done by distributing the questionnaire to a sample of 10 participants selected randomly from both countries. The responses from those individuals were subjected to a factor analysis. As a result, a minor change to certain terminology was made to some questions and the total number of questions was reduced to 23 questions. The content validity was finally assessed by discussion and rating by academics and students.
A pilot questionnaire was given to 10 participants and then re-given to them after 45 days to test reliability and reproducibility. The Cronbach’s alpha was used to test the reliability, the values for the questions ranged from 0.82 to 0.95 with an overall Cronbach’s alpha of 0.92 showing excellent reliability.
Two hundred hard copies (paper forms) were randomly distributed among populations. In addition, soft copies of the questionnaire using my easy survey website ( www.myeasysurvey.com ) were available. A systematic random sampling technique was used when questionnaires were distributed. The participants were selected from Riyadh Colleges of Dentistry and Pharmacy directory list that included all students’ names and every fourth name (aged 18 years and above) was chosen. Every third customer entering some pharmacy stores in both countries was selected to fill in a questionnaire. A total of 200 questionnaires were distributed, participants were requested to fill in the questionnaires after reading and signing an informed consent statement. After three months, 166 filled questionnaires were returned. In Saudi Arabia; all hundred distributed questionnaires were filled and returned while only 61 were returned in India. Five additional questionnaires (late reporting) from Saudi Arabia were also included in the study. Collected data was analyzed using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) software analysis tool (version 18). Chi square test with p < 0.05 was used to check for significance of differences in responses.
Total of 166 questionnaires from paper and online versions were filled and returned with a response rate of 83%. From those, 105 came from Saudi populations and 61 from Indian populations. There were 48 females and 117 males with an indeterminate case. Of these, 84 were students, 62 had bachelor degrees, 11 had postgraduate degrees, and 9 were indeterminate ( Figure 1 ).

Study populations divided into different categories
Significant variations between participants of different cultures, genders and educational levels have been found upon comparison of their daily practices when using pharmaceutical preparations ( Tables 1 – 3 ). Pharmaceutical malpractices have been noticed from populations in both countries with significant differences in certain responses from each one ( Table 1 ). On gender basis; females were found to be notably more curious than males when dealing with pharmaceuticals ( Table 2 ). Remarkable variations between participants of different educational levels were found when using pharmaceutical products ( Table 3 ).
Saudi and Indian populations’ safety measures when using pharmaceuticals
Differences in responses about pharmaceuticals safety practices based on gender basis
Level of education in relation to participants’ responses of pharmaceuticals safety
Comparison of the safety measures practiced by the study participants when using pharmaceuticals has been done on the basis of culture, gender and education. The study asked about all pharmaceutical preparations that people were using on their daily life including prescription and OTC medications, cosmetic and various health care products. Selecting people from different communities would significantly help in understanding some of the leading factors to pharmaceuticals safety practices. Especially within Saudi and Indian communities where there are many challenges to health care services although their governments have given high priority to the development of health care systems ( 28 – 30 ). On the other hand, comparing participants of both genders and different educational levels for their attitudes when using pharmaceuticals had determined how those factors would affect their safety measures when using pharmaceuticals and hence their health and well being.
Analysis of the data revealed that most of the involved populations did not usually obtain full information from pharmacists about the pharmaceutical product they purchase in pharmacy stores ( Tables 1 – 3 ). This could be due to self dependence on reading the products’ labels. However, the results showed that more than 60% of the respondents did not try to read the leaflets of their medications. Females and postgraduates were more curious to read such leaflets. This could be explained as the majority (> 70%) of the males and graduates could not understand the terminology found in the leaflets ( Tables 2 and and3 3 ).
A few (17%) of the participants were careful enough to ask the pharmacist what to do with their medications leftover. This explains why more than half of them (> 50%) stored the leftover until further needed. Females and postgraduates were significantly the best in dealing with their medications leftover ( Tables 2 and and3). 3 ). More than half of the total participants shared their prescribed medications with others while about three quarters of them use some medications for purposes other than those labeled on the package without consultation. With respect to educational levels, it was found that, the higher the educational degree, the lesser the percentage of such malpractices ( Table 3 ). Sharing and repeating prescription medications is a common habit in developing countries where the strict laws for dispensing prescription drugs are lacking. Although 40% of the study participants repeated their prescribed medications whenever they felt sick, Saudi and postgraduate populations significantly avoided such habit when compared to Indian and graduate ones, respectively ( Tables 1 and and3 3 ).
Saudi, female and postgraduate participants were found to be remarkably more aware about the suitable instructions to be followed to ensure the safe storage of pharmaceutical preparations at home ( Tables 1 – 3 ). About two third of the total population thought that humid places (kitchens and bathrooms) or dining tables were the best places to keep pharmaceuticals. There were no significant differences between either genders or people with different education levels or from different cultures regarding this matter. This might be due to ease of accessibility and/or avoidance of forgetting taking the medicaments on their respective timing. Participants were used to practice such despite the damage occurred to certain products if kept in those places. More than three quarters of participants stored their medications in the presence of adolescents noting that Indian-, female- and student- participants were found to engage more in such behavioral mistakes ( Tables 1 – 3 ). The latter might lead to some intentional drug intoxications by those teenagers and increased rates of suicides.
Although all of the populations involved in the study were educated, most of them did not care to keep a list of emergency numbers or contacts of the closest drug poison centers in case of accidents or drug poisoning. About three quarters of the participants did not keep standard measurement tool for accurate drug dosage or check the approval of regulation authorities for food and drug safety (RAFDS) of the pharmaceuticals upon purchasing from pharmacies or retail markets. Some participants stated that if the product was available in the market, they thought no need to check this as it should have been approved already while others believed that it was hard to go through the product’s label and understand it. More than three quarters of the participants were found not to bother to update themselves about medications. Saudi-and female- participants were particularly more interested for being updated to be the first to know about harmful and useless products so they could avoid any complications before they occur ( Tables 1 and and2 2 ).
Indicating all precautions about pharmaceuticals would be extremely difficult. The prudent alternative is to make reasonable judgments based on the best available evidences combined with successful experiences in health care. ( 31 ) One of the limitations of the study is the difficulty to access different families in order to ask them about their attitudes when using pharmaceutical products. From each house, only one questionnaire is to be filled and represents what they usually do. The responses from Saudi Arabia were higher than that from India as the study was mainly done in Saudi Arabia and the distance played a factor on that. Accordingly, this is considered a snapshot study in order to achieve its main goal to capture an insight into the different individuals practice towards pharmaceuticals that they are using and keeping at home in two developing countries.
Increased vulnerabilities of drug consumers might be due to increased errors, most of which might be unintentional or due to the consumer’s carelessness. Although the limited number of samples, this pilot study focused on the common mistakes that the consumers of pharmaceuticals usually make and highlighted their increased percentages between those consumers. In addition, the study discussed the predisposing factors and reasons of such practices. A detailed study with a greater sample size is still necessary to elaborate on the factors unreached by this study.
Neglecting such malpractices can have a serious negative impact not only on individuals and community but also on the national economy. Hence, increasing population awareness about self medication, drug expiration, medications labels and optimum storage conditions would minimize the drug adverse events and even be life saving. The former would be achieved by the participation of health care professionals and researchers that should underline those mistakes and the reasons for their occurrence. People work in pharmaceutical industry also have a great responsibility to improve medication safety by supplying the market with products that are stable in most conditions, easily identified from each others with labels which are easy to be read and understood. The role of policy makers comes afterwards to set the rules which aim to minimize the index of errors to minimum, hence, improving the medication and patient safety practices.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Dr Sharat Pani for his help and support during the work of the study.
- Sign In / Manage Profile

- Learn About Membership
- Join AMWA Now
- Access Member Benefits
- Member Directory
- Recognition & Awards
- AMWA Code of Ethics
- AMWA Education
- Online Learning
- Live Webinars
- Essential Skills
- ES Certificate
- Onsite Training
- Events Calendar
- AMWA Career
- Search the Directory
- Create a Listing
- Compensation and Salary Information
- Advance Your Professional Career
- Expert Tips for Freelance Medical Writing
- Guide to Becoming a Medical Writer
- Guide to Regulatory Writing
- Medical Editing Guide
- Value of Medical Writing
- Employer Resources
- About Medical Communication
- View the Current MWCs
- About the MWC Commission
- AMWA Resources
- Current Issue
- Read Recent Issues
- Past Issue Archive
- Instructions for Contributors
- Index (1985-2023)
- Medical Communication News
- Member Resource Library
- Mini Tutorials
- Position Statements and Guidelines
- Regulatory Writer Training eBook
- Online Store
- AMWA Event Calendar
- Registration
- Onsite Experience
- Sponsors and Exhibitors
- AMWA Online Learning
Expand Your Skills to Write for the Pharmaceutical Industry
Let’s explore the distinct types of writing in this niche, then identify the challenges you must overcome to succeed as a writer in this rapidly expanding industry.
Types of Writing for the Pharmaceutical Industry
If you’re a veteran medical writer, you already have a solid understanding of these broad types of medical writing :
- Regulatory writing
- Scientific publications
- Health communications
- Education for professionals
- Promotional writing
- Grantsmanship
Whether you write for a pharmaceutical company, medical device company, or some other type of organization, pharmaceutical content can fall into several of the above categories.
Writers for the pharmaceutical industry are likely to do one (or more) of the following types of writing, which are further described in The Writing Cooperative ’s “ Writing for the Pharmaceutical Industry ”:
- Pharmaceutical marketing communications. Medical drugs and devices are marketed to consumers and health care professionals. As a medical marketing communicator, you’ll need to write plain language summaries of critical information—from drug contraindications to clear indications for use. You will also craft content such as slide decks and brochures to educate physicians about these products. If you work for a health care organization rather than a drug or medical device company, you might create content for the hospital’s website, newsletter, or other marketing materials.
- Regulatory writing . Writers in this niche focus on documents required by regulatory agencies such as the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). You could write manuals for conducting clinical trials (known as investigator brochures), clinical study reports, or submissions such as Investigational New Drug Applications (INDs), Marketing Authorization Applications (MAAs), or New Drug Applications (NDAs).
- Continuing medical education (CME) course writing . Like professionals in other industries, doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals must earn continuing education credits to maintain their licenses. Writing content for these courses is a lucrative, rewarding option for medical communicators with a love for learning.
- Technical writing. Pharmaceutical technical writers create technical documentation such as medical device user manuals or reference guides. This type of writing requires incredible attention to detail. The writing can seem dry—especially for those shifting from health communication or medical marketing—but a great technical writer can also enjoy the satisfaction of translating dense information into helpful material for a variety of readers.
Challenges of Writing for the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical field is increasingly fast‑paced. From novel drugs to the development of generic specialty medications, the rapid changes can feel overwhelming for medical writers who must keep up with changing trends and regulations.
Here are some of the greatest challenges of crafting documents for this industry:
Lack of standardized training
The baseline experience of regulatory writers is uneven or absent due to the lack of formal, standardized training in many organizations. Regulatory writer training is necessary, but it’s difficult to create because it consists of so many components, including hands‑on education. Extensive training also takes place over multiple years.
Writers for the pharmaceutical industry—especially those involved in regulatory document creation—should have the following:
- High‑level knowledge of the drug development process
- Strong medical writing skills
- Technical aptitude with a variety of resources, from Adobe Acrobat to Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) Glossary
AMWA’s training roadmap for regulatory writers offers a helpful outline of the regulatory topics that are most important and demonstrates how certain topics and skills build on the preceding ones.
Rapidly evolving therapies and standards
Addressing this challenge requires a deep commitment to continued learning. In Managed Care Executive ’s January article “Top Issues Facing Pharma in 2020,” author Frieda Wiley, PharmD, reviewed several hot-button topics in the pharmaceutical industry’s “era of exponential change.”
In this industry, you might write about a variety of therapeutic categories with new products every year. You could find yourself creating documents covering everything from gene therapy to specialty drugs for rare diseases and disorders. You should also be prepared for last‑minute document revisions due to late‑breaking study results or urgent regulatory changes.
Attention to detail
Writing for the pharmaceutical industry is not for everyone. Writers must be fastidious and undistracted—even when the topics are highly technical or dry.
The pharmaceutical industry can be challenging even for experienced medical writers . The key is to commit to learning, maintain unwavering attention to detail, and determine a niche that maximizes your background and skills.

November 16, 2020 at 8:00 AM
American Medical Writers Association
AMWA is the leading resource for medical communicators. The AMWA Blog is developed in partnership with community members who work every day to create clear communications that lead to better health and well-being.
View all posts >
Blog subscribe.
- Career development (43)
- Core knowledge and skills (37)
- Freelancing (28)
- Health communication (17)
- Writing and editing mechanics (17)
- Soft Skills (15)
- Getting Started (11)
- Regulatory writing (11)
- Scientific publications (11)
- Management & Leadership (8)
- Education for professionals (6)
- Grantsmanship (3)
- Promotional writing (1)
- Sales Training (1)
American Medical Writers Association 9841 Washingtonian Blvd, Suite 500-26 Gaithersburg, MD 20878
phone: 240. 238. 0940 fax: 301. 294. 9006 [email protected]
About Us Contact AMWA Staff © 2023 AMWA / Policies
QUICK LINKS
- AMWA Journal
- Certification
- Engage Online Community
- Medical Writing & Communication Conference
CONNECT WITH US
- Support AMWA
- Advertise with AMWA
Membership Management Software Powered by YourMembership :: Legal
Synthetic Chemistry
In-vitro biology services, in-vitro adme services, route scouting, non-gmp kilo lab, analytical support services.

A sneak peek into our facility
Piramal has been offering from mg to gm scale discovery chemistries to its customers from North America, Europe and Asia
Piramal’s in vitro Biology is designed to provide best in class support to our clients to enable their preclinical drug discovery.
Piramal's in-vitro labs provide ADME services for faster and improved decision making for our Chemistry clients
Assisting our partners in discovering and developing efficient and cost effective routes
Piramal’s fully-equipped kilo-lab allows for rapid development of scalable and robust chemical processes using advanced process methodologies
The chemists at Piramal are supported by a specialist & fully dedicated analytical team which operates 24/7 with suites containing advanced analytical equipment
Piramal Discovery Solutions offers a comprehensive range of Contract Research Services from our state-of-the-art research centre in India to support drug discovery activities.
Development, process r&d services, pre-formulation studies, pharmaceutical drug development services, regulatory services, clinical trial services.

Process development for small molecule intermediates, APIs and HPAPIs
Expert approach ensures quality of drugs from discovery to commercial supply
Pharmaceutical Development of oral solids, liquids, creams, ointments, and sterile injectable.
Range of services, including method development, stability studies, validation and transfer
Expert clinical & regulatory support across all phases of drug development programs
Clinical Trial Manufacturing, Packaging and Supply Services using our global network
Piramal offers a comprehensive range of development services to help the customer address complex drug development challenges and bring more products to the market faster.
Manufacturing, api manufacturing, finished dosage manufacturing.
- Oral Solids
- Sterile Injectables
- Liquids, Creams and Ointments
- Cytotoxic and Potent Compounds
Lifecycle Management

We provide the manufacture and supply of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) on an integrated manufacturing model across North America, Europe and Asia
Piramal Pharma Solutions offers the development and manufacturing of High Potency API services from its Riverview facility
With very small quantities of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) or drug-able candidate molecules
Piramal offers contract manufacturing services for a wide variety of solid dose forms. Our global manufacturing sites located across North America, Europe and India offer the highest standards of quality and service to the customers.
Antibody drug conjugation, proof-of-concept studies, process development and scale up, adc manufacturing, adc fill/finish, analytical development services.
Piramal offers a fast-track early stage development service for your ADC programmes. Whether you are selecting your candidate mAb, linker or toxin
Piramal offers ADC process development and scale-up through Tox manufacture and into GMP manufacture
World-leading multi-product facility for clinical and commercial manufacturing of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs)
Piramal offers aseptic filling of ADC drug product through our FDA-inspected state-of- the-art manufacturing facility in Lexington, KY
Analytical development team covers a wide range of analytical methods from small molecule analysis through to cell killing assays and ELISA development
Piramal is the world leader in delivering customer-centric solutions in the field of Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs) to global pharmaceutical companies.
Generic apis, mumbai, india, generic api products.
- API Product List
- APIs (Under Development)
- Peptide API Product List
- Peptide APIs (Under Development)

We have an experienced team of over 28 scientists including 8 Ph.D.’s dedicated to innovation in new product development, cost optimization, and novel route scouting projects
Piramal’s Generic API division offers an indigenous basket of off-patent APIs for global markets. With the declining pipeline of new drugs in the pharmaceutical industry, our customers are looking for off-patent APIs with competitive cost and quality.
Nutrition solutions.
- Foods & Beverages
- Staple Foods
- Infant Nutrition
- Bakery Foods
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals
- Dry-Encapsulated
- Dry-Cold Water Soluble
- Oily-Liquid
- Animal Nutrition
- Customized Vitamin Mineral Premix-Powder Form
- Customized Oily & Water Miscible Vitamin Products
- Retinol & Diluted Forms
- Other Oily Forms For Cosmetic Industry
- Institutional
- Micro Nutrient Powder(MNP)
- Vitamin A Solution
- Premixes For Ready to Eat Therapeutic & Supplementary
- MOH Mandated Fortification Programs
Product List

With key focus on research and strong manufacturing capabilities, we deliver a portfolio of premium solutions to customers in more than 80 countries
Piramal Nutrition Solutions (PNS), division of Piramal Enterprises Limited (PEL) is one of the leading manufacturers of Straight Vitamins and Mineral premixes.

Dear Partners,
Necessitated by the unprecedented situation created by Covid-19, several industry events and tradeshows across the world have been postponed or stand cancelled. While we were looking forward to meet you, we at Piramal Pharma Solutions have had to take several precautionary measures to protect both our employees and customers, worldwide.
As we move forward in these extraordinary times, we want to assure you that that we are operational by taking the right safety measures and abundant precautions to ensure that we continue to support you and your patients.
While all of us are working remotely for now, you can schedule a discussion with us and we would be glad to help ensure you meet your pharmaceutical development and supply needs and thereby, your clinical and commercial timelines.
Please feel free to reach out to us at: [email protected]
Our best wishes to colleagues, friends and family.
Best Regards, Piramal Pharma Solutions
Thank You For Your Interest. Please Enter Your Details

Technical writing is not a new idea. Any type of communication written for and about industry and business with a focus on products and/or services is technical writing. Almost everyone within a company has written a form of technical document – from the résumé that was submitted to gain employment to the email sent to a co-worker to writing an investigative report. According to a survey of business leaders, as many as two-thirds of salaried employees have some writing responsibility, and all employees must have writing ability, especially with the increase in company email communication.
Technical writing skills are extremely important for any industry, but even more so when manufacturing pharmaceutical drugs. In this industry, if a batch record step is unclear or contains a mistake, it could have several types of negative consequences. Product could be unusable and clients could be lost if the mistake is caught. Employees could be hurt and lawsuits filed. Or, worse, the mistake could escape attention and end up impacting a patient, causing harm or death. The importance of good technical writing cannot be ignored as the science of pharmaceutical drug manufacturing depends on clear and accurate reporting. An otherwise meticulous document can appear flawed if it is poorly written wasting company time and resources.
It is difficult, however, to find employees who have content knowledge of their profession and also the skills needed to write a technical document. It is even rarer to find an employee who has taken a course in technical writing, and, as many colleges do not offer technical writing as a concentration in the English department, it is even harder to find an employee who has a degree in technical writing. With this information, it is not hard to believe the statistic that one-fourth of college graduates are not only poor writers, but lack proper communication skills altogether.
The Journal for Quality and Participation reports on several companies that lost big when it came to poor writing. Computer company Coleco eventually went out of business when customers who purchased its new line of computers found the instruction manual unreadable and returned the items. An oil company spent thousands of dollars to develop a new pesticide that had been written five years earlier by a technician in the same company but was so poorly written no one finished the report. A nuclear plant sent in a sales order for “ten foot long lengths” and instead of getting the ten-foot lengths they wanted, they instead received ten one-foot lengths. And, the list goes on.
According to the previously mentioned survey of business leaders, a little more than forty percent of companies offered or required additional training for employees with writing deficiencies. This training came with an annual cost of as much as three billion dollars. Add in the cost of poor writing resulting in liability to a company and that number grows substantially. Having just one staff technical writer could bring down this cost tremendously. Technical writers are diverse enough to fit into the pharmaceutical industry. Well-educated writers are able to explore a product and communicate its usefulness, process, what it means, and how it should be used clearly to the reader using as few words as possible.
In the pharmaceutical industry, Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) require instruction documents like Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) to be error free and written in an orderly fashion. It is as important for manufacturing documentation, reporting on problems, laboratory test methods, batch production records, etc. to all be crystal clear in its instructions. If employees are lacking in the skills to create crystal-clear, error-free instructions, then how are companies compensating for the deficit?
By having the necessary skills to research, understand complicated information, and tailor writing to many different readers, a technical writer within the pharmaceutical company is essential. By having a staff technical writer, companies can also save on training others within the company on the traits of technical writing. Any good technical writer can put together a session for others in the company detailing the traits common to technical writing and strategies for using them. Everyone within the company producing documents must be able to communicate detailed manufacturing procedures with simplification and directness reaching the end goal quickly and effectively. The steps must be written with extreme accuracy as lives depend on it.
A technical writing session for employees should include an introduction to technical writing. A brief description of clarity, conciseness, document design, audience, and accuracy are helpful. Then, the session should focus on strategies for using these traits in company documents like SOPs and batch production records. See Figure 1.
Figure 1: Technical Writing Strategies for SOPs
By creating good quality content and having the necessary skill to tailor a document to achieve maximum clarity, technical writers can help achieve positive results for any business. More importantly, they can train others within the company to produce a more sound technical document. Customers and clients will value the consistent professional look in company documents and communications and will feel informed and trusting of the information provided to them. This, in turn, can bring in more customers and clients, increase value for stakeholders, and improve employee relations throughout the company. By hiring a technical writer, not only is your business going to increase but you save on the three billion dollars’ worth of training writing-deficient employees each year and decrease the problems resulting from unclear writing plaguing businesses.
Be sure to evaluate the technical writing capabilities of Contract Development and Manufacuring Organizations (CDMOs) before starting your next project. Piramal Pharma Solutions knows the importance of producing sound, technical documents in the pharmaceutical industry. We employ technical writing to ensure more understandable SOPs and facilitate more executable batch records. Clients appreciate the consistency among the documentation and our employees appreciate the clarity of instructions and guidelines. Overall, we are more efficient as our documents become more efficient.
References: “Writing: A Ticket to Work…Or a Ticket out: A Survey of Business Leaders.” The National Commission on Writing. 2004. “Total Quality Business Writing.” The Journal for Quality and Participation . 1995.
Posted in Blogs on Oct 31, 2016


- Environment
- Information Science
- Social Issues
- Argumentative
- Cause and Effect
- Classification
- Compare and Contrast
- Descriptive
- Exemplification
- Informative
- Controversial
- Exploratory
- What Is an Essay
- Length of an Essay
- Generate Ideas
- Types of Essays
- Structuring an Essay
- Outline For Essay
- Essay Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body of an Essay
- Writing a Conclusion
- Essay Writing Tips
- Drafting an Essay
- Revision Process
- Fix a Broken Essay
- Format of an Essay
- Essay Examples
- Essay Checklist
- Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay Writing Service
- Admission Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Essay
- Academic Ghostwriting
- Write My Book Report
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Do My Assignment
- Buy College Papers
- Capstone Project Writing Service
- Buy Research Paper
- Custom Essays for Sale
Can’t find a perfect paper?
- Free Essay Samples
- Corporations
Pharmaceutical Industry
Updated 23 January 2024
Subject Corporations , Marketing , Europe
Downloads 29
Category Business , Economics , World
Topic Company
Summarily, this paper investigates the marketing dynamics that can apply in the European Union pharmaceutical sector in promoting a new medicine. The competition in the pharmaceutical industry in the European Union is intense; hence different companies have to develop unique methods of marketing their products. It is critical to employ the best model to ensure competitiveness in an industry that sees new entrants every time. Notably, it has been identified that pricing strategies are instrumental in ensuring survival of the product in the marketing despite intensive completion from existing medicine. Understanding the best pricing model is critical to the success of a company since many customers will tend to purchase products from companies that have lower rates. Additionally, this research paper discussed the trend in the EU pharmaceutical industry and how it affects companies` intentions to invest in research and development for innovation. The research indicates that companies that are focused on research and development have a better opportunity to have competitive pricing strategies as opposed to other actors in the industry. Other important aspects of this explorative research undertaking are the patent debate and reimbursement and how it impacts pricing strategies adopted by firms as a marketing tool. Companies that can successfully ensure they patent their products develop the best pricing model, which is vital in enhancing increased sales. Moreover, the research recommendations derive important insights on marketing that can assist a manager to apply pricing strategies and innovation as the best weapon to ensure survival in the highly competitive EU pharmaceutical market. The information is critical for new entrants in the industry since they will get a better understanding of the best marketing strategies they can use to attract a substantive customer base.
II. Introduction
The accessibility of health services is a human right issue within the European Union and hence, access to the necessary medicines is a government priority. The pricing system of the pharmaceuticals and the models of supply systems are critical elements in the achievement of the healthcare goals. The current initiatives by WHO on health systems aim at improving access, appropriate use and accessibility of medicine (Bigdeli et al., 2014). European countries in particular, have adopted policies on pricing and funding that are uniform so as to deliver quality medicine to their citizens. The pharmaceutical sector in the European market is regulated intensively as it is viewed to be a health, industrial and budgetary matter that is worthy of attention by all the stakeholders.
The self-medication market has experienced great sales in the EU market causing an alarm, hence necessitating the governments to introduce regulations that are based on the benefits and the possible risks that consumers derive from the medicines. Essentially, increase in the cases of self-medication has led to accessibility of healthcare to a lot of people in the EU but there are legitimate concerns over the misuse of the drugs.
Governmental control on pharmaceutical economics is influenced by factors that are crucial to the wellbeing of the population. Interestingly, the purchase model is not uniform, and the government has to strengthen the moral complexity regarding the right to access healthcare for the European populations. Pharmaceutical marketing has a life cycle in the European market that involves scanning to ensure that it is safe for use and further, an authorization is done for pricing and reimbursement. Additionally, the final stage in the cycle ensures responsible use of the pharmaceuticals to guarantee effectiveness of medicinal products in the long haul.
Nature and Scope of the Problem
The pharmaceutical industry in the EU region has an influential wave that shapes the government policy because of its impact in the achievement of healthcare objectives. Notably, this industry exhibits high levels of competition due to the pressure from various stakeholders on the discovery of new and better medicine. Pharmaceutical sector has over time been identified to have the greatest return on investment around the world.
Pharmaceuticals can be sold over the counter or as prescription drugs which necessitates for the application of an appropriate marketing strategy. The market that should be targeted as a result of the different end users could be medical professionals or the end consumers. The pricing strategy is a common challenge that faces the players in the pharmaceutical industry, especially, during marketing campaigns. The EU and individual governments are critical players in the overall architecture of marketing and authorization of new drugs in this market niche. Normally, EMA has a history of rejecting new medicines which leads to a lot of losses on new entrants in this industry.
This paper will delve on to the methods that are applied by the pharmaceuticals companies in developing pricing systems in a highly competitive environment. The pricing models adopted by the companies have an impact on the brand image, the company`s positioning and the reception by the customers. Information used in this research will be an explorative discussion about academic writings that are relevant to the topic of inquiry. In essence, the best pricing model exploits that balance that is established as a result of forces of demand and supply.
III. Background Information
The pharmaceutical industry in Europe has a great reputation around the world because of the existing track record that emanates from scientific innovation that contributes to discovery of new medicine. This topic was selected for dissertation because of the relevance of the pharmaceutical industry to economic growth of the European countries. A transformative and active drug manufacturing industry has a fundamental influence on trade, healthcare and development of science. Essentially, pharmaceuticals production is promoted by an economy that is knowledge-based.
A manager overseeing a marketing department with plans to introduce new pharmaceutical products in EU region must take into considerations the current dynamics of this industry to adopt the appropriate tools for successful launch. Concerns over investment on a new medicine have been raised by the major players in the industry due to the rising costs on research. Moreover, the regulatory authorities are adopting price austerity measures, while the authorizing agencies are introducing stringent regulations on quality and achievement of health objectives.
Research Objectives
Providing an understanding of the strategic pricing of new pharmaceutical products in the EU.
Providing recommendations to the new entrants about the pricing strategy of products.
Determining how patents influence the pricing of pharmaceuticals in the EU.
IV. Analysis of Trends in the Industry
New drugs are subjected to the rules that regulate the pharmaceutical industry in EU and at the national levels of the respective member states. Under the national competencies there are provisions that relate to allocation of resources, pricing of drugs and medicinal products reimbursement. The issue of ethics in the medicinal drugs corporations has gained a public momentum because many payments are made from the exchequer. The impact of globalization on the pharmaceutical market in EU has led to increased competition, as well as introduction of new opportunities. The manager of new entrants in the EU market should maneuver the rigid regulations to secure the most appropriate price for the product. Noteworthy, medicinal products face unwarranted trade barriers that create uncertainties over the authorization of marketing and pricing of new pharmaceutical products.
Source: Pharmaceutical industry regulators
Essentially, this figure shows in percentages the commitment of various countries to research and development in the pharmaceutical industry.
The pharmaceutical industry has evolved in contemporary times because of intervention by the EU through legislative and non-legislative rules with the ultimate aim of addressing the challenges that make it difficult for industry players to invest in research and innovation. Furthermore, there are major trends in the sector initiated by the governmental agencies to improve the competition policy so as to maintain the integrity of the pharmaceuticals market. ”Transparency Directive” frameworks have been developed with the objective of making the national pricing models better and open to public scrutiny (Babar, 2015). Understandably, the regulations by the various agencies are a trend that is necessary so as to ensure that drugs are viable economically and by adding of therapeutic gains to the users.
Analysis of Industry Trends from a Governmental Perspective
The issue of drug prices and reimbursement is a dicey matter in EU member states because it influences accessibility of medicine to patients due to factors such as affordability and availability. The appraisals for new drugs that are in line for launching have to comply with the different national regulations of the EU member states. The adoption of an external price referencing is not desirable as an industry trend because pharmaceutical companies introduce their product at a lower price in a particular market segment with the hope that they will increase it in another market.
Figure 1 above illustrates the major regions that engage in the pharmaceutical industry in the region. It is evident that Germany has a wider share as manufacturers; hence, they are at an upper hand in creating pricing strategies in the industry.
Policy changes that have been introduced via Lisbon Treaty gave EU a mandate to monitor the health systems of the member countries. Noteworthy, the EU policy instrument that have been adopted as a trend for the pharmaceutical market have made it attractive for patients to buy alternative generics so as to save costs. Healthcare in EU countries is usually a governmental responsibility that is implemented through a partnership with the insurance companies and any action taken at the regional level is meant to complement the national policies of respective countries. However, the issue of brexit has had a significant impact in the manner in which the EU countries relate in the pharmaceutical industry. It is difficult to develop policies that suit all countries in the European Union. The United Kingdom, for instance, is not part of the policies made by the EU (Lorgelly, 2018). Brexit has affected the pharmaceutical industry in a negative way since it is difficult to develop policies that are embraced by all the member countries (Song, 2016). It has affected the development of binding laws and regulations.
Essentially, in contemporary times manufacturers that have launched new pharmaceutical products enjoy some level of exclusivity on their patents thus enabling them to set prices that will cover all the costs incurred. The costs that are incurred in producing new pharmaceutical products have increased in modern times and the manufacturing companies are unable to assess them accurately (Enzmann, H., 2016). A scope of the regulations have been initiated by the governmental agencies in order to address the factors that lean on the demand side, consisting of patients and medical professionals, and the supply side that addresses market elasticity and the pharmaceuticals. The EU health laws and policies have been critical in establishing an industry that is guided by common regulations (Hervey et al., 2017). It becomes difficult for different companies to hike prices of pharmaceuticals since there is a set standard; hence, reducing monopoly and unfair competition.
V. Methodological Approach
The method applied in this research paper is exploratory because it involves an analysis of academic enquiries that have been conducted in this field. The data sources that are used in the paper are mainly reports from governmental agencies and reputable scholars that have an interest in the topic being discussed. In essence the justification of the methodology stems from the need to understand from a policy perspective the hurdles and opportunities that present for drug discoverers as they seek to gain market entry into the EU.
Essentially, an integral part of the research methodology that was applied in this study was a skimming of the pharmaceutical policies that have been introduced within the EU framework to control pricing and purchasing of medicines. The academic sources used in this review are seminar papers that have relevant information on the topic and other authoritative policy documents that have been influential in the development of legislations and regulations in the pharmaceutical industry. The scope of this explorative research is broad covering all aspects that have an impact on the development of a pricing strategy for a medicinal product in the EU market. Additionally, there is inclusion of the multi-dimensional nature of pharmaceutical marketing norms so as to come up with recommendations that can assist new entrants in setting the most appropriate prices (Hanf, 2011). The key phrases that are critical in this research paper include reimbursement policies, price regulations and market authorization.
Notably, the explorative study investigates the impact of generic medicine in influencing drug pricing policies at the country level. The issue of competition between the generics and the branded drugs that have IP rights has a bearing on the pricing strategies as different member states of the EU and their different regulations. The regulatory regimes of EU countries have been considered extensively in developing recommendations for a company that is a new entrant in this market niche.
Generic drugs are usually copies of drugs that have already been branded and they accomplish the same treatment goal that is intended by the manufacturers of the branded medicine. The competition challenge that is existent in the European market stems from the issue of generic and brand drugs in which the latter has gained prominence among the consumers due to their affordability. The non-patented pharmaceuticals have been problematic because they interfere with the market prices. The market for generic medicine has expanded significantly in the EU market contributing about half of the consumed pharmaceutical products. Governments are facing challenges on promoting the use of generic medicine to promote access to healthcare while at the same time ensuring that are innovations in the pharmaceutical industry (Herr, and Suppliet, 2012).
This paper studies diverse methods for pricing of new pharmaceuticals on the European market. This includes medicines developed for humans, without pharmaceutical equipment. Different strategies will be discussed along with their consequences for the selling company regarding finances, customers and brand image. Before jumping into further detail, there are a couple of concepts that need to be explained.
Porter`s 5 Forces of Analysis
The pharmaceutical industry has a lot of stakeholders that have vested interest and in some other cases power to control the market dynamics and the prices. Pharmaceutical companies have to invest on stakeholder management so as to address various interests that interplay in negotiating for prices and ensuring that customer needs are satisfied. The pharmaceutical industry is based on innovation and the pricing system is hinged on the competition policy. European Union enforces the authorization regulations for drug manufacturing companies within the body`s jurisdiction. Pharmaceutical companies in contemporary times have to satisfy the perceptions on value from stakeholders such as payers to be given access to markets (Sendyona et al., 2016). The growth and factors that influence economic success of companies operating in the pharmaceutical sector depend on the level of innovation and the investments on research and development. The marketing campaigns of pharmaceutical manufacturers should have clear and concise messages that appeal to the needs of the customers.
A new entrant in the pharmaceutical industry in Europe should consider factors relating to their customer base, the competitors and the capacity of the organization to position itself in a particular market niche. Noteworthy, a new pharmaceutical organization must establish clarity in terms of ensuring that it possesses a differential advantage and a clear understanding of the target market. The products offered by a drug manufacturing organization must be memorable to the consumers in order to create a relationship that develops to loyalty (Vogler and Martikainen, 2015. The differential advantage that is enhanced by the introduction of new pharmaceutical product has to be credible from the analysis of a consumer. Additionally, the innovation introduced in new products is supposed to give the companies a competitive edge in the market.
Competition in the Industry
The pharmaceutical sector in Europe exhibits intensive competition and the participants are in the private sector, as well as government agencies. The factors that influence competition are price, reliability of the products and customer service. Claim to patents and the manufacturing rights guarantee the new entrants a chance for survival in the market. Changes in the industry because of acquisitions and mergers have an influential role in the development of the pharmaceutical sector (Margaret, 2007). A new entrant in a highly rigid market in terms of regulation should have distinctive advantages over other competitors.
The critical element that is valuable for new entrants in the pharmaceutical industry lies in the development of a branding policy that creates an identity for a product. Customers are attracted to drugs that have closer associations and a strong perception on quality (Fernandez Utges Manley, 2015). The position of a new product is important because it is hinged on consumer needs and preferences, an undertaking that can assist a corporation to dominate the market.
The power of the suppliers
Pharmaceutical companies have to put into considerations various aspects of the market they ventures are located before implementing pricing strategies. Essentially, to address the pricing challenges new entrants can create market segments with the aim of offering products that address the specific needs of a particular group in a population.
Substitutes
The main concern for the pharmaceutical market is the existence of substitutes because they have the capacity to devalue the branded products hence creating a risk of vulnerability. Furthermore, the impact of globalization in the pharmaceutical industry has led to an increase in the manufacturers in the hope of reaping super profits. The aspect relating to expiry of patents is problematic because it encourages the production of generics that compete with the branded drugs. Pharmaceutical corporations have a responsibility to capitalize on the opportunities that are induced by the influence of globalization and neuter threats that are posed by the saturation of the markets (Colak, 2014). Launching new branded drugs demands an introduction of a marketing infrastructure that will aid in the building of a reputation for the brand. The competition from the herbal drugs can be quelled mainly due to their inability to prevent health conditions such as cancer.
PESTEL Analysis
1) Political
Politicians on their part view of process of pricing for the pharmaceuticals to be exploitative and a preoccupation of cartels whose intention is to profit from the public. The companies are forced to engage a wide array of stakeholders to understand the complex process of pricing that is primarily determined by valuation. Pricing attracts political attention; hence, becoming a source of debate on the issue (Löfgren, 2017). The pharmaceutical industry is attracting attention from the policy makers because of its role in the achievement of the healthcare goals. Notably, healthcare services have become expensive and this is a responsibility that EU countries national governments have taken as a burden that over time has morphed to be an election agenda. The repercussions on the industry are stringent measures by governments that are under pressure to deliver on healthcare by the citizens.
2) Economical
The high competition levels in the pharmaceutical industry has contributed to innovation leading to introduction of new products and market entrants that are facing hurdles in gaining foothold in the sector. However, more companies have been established in the industry and there is a growing portfolio of the products in this segment and eventually the economic benefits have been extended to the public through buying shares and securities from the listed drug manufacturers.
The social aspect of pharmaceutical companies in the EU region is mainly on the commitment to their corporate responsibility. The mainstay of pharmaceutical companies is the achievement of a social need by delivering quality healthcare. Drug manufacturing companies are more responsive to the issues in the society by driving innovations that contribute to wellbeing of the society. Drugs manufacturing companies must adhere to established systems of social accountability, corporate compliance, philanthropy and ethics.
4) Technological
Innovation has been a major driver of developments in drug manufacturing sector in the EU region due to the pressure to develop better drugs and the competition emerging from the generics leading to reduced prices of branded medicine. Undoubtedly, the EU market is highly competitive and industry players have to invest heavily on research and innovation so as to remain relevant and come up with products that address the contemporary health challenges. Companies have a risk of being defined as venerable in case the health products they produce are inferior compared to those offered by the competitors.
5) Environmental
The aspect of compliance in the pharmaceutical sector has been reinforced because of the underlying factors relating to customer preference by demanding quality and a fair pricing for medicines. Consumers of the products solely depend on the trust that is established between them and the regulatory authority to protect their interest in the sector. The overhead costs that are associated with the regulation and compliance requirements reduce the investments that are directed towards innovation. The research initiatives undertaken by the companies in the pharmaceutical industry are focusing on the aging generation because they are biggest consumers of the drugs.
The political environment and the society in general have great influence in the functionality and operations conducted by pharmaceutical companies, especially on matters ethics. However, regulatory authorities have greater mandate in ensuring that there is compliance with the laws for consumer protection. Essentially it is incumbent upon the company to demonstrate its compliance to safety standards and the effectiveness of administering the drugs manufactured on the patients.
VI. Contemporary Pricing Strategies in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Drug pricing has remained as a contentious issue that has affected the entry of new players in the EU market due to the risk of intensive competition from well-established companies. Noteworthy, price strategies in this unique market are affected by the market forces, intensive political scrutiny and pricing regulations that discourage introduction of new products because of the rigidity of market entry (Aaker and McLoughlin, 2010). In essence, developing the appropriate pricing system is critical because it will offer immense value. Drug manufacturers are facing a lot of challenges in contemporary times, especially with regard to the introduction of new drugs to improve the standard of care with no peer to support the evaluation. It is; therefore, critical for companies to develop effective marketing approach in the industry (Lidstone and MacLennan, 2017). Having a sound marketing plan is vital sine it will increase the customer base of the pharmaceutical products.
Determination of the pricing for a pharmaceutical product
The contemporary times pricing norms for new products in the pharmaceutical industry are determined by their effectiveness in terms of therapeutic gains to the consumer. The main determinant that eventually leads to price wars is the therapeutic advance that embodies a drug that is introduced in the market (Carone et al., 2012). Drugs that have greater therapeutic results on the patients may have their prices twice those of comparable levels. Competitive pressures play a significant role in terms as launch prices are influenced by the pricing of the substitutes. Duplicate products such as generic drugs are essential in the development of pricing strategies for the pharmaceutical industry.
Pharmaceutical company have caused a media uproar due to increase in the prices of drug which is not related to the rate of inflation. In essence, there are numerous issues that affect the pricing system that is adopted by EU countries in an effort to control the pharmaceutical industry. The services of an auditor are in most cases necessary in determining the unfair practices that could be sanctioned by stakeholders in the industry. The pricing strategy in the EU has had to be developed effectively to ensure there is fairness in the market (Faulkner et al., 2016). It has also been a key strategy used by companies to ensure they have a competitive edge in the market.
Pricing strategies have a major impact on timing that launch of new products is done and the reception by the target market. Countries that institute price controls in their market make it difficult for external players and new entrants to gain entry into the EU pharmaceutical industry (Margaret, 2007). The legal framework has also made the pricing regime in the EU regime complicated because of allowing the import of parallel substitutes. Price regulation practices in one region affects the pricing strategies of the domestic firms and entry of external investors in the market.
Pricing Regulations
Price change is impactful on supply of drugs within the EU and the method applied in reimbursement influences the relationship and the memorability of a particular brand. Essentially, a cross-reference pricing system is adopted because it is agreeable among the decision makers. Furthermore, there are greater incentives with regard to strong incentives that are introduced due to effect of spill-overs as a result of impact by foreign drug prices (Vogler and Martikainen, 2015). However, to alleviate the problems that are associated with cross-referencing in pricing and index that considers all the countries should be created in determination of the definite price for reimbursement.
Challenges facing pharmaceutical industries in percentages
Source: EU policy documents.
Figure 2 provides an overview of the challenges players in the pharmaceutical industry face. The major problem is increased manufacturing cost, which influences the pricing of the products. Additionally, the increased customer expectation to lower the prices of the products also forms part of the big challenges the industry faces. It becomes difficult to balance between the customer expectation and the profitability of the company.
Introducing a new pharmaceutical product in a market like EU that adopts a differential pricing system can be transformative because it gives incentive for the innovators that introduce new drugs in the market. The dicey issue that investors in the pharmaceutical industry is the inability to recover costs that relate to research and development (Ruggeri and Nolte, 2013). In Europe, the prices of the pharmaceuticals are decided at the national government`s level. Drugs are provided as a form of subsidy which is supposed to be reimbursed by the payers. In case, the health insurance is introduced by a company that enjoys monopoly, then, there is high likelihood that it will influence the drug prices. In essence, the manufacturers do not have the opportunity to negotiate the prices of the medicines in the various countries within the EU framework (Simoens, 2012). Notably, adopting profit maximization strategies can only be effective with delayed distribution of innovative medicines or ultimately avoiding their access which affects access of healthcare impacting on welfare. The patients in a very competitive market for pharmaceuticals are denied access to new medicine.
The regulatory pathway for the European Union is developed by the European Union Medicines Agency (EMEA) that has legislative authority with regard to allowing industry players to introduce new products. New market entrants have to be aware of the existing pricing systems and they have to negotiate with the national governments and agree on a refund rate. Essentially, there is a determination of the additional benefits that patients will derive from the new drug to another comparative product that is expedient (Kyle, 2007). The negotiations for refund rates are negotiated in case there is an identifiable benefit that will accrue to consumers by using a particular pharmaceutical product compared to another. Noteworthy, the pricing strategy for a new entrant is determined by their ability to come up a with a product differentiation that will lead to therapeutic benefits for the consumers. A pharmaceutical company that introduces a medicine with additional benefits has a legitimate basis to charge a higher price as part of the comparative therapy.
VII. Challenges Facing New Pharmaceuticals in EU Market
New pharmaceutical companies in the European market face great challenges due to the rigidity of the regulations and the complexities of the pricing systems. In essence, an additional benefit emanating from investment in innovation will guarantee a new entrant in the pharmaceutical industry a greater power in the negotiation of a higher price compared to other substitutes in the market. The major issue of contention that is existent between entrant pharmaceutical companies and the regulatory authorities stems from the selection of a comparative therapy that is an under-priced generic product (Cravens and Glover, 1995). Market authorization and pricing is approved upon evaluation of the dossiers that are delivered by the pharmaceutical companies with the ultimate aim of ensuring that the consumer is protected from exploitation by the manufacturers.
The price negotiation for drug discoverers as players in the pharmaceutical sector should start in initial stages so as to define the impact expected from a project and the end points that will be realized. The trial design is critical in the determination of the pricing and the model reimbur
Deadline is approaching?
Wait no more. Let us write you an essay from scratch
Related Essays
Related topics.
Find Out the Cost of Your Paper
Type your email
By clicking “Submit”, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy policy. Sometimes you will receive account related emails.
404 Not found

- Order Now
Quality In Pharmaceutical Industry Management Essay
Published Date: 23 Mar 2015
Disclaimer: This essay has been written and submitted by students and is not an example of our work. Please click this link to view samples of our professional work witten by our professional essay writers . Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of EssayCompany.
since any minor failure in fulfilling the standards of quality among all the phases of production process can lead to serious damages on the end user's health or even life. Moreover, quality impacts the success of a business financially as any defect in quality may result in a bad reputation and lead to serious financial damages.
All production stages need quality assurance activities at several points (Shah, 2004), consequently, quality must be considered from various points of view. It is not about products and services anymore; there are also other aspects to be taken into consideration like processes, employees, suppliers and business partners in general.
Various standards are the applicable around the World, the majority of which compliant or inspired to the wide framework of General Manufacturing Practices ("GMP").
This essay analyses some of the quality issues related to the application of these standards in secondary production of tablets, the most common drug dosage form today (http://www.pharmamanufacturing.com/articles/2008/096.html). The aim is to highlight in particular the impact on quality of product transfers both internally (across the production line) and externally (through supply chain and distribution).
Secondary manufacturing is the supply chain node where the inert materials (called "excipients") are added to active ingredients ("API") produced in the primary manufacturing step and the final product is made available for market distribution through market warehouses/distribution centres, wholesalers and retailers/hospitals (article: "Pharmaceutical supply chains: key issues and strategies for optimisation").
Firstly, the quality issue is introduced, with a particular attention to GMP framework; then some strategic and design issues in the pharmaceutical supply chain are analysed, highlighting the importance of applying quality standards on all the steps and some suggestions are given; thirdly, the production line of solid doses is analysed and some suggestions to increase the quality of the product are provided.
Quality framework in the Pharmaceutical Industry
GMP is a legal system originally inspired by Food and Drugs Administration ("FDA") concerning the minimum level of quality which is necessary to obtain in pharmaceutical and medical industries. By observing these guidelines, companies can assure drugs' specification, effectiveness, quality, purity and safety. Over 100 countries obey GMP as one of their standards, using it as the base of their quality system. This framework provides testing procedures, laboratory based examinations and measures of proportion and weight of the ingredients to be applied before, during and after manufacturing process to make sure that the predefined requirements match the finished product.(pharmainfo,2009)
While in other markets, segmentation results in various approaches to investments in product's quality, in the pharmaceutical industry, since people's health is involved, businesses must try not to compromise on quality. Releasing low quality pharmaceutical products may result in hazards and as a consequence in customer claims, which will end into financial losses. Therefore having products with good quality that provide effective healthcare for customers will improve their trust in the product and provide a financial benefit to the company.
On the other hand overspending on quality is not always a good idea. In the very high levels of quality, every small step forward will be tremendously expensive resulting in products that are not significantly better than rivals, but with higher prices. This approach is not suitable from a business point of view as, in order to maintain a competitive position in the market, companies should renounce to part of their profit margins. Hence, spending on quality should be a trade-off between higher profits and appropriate quality levels.
Expenditures should be definitely focused on the production system, but this could be inefficient if not supported by adequate supply and distribution management systems which guarantee product's reliability as illustrated in the next paragraphs.
Quality issues in the extended supply chain
Nowadays competition is not anymore a matter of independent entities interacting in the marketplace: competitive advantage lies in developing strong partnership as "supply chains compete, not companies" (Christopher cited in www.emeraldinsight.com/1750-6123.htm). Consequently, effective quality management systems should be extended to cover suppliers' and sub-suppliers' manufacturing processes and sourcing strategy should be assessed to identify possible improvements (Rathore and Low, 2010).
As raw material plays a significant role in producing quality and safe drugs; the route towards developing quality pharmaceutical products starts with selecting proper ingredients.
In secondary manufacturing processes, two main families of raw material are managed: excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredients ("API"). While the latters are already heavily regulated, controls on the formers, generally considered safe being originated from the food industry, are becoming increasingly important due to emerging of new excipients (http://www.touchbriefings.com/pdf/890/PT04_rafidison.pdf). These raw materials contribute the most to product variability and, as manufacturers are legally responsible for their quality, it is essential to put in place proper raw material management systems to minimise possible negative impacts on production's performance facilitating implementation of Quality by Design.
Nowadays most of the pharmaceutical raw material is providing from China and India. They are the main producers of raw material especially for third world countries. Besides all the rules and regulation about the quality and control limit, sometimes the quality of the product they are producing is not acceptable. By having an efficient laboratory and lab technicians it is possible to control the raw material which is coming to the factory and send back the raw material which is not in the control limit.
Perfect! Thanks, I'll add/search for references on that!
As the survey conducted in 2006 by Aberdeen Group (cited in Littlefield, 2007) indicates, pharmaceutical companies could achieve compliance and traceability success not only by automating raw material but also finished product traceability, eliminating manual activities.
Stakeholders along the whole pharmaceutical supply chain recognise the critical importance of solutions like bar coding and radio frequency identification ("RFID") to track products from manufacturing plants to retailers as the extension of traceability to the single final product maximizes quality management and safety control (ZIT, 2008). Their usage is encouraged by: regulatory agencies aiming to ensure product security eliminating inefficient paper-based systems (FALKEN Secure Networks, 2009); providers interested in quality of care and patient safety; suppliers looking for effective and cheaper methods to control inventory improving productivity and profitability (ZIT, 2008).
Track-and-trace systems are frequently used to support forward logistics activities and stem sales of counterfeited drugs, estimated to reach $75 billion in 2010 (Centre for Medicines in the Public Interest cited in ZIT, 2008); however, it could be beneficial to reverse supply chain logistics as well, considering that returns handled annually worth approximately $2 billion (Health Distribution Management Association cited in ZIT, 2008), varying between 3 and 6% of annual sales (Hunter et al. cited in Kumar and Dieveney and Dieveney, 2009).
In the majority of cases, distribution and returns are handled by third party providers (Valero cited in Kumar and Dieveney and Dieveney, 2009) not being a core competency of pharmaceutical companies and batch visibility is lost as products proceed through the supply chain (ZIT, 2008): some technology providers, as for example Falken Secure Networks (2009), are promoting the introduction of a tracking system based on RFID technology common to all players in the supply chain to improve visibility, collaboration, real-time information flow and reverse logistics efficiency. Reduction of losses along both forward and reverse logistics processes would offset costs for implementing the system (Kumar and Dieveney and Dieveney, 2009). Such systems seem to be effective: Pfizer, for example, implemented it since 2006 to limit losses for one of the most counterfeit drugs like Viagra in the United States (O'Connor, 2006).
Quality issues from the production point of view
Most of the companies in various industries are competing to improve the processes of quality management in the production process; however, quality has always been a low priority in pharmaceutical industry. This has become an issue since companies had to pay more than $700 million on observances because of low quality since 2001. On the other hand it causes a remarkable reduction in revenue. The compliances take large amount of effort to address from management level of the company, which is the most expensive human resource level, and in some cases caused up to 20% increase in unit cost.
Pharmaceutical industry managers are usually resistant to applying quality management in their companies because they believe that having regulations related to quality reduces the agility of company confronting the changes. Meanwhile, some companies in this industry have managed to use quality management and also minimizing the risk of regulations. Â
Having these issues, most companies decided to just throw away the defected produces in production line to make sure that customers receive high quality product. This is neither cost effective nor sustainable. Therefore, quality management among the whole processes seems to be essential rather than just monitoring the final product.
To enjoy the benefits of quality management as well as avoiding the regulations, managers tend to build a cultural inspiration among the people involved by defining, fully understanding and being committed to the quality objectives of the company. These objectives must be clear, measurable and comprehensible. Managers will exactly know what to focus in the production process to resolve the bottlenecks and produce quality products. (Dsouza, 2007)
The initial idea for making a tablet was first developed by machinery as the tablets cannot be made by pressing powders. As the result of above phenomenon, the very old traditional methods to make tablets, forced tablet producers to first make granules in a pot named the mixer blender granulating machine: this step is called "granulation". Wet granules, being made in a granulator, does not come to equal shapes and sizes and it has to be passed through a calibrating mill in which the mesh sizes of prepared granules can be made more uniformed granules. These uniformed granules led to a fluid bed drying machine where they will be dried thoroughly by the help of hot air and fluidization of the particles inside a container. Then again the particles have to be uniformed in a dry calibrating mill before going into final blender. After the preparation of the powder it will be formed by tablet press machine: this step is called "compression". Prepared tablets are then subject to coating in a machine called coater. After further quality controls, the final stage for tablets is packaging them in bottles, strips or blisters (Shah, 2004).
For each packaging system, there are different machines involved in order to protect the prepared tablets against moisture, light, temperature and most importantly against contamination.
The above procedure ever since the old times still remain the same but with much more sophistication to ensure a wider range of protection of the prepared tablets against possible above environmental effects. Such protection has hence being defined by guidance described as GMP and cGMP (can we add some details on this?).
We can put something here but it is just going to be the explanation and I don't think he is going to like it. My recommendation is not to write anymore but if you have useful information which can be add to this part and relevant to it tell me.
I just was saying, can we add:
- a reference that certifies that GMP/cGMP state that
- can we introduce cGMP in the Rules/regulations part as we don't cite it
Transferring the raw material and semi finished product
Historically, the procedure of transferring material from one machine to another during the production process was performed manually by operators. The human involvement during the pharmaceutical manufacturing process is critical for three reasons: firstly, it could affect quality of products consequently to unavoidable human errors; secondly, it could damage the product by direct contamination as a lack of employees' hygiene and sanitation can threaten quality as well; lastly, safety of employees themselves can be undermined by inhaling small particles of simple drugs at production line.
Consequently, with development of technology, more modern and automated methods were utilized to minimize the risk of contamination: the evacuation of products from one machine to the next was then helped by vacuum through special containers which involved vacuum pump and filters. Benefits achieved with this method were offset by high costs and complexity. Subsequently, a further improvement has been achieved exploiting gravity with the use of lifters enabling the product to circle around the production line in a closed loop system. This method was found to be safe, practical and also less expensive than the vacuum. For such method, special product containers were created which had a loading port on top and unloading port at the bottom, both being facilitated for manual operation or pneumatic valve for automatic operation. In some cases when a more difficult powder or wet granules was involved, a helping vibrator could also be installed to ease down the product in to these containers. These containers were made by special shape and angles so as to be able to empty all products into the next unit and it also could be attached to a lifting device.
As shown above, the presence of humans along the solid dose line can negatively affect the quality of product. To avoid the massive consequences of this, which can cause financial disasters for the business, companies could provide their employees with professional training and proper hygiene facilities as having skills and appropriate training material and constant development minimizes the errors, optimizes the efficiency and therefore improves the quality. This results in continue personnel training investments and would not completely avoid errors and contamination risks.
Differently they could opt for investments in automation which can help pharmaceutical factories to minimize operators contact with the product during the process. By reducing or even eliminating operator's involvement it is in fact possible to lower occurrence of human fault.
Suggestion for a new layout of the plants
Traditionally, pharmaceutical companies had a flat layout and there are still many factories (Reference) which are following this instruction because of its simplicity. With this layout operators have a direct contact with product as they are responsible for manually transferring the powder from one machine to the next; all machineries are in a horizontal line like the lay out below:
[Insert picture]
As shown above in this essay, technology developments leaded to the introduction of vacuum and lifters Although this method is very useful and shows a first tendency to move the production flow to a vertical layout, as shown in the picture below, this is still based on a flat factory and thereby is quite expensive and presents some technical disadvantages.
Our suggestion to improve production quality is to exploit gravity, building new pharmaceutical factories with a 4 or 5 floors layout instead of wider flat buildings.
The most important advantage of making the factory in different levels is that instead of putting the machinery in a horizontal line, it is possible to put it vertically. It is obvious that much more precaution has to be taken into account when some dangerous materials like hormones, anticancer drugs and biological and sensitive drugs are being processed. Nowadays, for this kind of material partial or total containment is designed and utilized. In such restricted areas no operators are allowed and the entire process is designed to be fully automated and monitored from an outside room using SCADA systems (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition), compliant to rules and regulations of FDA and according to CFR21 part 11 Guidance. These systems control and monitor each and every single step of the process and record all parameters according to the validation documentations for regular and future revalidation in case of need. Such containments involve some very advanced and patented technologies and since no human is involved the risk of mistake are considerably minimized; this technology, however, is extremely expensive and cannot be used by the majority of pharmaceutical companies.
What is the problem here?
Just two things:
CFR21 part 11 Guidance Æ’Â what's that? Could you add further details as the reader doesn't know what is that?
Some further details also on this "validation documentations for regular and future revalidation"?
This (what?)( The reason the pharmaceutical companies are not using this technology which is expensive. Elena isn't it clear? No, sorry....it seems like we are suggesting the new layout to substitute the containment areas...) is the reason why we are suggesting this layout which is much cheaper and can be equally efficient. By using this layout we can minimize operator's presence and omit some extra machinery like vacuum and lifter.
This is our suggested layout.
By this method it is possible:
To reduce the human involvement and unwilling effects on the products;
To protect operators from possible harmful effects of raw material and semi-finished products;
To protect the environment against possible and constant distribution of product's particles and chemicals;
To control containment with regular and pre-determined conditions such as temperature and humidity;
To guarantee total protection against possible contamination coming from operators, environment or even from the equipment itself;
To reduce to a minimum creation of dust inside the powder-making room due to the closed loop created with this layout.
Conclusions
This essay shows the importance of product transfers as a key area on which pharmaceutical companies should work to gain quality improvement. The main focus is on production line for solid doses, the most common drugs dosage form today.
The theme of transferring material has been analysed from two points of view: external and internal to the production plant. The first refers both to supply management and the importance of properly managing raw material as it is fundamental to reduce product variability as well as to management of forward and reverse logistics. The second refers to the transfer of raw material and semi-finished product along the production line and the importance of reducing or eliminating direct human interaction as it can generate threats to product quality as well as to employees' safety.
Some suggestions for improvement are given on both aspects: the introduction of an integrated supply and distribution system would enable raw materials traceability, avoid drugs' counterfeiting and help returns management while the redesign of factory's layout can help generate higher quality levels by improving process automation and reducing to a minimum human contamination.
RAJ,G.,2009, REGULATORY ASPECTS AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT IN GENERIC PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRY, [Online] Available at: http://www.pharmainfo.net/gabrie/publications/regulatory-aspects-and-quality-management-generic-pharmaceutical-industry-fourrt [December 2010]
Dsouza, A., Keeling, D. and Phillips, R., 2007. Improving quality in pharma manufacturing. The McKinsey Quarterly.

Our Service Portfolio
- Essay Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Assignment Writing Service
- Coursework Writting Service
- Article Writting Service

Want To Place An Order Quickly?
Then shoot us a message on Whatsapp, WeChat or Gmail. We are available 24/7 to assist you.

Do not panic, you are at the right place

Visit Our essay writting help page to get all the details and guidence on availing our assiatance service.
Get 20% Discount, Now £19 £14 / Per Page 14 days delivery time
Our writting assistance service is undoubtedly one of the most affordable writting assistance services and we have highly qualified professionls to help you with your work. So what are you waiting for, click below to order now.
Get An Instant Quote

I DON'T WANT DISCOUNT
Our experts are ready to assist you, call us to get a free quote or order now to get succeed in your academics writing.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Introduction. The quality in the pharmaceutical industry has become a very important topic. Since the world has gathered together to harmonize its practices and guides and the launching of the FDA current good manufacturing practices - the cGMP; for the 21st century - there has been a growing awareness for the significance of the quality of the pharmaceutical products (Woodcock, 2004).
GMP is a legal system originally inspired by Food and Drugs Administration ("FDA") concerning the minimum level of quality which is necessary to obtain in pharmaceutical and medical industries. By observing these guidelines, companies can assure drugs' specification, effectiveness, quality, purity and safety. Over 100 countries obey GMP ...
all of the time. Quality risk management is defined as a technique for assessing risk, controlling risk, communicating risk, and reviewing risk to the drug-quality. product's It is a widely used tool in the pharmaceutical business for assessing medication risk 'Q' - Quality Topics i.e. Those related to chemical and Pharmaceutical Quality Assuarance
Quality Assurance (QA) is a wide concept and covers all aspects that could have an impact on the quality of prescribed pharmaceutical products. The objectives of QA are: to ensure that the prescribed medicine competently provides the desired effect to the person taking it; to protect patients from accidentally being administered an incorrect or ...
1.1 Introduction. The pharmaceutical precinct relies blisteringly on quality control and quality assurance. Drugs must be promoted as safe and clinically effective with uniform and foreseeable functioning. Novel and improved therapeutics are being developed at a galloping pace.
Pharmaceutical industry has a responsibility of developing, producing and marketing of drugs licensed for medication purposes. It is the only body allowed in dealing with drugs having met the set conditions, which vary from country to country. This research paper will analyze the pharmaceutical industry based on its market size, research and ...
Quality is one of the most important management principles for any organization regardless of industry. This is particularly true for the pharmaceutical sector: maintaining quality product standards is essential for the prevention and treatment of numerous medical disorders. Although the pharmaceutical industry has been around for centuries, in ...
Quality audit is a review and evaluation of all or part of a quality system. with the specifi c purpose of imp roving it. It is one of th e mean s to examine pharmacy programs and ensures that the ...
Effective Quality Assurance (QA) is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry for several reasons:-. Patient Safety:- The primary goal of QA in the pharmaceutical industry is to ensure the safety of patients. QA measures are in place to prevent the distribution of unsafe or ineffective products that could harm patients.
Pharmaceutical Industry the Purpose of. This relationship has an effect on the payment rates that CMS sets. Higher cost pharmaceutical therapies are systematically reimbursed below acquisition cost (i.e., the payment system is biased against full reimbursement for higher cost therapies). Reimbursement compared to acquisition cost for the top IO ...
From the researcher's point of view, big pharmaceutical corporations are putting huge profits on top of patients, spiraling shammed public relations campaigns and more. Before the recent changes, Medicare CEOs and these companies had been reported to have involved in frauds worth billions of shillings. We will write a custom essay on your topic.
One aspect of pharmaceutical quality assurance that is very important, and that anyone working in the industry should be aware of, is technical writing. Technical writing is different from other kinds of writing, because it is focused first and foremost on clarity. Long sentences and descriptions might work well in an article or book, but not ...
Objectives. The purpose of this study was to highlight the common errors and pharmaceutical malpractices that people usually engage in on a daily basis and to correlate these to culture, gender and educational levels. This may spread awareness in an easy and understandable manner and provide certain guidelines to drug consumers ensuring that ...
The pharmaceutical industry can be challenging even for experienced medical writers. The key is to commit to learning, maintain unwavering attention to detail, and determine a niche that maximizes your background and skills. Categories: Career development , Regulatory writing.
Bringing Access And Quality Together. As the pharmaceutical industry moves ahead, the essential task is to meld the innovation seen in drug development with the imperatives of access and quality care.
The social component of ESG ratings in pharma can be divided into three main topics: Employee management: Driving employee satisfaction, ensuring a diversified workforce through strategic sourcing, and providing increased transparency over gender pay ratios. Health and safety: Compliance with health standards and deployment of proactive safety ...
Pharmaceutical companies research, develop, market, and/or distribute drugs. Some of the major pharmaceutical companies (a.k.a. Big Pharma) in the world are Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Sanofi Aventis. Biotechnology companies may also produce drugs but use derivatives of biological systems or living organisms.
A technical writing session for employees should include an introduction to technical writing. A brief description of clarity, conciseness, document design, audience, and accuracy are helpful. Then, the session should focus on strategies for using these traits in company documents like SOPs and batch production records. See Figure 1.
The pharmaceutical industry in Europe has a great reputation around the world because of the existing track record that emanates from scientific innovation that contributes to discovery of new medicine. This topic was selected for dissertation because of the relevance of the pharmaceutical industry to economic growth of the European countries.
1. Introduction. The quality in the pharmaceutical industry has become a very important topic. Since the world has gathered together to harmonize its practices and guides and the launching of the FDA current good manufacturing practices - the cGMP; for the 21st century - there has been a growing awareness for the significance of the quality of the pharmaceutical products (Woodcock, 2004).
In spite from the extensive investment in research and development int the Cadain pharmaceutical industry, considerable gaps available over […] Wie to Write a Pharmacy School Admission Essential. Healthcare may not may to write much essays in their day jobs, but many of them had to write einer essay to get into pharmacy school.
Disclaimer: This essay has been written and submitted by students and is not an example of our work. Please click this link to view samples of our professional work witten by our professional essay writers.Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of EssayCompany.
www.wjpps.com │ Vol 10, Issue 11, 2021.│ ISO 9001:2015 Certified Journal │ 1830 Yutika et al. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences The industry does a lot to advance the health and well-being of people around the world. Developing vaccines and drugs to reduce and treat disease is only part of the role of industry