

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, should college athletes be paid an expert debate analysis.
Extracurriculars

The argumentative essay is one of the most frequently assigned types of essays in both high school and college writing-based courses. Instructors often ask students to write argumentative essays over topics that have “real-world relevance.” The question, “Should college athletes be paid?” is one of these real-world relevant topics that can make a great essay subject!
In this article, we’ll give you all the tools you need to write a solid essay arguing why college athletes should be paid and why college athletes should not be paid. We'll provide:
- An explanation of the NCAA and what role it plays in the lives of student athletes
- A summary of the pro side of the argument that's in favor of college athletes being paid
- A summary of the con side of the argument that believes college athletes shouldn't be paid
- Five tips that will help you write an argumentative essay that answers the question "Should college athletes be paid?"

The NCAA is the organization that oversees and regulates collegiate athletics.
What Is the NCAA?
In order to understand the context surrounding the question, “Should student athletes be paid?”, you have to understand what the NCAA is and how it relates to student-athletes.
NCAA stands for the National Collegiate Athletic Association (but people usually just call it the “N-C-double-A”). The NCAA is a nonprofit organization that serves as the national governing body for collegiate athletics.
The NCAA specifically regulates collegiate student athletes at the organization’s 1,098 “member schools.” Student-athletes at these member schools are required to follow the rules set by the NCAA for their academic performance and progress while in college and playing sports. Additionally, the NCAA sets the rules for each of their recognized sports to ensure everyone is playing by the same rules. ( They also change these rules occasionally, which can be pretty controversial! )
The NCAA website states that the organization is “dedicated to the well-being and lifelong success of college athletes” and prioritizes their well-being in academics, on the field, and in life beyond college sports. That means the NCAA sets some pretty strict guidelines about what their athletes can and can't do. And of course, right now, college athletes can't be paid for playing their sport.
As it stands, NCAA athletes are allowed to receive scholarships that cover their college tuition and related school expenses. But historically, they haven't been allowed to receive additional compensation. That meant athletes couldn't receive direct payment for their participation in sports in any form, including endorsement deals, product sponsorships, or gifts.
Athletes who violated the NCAA’s rules about compensation could be suspended from participating in college sports or kicked out of their athletic program altogether.

The Problem: Should College Athletes Be Paid?
You know now that one of the most well-known functions of the NCAA is regulating and limiting the compensation that student-athletes are able to receive. While many people might not question this policy, the question of why college athletes should be paid or shouldn't be paid has actually been a hot-button topic for several years.
The fact that people keep asking the question, “Should student athletes be paid?” indicates that there’s some heat out there surrounding this topic. The issue is frequently debated on sports talk shows , in the news media , and on social media . Most recently, the topic re-emerged in public discourse in the U.S. because of legislation that was passed by the state of California in 2019.
In September 2019, California governor Gavin Newsome signed a law that allowed college athletes in California to strike endorsement deals. An endorsement deal allows athletes to be paid for endorsing a product, like wearing a specific brand of shoes or appearing in an advertisement for a product.
In other words, endorsement deals allow athletes to receive compensation from companies and organizations because of their athletic talent. That means Governor Newsome’s bill explicitly contradicts the NCAA’s rules and regulations for financial compensation for student-athletes at member schools.
But why would Governor Newsome go against the NCAA? Here’s why: the California governor believes that it's unethical for the NCAA to make money based on the unpaid labor of its athletes . And the NCAA definitely makes money: each year, the NCAA upwards of a billion dollars in revenue as a result of its student-athlete talent, but the organization bans those same athletes from earning any money for their talent themselves. With the new California law, athletes would be able to book sponsorships and use agents to earn money, if they choose to do so.
The NCAA’s initial response to California’s new law was to push back hard. But after more states introduced similar legislation , the NCAA changed its tune. In October 2019, the NCAA pledged to pass new regulations when the board voted unanimously to allow student athletes to receive compensation for use of their name, image, and likeness.
Simply put: student athletes can now get paid through endorsement deals.
In the midst of new state legislation and the NCAA’s response, the ongoing debate about paying college athletes has returned to the spotlight. Everyone from politicians, to sports analysts, to college students are arguing about it. There are strong opinions on both sides of the issue, so we’ll look at how some of those opinions can serve as key points in an argumentative essay.

Let's take a look at the arguments in favor of paying student athletes!
The Pros: Why College Athletes Should B e Paid
Since the argument about whether college athletes should be paid has gotten a lot of public attention, there are some lines of reasoning that are frequently called upon to support the claim that college athletes should be paid.
In this section, we'll look at the three biggest arguments in favor of why college athletes should be paid. We'll also give you some ideas on how you can support these arguments in an argumentative essay.
Argument 1: The Talent Should Receive Some of the Profits
This argument on why college athletes should be paid is probably the one people cite the most. It’s also the easiest one to support with facts and evidence.
Essentially, this argument states that the NCAA makes millions of dollars because people pay to watch college athletes compete, and it isn’t fair that the athletes don't get a share of the profits
Without the student athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t earn over a billion dollars in annual revenue , and college and university athletic programs wouldn’t receive hundreds of thousands of dollars from the NCAA each year. In fact, without student athletes, the NCAA wouldn’t exist at all.
Because student athletes are the ones who generate all this revenue, people in favor of paying college athletes argue they deserve to receive some of it back. Otherwise, t he NCAA and other organizations (like media companies, colleges, and universities) are exploiting a bunch of talented young people for their own financial gain.
To support this argument in favor of paying college athletes, you should include specific data and revenue numbers that show how much money the NCAA makes (and what portion of that actually goes to student athletes). For example, they might point out the fact that the schools that make the most money in college sports only spend around 10% of their tens of millions in athletics revenue on scholarships for student-athletes. Analyzing the spending practices of the NCAA and its member institutions could serve as strong evidence to support this argument in a “why college athletes should be paid” essay.

I've you've ever been a college athlete, then you know how hard you have to train in order to compete. It can feel like a part-time job...which is why some people believe athletes should be paid for their work!
Argument 2: College Athletes Don’t Have Time to Work Other Jobs
People sometimes casually refer to being a student-athlete as a “full-time job.” For many student athletes, this is literally true. The demands on a student-athlete’s time are intense. Their days are often scheduled down to the minute, from early in the morning until late at night.
One thing there typically isn’t time for in a student-athlete’s schedule? Working an actual job.
Sports programs can imply that student-athletes should treat their sport like a full-time job as well. This can be problematic for many student-athletes, who may not have any financial resources to cover their education. (Not all NCAA athletes receive full, or even partial, scholarships!) While it may not be expressly forbidden for student-athletes to get a part-time job, the pressure to go all-in for your team while still maintaining your eligibility can be tremendous.
In addition to being a financial burden, the inability to work a real job as a student-athlete can have consequences for their professional future. Other college students get internships or other career-specific experience during college—opportunities that student-athletes rarely have time for. When they graduate, proponents of this stance argue, student-athletes are under-experienced and may face challenges with starting a career outside of the sports world.
Because of these factors, some argue that if people are going to refer to being a student-athlete as a “full-time job,” then student-athletes should be paid for doing that job.
To support an argument of this nature, you can offer real-life examples of a student-athlete’s daily or weekly schedule to show that student-athletes have to treat their sport as a full-time job. For instance, this Twitter thread includes a range of responses from real student-athletes to an NCAA video portraying a rose-colored interpretation of a day in the life of a student-athlete.
Presenting the Twitter thread as one form of evidence in an essay would provide effective support for the claim that college athletes should be paid as if their sport is a “full-time job.” You might also take this stance in order to claim that if student-athletes aren’t getting paid, we must adjust our demands on their time and behavior.
Argument 3: Only Some Student Athletes Should Be Paid
This take on the question, “Should student athletes be paid?” sits in the middle ground between the more extreme stances on the issue. There are those who argue that only the student athletes who are big money-makers for their university and the NCAA should be paid.
The reasoning behind this argument? That’s just how capitalism works. There are always going to be student-athletes who are more talented and who have more media-magnetizing personalities. They’re the ones who are going to be the face of athletic programs, who lead their teams to playoffs and conference victories, and who are approached for endorsement opportunities.
Additionally, some sports don't make money for their schools. Many of these sports fall under Title IX, which states that no one can be excluded from participation in a federally-funded program (including sports) because of their gender or sex. Unfortunately, many of these programs aren't popular with the public , which means they don't make the same revenue as high-dollar sports like football or basketball .
In this line of thinking, since there isn’t realistically enough revenue to pay every single college athlete in every single sport, the ones who generate the most revenue are the only ones who should get a piece of the pie.
To prove this point, you can look at revenue numbers as well. For instance, the womens' basketball team at the University of Louisville lost $3.8 million dollars in revenue during the 2017-2018 season. In fact, the team generated less money than they pay for their coaching staff. In instances like these, you might argue that it makes less sense to pay athletes than it might in other situations (like for University of Alabama football, which rakes in over $110 million dollars a year .)

There are many people who think it's a bad idea to pay college athletes, too. Let's take a look at the opposing arguments.
The Cons: Why College Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid
People also have some pretty strong opinions about why college athletes shouldn't be paid. These arguments can make for a pretty compelling essay, too!
In this section, we'll look at the three biggest arguments against paying college athletes. We'll also talk about how you can support each of these claims in an essay.
Argument 1: College Athletes Already Get Paid
On this side of the fence, the most common reason given for why college athletes should not be paid is that they already get paid: they receive free tuition and, in some cases, additional funding to cover their room, board, and miscellaneous educational expenses.
Proponents of this argument state that free tuition and covered educational expenses is compensation enough for student-athletes. While this money may not go straight into a college athlete's pocket, it's still a valuable resource . Considering most students graduate with nearly $30,000 in student loan debt , an athletic scholarship can have a huge impact when it comes to making college affordable .
Evidence for this argument might look at the financial support that student-athletes receive for their education, and compare those numbers to the financial support that non-athlete students receive for their schooling. You can also cite data that shows the real value of a college tuition at certain schools. For example, student athletes on scholarship at Duke may be "earning" over $200,000 over the course of their collegiate careers.
This argument works to highlight the ways in which student-athletes are compensated in financial and in non-financial ways during college , essentially arguing that the special treatment they often receive during college combined with their tuition-free ride is all the compensation they have earned.

Some people who are against paying athletes believe that compensating athletes will lead to amateur athletes being treated like professionals. Many believe this is unfair and will lead to more exploitation, not less.
Argument 2: Paying College Athletes Would Side-Step the Real Problem
Another argument against paying student athletes is that college sports are not professional sports , and treating student athletes like professionals exploits them and takes away the spirit of amateurism from college sports .
This stance may sound idealistic, but those who take this line of reasoning typically do so with the goal of protecting both student-athletes and the tradition of “amateurism” in college sports. This argument is built on the idea that the current system of college sports is problematic and needs to change, but that paying student-athletes is not the right solution.
Instead, this argument would claim that there is an even better way to fix the corrupt system of NCAA sports than just giving student-athletes a paycheck. To support such an argument, you might turn to the same evidence that’s cited in this NPR interview : the European model of supporting a true minor league system for most sports is effective, so the U.S. should implement a similar model.
In short: creating a minor league can ensure athletes who want a career in their sport get paid, while not putting the burden of paying all collegiate athletes on a university.
Creating and supporting a true professional minor league would allow the students who want to make money playing sports to do so. Universities could then confidently put earned revenue from sports back into the university, and student-athletes wouldn’t view their college sports as the best and only path to a career as a professional athlete. Those interested in playing professionally would be able to pursue this dream through the minor leagues instead, and student athletes could just be student athletes.
The goal of this argument is to sort of achieve a “best of both worlds” solution: with the development and support of a true minor league system, student-athletes would be able to focus on the foremost goal of getting an education, and those who want to get paid for their sport can do so through the minor league. Through this model, student-athletes’ pursuit of their education is protected, and college sports aren’t bogged down in ethical issues and logistical hang-ups.
Argument 3: It Would Be a Logistical Nightmare
This argument against paying student athletes takes a stance on the basis of logistics. Essentially, this argument states that while the current system is flawed, paying student athletes is just going to make the system worse. So until someone can prove that paying collegiate athletes will fix the system, it's better to maintain the status quo.
Formulating an argument around this perspective basically involves presenting the different proposals for how to go about paying college athletes, then poking holes in each proposed approach. Such an argument would probably culminate in stating that the challenges to implementing pay for college athletes are reason enough to abandon the idea altogether.
Here's what we mean. One popular proposed approach to paying college athletes is the notion of “pay-for-play.” In this scenario, all college athletes would receive the same weekly stipend to play their sport .
In this type of argument, you might explain the pay-for-play solution, then pose some questions toward the approach that expose its weaknesses, such as: Where would the money to pay athletes come from? How could you pay athletes who play certain sports, but not others? How would you avoid Title IX violations? Because there are no easy answers to these questions, you could argue that paying college athletes would just create more problems for the world of college sports to deal with.
Posing these difficult questions may persuade a reader that attempting to pay college athletes would cause too many issues and lead them to agree with the stance that college athletes should not be paid.

5 Tips for Writing About Paying College Athletes
If you’re assigned the prompt “Should college athletes be paid," don't panic. There are several steps you can take to write an amazing argumentative essay about the topic! We've broken our advice into five helpful tips that you can use to persuade your readers (and ace your assignment).
Tip 1: Plan Out a Logical Structure for Your Essay
In order to write a logical, well-organized argumentative essay, one of the first things you need to do is plan out a structure for your argument. Using a bare-bones argumentative outline for a “why college athletes should be paid” essay is a good place to start.
Check out our example of an argumentative essay outline for this topic below:
- The thesis statement must communicate the topic of the essay: Whether college athletes should be paid, and
- Convey a position on that topic: That college athletes should/ should not be paid, and
- State a couple of defendable, supportable reasons why college athletes should be paid (or vice versa).
- Support Point #1 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #2 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #3 with evidence
- New body paragraph addressing opposing viewpoints
- Concluding paragraph
This outline does a few things right. First, it makes sure you have a strong thesis statement. Second, it helps you break your argument down into main points (that support your thesis, of course). Lastly, it reminds you that you need to both include evidence and explain your evidence for each of your argumentative points.
While you can go off-book once you start drafting if you feel like you need to, having an outline to start with can help you visualize how many argumentative points you have, how much evidence you need, and where you should insert your own commentary throughout your essay.
Remember: the best argumentative essays are organized ones!
Tip 2: Create a Strong Thesis
T he most important part of the introduction to an argumentative essay claiming that college athletes should/should not be paid is the thesis statement. You can think of a thesis like a backbone: your thesis ties all of your essay parts together so your paper can stand on its own two feet!
So what does a good thesis look like? A solid thesis statement in this type of argumentative essay will convey your stance on the topic (“Should college athletes be paid?”) and present one or more supportable reasons why you’re making this argument.
With these goals in mind, here’s an example of a thesis statement that includes clear reasons that support the stance that college athletes should be paid:
Because the names, image, and talents of college athletes are used for massive financial gain, college athletes should be able to benefit from their athletic career in the same way that their universities do by getting endorsements.
Here's a thesis statement that takes the opposite stance--that college athletes shouldn’t be paid --and includes a reason supporting that stance:
In order to keep college athletics from becoming over-professionalized, compensation for college athletes should be restricted to covering college tuition and related educational expenses.
Both of these sample thesis statements make it clear that your essay is going to be dedicated to making an argument: either that college athletes should be paid, or that college athletes shouldn’t be paid. They both convey some reasons why you’re making this argument that can also be supported with evidence.
Your thesis statement gives your argumentative essay direction . Instead of ranting about why college athletes should/shouldn’t be paid in the remainder of your essay, you’ll find sources that help you explain the specific claim you made in your thesis statement. And a well-organized, adequately supported argument is the kind that readers will find persuasive!
Tip 3: Find Credible Sources That Support Your Thesis
In an argumentative essay, your commentary on the issue you’re arguing about is obviously going to be the most fun part to write. But great essays will cite outside sources and other facts to help substantiate their argumentative points. That's going to involve—you guessed it!—research.
For this particular topic, the issue of whether student athletes should be paid has been widely discussed in the news media (think The New York Times , NPR , or ESPN ).
For example, this data reported by the NCAA shows a breakdown of the gender and racial demographics of member-school administration, coaching staff, and student athletes. These are hard numbers that you could interpret and pair with the well-reasoned arguments of news media writers to support a particular point you’re making in your argument.
Though this may seem like a topic that wouldn’t generate much scholarly research, it’s worth a shot to check your library database for peer-reviewed studies of student athletes’ experiences in college to see if anything related to paying student athletes pops up. Scholarly research is the holy grail of evidence, so try to find relevant articles if you can.
Ultimately, if you can incorporate a mix of mainstream sources, quantitative or statistical evidence, and scholarly, peer-reviewed sources, you’ll be on-track to building an excellent argument in response to the question, “Should student athletes be paid?”

Having multiple argumentative points in your essay helps you support your thesis.
Tip 4: Develop and Support Multiple Points
We’ve reviewed how to write an intro and thesis statement addressing the issue of paying college athletes, so let’s talk next about the meat and potatoes of your argumentative essay: the body paragraphs.
The body paragraphs that are sandwiched between your intro paragraph and concluding paragraph are where you build and explain your argument. Generally speaking, each body paragraph should do the following:
- Start with a topic sentence that presents a point that supports your stance and that can be debated,
- Present summaries, paraphrases, or quotes from credible sources--evidence, in other words--that supports the point stated in the topic sentence, and
- Explain and interpret the evidence presented with your own, original commentary.
In an argumentative essay on why college athletes should be paid, for example, a body paragraph might look like this:
Thesis Statement : College athletes should not be paid because it would be a logistical nightmare for colleges and universities and ultimately cause negative consequences for college sports.
Body Paragraph #1: While the notion of paying college athletes is nice in theory, a major consequence of doing so would be the financial burden this decision would place on individual college sports programs. A recent study cited by the NCAA showed that only about 20 college athletic programs consistently operate in the black at the present time. If the NCAA allows student-athletes at all colleges and universities to be paid, the majority of athletic programs would not even have the funds to afford salaries for their players anyway. This would mean that the select few athletic programs that can afford to pay their athletes’ salaries would easily recruit the most talented players and, thus, have the tools to put together teams that destroy their competition. Though individual athletes would benefit from the NCAA allowing compensation for student-athletes, most athletic programs would suffer, and so would the spirit of healthy competition that college sports are known for.
If you read the example body paragraph above closely, you’ll notice that there’s a topic sentence that supports the claim made in the thesis statement. There’s also evidence given to support the claim made in the topic sentence--a recent study by the NCAA. Following the evidence, the writer interprets the evidence for the reader to show how it supports their opinion.
Following this topic sentence/evidence/explanation structure will help you construct a well-supported and developed argument that shows your readers that you’ve done your research and given your stance a lot of thought. And that's a key step in making sure you get an excellent grade on your essay!
Tip 5: Keep the Reader Thinking
The best argumentative essay conclusions reinterpret your thesis statement based on the evidence and explanations you provided throughout your essay. You would also make it clear why the argument about paying college athletes even matters in the first place.
There are several different approaches you can take to recap your argument and get your reader thinking in your conclusion paragraph. In addition to restating your topic and why it’s important, other effective ways to approach an argumentative essay conclusion could include one or more of the following:
While you don’t want to get too wordy in your conclusion or present new claims that you didn’t bring up in the body of your essay, you can write an effective conclusion and make all of the moves suggested in the bulleted list above.
Here’s an example conclusion for an argumentative essay on paying college athletes using approaches we just talked about:
Though it’s true that scholarships and financial aid are a form of compensation for college athletes, it’s also true that the current system of college sports places a lot of pressure on college athletes to behave like professional athletes in every way except getting paid. Future research should turn its attention to the various inequities within college sports and look at the long-term economic outcomes of these athletes. While college athletes aren't paid right now, that doesn’t necessarily mean that a paycheck is the best solution to the problem. To avoid the possibility of making the college athletics system even worse, people must consider the ramifications of paying college students and ensure that paying athletes doesn't create more harm than good.
This conclusion restates the argument of the essay (that college athletes shouldn't be paid and why), then uses the "Future Research" tactic to make the reader think more deeply about the topic.
If your conclusion sums up your thesis and keeps the reader thinking, you’ll make sure that your essay sticks in your readers' minds.

Should College Athletes Be Paid: Next Steps
Writing an argumentative essay can seem tough, but with a little expert guidance, you'll be well on your way to turning in a great paper . Our complete, expert guide to argumentative essays can give you the extra boost you need to ace your assignment!
Perhaps college athletics isn't your cup of tea. That's okay: there are tons of topics you can write about in an argumentative paper. We've compiled 113 amazing argumentative essay topics so that you're practically guaranteed to find an idea that resonates with you.
If you're not a super confident essay writer, it can be helpful to look at examples of what others have written. Our experts have broken down three real-life argumentative essays to show you what you should and shouldn't do in your own writing.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Pros and Cons
Do you know how to improve your profile for college applications.
See how your profile ranks among thousands of other students using CollegeVine. Calculate your chances at your dream schools and learn what areas you need to improve right now — it only takes 3 minutes and it's 100% free.
Show me what areas I need to improve
What’s Covered:
History of the debate: should college athletes be paid, why college athletes should be paid.
- Why College Athletes Shouldn’t Be Paid
- Where To Get Your Essay Edited For Free
College athletics provide big benefits for many schools: they increase their profile, generate millions of dollars in revenue, and have led to one of the most contentious questions in sports— should college athletes be paid? Like other difficult questions, there are good arguments on both sides of the issue of paying college athletes.
Historically, the debates over paying college athletes have only led to more questions, which is why it’s raged on for more than a century. Perhaps the earliest group to examine the quandary was Andrew Carnegie’s Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching, which produced a mammoth study in 1929 of amateur athletes and the profits they generate for their universities. You don’t have to get past the preface to find questions that feel at home in today’s world:
- “What relation has this astonishing athletic display to the work of an intelligence agency like a university?”
- “How do students, devoted to study, find either the time or the money to stage so costly a performance?”
Many of the questions asked way back in 1929 continue to resurface today, and many of them have eventually ended up seeking answers in court. The first case of note came in the 1950s, when the widow of Fort Lewis football player Ray Dennison took the college all the way to the Colorado Supreme Court in an effort to collect a death benefit after he was killed playing football. She lost the case, but future generations would have more success and have slowly whittled away at arguments against paying athletes.
The most noticeable victory for athletes occurred in 2019, when California Governor, Gavin Newsom, signed legislation effectively allowing college athletes in the state to earn compensation for the use of their likeness, sign endorsement deals, and hire agents to represent them.
The court fights between college athletes and the NCAA continue today—while not exactly about payment, a case regarding whether or not schools can offer athletes tens of thousands of dollars in education benefits such as computers, graduate scholarships, tutoring, study abroad, and internships was heard by the U.S. Supreme Court in March 2021. A decision is expected in June 2021.
There are a number of great reasons to pay college athletes, many of which will not only improve the lives of student-athletes, but also improve the product on the field and in the arena.
College Athletes Deserve to Get Paid
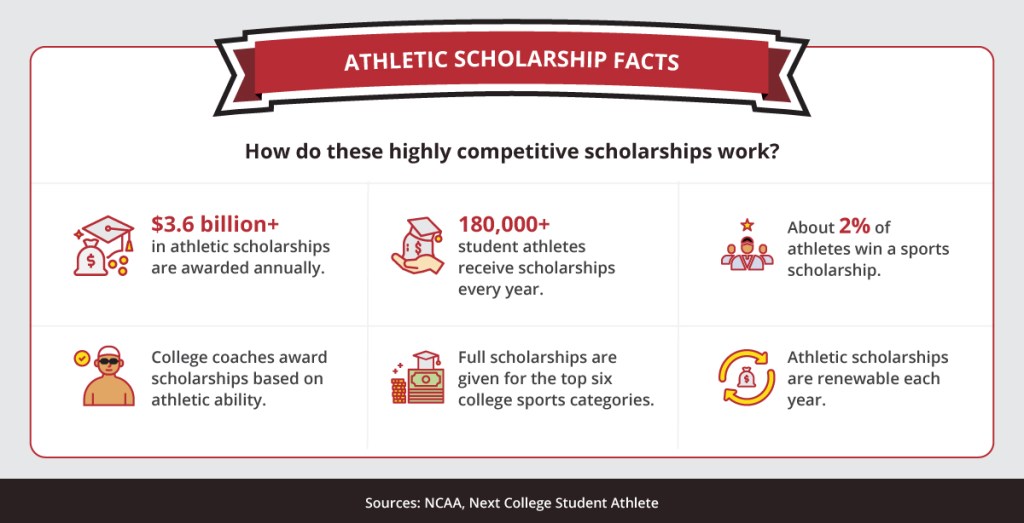
In 2019, the NCAA reported $18.9 billion in total athletics revenue. This money is used to finance a variety of paid positions that support athletics at colleges and universities, including administrators, directors, coaches, and staff, along with other employment less directly tied to sports, such as those in marketing and media. The only people not receiving a paycheck are the stars of the show: the athletes.
A testament to the disparate allocation of funds generated by college sports, of the $18.9 billion in athletics revenue in 2019, $3.6 billion went toward financial aid for student-athletes, and $3.7 billion was used for coaches’ compensation. A February 2020 USA Today article found that the average total pay for Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) college football head coaches in 2020-21 was $2.7 million. The highest-paid college football coach—the University of Alabama’s Nick Saban—earns $9.3 million a year and is the highest-paid public employee in the country. He is not alone, college coaches dominate the list of public employees with the largest salaries.
If there’s money to provide college coaches with lavish seven-figure salaries (especially at public institutions), why shouldn’t there be funds to pay college athletes?
Vital Support for Athletes
A 2011 study published by the National College Players Association (NCPA) found that an overwhelming number of students on full athletics scholarships live below the federal poverty line—85% of athletes who live on campus and 86% athletes who live off-campus. “Full scholarship” itself is a misnomer; the same study found that the average annual scholarship for FBS athletes on “full” scholarships was actually $3,222. Find out more information about athletic scholarships .
Paying student-athletes would help eliminate the need for these student-athletes to take out loans, burden their families for monetary support, or add employment to their already busy schedules. The NCAA limits in-season practice time to 20 hours a week, but a 2008 NCAA report shows that in-season student-athletes commonly spent upward of 30 and 40 hours a week engaged in “athletic activities.”
Encouraged to Stay in College Longer
A report produced by the NCPA and Drexel University estimated the average annual fair market value of big-time college football and men’s basketball players between 2011 and 2015 was $137,357 and $289,031, respectively, and concluded that football players only receive about 17% of their fair market value, while men’s basketball players receive approximately 8% of theirs.
If colleges paid athletes even close to their worth, they would provide an incentive for the athletes to stay in college and earn degrees, rather than leaving college for a paycheck. This would also help keep top talents playing for college teams, improve the level of competition, and potentially lead to even higher revenue. On a side note, this would incentivize athletes to complete their degree, making them more employable after the end of their athletic career.
Limit Corruption
Just because there are rules prohibiting the compensation of college athletes doesn’t mean it doesn’t happen, and over the years there have been numerous scandals. For example, in 2009, six ex-University of Toledo players were indicted in a point-shaving scheme , and in 2010, Reggie Bush returned his Heisman Trophy after allegations that he was given hundreds of thousands of dollars from sports agents while he played for USC.
Paying college athletes will likely not totally eliminate corruption from college sports, but putting athletes in a less-precarious financial position would be a good step toward avoiding external influence, especially when you consider some of the players involved in the University of Toledo point-shaving scandal were paid as little as $500.
It’s a Job (and a Dangerous One)
As mentioned before, college athletes can put in upward of 40 hours a week practicing, training, and competing—being a “student-athlete” is a challenge when you’re devoting full-time hours to athletics. A New York Times study found a 0.20-point difference in average GPA between recruited male athletes and non-athletes. The difference is less pronounced among females, with non-athletes averaging a 3.24 GPA and recruited women athletes at 3.18.
It’s not just the time commitment that playing college athletics puts on student-athletes, it’s the risk to their health. A 2009-2010 CDC report found that more than 210,000 injuries are sustained by NCAA student-athletes each year. Full athletic scholarships are only guaranteed a year at a time, meaning student-athletes are one catastrophic injury away from potentially losing their scholarship. That is to say nothing of the lasting effects of an injury, like head traumas , which made up 7.4% of all injuries in college football players between 2004 and 2009.

Discover your chances at hundreds of schools
Our free chancing engine takes into account your history, background, test scores, and extracurricular activities to show you your real chances of admission—and how to improve them.
Why College Athletes Should Not Be Paid
There are a lot of great reasons why college athletes should be paid, but there are also some compelling reasons why college athletes should not be paid—and why not paying athletes is actually good for both the institutions and athletes.
Compensation Conundrum
One of the most common reasons cited against paying college players is compensation. Will all college athletes get compensated equally? For example, will the star quarterback receive the same amount as the backup catcher on the softball team? A 2014 CNBC article estimated that Andrew Wiggins, a University of Kansas forward (and soon-to-be first-overall draft pick), had a fair market value of around $1.6 million.
Similarly, will compensation take into account talent? Will the All-American point guard get the same amount as the captain of the swim team? In all likelihood, paying college athletes will benefit big-time, revenue-generating sports and hurt less popular sports.
Eliminate Competitive Balance
According to the NCAA , in 2019, the 65 Power Five schools exceeded revenue by $7 million, while all other Division I colleges had a $23 million deficit between expenses and revenue. If college athletes were to get paid, then large, well-funded schools such as those of the Power Five would be best positioned to acquire top talent and gain a competitive advantage.
From a student’s point of view, paying college athletes will alter their college experience. No longer would fit, college, university reputation, and values factor into their college decisions—rather, choices would be made simply based on who was offering the most money.
Professionalism vs. the Classroom
There’s a feeling that paying college athletes sends the wrong message and incentivizes them to focus on athletics instead of academics, when the reality is that very few college athletes will go on to play sports professionally. Just 1.6% of college football players will take an NFL field. NCAA men’s basketball players have even slimmer odds of playing in a major professional league ( 1.2% ), while the chances of a professional career are particularly grim for women basketball players, at a mere 0.8% .
Although the odds of a college athlete turning pro are low, the probability of them earning a degree is high, thanks in part to the academic support athletes are given. According to data released by the NCAA, 90% of Division I athletes enrolled in 2013 earned a degree within six years.
It Will End Less-Popular, Unprofitable Sports
If colleges and universities pay their athletes, there is a fear that resources will only go to popular, revenue-generating sports. Programs like football and men’s basketball would likely benefit greatly, but smaller, unprofitable sports such as gymnastics, swimming and diving, tennis, track and field, volleyball, and wrestling could find themselves at best cash-strapped and, at the worst, cut altogether.
It’s just not less-popular sports that paying athletes could threaten—women’s programs could also find themselves in the crosshairs of budget-conscious administrators. Keep in mind, it was just in March 2021 that the NCAA made national news for its unequal treatment of the men’s and women’s NCAA basketball tournaments.
Financial Irresponsibility
Former ESPN, and current FOX Sports, personality Colin Cowherd made news in 2014 when he voiced a popular argument against paying college athletes: financial irresponsibility. In Cowherd’s words:
“I don’t think paying all college athletes is great… Not every college is loaded, and most 19-year-olds [are] gonna spend it—and let’s be honest, they’re gonna spend it on weed and kicks! And spare me the ‘they’re being extorted’ thing. Listen, 90 percent of these college guys are gonna spend it on tats, weed, kicks, Xboxes, beer and swag. They are, get over it!”
A look at the professional ranks bolsters Cowherd’s argument about athletes’ frivolous spending. According to CNBC , 60% of NBA players go broke within five years of departing the league and 78% of former NFL players experience financial distress two years after retirement.
Writing an Essay on This? Where to Get Your Essay Edited for Free
Writing an essay on whether college athletes should or shouldn’t be paid? CollegeVine can help! Our peer review tool allows you to receive feedback and learn the strengths and weaknesses of your essay for free.
Looking for more debate, speech, or essay topics? Check out these other CollegeVine articles for ideas:
- 52 Argumentative Essays Ideas that are Actually Interesting
- 52 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
- 60 Debate Topics for High Schoolers

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
The Case for Paying College Athletes
The case against paying college athletes, the era of name, image, and likeness (nil) profiting, why should college athletes be paid, is it illegal for college athletes to get paid, what percentage of americans support paying college athletes, the bottom line, should college athletes be paid.
The Case For and Against
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Headshot-4c571aa3d8044192bcbd7647dd137cf1.jpg)
Should college athletes be able to make money from their sport? When the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) was founded in 1906, the organization’s answer was a firm “no,” as it sought to “ensure amateurism in college sports.”
Despite the NCAA’s official stance, the question has long been debated among college athletes, coaches, sports fans, and the American public. The case for financial compensation saw major developments in June 2021, when the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the NCAA cannot limit colleges from offering student-athletes “education-related benefits.”
In response, the NCAA issued an interim policy stating that its student-athletes were permitted to profit off their name, image, and likeness (NIL) , but not to earn a salary. This policy will remain in place until a more “permanent solution” can be found in conjunction with Congress.
Meanwhile, the landscape continues to shift, with new cases, decisions, and state legislation being brought forward. College athletes are currently permitted to receive “cost of attendance” stipends (up to approximately $6,000), unlimited education-related benefits, and awards. A 2023 survey found that 67% of U.S. adults favor paying college athletes with direct compensation.
Key Takeaways
- Despite the NCAA reporting nearly $1.3 billion in revenue in 2023, student-athletes are restricted to limited means of compensation.
- Although college sports regularly generate valuable publicity and billions of dollars in revenue for schools, even the highest-grossing college athletes tend to see only a small fraction of this.
- One argument for paying college athletes is the significant time commitment that their sport requires, which can impact their ability to earn income and divert time and energy away from academic work.
- Student-athletes may face limited prospects after college for a variety of reasons, including a high risk of injury, fierce competition to enter professional leagues, and lower-than-average graduation rates.
- The developing conversation around paying college athletes must take into account the practical challenges of determining and administering compensation, as well as the potential impacts on players and schools.
There are numerous arguments in support of paying college athletes, many of which focus on ameliorating the athletes’ potential risks and negative impacts. Here are some of the typical arguments in favor of more compensation.
Financial Disparity
College sports generate billions of dollars in revenue for networks, sponsors, and institutions (namely schools and the NCAA). There is considerable money to be made from advertising and publicity, historically, most of which has not benefited those whose names, images, and likenesses are featured within it.
Of the 2019 NCAA Division I revenues ($15.8 billion in total), only 18.2% was returned to athletes through scholarships, medical treatment, and insurance. Additionally, any other money that goes back to college athletes is not distributed equally. An analysis of players by the National Bureau of Economic Research found major disparities between sports and players.
Nearly 50% of men’s football and basketball teams, the two highest revenue-generating college sports, are made up of Black players. However, these sports subsidize a range of other sports (such as men’s golf and baseball, and women’s basketball, soccer, and tennis) where only 11% of players are Black and which also tend to feature players from higher-income neighborhoods. In the end, financial redistribution between sports effectively funnels resources away from students who are more likely to be Black and come from lower-income neighborhoods toward those who are more likely to be White and come from higher-income neighborhoods.
Exposure and Marketing Value
Colleges’ finances can benefit both directly and indirectly from their athletic programs. The “Flutie Effect,” named after Boston College quarterback Doug Flutie, is an observed phenomenon whereby college applications and enrollments seem to increase after an unexpected upset victory or national football championship win by that college’s team. Researchers have also suggested that colleges that spend more on athletics may attract greater allocations of state funding and boost private donations to institutions.
Meanwhile, the marketing of college athletics is valued in the millions to billions of dollars. In 2023, the NCAA generated nearly $1.3 billion in revenue, $945.1 million of which came from media rights fees. In 2022, earnings from March Madness represented nearly 90% of the NCAA’s total revenue. Through this, athletes give schools major exposure and allow them to rack up huge revenues, which argues for making sure the players benefit, too.
Opportunity Cost, Financial Needs, and Risk of Injury
Because participation in college athletics represents a considerable commitment of time and energy, it necessarily takes away from academic and other pursuits, such as part-time employment. In addition to putting extra financial pressure on student-athletes, this can impact athletes’ studies and career outlook after graduation, particularly for those who can’t continue playing after college, whether due to injury or the immense competition to be accepted into a professional league.
Earning an income from sports and their significant time investment could be a way to diminish the opportunity cost of participating in them. This is particularly true in case of an injury that can have a long-term effect on an athlete’s future earning potential.
Arguments against paying college athletes tend to focus on the challenges and implications of a paid-athlete system. Here are some of the most common objections to paying college athletes.
Existing Scholarships
Opponents of a paid-athlete system tend to point to the fact that some college athletes already receive scholarships , some of which cover the cost of their tuition and other academic expenses in full. These are already intended to compensate athletes for their work and achievements.
Financial Implications for Schools
One of the main arguments against paying college athletes is the potential financial strain on colleges and universities. The majority of Division I college athletics departments’ expenditures actually surpass their revenues, with schools competing for players by hiring high-profile coaches, constructing state-of-the-art athletics facilities, and offering scholarships and awards.
With the degree of competition to attract talented athletes so high, some have pointed out that if college athletes were to be paid a salary on top of existing scholarships, it might unfairly burden those schools that recruit based on the offer of a scholarship.

‘Amateurism’ and the Challenges of a Paid-Athlete System
Historically, the NCAA has sought to promote and preserve a spirit of “amateurism” in college sports, on the basis that fans would be less interested in watching professional athletes compete in college sports, and that players would be less engaged in their academic studies and communities if they were compensated with anything other than scholarships.
The complexity of determining levels and administration of compensation across an already uneven playing field also poses a practical challenge. What would be the implications concerning Title IX legislation, for example, since there is already a disparity between male and female athletes and sports when it comes to funding, resources, opportunities, compensation, and viewership?
Another challenge is addressing the earnings potential of different sports (as many do not raise revenues comparable to high-profile sports like men’s football and basketball) or of individual athletes on a team. Salary disparities would almost certainly affect team morale and drive further competition between schools to bid for the best athletes.
In 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the NCAA violated antitrust laws with its rules around compensation, holding that the NCAA’s current rules were “more restrictive than necessary” and that the NCAA could no longer “limit education-related compensation or benefits” for Division I football and basketball players.
In response, the NCAA released an interim policy allowing college athletes to benefit from their name, image, and likeness (NIL) , essentially providing the opportunity for players to profit off their personal brand through social media and endorsement deals. States then introduced their own rules around NIL, as did individual schools, whose coaches or compliance departments maintain oversight of NIL deals and the right to object to them in case of conflict with existing agreements.
Other court cases against the NCAA have resulted in legislative changes that now allow students to receive “cost of attendance” stipends up to a maximum of around $6,000 as well as unlimited education-related benefits and awards.
The future of NIL rules and student-athlete compensation remains to be seen. According to the NCAA, the intention is to “develop a national law that will help colleges and universities, student-athletes, and their families better navigate the name, image, and likeness landscape.” However, no timeline has been specified as of yet.
Common arguments in support of paying college athletes tend to focus on players’ financial needs, their high risk of injury, and the opportunity cost they face (especially in terms of academic achievement, part-time work, and long-term financial and career outlook). Proponents of paying college athletes also point to the extreme disparity between the billion-dollar revenues of schools and the NCAA and current player compensation.
Although the NCAA once barred student-athletes from earning money from their sport, legislation around compensating college athletes is changing. In 2021, the NCAA released an interim policy permitting college athletes to profit off their name, image, and likeness (NIL) through social media and endorsement and sponsorship deals. However, current regulations and laws vary by state.
In 2023, a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults found that 67% of respondents were in favor of paying college athletes with direct compensation. Sixty-four percent said they supported athletes’ rights to obtain employee status, and 59% supported their right to collectively bargain as a labor union .
Although the NCAA is under growing pressure to share its billion-dollar revenues with the athletes it profits from, debate remains around whether, how, and how much college athletes should be paid. Future policy and legislation will need to take into account the financial impact on schools and athletes, the value of exposure and marketing, pay equity and employment rights, pay administration, and the nature of the relationship between college athletes and the institutions they represent.
NCAA. “ History .”
Marquette Sports Law Review. “ Weakening Its Own Defense? The NCAA’s Version of Amateurism ,” Page 260 (Page 5 of PDF).
U.S. Supreme Court. “ National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston et al. ”
NCAA. “ NCAA Adopts Interim Name, Image and Likeness Policy .”
PBS NewsHour. “ Analysis: Who Is Winning in the High-Revenue World of College Sports? ”
Sportico. “ 67% of Americans Favor Paying College Athletes: Sportico/Harris Poll .”
Sportico. “ NCAA Took in Record Revenue in 2023 on Investment Jump .”
National Bureau of Economic Research. “ Revenue Redistribution in Big-Time College Sports .”
Appalachian State University, Walker College of Business. “ The Flutie Effect: The Influence of College Football Upsets and National Championships on the Quantity and Quality of Students at a University .”
Grand Canyon University. “ Should College Athletes Be Paid? ”
Flagler College Gargoyle. “ Facing Inequality On and Off the Court: The Disparities Between Male and Female Athletes .”
U.S. Department of Education. “ Title IX and Sex Discrimination .”
Congressional Research Service Reports. “ National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston and the Debate Over Student Athlete Compensation .”
NCSA College Recruiting. “ NCAA Name, Image, Likeness Rule .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-151311702-a935ed8794c64194a53b5741d4be05f3.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Should College Athletes Get Paid?
Should college athletes be getting paid? That’s a question that has been a topic of discussion for quite some time and has even influenced laws and regulations. With college athletes’ busy schedules, hard work, and sacrifice, some believe that college athletes should be getting paid. Still, others believe that they should not be getting paid due to the fact that they are still college students and making money from sources outside of play. Our editorial staff was asked a few questions about their personal opinion on this topic. College is oftentimes looked at as a developmental stage for athletes to advance and grow their skills before possibly having the chance to go professional. Therefore, the editors were asked if money was involved if that would affect the developmental stage. Their answers varied, some stating that it would affect the developmental stage, making things “very convoluted,” while others think money is already involved for athletes who have received scholarships. They then were asked if athletes getting paid would affect the fairness of the game. They all agreed it would not affect the fairness of the game, although some editors went on to explain exceptions. These exceptions included some schools paying athletes and some not, difference in pay, and what is considered professional versus amateur. One editor said, “College athletes already don’t get paid because of the fact that they are not yet professional athletes. Paying them would blur the distinct boundary between the two.” As mentioned, college athletes already don’t get paid due to the fact they are not professional athletes and still students who take classes and have their academic responsibilities. If athletes were to get paid, it raises the question of, “Should athletes that are getting Cs and Ds be getting paid at the same level of athletes who are receiving As and Bs?” With that being said, the editorial staff was asked if they think academics should impact an athletes level of pay. While there were mixed answers, one editor commented, “Academics most definitely should impact their pay, but their ability to play, as well.” Another editor brought up a good point: “Why not pay everyone that’s getting really good grades in class?” Say college athletes do get paid, how would the level of pay be determined amongst each athlete? Each editor shed a different light on this question. One editor said that it could potentially be determined by performance, amount of time played, and how much money the team creates for the University. A second editor mentioned it being based on the division of the school and possibly playing time, but not the performance of each player. A third editor shared that they believe it could be based on similar factors that determine a professional athlete’s pay. Lastly, after considering all the questions they previously answered they were all individually asked if they think athletes should be paid or not. Their responses were as followed: Editor One: “I don’t think they should be paid. That’s what brand deals and sponsorships are for at the college level. I’ve seen many athletes partner with big and small companies for brand deals where they either get products or money.” Editor Two: “I do not think college athletes should be paid as a wage-based job. A lot of college athletes get scholarships and other financial benefits from their sports. However, I think athletes should have the right to their own name and brand. So, getting paid through sponsorships or merch with their name on it should be totally fine.” Editor Three: “I don’t think college athletes should be paid at all, especially considering that many, if not all, of them are already being paid in scholarships. I have heard complaints that many college athletes lack time to have a job due to practices and academic work, but the non-athletes who are able to have a job most likely have their money going towards tuition. Any additional pay given to a college athlete would be ridiculous.” Overall, it is clear that there are many factors to this debate, and there may not be an answer any time soon.
Related Articles
A year in review at mu.
A lot can change in one year, and like most years, 2016 was no different. While 2016 has brought on a little more change than some can handle, it is perhaps a year that no one will forget. At Monmouth University, 2016 has been a year of highs and lows.
Does MU Fall “Flat” in Cleaning Construction?
The construction of the University’s latest building, Pozycki Hall, has inconveniently stripped students of a vast majority of parking spaces – that is old news. Now, however, another problem caused by the site has come into question by The Outlook: car problems potentially caused by inadequate clean-up of the construction.

COVID-19 Pandemic: One Year Later
It’s been a full year since the University, and the world for that matter, shut down due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Despite the pandemic seemingly being on its last legs, some editors still worry for their job prospects after graduation.
Home — Essay Samples — Life — Paying College Athletes — Whether College Athletes Should Be Paid: An Argumentative Perspective
Whether College Athletes Should Be Paid: an Argumentative Perspective
- Categories: College Tuition Paying College Athletes Student Athletes
About this sample

Words: 740 |
Published: Mar 18, 2021
Words: 740 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Works Cited
- Meshefejian, N. (2019). Pay for Play: Why NCAA Athletes Should Be Compensated. Journal of Law and Politics, 34(4), 765-789.
- Lemmons, L. (2019). Pay College Athletes? They're Already Paid in Education. USA Today. Retrieved from https://www.usatoday.com/story/sports/columnist/brennan/2019/09/20/pay-college-athletes-theyre-already-paid-education/2383885001/
- Suggs, W. (2020). NCAA Athletes Deserve to Be Paid for Their Name, Image and Likeness. The Washington Post. Retrieved from https://www.washingtonpost.com/opinions/2020/12/15/ncaa-athletes-deserve-be-paid-their-name-image-likeness/
- Branch, J. (2011). The Shame of College Sports. The Atlantic. Retrieved from https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2011/10/the-shame-of-college-sports/308643/
- Edelman, M. (2022). The Economic Case for Paying College Athletes. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/modeledbehavior/2022/01/28/the-economic-case-for-paying-college-athletes/?sh=39da6319645b
- Hawkins, A. (2019). Why College Athletes Should Get Paid—and Why They're Already Worth Millions. The Verge. Retrieved from https://www.theverge.com/2019/3/20/18261744/college-athletes-pay-ncaa-basketball-football-players
- Coates, D., & Zhang, L. (2016). Does Paying College Athletes Help or Hurt Other Students? An Empirical Analysis of the "Price of Football". SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2806700
- Staurowsky, E. J. (2019). The Case for Paying College Athletes. Inside Higher Ed. Retrieved from https://www.insidehighered.com/views/2019/09/04/its-time-think-about-how-pay-college-athletes-opinion
- Murphy, A. (2021). The Case for Paying College Athletes. The Balance. Retrieved from https://www.thebalance.com/should-college-athletes-be-paid-4160789
- Smith, D. (2018). The Real Cost of College Athletics. The Atlantic. Retrieved from https://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2018/11/why-do-colleges-have-sports-teams/575155/

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Education Life

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 788 words
3 pages / 1316 words
2 pages / 711 words
2 pages / 1061 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Paying College Athletes
In the past five to ten years, there has been a controversial question going around: should students who play a sport get paid as a reward of being a College Athlete? The answer is no. Student athletes should not get paid [...]
The question of whether coaches and players should receive equal compensation in the realm of professional sports is a topic that has sparked intense debate. The Should Coaches and Players Make the Same Amount of Money Essay [...]
The discussion whether the college athletes should be paid has been re-hashed several times. There are those who advocates in favor and many against the idea of paying athlete who plays sports for their colleges. Many reasons [...]
Should college athletes be paid? This essay argues that student athletes at universities around the country should not only obtain a percentage of income made off their athletic performance but also pursue business deals and [...]
Should college athletes be paid? The intensity of the argument to pay college athletes has escalated in the past few years. Picture a world where every college athlete was paid by their schools to play. The controversy it would [...]
On common on average only 1/3 of college athletes are given a scholarship and a majority are half as much as a full scholarships as stated by the National Collegiate Athletic Association. From that 1/3 about two percent make it [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Reasons Why or Why Not
January 3, 2022
Tables of Contents
Why are college athletes not getting paid by their schools?
How do student athlete scholarships work, what are the pros and cons of compensation for college athletes, keeping education at the center of college sports.
Since its inception in 1906, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) has governed intercollegiate sports and enforced a rule prohibiting college athletes to be paid. Football, basketball, and a handful of other college sports began to generate tremendous revenue for many schools in the mid-20th century, yet the NCAA continued to prohibit payments to athletes. The NCAA justified the restriction by claiming it was necessary to protect amateurism and distinguish “student athletes” from professionals.
The question of whether college athletes should be paid was answered in part by the Supreme Court’s June 21, 2021, ruling in National Collegiate Athletic Association v. Alston, et. al. The decision affirmed a lower court’s ruling that blocked the NCAA from enforcing its rules restricting the compensation that college athletes may receive.
- As a result of the NCAA v. Alston ruling, college athletes now have the right to profit from their name, image, and likeness (NIL) while retaining the right to participate in their sport at the college level. (The prohibition against schools paying athletes directly remains in effect.)
- Several states have passed laws that allow such compensation. Colleges and universities in those states must abide by these new laws when devising and implementing their own policies toward NIL compensation for college athletes.
Participating in sports benefits students in many ways: It helps them focus, provides motivation, builds resilience, and develops other skills that serve students in their careers and in their lives. The vast majority of college athletes will never become professional athletes and are happy to receive a full or partial scholarship that covers tuition and education expenses as their only compensation for playing sports.
Athletes playing Division I football, basketball, baseball, and other sports generate revenue for their schools and for third parties such as video game manufacturers and media companies. Many of these athletes believe it’s unfair for schools and businesses to profit from their hard work and talent without sharing the profits with them. They also point out that playing sports entails physical risk in addition to a considerable investment in time and effort.
This guide considers the reasons for and against paying college athletes, and the implications of recent court rulings and legislation on college athletes, their schools, their sports, and the role of the NCAA in the modern sports environment.
Back To Top
The reasons why college athletes aren’t paid go back to the first organized sports competitions between colleges and universities in the late 19th century. Amateurism in college sports reflects the “ aristocratic amateurism ” of sports played in Europe at the time, even though most of the athletes at U.S. colleges had working-class backgrounds.
By the early 20th century, college football had gained a reputation for rowdiness and violence, much of which was attributed to the teams’ use of professional athletes. This led to the creation of the NCAA, which prohibited professionalism in college sports and enforced rules restricting compensation for college athletes. The rules are intended to preserve the amateurism of student participants. The NCAA justified the rules on two grounds:
- Fans would lose interest in the games if the players were professional athletes.
- Limiting compensation to capped scholarships ensures that college athletes remain part of the college community.
NCAA rules also prohibited college athletes from receiving payment to “ advertise, recommend, or promote ” any commercial product or service. Athletes were barred from participating in sports if they signed a contract to be represented by an agent as well. As a result of the NIL court decision, the NCAA will no longer enforce its rule relating to compensation for NIL activities and will allow athletes to sign contracts with agents.
Major college sports now generate billions in revenue for their schools each year
For decades, colleges and universities have operated under the assumption that scholarships are sufficient compensation for college athletes. Nearly all college sports cost more for the schools to operate than they generate in revenue for the institution, and scholarships are all that participants expect.
But while most sports don’t generate revenue, a handful, notably football and men’s and women’s basketball, stand out as significant exceptions to the rule:
- Many schools that field teams in the NCAA’s Division I football tier regularly earn tens of millions of dollars each year from the sport.
- The NCAA tournaments for men’s and women’s Division I basketball championships generated more than $1 billion in 2019 .
Many major colleges and universities generate a considerable amount of money from their athletic teams:
- The Power Five college sports conferences — the Atlantic Coast Conference (ACC), Big Ten, Big 12, Pac 12, and Southeastern Conference (SEC) — generated more than $2.9 billion in revenue from sports in fiscal 2020, according to federal tax records reported by USA Today .
- This figure represents an increase of $11 million from 2019, a total that was reduced because of restrictions related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- In the six years prior to 2020, the conferences recorded collective annual revenue increases averaging about $252 million.
What are name, image, likeness agreements for student athletes?
In recent years some college athletes at schools that field teams in the NCAA’s highest divisions have protested the restrictions placed on their ability to be compensated for third parties’ use of their name, image, and likeness. During the 2021 NCAA Division I basketball tournament known familiarly as March Madness, several players wore shirts bearing the hashtag “ #NotNCAAProperty ” to call attention to their objections.
Following the decision in NCAA v. Alston, the NCAA enacted a temporary policy allowing college athletes to enter into NIL agreements and other endorsements. The interim policy will be in place until federal legislation is enacted or new NCAA rules are created governing NIL contracts for college athletes.
- Student athletes are now able to sign endorsement deals, profit from their use of social media, and receive compensation for personal appearances and signing autographs.
- If they attend a school located in a state that has enacted NIL legislation, they are subject to any restrictions present in those state laws. As of mid-August 2021, 40 states had enacted laws governing NIL contracts for college athletes.
- If their school is in a state without such a law, the college or university will determine its own NIL policies, although the NCAA prohibits pay-for-play and improper recruiting inducements.
- Student athletes are allowed to sign with sports agents and enter into agreements with school boosters so long as the deals abide by state laws and school policies.
Within weeks of the NCAA policy change, premier college athletes began signing NIL agreements with the potential to earn them hundreds of thousands of dollars .
- Bryce Young, a sophomore quarterback for the University of Alabama, has nearly $1 million in endorsement deals.
- Quarterback Quinn Ewers decided to skip his last year of high school and enroll early at Ohio State University so he could make money from endorsements.
- A booster for the University of Miami pledged to pay each member of the school’s football team $500 for endorsing his business.
How will the change affect college athletes and their schools?
The repercussions of court decisions and state laws that allow college athletes to sign NIL agreements continue to be felt at campuses across the country, even though schools and athletes have received little guidance on how to manage the process.
- The top high school athletes in football, basketball, and other revenue-generating college sports will consider their potential for endorsement earnings while being recruited by various schools.
- The first NIL agreements highlight the disparity between what elite college athletes can expect to earn and what other athletes may realize. On one NIL platform, the average amount earned by Division I athletes was $471, yet one athlete made $210,000 in July alone.
- Most NIL deals at present are for small amounts, typically about $100 in free apparel, in exchange for endorsing a product on social media.
The presidents and other leaders of colleges and universities that field Division I sports have not yet responded to the changes in college athlete compensation other than to reiterate that they do not operate for-profit sports franchises. However, the NCAA requires that Division I sports programs be self-supporting, in contrast to sports programs at Division II and III institutions, which receive funding directly from their schools.
Many members of the Power 5 sports conferences have reported shortfalls in their operations, leading analysts to anticipate major structural reforms in the governing of college sports in the near future. The recent changes have also caused some people to believe the NCAA is no longer relevant or necessary.

How do highly competitive athletic scholarships work? According to the NCAA and Next College Student Athlete: $3.6 billion+ in athletic scholarships are awarded annually, and 180,000+ student athletes receive scholarships every year. Additionally, about 2% of athletes win a sports scholarship; college coaches award scholarships based on athletic ability; full scholarships are given for the top six college sports categories; and athletic scholarships are renewable each year.
The primary financial compensation student athletes receive is a scholarship that pays all or part of their tuition and other college-related expenses. Other forms of financial assistance available to student athletes include grants, loans, and merit aid .
- Grants are also called “gift aid,” because students are not expected to pay them back (with some exceptions, such as failing to complete the course of study for which the grant was awarded). Grants are awarded based on a student’s financial need. The four types of grants awarded by the U.S. Department of Education are Federal Pell Grants , Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grants , Iraq and Afghanistan Service Grants , and Teacher Education Assistance for College or Higher Education (TEACH) Grants .
- Loans are available to cover education expenses from government agencies and private banks. Students must pay the loans back over a specified period after graduating from or leaving school, including interest charges. EducationData.org estimates that as of 2020, the average amount of school-related debt owed by college graduates was $37,693.
- Merit aid is awarded based on the student’s academic, athletic, artistic, and other achievements. Athletic scholarships are a form of merit aid that typically cover one academic year at a time and are renewable each year, although some are awarded for up to four years.
Full athletic scholarships vs. partial scholarships
When most people think of a student athlete scholarship, they have in mind a full-ride scholarship that covers nearly all college-related expenses. However, most student athletes receive partial scholarships that may pay tuition but not college fees and living expenses, for example.
A student athlete scholarship is a nonguaranteed financial agreement between the school and the student. The NCAA refers to full-ride scholarships awarded to student athletes entering certain Division I sports programs as head count scholarships because they are awarded per athlete. Conversely, equivalency sports divide scholarships among multiple athletes, some of whom may receive a full scholarship and some a partial scholarship. Equivalency awards are divided among a team’s athletes at the discretion of the coaches, as long as they do not exceed the allowed scholarships for their sport.
These Division I sports distribute scholarships per head count:
- Men’s football
- Men’s basketball
- Women’s basketball
- Women’s volleyball
- Women’s gymnastics
- Women’s tennis
These are among the Division I equivalency sports for men:
- Track and field
- Cross-country
These are the Division I equivalency sports for women:
- Field hockey
All Division II and National Association of Intercollegiate Athletics (NAIA) sports programs distribute scholarships on an equivalency basis. Division III sports programs do not award sports scholarships, although other forms of financial aid are available to student athletes at these schools.
How college athletic scholarships are awarded
In most cases, the coaching staff of a team determines which students will receive scholarships after spending time scouting and recruiting. The NCAA imposes strict rules for recruiting student athletes and provides a guide to help students determine their eligibility to play college sports.
Once a student has received a scholarship offer from a college or university, the person may sign a national letter of intent (NLI), which is a voluntary, legally binding contract between an athlete and the school committing the student to enroll and play the designated sport for that school only. The school agrees to provide financial aid for one academic year as long as the student is admitted and eligible to receive the aid.
After the student signs an NLI, other schools are prohibited from recruiting them. Students who have signed an NLI may ask the school to release them from the commitment; if a student attends a school other than the one with which they have an NLI agreement, they lose one full year of eligibility and must complete a full academic year at the new school before they can compete in their sport.
Very few student athletes are awarded a full scholarship, and even a “full” scholarship may not pay for all of a student’s college and living expenses. The average Division I sports scholarship in the 2019-20 fiscal year was about $18,000, according to figures compiled by ScholarshipStats.com, although some private universities had average scholarship awards that were more than twice that amount. However, EducationData.org estimates that the average cost of one year of college in the U.S. is $35,720. They estimate the following costs by type of school.
- The average annual cost for an in-state student attending a public four-year college or university is $25,615.
- Average in-state tuition for one year is $9,580, and out-of-state tuition costs an average of $27,437.
- The average cost at a private university is $53,949 per academic year, about $37,200 of which is tuition and fees.
Student athlete scholarship resources
- College Finance, “Full-Ride vs. Partial-Ride Athletic Scholarships” — The college expenses covered by full athletic scholarships, how to qualify for partial athletic scholarships, and alternatives to scholarships for paying college expenses
- Student First Educational Consulting, “Athletic Scholarship Issues for 2021-2022 and Beyond” — A discussion of the decline in the number of college athletic scholarships as schools drop athletic programs, and changes to the rules for college athletes transferring to new schools
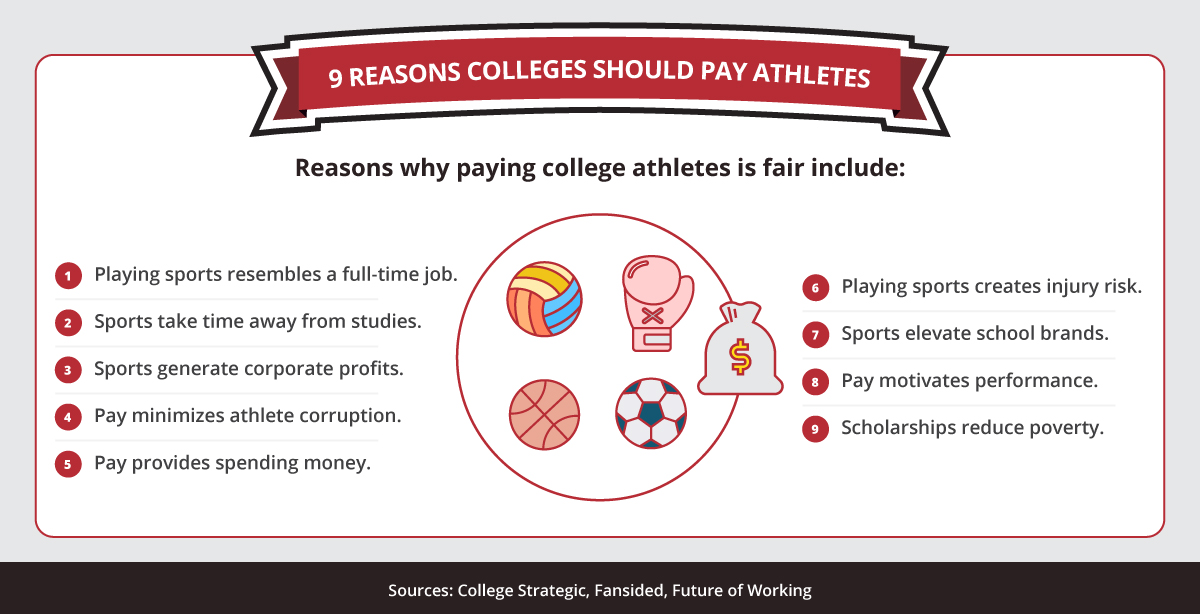
According to College Strategic, Fansided, and Future of Working, reasons why paying college athletes is fair include: 1. Playing sports resembles a full-time job. 2. Sports take time away from studies. 3. Sports generate corporate profits. 4. Pay minimizes athlete corruption. 5. Pay provides spending money. 6. Playing sports creates injury risk. 7. Sports elevate school brands. 8. Pay motivates performance. 9. Scholarships reduce poverty.
There are many reasons why student athletes should be paid, but there are also valid reasons why student athletes should not be paid in certain circumstances. The lifting of NCAA restrictions on NIL agreements for college athletes has altered the landscape of major college sports but will likely have little or no impact on the majority of student athletes, who will continue to compete as true amateurs.
Reasons why student athletes should be paid
The argument raised most often in favor of allowing college athletes to receive compensation is that colleges and universities profit from the sports they play but do not share the proceeds with the athletes who are the ultimate source of that profit.
- In 2017 (the most recent year for which figures are available), the NCAA recorded $1.07 billion in revenue. The organization’s president earned $2.7 million in 2018, and nine other NCAA executives had salaries greater than $500,000 that year.
- Elite college coaches earn millions of dollars a year in salary, topped by University of Alabama football coach Nick Saban’s $9.3 million annual salary.
- Many of the athletes at leading football and basketball programs are from low-income families, and the majority will not become professional athletes.
- College athletes take great physical risks to play their sports and put their future earning potential at risk. In school they may be directed toward nonchallenging courses, which denies them the education their fellow students receive.
Reasons why student athletes should not be paid
Opponents to paying college athletes rebut these arguments by pointing to the primary role of colleges and universities: to provide students with a rewarding educational experience that prepares them for their professional careers. These are among the reasons they give for not paying student athletes.
- Scholarships are the fairest form of compensation for student athletes considering the financial strain that college athletic departments are under. Most schools in Division I, II, and III spend more money on athletics than they receive in revenue from the sports.
- College athletes who receive scholarships are presented with an opportunity to earn a valuable education that will increase their earning power throughout their career outside of sports. A Gallup survey of NCAA athletes found that 70% graduate in four years or fewer , compared to 65% of all undergraduate students.
- Paying college athletes will “ diminish the spirit of amateurism ” that distinguishes college sports from their professional counterparts. Limiting compensation for playing a sport to the cost of attending school avoids creating a separate class of students who are profiting from their time in school.
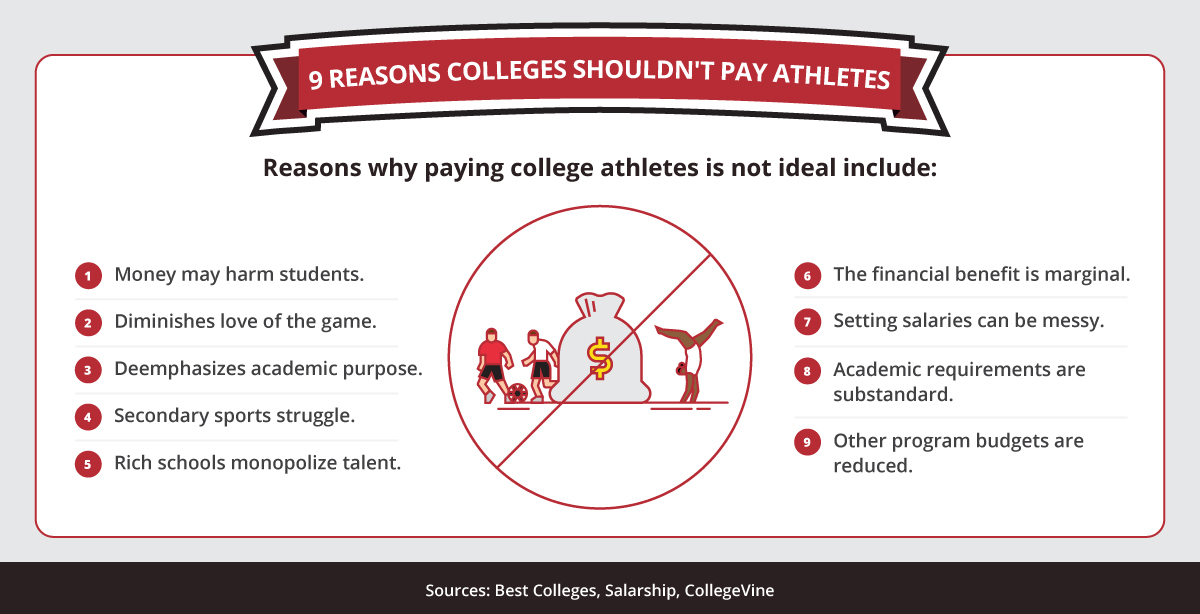
According to Best Colleges, Salarship, and CollegeVine, reasons why paying college athletes is less than ideal include: 1. Money may harm students. 2. Pay diminishes love of the game. 3. Pay deemphasizes academic purpose. 4. Secondary sports struggle. 5. Rich schools monopolize talent. 6. The financial benefit is marginal. 7. Setting salaries can be messy. 8. Academic requirements are substandard. 9. Other program budgets are reduced.
How do college athlete endorsements work?
Soon after the Supreme Court released its decision in NCAA v. Alston, the NCAA issued guidelines for schools that allow college athletes to make money from product endorsements, social media accounts, autographs, and other uses of their name, image, or likeness. This counters the NCAA’s longstanding opposition to student athletes profiting from endorsements. At present, implementation of the guidelines varies from school to school and state to state, which means athletes at some institutions may benefit more from NIL agreements than those attending other schools.
Several NIL consultancy firms are actively soliciting endorsements from college athletes in the aftermath of the rule change.
- Highly touted 19-year-old basketball recruit Hercy Miller, who joined the Tennessee State University basketball team in 2021, signed a $2 million endorsement deal with Web Apps America.
- University of Michigan quarterback Cade McNamara has entered into an endorsement deal with cryptocurrency company More Management that will pay him in cryptocurrency .
- Twin sisters Haley and Hanna Cavinder of the Fresno State University basketball team have marketing agreements to promote Boost Mobile and Six Star Pro Nutrition to the 3.3 million followers of their TikTok account.
- Gable Steveson, a wrestler for the University of Minnesota, entered into an endorsement deal with the delivery service Gopuff; Steveson has 245,000 followers on Instagram and 30,000 on Twitter.
Despite the rush of high-profile college athletes signing endorsement deals, some educators and analysts express concern about the impact of the endorsements on schools, athletes, and college sports.
- Schools with more favorable endorsement rules may entice student athletes away from the schools they are currently attending.
- Likewise, states that have enacted endorsement laws that provide more earning potential for college athletes may see more top recruits choosing to attend schools in those states.
- The time college athletes spend meeting the requirements of their endorsement contracts could detract from study and practice time. This can have an adverse effect on their education and athletic careers — if they are unable to maintain grade requirements, for example, they may be disqualified from playing.
- If a college athlete’s performance in the sport declines, they may be less likely to attract and retain endorsement deals. While the NCAA has banned NIL agreements based on the athlete meeting specific performance criteria, the group acknowledges that a student’s athletic performance may enhance their NIL value .
- Because of complicated contracts and tax laws, student athletes will have to rely on agents, advisers, and managers, which may leave them vulnerable to exploitation.
From the onset of intercollegiate sports, students have benefited from their participation by learning dedication to their sport, building relationships, and being part of a team. Sports allow students to acquire many important values, such as fair competition and physical and mental health. Education should remain at the forefront of all aspects of college, including sports, whether or not collegiate athletes are paid.
Infographic Source
Best Colleges, “Should College Athletes Be Paid?”
College Strategic, “Why College Athletes Should Be Paid”
CollegeVine, “Should College Athletes Be Paid? Pros and Cons”
Fansided, “64 Reasons College Athletes Need to Be Paid”
Future of Working, “17 Advantages and Disadvantages of Paying College Athletes”
NCAA, “Scholarships”
Next College Student Athlete, “What Are the Different Types of Offers I Could Get?”
Salarship, “Should College Athletes Be Paid: Pros and Cons”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.
Should College Athletes Be Paid? Essay Examples & Guide
- 👍 Advantages
- 👎 Disadvantages
- 💡 Essay Topics
- 📑 Outlining Your Paper
- 💸 Essay Example #1
- 🙅 Essay Example #2
🔗 References
There are a lot of benefits of doing sports in college, for everyone except the athletes themselves. Surely, your sports achievements can get you recognition and respect. But the issue here is not being paid at all.
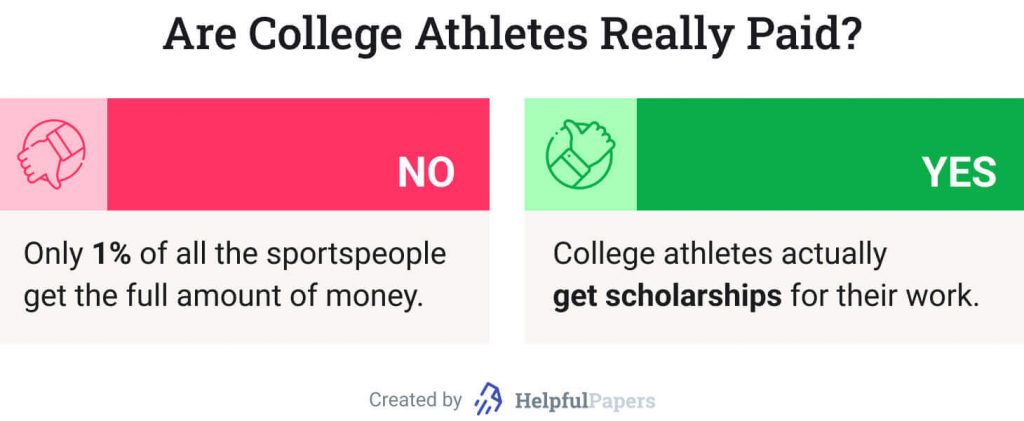
You see, sport is arduous labor. And any labor, according to common sense, must be rewarded with a salary. On the other hand, doing sports for the sake of sports can also be justified. There is no clear answer for “Should college athletes be paid?”. Writing an essay, though, can help you find it.
⚖️ Should College Athletes Be Paid: Pros and Cons
This matter is very recent. Therefore, there is a lot of space for discussion here. Some may say that athletes are paid. They actually get scholarships for their work.
Others may argue that only 1% of all the sportspeople get the full amount of money. Both statements are true, and the correct answer doesn’t really exist. To help you form your own opinion on the topic, here are some pros and cons:
- It would be fair to pay sportspeople for their hard work.
- The sport takes a lot of time from studies, and it must be compensated.
- The health risk is very high, and the reward for it is a must.
- The sport would become an excellent alternative for a work-study job.
- Many athletes’ families require monetary support, which athlete payments can give.
- A lot more people would be attracted to doing sports.
- The athletes already enjoy enough compensations.
- The amount of actual future sports pros is depressing.
- It can undermine the overall studying experience.
- Most of the sports programs cannot afford salaries.
- It would create room for inequity.
- Mixing studying and sports would become even more difficult due to increased demand.
- The concept of playing for the love of sports would cease to exist.
We will look into them deeper in the next section.
👍 Paying College Athletes: Advantages
- It is simply fair to pay athletes for their endeavors. A single sportsperson can generate millions of dollars for their college. It would be only fair if the stars themselves got at least some of this money.
- It is a great way to compensate for taking away from studies. Sport is a time-consuming activity. And time is a valuable thing when you are a student. Let’s not forget that college athletes also need time to study. Or at least compensation for the time they put into the sport.
- The money would at least partially make up for possible injuries. While health is priceless, risking it must be rewarded properly. And that’s exactly what college athletes do. They put their well-being on the line for their universities. Unfortunately, universities don’t seem to give the favor back.
- It would be a great way to substitute work. An average athlete puts 40 hours a week into doing sports for his college. You can easily compare this amount of time to a generic work-study job. The only difference is the latter brings you money, and the former does not.
- It’s a great way to motivate athletes to continue their sports careers. After graduation, the majority of college athletes will stop playing for their team. They are far more likely to simply find a job and get a steady income. Paying them would make a choice between sports and career not that obvious.
- It would support a lot of students’ families. While college sportspeople bath in success, their families often suffer financially. Sustaining a starting athlete can be really costly at times. That’s where a salary would be a saving grace for struggling families.
- It is a great motivation for more students to pursue a sports career. The possibility of making money will attract more people into playing for a sports team. And that brings a better chance to find young talent.
👎 Paying College Athletes: Disadvantages
- The athletes already have their compensations. The coach’s advice, the medical treatment, the strength training. All of these cost money. But the athletes don’t have to pay a single cent for these and many other services. They are provided for free as compensation already.
- Not a lot of athletes will actually become professionals. Out of all college athletes, a mere 2% go pro as a result. Most of them see doing sports as a way to receive education and nothing more.
- It can harm other colleges’ programs. Since the salary would come from the college budget, there would be inevitable cutbacks. As a result, every student in the institution suffers.
- There are not many sports that make a profit. More often than not, sport doesn’t bring a lot of money. Exceptions are basketball and football. Should football players make more money than, for example, swimmers? Here’s where the next issue occurs.
- Possible inequity. You see, if some students participate in a sport that has no profit, then why pay them? As a result of such logic, whole college teams will cease to exist.
- Possible study problems. With the appearance of salaries, the expectations from the players will rise. Attending training sessions and games will become a definite must. No skips would be allowed. In this case, ping-ponging your priorities from sports to studies is much more difficult.
- The love for the game would go away. College students play sports mostly because they want to do what they love. Paying them might destroy the compassion for doing sport. The amateur leagues will be filled with players who are in it for the money and nothing else.
💡 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Topics
- Balancing college sports and academic mission .
- Payments to collegiate athletes .
- Top college athletes are worth six figures.
- Title IX in the female sports development .
- Kids and sports: Lack of professional sports guides .
- College athletes do not deserve the degrees they’re studying for.
- Steroid abuse in the world of sports .
- Shortage of officials at the high school sports level .
- College sports should be made professional.
- Steroid use effects on professional young athletes .
- Is it justified for college athletes to be paid ?
- College sports should not require missing classes.
- Professional athletes allowed to use steroids.
- Paying college athletes: Reinforcing privilege or promoting growth ?
- If colleges pay college athletes, it would increase the disparity between small and bigger college teams.
- School athletes and drug tests.
- Arguments for adequate remuneration for college athletes .
- The NCAA definition of college athletes as amateurs is outdated.
- Sports-related problems and conflicts.
- African American studies. Negro baseball league.
- The moral side: “A gentlemen never competes for money” (Walter Camp).
- Running injuries, workout and controversies.
- Should college athletes be paid ?
- Ed O’Bannon’s lawsuit: Using athletes’ images in video games.
- Does youth sports play a part in character formation?
- Children participation in sports .
- Where does college sports money go?
- Sports analysis: steroids and HGH in sports.
- Steroid usage in professional sports.
- College athletes work as marketers for their college, as their success in sports improves admission rates.
- Physical activity and sports team participation.
- Using performance-enhancing drugs and in the world of sport .
- Research handbook of employment relations in sport .
- Successfully luring college athletes .
- College athletes should be paid .
Haven’t found anything inspiring in the list above? Try using our topic-generating tool !
📑 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Outline
Before writing your work, the first thing you want to do is outline. An argumentative-style essay would be perfect for writing on our topic.
We will go with a generic 5-paragraph format :
- Hook. A flashy sentence or two to evoke interest in your work. A joke or a shocking fact, for example.
- Background information. General info that the reader needs to know before going deeper into the essay.
- Thesis statement. It is a sentence that reflects the main idea of the further text. It leaves room for debate and briefly showcases the arguments you will discuss further.
- Body. The body is the biggest part of your work. In our case, it will be three paragraphs long. Each paragraph names and explains the argument you want to make.
- Conclusion. The end of your essay. Nothing new should be added. Just restate your thesis, summarize the points you made in the body, and be done with it.
💸 Why College Athletes Should Be Paid Essay Example
In 2017 National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) made over $1.04 billion in revenue. None of the college athletes have seen any part of this sum. A survey made the same year showed 60% of the sportspeople to be satisfied with the scholarship-only payments. The situation, however, has drastically changed over the years. The same 60% now agree that college athletes need monetary compensation. While college athletes' payments are a controversial topic, their hard work and health must be fairly compensated no matter what, and a salary seems to be the best way for it.
It is no surprise that doing sports consumes a solid number of things. Time is one of them. An average college student puts in their sports activities 35 hours a week. It can be compared to having a generic work-study job. The only difference is the job brings you money as any hard labor should. However, in the case of college sport, it seems to profit anyone but the athletes themselves. While the NCAA executives make six-figure salaries, the players, the actual stars of the competition, have the status of the unpaid workforce.
Another thing consumed by sports activities is health. In 2017 over 60% of all Division I players were reported to suffer a major injury. Although, this phenomenal danger to athletes' well-being seems to go unnoticed as well. The only "compensation" provided to people who risk their soundness for the sake of university is education itself. Usually, the health risk is considered a reason for a salary raise. Unfortunately, in our case, there is nothing to give a raise to.
Putting yourself to the fullest in any activity must be rewarded. And the sportspeople truly give it their best. Time, passion, health, everything is given. And for now, everything they give is given for nothing.
🙅 College Athletes Should Not Be Paid Essay Example
There are hundreds of sports college athletes do. Only two of them bring the college profit. The issue of paying the students involved with the college sports activities has been around for a while. Some are satisfied with their scholarship and the possibility to get an education. Others, however, demand more tangible rewards for their achievements. While payments may seem justified, the fact that the athletes already receive enough compensation for their work via scholarship and education is often overlooked.
National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) reports more than $3.6 billion in athletic scholarships to be provided annually to more than 180,000 student-athletes. A simple calculation shows $20.000 a year for each athlete. This sum is more than enough to cover the average cost of an academic year of $17,797.
Furthermore, most college athletic programs make barely enough money to sustain themselves, not to mention paying salaries. The only two kinds of sport that make enough profit to afford salaries are football and basketball. Others, sadly, do not. And this fact creates a significant equity problem. Do we pay all players equally? And if not, who do we pay more? All these questions remain unanswered.
While it seems just, creating salaries brings more problems than solves. The extent of the compensation necessary is, of course, negotiable. But all efforts made by college athletes are compensated in some way. That is a fact.
We hope that this info helped you with your assignment. Make sure to let us know what part you’ve found the most useful in the comments. And also, check out our title page maker . And good luck with your studies!
- 16 college athletes already getting paid under new NCAA rule
- Should College Athletes Be Paid? | BestColleges
- Should College Athletes Be Paid? Reasons Why or Why Not
- All college athletes in California can now get paid – KTVU
- Pay for Play: Should College Athletes Be Compensated?
Research Paper Analysis: How to Analyze a Research Article + Example
Film analysis: example, format, and outline + topics & prompts.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
An Argument For Not Allowing College Athletes To Earn Compensation
NPR's Mary Louise Kelly speaks with Ekow Yankah, author of The New Yorker essay, "Why N.C.A.A. Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid," about the NCAA's decision to allow college athletes to earn compensation.
MARY LOUISE KELLY, HOST:
The NCAA makes close to a billion dollars in revenue each school year, but college players see none of that money. Now that might change. Yesterday, the NCAA's Board of Governors voted to permit student-athletes to benefit from the use of their name, image and likeness. Now, some see this as addressing an unfair practice of exploitative behavior by the NCAA. Others see this as a lousy idea.
Here to discuss is Ekow Yankah. He's a professor at Cardozo School of Law. He has written about this, an essay in The New Yorker back in 2015 titled "Why NCAA Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid." He joins me now from London.
Welcome to ALL THINGS CONSIDERED.
EKOW YANKAH: Thank you for having me.
KELLY: What did you make of this announcement yesterday?
YANKAH: Like most people, we're all sort of waiting to see what the announcement means. The NCAA often tries to do the vaguely right thing when it has absolutely no other choice. So I take it that this is a capitulation of what they see coming down the pike in terms of a slew of laws that are passing from state to state and threatened federal action.
KELLY: But I gather you think this is a lousy idea. You're in the lousy idea camp. How come?
YANKAH: Well, I'm torn about the name and likeness issue, which is slightly different than paying the athletes. But at bottom, the reason I'm concerned is because I think this will be awfully hard to distinguish from salaries. I consistently worry about the continued professionalization of college athletics.
Look; there's no question that the current system is deeply exploitative and deeply problematic. I guess my baseline worry is many people - I think people in good faith - see the exploitation, and they say the answer is to pay these young athletes some amount of money while they're playing football or basketball. I look, and I say the answer is to make sure that these young men - and with the revenue generated in sports, it's typically young men - that they get the thing that they were promised that was of value. That is to say they get a college degree that was of value.
And one of the things I worry about is how many of, at least the listeners to NPR, those who have opportunity and resources - how many of them would trade a college degree for their child for three years of their child being paid in college? I doubt that's a trade that your listeners would make. Those are not the dreams I have for my children.
KELLY: So in your view, should anything change in the current system?
YANKAH: Yeah. I think everybody agrees that the current system needs to be changed and that the corruption of the current system is untenable and, indeed, deeply racially scarred. I'm not interested in whether or not even my beloved Wolverines crank out three or four professionals a year. I'm interested in universities that can crank out generations of black lawyers and doctors and engineers.
It seems to me that the best way to make sure that we are actually serving these young men is to do our best to support and create a true minor league system.
KELLY: Similar to the way it works in Europe already.
YANKAH: Similar to the way it works in Europe. Young kids who want to play for Manchester United are playing in soccer camps from when they're young. Every year, they get cut down. But the ones who dream of playing on the big stage pursue through the minor league system - and similar to the way it works in baseball and, by the way, similar to the way it works in hockey in the United States.
KELLY: I want to make this personal. You played soccer a little bit in college. New college athlete - would you have wanted to get paid?
YANKAH: Maybe in this way I'm a little bit pushed the other way. I played very briefly when Michigan was a club team. In order to keep playing, I would've had to pay money to play. I was working a full-time job in college on top of scholarships. I would've been thrilled to be able to play, just not to pay. And so in this way, I am one of the people who truly thinks that sports are actually a part of an education. You know, we don't think of the dancers as not students, and we don't think of the chess players as not students.
KELLY: The chess team isn't bringing in a billion dollars every year, though.
YANKAH: No, that's true. That's absolutely right. And I think, you know, that's a concern. On the other hand, if there was a true professional league where the students who wanted to make their money could go make their money, then the university could look the student-athletes in the eye and be quite clear that the revenue generation was more about the university than any particular student-athlete. That is to say if your skills are the kind for which you can get paid, you can go to the minor league and get paid.
KELLY: That's Ekow Yankah. He is a professor at Cardozo School of Law, and he wrote an essay for The New Yorker titled "Why NCAA Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid."
Ekow Yankah, thanks.
YANKAH: Thank you for having me.
Copyright © 2019 NPR. All rights reserved. Visit our website terms of use and permissions pages at www.npr.org for further information.
NPR transcripts are created on a rush deadline by an NPR contractor. This text may not be in its final form and may be updated or revised in the future. Accuracy and availability may vary. The authoritative record of NPR’s programming is the audio record.
College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid? Essay
College sport becomes more popular with the public because of its entertaining and mass character. Furthermore, college sport is a necessary part of the American youth’s culture. That is why the problematic questions associated with the aspects of college sport attract the large audience to discussing the issues.
Today, the question of paying college athletes salaries is actively discussed within the society because the profits gained by athletes for their teams and colleges increase regularly. From this point, the issue is in the necessity to encourage the athletes’ activities and provide them with some merits. Many researchers state that it is unfairly for colleges to gain all the possible benefits from the athletes’ successful performance without paying salaries (Johnson).
Nevertheless, it is also impossible to speak about the absence of financial benefits for the athletes because there are different kinds of special scholarships provided by colleges for their student-athletes. Thus, college athletes should not be paid because they receive their wages in the form of scholarships, college sport cannot be compared with the commercialized professional sports industry, and there is no effective system to provide athletes with salaries according to their efforts and performance.
The supporters of the idea to provide college athletes with salaries develop their arguments referring to the necessity to guarantee the students’ compensation for successful performance. However, student-athletes receive their regular scholarships without any dependence on performance in this or that season.
This scholarship is rather advantageous for them because it provides financial assistance and accentuates their role for the college’s development with references to the sports successes. College athletes can generate significant annual revenues for college teams, but different colleges perform differently in competitions.
From this point, the dependence of regular salaries on the athletes and team’s performance can be discussed as a kind of discrimination (Donaldson). That is why all the student-athletes receive the fixed scholarships which can vary about definite bonuses. Thus, the system based on scholarships can be discussed as more effective and advantageous for students about their successes as sportsmen.
It is possible to speak about only additional payments and bonuses for successful athletes without changing the current system of scholarships.Furthermore, those athletes who begin to receive wages for their performance should be discussed as professional sportsmen for whom sport is a kind of job.
College athletes are amateurs who can be successful or not in their performance. The necessity to pay each college athlete can be rather risky for many colleges where the sport is not developed. Moreover, the utilization of significant financial resources in colleges in the form of athletes’ wages is the source for increasing the corruption within the educational institutions (Johnson).
Sport in college is the part of the educational program, and it cannot be discussed as part of the commercialized industry with references to the professional sport. College athletes are not professionals in spite of the fact their sport results can be rather high.
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) does not support the idea of paying students for their sports successes because it is necessary to follow the standard rules of paying any wages for all the colleges and all the athletes without references to their performance (Johnson).
Colleges’ merits in relation to the athletes’ successes are different, and “it would be a burden for the majority of schools that don’t profit from athletics”, and moreover, “paying players could also introduce legal uncertainties ranging from the impact on Title IX to questions about workers compensation and unionization” (Cohen).
Thus, the new approach to the whole system of funding colleges and paying students is necessary. However, it is possible to speak about the professional career of a sportsman after graduating from college without concentrating on similar issues.
The implementation of a new system of paying college athletes should be developed with references to such important questions as the principles of distribution of resources among the athletes and the position of colleges which do not receive any profits from their college athletes.
It is significant to pay attention to the fact that only several colleges can gain real benefits from college sports competitions because of the high performance of their teams. The majority of college teams do not demonstrate extremely high results to provide their colleges with billions of profits. That is why, it is more rationally to discuss the question of paying students locally, basing on the definite bonus system.
If student-athletes are paid for their performance, they become equal in their status to professional sportsmen. From this perspective, the situation of providing students with special wages and regular salaries can influence the change in accents within the educational system.
It is important to avoid the evolution of the college sport into commerce, market, and the professional sports industry. Although the participation of athletes in college sports competitions which can provide the college with profits can be discussed as exploitation, the balance is preserved because of providing students’ scholarships for athletes.
Works Cited
Cohen, Ben. The Case for Paying College Athletes . 2011.
Donaldson, James. Standing above the Crowd: Execute Your Game Plan to Become the Best You Can Be . USA: Trinadigm, 2011. Print.
Johnson, Dennis. Point/Counterpoint: Paying College Athletes . 2012.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, August 16). College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid? https://ivypanda.com/essays/college-athletics-should-college-athletes-be-paid/
"College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid?" IvyPanda , 16 Aug. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/college-athletics-should-college-athletes-be-paid/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid'. 16 August.
IvyPanda . 2022. "College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid?" August 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/college-athletics-should-college-athletes-be-paid/.
1. IvyPanda . "College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid?" August 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/college-athletics-should-college-athletes-be-paid/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "College Athletics: Should College Athletes Be Paid?" August 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/college-athletics-should-college-athletes-be-paid/.
- Student-Athletes and Socialization
- Importance of Education to Student-Athletes
- Stress Management Skills of Student-Athletes
- Student Athletes' Employee Status and Compensation
- The Merits and Demerits of Paying Student-Athletes for Participating In College Sports
- Money Compensation for Student-Athletes
- Sleep Problems Among Student-Athletes
- Student-Athletes Compensation: Utilitarian View
- Commercialized Media and Cultural System on Prevailing Power Structure
- Recalling the Great UNC Sports Scandal
- Cycling Culture in France
- The Structural Sources of the Issue of ‘Juiced’ Athletes According to Mills’ Theory
- Mills and Juiced Athletes Problem
- Professional Sports Governance Issue
- Hockey Violence Intervention
Persuasive Essay on College Athletes Should Be Paid
Student-athletes sacrifice a lot of time and effort to be where they are. During the week, these athletes will participate in very challenging practices and games while also having to perform well in school. All the responsibilities of a student-athlete, in addition to maintaining a life outside of school, is a full-time task. In division-one schools the big question is, do these athletes deserve to be paid?
College level athletes always have very loaded schedules. Every day, these athletes have a lot of different tasks to complete. Some of these tasks include, workouts, practices, games, homework, social lives, and some even have jobs. The duties of a student-athlete can be overwhelming and saying that they work hard is an understatement. Surely, all this hard work must be paying off for the athletes, right?
Unfortunately for the athletes, they aren’t allowed to be paid for their involvement in any school’s athletic programs. A lot of people have a problem with this because the athletes produce so much revenue for the NCAA, but they get none of it. The NCAA governs intercollegiate athletics, and they make a lot of money doing it. For example, in the 2010-2011 fiscal year, the president of the NCAA, Mark Emmert, said that the projected total revenue for said year was 757 million dollars. Of that amount, 452.2 million dollars was distributed to division-one schools (Johnson).
Because of the restriction on paying student-athletes, some of these players that don’t have very big scholarships may have to try to find jobs, which just adds to their busy week. If the athletes were compensated through their programs, it would eliminate the need for them to get jobs. In turn, they would be able to focus more on their sports and classes. Also, there would be more job openings for the students who have more available schedules than student-athletes. This is especially good news for normal students because majority of them don’t have big scholarships either.
Speaking of scholarships, every year the 30 biggest universities in the country generate over 100 million dollars each. However, most of the universities spend more money than they make, on scholarships and expenses related to their programs. Even though these colleges make so much money, they spend even more. Paying the athletes would mean other, smaller, athletic programs will eventually get cut to keep the programs that generate money alive (Mcdavis).
Sponsorships are another way that players could be paid without the school’s revenue being affected. Star athletes who have their name out there are likely to be known by some of the top sports brands. The issue is that the players aren’t allowed to receive any revenue from their involvement with the school. If a player is caught accepting money from their involvement with the school, they can have their scholarship revoked and even get expelled from the school. So, with sponsorships not being a realistic option, athletes will want to work hard for scholarships instead.
If the payment of athletes was allowed, competition among athletes for scholarships and sponsorships will increase. Increased competition often leads to an increase in the usage of performance enhancing drugs (PEDs). This competition would all be taking place at the high school level in this scenario. Now, you’re looking at high school age athletes taking hormones at a critical point in their life, all for a shot at playing at a division-one school. A dangerous epidemic among teens could develop if we begin paying division-one athletes, but that’s not all.
Still assuming that student-athletes are allowed to be paid, most colleges wouldn’t be able to keep up with the big ones that make hundreds of millions of dollars. Star athletes would go to the big schools because they’ll make the most money there. After a while of this process, super teams would form from the big schools, generating more and more income from viewership and sponsorships. The big universities will just continue recruiting star players because they have the power to do so, and the cycle repeats. Small universities would eventually be drowned out and the big guys will be running the show (Mcdavis).
Enlarging the pool of money available for scholarships to athletes, would decrease the pool of money available for scholarships to normal students. In terms of fairness, that decision does not make sense. Normal students need money just as much as student-athletes, if not worse. If one college offers a bigger scholarship than another, the student will likely go to that school, disregarding other variables.
The NCAA makes a ton of money from fans watching athletics, and so do the universities. However, while players are the main source of the revenue, the expenses to cover all the universities’ programs and scholarships make it unfavorable to pay athletes. Paying division-one athletes would indirectly end up promoting a dangerous amount of competition for young athletes. It would also hurt many other universities, causing them to close an enormous number of athletic programs in the long run. Said universities are likely to lose a chunk of their student body as well. There are more reasons to restrict athletes getting paid than not. It would be unfair, unsafe, and a flat-out bad idea.
Works Cited
Johnson, Dennis A., and John Acquaviva. "Point/counterpoint: paying college athletes." The Sport Journal, vol. 15, no. 1, annual 2012. Gale Academic OneFile, link.gale.com/apps/doc/A322563607/AONE?u=anke52316&sid=oclc&xid=e3899b0c. Accessed 4 Oct. 2021.
Mcdavis, Cody J. “Don't Pay College Athletes.” The New York Times, 26 Feb. 2019, p. A23(L). Gale Academic OneFile, https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A575860557/AONE?u=anke52316&sid=bookmark-AONE&xid=630b749c. Accessed 4 Oct. 2021.
Related Samples
- Essay on: How Covid-19 Changed Our Habits In Life
- What it means to be a good student
- Argumentative Essay Example on Cursive Writing
- Personal Essay Sample: Hurricane IDA
- Essay On Significance Of Independence In My Life
- Narrative Essay on My Strengths and Weaknesses in Essay Writing
- Beauty Pageants And Self Esteem Essay Example
- Reflective Essay about Trust
- Persuasive Essay on Trigger Warnings
- Narrative Essay Example: My Perfect Vacation
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Students
Argumentative Essay On Should College Athletes Be Paid? An Argumentative Essay
Type of paper: Argumentative Essay
Topic: Students , Education , Sports , College , Athletes , Law , United States , College Sports
Words: 1700
Published: 10/06/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Institutions of higher learning in the United States spend millions of dollars to recruit and train college athletes. These college athletes participate in various events at the expense of their time as students. If in return for their hard work, college athletes get nothing more than a scholarship and health protection, then it is absolutely unfair. This is because everyone around them gets some benefits – from the college coach who earns a decent salary of close to $100,000 a year to the media houses that profit from adverts and the entities that advertise at these college sporting events. Therefore, there the exclusion of college athletes from the list of paid beneficiaries in college sports is highly unethical and amoral. This is because everyone benefits from it, except the real participants who are at the forefront and risking their lives and doing the hard work. Moreover, college athletes literally “earn their keep”. In other words, they earn the right to be given valuable consideration for their contribution to their schools. This is because in the early 20th Century, college sports were nothing more than a tool for exercising and socializing. This is because college athletes only did some basic activities and they tend to use the rest of the time to socialize and carry out various activities. In the 21st Century, the dynamics and variables are a lot different from what existed on US college campuses 90 years ago. Today, there is a systematic move towards a process whereby universities invest a lot of money into their sporting infrastructure and sports training systems. In 2006, “Rutgers University invested as much as US$102 million in the renovation of its stadium for college sports”. This is a facility that nations in more than half of the countries of the world will dream of owning as a national sports stadium. This goes to show that college athletics is more than just about exercising, keeping fit and socializing. It has grown to more than just that. Therefore, there is more to sports in colleges than just infrastructure. There is competition and there is the need for dedication that goes beyond just the normal. Hence, there is an absolute requirement to ensure that the very people for whom these facilities were created are given what they duly deserve, a remuneration commensurate to the utilization of these facilities. The level of competition in college athletics is also really intense. Therefore, institutions of higher learning provide various offers to students which are short of being packaged as salaries. If a college student is getting an annual $100,000 scholarship for being an athlete, then it can be said that such an individual is literally being paid far beyond the minimum wage for his contributions to the school. Although many institutions give sportsmen and women scholarships of less than $20,000, there is a general disparity and this disparity is a reflection of the competition in the industry. Those who argue against providing a salary to college students claim that it will spark an unnecessary race towards providing too much money to students and this will cause most of them to lose focus on what they are in school for – academics. As a matter of fact, that is already happening with the extremely huge margins and differences between institutions’ scholarships to their athletes. Therefore, that argument that unnecessary competition will accompany paying sportsmen and women in colleges is not valid. It must also be recalled that internally, there are many activities and processes that go on in institutions of higher learning that provide sufficient motivation to athletes. Therefore, providing a standardized system of paying these athletes can help them to start planning their lives as sportsmen and women even before they graduate from college. This is because tying the motivation to only education creates major problems. First of all, most student athletes spend too much time training and they do not get the best of grades. Thus, when they graduate, they might only have one option – to go professional. This might not work out for most of them. And many of them end up like high-school graduates and others end up worse as drug addicts and criminals because they do not have the means to live the kind of life they ought to be living as college graduates. The only solution is to provide a fair value for the effort of each college athlete and manage their earnings well so they can have a smooth transition after graduation either into a career, entrepreneurship or professional sports. In the legal sense, it can be argued that the failure to pay college athletes is unconstitutional and goes against the civil liberties of the United States. The fundamental basis for the US constitution asserts that all human beings are created equally. And hence, there is the need for equal and fair treatment of all American people. “The doctrine of equal pay for equal work was introduced to the laws of our country as an extension of the Nineteenth Amendment which granted women in the United States the right to vote”. “The Nineteenth Amendment gave rise to the Equal Pay Act 1963 which created a new frontier for the provision of fair and equal remuneration for a given volume of work without prejudice for the gender and other features of an individual”. The doctrine of the Nineteenth Amendment formed a major part of the argument and demands of the members of the Civil Rights Movement. This culminated in the creation of a system through which all forms of discrimination were critically reviewed by the legal system and practices that discriminated against people for their features were abolished. There are many educational rules that make it difficult for the provision of fair value of remuneration to college athletes. These regulations are meant to get students to focus on their studies and get educational institutions to concentrate on educating people. In spite of this, it can be identified that educational institutions are able to get around these requirements and they use various techniques and means to recruit the best athletes and spend a lot of money on sporting facilities. They therefore find ways of evading the limits placed on them to achieve their goals and make their heads and leaders look good in the eyes of stakeholders like the alumni. However, the poor students who are individual and do not have much of a voice end up working hard and putting in their best for absolutely nothing. This is simply because they do not have the same power to override the rules. It must be recalled that the US Constitution is the primary law of the country. And as such, all laws by institutions like the Department of Education and others are subject to the laws of the United States. It is apparent that many college athletes do so much work that is not different from what amateurs and professionals in the same sports do. These professionals and amateurs get a fair value for their effort and they claim it and carry on with their lives. The only difference here is that college athletes have decided to get a better future for themselves by studying something that will benefit them. This makes it illegal because they put in a given quantum of effort that their professional and amateur counterparts also do. So on the basis of equality and the doctrine of “equal work for equal pay”, it is apparent that all laws barring college athletes from achieving a fair remuneration is illegal and is inconsistent with the US Constitution. It must also be added that that the core value of the United States is on the basis of Capitalist ideologies. The government and the state only have the obligation to work as an invisible hand that guides activities in our country. They should not dictate anything to anyone nor force anyone to do anything. In this case, it is apparent that the classical ideals of Adam Smith towards capitalism are breached in the United States when college athletes are denied the right to a fair salary. This is because they are being made to work and achieve results that are not rewarded adequately is no different from activities in a Communist country where people are to work for a stipend from the government. Therefore, these rules preventing college athletes from gaining a fair salary are not in the right spirit of the American social values. Finally, college sports are meant to help groom intellectual and smart professionals who will take over the sporting arena of the country and achieve international laurels for the United States. However, from the way college students are being made to play for little or no remuneration, it is clear that most of them are going to lose their interest and desire to build their competencies and sacrifice for the development of their careers. In conclusion, it can be identified that student sportsmen and women are being delved a negative deal because they are the only ones who do not benefit when college sports do not yield them remuneration. This is morally problematic as college sports yield benefits to all stakeholders except these college athletes who get little or no economic benefits from their sports. Viewing this from the US Constitution, this practice is wrong and does not encourage equality. The doctrine of equal work for equal pay is disregarded because college athletes do equal work as amateur and professionals sports participants. It is further argued that not paying college sportsmen and women is against the US’ tradition of capitalism and this goes on to have a detrimental influence on the development of sports in the United States.
Works Cited
Alfred, Richard, et al. Performance: The Dynamic of Results in Postsecondary Organizations. Larnham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2013. Print. Critchlow, Donald. Phyllis Schlafly and Grassroots Conservatism: A Woman's Crusade. . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Presss, 2011. Print. Weir, Robert. Workers in America: A Historical Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara: ABC CLIO, 2012. Print.

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 131
This paper is created by writer with
ID 258344070
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Example of essay on public relations, intellectual property report examples, nas t shirt business proposal research paper examples, example of managerial control report report, what is the effect of financial crisis on employment in uk after 2008 literature review, research paper on the meaning of work, controversy concerning the reader essay sample, example of gender matters essay, essay on frederick douglass journey to literacy, course work on western religious philosophy, example of report on the game of golf, free essay on rising fuel prices and its effect on the airline industry and fuel hedging, critiques of essays critical thinking samples, starbucks case study sample, free discrimination in the social world essay example, short answer essays examples, stereotyping problem case study example, good example of argumentative essay on music morals, japans state secret law article review examples, researched argument part 1 research paper sample, exploration of how race works as a political ideology essay, good essay on step two, mending essays, impatience essays, inventory control essays, occupancy essays, egotism essays, idolatry essays, informant essays, egoism essays, impressionist essays, duplessis essays, delimitations essays, bongar essays, derails essays, abducts essays, protein reports, evidence reports, ireland reports, talent reports, kinship reports, hamlet reports.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
- Share full article
Advertisement
What Would Paying Student Athletes Look Like?
A college team’s vote to unionize adds pressure on the N.C.A.A. to abandon rules that forbid paying student athletes like employees.

By Joe Nocera and Ephrat Livni
“Unions are tricky for college sports,” Jay Bilas, the ESPN college basketball analyst, said over the phone the other day, “because you’ve got public and private institutions and different state laws.”
“It’s not impossible to have a union of college athletes,” he said, “but it would be difficult.”
Bilas, who is a vocal critic of the National Collegiate Athletic Association, was referring, of course, to the news on Tuesday that the Dartmouth College men’s basketball team had voted 13 to 2 to form a union . He was skeptical that this latest shot across the N.C.A.A.’s bow would lead anywhere. Still, it was the latest example of the pressure the association is under to finally abandon “amateurism” — the N.C.A.A.’s long-held dogma that prevents college athletes from being paid. Of course over the past few years, many athletes have been able to put money in their pockets, thanks to so-called NIL payments (NIL stands for name, image and likeness). But that’s an ad hoc system, organized largely by supporters of the athletic department, that allows some athletes to bring in millions while others make nothing. It’s not the same as universities paying athletes they employ.
Bilas said it was clear that schools would soon have to pay their athletes in sports that bring in a lot of money, like football and men’s basketball. And he’s not the only one. Jeffrey Kessler, the lawyer who won the big antitrust case against the N.C.A.A. before a unanimous Supreme Court in 2021, has another case against the organization that is scheduled to go to trial in January. The suit alleges that college athletes have been illegally deprived of any payment for having their names, images and likenesses used in promotional broadcasting that have earned millions for big athletic conferences like the Big Ten. If he were to win that case — and the odds are in his favor — the N.C.A.A. and the conferences could be liable for up to $4 billion.
Although the N.C.A.A. remains stubbornly resistant to settling the antitrust cases against it, the prospect of paying billions in damages might finally bring the organization to the table. Either through a court victory or a settlement, the litigation could, Kessler said, lead to “the complete transformation of the current structure so that the athletes who generate all the revenue can receive fair compensation for what they are contributing.”
But if a new structure arose to compensate players, what would it look like? Andy Schwarz, an economist deeply involved in the fight to transform the N.C.A.A., told me that he could very well see unions playing a part — but it would be a different kind of union from what the Dartmouth players were trying to do. “You would have conference-level unions to negotiate the terms of employment and to enshrine in contracts the rights and duties of an athlete,” he wrote in an email. “In my view, the schools would provide the education and the conferences would be employing the athletes to be participants on a television program.” In other words, each conference would agree to a kind of collective bargaining agreement with a players’ association, just like professional sports.
Which still leaves the question of how individual players are paid under the umbrella of the collective bargaining agreement. Bilas told me that whenever he had been asked that question, he replied: “This is really simple. Just have a contract between the athlete and the school. Just like the rest of American business does.”
The contract could be about more than just compensation. It could have buyout clauses that would include financial penalties if a player jumped to another school, or if a school cut the player loose. It could be multiyear, which would create incentives for athletes to stay in school beyond freshman year. There could even be a clause to ensure the athlete receives a real education rather than “majoring in eligibility” as is so often the case today.
“At first,” Bilas said, “some players will be overpaid and some others might be underpaid, but pretty soon, a market will be established, and you’ll know what players are worth.”
Would Bilas’s idea further separate the major sports schools, like Ohio State and Alabama, from the smaller schools, like Ball State or Eastern Michigan, that won’t have the money to pay their athletes? Sure. But that divide already exists.
“The walls are rapidly closing in on the N.C.A.A.,” Kessler said. “Nine Supreme Court justices have recognized how exploitative this system is. How long can they hang on? It’s up to them. They can participate in the resolution and come up with a system for everybody or they can go kicking and screaming into the night.” — Joe Nocera
HERE’S WHAT’S HAPPENING
President Biden goes after big business and billionaires. In his State of the Union address , Biden signaled that he wanted to raise taxes on corporations and wealthy people. The policy wish list presented a contrast with Donald J. Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee, even if it is unlikely to become law while the G.O.P. controls both the House and the Senate.
China revealed its economic growth target. The Chinese premier, Li Qiang, said that the world’s second biggest economy would aim for 5 percent growth in 2024 , the same as last year. But he dashed investors’ hopes that Beijing would also announce measures to stimulate the economy, with some analysts saying that slow growth was the new normal.
Apple reversed course to allow a competing app store in Europe. The move to allow Epic Games to develop a game store for iPhones and iPads in Europe highlights how Apple is changing its operations to comply with the Digital Markets Act , a sweeping new law designed to help small businesses compete with the biggest. It came days after Apple was fined 1.8 billion euros ($1.95 billion) for thwarting competition from rival music streaming services through its dominant App Store.
TikTok comes under new pressure from U.S. lawmakers. The House Select Committee on the Chinese Communist Party introduced a bill that would ban TikTok from U.S. app stores unless ByteDance, its Chinese parent company, divests. The company urged its users to tell their representatives in Washington to vote against the bill, leading to Congressional offices being overwhelmed with calls.
Three questions for Rohit Chopra
One year after a rapid run on deposits at regional banks set off fears of a financial crisis, forcing government intervention, banks are gearing up for a big fight with their regulators.
Those regulators want to roll out a new proposal for banks to set aside more liquid funds to weather an emergency — a risk that the $1 billion rescue of New York Community Bank by private investors on Wednesday drove home.
But big banks are already pushing back on an existing plan to force them to hold more capital. And their protests could be successful: Jay Powell, the Fed chair, this week signaled that plans to make the biggest banks hold more capital may be overhauled.
DealBook spoke to Rohit Chopra, who leads the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, about what went wrong last year and how to fix it. His answers have been lightly edited for brevity and clarity.
What do you think of Powell’s signal that regulators may retreat from new capital requirements for big banks?
There has not been a final rule published. That’s an ongoing rule-making. But large banks need more skin in the game. Certainly, a lot of the financial industry told us in 2022 that everything is great: “We don’t see any risk of significant failure on the horizon.” And then last March, we had a domino effect of several banks going down, and, absent emergency intervention, more would have gone down. So I don’t think we live in a world where we can count on large banks always being OK. And because they take a lot of insured deposits, they get a lot of implicit and explicit federal subsidies and their failure can cause global financial crises, we gotta make sure that their shareholders are the ones who hold the bag when things go wrong. That’s the reason for doing it.
What other solutions are available?
We have a system right now where smaller banks have limits, but the very largest essentially can hand out free unlimited deposit insurance because there’s a perception that they would be rescued if they screwed up, that they’re implicitly insured. That, to me, seems fundamentally unfair. I would favor raising the cap on deposit insurance substantially so that there is some parity between small players and the biggest players.
I also favor more limitations on banks that are deeply dependent on these so-called uninsured deposits. When we look at Silicon Valley Bank, it was very fast growing, deeply dependent on uninsured deposits. There’s obviously more that could be done, but I’d certainly put those on the list.
Is the situation at NYCB, whose problems have been driven by mounting commercial real estate losses, a repeat of last year?
The issues we saw last year were not closely tied to commercial real estate. We have a lot of things that are still unresolved to make sure last year’s bank failures don’t recur. But at the same time, there’s the impending risks, and safeguarding the system for that, which includes commercial real estate.
Thanks for reading! We’ll see you Monday. In the meantime, remember, clocks in the United States spring forward tonight.
We’d like your feedback. Please email thoughts and suggestions to [email protected] .
Ephrat Livni reports from Washington on the intersection of business and policy for DealBook. Previously, she was a senior reporter at Quartz, covering law and politics, and has practiced law in the public and private sectors. More about Ephrat Livni
Inside the World of Sports
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping professional, collegiate and amateur athletics..
Baseball Season: Fans of the sport in South Korea have embraced Shohei Ohtani , the superstar from Japan, despite a longtime rivalry and history between the two countries.
Unionization Efforts: How is a football team different from a marching band? The National Labor Relations Board is considering this question as it tries to determine whether some college athletes should be deemed employees .
Delayed Gratification: Doping rules, legal challenges and endless appeals have left some Olympic medalists waiting for their golds .
The Worst Job in College Basketball: South Carolina Salkehatchie had no budget, players or running water when Matt Lynch arrived. One season in, the first publicly gay head coach is figuring out how to win , on the court and off.
How the Kelces Made Crying Cool: Tears in men’s sports were once considered a sign of weakness. But Jason and Travis Kelce have regularly put their emotions on full display .
March Madness brings in millions for colleges. But athletes still provide 'free' labor.
The earning potential for many athletes is often never greater than it is during their time spent as part of powerhouse college athletic programs..
With employees nationwide getting ready to partake in their annual March Madness office pools , college athletes have never been closer to recognition as valued employees themselves.
In February, a National Labor Relations Board regional director ordered a union election for the Dartmouth College men’s basketball team , finding that the players are entitled to unionize as school employees under the National Labor Relations Act. The board’s decision is just one part of a rapidly evolving legal landscape that seems increasingly receptive to the idea that college athletes should be fairly compensated for the profits they produce for their schools.
The board’s decision aligns with the Supreme Court’s 2021 ruling in NCAA v. Alston , which signaled clearly that colleges and universities are not exempt from antitrust laws when it comes to profiting from student-athletes without fairly compensating them.
Antitrust laws exist to ensure fair competition in a free-market economy. Top college athletes should be allowed to operate competitively in the open marketplace. In fact, many Division I athletes drive sports programs that generate outrageously large profits for their schools. The Ohio State University athletic program, for example, raked in more than $250 million in revenue in just the fiscal year 2022.
But should college athletes be compensated as employees when they already receive non-employee-based compensation?
The Dartmouth NLRB decision on Feb. 5 found that “the players (play basketball) in exchange for compensation” but also that Dartmouth “does not provide (the players) with monetary compensation.”
How then are the players compensated? Athletic scholarships could be construed as compensation, but Ivy League schools don’t offer them.
Instead, the board found that the players were offered something arguably “more valuable” than an athletic scholarship: an “early read” of their applications or access to a “special admission process” to gain entry into a highly selective college, in addition to unconditional financial aid, athletic apparel and other amenities.
Supreme Court opened the door for NIL compensation
But the Supreme Court's unanimous decision in the Alston case in June 2021 suggests that college athletes are entitled to more than just non-cash compensation.
At oral argument, Justice Elena Kagan chastised the NCAA for appropriating the athletes’ “amateur” status as a basis to deny them compensation and, in a fiery concurring opinion, Justice Brett Kavanaugh invited broader challenges to the NCAA’s student-athlete compensation rules.
Is it safe for women to run? Being a female runner shouldn't be dangerous. Laken Riley's death reminds us it is.
Just weeks later, the force of the Alston ruling greased the skids for a combination of state law and NCAA regulation changes, through which college athletes acquired the ability to lawfully monetize their names, images and likenesses (NIL).
By accepting money from businesses in exchange for allowing them to use a personal likeness or image in advertisements, Division I athletes can now earn hundreds of thousands of dollars upon enrollment, often with the assistance of school-affiliated NIL collectives , which exist to source such opportunities for them.
Top Division I earners can reap millions , with USC freshman basketball player Bronny James (son of LeBron James) worth an estimated $5.9 million .
Shouldn’t a formal wage-based compensation scheme be offset by the value of the scholarships college athletes receive, in addition to any NIL earnings? The potential for those earnings, in addition to scholarship money and related benefits, is surely more than sufficient compensation for college water polo players or fencers, for example, particularly because the vast majority of them complete the degrees they were promised when recruited.
But the calculus is often different for athletes propping up massive revenue-generating institutions such as football or basketball.
The vast majority of those student-athletes never turn professional. Far from it − many of them are “used up” and “cast aside” without ever completing their degrees, as Justice Samuel Alito pointed out at oral argument in the Alston case.
Consequently, their earning potential is often never greater than it is during their time spent as part of powerhouse college athletic programs. The subtext of Alston is that those student-athletes should be permitted to capitalize on that potential. Those athletes now have the Dartmouth basketball team to thank for furthering their case to be valued as employees.
The irony? According to the college, Dartmouth basketball operates at a loss .
The real March Madness: Why don't NCAA schools pay college athletes who make them billions?
Will colleges recognize athletes as employees?
The Dartmouth NLRB decision, moving college athletes ever closer to formal recognition as “employees,” is all the more important as the NCAA seeks to enforce rules that limit NIL earning power. Most recently, the attorneys general of Tennessee and Virginia sued in federal court to prevent the NCAA from enforcing those rules, which prohibit student-athletes from negotiating NIL deals during the recruitment process.
The presiding judge has already ruled in favor of the athletes, finding that the states are likely to succeed on the merits of their claims because the “NCAA's prohibition likely violates federal antitrust law and harms student-athletes .”
The NIL litigation comes just as the 3rd Circuit Court of Appeals considers whether college athletes are employees under the Fair Labor Standards Act, which sets minimum wage and overtime pay requirements. In that case, Johnson v. NCAA , a group of Division I athletes sued on the theory that they should be paid as employees under the FLSA for their time engaged in athletic activities on behalf of their schools. A ruling for the athletes would allow the case to move forward toward trial in the federal district court.
The net effect of the Dartmouth NLRB decision would be to bring athletes one step closer to unprecedented bargaining and earning power over colleges and universities that have, in many cases, enjoyed outsize institutional growth as a direct result of those athletes’ revenue-generating efforts.
College athletes deserve to be compensated appropriately for their efforts, commensurate with the economic benefits their hard work confers upon their schools.
Of course, there remains the question of how any formal compensation scheme should be structured. As far as the law is concerned, the process of answering that question is well underway, and rightly so.
Alex Talel is an attorney and author. He served as law clerk to Judge Jon O. Newman of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 2nd Circuit and to Judge Sidney H. Stein of the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Introduction paragraph with a thesis statement that establishes an arguable claim . The thesis statement must communicate the topic of the essay: Whether college athletes should be paid, and Convey a position on that topic: That college athletes should/should not be paid, and ; State a couple of defendable, supportable reasons why college athletes should be paid (or vice versa).
College Athletes Deserve to Get Paid. In 2019, the NCAA reported $18.9 billion in total athletics revenue. This money is used to finance a variety of paid positions that support athletics at colleges and universities, including administrators, directors, coaches, and staff, along with other employment less directly tied to sports, such as those ...
College athletes are currently permitted to receive "cost of attendance" stipends (up to approximately $6,000), unlimited education-related benefits, and awards. A 2023 survey found that 67% ...
Now, the N.C.A.A. has approved a historic change to allow student-athletes to be compensated for use of their N.I.L., with schools and conferences allowed to adopt their own additional policies ...
Pro 3 College athletes are often valued at more than $1 million, but they (and their families) frequently live below the poverty line. A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that the top two college football positions-the quarterback and wide receiver-were worth $2.4 million and $1.3 million per year respectively, while starting men's basketball players in the Power ...
A lot of college athletes get scholarships and other financial benefits from their sports. However, I think athletes should have the right to their own name and brand. So, getting paid through sponsorships or merch with their name on it should be totally fine." Editor Three: "I don't think college athletes should be paid at all ...
For more than a century, or as long as the N.C.A.A. has presided over college sports, athletes had no legal way to earn anything more tangible from their achievements than plaques and trophies.
Some argue student-athletes are "paid" through full scholarships, something most college students can only dream about — and that's partially true. According to the NCAA, over 150,000 Division I and Division II student-athletes receive $2.9 billion in scholarships each year (Division III schools don't offer athletic scholarships).
Between 1985-1986 and 2009-2010 at 44 universities in one of the five major conferences, average compensation expressed in 2009-2010 dollars increased for full professors from $107,400 to $141,600, for presidents from $294,400 to $559,700, and for head football coaches from $273,300 to $2,054,700.10.
One of the good reasons why college athletes should be paid is that it provides athletes to get good exposure. Every Saturday there are a bunch of college football games, top performers get rewarded with awards, for example the player of the week, and that goes for all sports. Exposure is a big thing in sports but some also agree it should be ...
Historically, spectacularly, wrong. A new national survey commissioned by Sportico in cooperation with The Harris Poll found that 67 percent of American adults believe college athletes should be ...
To see that dependable college athletes are getting paid for their skills on the field. The typical Division I college athlete devotes 43.3 hours per week to his sport which is 3.3 more hours than the typical American work week which means they have no time to work a job to make money.
Persuasive arguments in this essay show that getting paid college athletes will help them support their family and limited the corruptions from NCAA and player may stay in college longer. These will truly help college athletes with their long work scheduled with games; practice and school work and make a better place where I believed lot people ...
Paragraph 1: Since college athletics programs are geared towards turning a profit at the end in terms of the revenue generated during the programs, it would only be fair to pay the athletes involved. Some of the revenues should be passed to the people who actually cause the fans to come to the pitch, the players.
Since its inception in 1906, the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) has governed intercollegiate sports and enforced a rule prohibiting college athletes to be paid. Football, basketball, and a handful of other college sports began to generate tremendous revenue for many schools in the mid-20th century, yet the NCAA continued to ...
📑 Should College Athletes Be Paid Essay Outline Our Experts can deliver a custom essay for a mere 11.00 9.35/page Learn more. Before writing your work, the first thing you want to do is outline. An argumentative-style essay would be perfect for writing on our topic.
NPR's Mary Louise Kelly speaks with Ekow Yankah, author of The New Yorker essay, "Why N.C.A.A. Athletes Shouldn't Be Paid," about the NCAA's decision to allow college athletes to earn compensation.
We will write a custom essay on your topic. Today, the question of paying college athletes salaries is actively discussed within the society because the profits gained by athletes for their teams and colleges increase regularly. From this point, the issue is in the necessity to encourage the athletes' activities and provide them with some merits.
Said universities are likely to lose a chunk of their student body as well. There are more reasons to restrict athletes getting paid than not. It would be unfair, unsafe, and a flat-out bad idea. Works Cited. Johnson, Dennis A., and John Acquaviva. "Point/counterpoint: paying college athletes." The Sport Journal, vol. 15, no. 1, annual 2012.
Paying college athletes will increase the competitiveness of various sports programs. Tiered payments given to professional players in sports like basketball motivate them to perform better. The hard work from professional athletes boosts their total wages from sponsorship deals and media events (Steckler, 2015).
Therefore, there the exclusion of college athletes from the list of paid beneficiaries in college sports is highly unethical and amoral. This is because everyone benefits from it, except the real participants who are at the forefront and risking their lives and doing the hard work. Moreover, college athletes literally "earn their keep".
Decent Essays. 1131 Words. 5 Pages. Open Document. An issue that has been a well-known topic of conversation recently is the subject of college athletes getting paid or not. This issue has been circulating amongst sports fans throughout the country. Everyone from the fans, players, parents, and media groups all have opinions on this matter.
Essay on Why Is Baseball the Highest Paid Sport Pay to Play in Civil Engineering: Analytical Essay College Athletes And Financial Reward College Athletes Should Get Paid: For And Against Paying Wages To College Athletes Why Football Should Be Banned among Children: Opinion Essay Cheerleading Is a Sport: Argumentative Essay Cheerleading Is not a ...
A college team's vote to unionize adds pressure on the N.C.A.A. to abandon rules that forbid paying student athletes like employees. By Joe Nocera and Ephrat Livni "Unions are tricky for ...
NCAA, a group of Division I athletes sued on the theory that they should be paid as employees under the FLSA for their time engaged in athletic activities on behalf of their schools. A ruling for ...
Getting paid is an incentive for them to perform better. This motivates them to become professional athletes. According to NCAA reports, less than 2% of college athletes become professional players. Offering them a work-study program or a stipend for playing can give them a reason to pursue their careers in athletics.