How Effective Is Online Learning? What the Research Does and Doesn’t Tell Us

- Share article
Editor’s Note: This is part of a series on the practical takeaways from research.
The times have dictated school closings and the rapid expansion of online education. Can online lessons replace in-school time?
Clearly online time cannot provide many of the informal social interactions students have at school, but how will online courses do in terms of moving student learning forward? Research to date gives us some clues and also points us to what we could be doing to support students who are most likely to struggle in the online setting.
The use of virtual courses among K-12 students has grown rapidly in recent years. Florida, for example, requires all high school students to take at least one online course. Online learning can take a number of different forms. Often people think of Massive Open Online Courses, or MOOCs, where thousands of students watch a video online and fill out questionnaires or take exams based on those lectures.
In the online setting, students may have more distractions and less oversight, which can reduce their motivation.
Most online courses, however, particularly those serving K-12 students, have a format much more similar to in-person courses. The teacher helps to run virtual discussion among the students, assigns homework, and follows up with individual students. Sometimes these courses are synchronous (teachers and students all meet at the same time) and sometimes they are asynchronous (non-concurrent). In both cases, the teacher is supposed to provide opportunities for students to engage thoughtfully with subject matter, and students, in most cases, are required to interact with each other virtually.
Coronavirus and Schools
Online courses provide opportunities for students. Students in a school that doesn’t offer statistics classes may be able to learn statistics with virtual lessons. If students fail algebra, they may be able to catch up during evenings or summer using online classes, and not disrupt their math trajectory at school. So, almost certainly, online classes sometimes benefit students.
In comparisons of online and in-person classes, however, online classes aren’t as effective as in-person classes for most students. Only a little research has assessed the effects of online lessons for elementary and high school students, and even less has used the “gold standard” method of comparing the results for students assigned randomly to online or in-person courses. Jessica Heppen and colleagues at the American Institutes for Research and the University of Chicago Consortium on School Research randomly assigned students who had failed second semester Algebra I to either face-to-face or online credit recovery courses over the summer. Students’ credit-recovery success rates and algebra test scores were lower in the online setting. Students assigned to the online option also rated their class as more difficult than did their peers assigned to the face-to-face option.
Most of the research on online courses for K-12 students has used large-scale administrative data, looking at otherwise similar students in the two settings. One of these studies, by June Ahn of New York University and Andrew McEachin of the RAND Corp., examined Ohio charter schools; I did another with colleagues looking at Florida public school coursework. Both studies found evidence that online coursetaking was less effective.

About this series
This essay is the fifth in a series that aims to put the pieces of research together so that education decisionmakers can evaluate which policies and practices to implement.
The conveners of this project—Susanna Loeb, the director of Brown University’s Annenberg Institute for School Reform, and Harvard education professor Heather Hill—have received grant support from the Annenberg Institute for this series.
To suggest other topics for this series or join in the conversation, use #EdResearchtoPractice on Twitter.
Read the full series here .
It is not surprising that in-person courses are, on average, more effective. Being in person with teachers and other students creates social pressures and benefits that can help motivate students to engage. Some students do as well in online courses as in in-person courses, some may actually do better, but, on average, students do worse in the online setting, and this is particularly true for students with weaker academic backgrounds.
Students who struggle in in-person classes are likely to struggle even more online. While the research on virtual schools in K-12 education doesn’t address these differences directly, a study of college students that I worked on with Stanford colleagues found very little difference in learning for high-performing students in the online and in-person settings. On the other hand, lower performing students performed meaningfully worse in online courses than in in-person courses.
But just because students who struggle in in-person classes are even more likely to struggle online doesn’t mean that’s inevitable. Online teachers will need to consider the needs of less-engaged students and work to engage them. Online courses might be made to work for these students on average, even if they have not in the past.
Just like in brick-and-mortar classrooms, online courses need a strong curriculum and strong pedagogical practices. Teachers need to understand what students know and what they don’t know, as well as how to help them learn new material. What is different in the online setting is that students may have more distractions and less oversight, which can reduce their motivation. The teacher will need to set norms for engagement—such as requiring students to regularly ask questions and respond to their peers—that are different than the norms in the in-person setting.
Online courses are generally not as effective as in-person classes, but they are certainly better than no classes. A substantial research base developed by Karl Alexander at Johns Hopkins University and many others shows that students, especially students with fewer resources at home, learn less when they are not in school. Right now, virtual courses are allowing students to access lessons and exercises and interact with teachers in ways that would have been impossible if an epidemic had closed schools even a decade or two earlier. So we may be skeptical of online learning, but it is also time to embrace and improve it.
A version of this article appeared in the April 01, 2020 edition of Education Week as How Effective Is Online Learning?
Sign Up for EdWeek Tech Leader
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- Why More and More Students Are Taking Online Classes? Words: 588
- Effectiveness of Online Quizzes to Assess Students’ Learning Words: 1752
- Education Theory for Online Learning Words: 590
- History and Evolution of Online Education Words: 836
- Online Education and E-Learning: Potential and Benefits Words: 2018
- Online Education as an Alternative to Traditional Schooling Words: 1421
- Online Courses by Traditional Universities Words: 5611
- Benefits and Drawbacks of Online Education: Analysis Words: 630
- Learning Methods: Online Learning Words: 928
- Online vs. Traditional Classroom Education Words: 1067
- Pros and Cons of Online Learning Words: 1102
- Information Technology Enabled Online Learning Words: 1099
- Online Learning vs. In-Person Learning Words: 580
- Learning Paradigms: On-Line Education Words: 1093
Effectiveness of Online Education
It is hard to dispute that online education has recently established itself as a significant component of current educational systems. As new technologies are developed, online learning continues to take on new forms. The majority of colleges, high schools, and other educational institutions throughout the world have embraced this method of instruction, and the number of students attending online classes is fast increasing. The current educational system and common practice have undergone significant modifications. Multiple causes, including technological advancements, better infrastructure, and enhanced communications, have contributed to this. Technology has made it feasible to learn online. When closely examined, this method of learning appears straightforward in comparison to classroom instruction. However, the use of online education still creates a number of contentious points of view since some people back this technique and provide their justifications, while others are opposed to it and provide equally solid justifications. Online learning connects teachers with students who may not be able to enroll in a regular classroom course, as well as provides flexibility in scheduling.
The online class system is proven to be a terrific alternative to conventional classrooms in the era of technology, despite the fact that some people still believe that traditional classes are the greatest way to study. Students that are committed to expanding their knowledge, picking up new abilities, and acquiring respectable credentials frequently sign up for the most useful courses (Moise et al ., 2021). Many applicants are now able to receive their education at home because of their devotion to this online learning. Online education is thus one of the most practical methods of learning for people who are disadvantageous owing to distance, considering its advantages. This lowers the expense of creating classrooms, buying books, and traveling (Arkorful and Abaidoo, 2018). Tuition fees are a cost that parents cannot avoid. Students can obtain all the necessary study materials, tests, and results since they can use contemporary technology.
Access to educational facilities is made simple by internet technology, which is commonly utilized by online schools. This made it simple for instructors, staff, and administrators to share information with students. Employing fewer staff members and lowering the cost of obtaining more materials from other universities lowers the institute’s operational expenses (Moise et al ., 2021). The flexibility of online mode of education allows students to study whenever it is most convenient for them. Students had to go outside of their comfort zones for a lengthy period to see professors. Moreover, their focus can be impaired as a result of the surroundings’ shift. Instead, online education gives students the option to pick the most conducive learning environment, which improves their comprehension (Davis et al ., 2019). Students enjoy learning more as a consequence than they would in a traditional classroom setting. It may be described as a student-centered setting that can only be provided via distant learning.
Another benefit of online learning is the accessibility of educational resources. Students who take classes online have unrestricted access to study resources, which allows them to learn successfully and quickly. However, because they are forced to take notes during lectures, students in a classroom might not have the most accurate notes compared to content posted online. In the past, schools had restrictions on how many pupils may study in a single classroom. The number of pupils enrolled in schools was constrained by the lack of resources like lecture halls and professors. Moreover, it has been discovered that online learning lessens the workload for teachers (Davis et al ., 2019). The teacher’s burden is decreased because the majority of the notes and books are available to the pupils online. This demonstrates that online learning is significantly more advantageous for students, teachers, and the institution as a whole and those present difficulties may be addressed by using more advanced technology and effective teaching methods.
Online learning has numerous benefits for changing the learning process, but it also has certain drawbacks. Modern computers’ technological constraints, which have an impact on the caliber of educational resources and the learning process in general, are one of the issues. For instance, sluggish Internet connections and download speeds have an impact on the accessibility of educational resources (Sadeghi, 2019). However, by utilizing modern, fast-access hardware and software components, this issue has been resolved, which makes downloading educational software and applications simpler. Better and faster computers are developing as computing power rises, improving access to online educational institutions.
Moreover, there is a significant social disadvantage to online schooling. The fact that learning occurs online demonstrates unequivocally that there are no intimate social ties among the members of the school community. They can just have chat sessions, which might not happen as frequently. This makes it challenging to comprehend some of the problems that impact students’ performance and prevents further discussion of those problems.
The fact that technology is always evolving is another issue with online learning. Technology is evolving quickly, which puts obstacles in the way of the sharing of broad knowledge. For instance, it can be exceedingly challenging to manage a student when they are given homework, an online exam, or any other test since the answers provided to the examiner could not be accurate (Ferri et al ., 2020). Not to be overlooked are the scientific areas that need both practical and research labor. As chemists’ chemicals and equipment needed for practical physics lessons cannot be emailed to a student, teaching such courses online results in a restricted quantity of learning resources.
For students who can attend a class every day, the classroom setting offers a beneficial learning environment. Students benefit from interaction when such a setting is created. Unlike the internet environment, it fosters social growth and the free interchange of ideas. Many students contribute to the implementation of worthwhile concepts that strengthen teamwork and group projects (Arkorful and Abaidoo, 2018). They can learn firsthand information when they collaborate with their professors. Additionally, it enables unrestricted interchange of ideas without restrictions to language while getting instant feedback from peers and teachers.
In conclusion, online education is advantageous for both students and professors, as well as the organization that provides these courses. As a result, it seems that most educational institutions benefit from the use of online learning. Online forums, new web-based software, and the modernization of e-learning systems may all help to overcome the issues that come with online learning, such as the lack of student feedback and the lack of adequate technology to provide online learning successfully. This demonstrates how e-learning may take the place of conventional classroom instruction. Even though there are a lot issues now, there is still opportunity for advancement and improvement, which will probably result in the future growth of online learning.
Reference List
Arkorful, V. and Abaidoo, N. (2018) ‘ The role of e-learning, advantages, and disadvantages of its adoption in higher education ’, International Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning , 12(1), pp. 29–42. Web.
Davis, N.L., Gough, M. and Taylor, L.L. (2019) ‘ Online teaching: advantages, obstacles, and tools for getting it right ’, Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism , 19(3), pp. 256–263. Web.
Ferri, F., Grifoni, P. and Guzzo, T. (2020) ‘ Online learning and emergency remote teaching: opportunities and challenges in emergency situations ’, Societies , 10(4), p. 86–88. Web.
Moise, D., Diaconu, A., Negescu, M.D.O. and Gombos, C.C. (2021) ‘ Online education during pandemic times: advantages and disadvantages ’ , European Journal of Sustainable Development , 10(4), pp. 63–69. Web.
Sadeghi, M. (2019) ‘ A shift from classroom to distance learning: advantages and limitations ’, International Journal of Research in English Education , 4(1), pp. 80–88. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2024, February 6). Effectiveness of Online Education. https://studycorgi.com/effectiveness-of-online-education/
"Effectiveness of Online Education." StudyCorgi , 6 Feb. 2024, studycorgi.com/effectiveness-of-online-education/.
StudyCorgi . (2024) 'Effectiveness of Online Education'. 6 February.
1. StudyCorgi . "Effectiveness of Online Education." February 6, 2024. https://studycorgi.com/effectiveness-of-online-education/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Effectiveness of Online Education." February 6, 2024. https://studycorgi.com/effectiveness-of-online-education/.
StudyCorgi . 2024. "Effectiveness of Online Education." February 6, 2024. https://studycorgi.com/effectiveness-of-online-education/.
This paper, “Effectiveness of Online Education”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: February 6, 2024 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Is Online Learning Effective?
A new report found that the heavy dependence on technology during the pandemic caused “staggering” education inequality. What was your experience?

By Natalie Proulx
During the coronavirus pandemic, many schools moved classes online. Was your school one of them? If so, what was it like to attend school online? Did you enjoy it? Did it work for you?
In “ Dependence on Tech Caused ‘Staggering’ Education Inequality, U.N. Agency Says ,” Natasha Singer writes:
In early 2020, as the coronavirus spread, schools around the world abruptly halted in-person education. To many governments and parents, moving classes online seemed the obvious stopgap solution. In the United States, school districts scrambled to secure digital devices for students. Almost overnight, videoconferencing software like Zoom became the main platform teachers used to deliver real-time instruction to students at home. Now a report from UNESCO , the United Nations’ educational and cultural organization, says that overreliance on remote learning technology during the pandemic led to “staggering” education inequality around the world. It was, according to a 655-page report that UNESCO released on Wednesday, a worldwide “ed-tech tragedy.” The report, from UNESCO’s Future of Education division, is likely to add fuel to the debate over how governments and local school districts handled pandemic restrictions, and whether it would have been better for some countries to reopen schools for in-person instruction sooner. The UNESCO researchers argued in the report that “unprecedented” dependence on technology — intended to ensure that children could continue their schooling — worsened disparities and learning loss for hundreds of millions of students around the world, including in Kenya, Brazil, Britain and the United States. The promotion of remote online learning as the primary solution for pandemic schooling also hindered public discussion of more equitable, lower-tech alternatives, such as regularly providing schoolwork packets for every student, delivering school lessons by radio or television — and reopening schools sooner for in-person classes, the researchers said. “Available evidence strongly indicates that the bright spots of the ed-tech experiences during the pandemic, while important and deserving of attention, were vastly eclipsed by failure,” the UNESCO report said. The UNESCO researchers recommended that education officials prioritize in-person instruction with teachers, not online platforms, as the primary driver of student learning. And they encouraged schools to ensure that emerging technologies like A.I. chatbots concretely benefited students before introducing them for educational use. Education and industry experts welcomed the report, saying more research on the effects of pandemic learning was needed. “The report’s conclusion — that societies must be vigilant about the ways digital tools are reshaping education — is incredibly important,” said Paul Lekas, the head of global public policy for the Software & Information Industry Association, a group whose members include Amazon, Apple and Google. “There are lots of lessons that can be learned from how digital education occurred during the pandemic and ways in which to lessen the digital divide. ” Jean-Claude Brizard, the chief executive of Digital Promise, a nonprofit education group that has received funding from Google, HP and Verizon, acknowledged that “technology is not a cure-all.” But he also said that while school systems were largely unprepared for the pandemic, online education tools helped foster “more individualized, enhanced learning experiences as schools shifted to virtual classrooms.” Education International, an umbrella organization for about 380 teachers’ unions and 32 million teachers worldwide, said the UNESCO report underlined the importance of in-person, face-to-face teaching. “The report tells us definitively what we already know to be true, a place called school matters,” said Haldis Holst, the group’s deputy general secretary. “Education is not transactional nor is it simply content delivery. It is relational. It is social. It is human at its core.”
Students, read the entire article and then tell us:
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
- Current Issue
- Past Issues
- Get New Issue Alerts
- American Academy of Arts and Sciences
Online Learning & the Transformation of Global Higher Education
This essay examines the global impact of online education in the decade following the widely publicized introduction of MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) in 2012—exploring the demographics and preferences of learners, the effectiveness of online learning, the surprising and substantial impact on the labor market, and the implications of scalability for reducing the cost of education. The essay concludes that online education has broadened the range of activities undertaken by leading universities and will continue to dramatically expand the population of learners with access to low-cost, high-quality education.
Richard C. Levin , a Fellow of the American Academy since 1998, is the former President of Yale University (1993–2013) and the former CEO of Coursera (2014–2017). He is the author of The Work of the University (2003) and The Worth of the University (2013).
In 2012, online education burst into public view with the publication of a New York Times article entitled, “The Year of the MOOC .” 1 The article described the sudden growth in popularity of Massive Open Online Courses and the startup platforms that provided them (Coursera, ed X , and Udacity). A balanced and judicious account, it nonetheless precipitated an avalanche of fears and hopes. Faculty questioned the effectiveness of online learning, but nonetheless feared that the MOOC would replace classroom teaching, reduce the demand for professors, and transform them into teaching assistants. By contrast, trustees hoped that online instruction might reverse, or at least arrest, the relentless increase of tuition, and they urged presidents to invest for fear of missing out. The trustees of the University of Virginia even attempted to fire their president over her reluctance to embrace technology with the alacrity that they expected. 2 Universities around the country rushed to sign up with ed X , a nonprofit joint venture of MIT and Harvard, or Coursera, a for-profit startup founded by two Stanford professors. European, Latin American, and Asian universities soon followed. By mid-2014, Coursera and ed X had more than one hundred fifty unique university partners between them, most of which ranked in the global top 200.
A decade later, some early goals have been met and others have not; some fears remain while many have been laid to rest. As is typical of overhyped innovations, imagined revolution has given way to evolution. Slowly and steadily, online learning is transforming postsecondary education around the world, both inside and outside the academy, in ways that were not fully anticipated in 2012.
Online education predates the Year of the MOOC by four decades. In 1971, the Open University began to televise courses throughout the United Kingdom. Two years later, Jim Gibbons at Stanford conducted fascinating experiments combining videotaped lectures with live, onsite tutoring, anticipating lessons relearned in the MOOC era. 3 Education scholar Linda Harasim is often credited with offering the first fully online, for-credit university course in 1986 (accessed primitively by dial-up modems over landline telephone infrastructure), although Harasim herself identifies numerous precursors elsewhere between 1981 and 1986. 4 The University of Phoenix began offering fully online bachelor’s and master’s degrees just three years later, and other for-profit organizations, as well as nonprofits, followed shortly after. A decade later, at the turn of the millennium, top-tier universities entered the arena, offering single courses via streaming video, but Fathom (Columbia), E -Cornell, and AllLearn (a joint venture of Oxford, Stanford, and Yale) failed to achieve scale or commercial viability. In 2008, a new venture, 2tor (later renamed 2 U ), developed a platform for hosting online degrees offered by established universities such as the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the University of Southern California, and received a share of tuition revenue for supplying the technology, assisting with course production, and recruiting students—chiefly through paid advertising.
By the Year of the MOOC , there were 7 million students enrolled in at least one online course through a U.S. university, and 1.5 million enrolled in fully online degree programs. 5 Most online degree programs charged tuition fees comparable to those paid by students on campus, and enrollment was typically less than enrollment in counterpart programs on campus. The MOOC promised something radically new and different—famous professors from top universities, massive scale, and low cost. For the first time, institutions of higher education could imagine achieving high quality, wide access, and affordability in the same offering.
Such imagining was possible only because MOOC s, unlike most online degree programs then and now, did not require the presence of a live instructor. Students watched videos, took quizzes and tests, and worked on collaborative projects with each other asynchronously, which meant that the same course could reach large numbers in different time zones at low cost per student. Asynchronous courses and degree programs built upon them had the potential to increase the number of students reached by a single faculty member from tens or hundreds to tens or hundreds of thousands, or more.
In this essay, I hope to shed light on the current and future impact of online learning on global higher education. To do this, I will begin by asking two questions about the demand for online postsecondary education: 1) who are the learners? and 2) what do they want to learn? The answers are surprising, especially to faculty and administrators in traditional higher education. I will also discuss who is supplying educational content online, how it is delivered, and whether it is effective. Finally, I will offer a perspective on two further questions: 1) can online education serve the learning needs of the global workforce in an era of rapid technological progress? and 2) can online education help universities around the world in their quest for the holy grail of high quality, accessibility, and affordability?
In 2012, the conversation among U.S. academics assumed that the audience for MOOC s would be pre-college or college-age students, principally residing in the United States. But, contrary to expectations, a 2015 Coursera survey revealed that only 11 percent of surveyed learners were under age 22, just under half were 22–45 years old, and the balance were over 45 years old. 6 And the learner population was, and remains, overwhelmingly international. By the end of 2022, only 21 percent of Coursera’s learners resided in North America. The rest were distributed around the world: 32 percent in Asia, 18 percent in Latin America, 17 percent in Europe, and 10 percent in the Middle East and Africa. Apart from the United States (19 percent) and India (16 percent), no single country has more than 10 percent of the learners on the platform. 7 These demographics have profound implications for the future of higher education. They demonstrate that the principal consequence of putting courses online has not been to transform teaching and learning on campus, but rather to extend the reach of universities beyond customary geographic and demographic boundaries to millions of learners around the world beyond the normal age of university students.
It is worth dwelling on this point. There are 19 million students enrolled in institutions of higher education in the United States and approximately 250 million enrolled worldwide. Enrollment in online courses will come to dwarf these numbers. By the end of 2022, Coursera alone had 118 million registered learners, growing at an annual rate of 22 percent. Putting university courses on Zoom during the early years of the COVID -19 pandemic to meet the needs of on-campus students was a transient accommodation. Reaching hundreds of millions who are not currently enrolled in higher education is a revolution.
In the early days at Coursera, the entire staff assembled weekly for updates from the leadership team. At the close of each meeting, one of the employees would relate a “learner story.” More than any quantitative evidence, these stories drove home the extraordinary impact of online courses on learners outside the traditional reach of higher education. One moving example was the story of an unemployed taxi driver in Tennessee who—after losing his home, being abandoned by his family, and suffering from depression—took an online writing course that gave him the confidence to enroll in a nearby state university, complete a degree, and get a job as a writer. Another was the story of a woman in Bangladesh who, after escaping from an abusive husband and fleeing to another city, took online business courses that prepared her to open what became a successful bakery. These are only two students among many whose lives were transformed by access to online education.
In the Year of the MOOC , as universities rushed to sign on with Coursera and ed X , their faculty and administrators assumed that a large audience would be available for courses across a wide range of subject matters in the liberal arts and sciences. Enrollments were widely distributed and remain so. But in 2013, once Coursera began to charge learners for certificates of successful completion, courses imparting job-relevant skills in business, technology, and data science produced over 80 percent of its revenue. A year later, when Coursera and ed X began offering sequences of courses from university partners, these skewed heavily toward practical subjects in business, technology, and data science. At the same time, Udacity abandoned its efforts in general education and concentrated its courses and “nanodegrees” entirely on computer science and data science. Reflecting these developments, Coursera’s survey of fifty-two thousand course completers in 2015 found that “educational benefit” was the principal motivation for 28 percent of those surveyed while “career benefit” motivated 52 percent. 8
The early MOOC platforms’ experience with vocationally oriented learners was paralleled by the emergence of scores, if not hundreds, of start-ups offering “microcredentials” through live “coding bootcamps” as well as online instruction in computer skills. None has achieved the scale of the MOOC platforms, but some have partnered successfully with universities to offer instruction on campuses. Microcredentials—a category that includes certificates of completion of MOOC s and multicourse sequences—have become a labor-market currency, especially in the technology sector. Jobseekers list these credentials on their resumes and LinkedIn profiles, and recruiters pay attention to them.
In 2016, a study of three thousand candidates for software engineering jobs found that completing Coursera and Udacity courses was the single best indicator of success in technical interviews. 9 In a more recent survey, 86 percent of employers agreed that microcredentials strengthened a candidate’s job application, and 74 percent believed that earning such credentials improved a candidate’s ability to perform well in an entry-level position. 10
Career-oriented courses and programs—especially those focused on the acquisition of business, computing, and data science skills—remain the principal source of enrollment and revenue for online providers. In 2022, they accounted for three-quarters of Coursera’s 39 million enrollments. Nonetheless, liberal arts subjects continue to flourish online. Of the sixteen Coursera courses with over one million cumulative enrollments, seven are liberal arts courses spanning the disciplines of psychology, neuroscience, economics, English, and Asian languages.
Universities hoping to reach off-campus audiences can post courses on their own websites or YouTube channels, and can also partner with a third-party platform to gain the advantages of potentially larger enrollments, likely lower costs of attracting those enrollments, and technology that supports a more interactive and personalized learning experience. After the Year of the MOOC , dozens of platforms emerged to work with universities to offer single courses and/or collections of courses (specializations, nanodegrees, micromaster’s, and other certificate programs). Among these were Future Learn in the United Kingdom, FUN in France, Swayyam and Simplilearn in India, and Chinese University MOOC (previously known as I -Course), Xuetang X , and CNMOOC in China. 11 Universities seeking to offer accredited degree programs, certificates, or executive education programs online can provide them on their own websites or use a third-party platform such as 2 U , Noodle, and Coursera (each based in the United States), or a number of strong competitors in India such as UpGrad, Eruditus, or Great Learning. In all these cases, the courses, programs, and degrees carry the university’s brand name. Some faculty have operated independently of their institutions by authoring their own courses on platforms such as Udemy or Teachable.
Online postsecondary instruction is not limited to the offerings of universities or freelance university faculty. Well before the Year of the MOOC , Skillsoft, Lynda.com, and others offered video libraries of short courses on business topics over the internet, taught chiefly by instructors with industry expertise but no academic affiliation. When the MOOC s revealed the enormous latent demand for job-related skills acquisition in business, technology, and data science, the field exploded. Hundreds of start-ups in the United States, Europe, India, and China began to offer courses and certificate programs in computing and data science taught by industry experts, wholly online or in hybrid format. Udacity was a pioneer in this movement. It pivoted from Stanford professors to industry experts as instructors as early as 2013. By 2016, even Coursera had begun to offer specializations and certificate programs under the sponsorship of leading companies such as Google in technology and PricewaterhouseCoopers in business. By the end of 2022, it had over 110 industry partners offering job-relevant courses alongside more than 185 universities providing education in both academic and professional subject matter. When a professor at the University of Michigan offers his #1-rated course on introductory programming in Python through Coursera, he is competing not only with courses offered by other professors on ed X or Coursera, as well as industry experts on Udacity, Udemy, Skillshare, Great Courses, Codeacademy, and Data Camp, but also with courses offered by Google, IBM , and Meta experts on the Coursera platform.
The ecosystem has continued to expand. By the end of 2022, there were at least 256 companies offering online or hybrid instruction in either postsecondary academic subjects or workforce skill development. One-third of these companies are based in North America, 23 percent in Europe, 16 percent in Latin America, and 10 percent in South Asia, with the balance divided evenly among Southeast Asia, Australia, the Middle East and North Africa, and Sub-Saharan Africa. 12
No one claims that an asynchronous, large-scale class can replicate the learning experience of the live, on-campus seminar involving a professor and ten to fifteen students. In such a setting, an excellent teacher can help a student master far more than the subject matter. Students learn how to form and defend an argument, and how to find flaws in the arguments of others. In short, students develop, through regular practice, the ability to think critically and independently. To date, this experience has not been replicated online at scale . Holding a synchronous online discussion with twelve people can produce all or most of the educational benefits of a physical classroom, but without realizing the access and affordability benefits associated with large-scale MOOC s.
The small seminar focused on developing the capacity for critical thinking is not, however, the norm in on-campus higher education worldwide. Lecture courses focused on content mastery account for a much larger share of enrollment. And there is evidence that asynchronous, scalable online courses produce better mastery of content than live lecture courses. Perhaps the most careful study of the subject was undertaken by physicist David E. Pritchard at MIT , who found through pre- and posttesting using ed X technology that learning gains in his introductory physics MOOC exceeded those in the traditional, live introductory physics lecture courses studied earlier by physicist Richard R. Hake, although they fell short of the learning gains realized in courses using interactive pedagogy. 13 Moreover, the learning gains experienced by the 1,080 study participants in Pritchard’s MOOC did not differ significantly across cohorts defined by educational background. 14
Why might learning be more effective in asynchronous online courses than in traditional live lecture courses? First, many studies have shown that retention improves dramatically by breaking lectures into short segments and interjecting quizzes at regular intervals of six to ten minutes, a standard feature of Coursera and ed X courses. Such practices have long been recommended for live teaching, but they remain far from universal. Second, several online platforms offer learners the opportunity to vary the instructor’s speed of delivery from one half to double the number of words per minute—helping learners who are having difficulty and preventing those who find the material easy from becoming bored. Third, online platforms typically have a replay button, so learners who fail an in-video quiz, or who otherwise have difficulty understanding the first time through, can watch a video segment again and again until the material is understood. Fourth, some platforms—Coursera among them—employ algorithms to detect learners having difficulty and guide them to review relevant earlier segments of the course. Fifth, some courses, especially those in the computer science and data science domains, weave interactive exercises throughout the lectures, enabling students to master concepts through practical application.
These observations about the effectiveness of online learning help to explain some of the reactions of teachers and students who were forced to go online during the COVID -19 pandemic. In general, teachers found interactive seminar classes worked better online than they expected, while lectures fared worse. The first of these impressions is understandable: conversation tended to work reasonably well in classes small enough to fit everyone on a single Zoom screen, even if the experience did not fully replicate the chemistry of live classroom interaction. The second impression is also understandable: given the overnight switch from the classroom to Zoom, most instructors were unaware of what had been learned about teaching lecture classes effectively online, and they simply replicated what they did in the classroom. Uninterrupted lectures of fifty or seventy-five minutes did not hold the attention of online learners who might otherwise have been mesmerized by the live presence of a charismatic lecturer. Moreover, in synchronous online lectures, students lacked the advantages of slowing the instructor down, or hitting the replay button, or receiving algorithmically driven guidance when they were confused. Some of the deficit of synchronous online lectures can be mitigated by recording them and making them available for replay. 15
For many students, particularly those in residential universities, moving classes online was unpopular, because they were deprived of live interaction with fellow classmates as well as the instructor. Overall, however, student reaction was positive. A survey published in April 2021 found that 73 percent of students would like to take some fully online courses in the future. 16 Many working adults attending late afternoon or evening classes at community colleges or state universities embraced online learning because it brought the benefit of eliminating a commute after the workday.
Recent advances in artificial intelligence, and especially radical breakthroughs in natural language–processing algorithms, promise quantum improvement in the effectiveness of online learning, but the inaccuracy of forecasts in the Year of the MOOC cautions against offering predictions with any confidence in the Year of Chat GPT .
A major surprise of the last decade is that online education has had a more profound impact on the labor market than on university campuses. Technological and demographic factors have created unprecedented demand for job-relevant training, and online instruction has provided a low-cost solution that has already reached significant scale, with the potential to grow ten- or one hundredfold in the years ahead.
Since the advent of distributed computing in the 1980s, digital technologies have spread across virtually every job and profession. Technology has created entirely new categories of jobs (for example, data scientists), changed the mix of skills required for most jobs (such as auto mechanics), and rendered many jobs obsolete (including telephone switchboard operators). Numerous studies document the shifts in demand for labor across job categories and skill requirements, and most project substantial further change in the years ahead. 17 These technology-induced changes in the demand for labor have been exacerbated in the United States and other developed countries by declining working-age populations—a joint consequence of long-term decline in birth rates, decreased legal immigration, and retirement of the large “baby boomer” generation. Among the consequences of these trends are substantial shortages of labor in job categories where demand is growing and technical skills are required, and a pool of unemployed or underemployed workers whose jobs have been replaced or substantially altered by technology. The solution to this problem is accessible, affordable skills training to prepare workers, from entry-level to midcareer, to fill vacancies in new or substantially altered job categories, or to retrain them for employment in established job categories.
At the entry level, this need for job-relevant skills acquisitions is well-met in countries with strong vocational education or apprenticeship programs, such as Germany, Sweden, Switzerland, and Singapore, but much less well-met by U.S. community colleges that are underresourced and torn between providing students with technical training and a pathway to four-year colleges. Online instruction is beginning to fulfill this need with microcredentials, in some instances integrated into community college curricula. Such credentials vary widely in quality and likely will not flourish without some mechanism for accreditation and accountability. But some offerings seem promising. Google, for example, offers five entry-level certificate programs that run six to eight months and train entry-level IT support staff, data analysts, project managers, user experience designers, and digital marketing specialists. These and more than twenty-five other entry-level certificate programs designed by leading companies (Meta, IBM , Intuit, Salesforce, and others) are available for just $39 or $49 per month on the Coursera platform. By the end of 2022, nearly 6 million learners had enrolled in entry-level certificate programs.
Providing low-cost, effective, and at-scale training and retraining for midcareer workers has been an elusive goal of many governments for decades, while most companies have focused their training resources on “onboarding” new employees rather than “upskilling” to help employees move up the ladder, or “reskilling” to assist workers in switching jobs, or adapting to changing skill requirements in their current jobs. Increasingly, however, companies are incorporating online resources into their training programs to upskill and reskill their employees, and governments are relying upon them for use in retraining the unemployed or underemployed in need of new skills. Leading online platforms such as Udemy, Coursera, Pluralsight, InStride, Degreed, and Guild Education have emerged to meet these needs in recent years, alongside earlier suppliers of shortform videos such as Skillsoft and LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com). Pluralsight, which is focused on digital skills training, claims to serve 70 percent of Fortune 500 companies, and over 18,000 business customers in all. Coursera serves nearly 4,000 business customers, and it also supports over 430 workforce training programs for governments in over 100 countries. Workforce training provides a substantial opportunity for higher education to expand its reach and social impact. Although one might expect Coursera’s industry partners to dominate its skills training activities, universities account for 44 percent of course enrollments by learners subscribed through companies or government agencies.
Because companies value online offerings for ease of use, low cost, and a curricular breadth impossible to replicate in-house, their use is likely to continue to grow rapidly, especially in imparting digital and technical skills. 18 Live training will not disappear. It is still the medium of choice for developing company culture, teamwork, and other “soft skills,” as well as for satisfying the desire of senior executives for “high-touch” contact with professors from leading business schools.
The experience of early and midcareer learners of relatively low educational attainment has somewhat modified the optimistic conclusion of early studies finding learning gains at all educational levels. Government agencies and nonprofits offering workforce development programs have found that unemployed and underemployed learners do not flourish in a purely independent, asynchronous learning environment. Some degree of regular interaction with live teachers or mentors improves their performance. In response, a host of new start-ups have emerged to provide the “hands-on” contact with users of high-quality asynchronous online courses and certificate programs. 19 Perhaps the new AI technologies will enable realization of the benefits of this kind of personalized support at greater scale and lower cost.
It is well known that the cost of higher education rises faster than inflation. But why? Two distinguished Princeton economists, William Baumol and William Bowen, provided the explanation of this persistent phenomenon more than a half-century ago. 20 They did so with reference to the performing arts, but the same logic applies to education.
The idea is simple. Productivity (the amount of output per worker) tends to increase over time in many sectors of the economy. The production of a gigabyte of computer memory requires only a miniscule fraction of the labor that was required forty years ago. Consequently, the price of computer memory has declined. By contrast, there is no productivity growth at all in chamber music. Labor input (a quartet, for example) stays constant over time, and, unless the size of the concert hall grows, output (in the form of tickets sold) also remains constant over time. Since inflation is just an average of all price changes in the economy, prices in sectors with high-productivity growth will rise more slowly than inflation, while prices in sectors with low-productivity growth (such as the performing arts) will rise faster than inflation.
The dynamics are no different in higher education. If the average number of students in a seminar remains fifteen, average enrollment in lecture courses remains 100 students, and a faculty member’s teaching load does not increase, the cost of educational services and the resulting prices (tuition and fees) will rise faster than inflation. There is only one way to reverse this tendency: the productivity of the university’s scarcest resource—its faculty—must increase.
Herein lies the promise of online education: it can provide at least a partial cure for the Baumol-Bowen “cost disease.” 21 By increasing the number of students a faculty member teaches, the incremental revenue from online instruction can help moderate the rise of on-campus tuition, while also supporting financial aid and other university investments.
Further, online education can be priced well below the potentially unsustainable level of on-campus tuition. In 2014, Georgia Tech priced its pioneering OMSCS (Online Master’s of Science in Computer Science) degree at $6,800, an 83 percent discount from its on-campus program. Coursera quickly followed this example, pricing its degrees well below comparable on-campus programs. Although many universities still price at on-campus levels, 2 U , the largest of the online degree platforms, began to discount the degrees of some of its partners after it acquired ed X in 2021. The benefits of low-cost online degree programs are beginning to accrue globally. By the end of 2022, eleven of the twenty universities offering degrees on Coursera were located outside the United States—in the United Kingdom, France, Italy, India, Australia, Mexico, Colombia, Chile, and Peru.
A decade ago, faculties in the United States and Western Europe feared that MOOC s created by top-tier universities might become widely used as a substitute for the professorate in the rest of academia, and the prospects facing graduate students seeking academic employment, already grim in many disciplines, would become even grimmer. It still seems unlikely that this will happen any time soon on U.S. and European campuses. But consider the question from the perspective of a country like India, with 37 million university students in 2020 and a declared policy objective of doubling the gross enrollment ratio by 2035. Given the growth rate of the population, this objective of the government’s National Educational Policy would require an enormous investment in faculty, staff, and brick-and-mortar facilities. The goal is almost certainly unattainable without the use of scalable online resources.
Coursera began licensing courses created by its university partners to a few universities in India, Central Asia, and the Middle East as a pilot project in 2016. After the formal launch of Coursera for Campus in 2019, when the start of the COVID -19 pandemic disrupted teaching and learning around the globe, Coursera responded by offering its entire catalog, free of charge, to any accredited universities that desired access. After the emergency protocols of the pandemic were dropped, Coursera resumed charging universities very modest licensing fees. At the end of 2022, 437 universities were subscribers, and 88 universities (nearly all in developing countries) were offering credit for Coursera courses created by leading universities. Some institutions supplemented the imported credit-bearing courses with resident faculty facilitation. Others offered them stand-alone.
In the Year of the MOOC , the educational activities of nearly all the world’s leading universities were no different than they had been fifty years before. Institutions offered high-quality undergraduate and graduate degree programs to full-time students on campus. Over the next fifty years, their educational mission will expand. Universities will offer online bachelor’s and master’s degree programs, online courses for credit on campus and off, courses and degrees for enterprises and government workforce-development programs, and courses for universities in developing countries enabling expanded accessibility and improved quality. A university’s “students” will no longer be concentrated among those between eighteen and thirty years of age. Entry-level and midcareer workers and professionals seeking career advancement, or wishing to change careers, will turn to universities to enhance their skills, and lifelong learners will enjoy access to liberal arts courses well into retirement. The social impact of universities will be greater than ever before, as hundreds of millions of learners around the world will have lifelong engagement with high-quality education, and access to opportunities that they never imagined possible.
- 1 Laura Pappano, “The Year of the MOOC ,” The New York Times, November 2, 2012.
- 2 Eric Kolenich, “10 Years Ago, UVA Fired and Rehired Its President, Fearing a Crisis that Never Materialized,” Richmond Times-Dispatch , June 27, 2022.
- 3 J. F. Gibbons, W. R. Kincheloe, and K. S. Down, “Tutored Videotape Instruction: A New Use of Electronics Media in Education,” Science 195 (4283) (1977): 1139–1146; and Andrew Myers, “ Lessons in Remote Learning from the 1970s: A Q&A with James Gibbons ,” Stanford University, August 14, 2020.
- 4 Linda Harasim, “Shift Happens: Online Education as a New Paradigm in Learning,” The Internet and Higher Education 3 (2000): 41–61.
- 5 See Tables 311.20 and 311.22 in Digest of Education Statistics 2020 (Washington, D.C.: National Center for Education Statistics, 2020).
- 6 “ Impact Revealed: Learner Outcomes in Open Online Courses ,” Coursera, September 2015.
- 7 Data and examples in this essay are drawn disproportionately from Coursera, because of the author’s personal experience as its Chief Executive Office from 2014 to 2017 and the company’s willingness to provide data. From the beginning, Coursera has been by far the largest platform for online university courses.
- 8 Chen Zhenghao, Brandon Alcorn, Gayle Christensen, et al., “Who’s Benefiting from MOOC s, and Why,” Harvard Business Review , September 22, 2015.
- 9 Aline Lerner, “Lessons from 3,000 Technical Interviews . . . or, How What You Do after Graduation Matters Way More Than Where You Went To School,” Business Insider , December 30, 2016. Only three characteristics had a significant correlation with performance on technical interviews: whether applicants had worked for an elite company, whether they had graduated from a “top computer science school,” and whether they had posted a Coursera or Udacity certificate on their LinkedIn profiles. The effect of completing a MOOC was the most strongly correlated, with an effect size more than double that of attending a top school. Moreover, the effect of completing a MOOC was far greater for those who had not attended a top school.
- 10 See Scott Shireman, “ New Coursera Survey Shows High Demand for Industry Micro-Credentials from Students and Employers in Tight Labor Market ,” Coursera, February 2, 2023.
- 11 The Report by Class Central , an online publication covering the MOOC industry, published a description of twenty-four Chinese MOOC platforms in early 2022: Rui Ma, “ Massive List of Chinese Online Course Platforms in 2022 ,” The Report , January 19, 2022. In early 2023, the same publication identified 29 additional active MOOC platforms in the rest of the world. See Laurie Pickard, Rui Ma, and Manoel Cortes Mendez, “ Massive List of MOOC Platforms Around the World in 2024 ,” The Report , April 10, 2023.
- 12 These data were provided by GSV Ventures, the cosponsor of the annual ASU - GSV Summit, the world’s largest gathering of edtech companies, investors, and university and industry partners.
- 13 David E. Pritchard, Kimberly F. Colvin, John Champaign, et al., “Learning in an Introductory Physics MOOC : All Cohorts Learn Equally Including in an On-Campus Class,” International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning 15 (4) (2014); and Richard R. Hake, “Interactive-Engagement vs Traditional Methods: A Six-Thousand Student Survey of Mechanics Test Data for Introductory Physics Courses,” American Journal of Physics 66 (1) (1998): 4–74.
- 14 Pritchard measured learning by the percentage decline in the proportion of test questions answered incorrectly. By this metric, high school graduates, college graduates, physics teachers, and PhDs were statistically indistinguishable.
- 15 Over the summer of 2020, well-resourced universities were able to provide support to faculty to help them modify their course designs to work more effectively online, but such resources were readily available only in a small fraction of developed-country institutions, and not at all in most of the developing world’s colleges and universities.
- 16 Lindsay McKenzie, “Students Want Online Learning Options Post-Pandemic,” Inside Higher Education , April 27, 2021.
- 17 The McKinsey Global Institute has published several comprehensive reviews of the effect of automation or digitalization on jobs and the skills required for them. As a point of entry, see McKinsey Global Institute, “Jobs Lost, Jobs Gained: What the Future of Work Will Mean for Jobs, Skills, and Wages,” November 28, 2017.
- 18 Fahim Ul Haq, “Five Reasons Why Online Learning Is the Future of Professional Development,” Forbes , March 26, 2021.
- 19 A notable example is Merit America, a nonprofit that provides classroom mentoring and job placement services for students as they complete Google certificates in IT support and data analytics. In their first five years of operation, three thousand program completers were placed in new jobs at average annual salary gains of $24,000. See Merit America, “ Merit America Alumni Experience a $24,000 Wage Increase 3+ Months Post-Program, According to University of Virginia Analysis .”
- 20 William J. Baumol and William G. Bowen, “On the Performing Arts: The Anatomy of Their Economic Problems,” The American Economic Review 55 (1/2) (1965): 495–502.
Advertisement
The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study
- Published: 06 September 2021
- Volume 27 , pages 429–450, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Hakan Ulum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1398-6935 1
81k Accesses
30 Citations
10 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students’ academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this study will provide a source to assist future studies with comparing the effect of online education on academic achievement before and after the pandemic. This meta-analysis study consists of 27 studies in total. The meta-analysis involves the studies conducted in the USA, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia. The studies included in the meta-analysis are experimental studies, and the total sample size is 1772. In the study, the funnel plot, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test were utilized to determine the publication bias, which has been found to be quite low. Besides, Hedge’s g statistic was employed to measure the effect size for the difference between the means performed in accordance with the random effects model. The results of the study show that the effect size of online education on academic achievement is on a medium level. The heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Information and communication technologies have become a powerful force in transforming the educational settings around the world. The pandemic has been an important factor in transferring traditional physical classrooms settings through adopting information and communication technologies and has also accelerated the transformation. The literature supports that learning environments connected to information and communication technologies highly satisfy students. Therefore, we need to keep interest in technology-based learning environments. Clearly, technology has had a huge impact on young people's online lives. This digital revolution can synergize the educational ambitions and interests of digitally addicted students. In essence, COVID-19 has provided us with an opportunity to embrace online learning as education systems have to keep up with the rapid emergence of new technologies.
Information and communication technologies that have an effect on all spheres of life are also actively included in the education field. With the recent developments, using technology in education has become inevitable due to personal and social reasons (Usta, 2011a ). Online education may be given as an example of using information and communication technologies as a consequence of the technological developments. Also, it is crystal clear that online learning is a popular way of obtaining instruction (Demiralay et al., 2016 ; Pillay et al., 2007 ), which is defined by Horton ( 2000 ) as a way of education that is performed through a web browser or an online application without requiring an extra software or a learning source. Furthermore, online learning is described as a way of utilizing the internet to obtain the related learning sources during the learning process, to interact with the content, the teacher, and other learners, as well as to get support throughout the learning process (Ally, 2004 ). Online learning has such benefits as learning independently at any time and place (Vrasidas & MsIsaac, 2000 ), granting facility (Poole, 2000 ), flexibility (Chizmar & Walbert, 1999 ), self-regulation skills (Usta, 2011b ), learning with collaboration, and opportunity to plan self-learning process.
Even though online education practices have not been comprehensive as it is now, internet and computers have been used in education as alternative learning tools in correlation with the advances in technology. The first distance education attempt in the world was initiated by the ‘Steno Courses’ announcement published in Boston newspaper in 1728. Furthermore, in the nineteenth century, Sweden University started the “Correspondence Composition Courses” for women, and University Correspondence College was afterwards founded for the correspondence courses in 1843 (Arat & Bakan, 2011 ). Recently, distance education has been performed through computers, assisted by the facilities of the internet technologies, and soon, it has evolved into a mobile education practice that is emanating from progress in the speed of internet connection, and the development of mobile devices.
With the emergence of pandemic (Covid-19), face to face education has almost been put to a halt, and online education has gained significant importance. The Microsoft management team declared to have 750 users involved in the online education activities on the 10 th March, just before the pandemic; however, on March 24, they informed that the number of users increased significantly, reaching the number of 138,698 users (OECD, 2020 ). This event supports the view that it is better to commonly use online education rather than using it as a traditional alternative educational tool when students do not have the opportunity to have a face to face education (Geostat, 2019 ). The period of Covid-19 pandemic has emerged as a sudden state of having limited opportunities. Face to face education has stopped in this period for a long time. The global spread of Covid-19 affected more than 850 million students all around the world, and it caused the suspension of face to face education. Different countries have proposed several solutions in order to maintain the education process during the pandemic. Schools have had to change their curriculum, and many countries supported the online education practices soon after the pandemic. In other words, traditional education gave its way to online education practices. At least 96 countries have been motivated to access online libraries, TV broadcasts, instructions, sources, video lectures, and online channels (UNESCO, 2020 ). In such a painful period, educational institutions went through online education practices by the help of huge companies such as Microsoft, Google, Zoom, Skype, FaceTime, and Slack. Thus, online education has been discussed in the education agenda more intensively than ever before.
Although online education approaches were not used as comprehensively as it has been used recently, it was utilized as an alternative learning approach in education for a long time in parallel with the development of technology, internet and computers. The academic achievement of the students is often aimed to be promoted by employing online education approaches. In this regard, academicians in various countries have conducted many studies on the evaluation of online education approaches and published the related results. However, the accumulation of scientific data on online education approaches creates difficulties in keeping, organizing and synthesizing the findings. In this research area, studies are being conducted at an increasing rate making it difficult for scientists to be aware of all the research outside of their expertise. Another problem encountered in the related study area is that online education studies are repetitive. Studies often utilize slightly different methods, measures, and/or examples to avoid duplication. This erroneous approach makes it difficult to distinguish between significant differences in the related results. In other words, if there are significant differences in the results of the studies, it may be difficult to express what variety explains the differences in these results. One obvious solution to these problems is to systematically review the results of various studies and uncover the sources. One method of performing such systematic syntheses is the application of meta-analysis which is a methodological and statistical approach to draw conclusions from the literature. At this point, how effective online education applications are in increasing the academic success is an important detail. Has online education, which is likely to be encountered frequently in the continuing pandemic period, been successful in the last ten years? If successful, how much was the impact? Did different variables have an impact on this effect? Academics across the globe have carried out studies on the evaluation of online education platforms and publishing the related results (Chiao et al., 2018 ). It is quite important to evaluate the results of the studies that have been published up until now, and that will be published in the future. Has the online education been successful? If it has been, how big is the impact? Do the different variables affect this impact? What should we consider in the next coming online education practices? These questions have all motivated us to carry out this study. We have conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis study that tries to provide a discussion platform on how to develop efficient online programs for educators and policy makers by reviewing the related studies on online education, presenting the effect size, and revealing the effect of diverse variables on the general impact.
There have been many critical discussions and comprehensive studies on the differences between online and face to face learning; however, the focus of this paper is different in the sense that it clarifies the magnitude of the effect of online education and teaching process, and it represents what factors should be controlled to help increase the effect size. Indeed, the purpose here is to provide conscious decisions in the implementation of the online education process.
The general impact of online education on the academic achievement will be discovered in the study. Therefore, this will provide an opportunity to get a general overview of the online education which has been practiced and discussed intensively in the pandemic period. Moreover, the general impact of online education on academic achievement will be analyzed, considering different variables. In other words, the current study will allow to totally evaluate the study results from the related literature, and to analyze the results considering several cultures, lectures, and class levels. Considering all the related points, this study seeks to answer the following research questions:
What is the effect size of online education on academic achievement?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the country?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the class level?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the lecture?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the online education approaches?
This study aims at determining the effect size of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, on students’ academic achievement in different courses by using a meta-analysis method. Meta-analysis is a synthesis method that enables gathering of several study results accurately and efficiently, and getting the total results in the end (Tsagris & Fragkos, 2018 ).
2.1 Selecting and coding the data (studies)
The required literature for the meta-analysis study was reviewed in July, 2020, and the follow-up review was conducted in September, 2020. The purpose of the follow-up review was to include the studies which were published in the conduction period of this study, and which met the related inclusion criteria. However, no study was encountered to be included in the follow-up review.
In order to access the studies in the meta-analysis, the databases of Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS were reviewed by utilizing the keywords ‘online learning and online education’. Not every database has a search engine that grants access to the studies by writing the keywords, and this obstacle was considered to be an important problem to be overcome. Therefore, a platform that has a special design was utilized by the researcher. With this purpose, through the open access system of Cukurova University Library, detailed reviews were practiced using EBSCO Information Services (EBSCO) that allow reviewing the whole collection of research through a sole searching box. Since the fundamental variables of this study are online education and online learning, the literature was systematically reviewed in the related databases (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) by referring to the keywords. Within this scope, 225 articles were accessed, and the studies were included in the coding key list formed by the researcher. The name of the researchers, the year, the database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS), the sample group and size, the lectures that the academic achievement was tested in, the country that the study was conducted in, and the class levels were all included in this coding key.
The following criteria were identified to include 225 research studies which were coded based on the theoretical basis of the meta-analysis study: (1) The studies should be published in the refereed journals between the years 2020 and 2021, (2) The studies should be experimental studies that try to determine the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement, (3) The values of the stated variables or the required statistics to calculate these values should be stated in the results of the studies, and (4) The sample group of the study should be at a primary education level. These criteria were also used as the exclusion criteria in the sense that the studies that do not meet the required criteria were not included in the present study.
After the inclusion criteria were determined, a systematic review process was conducted, following the year criterion of the study by means of EBSCO. Within this scope, 290,365 studies that analyze the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement were accordingly accessed. The database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) was also used as a filter by analyzing the inclusion criteria. Hence, the number of the studies that were analyzed was 58,616. Afterwards, the keyword ‘primary education’ was used as the filter and the number of studies included in the study decreased to 3152. Lastly, the literature was reviewed by using the keyword ‘academic achievement’ and 225 studies were accessed. All the information of 225 articles was included in the coding key.
It is necessary for the coders to review the related studies accurately and control the validity, safety, and accuracy of the studies (Stewart & Kamins, 2001 ). Within this scope, the studies that were determined based on the variables used in this study were first reviewed by three researchers from primary education field, then the accessed studies were combined and processed in the coding key by the researcher. All these studies that were processed in the coding key were analyzed in accordance with the inclusion criteria by all the researchers in the meetings, and it was decided that 27 studies met the inclusion criteria (Atici & Polat, 2010 ; Carreon, 2018 ; Ceylan & Elitok Kesici, 2017 ; Chae & Shin, 2016 ; Chiang et al. 2014 ; Ercan, 2014 ; Ercan et al., 2016 ; Gwo-Jen et al., 2018 ; Hayes & Stewart, 2016 ; Hwang et al., 2012 ; Kert et al., 2017 ; Lai & Chen, 2010 ; Lai et al., 2015 ; Meyers et al., 2015 ; Ravenel et al., 2014 ; Sung et al., 2016 ; Wang & Chen, 2013 ; Yu, 2019 ; Yu & Chen, 2014 ; Yu & Pan, 2014 ; Yu et al., 2010 ; Zhong et al., 2017 ). The data from the studies meeting the inclusion criteria were independently processed in the second coding key by three researchers, and consensus meetings were arranged for further discussion. After the meetings, researchers came to an agreement that the data were coded accurately and precisely. Having identified the effect sizes and heterogeneity of the study, moderator variables that will show the differences between the effect sizes were determined. The data related to the determined moderator variables were added to the coding key by three researchers, and a new consensus meeting was arranged. After the meeting, researchers came to an agreement that moderator variables were coded accurately and precisely.
2.2 Study group
27 studies are included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies that are included in the analysis is 1772. The characteristics of the studies included are given in Table 1 .
2.3 Publication bias
Publication bias is the low capability of published studies on a research subject to represent all completed studies on the same subject (Card, 2011 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Similarly, publication bias is the state of having a relationship between the probability of the publication of a study on a subject, and the effect size and significance that it produces. Within this scope, publication bias may occur when the researchers do not want to publish the study as a result of failing to obtain the expected results, or not being approved by the scientific journals, and consequently not being included in the study synthesis (Makowski et al., 2019 ). The high possibility of publication bias in a meta-analysis study negatively affects (Pecoraro, 2018 ) the accuracy of the combined effect size, causing the average effect size to be reported differently than it should be (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). For this reason, the possibility of publication bias in the included studies was tested before determining the effect sizes of the relationships between the stated variables. The possibility of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
2.4 Selecting the model
After determining the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study, the statistical model used to calculate the effect sizes was selected. The main approaches used in the effect size calculations according to the differentiation level of inter-study variance are fixed and random effects models (Pigott, 2012 ). Fixed effects model refers to the homogeneity of the characteristics of combined studies apart from the sample sizes, while random effects model refers to the parameter diversity between the studies (Cumming, 2012 ). While calculating the average effect size in the random effects model (Deeks et al., 2008 ) that is based on the assumption that effect predictions of different studies are only the result of a similar distribution, it is necessary to consider several situations such as the effect size apart from the sample error of combined studies, characteristics of the participants, duration, scope, and pattern of the study (Littell et al., 2008 ). While deciding the model in the meta-analysis study, the assumptions on the sample characteristics of the studies included in the analysis and the inferences that the researcher aims to make should be taken into consideration. The fact that the sample characteristics of the studies conducted in the field of social sciences are affected by various parameters shows that using random effects model is more appropriate in this sense. Besides, it is stated that the inferences made with the random effects model are beyond the studies included in the meta-analysis (Field, 2003 ; Field & Gillett, 2010 ). Therefore, using random effects model also contributes to the generalization of research data. The specified criteria for the statistical model selection show that according to the nature of the meta-analysis study, the model should be selected just before the analysis (Borenstein et al., 2007 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Within this framework, it was decided to make use of the random effects model, considering that the students who are the samples of the studies included in the meta-analysis are from different countries and cultures, the sample characteristics of the studies differ, and the patterns and scopes of the studies vary as well.
2.5 Heterogeneity
Meta-analysis facilitates analyzing the research subject with different parameters by showing the level of diversity between the included studies. Within this frame, whether there is a heterogeneous distribution between the studies included in the study or not has been evaluated in the present study. The heterogeneity of the studies combined in this meta-analysis study has been determined through Q and I 2 tests. Q test evaluates the random distribution probability of the differences between the observed results (Deeks et al., 2008 ). Q value exceeding 2 value calculated according to the degree of freedom and significance, indicates the heterogeneity of the combined effect sizes (Card, 2011 ). I 2 test, which is the complementary of the Q test, shows the heterogeneity amount of the effect sizes (Cleophas & Zwinderman, 2017 ). I 2 value being higher than 75% is explained as high level of heterogeneity.
In case of encountering heterogeneity in the studies included in the meta-analysis, the reasons of heterogeneity can be analyzed by referring to the study characteristics. The study characteristics which may be related to the heterogeneity between the included studies can be interpreted through subgroup analysis or meta-regression analysis (Deeks et al., 2008 ). While determining the moderator variables, the sufficiency of the number of variables, the relationship between the moderators, and the condition to explain the differences between the results of the studies have all been considered in the present study. Within this scope, it was predicted in this meta-analysis study that the heterogeneity can be explained with the country, class level, and lecture moderator variables of the study in terms of the effect of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, and it has an impact on the students’ academic achievement in different lectures. Some subgroups were evaluated and categorized together, considering that the number of effect sizes of the sub-dimensions of the specified variables is not sufficient to perform moderator analysis (e.g. the countries where the studies were conducted).
2.6 Interpreting the effect sizes
Effect size is a factor that shows how much the independent variable affects the dependent variable positively or negatively in each included study in the meta-analysis (Dinçer, 2014 ). While interpreting the effect sizes obtained from the meta-analysis, the classifications of Cohen et al. ( 2007 ) have been utilized. The case of differentiating the specified relationships of the situation of the country, class level, and school subject variables of the study has been identified through the Q test, degree of freedom, and p significance value Fig. 1 and 2 .
3 Findings and results
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement. Before determining the effect sizes in the study, the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
When the funnel plots are examined, it is seen that the studies included in the analysis are distributed symmetrically on both sides of the combined effect size axis, and they are generally collected in the middle and lower sections. The probability of publication bias is low according to the plots. However, since the results of the funnel scatter plots may cause subjective interpretations, they have been supported by additional analyses (Littell et al., 2008 ). Therefore, in order to provide an extra proof for the probability of publication bias, it has been analyzed through Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test (Table 2 ).
Table 2 consists of the results of the rates of publication bias probability before counting the effect size of online education on academic achievement. According to the table, Orwin Safe N analysis results show that it is not necessary to add new studies to the meta-analysis in order for Hedges g to reach a value outside the range of ± 0.01. The Duval and Tweedie test shows that excluding the studies that negatively affect the symmetry of the funnel scatter plots for each meta-analysis or adding their exact symmetrical equivalents does not significantly differentiate the calculated effect size. The insignificance of the Egger tests results reveals that there is no publication bias in the meta-analysis study. The results of the analysis indicate the high internal validity of the effect sizes and the adequacy of representing the studies conducted on the relevant subject.
In this study, it was aimed to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement after testing the publication bias. In line with the first purpose of the study, the forest graph regarding the effect size of online education on academic achievement is shown in Fig. 3 , and the statistics regarding the effect size are given in Table 3 .
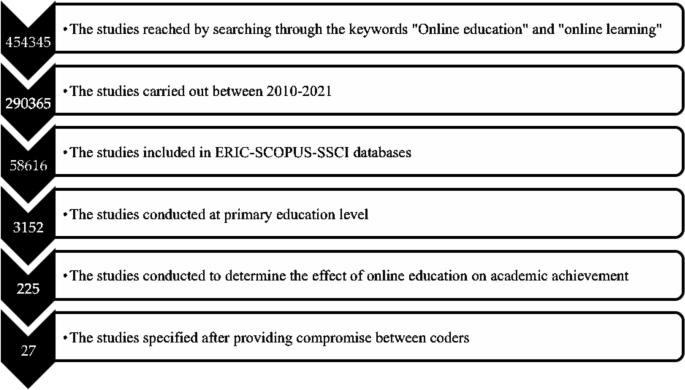
The flow chart of the scanning and selection process of the studies
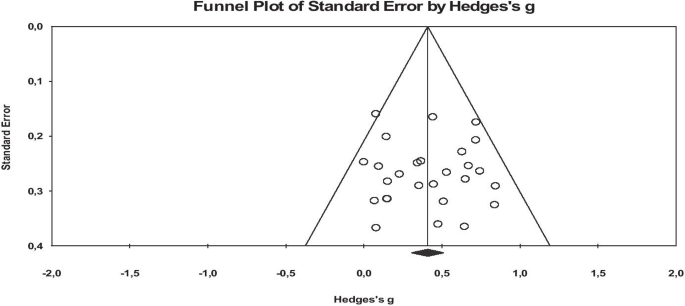
Funnel plot graphics representing the effect size of the effects of online education on academic success
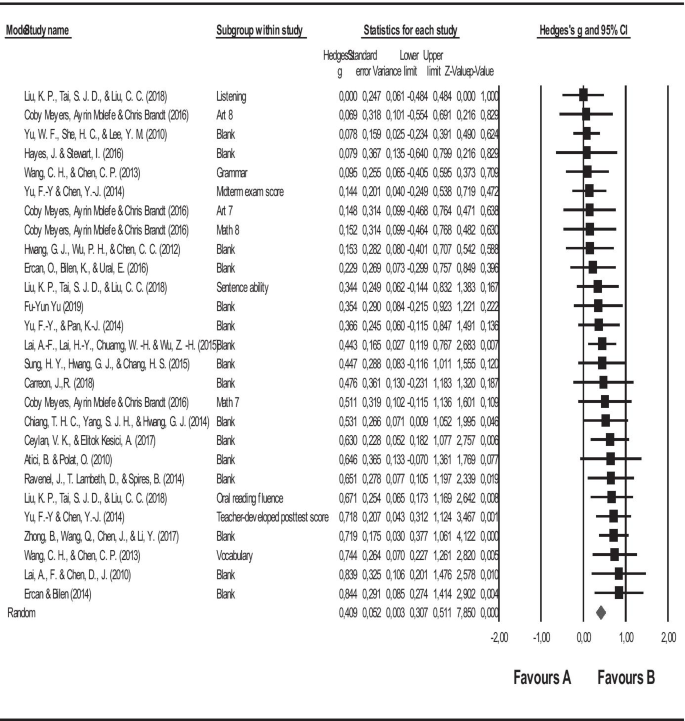
Forest graph related to the effect size of online education on academic success
The square symbols in the forest graph in Fig. 3 represent the effect sizes, while the horizontal lines show the intervals in 95% confidence of the effect sizes, and the diamond symbol shows the overall effect size. When the forest graph is analyzed, it is seen that the lower and upper limits of the combined effect sizes are generally close to each other, and the study loads are similar. This similarity in terms of study loads indicates the similarity of the contribution of the combined studies to the overall effect size.
Figure 3 clearly represents that the study of Liu and others (Liu et al., 2018 ) has the lowest, and the study of Ercan and Bilen ( 2014 ) has the highest effect sizes. The forest graph shows that all the combined studies and the overall effect are positive. Furthermore, it is simply understood from the forest graph in Fig. 3 and the effect size statistics in Table 3 that the results of the meta-analysis study conducted with 27 studies and analyzing the effect of online education on academic achievement illustrate that this relationship is on average level (= 0.409).
After the analysis of the effect size in the study, whether the studies included in the analysis are distributed heterogeneously or not has also been analyzed. The heterogeneity of the combined studies was determined through the Q and I 2 tests. As a result of the heterogeneity test, Q statistical value was calculated as 29.576. With 26 degrees of freedom at 95% significance level in the chi-square table, the critical value is accepted as 38.885. The Q statistical value (29.576) counted in this study is lower than the critical value of 38.885. The I 2 value, which is the complementary of the Q statistics, is 12.100%. This value indicates that the accurate heterogeneity or the total variability that can be attributed to variability between the studies is 12%. Besides, p value is higher than (0.285) p = 0.05. All these values [Q (26) = 29.579, p = 0.285; I2 = 12.100] indicate that there is a homogeneous distribution between the effect sizes, and fixed effects model should be used to interpret these effect sizes. However, some researchers argue that even if the heterogeneity is low, it should be evaluated based on the random effects model (Borenstein et al., 2007 ). Therefore, this study gives information about both models. The heterogeneity of the combined studies has been attempted to be explained with the characteristics of the studies included in the analysis. In this context, the final purpose of the study is to determine the effect of the country, academic level, and year variables on the findings. Accordingly, the statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the countries where the studies were conducted are given in Table 4 .
As seen in Table 4 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ significantly according to the countries where the studies were conducted in. Q test results indicate the heterogeneity of the relationships between the variables in terms of countries where the studies were conducted in. According to the table, the effect of online education on academic achievement was reported as the highest in other countries, and the lowest in the US. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 5 .
As seen in Table 5 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the class level. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in the 4 th class. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 6 .
As seen in Table 6 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the school subjects included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in ICT subject.
The obtained effect size in the study was formed as a result of the findings attained from primary studies conducted in 7 different countries. In addition, these studies are the ones on different approaches to online education (online learning environments, social networks, blended learning, etc.). In this respect, the results may raise some questions about the validity and generalizability of the results of the study. However, the moderator analyzes, whether for the country variable or for the approaches covered by online education, did not create significant differences in terms of the effect sizes. If significant differences were to occur in terms of effect sizes, we could say that the comparisons we will make by comparing countries under the umbrella of online education would raise doubts in terms of generalizability. Moreover, no study has been found in the literature that is not based on a special approach or does not contain a specific technique conducted under the name of online education alone. For instance, one of the commonly used definitions is blended education which is defined as an educational model in which online education is combined with traditional education method (Colis & Moonen, 2001 ). Similarly, Rasmussen ( 2003 ) defines blended learning as “a distance education method that combines technology (high technology such as television, internet, or low technology such as voice e-mail, conferences) with traditional education and training.” Further, Kerres and Witt (2003) define blended learning as “combining face-to-face learning with technology-assisted learning.” As it is clearly observed, online education, which has a wider scope, includes many approaches.
As seen in Table 7 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to online education approaches included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in Web Based Problem Solving Approach.
4 Conclusions and discussion
Considering the developments during the pandemics, it is thought that the diversity in online education applications as an interdisciplinary pragmatist field will increase, and the learning content and processes will be enriched with the integration of new technologies into online education processes. Another prediction is that more flexible and accessible learning opportunities will be created in online education processes, and in this way, lifelong learning processes will be strengthened. As a result, it is predicted that in the near future, online education and even digital learning with a newer name will turn into the main ground of education instead of being an alternative or having a support function in face-to-face learning. The lessons learned from the early period online learning experience, which was passed with rapid adaptation due to the Covid19 epidemic, will serve to develop this method all over the world, and in the near future, online learning will become the main learning structure through increasing its functionality with the contribution of new technologies and systems. If we look at it from this point of view, there is a necessity to strengthen online education.
In this study, the effect of online learning on academic achievement is at a moderate level. To increase this effect, the implementation of online learning requires support from teachers to prepare learning materials, to design learning appropriately, and to utilize various digital-based media such as websites, software technology and various other tools to support the effectiveness of online learning (Rolisca & Achadiyah, 2014 ). According to research conducted by Rahayu et al. ( 2017 ), it has been proven that the use of various types of software increases the effectiveness and quality of online learning. Implementation of online learning can affect students' ability to adapt to technological developments in that it makes students use various learning resources on the internet to access various types of information, and enables them to get used to performing inquiry learning and active learning (Hart et al., 2019 ; Prestiadi et al., 2019 ). In addition, there may be many reasons for the low level of effect in this study. The moderator variables examined in this study could be a guide in increasing the level of practical effect. However, the effect size did not differ significantly for all moderator variables. Different moderator analyzes can be evaluated in order to increase the level of impact of online education on academic success. If confounding variables that significantly change the effect level are detected, it can be spoken more precisely in order to increase this level. In addition to the technical and financial problems, the level of impact will increase if a few other difficulties are eliminated such as students, lack of interaction with the instructor, response time, and lack of traditional classroom socialization.
In addition, COVID-19 pandemic related social distancing has posed extreme difficulties for all stakeholders to get online as they have to work in time constraints and resource constraints. Adopting the online learning environment is not just a technical issue, it is a pedagogical and instructive challenge as well. Therefore, extensive preparation of teaching materials, curriculum, and assessment is vital in online education. Technology is the delivery tool and requires close cross-collaboration between teaching, content and technology teams (CoSN, 2020 ).
Online education applications have been used for many years. However, it has come to the fore more during the pandemic process. This result of necessity has brought with it the discussion of using online education instead of traditional education methods in the future. However, with this research, it has been revealed that online education applications are moderately effective. The use of online education instead of face-to-face education applications can only be possible with an increase in the level of success. This may have been possible with the experience and knowledge gained during the pandemic process. Therefore, the meta-analysis of experimental studies conducted in the coming years will guide us. In this context, experimental studies using online education applications should be analyzed well. It would be useful to identify variables that can change the level of impacts with different moderators. Moderator analyzes are valuable in meta-analysis studies (for example, the role of moderators in Karl Pearson's typhoid vaccine studies). In this context, each analysis study sheds light on future studies. In meta-analyses to be made about online education, it would be beneficial to go beyond the moderators determined in this study. Thus, the contribution of similar studies to the field will increase more.
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of online education on academic achievement. In line with this purpose, the studies that analyze the effect of online education approaches on academic achievement have been included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies included in the meta-analysis is 1772. While the studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in the US, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia, the studies carried out in Europe could not be reached. The reason may be attributed to that there may be more use of quantitative research methods from a positivist perspective in the countries with an American academic tradition. As a result of the study, it was found out that the effect size of online education on academic achievement (g = 0.409) was moderate. In the studies included in the present research, we found that online education approaches were more effective than traditional ones. However, contrary to the present study, the analysis of comparisons between online and traditional education in some studies shows that face-to-face traditional learning is still considered effective compared to online learning (Ahmad et al., 2016 ; Hamdani & Priatna, 2020 ; Wei & Chou, 2020 ). Online education has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of online learning compared to face-to-face learning in the classroom is the flexibility of learning time in online learning, the learning time does not include a single program, and it can be shaped according to circumstances (Lai et al., 2019 ). The next advantage is the ease of collecting assignments for students, as these can be done without having to talk to the teacher. Despite this, online education has several weaknesses, such as students having difficulty in understanding the material, teachers' inability to control students, and students’ still having difficulty interacting with teachers in case of internet network cuts (Swan, 2007 ). According to Astuti et al ( 2019 ), face-to-face education method is still considered better by students than e-learning because it is easier to understand the material and easier to interact with teachers. The results of the study illustrated that the effect size (g = 0.409) of online education on academic achievement is of medium level. Therefore, the results of the moderator analysis showed that the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ in terms of country, lecture, class level, and online education approaches variables. After analyzing the literature, several meta-analyses on online education were published (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Machtmes & Asher, 2000 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ). Typically, these meta-analyzes also include the studies of older generation technologies such as audio, video, or satellite transmission. One of the most comprehensive studies on online education was conducted by Bernard et al. ( 2004 ). In this study, 699 independent effect sizes of 232 studies published from 1985 to 2001 were analyzed, and face-to-face education was compared to online education, with respect to success criteria and attitudes of various learners from young children to adults. In this meta-analysis, an overall effect size close to zero was found for the students' achievement (g + = 0.01).
In another meta-analysis study carried out by Zhao et al. ( 2005 ), 98 effect sizes were examined, including 51 studies on online education conducted between 1996 and 2002. According to the study of Bernard et al. ( 2004 ), this meta-analysis focuses on the activities done in online education lectures. As a result of the research, an overall effect size close to zero was found for online education utilizing more than one generation technology for students at different levels. However, the salient point of the meta-analysis study of Zhao et al. is that it takes the average of different types of results used in a study to calculate an overall effect size. This practice is problematic because the factors that develop one type of learner outcome (e.g. learner rehabilitation), particularly course characteristics and practices, may be quite different from those that develop another type of outcome (e.g. learner's achievement), and it may even cause damage to the latter outcome. While mixing the studies with different types of results, this implementation may obscure the relationship between practices and learning.
Some meta-analytical studies have focused on the effectiveness of the new generation distance learning courses accessed through the internet for specific student populations. For instance, Sitzmann and others (Sitzmann et al., 2006 ) reviewed 96 studies published from 1996 to 2005, comparing web-based education of job-related knowledge or skills with face-to-face one. The researchers found that web-based education in general was slightly more effective than face-to-face education, but it is insufficient in terms of applicability ("knowing how to apply"). In addition, Sitzmann et al. ( 2006 ) revealed that Internet-based education has a positive effect on theoretical knowledge in quasi-experimental studies; however, it positively affects face-to-face education in experimental studies performed by random assignment. This moderator analysis emphasizes the need to pay attention to the factors of designs of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The designs of the studies included in this meta-analysis study were ignored. This can be presented as a suggestion to the new studies that will be conducted.
Another meta-analysis study was conducted by Cavanaugh et al. ( 2004 ), in which they focused on online education. In this study on internet-based distance education programs for students under 12 years of age, the researchers combined 116 results from 14 studies published between 1999 and 2004 to calculate an overall effect that was not statistically different from zero. The moderator analysis carried out in this study showed that there was no significant factor affecting the students' success. This meta-analysis used multiple results of the same study, ignoring the fact that different results of the same student would not be independent from each other.
In conclusion, some meta-analytical studies analyzed the consequences of online education for a wide range of students (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ), and the effect sizes were generally low in these studies. Furthermore, none of the large-scale meta-analyzes considered the moderators, database quality standards or class levels in the selection of the studies, while some of them just referred to the country and lecture moderators. Advances in internet-based learning tools, the pandemic process, and increasing popularity in different learning contexts have required a precise meta-analysis of students' learning outcomes through online learning. Previous meta-analysis studies were typically based on the studies, involving narrow range of confounding variables. In the present study, common but significant moderators such as class level and lectures during the pandemic process were discussed. For instance, the problems have been experienced especially in terms of eligibility of class levels in online education platforms during the pandemic process. It was found that there is a need to study and make suggestions on whether online education can meet the needs of teachers and students.
Besides, the main forms of online education in the past were to watch the open lectures of famous universities and educational videos of institutions. In addition, online education is mainly a classroom-based teaching implemented by teachers in their own schools during the pandemic period, which is an extension of the original school education. This meta-analysis study will stand as a source to compare the effect size of the online education forms of the past decade with what is done today, and what will be done in the future.
Lastly, the heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
*Studies included in meta-analysis
Ahmad, S., Sumardi, K., & Purnawan, P. (2016). Komparasi Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Antara Pembelajaran Menggunakan Sistem Pembelajaran Online Terpadu Dengan Pembelajaran Klasikal Pada Mata Kuliah Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education, 2 (2), 286–292.
Article Google Scholar
Ally, M. (2004). Foundations of educational theory for online learning. Theory and Practice of Online Learning, 2 , 15–44. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://eddl.tru.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/01_Anderson_2008-Theory_and_Practice_of_Online_Learning.pdf
Arat, T., & Bakan, Ö. (2011). Uzaktan eğitim ve uygulamaları. Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi , 14 (1–2), 363–374. https://doi.org/10.29249/selcuksbmyd.540741
Astuti, C. C., Sari, H. M. K., & Azizah, N. L. (2019). Perbandingan Efektifitas Proses Pembelajaran Menggunakan Metode E-Learning dan Konvensional. Proceedings of the ICECRS, 2 (1), 35–40.
*Atici, B., & Polat, O. C. (2010). Influence of the online learning environments and tools on the student achievement and opinions. Educational Research and Reviews, 5 (8), 455–464. Retrieved on the 11th of October, 2020 from https://academicjournals.org/journal/ERR/article-full-text-pdf/4C8DD044180.pdf
Bernard, R. M., Abrami, P. C., Lou, Y., Borokhovski, E., Wade, A., Wozney, L., et al. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta- analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 3 (74), 379–439. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074003379
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis . Wiley.
Book Google Scholar
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L., & Rothstein, H. (2007). Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects . UK: Wiley.
Card, N. A. (2011). Applied meta-analysis for social science research: Methodology in the social sciences . Guilford.
Google Scholar
*Carreon, J. R. (2018 ). Facebook as integrated blended learning tool in technology and livelihood education exploratory. Retrieved on the 1st of October, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1197714.pdf
Cavanaugh, C., Gillan, K. J., Kromrey, J., Hess, M., & Blomeyer, R. (2004). The effects of distance education on K-12 student outcomes: A meta-analysis. Learning Point Associates/North Central Regional Educational Laboratory (NCREL) . Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED489533.pdf
*Ceylan, V. K., & Elitok Kesici, A. (2017). Effect of blended learning to academic achievement. Journal of Human Sciences, 14 (1), 308. https://doi.org/10.14687/jhs.v14i1.4141
*Chae, S. E., & Shin, J. H. (2016). Tutoring styles that encourage learner satisfaction, academic engagement, and achievement in an online environment. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1371–1385. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2015.1009472
*Chiang, T. H. C., Yang, S. J. H., & Hwang, G. J. (2014). An augmented reality-based mobile learning system to improve students’ learning achievements and motivations in natural science inquiry activities. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (4), 352–365. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gwo_Jen_Hwang/publication/287529242_An_Augmented_Reality-based_Mobile_Learning_System_to_Improve_Students'_Learning_Achievements_and_Motivations_in_Natural_Science_Inquiry_Activities/links/57198c4808ae30c3f9f2c4ac.pdf
Chiao, H. M., Chen, Y. L., & Huang, W. H. (2018). Examining the usability of an online virtual tour-guiding platform for cultural tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 23 (29–38), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.05.002
Chizmar, J. F., & Walbert, M. S. (1999). Web-based learning environments guided by principles of good teaching practice. Journal of Economic Education, 30 (3), 248–264. https://doi.org/10.2307/1183061
Cleophas, T. J., & Zwinderman, A. H. (2017). Modern meta-analysis: Review and update of methodologies . Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55895-0
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Observation. Research Methods in Education, 6 , 396–412. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nabil_Ashraf2/post/How_to_get_surface_potential_Vs_Voltage_curve_from_CV_and_GV_measurements_of_MOS_capacitor/attachment/5ac6033cb53d2f63c3c405b4/AS%3A612011817844736%401522926396219/download/Very+important_C-V+characterization+Lehigh+University+thesis.pdf
Colis, B., & Moonen, J. (2001). Flexible Learning in a Digital World: Experiences and Expectations. Open & Distance Learning Series . Stylus Publishing.
CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. Retrieved on the 3rd of September, 2021 from https://www.cosn.org/sites/default/files/COVID-19%20Member%20Exclusive_0.pdf
Cumming, G. (2012). Understanding new statistics: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. New York, USA: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203807002
Deeks, J. J., Higgins, J. P. T., & Altman, D. G. (2008). Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses . In J. P. T. Higgins & S. Green (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 243–296). Sussex: John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470712184.ch9
Demiralay, R., Bayır, E. A., & Gelibolu, M. F. (2016). Öğrencilerin bireysel yenilikçilik özellikleri ile çevrimiçi öğrenmeye hazır bulunuşlukları ilişkisinin incelenmesi. Eğitim ve Öğretim Araştırmaları Dergisi, 5 (1), 161–168. https://doi.org/10.23891/efdyyu.2017.10
Dinçer, S. (2014). Eğitim bilimlerinde uygulamalı meta-analiz. Pegem Atıf İndeksi, 2014(1), 1–133. https://doi.org/10.14527/pegem.001
*Durak, G., Cankaya, S., Yunkul, E., & Ozturk, G. (2017). The effects of a social learning network on students’ performances and attitudes. European Journal of Education Studies, 3 (3), 312–333. 10.5281/zenodo.292951
*Ercan, O. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes . European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Ercan, O., & Bilen, K. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes. European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23.
*Ercan, O., Bilen, K., & Ural, E. (2016). “Earth, sun and moon”: Computer assisted instruction in secondary school science - Achievement and attitudes. Issues in Educational Research, 26 (2), 206–224. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Field, A. P. (2003). The problems in using fixed-effects models of meta-analysis on real-world data. Understanding Statistics, 2 (2), 105–124. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328031us0202_02
Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 63 (3), 665–694. https://doi.org/10.1348/00071010x502733
Geostat. (2019). ‘Share of households with internet access’, National statistics office of Georgia . Retrieved on the 2nd September 2020 from https://www.geostat.ge/en/modules/categories/106/information-and-communication-technologies-usage-in-households
*Gwo-Jen, H., Nien-Ting, T., & Xiao-Ming, W. (2018). Creating interactive e-books through learning by design: The impacts of guided peer-feedback on students’ learning achievements and project outcomes in science courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society., 21 (1), 25–36. Retrieved on the 2nd of October, 2020 https://ae-uploads.uoregon.edu/ISTE/ISTE2019/PROGRAM_SESSION_MODEL/HANDOUTS/112172923/CreatingInteractiveeBooksthroughLearningbyDesignArticle2018.pdf
Hamdani, A. R., & Priatna, A. (2020). Efektifitas implementasi pembelajaran daring (full online) dimasa pandemi Covid-19 pada jenjang Sekolah Dasar di Kabupaten Subang. Didaktik: Jurnal Ilmiah PGSD STKIP Subang, 6 (1), 1–9.
Hart, C. M., Berger, D., Jacob, B., Loeb, S., & Hill, M. (2019). Online learning, offline outcomes: Online course taking and high school student performance. Aera Open, 5(1).
*Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86 (3), 397–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12114
Horton, W. K. (2000). Designing web-based training: How to teach anyone anything anywhere anytime (Vol. 1). Wiley Publishing.
*Hwang, G. J., Wu, P. H., & Chen, C. C. (2012). An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Computers and Education, 59 (4), 1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.009
*Kert, S. B., Köşkeroğlu Büyükimdat, M., Uzun, A., & Çayiroğlu, B. (2017). Comparing active game-playing scores and academic performances of elementary school students. Education 3–13, 45 (5), 532–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2016.1140800
*Lai, A. F., & Chen, D. J. (2010). Web-based two-tier diagnostic test and remedial learning experiment. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 8 (1), 31–53. https://doi.org/10.4018/jdet.2010010103
*Lai, A. F., Lai, H. Y., Chuang W. H., & Wu, Z.H. (2015). Developing a mobile learning management system for outdoors nature science activities based on 5e learning cycle. Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Learning, ICEL. Proceedings of the International Association for Development of the Information Society (IADIS) International Conference on e-Learning (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, July 21–24, 2015). Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562095.pdf
Lai, C. H., Lin, H. W., Lin, R. M., & Tho, P. D. (2019). Effect of peer interaction among online learning community on learning engagement and achievement. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies (IJDET), 17 (1), 66–77.
Littell, J. H., Corcoran, J., & Pillai, V. (2008). Systematic reviews and meta-analysis . Oxford University.
*Liu, K. P., Tai, S. J. D., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Enhancing language learning through creation: the effect of digital storytelling on student learning motivation and performance in a school English course. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66 (4), 913–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9592-z
Machtmes, K., & Asher, J. W. (2000). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of telecourses in distance education. American Journal of Distance Education, 14 (1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923640009527043
Makowski, D., Piraux, F., & Brun, F. (2019). From experimental network to meta-analysis: Methods and applications with R for agronomic and environmental sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024_1696-1
* Meyers, C., Molefe, A., & Brandt, C. (2015). The Impact of the" Enhancing Missouri's Instructional Networked Teaching Strategies"(eMINTS) Program on Student Achievement, 21st-Century Skills, and Academic Engagement--Second-Year Results . Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness. Retrieved on the 14 th November, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562508.pdf
OECD. (2020). ‘A framework to guide an education response to the COVID-19 Pandemic of 2020 ’. https://doi.org/10.26524/royal.37.6
Pecoraro, V. (2018). Appraising evidence . In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 99–114). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_9
Pigott, T. (2012). Advances in meta-analysis . Springer.
Pillay, H. , Irving, K., & Tones, M. (2007). Validation of the diagnostic tool for assessing Tertiary students’ readiness for online learning. Higher Education Research & Development, 26 (2), 217–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360701310821
Prestiadi, D., Zulkarnain, W., & Sumarsono, R. B. (2019). Visionary leadership in total quality management: efforts to improve the quality of education in the industrial revolution 4.0. In the 4th International Conference on Education and Management (COEMA 2019). Atlantis Press
Poole, D. M. (2000). Student participation in a discussion-oriented online course: a case study. Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 33 (2), 162–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/08886504.2000.10782307
Rahayu, F. S., Budiyanto, D., & Palyama, D. (2017). Analisis penerimaan e-learning menggunakan technology acceptance model (Tam)(Studi Kasus: Universitas Atma Jaya Yogyakarta). Jurnal Terapan Teknologi Informasi, 1 (2), 87–98.
Rasmussen, R. C. (2003). The quantity and quality of human interaction in a synchronous blended learning environment . Brigham Young University Press.
*Ravenel, J., T. Lambeth, D., & Spires, B. (2014). Effects of computer-based programs on mathematical achievement scores for fourth-grade students. i-manager’s Journal on School Educational Technology, 10 (1), 8–21. https://doi.org/10.26634/jsch.10.1.2830
Rolisca, R. U. C., & Achadiyah, B. N. (2014). Pengembangan media evaluasi pembelajaran dalam bentuk online berbasis e-learning menggunakan software wondershare quiz creator dalam mata pelajaran akuntansi SMA Brawijaya Smart School (BSS). Jurnal Pendidikan Akuntansi Indonesia, 12(2).
Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effective- ness of Web-based and classroom instruction: A meta-analysis . Personnel Psychology, 59 (3), 623–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2006.00049.x
Stewart, D. W., & Kamins, M. A. (2001). Developing a coding scheme and coding study reports. In M. W. Lipsey & D. B. Wilson (Eds.), Practical metaanalysis: Applied social research methods series (Vol. 49, pp. 73–90). Sage.
Swan, K. (2007). Research on online learning. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 11 (1), 55–59.
*Sung, H. Y., Hwang, G. J., & Chang, Y. C. (2016). Development of a mobile learning system based on a collaborative problem-posing strategy. Interactive Learning Environments, 24 (3), 456–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2013.867889
Tsagris, M., & Fragkos, K. C. (2018). Meta-analyses of clinical trials versus diagnostic test accuracy studies. In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 31–42). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_4
UNESCO. (2020, Match 13). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. Retrieved on the 14 th November 2020 from https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/ coronavirus-school-closures
Usta, E. (2011a). The effect of web-based learning environments on attitudes of students regarding computer and internet. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28 (262–269), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.051
Usta, E. (2011b). The examination of online self-regulated learning skills in web-based learning environments in terms of different variables. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 10 (3), 278–286. Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ944994.pdf
Vrasidas, C. & MsIsaac, M. S. (2000). Principles of pedagogy and evaluation for web-based learning. Educational Media International, 37 (2), 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/095239800410405
*Wang, C. H., & Chen, C. P. (2013). Effects of facebook tutoring on learning english as a second language. Proceedings of the International Conference e-Learning 2013, (2009), 135–142. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562299.pdf
Wei, H. C., & Chou, C. (2020). Online learning performance and satisfaction: Do perceptions and readiness matter? Distance Education, 41 (1), 48–69.
*Yu, F. Y. (2019). The learning potential of online student-constructed tests with citing peer-generated questions. Interactive Learning Environments, 27 (2), 226–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1458040
*Yu, F. Y., & Chen, Y. J. (2014). Effects of student-generated questions as the source of online drill-and-practice activities on learning . British Journal of Educational Technology, 45 (2), 316–329. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12036
*Yu, F. Y., & Pan, K. J. (2014). The effects of student question-generation with online prompts on learning. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (3), 267–279. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.565.643&rep=rep1&type=pdf
*Yu, W. F., She, H. C., & Lee, Y. M. (2010). The effects of web-based/non-web-based problem-solving instruction and high/low achievement on students’ problem-solving ability and biology achievement. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 47 (2), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703291003718927
Zhao, Y., Lei, J., Yan, B, Lai, C., & Tan, S. (2005). A practical analysis of research on the effectiveness of distance education. Teachers College Record, 107 (8). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2005.00544.x
*Zhong, B., Wang, Q., Chen, J., & Li, Y. (2017). Investigating the period of switching roles in pair programming in a primary school. Educational Technology and Society, 20 (3), 220–233. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://repository.nie.edu.sg/bitstream/10497/18946/1/ETS-20-3-220.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Primary Education, Ministry of Turkish National Education, Mersin, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hakan Ulum .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ulum, H. The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study. Educ Inf Technol 27 , 429–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Download citation
Received : 06 December 2020
Accepted : 30 August 2021
Published : 06 September 2021
Issue Date : January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online education
- Student achievement
- Academic success
- Meta-analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study
Primary Education, Ministry of Turkish National Education, Mersin, Turkey
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students’ academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this study will provide a source to assist future studies with comparing the effect of online education on academic achievement before and after the pandemic. This meta-analysis study consists of 27 studies in total. The meta-analysis involves the studies conducted in the USA, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia. The studies included in the meta-analysis are experimental studies, and the total sample size is 1772. In the study, the funnel plot, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test were utilized to determine the publication bias, which has been found to be quite low. Besides, Hedge’s g statistic was employed to measure the effect size for the difference between the means performed in accordance with the random effects model. The results of the study show that the effect size of online education on academic achievement is on a medium level. The heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
Introduction
Information and communication technologies have become a powerful force in transforming the educational settings around the world. The pandemic has been an important factor in transferring traditional physical classrooms settings through adopting information and communication technologies and has also accelerated the transformation. The literature supports that learning environments connected to information and communication technologies highly satisfy students. Therefore, we need to keep interest in technology-based learning environments. Clearly, technology has had a huge impact on young people's online lives. This digital revolution can synergize the educational ambitions and interests of digitally addicted students. In essence, COVID-19 has provided us with an opportunity to embrace online learning as education systems have to keep up with the rapid emergence of new technologies.
Information and communication technologies that have an effect on all spheres of life are also actively included in the education field. With the recent developments, using technology in education has become inevitable due to personal and social reasons (Usta, 2011a ). Online education may be given as an example of using information and communication technologies as a consequence of the technological developments. Also, it is crystal clear that online learning is a popular way of obtaining instruction (Demiralay et al., 2016 ; Pillay et al., 2007 ), which is defined by Horton ( 2000 ) as a way of education that is performed through a web browser or an online application without requiring an extra software or a learning source. Furthermore, online learning is described as a way of utilizing the internet to obtain the related learning sources during the learning process, to interact with the content, the teacher, and other learners, as well as to get support throughout the learning process (Ally, 2004 ). Online learning has such benefits as learning independently at any time and place (Vrasidas & MsIsaac, 2000 ), granting facility (Poole, 2000 ), flexibility (Chizmar & Walbert, 1999 ), self-regulation skills (Usta, 2011b ), learning with collaboration, and opportunity to plan self-learning process.
Even though online education practices have not been comprehensive as it is now, internet and computers have been used in education as alternative learning tools in correlation with the advances in technology. The first distance education attempt in the world was initiated by the ‘Steno Courses’ announcement published in Boston newspaper in 1728. Furthermore, in the nineteenth century, Sweden University started the “Correspondence Composition Courses” for women, and University Correspondence College was afterwards founded for the correspondence courses in 1843 (Arat & Bakan, 2011 ). Recently, distance education has been performed through computers, assisted by the facilities of the internet technologies, and soon, it has evolved into a mobile education practice that is emanating from progress in the speed of internet connection, and the development of mobile devices.
With the emergence of pandemic (Covid-19), face to face education has almost been put to a halt, and online education has gained significant importance. The Microsoft management team declared to have 750 users involved in the online education activities on the 10 th March, just before the pandemic; however, on March 24, they informed that the number of users increased significantly, reaching the number of 138,698 users (OECD, 2020 ). This event supports the view that it is better to commonly use online education rather than using it as a traditional alternative educational tool when students do not have the opportunity to have a face to face education (Geostat, 2019 ). The period of Covid-19 pandemic has emerged as a sudden state of having limited opportunities. Face to face education has stopped in this period for a long time. The global spread of Covid-19 affected more than 850 million students all around the world, and it caused the suspension of face to face education. Different countries have proposed several solutions in order to maintain the education process during the pandemic. Schools have had to change their curriculum, and many countries supported the online education practices soon after the pandemic. In other words, traditional education gave its way to online education practices. At least 96 countries have been motivated to access online libraries, TV broadcasts, instructions, sources, video lectures, and online channels (UNESCO, 2020 ). In such a painful period, educational institutions went through online education practices by the help of huge companies such as Microsoft, Google, Zoom, Skype, FaceTime, and Slack. Thus, online education has been discussed in the education agenda more intensively than ever before.
Although online education approaches were not used as comprehensively as it has been used recently, it was utilized as an alternative learning approach in education for a long time in parallel with the development of technology, internet and computers. The academic achievement of the students is often aimed to be promoted by employing online education approaches. In this regard, academicians in various countries have conducted many studies on the evaluation of online education approaches and published the related results. However, the accumulation of scientific data on online education approaches creates difficulties in keeping, organizing and synthesizing the findings. In this research area, studies are being conducted at an increasing rate making it difficult for scientists to be aware of all the research outside of their expertise. Another problem encountered in the related study area is that online education studies are repetitive. Studies often utilize slightly different methods, measures, and/or examples to avoid duplication. This erroneous approach makes it difficult to distinguish between significant differences in the related results. In other words, if there are significant differences in the results of the studies, it may be difficult to express what variety explains the differences in these results. One obvious solution to these problems is to systematically review the results of various studies and uncover the sources. One method of performing such systematic syntheses is the application of meta-analysis which is a methodological and statistical approach to draw conclusions from the literature. At this point, how effective online education applications are in increasing the academic success is an important detail. Has online education, which is likely to be encountered frequently in the continuing pandemic period, been successful in the last ten years? If successful, how much was the impact? Did different variables have an impact on this effect? Academics across the globe have carried out studies on the evaluation of online education platforms and publishing the related results (Chiao et al., 2018 ). It is quite important to evaluate the results of the studies that have been published up until now, and that will be published in the future. Has the online education been successful? If it has been, how big is the impact? Do the different variables affect this impact? What should we consider in the next coming online education practices? These questions have all motivated us to carry out this study. We have conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis study that tries to provide a discussion platform on how to develop efficient online programs for educators and policy makers by reviewing the related studies on online education, presenting the effect size, and revealing the effect of diverse variables on the general impact.
There have been many critical discussions and comprehensive studies on the differences between online and face to face learning; however, the focus of this paper is different in the sense that it clarifies the magnitude of the effect of online education and teaching process, and it represents what factors should be controlled to help increase the effect size. Indeed, the purpose here is to provide conscious decisions in the implementation of the online education process.
The general impact of online education on the academic achievement will be discovered in the study. Therefore, this will provide an opportunity to get a general overview of the online education which has been practiced and discussed intensively in the pandemic period. Moreover, the general impact of online education on academic achievement will be analyzed, considering different variables. In other words, the current study will allow to totally evaluate the study results from the related literature, and to analyze the results considering several cultures, lectures, and class levels. Considering all the related points, this study seeks to answer the following research questions:
- What is the effect size of online education on academic achievement?
- How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the country?
- How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the class level?
- How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the lecture?
- How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the online education approaches?
This study aims at determining the effect size of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, on students’ academic achievement in different courses by using a meta-analysis method. Meta-analysis is a synthesis method that enables gathering of several study results accurately and efficiently, and getting the total results in the end (Tsagris & Fragkos, 2018 ).
Selecting and coding the data (studies)
The required literature for the meta-analysis study was reviewed in July, 2020, and the follow-up review was conducted in September, 2020. The purpose of the follow-up review was to include the studies which were published in the conduction period of this study, and which met the related inclusion criteria. However, no study was encountered to be included in the follow-up review.
In order to access the studies in the meta-analysis, the databases of Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS were reviewed by utilizing the keywords ‘online learning and online education’. Not every database has a search engine that grants access to the studies by writing the keywords, and this obstacle was considered to be an important problem to be overcome. Therefore, a platform that has a special design was utilized by the researcher. With this purpose, through the open access system of Cukurova University Library, detailed reviews were practiced using EBSCO Information Services (EBSCO) that allow reviewing the whole collection of research through a sole searching box. Since the fundamental variables of this study are online education and online learning, the literature was systematically reviewed in the related databases (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) by referring to the keywords. Within this scope, 225 articles were accessed, and the studies were included in the coding key list formed by the researcher. The name of the researchers, the year, the database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS), the sample group and size, the lectures that the academic achievement was tested in, the country that the study was conducted in, and the class levels were all included in this coding key.
The following criteria were identified to include 225 research studies which were coded based on the theoretical basis of the meta-analysis study: (1) The studies should be published in the refereed journals between the years 2020 and 2021, (2) The studies should be experimental studies that try to determine the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement, (3) The values of the stated variables or the required statistics to calculate these values should be stated in the results of the studies, and (4) The sample group of the study should be at a primary education level. These criteria were also used as the exclusion criteria in the sense that the studies that do not meet the required criteria were not included in the present study.
After the inclusion criteria were determined, a systematic review process was conducted, following the year criterion of the study by means of EBSCO. Within this scope, 290,365 studies that analyze the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement were accordingly accessed. The database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) was also used as a filter by analyzing the inclusion criteria. Hence, the number of the studies that were analyzed was 58,616. Afterwards, the keyword ‘primary education’ was used as the filter and the number of studies included in the study decreased to 3152. Lastly, the literature was reviewed by using the keyword ‘academic achievement’ and 225 studies were accessed. All the information of 225 articles was included in the coding key.
It is necessary for the coders to review the related studies accurately and control the validity, safety, and accuracy of the studies (Stewart & Kamins, 2001 ). Within this scope, the studies that were determined based on the variables used in this study were first reviewed by three researchers from primary education field, then the accessed studies were combined and processed in the coding key by the researcher. All these studies that were processed in the coding key were analyzed in accordance with the inclusion criteria by all the researchers in the meetings, and it was decided that 27 studies met the inclusion criteria (Atici & Polat, 2010 ; Carreon, 2018 ; Ceylan & Elitok Kesici, 2017 ; Chae & Shin, 2016 ; Chiang et al. 2014 ; Ercan, 2014 ; Ercan et al., 2016 ; Gwo-Jen et al., 2018 ; Hayes & Stewart, 2016 ; Hwang et al., 2012 ; Kert et al., 2017 ; Lai & Chen, 2010 ; Lai et al., 2015 ; Meyers et al., 2015 ; Ravenel et al., 2014 ; Sung et al., 2016 ; Wang & Chen, 2013 ; Yu, 2019 ; Yu & Chen, 2014 ; Yu & Pan, 2014 ; Yu et al., 2010 ; Zhong et al., 2017 ). The data from the studies meeting the inclusion criteria were independently processed in the second coding key by three researchers, and consensus meetings were arranged for further discussion. After the meetings, researchers came to an agreement that the data were coded accurately and precisely. Having identified the effect sizes and heterogeneity of the study, moderator variables that will show the differences between the effect sizes were determined. The data related to the determined moderator variables were added to the coding key by three researchers, and a new consensus meeting was arranged. After the meeting, researchers came to an agreement that moderator variables were coded accurately and precisely.
Study group
27 studies are included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies that are included in the analysis is 1772. The characteristics of the studies included are given in Table Table1 1 .
The characteristics of the studies included in the meta-analysis
| = | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | 2010 | 3 |
| 2012 | 1 | |
| 2013 | 2 | |
| 2014 | 6 | |
| 2015 | 2 | |
| 2016 | 6 | |
| 2017 | 2 | |
| 2018 | 4 | |
| 2019 | 1 | |
| Level | 4. Class | 2 |
| 5. Class | 6 | |
| 6. Class | 9 | |
| 7. Class | 5 | |
| 8. Class | 5 | |
| School Subjects | Art | 2 |
| Biology | 1 | |
| ICT | 3 | |
| English | 5 | |
| Math | 4 | |
| Nature | 3 | |
| Science | 6 | |
| Social Sciences | 3 | |
| Countries | USA | 4 |
| Others | 4 | |
| Taiwan | 15 | |
| Turkey | 4 |
Publication bias
Publication bias is the low capability of published studies on a research subject to represent all completed studies on the same subject (Card, 2011 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Similarly, publication bias is the state of having a relationship between the probability of the publication of a study on a subject, and the effect size and significance that it produces. Within this scope, publication bias may occur when the researchers do not want to publish the study as a result of failing to obtain the expected results, or not being approved by the scientific journals, and consequently not being included in the study synthesis (Makowski et al., 2019 ). The high possibility of publication bias in a meta-analysis study negatively affects (Pecoraro, 2018 ) the accuracy of the combined effect size, causing the average effect size to be reported differently than it should be (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). For this reason, the possibility of publication bias in the included studies was tested before determining the effect sizes of the relationships between the stated variables. The possibility of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
Selecting the model
After determining the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study, the statistical model used to calculate the effect sizes was selected. The main approaches used in the effect size calculations according to the differentiation level of inter-study variance are fixed and random effects models (Pigott, 2012 ). Fixed effects model refers to the homogeneity of the characteristics of combined studies apart from the sample sizes, while random effects model refers to the parameter diversity between the studies (Cumming, 2012 ). While calculating the average effect size in the random effects model (Deeks et al., 2008 ) that is based on the assumption that effect predictions of different studies are only the result of a similar distribution, it is necessary to consider several situations such as the effect size apart from the sample error of combined studies, characteristics of the participants, duration, scope, and pattern of the study (Littell et al., 2008 ). While deciding the model in the meta-analysis study, the assumptions on the sample characteristics of the studies included in the analysis and the inferences that the researcher aims to make should be taken into consideration. The fact that the sample characteristics of the studies conducted in the field of social sciences are affected by various parameters shows that using random effects model is more appropriate in this sense. Besides, it is stated that the inferences made with the random effects model are beyond the studies included in the meta-analysis (Field, 2003 ; Field & Gillett, 2010 ). Therefore, using random effects model also contributes to the generalization of research data. The specified criteria for the statistical model selection show that according to the nature of the meta-analysis study, the model should be selected just before the analysis (Borenstein et al., 2007 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Within this framework, it was decided to make use of the random effects model, considering that the students who are the samples of the studies included in the meta-analysis are from different countries and cultures, the sample characteristics of the studies differ, and the patterns and scopes of the studies vary as well.
Heterogeneity
Meta-analysis facilitates analyzing the research subject with different parameters by showing the level of diversity between the included studies. Within this frame, whether there is a heterogeneous distribution between the studies included in the study or not has been evaluated in the present study. The heterogeneity of the studies combined in this meta-analysis study has been determined through Q and I 2 tests. Q test evaluates the random distribution probability of the differences between the observed results (Deeks et al., 2008 ). Q value exceeding 2 value calculated according to the degree of freedom and significance, indicates the heterogeneity of the combined effect sizes (Card, 2011 ). I 2 test, which is the complementary of the Q test, shows the heterogeneity amount of the effect sizes (Cleophas & Zwinderman, 2017 ). I 2 value being higher than 75% is explained as high level of heterogeneity.
In case of encountering heterogeneity in the studies included in the meta-analysis, the reasons of heterogeneity can be analyzed by referring to the study characteristics. The study characteristics which may be related to the heterogeneity between the included studies can be interpreted through subgroup analysis or meta-regression analysis (Deeks et al., 2008 ). While determining the moderator variables, the sufficiency of the number of variables, the relationship between the moderators, and the condition to explain the differences between the results of the studies have all been considered in the present study. Within this scope, it was predicted in this meta-analysis study that the heterogeneity can be explained with the country, class level, and lecture moderator variables of the study in terms of the effect of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, and it has an impact on the students’ academic achievement in different lectures. Some subgroups were evaluated and categorized together, considering that the number of effect sizes of the sub-dimensions of the specified variables is not sufficient to perform moderator analysis (e.g. the countries where the studies were conducted).
Interpreting the effect sizes
Effect size is a factor that shows how much the independent variable affects the dependent variable positively or negatively in each included study in the meta-analysis (Dinçer, 2014 ). While interpreting the effect sizes obtained from the meta-analysis, the classifications of Cohen et al. ( 2007 ) have been utilized. The case of differentiating the specified relationships of the situation of the country, class level, and school subject variables of the study has been identified through the Q test, degree of freedom, and p significance value Fig. 1 and and2 2 .

The flow chart of the scanning and selection process of the studies

Funnel plot graphics representing the effect size of the effects of online education on academic success
Findings and results
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement. Before determining the effect sizes in the study, the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
When the funnel plots are examined, it is seen that the studies included in the analysis are distributed symmetrically on both sides of the combined effect size axis, and they are generally collected in the middle and lower sections. The probability of publication bias is low according to the plots. However, since the results of the funnel scatter plots may cause subjective interpretations, they have been supported by additional analyses (Littell et al., 2008 ). Therefore, in order to provide an extra proof for the probability of publication bias, it has been analyzed through Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test (Table (Table2 2 ).
Reliability tests results representing the probability of publication bias
| Orwin’s Safe N | Duval & Tweedie | Egger’s test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0.01 Hedges )* | Trimmed | Observed/Added | ( ) |
| 1073 | 0 | 0.407 (0.408) | 0.849 |
* Represents the required number of papers for Hedges g co-efficiency to reach a rate out of 0.01 range
Table Table2 2 consists of the results of the rates of publication bias probability before counting the effect size of online education on academic achievement. According to the table, Orwin Safe N analysis results show that it is not necessary to add new studies to the meta-analysis in order for Hedges g to reach a value outside the range of ± 0.01. The Duval and Tweedie test shows that excluding the studies that negatively affect the symmetry of the funnel scatter plots for each meta-analysis or adding their exact symmetrical equivalents does not significantly differentiate the calculated effect size. The insignificance of the Egger tests results reveals that there is no publication bias in the meta-analysis study. The results of the analysis indicate the high internal validity of the effect sizes and the adequacy of representing the studies conducted on the relevant subject.
In this study, it was aimed to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement after testing the publication bias. In line with the first purpose of the study, the forest graph regarding the effect size of online education on academic achievement is shown in Fig. 3 , and the statistics regarding the effect size are given in Table Table3 3 .

Forest graph related to the effect size of online education on academic success
The findings related to the effect size of online education on academic success
| Effect Size Model | n | Effect Size (d) | Lower limit | Upper Limit | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Effect | 27 | 0.407 | 0.313 | 0.502 | 29.579 | 0.285 |
| Random Effect | 27 | 0.409 | 0.307 | 0.511 |
n: the Number of Studies included in Meta-Analysis; Hedges g: average effect size
p: significance level of the effect size; S error : standard error; EB low – EB up : lower and upper limits of the effect size
The square symbols in the forest graph in Fig. 3 represent the effect sizes, while the horizontal lines show the intervals in 95% confidence of the effect sizes, and the diamond symbol shows the overall effect size. When the forest graph is analyzed, it is seen that the lower and upper limits of the combined effect sizes are generally close to each other, and the study loads are similar. This similarity in terms of study loads indicates the similarity of the contribution of the combined studies to the overall effect size.
Figure 3 clearly represents that the study of Liu and others (Liu et al., 2018 ) has the lowest, and the study of Ercan and Bilen ( 2014 ) has the highest effect sizes. The forest graph shows that all the combined studies and the overall effect are positive. Furthermore, it is simply understood from the forest graph in Fig. 3 and the effect size statistics in Table Table3 3 that the results of the meta-analysis study conducted with 27 studies and analyzing the effect of online education on academic achievement illustrate that this relationship is on average level (= 0.409).
After the analysis of the effect size in the study, whether the studies included in the analysis are distributed heterogeneously or not has also been analyzed. The heterogeneity of the combined studies was determined through the Q and I 2 tests. As a result of the heterogeneity test, Q statistical value was calculated as 29.576. With 26 degrees of freedom at 95% significance level in the chi-square table, the critical value is accepted as 38.885. The Q statistical value (29.576) counted in this study is lower than the critical value of 38.885. The I 2 value, which is the complementary of the Q statistics, is 12.100%. This value indicates that the accurate heterogeneity or the total variability that can be attributed to variability between the studies is 12%. Besides, p value is higher than (0.285) p = 0.05. All these values [Q (26) = 29.579, p = 0.285; I2 = 12.100] indicate that there is a homogeneous distribution between the effect sizes, and fixed effects model should be used to interpret these effect sizes. However, some researchers argue that even if the heterogeneity is low, it should be evaluated based on the random effects model (Borenstein et al., 2007 ). Therefore, this study gives information about both models. The heterogeneity of the combined studies has been attempted to be explained with the characteristics of the studies included in the analysis. In this context, the final purpose of the study is to determine the effect of the country, academic level, and year variables on the findings. Accordingly, the statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the countries where the studies were conducted are given in Table Table4 4 .
The dispersion of the studies according to the countries and the heterogeneity test results
| Country | Confidence interval (%95) | Heterogeneity test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Effect size (d) | Lower limit | Upper limit | Q | sd | |||
| Academic Success | Turkey | 4 | 0.575 | 0.304 | 0.846 | 5.306 | 3 | 0.151 |
| Taiwan | 15 | 0.370 | 0.236 | 0.503 | ||||
| USA | 4 | 0.218 | -0.0092 | 0.528 | ||||
| Others | 4 | 0.596 | 0.345 | 0.847 | ||||
As seen in Table Table4, 4 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ significantly according to the countries where the studies were conducted in. Q test results indicate the heterogeneity of the relationships between the variables in terms of countries where the studies were conducted in. According to the table, the effect of online education on academic achievement was reported as the highest in other countries, and the lowest in the US. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table Table5 5 .
The dispersion of the studies according to the class level and the heterogeneity test results
| Level | Confidence interval (%95) | Heterogeneity test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Effect size (d) | Lower limit | Upper limit | Q | Sd | |||
| Academic Success | 4. Class | 2 | 0.588 | 0.211 | 0.965 | 2.427 | 4 | 0.658 |
| 5. Class | 6 | 0.395 | 0.203 | 0.587 | ||||
| 6. Class | 9 | 0.472 | 0.272 | 0.671 | ||||
| 7. Class | 5 | 0.358 | 0.055 | 0.660 | ||||
| 8. Class | 5 | 0.266 | -0.007 | 0.539 | ||||
As seen in Table Table5, 5 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the class level. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in the 4 th class. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table Table6 6 .
The dispersion of the studies according to the school subjects and the heterogeneity test results
| Subjects | Confidence interval (%95) | Heterogeneity test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Effect size (d) | Lower limit | Upper limit | Q | Sd | |||
| Academic Success | Art | 2 | 0.109 | -0.329 | 0.547 | 10.996 | 7 | 0.139 |
| Biology | 1 | 0.078 | -0.234 | 0.391 | ||||
| ICT | 3 | 0.659 | 0.406 | 0.913 | ||||
| English | 5 | 0.365 | 0.075 | 0.656 | ||||
| Math | 4 | 0.386 | 0.077 | 0.695 | ||||
| Nature | 3 | 0.405 | 0.159 | 0.651 | ||||
| Science | 6 | 0.534 | 0.294 | 0.774 | ||||
| Social Sciences | 3 | 0.409 | 0.063 | 0.756 | ||||
As seen in Table Table6, 6 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the school subjects included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in ICT subject.
The obtained effect size in the study was formed as a result of the findings attained from primary studies conducted in 7 different countries. In addition, these studies are the ones on different approaches to online education (online learning environments, social networks, blended learning, etc.). In this respect, the results may raise some questions about the validity and generalizability of the results of the study. However, the moderator analyzes, whether for the country variable or for the approaches covered by online education, did not create significant differences in terms of the effect sizes. If significant differences were to occur in terms of effect sizes, we could say that the comparisons we will make by comparing countries under the umbrella of online education would raise doubts in terms of generalizability. Moreover, no study has been found in the literature that is not based on a special approach or does not contain a specific technique conducted under the name of online education alone. For instance, one of the commonly used definitions is blended education which is defined as an educational model in which online education is combined with traditional education method (Colis & Moonen, 2001 ). Similarly, Rasmussen ( 2003 ) defines blended learning as “a distance education method that combines technology (high technology such as television, internet, or low technology such as voice e-mail, conferences) with traditional education and training.” Further, Kerres and Witt (2003) define blended learning as “combining face-to-face learning with technology-assisted learning.” As it is clearly observed, online education, which has a wider scope, includes many approaches.
As seen in Table Table7, 7 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to online education approaches included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in Web Based Problem Solving Approach.
The dispersion of the studies according to the online education approaches and the heterogeneity test results
| Subjects | Confidence interval (%95) | Heterogeneity test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Effect size (d) | Lower limit | Upper limit | Q | Sd | |||
| Online Education Approaches | Computer Assisted Learning | 2 | 0.433 | 0.054 | 0.812 | 10.245 | 7 | 0.175 |
| Online Learning Environments | 11 | 0.416 | 0.263 | 0.569 | ||||
| Digital Story Telling | 3 | 0.332 | 0.049 | 0.615 | ||||
| Blended Learning | 2 | 0.586 | 0.208 | 0.964 | ||||
| Mobile Learning | 3 | 0.463 | 0.216 | 0.711 | ||||
| Learning by Social Networks | 2 | 0.409 | 0.049 | 0.768 | ||||
| Web Based Problem Solving | 2 | 0.842 | 0.417 | 1.267 | ||||
| Web Based Learning | 2 | 0.096 | -0.176 | 0.368 | ||||
Conclusions and discussion
Considering the developments during the pandemics, it is thought that the diversity in online education applications as an interdisciplinary pragmatist field will increase, and the learning content and processes will be enriched with the integration of new technologies into online education processes. Another prediction is that more flexible and accessible learning opportunities will be created in online education processes, and in this way, lifelong learning processes will be strengthened. As a result, it is predicted that in the near future, online education and even digital learning with a newer name will turn into the main ground of education instead of being an alternative or having a support function in face-to-face learning. The lessons learned from the early period online learning experience, which was passed with rapid adaptation due to the Covid19 epidemic, will serve to develop this method all over the world, and in the near future, online learning will become the main learning structure through increasing its functionality with the contribution of new technologies and systems. If we look at it from this point of view, there is a necessity to strengthen online education.
In this study, the effect of online learning on academic achievement is at a moderate level. To increase this effect, the implementation of online learning requires support from teachers to prepare learning materials, to design learning appropriately, and to utilize various digital-based media such as websites, software technology and various other tools to support the effectiveness of online learning (Rolisca & Achadiyah, 2014 ). According to research conducted by Rahayu et al. ( 2017 ), it has been proven that the use of various types of software increases the effectiveness and quality of online learning. Implementation of online learning can affect students' ability to adapt to technological developments in that it makes students use various learning resources on the internet to access various types of information, and enables them to get used to performing inquiry learning and active learning (Hart et al., 2019 ; Prestiadi et al., 2019 ). In addition, there may be many reasons for the low level of effect in this study. The moderator variables examined in this study could be a guide in increasing the level of practical effect. However, the effect size did not differ significantly for all moderator variables. Different moderator analyzes can be evaluated in order to increase the level of impact of online education on academic success. If confounding variables that significantly change the effect level are detected, it can be spoken more precisely in order to increase this level. In addition to the technical and financial problems, the level of impact will increase if a few other difficulties are eliminated such as students, lack of interaction with the instructor, response time, and lack of traditional classroom socialization.
In addition, COVID-19 pandemic related social distancing has posed extreme difficulties for all stakeholders to get online as they have to work in time constraints and resource constraints. Adopting the online learning environment is not just a technical issue, it is a pedagogical and instructive challenge as well. Therefore, extensive preparation of teaching materials, curriculum, and assessment is vital in online education. Technology is the delivery tool and requires close cross-collaboration between teaching, content and technology teams (CoSN, 2020 ).
Online education applications have been used for many years. However, it has come to the fore more during the pandemic process. This result of necessity has brought with it the discussion of using online education instead of traditional education methods in the future. However, with this research, it has been revealed that online education applications are moderately effective. The use of online education instead of face-to-face education applications can only be possible with an increase in the level of success. This may have been possible with the experience and knowledge gained during the pandemic process. Therefore, the meta-analysis of experimental studies conducted in the coming years will guide us. In this context, experimental studies using online education applications should be analyzed well. It would be useful to identify variables that can change the level of impacts with different moderators. Moderator analyzes are valuable in meta-analysis studies (for example, the role of moderators in Karl Pearson's typhoid vaccine studies). In this context, each analysis study sheds light on future studies. In meta-analyses to be made about online education, it would be beneficial to go beyond the moderators determined in this study. Thus, the contribution of similar studies to the field will increase more.
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of online education on academic achievement. In line with this purpose, the studies that analyze the effect of online education approaches on academic achievement have been included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies included in the meta-analysis is 1772. While the studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in the US, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia, the studies carried out in Europe could not be reached. The reason may be attributed to that there may be more use of quantitative research methods from a positivist perspective in the countries with an American academic tradition. As a result of the study, it was found out that the effect size of online education on academic achievement (g = 0.409) was moderate. In the studies included in the present research, we found that online education approaches were more effective than traditional ones. However, contrary to the present study, the analysis of comparisons between online and traditional education in some studies shows that face-to-face traditional learning is still considered effective compared to online learning (Ahmad et al., 2016 ; Hamdani & Priatna, 2020 ; Wei & Chou, 2020 ). Online education has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of online learning compared to face-to-face learning in the classroom is the flexibility of learning time in online learning, the learning time does not include a single program, and it can be shaped according to circumstances (Lai et al., 2019 ). The next advantage is the ease of collecting assignments for students, as these can be done without having to talk to the teacher. Despite this, online education has several weaknesses, such as students having difficulty in understanding the material, teachers' inability to control students, and students’ still having difficulty interacting with teachers in case of internet network cuts (Swan, 2007 ). According to Astuti et al ( 2019 ), face-to-face education method is still considered better by students than e-learning because it is easier to understand the material and easier to interact with teachers. The results of the study illustrated that the effect size (g = 0.409) of online education on academic achievement is of medium level. Therefore, the results of the moderator analysis showed that the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ in terms of country, lecture, class level, and online education approaches variables. After analyzing the literature, several meta-analyses on online education were published (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Machtmes & Asher, 2000 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ). Typically, these meta-analyzes also include the studies of older generation technologies such as audio, video, or satellite transmission. One of the most comprehensive studies on online education was conducted by Bernard et al. ( 2004 ). In this study, 699 independent effect sizes of 232 studies published from 1985 to 2001 were analyzed, and face-to-face education was compared to online education, with respect to success criteria and attitudes of various learners from young children to adults. In this meta-analysis, an overall effect size close to zero was found for the students' achievement (g + = 0.01).
In another meta-analysis study carried out by Zhao et al. ( 2005 ), 98 effect sizes were examined, including 51 studies on online education conducted between 1996 and 2002. According to the study of Bernard et al. ( 2004 ), this meta-analysis focuses on the activities done in online education lectures. As a result of the research, an overall effect size close to zero was found for online education utilizing more than one generation technology for students at different levels. However, the salient point of the meta-analysis study of Zhao et al. is that it takes the average of different types of results used in a study to calculate an overall effect size. This practice is problematic because the factors that develop one type of learner outcome (e.g. learner rehabilitation), particularly course characteristics and practices, may be quite different from those that develop another type of outcome (e.g. learner's achievement), and it may even cause damage to the latter outcome. While mixing the studies with different types of results, this implementation may obscure the relationship between practices and learning.
Some meta-analytical studies have focused on the effectiveness of the new generation distance learning courses accessed through the internet for specific student populations. For instance, Sitzmann and others (Sitzmann et al., 2006 ) reviewed 96 studies published from 1996 to 2005, comparing web-based education of job-related knowledge or skills with face-to-face one. The researchers found that web-based education in general was slightly more effective than face-to-face education, but it is insufficient in terms of applicability ("knowing how to apply"). In addition, Sitzmann et al. ( 2006 ) revealed that Internet-based education has a positive effect on theoretical knowledge in quasi-experimental studies; however, it positively affects face-to-face education in experimental studies performed by random assignment. This moderator analysis emphasizes the need to pay attention to the factors of designs of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The designs of the studies included in this meta-analysis study were ignored. This can be presented as a suggestion to the new studies that will be conducted.
Another meta-analysis study was conducted by Cavanaugh et al. ( 2004 ), in which they focused on online education. In this study on internet-based distance education programs for students under 12 years of age, the researchers combined 116 results from 14 studies published between 1999 and 2004 to calculate an overall effect that was not statistically different from zero. The moderator analysis carried out in this study showed that there was no significant factor affecting the students' success. This meta-analysis used multiple results of the same study, ignoring the fact that different results of the same student would not be independent from each other.
In conclusion, some meta-analytical studies analyzed the consequences of online education for a wide range of students (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ), and the effect sizes were generally low in these studies. Furthermore, none of the large-scale meta-analyzes considered the moderators, database quality standards or class levels in the selection of the studies, while some of them just referred to the country and lecture moderators. Advances in internet-based learning tools, the pandemic process, and increasing popularity in different learning contexts have required a precise meta-analysis of students' learning outcomes through online learning. Previous meta-analysis studies were typically based on the studies, involving narrow range of confounding variables. In the present study, common but significant moderators such as class level and lectures during the pandemic process were discussed. For instance, the problems have been experienced especially in terms of eligibility of class levels in online education platforms during the pandemic process. It was found that there is a need to study and make suggestions on whether online education can meet the needs of teachers and students.
Besides, the main forms of online education in the past were to watch the open lectures of famous universities and educational videos of institutions. In addition, online education is mainly a classroom-based teaching implemented by teachers in their own schools during the pandemic period, which is an extension of the original school education. This meta-analysis study will stand as a source to compare the effect size of the online education forms of the past decade with what is done today, and what will be done in the future.
Lastly, the heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
*Studies included in meta-analysis
- Ahmad S, Sumardi K, Purnawan P. Komparasi Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Antara Pembelajaran Menggunakan Sistem Pembelajaran Online Terpadu Dengan Pembelajaran Klasikal Pada Mata Kuliah Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education. 2016; 2 (2):286–292. doi: 10.17509/jmee.v2i2.1491. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ally, M. (2004). Foundations of educational theory for online learning. Theory and Practice of Online Learning, 2 , 15–44. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://eddl.tru.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/01_Anderson_2008-Theory_and_Practice_of_Online_Learning.pdf
- Arat, T., & Bakan, Ö. (2011). Uzaktan eğitim ve uygulamaları. Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi , 14 (1–2), 363–374. 10.29249/selcuksbmyd.540741
- Astuti CC, Sari HMK, Azizah NL. Perbandingan Efektifitas Proses Pembelajaran Menggunakan Metode E-Learning dan Konvensional. Proceedings of the ICECRS. 2019; 2 (1):35–40. doi: 10.21070/picecrs.v2i1.2395. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- *Atici, B., & Polat, O. C. (2010). Influence of the online learning environments and tools on the student achievement and opinions. Educational Research and Reviews, 5 (8), 455–464. Retrieved on the 11th of October, 2020 from https://academicjournals.org/journal/ERR/article-full-text-pdf/4C8DD044180.pdf
- Bernard RM, Abrami PC, Lou Y, Borokhovski E, Wade A, Wozney L, et al. How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta- analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research. 2004; 3 (74):379–439. doi: 10.3102/00346543074003379. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Borenstein, M., Hedges, L., & Rothstein, H. (2007). Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects . UK: Wiley. [ PubMed ]
- Card NA. Applied meta-analysis for social science research: Methodology in the social sciences. Guilford; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- *Carreon, J. R. (2018 ). Facebook as integrated blended learning tool in technology and livelihood education exploratory. Retrieved on the 1st of October, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1197714.pdf
- Cavanaugh, C., Gillan, K. J., Kromrey, J., Hess, M., & Blomeyer, R. (2004). The effects of distance education on K-12 student outcomes: A meta-analysis. Learning Point Associates/North Central Regional Educational Laboratory (NCREL) . Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED489533.pdf
- *Ceylan, V. K., & Elitok Kesici, A. (2017). Effect of blended learning to academic achievement. Journal of Human Sciences, 14 (1), 308. 10.14687/jhs.v14i1.4141
- *Chae, S. E., & Shin, J. H. (2016). Tutoring styles that encourage learner satisfaction, academic engagement, and achievement in an online environment. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1371–1385. 10.1080/10494820.2015.1009472
- *Chiang, T. H. C., Yang, S. J. H., & Hwang, G. J. (2014). An augmented reality-based mobile learning system to improve students’ learning achievements and motivations in natural science inquiry activities. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (4), 352–365. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gwo_Jen_Hwang/publication/287529242_An_Augmented_Reality-based_Mobile_Learning_System_to_Improve_Students'_Learning_Achievements_and_Motivations_in_Natural_Science_Inquiry_Activities/links/57198c4808ae30c3f9f2c4ac.pdf
- Chiao HM, Chen YL, Huang WH. Examining the usability of an online virtual tour-guiding platform for cultural tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education. 2018; 23 (29–38):1. doi: 10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.05.002. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chizmar, J. F., & Walbert, M. S. (1999). Web-based learning environments guided by principles of good teaching practice. Journal of Economic Education, 30 (3), 248–264. 10.2307/1183061
- Cleophas, T. J., & Zwinderman, A. H. (2017). Modern meta-analysis: Review and update of methodologies . Switzerland: Springer. 10.1007/978-3-319-55895-0
- Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Observation. Research Methods in Education, 6 , 396–412. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nabil_Ashraf2/post/How_to_get_surface_potential_Vs_Voltage_curve_from_CV_and_GV_measurements_of_MOS_capacitor/attachment/5ac6033cb53d2f63c3c405b4/AS%3A612011817844736%401522926396219/download/Very+important_C-V+characterization+Lehigh+University+thesis.pdf
- Colis B, Moonen J. Flexible Learning in a Digital World: Experiences and Expectations. Open & Distance Learning Series. Stylus Publishing; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. Retrieved on the 3rd of September, 2021 from https://www.cosn.org/sites/default/files/COVID-19%20Member%20Exclusive_0.pdf
- Cumming, G. (2012). Understanding new statistics: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. New York, USA: Routledge. 10.4324/9780203807002
- Deeks, J. J., Higgins, J. P. T., & Altman, D. G. (2008). Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses . In J. P. T. Higgins & S. Green (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 243–296). Sussex: John Wiley & Sons. 10.1002/9780470712184.ch9
- Demiralay, R., Bayır, E. A., & Gelibolu, M. F. (2016). Öğrencilerin bireysel yenilikçilik özellikleri ile çevrimiçi öğrenmeye hazır bulunuşlukları ilişkisinin incelenmesi. Eğitim ve Öğretim Araştırmaları Dergisi, 5 (1), 161–168. 10.23891/efdyyu.2017.10
- Dinçer, S. (2014). Eğitim bilimlerinde uygulamalı meta-analiz. Pegem Atıf İndeksi, 2014(1), 1–133. 10.14527/pegem.001
- *Durak, G., Cankaya, S., Yunkul, E., & Ozturk, G. (2017). The effects of a social learning network on students’ performances and attitudes. European Journal of Education Studies, 3 (3), 312–333. 10.5281/zenodo.292951
- *Ercan, O. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes . European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23. 10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
- Ercan O, Bilen K. Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes. European Journal of Educational Research. 2014; 3 (1):9–23. doi: 10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- *Ercan, O., Bilen, K., & Ural, E. (2016). “Earth, sun and moon”: Computer assisted instruction in secondary school science - Achievement and attitudes. Issues in Educational Research, 26 (2), 206–224. 10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
- Field, A. P. (2003). The problems in using fixed-effects models of meta-analysis on real-world data. Understanding Statistics, 2 (2), 105–124. 10.1207/s15328031us0202_02
- Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 63 (3), 665–694. 10.1348/00071010x502733 [ PubMed ]
- Geostat. (2019). ‘Share of households with internet access’, National statistics office of Georgia . Retrieved on the 2nd September 2020 from https://www.geostat.ge/en/modules/categories/106/information-and-communication-technologies-usage-in-households
- *Gwo-Jen, H., Nien-Ting, T., & Xiao-Ming, W. (2018). Creating interactive e-books through learning by design: The impacts of guided peer-feedback on students’ learning achievements and project outcomes in science courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society., 21 (1), 25–36. Retrieved on the 2nd of October, 2020 https://ae-uploads.uoregon.edu/ISTE/ISTE2019/PROGRAM_SESSION_MODEL/HANDOUTS/112172923/CreatingInteractiveeBooksthroughLearningbyDesignArticle2018.pdf
- Hamdani, A. R., & Priatna, A. (2020). Efektifitas implementasi pembelajaran daring (full online) dimasa pandemi Covid-19 pada jenjang Sekolah Dasar di Kabupaten Subang. Didaktik: Jurnal Ilmiah PGSD STKIP Subang, 6 (1), 1–9.
- Hart, C. M., Berger, D., Jacob, B., Loeb, S., & Hill, M. (2019). Online learning, offline outcomes: Online course taking and high school student performance. Aera Open, 5(1).
- *Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86 (3), 397–411. 10.1111/bjep.12114 [ PubMed ]
- Horton WK. Designing web-based training: How to teach anyone anything anywhere anytime. Wiley Publishing; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- *Hwang, G. J., Wu, P. H., & Chen, C. C. (2012). An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Computers and Education, 59 (4), 1246–1256. 10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.009
- *Kert, S. B., Köşkeroğlu Büyükimdat, M., Uzun, A., & Çayiroğlu, B. (2017). Comparing active game-playing scores and academic performances of elementary school students. Education 3–13, 45 (5), 532–542. 10.1080/03004279.2016.1140800
- *Lai, A. F., & Chen, D. J. (2010). Web-based two-tier diagnostic test and remedial learning experiment. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 8 (1), 31–53. 10.4018/jdet.2010010103
- *Lai, A. F., Lai, H. Y., Chuang W. H., & Wu, Z.H. (2015). Developing a mobile learning management system for outdoors nature science activities based on 5e learning cycle. Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Learning, ICEL. Proceedings of the International Association for Development of the Information Society (IADIS) International Conference on e-Learning (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, July 21–24, 2015). Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562095.pdf
- Lai CH, Lin HW, Lin RM, Tho PD. Effect of peer interaction among online learning community on learning engagement and achievement. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies (IJDET) 2019; 17 (1):66–77. doi: 10.4018/IJDET.2019010105. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Littell JH, Corcoran J, Pillai V. Systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Oxford University; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- *Liu, K. P., Tai, S. J. D., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Enhancing language learning through creation: the effect of digital storytelling on student learning motivation and performance in a school English course. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66 (4), 913–935. 10.1007/s11423-018-9592-z
- Machtmes, K., & Asher, J. W. (2000). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of telecourses in distance education. American Journal of Distance Education, 14 (1), 27–46. 10.1080/08923640009527043
- Makowski, D., Piraux, F., & Brun, F. (2019). From experimental network to meta-analysis: Methods and applications with R for agronomic and environmental sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. 10.1007/978-94-024_1696-1
- * Meyers, C., Molefe, A., & Brandt, C. (2015). The Impact of the" Enhancing Missouri's Instructional Networked Teaching Strategies"(eMINTS) Program on Student Achievement, 21st-Century Skills, and Academic Engagement--Second-Year Results . Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness. Retrieved on the 14 th November, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562508.pdf
- OECD. (2020). ‘A framework to guide an education response to the COVID-19 Pandemic of 2020 ’. 10.26524/royal.37.6
- Pecoraro, V. (2018). Appraising evidence . In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 99–114). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. 10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_9
- Pigott T. Advances in meta-analysis. Springer; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pillay, H. , Irving, K., & Tones, M. (2007). Validation of the diagnostic tool for assessing Tertiary students’ readiness for online learning. Higher Education Research & Development, 26 (2), 217–234. 10.1080/07294360701310821
- Prestiadi, D., Zulkarnain, W., & Sumarsono, R. B. (2019). Visionary leadership in total quality management: efforts to improve the quality of education in the industrial revolution 4.0. In the 4th International Conference on Education and Management (COEMA 2019). Atlantis Press
- Poole, D. M. (2000). Student participation in a discussion-oriented online course: a case study. Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 33 (2), 162–177. 10.1080/08886504.2000.10782307
- Rahayu FS, Budiyanto D, Palyama D. Analisis penerimaan e-learning menggunakan technology acceptance model (Tam)(Studi Kasus: Universitas Atma Jaya Yogyakarta) Jurnal Terapan Teknologi Informasi. 2017; 1 (2):87–98. doi: 10.21460/jutei.2017.12.20. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rasmussen RC. The quantity and quality of human interaction in a synchronous blended learning environment. Brigham Young University Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- *Ravenel, J., T. Lambeth, D., & Spires, B. (2014). Effects of computer-based programs on mathematical achievement scores for fourth-grade students. i-manager’s Journal on School Educational Technology, 10 (1), 8–21. 10.26634/jsch.10.1.2830
- Rolisca, R. U. C., & Achadiyah, B. N. (2014). Pengembangan media evaluasi pembelajaran dalam bentuk online berbasis e-learning menggunakan software wondershare quiz creator dalam mata pelajaran akuntansi SMA Brawijaya Smart School (BSS). Jurnal Pendidikan Akuntansi Indonesia, 12(2).
- Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effective- ness of Web-based and classroom instruction: A meta-analysis . Personnel Psychology, 59 (3), 623–664. 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2006.00049.x
- Stewart DW, Kamins MA. Developing a coding scheme and coding study reports. In: Lipsey MW, Wilson DB, editors. Practical metaanalysis: Applied social research methods series. Sage; 2001. pp. 73–90. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swan K. Research on online learning. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks. 2007; 11 (1):55–59. [ Google Scholar ]
- *Sung, H. Y., Hwang, G. J., & Chang, Y. C. (2016). Development of a mobile learning system based on a collaborative problem-posing strategy. Interactive Learning Environments, 24 (3), 456–471. 10.1080/10494820.2013.867889
- Tsagris, M., & Fragkos, K. C. (2018). Meta-analyses of clinical trials versus diagnostic test accuracy studies. In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 31–42). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. 10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_4
- UNESCO. (2020, Match 13). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. Retrieved on the 14 th November 2020 from https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/ coronavirus-school-closures
- Usta E. The effect of web-based learning environments on attitudes of students regarding computer and internet. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011; 28 (262–269):1. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.051. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Usta, E. (2011b). The examination of online self-regulated learning skills in web-based learning environments in terms of different variables. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 10 (3), 278–286. Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ944994.pdf
- Vrasidas, C. & MsIsaac, M. S. (2000). Principles of pedagogy and evaluation for web-based learning. Educational Media International, 37 (2), 105–111. 10.1080/095239800410405
- *Wang, C. H., & Chen, C. P. (2013). Effects of facebook tutoring on learning english as a second language. Proceedings of the International Conference e-Learning 2013, (2009), 135–142. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562299.pdf
- Wei HC, Chou C. Online learning performance and satisfaction: Do perceptions and readiness matter? Distance Education. 2020; 41 (1):48–69. doi: 10.1080/01587919.2020.1724768. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- *Yu, F. Y. (2019). The learning potential of online student-constructed tests with citing peer-generated questions. Interactive Learning Environments, 27 (2), 226–241. 10.1080/10494820.2018.1458040
- *Yu, F. Y., & Chen, Y. J. (2014). Effects of student-generated questions as the source of online drill-and-practice activities on learning . British Journal of Educational Technology, 45 (2), 316–329. 10.1111/bjet.12036
- *Yu, F. Y., & Pan, K. J. (2014). The effects of student question-generation with online prompts on learning. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (3), 267–279. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.565.643&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- *Yu, W. F., She, H. C., & Lee, Y. M. (2010). The effects of web-based/non-web-based problem-solving instruction and high/low achievement on students’ problem-solving ability and biology achievement. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 47 (2), 187–199. 10.1080/14703291003718927
- Zhao, Y., Lei, J., Yan, B, Lai, C., & Tan, S. (2005). A practical analysis of research on the effectiveness of distance education. Teachers College Record, 107 (8). 10.1111/j.1467-9620.2005.00544.x
- *Zhong, B., Wang, Q., Chen, J., & Li, Y. (2017). Investigating the period of switching roles in pair programming in a primary school. Educational Technology and Society, 20 (3), 220–233. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://repository.nie.edu.sg/bitstream/10497/18946/1/ETS-20-3-220.pdf
Department of Education
How effective is online learning what the research does and doesn't tell us.
Susanna Loeb, Professor of Education, on the effectiveness of online learning for K-12 students.
In the fifth essay of the Education Week series "Weighing the Research: What Works, What Doesn't," Professor of Education Susanna Loeb explores the effectiveness of online learning in K-12 education. "It is not surprising that in-person courses are, on average, more effective. Being in person with teachers and other students creates social pressures and benefits that can help motivate students to engage. Some students do as well in online courses as in in-person courses, some may actually do better, but, on average, students do worse in the online setting, and this is particularly true for students with weaker academic backgrounds."
How Effective Is Online Learning? What the Research Does and Doesn't Tell Us — Education Week
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 25 January 2021
Online education in the post-COVID era
- Barbara B. Lockee 1
Nature Electronics volume 4 , pages 5–6 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
140k Accesses
228 Citations
337 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make it work — could permanently change how education is delivered.
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced the world to engage in the ubiquitous use of virtual learning. And while online and distance learning has been used before to maintain continuity in education, such as in the aftermath of earthquakes 1 , the scale of the current crisis is unprecedented. Speculation has now also begun about what the lasting effects of this will be and what education may look like in the post-COVID era. For some, an immediate retreat to the traditions of the physical classroom is required. But for others, the forced shift to online education is a moment of change and a time to reimagine how education could be delivered 2 .

Looking back
Online education has traditionally been viewed as an alternative pathway, one that is particularly well suited to adult learners seeking higher education opportunities. However, the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has required educators and students across all levels of education to adapt quickly to virtual courses. (The term ‘emergency remote teaching’ was coined in the early stages of the pandemic to describe the temporary nature of this transition 3 .) In some cases, instruction shifted online, then returned to the physical classroom, and then shifted back online due to further surges in the rate of infection. In other cases, instruction was offered using a combination of remote delivery and face-to-face: that is, students can attend online or in person (referred to as the HyFlex model 4 ). In either case, instructors just had to figure out how to make it work, considering the affordances and constraints of the specific learning environment to create learning experiences that were feasible and effective.
The use of varied delivery modes does, in fact, have a long history in education. Mechanical (and then later electronic) teaching machines have provided individualized learning programmes since the 1950s and the work of B. F. Skinner 5 , who proposed using technology to walk individual learners through carefully designed sequences of instruction with immediate feedback indicating the accuracy of their response. Skinner’s notions formed the first formalized representations of programmed learning, or ‘designed’ learning experiences. Then, in the 1960s, Fred Keller developed a personalized system of instruction 6 , in which students first read assigned course materials on their own, followed by one-on-one assessment sessions with a tutor, gaining permission to move ahead only after demonstrating mastery of the instructional material. Occasional class meetings were held to discuss concepts, answer questions and provide opportunities for social interaction. A personalized system of instruction was designed on the premise that initial engagement with content could be done independently, then discussed and applied in the social context of a classroom.
These predecessors to contemporary online education leveraged key principles of instructional design — the systematic process of applying psychological principles of human learning to the creation of effective instructional solutions — to consider which methods (and their corresponding learning environments) would effectively engage students to attain the targeted learning outcomes. In other words, they considered what choices about the planning and implementation of the learning experience can lead to student success. Such early educational innovations laid the groundwork for contemporary virtual learning, which itself incorporates a variety of instructional approaches and combinations of delivery modes.
Online learning and the pandemic
Fast forward to 2020, and various further educational innovations have occurred to make the universal adoption of remote learning a possibility. One key challenge is access. Here, extensive problems remain, including the lack of Internet connectivity in some locations, especially rural ones, and the competing needs among family members for the use of home technology. However, creative solutions have emerged to provide students and families with the facilities and resources needed to engage in and successfully complete coursework 7 . For example, school buses have been used to provide mobile hotspots, and class packets have been sent by mail and instructional presentations aired on local public broadcasting stations. The year 2020 has also seen increased availability and adoption of electronic resources and activities that can now be integrated into online learning experiences. Synchronous online conferencing systems, such as Zoom and Google Meet, have allowed experts from anywhere in the world to join online classrooms 8 and have allowed presentations to be recorded for individual learners to watch at a time most convenient for them. Furthermore, the importance of hands-on, experiential learning has led to innovations such as virtual field trips and virtual labs 9 . A capacity to serve learners of all ages has thus now been effectively established, and the next generation of online education can move from an enterprise that largely serves adult learners and higher education to one that increasingly serves younger learners, in primary and secondary education and from ages 5 to 18.
The COVID-19 pandemic is also likely to have a lasting effect on lesson design. The constraints of the pandemic provided an opportunity for educators to consider new strategies to teach targeted concepts. Though rethinking of instructional approaches was forced and hurried, the experience has served as a rare chance to reconsider strategies that best facilitate learning within the affordances and constraints of the online context. In particular, greater variance in teaching and learning activities will continue to question the importance of ‘seat time’ as the standard on which educational credits are based 10 — lengthy Zoom sessions are seldom instructionally necessary and are not aligned with the psychological principles of how humans learn. Interaction is important for learning but forced interactions among students for the sake of interaction is neither motivating nor beneficial.
While the blurring of the lines between traditional and distance education has been noted for several decades 11 , the pandemic has quickly advanced the erasure of these boundaries. Less single mode, more multi-mode (and thus more educator choices) is becoming the norm due to enhanced infrastructure and developed skill sets that allow people to move across different delivery systems 12 . The well-established best practices of hybrid or blended teaching and learning 13 have served as a guide for new combinations of instructional delivery that have developed in response to the shift to virtual learning. The use of multiple delivery modes is likely to remain, and will be a feature employed with learners of all ages 14 , 15 . Future iterations of online education will no longer be bound to the traditions of single teaching modes, as educators can support pedagogical approaches from a menu of instructional delivery options, a mix that has been supported by previous generations of online educators 16 .
Also significant are the changes to how learning outcomes are determined in online settings. Many educators have altered the ways in which student achievement is measured, eliminating assignments and changing assessment strategies altogether 17 . Such alterations include determining learning through strategies that leverage the online delivery mode, such as interactive discussions, student-led teaching and the use of games to increase motivation and attention. Specific changes that are likely to continue include flexible or extended deadlines for assignment completion 18 , more student choice regarding measures of learning, and more authentic experiences that involve the meaningful application of newly learned skills and knowledge 19 , for example, team-based projects that involve multiple creative and social media tools in support of collaborative problem solving.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, technological and administrative systems for implementing online learning, and the infrastructure that supports its access and delivery, had to adapt quickly. While access remains a significant issue for many, extensive resources have been allocated and processes developed to connect learners with course activities and materials, to facilitate communication between instructors and students, and to manage the administration of online learning. Paths for greater access and opportunities to online education have now been forged, and there is a clear route for the next generation of adopters of online education.
Before the pandemic, the primary purpose of distance and online education was providing access to instruction for those otherwise unable to participate in a traditional, place-based academic programme. As its purpose has shifted to supporting continuity of instruction, its audience, as well as the wider learning ecosystem, has changed. It will be interesting to see which aspects of emergency remote teaching remain in the next generation of education, when the threat of COVID-19 is no longer a factor. But online education will undoubtedly find new audiences. And the flexibility and learning possibilities that have emerged from necessity are likely to shift the expectations of students and educators, diminishing further the line between classroom-based instruction and virtual learning.
Mackey, J., Gilmore, F., Dabner, N., Breeze, D. & Buckley, P. J. Online Learn. Teach. 8 , 35–48 (2012).
Google Scholar
Sands, T. & Shushok, F. The COVID-19 higher education shove. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/3o2vHbX (16 October 2020).
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T. & Bond, M. A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/38084Lh (27 March 2020).
Beatty, B. J. (ed.) Hybrid-Flexible Course Design Ch. 1.4 https://go.nature.com/3o6Sjb2 (EdTech Books, 2019).
Skinner, B. F. Science 128 , 969–977 (1958).
Article Google Scholar
Keller, F. S. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 1 , 79–89 (1968).
Darling-Hammond, L. et al. Restarting and Reinventing School: Learning in the Time of COVID and Beyond (Learning Policy Institute, 2020).
Fulton, C. Information Learn. Sci . 121 , 579–585 (2020).
Pennisi, E. Science 369 , 239–240 (2020).
Silva, E. & White, T. Change The Magazine Higher Learn. 47 , 68–72 (2015).
McIsaac, M. S. & Gunawardena, C. N. in Handbook of Research for Educational Communications and Technology (ed. Jonassen, D. H.) Ch. 13 (Simon & Schuster Macmillan, 1996).
Irvine, V. The landscape of merging modalities. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/2MjiBc9 (26 October 2020).
Stein, J. & Graham, C. Essentials for Blended Learning Ch. 1 (Routledge, 2020).
Maloy, R. W., Trust, T. & Edwards, S. A. Variety is the spice of remote learning. Medium https://go.nature.com/34Y1NxI (24 August 2020).
Lockee, B. J. Appl. Instructional Des . https://go.nature.com/3b0ddoC (2020).
Dunlap, J. & Lowenthal, P. Open Praxis 10 , 79–89 (2018).
Johnson, N., Veletsianos, G. & Seaman, J. Online Learn. 24 , 6–21 (2020).
Vaughan, N. D., Cleveland-Innes, M. & Garrison, D. R. Assessment in Teaching in Blended Learning Environments: Creating and Sustaining Communities of Inquiry (Athabasca Univ. Press, 2013).
Conrad, D. & Openo, J. Assessment Strategies for Online Learning: Engagement and Authenticity (Athabasca Univ. Press, 2018).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA
Barbara B. Lockee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Barbara B. Lockee .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lockee, B.B. Online education in the post-COVID era. Nat Electron 4 , 5–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-00534-0
Download citation
Published : 25 January 2021
Issue Date : January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-00534-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
A comparative study on the effectiveness of online and in-class team-based learning on student performance and perceptions in virtual simulation experiments.
BMC Medical Education (2024)
Development and validation of the antecedents to videoconference fatigue scale in higher education (AVFS-HE)
- Benjamin J. Li
- Andrew Z. H. Yee
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Leveraging privacy profiles to empower users in the digital society
- Davide Di Ruscio
- Paola Inverardi
- Phuong T. Nguyen
Automated Software Engineering (2024)
Global public concern of childhood and adolescence suicide: a new perspective and new strategies for suicide prevention in the post-pandemic era
- Dong Keon Yon
World Journal of Pediatrics (2024)
The influencing factors and predictability of primary school students’ learning performance in online supplementary classes
Quick links.
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

Creative samples from the experts
↑ Return to Essay Samples
Argumentative Essay: Online Learning and Educational Access
Conventional learning is evolving with the help of computers and online technology. New ways of learning are now available, and improved access is one of the most important benefits available. People all around the world are experiencing improved mobility as a result of the freedom and potential that online learning provides, and as academic institutions and learning organisations adopt online learning technologies and remote-access learning, formal academic education is becoming increasingly legitimate. This essay argues the contemporary benefits of online learning, and that these benefits significantly outweigh the issues, challenges and disadvantages of online learning.
Online learning is giving people new choices and newfound flexibility with their personal learning and development. Whereas before, formal academic qualifications could only be gained by participating in a full time course on site, the internet has allowed institutions to expand their reach and offer recognized courses on a contact-partial, or totally virtual, basis. Institutions can do so with relatively few extra resources, and for paid courses this constitutes excellent value, and the student benefits with greater educational access and greater flexibility to learn and get qualified even when there lots of other personal commitments to deal with.
Flexibility is certainly one of the most important benefits, but just as important is educational access. On top of the internet’s widespread presence in developed countries, the internet is becoming increasingly available in newly developed and developing countries. Even without considering the general informational exposure that the internet delivers, online academic courses and learning initiatives are becoming more aware of the needs of people from disadvantaged backgrounds, and this means that people from such backgrounds are in a much better position to learn and progress than they used to be.
The biggest argument that raises doubt over online learning is the quality of online courses in comparison to conventional courses. Are such online courses good enough for employers to take notice? The second biggest argument is the current reality that faces many people from disadvantaged backgrounds, despite the improvements made in this area in recent years – they do not have the level of basic access needed to benefit from online learning. In fact, there are numerous sources of evidence that claim disadvantaged students are not receiving anywhere near the sort of benefits that online learning institutions and promoters are trying to instigate. Currently there are many organisations, campaigns and initiatives that are working to expand access to higher education. With such high participation, it can be argued that it is only a matter of time before the benefits are truly realised, but what about the global online infrastructure?
There is another argument that is very difficult to dispel, and that is the response of different types of students to the online learning paradigm. Evidence shows that there are certain groups of students that benefit from college distance learning much more than other groups. In essence, students must be highly motivated and highly disciplined if they are to learn effectively in their own private environment.

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.
Information
- Author Services

Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Assessing the impact of online-learning effectiveness and benefits in knowledge management, the antecedent of online-learning strategies and motivations: an empirical study.

1. Introduction
2. literature review and research hypothesis, 2.1. online-learning self-efficacy terminology, 2.2. online-learning monitoring terminology, 2.3. online-learning confidence in technology terminology, 2.4. online-learning willpower terminology, 2.5. online-learning attitude terminology, 2.6. online-learning motivation terminology, 2.7. online-learning strategies and online-learning effectiveness terminology, 2.8. online-learning effectiveness terminology, 3. research method, 3.1. instruments, 3.2. data analysis and results, 4.1. reliability and validity analysis, 4.2. hypothesis result, 5. discussion, 6. conclusions, 7. limitations and future directions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- UNESCO. COVID-19 Educational Disruption and Response ; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2020. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moore, D.R. E-learning and the science of instruction: Proven guidelines for consumers and designers of multimedia learning. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2006 , 54 , 197–200. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- McDonald, E.W.; Boulton, J.L.; Davis, J.L. E-learning and nursing assessment skills and knowledge–An integrative review. Nurse Educ. Today 2018 , 66 , 166–174. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Homan, S.R.; Wood, K. Taming the mega-lecture: Wireless quizzing. Syllabus Sunnyvale Chatsworth 2003 , 17 , 23–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emran, M.A.; Shaalan, K. E-podium technology: A medium of managing knowledge at al buraimi university college via mlearning. In Proceedings of the 2nd BCS International IT Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 9–10 March 2014; pp. 1–4. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tenório, T.; Bittencourt, I.I.; Isotani, S.; Silva, A.P. Does peer assessment in on-line learning environments work? A systematic review of the literature. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016 , 64 , 94–107. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sheshasaayee, A.; Bee, M.N. Analyzing online learning effectiveness for knowledge society. In Information Systems Design and Intelligent Applications ; Bhateja, V., Nguyen, B., Nguyen, N., Satapathy, S., Le, D.N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 995–1002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Panigrahi, R.; Srivastava, P.R.; Sharma, D. Online learning: Adoption, continuance, and learning outcome—A review of literature. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 2018 , 43 , 1–14. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alias, N.; Othman, M.S.; Alzahrani, A.I.; Alfarraj, O.; Saged, A.A. Use of e-learning by university students in Malaysian higher educational institutions: A case in Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. IEEE Access 2018 , 6 , 14268–14276. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Yahaya, N.; Aldraiweesh, A.A.; Alamri, M.M.; Aljarboa, N.A.; Alturki, U. Integrating technology acceptance model with innovation diffusion theory: An empirical investigation on students’ intention to use E-learning systems. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 26797–26809. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gunawan, I.; Hui, L.K.; Ma’sum, M.A. Enhancing learning effectiveness by using online learning management system. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Education and Technology (ICET), Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2021; pp. 48–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Tangworakitthaworn, P.; Gilbert, L. Individual learning effectiveness based on cognitive taxonomies and constructive alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference (Tencon), Osaka, Japan, 16–19 November 2020; pp. 1002–1006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pee, L.G. Enhancing the learning effectiveness of ill-structured problem solving with online co-creation. Stud. High. Educ. 2020 , 45 , 2341–2355. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kintu, M.J.; Zhu, C.; Kagambe, E. Blended learning effectiveness: The relationship between student characteristics, design features and outcomes. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2017 , 14 , 1–20. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Wang, M.H.; Vogel, D.; Ran, W.J. Creating a performance-oriented e-learning environment: A design science approach. Inf. Manag. 2011 , 48 , 260–269. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Hew, K.F.; Cheung, W.S. Students’ and instructors’ use of massive open online courses (MOOCs): Motivations and challenges. Educ. Res. Rev. 2014 , 12 , 45–58. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bryant, J.; Bates, A.J. Creating a constructivist online instructional environment. TechTrends 2015 , 59 , 17–22. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lee, M.C. Explaining and predicting users’ continuance intention toward e-learning: An extension of the expectation–confirmation model. Comput. Educ. 2010 , 54 , 506–516. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lin, K.M. E-Learning continuance intention: Moderating effects of user e-learning experience. Comput. Educ. 2011 , 56 , 515–526. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huang, E.Y.; Lin, S.W.; Huang, T.K. What type of learning style leads to online participation in the mixed-mode e-learning environment? A study of software usage instruction. Comput. Educ. 2012 , 58 , 338–349. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chu, T.H.; Chen, Y.Y. With good we become good: Understanding e-learning adoption by theory of planned behavior and group influences. Comput. Educ. 2016 , 92 , 37–52. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 1977 , 84 , 191–215. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Torkzadeh, G.; Van Dyke, T.P. Development and validation of an Internet self-efficacy scale. Behav. Inform. Technol. 2001 , 20 , 275–280. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Saadé, R.G.; Kira, D. Computer anxiety in e-learning: The effect of computer self-efficacy. J. Inform. Technol. Educ. Res. 2009 , 8 , 177–191. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Tucker, J.; Gentry, G. Developing an E-Learning strategy in higher education. In Proceedings of the SITE 2009–Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference, Charleston, SC, USA, 2–6 March 2009; pp. 2702–2707. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, H.M.; Huang, R.H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J. Characteristics of distance learners: Research on relationships of learning motivation, learning strategy, self-efficacy, attribution and learning results. Open Learn. J. Open Distance Elearn. 2008 , 23 , 17–28. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mahmud, B.H. Study on the impact of motivation, self-efficacy and learning strategies of faculty of education undergraduates studying ICT courses. In Proceedings of the 4th International Postgraduate Research Colloquium (IPRC) Proceedings, Bangkok, Thailand, 29 October 2009; pp. 59–80. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yusuf, M. Investigating relationship between self-efficacy, achievement motivation, and self-regulated learning strategies of undergraduate Students: A study of integrated motivational models. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011 , 15 , 2614–2617. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- De la Fuente, J.; Martínez-Vicente, J.M.; Peralta-Sánchez, F.J.; GarzónUmerenkova, A.; Vera, M.M.; Paoloni, P. Applying the SRL vs. ERL theory to the knowledge of achievement emotions in undergraduate university students. Front. Psychol. 2019 , 10 , 2070. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Ahmadi, S. Academic self-esteem, academic self-efficacy and academic achievement: A path analysis. J. Front. Psychol. 2020 , 5 , 155. [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyen, E.L.; Aust, R.J.; Bui, Y.N. Assessing and monitoring student progress in an E-learning personnel preparation environment. Teach. Educ. Spec. Educ. 2002 , 25 , 187–198. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Dunlosky, J.; Kubat-Silman, A.K.; Christopher, H. Training monitoring skills improves older adults’ self-paced associative learning. Psychol. Aging 2003 , 18 , 340–345. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, H.J. Research on the relationship between English learning motivation. Self-monitoring and Test Score. Ethnic Educ. Res. 2005 , 6 , 66–71. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenberg, M.J. E-Learning: Strategies for Delivering Knowledge in the Digital Age ; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhat, S.A.; Bashir, M. Measuring ICT orientation: Scale development & validation. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018 , 23 , 1123–1143. [ Google Scholar ]
- Achuthan, K.; Francis, S.P.; Diwakar, S. Augmented reflective learning and knowledge retention perceived among students in classrooms involving virtual laboratories. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2017 , 22 , 2825–2855. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hu, X.; Yelland, N. An investigation of preservice early childhood teachers’ adoption of ICT in a teaching practicum context in Hong Kong. J. Early Child. Teach. Educ. 2017 , 38 , 259–274. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fraillon, J.; Ainley, J.; Schulz, W.; Friedman, T.; Duckworth, D. Preparing for Life in a Digital World: The IEA International Computer and Information Literacy Study 2018 International Report ; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huber, S.G.; Helm, C. COVID-19 and schooling: Evaluation, assessment and accountability in times of crises—Reacting quickly to explore key issues for policy, practice and research with the school barometer. Educ. Assess. Eval. Account. 2020 , 32 , 237–270. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Eickelmann, B.; Gerick, J. Learning with digital media: Objectives in times of Corona and under special consideration of social Inequities. Dtsch. Schule. 2020 , 16 , 153–162. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shehzadi, S.; Nisar, Q.A.; Hussain, M.S.; Basheer, M.F.; Hameed, W.U.; Chaudhry, N.I. The role of e-learning toward students’ satisfaction and university brand image at educational institutes of Pakistan: A post-effect of COVID-19. Asian Educ. Dev. Stud. 2020 , 10 , 275–294. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Miller, E.M.; Walton, G.M.; Dweck, C.S.; Job, V.; Trzesniewski, K.; McClure, S. Theories of willpower affect sustained learning. PLoS ONE 2012 , 7 , 38680. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Moriña, A.; Molina, V.M.; Cortés-Vega, M.D. Voices from Spanish students with disabilities: Willpower and effort to survive university. Eur. J. Spec. Needs Educ. 2018 , 33 , 481–494. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Koballa, T.R., Jr.; Crawley, F.E. The influence of attitude on science teaching and learning. Sch. Sci. Math. 1985 , 85 , 222–232. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chao, C.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chuang, K.Y. Exploring students’ learning attitude and achievement in flipped learning supported computer aided design curriculum: A study in high school engineering education. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2015 , 23 , 514–526. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Stefan, M.; Ciomos, F. The 8th and 9th grades students’ attitude towards teaching and learning physics. Acta Didact. Napocensia. 2010 , 3 , 7–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sedighi, F.; Zarafshan, M.A. Effects of attitude and motivation on the use of language learning strategies by Iranian EFL University students. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Shiraz Univ. 2007 , 23 , 71–80. [ Google Scholar ]
- Megan, S.; Jennifer, H.C.; Stephanie, V.; Kyla, H. The relationship among middle school students’ motivation orientations, learning strategies, and academic achievement. Middle Grades Res. J. 2013 , 8 , 1–12. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nasser, O.; Majid, V. Motivation, attitude, and language learning. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011 , 29 , 994–1000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Özhan, Ş.Ç.; Kocadere, S.A. The effects of flow, emotional engagement, and motivation on success in a gamified online learning environment. J. Educ. Comput. Res. 2020 , 57 , 2006–2031. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, A.P.; Che, H.S. A research on the relationship between learning anxiety, learning attitude, motivation and test performance. Psychol. Dev. Educ. 2005 , 21 , 55–59. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin, C.H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zheng, B.B. The roles of learning strategies and motivation in online language learning: A structural equation modeling analysis. Comput. Educ. 2017 , 113 , 75–85. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Deschênes, M.F.; Goudreau, J.; Fernandez, N. Learning strategies used by undergraduate nursing students in the context of a digital educational strategy based on script concordance: A descriptive study. Nurse Educ. Today 2020 , 95 , 104607. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Jerusalem, M.; Schwarzer, R. Self-efficacy as a resource factor in stress appraisal processes. In Self-Efficacy: Thought Control of Action ; Schwarzer, R., Ed.; Hemisphere Publishing Corp: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 195–213. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zimmerman, B.J. Becoming a self-regulated learner: An overview. Theory Pract. 2002 , 41 , 64–70. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pintrich, P.R.; Smith, D.A.F.; García, T.; McKeachie, W.J. A Manual for the Use of the Motivated Strategies Questionnaire (MSLQ) ; University of Michigan, National Center for Research to Improve Post Secondary Teaching and Learning: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Knowles, E.; Kerkman, D. An investigation of students attitude and motivation toward online learning. InSight Collect. Fac. Scholarsh. 2007 , 2 , 70–80. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective , 7th ed.; Pearson Education International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981 , 18 , 39–50. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) ; Sage: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2016. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kiliç-Çakmak, E. Learning strategies and motivational factors predicting information literacy self-efficacy of e-learners. Aust. J. Educ. Technol. 2010 , 26 , 192–208. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Zheng, C.; Liang, J.C.; Li, M.; Tsai, C. The relationship between English language learners’ motivation and online self-regulation: A structural equation modelling approach. System 2018 , 76 , 144–157. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- May, M.; George, S.; Prévôt, P. TrAVis to enhance students’ self-monitoring in online learning supported by computer-mediated communication tools. Int. J. Comput. Inform. Syst. Ind. Manag. Appl. 2011 , 3 , 623–634. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rafart, M.A.; Bikfalvi, A.; Soler, J.; Poch, J. Impact of using automatic E-Learning correctors on teaching business subjects to engineers. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2019 , 35 , 1630–1641. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee, P.M.; Tsui, W.H.; Hsiao, T.C. A low-cost scalable solution for monitoring affective state of students in E-learning environment using mouse and keystroke data. In Intelligent Tutoring Systems ; Cerri, S.A., Clancey, W.J., Papadourakis, G., Panourgia, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 679–680. [ Google Scholar ]
- Metz, D.; Karadgi, S.S.; Müller, U.J.; Grauer, M. Self-Learning monitoring and control of manufacturing processes based on rule induction and event processing. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information, Process, and Knowledge Management eKNOW, Valencia, Spain, 21–25 November 2012; pp. 78–85. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fitch, J.L.; Ravlin, E.C. Willpower and perceived behavioral control: Intention-behavior relationship and post behavior attributions. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J. 2005 , 33 , 105–124. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sridharan, B.; Deng, H.; Kirk, J.; Brian, C. Structural equation modeling for evaluating the user perceptions of e-learning effectiveness in higher education. In Proceedings of the ECIS 2010: 18th European Conference on Information Systems, Pretoria, South Africa, 7–9 June 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tarhini, A.; Hone, K.; Liu, X. The effects of individual differences on e-learning users’ behaviour in developing countries: A structural equation model. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014 , 41 , 153–163. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- de Leeuw, R.A.; Logger, D.N.; Westerman, M.; Bretschneider, J.; Plomp, M.; Scheele, F. Influencing factors in the implementation of postgraduate medical e-learning: A thematic analysis. BMC Med. Educ. 2019 , 19 , 300. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ Green Version ]
- Erenler, H.H.T. A structural equation model to evaluate students’ learning and satisfaction. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2020 , 28 , 254–267. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fee, K. Delivering E-learning: A complete strategy for design, application and assessment. Dev. Learn. Organ. 2013 , 27 , 40–52. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- So, W.W.N.; Chen, Y.; Wan, Z.H. Multimedia e-Learning and self-regulated science learning: A study of primary school learners’ experiences and perceptions. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2019 , 28 , 508–522. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Variables | Category | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 243 | 51.81 |
| Female | 226 | 48.19 | |
| Education program level | Undergraduate program | 210 | 44.78 |
| Master program | 154 | 32.84 | |
| Doctoral program | 105 | 22.39 | |
| Online learning tools | Smartphone | 255 | 54.37 |
| Computer/PC | 125 | 26.65 | |
| Tablet | 89 | 18.98 | |
| Online learning media | Google Meet | 132 | 28.14 |
| Microsoft Teams | 99 | 21.11 | |
| Zoom | 196 | 41.79 | |
| Others | 42 | 8.96 |
| Construct | Measurement Items | Factor Loading/Coefficient (t-Value) | AVE | Composite Reliability | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Online Learning Benefit (LBE) | LBE1 | 0.88 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 0.75 |
| LBE2 | 0.86 | ||||
| LBE3 | 0.71 | ||||
| Online-learning effectiveness (LEF) | LEF1 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.90 | 0.84 |
| LEF2 | 0.88 | ||||
| LEF3 | 0.90 | ||||
| Online-learning motivation (LMT) | LMT1 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.91 | 0.85 |
| LMT2 | 0.91 | ||||
| LMT3 | 0.85 | ||||
| Online-learning strategies (LST) | LST1 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.84 |
| LST2 | 0.87 | ||||
| LST3 | 0.83 | ||||
| Online-learning attitude (OLA) | OLA1 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.84 |
| OLA2 | 0.83 | ||||
| OLA3 | 0.87 | ||||
| Online-learning confidence-in-technology (OLC) | OLC1 | 0.87 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.76 |
| OLC2 | 0.71 | ||||
| OLC3 | 0.89 | ||||
| Online-learning monitoring (OLM) | OLM1 | 0.88 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 0.83 |
| OLM2 | 0.91 | ||||
| OLM3 | 0.79 | ||||
| Online-learning self-efficacy (OLS) | OLS1 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.84 | 0.73 |
| OLS2 | 0.81 | ||||
| OLS3 | 0.89 | ||||
| Online-learning willpower (OLW) | OLW1 | 0.91 | 0.69 | 0.87 | 0.77 |
| OLW2 | 0.84 | ||||
| OLW3 | 0.73 |
| LBE | LEF | LMT | LST | OLA | OLC | OLM | OLS | OLW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBE | |||||||||
| LEF | 0.82 | ||||||||
| LMT | 0.81 | 0.80 | |||||||
| LST | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.86 | ||||||
| OLA | 0.69 | 0.63 | 0.78 | 0.81 | |||||
| OLC | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.72 | ||||
| OLM | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.63 | 0.83 | |||
| OLS | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.75 | ||
| OLW | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.79 |
| LBE | LEF | LMT | LST | OLA | OLC | OLM | OLS | OLW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBE1 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.63 | 0.74 |
| LBE2 | 0.86 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.73 | 0.79 |
| LBE3 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.53 |
| LEF1 | 0.63 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.51 | 0.62 | 0.69 | 0.46 | 0.57 |
| LEF2 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.55 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.52 | 0.69 |
| LEF3 | 0.72 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.69 |
| LMT1 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.63 | 0.74 |
| LMT2 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.88 | 0.61 | 0.67 |
| LMT3 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.69 |
| LST1 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.90 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.57 | 0.39 | 0.57 |
| LST2 | 0.74 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.61 | 0.48 | 0.63 |
| LST3 | 0.72 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.72 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.69 |
| OLA1 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.69 |
| OLA2 | 0.51 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.83 | 0.58 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.43 |
| OLA3 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.70 | 0.87 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.47 |
| OLC1 | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.91 |
| OLC2 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.46 | 0.39 | 0.47 |
| OLC3 | 0.81 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.89 | 0.80 | 0.66 | 0.75 |
| OLM1 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.88 | 0.61 | 0.69 |
| OLM2 | 0.86 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.63 | 0.57 | 0.75 | 0.91 | 0.73 | 0.79 |
| OLM3 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.47 | 0.39 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 0.73 |
| OLS1 | 0.41 | 0.23 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.39 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.69 | 0.49 |
| OLS2 | 0.45 | 0.41 | 0.48 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.52 | 0.81 | 0.49 |
| OLS3 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.49 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.89 | 0.82 |
| OLW1 | 0.78 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.65 | 0.53 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.91 |
| OLW2 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.51 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.87 | 0.84 |
| OLW3 | 0.57 | 0.49 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.73 |
| Hypothesis | Path | Standardized Path Coefficient | t-Value | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | OLS → LST | 0.29 *** | 2.14 | Accepted |
| H2 | OLM → LST | 0.24 *** | 2.29 | Accepted |
| H3 | OLC → LST | 0.28 *** | 1.99 | Accepted |
| H4 | OLC → LMT | 0.36 *** | 2.96 | Accepted |
| H5 | OLW → LMT | 0.26 *** | 2.55 | Accepted |
| H6 | OLA → LMT | 0.34 *** | 4.68 | Accepted |
| H7 | LMT → LST | 0.71 *** | 4.96 | Accepted |
| H8 | LMT → LEF | 0.60 *** | 5.89 | Accepted |
| H9 | LST → LEF | 0.32 *** | 3.04 | Accepted |
| H10 | LEF → LBE | 0.81 *** | 23.6 | Accepted |
| MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
Share and Cite
Hongsuchon, T.; Emary, I.M.M.E.; Hariguna, T.; Qhal, E.M.A. Assessing the Impact of Online-Learning Effectiveness and Benefits in Knowledge Management, the Antecedent of Online-Learning Strategies and Motivations: An Empirical Study. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052570
Hongsuchon T, Emary IMME, Hariguna T, Qhal EMA. Assessing the Impact of Online-Learning Effectiveness and Benefits in Knowledge Management, the Antecedent of Online-Learning Strategies and Motivations: An Empirical Study. Sustainability . 2022; 14(5):2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052570
Hongsuchon, Tanaporn, Ibrahiem M. M. El Emary, Taqwa Hariguna, and Eissa Mohammed Ali Qhal. 2022. "Assessing the Impact of Online-Learning Effectiveness and Benefits in Knowledge Management, the Antecedent of Online-Learning Strategies and Motivations: An Empirical Study" Sustainability 14, no. 5: 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052570
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
How does virtual learning impact students in higher education?
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, stephanie riegg cellini stephanie riegg cellini nonresident senior fellow - governance studies , brown center on education policy.
August 13, 2021
In 2020, the pandemic pushed millions of college students around the world into virtual learning. As the new academic year begins, many colleges in the U.S. are poised to bring students back to campus, but a large amount of uncertainty remains. Some institutions will undoubtedly continue to offer online or hybrid classes, even as in-person instruction resumes. At the same time, low vaccination rates, new coronavirus variants, and travel restrictions for international students may mean a return to fully online instruction for some U.S. students and many more around the world.
Public attention has largely focused on the learning losses of K-12 students who shifted online during the pandemic. Yet, we may have reason to be concerned about postsecondary students too. What can we expect from the move to virtual learning? How does virtual learning impact student outcomes? And how does it compare to in-person instruction at the postsecondary level?
Several new papers shed light on these issues, building on previous work in higher education and assessing the efficacy of online education in new contexts. The results are generally consistent with past research: Online coursework generally yields worse student performance than in-person coursework. The negative effects of online course-taking are particularly pronounced for less-academically prepared students and for students pursuing bachelor’s degrees. New evidence from 2020 also suggests that the switch to online course-taking in the pandemic led to declines in course completion. However, a few new studies point to some positive effects of online learning, too. This post discusses this new evidence and its implications for the upcoming academic year.
Evaluating online instruction in higher education
A number of studies have assessed online versus in-person learning at the college level in recent years. A key concern in this literature is that students typically self-select into online or in-person programs or courses, confounding estimates of student outcomes. That is, differences in the characteristics of students themselves may drive differences in the outcome measures we observe that are unrelated to the mode of instruction. In addition, the content, instructor, assignments, and other course features might differ across online and in-person modes as well, which makes apples-to-apples comparisons difficult.
The most compelling studies of online education draw on a random assignment design (i.e., randomized control trial or RCT) to isolate the causal effect of online versus in-person learning. Several pathbreaking studies were able to estimate causal impacts of performance on final exams or course grades in recent years. Virtually all of these studies found that online instruction resulted in lower student performance relative to in-person instruction; although in one case , students with hybrid instruction performed similarly to their in-person peers. Negative effects of online course-taking were particularly pronounced for males and less-academically prepared students.
A new paper by Kofoed and co-authors adds to this literature looking specifically at online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in a novel context: the U.S. Military Academy at West Point. When many colleges moved classes completely online or let students choose their own mode of instruction at the start of the pandemic, West Point economics professors arranged to randomly assign students to in-person or online modes of learning. The same instructors taught one online and one in-person economics class each, and all materials, exams, and assignments were otherwise identical, minimizing biases that otherwise stand in the way of true comparisons. They find that online education lowered a student’s final grade by about 0.2 standard deviations. Their work also confirms the results of previous papers, finding that the negative effect of online learning was driven by students with lower academic ability. A follow-up survey of students’ experiences suggests that online students had trouble concentrating on their coursework and felt less connected to both their peers and instructors relative to their in-person peers.
Cacault et al. (2021) also use an RCT to assess the effects of online lectures in a Swiss university. The authors find that having access to a live-streamed lecture in addition to an in-person option improves the achievement of high-ability students, but lowers the achievement of low-ability students. The key to understanding this two-pronged effect is the counterfactual: When streamed lectures substitute for no attendance (e.g., if a student is ill), they can help students, but when streaming lectures substitute for in-person attendance, they can hurt students.
Broader impacts of online learning
One drawback of RCTs is that these studies are typically limited to a single college and often a single course within that college, so it is not clear if the results generalize to other contexts. Several papers in the literature draw on larger samples of students in non-randomized settings and mitigate selection problems with various econometric methods. These papers find common themes: Students in online courses generally get lower grades, are less likely to perform well in follow-on coursework, and are less likely to graduate than similar students taking in-person classes.
In a recent paper , my co-author Hernando Grueso and I add to this strand of the literature, expanding it to a very different context. We draw on data from the country of Colombia, where students take a mandatory exit exam when they graduate. Using these data, we can assess test scores as an outcome, rather than (more subjective) course grades used in other studies. We can also assess performance across a wide range of institutions, degree programs, and majors.
We find that bachelor’s degree students in online programs perform worse on nearly all test score measures—including math, reading, writing, and English—relative to their counterparts in similar on-campus programs. Results for shorter technical certificates, however, are more mixed. While online students perform significantly worse than on-campus students on exit exams in private institutions, they perform better in SENA, the main public vocational institution in the country, suggesting substantial heterogeneity across institutions in the quality of online programming. Interviews with SENA staff indicate that SENA’s approach of synchronous learning and real-world projects may be working for some online students, but we cannot definitively call this causal evidence, particularly because we can only observe the students who graduate.
A new working paper by Fischer et al. pushes beyond near-term outcomes, like grades and scores, to consider longer-term outcomes, like graduation and time-to-degree, for bachelor’s degree-seeking students in a large public university in California. They find reason to be optimistic about online coursework: When students take courses required for their major online, they are more likely to graduate in four years and see a small decrease in time-to-degree relative to students taking the requirements in-person.
On the other hand, new work considering course completion during the pandemic is less promising. Looking at student outcomes in spring 2020 in Virginia’s community college system, Bird et al. find that the switch to online instruction resulted in an 8.5% reduction in course completion. They find that both withdrawals and failures rose. They also confirm findings in the literature that negative impacts are more extreme among less-academically-prepared students.
Online learning in the fall and beyond
Much more research on virtual learning will undoubtedly be forthcoming post-pandemic. For now, college professors and administrators should consider that college students pushed online may be less prepared for future follow-on classes, their GPAs may be lower, course completion may suffer, and overall learning may have declined relative to in-person cohorts in previous years. These results seem particularly problematic for students with less academic preparation and those in bachelor’s degree programs.
The research is less clear on the impact of virtual instruction on college completion. Although course completion rates appear to be lower for online courses relative to in-person, the evidence is mixed on the impact of virtual instruction on graduation and time-to-degree. The negative learning impacts, reduced course completion, and lack of connection with other students and faculty in a virtual environment could ultimately reduce college completion rates. On the other hand, there is also evidence that the availability of online classes may allow students to move through their degree requirement more quickly.
As the fall semester approaches, colleges will need to make critical choices about online, hybrid, and in-person course offerings. Maintaining some of the most successful online courses will enhance flexibility at this uncertain time and allow some students to continue to make progress on their degrees if they get sick or cannot return to campus for other reasons. For those transitioning back to campus, administrators might consider additional in-person programming, review sessions, tutoring, and other enhanced supports as students make up for learning losses associated with the virtual instruction of the past year.
Related Content
Stephanie Riegg Cellini, Kathryn J. Blanchard
July 22, 2021
Daphna Bassok, Lauren Bauer, Stephanie Riegg Cellini, Helen Shwe Hadani, Michael Hansen, Douglas N. Harris, Brad Olsen, Richard V. Reeves, Jon Valant, Kenneth K. Wong
March 12, 2021
Education Policy Higher Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Jack Malamud, Cameron F. Kerry, Mark MacCarthy, Katharine Meyer, Tom Wheeler
July 10, 2024
Sofoklis Goulas
June 27, 2024
Phillip Levine, Luke Pardue
June 5, 2024
Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
- Introduction
- Thesis Statement
Background study
- Impacts of online education
Introduction to Online Education
Online learning is one of the new innovative study methods that have been introduced in the pedagogy field. In the last few years, there has been a great shift in the training methods. Students can now learn remotely using the internet and computers.
Online learning comes in many forms and has been developing with the introduction of new technologies. Most universities, high schools, and other institutions in the world have all instituted this form of learning, and the student population in the online class is increasing fast. There has been a lot of research on the impacts of online education as compared to ordinary classroom education.
If the goal is to draw a conclusion of online education, considerable differences between the online learning environment and classroom environment should be acknowledged. In the former, teachers and students don’t meet physically as opposed to the latter, where they interact face to face. In this essay, the challenges and impact of online classes on students, teachers, and institutions involved were examined.
Thesis Statement about Online Classes
Thus, the thesis statement about online classes will be as follows:
Online learning has a positive impact on the learners, teachers, and the institution offering these courses.
Online learning or E learning is a term used to describe various learning environments that are conducted and supported by the use of computers and the internet. There are a number of definitions and terminologies that are used to describe online learning.
These include E learning, distance learning, and computer learning, among others (Anon, 2001). Distant learning is one of the terminologies used in E learning and encompasses all learning methods that are used to train students that are geographically away from the training school. Online learning, on the other hand, is used to describe all the learning methods that are supported by the Internet (Moore et al., 2011).
Another terminology that is used is E learning which most authors have described as a learning method that is supported by the use of computers, web-enabled communication, and the use of new technological tools that enhance communication (Spector, 2008). Other terminologies that are used to describe this form of online learning are virtual learning, collaborative learning, web-based learning, and computer-supported collaborative learning (Conrad, 2006).
Impacts of Online Classes on Students
Various studies and articles document the merits, demerits, and challenges of online studies. These studies show that online study is far beneficial to the students, teachers, and the institution in general and that the current challenges can be overcome through technological advancement and increasing efficiency of the learning process.
One of the key advantages of online learning is the ability of students to study in their own comfort. For a long time, students had to leave their comfort areas and attend lectures. This change in environment causes a lack of concentration in students. In contrast, E-learning enables the students to choose the best environment for study, and this promotes their ability to understand. As a result, students enjoy the learning process as compared to conventional classroom learning.
Another benefit is time and cost savings. Online students are able to study at home, and this saves them travel and accommodation costs. This is in contrast with the classroom environment, where learners have to pay for transport and accommodation costs as well as any other costs associated with the learning process.
Online study has been found to reduce the workload on the tutors. Most of the online notes and books are availed to the students, and this reduces the teacher’s workload. Due to the availability of teaching materials online, tutors are not required to search for materials. Teachers usually prepare lessons, and this reduces the task of training students over and over again.
Accessibility to learning materials is another benefit of online learning. Students participating in online study have unlimited access to learning materials, which gives them the ability to study effectively and efficiently. On the other hand, students in the classroom environment have to take notes as the lecture progress, and these notes may not be accurate as compared to the materials uploaded on the websites.
Unlimited resources are another advantage of online study. Traditionally, learning institutions were limited in the number of students that could study in the classroom environment. The limitations of facilities such as lecture theaters and teachers limited student enrollment in schools (Burgess & Russell, 2003).
However, with the advent of online studies, physical limitations imposed by classrooms, tutors, and other resources have been eliminated. A vast number of students can now study in the same institution and be able to access the learning materials online. The use of online media for training enables a vast number of students to access materials online, and this promotes the learning process.
Promoting online study has been found by most researchers to open the students to vast resources that are found on the internet. Most of the students in the classroom environment rely on the tutors’ notes and explanations for them to understand a given concept.
However, students using the web to study most of the time are likely to be exposed to the vast online educational resources that are available. This results in the students gaining a better understanding of the concept as opposed to those in the classroom environment (Berge & Giles, 2008).
An online study environment allows tutors to update their notes and other materials much faster as compared to the classroom environment. This ensures that the students receive up-to-date information on a given study area.
One of the main benefits of E-learning to institutions is the ability to provide training to a large number of students located in any corner of the world. These students are charged training fees, and this increases the money available to the institution. This extra income can be used to develop new educational facilities, and these will promote education further (Gilli et al., 2002).
Despite the many advantages that online study has in transforming the learning process, there are some challenges imposed by the method. One of the challenges is the technological limitations of the current computers, which affect the quality of the learning materials and the learning process in general.
Low download speed and slow internet connectivity affect the availability of learning materials. This problem is, however, been reduced through the application of new software and hardware elements that have high access speeds. This makes it easier to download learning materials and applications. As computing power increases, better and faster computers are being unveiled, and these will enable better access to online study facilities.
Another disadvantage of online learning as compared to the classroom environment is the lack of feedback from the students. In the classroom environment, students listen to the lecture and ask the tutors questions and clarifications any issues they didn’t understand. In the online environment, the response by the teacher may not be immediate, and students who don’t understand a given concept may find it hard to liaise with the teachers.
The problem is, however, been circumvented by the use of simple explanation methods, slideshows, and encouraging discussion forums between the teachers and students. In the discussion forums, students who don’t understand a concept can leave a comment or question, which will be answered by the tutor later.
Like any other form of learning, online studies have a number of benefits and challenges. It is, therefore, not logical to discredit online learning due to the negative impacts of this training method. Furthermore, the benefits of e-learning far outweigh the challenges.
Conclusion about Online Education
In culmination, a comparative study between classroom study and online study was carried out. The study was done by examining the findings recorded in books and journals on the applicability of online learning to students. The study revealed that online learning has many benefits as compared to conventional learning in the classroom environment.
Though online learning has several challenges, such as a lack of feedback from students and a lack of the proper technology to effectively conduct online learning, these limitations can be overcome by upgrading the E-Leaning systems and the use of online discussion forums and new web-based software.
In conclusion, online learning is beneficial to the students, tutors, and the institution offering these courses. I would therefore recommend that online learning be implemented in all learning institutions, and research on how to improve this learning process should be carried out.
Anon, C. (2001). E-learning is taking off in Europe. Industrial and Commercial Training , 33 (7), 280-282.
Berge, Z., & Giles, L. (2008). Implementing and sustaining e-learning in the workplace. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies , 3(3), 44-53.
Burgess, J. & Russell, J. (2003).The effectiveness of distance learning initiatives in organizations. Journal of Vocational Behaviour , 63 (2),289-303.
Conrad, D. (2006). E-Learning and social change, Perspectives on higher education in the digital age . New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Gilli, R., Pulcini, M., Tonchia, S. & Zavagno, M. (2002), E-learning: A strategic Instrument. International Journal of Business Performance Management , 4 (1), 2-4.
Moore, J. L., Camille, D. & Galyen, K. (2011). E-Learning, online learning and distance learning environments: Are they the same? Internet and Higher Education, 14(1), 129-135.
Spector, J., Merrill, M., Merrienboer, J. & Driscoll, M. P. (2008). Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (3rd ed.), New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- General Curriculum for Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Learners
- Student Survival Guide to Research
- Students With Children and Teachers’ High Expectations
- Nursing Terminologies: NANDA International
- Tutoring Programs for College Students
- Strategies for Motivating Students
- Importance of Sexual Education in School
- New School Program in Seattle
- General Education Courses
- E-learning as an Integral Part of Education System
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, December 19). Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/
"Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." IvyPanda , 19 Dec. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay'. 19 December.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." December 19, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
1. IvyPanda . "Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." December 19, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." December 19, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.

Capturing the benefits of remote learning
How education experts are applying lessons learned in the pandemic to promote positive outcomes for all students
Vol. 52 No. 6 Print version: page 46
- Schools and Classrooms

With schools open again after more than a year of teaching students outside the classroom, the pandemic sometimes feels like a distant memory. The return to classrooms this fall brings major relief for many families and educators. Factors such as a lack of reliable technology and family support, along with an absence of school resources, resulted in significant academic setbacks, not to mention stress for everyone involved.
But for all the downsides of distance learning, educators, psychologists, and parents have seen some benefits as well. For example, certain populations of students found new ways to be more engaged in learning, without the distractions and difficulties they faced in the classroom, and the general challenges of remote learning and the pandemic brought mental health to the forefront of the classroom experience.
Peter Faustino, PsyD, a school psychologist in Scarsdale, New York, said the pandemic also prompted educators and school psychologists to find creative new ways of ensuring students’ emotional and academic well-being. “So many students were impacted by the pandemic, so we couldn’t just assume they would find resources on their own,” said Faustino. “We had to work hard at figuring out new ways to connect with them.”
Here are some of the benefits of distance learning that school psychologists and educators have observed and the ways in which they’re implementing those lessons post-pandemic, with the goal of creating a more equitable, productive environment for all students.
Prioritizing mental health
Faustino said that during the pandemic, he had more mental health conversations with students, families, and teachers than ever. “Because COVID-19 affected everyone, we’re now having mental health discussions as school leaders on a daily and weekly basis,” he said.
This renewed focus on mental health has the potential to improve students’ well-being in profound ways—starting with helping them recover from the pandemic’s effects. In New York City, for example, schools are hiring more than 600 new clinicians, including psychologists , to screen students’ mental health and help them process pandemic-related trauma and adjust to the “new normal” of attending school in person.
Educators and families are also realizing the importance of protecting students’ mental health more generally—not only for their health and safety but for their learning. “We’ve been seeing a broader appreciation for the fact that mental health is a prerequisite for learning rather than an extracurricular pursuit,” said Eric Rossen, PhD, director of professional development and standards at the National Association of School Psychologists.
As a result, Rossen hopes educators will embed social and emotional learning components into daily instruction. For example, teachers could teach mindfulness techniques in the classroom and take in-the-moment opportunities to help kids resolve conflicts or manage stress.
Improved access to mental health resources in schools is another positive effect. Because of physical distancing guidelines, school leaders had to find ways to deliver mental health services remotely, including via online referrals and teletherapy with school psychologists and counselors.
Early in the pandemic, Faustino said he was hesitant about teletherapy’s effectiveness; now, he hopes to continue offering a virtual option. Online scheduling and remote appointments make it easier for students to access mental health resources, and some students even enjoy virtual appointments more, as they can attend therapy in their own spaces rather than showing up in the counselor’s office. For older students, Faustino said that level of comfort often leads to more productive, open conversations.
Autonomy as a key to motivation
Research suggests that when students have more choices about their materials and activities, they’re more motivated—which may translate to increased learning and academic success. In a 2016 paper, psychology researcher Allan Wigfield, PhD, and colleagues make the case that control and autonomy in reading activities can improve both motivation and comprehension ( Child Development Perspectives , Vol. 10, No. 3 ).
During the period of online teaching, some students had opportunities to learn at their own pace, which educators say improved their learning outcomes—especially in older students. In a 2020 survey of more than 600 parents, researchers found the second-most-valued benefit of distance learning was flexibility—not only in schedule but in method of learning.
In a recent study, researchers found that 18% of parents pointed to greater flexibility in a child’s schedule or way of learning as the biggest benefit or positive outcome related to remote learning ( School Psychology , Roy, A., et al., in press).
This individualized learning helps students find more free time for interests and also allows them to conduct their learning at a time they’re most likely to succeed. During the pandemic, Mark Gardner, an English teacher at Hayes Freedom High School in Camas, Washington, said he realized how important student-centered learning is and that whether learning happens should take precedence over how and when it occurs.
For example, one of his students thrived when he had the choice to do work later at night because he took care of his siblings during the day. Now, Gardner posts homework online on Sundays so students can work at their own pace during the week. “Going forward, we want to create as many access points as we can for kids to engage with learning,” he said.
Rosanna Breaux , PhD, an assistant professor of psychology and assistant director of the Child Study Center at Virginia Tech, agrees. “I’d like to see this flexibility continue in some way, where—similar to college—students can guide their own learning based on their interests or when they’re most productive,” she said.
During the pandemic, many educators were forced to rethink how to keep students engaged. Rossen said because many school districts shared virtual curricula during the period of remote learning, older students could take more challenging or interesting courses than they could in person. The same is true for younger students: Megan Hibbard, a teacher in White Bear Lake, Minnesota, said many of her fifth graders enjoyed distance learning more than in-person because they could work on projects that aligned with their interests.
“So much of motivation is discovering the unique things the student finds interesting,” said Hunter Gehlbach, PhD, a professor and vice dean at the Johns Hopkins School of Education. “The more you can facilitate students spending more time on the things they’re really interested in, the better.”
Going forward, Rossen hopes virtual curricula will allow students greater opportunities to pursue their interests, such as by taking AP classes, foreign languages, or vocational electives not available at their own schools.
Conversely, Hibbard’s goal is to increase opportunities for students to pursue their interests in the in-person setting. For example, she plans to increase what she calls “Genius Hours,” a time at the end of the school day when students can focus on high-interest projects they’ll eventually share with the class.
Better understanding of children's needs
One of the most important predictors of a child’s success in school is parental involvement in their education. For example, in a meta-analysis of studies, researchers linked parental engagement in their middle schoolers’ education with greater measures of success (Hill, N. E., & Tyson, D. F., Developmental Psychology , Vol. 45, No. 3, 2009).
During the pandemic, parents had new opportunities to learn about their kids and, as a result, help them learn. According to a study by Breaux and colleagues, many parents reported that the pandemic allowed them a better understanding of their child’s learning style, needs, or curriculum.
James C. Kaufman , PhD, a professor of educational psychology at the University of Connecticut and the father of an elementary schooler and a high schooler, said he’s had a front-row seat for his sons’ learning for the first time. “Watching my kids learn and engage with classmates has given me some insight in how to parent them,” he said.
Stephen Becker , PhD, a pediatric psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said some parents have observed their children’s behavior or learning needs for the first time, which could prompt them to consider assessment and Individualized Education Program (IEP) services. Across the board, Gehlbach said parents are realizing how they can better partner with schools to ensure their kids’ well-being and academic success.
For example, Samantha Marks , PsyD, a Florida-based clinical psychologist, said she realized how much help her middle school daughter, a gifted and talented student with a 504 plan (a plan for how the school will offer support for a student’s disability) for anxiety, needed with independence. “Bringing the learning home made it crystal clear what we needed to teach our daughter to be independent and improve executive functioning” she said. “My takeaway from this is that more parents need to be involved in their children’s education in a healthy, helpful way.”
Marks also gained a deeper understanding of her daughter’s mental health needs. Through her 504 plan, she received help managing her anxiety at school—at home, though, Marks wasn’t always available to help, which taught her the importance of helping her daughter manage her anxiety independently.
Along with parents gaining a deeper understanding of their kids’ needs, the pandemic also prompted greater parent participation in school. For example, Rossen said his kids’ school had virtual school board meetings; he hopes virtual options continue for events like back-to-school information sessions and parenting workshops. “These meetings are often in the evening, and if you’re a single parent or sole caregiver, you may not want to pay a babysitter in order to attend,” he said.
Brittany Greiert, PhD, a school psychologist in Aurora, Colorado, says culturally and linguistically diverse families at her schools benefited from streamlined opportunities to communicate with administrators and teachers. Her district used an app that translates parent communication into 150 languages. Parents can also remotely participate in meetings with school psychologists or teachers, which Greiert says she plans to continue post-pandemic.
Decreased bullying
During stay-at-home orders, kids with neurodevelopmental disorders experienced less bullying than pre-pandemic (McFayden, T. C., et al., Journal of Rural Mental Health , No. 45, Vol. 2, 2021). According to 2019 research, children with emotional, behavioral, and physical health needs experience increased rates of bullying victimization ( Lebrun-Harris, L. A., et al., ), and from the U.S. Department of Education suggests the majority of bullying takes place in person and in unsupervised areas (PDF) .
Scott Graves , PhD, an associate professor of educational studies at The Ohio State University and a member of APA’s Coalition for Psychology in Schools and Education (CPSE), said the supervision by parents and teachers in remote learning likely played a part in reducing bullying. As a result, he’s less worried his Black sons will be victims of microaggressions and racist behavior during online learning.
Some Asian American families also report that remote learning offered protection against racism students may have experienced in person. Shereen Naser, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at Cleveland State University and a member of CPSE, and colleagues found that students are more comfortable saying discriminatory things in school when their teachers are also doing so; Naser suspects this trickle-down effect is less likely to happen when students learn from home ( School Psychology International , 2019).
Reductions in bullying and microaggressions aren’t just beneficial for students’ long-term mental health. Breaux said less bullying at school results in less stress, which can improve students’ self-esteem and mood—both of which impact their ability to learn.
Patricia Perez, PhD, an associate professor of international psychology at The Chicago School of Professional Psychology and a member of CPSE, said it’s important for schools to be proactive in providing spaces for support and cultural expression for students from vulnerable backgrounds, whether in culture-specific clubs, all-school assemblies that address racism and other diversity-related topics, or safe spaces to process feelings with teachers.
According to Rossen, many schools are already considering how to continue supporting students at risk for bullying, including by restructuring the school environment.
One principal, Rossen said, recently switched to single-use bathrooms to avoid congregating in those spaces once in-person learning commences to maintain social distancing requirements. “The principal received feedback from students about how going to the bathroom is much less stressful for these students in part due to less bullying,” he said.
More opportunities for special needs students
In Becker and Breaux’s research, parents of students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), particularly those with a 504 plan and IEP, reported greater difficulties with remote learning. But some students with special learning needs—including those with IEPs and 504 plans—thrived in an at-home learning environment. Recent reporting in The New York Times suggests this is one reason many students want to continue online learning.
According to Cara Laitusis, PhD, a principal research scientist at Educational Testing Service ( ETS ) and a member of CPSE, reduced distractions may improve learning outcomes for some students with disabilities that impact attention in a group setting. “In assessments, small group or individual settings are frequently requested accommodations for some students with ADHD, anxiety, or autism. Being in a quiet place alone without peers for part of the instructional day may also allow for more focus,” she said. However, she also pointed out the benefits of inclusion in the classroom for developing social skills with peers.
Remote learning has improved academic outcomes for students with different learning needs, too. Marks said her seventh-grade daughter, a visual learner, appreciated the increase in video presentations and graphics. Similarly, Hibbard said many of her students who struggle to grasp lessons on the first try have benefited from the ability to watch videos over again until they understand. Post-pandemic, she plans to record bite-size lessons—for example, a 1-minute video of a long division problem—so her students can rewatch and process at their own rate.
Learners with anxiety also appreciate the option not to be in the classroom, because the social pressures of being surrounded by peers can make it hard to focus on academics. “Several of my students have learned more in the last year simply due to the absence of anxiety,” said Rosie Reid, an English teacher at Ygnacio Valley High School in Concord, California, and a 2019 California Teacher of the Year. “It’s just one less thing to negotiate in a learning environment.”
On online learning platforms, it’s easier for kids with social anxiety or shyness to participate. One of Gardner’s students with social anxiety participated far more in virtual settings and chats. Now, Gardner is brainstorming ways to encourage students to chat in person, such as by projecting a chat screen on the blackboard.
Technology has helped school psychologists better engage students, too. For example, Greiert said the virtual setting gave her a new understanding of her students’ personalities and needs. “Typing out their thoughts, they were able to demonstrate humor or complex thoughts they never demonstrated in person,” she said. “I really want to keep incorporating technology into sessions so kids can keep building on their strengths.”
Reid says that along with the high school students she teaches, she’s seen her 6-year-old daughter benefit from learning at her own pace in the familiarity of her home. Before the pandemic, she was behind academically, but by guiding her own learning—writing poems, reading books, playing outside with her siblings—she’s blossomed. “For me, as both a mother and as a teacher, this whole phenomenon has opened the door to what education can be,” Reid said.
Eleanor Di Marino-Linnen, PhD, a psychologist and superintendent of the Rose Tree Media School District in Media, Pennsylvania, says the pandemic afforded her district a chance to rethink old routines and implement new ones. “As challenging as it is, it’s definitely an exciting time to be in education when we have a chance to reenvision what schools have looked like for many years,” she said. “We want to capitalize on what we’ve learned.”
Further reading
Why are some kids thriving during remote learning? Fleming, N., Edutopia, 2020
Remote learning has been a disaster for many students. But some kids have thrived. Gilman, A., The Washington Post , Oct. 3, 2020
A preliminary examination of key strategies, challenges, and benefits of remote learning expressed by parents during the COVID-19 pandemic Roy, A., et al., School Psychology , in press
Remote learning during COVID-19: Examining school practices, service continuation, and difficulties for adolescents with and without attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder Becker S. P., et al., Journal of Adolescent Health , 2020
Recommended Reading

Contact APA
You may also like.
A study of effectiveness of online learning
- February 2021
- Conference: National Confrence DYPIMS 2021

- Balaji Institute of international business

Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Landra Rezabek
- Dr Jyoti Agarwal
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay On Online Education: In 100 Words, 150 Words, and 200 Words
- Updated on
- Apr 26, 2024

Online education has emerged as a significant transformation in the global education landscape, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic . This essay explores the various facets of online education, from its inception to its advantages and disadvantages and its impact on learners and educators alike. The evolution of online education presents a new horizon for accessible and flexible learning .

Table of Contents
- 1 Essay on Online Education in 100 words
- 2 Essay on Online Education in 150 words
- 3 Essay on Online Education in 200 words
- 4 Short Essay on Online Education
Also Read: English Essay Topics
Also Read: How to Write an Essay in English
Also Read: Speech on Republic Day for Class 12th
Essay on Online Education in 100 words
Online education is a modern educational paradigm where students access instructional content through the internet. This innovative approach has gained immense popularity, especially after the pandemic, owing to its convenience and adaptability. It has enabled students of all ages to acquire knowledge from the comfort of their homes, transcending geographical barriers. Online education offers a diverse range of courses and resources, fostering continuous learning. However, it also presents challenges, such as dependency on technology and potential disengagement from the physical world.
Also Read: The Beginner’s Guide to Writing an Essay
Essay on Online Education in 150 words
Online education marks a revolutionary shift in how we acquire knowledge. It harnesses the power of the internet to deliver educational content to students, making learning more flexible and accessible. Technology advancements have accelerated the development of online education, enabling educational institutions to provide a wide range of courses and programmes through digital platforms.
One of the primary advantages of online education is its ability to cater to a diverse audience, regardless of geographical location or physical limitations. It eliminates the need for commuting and offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional classroom learning. However, online education also comes with its challenges. It requires self-discipline and motivation as students often learn independently. Additionally, prolonged screen time can have adverse effects on students’ physical and mental well-being, potentially leading to social disconnection.
Essay on Online Education in 200 words
Online education has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, with the internet serving as the conduit for delivering educational content. This transformation has been accelerated, particularly in response to the global pandemic. Online education transcends the boundaries of traditional learning, offering students the opportunity to acquire knowledge and skills from anywhere in the world.
One of the most compelling aspects of online education is its flexibility. Learners can access course materials and engage with instructors at their convenience, breaking free from rigid schedules. Moreover, this mode of education has expanded access to a vast array of courses, allowing individuals to pursue their interests and career goals without geographical constraints.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the challenges associated with online education. It demands a high degree of self-discipline, as students must navigate the coursework independently. Prolonged screen time can have adverse effects on health and may lead to a sense of disconnection from society.
In conclusion, online education represents a significant shift in how we approach learning. It offers unprecedented access and flexibility but also requires learners to adapt to a more self-directed approach to education. Striking a balance between the benefits and challenges of online education is key to harnessing its full potential.
Also Read: Essay on Fire Safety in 200 and 500+ words in English for Students
Short Essay on Online Education
Find a sample essay on online education below:
An organised argument backed up by proof and examples is the key to writing a convincing essay. Create a clear thesis statement at the outset, follow a logical progression of points, and then summarise your main points.
To improve readability, use clear and concise language, break your essay into paragraphs with clear topic sentences, and vary your sentence structure.
If you’re struggling to meet the word count, review your content to see if you can expand on your ideas, provide more examples, or include additional details to support your arguments. Additionally, check for any redundancies or irrelevant information that can be removed.
Related Reads
We hope that this essay on Online Education helps. For more amazing daily reads related to essay writing , stay tuned with Leverage Edu .
Manasvi Kotwal
Manasvi's flair in writing abilities is derived from her past experience of working with bootstrap start-ups, Advertisement and PR agencies as well as freelancing. She's currently working as a Content Marketing Associate at Leverage Edu to be a part of its thriving ecosystem.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Home — Essay Samples — Education — E-Learning — Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Online Courses
Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Online Courses
- Categories: E-Learning Teaching Philosophy
About this sample

Words: 432 |
Published: Aug 1, 2022
Words: 432 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1538 words
1 pages / 575 words
5 pages / 2159 words
3 pages / 1214 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on E-Learning
As a college student, the choice between taking courses online or in-person can be a difficult one. While online classes provide flexibility and convenience, they also come with their own set of challenges. In this essay, we [...]
In conclusion, both online learning and classroom learning offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Online learning provides flexibility and access to a wide range of resources, while classroom learning offers immediate [...]
Online learning has gained prominence, offering flexibility and accessibility, but it also presents unique challenges to teacher-student relationships. This qualitative essay embarks on an in-depth exploration of teacher-student [...]
The emergence of e-learning has revolutionized the way we approach education. With the advancement of technology, traditional classroom settings are no longer the sole method of learning. E-learning, also known as online [...]
10 Minute School is the largest online educational platform of Bangladesh. It was introduced or created by Ayman Sadiq with his goal to destroy all kinds of barriers of ensuring quality education to all across Bangladesh. It can [...]
Technology is a method of doing things or solving issues for the greater good of humanity. Technology is also a human activity that involves the design and development of products that make human life easier, such as machines, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Essay on Online Education | Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Education Essay
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Essay on Online Education: Online learning is one of the imminent trends in the education sector around the globe. This mode of learning is done through the internet. With advanced and upgraded technologies, this mode of learning has been made simpler. Online Education is also preferred in higher learning Institutions. This article will render the students about online education, its outcomes, and advantage in short and long essays on Online Education.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Long and Short Essays on Online Education for Students and Children in English
We provide children and students with essay samples on a long essay of 500 words and a short essay on Online Education in Lockdown of 150 words on the topic “Online education in India Essay” for reference.
Short Essay on Online Education 150 Words in English
Short Essay on Online Education advantages and Disadvantages is helpful to students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
Education is an integral part of people’s lives; it will either make them or break them in the prospect depending on their careers. Education is broadly diverse today compared to the 1950s because of progressions in teaching methods and other prominent inventions that implement more apparent teaching techniques.
In E-learning, the students study from home or any other place, that is most convenient for them. They can acquire learning material online. The study materials in online education could be texts, audio, notes, videos, and images. However, the method of study has its benefits and various drawbacks too.
Online education is suitable for those who can not visit or obtain the traditional education method for one reason or the other. Nearly 6.1 million college students are currently attending online courses, and this number is growing by around 30 percent yearly.
Online education provides a myriad of advantages for people, as well as companies because it allows for, among others, flexibility. A great way to benefit more from online education is to consolidate online education and traditional ways of teaching.

Online Education Essay 500 Words in English
Long Essay on Online Education 400 Words in English is helpful to students of classes 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12.
Introduction: Online education is an amenable instructional delivery process that includes any learning that takes place via the internet. Online learning enables educators to communicate with students who may not be capable of enrolling in a traditional classroom course and assists students who need to work on their own schedule and at their own speed.
Every discipline is registering a surge in the volume of distance learning and imparting of online degrees, with remarkable pace. Schools and institutions that offer online education are also growing in number. Students pursuing degrees through online methods must be scrupulous in ensuring their coursework is completed through a valued and credentialed university.
Online education is known to offer the benefit of synergy. Here, the format employed makes room for dynamic communications between students and the teachers. Through these communications, sources are shared, and an open-ended synergy evolves through a learning process. When each person bestows a view or opinion through discussions and comments on others’ work course, it benefits the student to learn better. This unique advantage is manifested in a student-centred virtual learning environment that online learning format alone can contribute.
With online classes, we don’t need to travel to a different city or commute long distances. We can stay where we are and keep our current job while we work toward improving our career with an online degree. Online education also helps digital nomads—someone who espouses a technology-enabled or location-independent lifestyle. We can watch lectures and complete our coursework wherever we are.
Whether we are a full-time or part-time online student, the online education experience provides a much more manageable schedule. Online education has gained much approval on account of its cheapness. Such is the fact that online courses are more affordable than those offered at schools or colleges. While studying in universities, we may have to spend some money such as transportation, lodging, and meals, online education may not require such expenses.
One of the important aspects of online learning is its inherent flexibility, however, there is a catch, one has to be extremely self-motivated. The best online students develop various approaches for staying up to date on their coursework. Things like setting aside time every week to study and create a workspace with minimal distractions can help immensely.
Conclusion on Online Education Essay
Online education’s potential advantages involve increased educational access; it provides a high-quality learning opportunity, improves student outcomes and skills, and expands educational choice options. Therefore, location, time, and quality are no longer considered factors in seeking degree courses or higher education because of online education.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Education Essay
Introduction to Online Education Essay: Online education refers to the type of knowledge which is imparted through the internet. Millions of people globally are enrolled in online courses and can learn from the comfort of their homes. Online education can come in different ways; they could be educational webinars and videos on the internet or even face to face learning on the laptop with the teacher, which utilises the internet.
Online education contributes a myriad of advantages for people, as well as companies because it provides flexibility among other work. This indicates that despite people’s physical locations, they can accomplish the same level of education by taking similar online courses.
Teachers and professors optimise the timelessness and focus of the learning curriculum while students are able to fit learning time into their hectic schedules. Online education offers extensive benefits to students by giving a manageable schedule, student enhancement and augmented education access and choice.
Advantages of Online Education
Online education enables us to learn from various mentors and teachers in different areas, increasing our knowledge and perspective. It reduces nervousness among students, as many are able to communicate more through online education than regular classes. One can learn from merely anyplace as long as they have an available internet device.
Online education normally provides a chance to study at our own speed as there is no rush. Most online courses are usually enjoyable and more comfortable compared to attending traditional classes. It spares you the inconvenience of having to travel to a particular destination every single day.
Online education usually is more affordable. Online education further happens to be comparatively cheaper in comparison to conventional educational approaches. Under traditional university programs, the students are required to compensate for transportation, textbooks, institutional facilities such as gyms, libraries, swimming pools, and other costs that expedite the cost of university education up. Online education, on its part, charges only for tuition and additional essential expenses. Virtual education thus offers both the wealthy and the poor an opportunity.
It allows one to learn innovative approaches through the internet and therefore become more skilful. In online education, if there are any variations in the syllabus, updates can be done instantly compared to conventional means of education.
Online education is flexible and adaptable since one can study at any time, even at midnight. It can help increase the grades of some people as compared to standard traditional education. Some people learn more through online education.
There is no need to wait for office hours to speak to the instructor; you can immediately access them through chat or email. There is considerably a large amount of educational information on the internet. Online education can also help one to be in the mix of a diverse group of people from varied educational, social, cultural and philosophical backgrounds. The subject matter is always available on the internet, unlike traditional education.
Disadvantages of Online Education
The advantages that online education brings to students are immense and indisputable. Pursuing an online course is an excellent option in education, particularly when traditional learning situations have many obstacles, such as commuting or distance. However, as everything has two sides, online education also has some fundamental drawbacks that can be inconvenient.
Using the computer too much can make the students prone to plagiarism. It can also cause vision problems as we sit near the laptop almost the whole day. Online education may also hinder physical development. Online education can be quite complicated for a person to be accountable for their own learning without someone to drive them to do something.
Online education detaches you from your classmates. One might need to put in extra time in some cases to understand the learning process. It is easier to cheat in an online exam than when in a class and hence may not be advisable during exams. Online education also gives one a lot of autonomy which may be critical for our learning. There are a number of distractions on the internet through adverts, and this might interrupt our learning. Online education also has significantly less self-assessment.
Online education has both advantages and shortcomings, but it is an excellent method of learning that can help develop a student’s performance. To succeed in online education, one should choose an ideal university and course to avoid pursuing education from among the various suspicious universities that employers may reject. The other most essential thing is to assure that one needs to maintain communication with the school faculty and fellow students. The important point is proper time administration that helps one manage our time to complete and submit prescribed assignments in time.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Effectiveness of Online Education and the Extent to which Online Courses can Replace Traditional Classroom Teaching

2022, The Effectiveness of Online Education and the Extent to which Online Courses can Replace Traditional Classroom Teaching.
Over the past few years, there has been an increase in institutions that have adopted online education as means of delivering educational content in different disciplines. The COVID-19 pandemic also contributed to most institutions of learning adopting online education. Online education is mostly delivered over the internet unlike the traditional mode of education which requires students to sit in a classroom with a lecturer Infront of them. Most online platforms incorporate rich graphics and interactive quizzes which enhance the learning experience of students.
Related Papers
Mahamadou tembely
Education providers are moving from traditional face-to-face environments to those that are completely electronic. The movement to online education requires applying new strategies to suit the new medium. Online education provides university equivalent courses for millions of students across the globe. This paper discusses the strengths, weaknesses, and potentiality of online education.
Paul D Bacsich
Eddie Mombera
Online Teaching allows people to access education from anywhere in the world and at any time that is convenient to the leaner, it offers flexibility, it is student self-paced in delivery of the course material. Online learning is a form of distance learning. Simonson & Berg (2016) defined online learning as a form of education where the courses are delivered to students through internet and communication between students is also through internet. Recently there has been a significant increase in the number and variety of online courses had been observed. Chidi et al. (2021) considers online learning as an education reform that has been encouraged by advancement in technology. Although online courses have been welcomed as a great opportunity by a number of students, others still see them as less useful than traditional face-to-face courses. In this paper , we will look at the advantages and disadvantages of online learning and further to that, the paper will evaluate the effectiveness of online education by examining perception on online teaching, and discuss the extent to which online courses can replace traditional classroom teaching.
Holly Seirup
More and more colleges and universities across the US have adopted online instruction (Allen & Seaman, 2015; Perreault, Waldman, Alexander, & Zhao, 2008). Ginn & Hammond (2012), offer an example of the growth in a report on the adoption of online instruction by National Association of Schools and Public Affairs and Administration members. The report chronicled the increase in offerings of online courses, certificates, and Master degree programs from eight online courses in the 1990s to 15 in 2003 and 39 in 2012. Online offerings and enrollments are expansive (Ni, 2013) as colleges and universities continue to rethink the concept of instructional effectiveness, innovative pedagogy, and student retention.
Massive Open Online Courses - Current Practice and Future Trends [Working Title]
Sabila Naseer
Digital Education is the innovative incorporation of modern technology and digital tools to assist the progress of the teaching and learning process. This concept was familiar for the last many years but during COVID-19 its urgent need was undrescored. However, in this chapter, both advantages and flaws of digital learning or online practices have been highlighted. The experts' given solutions both on a national and international level to overcome the flaws have also been discussed. To make this set-up more smooth for the students, teachers, as well as the community for upcoming ages, have also been foregrounded to deal with any calamity.
isara solutions
Interal Res journa Managt Sci Tech
The outbreak of COVID-19 had led to the shutdown of all the educational institutes, although maintaining the process of learning and teaching is crucial for all the economies. e-learning evolved to be the most optimum tool for distributing education to remote locations. The Government of India has introduced numerous programmes for making changes in the current scenarios of education at school, undergraduate and postgraduate level to impart education to all the sections of society. The present study aims to analyze the technologies employed by the formal Indian institutions to conduct online classes and factors impacting the choice as no study has examined the technology adopted by universities in the situation like COVID-19 epidemic. Quantitative study was conducted with the help of mailed-questionnaire and responses were gathered from 187 respondents. Hypothesis were constructed and statistically tested with the chi-square and sample t-test. The results highlighted that Zoom, StarLeaf and Canvas are most used e-learning softwares as they provide the feature of locking the room and ease in integration with the other softwares. However, these platforms were not seen as the future of the education system.
Apeejay Journal of Management & Technology
Simple Sharma
The online courses has become a different platform for learning which has grown rapidly in last decade due to its attractiveness. There are three main pillars of online courses which make them successful i.e. instructor, student and technology. Online courses push student towards boosting their knowledge, confidence and enhance their skills not only this people can also take online courses while doing other jobs, even while completing their degrees and maintaining status of their families. Students' satisfaction is important part and parcel of online courses, as it depends on student performance & also on quality aspect of online courses. Interaction is considered as an important factor for round about development of students & learner-student interaction is deliberated as enhancing the progress of students in field of education. It is cleared from facts in this review that new technologies have expanded prospective interaction among student & instructor, but careful planning should be done on part of instructor to have great growth on part of student. No doubt new technologies in this field has put great advantages but due to one way communication learners face many challenges and got the feeling of isolation as compared to offline learning. In offline learning which is also called traditional classroom learning, there is two way communication which leads to transparency and evolution of new ideas. But still learners are adopting the online courses due to short term duration and time flexibility. This review focus on various benefits on part of student, interaction of learner & instructor, challenges & key points that highlighted the online education importance in today's scenario.
Online Education’s Effectiveness: Online Courses vs. Traditional Classroom Teaching
Yumna Fatehi
The effectiveness of online education is argued by researchers who held different views in this respect. Some studies questioned that online courses could replace traditional classroom teaching. On the other hand, other studies emphasized the appropriateness of online courses, especially when abiding by certain requirements that can make online courses efficient. The study discusses these different views and sheds light on the appropriate conditions for successful online learning.
Muhammad Nabeel Siddiqui
The effectiveness of online studying is disputable .some people believe that it is much more constructive than traditional classroom based training while others do not. This essay will discuss the positive and negative aspects of online study
Journal of Technology …
Debra Sprague
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Flavius Marcau
Karim (Omid) Hajhashemi
Nur Azmina Md arif
Dana Mathews
Hayden Wimmer
Business and Management Studies by RedFame
Prof. Dr. Samir Abdelaziz
Indian Journal of School Health and Wellbeing
Satbir Bedi , Vikas Baniwal
Benita Jones
Academia Letters
Jace Hargis
sciencepub.net
Ahmad Shahidian
TURKISH ONLINE JOURNAL OF DESIGN ART COMMUNICATION
Serhat Yılmaz
Philip Lippel
Ludovika Jannoke
IOSR Journals
The Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government
Chanchal Sachdeva Suri
Phunziroh Masanjala
International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
Saumendra Mohanty
Gayaz Ahmed
Acta Universitatis Bohemiae Meridionalis
Dr. Ravindra R Kaikini
Nova Science Publishers
Yaron Ghilay
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
24/7 writing help on your phone
To install StudyMoose App tap and then “Add to Home Screen”
The Effectiveness of Online Classes
Save to my list
Remove from my list

- Boghikian-Whitby, S., & Mortagy, Y. (2016). Student preferences and performance in online and face-to-face classes using Myers-Briggs Indicator: A longitudinal quasi-experimental study. Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology, 13, 89-109. Retrieved from Directory of Open Access Journals database. (edsdoj.05e34e0e5acc4d978e41b80b6b07fe05)
- Bosshardt, W., & Chiang, E. P. (2016). Targeting teaching lecture capture learning: do students perform better compared to face-to-face classes? Southern Economic Journal, 82(3), 1021-1038. https://doi.org/10.1002/soej.12084
- Flanagan, J. L. (2012). Online versus face-to-face instruction: analysis of gender and course format in undergraduate business statistics courses. Academy of Business Research Journal, 2, 89-98. Retrieved from Business Source Complete database. (Accession No. 86173757)
- Frass, L. R., Rucker, R. D., & Washington, G. (2017). An overview of how four institutions prepare faculty to teach online. Journal of Online Higher Education, 1(1), 1-7. Retrieved from Directory of Open Access Journals database. (edsdoj.9c202c058f634dfeb7accd277bdc2ef3)
- Ganesh, G., Paswan, A., & Sun, Q. (2015). Are face-to-face classes more effective than online classes? an empirical examination. Marketing Education Review, 25(2), 67-81. https://doi.org/10.1080/10528008.2015.1029851
- Paquette, K. R., Corbett, F., & Casses, M. (2015). Student evaluation response rates of teacher performance in higher education online classes. Quarterly Review of Distance Education, 16(4), 71-82. Retrieved from Academic Search Complete database. (Accession No. 114746037)
- Publication manual of the American Psychological Association. (6th ed.). (2010). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association
The Effectiveness of Online Classes. (2021, Dec 07). Retrieved from https://studymoose.com/the-effectiveness-of-online-classes-essay
"The Effectiveness of Online Classes." StudyMoose , 7 Dec 2021, https://studymoose.com/the-effectiveness-of-online-classes-essay
StudyMoose. (2021). The Effectiveness of Online Classes . [Online]. Available at: https://studymoose.com/the-effectiveness-of-online-classes-essay [Accessed: 23 Jul. 2024]
"The Effectiveness of Online Classes." StudyMoose, Dec 07, 2021. Accessed July 23, 2024. https://studymoose.com/the-effectiveness-of-online-classes-essay
"The Effectiveness of Online Classes," StudyMoose , 07-Dec-2021. [Online]. Available: https://studymoose.com/the-effectiveness-of-online-classes-essay. [Accessed: 23-Jul-2024]
StudyMoose. (2021). The Effectiveness of Online Classes . [Online]. Available at: https://studymoose.com/the-effectiveness-of-online-classes-essay [Accessed: 23-Jul-2024]
- Traditional Classes VS Online Classes Pages: 2 (464 words)
- Pros and Cons of Sync and Async Learning in Online Classes Pages: 1 (277 words)
- Why are More and More Students Taking Online Classes? Pages: 3 (725 words)
- Choosing Online Classes: A Productive Solution for Busy Professionals Pages: 4 (1042 words)
- Online vs Traditional Classes: A Student Performance Comparison Pages: 3 (638 words)
- Blended Learning: The Best From Traditional and Online Classes Pages: 3 (828 words)
- Instant Online Loans No Credit Check – A Simple Online Application Pages: 2 (411 words)
- Gender is the division of individuals into two classes men Pages: 5 (1444 words)
- What effects did World War I have on social classes? Pages: 7 (1805 words)
- Divided America Into Classes Pages: 9 (2499 words)

👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Most online courses, however, particularly those serving K-12 students, have a format much more similar to in-person courses. The teacher helps to run virtual discussion among the students ...
Nashville, TN 3720 3 USA. t [email protected]. Abstract. The physical "brick and mortar" classroom is starting to lose its monopoly as the place of. learning. The Internet has made ...
Effectiveness of Online Education. Words: 1113 Pages: 4. It is hard to dispute that online education has recently established itself as a significant component of current educational systems. As new technologies are developed, online learning continues to take on new forms. The majority of colleges, high schools, and other educational ...
218. A UNESCO report says schools' heavy focus on remote online learning during the pandemic worsened educational disparities among students worldwide. Amira Karaoud/Reuters. By Natalie Proulx ...
This essay examines the global impact of online education in the decade following the widely publicized introduction of MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses) in 2012—exploring the demographics and preferences of learners, the effectiveness of online learning, the surprising and substantial impact on the labor market, and the implications of scalability for reducing the cost of education.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students' academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this ...
However, contrary to the present study, the analysis of comparisons between online and traditional education in some studies shows that face-to-face traditional learning is still considered effective compared to online learning (Ahmad et al., 2016; Hamdani & Priatna, 2020; Wei & Chou, 2020). Online education has advantages and disadvantages.
In the fifth essay of the Education Week series "Weighing the Research: What Works, What Doesn't," Professor of Education Susanna Loeb explores the effectiveness of online learning in K-12 education. "It is not surprising that in-person courses are, on average, more effective.
The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make it work ...
This essay argues the contemporary benefits of online learning, and that these benefits significantly outweigh the issues, challenges and disadvantages of online learning. Online learning is giving people new choices and newfound flexibility with their personal learning and development. Whereas before, formal academic qualifications could only ...
Recognition of the potential advantages of online instruction isn't new. A paper published back in 2001 noted that online courses could "address a variety of learning styles," allow ...
Online learning is one of the educational solutions for students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Worldwide, most universities have shifted much of their learning frameworks to an online learning model to limit physical interaction between people and slow the spread of COVID-19. The effectiveness of online learning depends on many factors, including student and instructor self-efficacy, attitudes ...
They find that online education lowered a student's final grade by about 0.2 standard deviations. Their work also confirms the results of previous papers, finding that the negative effect of ...
This change in environment causes a lack of concentration in students. In contrast, E-learning enables the students to choose the best environment for study, and this promotes their ability to understand. As a result, students enjoy the learning process as compared to conventional classroom learning.
"Research generally shows that online learning can be as effective as in-person instruction, if you have a good setup," Gill says. But what most schools were doing in the spring wasn't true online learning, she adds. "Teachers didn't have prepared online content, so they were trying to convert what they normally do to an online platform.
This systematic analysis examines effectiveness research on online and blended learning from schools, particularly relevant during the Covid-19 pandemic, and also educational games, computer-supported cooperative learning (CSCL) and computer-assisted instruction (CAI), largely used in schools but with potential for outside school.
In a recent study, researchers found that 18% of parents pointed to greater flexibility in a child's schedule or way of learning as the biggest benefit or positive outcome related to remote learning ( School Psychology, Roy, A., et al., in press).
Online learning, ideally means Educational technology is the combined use o f hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to fa cilitate learning. Educati onal technology. creates ...
Essay on Online Education in 200 words. Online education has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, with the internet serving as the conduit for delivering educational content. This transformation has been accelerated, particularly in response to the global pandemic. Online education transcends the boundaries of traditional learning ...
Effectiveness of Online Teaching and Online Courses. In the past few years and even more so recently with the challenges created by the Covid epidemic, there seems to be a growing interest in the role that online teaching can play in the field of education. It has prompted the educated elite to examine how online teaching can improve academic ...
Essay on Online Education: Online learning is one of the imminent trends in the education sector around the globe. This mode of learning is done through the internet. With advanced and upgraded technologies, this mode of learning has been made simpler. Online Education is also preferred in higher learning Institutions. This article will render the […]
The evaluation and discussions will be informed by existing literature on online learning that has been published in peer-reviewed journals and published books on the subject. 2.0 The Effectiveness of Online Education Al Rawashdeh et al (2021) states that online learning involves the use of text, images, and sound to engage the learner hence ...
The effectiveness of online education has shown a number of advantages due to increased flexibility and learning opportunities: easy access to experts, exposure to educational environments, a wide range of types of courses, and joining student communities. There are also several disadvantages of online education, such as: internet browsing ...
As if that was not good enough, the younger generations are being offered courses online, making K-12 online education popular. Whether students decide to pursue their education, regardless of whether they choose a traditional face-to-face school setting or courses being taught online, studies in previous years found that online courses can be beneficial for some and convenient.