227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples
If you’re looking for a good depression research title, you’re at the right place! StudyCorgi has prepared a list of titles for depression essays and research questions that you can use for your presentation, persuasive paper, and other writing assignments. Read on to find your perfect research title about depression!

🙁 TOP 7 Depression Title Ideas
🏆 best research topics on depression, ❓ depression research questions, 👍 depression research topics & essay examples, 📝 argumentative essay topics about depression, 🌶️ hot depression titles for a paper, 🔎 creative research topics about depression, 🎓 most interesting depression essay topics, 💡 good titles for depression essays.
- Depression and Solutions in Psychiatry
- Depression as It Relates to Obesity
- Depression: Case Conceptualization and Treatment Planning
- Teenage Depression: Causes and Symptoms
- The Concept of Postpartum Depression
- History and Treatment of Depression
- Components of the Treatment of Depression
- Social Media as a Cause of Anxiety and Depression Anxiety and depression are considerable problems for world society. Numerous studies have linked high social media use with high levels of anxiety and depression.
- Geriatric Depression Scale, Clock Drawing Test and Mini-Mental Status Examination Depression is a common condition among geriatric patients. Around 5 million older adults in the US experience significant morbidity from depression.
- Does Social Media Use Contribute to Depression? Social media is a relatively new concept in a modern world. It combines technology and social tendencies to enhance interaction through Internet-based gadgets and applications.
- Transition Phase of Depression and Its’ Challenges Providing psychoeducation to people with mild to moderate depression, strategies for recognizing and addressing conflict and reluctance are discussed in this paper
- Adolescent Mental Health: Depression This paper includes depression background discussion, including its signs, prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment, and a plan of treatment with three interventions to address this chronic health disease.
- Action Research in Treating Depression With Physical Exercise Depression is one of the most common mental health disorders in the United States. The latest statistics showed that depression does not discriminate against age.
- Impact of Depression on a Family The article makes a very powerful argument about the effects of depression on the relatives of the patient by identifying the major factors that put the family into a challenging position.
- Depression and Depressive Disorders Depression is one of the leading causes of disability in the world. Symptoms are feelings of sadness and guilt, changes in sleeping patterns changes in appetite, and other.
- The Rise of Depression in the Era of the Internet Understanding how the Internet affects human lives is essential in ascertaining the reasons for the growing loneliness in the intrinsically connected world.
- Application of Analysis of Variance in the Analysis of HIV/AIDS-Related Depression Cases Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a commonly used approach in the testing of the equality of various means using variance.
- Major Types of Depression This paper will review and analyze two scholarly articles concerning depression, its sings in male and female patients, and its connection and similarity to other disorders.
- Major Depression’ Symptoms and Treatment – Psychology A continuous sense of tiredness, unhappiness, and hopelessness are key signs of clinical or major depression. Such mood changes alter the daily life programs of an individual for sometimes.
- Depression: Psychoeducational Intervention This paper considers the peculiarities of the application of psychoeducation in depression, including advantages, limitations, and ethical aspects.
- Mitigating Postnatal Depression in New Mothers: A Recreational Program Plan Post-natal depression is a popular form of depression in women. This paper presents an activity plan for the use of leisure as a therapeutic response to post-natal depression.
- Baby Blues: What We Know About Postpartum Depression The term Postpartum Depression describes a wide variety of physical and emotional adjustments experienced by a significant number of new mothers.
- Self-Esteem and Depression in Quantitative Research The topic that has been proposed for quantitative research pertains to the problem of the relationship between self-esteem and depression.
- Smoking Cessation and Depression It was estimated that nicotine affects the human’s reward system. As a result, smoking cessation might lead to depression and other mental disorder.
- Predicting Barriers to Treatment for Depression Mental health issues such as depression and drug abuse are the most frequent among teenagers and young adults. In this age range, both disorders tend to co-occur.
- Relation Between the COVID-19 Pandemic and Depression The paper is to share an insight into the detrimental effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of thousands of people and provide advice on how to reduce its impact.
- Post-operative Breast Cancer Patients With Depression: Annotated Bibliography This paper is an annotated bibliography about risk reduction strategies at the point of care: Post-operative breast cancer patients who are experiencing depression.
- Is Creativity A Modern Panacea From Boredom and Depression? Communication, daily life, and working patterns become nothing but fixed mechanisms that are deprived of any additional thoughts and perspectives.
- Depression and Other Antecedents of Obesity Defeating the inertia about taking up a regular programme of sports and exercise can be a challenging goal. Hence, more advocacy campaigns focus on doing something about obesity with a more prudent diet.
- Depression in Adolescence as a Contemporary Issue Depression in adolescents is not medically different from adult depression but is caused by developmental and social challenges young people encounter.
- Depression and Workplace Violence The purpose of this paper is to provide an in-depth analysis how can workplace violence and verbal aggression be reduced or dealt with by employees.
- Treating Mild Depression: Psychotherapy and Pharmacotherapy The project intends to investigate the comparative effectiveness of the treatments that are currently used for mild depression.
- Anxiety, Depression, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Currently, many people experience anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder that affect their general health.
- Depression and Anxiety: Mary’s Case Mary’s husband’s death precipitated her depression and anxiety diagnosis. She feels lonely and miserable as she struggles with her daily endeavors with limited emotional support.
- What Are the Characteristics and Causes of Depression?
- Why Are Athletes Vulnerable to Depression?
- Why and How Adolescents Are Affected by Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Clinical Depression?
- Does Depression Assist Eating Disorders?
- What Should You Know About Depression?
- How Can Mother Nature Lower Depression and Anxiety?
- How Can Video Games Relieve Stress and Reduce Depression?
- When Does Teacher Support Reduce Depression in Students?
- Why Are Teenagers Affected by Depression?
- How Teens and Depression Today?
- Are Mental Health Issues Like Depression Related to Race?
- What Does Depression Mean?
- How Did the Depression Affect France?
- How Does Depression Stop?
- When Postpartum Depression Leads to Psychosis?
- How Do Medication and Therapy Combat Depression?
- What Are the Leading Causes of Depression?
- What About Drugs for Anxiety and Depression?
- What’s the Big Deal About Anxiety and Depression in Students?
- How Should Childhood Depression and Anxiety Be?
- How Do Gender Stereotypes Warp Our View of Depression?
- What Are the Signs of Teenage Depression?
- Are Testosterone Levels and Depression Risk Linked Based on Partnering and Parenting?
- How Psychology Helps People With Depression?
- How Should Childhood Depression and Anxiety Be Treated or Dealt With?
- African American Children Suffering From Anxiety and Depression Depression and anxiety are common among African American children and adolescents, and they face significant barriers to receiving care and treatment.
- Effects of Music Therapy on Depressed Elderly People Music therapy has been shown to have positive effects among people, and thus the aim was to assess the validity of such claims using elderly people.
- Depression in the Contemporary Society Public awareness about depression has increased in recent years, with more attention dedicated to the need for addressing this serious mental health illness and less stigmatization.
- Physiological Psychology. Postpartum Depression Depression is a focal public health question. In the childbearing period, it is commoner in females than in males with a 2:1 ratio.
- Adolescent Depression: Modern Issues and Resources Teenagers encounter many challenging health-related issues; mental health conditions are one of them. This paper presents the aspects of depression in adolescents.
- Depression Among Rich People Analysis Among the myriad differences between rich and poor people is the manner in which they are influenced by and respond to depression.
- Theories in Depression Treatment This study analyzes the theories pertinent to depression treatment, reviews relevant evidence, defines key concepts of the project, and explains the framework chosen for it.
- The Postnatal (Postpartum) Depression’ Concept Postnatal or postpartum depression (PPD) is a subtype of depression which is experienced by women within the first half a year after giving birth.
- The Efficacy of Medication in Depression’ Treatment This paper attempts to provide a substantial material for the participation in an argument concerning the clinical effectiveness of antidepressant medications.
- Depression and Cognitive Psychotherapy Approaches Cognitive psychotherapy offers various techniques to cope with emotional problems. This paper discusses the most effective cognitive approaches.
- Women’s Mental Health Disorder: Major Depression The mental health disorder paper aims to explore major depression, its symptoms, assessment, and intervention strategies appropriate for women.
- Early Diagnosis of Depression Among Young Adults The purpose of this study was to discover sociodemographic and health traits related to depression sufferers’ usage of various mental health services.
- Depression in Middle-Aged African Women The research study investigates depression in middle-aged African women because the mental health of the population is a serious concern of the modern healthcare sector.
- Early Diagnosis of Depression Among Young Adults The paper shows a need for early identification of depression symptoms in primary care practice. PHQ-2 and PHQ-9 are useful tools for portraying symptoms.
- Early Diagnosis of Depression: Public Health Depression in young adults has become a significant health problem across the US. It causes persistent feelings of loss of interest in activities and sadness.
- Depression and Social Media in Scientific vs. Popular Articles The damage can come in the form of misinformation, which can result in an unjustified and unnecessary self-restriction of social media.
- Depression in Adolescence: Causes and Treatment Depression amongst young adults at the puberty stage comes in hand with several causes that one cannot imagine, and depression happens or is triggered by various reasons.
- Addressing Depression Among Native Youths The current paper aims to utilize a Medicine Wheel model and a social work paradigm to manage depression among Native American Indian youths.
- Psychological Assessments and Intervention Strategies for Depression The article presents two case studies highlighting the importance of psychological assessments and intervention strategies for individuals experiencing depression.
- The Impact of Postpartum Maternal Depression on Postnatal Attachment This paper examines the influence of postpartum maternal depression on postnatal infant attachment, discusses the adverse effects of depression on attachment.
- Marijuana Effects on Risk of Anxiety and Depression The current paper aims to find out whether medical cannabis can positively affect anxiety and depression and the process of their treatment.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety and Depression Cognitive behavioral therapy analyzes the unconscious processes influencing the normal functioning of the human body, causing different pathologies.
- Hypnotherapy as an Effective Method for Treating Depression This paper explores the use of hypnotherapy as a treatment for depression and highlights the advantages of hypnosis in addressing depressive symptoms.
- Postpartum Depression in Women and Men The focus of the paper is health problems that affect women after giving birth to a child, such as depression. The author proposes that men also experience postpartum depression.
- Repression and Depression in “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman In “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman, the author highlighted the connection between repression and depression.
- Men and Depression: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Depression in men and women has several incompatibilities as males suffer from health problems more often than women as they rarely express their emotions.
- Promotion of Change Regarding Adolescent Depression In the essay, the author describes the methods to evaluate the symptoms of a patient who has been referred for counseling with depression.
- Interventions to Cope With Depression Depression is characterized by sadness, anxiety, feelings of worthlessness, and helplessness. These feelings do not necessarily relate to life events.
- Bipolar Depression and Bipolar Mania Although all bipolar disorders are characterized by periods of extreme mood, the main difference between them is the severity of the condition itself.
- Post-Stroke Anxiety and Depression The purpose of the given study is to ascertain how cognitive behavior therapy affects individuals with post-stroke ischemia in terms of depression reduction.
- Depression and Anxiety Management The medical staff will investigate the treatment modalities currently being utilized for the large population of patients experiencing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Depression in Hispanic Culture There are different ways in which culture or ethnicity can impact the treatment of the development of mental health disorders.
- Impacts of Stress of Low Income on the Risk of Depression in Children Socioeconomic hardships lead to a decline in the quality of parenting and the development of psychological and behavioral problems in children.
- The Causes of Depression and How to Overcome It In this self-reflection essay, the author describes the causes of his depression and the steps he is taking to overcome it.
- Is depression a biological condition or a result of unrealistic expectations?
- Should employers be legally required to provide support to workers with depression?
- Do the media portrayals of depression accurately reflect people’s experiences?
- Social media contributes to depression rates by eliciting the feeling of loneliness.
- Should mental health screening be mandatory in schools?
- Should depression be reclassified as a neurological disorder?
- Antidepressants are an overused quick-fix solution to depression.
- Should non-pharmacological treatments for depression be prioritized?
- Should depression be considered a disability?
- The use of electroconvulsive therapy for depression should be banned.
- Depression: Diagnostics and Treatment Depression, when it remains unchecked, can cause detrimental effects to individuals, such as suicide, which will eventually equate to mental disorders.
- Depression and Anxiety in Mental Health Nurses Depression and anxiety are the most common mental diseases in humans. Nurses who work in mental health are at significant risk of getting psychiatric illnesses.
- Psychedelics in Depression and Anxiety Treatment Mental illnesses have become an essential part of health in the last few decades, with sufficient attention being devoted to interventions that resolve them.
- Depression and Anxiety Among African-American Children Depression and anxiety are common among African-American children and adolescents, but they face significant barriers to receiving care and treatment due to their age and race.
- Why Are Physical Activities Treatments for Depression? In this paper, the connection between physical activities and depression will be analyzed, and the common counterargument will be discussed.
- Depression in the Older Population The paper discusses depression is an actual clinical disorder for older people with specific reasons related to their age.
- Nutrition and Depression: A Psychological Perspective When discussing nutrition in toddlers and certain behavioral patterns, one of the first standpoints to pay attention to is the humanistic perspective.
- Social Media and Depression in Adolescents: The Causative Link This paper explores how social media causes depression in adolescents during the social-emotional stage of life.
- Physical Activities as Treatment for Depression This paper will discuss what factors are improved via physical exercise and how they help with treating depression.
- “Yoga for Depression” Article by The Minded Institute One can say that depression is both the biological and mental Black Death of modern humanity in terms of prevalence and negative impact on global health.
- Therapeutic Interventions for the Older Adult With Depression and Dementia The paper researches the therapeutic interventions which relevant for the older people with depression and dementia nowadays.
- Depression Among Patients With Psoriasis Considering psoriasis as the cause of the development of depressive disorders, many researchers assign a decisive role to the severe skin itching that accompanies psoriasis.
- Qi Gong Practices’ Effects on Depression Qi Gong is a set of physical and spiritual practices aimed at the balance of mind, body, and soul and the article demonstrates whether it is good or not at treating depression.
- The Effects of Forgiveness Therapy on Depression for Women The study analyzes the impact of forgiveness therapy on the emotional state of women who have experienced emotional abuse.
- How Covid-19 Isolation Contributed to Depression and Adolescent Suicide The pandemic affected adolescents because of stringent isolation measures, which resulted in mental challenges such as depression and anxiety, hence suicidal thoughts.
- Depression and Anxiety in Older Generation Depression and anxiety represent severe mental disorders that require immediate and prolonged treatment for patients of different ages.
- Coping with Depression After Loss of Loved Ones This case is about a 60-year-old man of African American origin. He suffered from depression after his wife’s death, which made him feel lonely and isolated.
- Postpartum Depression Screening Program Evaluation In order to manage the depression of mothers who have just delivered, it is important to introduce a routine postpartum depression-screening program in all public hospitals.
- Depression: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment Depression interferes with daily routine, wasting valuable time and lowering production. Persistent downs or blues, sadness, and anger may be signs of depression.
- Adolescent Males With Depression: Poly-Substance Abuse Depression is the most crucial aspect that makes young males indulge in poly-substance abuse. There are various ways in which male adolescents express their depression.
- The Health of the Elderly: Depression and Severe Emotional Disturbance This study is intended for males and females over the age of 50 years who are likely to suffer from depression and severe emotional disturbance.
- Suicidal Ideation & Depression in Elderly Living in Nursing Home vs. With Family This paper attempts to compare the incidence of suicidal ideation and depression among elderly individuals living in nursing homes and those living with family in the community.
- Major Depression: Symptoms and Treatment Major depression is known as clinical depression, which is characterized by several symptoms. There are biological, psychological, social, and evolutionary causes of depression.
- Health Disparity Advocacy: Clinical Depression in the U.S. Recent statistics show that approximately more than 10 million people suffer from severe depression each year in the U.S..
- Serum Neurotrophic Factors in Adolescent Depression by Pallavi et al. The research hypothesis of the article is to compare the serum concentration of neurotrophic factors in depression patients and healthy control.
- The Treatment of Anxiety and Depression The meta-analysis provides ample evidence, which indicates that CES is not only effective but also safe in the treatment of anxiety and depression.
- Depression Intervention Among Diabetes Patients The research examines the communication patterns used by depression care specialist nurses when communicating with patients suffering from diabetes.
- Postnatal Depression in New Mothers and Its Prevention Leisure activities keep new mothers suffering from postnatal depression busy and enable them to interact with other members of the society.
- Literature Evaluation on the Depression Illness The evaluation considers the articles that study such medical illness as depression from different planes of its perception.
- Treatment of Major Depression The purpose of the paper is to identify the etiology and the treatment of major depression from a psychoanalytic and cognitive perspective.
- Edinburgh Depression Screen for Treating Depression Edinburgh Depression screen is also known as Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale which is used to screen pregnant and postnatal women for emotional distress.
- Depression Treatment Variants in the US There is a debate regarding the best formula for depression treatment whereby some argue for using drugs, whereas others are advocating for therapy.
- Depression in the Elderly: Treatment Options Professionals may recommend various treatment options, including the use of antidepressants, psychotherapy such as cognitive-behavioral therapy.
- Depression Treatments and Therapeutic Strategies This article examines the effectiveness of different depression treatments and reviews the therapeutic strategies, which can be helpful if the initial treatment fails.
- Can physical exercise alone effectively treat depression?
- Art therapy as a complementary treatment for depression.
- Is there a link between perfectionism and depression?
- The influence of sleep patterns on depression treatment outcomes.
- Can exposure to nature and green spaces decrease depression rates in cities?
- The relationship between diet and depression symptoms.
- The potential benefits of psychedelic-assisted therapy in treating depression.
- The role of outdoor experiences in alleviating depression symptoms.
- The relationship between depression and physical health in older adults.
- The role of workplace culture in preventing employee depression.
- Depression and the Nervous System Depression is a broad condition that is associated with failures in many parts of the nervous system. It can be both the cause and the effect of this imbalance.
- Depression: Types, Symptoms, Etiology & Management Depression differs from other disorders, connected with mood swings, and it may present a serious threat to the individual’s health condition.
- The Effect of Music Therapy on Depression One major finding of study is that music therapy alleviates depression among the elderly. Music therapy could alleviate depression.
- Post-Natal Depression as an Affective Disorder Postpartum or post-natal depression (PPD) is a serious issue that can potentially be destructive to both infant and mother.
- “Neighborhood Racial Discrimination and the Development of Major Depression” by Russell The study investigates how neighborhood racial discrimination influences this severe mental disorder among African American Women.
- Adolescent Depression and Physical Health Depression in adolescents and young people under 24 is a factor that affects their physical health negatively and requires intervention from various stakeholders.
- Family Support to a Veteran With Depression Even the strongest soldiers become vulnerable to multiple health risks and behavioral changes, and depression is one of the problems military families face.
- Alcohol and Depression Article by Churchill and Farrell The selected article for this discussion is “Alcohol and Depression: Evidence From the 2014 Health Survey for England” by Sefa Awaworyi Churchill and Lisa Farrell.
- Negative Effects of Depression in Adolescents on Their Physical Health Mental disorders affect sleep patterns, physical activity, digestive and cardiac system. The purpose of the paper to provide information about adverse impacts of depression on health.
- Elderly Depression: Symptoms, Consequences, Behavior, and Therapy The paper aims to identify symptoms, behavioral inclinations of older adults, consequences of depression, and treatment ways.
- Depression in Feminist Literature of the 1890s The aim of the work is to analyze the cause of female sickness, which is their inability to express themselves and the pitiful place of a female in the society of that time.
- Major Depression Disorder: Causes and Treatment Loss in weight and appetite are some of the symptoms that a patient diagnosed with Major Depression Disorder could manifest.
- Mood Disorders: Depression Concepts Description The essay describes the nature of depression, its causes, characteristics, consequences, and possible ways of treatment.
- Geriatric Depression Diagnostics Study Protocol The research question is: how does the implementation of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines affect the accuracy of diagnosing of depression?
- Mental Health Association of Depression and Alzheimer’s in the Elderly Depression can be a part of Alzheimer’s disease. Elderly people may have episodes of depression, but these episodes cannot be always linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
- Protective Factors Against Youthful Depression Several iterations of multiple correlation, step-wise and hierarchical regression yielded inconclusive results about the antecedents of youthful depression.
- Depression and Related Psychological Issues Depression as any mental disorder can be ascribed, regarding the use of psychoanalysis, to a person`s inability to control his destructive or sexual instincts or impulses.
- Television Habituation and Adolescent Depression The paper investigates the theory that there is a link between heavy TV viewing and adolescent depression and assess the strength of association.
- Occupational Psychology: Depression Counselling The case involves a 28-year-old employee at Data Analytics Ltd. A traumatic event affected his mental health, causing depression and reduced performance.
- Psychotherapeutic Group: Treatment of Mild-To-Moderate Depression The aim of this manual is to provide direction and employ high-quality sources dedicated to mild-to-moderate depression and group therapy to justify the choices made for the group.
- “Depression and Ways of Coping With Stress” by Orzechowska et al. The study “Depression and Ways of Coping With Stress” by Orzechowska et al. aimed the solve an issue pertinent to nursing since depression can influence any patient.
- Postpartum Depression: Evidence-Based Practice Postpartum or postnatal depression refers to a mood disorder that can manifest in a large variety of symptoms and can range from one person to another.
- Effectiveness of Telenursing in Reducing Readmission, Depression, and Anxiety The project is dedicated to testing the effectiveness of telenursing in reducing readmission, depression, and anxiety, as well as improving general health outcomes.
- Adult Depression Treatment in the United States This study characterizes the treatment of adult depression in the US. It is prompted by the findings of earlier studies, which discover the lack of efficient depression care.
- Nurses’ Interventions in Postnatal Depression Treatment This investigation evaluates the effect of nurses’ interventions on the level of women’s postnatal depression and their emotional state.
- Postpartum Depression: Evidence-Based Care Outcomes In this evidence-based study, the instances of potassium depression should be viewed as the key dependent variable that will have to be monitored in the course of the analysis.
- Postpartum Depression: Diagnosis and Treatment This paper aims to discuss the peculiarities of five one-hour classes on depression awareness, to implement this intervention among first-year mothers, and to evaluate its worth during the first year after giving birth.
- Homelessness and Depression Among Illiterate People There are various myths people have about homelessness and depression. For example, many people believe that only illiterate people can be homeless.
- Postpartum Depression In First-time Mothers The most common mental health problem associated with childbirth remains postpartum depression, which can affect both sexes, and negatively influences the newborn child.
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Postpartum Depression Postpartum depression has many explanations, but the usual way of referring to this disease is linked to psychological problems.
- What Is Postpartum Depression? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment The prevalence of postpartum depression is quite high as one in seven new American mothers develops this health issue.
- Predictors of Postpartum Depression The phenomenon of postpartum depression affects the quality of women’s lives, as well as their self-esteem and relationships with their child.
- Depression and Self-Esteem: Research Problem Apart from descriptively studying the relationship between depression and self-esteem, a more practical approach can be used to check how interventions for enhancing self-esteem might affect depression.
- The Relationship Between Depression and Self-Esteem The topic which is proposed to be studied is the relationship between depression and self-esteem. Self-esteem can be defined as individual’s subjective evaluation of his or her worth.
- The Impact of Depression on Motherhood This work studies the impact of depression screening on prenatal and posts natal motherhood and effects on early interventions using a literature review.
- Depression in Female Cancer Patients and Survivors Depression is often associated with fatigue and sleep disturbances that prevent females from thinking positively and focusing on the treatment and its outcomes.
- Depression in Cardiac or Diabetic Patients The paper develops a framework through which risk factors associated with the development of MDD among adult patients with heart disease or diabetes can be easily identified.
- The Geriatric Population’s Depression This paper discusses how does the implementation of National Institute for Health and Care guidelines affect the accuracy of diagnosing of depression in the geriatric population.
- Problem of Depression: Recognition and Management Depression is a major health concern, which is relatively prevalent in the modern world. Indeed, in the US, 6.7 % of adults experienced an episode of the Major Depressive Disorder in 2015.
- Health and Care Excellence in Depression Management The introduction of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines can affect the accuracy of diagnosing and quality of managing depression.
- Impact of COVID-19 on Depression and Suicide Rates among Adolescents and Young People The purpose of this paper is to explore the influence of coronavirus on these tragic numbers.
- Mild Depression: Psychotherapy or Pharmacotherapy The research question in this paper is: in psychiatric patients with mild depression, what is the effect of psychotherapy on health compared with pharmacotherapy?
- Postpartum Bipolar Disorder and Depression The results of the Mood Disorder Questionnaire screening of a postpartum patient suggest a bipolar disorder caused by hormonal issues and a major depressive episode.
- Bipolar Disorder or Manic Depression Bipolar disorder is a mental illness characterized by unusual mood changes that shift from manic to depressive extremes. In the medical field, it`s called manic depression.
- The Improvement of Depression Management The present paper summarizes the context analysis that was prepared for a change project aimed at the improvement of depression management.
- Depression Management in US National Guidelines The project offers the VEGA medical center to implement the guidelines for depression management developed by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
- Women’s Health and Major Depression Symptoms The client’s complaints refer to sleep problems, frequent mood swings (she gets sad a lot), and the desire to stay away from social interactions.
- Predictors of Postpartum Depression: Who Is at Risk? The article “Predictors of Postpartum Depression” by Katon, Russo, and Gavin focuses on the identification of risk factors related to postnatal depression.
- Depression and Its Treatment: Racial and Ethnic Disparities The racial and ethnic disparities in depression treatment can be used for the development of quality improvement initiatives aimed at the advancement of patient outcomes.
- Lamotrigine for Bipolar Depression Management Lamotrigine sold as Lamictal is considered an effective medication helping to reduce some symptoms that significantly affect epileptic and bipolar patients’ quality of life.
- Citalopram, Methylphenidate in Geriatric Depression Citalopram typically ranges among 10-20 antidepressants for its cost-effectiveness and positive effect on patients being even more effective than reboxetine and paroxetine.
- Depression and Self-Esteem Relationship Self-esteem can be defined as an “individual’s subjective evaluation of his or her worth as a person”; it does not necessarily describe one’s real talents.
- Postpartum Depression: Methods for the Prevention Postpartum depression is a pressing clinical problem that affects new mothers, infants, and other family members. The prevalence of postpartum depression ranges between 13 and 19 percent.
- Anxiety and Depression Among Females with Cancer The study investigated the prevalence of and the potential factors of risk for anxiety and/or depression among females with early breast cancer during the first 5 years.
- Post-Partum Depression and Perinatal Dyadic Psychotherapy Post-partum depression affects more than ten percent of young mothers, and a method Perinatal Dyadic Psychotherapy is widely used to reduce anxiety.
- VEGA Medical Center: Detection of Depression Practice guidelines for the psychiatric evaluation of adults, and they can be employed to solve the meso-level problem of the VEGA medical center and its nurses.
- Depression in Obstetrics and Gynecology: Research This essay analyzes a clinical research article “Improving care for depression in obstetrics and gynecology: A randomized controlled trial” by Melville et al.
- Postpartum Depression, Prevention and Treatment Postpartum depression is a common psychiatric condition in women of the childbearing age. They are most likely to develop the disease within a year after childbirth.
- Smoking Cessation and Depression Problem The aim of the study is to scrutinize the issues inherent in the process of smoking cessation and align them with the occurrence of depression in an extensive sample of individuals.
- Evidence-Based Pharmacology: Major Depression In this paper, a certain attention to different treatment approaches that can be offered to patients with depression will be paid, including the evaluation of age implications.
- Treatment of Depression in Lesbians The aim of this paper is to review a case study of 45 years old lesbian woman who seeks treatment for depression and to discuss the biophysical, psychological, sociocultural, health system.
- Women’s Health: Predictors of Postpartum Depression The article written by Katon, Russo, and Gavin is focused on women’s health. It discusses predictors of postpartum depression (PPD), including sociodemographic and clinic risk factors.
- Depression Treatment and Management Treatment could be started only after patient is checked whether he has an allergy to the prescribed pills or not. If he is not allergic, he should also maintain clinical tests for depression.
- Depression and Thyroid Issues in Young Woman Young people are busy at studies or at work and do not pay much attention to primary symptoms unless they influence the quality of life.
- Counseling Depression: Ethical Aspects This paper explores the ethical aspects required to work with a widower who diminished passion for food, secluding himself in the house, portraying signs of depression.
- Postpartum Depression as Serious Mental Health Problem The research study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a two-step behavioral and educational intervention on the symptoms of postpartum depression in young mothers.
- European Alliances, Wars, Dictatorships and Depression The decades leading to World War I had unusual alignments. The European nations were still scrambling for Asia, Africa and parts of undeveloped Europe.
- Women’s Health: Depression as a Psychological Factor Women who identify themselves as lesbian are likely to experience depression. Biophysical, psychological, sociocultural, behavioral, and health system factors should be taken into consideration.
- Childhood Obesity and Depression Intervention The main intervention to combat depressive moods in adolescents should be linked to improving the psychological health of young people in cooperation with schools.
- Postnatal Depression Prevalence and Effects The paper analyzes the prevalence and risk factors of Postnatal (Postpartum) Depression as well as investigates the effect on the newborns whose mothers suffer from this condition.
- Depression in Older Adults Depression is one of the most common mental illnesses in the world. Evidence-based holistic intervention would provide more effective treatment for elderly patients with depression.
- Placebo and Treatments for Depression Natural alternative treatments for depression actually work better than the biochemical alternatives like antidepressants.
- Care for Depression in Obstetrics and Gynecology This work analyzes the article developed by Melville et al. in which discusses the theme of depression in obstetrics and gynecology and improving care for it.
- Depression Screening in Primary Care Screening for depression in patients suffering from long term conditions (LTCs) or persistent health problems of the body, could largely be erroneous.
- Patients with Depression’ Care: Betty Case Betty, a 45 years old woman, is referred to a local clinic because of feeling depressed. She has a history of three divorces and thinks that she is tired of living the old way.
- Clinical Depression Treatment: Issues and Solvings The paper describes and justifies the design selected for research on depression treatment. It also identifies ethical issues and proposes ways of addressing them.
- Depression in Older Persons – Psychology This article presents the research findings of a study conducted in Iran to assess how effective integrative and instrumental therapies are in the management of depression in older persons.
- Depression in the Elderly – Psychology This paper discusses how a person would know whether a relative had clinical depression or was sad due to specific changes or losses in life.
- Depression in the Elderly Depression can be defined as a state of anxiety, sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness. It can affect people across all ages, who present with diverse signs and symptoms
- Postnatal Depression: Prevalence of Postnatal Depression in Bahrain The study was aimed at estimating the prevalence of postnatal depression among 237 Bahraini women who attended checkups in 20 clinical centres over a period of 2 months.
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/depression-essay-topics/
"227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/depression-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/depression-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/depression-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "227 Depression Research Topics & Essay Titles + Examples." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/depression-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Depression were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 22, 2024 .
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
7 Depression Research Paper Topic Ideas
Nancy Schimelpfening, MS is the administrator for the non-profit depression support group Depression Sanctuary. Nancy has a lifetime of experience with depression, experiencing firsthand how devastating this illness can be.
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
In psychology classes, it's common for students to write a depression research paper. Researching depression may be beneficial if you have a personal interest in this topic and want to learn more, or if you're simply passionate about this mental health issue. However, since depression is a very complex subject, it offers many possible topics to focus on, which may leave you wondering where to begin.
If this is how you feel, here are a few research titles about depression to help inspire your topic choice. You can use these suggestions as actual research titles about depression, or you can use them to lead you to other more in-depth topics that you can look into further for your depression research paper.
What Is Depression?
Everyone experiences times when they feel a little bit blue or sad. This is a normal part of being human. Depression, however, is a medical condition that is quite different from everyday moodiness.
Your depression research paper may explore the basics, or it might delve deeper into the definition of clinical depression or the difference between clinical depression and sadness .
What Research Says About the Psychology of Depression
Studies suggest that there are biological, psychological, and social aspects to depression, giving you many different areas to consider for your research title about depression.
Types of Depression
There are several different types of depression that are dependent on how an individual's depression symptoms manifest themselves. Depression symptoms may vary in severity or in what is causing them. For instance, major depressive disorder (MDD) may have no identifiable cause, while postpartum depression is typically linked to pregnancy and childbirth.
Depressive symptoms may also be part of an illness called bipolar disorder. This includes fluctuations between depressive episodes and a state of extreme elation called mania. Bipolar disorder is a topic that offers many research opportunities, from its definition and its causes to associated risks, symptoms, and treatment.
Causes of Depression
The possible causes of depression are many and not yet well understood. However, it most likely results from an interplay of genetic vulnerability and environmental factors. Your depression research paper could explore one or more of these causes and reference the latest research on the topic.
For instance, how does an imbalance in brain chemistry or poor nutrition relate to depression? Is there a relationship between the stressful, busier lives of today's society and the rise of depression? How can grief or a major medical condition lead to overwhelming sadness and depression?
Who Is at Risk for Depression?
This is a good research question about depression as certain risk factors may make a person more prone to developing this mental health condition, such as a family history of depression, adverse childhood experiences, stress , illness, and gender . This is not a complete list of all risk factors, however, it's a good place to start.
The growing rate of depression in children, teenagers, and young adults is an interesting subtopic you can focus on as well. Whether you dive into the reasons behind the increase in rates of depression or discuss the treatment options that are safe for young people, there is a lot of research available in this area and many unanswered questions to consider.
Depression Signs and Symptoms
The signs of depression are those outward manifestations of the illness that a doctor can observe when they examine a patient. For example, a lack of emotional responsiveness is a visible sign. On the other hand, symptoms are subjective things about the illness that only the patient can observe, such as feelings of guilt or sadness.
An illness such as depression is often invisible to the outside observer. That is why it is very important for patients to make an accurate accounting of all of their symptoms so their doctor can diagnose them properly. In your depression research paper, you may explore these "invisible" symptoms of depression in adults or explore how depression symptoms can be different in children .
How Is Depression Diagnosed?
This is another good depression research topic because, in some ways, the diagnosis of depression is more of an art than a science. Doctors must generally rely upon the patient's set of symptoms and what they can observe about them during their examination to make a diagnosis.
While there are certain laboratory tests that can be performed to rule out other medical illnesses as a cause of depression, there is not yet a definitive test for depression itself.
If you'd like to pursue this topic, you may want to start with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). The fifth edition, known as DSM-5, offers a very detailed explanation that guides doctors to a diagnosis. You can also compare the current model of diagnosing depression to historical methods of diagnosis—how have these updates improved the way depression is treated?
Treatment Options for Depression
The first choice for depression treatment is generally an antidepressant medication. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most popular choice because they can be quite effective and tend to have fewer side effects than other types of antidepressants.
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is another effective and common choice. It is especially efficacious when combined with antidepressant therapy. Certain other treatments, such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), are most commonly used for patients who do not respond to more common forms of treatment.
Focusing on one of these treatments is an option for your depression research paper. Comparing and contrasting several different types of treatment can also make a good research title about depression.
A Word From Verywell
The topic of depression really can take you down many different roads. When making your final decision on which to pursue in your depression research paper, it's often helpful to start by listing a few areas that pique your interest.
From there, consider doing a little preliminary research. You may come across something that grabs your attention like a new study, a controversial topic you didn't know about, or something that hits a personal note. This will help you narrow your focus, giving you your final research title about depression.
Remes O, Mendes JF, Templeton P. Biological, psychological, and social determinants of depression: A review of recent literature . Brain Sci . 2021;11(12):1633. doi:10.3390/brainsci11121633
National Institute of Mental Health. Depression .
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition . American Psychiatric Association.
National Institute of Mental Health. Mental health medications .
Ferri, F. F. (2019). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2020 E-Book: 5 Books in 1 . Netherlands: Elsevier Health Sciences.
By Nancy Schimelpfening Nancy Schimelpfening, MS is the administrator for the non-profit depression support group Depression Sanctuary. Nancy has a lifetime of experience with depression, experiencing firsthand how devastating this illness can be.
434 Depression Essay Titles & Research Topics: Argumentative, Controversial, and More
Depression is undeniably one of the most prevalent mental health conditions globally, affecting approximately 5% of adults worldwide. It often manifests as intense feelings of hopelessness, sadness, and a loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities. Many also experience physical symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and appetite changes. Recognizing and addressing this mental disorder is extremely important to save lives and treat the condition.
In this article, we’ll discuss how to write an essay about depression and introduce depression essay topics and research titles for students that may be inspirational.
- 🔝 Top Depression Essay Titles
- ✅ Essay Prompts
- 💡 Research Topics
- 🔎 Essay Titles
- 💭 Speech Topics
- 📝 Essay Structure
🔗 References
🔝 top 12 research titles about depression.
- How is depression treated?
- Depression: Risk factors.
- The symptoms of depression.
- What types of depression exist?
- Depression in young people.
- Differences between anxiety and depression.
- The parents’ role in depression therapy.
- Drugs as the root cause of depression.
- Dangerous consequences of untreated depression.
- Effect of long-term depression.
- Different stages of depression.
- Treatment for depression.
✅ Prompts for Essay about Depression
Struggling to find inspiration for your essay? Look no further! We’ve put together some valuable essay prompts on depression just for you!
Prompt for Personal Essay about Depression
Sharing your own experience with depression in a paper can be a good idea. Others may feel more motivated to overcome their situation after reading your story. You can also share valuable advice by discussing things or methods that have personally helped you deal with the condition.
For example, in your essay about depression, you can:
- Tell about the time you felt anxious, hopeless, or depressed;
- Express your opinion on depression based on the experiences from your life;
- Suggest a way of dealing with the initial symptoms of depression ;
- Share your ideas on how to protect mental health at a young age.
How to Overcome Depression: Essay Prompt
Sadness is a common human emotion, but depression encompasses more than just sadness. As reported by the National Institute of Mental Health, around 21 million adults in the United States, roughly 8.4% of the total adult population , faced at least one significant episode of depression in 2020. When crafting your essay about overcoming depression, consider exploring the following aspects:
- Depression in young people and adolescents;
- The main causes of depression;
- The symptoms of depression;
- Ways to treat depression;
- Help from a psychologist (cognitive behavioral therapy or interpersonal therapy ).
Postpartum Depression: Essay Prompt
The birth of a child often evokes a spectrum of powerful emotions, spanning from exhilaration and happiness to apprehension and unease. It can also trigger the onset of depression. Following childbirth, many new mothers experience postpartum “baby blues,” marked by shifts in mood, bouts of tears, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. To shed light on the subject of postpartum depression, explore the following questions:
- What factors may increase the risk of postpartum depression?
- Is postpartum depression predictable?
- How to prevent postpartum depression?
- What are the symptoms of postpartum depression?
- What kinds of postpartum depression treatments exist?
Prompt for Essay about Teenage Depression
Teenage depression is a mental health condition characterized by sadness and diminishing interest in daily activities. It can significantly impact a teenager’s thoughts, emotions, and behavior, often requiring long-term treatment and support.
By discussing the primary symptoms of teenage depression in your paper, you can raise awareness of the issue and encourage those in need to seek assistance. You can pay attention to the following aspects:
- Emotional changes (feelings of sadness, anger, hopelessness, guilt, etc.);
- Behavioral changes (loss of energy and appetite , less attention to personal hygiene, self-harm, etc.);
- New addictions (drugs, alcohol, computer games, etc.).
💡 Research Topics about Depression
- The role of genetics in depression development.
- The effectiveness of different psychotherapeutic interventions for depression.
- Anti-depression non-pharmacological and medication treatment .
- The impact of childhood trauma on the onset of depression later in life.
- Exploring the efficacy of antidepressant medication in different populations.
- The impact of exercise on depression symptoms and treatment outcomes.
- Mild depression: pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy .
- The relationship between sleep disturbances and depression.
- The role of gut microbiota in depression and potential implications for treatment.
- Investigating the impact of social media on depression rates in adolescents.
- Depression, dementia, and delirium in older people .
- The efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy in preventing depression relapse.
- The influence of hormonal changes on depression risk.
- Assessing the effectiveness of self-help and digital interventions for depression.
- Herbal and complementary therapies for depression .
- The relationship between personality traits and vulnerability to depression.
- Investigating the long-term consequences of untreated depression on physical health.
- Exploring the link between chronic pain and depression.
- Depression in the elderly male .
- The impact of childhood experiences on depression outcomes in adulthood.
- The use of ketamine and other novel treatments for depression.
- The effect of stigma on depression diagnosis and treatment.
- The conducted family assessment: cases of depression .
- The role of social support in depression recovery.
- The effectiveness of online support groups for individuals with depression.
- Depression and cognitive decline in adults.
- Depression: PICOT question component exploration .
- Exploring the impact of nutrition and dietary patterns on depression symptoms.
- Investigating the efficacy of art-based therapies in depression treatment.
- The role of neuroplasticity in the development and treatment of depression.
- Depression among HIV-positive women .
- The influence of gender on depression prevalence and symptomatology.
- Investigating the impact of workplace factors on depression rates and outcomes.
- The efficacy of family-based interventions in reducing depression symptoms in teenagers.
- Frontline nurses’ burnout, anxiety, depression, and fear statuses .
- The role of early-life stress and adversity in depression vulnerability.
- The impact of various environmental factors on depression rates.
- Exploring the link between depression and cardiovascular health .
- Depression detection in adults in nursing practice .
- Virtual reality as a therapeutic tool for depression treatment.
- Investigating the impact of childhood bullying on depression outcomes.
- The benefits of animal-assisted interventions in depression management.
- Depression and physical exercise .
- The relationship between depression and suicidal behavior .
- The influence of cultural factors on depression symptom expression.
- Investigating the role of epigenetics in depression susceptibility.
- Depression associated with cognitive dysfunction .
- Exploring the impact of adverse trauma on the course of depression.
- The efficacy of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating depression.
- The relationship between depression and substance use disorders .
- Depression and anxiety among college students .
- Investigating the effectiveness of group therapy for depression.
- Depression and chronic medical conditions .
Psychology Research Topics on Depression
- The influence of early attachment experiences on the development of depression.
- The impact of negative cognitive biases on depression symptomatology.
- Depression treatment plan for a queer patient .
- Examining the relationship between perfectionism and depression.
- The role of self-esteem in depression vulnerability and recovery.
- Exploring the link between maladaptive thinking styles (e.g., rumination, catastrophizing) and depression.
- Investigating the impact of social support on depression outcomes and resilience.
- Identifying depression in young adults at an early stage .
- The influence of parenting styles on the risk of depression in children and adolescents.
- The role of self-criticism and self-compassion in depression treatment.
- Exploring the relationship between identity development and depression in emerging adulthood.
- The role of learned helplessness in understanding depression and its treatment.
- Depression in the elderly .
- Examining the connection between self-efficacy beliefs and depression symptoms.
- The influence of social comparison processes on depression and body image dissatisfaction .
- Exploring the impact of trauma-related disorders on depression.
- The role of resilience factors in buffering against the development of depression.
- Investigating the relationship between personality traits and depression.
- Depression and workplace violence .
- The impact of cultural factors on depression prevalence and symptom presentation.
- Investigating the effects of chronic stress on depression risk.
- The role of coping strategies in depression management and recovery.
- The correlation between discrimination/prejudice and depression/anxiety .
- Exploring the influence of gender norms and societal expectations on depression rates.
- The impact of adverse workplace conditions on employee depression.
- Investigating the effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating depression.
- Cognitive behavior and depression in adolescents .
- Childhood emotional neglect and adult depression.
- The influence of perceived social support on treatment outcomes in depression.
- The effects of childhood bullying on the development of depression.
- The impact of intergenerational transmission of depression within families.
- Depression in children: symptoms and treatments .
- Investigating the link between body dissatisfaction and depression in adolescence.
- The influence of adverse life events and chronic stressors on depression risk.
- The effects of peer victimization on the development of depression in adolescence.
- Counselling clients with depression and addiction .
- The role of experiential avoidance in depression and its treatment.
- The impact of social media use and online interactions on depression rates.
- Depression management in adolescent .
- Exploring the relationship between emotional intelligence and depression symptomatology.
- Investigating the influence of cultural values and norms on depression stigma and help-seeking behavior.
- The effects of childhood maltreatment on neurobiological markers of depression.
- Psychological and emotional conditions of suicide and depression .
- Exploring the relationship between body dissatisfaction and depression.
- The influence of self-worth contingencies on depression vulnerability and treatment response.
- The impact of social isolation and loneliness on depression rates.
- Psychology of depression among college students .
- The effects of perfectionistic self-presentation on depression in college students.
- The role of mindfulness skills in depression prevention and relapse prevention.
- Investigating the influence of adverse neighborhood conditions on depression risk.
- Personality psychology and depression .
- The impact of attachment insecurity on depression symptomatology.
Postpartum Depression Research Topics
- Identifying risk factors for postpartum depression.
- Exploring the role of hormonal changes in postpartum depression.
- “Baby blues” or postpartum depression and evidence-based care .
- The impact of social support on postpartum depression.
- The effectiveness of screening tools for early detection of postpartum depression.
- The relationship between postpartum depression and maternal-infant bonding .
- Postpartum depression educational program results .
- Identifying effective interventions for preventing and treating postpartum depression.
- Examining the impact of cultural factors on postpartum depression rates.
- Investigating the role of sleep disturbances in postpartum depression.
- Depression and postpartum depression relationship .
- Exploring the impact of a traumatic birth experience on postpartum depression.
- Assessing the impact of breastfeeding difficulties on postpartum depression.
- Understanding the role of genetic factors in postpartum depression.
- Postpartum depression: consequences .
- Investigating the impact of previous psychiatric history on postpartum depression risk.
- The potential benefits of exercise on postpartum depression symptoms.
- The efficacy of psychotherapeutic interventions for postpartum depression.
- Postpartum depression in the twenty-first century .
- The influence of partner support on postpartum depression outcomes.
- Examining the relationship between postpartum depression and maternal self-esteem.
- The impact of postpartum depression on infant development and well-being.
- Maternal mood symptoms in pregnancy and postpartum depression .
- The effectiveness of group therapy for postpartum depression management.
- Identifying the role of inflammation and immune dysregulation in postpartum depression.
- Investigating the impact of childcare stress on postpartum depression.
- Postpartum depression among low-income US mothers .
- The role of postnatal anxiety symptoms in postpartum depression.
- The impact of postpartum depression on the marital relationship.
- The influence of postpartum depression on parenting practices and parental stress.
- Postpartum depression: symptoms, role of cultural factors, and ways to support .
- Investigating the efficacy of pharmacological treatments for postpartum depression.
- The impact of postpartum depression on breastfeeding initiation and continuation.
- The relationship between postpartum depression and post-traumatic stress disorder .
- Postpartum depression and its identification .
- The impact of postpartum depression on cognitive functioning and decision-making.
- Investigating the influence of cultural norms and expectations on postpartum depression rates.
- The impact of maternal guilt and shame on postpartum depression symptoms.
- Beck’s postpartum depression theory: purpose, concepts, and significance .
- Understanding the role of attachment styles in postpartum depression vulnerability.
- Investigating the effectiveness of online support groups for women with postpartum depression.
- The impact of socioeconomic factors on postpartum depression prevalence.
- Perinatal depression: research study and design .
- The efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions for postpartum depression.
- Investigating the influence of birth spacing on postpartum depression risk.
- The role of trauma history in postpartum depression development.
- The link between the birth experience and postnatal depression .
- How does postpartum depression affect the mother-infant interaction and bonding ?
- The effectiveness of home visiting programs in preventing and managing postpartum depression.
- Assessing the influence of work-related stress on postpartum depression.
- The relationship between postpartum depression and pregnancy-related complications.
- The role of personality traits in postpartum depression vulnerability.
🔎 Depression Essay Titles
Depression essay topics: cause & effect.
- The effects of childhood trauma on the development of depression in adults.
- The impact of social media usage on the prevalence of depression in adolescents.
- “Predictors of Postpartum Depression” by Katon et al.
- The effects of environmental factors on depression rates.
- The relationship between academic pressure and depression among college students.
- The relationship between financial stress and depression.
- The best solution to predict depression because of bullying .
- How does long-term unemployment affect mental health ?
- The effects of unemployment on mental health, particularly the risk of depression.
- The impact of genetics and family history of depression on an individual’s likelihood of developing depression.
- The relationship between depression and substance abuse .
- Child abuse and depression .
- The role of gender in the manifestation and treatment of depression.
- The effects of chronic stress on the development of depression.
- The link between substance abuse and depression.
- Depression among students at Elon University .
- The influence of early attachment styles on an individual’s vulnerability to depression.
- The effects of sleep disturbances on the severity of depression.
- Chronic illness and the risk of developing depression.
- Depression: symptoms and treatment .
- Adverse childhood experiences and the likelihood of experiencing depression in adulthood.
- The relationship between chronic illness and depression.
- The role of negative thinking patterns in the development of depression.
- Effects of depression among adolescents .
- The effects of poor body image and low self-esteem on the prevalence of depression.
- The influence of social support systems on preventing symptoms of depression.
- The effects of child neglect on adult depression rates.
- Depression caused by hormonal imbalance .
- The link between perfectionism and the risk of developing depression.
- The effects of a lack of sleep on depression symptoms.
- The effects of childhood abuse and neglect on the risk of depression.
- Social aspects of depression and anxiety .
- The impact of bullying on the likelihood of experiencing depression.
- The role of serotonin and neurotransmitter imbalances in the development of depression.
- The impact of a poor diet on depression rates.
- Depression and anxiety run in the family .
- The effects of childhood poverty and socioeconomic status on depression rates in adults.
- The impact of divorce on depression rates.
- The relationship between traumatic life events and the risk of developing depression.
- The influence of personality traits on susceptibility to depression.
- The impact of workplace stress on depression rates.
- Depression in older adults: causes and treatment .
- The impact of parental depression on children’s mental health outcomes.
- The effects of social isolation on the prevalence and severity of depression.
- The role of cultural factors in the manifestation and treatment of depression.
- The relationship between childhood bullying victimization and future depressive symptoms.
- The impact of early intervention and prevention programs on reducing the risk of postpartum depression.
- Treating mood disorders and depression .
- How do hormonal changes during pregnancy contribute to the development of depression?
- The effects of sleep deprivation on the onset and severity of postpartum depression.
- The impact of social media on depression rates among teenagers.
- The role of genetics in the development of depression.
- The impact of bullying on adolescent depression rates.
- Mental illness, depression, and wellness issues .
- The effects of a sedentary lifestyle on depression symptoms.
- The correlation between academic pressure and depression in students.
- The relationship between perfectionism and depression.
- The correlation between trauma and depression in military veterans.
- Anxiety and depression during childhood and adolescence .
- The impact of racial discrimination on depression rates among minorities.
- The relationship between chronic pain and depression.
- The impact of social comparison on depression rates among young adults.
- The effects of childhood abuse on adult depression rates.
Depression Argumentative Essay Topics
- The role of social media in contributing to depression among teenagers.
- The effectiveness of antidepressant medication: an ongoing debate.
- Depression treatment: therapy or medications ?
- Should depression screening be mandatory in schools and colleges?
- Is there a genetic predisposition to depression?
- The stigma surrounding depression: addressing misconceptions and promoting understanding.
- Implementation of depression screening in primary care .
- Is psychotherapy more effective than medication in treating depression?
- Is teenage depression overdiagnosed or underdiagnosed: a critical analysis.
- The connection between depression and substance abuse: untangling the relationship.
- Humanistic therapy of depression .
- Should ECT (electroconvulsive therapy) be a treatment option for severe depression?
- Where is depression more prevalent: in urban or rural communities? Analyzing the disparities.
- Is depression a result of chemical imbalance in the brain? Debunking the myth.
- Depression: a serious mental and behavioral problem .
- Should depression medication be prescribed for children and adolescents?
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in managing depression.
- Should depression in the elderly be considered a normal part of aging?
- Is depression hereditary? Investigating the role of genetics in depression risk.
- Different types of training in managing the symptoms of depression .
- The effectiveness of online therapy platforms in treating depression.
- Should psychedelic therapy be explored as an alternative treatment for depression?
- The connection between depression and cardiovascular health: Is there a link?
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in preventing depression relapse.
- Depression as a bad a clinical condition .
- Should mind-body interventions (e.g., yoga , meditation) be integrated into depression treatment?
- Should emotional support animals be prescribed for individuals with depression?
- The effectiveness of peer support groups in decreasing depression symptoms.
- The use of antidepressants: are they overprescribed or necessary for treating depression?
- Adult depression and anxiety as a complex problem .
- The effectiveness of therapy versus medication in treating depression.
- The stigma surrounding depression and mental illness: how can we reduce it?
- The debate over the legalization of psychedelic drugs for treating depression.
- The relationship between creativity and depression: does one cause the other?
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy for generalized anxiety disorder and depression .
- The role of childhood trauma in shaping adult depression: Is it always a causal factor?
- The debate over the medicalization of sadness and grief as forms of depression.
- Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or meditation, are effective in treating depression.
- Depression as a widespread mental condition .
Controversial Topics about Depression
- The existence of “chemical imbalance” in depression: fact or fiction?
- The over-reliance on medication in treating depression: are alternatives neglected?
- Is depression overdiagnosed and overmedicated in Western society?
- Measurement of an individual’s level of depression .
- The role of Big Pharma in shaping the narrative and treatment of depression.
- Should antidepressant advertisements be banned?
- The inadequacy of current diagnostic criteria for depression: rethinking the DSM-5.
- Is depression a biological illness or a product of societal factors?
- Literature review on depression .
- The overemphasis on biological factors in depression treatment: ignoring environmental factors.
- Is depression a normal reaction to an abnormal society?
- The influence of cultural norms on the perception and treatment of depression.
- Should children and adolescents be routinely prescribed antidepressants?
- The role of family in depression treatment .
- The connection between depression and creative genius: does depression enhance artistic abilities?
- The ethics of using placebo treatment for depression studies.
- The impact of social and economic inequalities on depression rates.
- Is depression primarily a mental health issue or a social justice issue?
- Depression disassembling and treating .
- Should depression screening be mandatory in the workplace?
- The influence of gender bias in the diagnosis and treatment of depression.
- The controversial role of religion and spirituality in managing depression.
- Is depression a result of individual weakness or societal factors?
- Abnormal psychology: anxiety and depression case .
- The link between depression and obesity: examining the bidirectional relationship.
- The connection between depression and academic performance : causation or correlation?
- Should depression medication be available over the counter?
- The impact of internet and social media use on depression rates: harmful or beneficial?
- Interacting in the workplace: depression .
- Is depression a modern epidemic or simply better diagnosed and identified?
- The ethical considerations of using animals in depression research.
- The effectiveness of psychedelic therapies for treatment-resistant depression.
- Is depression a disability? The debate on workplace accommodations.
- Polysubstance abuse among adolescent males with depression .
- The link between depression and intimate partner violence : exploring the relationship.
- The controversy surrounding “happy” pills and the pursuit of happiness.
- Is depression a choice? Examining the role of personal responsibility.
Good Titles for Depression Essays
- The poetic depictions of depression: exploring its representation in literature.
- The melancholic symphony: the influence of depression on classical music.
- Moderate depression symptoms and treatment .
- Depression in modern music: analyzing its themes and expressions.
- Cultural perspectives on depression: a comparative analysis of attitudes in different countries.
- Contrasting cultural views on depression in Eastern and Western societies.
- Diagnosing depression in the older population .
- The influence of social media on attitudes and perceptions of depression in global contexts.
- Countries with progressive approaches to mental health awareness.
- From taboo to acceptance: the evolution of attitudes towards depression.
- Depression screening tool in acute settings .
- The Bell Jar : analyzing Sylvia Plath’s iconic tale of depression .
- The art of despair: examining Frida Kahlo’s self-portraits as a window into depression.
- The Catcher in the Rye : Holden Caulfield’s battle with adolescent depression.
- Music as therapy: how jazz artists turned depression into art.
- Depression screening tool for a primary care center .
- The Nordic paradox: high depression rates in Scandinavian countries despite high-quality healthcare.
- The Stoic East: how Eastern philosophies approach and manage depression.
- From solitude to solidarity: collective approaches to depression in collectivist cultures.
- The portrayal of depression in popular culture: a critical analysis of movies and TV shows.
- The depression screening training in primary care .
- The impact of social media influencers on depression rates among young adults.
- The role of music in coping with depression: can specific genres or songs help alleviate depressive symptoms?
- The representation of depression in literature: a comparative analysis of classic and contemporary works.
- The use of art as a form of self-expression and therapy for individuals with depression.
- Depression management guidelines implementation .
- The role of religion in coping with depression: Christian and Buddhist practices.
- The representation of depression in the video game Hellblade: Senua’s Sacrifice .
- The role of nature in coping with depression: can spending time outdoors help alleviate depressive symptoms?
- The effectiveness of dance/movement therapy in treating depression among older adults.
- The National Institute for Health: depression management .
- The portrayal of depression in stand-up comedy: a study of comedians like Maria Bamford and Chris Gethard.
- The role of spirituality in coping with depression: Islamic and Hindu practices .
- The portrayal of depression in animated movies : an analysis of Inside Out and The Lion King .
- The representation of depression by fashion designers like Alexander McQueen and Rick Owens.
- Depression screening in primary care .
- The portrayal of depression in documentaries: an analysis of films like The Bridge and Happy Valley .
- The effectiveness of wilderness therapy in treating depression among adolescents.
- The connection between creativity and depression: how art can help heal.
- The role of Buddhist and Taoist practices in coping with depression.
- Mild depression treatment research funding sources .
- The portrayal of depression in podcasts: an analysis of the show The Hilarious World of Depression .
- The effectiveness of drama therapy in treating depression among children and adolescents.
- The representation of depression in the works of Vincent van Gogh and Edvard Munch.
- Depression in young people: articles review .
- The impact of social media on political polarization and its relationship with depression.
- The role of humor in coping with depression: a study of comedians like Ellen DeGeneres.
- The portrayal of depression in webcomics: an analysis of the comics Hyperbole and a Half .
- The effect of social media on mental health stigma and its relationship with depression.
- Depression and the impact of human services workers .
- The masked faces: hiding depression in highly individualistic societies.
💭 Depression Speech Topics
Informative speech topics about depression.
- Different types of depression and their symptoms.
- The causes of depression: biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
- How depression and physical issues are connected .
- The prevalence of depression in different age groups and demographics.
- The link between depression and anxiety disorders .
- Physical health: The effects of untreated depression.
- The role of genetics in predisposing individuals to depression.
- What you need to know about depression .
- How necessary is early intervention in treating depression?
- The effectiveness of medication in treating depression.
- The role of exercise in managing depressive symptoms.
- Depression in later life: overview .
- The relationship between substance abuse and depression.
- The impact of trauma on depression rates and treatment.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness meditation in managing depressive symptoms.
- Enzymes conversion and metabolites in major depression .
- The benefits and drawbacks of electroconvulsive therapy for severe depression.
- The effect of gender and cultural norms on depression rates and treatment.
- The effectiveness of alternative therapies for depression, such as acupuncture and herbal remedies .
- The importance of self-care in managing depression.
- Symptoms of anxiety, depression, and peritraumatic dissociation .
- The role of support systems in managing depression.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating depression.
- The benefits and drawbacks of online therapy for depression.
- The role of spirituality in managing depression.
- Depression among minority groups .
- The benefits and drawbacks of residential treatment for severe depression.
- What is the relationship between childhood trauma and adult depression?
- How effective is transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for treatment-resistant depression?
- The benefits and drawbacks of art therapy for depression.
- Mood disorder: depression and bipolar .
- The impact of social media on depression rates.
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) in treating depression.
- Depression in older people .
- The impact of seasonal changes on depression rates and treatment options.
- The impact of depression on daily life and relationships, and strategies for coping with the condition.
- The stigma around depression and the importance of seeking help.
Persuasive Speech Topics about Depression
- How important is it to recognize the signs and symptoms of depression ?
- How do you support a loved one who is struggling with depression?
- The importance of mental health education in schools to prevent and manage depression.
- Social media: the rise of depression and anxiety .
- Is there a need to increase funding for mental health research to develop better treatments for depression?
- Addressing depression in minority communities: overcoming barriers and disparities.
- The benefits of including alternative therapies , such as yoga and meditation, in depression treatment plans.
- Challenging media portrayals of depression: promoting accurate representations.
- Two sides of depression disease .
- How social media affects mental health: the need for responsible use to prevent depression.
- The importance of early intervention: addressing depression in schools and colleges.
- The benefits of seeking professional help for depression.
- There is a need for better access to mental health care, including therapy and medication, for those suffering from depression.
- Depression in adolescents and suitable interventions .
- How do you manage depression while in college or university?
- The role of family and friends in supporting loved ones with depression and encouraging them to seek help.
- The benefits of mindfulness and meditation for depression.
- The link between sleep and depression, and how to improve sleep habits.
- How do you manage depression while working a high-stress job?
- Approaches to treating depression .
- How do you manage depression during pregnancy and postpartum?
- The importance of prioritizing employee mental health and providing resources for managing depression in the workplace.
- How should you manage depression while caring for a loved one with a chronic illness?
- How to manage depression while dealing with infertility or pregnancy loss.
- Andrew Solomon: why we can’t talk about depression .
- Destigmatizing depression: promoting mental health awareness and understanding.
- Raising funds for depression research: investing in mental health advances.
- The power of peer support: establishing peer-led programs for depression.
- Accessible mental health services: ensuring treatment for all affected by depression.
- Evidence-based screening for depression in acute care .
- The benefits of journaling for mental health: putting your thoughts on paper to heal.
- The power of positivity: changing your mindset to fight depression .
- The healing power of gratitude in fighting depression.
- The connection between diet and depression: eating well can improve your mood.
- Teen depression and suicide in Soto’s The Afterlife .
- The benefits of therapy for depression: finding professional help to heal.
- The importance of setting realistic expectations when living with depression.
📝 How to Write about Depression: Essay Structure
We’ve prepared some tips and examples to help you structure your essay and communicate your ideas.
Essay about Depression: Introduction
An introduction is the first paragraph of an essay. It plays a crucial role in engaging the reader, offering the context, and presenting the central theme.
A good introduction typically consists of 3 components:
- Hook. The hook captures readers’ attention and encourages them to continue reading.
- Background information. Background information provides context for the essay.
- Thesis statement. A thesis statement expresses the essay’s primary idea or central argument.
Hook : Depression is a widespread mental illness affecting millions worldwide.
Background information : Depression affects your emotions, thoughts, and behavior. If you suffer from depression, engaging in everyday tasks might become arduous, and life may appear devoid of purpose or joy.
Depression Essay Thesis Statement
A good thesis statement serves as an essay’s road map. It expresses the author’s point of view on the issue in 1 or 2 sentences and presents the main argument.
Thesis statement : The stigma surrounding depression and other mental health conditions can discourage people from seeking help, only worsening their symptoms.
Essays on Depression: Body Paragraphs
The main body of the essay is where you present your arguments. An essay paragraph includes the following:
- a topic sentence,
- evidence to back up your claim,
- explanation of why the point is essential to the argument;
- a link to the next paragraph.
Topic sentence : Depression is a complex disorder that requires a personalized treatment approach, comprising both medication and therapy.
Evidence : Medication can be prescribed by a healthcare provider or a psychiatrist to relieve the symptoms. Additionally, practical strategies for managing depression encompass building a support system, setting achievable goals, and practicing self-care.
Depression Essay: Conclusion
The conclusion is the last part of your essay. It helps you leave a favorable impression on the reader.
The perfect conclusion includes 3 elements:
- Rephrased thesis statement.
- Summary of the main points.
- Final opinion on the topic.
Rephrased thesis: In conclusion, overcoming depression is challenging because it involves a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors that affect an individual’s mental well-being.
Summary: Untreated depression heightens the risk of engaging in harmful behaviors such as substance abuse and can also result in negative thought patterns, diminished self-esteem, and distorted perceptions of reality.
We hope you’ve found our article helpful and learned some new information. If so, feel free to share it with your friends. You can also try our free online topic generator !
- Pain, anxiety, and depression – Harvard Health | Harvard Health Publishing
- Depression-related increases and decreases in appetite reveal dissociable patterns of aberrant activity in reward and interoceptive neurocircuitry – PMC | National Library of Medicine
- How to Get Treatment for Postpartum Depression – The New York Times
- What Is Background Information and What Purpose Does It Serve? | Indeed.com
- Thesis | Harvard College Writing Center
- Topic Sentences: How Do You Write a Great One? | Grammarly Blog
725 Research Proposal Topics & Title Ideas in Education, Psychology, Business, & More
414 proposal essay topics for projects, research, & proposal arguments.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Evolution and emerging trends in depression research from 2004 to 2019: a literature visualization analysis.

- 1 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2 School of Life Sciences, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Depression has become a major threat to human health, and researchers around the world are actively engaged in research on depression. In order to promote closer research, the study of the global depression knowledge map is significant. This study aims to map the knowledge map of depression research and show the current research distribution, hotspots, frontiers, and trends in the field of depression research, providing researchers with worthwhile information and ideas. Based on the Web of Science core collection of depression research from 2004 to 2019, this study systematically analyzed the country, journal, category, author, institution, cited article, and keyword aspects using bibliometric and data visualization methods. A relationship network of depression research was established, highlighting the highly influential countries, journals, categories, authors, institutions, cited articles, and keywords in this research field. The study identifies great research potential in the field of depression, provides scientific guidance for researchers to find potential collaborations through collaboration networks and coexistence networks, and systematically and accurately presents the hotspots, frontiers, and shortcomings of depression research through the knowledge map of global research on depression with the help of information analysis and fusion methods, which provides valuable information for researchers and institutions to determine meaningful research directions.
Introduction
Health issues are becoming more and more important to people due to the continuous development of health care. The social pressures on people are becoming more and more pronounced in a social environment that is developing at an increasing rate. Prolonged exposure to stress can have a negative impact on brain development ( 1 ), and depression is one of the more typical disorders that accompany it. Stress will increase the incidence of depression ( 2 ), depression has become a common disease ( 3 ), endangering people's physical health. Depression is a debilitating mental illness with mood disorders, also known as major depression, clinical depression, or melancholia. In human studies of the disease, it has been found that depression accounts for a large proportion of the affected population. According to the latest data from the World Health Organization (WHO) statistics in 2019, there are more than 350 million people with depression worldwide, with an increase of about 18% in the last decade and an estimated lifetime prevalence of 15% ( 4 ), it is a major cause of global disability and disease burden ( 5 ), and depression has quietly become a disease that threatens hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
Along with the rise of science communication research, the quantification of science is also flourishing. As a combination of “data science” and modern science, bibliometrics takes advantage of the explosive growth of research output in the era of big data, and uses topics, authors, publications, keywords, references, citations, etc. as research targets to reveal the current status and impact of the discipline more accurately and scientifically. Whereas, there is not a wealth of bibliometric studies related to depression. Fusar-Poli et al. ( 6 ) used bibliometrics to systematically evaluate cross-diagnostic psychiatry. Hammarström et al. ( 7 ) used bibliometrics to analyze the scientific quality of gender-related explanatory models of depression in the medical database PubMed. Tran et al. ( 8 ) used the bibliometric analysis of research progress and effective interventions for depression in AIDS patients. Wang et al. ( 9 ) used bibliometric methods to analyze scientific studies on the comorbidity of pain and depression. Shi et al. ( 10 ) performed a bibliometric analysis of the top 100 cited articles on biomarkers in the field of depression. Dongping et al. ( 11 ) used bibliometric analysis of studies on the association between depression and gut flora. An Chunping et al. ( 12 ) analyzed the literature on acupuncture for depression included in PubMed based on bibliometrics. Yi and Xiaoli ( 13 ) used a bibliometric method to analyze the characteristics of the literature on the treatment of depression by Chinese medicine in the last 10 years. Zhou and Yan ( 14 ) used bibliometric method to analyze the distribution of scientific and technological achievements on depression in Peoples R China. Guaijuan ( 15 ) performed a bibliometric analysis of the interrelationship between psoriasis and depression. Econometric analysis of the relationship between vitamin D deficiency and depression was performed by Yunzhi et al. ( 16 ) and Shauni et al. ( 17 ) performed a bibliometric analysis of domestic and international research papers on depression-related genes from 2003 to 2007. A previous review of depression-related bibliometric studies revealed that there is no bibliometric analysis of global studies in the field of depression, including country network analysis, journal network analysis, category network analysis, author network analysis, institutional network analysis, literature co-citation analysis, keyword co-presentation analysis, and cluster analysis.
The aim of this study was to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature-based data mining and metrics analysis of depression-related research. More specifically, this analysis focuses on cooperative network and co-presentation analysis, based on the 36,477 papers included in the Web of Science Core Collection database from 2004 to 2019, and provides an in-depth analysis of cooperative network, co-presentation network, and co-citation through modern metrics and data visualization methods. Through the mining of key data, the data correlation is further explored, and the results obtained can be used to scientifically and reasonably predict the depression-related information. This study aims to show the spatial and temporal distribution of research countries, journals, authors, and institutions in the field of depression in a more concise manner through a relational network. A deeper understanding of the internal structure of the research community will help researchers and institutions to establish more accurate and effective global collaborations, in line with the trend of human destiny and globalization. In addition, the study will allow for the timely identification of gaps in current research. A more targeted research direction will be established, a more complete picture of the new developments in the field of depression today will be obtained, and the research protocol will be informed for further adjustments. The results of these analyses will help researchers understand the evolution of this field of study. Overall, this paper uses literature data analysis to find research hotspots in the field of depression, analyze the knowledge structure within different studies, and provide a basis for predicting research frontiers. This study analyzed the literature in the field of depression using CiteSpace 5.8.R2 (64-bit) to analyze collaborative networks, including country network analysis, journal network analysis, category network analysis, researcher network analysis, and institutional network analysis using CiteSpace 5.8.R2 (64-bit). In addition, literature co-citation, keyword co-presentation, and cluster analysis of depression research hotspots were also performed. Thus, exploring the knowledge dimensions of the field, quantifying the research patterns in the field, and uncovering emerging trends in the field will help to obtain more accurate and complete information. The large amount of current research results related to depression will be presented more intuitively and accurately with the medium of information technology, and the scientific evaluation of research themes and trend prediction will be provided from a new perspective.
Data Sources
The data in this paper comes from the Web of Science (WoS) core collection. The time years were selected as 2004–2019. First, the literature was retrieved after entering “depression” using the title search method. A total of 73,829 articles, excluding “depression” as “suppression,” “decline,” “sunken,” “pothole,” “slump,” “low pressure,” “frustration.” The total number of articles with other meanings such as “depression” was 5,606, and the total number of valid articles related to depression was 68,223. Next, the title search method was used to search for studies related to “major depressive disorder” not “depression,” and a total of 8,070 articles were retrieved. For the two search strategies, a total of 76,293 records were collected. The relevant literature retrieved under the two methods were combined and exported in “plain text” file format. The exported records included: “full records and references cited.” CiteSpace processed the data to obtain 41,408 valid records, covering all depression-related research articles for the period 2004–2019, and used this as the basis for analysis.
Processing Tools
CiteSpace ( 18 ), developed by Chao-Mei Chen, a professor in the School of Information Science and Technology at Drexel University, is a Java-based program with powerful data visualization capabilities and is one of the most widely used knowledge mapping tools. The software version used in this study is CiteSpace 5.8.R2 (64-bit).
Methods of Analysis
This study uses bibliometrics and data visualization as analytical methods. First, the application of bibliometrics to the field of depression helped to identify established and emerging research clusters, demonstrating the value of research in this area. Second, data visualization provides multiple perspectives on the data, presenting correlations in a clearer “knowledge graph” that can reveal underestimated and overlooked trends, patterns, and differences ( 19 ). CiteSpace is mainly based on the “co-occurrence clustering idea,” which extracts the information units (keywords, authors, institutions, countries, journals, etc.) in the data by classification, and then further reconstructs the data in the information units to form networks based on different types and strengths of connections (e.g., keyword co-occurrence, author collaboration, etc.). The resulting networks include nodes and links, where the nodes represent the information units of the literature and the links represent the existence of connections (co-occurrence) between the nodes. Finally, the network is measured, statistically analyzed, and presented in a visual way. The analysis needs to focus on: the overall structure of the network, key nodes and paths. The key evaluation indicators in this study are: betweenness centrality, year, keyword frequency, and burst strength. Betweenness centrality (BC) is the number of times a node acts as the shortest bridge between two other nodes. The higher the number of times a node acts as an “intermediary,” the greater its betweenness centrality. Betweenness centrality is a measure of the importance of articles found and measured by nodes in the network by labeling the category (or authors, journals, institutions, etc.) with purple circles. There may be many shortest paths between two nodes in the network, and by counting all the shortest paths of any two nodes in the network, if many of the shortest paths pass through a node, then the node is considered to have high betweenness centrality. In CiteSpace, nodes with betweenness centrality over 0.1 are called critical nodes. Year, which represents the publication time of the article. Frequency, which represents the number of occurrences. Burst strength, an indicator used to measure articles with sudden rise or sudden decline in citations. Nodes with high burst strength usually represent a shift in a certain research area and need to be focused on, and the burst article points are indicated in red. The nodes and their sizes and colors are first analyzed initially, and further analyzed by betweenness centrality indicators for evaluation. Each node represents an article, and the larger the node, the greater the frequency of the keyword word and the greater the relevance to the topic. Similarly, the color of the node represents time: the warmer the color, the more recent the time; the colder the color, the older the era; the node with a purple outer ring is a node with high betweenness centrality; the color of each annual ring can determine the time distribution: the color of the annual ring represents the corresponding time, and the thickness of one annual ring is proportional to the number of articles within the corresponding time division; the dominant color can reflect the relative concentration of the emergence time; the node The appearance of red annual rings in the annual rings means hot spots, and the frequency of citations has been or is still increasing rapidly.
Large-Scale Assessment
Country analysis.
During the period 2004–2019, a total of 157 countries/territories have conducted research on depression, which is about 67.38% of 233 countries/territories worldwide. This shows that depression is receiving attention from many countries/regions around the world. Figure 1 shows the geographical distribution of published articles for 157 countries. The top 15 countries are ranked according to the number of articles published. Table 1 lists the top 15 countries with the highest number of publications in the field of depression worldwide from 2004 to 2019. These 15 countries include 4 Asian countries (Peoples R China, Japan, South Korea, Turkey), 2 North American countries (USA, Canada), 1 South American country (Brazil), 7 European countries (UK, Germany, Netherlands, Italy, France, Spain, Sweden), and 1 Oceania country (Australia).
Figure 1 . Geographical distributions of publications, 2004–2019.
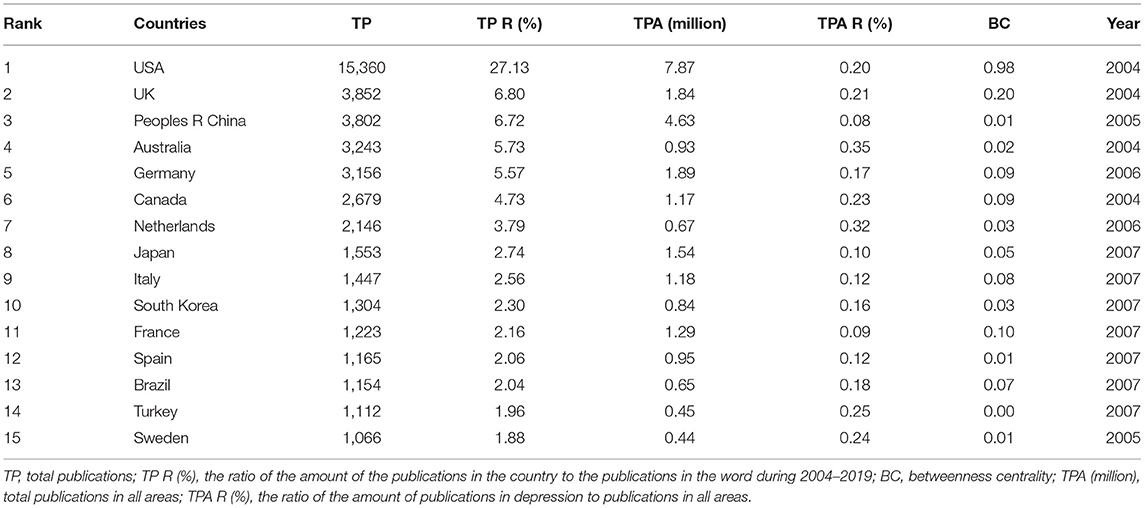
Table 1 . The top 15 productive countries.
Overall, the main distribution of these articles is in USA and some European countries, such as UK, Germany, Netherlands, Italy, France, Spain, and Sweden. This means that these countries are more interested and focused on research on depression compared to others. The total number of publications across all research areas in the Web of Science core collection is similar to the distribution of depression research areas, with the trend toward USA, UK, and Peoples R China as leading countries being unmistakable, and USA has been a leader in the field of depression, with far more articles published than any other country. It can also be seen that USA is the country with the highest betweenness centrality in the network of national collaborations analyzed in this paper. USA research in the field of depression is closely linked to global research, and is an important part of the global collaborative network for depression research. As of 2019, the total number of articles published in depression performance research in USA represents 27.13% of the total number of articles published in depression worldwide, which is ~4 times more than the second-place country, UK, which is far ahead of other countries. Peoples R China, as the third most published country, has a dominant number of articles, but its betweenness centrality is 0.01, reflecting the fact that Peoples R China has less collaborative research with other countries, so Peoples R China should strengthen its foreign collaborative research and actively establish global scientific research partnerships to seek development and generate breakthroughs in cooperation. The average percentage of scientific research on depression in each country is about 0.19%, also highlighting the urgent need to address depression as one of the global human health problems. The four Asian countries included in the top 15 countries are Peoples R China, Japan, South Korea, and Turkey, with Peoples R China ranking third with 6.72% of the total number of all articles counted. The distribution may be explained by the fact that Peoples R China is the largest developing country with a rapid development rate as the largest. Along with the steady rise in the country's economic power, people are creating economic benefits and their health is becoming a consumable commodity. The lifetime prevalence and duration of depression varies by country and region ( 2 ), but the high prevalence and persistence of depression worldwide confirms the increasing severity of the disease worldwide. The WHO estimates that more than 300 million people, or 4.4% of the world's population, suffer from depression ( 20 ), with the number of people suffering from depression increasing at a patient rate of 18.4% between 2005 and 2015. Depression, one of the most prevalent mental illnesses of our time, has caused both physical and psychological harm to many people, and it has become the leading cause of disability worldwide today, and in this context, there is increased interest and focus on research into depression. It is expected that a more comprehensive understanding of depression and finding ways to prevent and cope with the occurrence of this disease can help people get rid of the pain and shadow brought by depression, obtain a healthy and comfortable physical and mental environment and physical health, and make Chinese contributions to the cause of human health. Undoubtedly, the occurrence of depressive illnesses in the context of irreversible human social development has stimulated a vigorous scientific research environment on depression in Peoples R China and other developing countries and contributed to the improvement of research capacity in these countries. Moreover, from a different perspective, the geographical distribution of articles in this field also represents the fundamental position of the country in the overall scientific and academic research field.
Growth Trend Analysis
Figure 2 depicts the distribution of 38,433 articles from the top 10 countries in terms of the number of publications and the trend of growth during 2004–2019.
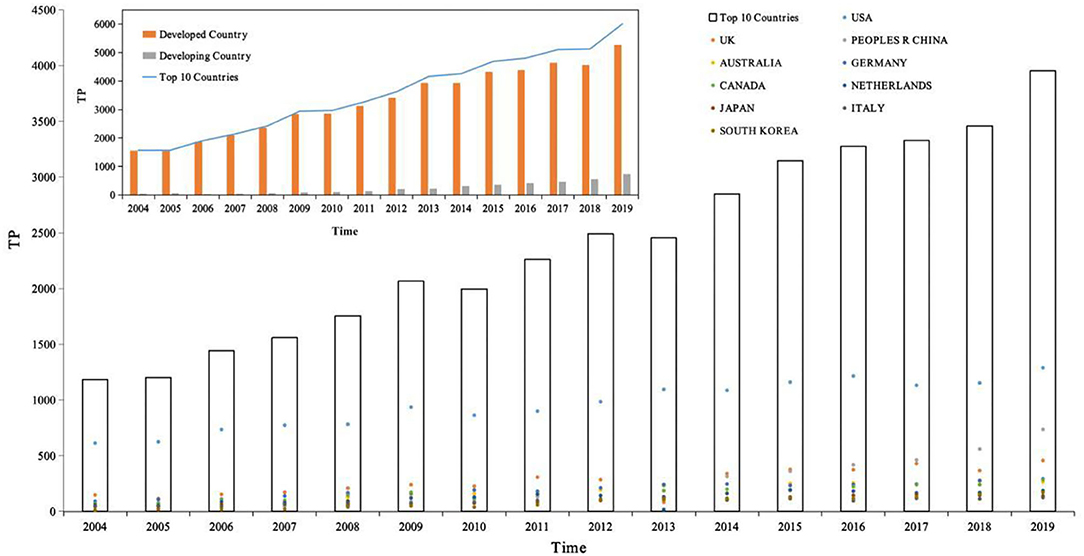
Figure 2 . The distribution of publications in top 10 productive countries, 2004–2019. Source: author's calculation. National development classification criteria refer to “Human Development Report 2020” ( 21 ).
First, the number of articles published per year for the top 10 countries in terms of productivity was counted and then the white bar chart in Figure 2 was plotted, with the year as the horizontal coordinate and total publications as the vertical coordinate, showing the distribution of the productivity of articles in the field of depression per year. The total number of publications for the period 2004–2019 is 38,433. Based on the white bars and line graphs in Figure 2 , we can divide this time period into three growth periods. The number of publications in each growth period is calculated based on the number of publications per year. As can be seen from the figure, the period 2004–2019 can be divided into three main growth periods, namely 2004–2009, 2010–2012, and 2013–2019, the first growth period being from 2004 to 2009, the number of publications totaled 6,749, accounting for 23.97% of all publications; from 2010 to 2012, the number of publications totaled 8,236, accounting for 17.56% of all publications; and from 2013 to 2019, the number of publications totaled 22,473, accounting for 58.47% of all publications. Of these, 2006 was the first year of sharp growth with an annual growth rate of 19.97%, 2009 was the second year of sharp growth with an annual growth rate of 17.64%, and 2008 was the third year of sharp growth with an annual growth rate of 16.09%. In the last 5 years, 2019 has also shown a sharp growth trend with a growth rate of 14.34%. Notably, in 2010 and 2013, there was negative growth with the growth rate of −3.39 and −1.45%. In the last 10 years, depression research has become one of the most valuable areas of human research. It can also be noted that the number of publications in the field of depression in these 10 countries has been increasing year after year.
Second, the analysis is conducted from the perspective of national development, divided into developed and developing countries, as shown in the orange bar chart in Figure 2 , where the horizontal coordinate is year and the vertical coordinate is total publications, comparing the article productivity variability between developed and developing countries. The top 10 most productive countries in the field of depression globally include nine developed countries and one developing country, respectively. During the period 2004–2019, 34,631 papers were published in developed countries and 3,802 papers were published in developing countries, with developed countries accounting for 90.11% of the 38,433 articles and developing countries accounting for 9.89%, and the total number of publications in developed countries was about 9 times higher than that in developing countries. During the period 2004–2019, the number of publications in developed countries showed negative growth in 2 years (2010 and 2013) with growth rates of −3.39 and −1.45%, respectively. The rest of the years showed positive growth with growth rates of 1.52% (2005), 19.97 (2006), 8.11 (2007), 12.70 (2008), 17.64 (2009), 13.22 (2011), 10.17 (2012), 16.09 (2014), 10.46 (2015), 4.10 (2016), 1.59 (2017), 3.91 (2018), and 14.34 (2019), showing three periods of positive growth: 2004–2009, 2011–2012, and 2014–2019, with the highest growth rate of 19.97% in 2006. Recent years have also shown a higher growth trend, with a growth rate of 14.34% in 2019. It is worth noting that developing countries have been showing positive growth in the number of articles in the period 2004–2019, with annual growth rates of 81.25 (2005), 17.24 (2006), 35.29 (2007), 19.57 (2008), 65.45 (2009), 13.19 (2010), 29.13 (2011), 54.89 (2012), 12.14 (2013), 36.36 (2014), 14.92 (2015), 16.02 (2016), 10.24 (2017), 21.17 (2018), and 31.37 (2019), with the highest growth rate of 81.25% in 2005. In the field of depression research, developed countries are still the main force and occupy an important position.
Further, 10 countries with the highest productivity in the field of depression are compared, total publications in the vertical coordinate, and the colored scatter plot contains 10 colored dots, representing 10 different countries. On the one hand, the variability of the contributions of different countries in the same time frame can be compared horizontally. On the other hand, it is possible to compare vertically the variability of the growth of different countries over time. Among them, USA, with about 40.29% of the world's publications in the field of depression, has always been a leader in the field of depression with its rich research results. Peoples R China, as the only developing country, ranks 3rd in the top 10 countries with high production of research papers in the field of depression, and Peoples R China's research in the field of depression has shown a rapid growth trend, and by 2016, it has jumped to become the 2nd largest country in the world, with the number of published papers increasing year by year, which has a broad prospect and great potential for development.
Distribution of Periodicals
Table 2 lists the top 15 journals in order of number of journal co-citations. In the field of depression, the top 15 cited journals accounted for 19.06% of the total number of co-citations, nearly one in five of the total number of journal co-citations. In particular, the top 3 journals were ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT (ARCHIVES OF GENERAL PSYCHIATRY), J AFFECT DISORDERS (JOURNAL OF AFFECTIVE DISORDERS), and AM J PSYCHIAT (AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY), with co-citation counts of 20,499, 20,302, and 20,143, with co-citation rates of 2.09, 2.07, and 2.06%, respectively. The main research area of ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT is Psychiatry; the main research area of the journal J AFFECT DISORDERS is Neurosciences and Neurology, Psychiatry; AM J PSYCHIAT is the main research area of Psychiatry, and the three journals have “psychiatry” in common, making them the most frequently co-cited journals in the field of depression.
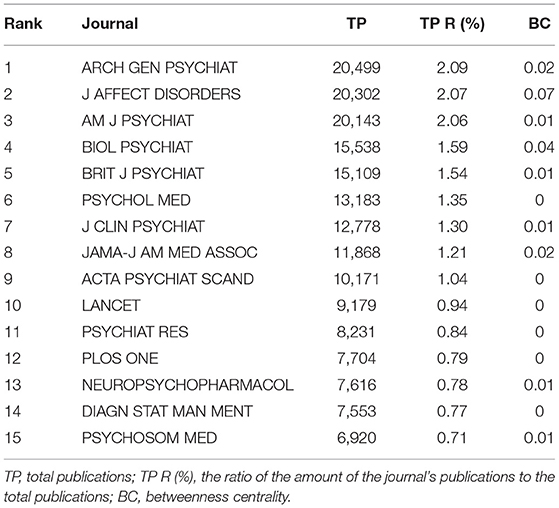
Table 2 . The top 15 co-cited journals.
Figure 3 shows the network relationship graph of the cited journals from 2004 to 2019. The figure takes g-index as the selection criteria, the scale factor k = 25 to include more nodes. Each node of the graph represents each journal, the node size represents the number of citation frequencies, the label size represents the size of the betweenness centrality of the journal in the network, and the links between journals represent the co-citation relationships. The journal co-citation map reflects the structure of the journals, indicating that there are links between journals and that the journals include similar research topics. These journals included research topics related to neuroscience, psychiatry, neurology, and psychology. The journal with betweenness centrality size in the top 1 was ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT, with betweenness centrality size of 0.07, and impact shadows of 14.48. ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT, has research themes of Psychiatry. In all, these journals in Figure 3 occupy an important position in the journal's co-citation network and have strong links with other journals.
Figure 3 . Prominent journals involved in depression. The betweenness centrality of a node in the network measures the importance of the position of the node in the network. Two types of nodes may have high betweenness centrality scores: (1) Nodes that are highly connected to other nodes, (2) Nodes are positioned between different groups of nodes. The lines represent the link between two different nodes.
Distribution of Categories
Table 3 lists the 15 most popular categories in the field of depression research during the period 2004–2019. In general, the main disciplines involved are neuroscience, psychology, pharmacy, medicine, and health care, which are closely related to human life and health issues. Of these, psychiatry accounted for 20.78%, or about one-five, making it the most researched category. The study of depression focuses on neuroscience, reflecting the essential characteristics of depression as a category of mental illness and better reflecting the fact that depression is an important link in the human public health care. In addition, Table 3 shows that the category with the highest betweenness centrality is Neuroscience, followed by Public, Environment & Occupational Health, and then Pharmacology & Pharmacy, with betweenness centrality of 0.16, 0.13, and 0.11, respectively. It is found that the research categories of depression are also centered on disciplines such as neuroscience, public health and pharmacology, indicating that research on depression requires a high degree of integration of multidisciplinary knowledge and integration of information from various disciplines in order to have a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the depression.
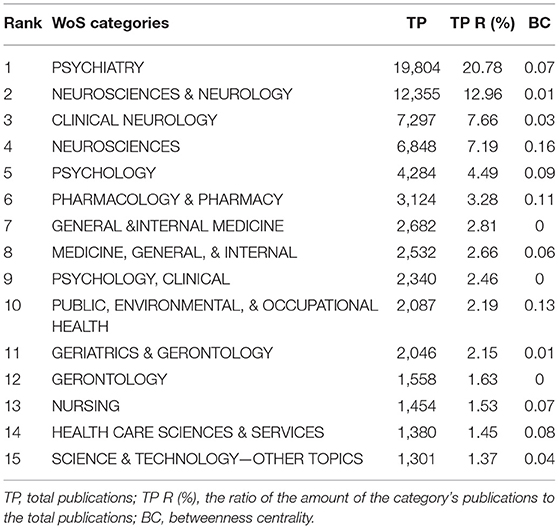
Table 3 . The top 15 productive categories, 2004–2019.
Figure 4 shows the nine categories with the betweenness centrality in the category research network, with Neuroscience being the node with the highest betweenness centrality in this network, meaning that Neuroscience is most strongly linked to all research categories in the field of depression research. Depression is a debilitating psychiatric disorder with mood disorders. It is worth noting that the development of depression not only has psychological effects on humans, but also triggers many somatic symptoms that have a bad impact on their daily work and life, giving rise to the second major mediating central point of research with public health as its theme. The somatization symptoms of depression often manifest as abnormalities in the cardiovascular system, and many studies have looked at the pathology of the cardiovascular system in the hope of finding factors that influence the onset of depression, mechanisms that trigger it or new ways to treat it. Thus, depression involves not only the nervous system, but also interacts with the human cardiovascular system, for example, and the complexity of depression dictates that the study of depression is an in-depth study based on complex systems.
Figure 4 . Prominent categories involved in depression, 2004–2019. The betweenness centrality of a node in the network measures the importance of the position of the node in the network. Two types of nodes may have high betweenness centrality scores: (1) Nodes that are highly connected to other nodes, (2) Nodes are positioned between different groups of nodes. The lines represent the link between two different nodes.
Author Statistics
The results of the analysis showed that there were many researchers working in the field of depression over the past 16 years, and 63 of the authors published at least 30 articles related to depression. Table 4 lists the 15 authors with the highest number of articles published. It includes the rank of the number of articles published, author, country, number of articles published in depression-related studies, total number of articles included in Web of Science, total number of citations, average number of citations, and H-index. According to the statistics, seven of the top 15 authors are from USA, three from the Netherlands, one from Canada, one from Australia, one from New Zealand, one from Italy, and one from Germany. From this, it can be seen that these productive authors are from developed countries, thus it can be inferred that developed countries have a better research environment, more advanced research technology and more abundant research funding. The evaluation indicators in the author co-occurrence network are frequency, betweenness centrality and time of first appearance. The higher the frequency, i.e., the higher the number of collaborative publications, the more collaboration, the higher the information dissemination rate, the three authors with the highest frequency in this author co-occurrence network are MAURIZIO FAVA, BRENDA W. J. H. PENNINX, MADHUKAR H. TRIVEDI; the higher the betweenness centrality, i.e., the closer the relationship with other authors, the more collaboration, the higher the information dissemination rate, the three authors with the highest betweenness centrality are the three authors with the highest betweenness centrality are MICHAEL E. THASE, A. JOHN RUSH; the time of first appearance, i.e., the longer the influence generated by the author's research, the higher the information dissemination rate; in addition, the impact factor and citations can also reflect the information dissemination efficiency of the authors.
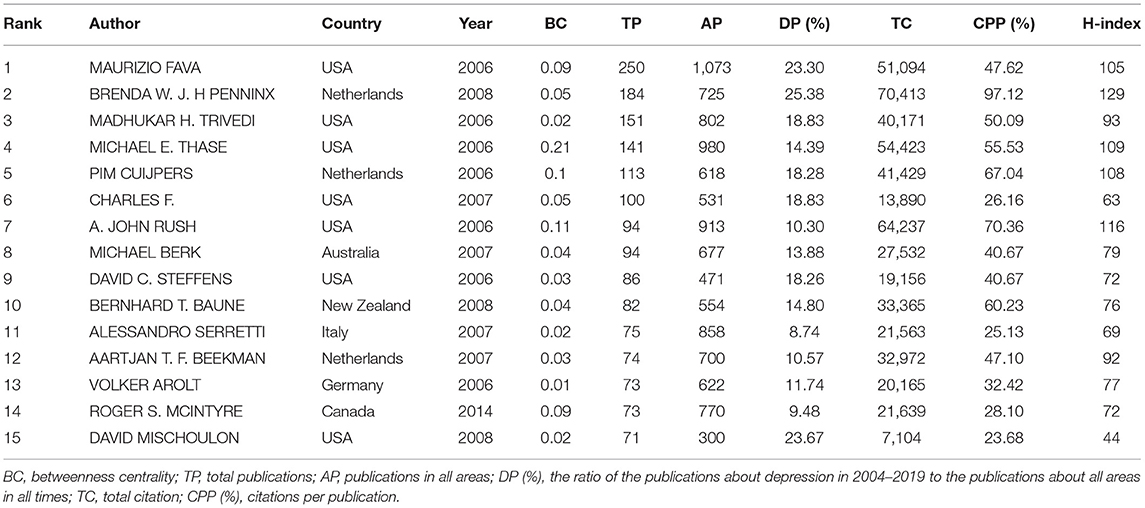
Table 4 . The top 15 authors in network of co-authorship, 2004–2019.
The timezone view ( Figure 5 ) in the author co-occurrence network clearly shows the updates and interactions of author collaborations, for example. All nodes are positioned in a two-dimensional coordinate with the horizontal axis of time, and according to the time of first posting, the nodes are set in different time zones, and their positions are sequentially upward with the time axis, showing a left-to-right, bottom-up knowledge evolution diagram. The time period 2004–2019 is divided into 16 time zones, one for each year, and each circle in the figure represents an author, and the time zone in which the circle appears is the year when the author first published an article in the data set of this study. The closer the color, the warmer the color, the closer the time, the colder the color, the older the era, the thickness of an annual circle, and the number of articles within the corresponding time division is proportional, the dominant color can reflect the relative concentration of the emergence time, the nodes appear in the annual circle of the red annual circle, that is, on behalf of the hot spot, the frequency of being cited was or is still increasing sharply. Nodes with purple outer circles are nodes with high betweenness centrality. The time zone view demonstrates the growth of author collaboration in the field, and it can be found from the graph that the number of author collaborations increases over time, and the frequency of publications in the author collaboration network is high; observe that the thickness of the warm annual rings in the graph is much greater than the thickness of the cold annual rings, which represents the increase of collaboration in time; there are many authors in all time zones, which indicates that there are many research collaborations and achievements in the field, and the field is in a period of collaborative prosperity. The linkage relationship between the sub-time-periods can be seen by the linkage relationship between the time periods, and it can be found from the figure that there are many linkages in the field in all time periods, which indicates that the author collaboration in the field of depression research is strong.
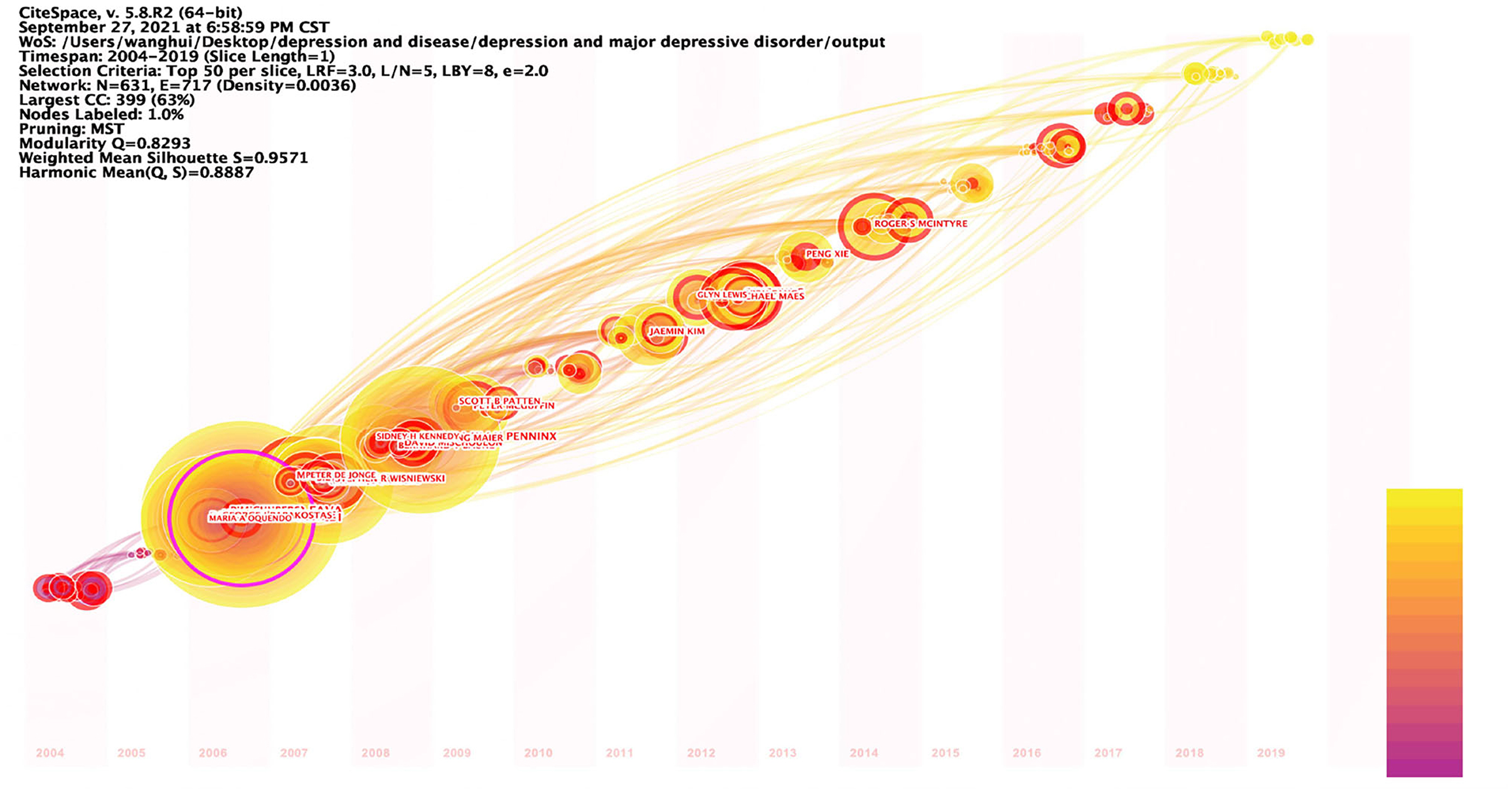
Figure 5 . Timezone view of the author's co-existing network in depression, 2004–2019. The circle represents the author, the time zone in which the circle appears is the year in which the author first published in this study dataset, the radius of the circle represents the frequency of appearance, the color represents the different posting times, the lines represent the connections between authors, and the time zone diagram shows the evolution of author collaboration.
Institutional Statistics
Table 5 lists the top 15 research institutions in network of co-authors' institutions. These include 10 American research institutions, two Netherlands research institutions, one UK research institution, one Canadian research institution and one Australian research institution, all of which, according to the statistics, are from developed countries. Of these influential research institutions, 66.7% are from USA. Figure 6 shows the collaborative network with these influential research institutions as nodes. Kings Coll London (0.2), Univ Michigan (0.17), Univ Toronto (0.15), Stanford Univ (0.14), Univ Penn (0.14), Univ Pittsburgh (0.14), Univ Melbourne (0.12), Virginia Commonwealth Univ (0.12), Columbia Univ (0.1), Duke Univ (0.1), Massachusetts Gen Hosp (0.1), Vrije Univ Amsterdam (0.1), with betweenness centrality >0.1. Kings Coll London has a central place in this collaborative network and is influential in the field of depression research. Table 6 lists the 15 institutions with the strong burst strength. The top 3 institutions are all from USA. Univ Copenhagen, Univ Illinois, Harvard Med Sch, Boston Univ, Univ Adelaide, Heidelberg Univ, Univ New South Wales, and Icahn Sch Med Mt Sinai have had strong burst strength in recent years. It suggests that these institutions may have made a greater contribution to the field of depression over the course of this year and more attention could be paid to their research.
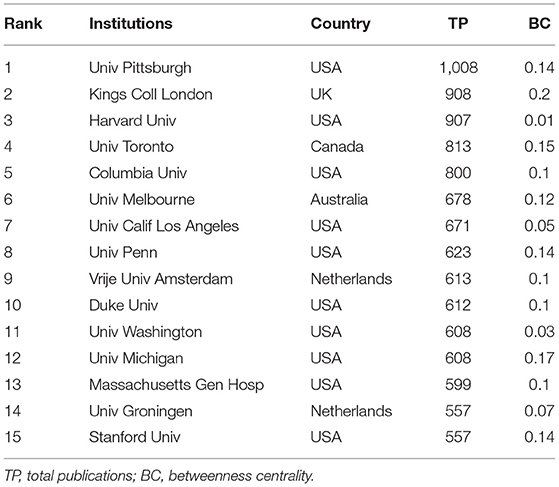
Table 5 . The top 15 institutions in network of co-authors' institutions, 2004–2019.
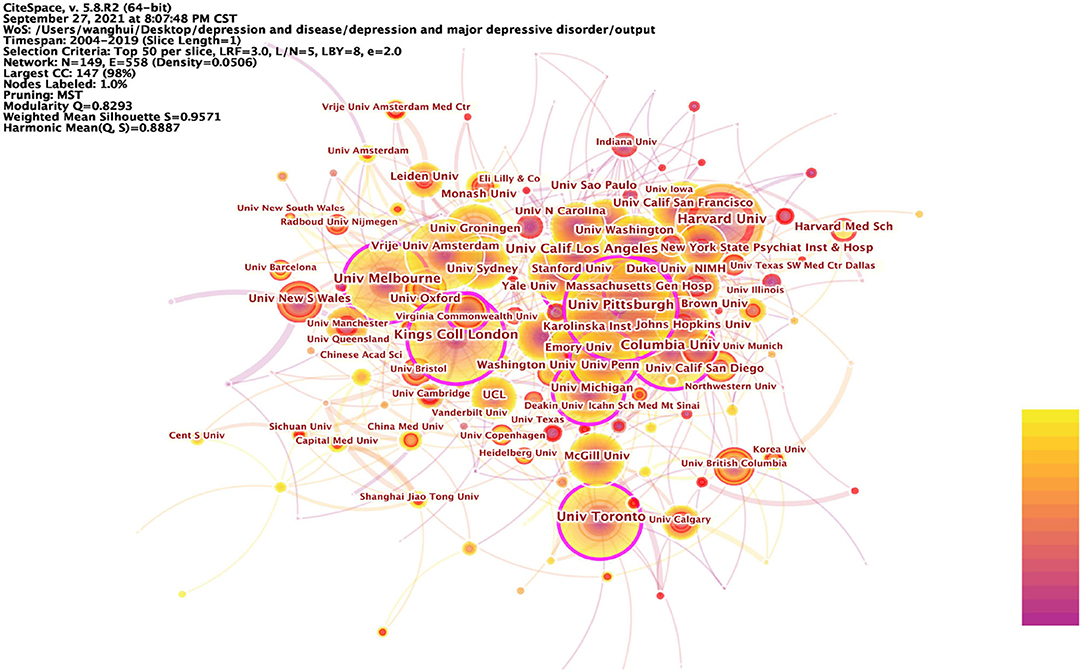
Figure 6 . Prominent institutions involved in depression, 2004–2019. The betweenness centrality of a node in the network measures the importance of the position of the node in the network. Two types of nodes may have high betweenness centrality scores: (1) Nodes that are highly connected to other nodes, (2) Nodes are positioned between different groups of nodes. The lines represent the link between two different nodes.
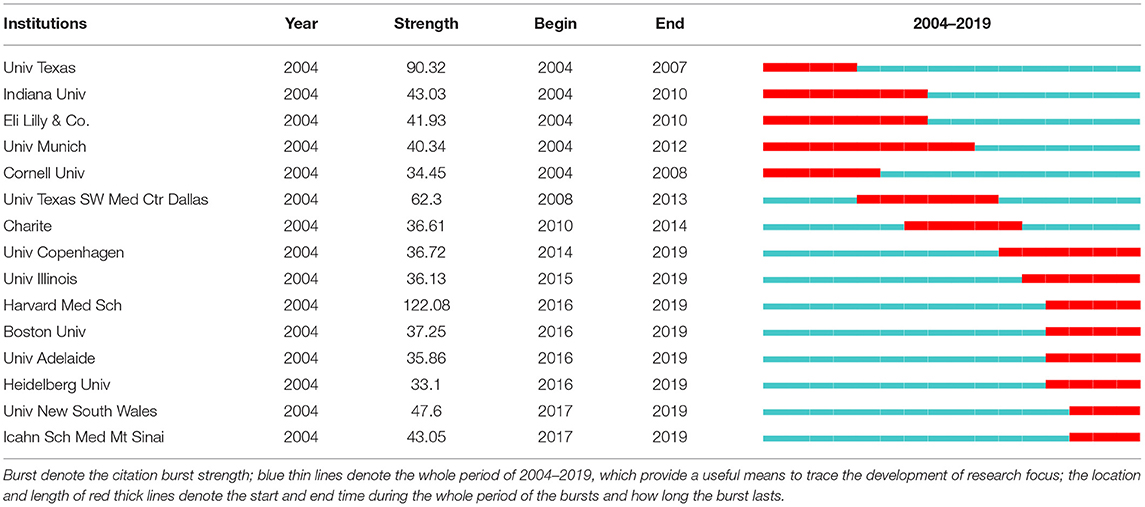
Table 6 . The top 15 institutions with the strongest citation bursts, 2004–2019.
Summing up the above analysis, it can be seen that the research institutions in USA are at the center of the depression research field, are at the top of the world in terms of quantity and quality of research, and are showing continuous growth in vitality. Research institutions in USA, as pioneers among all research institutions, lead and drive the development of depression research and play an important role in cutting-edge research in the field of depression.
Article Citations
Table 7 lists the 16 articles that have been cited more than 1,000 times within the statistical range of this paper from 2004 to 2019. As can be seen from the table, the most cited article was written by Dowlati et al. from Canada and published in BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY 2010, which was cited 2,556 times. In addition, 11 of these 16 highly cited articles were from the USA. Notably, two articles by Kroenke, K as first author appear in this list, ranked 7th and 11th, respectively. In addition, there are three articles from Canada, one article from Switzerland, and one article from the UK. And interestingly, all of these countries are developed countries. It can be reflected that developed countries have ample research experience and high quality of research in the field of depression research. On the other hand, it also reflects that depression is a key concern in developed countries. These highly cited articles provide useful information to many researchers and are of high academic and exploratory value.
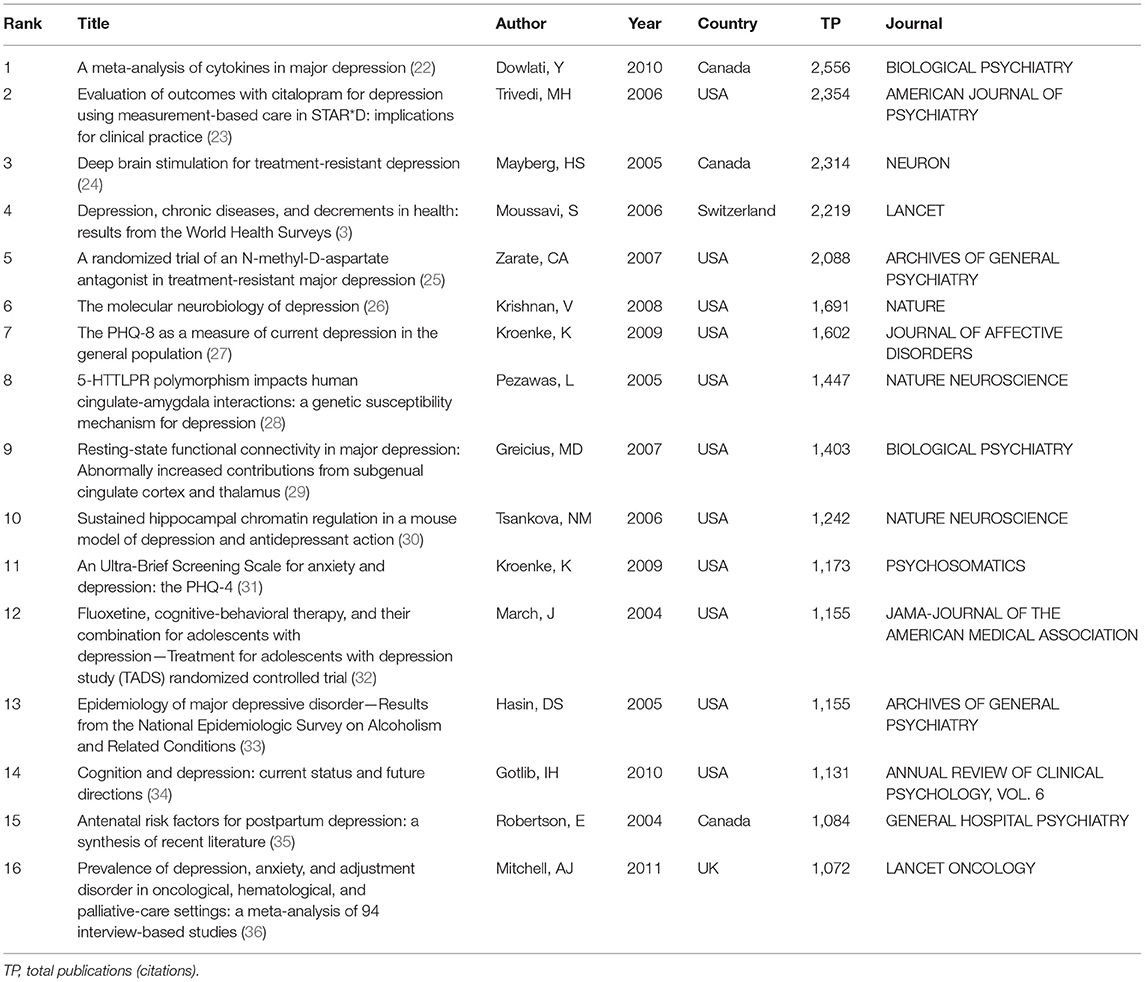
Table 7 . The top 15 frequency cited articles, 2004–2019.
Research Hotspots Ang Frontiers
Keyword analysis.
The keyword analysis of depression yielded the 25 most frequent keywords in Table 8 and the keyword co-occurrence network in Figure 7 . Also, the data from this study were detected by burst, the 25 keywords with the strongest burst strength were obtained in Table 9 . These results bring out the popular and cutting-edge research directions in the field clearly.
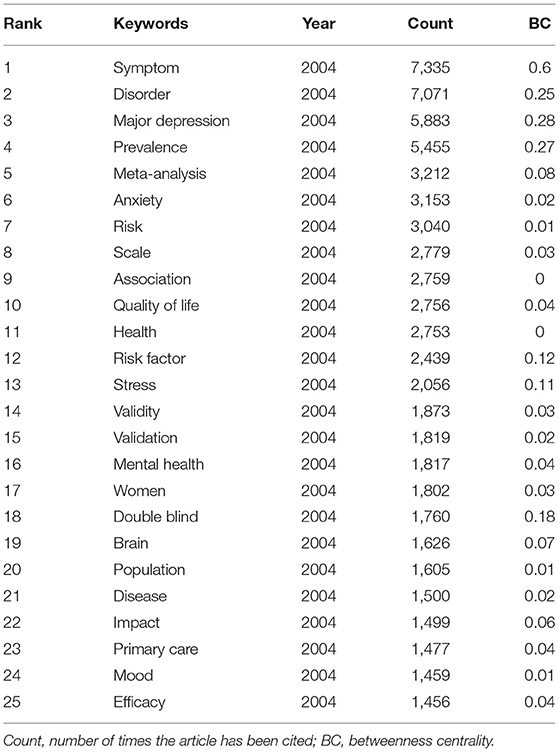
Table 8 . Top 25 frequent keywords in the period of 2004–2019.
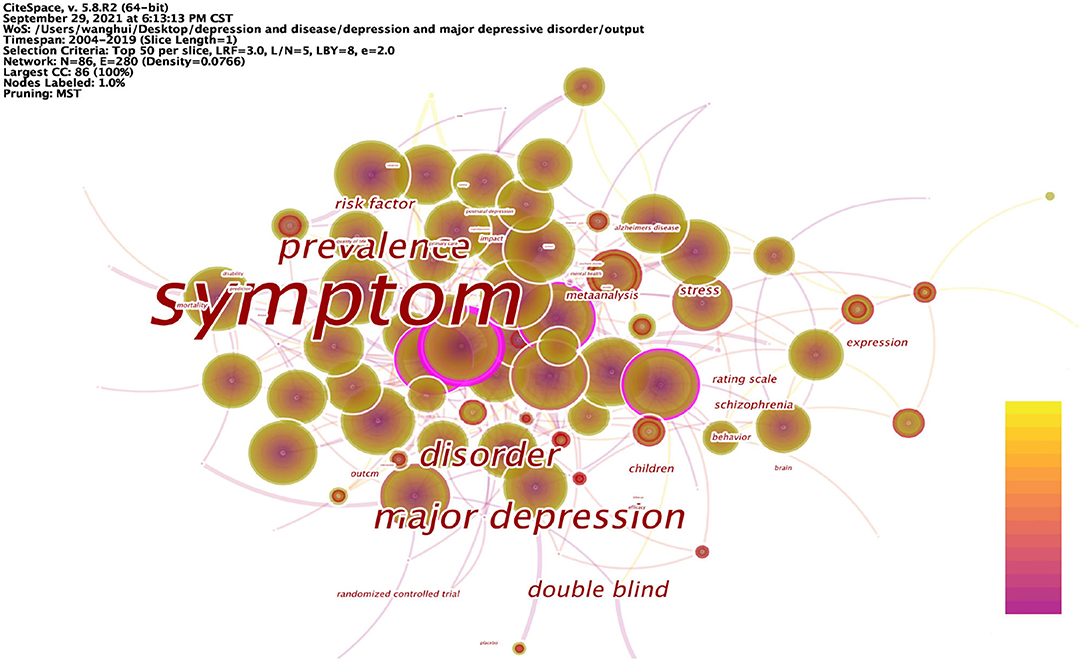
Figure 7 . Keyword co-occurrence network in depression, 2004–2019.
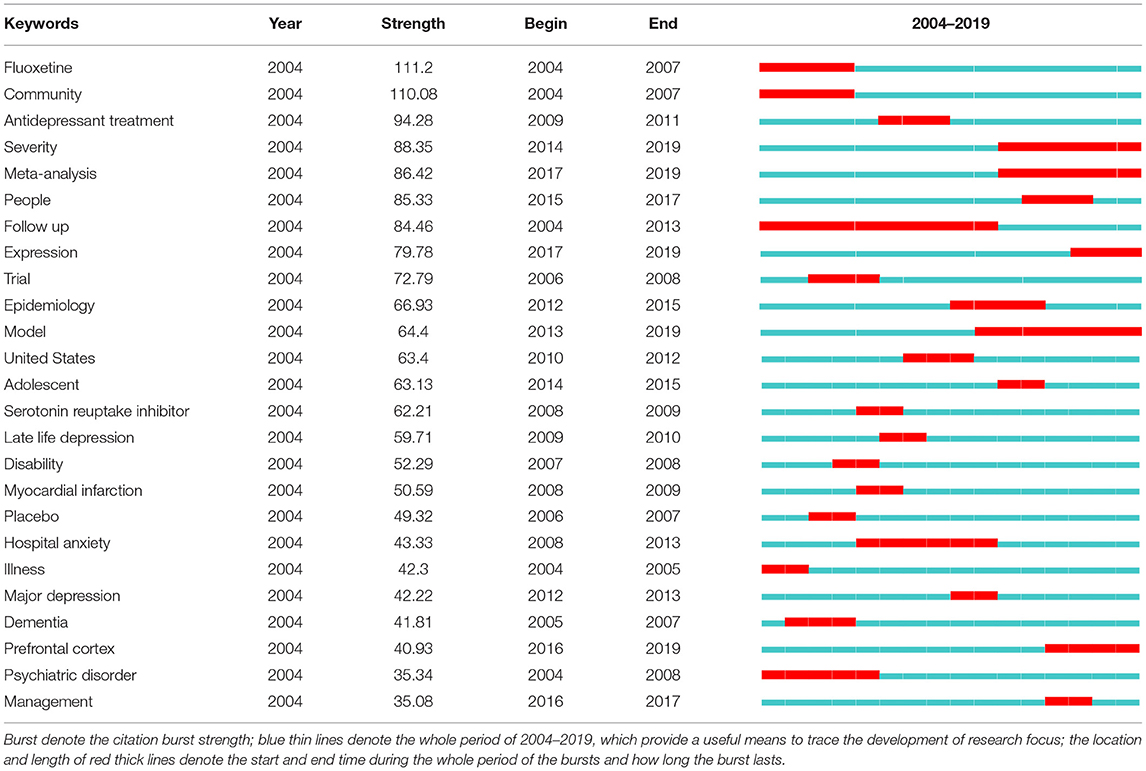
Table 9 . Top 25 keywords with strongest citation bursts in the period of 2004–2019.
The articles on depression during 2004–2019 were analyzed in 1-year time slices, and the top 25 keywords with the highest frequency of occurrence were selected from each slice to obtain the keyword network shown in Table 8 . The top 25 keywords with the highest frequencies were: symptom, disorder, major depression, prevalence, meta-analysis, anxiety, risk, scale, association, quality of life, health, risk factor, stress, validity, validation, mental health, women, double blind, brain, population, disease, impact, primary care, mood, and efficacy. High-frequency nodes respond to popular keywords and are an important basis for the field of depression research.
Figure 7 shows the co-occurrence network mapping of keywords regarding depression research. Each circle in the figure is a node representing a keyword, and the greater the betweenness centrality, the more critical the position of the node in the network. The top 10 keywords in terms of betweenness centrality are: symptom (0.6), major depression (0.28), prevalence (0.27), disorder (0.25), double blind (0.18), risk factor (0.12), stress (0.11), children (0.1), schizophrenia (0.1), and expression (0.1). Nodes with high betweenness centrality reflect that the keyword forms a co-occurrence relationship with multiple other keywords in the domain. A higher betweenness centrality indicates that it is more related to other keywords, and therefore, the node plays an important role in the study. Relatively speaking, these nodes represent the main research directions in the field of depression; they are also the key research directions in this period, and to a certain extent, represent the research hotspots in this period.
Burst detection was performed on the keywords, and the 25 keywords with the strongest strength were extracted, as shown in Table 9 . These keywords contain: fluoxetine, community, follow up, illness, psychiatric disorder, dementia, trial, placebo, disability, serotonin reuptake inhibitor, myocardial infarction, hospital anxiety, antidepressant treatment, late life depression, United States, epidemiology, major depression, model, severity, adolescent, people, prefrontal cortex, management, meta-analysis, and expression. The keywords that burst earlier include fluoxetine (2004), community (2004), follow up (2004), illness (2004), and psychiatric disorder (2004), are keywords that imply that researchers focused on themes early in the field of depression. As researchers continue to explore, the study of depression is changing day by day, and the keywords that have burst in recent years are people (2015), prefrontal cortex (2016), management (2016), meta-analysis (2017), and expression (2017). Reflecting the fact that depression research in recent years has mainly focused on human subjects, the focus has been on the characterization of populations with depression onset. The relationship between depression and the brain has aroused the curiosity of researchers, what exactly are the causes that trigger depression and what are the effects of depression for the manifestation of depression have caused a wide range of discussions in the research community, and the topics related to it have become the most popular studies and have been the focus of research in recent years. All of these research areas showed considerable growth, indicating that research into this area is gaining traction, suggesting that it is becoming a future research priority. The keywords with the strongest burst strength are fluoxetine (111.2), community (110.08), antidepressant treatment (94.28), severity (88.35), meta-analysis (86.42), people (85.33), and follow up (84.46). The rapid growth of research based on these keywords indicates that these topics are the most promising and interesting. The keywords that has been around the longest burst are follow up (2004–2013), model (2013–2019), hospital anxiety (2008–2013), severity (2014–2019), and psychiatric disorder (2004–2008), researchers have invested a lot of research time in these research directions, making many research results, and responding to the exploratory value and significance of research on these topics. At the same time, the longer duration of burst also proves that these research directions have research potential and important value.
Research Hotspots
Hotspots must mainly have the characteristics of high frequency, high betweenness centrality, strong burst, and time of emergence can be used as secondary evaluation indicators. The higher the number of occurrences, the higher the degree of popularity and attention. The higher betweenness centrality means the greater the influence and the higher the importance. Nodes with strong burst usually represent key shift nodes and need to be focused on. The time can be dynamically adjusted according to the target time horizon of the analysis. Thus, based on the results of statistical analysis, it is clear that the research hotspots in the field of depression can be divided into four main areas: etiology (external factors, internal factors), impact (quality of life, disease symptoms, co-morbid symptoms), treatment (interventions, drug development, care modalities), and assessment (population, size, symptoms, duration of disease, morbidity, mortality, effectiveness).
Risk factors for depression include a family history of depression, early life abuse and neglect, and female sexuality and recent life stressors. Physical illnesses also increase the risk of depression, particularly increasing the prevalence associated with metabolic (e.g., cardiovascular disease) and autoimmune disorders.
Research on the etiology of depression can be divided into internal and external factors. In recent years, researchers have increasingly focused on the impact of external factors on depression. Depression is influenced by environmental factors related to social issues, such as childhood experiences, social interactions, and lifestyles. Adverse childhood experiences are risk factors for depression and anxiety in adolescence ( 37 ) and are a common pathway to depression in adults ( 38 ). Poor interpersonal relationships with classmates, family, teachers, and friends increase the prevalence of depression in adolescents ( 39 ). Related studies assessed three important, specific indicators of the self-esteem domain: social confidence, academic ability, and appearance ( 40 ). The results suggest that these three dimensions of self-esteem are key risk factors for increased depressive symptoms in Chinese adolescents. The vulnerability model ( 41 ) suggests that low self-esteem is a causal risk factor for depression, and low self-esteem is thought to be one of the main causes of the onset and progression of depression, with individuals who exhibit low self-esteem being more likely to develop social anxiety and social withdrawal, and thus having a sense of isolation ( 42 ), which in turn leads to subsequent depression. Loneliness predicts depression in adolescents. Individuals with high levels of loneliness experience more stress and tension from psychological and physical sources in their daily lives, which, combined with insufficient care from society, can lead to depression ( 43 ). A mechanism of association exists between life events and mood disorders, with negative life events being directly associated with depressive symptoms ( 44 ). In a cross-sectional study conducted in Shanghai, the prevalence of depression was higher among people who worked longer hours, and daily lifestyle greatly influenced the prevalence of depression ( 45 ). A number of studies in recent years have presented a number of interesting ideas, and they suggest that depression is related to different environmental factors, such as temperature, sunlight hours, and air pollution. Environmental factors have been associated with suicidal behavior. Traffic noise is a variable that triggers depression and is associated with personality disorders such as depression ( 46 ). The harmful effects of air pollution on mental health, inhalation of air pollutants can trigger neuroinflammation and oxidative stress and induce dopaminergic neurotoxicity. A study showed that depression was associated with an increase in ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) ( 47 ).
Increased inflammation is a feature of many diseases and even systemic disorders, such as some autoimmune diseases [e.g., type 1 diabetes ( 48 ) or rheumatoid arthritis ( 49 )] and infectious diseases [e.g., hepatitis and sepsis ( 50 )], are associated with an inflammatory response and have been found to increase the risk of depression. A growing body of evidence supports a bidirectional association between depression and inflammatory processes, with stressors and pathogens leading to excessive or prolonged inflammatory responses when combined with predisposing factors (e.g., childhood adversity and modifying factors such as obesity). The resulting illnesses (e.g., pain, sleep disorders), depressive symptoms, and negative health (e.g., poor diet, sedentary lifestyle) may act as mediating pathways leading to inflammation and depression. In terms of mechanistic pathways, cytokines induce depression by affecting different mood-related processes. Elevated inflammatory signals can dysregulate the metabolism of neurotransmitters, damaging neurons, and thus altering neural activity in the brain. In addition cytokines can modulate depression by regulating hormone levels. Inflammation can have different effects on different populations depending on individual physiology, and even lower levels of inflammation may have a depressive effect on vulnerable individuals. This may be due to lower parasympathetic activity, poorer sensitivity to glucocorticoid inhibitory feedback, a greater response to social threat in the anterior oral cortex or amygdala and a smaller hippocampus. Indeed, these are all factors associated with major depression that can affect the sensitivity to the inhibitory consequences of inflammatory stimuli.
Depression triggers many somatization symptoms, which can manifest as insomnia, menopausal syndrome, cardiovascular problems, pain, and other somatic symptoms. There is a link between sleep deprivation and depression, with insomnia being a trigger and maintenance of depression, and more severe insomnia and chronic symptoms predicting more severe depression. Major depression is considered to be an independent risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease and a predictor of cardiovascular events ( 51 ). Patients with depression are extremely sensitive to pain and have increased pain perception ( 52 ) and is associated with an increased risk of suicide ( 53 , 54 ), and generally the symptoms of these pains are not relieved by medication.
Studies have shown that depression triggers an inflammatory response, promoting an increase in cytokines in response to stressors vs. pathogens. For example, mild depressive symptoms have been associated with an amplified and prolonged inflammatory response ( 55 , 56 ) following influenza vaccination in older adults and pregnant women. Among women who have recently given birth, those with a lifetime history of major depression have greater increases in both serum IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptors after delivery than women without a history of depression ( 57 ). Pro-inflammatory agents, such as interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha), for specific somatization disorders [e.g., hepatitis C or malignant melanoma ( 58 , 59 )], although effective for somatic disorders, pro-inflammatory therapy often leads to psychiatric side effects. Up to 80% of patients treated with IFN-α have been reported to suffer from mild to moderate depressive symptoms.
Clinical trials have shown better antidepressant treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs compared to placebo, either as monotherapy ( 60 , 61 ) or as an add-on treatment ( 62 – 65 ) to antidepressants ( 66 , 67 ). However, findings like whether NSAIDs can be safely used in combination with antidepressants are controversial. Patients with depression often suffer from somatic co-morbidities, which must be included in the benefit/risk assessment. It is important to consider the type of medication, duration of treatment, and dose, and always balance the potential treatment effect with the risk of adverse events in individual patients. Depression, childhood adversity, stressors, and diet all affect the gut microbiota and promote gut permeability, another pathway that enhances the inflammatory response, and effective depression treatment may have profound effects on mood, inflammation, and health. Early in life gut flora colonization is associated with hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activation and affects the enteric nervous system, which is associated with the risk of major depression, gut flora dysbiosis leads to the onset of TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses, and pro-inflammatory factors are closely associated with depression. Clinical studies have shown that in the gut flora of depressed patients, pro-inflammatory bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae and Desulfovibrio are enriched, while short-chain fatty acid producing bacteria are reduced, and some of these bacterial taxa may transmit peripheral inflammation into the brain via the brain-gut axis ( 68 ). In addition, gut flora can affect the immune system by modulating neurotransmitters (5-hydroxytryptamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, norepinephrine, etc.), which in turn can influence the development of depression ( 69 ). Therefore, antidepressant drugs targeting gut flora are a future research direction, and diet can have a significant impact on mood by regulating gut flora.
As the molecular basis of clinical depression remains unclear, and treatments and therapeutic effects are limited and associated with side effects, researchers have worked to discover new treatment modalities for depression. High-amplitude low-frequency musical impulse stimulation as an additional treatment modality seems to produce beneficial effects ( 70 ). Studies have found electroconvulsive therapy to be one of the most effective antidepressant treatment therapies ( 71 ). Physical exercise can promote molecular changes that lead to a shift from a chronic pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state in the peripheral and central nervous system ( 72 ). Aromatherapy is widely used in the treatment of central nervous system disorders ( 73 ). By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, qigong can be effective in reducing depression ( 74 ). The exploration of these new treatment modalities provides more reference options for the treatment of depression.
Large-scale assessments of depression have found that the probability of developing depression varies across populations. Depression affects some specific populations more significantly, for example: adolescents, mothers, and older adults. Depression is one of the disorders that predispose to adolescence, and depression is associated with an increased risk of suicide among college students ( 75 ). Many women develop depression after childbirth. Depression that develops after childbirth is one of the most common complications for women in the postpartum period ( 76 ). The health of children born to mothers who suffer from postpartum depression can also be adversely affected ( 77 ). Depression can cause many symptoms within the central nervous system, especially in the elderly population ( 78 ).
Furthermore, one of the most consistent findings of the association between inflammation and depression is the elevated levels of peripheral pro-inflammatory markers in depressed individuals, and peripheral pro-inflammatory marker levels can also be used as a basis for the assessment of depressed patients. Studies have shown that the following pro-inflammatory markers have been found to be at increased levels in depressed individuals: CRP ( 79 , 80 ), IL-6 ( 22 , 79 , 81 , 82 ), TNF–α, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) ( 79 , 82 ), however, this association is not unidirectional and the subsequent development of depression also increases pro-inflammatory markers ( 82 , 83 ). These biomarkers are of great interest, and depressed patients with increased inflammatory markers may represent a relatively drug-resistant population.
Frontier Analysis
The exploration and analysis of frontier areas of depression were based on the results of the analysis of the previous section on keywords. According to the evaluation index and analysis idea of this study, the frontier research topics need to have the following four characteristics: low to medium frequency, strong burst, high betweenness centrality, and the research direction in recent years. Therefore, combining the results of keyword analysis and these characteristics, it can be found that the frontier research on depression also becomes clear.
Research on Depression Characterized by Psychosexual Disorders
Exploration of biological mechanisms based on depression-associated neurological disorders and analysis of depression from a neurological perspective have always been the focus of research. Activation of neuroinflammatory pathways may contribute to the development of depression ( 84 ). A research model based on the microbial-gut-brain axis facilitates the neurobiology of depression ( 85 ). Some probiotics positively affect the central nervous system due to modulation of neuroinflammation and thus may be able to modulate depression ( 86 ). The combination of environmental issues and the neurobiological study of depression opens new research directions ( 46 ).
Research on Relevant Models of Depression
How to develop a model that meets the purpose of the study determines the outcome of the study and has become the direction that researchers have been exploring in recent years. Martínez et al. ( 87 ) developed a predictive model to assess factors that modify the treatment pathway for postpartum depression. Nie et al. ( 88 ) extended the work on predictive modeling of treatment-resistant depression to establish a predictive model for treatment-resistant depression. Rational modeling methods and behavioral testing facilitate a more comprehensive exploration of depression, with richer studies and more scientifically valid findings.
Research and Characterization of the Depressed Patient Population
Current research on special groups and depression has received much attention. In a study of a group of children, 4% were found to suffer from depression ( 89 ). The diagnosis and treatment of mental health disorders is an important component of pediatric care. Second, some studies of populations with distinct characteristics have been based primarily on female populations. Maternal perinatal depression is also a common mental disorder with a prevalence of over 10% ( 90 ). In addition, geriatric depression is a chronic and specific disorder ( 91 ). Studies based on these populations highlight the characteristics of the disorder more directly than large-scale population explorations and are useful for conducting extended explorations from specific to generalized.
Somatic Comorbidities Associated With Depression
Depression often accompanies the onset and development of many other disorders, making the study of physical comorbidities associated with depression a new landing place for depression research. Depression is a complication of many neurological or psychopathological disorders. Depression is a common co-morbidity of glioblastoma multiforme ( 92 ). Depression is an important disorder associated with stroke ( 93 ). Chronic liver disease is associated with depression ( 94 ). The link between depressive and anxiety states and cancer has been well-documented ( 95 ). In conclusion, depression is associated with an increased risk of lung, oral, prostate, and skin cancers, an increased risk of cancer-specific death from lung, bladder, breast, colorectal, hematopoietic system, kidney, and prostate cancers, and an increased risk of all-cause mortality in lung cancer patients. The early detection and effective intervention of depression and its complications has public health and clinical implications.
Research on Mechanisms of Depression
Research based on the mechanisms of depression includes the study of disease pathogenesis, the study of drug action mechanisms, and the study of disease treatment mechanisms. Research on the pathogenesis of depression has focused more on the study of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Social pressure can change the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis ( 96 ). Studies on the mechanism of action of drugs are mostly based on their effects on the central nervous system. The antidepressant effects of Tanshinone IIA are mediated by the ERK-CREB-BDNF pathway in the hippocampus of mice ( 97 ). Research on the mechanisms of depression treatment has also centered on the central nervous system. It has been shown that the vagus nerve can transmit signals to the brain that can lead to a reduction in depressive behavior ( 98 ).
In this study, based on the 2004–2019 time period, this wealth of data is effectively integrated through data analysis and processing to reproduce the research process in a particular field and to co-present global trends in homogenous fields while organizing past research.
Journals that have made outstanding contributions in this field include ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT, J AFFECT DISORDERS and AM J PSYCHIAT. PSYCHIATRY, NEUROSCIENCES & NEUROLOGY and CLINICAL NEUROLOGY are the three most popular categories. The three researchers with the highest number of articles were MAURIZIO FAVA (USA), BRENDA W. J. H. PENNINX (NETHERLANDS) and MADHUKAR H TRIVEDI (USA). Univ Pittsburgh (USA), Kings Coll London (UK) and Harvard Univ (USA) are three of the most productive and influential research institutions. A Meta-Analysis of Cytokines in Major Depression, Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: Implications for clinical practice and Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression are key articles. Through keyword analysis, a distribution network centered on depression was formed. Although there are good trends in the research on depression, there are still many directions to be explored in depth. Some recommendations regarding depression are as follows.
(1) The prevention of depression can be considered by focusing on treating external factors and guiding the individual.
Faced with the rising incidence of depression worldwide and the difficulty of treating depression, researchers can think more about how to prevent the occurrence of depression. Depressed moods are often the result of stress, not only social pressures on the individual, but also environmental pressures in the developmental process, which in turn have an unhealthy relationship with the body and increase the likelihood of depression. The correlation between external factors and depression is less well-studied, but the control of external factors may be more effective in the short term than in the long term, and may be guided by self-adjustment to avoid major depressive disorder.
(2) The measurement and evaluation of the degree of depression should be developed in the direction of precision.
In the course of research, it has been found that the Depression Rating Scale is mostly used for the detection and evaluation of depression. This kind of assessment is more objective, but it still lacks accuracy, and the research on measurement techniques and methods is less, which is still at a low stage. Patients with depression usually have a variety of causes, conditions, and duration of illness that determine the degree of depression. Therefore, whether these scales can truly accurately measure depression in depressed patients needs further consideration. Accurate measurement is an important basis for evidence-based treatment of depression, and thus how to achieve accurate measurement of depression is a research direction that researchers can move toward.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for further research to address these issues.
A systematic analysis of research in the field of depression in this study concludes that the distribution of countries, journals, categories, authors, institutions, and citations may help researchers and research institutions to establish closer collaboration, develop appropriate publication plans, grasp research hotspots, identify valuable research ideas, understand current emerging research, and determine research directions. In addition, there are still some limitations that can be overcome in future work. First, due to the lack of author and address information in older published articles, it may not be possible to accurately calculate their collaboration; second, although the data scope of this paper is limited to the Web of Science, it can adequately meet our objectives.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author Contributions
HW conceived and designed the analysis, collected the data, performed the analysis, and wrote the paper. XT, XW, and YW conceived and designed the analysis. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 81973495.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR, Heim C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2009) 10:434–45. doi: 10.1038/nrn2639
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Kessler RC, Bromet EJ. The epidemiology of depression across cultures. Annu Rev Public Health. (2013) 34:119–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031912-114409
3. Moussavi S, Chatterji S, Verdes E, Tandon A, Patel V, Ustun B. Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: results from the World Health Surveys. Lancet. (2007) 370:851–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61415-9
4. Peter Heutink MR. The genetics of MDD – a review of challenges and opportunities. J Depress Anxiety. (2014) 3:150. doi: 10.4172/2167-1044.1000150
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
5. Melchior M, Caspi A, Milne BJ, Danese A, Poulton R, Moffitt TE. Work stress precipitates depression and anxiety in young, working women and men. Psychol Med. (2007) 37:1119–29. doi: 10.1017/S0033291707000414
6. Fusar-Poli P, Solmi M, Brondino N, Davies C, Chae C, Politi P, et al. Transdiagnostic psychiatry: a systematic review. World Psychiatry. (2019) 18:192–207. doi: 10.1002/wps.20631
7. Hammarström A, Lehti A, Danielsson U, Bengs C, Johansson EE. Gender-related explanatory models of depression: a critical evaluation of medical articles. Public Health. (2009) 123:689–93. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2009.09.010
8. Tran BX, Ho RCM, Ho CSH, Latkin CA, Phan HT, Ha GH, et al. Depression among patients with HIV/AIDS: research development and effective interventions (gapresearch). Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:1772. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16101772
9. Wang XQ, Peng MS, Weng LM, Zheng YL, Zhang ZJ, Chen PJ. Bibliometric study of the comorbidity of pain and depression research. Neural Plast. (2019) 2019:1657498. doi: 10.1155/2019/1657498
10. Shi S, Gao Y, Sun Y, Liu M, Shao L, Zhang J, et al. The top-100 cited articles on biomarkers in the depression field: a bibliometric analysis. Psychol Heal Med. (2020) 26:533–42. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2020.1752924
11. Dongping G, Ami D, Ranran D, Yuan Y, Xiaobei S, Xiaoyao W, et al. A study of the relationship between depression and intestinal flora based on bibliometrics. China Med Her. (2017) 14:173–6.
12. Chunping A, Haiyan W, Nina H, Pinghui H. Bibiometrics analysis of acupuncture for treating depression based on GoPubMed. J Clin Acupunct Moxibustion. (2017) 33:54–7.
13. Yi Y, Xiaoli W. Bibiometrics analysis of acupuncture for treating depression based on GoPubMed. Mod Chinese Med. (2012) 14:35–8. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.2012.09.013
CrossRef Full Text
14. Zhou X, Yan F. Analysis on scientific and technological achievements in the field of depression during 1999-2017. J Prev Med Inf. (2019) 35:777–82.
15. Guaijuan W. Bibliometric analysis of literatures of psoriasis and depression based on GoPubmed. J Dermatol Venereol. (2017) 39:391–4.
16. Yunzhi C, Jie G, Yihui C, Chen G, Chen W, Wang H, et al. A Bibliometric analysis on research of vitamin D deficiency and depression caused. J Guiyang Coll Tradit Chinese Med. (2016) 38:32–5.
17. Shaoni L, Shumin R, Chunhui Z, Yongxiao T, Qizheng Z. Bibliometric analysis of depression-related genes. Chinese J Med Libr Inf Sci. (2009) 18:75–8.
18. Chen C. CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. (2014) 57:359–77. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
19. Elgendi M. Scientists need data visualization training. Nat Biotechnol. (2017) 35:990–1. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3986
20. World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates (2017).
Google Scholar
21. World Health Organization. Human Development Report 2020 (2020).
22. Dowlati Y, Herrmann N, Swardfager W, Liu H, Sham L, Reim EK, et al. A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol Psychiatry. (2010) 67:446–57. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.033
23. Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Warden D, Ritz L, et al. Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR * D: implications for clinical practice. Am J Psychiatry. (2006) 163:28–40. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.163.1.28
24. Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D, Hamani C, et al. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron. (2005) 45:651–60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.02.014
25. Zarate CA, Jr., Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, et al. A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry . (2006) 67:793–802. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.90
26. Krishnan V, Nestler EJ. The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature. (2008) 455:894–902. doi: 10.1038/nature07455
27. Kroenke K, Strine TW, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Berry JT, Mokdad AH. The PHQ-8 as a measure of current depression in the general population. J Affect Disord. (2009) 114:163–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2008.06.026
28. Pezawas L, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Drabant EM, Verchinski BA, Munoz KE, Kolachana BS, et al. 5-HTTLPR polymorphism impacts human cingulate-amygdala interactions: a genetic susceptibility mechanism for depression. Nat Neurosci. (2005) 8:828–34. doi: 10.1038/nn1463
29. Greicius MD, Flores BH, Menon V, Glover GH, Solvason HB, Kenna H, et al. Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biol Psychiatry. (2007) 62:429–37. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.020
30. Tsankova NM, Berton O, Renthal W, Kumar A, Neve RL, Nestler EJ. Sustained hippocampal chromatin regulation in a mouse model of depression and antidepressant action. Nat Neurosci. (2006) 9:519–25. doi: 10.1038/nn1659
31. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Löwe B. An Ultra-Brief Screening Scale for anxiety and depression: the PHQ−4. Psychosomatics. (2009) 50:613–21. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3182(09)70864-3
32. March J, Silva S, Petrycki S, Curry J, Wells K, Fairbank J, et al. Fluoxetine, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and their combination for adolescents with depression: Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study (TADS) randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr. (2005) 146:145. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.10.032
33. Hasin DS, Goodwin RD, Stinson FS, Grant BF. Epidemiology of major depressive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2005) 62:1097. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.10.1097
34. Gotlib IH, Joormann J. Cognition and depression: current status and future directions. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. (2010) 6:285–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131305
35. Robertson E, Grace S, Wallington T, Stewart DE. Antenatal risk factors for postpartum depression: a synthesis of recent literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. (2004) 26:289–95. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2004.02.006
36. Mitchell AJ, Chan M, Bhatti H, Halton M, Grassi L, Johansen C, et al. Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and adjustment disorder in oncological, haematological, and palliative-care settings: a meta-analysis of 94 interview-based studies. Lancet Oncol. (2011) 12:160–74. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70002-X
37. Wang D, Jiang Q, Yang Z, Choi JK. The longitudinal influences of adverse childhood experiences and positive childhood experiences at family, school, and neighborhood on adolescent depression and anxiety. J Affect Disord. (2021) 292:542–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.108
38. LeMasters K, Bates LM, Chung EO, Gallis JA, Hagaman A, Scherer E, et al. Adverse childhood experiences and depression among women in rural Pakistan. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:400. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10409-4
39. Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Lee YT, Chen L. Cumulative interpersonal relationship risk and resilience models for bullying victimization and depression in adolescents. Pers Individ Dif. (2020) 155:109706. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.109706
40. Zhou J, Li X, Tian L, Huebner ES. Longitudinal association between low self-esteem and depression in early adolescents: the role of rejection sensitivity and loneliness. Psychol Psychother Theor Res Pract. (2020) 93:54–71. doi: 10.1111/papt.12207
41. Butler AC, Hokanson JE, Flynn HA. A comparison of self-esteem lability and low trait self-esteem as vulnerability factors for depression. J Pers Soc Psychol. (1994) 66:166–77. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.66.1.166
42. Watson J, Nesdale D. Rejection sensitivity, social withdrawal, and loneliness in young adults. J Appl Soc Psychol. (2012) 42:1984–2005. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2012.00927.x
43. Teo AR, Marsh HE, Forsberg CW, Nicolaidis C, Chen JI, Newsom J, et al. Loneliness is closely associated with depression outcomes and suicidal ideation among military veterans in primary care. J Affect Disord. (2018) 230:42–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.01.003
44. Sarubin N, Goerigk S, Padberg F, Übleis A, Jobst A, Erfurt L, et al. Self-esteem fully mediates positive life events and depressive symptoms in a sample of 173 patients with affective disorders. Psychol Psychother Theor Res Pract. (2020) 93:21–35. doi: 10.1111/papt.12205
45. Li Z, Dai J, Wu N, Jia Y, Gao J, Fu H. Effect of long working hours on depression and mental well-being among employees in Shanghai: the role of having leisure hobbies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:4980. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244980
46. Díaz J, López-Bueno JA, López-Ossorio JJ, Gónzález JL, Sánchez F, Linares C. Short-term effects of traffic noise on suicides and emergency hospital admissions due to anxiety and depression in Madrid (Spain). Sci Total Environ. (2020) 710:136315. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136315
47. Fan SJ, Heinrich J, Bloom MS, Zhao TY, Shi TX, Feng WR, et al. Ambient air pollution and depression: a systematic review with meta-analysis up to 2019. Sci Total Environ . (2020) 701:134721. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134721
48. Korczak DJ, Pereira S, Koulajian K, Matejcek A, Giacca A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and major depressive disorder: evidence for a biological link. Diabetologia. (2011) 54:2483–93. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2240-3
49. Dickens C, McGowan L, Clark-Carter D, Creed F. Depression in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. (2002) 64:52–60. doi: 10.1097/00006842-200201000-00008
50. Benros ME, Waltoft BL, Nordentoft M, Ostergaard SD, Eaton WW, Krogh J, et al. Autoimmune diseases and severe infections as risk factors for mood disorders a nationwide study. JAMA Psychiatry. (2013) 70:812–20. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.1111
51. Charlson FJ, Stapelberg NJC, Baxter AJ, Whiteford HA. Should global burden of disease estimates include depression as a risk factor for coronary heart disease? BMC Med. (2011) 9:47. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-9-47
52. Velly AM, Mohit S. Epidemiology of pain and relation to psychiatric disorders. Prog Neuro Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2018) 87:159–67. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.05.012
53. Razali SM, Khalib AQ. Pain symptoms in Malay patients with major depression. Asian J Psychiatr. (2012) 5:297–302. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2012.02.015
54. Bahk WM, Park S, Jon DI, Yoon BH, Min KJ, Hong JP. Relationship between painful physical symptoms and severity of depressive symptomatology and suicidality. Psychiatry Res. (2011) 189:357–61. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.01.009
55. Glaser R, Robles TF, Sheridan J, Malarkey WB, Kiecolt-Glaser JK. Mild depressive symptoms are associated with amplified and prolonged inflammatory responses after influenza virus vaccination in older adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2003) 60:1009–14. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.60.10.1009
56. Christian LM, Franco A, Iams JD, Sheridan J, Glaser R. Depressive symptoms predict exaggerated inflammatory responses to an in vivo immune challenge among pregnant women. Brain Behav Immun. (2010) 24:49–53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.05.055
57. Maes M, Ombelet W, De Jongh R, Kenis G, Bosmans E. The inflammatory response following delivery is amplified in women who previously suffered from major depression, suggesting that major depression is accompanied by a sensitization of the inflammatory response system. J Affect Disord. (2001) 63:85–92. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(00)00156-7
58. Friebe A, Horn M, Schmidt F, Janssen G, Schmid-Wendtner MH, Volkenandt M, et al. Dose-dependent development of depressive symptoms during adjuvant interferon-α treatment of patients with malignant melanoma. Psychosomatics . (2010) 51:466–73. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3182(10)70738-6
59. Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Santinami M, Testori A, Kruit WH, Marsden J, et al. Adjuvant therapy with pegylated interferon alfa-2b versus observation alone in resected stage III melanoma: final results of EORTC 18991, a randomised phase III trial. Lancet. (2008) 372:117–26. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61033-8
60. Tyring S, Gottlieb A, Papp K, Gordon K, Leonardi C, Wang A, et al. Etanercept and clinical outcomes, fatigue, and depression in psoriasis: double-blind placebo-controlled randomised phase III trial. Lancet. (2006) 367:29–35. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67763-X
61. Iyengar RL, Gandhi S, Aneja A, Thorpe K, Razzouk L, Greenberg J, et al. NSAIDs are associated with lower depression scores in patients with osteoarthritis. Am J Med . (2013) 126:1017.e11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.02.037
62. Müller N, Schwarz MJ, Dehning S, Douhe A, Cerovecki A, Goldstein-Müller B, et al. The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib has therapeutic effects in major depression: results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, add-on pilot study to reboxetine. Mol Psychiatry. (2006) 11:680–4. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001805
63. Akhondzadeh S, Jafari S, Raisi F, Nasehi AA, Ghoreishi A, Salehi B, et al. Clinical trial of adjunctive celecoxib treatment in patients with major depression: a double blind and placebo controlled trial. Depress Anxiety. (2009) 26:607–11. doi: 10.1002/da.20589
64. Abbasi SH, Hosseini F, Modabbernia A, Ashrafi M, Akhondzadeh S. Effect of celecoxib add-on treatment on symptoms and serum IL-6 concentrations in patients with major depressive disorder: Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Affect Disord. (2012) 141:308–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.03.033
65. Majd M, Hashemian F, Hosseinib SM, Shariatpanahi MV, Sharifid A. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of celecoxib augmentation of sertraline in treatment of drug-naive depressed women: a pilot study. Iran J Pharm Res. (2015) 14:891–9. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2015.1637
66. Warner-Schmidt JL, Vanover KE, Chen EY, Marshall JJ, Greengard P. Antidepressant effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are attenuated by antiinflammatory drugs in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2011) 108:9262–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104836108
67. Uher R, E TK, Tracy D, Wolfgang M, Ole M, Joanna H, et al. An inflammatory biomarker as a differential predictor of outcome of depression treatment with escitalopram and nortriptyline. Am J Psychiatry. (2014) 171:1278–86. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14010094
68. Simpson CA, Diaz-Arteche C, Eliby D, Schwartz OS, Simmons JG, Cowan CSM. The gut microbiota in anxiety and depression – a systematic review. Clin Psychol Rev. (2021) 83:101943. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101943
69. Yang Z, Li J, Gui X, Shi X, Bao Z, Han H, et al. Updated review of research on the gut microbiota and their relation to depression in animals and human beings. Mol Psychiatry. (2020) 25:2759–72. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0729-1
70. Sigurdardóttir GA, Nielsen PM, Rønager J, Wang AG. A pilot study on high amplitude low frequency–music impulse stimulation as an add-on treatment for depression. Brain Behav. (2019) 9:e01399. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1399
71. Maffioletti E, Gennarelli M, Gainelli G, Bocchio-Chiavetto L, Bortolomasi M, Minelli A. BDNF genotype and baseline serum levels in relation to electroconvulsive therapy effectiveness in treatment-resistant depressed patients. J ECT. (2019) 35:189–94. doi: 10.1097/YCT.0000000000000583
72. Ignácio ZM, da Silva RS, Plissari ME, Quevedo J, Réus GZ. Physical exercise and neuroinflammation in major depressive disorder. Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 56:8323–35. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01670-1
73. Lu Z, Zhang T, Wang X, Wang J, Shen J, Xiao Z, et al. Zwitterionic polymer-based nanoparticles encapsulated with linalool for regulating central nervous system. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. (2020) 6:442–9. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01451
74. Koo JW, Chaudhury D, Han MH, Nestler EJ. Role of mesolimbic brain-derived neurotrophic factor in depression. Biol Psychiatry. (2019) 86:738–48. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.05.020
75. Seppälä EM, Bradley C, Moeller J, Harouni L, Nandamudi D, Brackett MA. Promoting mental health and psychological thriving in university students: a randomized controlled trial of three well-being interventions. Front Psychiatry. (2020) 11:590. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00590
76. Weissman M, Olfson M. Depression in women: implications for health care research. Science. (1995) 269:799–801. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2020.305798
77. Savory K, Garay SM, Sumption LA, Kelleher JS, Daughters K, Janssen AB, et al. Prenatal symptoms of anxiety and depression associated with sex differences in both maternal perceptions of one year old infant temperament and researcher observed infant characteristics. J Affect Disord. (2020) 264:383–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.057
78. Eraydin IE, Mueller C, Corbett A, Ballard C, Brooker H, Wesnes K, et al. Investigating the relationship between age of onset of depressive disorder and cognitive function. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2019) 34:38–46. doi: 10.1002/gps.4979
79. Howren MB, Lamkin DM, Suls J. Associations of depression with c-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. (2009) 71:171–86. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181907c1b
80. Wium-Andersen MK, Ørsted DD, Nielsen SF, Nordestgaard BG. Elevated C-reactive protein levels, psychological distress, and depression in 73131 individuals. JAMA Psychiatry. (2013) 70:176–84. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamapsychiatry.102
81. Liu Y, Ho RCM, Mak A. Interleukin (IL)-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and soluble interleukin-2 receptors (sIL-2R) are elevated in patients with major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. J Affect Disord. (2012) 139:230–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.08.003
82. Dahl J, Ormstad H, Aass HCD, Malt UF, Bendz LT, Sandvik L, et al. The plasma levels of various cytokines are increased during ongoing depression and are reduced to normal levels after recovery. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2014) 45:77–86. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.03.019
83. Khandaker GM, Pearson RM, Zammit S, Lewis G, Jones PB. Association of serum interleukin 6 and C-reactive protein in childhood with depression and psychosis in young adult life a population-based longitudinal study. JAMA Psychiatry. (2014) 71:1121–8. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.1332
84. Zhang Z, xuan, Li E, Yan J, ping, Fu W, Shen P, Tian SW, et al. Apelin attenuates depressive-like behavior and neuroinflammation in rats co-treated with chronic stress and lipopolysaccharide. Neuropeptides. (2019) 77:101959. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2019.101959
85. Tian P, O'Riordan KJ, Lee Y, kun, Wang G, Zhao J, Zhang H, et al. Towards a psychobiotic therapy for depression: Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 reverses chronic stress-induced depressive symptoms and gut microbial abnormalities in mice. Neurobiol Stress. (2020) 12:100216. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2020.100216
86. Paiva IHR, Duarte-Silva E, Peixoto CA. The role of prebiotics in cognition, anxiety, and depression. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2020) 34:1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2020.03.006
87. Martínez P, Vöhringer PA, Rojas G. Barreiras de acesso a tratamento para mães com depressão pós-parto em centros de atenção primária: Um modelo preditivo. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. (2016) 24:e2675. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.0982.2675
88. Nie Z, Vairavan S, Narayan VA, Ye J, Li QS. Predictive modeling of treatment resistant depression using data from STARD and an independent clinical study. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0197268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197268
89. Elmore AL, Crouch E. The Association of adverse childhood experiences with anxiety and depression for children and youth, 8 to 17 years of age. Acad Pediatr. (2020) 20:600–8. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2020.02.012
90. Cheng B, Wang X, Zhou Y, Li J, Zhao Y, Xia S, et al. Regional cerebral activity abnormality in pregnant women with antenatal depression. J Affect Disord. (2020) 274:381–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.107
91. Senel B, Özel-Kizil ET, Sorgun MH, Tezcan-Aydemir S, Kirici S. Transcranial sonography imaging of brainstem raphe, substantia nigra and cerebral ventricles in patients with geriatric depression. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2020) 35:702–11. doi: 10.1002/gps.5287
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text
92. Mugge L, Mansour TR, Crippen M, Alam Y, Schroeder J. Depression and glioblastoma, complicated concomitant diseases: a systemic review of published literature. Neurosurg Rev. (2020) 43:497–511. doi: 10.1007/s10143-018-1017-2
93. Allida S, Kl C, Cf H, Lang H, House A, Ml H. Pharmacological, psychological, and non-invasive brain stimulation interventions for treating depression after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 1:CD003437. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003437.pub4
94. Lee K, Otgonsuren M, Younoszai Z, Mir HM, Younossi ZM. Association of chronic liver disease with depression: a population-based study. Psychosomatics. (2013) 54:52–9. doi: 10.1016/j.psym.2012.09.005
95. Wang YH, Li JQ, Shi JF, Que JY, Liu JJ, Lappin JM, et al. Depression and anxiety in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Mol Psychiatry. (2020) 25:1487–99. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0595-x
96. Colaianna M, Schiavone S, Zotti M, Tucci P, Morgese MG, Bäckdahl L, et al. Neuroendocrine profile in a rat model of psychosocial stress: relation to oxidative stress. Antioxida Redox Signal. (2013) 18:1385–99. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4569
97. Lu J, Zhou H, Meng D, Zhang J, Pan K, Wan B, et al. Tanshinone IIA Improves depression-like behavior in mice by activating the ERK-CREB-BDNF signaling pathway. Neuroscience. (2020) 430:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.01.026
98. McVey Neufeld KA, Bienenstock J, Bharwani A, Champagne-Jorgensen K, Mao YK, West C, et al. Oral selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors activate vagus nerve dependent gut-brain signalling. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:14290. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50807-8
Keywords: depression, major depressive disorder, bibliometrics, visual analysis, knowledge graphs, CiteSpace
Citation: Wang H, Tian X, Wang X and Wang Y (2021) Evolution and Emerging Trends in Depression Research From 2004 to 2019: A Literature Visualization Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 12:705749. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.705749
Received: 06 May 2021; Accepted: 05 October 2021; Published: 29 October 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Tian, Wang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yun Wang, wangyun@bucm.edu.cn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
163 In Depth Depression Research Topics To Use

Your professor probably wants every student to write an amazing research paper on depression. We know; that expectations are high. If you want to get a top grade, then you need to learn how to find the best depression research topics possible. Your teacher wants to read something interesting. He wants to see that you have dedicated enough time and effort to find an original idea. Bottom line, you need to make sure your topic is unique and highly interesting. You need to write the essay perfectly as well.
Remember, a good topic can earn you some bonus points. Why would you want to miss out on these when we have a list of 163 depression research topics right here on this page? Did you know that our list of topics is free to use as you see fit? You are allowed to reword any of our topics, as long as it helps you write a great essay. Also, we will never ask a student to give us any credit for using any of our ideas. Our company is here to help as many students as possible get the best possible grades on their difficult research papers on depression.
What to Write About in Your Depression Research Papers?
So, what can you write about in your next depression research papers? We will assume you are in psychology class for this blog post, even though any student can write a research paper about depression . We all know what depression is. It’s a serious medical condition that affects the way people act, feel and even think negatively. However, you could discuss the differences between depression and sadness or even other medical conditions.
Another great idea is to talk about the different types of depression. You can compare them, of course. Postpartum depression, major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, and mania – are just some of the things you can talk about with depression.
Next, you can talk about the many causes of depression, as well as the important signs and symptoms of this medical problem. Another interesting idea would be to talk about people who are most at risk of depression (and discuss the risk factors that lead to depression).
Of course, you could also discuss modern methods of diagnosing depression, as well as some of the most important or prominent treatment options for this medical issue. And remember, don’t be afraid to write your depression research papers on controversial topics. We have some very interesting ideas in our list of 163 awesome depression topics. Check them out below:
Interesting Depression Research Questions
Let’s start our list with the most interesting depression research questions possible. Check out these ideas and pick one right now:
- Discuss the effects of cognitive-behavioral group therapy on depression
- Depression leads to low self-esteem
- Analyze the effects of art therapy on depression
- The effects of depression on social life
- The link between social media and depression
- Research the top 3 causes of depression
- Reasons to take depression very seriously
- Depression in veterans in the United States
- Music therapy and its effects on depression
Research Paper About Depression For Middle School
Yes, even middle school children can write a paper about depression. Here are some ideas for a research paper about depression in middle school:
- What is depression?
- Compare depression with sadness
- What causes depression?
- Discuss the symptoms of depression
- How can depression be diagnosed?
- Best treatments for depression in the UK
- What is a major depressive disorder?
- Talk about depression in autistic children
- Negative effects of Facebook on people suffering from depression
- Health problems associated with depression
Teen Depression Research Paper
Want to write an awesome teen depression research paper? Check out these ideas and pick the one you like the most:
- Analyze the causes of depression in teens in the UK
- Methods to treat depression in teenagers
- Effects of physical activity on depressive teens
- Depression and anxiety in teens in the US
- Teen depression caused by the Covid 19 pandemic
- Symptoms of depression in young adults
- Why are teens prone to depression?
- Effects of depression on school activities
Psychology Research Topics
Do you want to write about depression and psychology? We have some of the best psychology research topics on the Internet right here:
- The psychological effects of depression
- Discuss the loss of interest in fun activities
- Hallucinations caused by the major depressive disorder
- Discuss the mental status examination procedure
- The effects of alcohol abuse on depression
- How does depression cause delusions?
- Why is depression so widespread in Japan?
- Analyze the monoamine theory as it relates to depression
- Discuss the Limbic Cortical Model for diagnosing depression
- The most effective depressive disorder diagnosis in 2022
Diagnosing Depression Topics
It’s not easy to write about diagnosing depression, but you can do it. Fortunately for you, we have some excellent diagnosing depression topics below:
- An in-depth look at the symptoms of depression
- A family history of depression
- Brain imaging for diagnosing depression
- The Beck Depression Inventory: Diagnosing Depression
- Drug use: a factor that causes depression
- Analyze the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression
- Keeping an eye on TSH and Thyroxine levels
- The link between hypogonadism and depression
- Cognitive testing for diagnosing depression
- The differences between depression and dementia
Causes of Depression Ideas
Talking about the many causes of depression can be a very interesting endeavor. Check out the following causes of depression ideas:
- Discuss the biopsychosocial model of depression
- Analyze the diathesis-stress model of depression
- The role of genetics in developing depression
- Childhood abuse and its effect on depression
- Genetic factors that influence the onset of depression
- An in-depth look at the 5-HTTLPR gene
- The link between HIV/AIDS and depression
- Discuss the seasonal affective disorder
- Can B2, B6, and B12 deficiency cause depression?
Most Interesting Psychology Topics
When you are looking for the most interesting psychology topics on the Web, you should visit this page directly. Here are our latest ideas:
- Social anxiety and its effects on depression
- Coping with depression as an autistic person
- Emotional abuse and its effects on depression
- Can financial problems cause depression?
- Love problems causing depression
- Talk about the early signs of depression in children
- Is domestic violence a cause of depression?
- Top 3 ways to treat the major depressive disorder
- Bullying and cyberbullying: two of the causes of depression
- Changes in brain activity in people suffering from depression
Drugs and Depression Ideas
Looking to write about drugs and how they relate to depression? Here are some amazing drugs and depression ideas for you:
- The link between drugs and depression
- Drug abuse leading to depression
- Best 3 drugs used to treat depression
- Using sertraline (Zoloft) to mitigate depression symptoms
- The pros and cons of fluoxetine (Prozac or Sarafem)
- Negative effects of citalopram (Celexa)
- How escitalopram (Lexapro) treats the symptoms of depression
- Prescribing paroxetine (Paxil or Brisdelle) for depression
- Dangerous health effects of taking fluvoxamine (Luvox) for depression
- Addiction problems with anti-depressive medication
Mental Health Research Paper Topics
Depression and mental health are closely related, so why not pick one of our awesome mental health research paper topics:
- The brain chemistry behind depression
- Changes in brain activity during a depressive episode
- Sleep problems caused by depression
- Tiredness: a feeling that never goes away
- What causes irritability and anger in patients diagnosed with depression?
- Headaches as a symptom of depression
- Chronic body aches and depression
- Is depression a mood disorder?
- Differences between depression and bipolar disorder
- Compare and contrast depression and the cyclothymic disorder
Topics for a Depression Presentation
Are you looking for the most interesting topics for a depression presentation? Don’t hesitate to pick any of these topics right now:
- The 3 main causes of depression in the United States
- Covid-19 induced depression among teenagers in the UK
- The symptoms of the major depressive disorder
- Physical or sexual abuse as a cause of depression
- Is depression affected by age?
- Medications that cause depression among the elderly
- How genes make some people more prone to depression
- Depression: A feeling of hopelessness that never goes away
- Signs you may be suffering from a mild case of depression
- The link between depression and memory loss
Depression Treatment Topics
Writing about various treatments for depression may not be an easy thing to do, but it’s certainly interesting. Here are some nice depression treatment topics:
- Discuss three types of treatments for depression
- Compare 4 of the most important drugs that alleviate depression symptoms
- Antidepressants: the good, the bad, the ugly
- Prescribing Adapin (doxepin) for depression
- Major side effects of Anafranil (clomipramine)
- Addiction problems with Aplenzin (bupropion)
- Medicinal marijuana and its effects on depression
- Physical exercise as a depression treatment
- The best mental health apps in 2022
- Benefits of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- What is the role of a mental health team?
Anxiety Research Paper Topics
Looking for the best anxiety research paper topics a student could ever wish for? Check out these ideas and choose the best one for your needs:
- The link between anxiety and depression
- Is anxiety the same as depression?
- What is anxiety?
- Why is anxiety dangerous?
- The symptoms of anxiety
- Treating anxiety in an effective way
- Covid-19-induced anxiety attacks
- Is depression a side-effect of anxiety?
- The emotions that trigger anxiety attacks
- Analyze the 4 levels of anxiety
Depression Symptoms Research Paper Topics
Our depression symptoms research paper topics are the absolute best – and the list has been recently updated. You can find our latest ideas below:
- Are you having a helpless outlook on your life?
- Is hating yourself a sign of depression?
- Symptoms of the Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Feeling tearful: is it a sign I am depressive?
- Inappropriate guilt and worthlessness: 2 of the symptoms of depression
- Low mood and sadness
- The symptoms of the Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
- Can depression lower your self-esteem?
- Can depression make you intolerant of other people?
- The symptoms of the major depressive syndrome
Good Research Topics for College
If you are a college student looking for the most interesting good research topics for college, you have arrived at the right place. Take a look at these awesome ideas:
- Effects of CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy)
- An in-depth look at the CDI measure
- Analyze catatonic depression
- Psychological evaluation to detect early signs of depression
- Alcoholism and its effects on depression
- Depression in law enforcement officers in the United States
- Cognitive therapy benefits
Controversial Topics on Depression
If you are looking for some controversial topics on depression, you are in luck. Our writers have just updated the list of topics, so you will surely find a unique topic below:
- Prescribing antidepressant medication to depression patients
- Forced treatment for people going through a major depression episode
- Addiction caused by antidepressant medication
- Depression on social media
- The lack of family support
Depression Topics for High School
High school students should pick topics that are a bit easier to write about. Here is our list of depression topics for high school students:
- The effects of social media on depression
- Childhood depression causes
- Write about the ways you can heal depression
- Can family help people suffering from depression?
- Physical activity as a cure for depression
- Depression caused by stress in the workplace
Depression and Sociology Ideas
Searching for some exceptional depression and sociology ideas? We have plenty of them below. Simply pick the one you like and start writing your paper today:
- Social problems caused by depression
- Feelings of loneliness
- Anger towards other people
- Irritability and frustration feelings
- The loss of interest in enjoyable activities
Coronavirus and Depression Ideas
Our writers have come up with some amazing coronavirus and depression ideas. You can check them out in the list below (and pick any of them for your next essay, of course):
- The effects of the pandemic on depression
- Analyze the rise in depression cases in the US
- Analyze the rise of depression cases in the United Kingdom
- Depression caused by the Covid 19 virus
- Problems with the lack of human interaction
Depression Topics for a Quick Paper
If you don’t want to spend too much time working on your essay, we recommend you pick one of our depression topics for a quick paper. Here are our best ideas so far:
- Any way to cure depression?
- List the major depression symptoms
- Explain how depression occurs
- The best therapy for depressive people
- Depression’s effect on your job
- Discuss postpartum depression
- Comorbid disorders associated with depression
- Yoga to alleviate depression symptoms
Need Some Writing Help From Our Experts?
Do you want to write a successful research paper, thesis, or dissertation about depression? Now you can get exceptional assistance from a team of experienced and highly skilled academic writers. All of our writers hold Ph.D. degrees in various fields, including psychology, sociology, and mental health.
Getting a high grade has never been easier. We will help you find a great topic, do the research and then write the paper for you. You just need to send us your requirements and we will write a custom paper for you in no time – in as little as 3 hours, if necessary. Get the best writing help fast from our experts today. Get in touch with us!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Call to +1 844 889-9952
222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples
📝 depression research papers examples, 💡 essay ideas on depression, 🎓 simple research topics about depression, 👍 good depression essay topics to write about, 🏆 best depression essay titles, ✍️ depression essay topics for college, 📣 depression discussion questions, ❓ depression research questions.
- The Correlation Between Discrimination/Prejudice and Depression/Anxiety Psychology essay sample: The purpose of this research proposal is to identify the components of the study about the correlation between discrimination/prejudice and depression/anxiety.
- Depression in Children: Symptoms and Treatments Psychology essay sample: Depression can make children not perform the duties they are assigned to do well. A caregiver can easily discover a small child’s depression by change of bowel habit.
- Depression and Postpartum Depression Relationship Psychology essay sample: This article discusses the relationship between depression and postpartum depression, the possible causes, and forms of the disease, its consequences for the woman's psyche.
- Depression as Bad a Clinical Condition Psychology essay sample: Specialists in mental health state that depression is the most common disorder they encounter on the daily basis. The following paper aims to provide evidence of the existence of it.
- Different Types of Training in Managing the Symptoms of Depression Psychology essay sample: The proposed study will compare the effectiveness of different types of training in managing the symptoms of depression. It will be considered by people with moderate depression.
- Postpartum Depression (PPD) and Its Identification Psychology essay sample: Katon, Russo, and Gavin focused on the problem of postpartum depression and its identification, because it is a common issue that leads to adverse health outcomes.
- Diseases of Modern Life Psychology essay sample: Bipolar disorder and major depression are two very similar mood disorders that are often confused and misdiagnosed.
- Mental Illness: Treatment Approaches and Challenges Psychology essay sample: The treatment of forensic populations, as with any clinical population, must be tailored to the individuals as well as to their mental illness.
- Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder and Antidepressants Psychology essay sample: The variety of mental disorders may often confuse terms of disease differentiation due to the lack of proper education. Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are examples of such confusion.
- Adult Depression and Anxiety as a Complex Problem Psychology essay sample: The presence of a physical disability is a major factor in developing a mental health condition due to the increase in dissatisfaction and the presence of multiple irritants.
- Abnormal Psychology: Anxiety and Depression Case Psychology essay sample: Abnormal psychology has many theories that emerged to describe the concept. It has components like biological, cognitive, behavioral as well as social-cultural models.
- American Adolescence. Teenage Problems Psychology essay sample: There are those psychological problems that youngsters cannot omit simply because of the society they currently live in.
- Treatment for Depressive and Bipolar Disorders Psychology essay sample: The study shows that an online intervention can be a part of treatment for people with BD, providing support not only for mania but also for depression.
- Psychology: Mental Health Issues Psychology essay sample: This paper contains a review of primary causes leading to mental illnesses along with available social and individual measures intended to cope with them.
- Depression Caused by Hormonal Imbalance, Socialisation of Children Psychology essay sample: Social life is utterly important for the mental health and socialization of children. They need parents to care about them and help to become a part of society.
- Divorce Effect on Children's Mental Health Psychology essay sample: The family dissolution process, a conflict between parents, custody issues, and negative post-divorce relationships adversely influence the mental health of children.
- Psychological Assessment Report Psychology essay sample: The client, Kyle Jones, is a 45-year-old professor working full-time at the Catholic University. The client’s cognitive functioning was impaired after a car accident.
- What You Need to Know About Depression Psychology essay sample: The article is devoted to depression: a definition is given, the causes, signs, types, and methods of therapy are considered.
- Personality Psychology and Depression Psychology essay sample: This paper presents an analysis of the connection between personality psychology and depression. Today, many attempts are made to investigate depressive symptoms.
- Interacting in the Workplace: Depression Psychology essay sample: Depression is a menace that affects a number of people in different ways. In the workplace, there are a number of ways used to tell whether a person is undergoing mental stress.
- Postpartum Depression. Consequences Psychology essay sample: These days more and more women approach the decision to have a baby very consciously, choosing the time when they are physically and emotionally prepared.
- Cognitive Behavior and Depression in Adolescents Psychology essay sample: People of different ages are prone to various psychological and emotional issues, especially in the current world that is transforming at a high pace.
- Social Problems Associated With Mental Illness and Health Promotion Psychology essay sample: Troubles with psychological health can create barriers to being employed, partially because mental illnesses are commonly stigmatized.
- Females’ Instagram Use and Psychological Well-Being Psychology essay sample: Sherlock and Wagstaff tested the hypothesis that the time spent by women on Instagram was positively correlated with body dissatisfaction, depression, and social comparison.
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy Psychology essay sample: Rational emotive behavior therapy is a therapy approach that involves the identification and replacement of negative behaviors with positive ones.
- Lack of Sleep at King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Psychology essay sample: This paper aims to explore the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation among KFUPM students and techniques for how they can manage time and stress to get adequate sleep.
- Aggression in Psychology Psychology essay sample: This emotion is difficult to define, and psychologists, judges, and lawyers have been trying to determine what actions should and should not be considered aggressive for a long time.
- Childhood Trauma: Disorders and Risky Behavior Psychology essay sample: Young people with a history of childhood abuse have a higher likelihood of participating in HIV risk behaviors such as having sex with multiple partners and having unprotected sex.
- Personality Psychology and Depression Psychology essay sample: The depression study in the personality psychology scope assesses the psychology models connection with personality traits, analyzing the depression propagation among adolescents.
- Depression in Young People: Articles Review Psychology essay sample: Depression is one of the mental health disorders progressively observed among the world population. The articles included in the annotated bibliography research this disease.
- Bipolar Type II Diagnosis and Treatment Psychology essay sample: The article examines the clinical differences between bipolar disorder type I and bipolar disorder type II since the difficulty in choosing a correct diagnosis.
- Concepts of Clinical Psychology Psychology essay sample: This paper revises three scholarly articles about mental disorders. Psychological disorders are a list of ailments with behavioral symptoms and can affect different areas of life.
- “Living With Depression” by Karp Psychology essay sample: In the article “Living with Depression: Illness and Identity Turning Points”, the author tries to investigate how different patients tend to interpret this incoherent illness.
- Resource Listing on Depression and Anxiety Psychology essay sample: This paper aims at creating a list of resources, including private agencies, counselors, websites, and publications that can help individuals.
- Two Sides of Depression Disease Psychology essay sample: Depression is a widespread disease in the modern world, and that is why people often do not fully understand how it works.
- Assessment of Counseling Methods: The Case Study Psychology essay sample: This paper explores the fallacies that emerge during the therapy of John, a young man indulging in substance abuse.
- Depression Among Minority Groups Psychology essay sample: Mental disorders stem from the existing or non-existence of internal emotional and psychological threats from which the individual lacks the mechanisms for control.
- Community of Single Mothers in California Psychology essay sample: This study is focused on the community of single mothers in San Bernardino County, California. The primary focus is on those single moms that have been diagnosed with depression.
- Causes and of Treatment Mood Disorders Psychology essay sample: Mood disorders are a group of mental diseases caused by chemical imbalances in the brain which causes the patient to have irregular changes in their moods.
- Early Separation and Suicide Psychology essay sample: When early separation occurs, a child who is not well taken care of can potentially succumb to mental problems, which can, in turn, act as a motivation for suicide.
- Mood Disorder: Depression and Bipolar Psychology essay sample: This discourse explores the link between depression and bipolar disorder, insofar as their etiology, assessment, diagnosis, and treatment are concerned.
- Postpartum Depression in the Twenty- First Century Psychology essay sample: A major assumption posited by researchers is that ‘social support’ is a key determinant in the prevention of postpartum depression.
- Differents Forms to Stress, Pandemic of Stress Psychology essay sample: In this paper, stress is a major problem in the world today. Many countries and many individuals and families are victims of stress-related problems.
- Depression: A Serious Mental and Behavioral Problem Psychology essay sample: Depression is a health problem that is difficult to diagnose. One way to help improve the detection of diagnosis is to use a genogram.
- Grief Response of Patients Diagnosed With Cancer Psychology essay sample: The beginning of anticipatory grief begins when as children, we realize that we will all die or lose a loved one at some point in life. This should prepare us for the loss.
- Depression Management in Adolescent Psychology essay sample: Adolescents are men and women in their transitional age from childhood to youth. Their age bracket is from ten to twenty-two.
- Depression and Physical Exercise Psychology essay sample: Physical activity and cognitive health are two inseparable concepts. Physical activity is a great way to reduce stress and cure depression.
- Psychological Disorder Analysis - Marla`S Diagnosis Psychology essay sample: In this case, the social cultural model is highly recommended as a form of treatment. This is because individuals from minority groups abandon therapy earlier than those from other groups.
- Depression in Older Person Psychology essay sample: The rising incidence of depression in older person has a correlation with age, gender, genetics, lifestyle, interpersonal relationship and the level of education.
- Maternal Mood Symptoms in Pregnancy and Postpartum Depression Psychology essay sample: As a woman, it is essential to understand postpartum depression and the fact that it can happen to any woman during or after pregnancy.
- Childhood Trauma Etiology Associated With Social and Mental Disorders Psychology essay sample: This paper will showcase the five themes that were revealed during the review process to better understand the associations between childhood trauma and various disorders.
- Stress and Anxiety Sources Amongst Students Psychology essay sample: This paper discusses some of the major sources of physiological, social, and psychological stress and anxiety in students.
- Group Therapy in Psychology: Strengths and Limitations Psychology essay sample: This paper aims to gather relevant data on group therapy in psychology, present its strengths and limitations, and outline the differences between group and individual approaches.
- Suicide in Adolescence Psychology essay sample: In the paper psychoeducational intervention for adolescents is developed and evaluated to improve suicide-related outcomes for high-risk students.
- Counselling Clients with Depression and Addiction Psychology essay sample: Clinicians should "understand that depression is associated with the racism or sexism that marginalized groups experience in their daily lives".
- Measurement of an Individual’s Level of Depression Psychology essay sample: Beck Depression Inventory is a systematic measurement of an individual's level of depression. Individuals who fall in the age group of 15 to 19 are the most vulnerable.
- Postpartum Depression Among Low-Income U.S. Mothers Psychology essay sample: Postpartum depression is a major issue, which takes place after a woman gives birth. The problem is more prominent and prevalent among mothers who have a low-socioeconomic status.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): Case Study Psychology essay sample: The case study about the patient with ASD will involve the identification of specific problems, the assessment of risk factors, and a review of models of abnormality.
- Psychological and Emotional Conditions of Suicide and Depression Psychology essay sample: Art and literature have been the niches that have allowed dissecting the issue of suicide without significant social reprimand toward the authors.
- Joan’s Case Conceptualization Psychology essay sample: The paper discusses Joan’s case. She is a 48-year-old woman who reports stress and depression. She has lost interest in relationships, exercise, and things she enjoys.
- Postpartum Depression: Symptoms, Role of Cultural Factors, and Ways To Support Psychology essay sample: Symptoms of postpartum depression differ from one woman to another and often range from mild to severe, they include intense irritability coupled with anger, insomnia, etc.
- Researching: Illness and Mental Health Psychology essay sample: The following paper will explain how mental health can be considered in ill patients and focused on a particular population
- Psychological Complications of Illness and Injuries Psychology essay sample: Depression associated with illness is a serious concern for patients, families, and healthcare professionals, as it might affect health outcomes
- Psychology of Depression Among College Students Psychology essay sample: Depression has serious effects among college students: poor academic performance, the development of suicidal thoughts, failed relationships, and loss of zeal for goal achievement.
- Military Resiliency Counseling and Care-Giving Psychology essay sample: This course aims to identify the key fears of people who have the problem of adapting to real life after participating in hostilities.
- Depression Associated with Cognitive Dysfunction Psychology essay sample: Low episodic memory performance precedes depression, which demonstrates that depression is associated with cognitive dysfunctions.
- Childhood Traumatic Experience Psychology essay sample: This paper examines the effect of childhood traumas on adulthood, including cognitive abilities, social behavior, and mental health, through the prism of scientific evidence.
- Depression and Anxiety Among College Students Psychology essay sample: The research question this paper tries to answer whether depression and anxiety are common in college students, and if so, what are the causes and possible consequences.
- Anxiety Disorder and Its Characteristics Psychology essay sample: This paper focuses on the fundamental characteristics of anxiety and its theories and treatment options imperially supported.
- People with Asperger's Syndrome: The Effects of Group Trainings Psychology essay sample: To effectively determine how group training affects adults and children with Asperger's syndrome, many researchers do use experimental research design.
- Resilience and Exposure to Trauma Relationship Psychology essay sample: This essay will discuss the relationship between stress, psychological stability, and mental health outcomes after distressing events.
- Emotion Regulation Therapy for Generalized Anxiety Disorder Psychology essay sample: Emotional Regulation Therapy demonstrates significant improvement in treating anxiety, depression, life satisfaction, ruminating, worrying, and being unable to manage feelings.
- Depression and Impact of Human Services Worker Psychology essay sample: Depression is a feeling of constant sadness and loss of interest, affecting how a person performs their day-to-day activities, it can stay for long without being recognized.
- DSM-5 Anxiety Disorders: Causes and Treatment Psychology essay sample: This research paper discusses the DSM-5 anxiety disorders reviewing the diagnosis, a case conceptualization, and a treatment plan.
- Cell Phones and Mental Health Psychology essay sample: Limited use of smartphones, current human companions, makes life easier and enjoyable, while excessive screen time may bring severe mental health consequences.
- Literature Review on Depression Psychology essay sample: The paper summarizes other researchers' work addressing the issue of depression using several databases and carries out a curative study on depression in full text.
- The Role of Family in Depression Treatment Psychology essay sample: Psychologists do a great job of helping people deal with their worries and fears because sometimes the patients have no one who could be trusted apart from the counselor.
- Stress Among Ethnic Minority Adolescents and Mindfulness Intervention Psychology essay sample: The purpose of the proposed research is to investigate the effect of a school-based mindfulness-based intervention on stress among ethnic minority adolescents.
- Professional Psychology: Obtaining a Counselor License Psychology essay sample: The paper is dedicated to the analysis of the profession of a psychologist. The aim is to create an algorithm, adherence to which will help obtain a license of a counselor.
- Couple Separation and Family Counseling Techniques Psychology essay sample: This paper aims to discuss advisory deliberations, expected effects due to separation, and the most effective family counseling techniques.
- Depression Disassembling and Treating Psychology essay sample: Depression is a pathology in its neglected form when the individual begins to have more severe symptoms - persistent nervous system disorders.
- Depressive Symptoms Statistics in the 1990s and Now Psychology essay sample: Between 1990 and 2010, the incidence of mental health problems and depression diagnoses in patients declined modestly.
- Anxiety and Decision Making: Literature Review Psychology essay sample: It is important to continue collecting the evidence to establish connections between levels of anxiety and computations that support decision-making.
- Psychology: Pluralism, Counselling Psychology Psychology essay sample: The reviewed articles were chosen for several reasons. First, they explore different topics in the field of counseling psychology.
- Experience of Childhood Trauma from Child Abuse/Maltreatment Psychology essay sample: This paper aims to analyze the experience of childhood trauma from child abuse/maltreatment, outcomes included, and relevant literature search results and annotated bibliography.
- Child Abuse and Depression Psychology essay sample: This essay argues that neglect, emotional distress, and limited access to psychological treatment during childhood alleviate depression and other mental conditions.
- Polysubstance Abuse Among Adolescent Males With Depression Psychology essay sample: Substance abuse among adolescents can be caused by depression. In this case, the adolescents down ply the idea of seeking psychological support
- Depression in Adolescents and Suitable Interventions Psychology essay sample: Critically, the issue of depression is pronounced in the age bracket due to confusion brought on by the changes happening and also peer pressure.
- Early-Life Stress and Behavioral Outcomes Psychology essay sample: The study aims to understand the mechanisms behind the long-lasting consequences of early-life stress exposure. It is accomplished by comparing the results of tests.
- Reducing Depressive Symptoms and Suicidal Tendencies in Adolescents Psychology essay sample: Cognitive-behavioral therapy addresses children, teenagers, adult survivors overcoming the harmful repercussions of early trauma for their unique mental and emotional needs.
- Aspects of Abnormal Psychology Psychology essay sample: Abnormal psychology studies psychological disorders and ways to improve the lives of those affected by them. There are several perspectives on the pathology.
- Depression: Symptoms and Treatment Psychology essay sample: Depression symptoms may be divided into three categories. The three categories are psychological, physical and social symptoms.
- Preventing Child Suicide: The Role of Family Therapy Psychology essay sample: Due to the increasing number of child suicide cases, more studies need to be done on various types of family therapy and other psychotherapies in preventing suicide.
- Experience of Trauma from Child Maltreatment Psychology essay sample: Summing up the findings of various researchers as well as using databases, studies confirm an undeniable influence of maltreatment on the later development and life of a child.
- Approaches for Treating Depression Psychology essay sample: Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is a type of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and one of the most effective approaches for treating depression.
- Managing Anxiety in Evidence-Based Practice Psychology essay sample: This EBP project proposal focuses on nonpharmacological treatment that does not involve the administration of drugs. It tries to effectively manage anxiety.
- Andrew Solomon: Why We Can't Talk About Depression Psychology essay sample: The main difficulty of depression lies in communicating the patient's condition to those around him. Many people use the word "depression" to describe a bad mood.
- Mental Health Disorders Most Commonly Found in Teenagers Psychology essay sample: The present essay focuses on anxiety, depression, and behavioral disorders because these mental health disorders are the most widely spread among teenagers.
- Approaches a Therapist Could Use to Help Lawrence Psychology essay sample: Lawrence thought he would never come out from underneath the hiding spot while he was despondent. Even some of the most severe depression, nonetheless, can be treated.
- The Link Between the Birth Experience and Postnatal Depression Psychology essay sample: This study offers an overview of the latest scholarly research surrounding postnatal depression to determine whether the birth experience contributes to postpartum depression.
- Evidence-Based Screening for Depression in Acute Care Psychology essay sample: EB analysis for the topic of depression to identify the need for an appropriate screening tool in addition to the PHQ-9 in the assessment evaluation process.
- Beck’s Postpartum Depression Theory: Purpose, Concepts, and Significance Psychology essay sample: This paper aims to describe, analyze and evaluate Beck's Postpartum Depression Theory, and discuss its purpose, concepts, and significance.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Depression Psychology essay sample: Treatment of psychological disorders requires the application of additional methods that might help with the physical state of people and their mental well-being.
- Teen Depression and Suicide in Soto “The Afterlife” Psychology essay sample: In “The Afterlife,” Gary Soto scrutinizes the challenges to teen mental health by portraying the protagonist observing from a side perspective the challenges faced by teenagers.
- Depression and Anxiety Run in the Family Psychology essay sample: This paper examines the possibilities of depression and anxiety in one family through the study of literature and applying one of the family theories.
- Humanistic Therapy of Depression Psychology essay sample: The mental health of the population is becoming a topical concern for numerous countries around the world, and, the need for effective and holistic treatments arises.
- Treating Mood Disorders and Depression Psychology essay sample: This paper discusses treating mood disorders. Medications, which are used to cure people with such diseases, always include a combination of various drugs.
- Major Depressive Disorder: Symptoms and Treatment Psychology essay sample: In the case described in the paper, symptoms can be observed that stand out in Major Depressive Disorder, which is characterized by losing interest in activities.
- Depression in Older Adults: Causes and Treatment Psychology essay sample: The main factors in the progression of depressive disorder in old age are traumatic life events, lifestyle, and chronic illness.
- Bullying: Collaborating with Parents to Increase Proactive Bystander Message Psychology essay sample: Bullying could potentially lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress. These symptoms could be typical also to the bystanders.
- Mental Illness, Depression, and Wellness Issues Psychology essay sample: Mental illness and depression are a silent plague and a sleeper problem that has slipped into millions' brains, hence being highlighted in various forms of media.
- Anxiety and Depression During Childhood and Adolescence Psychology essay sample: Attachment can be defined as the bond shared between two or more persons. People may have emotional closeness with one another.
- Depression as a Widespread Mental Condition Psychology essay sample: The paper investigates depression among individuals as it is a widespread mental condition. It focuses on the effects of depression that result from this condition.
- Teenagers’ Depression Experiment Psychology essay sample: There are many reasons why teenagers become depressed. All of these traumatize the child's psyche and prevent him or her from feeling like a full member of society.
- The Best Solution to Predict Depression Because of Bullying Psychology essay sample: This paper examines interventions to prove that the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program is the most effective solution for predicting depression provoked by bullying.
- Depression Among Students at Elon University Psychology essay sample: This paper entails an analysis of the problem of depression in colleges, specifically, at Elon University, and it includes its causes and suggested remedies.
- Effects of Depression Among Adolescents Psychology essay sample: Depression is a problem that affects all demographics, but this paper focuses on adolescents as its main point of discussion. Depression is a major cause of mental health.
- Social Aspects of Depression and Anxiety Psychology essay sample: Depression and anxiety disorders are problems that bring the mental state out of balance and significantly complicate normal life.
- Discussion Board-Anxiety and Depression Psychology essay sample: The article addresses the urgent need for early intervention and support to prevent suicide in individuals suffering from severe depression.
- Exercise Therapy for Patients With Depression and Anxiety
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Depression
- Yoga Therapy and Depression Symptom in Adult Patients
- Dysthymic Disorder Depression Therapy Symptoms
- Depression in Later Life Overview Older populations have significantly high rates of depression due to life contexts or underlying medical conditions leading to poor quality of life and other health risks.
- Childhood Mistreatment and Adolescent and Young Adult Depression
- Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation as an Add-on Treatment to Cognitive-Behavior Therapy in First Episode Drug-Nave Major Depression Patients
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy and the Application for Psychotic Depression
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Depression and Anxiety Attacks
- Herbal and Complementary Therapies for Depression The paper dwells on the pharmacological effects of herbal and complementary therapies used for depression and nursing implications.
- Metacognitive Therapy for Depression in Adults
- Relationship Between Depression and Subtypes of Early Life Stress in Adult Psychiatric Patients
- Family Therapy and Chronic Depression
- Cognitive Group Therapy for Depression in Adults
- Social Media: The Rise of Depression and Anxiety The increased use of social media in contemporary society adversely affects individuals resulting in depression and anxiety, particularly in those who use it regularly.
- Depression and Anxiety Among Adult Children of Alcoholics
- Managing Postpartum Depression Through Medications and Therapy
- Electroconvulsive Therapy for Severe Depression
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy and Its Effects on Depression
- Depression and Workplace Violence Workplace violence is a growing problem and is recognized as “a critical safety and health hazard” in the United States.
- Flowers Therapy and Easiest Ways to Deal With Depression
- Risk Factors for Adult Depression: Adverse Childhood Experiences and Personality Functioning
- Depression: Medication Versus Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Adolescents
- Approaching Depression Through the Solution Focused Brief Therapy Approach
- Depression in the Elderly Depression normally makes the elderly not to take pleasure in life as fully as they would wish. Normally, depression poses a serious threat on vigor.
- Adjunctive Bright Light Therapy for Bipolar Depression
- Depression and Anxiety Prevention Based on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for At-Risk Adolescents
- Resting-State Functional Connectivity of Brain With Electroconvulsive Therapy in Depression
- Depression: Major Depressive Disorder and Major Life Changes
- Depression in the Elderly Male The research is dedicated to the problems and dangers that may be caused by depression and how it can be avoided or resolved.
- Multimodal Psychotherapeutic Inpatient Therapy of Depression in Patients With High Cytokine Production
- Music Therapy Improve Depression Among Older Adults
- Talk Therapy for Depression or Bipolar Disorder
- Clinical Improvement and Neural Reactivity in Adolescents Treated With Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety and Depression
- How Depression and Physical Issues Are Connected Depression is commonly associated with various symptoms, such as guilt, sadness, hopelessness, and irritability.
- Life After Depression With Hypno Psychotherapy
- Antidepressant Treatment for Depression: Total Therapy Duration
- Cognitive Group Therapy for Adult Depression
- The Relationship Between Adult Attachment Classification and Symptoms of Depression
- Anxiety and Depression in the Workplace This paper looks at the issues of anxiety and depression in the workplace with the focus on causes and ways of dealing with it as part of daily management exercise.
- Adolescent Depression and Cognitive Behavior Therapy
- Virtual Reality Group Therapy for the Treatment of Depression
- The New Therapy Technique for Depression
- Group Therapy for Heart Patients With Depression
- Depression Screening & Treatment in the Workplace The current paper states that depression and treatment have the potential of changing the financial position of employees and employers.
- Oriental Therapy: Alternative Treatment for Depression
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Treatment for Adult Severe Depression
- Aaron Becks and Cognitive Behavior Therapy for Depression
- Massage Therapy Reducing Pain, Depression, and Anxiety in Hand Osteoarthritis Patients
- How Does Depression Affect an Individual’s Overall Quality of Life?
- Why Is Depression Hard to Overcome?
- How Does Depression Affect an Individual’s Overall Quality of Life?
- What Are the Major Types of Depression, and How Do They Differ?
- Why Is Early Diagnosis and Treatment Crucial in Managing Depression?
- Is Meditation a Good Way to Help People in Depression?
- Who Is More Susceptible to Depression, and Are There Specific Risk Factors?
- What Are the More Inconspicuous Symptoms of Depression?
- Can Depression Be a Chronic Condition, and How Is It Managed Over Time?
- What Is the Difference Between Clinical Depression and Normal Depression?
- Is Overthinking One of the Main Causes of Depression?
- How Does Depression Impact the Brain’s Functioning and Chemistry?
- Are There Physical Health Complications Associated with Long-Term Depression?
- What Role Do Genetics Play in the Development of Depression?
- Can Marijuana Help with Depression?
- What Is the Relationship Between Depression and Other Mental Health Disorders?
- Are There Good Habits That Help Overcome Depression?
- How Does Depression Affect Different Age Groups, From Children to Seniors?
- What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Depression? Why Is It Essential to Seek Professional Help for Depression?
- Is There an Evolutionary Explanation for Depression?
- Can Depression Be Managed Without Medication, Using Therapy Alone?
- How Does Depression Affect Our Daily Life?
- What Is the Difference Between Depression and Laziness?
- Are There Lifestyle Changes That Can Help Alleviate the Symptoms of Depression?
- What Is the Relationship Between Anxiety and Depression?
- Can Antidepressants Really Help Ease or Cure Depression?
- Who Are the Key Figures in the History of Depression Research and Treatment?
- Do Certain Life Events or Traumas Trigger Episodes of Depression?
- How Is Major Depression Different from Bipolar Depression?
- Can Depression in Children Manifest Differently Than in Adults?
- Does Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Have an Effect in Depression Level?
- How Does Depression Affect the Teenage Generation?
- Does Working Past Age 65 Protect Against Depression?
- Does Regular Exercise Reduce Stress Levels and Thus Reduce Symptoms of Depression?
- How Medication and Therapy Combat Depression?
- Does Depression Lead to Suicide and Decreased Life Expectancy?
- How Does Diabetes Not Cause Depression?
- Does Emotional Intelligence Mediate the Relation Between Mindfulness and Anxiety and Depression in Adolescents?
- How Does the Cognitive Theory Explain the Etiology of Depression?
- Does Parent Depression Correspond With Child Depression?
- Does Social Anxiety and Stress Lead to Depression?
- Does Positive Psychology Ease Symptoms of Depression?
- How Does Depression Affect Productivity?
- Does Depression Cause Cancer?
- Does Poverty Impact Depression in African American Adolescents and the Development of Suicidal Ideations?
- How Cognitive Reserves Does Moderates Effects of White Matter Hyperintensity on Depressive Symptoms and Cognitive Function in Late-Life Depression?
- How Cognitive Therapy for Depression Reduces Interpersonal Problems?
- How Does Self-Esteem Interact With Adolescent Depression?
- Does Maternal Depression Hurt Parent-Child Attachment?
- Does Fruit and Vegetable Consumption During Adolescence Predict Adult Depression?
- How Can Depression Take Over Someone’s Life?
- How Has Depression Changed My Life Essay?
- Does the Average Person Experience Depression Throughout Their Life?
- Can Experiencing Depression Throughout All Life?
Cite this page
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
PsychologyWriting. (2023, October 8). 222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/depression-research-topics/
"222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples." PsychologyWriting , 8 Oct. 2023, psychologywriting.com/topics/depression-research-topics/.
PsychologyWriting . (2023) '222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples'. 8 October.
PsychologyWriting . 2023. "222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples." October 8, 2023. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/depression-research-topics/.
1. PsychologyWriting . "222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples." October 8, 2023. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/depression-research-topics/.
Bibliography
PsychologyWriting . "222 Depression Research Topics & Essay Examples." October 8, 2023. https://psychologywriting.com/topics/depression-research-topics/.
- Intelligence
- Sigmund Freud
- Psychotherapy
- Child Development
- Abraham Maslow
- Child Abuse
Research Topics & Ideas: Mental Health
100+ Mental Health Research Topic Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project
If you’re just starting out exploring mental health topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of mental health-related research topics and ideas.
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Mental Health Topic Ideas
- Mood disorders
- Anxiety disorders
- Psychotic disorders
- Personality disorders
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Neurodevelopmental disorders
- Eating disorders
- Substance-related disorders

Mood Disorders
Research in mood disorders can help understand their causes and improve treatment methods. Here are a few ideas to get you started.
- The impact of genetics on the susceptibility to depression
- Efficacy of antidepressants vs. cognitive behavioural therapy
- The role of gut microbiota in mood regulation
- Cultural variations in the experience and diagnosis of bipolar disorder
- Seasonal Affective Disorder: Environmental factors and treatment
- The link between depression and chronic illnesses
- Exercise as an adjunct treatment for mood disorders
- Hormonal changes and mood swings in postpartum women
- Stigma around mood disorders in the workplace
- Suicidal tendencies among patients with severe mood disorders
Anxiety Disorders
Research topics in this category can potentially explore the triggers, coping mechanisms, or treatment efficacy for anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between social media and anxiety
- Exposure therapy effectiveness in treating phobias
- Generalised Anxiety Disorder in children: Early signs and interventions
- The role of mindfulness in treating anxiety
- Genetics and heritability of anxiety disorders
- The link between anxiety disorders and heart disease
- Anxiety prevalence in LGBTQ+ communities
- Caffeine consumption and its impact on anxiety levels
- The economic cost of untreated anxiety disorders
- Virtual Reality as a treatment method for anxiety disorders
Psychotic Disorders
Within this space, your research topic could potentially aim to investigate the underlying factors and treatment possibilities for psychotic disorders.
- Early signs and interventions in adolescent psychosis
- Brain imaging techniques for diagnosing psychotic disorders
- The efficacy of antipsychotic medication
- The role of family history in psychotic disorders
- Misdiagnosis and delayed treatment of psychotic disorders
- Co-morbidity of psychotic and mood disorders
- The relationship between substance abuse and psychotic disorders
- Art therapy as a treatment for schizophrenia
- Public perception and stigma around psychotic disorders
- Hospital vs. community-based care for psychotic disorders

Personality Disorders
Research topics within in this area could delve into the identification, management, and social implications of personality disorders.
- Long-term outcomes of borderline personality disorder
- Antisocial personality disorder and criminal behaviour
- The role of early life experiences in developing personality disorders
- Narcissistic personality disorder in corporate leaders
- Gender differences in personality disorders
- Diagnosis challenges for Cluster A personality disorders
- Emotional intelligence and its role in treating personality disorders
- Psychotherapy methods for treating personality disorders
- Personality disorders in the elderly population
- Stigma and misconceptions about personality disorders
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
Within this space, research topics could focus on the causes, symptoms, or treatment of disorders like OCD and hoarding.
- OCD and its relationship with anxiety disorders
- Cognitive mechanisms behind hoarding behaviour
- Deep Brain Stimulation as a treatment for severe OCD
- The impact of OCD on academic performance in students
- Role of family and social networks in treating OCD
- Alternative treatments for hoarding disorder
- Childhood onset OCD: Diagnosis and treatment
- OCD and religious obsessions
- The impact of OCD on family dynamics
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder: Causes and treatment
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Research topics in this area could explore the triggers, symptoms, and treatments for PTSD. Here are some thought starters to get you moving.
- PTSD in military veterans: Coping mechanisms and treatment
- Childhood trauma and adult onset PTSD
- Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing (EMDR) efficacy
- Role of emotional support animals in treating PTSD
- Gender differences in PTSD occurrence and treatment
- Effectiveness of group therapy for PTSD patients
- PTSD and substance abuse: A dual diagnosis
- First responders and rates of PTSD
- Domestic violence as a cause of PTSD
- The neurobiology of PTSD

Neurodevelopmental Disorders
This category of mental health aims to better understand disorders like Autism and ADHD and their impact on day-to-day life.
- Early diagnosis and interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder
- ADHD medication and its impact on academic performance
- Parental coping strategies for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
- Autism and gender: Diagnosis disparities
- The role of diet in managing ADHD symptoms
- Neurodevelopmental disorders in the criminal justice system
- Genetic factors influencing Autism
- ADHD and its relationship with sleep disorders
- Educational adaptations for children with neurodevelopmental disorders
- Neurodevelopmental disorders and stigma in schools
Eating Disorders
Research topics within this space can explore the psychological, social, and biological aspects of eating disorders.
- The role of social media in promoting eating disorders
- Family dynamics and their impact on anorexia
- Biological basis of binge-eating disorder
- Treatment outcomes for bulimia nervosa
- Eating disorders in athletes
- Media portrayal of body image and its impact
- Eating disorders and gender: Are men underdiagnosed?
- Cultural variations in eating disorders
- The relationship between obesity and eating disorders
- Eating disorders in the LGBTQ+ community
Substance-Related Disorders
Research topics in this category can focus on addiction mechanisms, treatment options, and social implications.
- Efficacy of rehabilitation centres for alcohol addiction
- The role of genetics in substance abuse
- Substance abuse and its impact on family dynamics
- Prescription drug abuse among the elderly
- Legalisation of marijuana and its impact on substance abuse rates
- Alcoholism and its relationship with liver diseases
- Opioid crisis: Causes and solutions
- Substance abuse education in schools: Is it effective?
- Harm reduction strategies for drug abuse
- Co-occurring mental health disorders in substance abusers

Choosing A Research Topic
These research topic ideas we’ve covered here serve as thought starters to help you explore different areas within mental health. They are intentionally very broad and open-ended. By engaging with the currently literature in your field of interest, you’ll be able to narrow down your focus to a specific research gap .
It’s important to consider a variety of factors when choosing a topic for your dissertation or thesis . Think about the relevance of the topic, its feasibility , and the resources available to you, including time, data, and academic guidance. Also, consider your own interest and expertise in the subject, as this will sustain you through the research process.
Always consult with your academic advisor to ensure that your chosen topic aligns with academic requirements and offers a meaningful contribution to the field. If you need help choosing a topic, consider our private coaching service.
You Might Also Like:

Good morning everyone. This are very patent topics for research in neuroscience. Thank you for guidance
What if everything is important, original and intresting? as in Neuroscience. I find myself overwhelmd with tens of relveant areas and within each area many optional topics. I ask myself if importance (for example – able to treat people suffering) is more relevant than what intrest me, and on the other hand if what advance me further in my career should not also be a consideration?
This information is really helpful and have learnt alot
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Advertisement
Major Depressive Disorder: Advances in Neuroscience Research and Translational Applications
- Open access
- Published: 13 February 2021
- Volume 37 , pages 863–880, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Zezhi Li 1 , 2 ,
- Meihua Ruan 3 ,
- Jun Chen 1 , 5 &
- Yiru Fang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8748-9085 1 , 4 , 5
44k Accesses
104 Citations
16 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
A Correction to this article was published on 17 May 2021
This article has been updated
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also referred to as depression, is one of the most common psychiatric disorders with a high economic burden. The etiology of depression is still not clear, but it is generally believed that MDD is a multifactorial disease caused by the interaction of social, psychological, and biological aspects. Therefore, there is no exact pathological theory that can independently explain its pathogenesis, involving genetics, neurobiology, and neuroimaging. At present, there are many treatment measures for patients with depression, including drug therapy, psychotherapy, and neuromodulation technology. In recent years, great progress has been made in the development of new antidepressants, some of which have been applied in the clinic. This article mainly reviews the research progress, pathogenesis, and treatment of MDD.
Similar content being viewed by others

Introduction
Neuroimaging advance in depressive disorder.
The cellular and molecular basis of major depressive disorder: towards a unified model for understanding clinical depression
Eleni Pitsillou, Sarah M. Bresnehan, … Tom C. Karagiannis
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Major depressive disorder (MDD) also referred to as depression, is one of the most severe and common psychiatric disorders across the world. It is characterized by persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure, low energy, worse appetite and sleep, and even suicide, disrupting daily activities and psychosocial functions. Depression has an extreme global economic burden and has been listed as the third largest cause of disease burden by the World Health Organization since 2008, and is expected to rank the first by 2030 [ 1 , 2 ]. In 2016, the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study demonstrated that depression caused 34.1 million of the total years lived with disability (YLDs), ranking as the fifth largest cause of YLD [ 3 ]. Therefore, the research progress and the clinical application of new discoveries or new technologies are imminent. In this review, we mainly discuss the current situation of research, developments in pathogenesis, and the management of depression.
Current Situation of Research on Depression
Analysis of published papers.
In the past decade, the total number of papers on depression published worldwide has increased year by year as shown in Fig. 1 A. Searching the Web of Science database, we found a total of 43,863 papers published in the field of depression from 2009 to 2019 (search strategy: TI = (depression$) or ts = ("major depressive disorder$")) and py = (2009 – 2019), Articles). The top 10 countries that published papers on the topic of depression are shown in Fig. 1 B. Among them, researchers in the USA published the most papers, followed by China. Compared with the USA, the gap in the total number of papers published in China is gradually narrowing (Fig. 1 C), but the quality gap reflected by the index (the total number of citations and the number of citations per paper) is still large, and is lower than the global average (Fig. 1 D). As shown in Fig. 1 E, the hot research topics in depression are as follows: depression management in primary care, interventions to prevent depression, the pathogenesis of depression, comorbidity of depression and other diseases, the risks of depression, neuroimaging studies of depression, and antidepressant treatment.
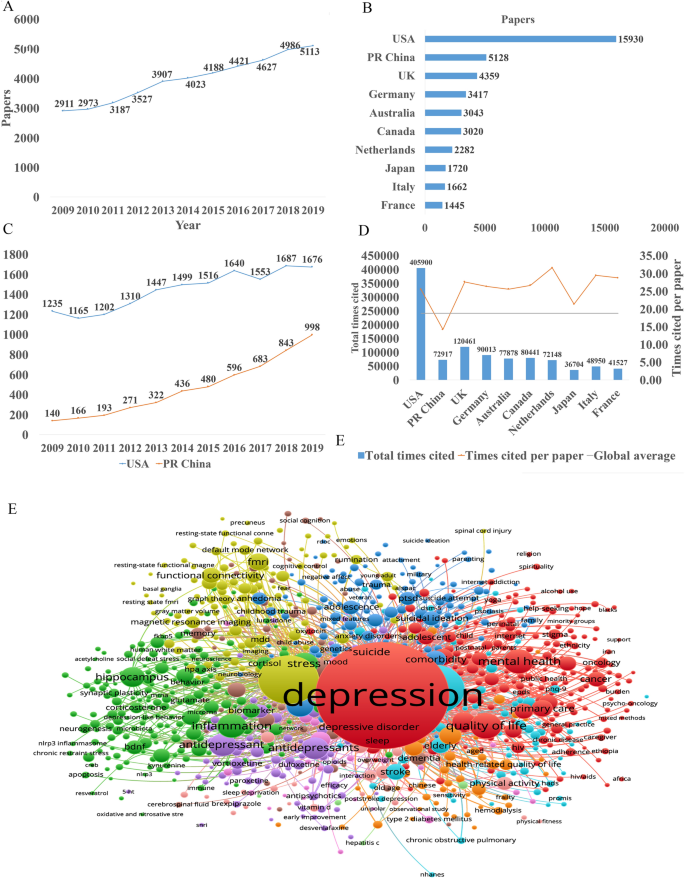
Analysis of published papers around the world from 2009 to 2019 in depressive disorder. A The total number of papers [from a search of the Web of Science database (search strategy: TI = (depression$) or ts = ("major depressive disorder$")) and py = (2009 – 2019), Articles)]. B The top 10 countries publishing on the topic. C Comparison of papers in China and the USA. D Citations for the top 10 countries and comparison with the global average. E Hot topics.
Analysis of Patented Technology Application
There were 16,228 patent applications in the field of depression between 2009 and 2019, according to the Derwent Innovation Patent database. The annual number and trend of these patents are shown in Fig. 2 A. The top 10 countries applying for patents related to depression are shown in Fig. 2 B. The USA ranks first in the number of depression-related patent applications, followed by China. The largest number of patents related to depression is the development of antidepressants, and drugs for neurodegenerative diseases such as dementia comorbid with depression. The top 10 technological areas of patents related to depression are shown in Fig. 2 C, and the trend in these areas have been stable over the past decade (Fig. 2 D).
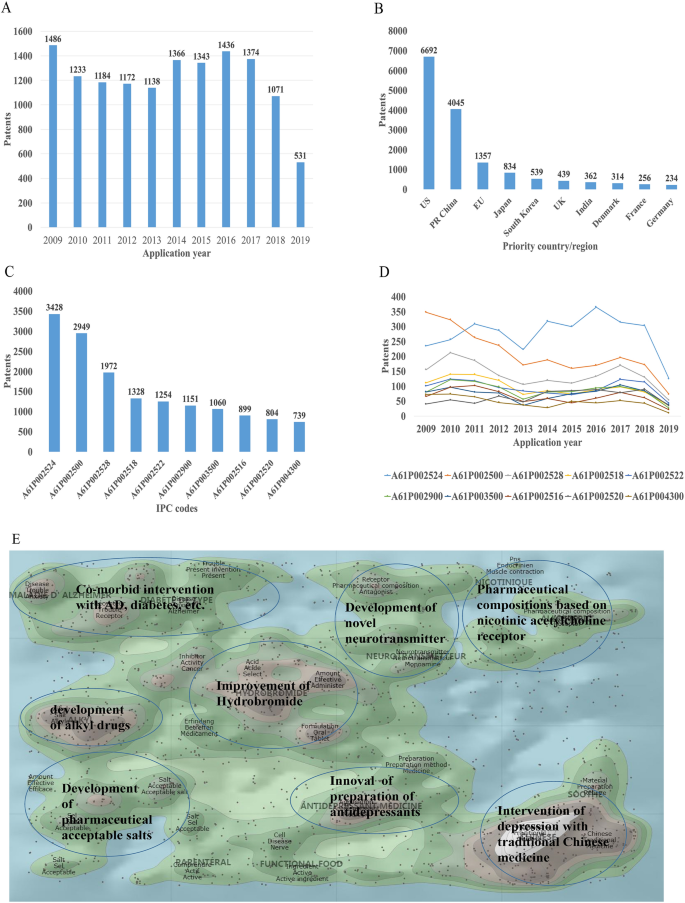
Analysis of patented technology applications from 2009 to 2019 in the field of depressive disorder. A Annual numbers and trends of patents (the Derwent Innovation patent database). B The top 10 countries/regions applying for patents. C The top 10 technological areas of patents. D The trend of patent assignees. E Global hot topic areas of patents.
Analysis of technical hotspots based on keyword clustering was conducted from the Derwent Innovation database using the "ThemeScape" tool. This demonstrated that the hot topic areas are as follows (Fig. 2 E): (1) improvement for formulation and the efficiency of hydrobromide, as well as optimization of the dosage; intervention for depression comorbid with AD, diabetes, and others; (3) development of alkyl drugs; (4) development of pharmaceutical acceptable salts as antidepressants; (5) innovation of the preparation of antidepressants; (6) development of novel antidepressants based on neurotransmitters; (7) development of compositions based on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; and (8) intervention for depression with traditional Chinese medicine.
Analysis of Clinical Trial
There are 6,516 clinical trials in the field of depression in the ClinicalTrials.gov database, and among them, 1,737 valid trials include the ongoing recruitment of subjects, upcoming recruitment of subjects, and ongoing clinical trials. These clinical trials are mainly distributed in the USA (802 trials), Canada (155), China (114), France (93), Germany (66), UK (62), Spain (58), Denmark (41), Sweden (39), and Switzerland (23). The indications for clinical trials include various types of depression, such as minor depression, depression, severe depression, perinatal depression, postpartum depression, and depression comorbid with other psychiatric disorders or physical diseases, such as schizophrenia, epilepsy, stroke, cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Parkinson's disease.
Based on the database of the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry website, a total of 143 clinical trials for depression have been carried out in China. According to the type of research, they are mainly interventional and observational studies, as well as a small number of related factor studies, epidemiological studies, and diagnostic trials. The research content involves postpartum, perinatal, senile, and other age groups with clinical diagnosis (imaging diagnosis) and intervention studies (drugs, acupuncture, electrical stimulation, transcranial magnetic stimulation). It also includes intervention studies on depression comorbid with coronary heart disease, diabetes, and heart failure.
New Medicine Development
According to the Cortellis database, 828 antidepressants were under development by the end of 2019, but only 292 of these are effective and active (Fig. 3 A). Large number of them have been discontinued or made no progress, indicating that the development of new drugs in the field of depression is extremely urgent.
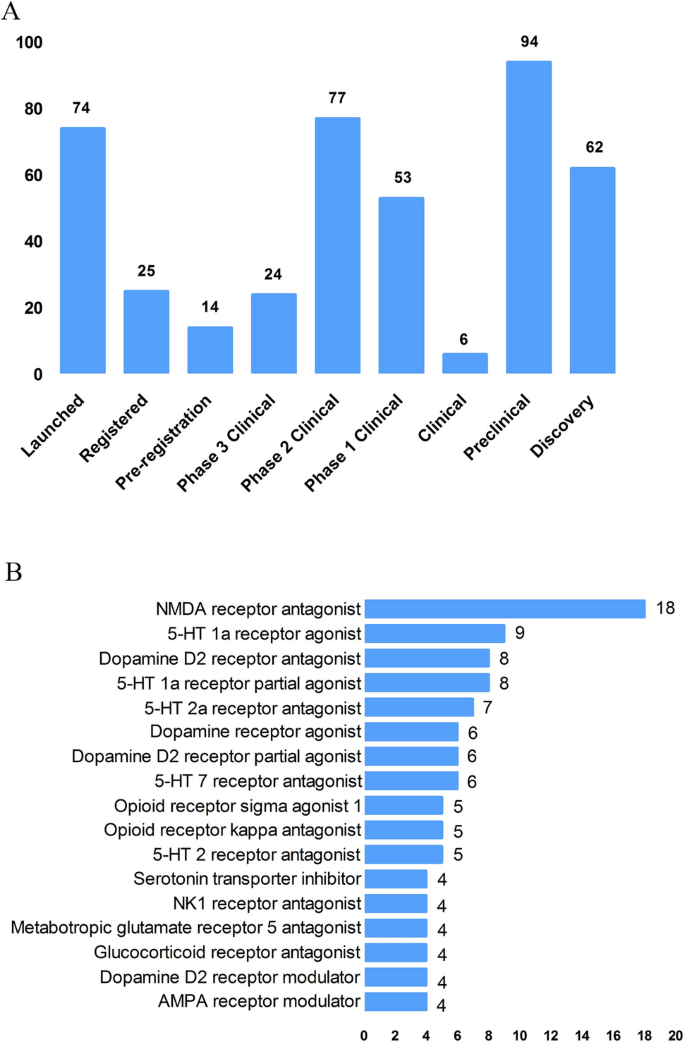
New medicine development from 2009 to 2019 in depressive disorder. A Development status of new candidate drugs. B Top target-based actions.
From the perspective of target-based actions, the most common new drugs are NMDA receptor antagonists, followed by 5-HT targets, as well as dopamine receptor agonists, opioid receptor antagonists and agonists, AMPA receptor modulators, glucocorticoid receptor antagonists, NK1 receptor antagonists, and serotonin transporter inhibitors (Fig. 3 B).
Epidemiology of Depression
The prevalence of depression varies greatly across cultures and countries. Previous surveys have demonstrated that the 12-month prevalence of depression was 0.3% in the Czech Republic, 10% in the USA, 4.5% in Mexico, and 5.2% in West Germany, and the lifetime prevalence of depression was 1.0% in the Czech Republic, 16.9% in the USA, 8.3% in Canada, and 9.0% in Chile [ 4 , 5 ]. A recent meta-analysis including 30 Countries showed that lifetime and 12-month prevalence depression were 10.8% and 7.2%, respectively [ 6 ]. In China, the lifetime prevalence of depression ranged from 1.6% to 5.5% [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. An epidemiological study demonstrated that depression was the most common mood disorder with a life prevalence of 3.4% and a 12-month prevalence of 2.1% in China [ 10 ].
Some studies have also reported the prevalence in specific populations. The National Comorbidity Survey-Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A) survey in the USA showed that the lifetime and 12-month prevalence of depression in adolescents aged 13 to 18 were 11.0% and 7.5%, respectively [ 11 ]. A recent meta-analysis demonstrated that lifetime prevalence and 12-month prevalence were 2.8% and 2.3%, respectively, among the elderly population in China [ 12 ].
Neurobiological Pathogenesis of Depressive Disorder
The early hypothesis of monoamines in the pathophysiology of depression has been accepted by the scientific community. The evidence that monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants promote monoamine neurotransmission supports this theory of depression [ 13 ]. So far, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are still the first-line antidepressants. However, there remain 1/3 to 2/3 of depressed patients who do not respond satisfactorily to initial antidepressant treatment, and even as many as 15%–40% do not respond to several pharmacological medicines [ 14 , 15 ]. Therefore, the underlying pathogenesis of depression is far beyond the simple monoamine mechanism.
Other hypotheses of depression have gradually received increasing attention because of biomarkers for depression and the effects pharmacological treatments, such as the stress-responsive hypothalamic pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis, neuroendocrine systems, the neurotrophic family of growth factors, and neuroinflammation.
Stress-Responsive HPA Axis
Stress is causative or a contributing factor to depression. Particularly, long-term or chronic stress can lead to dysfunction of the HPA axis and promote the secretion of hormones, including cortisol, adrenocorticotropic hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, arginine vasopressin, and vasopressin. About 40%–60% of patients with depression display a disturbed HPA axis, including hypercortisolemia, decreased rhythmicity, and elevated cortisol levels [ 16 , 17 ]. Mounting evidence has shown that stress-induced abnormality of the HPA axis is associated with depression and cognitive impairment, which is due to the increased secretion of cortisol and the insufficient inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor regulatory feedback [ 18 , 19 ]. In addition, it has been reported that the increase in cortisol levels is related to the severity of depression, especially in melancholic depression [ 20 , 21 ]. Further, patients with depression whose HPA axis was not normalized after treatment had a worse clinical response and prognosis [ 22 , 23 ]. Despite the above promising insights, unfortunately previous studies have shown that treatments regulating the HPA axis, such as glucocorticoid receptor antagonists, do not attenuate the symptoms of depressed patients [ 24 , 25 ].
Glutamate Signaling Pathway
Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter released by synapses in the brain; it is involved in synaptic plasticity, cognitive processes, and reward and emotional processes. Stress can induce presynaptic glutamate secretion by neurons and glutamate strongly binds to ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) including N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptors (AMPARs) [ 26 ] on the postsynaptic membrane to activate downstream signal pathways [ 27 ]. Accumulating evidence has suggested that the glutamate system is associated with the incidence of depression. Early studies have shown increased levels of glutamate in the peripheral blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain of depressed patients [ 28 , 29 ], as well as NMDAR subunit disturbance in the brain [ 30 , 31 ]. Blocking the function of NMDARs has an antidepressant effect and protects hippocampal neurons from morphological abnormalities induced by stress, while antidepressants reduce glutamate secretion and NMDARs [ 32 ]. Most importantly, NMDAR antagonists such as ketamine have been reported to have profound and rapid antidepressant effects on both animal models and the core symptoms of depressive patients [ 33 ]. On the other hand, ketamine can also increase the AMPAR pathway in hippocampal neurons by up-regulating the AMPA glutamate receptor 1 subunit [ 34 ]. Further, the AMPAR pathway may be involved in the mechanism of antidepressant effects. For example, preclinical studies have indicated that AMPAR antagonists might attenuate lithium-induced depressive behavior by increasing the levels of glutamate receptors 1 and 2 in the mouse hippocampus [ 35 ].
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
Contrary to glutamate, GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter. Although GABA neurons account for only a small proportion compared to glutamate, inhibitory neurotransmission is essential for brain function by balancing excitatory transmission [ 36 ]. Number of studies have shown that patients with depression have neurotransmission or functional defects of GABA [ 37 , 38 ]. Schür et al ., conducted a meta-analysis of magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies, which showed that the brain GABA level in depressive patients was lower than that in healthy controls, but no difference was found in depressive patients in remission [ 39 ]. Several postmortem studies have shown decreased levels of the GABA synthase glutamic acid decarboxylase in the prefrontal cortex of patients with depression [ 40 , 41 ]. It has been suggested that a functional imbalance of the GABA and glutamate systems contributes to the pathophysiology of depression, and activation of the GABA system might induce antidepressant activity, by which GABA A receptor mediators α2/α3 are considered potential antidepressant candidates [ 42 , 43 ]. Genetic mouse models, such as the GABA A receptor mutant mouse and conditional the Gad1-knockout mouse (GABA in hippocampus and cerebral cortex decreased by 50%) and optogenetic methods have verified that depression-like behavior is induced by changing the level of GABA [ 44 , 45 ].
Neurotrophin Family
The neurotrophin family plays a key role in neuroplasticity and neurogenesis. The neurotrophic hypothesis of depression postulates that a deficit of neurotrophic support leads to neuronal atrophy, the reduction of neurogenesis, and the destruction of glia support, while antidepressants attenuate or reverse these pathophysiological processes [ 46 ]. Among them, the most widely accepted hypothesis involves brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). This was initially triggered by evidence that stress reduces the BDNF levels in the animal brain, while antidepressants rescue or attenuate this reduction [ 47 , 48 ], and agents involved in the BDNF system have been reported to exert antidepressant-like effects [ 49 , 50 ]. In addition, mounting studies have reported that the BDNF level is decreased in the peripheral blood and at post-mortem in depressive patients, and some have reported that antidepressant treatment normalizes it [ 51 , 52 ]. Furthermore, some evidence also showed that the interaction of BDNF and its receptor gene is associated with treatment-resistant depression [ 15 ].
Recent studies reported that depressed patients have a lower level of the pro-domain of BDNF (BDNF pro-peptide) than controls. This is located presynaptically and promotes long-term depression in the hippocampus, suggesting that it is a promising synaptic regulator [ 53 ].
Neuroinflammation
The immune-inflammation hypothesis has attracted much attention, suggesting that the interactions between inflammatory pathways and neural circuits and neurotransmitters are involved in the pathogenesis and pathophysiological processes of depression. Early evidence found that patients with autoimmune or infectious diseases are more likely to develop depression than the general population [ 54 ]. In addition, individuals without depression may display depressive symptoms after treatment with cytokines or cytokine inducers, while antidepressants relieve these symptoms [ 55 , 56 ]. There is a complex interaction between the peripheral and central immune systems. Previous evidence suggested that peripheral inflammation/infection may spread to the central nervous system in some way and cause a neuroimmune response [ 55 , 57 ]: (1) Some cytokines produced in the peripheral immune response, such as IL-6 and IL-1 β, can leak into the brain through the blood-brain barrier (BBB). (2) Cytokines entering the central nervous system act directly on astrocytes, small stromal cells, and neurons. (3) Some peripheral immune cells can cross the BBB through specific transporters, such as monocytes. (4) Cytokines and chemokines in the circulation activate the central nervous system by regulating the surface receptors of astrocytes and endothelial cells at the BBB. (5) As an intermediary pathway, the immune inflammatory response transmits peripheral danger signals to the center, amplifies the signals, and shows the external phenotype of depressive behavior associated with stress/trauma/infection. (6) Cytokines and chemokines may act directly on neurons, change their plasticity and promote depression-like behavior.
Patients with depression show the core feature of the immune-inflammatory response, that is, increased concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines and their receptors, chemokines, and soluble adhesion molecules in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid [ 58 , 59 , 60 ]. Peripheral immune-inflammatory response markers not only change the immune activation state in the brain that affects explicit behavior, but also can be used as an evaluation index or biological index of antidepressant therapy [ 61 , 62 ]. Li et al . showed that the level of TNF-α in patients with depression prior to treatment was higher than that in healthy controls. After treatment with venlafaxine, the level of TNF-α in patients with depression decreased significantly, and the level of TNF-α in the effective group decreased more [ 63 ]. A recent meta-analysis of 1,517 patients found that antidepressants significantly reduced peripheral IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10, and CCL-2, suggesting that antidepressants reduce markers of peripheral inflammatory factors [ 64 ]. Recently, Syed et al . also confirmed that untreated patients with depression had higher levels of inflammatory markers and increased levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines after antidepressant treatment, while increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were found in non-responders [ 62 ]. Clinical studies have also found that anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as monoclonal antibodies and other cytokine inhibitors, may play an antidepressant role by blocking cytokines. The imbalance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines may be involved in the pathophysiological process of depression.
In addition, a recent study showed that microglia contribute to neuronal plasticity and neuroimmune interaction that are involved in the pathophysiology of depression [ 65 ]. When activated microglia promote inflammation, especially the excessive production of pro-inflammatory factors and cytotoxins in the central nervous system, depression-like behavior can gradually develop [ 65 , 66 ]. However, microglia change polarization as two types under different inflammatory states, regulating the balance of pro- and anti-inflammatory factors. These two types are M1 and M2 microglia; the former produces large number of pro-inflammatory cytokines after activation, and the latter produces anti-inflammatory cytokines. An imbalance of M1/M2 polarization of microglia may contribute to the pathophysiology of depression [ 67 ].
Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis
The microbiota-gut-brain axis has recently gained more attention because of its ability to regulate brain activity. Many studies have shown that the microbiota-gut-brain axis plays an important role in regulating mood, behavior, and neuronal transmission in the brain [ 68 , 69 ]. It is well established that comorbidity of depression and gastrointestinal diseases is common [ 70 , 71 ]. Some antidepressants can attenuate the symptoms of patients with irritable bowel syndrome and eating disorders [ 72 ]. It has been reported that gut microbiome alterations are associated with depressive-like behaviors [ 73 , 74 ], and brain function [ 75 ]. Early animal studies have shown that stress can lead to long-term changes in the diversity and composition of intestinal microflora, and is accompanied by depressive behavior [ 76 , 77 ]. Interestingly, some evidence indicates that rodents exhibit depressive behavior after fecal transplants from patients with depression [ 74 ]. On the other hand, some probiotics attenuated depressive-like behavior in animal studies, [ 78 ] and had antidepressant effects on patients with depression in several double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials [ 79 , 80 ].
The potential mechanism may be that gut microbiota can interact with the brain through a variety of pathways or systems, including the HPA axis, and the neuroendocrine, autonomic, and neuroimmune systems [ 81 ]. For example, recent evidence demonstrated that gut microbiota can affect the levels of neurotransmitters in the gut and brain, including serotonin, dopamine, noradrenalin, glutamate, and GABA [ 82 ]. In addition, recent studies showed that changes in gut microbiota can also impair the gut barrier and promote higher levels of peripheral inflammatory cytokines [ 83 , 84 ]. Although recent research in this area has made significant progress, more clinical trials are needed to determine whether probiotics have any effect on the treatment of depression and what the potential underlying mechanisms are.
Other Systems and Pathways
There is no doubt that several other systems or pathways are also involved in the pathophysiology of depression, such as oxidant-antioxidant imbalance [ 85 ], mitochondrial dysfunction [ 86 , 87 ], and circadian rhythm-related genes [ 88 ], especially their critical interactions ( e.g. interaction between the HPA and mitochondrial metabolism [ 89 , 90 ], and the reciprocal interaction between oxidative stress and inflammation [ 2 , 85 ]). The pathogenesis of depression is complex and all the hypotheses should be integrated to consider the many interactions between various systems and pathways.
Advances in Various Kinds of Research on Depressive Disorder
Genetic, molecular, and neuroimaging studies continue to increase our understanding of the neurobiological basis of depression. However, it is still not clear to what extent the results of neurobiological studies can help improve the clinical and functional prognosis of patients. Therefore, over the past 10 years, the neurobiological study of depression has become an important measure to understand the pathophysiological mechanism and guide the treatment of depression.
Genetic Studies
Previous twin and adoption studies have indicated that depression has relatively low rate of heritability at 37% [ 91 ]. In addition, environmental factors such as stressful events are also involved in the pathogenesis of depression. Furthermore, complex psychiatric disorders, especially depression, are considered to be polygenic effects that interact with environmental factors [ 13 ]. Therefore, reliable identification of single causative genes for depression has proved to be challenging. The first genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for depression was published in 2009, and included 1,738 patients and 1,802 controls [ 92 , 93 ]. Although many subsequent GWASs have determined susceptible genes in the past decade, the impact of individual genes is so small that few results can be replicated [ 94 , 95 ]. So far, it is widely accepted that specific single genetic mutations may play minor and marginal roles in complex polygenic depression. Another major recognition in GWASs over the past decade is that prevalent candidate genes are usually not associated with depression. Further, the inconsistent results may also be due to the heterogeneity and polygenic nature of genetic and non-genetic risk factors for depression as well as the heterogeneity of depression subtypes [ 95 , 96 ]. Therefore, to date, the quality of research has been improved in two aspects: (1) the sample size has been maximized by combining the data of different evaluation models; and (2) more homogenous subtypes of depression have been selected to reduce phenotypic heterogeneity [ 97 ]. Levinson et al . pointed out that more than 75,000 to 100,000 cases should be considered to detect multiple depression associations [ 95 ]. Subsequently, several recent GWASs with larger sample sizes have been conducted. For example, Okbay et al . identified two loci associated with depression and replicated them in separate depression samples [ 98 ]. Wray et al . also found 44 risk loci associated with depression based on 135,458 cases and 344,901 controls [ 99 ]. A recent GWAS of 807,553 individuals with depression reported that 102 independent variants were associated with depression; these were involved in synaptic structure and neural transmission, and were verified in a further 1,507,153 individuals [ 100 ]. However, even with enough samples, GWASs still face severe challenges. A GWAS only marks the region of the genome and is not directly related to the potential biological function. In addition, a genetic association with the indicative phenotype of depression may only be part of many pathogenic pathways, or due to the indirect influence of intermediate traits in the causal pathway on the final result [ 101 ].
Given the diversity of findings, epigenetic factors are now being investigated. Recent studies indicated that epigenetic mechanisms may be the potential causes of "loss of heritability" in GWASs of depression. Over the past decade, a promising discovery has been that the effects of genetic information can be directly influenced by environment factors, and several specific genes are activated by environmental aspects. This process is described as interactions between genes and the environment, which is identified by the epigenetic mechanism. Environmental stressors cause alterations in gene expression in the brain, which may cause abnormal neuronal plasticity in areas related to the pathogenesis of the disease. Epigenetic events alter the structure of chromatin, thereby regulating gene expression involved in neuronal plasticity, stress behavior, depressive behavior, and antidepressant responses, including DNA methylation, histone acetylation, and the role of non-coding RNA. These new mechanisms of trans-generational transmission of epigenetic markers are considered a supplement to orthodox genetic heredity, providing the possibility for the discovery of new treatments for depression [ 102 , 103 ]. Recent studies imply that life experiences, including stress and enrichment, may affect cellular and molecular signaling pathways in sperm and influence the behavioral and physiological phenotypes of offspring in gender-specific patterns, which may also play an important role in the development of depression [ 103 ].
Brain Imaging and Neuroimaging Studies
Neuroimaging, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and molecular imaging, provides a non-invasive technique for determining the underlying etiology and individualized treatment for depression. MRI can provide important data on brain structure, function, networks, and metabolism in patients with depression; it includes structural MRI (sMRI), functional MRI (fMRI), diffusion tensor imaging, and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Previous sMRI studies have found damaged gray matter in depression-associated brain areas, including the frontal lobe, anterior cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, putamen, thalamus, and amygdala. sMRI focuses on the thickness of gray matter and brain morphology [ 104 , 105 ]. A recent meta-analysis of 2,702 elderly patients with depression and 11,165 controls demonstrated that the volumes of the whole brain and hippocampus of patients with depression were lower than those of the control group [ 106 ]. Some evidence also showed that the hippocampal volume in depressive patients was lower than that of controls, and increased after treatment with antidepressants [ 107 ] and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) [ 108 ], suggesting that the hippocampal volume plays a critical role in the development, treatment response, and clinical prognosis of depression. A recent study also reported that ECT increased the volume of the right hippocampus, amygdala, and putamen in patients with treatment-resistant depression [ 109 ]. In addition, postmortem research supported the MRI study showing that dentate gyrus volume was decreased in drug-naive patients with depression compared to healthy controls, and was potentially reversed by treatment with antidepressants [ 110 ].
Diffusion tensor imaging detects the microstructure of the white matter, which has been reported impaired in patients with depression [ 111 ]. A recent meta-analysis that included first-episode and drug-naïve depressive patients showed that the decrease in fractional anisotropy was negatively associated with illness duration and clinical severity [ 112 ].
fMRI, including resting-state and task-based fMRI, can divide the brain into self-related regions, such as the anterior cingulate cortex, posterior cingulate cortex, medial prefrontal cortex, precuneus, and dorsomedial thalamus. Many previous studies have shown the disturbance of several brain areas and intrinsic neural networks in patients with depression which could be rescued by antidepressants [ 113 , 114 , 115 , 116 ]. Further, some evidence also showed an association between brain network dysfunction and the clinical correlates of patients with depression, including clinical symptoms [ 117 ] and the response to antidepressants [ 118 , 119 ], ECT [ 120 , 121 ], and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation [ 122 ].
It is worth noting that brain imaging provides new insights into the large-scale brain circuits that underlie the pathophysiology of depressive disorder. In such studies, large-scale circuits are often referred to as “networks”. There is evidence that a variety of circuits are involved in the mechanisms of depressive disorder, including disruption of the default mode, salience, affective, reward, attention, and cognitive control circuits [ 123 ]. Over the past decade, the study of intra-circuit and inter-circuit connectivity dysfunctions in depression has escalated, in part due to advances in precision imaging and analysis techniques [ 124 ]. Circuit dysfunction is a potential biomarker to guide psychopharmacological treatment. For example, Williams et al . found that hyper-activation of the amygdala is associated with a negative phenotype that can predict the response to antidepressants [ 125 ]. Hou et al . showed that the baseline characteristics of the reward circuit predict early antidepressant responses [ 126 ].
Molecular imaging studies, including single photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography, focus on metabolic aspects such as amino-acids, neurotransmitters, glucose, and lipids at the cellular level in patients with depression. A recent meta-analysis examined glucose metabolism and found that glucose uptake dysfunction in different brain regions predicts the treatment response [ 127 ].
The most important and promising studies were conducted by the ENIGMA (Enhancing NeuroImaging Genetics through Meta Analysis) Consortium, which investigated the human brain across 43 countries. The ENIGMA-MDD Working Group was launched in 2012 to detect the structural and functional changes associated with MDD reliably and replicate them in various samples around the world [ 128 ]. So far, the ENIGMA-MDD Working Group has collected data from 4,372 MDD patients and 9,788 healthy controls across 14 countries, including 45 cohorts [ 128 ]. Their findings to date are shown in Table 1 [ 128 , 129 , 130 , 131 , 132 , 133 , 134 , 135 , 136 , 137 ].
Objective Index for Diagnosis of MDD
To date, the clinical diagnosis of depression is subjectively based on interviews according to diagnostic criteria ( e.g. International Classification of Diseases and Diagnostic and Statistical Manual diagnostic systems) and the severity of clinical symptoms are assessed by questionnaires, although patients may experience considerable differences in symptoms and subtypes [ 138 ]. Meanwhile, biomarkers including genetics, epigenetics, peripheral gene and protein expression, and neuroimaging markers may provide a promising supplement for the development of the objective diagnosis of MDD, [ 139 , 140 , 141 ]. However, the development of reliable diagnosis for MDD using biomarkers is still difficult and elusive, and all methods based on a single marker are insufficiently specific and sensitive for clinical use [ 142 ]. Papakostas et al . showed that a multi-assay, serum-based test including nine peripheral biomarkers (soluble tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor type II, resistin, prolactin, myeloperoxidase, epidermal growth factor, BDNF, alpha1 antitrypsin, apolipoprotein CIII, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and cortisol) yielded a specificity of 81.3% and a sensitivity of 91.7% [ 142 ]. However, the sample size was relatively small and no other studies have yet validated their results. Therefore, further studies are needed to identify biomarker models that integrate all biological variables and clinical features to improve the specificity and sensitivity of diagnosis for MDD.
Management of Depression
The treatment strategies for depression consist of pharmacological treatment and non-pharmacological treatments including psychotherapy, ECT [ 98 ], and transcranial magnetic stimulation. As psychotherapy has been shown to have effects on depression including attenuating depressive symptoms and improving the quality of life [ 143 , 144 ]; several practice guidelines are increasingly recommending psychotherapy as a monotherapy or in combination with antidepressants [ 145 , 146 ].
Current Antidepressant Treatment
Antidepressants approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are shown in Table 2 . Due to the relatively limited understanding of the etiology and pathophysiology of depression, almost all the previous antidepressants were discovered by accident a few decades ago. Although most antidepressants are usually safe and effective, there are still some limitations, including delayed efficacy (usually 2 weeks) and side-effects that affect the treatment compliance [ 147 ]. In addition, <50% of all patients with depression show complete remission through optimized treatment, including trials of multiple drugs with and without simultaneous psychotherapy. In the past few decades, most antidepressant discoveries focused on finding faster, safer, and more selective serotonin or norepinephrine receptor targets. In addition, there is an urgent need to develop new approaches to obtain more effective, safer, and faster antidepressants. In 2019, the FDA approved two new antidepressants: Esketamine for refractory depression and Bresanolone for postpartum depression. Esmolamine, a derivative of the anesthetic drug ketamine, was approved by the FDA for the treatment of refractory depression, based on a large number of preliminary clinical studies [ 148 ]. For example, several randomized controlled trials and meta-analysis studies showed the efficacy and safety of Esketamine in depression or treatment-resistant depression [ 26 , 149 , 150 ]. Although both are groundbreaking new interventions for these debilitating diseases and both are approved for use only under medical supervision, there are still concerns about potential misuse and problems in the evaluation of mental disorders [ 151 ].
To date, although several potential drugs have not yet been approved by the FDA, they are key milestones in the development of antidepressants that may be modified and used clinically in the future, such as compounds containing dextromethorphan (a non-selective NMDAR antago–nist), sarcosine (N-methylglycine, a glycine reuptake inhibitor), AMPAR modulators, and mGluR modulators [ 152 ].
Neuromodulation Therapy
Neuromodulation therapy acts through magnetic pulse, micro-current, or neural feedback technology within the treatment dose, acting on the central or peripheral nervous system to regulate the excitatory/inhibitory activity to reduce or attenuate the symptoms of the disease.
ECT is one of most effective treatments for depression, with the implementation of safer equipment and advancement of techniques such as modified ECT [ 153 ]. Mounting evidence from randomized controlled trial (RCT) and meta-analysis studies has shown that rTMS can treat depressive patients with safety [ 154 ]. Other promising treatments for depression have emerged, such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) [ 155 ], transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)[ 156 ], vagal nerve stimulation [ 157 ], deep brain stimulation [ 158 ] , and light therapy [ 159 ], but some of them are still experimental to some extent and have not been widely used. For example, compared to tDCS, tACS displays less sensory experience and adverse reactions with weak electrical current in a sine-wave pattern, but the evidence for the efficacy of tACS in the treatment of depression is still limited [ 160 ]. Alexander et al . recently demonstrated that there was no difference in efficacy among different treatments (sham, 10-Hz and 40-Hz tACS). However, only the 10-Hz tACS group had more responders than the sham and 40-Hz tACS groups at week 2 [ 156 ]. Further RCT studies are needed to verify the efficacy of tACS. In addition, the mechanism of the effect of neuromodulation therapy on depression needs to be further investigated.
Precision Medicine for Depression
Optimizing the treatment strategy is an effective way to improve the therapeutic effect on depression. However, each individual with depression may react very differently to different treatments. Therefore, this raises the question of personalized treatment, that is, which patients are suitable for which treatment. Over the past decade, psychiatrists and psychologists have focused on individual biomarkers and clinical characteristics to predict the efficiency of antidepressants and psychotherapies, including genetics, peripheral protein expression, electrophysiology, neuroimaging, neurocognitive performance, developmental trauma, and personality [ 161 ]. For example, Bradley et al . recently conducted a 12-week RCT, which demonstrated that the response rate and remission rates of the pharmacogenetic guidance group were significantly higher than those of the non-pharmacogenetic guidance group [ 162 ].
Subsequently, Greden et al . conducted an 8-week RCT of Genomics Used to Improve Depression Decisions (GUIDED) on 1,167 MDD patients and demonstrated that although there was no difference in symptom improvement between the pharmacogenomics-guided and non- pharmacogenomics-guided groups, the response rate and remission rate of the pharmacogenomics-guided group increased significantly [ 163 ].
A recent meta-analysis has shown that the baseline default mode network connectivity in patients with depression can predict the clinical responses to treatments including cognitive behavioral therapy, pharmacotherapy, ECT, rTMS, and transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation [ 164 ]. However, so far, the biomarkers that predict treatment response at the individual level have not been well applied in the clinic, and there is still a lot of work to be conducted in the future.
Future Perspectives
Although considerable progress has been made in the study of depression during a past decade, the heterogeneity of the disease, the effectiveness of treatment, and the gap in translational medicine are critical challenges. The main dilemma is that our understanding of the etiology and pathophysiology of depression is inadequate, so our understanding of depression is not deep enough to develop more effective treatment. Animal models still cannot fully simulate this heterogeneous and complex mental disorder. Therefore, how to effectively match the indicators measured in animals with those measured in genetic research or the development of new antidepressants is another important challenge.
Change history
17 may 2021.
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00694-9
Dadi AF, Miller ER, Bisetegn TA, Mwanri L. Global burden of antenatal depression and its association with adverse birth outcomes: an umbrella review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20: 173
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhu S, Zhao L, Fan Y, Lv Q, Wu K, Lang X. Interaction between TNF-alpha and oxidative stress status in first-episode drug-naive schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 114: 104595
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Disease GBD, Injury I, Prevalence C. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390: 1211–1259
Article Google Scholar
Andrade L, Caraveo-Anduaga JJ, Berglund P, Bijl RV, De Graaf R, Vollebergh W, et al. The epidemiology of major depressive episodes: results from the International Consortium of Psychiatric Epidemiology (ICPE) Surveys. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 2003, 12: 3–21
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kessler RC, Bromet EJ. The epidemiology of depression across cultures. Annu Rev Public Health 2013, 34: 119–138
Lim GY, Tam WW, Lu Y, Ho CS, Zhang MW, Ho RC. Prevalence of depression in the community from 30 countries between 1994 and 2014. Sci Rep 2018, 8: 2861
Liu J, Yan F, Ma X, Guo HL, Tang YL, Rakofsky JJ, et al. Prevalence of major depressive disorder and socio-demographic correlates: Results of a representative household epidemiological survey in Beijing, China. J Affect Disord 2015, 179: 74–81
Zhang YS, Rao WW, Cui LJ, Li JF, Li L, Ng CH, et al. Prevalence of major depressive disorder and its socio-demographic correlates in the general adult population in Hebei province, China. J Affect Disord 2019, 252: 92–98
Ma X, Xiang YT, Cai ZJ, Li SR, Xiang YQ, Guo HL, et al. Prevalence and socio-demographic correlates of major depressive episode in rural and urban areas of Beijing, China. J Affect Disord 2009, 115: 323–330
Huang Y, Wang Y, Wang H, Liu Z, Yu X, Yan J, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6: 211–224
Avenevoli S, Swendsen J, He JP, Burstein M, Merikangas KR. Major depression in the national comorbidity survey-adolescent supplement: prevalence, correlates, and treatment. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2015, 54(37–44): e32
Google Scholar
Wang F, Zhang QE, Zhang L, Ng CH, Ungvari GS, Yuan Z, et al. Prevalence of major depressive disorder in older adults in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 2018, 241: 297–304
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ. The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nature 2008, 455: 894–902
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry 2006, 163: 1905–1917
Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Chen J, Fan J, Guan Y, et al. The role of BDNF, NTRK2 gene and their interaction in development of treatment-resistant depression: data from multicenter, prospective, longitudinal clinic practice. J Psychiatr Res 2013, 47: 8–14
Murphy BE. Steroids and depression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1991, 38: 537–559
Pariante CM, Lightman SL. The HPA axis in major depression: classical theories and new developments. Trends Neurosci 2008, 31: 464–468
Keller J, Gomez R, Williams G, Lembke A, Lazzeroni L, Murphy GM Jr, et al. HPA axis in major depression: cortisol, clinical symptomatology and genetic variation predict cognition. Mol Psychiatry 2017, 22: 527–536
Gomez RG, Fleming SH, Keller J, Flores B, Kenna H, DeBattista C, et al. The neuropsychological profile of psychotic major depression and its relation to cortisol. Biol Psychiatry 2006, 60: 472–478
Lamers F, Vogelzangs N, Merikangas KR, de Jonge P, Beekman AT, Penninx BW. Evidence for a differential role of HPA-axis function, inflammation and metabolic syndrome in melancholic versus atypical depression. Mol Psychiatry 2013, 18: 692–699
Nandam LS, Brazel M, Zhou M, Jhaveri DJ. Cortisol and major depressive disorder-translating findings from humans to animal models and back. Front Psychiatry 2019, 10: 974
Owashi T, Otsubo T, Oshima A, Nakagome K, Higuchi T, Kamijima K. Longitudinal neuroendocrine changes assessed by dexamethasone/CRH and growth hormone releasing hormone tests in psychotic depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33: 152–161
Mickey BJ, Ginsburg Y, Sitzmann AF, Grayhack C, Sen S, Kirschbaum C, et al. Cortisol trajectory, melancholia, and response to electroconvulsive therapy. J Psychiatr Res 2018, 103: 46–53
Stetler C, Miller GE. Depression and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activation: a quantitative summary of four decades of research. Psychosom Med 2011, 73: 114–126
Aubry JM. CRF system and mood disorders. J Chem Neuroanat 2013, 54: 20–24
Correia-Melo FS, Leal GC, Vieira F, Jesus-Nunes AP, Mello RP, Magnavita G, et al. Efficacy and safety of adjunctive therapy using esketamine or racemic ketamine for adult treatment-resistant depression: A randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority study. J Affect Disord 2020, 264: 527–534
Duman RS, Voleti B. Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents. Trends Neurosci 2012, 35: 47–56
Sanacora G, Zarate CA, Krystal JH, Manji HK. Targeting the glutamatergic system to develop novel, improved therapeutics for mood disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008, 7: 426–437
Hashimoto K. The role of glutamate on the action of antidepressants. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2011, 35: 1558–1568
Gray AL, Hyde TM, Deep-Soboslay A, Kleinman JE, Sodhi MS. Sex differences in glutamate receptor gene expression in major depression and suicide. Mol Psychiatry 2015, 20: 1057–1068
Chandley MJ, Szebeni A, Szebeni K, Crawford JD, Stockmeier CA, Turecki G, et al. Elevated gene expression of glutamate receptors in noradrenergic neurons from the locus coeruleus in major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2014, 17: 1569–1578
Musazzi L, Treccani G, Mallei A, Popoli M. The action of antidepressants on the glutamate system: regulation of glutamate release and glutamate receptors. Biol Psychiatry 2013, 73: 1180–1188
Kadriu B, Musazzi L, Henter ID, Graves M, Popoli M, Zarate CA Jr. Glutamatergic Neurotransmission: Pathway to Developing Novel Rapid-Acting Antidepressant Treatments. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2019, 22: 119–135
Beurel E, Grieco SF, Amadei C, Downey K, Jope RS. Ketamine-induced inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 contributes to the augmentation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor signaling. Bipolar Disord 2016, 18: 473–480
Gould TD, O’Donnell KC, Dow ER, Du J, Chen G, Manji HK. Involvement of AMPA receptors in the antidepressant-like effects of lithium in the mouse tail suspension test and forced swim test. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54: 577–587
Duman RS, Sanacora G, Krystal JH. Altered Connectivity in Depression: GABA and Glutamate Neurotransmitter Deficits and Reversal by Novel Treatments. Neuron 2019, 102: 75–90
Ghosal S, Hare B, Duman RS. Prefrontal Cortex GABAergic Deficits and Circuit Dysfunction in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Chronic Stress and Depression. Curr Opin Behav Sci 2017, 14: 1–8
Fee C, Banasr M, Sibille E. Somatostatin-positive gamma-aminobutyric acid interneuron deficits in depression: Cortical microcircuit and therapeutic perspectives. Biol Psychiatry 2017, 82: 549–559
Schur RR, Draisma LW, Wijnen JP, Boks MP, Koevoets MG, Joels M, et al. Brain GABA levels across psychiatric disorders: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of (1) H-MRS studies. Hum Brain Mapp 2016, 37: 3337–3352
Guilloux JP, Douillard-Guilloux G, Kota R, Wang X, Gardier AM, Martinowich K, et al. Molecular evidence for BDNF- and GABA-related dysfunctions in the amygdala of female subjects with major depression. Mol Psychiatry 2012, 17: 1130–1142
Karolewicz B, Maciag D, O’Dwyer G, Stockmeier CA, Feyissa AM, Rajkowska G. Reduced level of glutamic acid decarboxylase-67 kDa in the prefrontal cortex in major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2010, 13: 411–420
Lener MS, Niciu MJ, Ballard ED, Park M, Park LT, Nugent AC, et al. Glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid systems in the pathophysiology of major depression and antidepressant response to ketamine. Biol Psychiatry 2017, 81: 886–897
Chen X, van Gerven J, Cohen A, Jacobs G. Human pharmacology of positive GABA-A subtype-selective receptor modulators for the treatment of anxiety. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2019, 40: 571–582
Ren Z, Pribiag H, Jefferson SJ, Shorey M, Fuchs T, Stellwagen D, et al. Bidirectional homeostatic regulation of a depression-related brain state by gamma-aminobutyric acidergic deficits and ketamine treatment. Biol Psychiatry 2016, 80: 457–468
Kolata SM, Nakao K, Jeevakumar V, Farmer-Alroth EL, Fujita Y, Bartley AF, et al. Neuropsychiatric phenotypes produced by GABA reduction in mouse cortex and hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43: 1445–1456
Duman RS, Li N. A neurotrophic hypothesis of depression: role of synaptogenesis in the actions of NMDA receptor antagonists. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2012, 367: 2475–2484
Albert PR, Benkelfat C, Descarries L. The neurobiology of depression—revisiting the serotonin hypothesis. I. Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2012, 367: 2378–2381
Li K, Shen S, Ji YT, Li XY, Zhang LS, Wang XD. Melatonin augments the effects of fluoxetine on depression-like behavior and hippocampal BDNF-TrkB signaling. Neurosci Bull 2018, 34: 303–311
Zhang JJ, Gao TT, Wang Y, Wang JL, Guan W, Wang YJ, et al. Andrographolide exerts significant antidepressant-like effects involving the hippocampal BDNF system in mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2019, 22: 585–600
Wang JQ, Mao L. The ERK pathway: Molecular mechanisms and treatment of depression. Mol Neurobiol 2019, 56: 6197–6205
Chiou YJ, Huang TL. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factors in taiwanese patients with drug-naive first-episode major depressive disorder: Effects of antidepressants. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2017, 20: 213–218
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Youssef MM, Underwood MD, Huang YY, Hsiung SC, Liu Y, Simpson NR, et al. Association of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and brain BDNF levels with major depression and suicide. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2018, 21: 528–538
Kojima M, Matsui K, Mizui T. BDNF pro-peptide: physiological mechanisms and implications for depression. Cell Tissue Res 2019, 377: 73–79
Jeon SW, Kim YK. Inflammation-induced depression: Its pathophysiology and therapeutic implications. J Neuroimmunol 2017, 313: 92–98
Miller AH, Raison CL. The role of inflammation in depression: from evolutionary imperative to modern treatment target. Nat Rev Immunol 2016, 16: 22–34
Zhao G, Liu X. Neuroimmune advance in depressive disorder. Adv Exp Med Biol 2019, 1180: 85–98
Li Z, Wang Z, Zhang C, Chen J, Su Y, Huang J, et al. Reduced ENA78 levels as novel biomarker for major depressive disorder and venlafaxine efficiency: Result from a prospective longitudinal study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 81: 113–121
Ambrosio G, Kaufmann FN, Manosso L, Platt N, Ghisleni G, Rodrigues ALS, et al. Depression and peripheral inflammatory profile of patients with obesity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 91: 132–141
Mao R, Zhang C, Chen J, Zhao G, Zhou R, Wang F, et al. Different levels of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in patients with unipolar and bipolar depression. J Affect Disord 2018, 237: 65–72
Enache D, Pariante CM, Mondelli V. Markers of central inflammation in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies examining cerebrospinal fluid, positron emission tomography and post-mortem brain tissue. Brain Behav Immun 2019, 81: 24–40
Haroon E, Daguanno AW, Woolwine BJ, Goldsmith DR, Baer WM, Wommack EC, et al. Antidepressant treatment resistance is associated with increased inflammatory markers in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 95: 43–49
Syed SA, Beurel E, Loewenstein DA, Lowell JA, Craighead WE, Dunlop BW, et al. Defective inflammatory pathways in never-treated depressed patients are associated with poor treatment response. Neuron 2018, 99(914–924): e913
Li Z, Qi D, Chen J, Zhang C, Yi Z, Yuan C, et al. Venlafaxine inhibits the upregulation of plasma tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in the Chinese patients with major depressive disorder: a prospective longitudinal study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38: 107–114
Kohler CA, Freitas TH, Stubbs B, Maes M, Solmi M, Veronese N, et al. Peripheral alterations in cytokine and chemokine levels after antidepressant drug treatment for major depressive disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55: 4195–4206
Innes S, Pariante CM, Borsini A. Microglial-driven changes in synaptic plasticity: A possible role in major depressive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 102: 236–247
Sochocka M, Diniz BS, Leszek J. Inflammatory response in the CNS: Friend or foe? Mol Neurobiol 2017, 54: 8071–8089
Zhang L, Zhang J, You Z. Switching of the microglial activation phenotype is a possible treatment for depression disorder. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12: 306
Sandhu KV, Sherwin E, Schellekens H, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Feeding the microbiota-gut-brain axis: diet, microbiome, and neuropsychiatry. Transl Res 2017, 179: 223–244
Gonzalez-Arancibia C, Urrutia-Pinones J, Illanes-Gonzalez J, Martinez-Pinto J, Sotomayor-Zarate R, Julio-Pieper M, et al. Do your gut microbes affect your brain dopamine? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2019, 236: 1611–1622
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Clarke G. Irritable bowel syndrome: a microbiome-gut-brain axis disorder? World J Gastroenterol 2014, 20: 14105–14125
Whitehead WE, Palsson O, Jones KR. Systematic review of the comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome with other disorders: what are the causes and implications? Gastroenterology 2002, 122: 1140–1156
Ruepert L, Quartero AO, de Wit NJ, van der Heijden GJ, Rubin G, Muris JW. Bulking agents, antispasmodics and antidepressants for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011: CD003460.
Marin IA, Goertz JE, Ren T, Rich SS, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Farber E, et al. Microbiota alteration is associated with the development of stress-induced despair behavior. Sci Rep 2017, 7: 43859
Zheng P, Zeng B, Zhou C, Liu M, Fang Z, Xu X, et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol Psychiatry 2016, 21: 786–796
Curtis K, Stewart CJ, Robinson M, Molfese DL, Gosnell SN, Kosten TR, et al. Insular resting state functional connectivity is associated with gut microbiota diversity. Eur J Neurosci 2019, 50: 2446–2452
O’Mahony SM, Marchesi JR, Scully P, Codling C, Ceolho AM, Quigley EM, et al. Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses. Biol Psychiatry 2009, 65: 263–267
Garcia-Rodenas CL, Bergonzelli GE, Nutten S, Schumann A, Cherbut C, Turini M, et al. Nutritional approach to restore impaired intestinal barrier function and growth after neonatal stress in rats. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006, 43: 16–24
Hao Z, Wang W, Guo R, Liu H. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (ATCC 27766) has preventive and therapeutic effects on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 104: 132–142
Messaoudi M, Violle N, Bisson JF, Desor D, Javelot H, Rougeot C. Beneficial psychological effects of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in healthy human volunteers. Gut Microbes 2011, 2: 256–261
Rudzki L, Ostrowska L, Pawlak D, Malus A, Pawlak K, Waszkiewicz N, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus Plantarum 299v decreases kynurenine concentration and improves cognitive functions in patients with major depression: A double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 100: 213–222
Foster JA, McVey Neufeld KA. Gut-brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci 2013, 36: 305–312
Mittal R, Debs LH, Patel AP, Nguyen D, Patel K, O’Connor G, et al. Neurotransmitters: The critical modulators regulating gut-brain axis. J Cell Physiol 2017, 232: 2359–2372
Diviccaro S, Giatti S, Borgo F, Barcella M, Borghi E, Trejo JL, et al. Treatment of male rats with finasteride, an inhibitor of 5alpha-reductase enzyme, induces long-lasting effects on depressive-like behavior, hippocampal neurogenesis, neuroinflammation and gut microbiota composition. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 99: 206–215
Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Wilson SJ, Bailey ML, Andridge R, Peng J, Jaremka LM, et al. Marital distress, depression, and a leaky gut: Translocation of bacterial endotoxin as a pathway to inflammation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 98: 52–60
Lindqvist D, Dhabhar FS, James SJ, Hough CM, Jain FA, Bersani FS, et al. Oxidative stress, inflammation and treatment response in major depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 76: 197–205
Czarny P, Wigner P, Galecki P, Sliwinski T. The interplay between inflammation, oxidative stress, DNA damage, DNA repair and mitochondrial dysfunction in depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2018, 80: 309–321
Xie X, Yu C, Zhou J, Xiao Q, Shen Q, Xiong Z, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates the depression-like behaviors and is associated with attenuating the disruption of mitochondrial bioenergetics in depressed mice. J Affect Disord 2020, 263: 166–174
Wang XL, Yuan K, Zhang W, Li SX, Gao GF, Lu L. Regulation of circadian genes by the MAPK pathway: Implications for rapid antidepressant action. Neurosci Bull 2020, 36: 66–76
Xie X, Shen Q, Yu C, Xiao Q, Zhou J, Xiong Z, et al. Depression-like behaviors are accompanied by disrupted mitochondrial energy metabolism in chronic corticosterone-induced mice. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2020, 200: 105607
Zhang LF, Shi L, Liu H, Meng FT, Liu YJ, Wu HM, et al. Increased hippocampal tau phosphorylation and axonal mitochondrial transport in a mouse model of chronic stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2012, 15: 337–348
Flint J, Kendler KS. The genetics of major depression. Neuron 2014, 81: 1214
Sullivan PF, de Geus EJ, Willemsen G, James MR, Smit JH, Zandbelt T, et al. Genome-wide association for major depressive disorder: a possible role for the presynaptic protein piccolo. Mol Psychiatry 2009, 14: 359–375
Dunn EC, Brown RC, Dai Y, Rosand J, Nugent NR, Amstadter AB, et al. Genetic determinants of depression: recent findings and future directions. Harv Rev Psychiatry 2015, 23: 1–18
Major Depressive Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric GC, Ripke S, Wray NR, Lewis CM, Hamilton SP, Weissman MM, et al. A mega-analysis of genome-wide association studies for major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2013, 18: 497–511.
Levinson DF, Mostafavi S, Milaneschi Y, Rivera M, Ripke S, Wray NR, et al. Genetic studies of major depressive disorder: why are there no genome-wide association study findings and what can we do about it? Biol Psychiatry 2014, 76: 510–512
Sullivan PF, Agrawal A, Bulik CM, Andreassen OA, Borglum AD, Breen G, et al. Psychiatric genomics: An update and an agenda. Am J Psychiatry 2018, 175: 15–27
Schwabe I, Milaneschi Y, Gerring Z, Sullivan PF, Schulte E, Suppli NP, et al. Unraveling the genetic architecture of major depressive disorder: merits and pitfalls of the approaches used in genome-wide association studies. Psychol Med 2019, 49: 2646–2656
Okbay A, Baselmans BM, De Neve JE, Turley P, Nivard MG, Fontana MA, et al. Genetic variants associated with subjective well-being, depressive symptoms, and neuroticism identified through genome-wide analyses. Nat Genet 2016, 48: 624–633
Wray NR, Ripke S, Mattheisen M, Trzaskowski M, Byrne EM, Abdellaoui A, et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat Genet 2018, 50: 668–681
Howard DM, Adams MJ, Clarke TK, Hafferty JD, Gibson J, Shirali M, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat Neurosci 2019, 22: 343–352
Ormel J, Hartman CA, Snieder H. The genetics of depression: successful genome-wide association studies introduce new challenges. Transl Psychiatry 2019, 9: 114
Uchida S, Yamagata H, Seki T, Watanabe Y. Epigenetic mechanisms of major depression: Targeting neuronal plasticity. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2018, 72: 212–227
Yeshurun S, Hannan AJ. Transgenerational epigenetic influences of paternal environmental exposures on brain function and predisposition to psychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2019, 24: 536–548
van Eijndhoven P, van Wingen G, Katzenbauer M, Groen W, Tepest R, Fernandez G, et al. Paralimbic cortical thickness in first-episode depression: evidence for trait-related differences in mood regulation. Am J Psychiatry 2013, 170: 1477–1486
Peng W, Chen Z, Yin L, Jia Z, Gong Q. Essential brain structural alterations in major depressive disorder: A voxel-wise meta-analysis on first episode, medication-naive patients. J Affect Disord 2016, 199: 114–123
Geerlings MI, Gerritsen L. Late-life depression, hippocampal volumes, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry 2017, 82: 339–350
Maller JJ, Broadhouse K, Rush AJ, Gordon E, Koslow S, Grieve SM. Increased hippocampal tail volume predicts depression status and remission to anti-depressant medications in major depression. Mol Psychiatry 2018, 23: 1737–1744
Joshi SH, Espinoza RT, Pirnia T, Shi J, Wang Y, Ayers B, et al. Structural plasticity of the hippocampus and amygdala induced by electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2016, 79: 282–292
Gryglewski G, Baldinger-Melich P, Seiger R, Godbersen GM, Michenthaler P, Klobl M, et al. Structural changes in amygdala nuclei, hippocampal subfields and cortical thickness following electroconvulsive therapy in treatment-resistant depression: longitudinal analysis. Br J Psychiatry 2019, 214: 159–167
Boldrini M, Santiago AN, Hen R, Dwork AJ, Rosoklija GB, Tamir H, et al. Hippocampal granule neuron number and dentate gyrus volume in antidepressant-treated and untreated major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38: 1068–1077
Liang S, Wang Q, Kong X, Deng W, Yang X, Li X, et al. White matter abnormalities in major depression biotypes identified by diffusion tensor imaging. Neurosci Bull 2019, 35: 867–876
Chen G, Guo Y, Zhu H, Kuang W, Bi F, Ai H, et al. Intrinsic disruption of white matter microarchitecture in first-episode, drug-naive major depressive disorder: A voxel-based meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2017, 76: 179–187
Brakowski J, Spinelli S, Dorig N, Bosch OG, Manoliu A, Holtforth MG, et al. Resting state brain network function in major depression - Depression symptomatology, antidepressant treatment effects, future research. J Psychiatr Res 2017, 92: 147–159
Dutta A, McKie S, Downey D, Thomas E, Juhasz G, Arnone D, et al. Regional default mode network connectivity in major depressive disorder: modulation by acute intravenous citalopram. Transl Psychiatry 2019, 9: 116
Meyer BM, Rabl U, Huemer J, Bartova L, Kalcher K, Provenzano J, et al. Prefrontal networks dynamically related to recovery from major depressive disorder: a longitudinal pharmacological fMRI study. Transl Psychiatry 2019, 9: 64
Muller VI, Cieslik EC, Serbanescu I, Laird AR, Fox PT, Eickhoff SB. Altered brain activity in unipolar depression revisited: Meta-analyses of neuroimaging studies. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74: 47–55
Connolly CG, Ho TC, Blom EH, LeWinn KZ, Sacchet MD, Tymofiyeva O, et al. Resting-state functional connectivity of the amygdala and longitudinal changes in depression severity in adolescent depression. J Affect Disord 2017, 207: 86–94
Godlewska BR, Browning M, Norbury R, Igoumenou A, Cowen PJ, Harmer CJ. Predicting treatment response in depression: The role of anterior cingulate cortex. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2018, 21: 988–996
Goldstein-Piekarski AN, Staveland BR, Ball TM, Yesavage J, Korgaonkar MS, Williams LM. Intrinsic functional connectivity predicts remission on antidepressants: a randomized controlled trial to identify clinically applicable imaging biomarkers. Transl Psychiatry 2018, 8: 57
Leaver AM, Vasavada M, Joshi SH, Wade B, Woods RP, Espinoza R, et al. Mechanisms of antidepressant response to electroconvulsive therapy studied with perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Biol Psychiatry 2019, 85: 466–476
Miskowiak KW, Macoveanu J, Jorgensen MB, Stottrup MM, Ott CV, Jensen HM, et al. Neural response after a single ECT session during retrieval of emotional self-referent words in depression: A randomized, sham-controlled fMRI study. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2018, 21: 226–235
Du L, Liu H, Du W, Chao F, Zhang L, Wang K, et al. Stimulated left DLPFC-nucleus accumbens functional connectivity predicts the anti-depression and anti-anxiety effects of rTMS for depression. Transl Psychiatry 2018, 7: 3
Williams LM. Defining biotypes for depression and anxiety based on large-scale circuit dysfunction: a theoretical review of the evidence and future directions for clinical translation. Depress Anxiety 2017, 34: 9–24
Williams LM. Precision psychiatry: a neural circuit taxonomy for depression and anxiety. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3: 472–480
Williams LM, Korgaonkar MS, Song YC, Paton R, Eagles S, Goldstein-Piekarski A, et al. Amygdala reactivity to emotional faces in the prediction of general and medication-specific responses to antidepressant treatment in the randomized iSPOT-D trial. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40: 2398–2408
Hou Z, Gong L, Zhi M, Yin Y, Zhang Y, Xie C, et al. Distinctive pretreatment features of bilateral nucleus accumbens networks predict early response to antidepressants in major depressive disorder. Brain Imaging Behav 2018, 12: 1042–1052
De Crescenzo F, Ciliberto M, Menghini D, Treglia G, Ebmeier KP, Janiri L. Is (18)F-FDG-PET suitable to predict clinical response to the treatment of geriatric depression? A systematic review of PET studies. Aging Ment Health 2017, 21: 889–894
Schmaal L, Pozzi E, T CH, van Velzen LS, Veer IM, Opel N, et al. ENIGMA MDD: seven years of global neuroimaging studies of major depression through worldwide data sharing. Transl Psychiatry 2020, 10: 172.
Schmaal L, Veltman DJ, van Erp TG, Samann PG, Frodl T, Jahanshad N, et al. Subcortical brain alterations in major depressive disorder: findings from the ENIGMA Major Depressive Disorder working group. Mol Psychiatry 2016, 21: 806–812
Schmaal L, Hibar DP, Samann PG, Hall GB, Baune BT, Jahanshad N, et al. Cortical abnormalities in adults and adolescents with major depression based on brain scans from 20 cohorts worldwide in the ENIGMA Major Depressive Disorder Working Group. Mol Psychiatry 2017, 22: 900–909
Frodl T, Janowitz D, Schmaal L, Tozzi L, Dobrowolny H, Stein DJ, et al. Childhood adversity impacts on brain subcortical structures relevant to depression. J Psychiatr Res 2017, 86: 58–65
Renteria ME, Schmaal L, Hibar DP, Couvy-Duchesne B, Strike LT, Mills NT, et al. Subcortical brain structure and suicidal behaviour in major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis from the ENIGMA-MDD working group. Transl Psychiatry 2017, 7: e1116
Tozzi L, Garczarek L, Janowitz D, Stein DJ, Wittfeld K, Dobrowolny H, et al. Interactive impact of childhood maltreatment, depression, and age on cortical brain structure: mega-analytic findings from a large multi-site cohort. Psychol Med 2020, 50: 1020–1031
de Kovel CGF, Aftanas L, Aleman A, Alexander-Bloch AF, Baune BT, Brack I, et al. No alterations of brain structural asymmetry in major depressive disorder: An ENIGMA consortium analysis. Am J Psychiatry 2019, 176: 1039–1049
Ho TC, Gutman B, Pozzi E, Grabe HJ, Hosten N, Wittfeld K, et al. Subcortical shape alterations in major depressive disorder: Findings from the ENIGMA major depressive disorder working group. Hum Brain Mapp 2020.
Han LKM, Dinga R, Hahn T, Ching CRK, Eyler LT, Aftanas L, et al. Brain aging in major depressive disorder: results from the ENIGMA major depressive disorder working group. Mol Psychiatry 2020.
van Velzen LS, Kelly S, Isaev D, Aleman A, Aftanas LI, Bauer J, et al. White matter disturbances in major depressive disorder: a coordinated analysis across 20 international cohorts in the ENIGMA MDD working group. Mol Psychiatry 2020, 25: 1511–1525
Lv X, Si T, Wang G, Wang H, Liu Q, Hu C, et al. The establishment of the objective diagnostic markers and personalized medical intervention in patients with major depressive disorder: rationale and protocol. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16: 240
Fabbri C, Hosak L, Mossner R, Giegling I, Mandelli L, Bellivier F, et al. Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task Force on Genetics: Genetics, epigenetics and gene expression markers of major depressive disorder and antidepressant response. World J Biol Psychiatry 2017, 18: 5–28
Li Z, Zhang C, Fan J, Yuan C, Huang J, Chen J, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and bipolar disorder in patients in their first depressive episode: 3-year prospective longitudinal study. Br J Psychiatry 2014, 205: 29–35
Gong Q, He Y. Depression, neuroimaging and connectomics: a selective overview. Biol Psychiatry 2015, 77: 223–235
Papakostas GI, Shelton RC, Kinrys G, Henry ME, Bakow BR, Lipkin SH, et al. Assessment of a multi-assay, serum-based biological diagnostic test for major depressive disorder: a pilot and replication study. Mol Psychiatry 2013, 18: 332–339
Kolovos S, Kleiboer A, Cuijpers P. Effect of psychotherapy for depression on quality of life: meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry 2016, 209: 460–468
Park LT, Zarate CA Jr. Depression in the primary care setting. N Engl J Med 2019, 380: 559–568
Health N C C F M . Depression: The treatment and management of depression in adults (updated edition) 2010.
Qaseem A, Barry MJ, Kansagara D. Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of P. Nonpharmacologic versus pharmacologic treatment of adult patients with major depressive disorder: A clinical practice guideline from the american college of physicians. Ann Intern Med 2016, 164: 350–359
Dodd S, Mitchell PB, Bauer M, Yatham L, Young AH, Kennedy SH, et al. Monitoring for antidepressant-associated adverse events in the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder: An international consensus statement. World J Biol Psychiatry 2018, 19: 330–348
Cristea IA, Naudet F. US Food and Drug Administration approval of esketamine and brexanolone. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6: 975–977
Zheng W, Cai DB, Xiang YQ, Zheng W, Jiang WL, Sim K, et al. Adjunctive intranasal esketamine for major depressive disorder: A systematic review of randomized double-blind controlled-placebo studies. J Affect Disord 2020, 265: 63–70
Popova V, Daly EJ, Trivedi M, Cooper K, Lane R, Lim P, et al. Efficacy and safety of flexibly dosed esketamine nasal spray combined with a newly initiated oral antidepressant in treatment-resistant depression: A Randomized Double-Blind Active-Controlled Study. Am J Psychiatry 2019, 176: 428–438
Turner EH. Esketamine for treatment-resistant depression: seven concerns about efficacy and FDA approval. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6: 977–979
Murrough JW, Abdallah CG, Mathew SJ. Targeting glutamate signalling in depression: progress and prospects. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2017, 16: 472–486
Gill SP, Kellner CH. Clinical practice recommendations for continuation and maintenance electroconvulsive therapy for depression: Outcomes from a review of the evidence and a consensus workshop held in Australia in May 2017. J ECT 2019, 35: 14–20
McClintock SM, Reti IM, Carpenter LL, McDonald WM, Dubin M, Taylor SF, et al. Consensus recommendations for the clinical application of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in the treatment of depression. J Clin Psychiatry 2018, 79.
Chase HW, Boudewyn MA, Carter CS, Phillips ML. Transcranial direct current stimulation: a roadmap for research, from mechanism of action to clinical implementation. Mol Psychiatry 2020, 25: 397–407
Alexander ML, Alagapan S, Lugo CE, Mellin JM, Lustenberger C, Rubinow DR, et al. Double-blind, randomized pilot clinical trial targeting alpha oscillations with transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Transl Psychiatry 2019, 9: 106
Akhtar H, Bukhari F, Nazir M, Anwar MN, Shahzad A. Therapeutic efficacy of neurostimulation for depression: Techniques, current modalities, and future challenges. Neurosci Bull 2016, 32: 115–126
Zhou C, Zhang H, Qin Y, Tian T, Xu B, Chen J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of deep brain stimulation in treatment-resistant depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2018, 82: 224–232
Li X, Li X. The antidepressant effect of light therapy from retinal projections. Neurosci Bull 2018, 34: 359–368
Shekelle PG, Cook IA, Miake-Lye IM, Booth MS, Beroes JM, Mak S. Benefits and harms of cranial electrical stimulation for chronic painful conditions, depression, anxiety, and insomnia: A systematic review. Ann Intern Med 2018, 168: 414–421
Kessler RC. The potential of predictive analytics to provide clinical decision support in depression treatment planning. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2018, 31: 32–39
Bradley P, Shiekh M, Mehra V, Vrbicky K, Layle S, Olson MC, et al. Improved efficacy with targeted pharmacogenetic-guided treatment of patients with depression and anxiety: A randomized clinical trial demonstrating clinical utility. J Psychiatr Res 2018, 96: 100–107
Greden JF, Parikh SV, Rothschild AJ, Thase ME, Dunlop BW, DeBattista C, et al. Impact of pharmacogenomics on clinical outcomes in major depressive disorder in the GUIDED trial: A large, patient- and rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J Psychiatr Res 2019, 111: 59–67
Long Z, Du L, Zhao J, Wu S, Zheng Q, Lei X. Prediction on treatment improvement in depression with resting state connectivity: A coordinate-based meta-analysis. J Affect Disord 2020, 276: 62–68
Download references
Acknowledgments
This review was supported by the National Basic Research Development Program of China (2016YFC1307100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81930033 and 81771465; 81401127), Shanghai Key Project of Science & Technology (2018SHZDZX05), Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical Engineering Foundation (YG2016MS48), Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (19XJ11006), the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen Municipality (SZSM201612006), the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (2012BAI01B04), and the Innovative Research Team of High-level Local Universities in Shanghai.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Clinical Research Center and Division of Mood Disorders of Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200030, China
Zezhi Li, Jun Chen & Yiru Fang
Department of Neurology, Ren Ji Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200127, China
Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Shanghai Information Center for Life Sciences, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai, 200031, China
Meihua Ruan
Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai, 200031, China
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Psychotic Disorders, Shanghai, 201108, China
Jun Chen & Yiru Fang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yiru Fang .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Li, Z., Ruan, M., Chen, J. et al. Major Depressive Disorder: Advances in Neuroscience Research and Translational Applications. Neurosci. Bull. 37 , 863–880 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00638-3
Download citation
Received : 30 May 2020
Accepted : 30 September 2020
Published : 13 February 2021
Issue Date : June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00638-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Major depressive disorder
- Pathogenesis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Health Topics
- Brochures and Fact Sheets
- Help for Mental Illnesses
- Clinical Trials
Teen Depression Study: Understanding Depression in Teenagers Join a Research Study: Enrolling nationally from around the country
Depression — also known as major depressive disorder or clinical depression — is a common but serious mood disorder that can interfere with how people feel, think, and handle daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. Although sadness can be a symptom of depression, it does not characterize the disorder. Symptoms of depression include sad or anxious mood, feelings of hopelessness or guilt, loss of interest in previous hobbies or activities, decreased energy, difficulty concentrating or sleeping, changes in appetite or weight, and persistent physical symptoms. People with depression experience symptoms nearly every day for at least two weeks. Learn more about depression .
Join A Study
For opportunities to participate in NIMH research on the NIH campus, visit the clinical research website . Travel and lodging assistance may be available.
Featured Studies
Featured studies include only those currently recruiting participants . Studies with the most recent start date appear first.
A Digitally Assisted Risk Reduction Platform for Youth at High Risk for Suicide
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 7, 2024 Eligibility: 13 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Columbia University, New York, New York, United States
Despite efforts to prevent suicide, US rates are climbing, and suicide is the second leading cause of death among youth. Digital tools, especially personal smartphones, are promising avenues to address these issues and can be used to provide a unique understanding of risk factors, including psychological distress, anhedonia and behavioral withdrawal, and sleep disturbance among high-risk individuals. This project aims to enhance the effectiveness of the delivery of preventative health care to youth at risk for suicide by developing a comprehensive digital platform that allows practitioners to integrate mobile sensing data and HIPAA-compliant client communication tools into their management of these young people.
Title: Safety and Feasibility of Individualized Low Amplitude Seizure Therapy (iLAST)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 4, 2024 Eligibility: 22 Years to 70 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Background:
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is used to treat people with severe depression. During ECT, the brain is given electric pulses that cause a seizure. Although it is effective, it can cause side effects, including memory loss. Researchers want to study a new way to give ECT called iLAST.
To see if iLAST is safe and feasible in treating depression.
Eligibility:
People ages 22 70 years old who have major depressive disorder and are eligible for ECT
Participants will be screened under protocol 01-M-0254. This includes:
Medical and psychiatric history and exam
Blood and urine tests
Participants will be inpatients at the Clinical Center. They study has 3 phases and will last up to 20 weeks.
Phase I will last 1 week. It includes:
MRI: Participants will lie in a scanner that takes pictures of the body
MEG: A cone over the participant s head will record brain activity.
TMS: A wire coil placed on the participant s scalp will produce an electrical current to affect brain activity.
SEP: An electrode on the participant s wrist will give a small electrical shock to test nerve function.
Phase II will last 2 and a half weeks. It includes:
Seven sessions of iLAST under general anesthesia. Participants may also get standard ECT.
EEG: A small electrode placed on the participant s scalp will record brain waves.
Interviews about mood, symptoms, and side effects. Participants facial expressions may be video recorded.
Phase III will last at least 1 week. It will include:
Standard ECT if needed. Participants will have sessions every other day, 3 times a week.
Sponsoring Institution: National Institute of Mental Health
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Youth With Treatment-Resistant Major Depressive Disorder
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 4, 2024 Eligibility: 13 Years to 17 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is one of the most impairing medical conditions in the world. Medication and some kinds of talk therapy are standard treatments for teens with MDD, but these do not work well for everyone. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has been approved to treat MDD in adults. TMS might help adolescents, too.
To test TMS combined with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in teens with MDD.
People aged 13 to 17 years with MDD that has not responded to treatment.
Participants will be screened. They will have a physical exam and psychiatric evaluation. They will have an MRI scan and a test of their heart function. They will enroll in 2 NIH protocols (01-M-0254 and 18-M-0037).
For 2 to 6 weeks, participants will have weekly CBT, a kind of talk therapy. They will taper off of their psychiatric medicines.
For 2 weeks, participants will come to the clinic every weekday. They will receive 3 or 4 sessions of TMS on each of those days. A wire coil will be held on their scalp. A brief electrical current in the coil creates a magnetic pulse that affects brain activity. They will receive 30 TMS pulses in 10-second bursts; these will be repeated 60 times in each 15-minute session. Participants may hear a click and feel a pulling sensation under the coil. They may feel their muscles twitch. Each day, they will have tests of concentration, thinking, and memory. Some may have a 3rd week of TMS.
Participants will remain in the study for 5 more weeks. They will begin taking their medications again.
Targeting Large-scale Networks in Depression With Real-time Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Neurofeedback
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 18, 2024 Eligibility: 18 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States
The purpose of this study is to develop a technique called real time fMRI neurofeedback.
This technique uses a regular MRI scanner, except that special software allows the researchers to measure activity in participants brain, using fMRI, and then give information, in the form of a feedback signal, which indicates brain activity in real time, while in the MRI scanner. The larger goal of this study is to develop ways to help people, including those with depression, better regulate brain activity. The researchers think that this may be helpful in managing psychiatric symptoms.
This study design has three phases, however, only two phases (phase 2 and 3) are considered to be a clinical trial. Phase 2 (part 2) was registered and is NCT05934604. This is the phase 3 (part 3) for this project and is funded by the National Institutes of Health.
Better Sleep Study
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 15, 2024 Eligibility: 12 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UCSF Nancy Friend Pritzker Psychiatry Building, San Francisco, California, United States
The overall aim of this proposal is a confirmatory efficacy trial sufficiently powered and designed to test the hypothesis that improving the relationship between biological circadian timing and waketime, a novel modifiable target, improves depression outcomes in a subgroup of adolescents with depression and a misaligned relationship between biological circadian timing and waketime utilizing a cognitive-behavioral sleep intervention.
Supporting Peer Interactions to Expand Access to Digital Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Spanish-speaking Patients
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 14, 2024 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Zuckerberg San Francisco General, San Francisco, California, United States
Investigators will evaluate the implementation of an evidence-based, Spanish-language, digital, cognitive-behavioral therapy intervention (SilverCloud) in primary care settings for Latino patients with depression and/or anxiety. 426 participants will be enrolled in a two-armed trial comparing self-guided vs. supported dCBT (SilverCloud). At the provider level, investigators will compare the efficacy of provider referrals with the use of a clinic patient registry to identify candidates who could benefit from a digital mental health intervention.
Acoustic Stimulation, Sleep, and Cognitive-Emotional Processes in Young Adults With Anxiety and Depression Symptoms
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 14, 2024 Eligibility: 18 Years to 25 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
In this study, the investigators will recruit young adults (ages 18-25 years) with elevated anxiety/depression symptoms and sleep disturbance. Participants will complete two overnights in a sleep lab. During one of the overnights, slow-wave activity will be enhanced by delivering sub-arousal auditory tones during slow-wave sleep using a headband device (Philips SmartSleep or Dreem 2). During the other overnight, tones will not be administered. Cognitive and emotional processes will be evaluated using behavioral task performance, self-report, and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). After the second overnight, participants will take the headband device home and wear it every night for approximately 2 weeks. For half of the participants, the headband will play tones every night and, for the other half, the headband will not play tones. Participants will then return for a final testing visit in which cognitive and emotional processes and anxiety/depression symptoms will be assessed using behavioral task performance and self-report.
Young Adults With Violent Behavior During Early Psychosis
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 29, 2024 Eligibility: 16 Years to 30 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York, New York, United States
This study aims to provide an evidence-based behavioral intervention to reduce violent behavior for individuals experiencing early psychosis.
SilverCloud as a School-Based Intervention for Vulnerable Youth
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 8, 2024 Eligibility: 13 Years to 22 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): NYU Langone Health, Brooklyn, New York, United States
The goal of this study is to test the efficacy and feasibility of a clinician-guided, app-based cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) program, SilverCloud, as a school-based mental health intervention for vulnerable youth. An open trial of SilverCloud will be conducted to determine preliminary efficacy in this sample and inform program refinements by collecting outcome self-report assessments and conducting interviews on feasibility and acceptability. After the program and its implementation strategy are refined, we will conduct an randomized controlled trial. Adolescents who screen positive for significant mental health symptoms and who are enrolled in their school-based health center (SBHC) will be randomized to receive SilverCloud or treatment as usual (TAU). Efficacy will be assessed through outcome self-reports. Feasibility and acceptability feedback will again be collected from participants, SBHC staff, and community members.
Enhanced Coordinated Specialty Care for Early Psychosis
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 1, 2024 Eligibility: Age N/A, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): McLean Hospital OnTrack Clinic, Belmont, Massachusetts, United States; Massachusetts General Hospital FEPP Clinic, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
The goal of this clinical trial is to compare engagement in treatment in coordinated specialty care (CSC) to five extra care elements (CSC 2.0) in first-episode psychosis. The main question it aims to answer is:
• Does the addition of certain elements of care increase the number of visits in treatment for first-episode psychosis?
Participants will either:
Receive care as usual (CSC) or
Receive care as usual (CSC) plus five additional care elements (CSC 2.0):
Individual peer support Digital outreach Care coordination Multi-family group therapy Cognitive remediation
Researchers will compare the standard of care (CSC) to CSC 2.0 to see if participants receiving CSC 2.0 have more visits to their clinic in their first year.
Neural Circuit Effects of Ketamine in Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 31, 2024 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, United States
This project is designed to examine the role of the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (sgACC) in anhedonia and anxiety in humans with depression, as well as the acute and sustained effects of ketamine on agACC activation and depression symptoms.
Causal Role of Delta-beta Coupling for Goal-directed Behavior in Anhedonic Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 24, 2024 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, United States
Anhedonia, the inability to seek-out and experience pleasure, is a common symptom in depression that predicts treatment-resistance and is sometimes exacerbated by first-line antidepressants. In our previous research, we found that anhedonia decreases goal-directed behavior and its related neural activity. In this study, we will investigate target engagement from five-consecutive days of stimulation for participants that are within a unipolar major depressive episode and also have high symptoms of anhedonia.
RESISTance Exercise for Depression Trial
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 1, 2024 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, United States
Depression is a leading cause of disability worldwide and current treatments are ineffective for many people. This trial will investigate the efficacy of a 16-week high vs low dose resistance exercise training program for the treatment of Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in 200 adults.
Inflammation and Depression in People With HIV
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: December 11, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Emory University Hospital, Atlanta, Georgia, United States; Grady Memorial Hospital, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
The purpose of this 10-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study is to determine whether inflammation impacts reward and motor neural circuitry to contribute to depressive symptoms like anhedonia and psychomotor slowing in people with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and depression. Sixty male and female patients with HIV who have depression, anhedonia and high inflammation and are stable on effective treatment for their HIV will be randomized to receive either the anti-inflammatory drug baricitinib or a placebo for 10 weeks. Participants will complete lab tests, medical and psychiatric assessments, neurocognitive testing, functional MRI (fMRI) scans, and optional spinal taps as part of the study. The total length of participation is about 5 months.
Emotional Cognition: Establishing Constructs and Neural-Behavioral Mechanisms in Older Adults With Depression
Study Type: Observational Start Date: December 11, 2023 Eligibility: 21 Years to 80 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, United States
This is a cross-sectional pilot study designed to establish hot and cold cognitive functions and underlying neurocircuitry in older adults with MDD. The investigators will study 60 participants aged 21-80 years old with MDD. All participants will undergo clinical and neurocognitive assessment, and Magnetoencephalography (MEG)/Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedures at one time point. The investigators will also enroll 60 demographically matched comparable, never-depressed healthy participants (controls) to establish cognitive benchmarks. Healthy controls will complete clinical and neurocognitive measures at one time point. To attain a balanced sample of adults across the lifespan, the investigators will enroll participants such that each age epoch (e.g., 21-30, 31-40, etc.) has a total of ten subjects (n=10) in both the healthy control cohort and depressed cohort.
Dopaminergic Therapy for Anhedonia - 2
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 21, 2023 Eligibility: 25 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Emory University Hospital, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
The purpose of this 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, study is to explore new treatment options for people with depression who have high inflammation and anhedonia. Seventy male and female participants with depression, between 25-55 years of age, with higher levels of inflammation and anhedonia will be randomized to receive L-DOPA or matched placebo over 8 weeks. Participants will complete lab tests, medical and psychiatric assessments, motivation and motor tasks, and MRI scans as part of the study. The total length of participation is approximately 10 to 12 weeks.
Risk and Resilience to Suicide Following Late-Life Spousal Bereavement
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 20, 2023 Eligibility: 65 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Pittsburgh (UPMC), Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
The purpose of the RISE study is to examine how the 24-hour rhythm of sleep and social activity relate to mood and suicidal ideation among older adults that recently lost a spouse or life partner.
Processes and Circuitry Underlying Threat Sensitivity as a Treatment Target for Co-morbid Anxiety and Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 8, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Laureate Institute for Brain Research, Tulsa, Oklahoma, United States
This mechanistic study uses an anti anxiety drug and brain imaging to study the threat processing system and associated brain circuits in people with depression, anxiety disorders and comorbid depression and anxiety disorders. In a double blind, placebo controlled crossover design, up to 65 individuals will be recruited who will have a diagnosis of major depressive disorder (MDD) and at least one anxiety disorder (AD) (AD-MDD group), up to 65 participants will have a diagnosis of MDD and no diagnosis of an AD and up to 65 participants will have no diagnosis of MDD and a diagnosis of at least one AD will be enrolled to participate in an two session study to obtain 150 completers (50 per group). All participants will receive a single dose of Lorazepam and placebo (order randomized) taken orally. After the ~2.5 hr screening session, participants will complete two identical ~5 hr experimental sessions, each of which include a 30 min eyeblink startle session and a 1 hr functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain scan session. The total time involved in the study is approximately 10.5 hours.
The main questions the study seeks to answer are:
are people with comorbid depression and anxiety different than those with depression alone in terms of their eyeblink startle response to threat? are people with comorbid depression and anxiety different than those with depression alone in terms of their brain activation in response to threat? are people with comorbid depression and anxiety different than those with depression alone in terms of their responses to anxiety drugs?
NIMH Rhythms and Blues Study: A Prospective Natural History Study of Motor Activity, Mood States, and Bipolar Disorder
Study Type: Observational Start Date: November 3, 2023 Eligibility: 12 Years to 70 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Mood disorders, such as bipolar disorder, can have serious effects on a person s life. People with bipolar disorder are more likely to have heart disease and abuse substances. In this natural history study, researchers would like to learn more about the connection between exercise and mental health in people with and without mood disorders.
To better understand relationships among physical activity, sleep, and mental health.
People aged 12 to 60 years with a history of a mood disorder. Healthy spouses and relatives with no mood disorders are also needed.
Participants will be in the study up to 2 years.
For up to 20 days in a row, at 4 times during the study, participants will:
Complete an electronic diary on their smartphone. Participants will answer questions about their mood, health, sleep, and daily activities.
Wear an activity monitor, like a wristwatch, that records how much they move.
Wear a light sensor, as a necklace, to record the amount of light in their environment.
Some participants will do additional tests. Twice during the study, for 3 days in a row, they will:
Wear monitors to record their temperature, heart rate, and sleep.
Provide saliva samples.
Complete cognitive tasks on their smartphone.
Participants will visit the NIH clinic 2 times. They will have a physical exam, with blood and urine tests. They will wear a heart monitor. They will ride a stationary bike for 30 minutes. They may have an imaging scan.
Some participants will stay overnight. They will go to sleep wearing a cap to measure their brain activity.
Self-guided Treatment for Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 12, 2023 Eligibility: 13 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Big Health, Inc., San Francisco, California, United States
This study will examine the efficacy and safety of a self-guided digital therapeutic app for the adjunct treatment of Major Depressive Disorder compared to a control app in adolescents and adults.
A Precision Medicine Approach to Target Engagement for Emotion Regulation
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 29, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, United States
The proposed study is designed to first test whether teaching people personalized or standardized emotion regulation skills leads to greater decreases in daily negative emotion intensity. Second, using data from an initial sample, the investigators will prospectively assign an independent sample of participants to receive their predicted optimal or non-optimal skills to determine if it is feasible and efficacious to match participants to the most appropriate training condition. Results of these studies may identify the mechanisms by which emotion regulation interventions impact emotional functioning and allow for the development of personalized, evidence-based, and scalable emotion regulation interventions.
Ketamine Tolerated Dose for Postpartum Depression and Pain After Cesarean Delivery
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 25, 2023 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Magee Womens Hospital of UPMC, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
The purpose of this study is to identify a tolerable dose for postpartum ketamine infusion using a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) 3+3 design. A loading dose over 1 hour will be the MTD variable to be tested, as our data suggest that ketamine side effects occur with the loading dose. The investigators hypothesize that subanesthetic ketamine dose will be well tolerated and any noted side effects will be rated acceptable by postpartum women following cesarean delivery.
Tele-PROTECT Therapy: Effectiveness, Empowerment, and Implementation
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 22, 2023 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York, United States
The purpose of this randomized trial is to conduct a fully powered effectiveness trial of video-delivered PROTECT (Tele-PROTECT) compared to a video-delivered depression education (DepEd) control condition to be delivered to 140 English- and Spanish-speaking NYC elder abuse victims. Investigators hypothesize three main aims:
Effectiveness Aim: Tele-PROTECT participants will have significantly greater and clinically meaningful reductions in depression when compared to the DepEd control; Abuse Impact Aim: Tele-PROTECT participants will demonstrate greater safety related empowerment compared to DepEd control, which can help participants take steps to reduce risk; Implementation Aim: Stakeholders' views of the factors impacting the implementation of Tele-PROTECT based on characteristics of the intervention, agency setting, and population served will contribute to a national dissemination of Tele-PROTECT
Participants will
Receive 9 weeks of tele health psychotherapy delivered by a Master's level mental health clinician from the Weill Cornell Medicine research team. Participants will be assigned to "Tele-PROTECT" or "DepEd" psychotherapy randomly. Participate in one baseline assessment and four follow-up assessments at weeks 3, 6, 9, and 12 administered by a trained member of the research team.
Brain Changes During Social Reward Psychotherapy for Mid- and Late-Life Suicidality
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 18, 2023 Eligibility: 50 Years to 80 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York, United States
The investigators hypothesized that during the 9-week course of Engage & Connect treatment there will be an increase in brain functions of the Positive Valence System which in turn will lead to reduction in suicidality.
Amplitude Titration to Improve ECT Clinical Outcomes
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 14, 2023 Eligibility: 50 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of New Mexico Health Science Center, Albuquerque, New Mexico, United States
A randomized controlled trial will compare hippocampal neuroplasticity, antidepressant, and cognitive outcomes between individualized amplitude and fixed 800 mA amplitude ECT in older depressed subjects (n = 25 per group, n = 50 total). Relative to fixed 800 mA ECT:
H1: Individualized amplitude arm will have improved RUL antidepressant outcome (IDS-C30 response rates and reduced BT electrode placement switch at V2).
H2: Individualized amplitude arm will have improved cognitive outcomes (DKEFS-Verbal Fluency
Alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4- Isoxazole Propionic Acid Receptor Components of the Anti-Depressant Ketamine Response
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 7, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, United States
The proposed study will assess the combined effect of perampanel and ketamine on the anti-depressant response in individuals with treatment resistant depression. The purpose of this study is to test the hypothesis that stimulation of Alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4- Isoxazole Propionic Acid receptors (AMPAR) is critical to the anti-depressant response of ketamine.
CBT+ for Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 1, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, United States
This study investigates the effects of a novel intervention approach, intentionally sequencing aerobic exercise immediately prior to therapy sessions (i.e., cognitive behavioral therapy [CBT]) to determine its effects on both specific and common factors underlying the antidepressant effect of CBT (i.e., mechanisms of CBT). To assess the utility of this treatment augmentation, investigators plan to conduct a randomized controlled trial involving 40 adults with Major Depressive Disorder who will watch a nature documentary while either resting quietly (termed 'CalmCBT') or exercising at a moderate intensity ('ActiveCBT') immediately prior to 8 weekly sessions of CBT. It is hypothesized that target CBT mechanisms of antidepressant action (i.e., self-reported working alliance and behavioral activation) will be more effectively engaged by ActiveCBT vs. CalmCBT.
OptimizeD Pilot Study
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: August 1, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 99 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Sangath, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India
This pilot study aims to explore and refine the trial procedures that will be implemented in a larger-scale clinical trial scheduled to commence in March 2024 (NCT05944926). As part of this study, 60 patients with moderate to severe depression will be randomized to either psychotherapy based on behavioral activation called the Healthy Activity Program (HAP) or antidepressant medication.
The pilot study has two primary objectives:
Evaluate the feasibility and acceptability of the study Collect essential outcome data in preparation for the larger trial
Treatment of Post-partum Depression Using an Behavioral Intervention Called ROSE (Reach Out, Stay Strong, Essentials for Mothers of Newborns) Delivered Using an Electronic App
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: July 17, 2023 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York, United States
A randomized trial of pregnant people at risk for postpartum depression comparing the InBloom app (n = 76) to ROSE (n = 76; weekly scheduled group), and two control groups. We will assess Depression at baseline and 1, 2 and 3 months, ROI at 3 months, Satisfaction at 1 and 3 months and Perceived Access at 1 and 3 months. Subject participation will last up to 8 months (minimum 17 weeks pregnant through 3 months postpartum).
Reducing Psychological Barriers to PrEP Persistence Among Pregnant and Postpartum Women in Cape Town, South Africa
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: July 1, 2023 Eligibility: Females, 15 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Gugulethu Midwife Obstetric Unit (MOU), Cape Town, Western Cape, South Africa
Pregnant women in South Africa (SA) are at high risk of HIV acquisition. Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) use during pregnancy is both safe and effective in preventing HIV. However, posttraumatic stress (associated with intimate partner violence and/or other traumas) and depression negatively impact PrEP adherence among women in SA. Addressing posttraumatic stress and depression will likely improve PrEP adherence and persistence (i.e., sustained PrEP adherence over time) during pregnancy and breastfeeding, which are periods of dramatically increased HIV risk. The overarching goal of this proposal is to develop and test the feasibility and acceptability of a cognitive behavioral intervention that targets common underlying factors of posttraumatic stress and depression to improve PrEP adherence and persistence during pregnancy and the postpartum transition. The specific aims of the project are to (1) explore the mechanisms by which posttraumatic stress and depression impact PrEP adherence and persistence during pregnancy via qualitative interviews; (2) develop a brief PrEP adherence and persistence intervention (~4 sessions) that reduces the negative impact of psychological mechanisms common to posttraumatic stress and depression on PrEP use, and builds behavioral skills to improve self-care; and (3) evaluate the feasibility, acceptability, and signals of preliminary efficacy of the intervention, which will be integrated into antenatal care, in a pilot randomized controlled trial. All data will be collected in the Midwife Obstetrics Unit (MOU) in Gugulethu, a peri-urban settlement and former township community outside of Cape Town, SA.
Virtual Patient Navigation During a Pandemic
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 29, 2023 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States
The sub-study will involve a rigorous mixed-methods design. The qualitative phase of the sub-study will consist of semi-structured interviews. During the semi-structured interviews, 10 eligible women will be recruited to identify barriers and facilitators to accessing virtual mental health services. This information will be used to adapt an evidence-based patient navigation intervention for virtual use and an engagement measure. For the intervention phase of the sub-study, 30 women with persistent postpartum depression symptoms will be recruited to participate in the adapted virtual navigator program using rapid cycle testing over a 2-month period.
[18F]PF-06445974 to Image PDE4B in Major Depressive Disorder Using PET
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 22, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 70 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a psychiatric condition. People with MDD have occasional bouts of depressive symptoms; these bouts are called major depressive episodes (MDEs). Researchers want to know if people having MDEs have lower levels of an enzyme called PDE4B in their brains.
To find out (1) if PDE4B can be detected in a person s brain using a special scanning method and (2) if brain PDE4B levels are lower in people having an MDE.
People aged 18-70 years with MDD. Healthy volunteers are also needed.
Participants will have up to 5 clinic visits.
Participants will be screened. They will have a physical exam with blood tests. They will have a test of their heart function. Some participants may have a psychiatric assessment; they will answer questions about their state of mind and related topics.
Participants will have magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. They will lie on a table that slides into a metal cylinder.
Participants will have a positron emission tomography (PET) scan. A needle will be used to guide a thin plastic tube (catheter) into a vein in one arm. An experimental substance called a radioactive tracer ([18F]PF-06445974) will be injected through the catheter. Participants will lie on a table that slides into a doughnut-shaped machine. The scan will last up to 4 hours with a 15-minute break.
Participants blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing will be monitored before, during, and after the PET scan. A second catheter will be inserted in the artery of the wrist so blood can be drawn during the scan.
Some participants may return for a second PET scan.
https://nimhcontent.nimh.nih.gov/start/surveys/?s=KE88DXXPLDFHHTF8
Determining the Role of Social Reward Learning in Social Anhedonia
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 14, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 35 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, United States; University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama, United States
This is a clinical trial study that aims to evaluate the specificity of the relationship between reduced sensitivity to social reward and social anhedonia at both behavioral and neural levels. Individuals who recently experienced their first-episode psychosis will be recruited. Participants will be randomized 1:1 to motivational interviewing or a time- and format-matched control probe. At pre- and post-probe, participants will perform two social reward learning tasks in the scanner. With this design feature, we will examine the relationship between sensitivity to social reward and reduced subjective experience of social pleasure at both the behavioral and neural levels.
Neuro-affective Response to Light in Depressed Adolescents and Young Adults
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 14, 2023 Eligibility: 12 Years to 30 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Western Psychiatric Hospital, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
The goal of this neuroimaging pilot study is to understand developmental differences in the impact of therapeutic wavelength light (blue light) versus a non-therapeutic wavelength (red light) on emotional brain function in depression. The main questions this study aims to answer are:
Does acute exposure to blue light (vs red light) stabilize emotional brain function in depressed individuals? Are stabilizing effects of blue light (vs red light) stronger for blue light in adolescents than young adults?
Participants will complete:
A magnetic resonance imaging brain scan, in which we will examine the effect of blue versus red light on emotional brain function at rest and in response to rewards and losses. A pupillometry test of sensitivity to blue vs red light Clinical interviews and surveys Screening measures for drug and alcohol use, MRI safety, and current pregnancy [if relevant] Home sleep tracking with sleep diary and actigraphy for one week
Toward Understanding Drivers of Patient Engagement With Digital Mental Health Interventions - Part II
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 7, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 75 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Jessica Morrow Lipschitz, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
This study is a clinical trial that evaluates what drives patient engagement and tests the impact of two strategies-automated motivational push messaging and coach support-to improve engagement with an evidence-based mobile app intervention for depression and/or anxiety.
Amygdala Neurofeedback for Depression - Large Scale Clinical Trial
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 1, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
The goal of this study is to evaluate whether rtfMRI-nf training to increase the amygdala response to positive memories may serve as a stand-alone intervention for major depressive disorder
EPI-MINN: Targeting Cognition and Motivation - National
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 30, 2023 Eligibility: 15 Years to 40 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Minnesota Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
The purpose of this study is to perform a practice-based research project designed to assess whether cognition and motivated behavior in early psychosis can be addressed as key treatment goals within real-world settings by using a 12-week mobile intervention program. Participants who are receiving care at coordinated specialty care (CSC) early psychosis clinics across the United States will be recruited to participate in this study. A qualifying CSC program will provide comprehensive clinical services such as psychotherapy, medication management, psychoeducation, and work or education support. This study will be conducted remotely, and participants can participate at home with their own electronic devices.
The aim of this study is to investigate a well-defined 12-week mobile intervention program specifically designed to target cognitive functioning and motivated behavior for individuals with early psychosis. Participants will complete a screening interview which will include diagnosis and symptom ratings, neurocognitive assessment, and self-reports of symptoms, behavior, and functioning. Then participants will be randomized to receive the 12-week mobile intervention, or an active control of treatment as usual. The investigators will test for differences in the clinical trajectories after training, and at two follow up appointments at 6 and 12 months post-training.
Neurostimulation Versus Therapy for Problems With Emotions
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 15, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, United States
The primary goal of this clinical trial is to evaluate the unique neural and behavioral effects of a one-session training combining emotion regulation skills training, with excitatory repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC). The secondary aim is to identify key changes in the emotion regulation neural network following the combined intervention versus each of the components alone. The third aim is to explore personalized biomarkers for response to emotion regulation training.
Participants will undergo brain imaging while engaging in an emotional regulation task. Participants will be randomly assigned to learn one of two emotion regulation skills. Participants will be reminded of recent stressors and will undergo different types of neurostimulation, targeted using fMRI (functional MRI) results. Participants who may practice their emotion regulation skills during neurostimulation in a one-time session. Following this training, participants will undergo another fMRI and an exit interview to assess for immediate neural and behavioral changes. Measures of emotion regulation will be assessed at a one week and a one month follow up visit.
Friendship Bench Mental Health Intervention for Adolescent Girls and Young Women in South African PrEP Delivery Settings
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 24, 2023 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years to 25 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Wits Reproductive Health Institute, Johannesburg, Gauteng, South Africa
Adolescent girls and young women (AGYW) at risk of HIV in sub-Saharan Africa, frequently (20-50%) have symptoms of common mental disorders, including depression, anxiety, and stress. These symptoms are associated with suboptimal adherence to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), a highly effective HIV prevention approach. In this project, the team seeks to address poor mental health and consequent impacts on PrEP adherence and among AGYW at risk of HIV by testing an evidence-based mental health intervention (the Youth Friendship Bench SA) adapted for PrEP delivery programs.
Depressed Mood Improvement Through Nicotine Dosing 3
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 15, 2023 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Vanderbilt Psychiatric Hosptial, Nashville, Tennessee, United States
Deficits in cognitive control are core features of late-life depression (LLD), contributing both to emotion dysregulation and problems with inhibiting irrelevant information, conflict detection, and working memory. Clinically characterized as executive dysfunction, these deficits are associated with poor response to antidepressants and higher levels of disability. Improvement of cognitive control network (CCN) dysfunction may benefit both mood and cognitive performance, however no current pharmacotherapy improves Cognitive Control Network deficits in LLD.
The study examines the hypothesis that nicotine acetylcholine receptor agonists enhance Cognitive Control Network function. This effect may resultantly improve mood and cognitive performance in LLD. Small, open-label studies of transdermal nicotine (TDN) patches have supported potential clinical benefit and provided support that transdermal nicotine administration engages the Cognitive Control Network.
This blinded study will expand past open-label trials supporting potential benefit in LLD. It will examine TDN's effect on depression severity and cognitive control functions measured by neuropsychological testing. The study will evaluate 60 eligible and enrolled participants over a 3-year period.
Depressed Mood Improvement Through Nicotine Dosing-3 (Depressed MIND3) Extension
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 15, 2023 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Vanderbilt Psychiatric Hospital, Nashville, Tennessee, United States
This is an open-label, extension to the blinded Depressed MIND 3 (Depressed Mood Improvement through nicotine dosing) study. It will evaluate longer-term safety and efficacy of Transdermal Nicotine Patches for potential benefit in cognitive and depression outcomes in elderly depressed participants. Subjects complete blinded randomized trial of Depressed MIND-3 will be eligible for continuation in this extension. This extension study will consist of up to 12 weeks of treatment and a 3 -week safety follow-up period.
Using Machine Learning to Optimize User Engagement and Clinical Response to Digital Mental Health Interventions
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 12, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Center for Anxiety and Related Disorders, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Digital mental health interventions are a cost-effective and efficient approach to expanding the accessibility and impact of psychological treatments; however, little guidance exists for selecting the most effective program for a given individual. In the proposed study, decision rules will develop for selecting the digital program that is most likely to be the optimal intervention for each user. These treatment recommendations can be implemented in the context of large healthcare delivery systems to improve the delivery of digital mental health interventions at scale.
The overarching aim of the current study is to better understand for whom and how leading digital interventions work in a large healthcare setting. The study builds on the existing literature and follows expert recommendations by using machine learning (ML) methods to develop precision treatment rules (PTRs) for three leading digital interventions for emotional disorders (e.g., anxiety, depression, and related mental health disorders). Specifically, ML methods will be used to develop PTRs to optimize clinical outcomes and associated intervention engagement. This study will leverage a unique partnership between Boston University (BU), SilverCloud Health (SC)--a leading provider of digital mental health care--and Kaiser Permanente (KP)--one of America's leading health care providers.
A clinical trial (RCT) will be conducted to evaluate the relative effectiveness of three distinct empirically supported digital mental health interventions (from SC's existing library of programs) in a sample recruited from KP primary care and other clinical settings. Data from this trial will be used to develop theoretically and empirically informed, reliable selection algorithms for managing treatment delivery decisions. Algorithms will be validated in a separate "holdout" dataset by examining whether allocation to predicted optimal treatment is associated with superior outcomes compared to allocation to a non-optimal treatment. The role of user engagement will be determined, and other mechanisms in treatment outcome.
Mechanisms of Depression and Anhedonia in Adolescents: Linking Sleep to Reward- and Stress-Related Brain Function
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 27, 2023 Eligibility: 14 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Oregon, Eugene, Oregon, United States
This research will use biobehavioral approaches to generate understanding about the linkages between sleep duration and timing, stressful life events, and depressive symptoms in adolescents, with a long-term aim of developing effective preventative interventions.
In-person vs. Virtual Delivery of a Group-based Prevention of Postpartum Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 13, 2023 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Denver Health Medical Center, Denver, Colorado, United States
The goal of this clinical trial is to test whether an established preventive intervention (group interpersonal therapy) delivered virtually shows the same benefits for preventing postpartum depression as it does when delivered in person.
Behavioral Activation and Medication Optimization For Improving Perioperative Mental Health In Older Adults Undergoing Oncologic Surgery
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 10, 2023 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States
Using a Hybrid Type 1 Effectiveness-Implementation randomized control trial (RCT) design, the investigators will test the effectiveness of a bundled behavioral activation and medication optimization in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety in older adults undergoing oncologic surgery (compared with usual care), while examining implementation outcomes.
AI-Based Fidelity Feedback to Enhance CBT
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 9, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): The Penn Collaborative for CBT and Implementation Science, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States
This study is being conducted together by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and Lyssn.io, Inc., ("Lyssn"), a technology start-up developing digital tools to support evidence-based psychotherapies (EBPs) for mental health disorders and addiction. This study will implement a technology to assess and enhance the quality of EBPs like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) that includes a user interface geared to clinical, supervision, and administrative workflows and needs, and then assess this technology for effectiveness in comparison to usual care.
There is a tremendous global burden of mental illness: Over 50 million American adults have a diagnosable mental health disorder, and major depression on its own is the leading cause of disability worldwide. In the face of this burden, clinical research has documented a variety of effective EBPs (e.g. CBT), and these psychotherapies are utilized on a massive scale. Systems have invested over $2 billion in training providers in specific EBPs. Once trained, however, therapists' adherence to the EBP, also called fidelity, is both crucial for effectiveness and difficult to assess. There is no scalable method to assess the fidelity and quality of EBPs in community practice settings. This is a foundational problem for healthcare systems.
Advances in speech processing and machine learning make technology a promising solution to this problem. The use of technology - instead of humans - to evaluate EBPs means that objective, performance-based feedback can be provided quickly, efficiently, cost-effectively, and without human error. If successful, the present research will be among the first examples of a method for building, monitoring, and assessing the quality of therapy that can scale up to large, real-world healthcare settings.
In this study, the investigators will implement an existing, fully-functional prototype (LyssnCBT) that includes a user interface geared to community mental health (CMH) clinical, supervision, and administrative workflows and needs, and then assess for effectiveness of psychotherapy supported by LyssnCBT in comparison to usual care.
This study will implement LyssnCBT in 5 community mental health agencies, beginning with a single-arm pilot field trial to identify and address any specific barriers to implementing the tool in a community mental health context. The study team will then conduct a larger study in community mental health agencies comparing LyssnCBT to services as usual.
Disruptions of Brain Networks and Sleep by Electroconvulsive Therapy
Study Type: Observational Start Date: March 7, 2023 Eligibility: 21 Years to 65 Years Location(s): Washington University School of Medicine/Barnes-Jewish Hospital, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) alleviates treatment-resistant depression (TRD) through repeated generalized seizures. The goal of this study is to evaluate how ECT impacts sleep-wake regulation and efficiency of information transfer in functional networks in different states of arousal.
Neuroactive Steroid to Treat Depressed Mood: A Trial for People With HIV
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 3, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years to 85 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
This study will determine the effects of pregnenolone on brain function, inflammation and depressive symptoms in people with HIV who have depression. Participants in this study will receive a pill of either pregnenolone or placebo, and can stay on their current antidepression medications. Brain imaging and behavioral assessments will be performed during the study.
A Digital Intervention for Post-Stroke Depression and Executive Dysfunction
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 1, 2023 Eligibility: 50 Years to 79 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, New York, United States
Individuals with stroke commonly experience both depression and cognitive difficulties. The goal of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of a treatment that combines a digital therapeutic (an iPad-based cognitive training program) with learning cognitive strategies. The hypotheses are that this treatment will improve cognitive skills, depression symptoms, daily function, and brain connectivity. In the short-term, the findings will inform the efficacy of the intervention and in the long-term, may support the use of the intervention to improve co-occurring cognitive and mood difficulties after stroke.
Perioperative Mental Health in Orthopedic Surgery
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 27, 2023 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States
This Hybrid 1 Study will test the effectiveness of a bundled intervention comprised of behavioral activation and medication optimization in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety in older adults undergoing Orthopedic surgery (compared with usual care), while examining implementation outcomes.
Factorial Optimization Trial to Test Effects of Coping Intervention Components
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 18, 2023 Eligibility: 9 Years to 12 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona, United States
This study will identify components for inclusion in a coping intervention package to reduce mental health problems among children exposed to high interparental conflict after parental separation/divorce. Reappraisal, distraction, and relaxation coping strategies are related to fewer mental health problems among children, making intervention components based on these strategies key candidates for inclusion in an optimized coping intervention. The primary aim is to experimentally assess the main and interactive effects of three digital intervention coping components (reappraisal, distraction, relaxation) on children's coping efficacy, emotional security, and internalizing and externalizing problems. Secondary aims are to assess indirect effects of the intervention components on children's coping efficacy, emotional security, and internalizing and externalizing problems through their cognitive, emotional, and behavioral reactions to post-separation/divorce interparental conflict events.
Mechanisms of Behavioral Activation (BA)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 30, 2023 Eligibility: 15 Years to 17 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Facility for Education and Research in Neuroscience (FERN), Atlanta, Georgia, United States; Child and Adolescent Mood Program (CAMP), Atlanta, Georgia, United States; Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
The investigators will be comparing brain (neural) activation of depressed adolescent patients before, during and after a course of Behavioral Activation (BA) therapy using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). In particular, the project seeks to determine whether BA targets different neural mechanisms for behavioral avoidance associated with low motivation as compared to threat avoidance. A group of healthy controls will also be scanned as a comparator group for behavioral and imaging measures.
Clinical Trial for Integrated Care to Help At Risk Teen (iCHART) Intervention
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 26, 2023 Eligibility: 12 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UPMC Center for Adolescent and Young Adult Health, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States; Children's Community Pediatrics (CCP- Waterdam) of Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh UPMC, McMurray, Pennsylvania, United States
This protocol will test the effectiveness of an intervention, iCHART (integrated Care to Help At-Risk Teens) and facilitate recruitment for other studies in the larger ETUDES Center grant, which are focused on treatment development for target risk factors for suicidal behavior, specifically, sleep, anhedonia, and stress related to cybervictimization. This study will recruit 900 adolescents which will be enrolled in a randomized controlled trial to test iCHART and will be randomized to iCHART or treatment as usual (TAU). Based on previous work, the investigators hypothesize that iCHART, compared to TAU, will decrease suicidal-related events by 50%, and the effects will be mediated by increases in referrals, treatment engagement, and safety planning. The investigators will use implementation science methods to assess contextual factors (i.e., barriers and facilitators) and implementation outcomes specifically, acceptability, feasibility, appropriateness, and cost for our predictive algorithm and iCHART to inform future implementation efforts and promote health equity.

Improving Mental Health Among the LGBTQ+ Community
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 25, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, United States
The overall aim of this program of research is to improve the mental health of people who identify as LGBTQ+ by increasing their social support through a brief intervention. The purpose of the proposed project is to establish the effectiveness of our empirically-supported, brief acceptance-based behavioral therapy (ABBT). To achieve the specific aims, the investigators will conduct a fully-powered, randomized clinical trial (n=240) with two treatment arms: treatment-as-usual (TAU) vs. ABBT.
Study of a PST-Trained Voice-Enabled Artificial Intelligence Counselor(SPEAC) for Adults With Emotional Distress (Phase 2)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 23, 2023 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UIMC Advanced Imaging Center, Chicago, Illinois, United States; Department of Medicine, Vitoux Program on Aging and Prevention, Chicago, Illinois, United States
Approximately 200 Participants with mild-to-moderate, untreated depression and/or anxiety will be randomly assigned (by chance, like flipping a coin) to 1 of 3 study groups: Lumen Coached Problem-Solving Treatment (PST) (n=100), Human Coached PST (n=50), and optional (delayed) Lumen Coached PST as waitlist control (n=50) to improve emotional health. All participants will complete assessments at baseline and at 18 weeks post randomization.
Depending on the group assignment the PST program will be delivered by Lumen, a virtual voice-based coach on a study iPad, or by a human coach in person for the first session and then via videoconference or phone for the remaining 7 sessions. Participants assigned to the waitlist control group can receive the Lumen coached PST on a study iPad after completing their 18-week follow-up assessment.
Participants will receive 8 coaching sessions to learn problem-solving skills and work on unresolved problems in daily living that may be interfering with their emotional well-being and contributing to depression and anxiety symptoms.
Suubi-Mhealth: A Mobile Health Intervention to Address Depression Among Youth
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 23, 2022 Eligibility: 14 Years to 17 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): International Center for Child Health and Development (ICHAD), Masaka, Uganda
The overall goal of this study is to develop an mHealth intervention (Suubi-Mhealth) for use among Ugandan youth (14-17 years) with comorbid HIV and depression, taking into account their unique contextual, cultural, and developmental needs. This digital therapy intervention delivered via a mobile application, will utilize the core tenets of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) found to improve depression and ART adherence.
Social Media-Based Parenting Program for Women With Postpartum Depressive Symptoms: Impact on Child Development
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 18, 2022 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States
The long-term goal is to develop effective parenting strategies to facilitate optimal child development for mothers suffering with PPD symptoms. The overall objective for this application is to study whether this program combined with online depression treatment leads to more responsive parenting (target) and signals improved child language, socioemotional and cognitive development (outcomes) compared to depression treatment alone. Findings from this application can be used to inform a future study to test the effectiveness and implementation of this social media-based parenting program.
Transcranial Electric Stimulation Therapy (TEST) for Treatment Resistant Depression (TRD
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 8, 2022 Eligibility: 25 Years to 64 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
People with TRD are often helped by electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). But ECT can affect memory and thinking. Researchers want to study a treatment called TEST that uses less electricity.
To study the safety and feasibility of TEST and assess its antidepressant effects.
Adults aged 25-64 with major depression that has not been relieved by current treatments.
Participants will be admitted to the NIH Clinical Center for 5 18 weeks over 2 3 treatment phases. Their medications may be adjusted.
Participants will be interviewed about their depression, side effects, and other treatments they are receiving. They will complete questionnaires. They will give blood and urine samples. Their brain waves and heart rhythm will be recorded. They will take tests of memory, attention, mental functioning, and thinking.
Participants will have magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the head and brain. They will lie on a table that slides in and out of the scanner. Pictures of brain chemicals will also be taken. They may complete tasks during the MRI.
Participants will receive TEST and/or sham treatments. They may receive optional ECT. An intravenous catheter will be placed in an arm vein to receive general anesthesia. Two electrodes will be placed on the front of their head. An electric current will be passed from the ECT machine through the electrodes. For sham treatments, they will not receive the electric current. Their breathing, heart rate, brain function, blood pressure, and body movements will be measured.
Participants will have 7 follow-up visits over 6 months. Visits can be done via telehealth.
Participation will last for up to 42 weeks.
Glutamatergic Adaptation to Stress as a Mechanism for Anhedonia and Treatment Response With Ketamine
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 8, 2022 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
The main purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of ketamine on decision-making and emotion processing in a sample of individuals diagnosed with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD).
Behavioral Activation and Medication Optimization In Older Adults Undergoing Cardiac Procedures
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 5, 2022 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Washington University in St. Louis, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States
This Hybrid 1 Study will test the effectiveness of a bundled intervention comprised of behavioral activation and medication optimization in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety in older adults undergoing cardiac surgery (compared with usual care), while examining implementation outcomes.
A Dyadic Approach to Perinatal Depression in Primary Care: Maternal Infant and Dyadic Care
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 1, 2022 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Amritha Bhat, Seattle, Washington, United States
The purpose of this study is to assess the effectiveness of a parenting intervention+usual care compared to usual care on postpartum depression and other mental health and parenting outcomes, as well as the feasibility and acceptability of the parenting intervention.
Evaluating tDCS Brain-stimulation in Depression Using MRI
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 20, 2022 Eligibility: 20 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), Los Angeles, California, United States
Patients, physicians, and those who fund depression research are keenly interested in depression treatments that do not involve taking medications. One promising candidate treatment is transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), a low-cost technique that involves placing electrodes on specific scalp locations and using a 9-volt battery to cause a small amount of electricity to pass through parts of the brain. Depending on the direction of electrical flow, tDCS can make brain cells (neurons) more likely or less likely to generate their own electrical signals. When evaluated as a treatment, tDCS is typically done in daily sessions over a period of two weeks.
One of the challenges of tDCS is to work out the best possible positioning of electrodes and direction of electricity flow to gradually cause lasting changes in brain activity in ways that might be expected to improve depression. To address this challenge, the investigators are using MRI to take pictures of the brain during tDCS. This data will help us better understand the short-term effects of tDCS in depression and help us learn how to customize future treatments to cause a lasting beneficial response.
Patients with depression between the ages of 20-55 years are eligible to take part in this research. Potential participants will undergo:
An assessment to confirm eligibility. This will take place over a secure videoconference call lasting no more than 3 hours.
Two in-person study visits lasting 30 min and 2-1/2 hours respectively. In the first visit, the investigators will use the MRI to take a picture of the brain and head structure to determine appropriate locations for placing the tDCS electrodes at the start of the second visit. Following electrode placement, an MRI scan will be performed to take pictures of the brain during tDCS. Depending on the study arm,
Participants may receive 'active' or 'sham' tDCS. The 'sham' condition is identical to the 'active' tDCS in every way except that it involves minimal tDCS and is designed to help rule out effects unrelated to the administered tDCS electricity. Participants may also be asked to perform a mental task during MRI.
All participants will be compensated $150 + parking upon completion of all study-visits.
CBT Enhanced With Social Cognitive Training vs. CBT Only With Depressed Youth
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 10, 2022 Eligibility: 13 Years to 17 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Judy Garber, Nashville, Tennessee, United States
Depression in youth is a serious public health concern for which more personalized treatments are needed. This randomized controlled trial will test the effect of an intervention aimed at enhancing social cognitive capacities (e.g., ability to take another's perspective), thereby making treatment of depression in youth more efficient and effective. Participants in the R33 (N=82) will be youth between ages 13- through 17-years-old currently experiencing depression. Youth will be randomized to either an enhanced CBT intervention that teaches social cognitive skills, particularly social perspective taking and theory of mind (CBTSCT) as compared to CBT only. The primary target is improvement in both social cognitive skills and depressive symptoms at post-treatment and at a 6-month follow-up.
Ketamine Versus Midazolam for Recurrence of Suicidality in Adolescents
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 3, 2022 Eligibility: 13 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, United States
This project aims to examine the efficacy of ketamine, a rapidly acting medication shown to decrease suicidality in adults in as short as hours or days, as opposed to weeks.
The study design is a double-blind, randomized, active-control trial of adolescents (ages 13-18 years) with recent suicidal behaviors (suicide attempt or increased suicidal ideation). All participants must be receiving standard of care treatment which may range broadly from both outpatient and inpatient programs which include clinically indicated psychosocial and/or psychopharmacological treatments. Ketamine/midazolam treatment will occur twice weekly during the first two weeks of the study, followed by weekly assessments through week 12.
Neural-Derived Plasma Exosomal MicroRNAs As Promising Novel Biomarkers for Suicidality and Treatment Outcome in Adolescents
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 1, 2022 Eligibility: 10 Years to 24 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UAB Huntsville Regional Medical Campus, Huntsville, Alabama, United States; University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama, United States
This study is dedicated to help identify biomarkers for depression and suicide. The purpose of the study is to better understand these links to improve medical and psychiatric care in the future. This research is also to test the effects of standard treatment of depression on improvement in depressive and suicidal behavior and on biomarkers (e.g. miRNA) for these disorders.
Brain, Emotions, and Mind-Wandering
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 23, 2022 Eligibility: 11 Years to 14 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Western Psychiatric Hospital, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Mood lability is an important transdiagnostic problem that is associated with poor psychosocial function and suicidal thoughts, and is a predictor of mood disorder onset, especially in youth at familial risk. Thus, particularly in youth with a family history of mood disorder, an intervention to target mood lability during a key period of development could improve outcomes. This study will allow us to test neurobehavioral mechanisms of a mindfulness-based intervention to target mood lability in early adolescents at high risk for developing mood disorders. Through this randomized controlled trial, the investigators will better understand how and for whom mindfulness interventions work, which will lead to more targeted interventions to improve emotion regulation during this key developmental period.
Improving Adherence to Homework During Therapy
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 1, 2022 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, United States
The purpose of this study is to expand Adhere.ly- a simple, HIPAA-compliant, web-based platform to help therapists engage clients in practicing therapeutic skills between sessions (homework) during mental health treatment by conducting a trial comparing standard therapy to therapy enhanced with Adhere.ly.
Treatment Research Investigating Depression Effects on Neuroimmune Targets (TRIDENT)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: August 30, 2022 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Miami, Miami, Florida, United States
The purpose of this randomized controlled trial is to understand how a cognitive-behavioral treatment (a form of psychological treatment) for depression changes the gut microbiome (micro-organisms that regulate the health of the gut), immune system, and the brain functioning in people living with HIV.
Remote State Representation in Early Psychosis
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: July 27, 2022 Eligibility: 18 Years to 30 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
The purpose of this study is to examine state representation in individuals aged 15-40 who have been diagnosed with a psychotic illness, as well as young adults who do not have a psychiatric diagnosis. State Representation is our ability to process information about our surroundings. The investigators will complete some observational tests as well as a cognitive training clinical trial.
Caregiver Stress and Sleep Study
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: July 15, 2022 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UPMC Western Behavioral Health, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
This study includes a randomized experimental component where therapists will systematically deliver an experimental behavioral probe or a supportive control condition. The aim is to evaluate effects on meaningful health-relevant measures including morning activation levels, depression symptoms, rumination, and aspects brain connectivity previously linked with depression.
Virtual Group Psychoeducational Discussions With Spanish-Speaking Mothers of Infants in Pediatric Primary Care
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 9, 2022 Eligibility: Females, 16 Years to 99 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center, Baltimore, Maryland, United States
The goal of the proposed research is to test the feasibility and acceptability of a virtual group session which is intended to be offered universally to Spanish-speaking parents of newborns/infants attending pediatric primary care. The virtual session is intended to (1) enhance patient/family education about postpartum depression (PPD) and (2) Provide an orientation to families regarding relevant clinic and community psychosocial support resources available. The investigators will conduct a single-arm, open pilot of the session, which will be co-delivered by existing clinic staff (including social work and community outreach staff). Session contents include (1) Introduction to clinic staff, contacts, and resources (2) A video-recorded testimonial of a patient with a history of perinatal depression followed by a group discussion about/reflection on the video; (3) Review of prevalence and signs of PPD; (4) Discussion of clinic PPD screening procedures and rationale for screening; (5) Discussion of self-care and mood monitoring; (6) Discussion of relevant local resources, including information about availability of primary care resources for parents (including uninsured parents) and information about resources addressing social needs. The overall aim of the project is to Develop and pilot a virtual group augmentation of standard individual well-child care to improve (1) clinic screening procedures, discussion about and initial management of maternal depressive symptoms with immigrant Latinas and (2) patient symptom recognition, symptom disclosure, and subsequent treatment engagement
Addressing Intimate Partner Violence, Mental Health, and HIV in Antenatal Care
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 26, 2022 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Malvern Clinic, Johannesburg, Gauteng, South Africa
This quasi-experimental feasibility study recruit n=40 participants from each of two public antenatal clinics in Johannesburg, South Africa. Using the Bowen et al. approach, key feasibility study questions will be those around acceptability, implementation, and promising effects on intermediate variable. While this pilot trial is not powered to determine efficacy, it can help establish whether intervention targets the appropriate intermediate mechanisms (i.e. primary endpoints of IPV exposure and depressive symptoms) and moves intended outcomes in the right direction (i.e. towards better adherence as measured by self-reported adherence).
WellPATH-PREVENT: A Mobile Intervention for Middle-Aged and Older Adults Hospitalized for Suicidal Ideation or Attempt
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 22, 2022 Eligibility: 50 Years to 90 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Weill Cornell Institute of Geriatric Psychiatry, Weill Cornell Medicine, White Plains, New York, United States
The goal of this project is to test whether WellPATH-PREVENT (a novel, mobile psychosocial intervention) improves a specific aspect of emotion regulation, i.e., cognitive reappraisal ability, and reduces suicide risk in middle-aged and older adults (50-90 years old) who have been discharged after a suicide-related hospitalization (i.e. for suicidal ideation or suicide attempt).
Examining the Effects of Estradiol on Neural and Molecular Response to Reward
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 20, 2022 Eligibility: Females, 45 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, United States
This proposal will examine the effects of estradiol administration on perimenopausal-onset (PO) anhedonia and psychosis symptoms as well as on brain function using simultaneous positron emission tomography and functional magnetic resonance imaging (PET-MR).
Sequential Bilateral Accelerated Theta Burst Stimulation in Adolescents With Suicidal Ideation
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 4, 2022 Eligibility: 12 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Rochester, Minnesota, United States
The purpose of this study is to gather information regarding the use of a new type of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) called theta burst stimulation (TBS) for suicidal ideation in adolescents with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). The investigators hope to learn if this TMS treatment improves suicidal ideation over 10 days and clinical outcomes over 1 year of follow-up.
Academic-Community EPINET (AC-EPINET)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 16, 2022 Eligibility: 16 Years to 35 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Vanderbilt's Early Psychosis Program - Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee, United States; The Early Psychosis Intervention Center (EPICENTER) at Ohio State, Columbus, Ohio, United States; Strong Ties Young Adults Program- University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York, United States; Program for Risk Evaluation and Prevention (PREP) - University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States; Early Psychosis Intervention Clinic-New Orleans (EPIC-NOLA) - Tulane University, New Orleans, Louisiana, United States; Prevention and Recovery Center for Early Psychosis, Indianapolis, Indiana, United States
The investigators propose to examine the effects of CSC services delivered via TH (CSC-TH) versus the standard clinic-based CSC model (CSC-SD) on engagement and outcomes in a 12-month, randomized trial.
Model-based Electrical Brain Stimulation
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 8, 2022 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California, United States; University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, United States
Neuropsychiatric disorders are a leading cause of disability worldwide with depressive disorders being one of the most disabling among them. Also, millions of patients do not respond to current medications or psychotherapy, which makes it critical to find an alternative therapy. Applying electrical stimulation at various brain targets has shown promise but there is a critical need to improve efficacy.
Given inter- and intra-subject variabilities in neuropsychiatric disorders, this study aims to enable personalizing the stimulation therapy via i) tracking a patient's own symptoms based on their neural activity, and ii) a model of how their neural activity responds to stimulation therapy. The study will develop the modeling elements needed to realize a model-based personalized closed-loop system for electrical brain stimulation to achieve this aim.
The study will provide proof-of-concept demonstration in epilepsy patients who already have intracranial electroencephalography (iEEG) electrodes implanted for their standard clinical monitoring unrelated to this study, and who consent to being part of the study.
Effectiveness RCT of Customized Adherence Enhancement
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 1, 2022 Eligibility: 18 Years to 89 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio, United States; The Nord Center, Lorain, Ohio, United States
Approximately one in two individuals with bipolar disorder (BD) are non-adherent with medication, often leading to severe and negative consequences. Unfortunately, there is no widely used evidence-based approach to target poor adherence among individuals with BD. Building upon positive efficacy trial results, the proposed project will test the effectiveness of technology-facilitated Customized Adherence Enhancement (CAE) vs. enhanced treatment as usual (eTAU) using a prospective randomized controlled design in public mental health care settings and preferentially enrolling poorly adherent/high-risk individuals with BD. Deliverables include a curriculum-driven adherence enhancement approach that can be implemented in public healthcare settings and which can improve outcomes for the most vulnerable groups of people with BD.
The PATHway Study: Primary Care Based Depression Prevention in Adolescents
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 1, 2022 Eligibility: 13 Years to 18 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois, United States; UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, United States; Advocate Aurora Health, Park Ridge, Illinois, United States; Northshore University HealthSystem, Glenview, Illinois, United States; UI Health, Chicago, Illinois, United States
Prevention of depressive disorders has become a key priority for the NIMH, but the investigators have no widely available public health strategy to reduce morbidity and mortality. To address this need, the investigators developed and evaluated the primary care based-technology "behavioral vaccine," Competent Adulthood Transition with Cognitive-Behavioral Humanistic and Interpersonal Therapy (CATCH-IT). The investigators will engage N=4 health systems representative of the United States health care system, and conduct a factorial design study to optimize the intervention in preparation for an implementation study and eventual dissemination.
Beyond Monoamines: The Role of the Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ Receptor in Major Depression
Study Type: Observational Start Date: December 29, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 45 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): McLean Hospital, Belmont, Massachusetts, United States
This study looks at the role of the Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ receptor system in the brain of individuals with current or past major depressive disorder (MDD). It also examines how individuals with a history of depression make certain decisions and which brain regions are involved in such decisions. Information collected through MRI, PET, biospecimens (i.e., blood, saliva) and behavioral tasks will be used to predict depressive symptoms in the future.
XEN1101 for Major Depressive Disorder
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 19, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, United States; Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, United States
This project is designed to examine the neuronal KCNQ2/3 potassium (K+) channel subtype as a novel treatment target for mood disorders through the administration of the KCNQ-selective channel opener XEN1101 (Xenon Pharmaceuticals).
Using Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) to Understand Hallucinations in Schizophrenia
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 13, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 55 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): McLean Hospital, Belmont, Massachusetts, United States
This study uses a noninvasive technique called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to study how hallucinations work in schizophrenia.
TMS is a noninvasive way of stimulating the brain, using a magnetic field to change activity in the brain. The magnetic field is produced by a coil that is held next to the scalp. In this study the investigators will be stimulating the brain to learn more about how TMS might improve these symptoms of schizophrenia.
Invasive Decoding and Stimulation of Altered Reward Computations in Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 6, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 80 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, New York, United States
Novel invasive neurostimulation stimulation strategies through neurosurgical interventions are emerging as a promising therapeutical strategy for major depressive disorder. These have been applied mostly to the anterior cingulate cortex, but other limbic brain regions have shown promise as anatomical targets for new neurostimulation strategies. The researchers seek to study neural activity in limbic brain areas implicated in decision behavior and mood regulation to identify novel targets for treatment through electrical stimulation. To do this, the study team will record local field potentials (LFPs) from the orbitofrontal cortex, hippocampus and amygdala of epilepsy participants undergoing invasive monitoring (intracranial encephalography, iEEG) during choice behavior. Leveraging the high co-morbidity of depression and intractable epilepsy (33-50%), neural responses will be compared to reward across depression status to identify abnormal responses in depression. Finally, the researchers will use these as biomarkers to guide development of neurostimulation strategies for the treatment of depression.
Predictors of Cognitive Outcomes in Geriatric Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 28, 2021 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, United States
This study will focus on examining effects of stress on long-term mood and cognitive outcomes of late-life depression. It will also example the neural underpinnings of these changes using structural and functional brain imaging. Understanding how effects of stress in older depressed adults, as well as factors that might minimize those effects, lead to particular mood and cognitive outcomes will inform future development of novel prevention strategies.
Biomarker-guided rTMS for Treatment Resistant Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 1, 2021 Eligibility: 22 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York, United States; Stanford University, Stanford, California, United States
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a treatment for depression. The investigators are continuing to learn how to optimize outcomes from rTMS treatment. The purpose of this research project is to use brain network connectivity patterns as measured by resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to confirm a way to optimize the use of rTMS to treat depression. In addition, the study aims to gain a better understanding of how rTMS influences brain networks.
Long-term Observation of Participants With Mood Disorders
Study Type: Observational Start Date: August 17, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
More than 12,000 people have taken part in research at the Experimental Therapeutics & Pathophysiology Branch at the National Institute of Mental Health Intramural Program. This has led to advances in the treatment of depression, bipolar disorder, and suicide risk. Researchers want to follow up with this group to see if they continue to have mental health symptoms and receive psychiatric treatments.
To learn the long-term impact of depression, bipolar disorder, and suicide risk.
Adults ages 18 and older who signed consent for Protocol 01-M-0254 over a year ago.
This study has 2 phases: an online phase and a telephone phase. It has no in-person or face-to-face contact.
In Phase 1, participants will fill out online surveys. They will access the surveys through the study website. The questions will focus on their current thoughts and feelings. The surveys will also ask about their current treatments for their mental health symptoms. At the end of the surveys, they will be asked if they would like to take part in Phase 2. If so, they will mark yes. Phase 2 includes a phone interview. They will be contacted by email to schedule the interview.
In Phase 2, participants will be asked more in-depth questions about how they are feeling. They will also be asked which psychiatric medicines and treatments they have used since they left NIH.
In both phases, participants can skip any questions they do not want to answer.
The online surveys will take 30 minutes to complete. The phone interview will last 1-4 hours.
The information that participants give in this study may be linked to their other NIH research records.
Fitness for Brain Optimization for Late-Life Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: August 4, 2021 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Cognitive impairment and brain abnormalities are common and persist after depression remission in those with Late Life Depression (LLD), compounding dementia risk in both individuals with acute and remitted LLD (rLLD). In this study, investigators will examine systemic neural and cognitive benefits of aerobic exercise training in older adults with remitted LLD. This will generate preliminary data regarding neural targets of aerobic exercise training that may translate to cognitive benefits in those with rLLD, a population who remains at high risk for dementia despite successful treatment of depression.
Depression Screening in Black Churches
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: August 1, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Columbia University Irving Medical Center Center, New York, New York, United States
The overall aim of this study is to employ Community Health Workers (CHWs) to screen for depression in 30 Black churches and compare the effectiveness of Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) (Intervention arm) to Referral As Usual (Control arm) on treatment engagement for depression. The investigators will assess patient-level outcomes (Mental-Health Related Quality of Life and depressive symptoms) at 3- and 6-months post-screening and conduct a mixed-methods process evaluation to assess multi-level facilitators and barriers of screening uptake.
PET Imaging of Cyclooxygenase in Participants With Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: July 20, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 70 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Researchers developed [11C]MC1, a radioligand for cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). COX-2 is an enzyme induced in the brain during inflammation. Researchers want to see the levels of COX-1 (measured as distribution volume VT) are elevated in the brain of two groups of mood disorders patients undergoing MDE relative to the control group.
To determine whether COX-1 and COX-2 are detectable in the brains of individuals with MDD experiencing a major depressive episode (MDE).
People aged 18-70 years with MDD and Healthy Volunteers aged 18 70 years.
Group A: MDD participants will be studied with the same dose of [11C]MC1 before and after administration of 600 mg celecoxib; the study is neither randomized nor placebo-controlled. Group B: MDD participants, both medicated and unmedicated, will be studied with [11C]PS13 and compared to healthy volunteers..
https://nimhcontent.nimh.nih.gov/start/surveys/?s=TJW4RA4WN3LDD988
A Wearable Morning Light Treatment for Postpartum Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 23, 2021 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States
This study will test a consumer health light therapy device (Re-Timer) for women with postpartum depression to better understand how it affects mood and the body clock (also called the circadian clock).
Eligible participants will be enrolled and randomized after baseline assessments. In addition to using the Re-Timer light for 5 weeks participants will complete questionnaires at various timepoints, record sleep information, wear an actigraph watch, and provide saliva samples. Additionally, the sleep of the participants' infants will also be monitored using an ankle-worn device (actigraph) and sleep diary at certain time-points as this may influence the mother's mood/sleep, and in turn affect the results.
The hypotheses regarding the bright light versus the placebo dim light of the study are:
morning bright light therapy will produce greater improvement from pre- to post-treatment on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression morning bright light therapy will lengthen the Phase angle difference (PAD) and this will mediate change in depression symptoms. morning bright light therapy will produce greater improvements on self-reported depression symptoms, excessive daytime sleepiness, maternal-infant bonding, social functioning, and sleep-related impairment from pre- to post-treatment.
Antidepressant Effects of TS-161 in Treatment-Resistant Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: June 10, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a common, chronic mental illness. It can take weeks to months for antidepressants to work. Researchers want to test a new drug that might act more rapidly.
To see if TS-161 will improve symptoms of depression in people with MDD.
Adults ages 18-65 with MDD without psychotic features.
Participants will be screened under a separate protocol. They will have blood tests. They will complete surveys about their symptoms.
Participants will have an inpatient visit at NIH. Participation may last 12-16 weeks.
During the first phase of the study, participants will be tapered off their psychiatric medicines. For 2 weeks they will have a drug-free period.
During Phase II participants will take TS-161 or placebo. They will take TS-161 for 3 weeks and placebo for 3 weeks. In between the 3-week time period, they will have 2-3 weeks where they will be drug free. Participants will also have the following tests during this time:
Interviews Physical exams Psychological tests and surveys about their symptoms Blood draws and urine samples They may complete tests of mood and thinking MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging): Participants will lie in a machine that takes pictures of their brain. Functional MRIs: They will perform tasks displayed on a computer screen inside the MRI scanner MEG (magnetoencephalography): Participants will lie down and do tasks of memory, attention, and thinking. A cone lowered on their head will record brain activity. Electrocardiograms to record the heart s electrical activity. Electrodes will be placed on the skin....
Life Experiences in Adolescents and the Development of Skills
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 19, 2021 Eligibility: 12 Years to 15 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Western Psychiatric Institute and Clinic, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
The primary objective of this study is to assess acquisition and retention of a Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)-based "cognitive restructuring" skill, among young adolescents (12-15 years of age) with elevated depression symptoms and with population-level variability in lifetime exposure to adverse childhood experiences. This study uses a repeated-measures, longitudinal design to investigate associations between adversity exposure and learning-related cognitive control processes in the context of elevated depression (Aim 1). Adversity exposure and cognitive control will be examined as direct predictors of cognitive restructuring skill acquisition and skill retention over six-months; an indirect pathway from adversity to skill acquisition through cognitive control will also be examined (Aim 2). The study also includes exploration of key characteristics of adversity, namely the type (threat of harm versus deprivation of resources) and developmental timing of exposure, as distinct predictors of skill acquisition (exploratory Aim 3).
Improving Attentional and Cognitive Control in the Psychological Treatment of Intrusive Thoughts
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 30, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 60 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
The investigators are conducting this study to learn more about the cognitive and attentional processes among individuals with three types of repetitive negative thinking (RNT): mental rituals (as seen in obsessive compulsive disorder, OCD), worries (as seen in generalized anxiety disorder, GAD), and ruminations (as seen in major depressive disorder, MDD). Specifically, the investigators are studying whether psychological treatment can help people with RNT who have trouble stopping unwanted thoughts and shifting their attention.
Effects of Theta Burst Stimulation on the Brain, Behavior, and Clinical Symptoms in Adults With Bipolar Disorder
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 6, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 35 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Bipolar Disorder (BD) is a common and highly debilitating psychiatric disorder, however, the predisposing brain mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, the investigators aim to examine the immediate effect of transcranial brain stimulation (TBS) on brain activity and emotions in adults with and without BD as a first stage toward understanding the predisposing brain mechanisms of BD. The investigators hypothesize that TBS will reduce brain activity while playing a game with rewards in all adults, but the TBS will reduce brain activity more in the adults with BD compared to adults without BD. Furthermore, the investigators hypothesize that this reduced brain activity will be associated with reduced BD symptoms, such as negative emotions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Following Esketamine for Major Depression and Suicidal Ideation for Relapse Prevention
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 5, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UAB Medicine | Heersink School of Medicine, Birmingham, Alabama, United States; Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, United States; Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, United States
This is a rater-blinded, randomized controlled trial. All patients will receive esketamine for treatment of Major Depression with Suicidal Ideation (MDSI). Subjects will be randomized (1:1) to receive CBT (computer-assisted) or TAU alone following esketamine.
Internet-delivered Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Depression and Anxiety in Latin American College Students
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: March 1, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Universidad Autonoma Metropolitana, Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico; Universidad Popular de Cesar, Valledupar, Colombia; Fundación Universitaria del Area Andina, Valledupar, Colombia; Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia, Medellín, Colombia; Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia; Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México, Mexico City, Mexico; Universidad la Salle, León, Mexico; Universidad Autonoma de Baja California, Ensenada, Mexico
The aim is to evaluate short term and longer term treatment effects of internet-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy compared to treatment as usual for college students with anxiety and/or depression in low-middle income countries of Latin America.
MicroRNA Correlates of Childhood Maltreatment and Suicidality
Study Type: Observational Start Date: February 26, 2021 Eligibility: 18 Years to 60 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Alabama, United States; UAB Huntsville Regional Medical Campus, Huntsville, Alabama, United States
This is a research study to find out if childhood trauma and stress are associated with depression or suicidal risk. The study will assess the effects of both short-term and long-term stress on biomarker (e.g. miRNA [MiRNA]) levels. miRNAs are a type of RNA (genetic material that is translated into protein) that are found in throughout the body and blood. They are called microRNA because their size is much smaller than typical RNA molecules. miRNAs are highly responsive to environment. This responsiveness is reflected in their expression in individuals who are affected by environment such as stress. The investigators are gathering genetic material, including DNA and RNA, from each participant. The RNA will be taken from the small vesicles and cells in the participant's blood and analyzed. The vesicles are small objects that occur normally in the blood and that contain RNA. This information may help us to understand the cause of mental illness and to improve medical and psychiatric care in the future. There will be 450 participants enrolled in this study.
Impact of Transcutaneous Vagal Nerve Stimulation on Stress Response in Major Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 29, 2021 Eligibility: 50 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Massachusetts General Hospital, Charlestown, Massachusetts, United States
This study will identify the sex-dependent impact of expiratory-gated transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) on the modulation of the stress response circuitry and associated physiology in major depressive disorder (MDD). We will evaluate a sample of 80 adults with recurrent MDD randomized to receive active or sham expiratory-gated tVNS during a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) session, with simultaneous mood and physiological assessments. We hypothesize that expiratory-gated tVNS will effectively modulate, in a sex-dependent manner, specific brainstem-cortical pathways of the stress circuitry and attenuate physiological deficits in MDD.
Lay-Delivered Behavioral Activation in Senior Centers
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 27, 2021 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Goddard Riverside Community Center and NORC, New York, New York, United States; Progress Village Senior Center, Tampa, Florida, United States; Oaks at Riverview Senior Center, Tampa, Florida, United States; JL Young Apartments (Senior Housing), Tampa, Florida, United States; Brandon Senior Center, Brandon, Florida, United States; GenPride Senior Center, Seattle, Washington, United States; West Seattle Senior Center, Seattle, Washington, United States; SAGE Center Brooklyn at Stonewall House, New York, New York, United States
In response to large numbers of senior center clients who suffer untreated depression and the dearth of geriatric mental health providers, the investigators have simplified Behavioral Activation to be delivered by lay volunteers ("Do More, Feel Better"; DMFB). The focus of Behavioral Activation is to guide clients to reengage in daily pleasant and rewarding activities, and reduce depressive symptoms. If the investigators can show that the lay delivery model has positive impact in comparison to MSW-delivered Behavioral Activation, the investigators will have identified an effective intervention that can be used by a large untapped workforce of older adult volunteers across the nation.
Slow Wave Induction by Propofol to Eliminate Depression (SWIPED)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 14, 2021 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Washington University School of Medicine/Barnes-Jewish Hospital, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States
Our hypothesis is that targeted propofol infusion in TRD patients will induce slow wave activity during sedation and augment subsequent sleep slow wave activity. We will recruit 15 participants for this open label single arm Phase I trial. All participants will undergo two propofol infusions 2-6 days apart, with each infusion maximizing expression of EEG slow waves. To minimize bias, there will be no specific gender or ethnic background consideration for enrollment. This will be a single site investigation at Washington University Medical Center.
Cognitive Fitness for Depression in Older Adults
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 15, 2020 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UConn Health, Farmington, Connecticut, United States
This research is being done to determine if computerized administered cognitive fitness activities will improve thinking and depression in older depressed adults who are being treated with antidepressants. The investigators are also interested in whether participating in the treatment will result in changes to brain activity measured with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Depression Prevention in Older Spousally-bereaved Adults
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 20, 2020 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UPMC: WPIC- Bellefield Towers, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Using an indicated prevention approach, investigators propose to enroll 150 spousally-bereaved adults aged 60 years and older in the first 6 months after spousal death who are at high risk for major depression disorder because of subthreshold symptoms of depression. A confirmatory efficacy trial will be conducted in which participants will be randomly assigned to (a) self-monitor sleep, meals, and physical activity for 12 weeks using digital monitoring plus motivational health coaching (WELL; n=75); or (b) enhanced usual care (EUC, usual care plus study assessments, n=75). Objective actigraphic measures of the 24-hour pattern of day and nighttime activity - known as the rest-activity rhythm - will be measured to evaluate circadian rhythms as a mediator of treatment outcomes. Participants will be assessed at baseline, months 1 & 2, post-intervention, and 3, 6,12, 18-months post-intervention. In addition, the investigators will include a subset of participants bereaved by COVID-19 (or suspected as bereaved by COVID-19). Participants in this subset will undergo the same research procedures as the main cohort. Participants in both the main cohort and subset determined to be fully eligible will be randomized into two groups with a total of: usual care (EUC;n=125) and WELL (WELL; n=125).
Social Reward and Its Effect on Brain Functions in Psychotherapies for Mid- and Late-Life Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 15, 2020 Eligibility: 50 Years to 85 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York, United States
Abnormalities in the Positive Valence System (PVS) are associated with depressive symptoms and reduced behavioral activation in mid- and late-life. This study will investigate the engagement of the PVS during exposure to social rewards, part of a novel streamlined psychotherapy for mid- and late-life depression. Use of computational modeling will enable identification of neuroimaging and behavioral profiles associated with greater treatment response, and may guide future personalization of psychotherapy.
PEERS Plus mHealth Enhanced Peer Support
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 15, 2020 Eligibility: 50 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
The goal of this intervention study is to design and learn whether peer support that is delivered through video chats and texting can decrease depression among older adults. Participants will be assigned to a peer support program where they will receive 8 video chats with a peer mentor who provide social support and supportive texts over 8 weeks.
Unobtrusive Monitoring of Affective Symptoms and Cognition Using Keyboard Dynamics (UnMASCK)
Study Type: Observational Start Date: September 17, 2020 Eligibility: 25 Years to 50 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, Illinois, United States
Mood disorders are associated with significant financial and health costs for the United States, partially due to cognitive problems in these patients that can worsen disease course and impair treatment response. This study proposes to use smartphone-based technology to monitor cognitive problems in patients with mood disorders by linking brain network changes with predicted worsening of mood symptoms. The proposed study will provide evidence for using smartphone-based passive sensing as a cost-effective way to predict illness course and treatment response.
Approach-Avoidance, Computational Framework for Predicting Behavioral Therapy Outcome (AAC-BeT)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: September 11, 2020 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Laureate Institute for Brain Research, Tulsa, Oklahoma, United States
Depression and anxiety disorders rank in the top ten causes of years lived with disability. Less than 50% of patients experiencing long-lasting improvements to current gold-standard treatments. Two gold-standard behavioral interventions include behavioral activation, focused on enhancing approach behavior towards meaningful activities, and exposure-based therapy, focused on decreasing avoidance and challenging negative expectations. While these interventions have divergent treatment targets, there is little knowledge to inform which strategies should be used in the frequent case of comorbid anxiety and depression. Approach-avoidance decision-making paradigms focus on assessing responses when faced with potential rewards and threats, tapping into processes important for both anxiety and depression as well as behavioral activation and exposure-based therapy.
For this study, investigators will recruit individuals reporting both anxiety and depression symptoms and randomize them to one of three different interventions: (1) behavioral activation, (2) exposure-based therapy, and a non-specific therapy approach (3) supportive therapy. Participants will complete clinical, self-report, behavioral, and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) assessments before and after therapy. Investigators will use a computational approach to model factors that may influence one's behavior during approach-avoidance decision-making, including drives to avoid threat versus approach reward and confidence versus uncertainty in one's decisions.
This project will accomplish the following aims (1) Determine how changes in brain and behavior responses during approach-avoidance conflict relate to changes in mental health symptoms with the different therapy approaches, (2) Determine the degree to which baseline brain and behavior responses during approach-avoidance conflict predict response to the different therapy approaches, above and beyond the influence of demographics and baseline symptom severity. In addition, by including peripheral blood draws and measures of grace matter volume, the project will also accomplish the following aims: (1) Determine whether kynrenine metabolites measures peripherally may be beneficial as a biomarker of treatment response and (2) determine whether there is an association between change in kynurenine metabolites and changes in gray matter volume with treatment.
Results will enhance understanding of how different psychotherapy approaches (behavioral activation, exposure-based therapy) may impact brain responses and decisions when faces with potential reward versus threat and approach versus avoidance drives. In addition, results will have important implications concerning the potential for a more personalized approach to psychotherapy, enhancing knowledge of which types of therapy strategies may be most beneficial for which individuals.
Designing an Implementation Strategy for Delivering Routine Mental Health Screening and Treatment
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: August 12, 2020 Eligibility: 16 Years to 30 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
African Americans living with chronic health conditions are more likely to experience depression and other mental health disorders than their healthy counterparts, and are more likely to experience severe depression than whites, but less likely to be diagnosed or receive treatment. One especially vulnerable group is patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), a genetic blood disorder that primarily affects people of African descent, many of whom live in disadvantaged circumstances and are cared for in under-resourced settings. SCD causes severe acute and chronic pain, end-organ damage, and early mortality. Patients transitioning from adolescence to adulthood (ages16-30) are at high risk for mental health disorders and suicide.
Using mobile technology, the investigators can provide high-quality, evidence-based behavioral mental health treatment that reaches patients in different settings. Digital cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is effective for treating depression and anxiety and can be brought to scale at low cost. Despite the promise of digital CBT, there are barriers to its widespread use, particularly in low-resource settings serving minorities. Qualitative data show that cultural factors-lack of relatability, representation, and perceived stigma regarding mental health treatment-limit engagement with digital CBT programs. Population-and setting-specific adaptations to interventions can lead to their successful implementation and wider use. The investigators will work with a digital CBT program to decrease stigma and make it more relatable and relevant to young adults with SCD, by devising changes to advertising and promotion, and tailoring communication with an integrated health coach, Aim 1: Use implementation science (ImS) and human-centered design methods to define the barriers to delivering routine mental health screening and digital CBT to adolescents and young adults with SCD. Aim 2: Rapidly iterate, test, and evaluate adaptations to the implementation strategy for a coach-enhanced digital mental health service. Aim 3: Demonstrate that a population-specific implementation strategy improves engagement with a digital CBT-based mental health service.
The investigators will capitalize on our mobile technology tools, interdisciplinary expertise, and community-based partnerships to investigate the implementation of digital CBT into low-resource clinics and community-based organizations serving adolescents and adults with sickle cell disease.
Recurrence Markers, Cognitive Burden and Neurobiological Homeostasis in Late-Life Depression
Study Type: Observational Start Date: June 1, 2020 Eligibility: 60 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, Illinois, United States
Late-life depression (LLD) is associated with disability, increased risk for cognitive decline and dementia, elevated suicide risk, and greater all-cause mortality. These outcomes are related to depression being a recurrent disorder, with repeated episodes over a patient's lifetime. Recurrence rates (defined as including both relapse and recurrence) are high in LLD.
The goals of this study are to identify neurobiological factors that predict recurrence risk, and examine how cognitive performance changes are both influenced by these neurobiological factors and also predict recurrence risk.
Engaging Black Youth in Depression and Suicide Prevention Treatment Within Urban Schools
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 31, 2020 Eligibility: 12 Years to 20 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): McSilver Institute for Poverty Policy and Research, New York, New York, United States
Completing evidence-based treatments for depression has been shown to be particularly problematic for Black adolescents. If Black adolescents' depression treatment needs are to be met, the engagement challenges and the factors that lessen the success of treatment in the "real world" must be addressed. The investigators will examine the effectiveness of the Making Connections Intervention (MCI) and investigate key mediators of both engagement and response to treatment for depression. The MCI is a 1-2 session, evidence-based intervention designed to improve engagement, perceived relevance, and treatment satisfaction among depressed, Black adolescents. The study also uses tailored outreach strategies for adolescents and parents by including innovative digital content such as a web page/app along with other digital products.
This study will address an important public health issue: How best to connect Black adolescents with depression to treatment in clinically meaningful ways, and how best to deliver evidence-based treatment to them through school-based services.
Mechanism of Action Underlying Ketamine's Antidepressant Effects: The AMPA Throughput Theory in Patients With Treatment-Resistant Major Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 21, 2020 Eligibility: 18 Years to 70 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Most drugs that treat mood disorders take a long time to work. Ketamine works within hours. A dose can last for a week or more. Certain receptors in the brain might help ketamine work. A drug that blocks these receptors might affect how it works.
To see if the antidepressant response of ketamine is linked to AMPA receptors.
Adults ages 18-70 with major depression disorder without psychotic features
Participants will be screened under protocol 01-M-0254. They will have blood tests and a physical exam.
Participants will stay at the NIH Clinical Center for 5 weeks.
Phase 1 lasts 4 weeks. For 2 weeks, participants will taper off their psychiatric medicine. Then they will have the following tests:
Blood draws Psychological tests MRI: Participants will lie in a machine that takes pictures of their brain. MEG: Participants will lie down and do tasks. A cone lowered on their head will record brain activity. Optional sleep tests: Electrodes on the scalp and body and belts around the body will monitor participants while they sleep. Optional TMS: Participants will do tasks while a wire coil is held on their scalp. An electrical current will pass through the coil that affects brain activity.
For phase 2, on day 0 participants will take the study drug or a placebo orally. While having a MEG, they will get ketamine infused into a vein in one arm while blood is drawn from a vein in the other arm. On day 1, participants will again take the study drug or a placebo orally. On days 3-7, they will repeat many of the phase 1 tests. Days 8 and 9 are optional and include an open label ketamine treatment and many of the phase 1 tests.
Multi-modal Assessment of Gamma-aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Function in Psychosis
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: January 16, 2020 Eligibility: 16 Years to 60 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States
The purpose of this study is to better understand mental illness and will test the hypotheses that while viewing affective stimuli, patient groups will show increased blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) signal by fMRI after lorazepam.
This study will enroll participants between the ages of 16 and 60, who have a psychotic illness (such as psychosis which includes conditions like schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and mood disorders). The study will also enroll eligible participants without any psychiatric illness, to compare their brains.
The study will require participants to have 3-4 sessions over a few weeks. The initial assessments (may be over two visits) will include a diagnostic interview and several questionnaires (qols) to assess eligibility. Subsequently, there will will be two separate functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) sessions in which lorazepam or placebo will be given prior to the MRI. During the fMRI the participants will also be asked to answer questions. Additionally, the participants will have their blood drawn, women of child bearing potential will have a urine pregnancy test, vital signs taken, and asked to complete more qols.
Brain Stimulation and Decision-making
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: November 11, 2019 Eligibility: 18 Years to 50 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia, United States
Decision-making is an important process that is frequently shown to be impaired in patients with depression. While a number of preclinical and clinical studies have identified key regions involved in this process, it remains unclear exactly how these regions are influencing choice behavior especially when choices become more challenging. The goal of this project is to understand how these regions, such as the cingulate cortex, impact difficult choice behavior. Specifically, the researchers are interested in learning how disruptions in cognitive control might impact choice preferences during difficult decisions in depressed patients. To do this, this study will recruit participants with depression (as well as healthy controls) to perform game-like tasks in the laboratory while undergoing TMS or TI.
Adolescent Attention to Emotion Study
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 16, 2019 Eligibility: Females, 13 Years to 15 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Western Psychiatric Institute and Clinic, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States
Rates of depression increase rapidly during adolescence, especially for girls, and, thus, research is needed to spur the development of novel interventions to prevent adolescent depression. This project seeks to determine if a novel visuocortical probe of affect-biased attention (i.e., steady-state visual evoked potentials derived from EEG) can 1) be used to prospectively predict depression using a multi-wave repeated measures design and 2) modify affect-biased attention and buffer subsequent mood reactivity using real time neurofeedback. This work could ultimately lead to improved identification of adolescents who are at high risk for depression and directly inform the development of mechanistic treatment targets to be used in personalized intervention prescriptions for high-risk youth.
Exploring the Effects of Corticosteroids on the Human Hippocampus
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 1, 2019 Eligibility: 18 Years to 50 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, United States
Chronic corticosteroid (CS) exposure is associated with changes in memory and the hippocampus in both humans and in animal models. The hippocampus has a high concentration of glucocorticoid receptors (GCRs), and the pre-clinical literature demonstrates shortening of apical dendrites in the CA3 region of the hippocampus and decreased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus (DG) following CS administration. In humans, both stress and CS exposure are associated with a decline in declarative memory performance (a process mediated by the hippocampus). Impairment in declarative memory and hippocampal atrophy are reported in patients with excessive CS release due to Cushing's disease, and, by our group, in patients receiving prescription CS therapy. These findings have important implications for patients with mood disorders, as a large subset of people with major depressive disorder (MDD) show evidence of HPA axis activation, elevated cortisol and, importantly, resistance to the effects of CSs on both the HPA axis and on declarative memory. Thus, resistance to corticosteroids appears to be a consequence of MDD.
this study will examine changes in declarative memory, as well as use state-of-the-art high-resolution multimodal neuroimaging, including structural and functional (i.e., task-based and resting state) MRI, in both men and women healthy controls, and, as an exploratory aim, a depressed group, given 3-day exposures to hydrocortisone (160 mg/day) or placebo. The study will translate preclinical findings to humans, provide valuable data on possible sex differences in the response to cortisol and, for the first time, identify specific hippocampal subfields (e.g., CA3/DG) in humans that are most sensitive to acute CS effects. Using resting state fMRI data and whole brain connectomics using graph theoretical approaches, we will determine the effects of cortisol exposure on functional brain networks. Furthermore, this will be the first study to use neuroimaging to compare the brain's response to CSs in people with depression vs. controls, and determine whether depressed people demonstrate glucocorticoid resistance within the hippocampus. We hypothesize that hippocampal response to acute CSs will be greatest in the CA3/DG subfield, greater in women than in men, and that depressed people will show a blunted hippocampal response to CSs compared to controls. A multidisciplinary research team with extensive experience in CS effects on the brain and hippocampal subfield neuroimaging, and a prior history of research collaboration, will conduct the project.
A Longitudinal Study of Inflammatory Pathways in Depression
Study Type: Observational Start Date: October 1, 2019 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Pine Rest Christian Mental Health Services, Grand Rapids, Michigan, United States
Suicide accounts for at least 1 million deaths globally each year. This is likely a significant underestimate, because suicide is under-reported in many countries. In the US, over 42,000 people die from suicide annually. Despite increased focus on identification and treatment, the rate of suicide has increased steadily over the past 15 years.
Our project aims both to improve our understanding of factors that increase the risk for suicide by comparing blood biomarkers associated with inflammation in patients with depression without suicidal behavior and patients with depression and suicidal behavior. The 160 individuals in this study will be followed with psychiatric assessments and blood samples at repeated time points over one year.
Effects of an ER Beta Agonist (Lilly Compound LY500307) on Estradiol-Withdrawal-Induced Mood Symptoms in Women With Past Perimenopausal Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 23, 2019 Eligibility: Females, 45 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Some women who had depression in the perimenopause may have mood symptoms again if they stop estrogen therapy. Estrogen acts in the brain and other tissues by binding to at least three types of estrogen receptors. One of these receptors, estrogen receptor beta may affect anxiety and depression. The drug LY500307 acts only on this receptor. In this study, researchers will initially give you estrogen and then suddenly stop estrogen after three weeks. Then they will study how LY500307 affects mood symptoms.
Objectives:
To study how withdrawing estradiol affects mood. To test the safety and side effects of LY500307.
Healthy women ages 45-65 who had depression related to perimenopause in recent years and whose mood systems got better with estradiol
-Participants will be screened with:
Medical history
Physical exam
Blood tests
Psychiatric interview
Gynecological exam
Participants able to get pregnant must use effective barrier birth control throughout the study. During the first 3 weeks, participants will wear an estrogen patch. It is 1x2 inches and will be replaced every 3 days. For the next 3 weeks, participants will take 3 study capsules every morning. They will not know if they get the study drug or placebo. Some participants will also take a progesterone-like drug for 1 week at the end of the medication phase of the study. Participants will have 9 one-hour study visits. They will have blood samples and vital signs taken. They will answer questions about mood and behavior symptoms. Participants will keep a daily log of these symptoms. Participants will have 2 transvaginal ultrasounds. A probe is temporarily placed 2-3 inches into the vaginal canal and sound waves are used to create pictures of the lining of the uturus. Participants will have a final visit 4 weeks after stopping the study drug. They will answer questions about mood and side effects.
Mechanisms of Rumination Change in Adolescent Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 1, 2019 Eligibility: 14 Years to 17 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, United States
This study will evaluate whether a newer treatment, rumination-focused cognitive behavioral treatment, which includes mindfulness and can be used to reduce ruminative habits, change ways in which key brain regions interact with each other (e.g.., often called connectivity), and whether these changes in habits and brain connectivity can reduce the risk for recurrence of depression in the next two years.
Concurrent fMRI-guided rTMS and Cognitive Therapy for the Treatment of Major Depressive Episodes
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 17, 2018 Eligibility: 18 Years to 75 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a treatment for depression. It stimulates the brain. Researchers want to see if using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans helps locate the best area for rTMS in each person. They also want to find other ways to make it more effective.
To study the effects of combining MRI- guided transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and talk therapy on the brain in people with depression.
Adults ages 18-75 with a major depressive disorder and current depression. If taking an antidepressant, should have been doing so for at least 4 weeks.
Participants will be screened with medical and psychiatric history, psychiatric evaluation, physical exam, and blood and urine tests.
Phase 1 is 1-4 visits in 1 week. Participants will have:
Brain MRI. Participants will lie on a table in a scanner. Questions about their medical history and psychology symptoms Tests of mood and thinking
Tests of brain activity. Participants may do tasks during these tests:
A cone with magnetic detectors is put on the head. A cap with electrodes is put on the scalp. TMS. A brief electrical current passes through a wire coil on the scalp. A metal disk will be placed on the arm. A nerve will be stimulated with a small electrical shock.
Phase 2 is about 6 to 7 weeks.
There will be 30 daily sessions of combined therapy and repetitive TMS (rTMS) for 6 weeks. Participants will receive rTMS and another therapy by computer. For rTMS, repeated pulses will pass through the coil.
This is followed by up to 3 additional visits, when:
Participants will repeat Phase 1 tests Participants will rate their depression symptoms.
Phase 3 is 3 visits over 3 months. Participants will rate their depression symptoms and repeat some of the previous questionnaires and tests of mood and thinking.
Brain Connectivity in Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 3, 2018 Eligibility: 18 Years to 70 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States; Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, United States
This study originally included 100 subjects with medication-refractory depression undergoing 10 Hz transcranial magnetic stimulation (10Hz-TMS) to the left dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), with the goal of having 60 completers with good quality data. Subjects were recruited from the TMS clinics at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Brigham & Women's Hospital, and Butler Hospital. Subjects underwent an hour-long MRI scanning session, an optional DNA-sample collection, up to three 20 minute neuronavigation sessions for marking the site of TMS stimulation, questionnaires, and a behavioral testing battery before and after their TMS treatment course. The task battery included the Emotion Conflict Resolution (ECR) task, Multi-Source Interference Task (MSIT), War Game (Gambling) task, and Associative Learning with Reversal task. Subjects' scores on the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS) and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) were assessed before and after the TMS course. MRI data was utilized to identify brain regions whose connectivity to the stimulation site co-varies with the aforementioned measures of symptom improvement. This was the only study group until August 30, 2022, and the primary outcome was analyzed for the 10Hz-TMS group.
Due to changes in clinical standard of care from 10Hz-TMS to a newer version of TMS termed intermittent theta burst (iTBS), in September 2022 a second group was added to include patients receiving this new form of TMS. This second group included another 100 patients with medication-refractory depression undergoing iTBS to the left dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), with the intent to have 80 completers. Massachusetts General Hospital was added as a data collection site in lieu of Butler Hospital. Subjects will undergo an hour-long MRI scanning session, up to three 20 minute neuronavigation sessions for marking the site of TMS stimulation, questionnaires, and a behavioral testing battery before and after their TMS treatment course. The task battery will included the Emotion Conflict Resolution (ECR) task, Multi-Source Interference Task (MSIT), Penn Emotion Recognition Test, the Suicide/Death Implicit Association Test, and Associative Learning with Reversal task. Subjects' scores on the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) were assessed before and after the TMS course. MRI data will be utilized to identify brain regions whose connectivity to the stimulation site co-varies with the aforementioned measures of symptom improvement.
An Adaptive Algorithm-Based Approach to Treatment for Adolescent Depression
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: February 26, 2018 Eligibility: 12 Years to 18 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): Institute for Translational Research in Children's Mental Health, Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of two adaptive treatment strategies (ATSs) for adolescent depression. The ATSs include delivery of an evidence-based psychotherapy (interpersonal psychotherapy for depressed adolescents, IPT-A), systematic symptom monitoring, and an empirically-derived algorithm that specifies whether, when, and how to augment IPT-A. Two hundred depressed adolescents (age 12-18) will be recruited to participate in a 16-week sequential multiple assignment randomized trial conducted in outpatient community mental health clinics. Adolescents will be randomized to the IPT-A ATS condition or the community clinic's usual care (UC). Adolescents in the IPT-A ATS condition who are insufficient responders will be randomized a second time to the addition of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or more intensive IPT-A (delivered twice per week). Research assessments will be administered at baseline and at weeks 4, 8, 12, 16, and 36.
Characterization and Treatment of Adolescent Depression
Study Type: Observational Start Date: December 28, 2017 Eligibility: 11 Years to 25 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
This research study seeks to find causes and treatments of depression in teenagers. The study goals are to increase our knowledge of treatments for depression and understand how the brain changes when teenagers have depression. The study will also compare teenagers with depression to those without mental health diagnoses.
This outpatient study is recruiting participants ages 11-17 who are depressed. They must have a pediatrician or other medical provider, be medically healthy, and able to perform research tasks. They may not currently be hospitalized, psychotic or actively suicidal. Teenagers with depression are eligible even if they are taking medication.
The study begins with an evaluation that includes clinical assessment, interviews, and questionnaires.
Visits may include paper-and-pencil and computer tests of mood, memory, and thinking; specialized computer games; and structural and brain imaging. If eligible, study participants may return several times a year for up to two years. This part of the study does not involve treatment. Participants may be eligible for outpatient treatment for up to 25 weeks. This includes evidenced-based "talk" therapy. Participants may choose either Interpersonal Psychotherapy for Adolescents (IPT-A) or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). If indicated, participants may opt to receive standard medication treatments along with psychotherapy. Research includes computer tasks and brain imaging.
All clinical evaluations, research tasks and visits are free of cost. Participants are compensated for research activities. Parents and teenager must agree to the teenager s participation in research.
The study is conducted at the NIH in Bethesda, Maryland and enrolls participants from the Washington DC Metro region within 50 miles of NIH. Transportation expenses are reimbursed by NIMH.
Neuropharmacologic Imaging and Biomarker Assessments of Response to Acute and Repeated-Dosed Ketamine Infusions in Major Depressive Disorder
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: May 25, 2017 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Most medications that treat depression take weeks or months to work. Researchers want to develop fast-acting treatments. One dose of ketamine has a rapid antidepressant effect. For most people, this lasts a week or less. Repeated doses of ketamine may help maintain this effect.
Main Study: To study the effects of ketamine in treating depression.
Ketamine Metabolites Substudy: To study how ketamine effects brain chemistry.
To study how ketamine effects the brain. This is done by looking at metabolites, which are created when a drug is broken down.
Main Study: People ages 18-65 with major depressive disorder and healthy volunteers
Ketamine Metabolites Substudy: Healthy volunteers ages 18-65
Main Study:
Participants will be screened in another study, with:
Medical and psychiatric history Psychiatric and physical exam Blood, urine, and heart tests
Participants will be inpatients at NIH for 4 phases totaling 14-20 weeks.
Phase I (2-7 weeks):
Gradually stop current medications MRI: Participants lie and perform tasks in a machine that takes pictures of the body. Mood and thinking tests Blood and urine tests Sleep test: Monitors on the skin record brain waves, breathing, heart rate, and movement during sleep. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: A coil on the scalp gives an electrical current that affects brain activity. Stress tests: Electrodes on the skin measure reactions to loud noises or electric shocks.
Phase I tests are repeated in Phases II and III and in the final visit.
Phase II (4-5 weeks):
4 weekly IV infusions of ketamine or a placebo during an MRI or MEG. For the MEG, a cone over the head records brain activity.
Phase III (optional):
8 infusions of ketamine over 4 weeks
Phase IV (optional):
Symptoms monitoring for 4 weeks Participants will have a final visit. They will be offered standard treatment at NIH for up to 2 months.
Ketamine Metabolites Substudy:
Participants will be inpatients at NIH for 4 days.
Study Procedures:
Mood and thinking tests
1 infusion of ketamine
Spinal tap and spinal catheter: Used to get samples of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This is a fluid that moves around and within the brain and spinal cord. Studying CSF will help us learn how ketamine effects brain chemistry
Imaging mGluR5 and Synaptic Density in Psychiatric Disorders
Study Type: Observational Start Date: January 11, 2017 Eligibility: 18 Years to 80 Years Location(s): Yale University PET Center, New Haven, Connecticut, United States
This research study is designed to look at the involvement of the glutamate system and synaptic density in depression and bipolar disorder. Each participant will undergo a screening appointment to determine study eligibility. Thereafter, the study will take 2 or 3 visits depending on schedule availability and will consist of a combination of one magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scan, one proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and/or one C13 MRS scans, and up to two positron emission tomography (PET) scans. Participants will also participate in cognitive testing. Depending on camera time, staff availability and subject schedule, total study participation may last 1-2 months.
Neurobiology of Suicide
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: December 1, 2015 Eligibility: 18 Years to 70 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
There are no good treatments for people considering suicide. Researchers want to study suicide with questions, blood tests, brain imaging, and sleep studies. They hope to better understand suicide, so they can help suicidal people.
To understand what happens in the brain when someone has thought about or attempted suicide.
Group 1: Adults ages 18 70 who have thought about or attempted suicide recently
Group 2: Adults ages 18 70 who have thought about or attempted suicide in the past
Group 3: Adults ages 18 70 who have depression or anxiety, but have never thought about suicide
Group 4: Healthy volunteers the same ages.
Participants will be screened in another protocol. Adults who have recently thought about or attempted suicide must be referred by a doctor. They may do up to 3 phases of this study. Groups 2, 3 and 4 will do only Phase 1 and will not get ketamine.
Phase 1: 1 week in hospital. Participants will have:
Physical exam.
Questions about thoughts and feelings.
Thinking and memory tests and simple tasks.
Blood and urine tests.
Two MRI scans. Participants will lie on a table that slides into a metal cylinder that takes pictures. They will have a coil over their head and earplugs and do a computer task.
Sleep test. Disks and bands will be placed on the body to monitor it during sleep.
Magnetic detectors on their head while they perform tasks.
A wrist monitor for activity and sleep.
Lumbar puncture (optional). A needle will collect fluid from the back.
Shock experiments (optional). Participants will observe pictures and sounds and feel a small shock on the hand.
Phase 2: 4 days in hospital. A thin plastic tube will be placed in each arm, one for blood draws, the other to get the drug ketamine once. Participants will repeat most of the Phase 1 tests.
Phase 3: up to 4 more ketamine doses over 2 weeks.
Participants will have follow-up calls or visits at 6 months and then maybe yearly for 5 years.
Ketamine Alcohol (in Treatment-Resistant Depression)
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 23, 2014 Eligibility: 21 Years to 65 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of Iowa Health Care, Iowa City, Iowa, United States
A single subanesthetic dose infusion of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist ketamine has rapid and robust antidepressant effects in patients with treatment-refractory major depressive disorder (TRD). A family history of an alcohol use disorder (Family History Positive, FHP) is one of the strongest identified predictors of an improved antidepressant response to ketamine. Like ketamine, alcohol is a functional NMDA receptor antagonist. FHP is associated with differential response to both alcohol, e.g. decreased body sway and plasma cortisol, and ketamine, e.g. blunted psychotomimetic side effects. One of the primary mechanistic hypotheses for ketamine's antidepressant action is the acute intrasynaptic release of glutamate from major output neurons, e.g. cortical pyramidal cells. Preliminary clinical studies have demonstrated this acute glutamate "surge" in response to subanesthetic dose ketamine. Based on these findings, the investigators hypothesize that ketamine's enhanced antidepressant efficacy in FHP TRD subjects is, at least in part, attributable to increased glutamate release relative to TRD subjects without a family history of alcohol use disorder (Family History Negative, FHN). The investigators also hypothesize that alcohol similarly augments glutamate release in this bio- logically-enriched subgroup, which may be a more objective biomarker than family history status. To test these hypotheses, the investigators have designed a now two-site, open-label study of 21-65 year old medically and neurologically healthy, currently moderately-to-severely depressed TRD patients. In total, the investigators plan to recruit 25 FHP and 25 FHN TRD subjects. All subjects must not have a lifetime substance use disorder (except nicotine or caffeine), no lifetime history of an alcohol use disorder and socially drink. The experimental portion consists of two phases. The preliminary first phase is a medication taper (if needed) and psychotropic medication-free period. The experimental second phase comprises two pharmacokinetically-defined basal-bolus alcohol and one subanesthetic dose (0.5mg/kg x 40 minute) ketamine infusions. The first alcohol infusion will establish the pharmacokinetic profile for a subsequent alcohol infusion occurring during 7T-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), both resting-state functional MRI (rs-fMRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to detect glutamate in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex/ventral anterior cingulate cortex (vmPFC/vACC). The ketamine infusion will also occur during 7T-MRI. The primary outcome measure is group mean change in Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) score from pre-ketamine infusion (baseline) to one week post-infusion, where the investigators observed ketamine's greatest antidepressant effect in FHP TRD. Additional outcome measures are vmPFC/vACC glutamate change in response to ketamine and alcohol challenge based on family history status. In summary, this study will provide key mechanistic information on ketamine's improved antidepressant efficacy in a biologically-enriched subgroup. This will contribute to the systematic development of more efficacious, personalized treatments for major depression in an effort to reduce its enormous public health burden.
Cellular Aging and Neurobiology of Depression Study
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: December 31, 2010 Eligibility: 21 Years to 60 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, California, United States
We are conducting an eight week longitudinal study to learn if blood levels of certain naturally occurring compounds and genetic markers differ between patients with depression and healthy adults who are not depressed, and if any such differences relate to memory performance, mood, and neurobiology. We are also interested in how the gut microbiome is affected by antidepressant treatment.
We will do this by comparing the unmedicated depressed patients with matched healthy controls at baseline and then following the depressed patients over the course of eight weeks of standardized antidepressant treatment to gauge which baseline abnormalities normalize over the course of treatment.
Development of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Techniques for Studying Mood and Anxiety Disorders
Study Type: Observational Start Date: December 6, 2006 Eligibility: 18 Years to 65 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
This study is intended to help develop new MRI imaging techniques for studying mood and anxiety disorders. Researchers believe that depression and anxiety disorders may cause structural and functional changes in the brain. This study will optimize the way MRI scans are collected to look at brain structure and examine how the brain behaves while subjects perform particular tasks.
Healthy normal subjects between 18 and 50 years of age who have never had a major psychiatric disorder and who have no first-degree relatives with mood disorders may be eligible for this study. Candidates are screened by phone with questions about their psychiatric and medical history, current emotional state and sleep pattern, and family history of psychiatric disorders. Candidates who pass the preliminary screening then undergo additional screening interviews and laboratory tests.
Participants undergo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and neuropsychological testing, as follows:
"<TAB>MRI scans: Subjects are asked to participate in an MRI study on one of several scanners to measure blood flow in the brain, concentrations of certain chemicals in the brain, or magnetic properties of the brain. MRI uses a strong magnet and radio waves to obtain pictures of the brain. The subject lies still on a narrow bed with a metal coil close to the head. For this study, subjects may be asked to wear a special coil on the neck to help measure blood flow. They may be asked to watch a screen presenting images or to do a task in which they respond to pictures or sounds and may be asked to return for additional scans.
"<TAB>Neuropsychological testing: Subjects may undergo tests of cognitive performance. Often, people with mood disorders have subtle changes in performance on these tests that allow researchers to pinpoint where brain abnormalities occur. Before the tests can be used in patients, they must be validated by using healthy subjects. These tests are presented either orally, in written form, or on a computer.
Family Study of Affective and Anxiety Spectrum Disorders
Study Type: Observational Start Date: May 21, 2004 Eligibility: 7 Years to 120 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
This study will examine how depression, anxiety, and migraine run in families. It will help in defining the risk factors for physical, mental, and health problems-as well as define ways that those problems may be prevented and treated.
A broad range of ages among family members will be included to evaluate the patterns of how these disorders are expressed throughout people's lives. Children of all ages will be included, and those ages 8 to 17 will be interviewed directly.
Assessments will be collected through criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV as well as the spectrum, or range, of mood disorders and co-existing conditions. A member of the study team will visit the participants at home or will do an interview by telephone. Participation will take approximately 3 to 4 hours. Children will complete questionnaires given by the research team as well as questionnaires that they will do by themselves. The questions will pertain to the children's health, including physical and mental health and medical history, social relationships, problems, skills, and ways of dealing with important or stressful issues in their lives. These questionnaires will take up to 1 hour to complete.
Health history gathered from adult participants will pertain to height, weight, exercise, and general function. Women will be asked about the use of oral contraceptives, estrogen, and progesterone. In addition, there will be questionnaires on personality and temperamental traits, that is, behavior and impulsiveness. Questions will also involve social intuition, family and other environmental factors, general functioning, and basic demographics such as ethnicity, race, socioeconomic status, marital status, education level, and employment history.
Families enrolled in this phase of the research will be invited to participate in the next phase. There would be follow-up to evaluate the development of mood disorders, subtypes, and syndromes across the lifespan.
The Psychobiology of Childhood Temperament
Study Type: Observational Start Date: November 10, 2003 Eligibility: 2 Months to 60 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
The purpose of this study is to use brain imaging technology to examine brain changes that occur in children when they are exposed to various kinds of emotional tasks and to determine if these changes are related to the child's temperament.
Studies suggest that the risk for developing mood and anxiety disorders in preschool children may be linked to differences in temperament. The relationship between temperament and risk or resilience may reflect the influences of brain activity on behavior at different stages of childhood development. Behavioral inhibition and mood or anxiety disorders have been linked to disturbances in the circuitry of several areas in the brain. However, the involvement of this circuitry in temperament remains unclear. This study will use functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to examine the function of different parts of the brain in children who have previously undergone temperament studies and have had their temperaments classified.
Two sets of studies will be performed in the current protocol. A small set of pilot studies will be performed in infants, by staff at the University of Maryland. In terms of the studies among infants, these subjects will initially be contacted by staff at Maryland and then will be seen at the NIH for up to three visits lasting between 4- to 5- hours during the first year of life. These subjects also will undergo visits at the University of Maryland throughout the first year of life.
This study will comprise up to four clinic visits. At Visit 1, children and their parents will meet with study staff individually and together for psychiatric interviews. Children will undergo a physical examination, medical history, a urine drug test, and practice in an fMRI simulator. Saliva samples will be collected from the children and tests will be given to assess stage of puberty, temperament, intelligence, feelings, experiences, and behavior. Other visits include fMRI scans of the brain and other tasks.
Studies of Brain Function and Course of Illness in Pediatric Bipolar Disorder
Study Type: Observational Start Date: January 1, 2002 Eligibility: 7 Years to 60 Years, Does Not Accept Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
This study seeks to learn more about the symptoms of severe mood dysregulation in children and adolescents ages 7-17. Children and adolescents with severe mood dysregulation (SMD) display chronic anger, sadness, or irritability, as well as hyperarousal (such as insomnia, distractibility, hyperactivity) and extreme responses to frustration (such as frequent, severe temper tantrums). Researchers will describe the moods and behaviors of children with these symptoms and use specialized testing and brain imaging to learn about the brain changes associated with this disorder.
Study of Neuro-Cognitive Correlates of Pediatric Anxiety Disorders
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: October 2, 2001 Eligibility: 8 Years to 65 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Study Description:
This study examines relations between neurocognitive and clinical features of pediatric anxiety disorders. The study uses neuro-cognitive tasks, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), as well as magneto- and electro-encephalography (M/EEG). Patients will be studied over one year, before and after receiving either one of two standard-of-care treatments: cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or fluoxetine, a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Healthy comparisons will be studied at comparable time points.
Primary Objectives:
To compare healthy youth and symptomatic, medication-free pediatric patients studied prior to receipt of treatment. The study seeks to detect relations between clinical features of anxiety disorders at baseline and a wide range of neurocognitive features associated with attention, memory, and response to motivational stimuli.
Secondary Objectives:
To document relations between baseline neurocognitive features and response to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or fluoxetine, as defined by the Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale (PARS) and Clinical Global Improvement (CGI) Scale. To document relations between post-treatment changes in neurocognitive features and anxiety symptoms on the PARS following treatment with Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or fluoxetine. To document relations among broad arrays of clinical, cognitive, and neural measures
Primary Endpoints:
Indices of percent-signal change in hypothesized brain regions, comprising amygdala, striatum, and prefrontal cortex (PFC) for each fMRI and MEG paradigm.
Secondary Endpoints:
Treatment-response as defined by a continuous measure, the Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale score (PARS), and a categorial measure, the Clinical Global Improvement (CGI) score. Levels of symptoms and behaviors evoked by tasks that engage attention, memory, and elicit responses to motivational stimuli.
Evaluation of Patients With Mood and Anxiety Disorders and Healthy Volunteers
Study Type: Observational Start Date: February 2, 2001 Eligibility: 3 Years to 99 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
The purpose of this protocol is to allow for the careful screening of patients and healthy volunteers for participation in research protocols in the Experimental Therapeutics and Pathophysiology Lab (ETPB) at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and for the collection of natural history data. In addition the protocol will allow clinicians to gain more experience in the use of a variety of polysomnographic and high-density EEG recordings. Subjects in this protocol will undergo an evaluation which may include: a psychiatric interview; a diagnostic interview; rating scales; a medical history; a physical exam; brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); electroencephalography (EEG); electrocardiography (EKG), magnetoencephalography (MEG); blood, saliva and urine laboratory evaluation; and a request for medical records. Subjects may also be asked to complete questionnaires about attitudes towards research and motivation for research participation. The data collected may also be linked with data from other mood and anxiety disorder protocols (e.g., brain imaging, DNA, psychophysiology tests, treatment studies, etc) for the purposes of better understanding the diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment response of patients with mood disorders. Parents of minors will be interviewed. Upon conclusion of the screening process, subjects will either be offered participation in a research protocol and will sign the appropriate informed consent, or will be considered not appropriate for participation in research and will be referred back into the community. The current protocol thus serves as an entry point for individuals with mood or anxiety disorders or healthy volunteers to enter NIMH IRB approved ETPB protocols.
The Role of Hormones in Postpartum Mood Disorders
Study Type: Interventional Start Date: April 26, 1996 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years to 50 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
Determine whether postpartum depression is triggered by the abrupt withdrawal of estrogen and progesterone.
The appearance of mood and behavioral symptoms during pregnancy and the postpartum period has been extensively reported. While there has been much speculation about possible biologically based etiologies for postpartum disorders (PPD), none has ever been confirmed. Preliminary results from two related studies (protocols 90-M-0088, 92-M-0174) provide evidence that women with menstrual cycle related mood disorder, but not controls, experience mood disturbances during exogenous replacement of physiologic levels of gonadal steroids. The present protocol is designed to create a "scaled-down" hormonal milieu of pregnancy and the puerperium in order to determine whether women who have had a previous episode of postpartum major effective episode will experience differential mood and behavioral effects compared with controls and to determine whether it is the abrupt withdrawal of gonadal steroids or the prolonged exposure to gonadal steroids that is associated with mood symptoms. Supraphysiologic plasma levels of gonadal steroids will be established, maintained, and then rapidly reduced, simulating the hormonal events that occur during pregnancy and parturition. This will be accomplished by administering estradiol and progesterone to women who are pretreated with a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist (Lupron). After eight weeks, administration of gonadal steroids will be stopped in one group of patients and controls, and a sudden decline in the plasma hormone levels will be precipitated. Another group will be maintained on supraphysiologic levels of estrogen and progesterone for an additional month. Outcome measures will include mood, behavioral and hormonal parameters (a separate protocol done in collaboration with NICHD).
Evaluation of the Genetics of Bipolar Disorder
Study Type: Observational Start Date: August 11, 1994 Eligibility: 18 Years and Older, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
This study looks to identify genes that may affect a person's chances of developing bipolar disorder (BP) and related conditions.
Study of Premenstrual Syndrome and Premenstrual Dysphoria
Study Type: Observational Start Date: March 9, 1984 Eligibility: Females, 18 Years to 50 Years, Accepts Healthy Volunteers Location(s): National Institutes of Health Clinical Center, Bethesda, Maryland, United States
The purpose of this study is to identify and describe the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Women who experience PMS symptoms will complete clinical interviews, self-rating scales, and evaluations of mood and endocrine function. A subgroup of women with severe PMS (Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder or PMDD) will be offered additional research studies that focus on: 1) identifying the endocrine changes that may be responsible for changes in mood and behavior during the premenstrual period, 2) evaluating treatments for PMS symptoms, and/or 3) identifying genetic factors in women with and without PMS. Women with recurrent brief depression will also be recruited to serve as a comparison group....
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
April 2, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
reputable news agency
Anxiety, depression associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease
by Elana Gotkine

Anxiety and depression are associated with an increased incidence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), according to a study published online March 19 in Scientific Reports .
Qian Li, from The Third People's Hospital of Chengdu in China, and colleagues gathered 24-hour pH monitoring data and baseline patient information for a cohort of 518 individuals with GERD. In addition, their psychological well-being was assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale.
The researchers identified statistically significant variation in anxiety levels based on gender and significant disparity in depression based on age and literacy levels. In the patient cohort, there was a significant positive correlation observed between severity of anxiety and depression and the 24-hour pH monitoring results. A higher anxiety level was associated with a higher level of GERD in a logistic regression modeling analysis; the incidence of GERD was increased in the presence of mild anxiety (odds ratio, 2.64). A causal relationship was seen for the moderately severe anxiety group with increased GERD incidence (odds ratio, 6.84). A higher incidence of GERD was seen in association with moderate-to-severe depression (odds ratio, 2.32). GERD prevalence was increased among men versus women (odds ratio, 2.29). In addition, increased body mass index was positively associated with GERD susceptibility (odds ratio, 1.07).
"There is a certain correlation between GERD and anxiety and depression, which provides theoretical references for individuals and clinical workers to focus on patients' psychological emotions when treating GERD," the authors write.
Copyright © 2024 HealthDay . All rights reserved.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

New report presents a global plan to combat prostate cancer
2 hours ago

Dogs may provide new insights into human aging and cognition
AI's ability to detect tumor cells could be key to more accurate bone cancer prognoses
3 hours ago
Novel pre-clinical models help advance therapeutic development for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections

Far-UVC light can virtually eliminate airborne virus in an occupied room, study shows
4 hours ago

Las Vegas mass shooting survivors continue to struggle with major depression, PTSD

Combining food taxes and subsidies can lead to healthier grocery purchases for low-income households
New insights into muscle health: How innervation influences the recovery process
5 hours ago
Simulations reveal mechanism behind protein buildup in Parkinson's disease

Increasing positive affect in adolescence could lead to improved health and well-being in adulthood
6 hours ago
Related Stories

Study finds GERD can induce occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis, but not vice versa
Feb 1, 2024

DDW: Psych disorders make GERD hard to Dx by symptoms alone
Jun 5, 2018
Gastroesophageal reflux disease raises risk for periodontitis: Study
Dec 29, 2022
GERD increases risk for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
May 8, 2023

pH-multichannel intraluminal impedance monitoring can ID GERD
Dec 29, 2023
Gastroesophageal reflux disease causally linked to lung cancer
Dec 30, 2022
Recommended for you
Exploring the factors that influence people's ability to detect lies online
10 hours ago

Scientists link certain gut bacteria to lower heart disease risk
9 hours ago

Pilot study shows ketogenic diet improves severe mental illness
Apr 1, 2024
International study uses AI to show how personality influences the expression of our genes
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Depression articles within Scientific Reports
Article 26 March 2024 | Open Access
Social defeat stress induces liver injury by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in C57BL/6J mice
- XiaoLei Gao
- , Tong Zhao
- & Guang-Biao Huang
Article 23 March 2024 | Open Access
The impact of mental health on health-related quality of life in patients with NF2-related Schwannomatosis
- Anna Freier
- , Anna C. Lawson McLean
- & Johannes Kruse
Article 19 March 2024 | Open Access
Thought habits and processing modes among Japanese university students do not influence dynamic associations between rumination and negative affect
- Kohei Kambara
- , Shushi Namba
- & Akiko Ogata
5-HT_FAsTR: a versatile, label-free, high-throughput, fluorescence-based microplate assay to quantify serotonin transport and release
- Lina Bukowski
- , Markus Emanuel Strøm
- & Steffen Sinning
Article 28 February 2024 | Open Access
Feasibility of online managing cancer and living meaningfully (CALM) in Chinese patients with metastatic breast cancer: a pilot randomized control trial
- Yening Zhang
- , Ying Pang
- & Lili Tang
Article 24 February 2024 | Open Access
Hippocampal volume changes after ( R,S )-ketamine administration in patients with major depressive disorder and healthy volunteers
- Jennifer W. Evans
- , Morgan C. Graves
- & Carlos A. Zarate Jr
Article 11 February 2024 | Open Access
Mental health disorders among medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic in the area with no mandatory lockdown: a multicenter survey in Tanzania
- Deogratius Bintabara
- , Joseph B. Singo
- & Festo K. Shayo
Article 30 January 2024 | Open Access
Anxiety, depression, and brain overwork in the general population of Mongolia
- Battuvshin Lkhagvasuren
- , Tetsuya Hiramoto
- & Tsolmon Jadamba
Article 11 January 2024 | Open Access
Clinical outcomes associated with antidepressant use in inflammatory bowel disease patients and a matched control cohort
- Djibril M. Ba
- , Sanjay Yadav
- & Matthew D. Coates
Article 10 January 2024 | Open Access
Neuroactive steroid effects on autophagy in a human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK) cell model
- Sofia V. Salvatore
- , Ma. Xenia G. Ilagan
- & Steven Mennerick
Article 09 January 2024 | Open Access
Individual-specific change points in circadian rest-activity rhythm and sleep in individuals tapering their antidepressant medication: an actigraphy study
- Olga Minaeva
- , Evelien Schat
- & Harriëtte Riese
Article 12 December 2023 | Open Access
The Prevalence of Behavioural Symptoms and Psychiatric Disorders in Hadza Children
- Dennis Ougrin
- , Emma Woodhouse
- & Ioannis Bakolis
Article 08 December 2023 | Open Access
Dog owner mental health is associated with dog behavioural problems, dog care and dog-facilitated social interaction: a prospective cohort study
- Ana Maria Barcelos
- , Niko Kargas
- & Daniel S. Mills
Article 24 November 2023 | Open Access
Association of executive function with suicidality based on resting-state functional connectivity in young adults with subthreshold depression
- Je-Yeon Yun
- , Soo-Hee Choi
- & Joon Hwan Jang
Article 09 November 2023 | Open Access
Selective dopamine D2 receptor deletion from Nkx6.2 expressing cells causes impaired cognitive, motivation and anxiety phenotypes in mice
- Lucila Bechelli
- , Eugenia Tomasella
- & Diego M. Gelman
Article 04 November 2023 | Open Access
Baseline markers of cortical excitation and inhibition predict response to theta burst stimulation treatment for youth depression
- Prabhjot Dhami
- , Sylvain Moreno
- & Faranak Farzan
Article 03 November 2023 | Open Access
Cross-cultural validation of the COVID-19 peritraumatic distress index (CPDI) among Spanish and Peruvian populations
- Fabian Böttcher
- , Bruno Pedraz-Petrozzi
- & Soledad Ballesteros
Article 30 October 2023 | Open Access
Personalized relapse prediction in patients with major depressive disorder using digital biomarkers
- Srinivasan Vairavan
- , Homa Rashidisabet
- & Vaibhav A. Narayan
Article 17 October 2023 | Open Access
Depression by gender and associated factors among older adults in India: implications for age-friendly policies
- , T. Muhammad
- & Preeti Pushpalata Zanwar
Article 12 October 2023 | Open Access
Prevalence of depression, anxiety and suicidal ideas and associated factors, in particular sensory impairments, in a population of Bashkortostan in Russia
- Mukharram M. Bikbov
- , Timur R. Gilmanshin
- & Jost B. Jonas
Article 11 October 2023 | Open Access
Depressive states in healthy subjects lead to biased processing in frontal-parietal ERPs during emotional stimuli
- Pengcheng Li
- , Mio Yokoyama
- & Tohru Yagi
Article 05 October 2023 | Open Access
Associations among the workplace violence, burnout, depressive symptoms, suicidality, and turnover intention in training physicians: a network analysis of nationwide survey
- , Sun Jung Myung
- & Kyung Sik Kim
Article 03 October 2023 | Open Access
Association of illness perception and alexithymia with fatigue in hemodialysis recipients: a single-center, cross-sectional study
- Yoko Tanemoto
- , Ui Yamada
- & Masahiro Hashizume
Article 29 September 2023 | Open Access
Reduced length of nodes of Ranvier and altered proteoglycan immunoreactivity in prefrontal white matter in major depressive disorder and chronically stressed rats
- José Javier Miguel-Hidalgo
- , Erik Hearn
- & Grazyna Rajkowska
Article 20 September 2023 | Open Access
Associations between pre-pandemic authoritative parenting, pandemic stressors, and children’s depression and anxiety at the initial stage of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Karina G. Heaton
- , Nicolas L. Camacho
- & Michael S. Gaffrey
Article 19 September 2023 | Open Access
Prevalence and factors associated with metabolic syndrome in first hospitalization for major depression disorder patients
- Zhongyu Tang
- , Yanping Zhen
- & Jun Ma
Article 18 September 2023 | Open Access
Nonpharmacological approaches for pain and symptoms of depression in people with osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analyses
- Claire V. Burley
- , Anne-Nicole Casey
- & Belinda J. Parmenter
Article 16 September 2023 | Open Access
Anxiety and depression from age 3 to 8 years in children with and without ADHD symptoms
- Christine Baalsrud Ingeborgrud
- , Beate Oerbeck
- & Kristin Romvig Overgaard
Article 15 September 2023 | Open Access
A standardized workflow for long-term longitudinal actigraphy data processing using one year of continuous actigraphy from the CAN-BIND Wellness Monitoring Study
- Anastasiya Slyepchenko
- , Rudolf Uher
- & Benicio N. Frey
Article 02 September 2023 | Open Access
Clustering and trajectories of key noncommunicable disease risk factors in Norway: the NCDNOR project
- Knut Eirik Dalene
- , Simon Lergenmuller
- & Inger Ariansen
Article 22 August 2023 | Open Access
Sex-differential association of suicide attempts with thyroid dysfunction in first-episode and drug-naïve young major depressive disorder patients with comorbid anxiety
- , Ying Yuan
- & Xiangyang Zhang
Article 14 August 2023 | Open Access
Metabolites for monitoring symptoms and predicting remission in patients with depression who received electroconvulsive therapy: a pilot study
- Takahito Uchida
- , Yuki Sugiura
- & Hiroyuki Uchida
Article 19 July 2023 | Open Access
Differential network interactions between psychosocial factors, mental health, and health-related quality of life in women and men
- Martin Weiß
- , Marthe Gründahl
- & Caroline Morbach
Article 07 July 2023 | Open Access
Perinatal depression and mental health uptake referral rate in an obstetric service
- Francisca Tato Fernandes
- , Ana Beatriz de Almeida
- & Paula Freitas
Article 23 June 2023 | Open Access
Shorter telomere length predicts poor antidepressant response and poorer cardiometabolic indices in major depression
- Ryan Rampersaud
- , Gwyneth W. Y. Wu
- & Owen M. Wolkowitz
Article 15 June 2023 | Open Access
Disparities in insecurity, social support, and family relationships in association with poor mental health among US adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
- , Siyi Wang
- & Lina Mu
Article 07 June 2023 | Open Access
A case study of an individual participant data meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy showed that prediction regions represented heterogeneity well
- Aurelio López Malo Vázquez de Lara
- , Parash Mani Bhandari
- & Yuying Zhang
Article 24 May 2023 | Open Access
Bayesian network analysis of antidepressant treatment trajectories
- Rosanne J. Turner
- , Karin Hagoort
- & Floortje E. Scheepers
Resting-state EEG delta and alpha power predict response to cognitive behavioral therapy in depression: a Canadian biomarker integration network for depression study
- Benjamin Schwartzmann
- , Lena C. Quilty
Article 22 May 2023 | Open Access
Depression and anxiety during and after episodes of COVID-19 in the community
- Caterina Alacevich
- , Inna Thalmann
- & Stavros Petrou
Article 18 May 2023 | Open Access
Prevalence and clinical correlates of abnormal lipid metabolism in first-episode and drug-naïve patients with major depressive disorder with abnormal glucose metabolism
- Quanfeng Zhu
- , Guojun Jiang
Article 10 May 2023 | Open Access
Exploring the role of empathy in prolonged grief reactions to bereavement
- Takuya Yoshiike
- , Francesco Benedetti
- & Kenichi Kuriyama
Article 03 May 2023 | Open Access
Reappraisal capacity is unrelated to depressive and anxiety symptoms
- Jack L. Andrews
- , Tim Dalgleish
- & Susanne Schweizer
Article 02 May 2023 | Open Access
Modeling the antidepressant treatment response to transcranial magnetic stimulation using an exponential decay function
- Yosef A. Berlow
- , Amin Zandvakili
- & Noah S. Philip
Article 25 April 2023 | Open Access
Predictive biosignature of major depressive disorder derived from physiological measurements of outpatients using machine learning
- Nicolas Ricka
- , Gauthier Pellegrin
- & Pierre A. Geoffroy
Article 19 April 2023 | Open Access
The impact of pharmaceutical form and simulated side effects in an open-label-placebo RCT for improving psychological distress in highly stressed students
- Alexander Winkler
- , Alannah Hahn
- & Christiane Hermann
Article 18 April 2023 | Open Access
Resting-state functional connectivity disruption between the left and right pallidum as a biomarker for subthreshold depression
- Yosuke Sato
- & Yasumasa Okamoto
Article 06 April 2023 | Open Access
Effects of left anodal transcranial direct current stimulation on hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis activity in depression: a randomized controlled pilot trial
- Bruno Pedraz-Petrozzi
- , Helena Sardinha
- & Michael Deuschle
Article 03 April 2023 | Open Access
Mortality was predicted by depression and functional dependence in a cohort of elderly adults of Italian descent from southern Brazil
- Emeline Pessin
- , Sandra C. Fuchs
- & Emilio H. Moriguchi
Article 27 March 2023 | Open Access
Genetic risk of depression is different in subgroups of dietary ratio of tryptophan to large neutral amino acids
- Bence Bruncsics
- , Gabor Hullam
- & Gabriella Juhasz
Browse broader subjects
- Psychiatric disorders
- Diseases of the nervous system
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychiatry
Evolution and Emerging Trends in Depression Research From 2004 to 2019: A Literature Visualization Analysis
1 School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Xuemei Tian
2 School of Life Sciences, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Xianrui Wang
Associated data.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Depression has become a major threat to human health, and researchers around the world are actively engaged in research on depression. In order to promote closer research, the study of the global depression knowledge map is significant. This study aims to map the knowledge map of depression research and show the current research distribution, hotspots, frontiers, and trends in the field of depression research, providing researchers with worthwhile information and ideas. Based on the Web of Science core collection of depression research from 2004 to 2019, this study systematically analyzed the country, journal, category, author, institution, cited article, and keyword aspects using bibliometric and data visualization methods. A relationship network of depression research was established, highlighting the highly influential countries, journals, categories, authors, institutions, cited articles, and keywords in this research field. The study identifies great research potential in the field of depression, provides scientific guidance for researchers to find potential collaborations through collaboration networks and coexistence networks, and systematically and accurately presents the hotspots, frontiers, and shortcomings of depression research through the knowledge map of global research on depression with the help of information analysis and fusion methods, which provides valuable information for researchers and institutions to determine meaningful research directions.
Introduction
Health issues are becoming more and more important to people due to the continuous development of health care. The social pressures on people are becoming more and more pronounced in a social environment that is developing at an increasing rate. Prolonged exposure to stress can have a negative impact on brain development ( 1 ), and depression is one of the more typical disorders that accompany it. Stress will increase the incidence of depression ( 2 ), depression has become a common disease ( 3 ), endangering people's physical health. Depression is a debilitating mental illness with mood disorders, also known as major depression, clinical depression, or melancholia. In human studies of the disease, it has been found that depression accounts for a large proportion of the affected population. According to the latest data from the World Health Organization (WHO) statistics in 2019, there are more than 350 million people with depression worldwide, with an increase of about 18% in the last decade and an estimated lifetime prevalence of 15% ( 4 ), it is a major cause of global disability and disease burden ( 5 ), and depression has quietly become a disease that threatens hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
Along with the rise of science communication research, the quantification of science is also flourishing. As a combination of “data science” and modern science, bibliometrics takes advantage of the explosive growth of research output in the era of big data, and uses topics, authors, publications, keywords, references, citations, etc. as research targets to reveal the current status and impact of the discipline more accurately and scientifically. Whereas, there is not a wealth of bibliometric studies related to depression. Fusar-Poli et al. ( 6 ) used bibliometrics to systematically evaluate cross-diagnostic psychiatry. Hammarström et al. ( 7 ) used bibliometrics to analyze the scientific quality of gender-related explanatory models of depression in the medical database PubMed. Tran et al. ( 8 ) used the bibliometric analysis of research progress and effective interventions for depression in AIDS patients. Wang et al. ( 9 ) used bibliometric methods to analyze scientific studies on the comorbidity of pain and depression. Shi et al. ( 10 ) performed a bibliometric analysis of the top 100 cited articles on biomarkers in the field of depression. Dongping et al. ( 11 ) used bibliometric analysis of studies on the association between depression and gut flora. An Chunping et al. ( 12 ) analyzed the literature on acupuncture for depression included in PubMed based on bibliometrics. Yi and Xiaoli ( 13 ) used a bibliometric method to analyze the characteristics of the literature on the treatment of depression by Chinese medicine in the last 10 years. Zhou and Yan ( 14 ) used bibliometric method to analyze the distribution of scientific and technological achievements on depression in Peoples R China. Guaijuan ( 15 ) performed a bibliometric analysis of the interrelationship between psoriasis and depression. Econometric analysis of the relationship between vitamin D deficiency and depression was performed by Yunzhi et al. ( 16 ) and Shauni et al. ( 17 ) performed a bibliometric analysis of domestic and international research papers on depression-related genes from 2003 to 2007. A previous review of depression-related bibliometric studies revealed that there is no bibliometric analysis of global studies in the field of depression, including country network analysis, journal network analysis, category network analysis, author network analysis, institutional network analysis, literature co-citation analysis, keyword co-presentation analysis, and cluster analysis.
The aim of this study was to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature-based data mining and metrics analysis of depression-related research. More specifically, this analysis focuses on cooperative network and co-presentation analysis, based on the 36,477 papers included in the Web of Science Core Collection database from 2004 to 2019, and provides an in-depth analysis of cooperative network, co-presentation network, and co-citation through modern metrics and data visualization methods. Through the mining of key data, the data correlation is further explored, and the results obtained can be used to scientifically and reasonably predict the depression-related information. This study aims to show the spatial and temporal distribution of research countries, journals, authors, and institutions in the field of depression in a more concise manner through a relational network. A deeper understanding of the internal structure of the research community will help researchers and institutions to establish more accurate and effective global collaborations, in line with the trend of human destiny and globalization. In addition, the study will allow for the timely identification of gaps in current research. A more targeted research direction will be established, a more complete picture of the new developments in the field of depression today will be obtained, and the research protocol will be informed for further adjustments. The results of these analyses will help researchers understand the evolution of this field of study. Overall, this paper uses literature data analysis to find research hotspots in the field of depression, analyze the knowledge structure within different studies, and provide a basis for predicting research frontiers. This study analyzed the literature in the field of depression using CiteSpace 5.8.R2 (64-bit) to analyze collaborative networks, including country network analysis, journal network analysis, category network analysis, researcher network analysis, and institutional network analysis using CiteSpace 5.8.R2 (64-bit). In addition, literature co-citation, keyword co-presentation, and cluster analysis of depression research hotspots were also performed. Thus, exploring the knowledge dimensions of the field, quantifying the research patterns in the field, and uncovering emerging trends in the field will help to obtain more accurate and complete information. The large amount of current research results related to depression will be presented more intuitively and accurately with the medium of information technology, and the scientific evaluation of research themes and trend prediction will be provided from a new perspective.
Data Sources
The data in this paper comes from the Web of Science (WoS) core collection. The time years were selected as 2004–2019. First, the literature was retrieved after entering “depression” using the title search method. A total of 73,829 articles, excluding “depression” as “suppression,” “decline,” “sunken,” “pothole,” “slump,” “low pressure,” “frustration.” The total number of articles with other meanings such as “depression” was 5,606, and the total number of valid articles related to depression was 68,223. Next, the title search method was used to search for studies related to “major depressive disorder” not “depression,” and a total of 8,070 articles were retrieved. For the two search strategies, a total of 76,293 records were collected. The relevant literature retrieved under the two methods were combined and exported in “plain text” file format. The exported records included: “full records and references cited.” CiteSpace processed the data to obtain 41,408 valid records, covering all depression-related research articles for the period 2004–2019, and used this as the basis for analysis.
Processing Tools
CiteSpace ( 18 ), developed by Chao-Mei Chen, a professor in the School of Information Science and Technology at Drexel University, is a Java-based program with powerful data visualization capabilities and is one of the most widely used knowledge mapping tools. The software version used in this study is CiteSpace 5.8.R2 (64-bit).
Methods of Analysis
This study uses bibliometrics and data visualization as analytical methods. First, the application of bibliometrics to the field of depression helped to identify established and emerging research clusters, demonstrating the value of research in this area. Second, data visualization provides multiple perspectives on the data, presenting correlations in a clearer “knowledge graph” that can reveal underestimated and overlooked trends, patterns, and differences ( 19 ). CiteSpace is mainly based on the “co-occurrence clustering idea,” which extracts the information units (keywords, authors, institutions, countries, journals, etc.) in the data by classification, and then further reconstructs the data in the information units to form networks based on different types and strengths of connections (e.g., keyword co-occurrence, author collaboration, etc.). The resulting networks include nodes and links, where the nodes represent the information units of the literature and the links represent the existence of connections (co-occurrence) between the nodes. Finally, the network is measured, statistically analyzed, and presented in a visual way. The analysis needs to focus on: the overall structure of the network, key nodes and paths. The key evaluation indicators in this study are: betweenness centrality, year, keyword frequency, and burst strength. Betweenness centrality (BC) is the number of times a node acts as the shortest bridge between two other nodes. The higher the number of times a node acts as an “intermediary,” the greater its betweenness centrality. Betweenness centrality is a measure of the importance of articles found and measured by nodes in the network by labeling the category (or authors, journals, institutions, etc.) with purple circles. There may be many shortest paths between two nodes in the network, and by counting all the shortest paths of any two nodes in the network, if many of the shortest paths pass through a node, then the node is considered to have high betweenness centrality. In CiteSpace, nodes with betweenness centrality over 0.1 are called critical nodes. Year, which represents the publication time of the article. Frequency, which represents the number of occurrences. Burst strength, an indicator used to measure articles with sudden rise or sudden decline in citations. Nodes with high burst strength usually represent a shift in a certain research area and need to be focused on, and the burst article points are indicated in red. The nodes and their sizes and colors are first analyzed initially, and further analyzed by betweenness centrality indicators for evaluation. Each node represents an article, and the larger the node, the greater the frequency of the keyword word and the greater the relevance to the topic. Similarly, the color of the node represents time: the warmer the color, the more recent the time; the colder the color, the older the era; the node with a purple outer ring is a node with high betweenness centrality; the color of each annual ring can determine the time distribution: the color of the annual ring represents the corresponding time, and the thickness of one annual ring is proportional to the number of articles within the corresponding time division; the dominant color can reflect the relative concentration of the emergence time; the node The appearance of red annual rings in the annual rings means hot spots, and the frequency of citations has been or is still increasing rapidly.
Large-Scale Assessment
Country analysis.
During the period 2004–2019, a total of 157 countries/territories have conducted research on depression, which is about 67.38% of 233 countries/territories worldwide. This shows that depression is receiving attention from many countries/regions around the world. Figure 1 shows the geographical distribution of published articles for 157 countries. The top 15 countries are ranked according to the number of articles published. Table 1 lists the top 15 countries with the highest number of publications in the field of depression worldwide from 2004 to 2019. These 15 countries include 4 Asian countries (Peoples R China, Japan, South Korea, Turkey), 2 North American countries (USA, Canada), 1 South American country (Brazil), 7 European countries (UK, Germany, Netherlands, Italy, France, Spain, Sweden), and 1 Oceania country (Australia).

Geographical distributions of publications, 2004–2019.
The top 15 productive countries.
TP, total publications; TP R (%), the ratio of the amount of the publications in the country to the publications in the word during 2004–2019; BC, betweenness centrality; TPA (million), total publications in all areas; TPA R (%), the ratio of the amount of publications in depression to publications in all areas .
Overall, the main distribution of these articles is in USA and some European countries, such as UK, Germany, Netherlands, Italy, France, Spain, and Sweden. This means that these countries are more interested and focused on research on depression compared to others. The total number of publications across all research areas in the Web of Science core collection is similar to the distribution of depression research areas, with the trend toward USA, UK, and Peoples R China as leading countries being unmistakable, and USA has been a leader in the field of depression, with far more articles published than any other country. It can also be seen that USA is the country with the highest betweenness centrality in the network of national collaborations analyzed in this paper. USA research in the field of depression is closely linked to global research, and is an important part of the global collaborative network for depression research. As of 2019, the total number of articles published in depression performance research in USA represents 27.13% of the total number of articles published in depression worldwide, which is ~4 times more than the second-place country, UK, which is far ahead of other countries. Peoples R China, as the third most published country, has a dominant number of articles, but its betweenness centrality is 0.01, reflecting the fact that Peoples R China has less collaborative research with other countries, so Peoples R China should strengthen its foreign collaborative research and actively establish global scientific research partnerships to seek development and generate breakthroughs in cooperation. The average percentage of scientific research on depression in each country is about 0.19%, also highlighting the urgent need to address depression as one of the global human health problems. The four Asian countries included in the top 15 countries are Peoples R China, Japan, South Korea, and Turkey, with Peoples R China ranking third with 6.72% of the total number of all articles counted. The distribution may be explained by the fact that Peoples R China is the largest developing country with a rapid development rate as the largest. Along with the steady rise in the country's economic power, people are creating economic benefits and their health is becoming a consumable commodity. The lifetime prevalence and duration of depression varies by country and region ( 2 ), but the high prevalence and persistence of depression worldwide confirms the increasing severity of the disease worldwide. The WHO estimates that more than 300 million people, or 4.4% of the world's population, suffer from depression ( 20 ), with the number of people suffering from depression increasing at a patient rate of 18.4% between 2005 and 2015. Depression, one of the most prevalent mental illnesses of our time, has caused both physical and psychological harm to many people, and it has become the leading cause of disability worldwide today, and in this context, there is increased interest and focus on research into depression. It is expected that a more comprehensive understanding of depression and finding ways to prevent and cope with the occurrence of this disease can help people get rid of the pain and shadow brought by depression, obtain a healthy and comfortable physical and mental environment and physical health, and make Chinese contributions to the cause of human health. Undoubtedly, the occurrence of depressive illnesses in the context of irreversible human social development has stimulated a vigorous scientific research environment on depression in Peoples R China and other developing countries and contributed to the improvement of research capacity in these countries. Moreover, from a different perspective, the geographical distribution of articles in this field also represents the fundamental position of the country in the overall scientific and academic research field.
Growth Trend Analysis
Figure 2 depicts the distribution of 38,433 articles from the top 10 countries in terms of the number of publications and the trend of growth during 2004–2019.

The distribution of publications in top 10 productive countries, 2004–2019. Source: author's calculation. National development classification criteria refer to “Human Development Report 2020” ( 21 ).
First, the number of articles published per year for the top 10 countries in terms of productivity was counted and then the white bar chart in Figure 2 was plotted, with the year as the horizontal coordinate and total publications as the vertical coordinate, showing the distribution of the productivity of articles in the field of depression per year. The total number of publications for the period 2004–2019 is 38,433. Based on the white bars and line graphs in Figure 2 , we can divide this time period into three growth periods. The number of publications in each growth period is calculated based on the number of publications per year. As can be seen from the figure, the period 2004–2019 can be divided into three main growth periods, namely 2004–2009, 2010–2012, and 2013–2019, the first growth period being from 2004 to 2009, the number of publications totaled 6,749, accounting for 23.97% of all publications; from 2010 to 2012, the number of publications totaled 8,236, accounting for 17.56% of all publications; and from 2013 to 2019, the number of publications totaled 22,473, accounting for 58.47% of all publications. Of these, 2006 was the first year of sharp growth with an annual growth rate of 19.97%, 2009 was the second year of sharp growth with an annual growth rate of 17.64%, and 2008 was the third year of sharp growth with an annual growth rate of 16.09%. In the last 5 years, 2019 has also shown a sharp growth trend with a growth rate of 14.34%. Notably, in 2010 and 2013, there was negative growth with the growth rate of −3.39 and −1.45%. In the last 10 years, depression research has become one of the most valuable areas of human research. It can also be noted that the number of publications in the field of depression in these 10 countries has been increasing year after year.
Second, the analysis is conducted from the perspective of national development, divided into developed and developing countries, as shown in the orange bar chart in Figure 2 , where the horizontal coordinate is year and the vertical coordinate is total publications, comparing the article productivity variability between developed and developing countries. The top 10 most productive countries in the field of depression globally include nine developed countries and one developing country, respectively. During the period 2004–2019, 34,631 papers were published in developed countries and 3,802 papers were published in developing countries, with developed countries accounting for 90.11% of the 38,433 articles and developing countries accounting for 9.89%, and the total number of publications in developed countries was about 9 times higher than that in developing countries. During the period 2004–2019, the number of publications in developed countries showed negative growth in 2 years (2010 and 2013) with growth rates of −3.39 and −1.45%, respectively. The rest of the years showed positive growth with growth rates of 1.52% (2005), 19.97 (2006), 8.11 (2007), 12.70 (2008), 17.64 (2009), 13.22 (2011), 10.17 (2012), 16.09 (2014), 10.46 (2015), 4.10 (2016), 1.59 (2017), 3.91 (2018), and 14.34 (2019), showing three periods of positive growth: 2004–2009, 2011–2012, and 2014–2019, with the highest growth rate of 19.97% in 2006. Recent years have also shown a higher growth trend, with a growth rate of 14.34% in 2019. It is worth noting that developing countries have been showing positive growth in the number of articles in the period 2004–2019, with annual growth rates of 81.25 (2005), 17.24 (2006), 35.29 (2007), 19.57 (2008), 65.45 (2009), 13.19 (2010), 29.13 (2011), 54.89 (2012), 12.14 (2013), 36.36 (2014), 14.92 (2015), 16.02 (2016), 10.24 (2017), 21.17 (2018), and 31.37 (2019), with the highest growth rate of 81.25% in 2005. In the field of depression research, developed countries are still the main force and occupy an important position.
Further, 10 countries with the highest productivity in the field of depression are compared, total publications in the vertical coordinate, and the colored scatter plot contains 10 colored dots, representing 10 different countries. On the one hand, the variability of the contributions of different countries in the same time frame can be compared horizontally. On the other hand, it is possible to compare vertically the variability of the growth of different countries over time. Among them, USA, with about 40.29% of the world's publications in the field of depression, has always been a leader in the field of depression with its rich research results. Peoples R China, as the only developing country, ranks 3rd in the top 10 countries with high production of research papers in the field of depression, and Peoples R China's research in the field of depression has shown a rapid growth trend, and by 2016, it has jumped to become the 2nd largest country in the world, with the number of published papers increasing year by year, which has a broad prospect and great potential for development.
Distribution of Periodicals
Table 2 lists the top 15 journals in order of number of journal co-citations. In the field of depression, the top 15 cited journals accounted for 19.06% of the total number of co-citations, nearly one in five of the total number of journal co-citations. In particular, the top 3 journals were ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT (ARCHIVES OF GENERAL PSYCHIATRY), J AFFECT DISORDERS (JOURNAL OF AFFECTIVE DISORDERS), and AM J PSYCHIAT (AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHIATRY), with co-citation counts of 20,499, 20,302, and 20,143, with co-citation rates of 2.09, 2.07, and 2.06%, respectively. The main research area of ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT is Psychiatry; the main research area of the journal J AFFECT DISORDERS is Neurosciences and Neurology, Psychiatry; AM J PSYCHIAT is the main research area of Psychiatry, and the three journals have “psychiatry” in common, making them the most frequently co-cited journals in the field of depression.
The top 15 co-cited journals.
TP, total publications; TP R (%), the ratio of the amount of the journal's publications to the total publications; BC, betweenness centrality .
Figure 3 shows the network relationship graph of the cited journals from 2004 to 2019. The figure takes g-index as the selection criteria, the scale factor k = 25 to include more nodes. Each node of the graph represents each journal, the node size represents the number of citation frequencies, the label size represents the size of the betweenness centrality of the journal in the network, and the links between journals represent the co-citation relationships. The journal co-citation map reflects the structure of the journals, indicating that there are links between journals and that the journals include similar research topics. These journals included research topics related to neuroscience, psychiatry, neurology, and psychology. The journal with betweenness centrality size in the top 1 was ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT, with betweenness centrality size of 0.07, and impact shadows of 14.48. ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT, has research themes of Psychiatry. In all, these journals in Figure 3 occupy an important position in the journal's co-citation network and have strong links with other journals.

Prominent journals involved in depression. The betweenness centrality of a node in the network measures the importance of the position of the node in the network. Two types of nodes may have high betweenness centrality scores: (1) Nodes that are highly connected to other nodes, (2) Nodes are positioned between different groups of nodes. The lines represent the link between two different nodes.
Distribution of Categories
Table 3 lists the 15 most popular categories in the field of depression research during the period 2004–2019. In general, the main disciplines involved are neuroscience, psychology, pharmacy, medicine, and health care, which are closely related to human life and health issues. Of these, psychiatry accounted for 20.78%, or about one-five, making it the most researched category. The study of depression focuses on neuroscience, reflecting the essential characteristics of depression as a category of mental illness and better reflecting the fact that depression is an important link in the human public health care. In addition, Table 3 shows that the category with the highest betweenness centrality is Neuroscience, followed by Public, Environment & Occupational Health, and then Pharmacology & Pharmacy, with betweenness centrality of 0.16, 0.13, and 0.11, respectively. It is found that the research categories of depression are also centered on disciplines such as neuroscience, public health and pharmacology, indicating that research on depression requires a high degree of integration of multidisciplinary knowledge and integration of information from various disciplines in order to have a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the depression.
The top 15 productive categories, 2004–2019.
TP, total publications; TP R (%), the ratio of the amount of the category's publications to the total publications; BC, betweenness centrality .
Figure 4 shows the nine categories with the betweenness centrality in the category research network, with Neuroscience being the node with the highest betweenness centrality in this network, meaning that Neuroscience is most strongly linked to all research categories in the field of depression research. Depression is a debilitating psychiatric disorder with mood disorders. It is worth noting that the development of depression not only has psychological effects on humans, but also triggers many somatic symptoms that have a bad impact on their daily work and life, giving rise to the second major mediating central point of research with public health as its theme. The somatization symptoms of depression often manifest as abnormalities in the cardiovascular system, and many studies have looked at the pathology of the cardiovascular system in the hope of finding factors that influence the onset of depression, mechanisms that trigger it or new ways to treat it. Thus, depression involves not only the nervous system, but also interacts with the human cardiovascular system, for example, and the complexity of depression dictates that the study of depression is an in-depth study based on complex systems.

Prominent categories involved in depression, 2004–2019. The betweenness centrality of a node in the network measures the importance of the position of the node in the network. Two types of nodes may have high betweenness centrality scores: (1) Nodes that are highly connected to other nodes, (2) Nodes are positioned between different groups of nodes. The lines represent the link between two different nodes.
Author Statistics
The results of the analysis showed that there were many researchers working in the field of depression over the past 16 years, and 63 of the authors published at least 30 articles related to depression. Table 4 lists the 15 authors with the highest number of articles published. It includes the rank of the number of articles published, author, country, number of articles published in depression-related studies, total number of articles included in Web of Science, total number of citations, average number of citations, and H-index. According to the statistics, seven of the top 15 authors are from USA, three from the Netherlands, one from Canada, one from Australia, one from New Zealand, one from Italy, and one from Germany. From this, it can be seen that these productive authors are from developed countries, thus it can be inferred that developed countries have a better research environment, more advanced research technology and more abundant research funding. The evaluation indicators in the author co-occurrence network are frequency, betweenness centrality and time of first appearance. The higher the frequency, i.e., the higher the number of collaborative publications, the more collaboration, the higher the information dissemination rate, the three authors with the highest frequency in this author co-occurrence network are MAURIZIO FAVA, BRENDA W. J. H. PENNINX, MADHUKAR H. TRIVEDI; the higher the betweenness centrality, i.e., the closer the relationship with other authors, the more collaboration, the higher the information dissemination rate, the three authors with the highest betweenness centrality are the three authors with the highest betweenness centrality are MICHAEL E. THASE, A. JOHN RUSH; the time of first appearance, i.e., the longer the influence generated by the author's research, the higher the information dissemination rate; in addition, the impact factor and citations can also reflect the information dissemination efficiency of the authors.
The top 15 authors in network of co-authorship, 2004–2019.
BC, betweenness centrality; TP, total publications; AP, publications in all areas; DP (%), the ratio of the publications about depression in 2004–2019 to the publications about all areas in all times; TC, total citation; CPP (%), citations per publication .
The timezone view ( Figure 5 ) in the author co-occurrence network clearly shows the updates and interactions of author collaborations, for example. All nodes are positioned in a two-dimensional coordinate with the horizontal axis of time, and according to the time of first posting, the nodes are set in different time zones, and their positions are sequentially upward with the time axis, showing a left-to-right, bottom-up knowledge evolution diagram. The time period 2004–2019 is divided into 16 time zones, one for each year, and each circle in the figure represents an author, and the time zone in which the circle appears is the year when the author first published an article in the data set of this study. The closer the color, the warmer the color, the closer the time, the colder the color, the older the era, the thickness of an annual circle, and the number of articles within the corresponding time division is proportional, the dominant color can reflect the relative concentration of the emergence time, the nodes appear in the annual circle of the red annual circle, that is, on behalf of the hot spot, the frequency of being cited was or is still increasing sharply. Nodes with purple outer circles are nodes with high betweenness centrality. The time zone view demonstrates the growth of author collaboration in the field, and it can be found from the graph that the number of author collaborations increases over time, and the frequency of publications in the author collaboration network is high; observe that the thickness of the warm annual rings in the graph is much greater than the thickness of the cold annual rings, which represents the increase of collaboration in time; there are many authors in all time zones, which indicates that there are many research collaborations and achievements in the field, and the field is in a period of collaborative prosperity. The linkage relationship between the sub-time-periods can be seen by the linkage relationship between the time periods, and it can be found from the figure that there are many linkages in the field in all time periods, which indicates that the author collaboration in the field of depression research is strong.

Timezone view of the author's co-existing network in depression, 2004–2019. The circle represents the author, the time zone in which the circle appears is the year in which the author first published in this study dataset, the radius of the circle represents the frequency of appearance, the color represents the different posting times, the lines represent the connections between authors, and the time zone diagram shows the evolution of author collaboration.
Institutional Statistics
Table 5 lists the top 15 research institutions in network of co-authors' institutions. These include 10 American research institutions, two Netherlands research institutions, one UK research institution, one Canadian research institution and one Australian research institution, all of which, according to the statistics, are from developed countries. Of these influential research institutions, 66.7% are from USA. Figure 6 shows the collaborative network with these influential research institutions as nodes. Kings Coll London (0.2), Univ Michigan (0.17), Univ Toronto (0.15), Stanford Univ (0.14), Univ Penn (0.14), Univ Pittsburgh (0.14), Univ Melbourne (0.12), Virginia Commonwealth Univ (0.12), Columbia Univ (0.1), Duke Univ (0.1), Massachusetts Gen Hosp (0.1), Vrije Univ Amsterdam (0.1), with betweenness centrality >0.1. Kings Coll London has a central place in this collaborative network and is influential in the field of depression research. Table 6 lists the 15 institutions with the strong burst strength. The top 3 institutions are all from USA. Univ Copenhagen, Univ Illinois, Harvard Med Sch, Boston Univ, Univ Adelaide, Heidelberg Univ, Univ New South Wales, and Icahn Sch Med Mt Sinai have had strong burst strength in recent years. It suggests that these institutions may have made a greater contribution to the field of depression over the course of this year and more attention could be paid to their research.
The top 15 institutions in network of co-authors' institutions, 2004–2019.
TP, total publications; BC, betweenness centrality .

Prominent institutions involved in depression, 2004–2019. The betweenness centrality of a node in the network measures the importance of the position of the node in the network. Two types of nodes may have high betweenness centrality scores: (1) Nodes that are highly connected to other nodes, (2) Nodes are positioned between different groups of nodes. The lines represent the link between two different nodes.
The top 15 institutions with the strongest citation bursts, 2004–2019.
Burst denote the citation burst strength; blue thin lines denote the whole period of 2004962019, which provide a useful means to trace the development of research focus; the location and length of red thick lines denote the start and end time during the whole period of the bursts and how long the burst lasts .
Summing up the above analysis, it can be seen that the research institutions in USA are at the center of the depression research field, are at the top of the world in terms of quantity and quality of research, and are showing continuous growth in vitality. Research institutions in USA, as pioneers among all research institutions, lead and drive the development of depression research and play an important role in cutting-edge research in the field of depression.
Article Citations
Table 7 lists the 16 articles that have been cited more than 1,000 times within the statistical range of this paper from 2004 to 2019. As can be seen from the table, the most cited article was written by Dowlati et al. from Canada and published in BIOLOGICAL PSYCHIATRY 2010, which was cited 2,556 times. In addition, 11 of these 16 highly cited articles were from the USA. Notably, two articles by Kroenke, K as first author appear in this list, ranked 7th and 11th, respectively. In addition, there are three articles from Canada, one article from Switzerland, and one article from the UK. And interestingly, all of these countries are developed countries. It can be reflected that developed countries have ample research experience and high quality of research in the field of depression research. On the other hand, it also reflects that depression is a key concern in developed countries. These highly cited articles provide useful information to many researchers and are of high academic and exploratory value.
The top 15 frequency cited articles, 2004–2019.
TP, total publications (citations) .
Research Hotspots Ang Frontiers
Keyword analysis.
The keyword analysis of depression yielded the 25 most frequent keywords in Table 8 and the keyword co-occurrence network in Figure 7 . Also, the data from this study were detected by burst, the 25 keywords with the strongest burst strength were obtained in Table 9 . These results bring out the popular and cutting-edge research directions in the field clearly.
Top 25 frequent keywords in the period of 2004–2019.
Count, number of times the article has been cited; BC, betweenness centrality .

Keyword co-occurrence network in depression, 2004–2019.
Top 25 keywords with strongest citation bursts in the period of 2004–2019.
Burst denote the citation burst strength; blue thin lines denote the whole period of 2004–2019, which provide a useful means to trace the development of research focus; the location and length of red thick lines denote the start and end time during the whole period of the bursts and how long the burst lasts .
The articles on depression during 2004–2019 were analyzed in 1-year time slices, and the top 25 keywords with the highest frequency of occurrence were selected from each slice to obtain the keyword network shown in Table 8 . The top 25 keywords with the highest frequencies were: symptom, disorder, major depression, prevalence, meta-analysis, anxiety, risk, scale, association, quality of life, health, risk factor, stress, validity, validation, mental health, women, double blind, brain, population, disease, impact, primary care, mood, and efficacy. High-frequency nodes respond to popular keywords and are an important basis for the field of depression research.
Figure 7 shows the co-occurrence network mapping of keywords regarding depression research. Each circle in the figure is a node representing a keyword, and the greater the betweenness centrality, the more critical the position of the node in the network. The top 10 keywords in terms of betweenness centrality are: symptom (0.6), major depression (0.28), prevalence (0.27), disorder (0.25), double blind (0.18), risk factor (0.12), stress (0.11), children (0.1), schizophrenia (0.1), and expression (0.1). Nodes with high betweenness centrality reflect that the keyword forms a co-occurrence relationship with multiple other keywords in the domain. A higher betweenness centrality indicates that it is more related to other keywords, and therefore, the node plays an important role in the study. Relatively speaking, these nodes represent the main research directions in the field of depression; they are also the key research directions in this period, and to a certain extent, represent the research hotspots in this period.
Burst detection was performed on the keywords, and the 25 keywords with the strongest strength were extracted, as shown in Table 9 . These keywords contain: fluoxetine, community, follow up, illness, psychiatric disorder, dementia, trial, placebo, disability, serotonin reuptake inhibitor, myocardial infarction, hospital anxiety, antidepressant treatment, late life depression, United States, epidemiology, major depression, model, severity, adolescent, people, prefrontal cortex, management, meta-analysis, and expression. The keywords that burst earlier include fluoxetine (2004), community (2004), follow up (2004), illness (2004), and psychiatric disorder (2004), are keywords that imply that researchers focused on themes early in the field of depression. As researchers continue to explore, the study of depression is changing day by day, and the keywords that have burst in recent years are people (2015), prefrontal cortex (2016), management (2016), meta-analysis (2017), and expression (2017). Reflecting the fact that depression research in recent years has mainly focused on human subjects, the focus has been on the characterization of populations with depression onset. The relationship between depression and the brain has aroused the curiosity of researchers, what exactly are the causes that trigger depression and what are the effects of depression for the manifestation of depression have caused a wide range of discussions in the research community, and the topics related to it have become the most popular studies and have been the focus of research in recent years. All of these research areas showed considerable growth, indicating that research into this area is gaining traction, suggesting that it is becoming a future research priority. The keywords with the strongest burst strength are fluoxetine (111.2), community (110.08), antidepressant treatment (94.28), severity (88.35), meta-analysis (86.42), people (85.33), and follow up (84.46). The rapid growth of research based on these keywords indicates that these topics are the most promising and interesting. The keywords that has been around the longest burst are follow up (2004–2013), model (2013–2019), hospital anxiety (2008–2013), severity (2014–2019), and psychiatric disorder (2004–2008), researchers have invested a lot of research time in these research directions, making many research results, and responding to the exploratory value and significance of research on these topics. At the same time, the longer duration of burst also proves that these research directions have research potential and important value.
Research Hotspots
Hotspots must mainly have the characteristics of high frequency, high betweenness centrality, strong burst, and time of emergence can be used as secondary evaluation indicators. The higher the number of occurrences, the higher the degree of popularity and attention. The higher betweenness centrality means the greater the influence and the higher the importance. Nodes with strong burst usually represent key shift nodes and need to be focused on. The time can be dynamically adjusted according to the target time horizon of the analysis. Thus, based on the results of statistical analysis, it is clear that the research hotspots in the field of depression can be divided into four main areas: etiology (external factors, internal factors), impact (quality of life, disease symptoms, co-morbid symptoms), treatment (interventions, drug development, care modalities), and assessment (population, size, symptoms, duration of disease, morbidity, mortality, effectiveness).
Risk factors for depression include a family history of depression, early life abuse and neglect, and female sexuality and recent life stressors. Physical illnesses also increase the risk of depression, particularly increasing the prevalence associated with metabolic (e.g., cardiovascular disease) and autoimmune disorders.
Research on the etiology of depression can be divided into internal and external factors. In recent years, researchers have increasingly focused on the impact of external factors on depression. Depression is influenced by environmental factors related to social issues, such as childhood experiences, social interactions, and lifestyles. Adverse childhood experiences are risk factors for depression and anxiety in adolescence ( 37 ) and are a common pathway to depression in adults ( 38 ). Poor interpersonal relationships with classmates, family, teachers, and friends increase the prevalence of depression in adolescents ( 39 ). Related studies assessed three important, specific indicators of the self-esteem domain: social confidence, academic ability, and appearance ( 40 ). The results suggest that these three dimensions of self-esteem are key risk factors for increased depressive symptoms in Chinese adolescents. The vulnerability model ( 41 ) suggests that low self-esteem is a causal risk factor for depression, and low self-esteem is thought to be one of the main causes of the onset and progression of depression, with individuals who exhibit low self-esteem being more likely to develop social anxiety and social withdrawal, and thus having a sense of isolation ( 42 ), which in turn leads to subsequent depression. Loneliness predicts depression in adolescents. Individuals with high levels of loneliness experience more stress and tension from psychological and physical sources in their daily lives, which, combined with insufficient care from society, can lead to depression ( 43 ). A mechanism of association exists between life events and mood disorders, with negative life events being directly associated with depressive symptoms ( 44 ). In a cross-sectional study conducted in Shanghai, the prevalence of depression was higher among people who worked longer hours, and daily lifestyle greatly influenced the prevalence of depression ( 45 ). A number of studies in recent years have presented a number of interesting ideas, and they suggest that depression is related to different environmental factors, such as temperature, sunlight hours, and air pollution. Environmental factors have been associated with suicidal behavior. Traffic noise is a variable that triggers depression and is associated with personality disorders such as depression ( 46 ). The harmful effects of air pollution on mental health, inhalation of air pollutants can trigger neuroinflammation and oxidative stress and induce dopaminergic neurotoxicity. A study showed that depression was associated with an increase in ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) ( 47 ).
Increased inflammation is a feature of many diseases and even systemic disorders, such as some autoimmune diseases [e.g., type 1 diabetes ( 48 ) or rheumatoid arthritis ( 49 )] and infectious diseases [e.g., hepatitis and sepsis ( 50 )], are associated with an inflammatory response and have been found to increase the risk of depression. A growing body of evidence supports a bidirectional association between depression and inflammatory processes, with stressors and pathogens leading to excessive or prolonged inflammatory responses when combined with predisposing factors (e.g., childhood adversity and modifying factors such as obesity). The resulting illnesses (e.g., pain, sleep disorders), depressive symptoms, and negative health (e.g., poor diet, sedentary lifestyle) may act as mediating pathways leading to inflammation and depression. In terms of mechanistic pathways, cytokines induce depression by affecting different mood-related processes. Elevated inflammatory signals can dysregulate the metabolism of neurotransmitters, damaging neurons, and thus altering neural activity in the brain. In addition cytokines can modulate depression by regulating hormone levels. Inflammation can have different effects on different populations depending on individual physiology, and even lower levels of inflammation may have a depressive effect on vulnerable individuals. This may be due to lower parasympathetic activity, poorer sensitivity to glucocorticoid inhibitory feedback, a greater response to social threat in the anterior oral cortex or amygdala and a smaller hippocampus. Indeed, these are all factors associated with major depression that can affect the sensitivity to the inhibitory consequences of inflammatory stimuli.
Depression triggers many somatization symptoms, which can manifest as insomnia, menopausal syndrome, cardiovascular problems, pain, and other somatic symptoms. There is a link between sleep deprivation and depression, with insomnia being a trigger and maintenance of depression, and more severe insomnia and chronic symptoms predicting more severe depression. Major depression is considered to be an independent risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease and a predictor of cardiovascular events ( 51 ). Patients with depression are extremely sensitive to pain and have increased pain perception ( 52 ) and is associated with an increased risk of suicide ( 53 , 54 ), and generally the symptoms of these pains are not relieved by medication.
Studies have shown that depression triggers an inflammatory response, promoting an increase in cytokines in response to stressors vs. pathogens. For example, mild depressive symptoms have been associated with an amplified and prolonged inflammatory response ( 55 , 56 ) following influenza vaccination in older adults and pregnant women. Among women who have recently given birth, those with a lifetime history of major depression have greater increases in both serum IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptors after delivery than women without a history of depression ( 57 ). Pro-inflammatory agents, such as interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha), for specific somatization disorders [e.g., hepatitis C or malignant melanoma ( 58 , 59 )], although effective for somatic disorders, pro-inflammatory therapy often leads to psychiatric side effects. Up to 80% of patients treated with IFN-α have been reported to suffer from mild to moderate depressive symptoms.
Clinical trials have shown better antidepressant treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs compared to placebo, either as monotherapy ( 60 , 61 ) or as an add-on treatment ( 62 – 65 ) to antidepressants ( 66 , 67 ). However, findings like whether NSAIDs can be safely used in combination with antidepressants are controversial. Patients with depression often suffer from somatic co-morbidities, which must be included in the benefit/risk assessment. It is important to consider the type of medication, duration of treatment, and dose, and always balance the potential treatment effect with the risk of adverse events in individual patients. Depression, childhood adversity, stressors, and diet all affect the gut microbiota and promote gut permeability, another pathway that enhances the inflammatory response, and effective depression treatment may have profound effects on mood, inflammation, and health. Early in life gut flora colonization is associated with hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activation and affects the enteric nervous system, which is associated with the risk of major depression, gut flora dysbiosis leads to the onset of TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses, and pro-inflammatory factors are closely associated with depression. Clinical studies have shown that in the gut flora of depressed patients, pro-inflammatory bacteria such as Enterobacteriaceae and Desulfovibrio are enriched, while short-chain fatty acid producing bacteria are reduced, and some of these bacterial taxa may transmit peripheral inflammation into the brain via the brain-gut axis ( 68 ). In addition, gut flora can affect the immune system by modulating neurotransmitters (5-hydroxytryptamine, gamma-aminobutyric acid, norepinephrine, etc.), which in turn can influence the development of depression ( 69 ). Therefore, antidepressant drugs targeting gut flora are a future research direction, and diet can have a significant impact on mood by regulating gut flora.
As the molecular basis of clinical depression remains unclear, and treatments and therapeutic effects are limited and associated with side effects, researchers have worked to discover new treatment modalities for depression. High-amplitude low-frequency musical impulse stimulation as an additional treatment modality seems to produce beneficial effects ( 70 ). Studies have found electroconvulsive therapy to be one of the most effective antidepressant treatment therapies ( 71 ). Physical exercise can promote molecular changes that lead to a shift from a chronic pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state in the peripheral and central nervous system ( 72 ). Aromatherapy is widely used in the treatment of central nervous system disorders ( 73 ). By activating the parasympathetic nervous system, qigong can be effective in reducing depression ( 74 ). The exploration of these new treatment modalities provides more reference options for the treatment of depression.
Large-scale assessments of depression have found that the probability of developing depression varies across populations. Depression affects some specific populations more significantly, for example: adolescents, mothers, and older adults. Depression is one of the disorders that predispose to adolescence, and depression is associated with an increased risk of suicide among college students ( 75 ). Many women develop depression after childbirth. Depression that develops after childbirth is one of the most common complications for women in the postpartum period ( 76 ). The health of children born to mothers who suffer from postpartum depression can also be adversely affected ( 77 ). Depression can cause many symptoms within the central nervous system, especially in the elderly population ( 78 ).
Furthermore, one of the most consistent findings of the association between inflammation and depression is the elevated levels of peripheral pro-inflammatory markers in depressed individuals, and peripheral pro-inflammatory marker levels can also be used as a basis for the assessment of depressed patients. Studies have shown that the following pro-inflammatory markers have been found to be at increased levels in depressed individuals: CRP ( 79 , 80 ), IL-6 ( 22 , 79 , 81 , 82 ), TNF–α, and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) ( 79 , 82 ), however, this association is not unidirectional and the subsequent development of depression also increases pro-inflammatory markers ( 82 , 83 ). These biomarkers are of great interest, and depressed patients with increased inflammatory markers may represent a relatively drug-resistant population.
Frontier Analysis
The exploration and analysis of frontier areas of depression were based on the results of the analysis of the previous section on keywords. According to the evaluation index and analysis idea of this study, the frontier research topics need to have the following four characteristics: low to medium frequency, strong burst, high betweenness centrality, and the research direction in recent years. Therefore, combining the results of keyword analysis and these characteristics, it can be found that the frontier research on depression also becomes clear.
Research on Depression Characterized by Psychosexual Disorders
Exploration of biological mechanisms based on depression-associated neurological disorders and analysis of depression from a neurological perspective have always been the focus of research. Activation of neuroinflammatory pathways may contribute to the development of depression ( 84 ). A research model based on the microbial-gut-brain axis facilitates the neurobiology of depression ( 85 ). Some probiotics positively affect the central nervous system due to modulation of neuroinflammation and thus may be able to modulate depression ( 86 ). The combination of environmental issues and the neurobiological study of depression opens new research directions ( 46 ).
Research on Relevant Models of Depression
How to develop a model that meets the purpose of the study determines the outcome of the study and has become the direction that researchers have been exploring in recent years. Martínez et al. ( 87 ) developed a predictive model to assess factors that modify the treatment pathway for postpartum depression. Nie et al. ( 88 ) extended the work on predictive modeling of treatment-resistant depression to establish a predictive model for treatment-resistant depression. Rational modeling methods and behavioral testing facilitate a more comprehensive exploration of depression, with richer studies and more scientifically valid findings.
Research and Characterization of the Depressed Patient Population
Current research on special groups and depression has received much attention. In a study of a group of children, 4% were found to suffer from depression ( 89 ). The diagnosis and treatment of mental health disorders is an important component of pediatric care. Second, some studies of populations with distinct characteristics have been based primarily on female populations. Maternal perinatal depression is also a common mental disorder with a prevalence of over 10% ( 90 ). In addition, geriatric depression is a chronic and specific disorder ( 91 ). Studies based on these populations highlight the characteristics of the disorder more directly than large-scale population explorations and are useful for conducting extended explorations from specific to generalized.
Somatic Comorbidities Associated With Depression
Depression often accompanies the onset and development of many other disorders, making the study of physical comorbidities associated with depression a new landing place for depression research. Depression is a complication of many neurological or psychopathological disorders. Depression is a common co-morbidity of glioblastoma multiforme ( 92 ). Depression is an important disorder associated with stroke ( 93 ). Chronic liver disease is associated with depression ( 94 ). The link between depressive and anxiety states and cancer has been well-documented ( 95 ). In conclusion, depression is associated with an increased risk of lung, oral, prostate, and skin cancers, an increased risk of cancer-specific death from lung, bladder, breast, colorectal, hematopoietic system, kidney, and prostate cancers, and an increased risk of all-cause mortality in lung cancer patients. The early detection and effective intervention of depression and its complications has public health and clinical implications.
Research on Mechanisms of Depression
Research based on the mechanisms of depression includes the study of disease pathogenesis, the study of drug action mechanisms, and the study of disease treatment mechanisms. Research on the pathogenesis of depression has focused more on the study of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Social pressure can change the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis ( 96 ). Studies on the mechanism of action of drugs are mostly based on their effects on the central nervous system. The antidepressant effects of Tanshinone IIA are mediated by the ERK-CREB-BDNF pathway in the hippocampus of mice ( 97 ). Research on the mechanisms of depression treatment has also centered on the central nervous system. It has been shown that the vagus nerve can transmit signals to the brain that can lead to a reduction in depressive behavior ( 98 ).
In this study, based on the 2004–2019 time period, this wealth of data is effectively integrated through data analysis and processing to reproduce the research process in a particular field and to co-present global trends in homogenous fields while organizing past research.
Journals that have made outstanding contributions in this field include ARCH GEN PSYCHIAT, J AFFECT DISORDERS and AM J PSYCHIAT. PSYCHIATRY, NEUROSCIENCES & NEUROLOGY and CLINICAL NEUROLOGY are the three most popular categories. The three researchers with the highest number of articles were MAURIZIO FAVA (USA), BRENDA W. J. H. PENNINX (NETHERLANDS) and MADHUKAR H TRIVEDI (USA). Univ Pittsburgh (USA), Kings Coll London (UK) and Harvard Univ (USA) are three of the most productive and influential research institutions. A Meta-Analysis of Cytokines in Major Depression, Evaluation of outcomes with citalopram for depression using measurement-based care in STAR*D: Implications for clinical practice and Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression are key articles. Through keyword analysis, a distribution network centered on depression was formed. Although there are good trends in the research on depression, there are still many directions to be explored in depth. Some recommendations regarding depression are as follows.
(1) The prevention of depression can be considered by focusing on treating external factors and guiding the individual.
Faced with the rising incidence of depression worldwide and the difficulty of treating depression, researchers can think more about how to prevent the occurrence of depression. Depressed moods are often the result of stress, not only social pressures on the individual, but also environmental pressures in the developmental process, which in turn have an unhealthy relationship with the body and increase the likelihood of depression. The correlation between external factors and depression is less well-studied, but the control of external factors may be more effective in the short term than in the long term, and may be guided by self-adjustment to avoid major depressive disorder.
(2) The measurement and evaluation of the degree of depression should be developed in the direction of precision.
In the course of research, it has been found that the Depression Rating Scale is mostly used for the detection and evaluation of depression. This kind of assessment is more objective, but it still lacks accuracy, and the research on measurement techniques and methods is less, which is still at a low stage. Patients with depression usually have a variety of causes, conditions, and duration of illness that determine the degree of depression. Therefore, whether these scales can truly accurately measure depression in depressed patients needs further consideration. Accurate measurement is an important basis for evidence-based treatment of depression, and thus how to achieve accurate measurement of depression is a research direction that researchers can move toward.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for further research to address these issues.
A systematic analysis of research in the field of depression in this study concludes that the distribution of countries, journals, categories, authors, institutions, and citations may help researchers and research institutions to establish closer collaboration, develop appropriate publication plans, grasp research hotspots, identify valuable research ideas, understand current emerging research, and determine research directions. In addition, there are still some limitations that can be overcome in future work. First, due to the lack of author and address information in older published articles, it may not be possible to accurately calculate their collaboration; second, although the data scope of this paper is limited to the Web of Science, it can adequately meet our objectives.
Data Availability Statement
Author contributions.
HW conceived and designed the analysis, collected the data, performed the analysis, and wrote the paper. XT, XW, and YW conceived and designed the analysis. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 81973495.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This essay analyzes a clinical research article "Improving care for depression in obstetrics and gynecology: A randomized controlled trial" by Melville et al. Postpartum Depression, Prevention and Treatment. Postpartum depression is a common psychiatric condition in women of the childbearing age.
The possible causes of depression are many and not yet well understood. However, it most likely results from an interplay of genetic vulnerability and environmental factors. Your depression research paper could explore one or more of these causes and reference the latest research on the topic. For instance, how does an imbalance in brain ...
All of our topics are interesting, so you won't get bored while writing your paper. You can use them for free - simply choose one and start writing! Table of contents hide. 1 Depression research topics for sociology papers. 2 Depression topics for history papers. 3 Depression research paper topics for health care papers.
1. Our Experts. can deliver a custom essay. for a mere 11.00 9.35/page 304 qualified. specialists online Learn more. Depression is undeniably one of the most prevalent mental health conditions globally, affecting approximately 5% of adults worldwide. It often manifests as intense feelings of hopelessness, sadness, and a loss of interest in ...
Its severe form, major depression is classified as a mood disorder. Latest Research and Reviews Genetic and phenotypic similarity across major psychiatric disorders: a systematic review and ...
As shown in Fig. Fig.1E, 1 E, the hot research topics in depression are as follows: depression management in primary care, interventions to prevent depression, ... The USA ranks first in the number of depression-related patent applications, followed by China. The largest number of patents related to depression is the development of ...
In this paper, we describe and present the vast, fragmented, and complex literature related to this topic. This review may be used to guide practice, public health efforts, policy, and research related to mental health and, specifically, depression. ... This paper discusses key areas in depression research; however, an exhaustive discussion of ...
CiteSpace processed the data to obtain 41,408 valid records, covering all depression-related research articles for the period 2004-2019, and used this as the basis for analysis. ... These journals included research topics related to neuroscience, psychiatry, neurology, and psychology. The journal with betweenness centrality size in the top 1 ...
Molecular Psychiatry - Advances in depression research: second special issue, 2020, with highlights on biological mechanisms, clinical features, co-morbidity, genetics, imaging, and treatment
This special depression issue has three articles by the late Nobel laureate Paul Greengard. In the first of those papers, Sagi et al. focus on parvalbumin interneurons, which are a major class of ...
In this essay, we have briefly reviewed a selected range of key discoveries that neuroscientific research has made on the topic of depressive disorders in the last decades. We have shown that depression has been linked to a wide range of abnormalities on different levels of neuroscientific description ranging from molecules and cells to brain ...
Mental Health Research Paper Topics. Depression and mental health are closely related, so why not pick one of our awesome mental health research paper topics: The brain chemistry behind depression. Changes in brain activity during a depressive episode. Sleep problems caused by depression.
Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder are examples of such confusion. Adult Depression and Anxiety as a Complex Problem. Psychology essay sample: The presence of a physical disability is a major factor in developing a mental health condition due to the increase in dissatisfaction and the presence of multiple irritants.
Here are a few ideas to get you started. The impact of genetics on the susceptibility to depression. Efficacy of antidepressants vs. cognitive behavioural therapy. The role of gut microbiota in mood regulation. Cultural variations in the experience and diagnosis of bipolar disorder.
The depression rate recorded between January and May 2020 — after the COVID-19 outbreak had begun in each country — ranged from 7% to 48%, with an average of about 25%. Even the lowest rates ...
Depression (also known as major depression, major depressive disorder, or clinical depression) is a common but serious mood disorder. It causes severe symptoms that affect how a person feels, thinks, and handles daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. To be diagnosed with depression, the symptoms must be present for at least 2 ...
This article explores effective and valid therapies for treating depression by addressing current and future research topics for different treatment categories. ... in the specific case of vortioxetine, have particular benefits in depression-related cognitive impairment. Indeed, vortioxetine is a very recent antidepressant with a multimodal ...
If you're one of more than 17 million adults or 3.2 million teens in the United States with major depression, you may know that treatment often falls short. The latest research on this common ...
The Research Domain Criteria framework (RDoC) was created in 2010 by the National Institute of Mental Health. The framework encourages researchers to examine functional processes that are implemented by the brain on a continuum from normal to abnormal. This way of researching mental disorders can help overcome inherent limitations in using all ...
As shown in Fig. 1E, the hot research topics in depression are as follows: depression management in primary care, interventions to prevent depression, ... The top 10 countries applying for patents related to depression are shown in Fig. 2B. The USA ranks first in the number of depression-related patent applications, followed by China. ...
Depression — also known as major depressive disorder or clinical depression — is a common but serious mood disorder that can interfere with how people feel, think, and handle daily activities, such as sleeping, eating, or working. Although sadness can be a symptom of depression, it does not characterize the disorder.
Anxiety and depression are associated with an increased incidence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), according to a study published online March 19 in Scientific Reports. Topics Conditions
Read the latest Research articles in Depression from Scientific Reports. ... The impact of mental health on health-related quality of life in patients with NF2-related Schwannomatosis.
Research suggests about half the people admitted to hospital after a head injury report major depression in the year after the accident, a rate 10 times higher than the general population.
Extensive studies have led to a variety of hypotheses for the molecular basis of depression and related mood disorders, but a definite pathogenic mechanism has yet to be defined. The monoamine hypothesis, in conjunction with the efficacy of antidepressants targeting monoamine systems, has long been the central topic of depression research.
CiteSpace processed the data to obtain 41,408 valid records, covering all depression-related research articles for the period 2004-2019, and used this as the basis for analysis. ... These journals included research topics related to neuroscience, psychiatry, neurology, and psychology. The journal with betweenness centrality size in the top 1 ...
1. What is the decision or change (e.g. clinical topic, practice guideline, system design, delivery of care) you are facing or struggling with where a summary of the evidence would be helpful? This proposal is to conduct an integrative meta-analysis of the change processes research in individual psychotherapy treatment for adults with depression to be used as part of updating the American ...