- +44 (0) 207 391 9032

Recent Posts
- Academic Integrity vs. Academic Dishonesty: Understanding the Key Differences
- How to Use AI to Enhance Your Thesis
- Guide to Structuring Your Narrative Essay for Success
- How to Hook Your Readers with a Compelling Topic Sentence
- Is a Thesis Writing Format Easy? A Comprehensive Guide to Thesis Writing
- The Complete Guide to Copy Editing: Roles, Rates, Skills, and Process
- How to Write a Paragraph: Successful Essay Writing Strategies
- Everything You Should Know About Academic Writing: Types, Importance, and Structure
- Concise Writing: Tips, Importance, and Exercises for a Clear Writing Style
- How to Write a PhD Thesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Success
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

22 Essay Question Words You Must Understand to Prepare a Well-Structured Essay
(Last updated: 3 June 2024)
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
Now, we may be experts in best essay writing , but we’re also the first to admit that tackling essay questions can be, well, a bit of a challenge. Essays first require copious amounts of background reading and research so you can include accurate facts in your writing. You then have to figure out how to present those facts in a convincing and systematic argument. No mean feat.
But the silver lining here is that presenting your argument doesn’t have to be stressful. This goes even if you’re a new student without much experience and ability. To write a coherent and well-structured essay , you just have to really understand the requirements of the question. And to understand the requirements of the question, you need to have a good hold on all the different question words. For example, 'justify', 'examine', and 'discuss', to name a few.
Lacking this understanding is a pitfall many students tumble into. But our guide on essay question words below should keep you firmly above on safe, essay-acing ground.
Definition of Question Words with Examples
No matter their nature, question words are key and must always be adhered to. And yet, many students often overlook them and therefore answer their essay questions incorrectly. You may be a font of all knowledge in your subject area, but if you misinterpret the question words in your essay title, your essay writing could be completely irrelevant and score poorly.
For example, if you are asked to compare the French and British upper houses of parliament, you won’t get many points by simply highlighting the differences between the two parliamentary systems.
So, what should you do? We advise you start by reading this guide – we’ve divided the question words either by ‘critical’ or ‘descriptive’ depending on their nature, which should help you identify the type of response your essay requires.
| Critical question words | Descriptive question words |
|---|---|
| Analyse | Define |
| Evaluate | Demonstrate |
| Justify | Describe |
| Critically evaluate | Elaborate |
| Review | Explain |
| Assess | Explore |
| Discuss | Identify |
| Examine | Illustrate |
| To what extent | Outline |
| Summarise | |
| Clarify | |
| Compare | |
| Contrast |

Question Words that Require a Critical Approach
Once you have done this, it’s also important that you critically (more on this word later) examine each part. You need to use important debates and evidence to look in depth at the arguments for and against, as well as how the parts interconnect. What does the evidence suggest? Use it to adopt a stance in your essay, ensuring you don’t simply give a narration on the key debates in the literature. Make your position known and tie this to the literature.
2. Evaluate
It is essential to provide information on both sides of the debate using evidence from a wide range of academic sources. Then you must state your position basing your arguments on the evidence that informed you in arriving at your position.
Also, you may want to consider arguments that are contrary to your position before stating a conclusion to your arguments. This will help present a balanced argument and demonstrate wide knowledge of the literature. Here, a critical approach becomes crucial. You need to explain why other possible arguments are unsatisfactory as well as why your own particular argument is preferable.
4. Critically evaluate
The key to tackling these question words is providing ample evidence to support your claims. Ensure that your analysis is balanced by shedding light on, and presenting a critique of, alternative perspectives. It is also important that you present extensive evidence taken from a varying range of sources.
State your conclusion clearly and state the reasons for this conclusion, drawing on factors and evidence that informed your perspective. Also try to justify your position in order to present a convincing argument to the reader.
Put another way, ‘review’ questions entail offering your opinion on the validity of the essay question. For example, you may be asked to review the literature on electoral reform in Great Britain. You'll need to give an overview of the literature. and any major arguments or issues that arose from it. You then need to comment logically and analytically on this material. What do you agree or disagree with? What have other scholars said about the subject? Are there any views that contrast with yours? What evidence are you using to support your assessment? Don’t forget to state your position clearly.
Review answers should not be purely descriptive; they must demonstrate a high level of analytical skill. The aim is not simply to regurgitate the works of other scholars, but rather to critically analyse these works.
However, when assessing a particular argument or topic, it is important that your thoughts on its significance are made clear. This must be supported by evidence, and secondary sources in the literature are a great start. Essentially, you need to convince the reader about the strength of your argument, using research to back up your assessment of the topic is essential. Highlight any limitations to your argument and remember to mention any counterarguments to your position.
Give a detailed examination of the topic by including knowledge of the various perspectives put forward by other scholars in relation to it. What are your thoughts on the subject based on the general debates in the literature? Remember to clearly state your position based on all the evidence you present.
You should also try to provide some context on why the issues and facts that you have closely examined are important. Have these issues and facts been examined differently by other scholars? If so, make a note of this. How did they differ in their approach and what are the factors that account for these alternative approaches?
‘Examine’ questions are less exploratory and discursive than some other types of question. They focus instead on asking you to critically examine particular pieces of evidence or facts to inform your analysis.
9. To what extent
Such questions require that you display the extent of your knowledge on a given subject and that you also adopt an analytical style in stating your position. This means that you must consider both sides of the argument, by present contrasting pieces of evidence. But ultimately, you must show why a particular set of evidence, or piece of information, is more valid for supporting your answer.

Question Words that Require a Descriptive Response
It is important that you provide more than one meaning if there are several of them as it shows that you are very familiar with the literature.
2. Demonstrate
Make sure you assert your position with these types of questions. It's even more important that you support your arguments with valid evidence in order to establish a strong case.
3. Describe
‘Describe’ question words focus less on the basic meaning of something, therefore, and more on its particular characteristics. These characteristics should form the building blocks of your answer.
4. Elaborate
In addition, always remember to back any claims with academic research. In explanatory answers it is important that you demonstrate a clear understanding of a research topic or argument. This comes across most convincingly if you present a clear interpretation of the subject or argument to the reader. Keep in mind any ‘what’, ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions as this will help you to structure a clear and logically coherent response. Coherence is extremely important in providing explanatory answers.
A somewhat detached, dispassionate tone can be particularly effective, in contrast to the more assertive, argumentative tone you might adopt for other types of essay question. Just remember that the key objective here is to give a nuanced account of a research topic or argument by examining its composite parts.
7. Identify
8. illustrate, 10. summarise, 11. clarify.
Such questions require you to shed light on a topic or, in some instances, break down a complex subject into simple parts. Coherence is very important for acing such questions, remembering to present your answer in a systematic manner.
12. Compare
Furthermore, you may also want to emphasise any differences, although the focus of your essay should be on establishing similarities.
13. Contrast

How to Strategically Structure Essay Based on Question Words
Understanding how to structure an essay based on question words is crucial for producing clear, focused, and compelling academic writing. The question words we analised above guide the direction of your response and dictate the type of content required. Recognising the demands of each question word allows you to strategically organise your essay, ensuring that your arguments are relevant and comprehensive. By mastering this approach, you can enhance the clarity and impact of your writing, making your academic work more persuasive and effective.
Here are a few more handy tips to bear in mind when addressing your essay questions:
When you first get your essay question, always try to understand exactly what the question means and what it is asking you to do. Look at the question word(s) and think about their meaning before you launch into planning what to write. Hopefully, our guide has shown you how to do this expertly.
Remember to read the question several times and consider any underlying assumptions behind the question. Highlight the key words and if possible, make a very basic draft outline of your response. This outline does not have to be detailed. But if you follow it as you write, it will help keep your response coherent and systematic.

How to write a first-class essay and ace your degree

Everything you need to know about exam resits

How to Identify Research Gaps
- essay writing
- essay writing service
- study skills
Writing Services
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Join 416 other subscribers.
Email Address
Understanding instruction words in academic essay titles
Posted in: essay-writing

Instruction or command words indicate what your tutor wants you to do in your written assignment. It's vital that you understand exactly what these instruction words mean so you can answer all parts of the essay question and provide a complete response.
Here's a list of some of the most common instruction/command words you'll see in essay questions (and examination questions as well), together with an explanation of what they mean.
Describe: Give a detailed account of…
Outline: Give the main features/general principles; don't include minor details.
Explain, account for, interpret: Describe the facts but also give causes and reasons for them. Depending on the context, these words may also suggest that you need to make the possible implications clear as well. For example: 'Explain X and its importance for Y'.
Comment on, criticise, evaluate, critically evaluate, assess: Judge the value of something. But first, analyse, describe and explain. Then go through the arguments for and against, laying out the arguments neutrally until the section where you make your judgement clear. Judgements should be backed by reasons and evidence.
Discuss, consider: The least specific of the instruction words. Decide, first of all, what the main issues are. Then follow the same procedures for Comment on, Criticise, Evaluate, Critically Evaluate and Assess.
Analyse: Break down into component parts. Examine critically or closely.
How far, how true, to what extent: These suggest there are various views on and various aspects to the subject. Outline some of them, evaluate their strengths and weaknesses, explore alternatives and then give your judgement.
Justify: Explain, with evidence, why something is the case, answering the main objections to your view as you go along.
Refute: Give evidence to prove why something is not the case.
Compare, contrast, distinguish, differentiate, relate: All require that you discuss how things are related to each other. Compare suggests you concentrate on similarities, which may lead to a stated preference, the justification of which should be made clear. These words suggest that two situations or ideas can be compared in a number of different ways, or from a variety of viewpoints. Contrast suggests you concentrate on differences.
Define: Write down the precise meaning of a word or phrase. Sometimes several co-existing definitions may be used and, possibly, evaluated.
Illustrate: Make clear and explicit; usually requires the use of carefully chosen examples.
State: Give a concise, clear explanation or account of…
Summarise: Give a concise, clear explanation or account of… presenting the main factors and excluding minor detail or examples (see also Outline).
Trace: Outline or follow the development of something from its initiation or point of origin.
Devise: Think up, work out a plan, solve a problem etc.
Apply (to): Put something to use, show how something can be used in a particular situation.
Identify: Put a name to, list something.
Indicate: Point out. This does not usually involve giving too much detail.
List: Make a list of a number of things. This usually involves simply remembering or finding out a number of things and putting them down one after the other.
Plan: Think about how something is to be done, made, organised, etc.
Report on: Describe what you have seen or done.
Review: Write a report on something.
Specify: Give the details of something.
Work out: Find a solution to a problem.
Adapted from: Coles, M. (1995), A Student’s Guide to Coursework Writing, University of Stirling, Stirling
Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
So wonderful can anyone get the information
Thanks Josphat!
This is a life saver, do you have a youtube channel where you talk about all this stuff? If so I would love to know about it 🙂 Rachelle
Thanks for your comment. We don't have a YouTube channel but stay tuned for more posts. You will also find additional self-directed learning resources in MySkills .
Quite helpful. I would definitely check this before my next essay.
Thank you, Dan.
Very helpful now I understand how construct my assignments and how to answer exam questions
I have understood it clearly;)
it is very useful for us to understand many instruction word and what we need to write down
There are some define of some words,and I find that there do have many common things for some words,but not all the same.Such as compare, contrast, distinguish, differentiate, relate,they all need people to compare but foucs on different ways.
Very helpful. Listed most of the words that might be misunderstood by foreign students. Now I know why my score of writing IELTS test is always 6, I even didn't get the point of what I was supposed to write!
I have already read all of this. And it gave me a brief instruction.
There are varied instruction words in essay questions. It's a good chance for me to have a overview of these main command words because I could response to requirements of questions precisely and without the risk of wandering off the topic.
When i encounter with an essay title with these instruction words above,I should understand exactly what these words mean so that i could know what my tutor would like me to do in the assignments.Also,these words may help me make an outline and read academic articles with percific purposes.
These words are accurate and appropriate. It is really helpful for me to response some assignment questions and I can know the orientation of my answers . I can also use these words to make an outline of my essay. However, in my view, for some instruction words which are confusing and hard to understand, it is better to give an example to help us understand.
It's the first time for me to recognise these instruction words , some of them are really similar with each other.
it is very helpful to my future study. it will be better to have some examples with it.
Bias-proof your GenAI: Strategies to mitigate algorithmic and human biases
As the world of Higher Education increasingly embraces the power of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI), the University is taking proactive steps to equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape. On 10 April, we started...

How to navigate Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) tools with confidence and integrity
Artificial intelligence (AI) is advancing rapidly, and new Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Elicit, Perplexity, Bard and Bing are now easily accessible online. As university students, how can you incorporate these emerging technologies into your studies and campus...
8 ways to beat procrastination
Whether you’re writing an assignment or revising for exams, getting started can be hard. Fortunately, there’s lots you can do to turn procrastination into action.

Welcome to GoodWritingHelp.com!
- How to Write an Essay
- Justification Essay
How to Write a Good Justification Essay
A justification essay is a common assignment at high school and college. Students are supposed to learn how to persuade someone in their points of view and how to express their thoughts clearly. This job is quite difficult, so you are able to improve your justification essay writing skills with the help of our professional writing guidelines.
Step One: Research Your Topic
If you want to persuade someone in the relevance and importance of your subject, you should be able to describe it in the best way. Your primary duty is to research your topic well and collect as many useful facts about it as possible. You will have to look through several books, periodicals, articles in the Internet, etc. to accumulate enough facts and arguments about your subject. Try to note all essential ideas to avoid losing them.
Step Two: Write an Outline
One cannot complete a good justification essay if he does not plan the process of writing carefully. You should plan your essay accurately and build a sound and informative piece of writing. Your outline contains all sections of your essay, all ideas, concepts, solutions and decisions. If you write down an informative outline, you will not miss any important point. You should also think about the structure of your justification essay. It should start from an introduction, proceed with the main body and finish with a denouement.
Step Three: Prepare a Sound Introduction
A good introductory part should clarify the choice of your topic, its relevance and importance. You should write in the most understandable and precise manner if you want to attract reader’s attention and to make him accept your point of view. You are able to improve your introduction with the help of bright quotations and a brilliant thesis statement that describes the whole idea of your analysis to your audience.
Step Four: Compose the Main Body
The main body of your justification essay should contain all essential ideas and quality arguments that support your opinion about the subject. Remember that you have to justify why you think in the definite way. Teachers often assign controversial topics in order to make students take the definite side in this discussion. Your duty is to prove to your audience that your point of view is better. You are able to present arguments starting from the least important ones and proceeding with the most essential arguments.
Step Five: Make a Good Conclusion
When you summarize your justification essay, you should enumerate its key points in brief. Moreover, you are able to write the final comment on your subject in order to leave space for suggestion to your readers.

How to Write a Good:
- Research Paper
- Dissertation
- Book Report
- Book Review
- Personal Statement
- Research Proposal
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Reaction Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Grant Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Movie Review
- Creative Writing
- Critical Thinking
- Article Critique
- Literature Review
- Research Summary
- English Composition
- Short Story
- Poem Analysis
- Reflection Paper
- Disciplines
Essay Types
- 5-Paragraph essay
- Admission essay
- Analytical essay
- Argumentative essay
- Cause and Effect essay
- Classification essay
- Compare and Contrast essay
- Critical essay
- Deductive essay
- Definition essay
- Descriptive essay
- Discussion essay
- Exploratory essay
- Expository essay
- Informal essay
- Narrative essay
- Personal essay
- Persuasive essay
- Research essay
- Response essay
- Scholarship essay
- 5-page essay
- Process essay
- Justification essay
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
- Writing effectively
Writing a rationale
How to write a rationale.
What is a rationale?
A rationale is when you are asked to give the reasoning or justification for an action or a choice you make.
There is a focus on the ‘ why ’ in a rationale: why you chose to do something, study or focus on something. It is a set of statements of purpose and significance and often addresses a gap or a need.
A rationale in Australian academic writing is rarely a whole task by itself. It is often a part of a bigger task. For example, a part of a lesson plan might be to provide a rationale for why you chose to teach particular content or use a certain resource or activity, or you may be asked to provide a rationale as to why you chose a particular theory to apply or a concept to support.
You may be called upon to provide a rationale:
prior to an action or decision; why you plan to do something and how, or
- after you have acted or decided something; reflecting, looking back, why you did something and how it worked or not.
You can use language to signal you are clearly providing a rationale in your writing. You can link your rationale to learning outcomes or aims for a lesson, activity or assessment task.
A model: problem-solution-rationale
A rationale can be provided by offering longer essay-based support for why it is important to do something in a certain way – in that sense, a whole paper can be a rationale.
However, a more specific or focused way of thinking about a rationale is how we can overtly show we are justifying our choices with the language we use.
One way of doing this is to consider the problem or issue requiring attention, the solution and then the rationale or justification for the solution (the ‘why’). This sets the rationale (the reason) within a context.
A diagnostic assessment determined that the students required more attention to addition and subtraction of mixed fractions. This activity intends to address this problem by having the children engage with the task with blocks before it is done with figures. The reason I chose to do this is because students have higher comprehension levels when presented with visual or tangible representations of abstract problems (Benson, 2016). I also did this as I wanted to allow the children to ‘play’ with maths, to see that it can be a fun activity and in doing so, to breakdown some of the ‘anti-mathematics prejudices’ that Gaines (2017, p. 4) talks about.
The important thing here is the language used to signal the rationale , in this case:
The reason I chose to do this is because … and I also did this as …
Another problem / solution / rationale example:
Scaffolding is the support provided by the teacher or a significant other, such as a classmate, which helps students in learning (Gibbons, 2015). Some students were having difficulty with the language at entry while others, particularly those who had completed the pre-tasks, had few problems. Therefore, in order to address this disparity in level and understanding, mixed-ability pairs were created where the more competent student helped the other. On reflection, this was an effective way to run the activity for two reasons : it allowed peer-to-peer teaching which solidified both students’ understanding; and it scaffolded the support in a way that allowed me to roam the room lending advice to pairs as needed.
The language used to signal our rationale in this example:
in order to and for two reasons …
Language to signal rationale
in order to
the reason this was done/chosen …
for the following reason(s) …
for two/three reasons …
Language for further justification - showing importance
This was important / significant because …
This meant that I could…
This enabled me to …
… which enabled / allowed me to…
… which pointed to / highlighted that / showed me that …
The key thing to remember about rationale writing is to stand back from the writing, look at it in a big picture sense and ask yourself, ‘ Have I explained why? ’ If that is clearly articulated, you have provided a rationale.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research and write about. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g., discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, relevant codes or standards or a specific timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise, instead you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia's asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
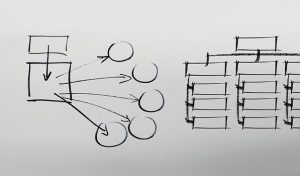
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
| Is clear, concise and well-structured | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under twenty in full. | Writes numbers under twenty as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed) | Uses humour (puns, sarcasm) |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- This essay argues…) | Writes in first person (I think, I found) |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject | Uses colloquial language e.g., mate |
Thesis statements
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
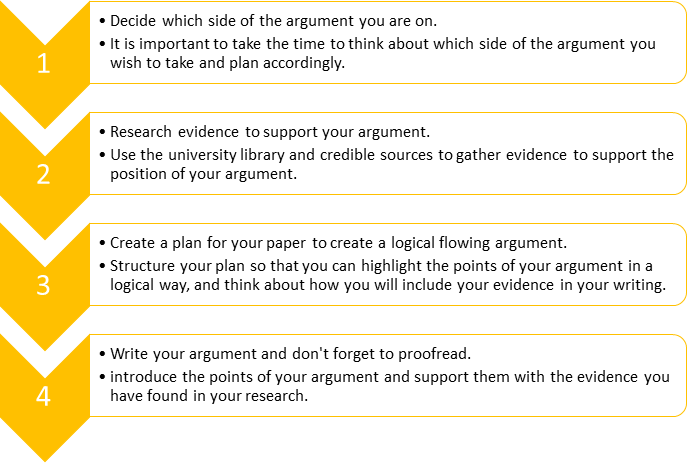
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that... • ...is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because... • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that.... • This evidence demonstrates that... • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that... |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates... • This evidence clearly demonstrates.... • This is important/significant because... • This data highlights... |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that... • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because... • Consequently, this leads to.... • The research presented therefore indicates... |

Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
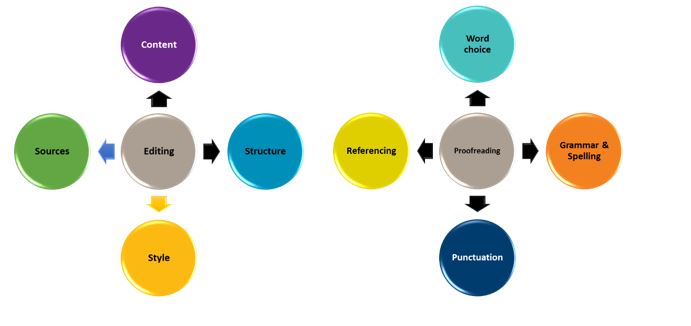
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Study Toolbox: Understanding Instructional Words in Essays, Assignments & Exams
- General Study Tips
- Note Taking
- Mind Mapping
- Searching Online Databases
- Searching Business Source Complete
- Searching CINAHL Ultimate
- Searching ProQuest Central
- Searching Science Direct
- Critically Evaluating Articles
- Critically Evaluating Websites
- Using Ebook Central
- Assignment Process
- Structure of an Academic Essay
- Understanding Instructional Words in Essays, Assignments & Exams
- Essay Checklist
- Literature Review
- APA Referencing
- Studying for Exams and Tests
- Tips for taking Exams
Before you can answer a question, you need to know what it means. When you are trying to understand the question look for instructional words, words that tell you what to do. Examples of these are analyse, describe and review.
Understanding Instructional Words
This table provides a list of instructional words and explains clearly what they require you to do in your essay, assignment or exam.
| Break down a topic into parts. Look in depth at each part using supporting arguments and evidence for and against. | |
| Present reasons and evidence to support or reject a position or viewpoint. | |
| Decide how important, useful, valuable or effective something is and give your reasons and evidence. | |
| Arrange information into groups. | |
| Present your opinion on the topic and back up your opinion with relevant evidence/information. | |
| Identify similarities between two or more topics/ideas. | |
| Identify differences between two or more topics/ideas. | |
| Identify and discuss both the similarities and differences between ideas/topics etc. | |
| Give your judgement about the value or truth of something. Discuss both positive and negative points. Support with evidence. | |
| Clearly state the exact meaning of something. | |
| Use examples or evidence to clarify and support your answer. | |
| Give a detailed account of something. No explanation or interpretation is required. | |
| Make a graph, chart or drawing to illustrate an idea. Label it and include a brief explanation. | |
| Present both sides of an issue/subject with evidence and then draw conclusions. | |
| Provide more detail with reasons and examples. | |
| Investigate closely a topic/issue etc. | |
| Make something clear by providing reasons and evidence. | |
| Select relevant details and discuss these. | |
| Examine a statement or idea and give a clear explanation/judgement of what it means. | |
| Use evidence to support an argument or idea. The aim is to convince the reader. | |
| Give a concise numbered list of things or ideas. | |
| Give the main points, do not include detail. | |
| Establish the truth of something using evidence. | |
| Show how things are connected or related to each other. | |
| Briefly and clearly present the main points. | |
| Give a concise account of the key points of the topic removing unnecessary detail. | |
| Describe the development or history of a topic from some point of origin. |
- Printable copy of Understanding Instructional Words This is a printable version of the table above. It provides a list of instructional words and explains what each requires you to do in your essay, assignment, test or exam.
- << Previous: Structure of an Academic Essay
- Next: Essay Checklist >>
- Last Updated: Jun 6, 2024 12:05 PM
- URL: https://sitacnz.libguides.com/Study_Toolbox
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Justify Your Methods in a Thesis or Dissertation

4-minute read
- 1st May 2023
Writing a thesis or dissertation is hard work. You’ve devoted countless hours to your research, and you want your results to be taken seriously. But how does your professor or evaluating committee know that they can trust your results? You convince them by justifying your research methods.
What Does Justifying Your Methods Mean?
In simple terms, your methods are the tools you use to obtain your data, and the justification (which is also called the methodology ) is the analysis of those tools. In your justification, your goal is to demonstrate that your research is both rigorously conducted and replicable so your audience recognizes that your results are legitimate.
The formatting and structure of your justification will depend on your field of study and your institution’s requirements, but below, we’ve provided questions to ask yourself as you outline your justification.
Why Did You Choose Your Method of Gathering Data?
Does your study rely on quantitative data, qualitative data, or both? Certain types of data work better for certain studies. How did you choose to gather that data? Evaluate your approach to collecting data in light of your research question. Did you consider any alternative approaches? If so, why did you decide not to use them? Highlight the pros and cons of various possible methods if necessary. Research results aren’t valid unless the data are valid, so you have to convince your reader that they are.
How Did You Evaluate Your Data?
Collecting your data was only the first part of your study. Once you had them, how did you use them? Do your results involve cross-referencing? If so, how was this accomplished? Which statistical analyses did you run, and why did you choose them? Are they common in your field? How did you make sure your data were statistically significant ? Is your effect size small, medium, or large? Numbers don’t always lend themselves to an obvious outcome. Here, you want to provide a clear link between the Methods and Results sections of your paper.
Did You Use Any Unconventional Approaches in Your Study?
Most fields have standard approaches to the research they use, but these approaches don’t work for every project. Did you use methods that other fields normally use, or did you need to come up with a different way of obtaining your data? Your reader will look at unconventional approaches with a more critical eye. Acknowledge the limitations of your method, but explain why the strengths of the method outweigh those limitations.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
What Relevant Sources Can You Cite?
You can strengthen your justification by referencing existing research in your field. Citing these references can demonstrate that you’ve followed established practices for your type of research. Or you can discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating other studies. Highlight the use of established techniques, tools, and measurements in your study. If you used an unconventional approach, justify it by providing evidence of a gap in the existing literature.
Two Final Tips:
● When you’re writing your justification, write for your audience. Your purpose here is to provide more than a technical list of details and procedures. This section should focus more on the why and less on the how .
● Consider your methodology as you’re conducting your research. Take thorough notes as you work to make sure you capture all the necessary details correctly. Eliminating any possible confusion or ambiguity will go a long way toward helping your justification.
In Conclusion:
Your goal in writing your justification is to explain not only the decisions you made but also the reasoning behind those decisions. It should be overwhelmingly clear to your audience that your study used the best possible methods to answer your research question. Properly justifying your methods will let your audience know that your research was effective and its results are valid.
Want more writing tips? Check out Proofed’s Writing Tips and Academic Writing Tips blogs. And once you’ve written your thesis or dissertation, consider sending it to us. Our editors will be happy to check your grammar, spelling, and punctuation to make sure your document is the best it can be. Check out our services for free .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Search suggestions update instantly to match the search query.

Essays: task words

Written Assignments
Explore what different task words mean and how they apply to your assignments
You'll need to understand what your assignments are asking you to do throughout your studies. Your assessments use 'task words' that explain what you need to do in your work.
Task words are the words or phrases in a brief that tell you what to do. Common examples of task words are 'discuss', 'evaluate', 'compare and contrast', and 'critically analyse'. These words are used in assessment marking criteria and will showcase how well you've answered the question.
None of these words have a fixed meaning. Your lecturers may have specific definitions for your subject or task so you should make sure you have a good idea of what these terms mean in your field. You can check this by speaking to your lecturer, checking your course handbook and reading your marking criteria carefully.
Task words and descriptions
- Account for : Similar to ‘explain’ but with a heavier focus on reasons why something is or is not the way it is.
- Analyse : This term has the widest range of meanings according to the subject. Make a justified selection of some of the essential features of an artefact, idea or issue. Examine how these relate to each other and to other ideas, in order to help better understand the topic. See ideas and problems in different ways, and provide evidence for those ways of seeing them.
- Assess : This has very different meanings in different disciplines. Measure or evaluate one or more aspect of something (for example, the effectiveness, significance or 'truth' of something). Show in detail the outcomes of these evaluations.
- Compare : Show how two or more things are similar.
- Compare and contrast : Show similarities and differences between two or more things.
- Contrast : Show how two or more things are different.
- Critically analyse : As with analysis, but questioning and testing the strength of your and others’ analyses from different perspectives. This often means using the process of analysis to make the whole essay an objective, reasoned argument for your overall case or position.
- Critically assess : As with “assess”, but emphasising your judgments made about arguments by others, and about what you are assessing from different perspectives. This often means making the whole essay a reasoned argument for your overall case, based on your judgments.
- Critically evaluate : As with 'evaluate', but showing how judgments vary from different perspectives and how some judgments are stronger than others. This often means creating an objective, reasoned argument for your overall case, based on the evaluation from different perspectives.
- Define : Present a precise meaning.
- Describe : Say what something is like. Give its relevant qualities. Depending on the nature of the task, descriptions may need to be brief or the may need to be very detailed.
- Discuss : Provide details about and evidence for or against two or more different views or ideas, often with reference to a statement in the title. Discussion often includes explaining which views or ideas seem stronger.
- Examine : Look closely at something. Think and write about the detail, and question it where appropriate.
- Explain : Give enough description or information to make something clear or easy to understand.
- Explore : Consider an idea or topic broadly, searching out related and/or particularly relevant, interesting or debatable points.
- Evaluate : Similar to “assess”, this often has more emphasis on an overall judgement of something, explaining the extent to which it is, for example, effective, useful, or true. Evaluation is therefore sometimes more subjective and contestable than some kinds of pure assessment.
- Identify : Show that you have recognised one or more key or significant piece of evidence, thing, idea, problem, fact, theory, or example.
- Illustrate : Give selected examples of something to help describe or explain it, or use diagrams or other visual aids to help describe or explain something.
- Justify : Explain the reasons, usually “good” reasons, for something being done or believed, considering different possible views and ideas.
- Outline : Provide the main points or ideas, normally without going into detail.
- Summarise : This is similar to 'outline'. State, or re-state, the most important parts of something so that it is represented 'in miniature'. It should be concise and precise.
- State : Express briefly and clearly.
Download our essay task words revision sheet
Download this page as a PDF for your essay writing revision notes.
Writing: flow and coherence

Writing clear sentences
Explore our top tips for writing clear sentences and download our help sheet.

Assignments usually ask you to demonstrate that you have immersed yourself in the course material and that you've done some thinking on your own; questions not treated at length in class often serve as assignments. Fortunately, if you've put the time into getting to know the material, then you've almost certainly begun thinking independently. In responding to assignments, keep in mind the following advice.
- Beware of straying. Especially in the draft stage, "discussion" and "analysis" can lead you from one intrinsically interesting problem to another, then another, and then ... You may wind up following a garden of forking paths and lose your way. To prevent this, stop periodically while drafting your essay and reread the assignment. Its purposes are likely to become clearer.
- Consider the assignment in relation to previous and upcoming assignments. Ask yourself what is new about the task you're setting out to do. Instructors often design assignments to build in complexity. Knowing where an assignment falls in this progression can help you concentrate on the specific, fresh challenges at hand.
Understanding some key words commonly used in assignments also may simplify your task. Toward this end, let's take a look at two seemingly impenetrable instructions: "discuss" and "analyze."
1. Discuss the role of gender in bringing about the French Revolution.
- "Discuss" is easy to misunderstand because the word calls to mind the oral/spoken dimension of communication. "Discuss" suggests conversation, which often is casual and undirected. In the context of an assignment, however, discussion entails fulfilling a defined and organized task: to construct an argument that considers and responds to an ample range of materials. To "discuss," in assignment language, means to make a broad argument about a set of arguments you have studied. In the case above, you can do this by
- pointing to consistencies and inconsistencies in the evidence of gendered causes of the Revolution;
- raising the implications of these consistencies and/or inconsistencies (perhaps they suggest a limited role for gender as catalyst);
- evaluating different claims about the role of gender; and
- asking what is gained and what is lost by focusing on gendered symbols, icons and events.
A weak discussion essay in response to the question above might simply list a few aspects of the Revolution—the image of Liberty, the executions of the King and Marie Antoinette, the cry "Liberte, Egalite, Fraternite!" —and make separate comments about how each, being "gendered," is therefore a powerful political force. Such an essay would offer no original thesis, but instead restate the question asked in the assignment (i.e., "The role of gender was very important in the French Revolution" or "Gender did not play a large role in the French Revolution").
In a strong discussion essay, the thesis would go beyond a basic restatement of the assignment question. You might test the similarities and differences of the revolutionary aspects being discussed. You might draw on fresh or unexpected evidence, perhaps using as a source an intriguing reading that was only briefly touched upon in lecture.
2. Analyze two of Chaucer's Canterbury Tales, including one not discussed in class, as literary works and in terms of sources/analogues.
The words "analyze" and "analysis" may seem to denote highly advanced, even arcane skills, possessed in virtual monopoly by mathematicians and scientists. Happily, the terms refer to mental activity we all perform regularly; the terms just need decoding. "Analyze" means two things in this specific assignment prompt.
- First, you need to divide the two tales into parts, elements, or features. You might start with a basic approach: looking at the beginning, middle, and end. These structural features of literary works—and of historical events and many other subjects of academic study—may seem simple or even simplistic, but they can yield surprising insights when examined closely.
- Alternatively, you might begin at a more complex level of analysis. For example, you might search for and distinguish between kinds of humor in the two tales and their sources in Boccaccio or the Roman de la Rose: banter, wordplay, bawdy jokes, pranks, burlesque, satire, etc.
Second, you need to consider the two tales critically to arrive at some reward for having observed how the tales are made and where they came from (their sources/analogues). In the course of your essay, you might work your way to investigating Chaucer's broader attitude toward his sources, which alternates between playful variation and strict adherence. Your complex analysis of kinds of humor might reveal differing conceptions of masculine and feminine between Chaucer and his literary sources, or some other important cultural distinction.
Analysis involves both a set of observations about the composition or workings of your subject and a critical approach that keeps you from noticing just anything—from excessive listing or summarizing—and instead leads you to construct an interpretation, using textual evidence to support your ideas.
Some Final Advice
If, having read the assignment carefully, you're still confused by it, don't hesitate to ask for clarification from your instructor. He or she may be able to elucidate the question or to furnish some sample responses to the assignment. Knowing the expectations of an assignment can help when you're feeling puzzled. Conversely, knowing the boundaries can head off trouble if you're contemplating an unorthodox approach. In either case, before you go to your instructor, it's a good idea to list, underline or circle the specific places in the assignment where the language makes you feel uncertain.
William C. Rice, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
Home » Microsoft Word » How to justify text in MS Word
How to justify text in MS Word
To simply put, a justified text is spaced so that the sides of your paragraphs are aligned to both the left and right margins.
MS Word automatically fills in spaces between words to achieve clean-cut edges rendering paragraph lines to be of the same length.

3 Ways to Justify Text in Word
- Using the Justify text-alignment button
- Using a shortcut key
- Using the Context menu
Lets get started.
Method 1: Using the Justify Text-alignment Button
Step 1: open an ms word document. .

Step 2: Select the text.
Select the text that you want to be justified. Then, go to the Home tab and select the Justify icon found under the Paragraph group.

This will justify the selected text.
Method 2: Using a Shortcut Key

Select the text you want to justify.
Now, hit the CTRL + J keys on your keyboard to justify the selected text.

There you have it! You’ve just used a shortcut key to justify text in Word!
Method 3: Using the Context Menu
Step 1: open a word document. .

Now that you have your document ready, go ahead and select the text that you want to be justified.

Step 3: Access the Context menu.
This will display the Paragraph dialogue box right in the middle of your screen.
On the dialogue box, under Indents and Spacing , click the Alignment drop-down menu and select Justified .

Click the OK button to save or Cancel to revert changes.

Voila! You’ve just used the context menu to justify text in Word.
We hope you’ve found this article helpful!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Adjusting Justification in Word: A Step-by-Step Guide
Adjusting justification in Word is a quick and simple process. It involves selecting the text you want to justify, clicking on the ‘Home’ tab, and then choosing your desired justification option from the ‘Paragraph’ group. Once you click on your chosen justification style, your text will instantly adjust.
After you complete the action, the text will align based on the justification you selected. If you chose left justification, it will align to the left, and if you chose right, it will align to the right. Center justification will center your text, and full justification will spread it out to align both left and right.
Introduction
When it comes to creating professional-looking documents, the justification of your text is a crucial element that often goes overlooked. Justification refers to the alignment of text within a document. It can affect the overall appearance and readability of your work. Whether you’re typing up an essay, a report, or a resume, knowing how to adjust the justification of your text in Microsoft Word is essential.
Not only does proper justification make your document look neater, but it also impacts how easily your readers can follow along. After all, we’ve all struggled to read a poorly formatted document at some point, right? This article is relevant to students, professionals, writers, and anyone in between who seeks to enhance their Word documents. Let’s dive into the step-by-step process of adjusting justification in Word.
Adjusting Justification in Word Tutorial
Before we get into the steps, let’s discuss what adjusting justification will accomplish. By following these steps, you’ll be able to change how your text lines up on the page. This is useful for meeting specific formatting guidelines, enhancing the flow of your document, or simply making it look more aesthetically pleasing.
Step 1: Select the Text
- Select the text you want to adjust.
Once you’ve highlighted the text, you’re ready to start adjusting the justification. Make sure you only select the text you want to change, as the justification will apply to whatever is highlighted.
Step 2: Click on the ‘Home’ Tab
Find and click on the ‘Home’ tab in the Word ribbon.
The ‘Home’ tab is where you’ll find most of the basic formatting options, including font type, size, and, of course, paragraph justification. It’s usually located at the top of your Word document.
Step 3: Choose the Justification Style
In the ‘Paragraph’ group, click on your desired justification style.
You’ll see four different options for justification: align text left, center, align text right, and justify. The icons are pretty self-explanatory, but feel free to hover over them with your cursor to see a tooltip with each one’s function.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved Readability | Adjusting justification can greatly improve the readability of your document. Proper alignment can make your text more organized and easy to follow, which is especially important for longer documents. |
| Professional Appearance | A well-justified document looks neat and professional. It gives the impression that you’ve put thought and care into the presentation of your work, which can be crucial in professional or academic settings. |
| Meets Formatting Requirements | Many documents, such as academic papers or business reports, have specific formatting guidelines that include text justification. Knowing how to adjust this in Word helps you meet those requirements with ease. |
| Drawback | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Uneven Spacing | Full justification, while making both sides of the text align, can sometimes create awkward spaces between words. This can disrupt the flow of reading if not adjusted properly. |
| Inconsistent Appearance | If used incorrectly, adjusting justification can make different sections of your document look inconsistent. It’s important to apply justification styles thoughtfully to maintain a cohesive look. |
| Overlooked Detail | Some may find adjusting justification to be an unnecessary detail that doesn’t impact the overall content. However, overlooking this aspect can detract from the professionalism of your document. |
Additional Information
Adjusting the justification in Word is more than just choosing how your text aligns. It’s about presenting your information in the clearest, most accessible way possible. Remember, the goal is to make your document as reader-friendly as possible.
For instance, if you’re working on a resume, you may want to use left justification for the main body to keep it clean and uniform. But maybe you decide to center-justify your name and contact information at the top to make it stand out. It’s these small details that can make a big difference.
Also, consider the type of document you’re creating. Novels and books usually use full justification because it creates a clean look that’s easy on the eyes for long reading sessions. On the other hand, business emails or letters often use left justification because it’s straightforward and conventional.
Lastly, don’t be afraid to mix and match different justifications in the same document. As long as it’s done tastefully, it can add visual interest and help guide the reader’s eye to the most important information.
- Click on the ‘Home’ tab.
- Choose your desired justification style.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is text justification.
Text justification refers to the alignment of text within a document. It can be aligned to the left, center, right, or justified, which aligns it evenly on both the left and right sides.
Can I justify a single word?
Justifying a single word wouldn’t make much sense, as justification affects how a line or paragraph of text aligns. If you’re looking to emphasize a single word, consider other formatting options like bold or italics.
Does justification affect document formatting?
Yes, how you justify your text can affect the overall formatting and appearance of your document. It’s an important aspect of document design.
Can I undo a justification change?
Absolutely. If you change your mind after justifying text, simply click ‘Undo’ or press ‘Ctrl + Z’ on your keyboard to revert the changes.
Why does full justification create uneven spaces between words?
Full justification aims to align both sides of the text to the margins, which can sometimes result in irregular spacing to fill the line fully. This can be adjusted manually if needed.
Adjusting justification in Word might seem like a small detail, but it’s one that can have a significant impact on the look and readability of your document. Whether you’re aligning to the left for a formal letter, centering for an invitation, or using full justification for a report, the power is in your hands to enhance your document’s presentation.
Remember, while content is king, presentation is queen. A well-justified document can speak volumes about your attention to detail and care for your audience. So next time you open up Word to start typing, take a moment to adjust your justification—it could make all the difference.

Matthew Burleigh has been writing tech tutorials since 2008. His writing has appeared on dozens of different websites and been read over 50 million times.
After receiving his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Computer Science he spent several years working in IT management for small businesses. However, he now works full time writing content online and creating websites.
His main writing topics include iPhones, Microsoft Office, Google Apps, Android, and Photoshop, but he has also written about many other tech topics as well.
Read his full bio here.
Share this:
Join our free newsletter.
Featured guides and deals
You may opt out at any time. Read our Privacy Policy
Related posts:
- How to Justify Text in Excel 2010
- How to Remove Section Breaks in Word Documents
- How to Insert Text Box in Google Docs
- How to Clear Formatting in Google Docs
- How to Subscript in Google Docs (An Easy 4 Step Guide)
- How to Do a Hanging Indent on Google Docs
- How to Center Text in Word [2023 Guide]
- How to Make All Columns the Same Width in Excel 2013
- How to Return to Normal View in Word 2010
- How to Select All in Word for Office 365
- How to Single Space in Word for Office 365
- How to Hide Formatting Marks in Word 2010
- How to Vertically Center Text in Word 2013
- How to Insert a Square Root Symbol in Word
- How to Double Space in Word Documents
- How to Remove Underline in Word for Office 365
- How Do I Do a Grammar Check on Word Documents?
- How to Remove Strikethrough in Google Docs (A Simple 4 Step Guide)
- How to Count Characters in Microsoft Word 2013 (A Quick 3 Step Guide)
- How to Save as doc Instead of docx in Word 2010 By Default

Understanding your assignment questions: A short guide
- Introduction
- Breaking down the question
Directive or task words
Task works for science based essays.
- Further reading and references
It is really important to understand the directive or task word used in your assignment.
This will indicate how you should write and what the purpose of the assignment in. The following examples show some task words and their definitions.
However, it is important to note that none of these words has a fixed meaning. The definitions given are a general guide, and interpretation of the words may vary according to the context and the discipline.
If you are unsure as the exactly what a lecturer means by a particular task word, you should ask for clarification.
Analyse : Break up into parts; investigate
Comment on : Identify and write about the main issues; give your reactions based on what you've read/ heard in lectures. Avoid just personal opinion.
Compare : Look for the similarities between two things. Show the relevance or consequences of these similarities concluding which is preferable.
Contrast : Identify the differences between two items or arguments. Show whether the differences are significant. Perhaps give reasons why one is preferable.
Criticise : Requires an answer that points out mistakes or weaknesses, and which also indicates any favourable aspects of the subject of the question. It requires a balanced answer.
Critically evaluate : Weigh arguments for and against something, assessing the strength of the evidence on both sides. Use criteria to guide your assessment of which opinions, theories, models or items are preferable.
Define : Give the exact meaning of. Where relevant, show you understand how the definition may be problematic.
Describe : To describe is to give an observational account of something and would deal with what happened, where it happened, when it happened and who was involved. Spell out the main aspects of an idea or topic or the sequence in which a series of things happened.
Discuss : Investigate or examine by argument; sift and debate; give reasons for and against; examine the implications.
Evaluate : Assess and give your judgement about the merit, importance or usefulness of something using evidence to support your argument.
Examine : Look closely into something
Explain : Offer a detailed and exact rationale behind an idea or principle, or a set of reasons for a situation or attitude. Make clear how and why something happens.
Explore : Examine thoroughly; consider from a variety of viewpoints
Illustrate : Make something clear and explicit, give examples of evidence
Justify : Give evidence that supports and argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made
Outline : Give the main points/features/general principles; show the main structure and interrelations; omit details and examples
State : Give the main features briefly and clearly
Summarise : Draw out the main points only; omit details and examples
To what extent... : Consider how far something is true, or contributes to a final outcome. Consider also ways in which it is not true.
Task Words:
How to write e.g., discuss, argue etc.
Subject Matter:
What you should be writing about.
Limiting Words:
May narrow or change the focus of your answer. (Important - they stop you from including irrelevant info)
Below are some examples of questions and tips on how you might think about answering them.
Compare acute and chronic pain in terms of pathophysiology and treatment
Compare - Make sure you are comparing and not just describing the two things in isolation
Acute and chronic pain - Subject matter
In terms of pathophysiology and treatment - Important limiting phrase - focus ONLY on these things. Use them as a lens to highlight the differences between acute and chronic pain.
Tip : Assignments that ask you to compare two things can be structured in different ways. You may choose to alternate continually between the two things, making direct comparisons and organising your essay according to themes. Alternatively, you may choose to discuss one thing fully and then the next. If you choose the second approach, you must make the links and comparisons between the two things completely clear.
With reference to any particular example enzyme, outline the key structural and functional properties of its active site
With reference to any particular example enzyme - Important limiting phase - focus your answer on a specific example. Use this example to help demonstrate your understanding.
Outline - Factual description is needed. You must demonstrate your knowledge and understanding.
The key structural and functional properties of its active site - Subject matter
Tip : Assignments that ask you to outline or describe are assessing your understanding of the topic. You must express facts clearly and precisely, using examples to illuminate them.
There is no convincing evidence for the existence of life outside our solar systems
There is - Task words not so obvious this time. Try turning the title into a question: 'Is there any convincing evidence for...?'
Convincing - Important limiting word- there may be evidence but you need to assess whether or not it is convincing.
For the existence of life outside of our solar system - Subject matter
Tip : Assignment titles that are on actually a question are often simply asking 'how true is this statement?' You must present reasons it could be true and reasons it might not be, supported by evidence and recognising the complexity of the statement.
To what extent can nuclear power provide a solution to environmental issues?
Discuss - Explore the topic from different angles, in a critical way (not purely descriptive)
Nuclear power - Subject matter
Provide a solution to - Limiting phrase: discuss ways it can and ways it can't- don't be afraid to take a position based on evidence.
Environmental issues - Subject matter. Might be an idea to define/ discuss what could be meant by environmental issues? This might be important for your argument.
Tip : If an assignment is asking a direct question, make sure your essay answers it. Address it directly in the introduction, make sure each paragraph contributes something towards your response to it, and reinforce your response in your conclusion.
Discuss the issue of patient autonomy in relation to at least one case study
The issue of patient autonomy - Subject matter
In relation to at least one case study - Important limiting phrase - don't just discuss the issue of patient autonomy in general; discuss it in the context of one or more case studies. You should use the case study to illustrate all of your points about patient autonomy.
Tip : Assignments that ask you to discuss in relation to a case study, or to a placement or own experience, usually want to see a clear link between theory and practice (reality).
- << Previous: Breaking down the question
- Next: Further reading and references >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 4:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.bham.ac.uk/asc/understandingassignments
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of justify
transitive verb
intransitive verb
maintain , assert , defend , vindicate , justify mean to uphold as true, right, just, or reasonable.
maintain stresses firmness of conviction.
assert suggests determination to make others accept one's claim.
defend implies maintaining in the face of attack or criticism.
vindicate implies successfully defending.
justify implies showing to be true, just, or valid by appeal to a standard or to precedent.
Examples of justify in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'justify.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Middle English justifien , from Anglo-French or Late Latin; Anglo-French justifier , from Late Latin justificare , from Latin justus — see just entry 1
14th century, in the meaning defined at transitive sense 1a
Phrases Containing justify
- justify oneself
Dictionary Entries Near justify
justifying space
Cite this Entry
“Justify.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/justify. Accessed 30 Jun. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of justify, legal definition, legal definition of justify, more from merriam-webster on justify.
Nglish: Translation of justify for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of justify for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, flower etymologies for your spring garden, 12 star wars words, 'swash', 'praya', and 12 more beachy words, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, games & quizzes.

Justification (Typesetting and Composition)
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
SEAN GLADWELL / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In typesetting and printing, the process or result of spacing text so that the lines come out even at the margins .
The lines of text on this page are left-justified— that is, the text is lined up evenly on the left side of the page but not on the right (which is called ragged right ). As a general rule, use left justification when preparing essays, reports, and research papers.
Pronunciation: jus-te-feh-KAY-shen
Examples and Observations
" Research papers follow a standard presentation format...Do not right- justify (align) your paper. The right margins should be ragged. Your computer will automatically justify your left margin." (Laurie Rozakis, Schaum's Quick Guide to Writing Great Research Papers . McGraw-Hill, 2007)
Manuscript Guidelines (Chicago Style)
"To avoid the appearance of inconsistent spacing between words and sentences, all text in a manuscript should be presented flush left (ragged right)--that is, lines should not be 'justified' to the right margin. To leave enough room for handwritten queries, margins of at least one inch should appear on all four sides of the hard copy." ( The Chicago Manual of Style , 16th ed. The University of Chicago Press, 2010)
Full Justification
"Left- justified margins are generally easier to read than full-justified margins that can produce irregular spaces between words and unwanted blocks of text. However, because left-justified (ragged-right) margins look informal, full-justified text is more appropriate for publications aimed at a broad readership that expects a more formal, polished appearance. Further, full justification is often useful with multiple-column formats because the spaces between the columns (called alleys ) need the definition that full justification provides." (Gerald J. Alred, Charles T. Brusaw, and Walter E. Oliu, The Business Writer's Handbook , 7th ed. Macmillan, 2003)
Justification on Resumes
"Do not set full justification on an ASCII resume . Instead, left justify all lines so the right margin is ragged." (Pat Criscito, How to Write Better Résumés and Cover Letters . Barron's Educational Series, 2008)
- What Is Justification in Page Layout and Typography?
- Common Keyboard Symbols: Names, Uses, and Styles
- Forced Justification for Aligning Text
- Margin (Composition Format) Definition
- How to Set Justified Text With CSS
- The Correct Usage of the HTML P and BR Elements
- 140 Key Copyediting Terms and What They Mean
- How to Use CSS to Center Images and Other HTML Objects
- What Is an Indentation?
- Definition and Examples of Spacing in Composition
- Formatting Papers in Chicago Style
- Publishing Your Family History Book
- Page Layout Measurements in Points and Picas
- Add a Single Line Break in Dreamweaver Design View
- How to Indent Paragraphs With CSS
- How to Use Pull Quotes to Add Visual Flare to Articles

Justify , justified , justification , or full justified is text that is both left-aligned and right-aligned. For example, this paragraph of text is justified. As you can see, there is no ragged edge on either the left or right side of the text. To make both sides of the text straight extra spacing is added between each of the words.
The last line of the paragraph is always left-aligned, as seen above.
The term "justify" is not a synonym for "align" or "alignment." These terms have different meanings. See the alignment definition for its meaning.
What is the keyboard shortcut for justify?
In Microsoft Word , use the Ctrl + J keyboard shortcut to justify any text. In Google Docs , use the Ctrl + Shift + J keyboard shortcut.
Related information
- How to align text in Microsoft Word, Writer, and Google Docs.
- How to align text in Microsoft Excel, Calc, and Google Sheets.
- How to align text on a web page in HTML or CSS.
Center , Left align , Margin , Right align , Typography terms , Word processor terms , Word wrap
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Meaning of justify
When being asked to justify some conclusion, is it same as to prove it?
My memory tells me that "justify" has been used to describe some informal verification, not necessarily formal proof. I wonder if it is true? If yes, in what sense is "justify" informal? For example, only need to prove necessarity not sufficiency?
Thanks and regards!
- terminology
- $\begingroup$ It probably depends strongly on context. In my experience it means anything from "provide some evidence" to "prove." $\endgroup$ – Qiaochu Yuan Commented May 30, 2011 at 14:15
- $\begingroup$ @Qiaochu: Thanks! Do you mean necessary condition of the conclusion by "evidence"? $\endgroup$ – Tim Commented May 30, 2011 at 14:26
- 2 $\begingroup$ Doesn't that depend on what you're being asked to justify? $\endgroup$ – Qiaochu Yuan Commented May 30, 2011 at 15:15
5 Answers 5
A computation, properly laid out, is of course a proof. However, many students, after years of multiple choice tests, have learned to take the point of view that the answer is the only thing that matters.
"Justify" can be a reminder that the problem will be graded carefully, that (contrary to their usual experience) a slapdash computation will not necessarily get full marks.
I do not think that "justify" carries any connotation of "you need only show necessity but not sufficiency."
"Prove," in a course context, can often mean that a more or less specific set of tools should be used. "Justify" has a more informal feel, but I do not think of it as carrying a lower level of precision.
- $\begingroup$ Yes, in hindsight this agrees with my experience as well. I guess one interpretation of "justify" is "make sure to use words." $\endgroup$ – Qiaochu Yuan Commented May 30, 2011 at 18:16
To me, "justify" means to lay out the mathematical thought process step by step, so that the line from the starting point to the ending point is connected.
It is a bit less formal than a proof, which has certain logical requirements, but it means, "show enough work so that I know that you get the whole thing."
"Justify," just like its buddy "show," really means "prove."
I also encounter "justify", other than as a synonym for "prove", in meta-mathematical discussion. Sometimes (a lot of the time) the author of a book will invent a notation for a particular object being studied. In this case he/she might "justify" the invented notation, which usually means giving a reason why it's not arbitrary.
For example, while the sum of real valued functions is a different operation than the sum of real numbers, the same symbol "+" is used. I don't think this is the best example, but there's a plethora of them if one looks.
I guess justify means don't assume away.
Some possible exam questions:
1 Prove Borel-Cantelli Lemma.
2 Show that the series given below satisfies the differential equation. Justify all your steps.
3 Show that the series given below satisfies the differential equation. You do not have to justify switching derivative and summation.
In case 2, the professor is saying one cannot assume certain steps are valid as was done in previous classes. In this class, we proved things we assumed away in previous classes. You are to prove them here as well.
In case 3, the professor is saying one can assume said steps are valid.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged terminology ..
- Featured on Meta
- Upcoming sign-up experiments related to tags
Hot Network Questions
- Movie about a planet where seeds must be harvested just right in order to liberate a valuable crystal within
- What is a positive coinductive type and why are they so bad?
- Geometry question about a six-pack of beer
- Is the zero vector necessary to do quantum mechanics?
- Can I get a refund for ICE due to cancelled regional bus service?
- Summation of arithmetic series
- Embedded terminal for Nautilus >= version 43
- Do Christians believe that Jews and Muslims go to hell?
- Duplicating Matryoshka dolls
- How is Victor Timely a variant of He Who Remains in the 19th century?
- Is it consistent with ZFC that the real line is approachable by sets with no accumulation points?
- A 90s (maybe) made-for-TV movie (maybe) about a group of trainees on a spaceship. There is some kind of emergency and all experienced officers die
- Integration of the product of two exponential functions
- What is the translation of misgendering in French?
- Are ordinary or qualified dividends taxed first?
- Was BCD a limiting factor on 6502 speed?
- How to Pick Out Strings of a Specified Length
- Have children's car seats not been proven to be more effective than seat belts alone for kids older than 24 months?
- Can you help me to identify the aircraft in a 1920s photograph?
- Folk stories and notions in mathematics that are likely false, inaccurate, apocryphal, or poorly founded?
- Navigation on Mars without Martian GPS
- How can a landlord receive rent in cash using western union
- How to make D&D easier for kids?
- Do known physical systems all have a unique time evolution?
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of justify verb from the Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary
| present simple I / you / we / they justify | /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪ/ /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪ/ |
| he / she / it justifies | /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪz/ /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪz/ |
| past simple justified | /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪd/ /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪd/ |
| past participle justified | /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪd/ /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪd/ |
| -ing form justifying | /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪɪŋ/ /ˈdʒʌstɪfaɪɪŋ/ |
- justify doing something How can they justify paying such huge salaries?
- justify somebody/something doing something The results of the inquiry did not justify them departing from their existing policy.
- justify something Her success had justified the faith her teachers had put in her.
- Can you really justify the destruction of such a fine old building?
- The decision is justified on the grounds that there is no realistic alternative.
- The events that followed served to justify our earlier decision.
- The extra effort involved would go a long way in helping to justify their high price tags.
- The meagre result hardly justified the risks they took to get it.
- The university could not easily justify spending the money on this.
- It would be difficult for an employer to justify dismissing someone on those grounds.
- on the grounds of something
- on the grounds that…
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
- justify something/yourself The senator made an attempt to justify his actions .
- justify something/yourself to somebody The Prime Minister has been asked to justify the decision to Parliament.
- You don't need to justify yourself to me.
- justify doing something He sought to justify taking these measures by citing the threat of a terrorist attack.
- justify somebody/something doing something The press release was intended to justify them sacking her.
- He found it very difficult to justify his decision.
- Can you justify that accusation?
- How will you justify this pay cut to your employees?
- justify something (specialist) to arrange lines of printed text so that one or both edges are straight
- He defended a morality in which the end justifies the means.
- That's only OK if you believe that the end justifies the means.
Nearby words
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of justify in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- How can you justify the employment of capital punishment ?
- New evidence from a self-confessed liar was not enough to justify a retrial .
- Manufacturers need large sales to justify offering a big variety in export markets .
- We are duty bound to justify how we spend our funds .
- They haven't been given these rights for all eternity - they should justify having them just like most other people have to.
- account (to someone ) for something
- accountability
- adumbration
- demythologize
- indefinably
- indescribably
- inexpressibly
- justificatory
- lay something out
- walk through something
- what is he, are they, etc. like? idiom
justify | American Dictionary
- justification
Examples of justify
Translations of justify.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
sink or swim
If you are left to sink or swim, you are given no help so that you succeed or fail completely by your own efforts.

Fakes and forgeries (Things that are not what they seem to be)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- justify yourself
- Translations
- All translations
To add justify to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add justify to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition of Question Words with Examples. Words such as 'explain', 'evaluate' or 'analyse' - typical question words used in essay titles - provide a useful indication of how your essay should be structured. They often require varying degrees of critical responses. Sometimes, they may simply require a descriptive answer.
Here's a list of some of the most common instruction/command words you'll see in essay questions (and examination questions as well), together with an explanation of what they mean. Describe: Give a detailed account of…. Outline: Give the main features/general principles; don't include minor details. Explain, account for, interpret: Describe ...
Step Four: Compose the Main Body. The main body of your justification essay should contain all essential ideas and quality arguments that support your opinion about the subject. Remember that you have to justify why you think in the definite way. Teachers often assign controversial topics in order to make students take the definite side in this ...
What is a rationale? A rationale is when you are asked to give the reasoning or justification for an action or a choice you make. There is a focus on the 'why' in a rationale: why you chose to do something, study or focus on something. It is a set of statements of purpose and significance and often addresses a gap or a need.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Justify: Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements.
Examine a statement or idea and give a clear explanation/judgement of what it means. Justify: Use evidence to support an argument or idea. The aim is to convince the reader. List: Give a concise numbered list of things or ideas. Outline: Give the main points, do not include detail. Prove: Establish the truth of something using evidence. Relate
Two Final Tips: When you're writing your justification, write for your audience. Your purpose here is to provide more than a technical list of details and procedures. This section should focus more on the why and less on the how. Consider your methodology as you're conducting your research.
Account for: Similar to 'explain' but with a heavier focus on reasons why something is or is not the way it is.; Analyse: This term has the widest range of meanings according to the subject.Make a justified selection of some of the essential features of an artefact, idea or issue. Examine how these relate to each other and to other ideas, in order to help better understand the topic.
In the context of an assignment, however, discussion entails fulfilling a defined and organized task: to construct an argument that considers and responds to an ample range of materials. To "discuss," in assignment language, means to make a broad argument about a set of arguments you have studied. In the case above, you can do this by
Method 1: Using the Justify Text-alignment Button. Step 1: Open an MS Word document. Step 2: Select the text. Select the text that you want to be justified. Then, go to the Home tab and select the Justify icon found under the Paragraph group. This will justify the selected text.
Step 2: Click on the 'Home' Tab. Find and click on the 'Home' tab in the Word ribbon. The 'Home' tab is where you'll find most of the basic formatting options, including font type, size, and, of course, paragraph justification. It's usually located at the top of your Word document.
Justify: Give evidence that supports and argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Outline: Give the main points/features/general principles; show the main structure and interrelations; omit details and examples. State: Give the main features briefly and clearly. Summarise: Draw out the main points only; omit details and ...
the statement. Conclude by listing the most important factors and justify why you agree/disagree. Define Clearly state the meaning, and list the qualities, traits and characteristics. Describe Provide a detailed explanation about how and why something happens. Discuss Make a case for or against an argument and reach a conclusion. Point out the
2 justify something/yourself (to somebody) justify (somebody/something) doing something to give an explanation or excuse for something or for doing something synonym defend The Secretary of Education has been asked to justify the decision to Congress. You don't need to justify yourself to me.
justify: [verb] to prove or show to be just, right, or reasonable. to show to have had a sufficient legal reason. to qualify (oneself) as a surety (see surety 3) by taking oath to the ownership of sufficient property.
In typesetting and printing, the process or result of spacing text so that the lines come out even at the margins . The lines of text on this page are left-justified— that is, the text is lined up evenly on the left side of the page but not on the right (which is called ragged right ). As a general rule, use left justification when preparing ...
Justify, justified, justification, or full justified is text that is both left-aligned and right-aligned. For example, this paragraph of text is justified. As you can see, there is no ragged edge on either the left or right side of the text. To make both sides of the text straight extra spacing is added between each of the words. The last line ...
JUSTIFY meaning: 1. to give or to be a good reason for: 2. If you justify yourself, you give a good reason for what…. Learn more.
To me, "justify" means to lay out the mathematical thought process step by step, so that the line from the starting point to the ending point is connected. It is a bit less formal than a proof, which has certain logical requirements, but it means, "show enough work so that I know that you get the whole thing." Share. Cite.
justify something/yourself The senator made an attempt to justify his actions. justify something/yourself to somebody The Prime Minister has been asked to justify the decision to Parliament. You don't need to justify yourself to me. justify doing something He sought to justify taking these measures by citing the threat of a terrorist attack.
JUSTIFY definition: 1. to give or to be a good reason for: 2. If you justify yourself, you give a good reason for what…. Learn more.
Analyse them.Key instruction words in as. tasksAnalyseWhen you analyse something you consider it carefully and in detail in order to understand. r explain it. To analyse, identify the main parts or ideas of a subject and examine or interpret the connections. m.Comment onWhen you comment on a subject or the ideas in a subject, you say something ...
does not provide an application form, any individual who otherwise indicates a specific desire to an employer or other covered entity to be considered for employment. Except for recordkeeping purposes, "Applicant" is also an individual who can prove that he or she hasthey have been deterred from applying for a job by an employer's or
rejection, or assignment of any executory contract or unexpired lease of the debtor not previously rejected under such section; "(3) provide for— "(A) the settlement or adjustment of any claim or interest belonging to the debtor or to the estate; or "(B) the retention and enforcement by the debtor, by the trustee, or
but does not include work of a kind that is excluded from this definition by the regulations. classof accreditation means a class of accreditation prescribed under section 54 (5). classof registration means a class of registration prescribed under section 6 (4). close associatehas the same meaning as it has in theHome Building Act 1989.