- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Psychological Steps Involved in Problem Solving
A mental process or a phenomenon dedicated towards solving problems by discovering and analyzing the problem is referred to as problem-solving. It is a process dedicated to finding not just any solution, but the best solution to resolve any problems. There is no such thing as one best way to solve every kind of problem, since there are unique problems depending upon the situation there are unique solutions too.

In psychology, problem solving doesn’t necessarily refer to solving psychological/mental issues of the brain. The process simply refers to solving every kind of problems in life in a proper manner. The idea of including the subject in psychology is because psychology deals with the overall mental process. And, tactfully using our thought process is what leads to the solution of any problems.
There are number of rigid psychological steps involved in problem solving, which is also referred as problem-solving cycle. The steps are in sequential order, and solving any problem requires following them one after another. But, we tend to avoid following this rigid set of steps, which is why it often requires us to go through the same steps over and over again until a satisfactory solution is reached.
Here are the steps involved in problem solving, approved by expert psychologists.
1. Identifying the Problem
Identifying the problem seems like the obvious first stem, but it’s not exactly as simple as it sounds. People might identify the wrong source of a problem, which will render the steps thus carried on useless.
For instance , let’s say you’re having trouble with your studies. identifying the root of your failure is your first priority. The problem here could be that you haven’t been allocating enough time for your studies, or you haven’t tried the right techniques. But, if you make an assumption that the problem here is the subject being too hard, you won’t be able to solve the problem.
2. Defining/Understanding the Problem

It’s vital to properly define the problem once it’s been identified. Only by defining the problem, further steps can be taken to solve it. While at it, you also need to take into consideration different perspectives to understand any problem; this will also help you look for solutions with different perspectives.
Now, following up with the previous example . Let’s say you have identified the problem as not being able to allocate enough time for your studies. You need to sort out the reason behind it. Have you just been procrastinating? Have you been too busy with work? You need to understand the whole problem and reasons behind it, which is the second step in problem solving.
3. Forming a Strategy
Developing a strategy is the next step to finding a solution. Each different situation will require formulating different strategies, also depending on individual’s unique preferences.
Now, you have identified and studied your problem. You can’t just simply jump into trying to solve it. You can’t just quit work and start studying. You need to draw up a strategy to manage your time properly. Allocate less time for not-so-important works, and add them to your study time. Your strategy should be well thought, so that in theory at least, you are able to manage enough time to study properly and not fail in the exams.
4. Organizing Information

Organizing the available information is another crucial step to the process. You need to consider
- What do you know about the problem?
- What do you not know about the problem?
Accuracy of the solution for your problem will depend on the amount of information available.
The hypothetical strategy you formulate isn’t the all of it either. You need to now contemplate on the information available on the subject matter. Use the aforementioned questions to find out more about the problem. Proper organization of the information will force you to revise your strategy and refine it for best results.
5. Allocating Resources
Time, money and other resources aren’t unlimited. Deciding how high the priority is to solve your problem will help you determine the resources you’ll be using in your course to find the solution. If the problem is important, you can allocate more resources to solving it. However, if the problem isn’t as important, it’s not worth the time and money you might spend on it if not for proper planning.
For instance , let’s consider a different scenario where your business deal is stuck, but it’s few thousand miles away. Now, you need to analyze the problem and the resources you can afford to expend to solve the particular problem. If the deal isn’t really in your favor, you could just try solving it over the phone, however, more important deals might require you to fly to the location in order to solve the issue.
6. Monitoring Progress

You need to document your progress as you are finding a solution. Don’t rely on your memory, no matter how good your memory is. Effective problem-solvers have been known to monitor their progress regularly. And, if they’re not making as much progress as they’re supposed to, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies.
Problem solving isn’t an overnight feat. You can’t just have a body like that of Brad Pitt after a single session in the gym. It takes time and patience. Likewise, you need to work towards solving any problem every day until you finally achieve the results. Looking back at the previous example , if everything’s according to plan, you will be allocating more and more time for your studies until finally you are confident that you’re improving. One way to make sure that you’re on a right path to solving a problem is by keeping track of the progress. To solve the problem illustrated in the first example, you can take self-tests every week or two and track your progress.
7. Evaluating the Results
Your job still isn’t done even if you’ve reached a solution. You need to evaluate the solution to find out if it’s the best possible solution to the problem. The evaluation might be immediate or might take a while. For instance , answer to a math problem can be checked then and there, however solution to your yearly tax issue might not be possible to be evaluated right there.
- Take time to identify the possible sources of the problem. It’s better to spend a substantial amount of time on something right, than on something completely opposite.
- Ask yourself questions like What, Why, How to figure out the causes of the problem. Only then can you move forward on solving it.
- Carefully outline the methods to tackle the problem. There might be different solutions to a problem, record them all.
- Gather all information about the problem and the approaches. More, the merrier.
- From the outlined methods, choose the ones that are viable to approach. Try discarding the ones that have unseen consequences.
- Track your progress as you go.
- Evaluate the outcome of the progress.
What are other people reading?

Divergent Thinking

Convergent Thinking

Convergent Vs Divergent Thinking
7.3 Problem-Solving
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
The study of human and animal problem solving processes has provided much insight toward the understanding of our conscious experience and led to advancements in computer science and artificial intelligence. Essentially much of cognitive science today represents studies of how we consciously and unconsciously make decisions and solve problems. For instance, when encountered with a large amount of information, how do we go about making decisions about the most efficient way of sorting and analyzing all the information in order to find what you are looking for as in visual search paradigms in cognitive psychology. Or in a situation where a piece of machinery is not working properly, how do we go about organizing how to address the issue and understand what the cause of the problem might be. How do we sort the procedures that will be needed and focus attention on what is important in order to solve problems efficiently. Within this section we will discuss some of these issues and examine processes related to human, animal and computer problem solving.
PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGIES
When people are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
Problems themselves can be classified into two different categories known as ill-defined and well-defined problems (Schacter, 2009). Ill-defined problems represent issues that do not have clear goals, solution paths, or expected solutions whereas well-defined problems have specific goals, clearly defined solutions, and clear expected solutions. Problem solving often incorporates pragmatics (logical reasoning) and semantics (interpretation of meanings behind the problem), and also in many cases require abstract thinking and creativity in order to find novel solutions. Within psychology, problem solving refers to a motivational drive for reading a definite “goal” from a present situation or condition that is either not moving toward that goal, is distant from it, or requires more complex logical analysis for finding a missing description of conditions or steps toward that goal. Processes relating to problem solving include problem finding also known as problem analysis, problem shaping where the organization of the problem occurs, generating alternative strategies, implementation of attempted solutions, and verification of the selected solution. Various methods of studying problem solving exist within the field of psychology including introspection, behavior analysis and behaviorism, simulation, computer modeling, and experimentation.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them (table below). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error. The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Further problem solving strategies have been identified (listed below) that incorporate flexible and creative thinking in order to reach solutions efficiently.
Additional Problem Solving Strategies :
- Abstraction – refers to solving the problem within a model of the situation before applying it to reality.
- Analogy – is using a solution that solves a similar problem.
- Brainstorming – refers to collecting an analyzing a large amount of solutions, especially within a group of people, to combine the solutions and developing them until an optimal solution is reached.
- Divide and conquer – breaking down large complex problems into smaller more manageable problems.
- Hypothesis testing – method used in experimentation where an assumption about what would happen in response to manipulating an independent variable is made, and analysis of the affects of the manipulation are made and compared to the original hypothesis.
- Lateral thinking – approaching problems indirectly and creatively by viewing the problem in a new and unusual light.
- Means-ends analysis – choosing and analyzing an action at a series of smaller steps to move closer to the goal.
- Method of focal objects – putting seemingly non-matching characteristics of different procedures together to make something new that will get you closer to the goal.
- Morphological analysis – analyzing the outputs of and interactions of many pieces that together make up a whole system.
- Proof – trying to prove that a problem cannot be solved. Where the proof fails becomes the starting point or solving the problem.
- Reduction – adapting the problem to be as similar problems where a solution exists.
- Research – using existing knowledge or solutions to similar problems to solve the problem.
- Root cause analysis – trying to identify the cause of the problem.
The strategies listed above outline a short summary of methods we use in working toward solutions and also demonstrate how the mind works when being faced with barriers preventing goals to be reached.
One example of means-end analysis can be found by using the Tower of Hanoi paradigm . This paradigm can be modeled as a word problems as demonstrated by the Missionary-Cannibal Problem :
Missionary-Cannibal Problem
Three missionaries and three cannibals are on one side of a river and need to cross to the other side. The only means of crossing is a boat, and the boat can only hold two people at a time. Your goal is to devise a set of moves that will transport all six of the people across the river, being in mind the following constraint: The number of cannibals can never exceed the number of missionaries in any location. Remember that someone will have to also row that boat back across each time.
Hint : At one point in your solution, you will have to send more people back to the original side than you just sent to the destination.
The actual Tower of Hanoi problem consists of three rods sitting vertically on a base with a number of disks of different sizes that can slide onto any rod. The puzzle starts with the disks in a neat stack in ascending order of size on one rod, the smallest at the top making a conical shape. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod obeying the following rules:
- 1. Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- 2. Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack or on an empty rod.
- 3. No disc may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
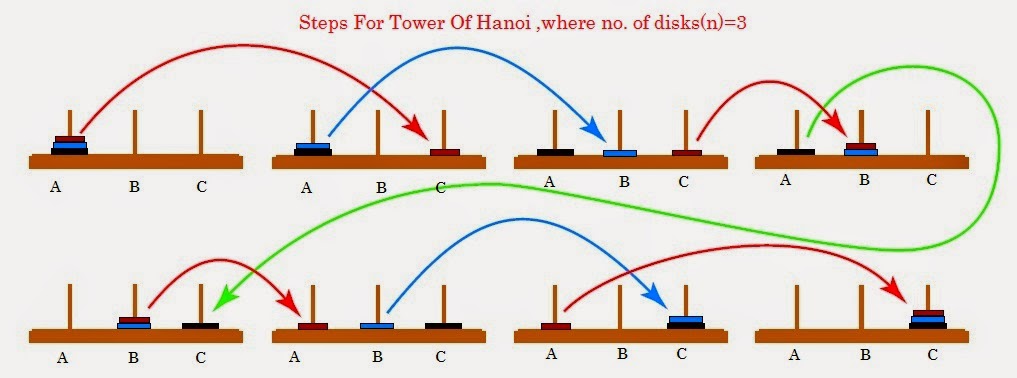
Figure 7.02. Steps for solving the Tower of Hanoi in the minimum number of moves when there are 3 disks.
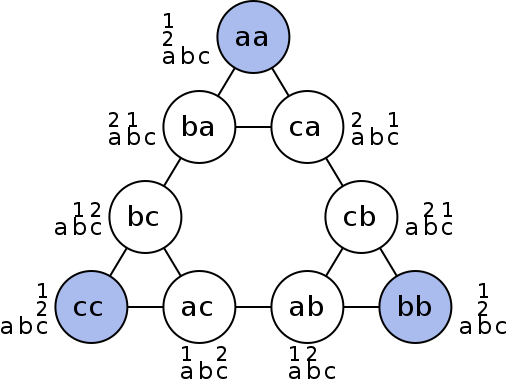
Figure 7.03. Graphical representation of nodes (circles) and moves (lines) of Tower of Hanoi.
The Tower of Hanoi is a frequently used psychological technique to study problem solving and procedure analysis. A variation of the Tower of Hanoi known as the Tower of London has been developed which has been an important tool in the neuropsychological diagnosis of executive function disorders and their treatment.
GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY AND PROBLEM SOLVING
As you may recall from the sensation and perception chapter, Gestalt psychology describes whole patterns, forms and configurations of perception and cognition such as closure, good continuation, and figure-ground. In addition to patterns of perception, Wolfgang Kohler, a German Gestalt psychologist traveled to the Spanish island of Tenerife in order to study animals behavior and problem solving in the anthropoid ape.
As an interesting side note to Kohler’s studies of chimp problem solving, Dr. Ronald Ley, professor of psychology at State University of New York provides evidence in his book A Whisper of Espionage (1990) suggesting that while collecting data for what would later be his book The Mentality of Apes (1925) on Tenerife in the Canary Islands between 1914 and 1920, Kohler was additionally an active spy for the German government alerting Germany to ships that were sailing around the Canary Islands. Ley suggests his investigations in England, Germany and elsewhere in Europe confirm that Kohler had served in the German military by building, maintaining and operating a concealed radio that contributed to Germany’s war effort acting as a strategic outpost in the Canary Islands that could monitor naval military activity approaching the north African coast.
While trapped on the island over the course of World War 1, Kohler applied Gestalt principles to animal perception in order to understand how they solve problems. He recognized that the apes on the islands also perceive relations between stimuli and the environment in Gestalt patterns and understand these patterns as wholes as opposed to pieces that make up a whole. Kohler based his theories of animal intelligence on the ability to understand relations between stimuli, and spent much of his time while trapped on the island investigation what he described as insight , the sudden perception of useful or proper relations. In order to study insight in animals, Kohler would present problems to chimpanzee’s by hanging some banana’s or some kind of food so it was suspended higher than the apes could reach. Within the room, Kohler would arrange a variety of boxes, sticks or other tools the chimpanzees could use by combining in patterns or organizing in a way that would allow them to obtain the food (Kohler & Winter, 1925).
While viewing the chimpanzee’s, Kohler noticed one chimp that was more efficient at solving problems than some of the others. The chimp, named Sultan, was able to use long poles to reach through bars and organize objects in specific patterns to obtain food or other desirables that were originally out of reach. In order to study insight within these chimps, Kohler would remove objects from the room to systematically make the food more difficult to obtain. As the story goes, after removing many of the objects Sultan was used to using to obtain the food, he sat down ad sulked for a while, and then suddenly got up going over to two poles lying on the ground. Without hesitation Sultan put one pole inside the end of the other creating a longer pole that he could use to obtain the food demonstrating an ideal example of what Kohler described as insight. In another situation, Sultan discovered how to stand on a box to reach a banana that was suspended from the rafters illustrating Sultan’s perception of relations and the importance of insight in problem solving.
Grande (another chimp in the group studied by Kohler) builds a three-box structure to reach the bananas, while Sultan watches from the ground. Insight , sometimes referred to as an “Ah-ha” experience, was the term Kohler used for the sudden perception of useful relations among objects during problem solving (Kohler, 1927; Radvansky & Ashcraft, 2013).
Solving puzzles.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (see figure) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
How long did it take you to solve this sudoku puzzle? (You can see the answer at the end of this section.)
Here is another popular type of puzzle (figure below) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Did you figure it out? (The answer is at the end of this section.) Once you understand how to crack this puzzle, you won’t forget.
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below (figure below). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).

What steps did you take to solve this puzzle? You can read the solution at the end of this section.
Pitfalls to problem solving.
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in the table below.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in the figure below? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in the figures above? Here are the answers.

Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
References:
Openstax Psychology text by Kathryn Dumper, William Jenkins, Arlene Lacombe, Marilyn Lovett and Marion Perlmutter licensed under CC BY v4.0. https://openstax.org/details/books/psychology
Review Questions:
1. A specific formula for solving a problem is called ________.
a. an algorithm
b. a heuristic
c. a mental set
d. trial and error
2. Solving the Tower of Hanoi problem tends to utilize a ________ strategy of problem solving.
a. divide and conquer
b. means-end analysis
d. experiment
3. A mental shortcut in the form of a general problem-solving framework is called ________.
4. Which type of bias involves becoming fixated on a single trait of a problem?
a. anchoring bias
b. confirmation bias
c. representative bias
d. availability bias
5. Which type of bias involves relying on a false stereotype to make a decision?
6. Wolfgang Kohler analyzed behavior of chimpanzees by applying Gestalt principles to describe ________.
a. social adjustment
b. student load payment options
c. emotional learning
d. insight learning
7. ________ is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for.
a. functional fixedness
c. working memory
Critical Thinking Questions:
1. What is functional fixedness and how can overcoming it help you solve problems?
2. How does an algorithm save you time and energy when solving a problem?
Personal Application Question:
1. Which type of bias do you recognize in your own decision making processes? How has this bias affected how you’ve made decisions in the past and how can you use your awareness of it to improve your decisions making skills in the future?
anchoring bias
availability heuristic
confirmation bias
functional fixedness
hindsight bias
problem-solving strategy
representative bias
trial and error
working backwards
Answers to Exercises
algorithm: problem-solving strategy characterized by a specific set of instructions
anchoring bias: faulty heuristic in which you fixate on a single aspect of a problem to find a solution
availability heuristic: faulty heuristic in which you make a decision based on information readily available to you
confirmation bias: faulty heuristic in which you focus on information that confirms your beliefs
functional fixedness: inability to see an object as useful for any other use other than the one for which it was intended
heuristic: mental shortcut that saves time when solving a problem
hindsight bias: belief that the event just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t
mental set: continually using an old solution to a problem without results
problem-solving strategy: method for solving problems
representative bias: faulty heuristic in which you stereotype someone or something without a valid basis for your judgment
trial and error: problem-solving strategy in which multiple solutions are attempted until the correct one is found
working backwards: heuristic in which you begin to solve a problem by focusing on the end result

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

Definition:
Problem Solving is the process of identifying, analyzing, and finding effective solutions to complex issues or challenges.
Key Steps in Problem Solving:
- Identification of the problem: Recognizing and clearly defining the issue that needs to be resolved.
- Analysis and research: Gathering relevant information, data, and facts to understand the problem in-depth.
- Formulating strategies: Developing various approaches and plans to tackle the problem effectively.
- Evaluation and selection: Assessing the viability and potential outcomes of the proposed solutions and selecting the most appropriate one.
- Implementation: Putting the chosen solution into action and executing the necessary steps to resolve the problem.
- Monitoring and feedback: Continuously evaluating the implemented solution and obtaining feedback to ensure its effectiveness.
- Adaptation and improvement: Modifying and refining the solution as needed to optimize results and prevent similar problems from arising in the future.
Skills and Qualities for Effective Problem Solving:
- Analytical thinking: The ability to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable components and analyze them thoroughly.
- Creativity: Thinking outside the box and generating innovative solutions.
- Decision making: Making logical and informed choices based on available data and critical thinking.
- Communication: Clearly conveying ideas, listening actively, and collaborating with others to solve problems as a team.
- Resilience: Maintaining a positive mindset, perseverance, and adaptability in the face of challenges.
- Resourcefulness: Utilizing available resources and seeking new approaches when confronted with obstacles.
- Time management: Effectively organizing and prioritizing tasks to optimize problem-solving efficiency.
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

48 Problem Solving
Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences, University of California, Santa Barbara
- Published: 03 June 2013
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Problem solving refers to cognitive processing directed at achieving a goal when the problem solver does not initially know a solution method. A problem exists when someone has a goal but does not know how to achieve it. Problems can be classified as routine or nonroutine, and as well defined or ill defined. The major cognitive processes in problem solving are representing, planning, executing, and monitoring. The major kinds of knowledge required for problem solving are facts, concepts, procedures, strategies, and beliefs. Classic theoretical approaches to the study of problem solving are associationism, Gestalt, and information processing. Current issues and suggested future issues include decision making, intelligence and creativity, teaching of thinking skills, expert problem solving, analogical reasoning, mathematical and scientific thinking, everyday thinking, and the cognitive neuroscience of problem solving. Common themes concern the domain specificity of problem solving and a focus on problem solving in authentic contexts.
The study of problem solving begins with defining problem solving, problem, and problem types. This introduction to problem solving is rounded out with an examination of cognitive processes in problem solving, the role of knowledge in problem solving, and historical approaches to the study of problem solving.
Definition of Problem Solving
Problem solving refers to cognitive processing directed at achieving a goal for which the problem solver does not initially know a solution method. This definition consists of four major elements (Mayer, 1992 ; Mayer & Wittrock, 2006 ):
Cognitive —Problem solving occurs within the problem solver’s cognitive system and can only be inferred indirectly from the problem solver’s behavior (including biological changes, introspections, and actions during problem solving). Process —Problem solving involves mental computations in which some operation is applied to a mental representation, sometimes resulting in the creation of a new mental representation. Directed —Problem solving is aimed at achieving a goal. Personal —Problem solving depends on the existing knowledge of the problem solver so that what is a problem for one problem solver may not be a problem for someone who already knows a solution method.
The definition is broad enough to include a wide array of cognitive activities such as deciding which apartment to rent, figuring out how to use a cell phone interface, playing a game of chess, making a medical diagnosis, finding the answer to an arithmetic word problem, or writing a chapter for a handbook. Problem solving is pervasive in human life and is crucial for human survival. Although this chapter focuses on problem solving in humans, problem solving also occurs in nonhuman animals and in intelligent machines.
How is problem solving related to other forms of high-level cognition processing, such as thinking and reasoning? Thinking refers to cognitive processing in individuals but includes both directed thinking (which corresponds to the definition of problem solving) and undirected thinking such as daydreaming (which does not correspond to the definition of problem solving). Thus, problem solving is a type of thinking (i.e., directed thinking).
Reasoning refers to problem solving within specific classes of problems, such as deductive reasoning or inductive reasoning. In deductive reasoning, the reasoner is given premises and must derive a conclusion by applying the rules of logic. For example, given that “A is greater than B” and “B is greater than C,” a reasoner can conclude that “A is greater than C.” In inductive reasoning, the reasoner is given (or has experienced) a collection of examples or instances and must infer a rule. For example, given that X, C, and V are in the “yes” group and x, c, and v are in the “no” group, the reasoning may conclude that B is in “yes” group because it is in uppercase format. Thus, reasoning is a type of problem solving.
Definition of Problem
A problem occurs when someone has a goal but does not know to achieve it. This definition is consistent with how the Gestalt psychologist Karl Duncker ( 1945 , p. 1) defined a problem in his classic monograph, On Problem Solving : “A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this goal is to be reached.” However, today researchers recognize that the definition should be extended to include problem solving by intelligent machines. This definition can be clarified using an information processing approach by noting that a problem occurs when a situation is in the given state, the problem solver wants the situation to be in the goal state, and there is no obvious way to move from the given state to the goal state (Newell & Simon, 1972 ). Accordingly, the three main elements in describing a problem are the given state (i.e., the current state of the situation), the goal state (i.e., the desired state of the situation), and the set of allowable operators (i.e., the actions the problem solver is allowed to take). The definition of “problem” is broad enough to include the situation confronting a physician who wishes to make a diagnosis on the basis of preliminary tests and a patient examination, as well as a beginning physics student trying to solve a complex physics problem.
Types of Problems
It is customary in the problem-solving literature to make a distinction between routine and nonroutine problems. Routine problems are problems that are so familiar to the problem solver that the problem solver knows a solution method. For example, for most adults, “What is 365 divided by 12?” is a routine problem because they already know the procedure for long division. Nonroutine problems are so unfamiliar to the problem solver that the problem solver does not know a solution method. For example, figuring out the best way to set up a funding campaign for a nonprofit charity is a nonroutine problem for most volunteers. Technically, routine problems do not meet the definition of problem because the problem solver has a goal but knows how to achieve it. Much research on problem solving has focused on routine problems, although most interesting problems in life are nonroutine.
Another customary distinction is between well-defined and ill-defined problems. Well-defined problems have a clearly specified given state, goal state, and legal operators. Examples include arithmetic computation problems or games such as checkers or tic-tac-toe. Ill-defined problems have a poorly specified given state, goal state, or legal operators, or a combination of poorly defined features. Examples include solving the problem of global warming or finding a life partner. Although, ill-defined problems are more challenging, much research in problem solving has focused on well-defined problems.
Cognitive Processes in Problem Solving
The process of problem solving can be broken down into two main phases: problem representation , in which the problem solver builds a mental representation of the problem situation, and problem solution , in which the problem solver works to produce a solution. The major subprocess in problem representation is representing , which involves building a situation model —that is, a mental representation of the situation described in the problem. The major subprocesses in problem solution are planning , which involves devising a plan for how to solve the problem; executing , which involves carrying out the plan; and monitoring , which involves evaluating and adjusting one’s problem solving.
For example, given an arithmetic word problem such as “Alice has three marbles. Sarah has two more marbles than Alice. How many marbles does Sarah have?” the process of representing involves building a situation model in which Alice has a set of marbles, there is set of marbles for the difference between the two girls, and Sarah has a set of marbles that consists of Alice’s marbles and the difference set. In the planning process, the problem solver sets a goal of adding 3 and 2. In the executing process, the problem solver carries out the computation, yielding an answer of 5. In the monitoring process, the problem solver looks over what was done and concludes that 5 is a reasonable answer. In most complex problem-solving episodes, the four cognitive processes may not occur in linear order, but rather may interact with one another. Although some research focuses mainly on the execution process, problem solvers may tend to have more difficulty with the processes of representing, planning, and monitoring.
Knowledge for Problem Solving
An important theme in problem-solving research is that problem-solving proficiency on any task depends on the learner’s knowledge (Anderson et al., 2001 ; Mayer, 1992 ). Five kinds of knowledge are as follows:
Facts —factual knowledge about the characteristics of elements in the world, such as “Sacramento is the capital of California” Concepts —conceptual knowledge, including categories, schemas, or models, such as knowing the difference between plants and animals or knowing how a battery works Procedures —procedural knowledge of step-by-step processes, such as how to carry out long-division computations Strategies —strategic knowledge of general methods such as breaking a problem into parts or thinking of a related problem Beliefs —attitudinal knowledge about how one’s cognitive processing works such as thinking, “I’m good at this”
Although some research focuses mainly on the role of facts and procedures in problem solving, complex problem solving also depends on the problem solver’s concepts, strategies, and beliefs (Mayer, 1992 ).
Historical Approaches to Problem Solving
Psychological research on problem solving began in the early 1900s, as an outgrowth of mental philosophy (Humphrey, 1963 ; Mandler & Mandler, 1964 ). Throughout the 20th century four theoretical approaches developed: early conceptions, associationism, Gestalt psychology, and information processing.
Early Conceptions
The start of psychology as a science can be set at 1879—the year Wilhelm Wundt opened the first world’s psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, and sought to train the world’s first cohort of experimental psychologists. Instead of relying solely on philosophical speculations about how the human mind works, Wundt sought to apply the methods of experimental science to issues addressed in mental philosophy. His theoretical approach became structuralism —the analysis of consciousness into its basic elements.
Wundt’s main contribution to the study of problem solving, however, was to call for its banishment. According to Wundt, complex cognitive processing was too complicated to be studied by experimental methods, so “nothing can be discovered in such experiments” (Wundt, 1911/1973 ). Despite his admonishments, however, a group of his former students began studying thinking mainly in Wurzburg, Germany. Using the method of introspection, subjects were asked to describe their thought process as they solved word association problems, such as finding the superordinate of “newspaper” (e.g., an answer is “publication”). Although the Wurzburg group—as they came to be called—did not produce a new theoretical approach, they found empirical evidence that challenged some of the key assumptions of mental philosophy. For example, Aristotle had proclaimed that all thinking involves mental imagery, but the Wurzburg group was able to find empirical evidence for imageless thought .
Associationism
The first major theoretical approach to take hold in the scientific study of problem solving was associationism —the idea that the cognitive representations in the mind consist of ideas and links between them and that cognitive processing in the mind involves following a chain of associations from one idea to the next (Mandler & Mandler, 1964 ; Mayer, 1992 ). For example, in a classic study, E. L. Thorndike ( 1911 ) placed a hungry cat in what he called a puzzle box—a wooden crate in which pulling a loop of string that hung from overhead would open a trap door to allow the cat to escape to a bowl of food outside the crate. Thorndike placed the cat in the puzzle box once a day for several weeks. On the first day, the cat engaged in many extraneous behaviors such as pouncing against the wall, pushing its paws through the slats, and meowing, but on successive days the number of extraneous behaviors tended to decrease. Overall, the time required to get out of the puzzle box decreased over the course of the experiment, indicating the cat was learning how to escape.
Thorndike’s explanation for how the cat learned to solve the puzzle box problem is based on an associationist view: The cat begins with a habit family hierarchy —a set of potential responses (e.g., pouncing, thrusting, meowing, etc.) all associated with the same stimulus (i.e., being hungry and confined) and ordered in terms of strength of association. When placed in the puzzle box, the cat executes its strongest response (e.g., perhaps pouncing against the wall), but when it fails, the strength of the association is weakened, and so on for each unsuccessful action. Eventually, the cat gets down to what was initially a weak response—waving its paw in the air—but when that response leads to accidentally pulling the string and getting out, it is strengthened. Over the course of many trials, the ineffective responses become weak and the successful response becomes strong. Thorndike refers to this process as the law of effect : Responses that lead to dissatisfaction become less associated with the situation and responses that lead to satisfaction become more associated with the situation. According to Thorndike’s associationist view, solving a problem is simply a matter of trial and error and accidental success. A major challenge to assocationist theory concerns the nature of transfer—that is, where does a problem solver find a creative solution that has never been performed before? Associationist conceptions of cognition can be seen in current research, including neural networks, connectionist models, and parallel distributed processing models (Rogers & McClelland, 2004 ).
Gestalt Psychology
The Gestalt approach to problem solving developed in the 1930s and 1940s as a counterbalance to the associationist approach. According to the Gestalt approach, cognitive representations consist of coherent structures (rather than individual associations) and the cognitive process of problem solving involves building a coherent structure (rather than strengthening and weakening of associations). For example, in a classic study, Kohler ( 1925 ) placed a hungry ape in a play yard that contained several empty shipping crates and a banana attached overhead but out of reach. Based on observing the ape in this situation, Kohler noted that the ape did not randomly try responses until one worked—as suggested by Thorndike’s associationist view. Instead, the ape stood under the banana, looked up at it, looked at the crates, and then in a flash of insight stacked the crates under the bananas as a ladder, and walked up the steps in order to reach the banana.
According to Kohler, the ape experienced a sudden visual reorganization in which the elements in the situation fit together in a way to solve the problem; that is, the crates could become a ladder that reduces the distance to the banana. Kohler referred to the underlying mechanism as insight —literally seeing into the structure of the situation. A major challenge of Gestalt theory is its lack of precision; for example, naming a process (i.e., insight) is not the same as explaining how it works. Gestalt conceptions can be seen in modern research on mental models and schemas (Gentner & Stevens, 1983 ).
Information Processing
The information processing approach to problem solving developed in the 1960s and 1970s and was based on the influence of the computer metaphor—the idea that humans are processors of information (Mayer, 2009 ). According to the information processing approach, problem solving involves a series of mental computations—each of which consists of applying a process to a mental representation (such as comparing two elements to determine whether they differ).
In their classic book, Human Problem Solving , Newell and Simon ( 1972 ) proposed that problem solving involved a problem space and search heuristics . A problem space is a mental representation of the initial state of the problem, the goal state of the problem, and all possible intervening states (based on applying allowable operators). Search heuristics are strategies for moving through the problem space from the given to the goal state. Newell and Simon focused on means-ends analysis , in which the problem solver continually sets goals and finds moves to accomplish goals.
Newell and Simon used computer simulation as a research method to test their conception of human problem solving. First, they asked human problem solvers to think aloud as they solved various problems such as logic problems, chess, and cryptarithmetic problems. Then, based on an information processing analysis, Newell and Simon created computer programs that solved these problems. In comparing the solution behavior of humans and computers, they found high similarity, suggesting that the computer programs were solving problems using the same thought processes as humans.
An important advantage of the information processing approach is that problem solving can be described with great clarity—as a computer program. An important limitation of the information processing approach is that it is most useful for describing problem solving for well-defined problems rather than ill-defined problems. The information processing conception of cognition lives on as a keystone of today’s cognitive science (Mayer, 2009 ).
Classic Issues in Problem Solving
Three classic issues in research on problem solving concern the nature of transfer (suggested by the associationist approach), the nature of insight (suggested by the Gestalt approach), and the role of problem-solving heuristics (suggested by the information processing approach).
Transfer refers to the effects of prior learning on new learning (or new problem solving). Positive transfer occurs when learning A helps someone learn B. Negative transfer occurs when learning A hinders someone from learning B. Neutral transfer occurs when learning A has no effect on learning B. Positive transfer is a central goal of education, but research shows that people often do not transfer what they learned to solving problems in new contexts (Mayer, 1992 ; Singley & Anderson, 1989 ).
Three conceptions of the mechanisms underlying transfer are specific transfer , general transfer , and specific transfer of general principles . Specific transfer refers to the idea that learning A will help someone learn B only if A and B have specific elements in common. For example, learning Spanish may help someone learn Latin because some of the vocabulary words are similar and the verb conjugation rules are similar. General transfer refers to the idea that learning A can help someone learn B even they have nothing specifically in common but A helps improve the learner’s mind in general. For example, learning Latin may help people learn “proper habits of mind” so they are better able to learn completely unrelated subjects as well. Specific transfer of general principles is the idea that learning A will help someone learn B if the same general principle or solution method is required for both even if the specific elements are different.
In a classic study, Thorndike and Woodworth ( 1901 ) found that students who learned Latin did not subsequently learn bookkeeping any better than students who had not learned Latin. They interpreted this finding as evidence for specific transfer—learning A did not transfer to learning B because A and B did not have specific elements in common. Modern research on problem-solving transfer continues to show that people often do not demonstrate general transfer (Mayer, 1992 ). However, it is possible to teach people a general strategy for solving a problem, so that when they see a new problem in a different context they are able to apply the strategy to the new problem (Judd, 1908 ; Mayer, 2008 )—so there is also research support for the idea of specific transfer of general principles.
Insight refers to a change in a problem solver’s mind from not knowing how to solve a problem to knowing how to solve it (Mayer, 1995 ; Metcalfe & Wiebe, 1987 ). In short, where does the idea for a creative solution come from? A central goal of problem-solving research is to determine the mechanisms underlying insight.
The search for insight has led to five major (but not mutually exclusive) explanatory mechanisms—insight as completing a schema, insight as suddenly reorganizing visual information, insight as reformulation of a problem, insight as removing mental blocks, and insight as finding a problem analog (Mayer, 1995 ). Completing a schema is exemplified in a study by Selz (Fridja & de Groot, 1982 ), in which people were asked to think aloud as they solved word association problems such as “What is the superordinate for newspaper?” To solve the problem, people sometimes thought of a coordinate, such as “magazine,” and then searched for a superordinate category that subsumed both terms, such as “publication.” According to Selz, finding a solution involved building a schema that consisted of a superordinate and two subordinate categories.
Reorganizing visual information is reflected in Kohler’s ( 1925 ) study described in a previous section in which a hungry ape figured out how to stack boxes as a ladder to reach a banana hanging above. According to Kohler, the ape looked around the yard and found the solution in a flash of insight by mentally seeing how the parts could be rearranged to accomplish the goal.
Reformulating a problem is reflected in a classic study by Duncker ( 1945 ) in which people are asked to think aloud as they solve the tumor problem—how can you destroy a tumor in a patient without destroying surrounding healthy tissue by using rays that at sufficient intensity will destroy any tissue in their path? In analyzing the thinking-aloud protocols—that is, transcripts of what the problem solvers said—Duncker concluded that people reformulated the goal in various ways (e.g., avoid contact with healthy tissue, immunize healthy tissue, have ray be weak in healthy tissue) until they hit upon a productive formulation that led to the solution (i.e., concentrating many weak rays on the tumor).
Removing mental blocks is reflected in classic studies by Duncker ( 1945 ) in which solving a problem involved thinking of a novel use for an object, and by Luchins ( 1942 ) in which solving a problem involved not using a procedure that had worked well on previous problems. Finding a problem analog is reflected in classic research by Wertheimer ( 1959 ) in which learning to find the area of a parallelogram is supported by the insight that one could cut off the triangle on one side and place it on the other side to form a rectangle—so a parallelogram is really a rectangle in disguise. The search for insight along each of these five lines continues in current problem-solving research.
Heuristics are problem-solving strategies, that is, general approaches to how to solve problems. Newell and Simon ( 1972 ) suggested three general problem-solving heuristics for moving from a given state to a goal state: random trial and error , hill climbing , and means-ends analysis . Random trial and error involves randomly selecting a legal move and applying it to create a new problem state, and repeating that process until the goal state is reached. Random trial and error may work for simple problems but is not efficient for complex ones. Hill climbing involves selecting the legal move that moves the problem solver closer to the goal state. Hill climbing will not work for problems in which the problem solver must take a move that temporarily moves away from the goal as is required in many problems.
Means-ends analysis involves creating goals and seeking moves that can accomplish the goal. If a goal cannot be directly accomplished, a subgoal is created to remove one or more obstacles. Newell and Simon ( 1972 ) successfully used means-ends analysis as the search heuristic in a computer program aimed at general problem solving, that is, solving a diverse collection of problems. However, people may also use specific heuristics that are designed to work for specific problem-solving situations (Gigerenzer, Todd, & ABC Research Group, 1999 ; Kahneman & Tversky, 1984 ).
Current and Future Issues in Problem Solving
Eight current issues in problem solving involve decision making, intelligence and creativity, teaching of thinking skills, expert problem solving, analogical reasoning, mathematical and scientific problem solving, everyday thinking, and the cognitive neuroscience of problem solving.
Decision Making
Decision making refers to the cognitive processing involved in choosing between two or more alternatives (Baron, 2000 ; Markman & Medin, 2002 ). For example, a decision-making task may involve choosing between getting $240 for sure or having a 25% change of getting $1000. According to economic theories such as expected value theory, people should chose the second option, which is worth $250 (i.e., .25 x $1000) rather than the first option, which is worth $240 (1.00 x $240), but psychological research shows that most people prefer the first option (Kahneman & Tversky, 1984 ).
Research on decision making has generated three classes of theories (Markman & Medin, 2002 ): descriptive theories, such as prospect theory (Kahneman & Tversky), which are based on the ideas that people prefer to overweight the cost of a loss and tend to overestimate small probabilities; heuristic theories, which are based on the idea that people use a collection of short-cut strategies such as the availability heuristic (Gigerenzer et al., 1999 ; Kahneman & Tversky, 2000 ); and constructive theories, such as mental accounting (Kahneman & Tversky, 2000 ), in which people build a narrative to justify their choices to themselves. Future research is needed to examine decision making in more realistic settings.
Intelligence and Creativity
Although researchers do not have complete consensus on the definition of intelligence (Sternberg, 1990 ), it is reasonable to view intelligence as the ability to learn or adapt to new situations. Fluid intelligence refers to the potential to solve problems without any relevant knowledge, whereas crystallized intelligence refers to the potential to solve problems based on relevant prior knowledge (Sternberg & Gregorenko, 2003 ). As people gain more experience in a field, their problem-solving performance depends more on crystallized intelligence (i.e., domain knowledge) than on fluid intelligence (i.e., general ability) (Sternberg & Gregorenko, 2003 ). The ability to monitor and manage one’s cognitive processing during problem solving—which can be called metacognition —is an important aspect of intelligence (Sternberg, 1990 ). Research is needed to pinpoint the knowledge that is needed to support intelligent performance on problem-solving tasks.
Creativity refers to the ability to generate ideas that are original (i.e., other people do not think of the same idea) and functional (i.e., the idea works; Sternberg, 1999 ). Creativity is often measured using tests of divergent thinking —that is, generating as many solutions as possible for a problem (Guilford, 1967 ). For example, the uses test asks people to list as many uses as they can think of for a brick. Creativity is different from intelligence, and it is at the heart of creative problem solving—generating a novel solution to a problem that the problem solver has never seen before. An important research question concerns whether creative problem solving depends on specific knowledge or creativity ability in general.
Teaching of Thinking Skills
How can people learn to be better problem solvers? Mayer ( 2008 ) proposes four questions concerning teaching of thinking skills:
What to teach —Successful programs attempt to teach small component skills (such as how to generate and evaluate hypotheses) rather than improve the mind as a single monolithic skill (Covington, Crutchfield, Davies, & Olton, 1974 ). How to teach —Successful programs focus on modeling the process of problem solving rather than solely reinforcing the product of problem solving (Bloom & Broder, 1950 ). Where to teach —Successful programs teach problem-solving skills within the specific context they will be used rather than within a general course on how to solve problems (Nickerson, 1999 ). When to teach —Successful programs teaching higher order skills early rather than waiting until lower order skills are completely mastered (Tharp & Gallimore, 1988 ).
Overall, research on teaching of thinking skills points to the domain specificity of problem solving; that is, successful problem solving depends on the problem solver having domain knowledge that is relevant to the problem-solving task.
Expert Problem Solving
Research on expertise is concerned with differences between how experts and novices solve problems (Ericsson, Feltovich, & Hoffman, 2006 ). Expertise can be defined in terms of time (e.g., 10 years of concentrated experience in a field), performance (e.g., earning a perfect score on an assessment), or recognition (e.g., receiving a Nobel Prize or becoming Grand Master in chess). For example, in classic research conducted in the 1940s, de Groot ( 1965 ) found that chess experts did not have better general memory than chess novices, but they did have better domain-specific memory for the arrangement of chess pieces on the board. Chase and Simon ( 1973 ) replicated this result in a better controlled experiment. An explanation is that experts have developed schemas that allow them to chunk collections of pieces into a single configuration.
In another landmark study, Larkin et al. ( 1980 ) compared how experts (e.g., physics professors) and novices (e.g., first-year physics students) solved textbook physics problems about motion. Experts tended to work forward from the given information to the goal, whereas novices tended to work backward from the goal to the givens using a means-ends analysis strategy. Experts tended to store their knowledge in an integrated way, whereas novices tended to store their knowledge in isolated fragments. In another study, Chi, Feltovich, and Glaser ( 1981 ) found that experts tended to focus on the underlying physics concepts (such as conservation of energy), whereas novices tended to focus on the surface features of the problem (such as inclined planes or springs). Overall, research on expertise is useful in pinpointing what experts know that is different from what novices know. An important theme is that experts rely on domain-specific knowledge rather than solely general cognitive ability.
Analogical Reasoning
Analogical reasoning occurs when people solve one problem by using their knowledge about another problem (Holyoak, 2005 ). For example, suppose a problem solver learns how to solve a problem in one context using one solution method and then is given a problem in another context that requires the same solution method. In this case, the problem solver must recognize that the new problem has structural similarity to the old problem (i.e., it may be solved by the same method), even though they do not have surface similarity (i.e., the cover stories are different). Three steps in analogical reasoning are recognizing —seeing that a new problem is similar to a previously solved problem; abstracting —finding the general method used to solve the old problem; and mapping —using that general method to solve the new problem.
Research on analogical reasoning shows that people often do not recognize that a new problem can be solved by the same method as a previously solved problem (Holyoak, 2005 ). However, research also shows that successful analogical transfer to a new problem is more likely when the problem solver has experience with two old problems that have the same underlying structural features (i.e., they are solved by the same principle) but different surface features (i.e., they have different cover stories) (Holyoak, 2005 ). This finding is consistent with the idea of specific transfer of general principles as described in the section on “Transfer.”
Mathematical and Scientific Problem Solving
Research on mathematical problem solving suggests that five kinds of knowledge are needed to solve arithmetic word problems (Mayer, 2008 ):
Factual knowledge —knowledge about the characteristics of problem elements, such as knowing that there are 100 cents in a dollar Schematic knowledge —knowledge of problem types, such as being able to recognize time-rate-distance problems Strategic knowledge —knowledge of general methods, such as how to break a problem into parts Procedural knowledge —knowledge of processes, such as how to carry our arithmetic operations Attitudinal knowledge —beliefs about one’s mathematical problem-solving ability, such as thinking, “I am good at this”
People generally possess adequate procedural knowledge but may have difficulty in solving mathematics problems because they lack factual, schematic, strategic, or attitudinal knowledge (Mayer, 2008 ). Research is needed to pinpoint the role of domain knowledge in mathematical problem solving.
Research on scientific problem solving shows that people harbor misconceptions, such as believing that a force is needed to keep an object in motion (McCloskey, 1983 ). Learning to solve science problems involves conceptual change, in which the problem solver comes to recognize that previous conceptions are wrong (Mayer, 2008 ). Students can be taught to engage in scientific reasoning such as hypothesis testing through direct instruction in how to control for variables (Chen & Klahr, 1999 ). A central theme of research on scientific problem solving concerns the role of domain knowledge.
Everyday Thinking
Everyday thinking refers to problem solving in the context of one’s life outside of school. For example, children who are street vendors tend to use different procedures for solving arithmetic problems when they are working on the streets than when they are in school (Nunes, Schlieman, & Carraher, 1993 ). This line of research highlights the role of situated cognition —the idea that thinking always is shaped by the physical and social context in which it occurs (Robbins & Aydede, 2009 ). Research is needed to determine how people solve problems in authentic contexts.
Cognitive Neuroscience of Problem Solving
The cognitive neuroscience of problem solving is concerned with the brain activity that occurs during problem solving. For example, using fMRI brain imaging methodology, Goel ( 2005 ) found that people used the language areas of the brain to solve logical reasoning problems presented in sentences (e.g., “All dogs are pets…”) and used the spatial areas of the brain to solve logical reasoning problems presented in abstract letters (e.g., “All D are P…”). Cognitive neuroscience holds the potential to make unique contributions to the study of problem solving.
Problem solving has always been a topic at the fringe of cognitive psychology—too complicated to study intensively but too important to completely ignore. Problem solving—especially in realistic environments—is messy in comparison to studying elementary processes in cognition. The field remains fragmented in the sense that topics such as decision making, reasoning, intelligence, expertise, mathematical problem solving, everyday thinking, and the like are considered to be separate topics, each with its own separate literature. Yet some recurring themes are the role of domain-specific knowledge in problem solving and the advantages of studying problem solving in authentic contexts.
Future Directions
Some important issues for future research include the three classic issues examined in this chapter—the nature of problem-solving transfer (i.e., How are people able to use what they know about previous problem solving to help them in new problem solving?), the nature of insight (e.g., What is the mechanism by which a creative solution is constructed?), and heuristics (e.g., What are some teachable strategies for problem solving?). In addition, future research in problem solving should continue to pinpoint the role of domain-specific knowledge in problem solving, the nature of cognitive ability in problem solving, how to help people develop proficiency in solving problems, and how to provide aids for problem solving.
Anderson L. W. , Krathwohl D. R. , Airasian P. W. , Cruikshank K. A. , Mayer R. E. , Pintrich P. R. , Raths, J., & Wittrock M. C. ( 2001 ). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. New York : Longman.
Baron J. ( 2000 ). Thinking and deciding (3rd ed.). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Bloom B. S. , & Broder B. J. ( 1950 ). Problem-solving processes of college students: An exploratory investigation. Chicago : University of Chicago Press.
Chase W. G. , & Simon H. A. ( 1973 ). Perception in chess. Cognitive Psychology, 4, 55–81.
Chen Z. , & Klahr D. ( 1999 ). All other things being equal: Acquisition and transfer of the control of variable strategy . Child Development, 70, 1098–1120.
Chi M. T. H. , Feltovich P. J. , & Glaser R. ( 1981 ). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science, 5, 121–152.
Covington M. V. , Crutchfield R. S. , Davies L. B. , & Olton R. M. ( 1974 ). The productive thinking program. Columbus, OH : Merrill.
de Groot A. D. ( 1965 ). Thought and choice in chess. The Hague, The Netherlands : Mouton.
Duncker K. ( 1945 ). On problem solving. Psychological Monographs, 58 (3) (Whole No. 270).
Ericsson K. A. , Feltovich P. J. , & Hoffman R. R. (Eds.). ( 2006 ). The Cambridge handbook of expertise and expert performance. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Fridja N. H. , & de Groot A. D. ( 1982 ). Otto Selz: His contribution to psychology. The Hague, The Netherlands : Mouton.
Gentner D. , & Stevens A. L. (Eds.). ( 1983 ). Mental models. Hillsdale, NJ : Erlbaum.
Gigerenzer G. , Todd P. M. , & ABC Research Group (Eds.). ( 1999 ). Simple heuristics that make us smart. Oxford, England : Oxford University Press.
Goel V. ( 2005 ). Cognitive neuroscience of deductive reasoning. In K. J. Holyoak & R. G. Morrison (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning (pp. 475–492). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Guilford J. P. ( 1967 ). The nature of human intelligence. New York : McGraw-Hill.
Holyoak K. J. ( 2005 ). Analogy. In K. J. Holyoak & R. G. Morrison (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning (pp. 117–142). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Humphrey G. ( 1963 ). Thinking: An introduction to experimental psychology. New York : Wiley.
Judd C. H. ( 1908 ). The relation of special training and general intelligence. Educational Review, 36, 28–42.
Kahneman D. , & Tversky A. ( 1984 ). Choices, values, and frames. American Psychologist, 39, 341–350.
Kahneman D. , & Tversky A. (Eds.). ( 2000 ). Choices, values, and frames. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Kohler W. ( 1925 ). The mentality of apes. New York : Liveright.
Larkin J. H. , McDermott J. , Simon D. P. , & Simon H. A. ( 1980 ). Expert and novice performance in solving physics problems. Science, 208, 1335–1342.
Luchins A. ( 1942 ). Mechanization in problem solving. Psychological Monographs, 54 (6) (Whole No. 248).
Mandler J. M. , & Mandler G. ( 1964 ). Thinking from associationism to Gestalt. New York : Wiley.
Markman A. B. , & Medin D. L. ( 2002 ). Decision making. In D. Medin (Ed.), Stevens’ handbook of experimental psychology, Vol. 2. Memory and cognitive processes (2nd ed., pp. 413–466). New York : Wiley.
Mayer R. E. ( 1992 ). Thinking, problem solving, cognition (2nd ed). New York : Freeman.
Mayer R. E. ( 1995 ). The search for insight: Grappling with Gestalt psychology’s unanswered questions. In R. J. Sternberg & J. E. Davidson (Eds.), The nature of insight (pp. 3–32). Cambridge, MA : MIT Press.
Mayer R. E. ( 2008 ). Learning and instruction. Upper Saddle River, NJ : Merrill Prentice Hall.
Mayer R. E. ( 2009 ). Information processing. In T. L. Good (Ed.), 21st century education: A reference handbook (pp. 168–174). Thousand Oaks, CA : Sage.
Mayer R. E. , & Wittrock M. C. ( 2006 ). Problem solving. In P. A. Alexander & P. H. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed., pp. 287–304). Mahwah, NJ : Erlbaum.
McCloskey M. ( 1983 ). Intuitive physics. Scientific American, 248 (4), 122–130.
Metcalfe J. , & Wiebe D. ( 1987 ). Intuition in insight and non-insight problem solving. Memory and Cognition, 15, 238–246.
Newell A. , & Simon H. A. ( 1972 ). Human problem solving. Englewood Cliffs, NJ : Prentice-Hall.
Nickerson R. S. ( 1999 ). Enhancing creativity. In R. J. Sternberg (Ed.), Handbook of creativity (pp. 392–430). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Nunes T. , Schliemann A. D. , & Carraher D. W , ( 1993 ). Street mathematics and school mathematics. Cambridge, England : Cambridge University Press.
Robbins P. , & Aydede M. (Eds.). ( 2009 ). The Cambridge handbook of situated cognition. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Rogers T. T. , & McClelland J. L. ( 2004 ). Semantic cognition: A parallel distributed processing approach. Cambridge, MA : MIT Press.
Singley M. K. , & Anderson J. R. ( 1989 ). The transfer of cognitive skill. Cambridge, MA : Harvard University Press.
Sternberg R. J. ( 1990 ). Metaphors of mind: Conceptions of the nature of intelligence. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg R. J. ( 1999 ). Handbook of creativity. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg R. J. , & Gregorenko E. L. (Eds.). ( 2003 ). The psychology of abilities, competencies, and expertise. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Tharp R. G. , & Gallimore R. ( 1988 ). Rousing minds to life: Teaching, learning, and schooling in social context. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Thorndike E. L. ( 1911 ). Animal intelligence. New York: Hafner.
Thorndike E. L. , & Woodworth R. S. ( 1901 ). The influence of improvement in one mental function upon the efficiency of other functions. Psychological Review, 8, 247–261.
Wertheimer M. ( 1959 ). Productive thinking. New York : Harper and Collins.
Wundt W. ( 1973 ). An introduction to experimental psychology. New York : Arno Press. (Original work published in 1911).
Further Reading
Baron, J. ( 2008 ). Thinking and deciding (4th ed). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Duncker, K. ( 1945 ). On problem solving. Psychological Monographs , 58(3) (Whole No. 270).
Holyoak, K. J. , & Morrison, R. G. ( 2005 ). The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Mayer, R. E. , & Wittrock, M. C. ( 2006 ). Problem solving. In P. A. Alexander & P. H. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed., pp. 287–304). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Sternberg, R. J. , & Ben-Zeev, T. ( 2001 ). Complex cognition: The psychology of human thought . New York: Oxford University Press.
Weisberg, R. W. ( 2006 ). Creativity . New York: Wiley.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

The Process of Problem Solving
- Editor's Choice
- Experimental Psychology
- Problem Solving

In a 2013 article published in the Journal of Cognitive Psychology , Ngar Yin Louis Lee (Chinese University of Hong Kong) and APS William James Fellow Philip N. Johnson-Laird (Princeton University) examined the ways people develop strategies to solve related problems. In a series of three experiments, the researchers asked participants to solve series of matchstick problems.
In matchstick problems, participants are presented with an array of joined squares. Each square in the array is comprised of separate pieces. Participants are asked to remove a certain number of pieces from the array while still maintaining a specific number of intact squares. Matchstick problems are considered to be fairly sophisticated, as there is generally more than one solution, several different tactics can be used to complete the task, and the types of tactics that are appropriate can change depending on the configuration of the array.
Louis Lee and Johnson-Laird began by examining what influences the tactics people use when they are first confronted with the matchstick problem. They found that initial problem-solving tactics were constrained by perceptual features of the array, with participants solving symmetrical problems and problems with salient solutions faster. Participants frequently used tactics that involved symmetry and salience even when other solutions that did not involve these features existed.
To examine how problem solving develops over time, the researchers had participants solve a series of matchstick problems while verbalizing their problem-solving thought process. The findings from this second experiment showed that people tend to go through two different stages when solving a series of problems.
People begin their problem-solving process in a generative manner during which they explore various tactics — some successful and some not. Then they use their experience to narrow down their choices of tactics, focusing on those that are the most successful. The point at which people begin to rely on this newfound tactical knowledge to create their strategic moves indicates a shift into a more evaluative stage of problem solving.
In the third and last experiment, participants completed a set of matchstick problems that could be solved using similar tactics and then solved several problems that required the use of novel tactics. The researchers found that participants often had trouble leaving their set of successful tactics behind and shifting to new strategies.
From the three studies, the researchers concluded that when people tackle a problem, their initial moves may be constrained by perceptual components of the problem. As they try out different tactics, they hone in and settle on the ones that are most efficient; however, this deduced knowledge can in turn come to constrain players’ generation of moves — something that can make it difficult to switch to new tactics when required.
These findings help expand our understanding of the role of reasoning and deduction in problem solving and of the processes involved in the shift from less to more effective problem-solving strategies.
Reference Louis Lee, N. Y., Johnson-Laird, P. N. (2013). Strategic changes in problem solving. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 25 , 165–173. doi: 10.1080/20445911.2012.719021
good work for other researcher
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.

Careers Up Close: Joel Anderson on Gender and Sexual Prejudices, the Freedoms of Academic Research, and the Importance of Collaboration
Joel Anderson, a senior research fellow at both Australian Catholic University and La Trobe University, researches group processes, with a specific interest on prejudice, stigma, and stereotypes.

Experimental Methods Are Not Neutral Tools
Ana Sofia Morais and Ralph Hertwig explain how experimental psychologists have painted too negative a picture of human rationality, and how their pessimism is rooted in a seemingly mundane detail: methodological choices.
APS Fellows Elected to SEP
In addition, an APS Rising Star receives the society’s Early Investigator Award.
Privacy Overview
Facilitating Complex Thinking
Problem-Solving
Somewhat less open-ended than creative thinking is problem-solving , the analysis and solution of tasks or situations that are complex or ambiguous and that pose difficulties or obstacles of some kind (Mayer & Wittrock, 2006). Problem-solving is needed, for example, when a physician analyzes a chest X-ray: a photograph of the chest is far from clear and requires skill, experience, and resourcefulness to decide which foggy-looking blobs to ignore, and which to interpret as real physical structures (and therefore real medical concerns). Problem-solving is also needed when a grocery store manager has to decide how to improve the sales of a product: should she put it on sale at a lower price, or increase publicity for it, or both? Will these actions actually increase sales enough to pay for their costs?
PROBLEM-SOLVING IN THE CLASSROOM
Problem-solving happens in classrooms when teachers present tasks or challenges that are deliberately complex and for which finding a solution is not straightforward or obvious. The responses of students to such problems, as well as the strategies for assisting them, show the key features of problem-solving. Consider this example and students’ responses to it. We have numbered and named the paragraphs to make it easier to comment about them individually:
Scene #1: A problem to be solved
A teacher gave these instructions: “Can you connect all of the dots below using only four straight lines?” She drew the following display on the chalkboard:

The problem itself and the procedure for solving it seemed very clear: simply experiment with different arrangements of four lines. But two volunteers tried doing it at the board, but were unsuccessful. Several others worked at it at their seats, but also without success.
Scene #2: Coaxing students to re-frame the problem
When no one seemed to be getting it, the teacher asked, “Think about how you’ve set up the problem in your mind—about what you believe the problem is about. For instance, have you made any assumptions about how long the lines ought to be? Don’t stay stuck on one approach if it’s not working!”
Scene #3: Alicia abandons a fixed response
After the teacher said this, Alicia indeed continued to think about how she saw the problem. “The lines need to be no longer than the distance across the square,” she said to herself. So she tried several more solutions, but none of them worked either.
The teacher walked by Alicia’s desk and saw what Alicia was doing. She repeated her earlier comment: “Have you assumed anything about how long the lines ought to be?”
Alicia stared at the teacher blankly, but then smiled and said, “Hmm! You didn’t actually say that the lines could be no longer than the matrix! Why not make them longer?” So she experimented again using oversized lines and soon discovered a solution:

Scene #4: Willem’s and Rachel’s alternative strategies
Meanwhile, Willem worked on the problem. As it happened, Willem loved puzzles of all kinds and had ample experience with them. He had not, however, seen this particular problem. “It must be a trick,” he said to himself because he knew from experience that problems posed in this way often were not what they first appeared to be. He mused to himself: “Think outside the box, they always tell you. . .” And that was just the hint he needed: he drew lines outside the box by making them longer than the matrix and soon came up with this solution:

When Rachel went to work, she took one look at the problem and knew the answer immediately: she had seen this problem before, though she could not remember where. She had also seen other drawing-related puzzles and knew that their solution always depended on making the lines longer, shorter, or differently angled than first expected. After staring at the dots briefly, she drew a solution faster than Alicia or even Willem. Her solution looked exactly like Willem’s.
This story illustrates two common features of problem-solving: the effect of degree of structure or constraint on problem-solving, and the effect of mental obstacles to solving problems. The next sections discuss each of these features and then look at common techniques for solving problems.
The Effect of Constraints: Well-Structured Versus Ill-Structured Problems
Problems vary in how much information they provide for solving a problem, as well as in how many rules or procedures are needed for a solution. A well-structured problem provides much of the information needed and can in principle be solved using relatively few clearly understood rules. Classic examples are the word problems often taught in math lessons or classes: everything you need to know is contained within the stated problem and the solution procedures are relatively clear and precise. An ill-structured problem has the converse qualities: the information is not necessarily within the problem, solution procedures are potentially quite numerous, and multiple solutions are likely (Voss, 2006). Extreme examples are problems like “How can the world achieve lasting peace?” or “How can teachers ensure that students learn?”
By these definitions, the nine-dot problem is relatively well-structured—though not completely. Most of the information needed for a solution is provided in Scene #1: there are nine dots shown and instructions given to draw four lines. But not all necessary information was given: students needed to consider lines that were longer than implied in the original statement of the problem. Students had to “think outside the box,” as Willem said—in this case, literally.
When a problem is well-structured, so are its solution procedures likely to be as well. A well-defined procedure for solving a particular kind of problem is often called an algorithm ; examples are the procedures for multiplying or dividing two numbers or the instructions for using a computer (Leiserson, et al., 2001). Algorithms are only effective when a problem is very well-structured and there is no question about whether the algorithm is an appropriate choice for the problem. In that situation, it pretty much guarantees a correct solution. They do not work well, however, with ill-structured problems, where they are ambiguities and questions about how to proceed or even about precisely what the problem is about. In those cases, it is more effective to use heuristics , which are general strategies—“rules of thumb,” so to speak—that do not always work but often do, or that provide at least partial solutions. When beginning research for a term paper, for example, a useful heuristic is to scan the library catalog for titles that look relevant. There is no guarantee that this strategy will yield the books most needed for the paper, but the strategy works enough of the time to make it worth trying.
In the nine-dot problem, most students began in Scene #1 with a simple algorithm that can be stated like this: “Draw one line, then draw another, and another, and another.” Unfortunately, this simple procedure did not produce a solution, so they had to find other strategies for a solution. Three alternatives are described in Scenes #3 (for Alicia) and 4 (for Willem and Rachel). Of these, Willem’s response resembled a heuristic the most: he knew from experience that a good general strategy that often worked for such problems was to suspect deception or trick in how the problem was originally stated. So he set out to question what the teacher had meant by the word line and came up with an acceptable solution as a result.
Common Obstacles to Solving Problems
The example also illustrates two common problems that sometimes happen during problem-solving. One of these is functional fixedness : a tendency to regard the functions of objects and ideas as fixed (German & Barrett, 2005). Over time, we get so used to one particular purpose for an object that we overlook other uses. We may think of a dictionary, for example, as necessarily something to verify spellings and definitions, but it also can function as a gift, a doorstop, or a footstool. For students working on the nine-dot matrix described in the last section, the notion of “drawing” a line was also initially fixed; they assumed it to be connecting dots but not extending lines beyond the dots. Functional fixedness sometimes is also called response set , the tendency for a person to frame or think about each problem in a series in the same way as the previous problem, even when doing so is not appropriate for later problems. In the example of the nine-dot matrix described above, students often tried one solution after another, but each solution was constrained by a set response not to extend any line beyond the matrix.
Functional fixedness and the response set are obstacles in problem representation , the way that a person understands and organizes information provided in a problem. If information is misunderstood or used inappropriately, then mistakes are likely—if indeed the problem can be solved at all. With the nine-dot matrix problem, for example, construing the instruction to draw four lines as meaning “draw four lines entirely within the matrix” means that the problem simply could not be solved. For another, consider this problem: “The number of water lilies on a lake doubles each day. Each water lily covers exactly one square foot. If it takes 100 days for the lilies to cover the lake exactly, how many days does it take for the lilies to cover exactly half of the lake?” If you think that the size of the lilies affects the solution to this problem, you have not represented the problem correctly. Information about lily size is not relevant to the solution and only serves to distract from the truly crucial information, the fact that the lilies double their coverage each day. (The answer, incidentally, is that the lake is half covered in 99 days; can you think why?)
Strategies to Assist Problem-Solving
Just as there are cognitive obstacles to problem-solving, there are also general strategies that help the process be successful, regardless of the specific content of a problem (Thagard, 2005). One helpful strategy is problem analysis —identifying the parts of the problem and working on each part separately. Analysis is especially useful when a problem is ill-structured. Consider this problem, for example: “Devise a plan to improve bicycle transportation in the city.” Solving this problem is easier if you identify its parts or component subproblems, such as (1) installing bicycle lanes on busy streets, (2) educating cyclists and motorists to ride safely, (3) fixing potholes on streets used by cyclists, and (4) revising traffic laws that interfere with cycling. Each separate subproblem is more manageable than the original, general problem. The solution of each subproblem contributes to the solution of the whole, though of course is not equivalent to a whole solution.
Another helpful strategy is working backward from a final solution to the originally stated problem. This approach is especially helpful when a problem is well-structured but also has elements that are distracting or misleading when approached in a forward, normal direction. The water lily problem described above is a good example: starting with the day when all the lake is covered (Day 100), ask what day would it, therefore, be half-covered (by the terms of the problem, it would have to be the day before, or Day 99). Working backward, in this case, encourages reframing the extra information in the problem (i. e. the size of each water lily) as merely distracting, not as crucial to a solution.
A third helpful strategy is analogical thinking —using knowledge or experiences with similar features or structures to help solve the problem at hand (Bassok, 2003). In devising a plan to improve bicycling in the city, for example, an analogy of cars with bicycles is helpful in thinking of solutions: improving conditions for both vehicles requires many of the same measures (improving the roadways, educating drivers). Even solving simpler, more basic problems is helped by considering analogies. A first-grade student can partially decode unfamiliar printed words by analogy to words he or she has learned already. If the child cannot yet read the word screen , for example, he can note that part of this word looks similar to words he may already know, such as seen or green, and from this observation derive a clue about how to read the word screen . Teachers can assist this process, as you might expect, by suggesting reasonable, helpful analogies for students to consider.
Video 5.4.1. Problem Solving explains strategies used for solving problems.
Many systems for problem-solving can be taught to learners (Pressley, 1995). There are problem-solving strategies to improve general problem solving (Burkell, Schneider, & Pressley, 1990; Mayer, 1987; Sternberg, 1988), scientific thinking (Kuhn, 1989), mathematical problem solving (Schoenfeld, 1989), and writing during the elementary years (Harris & Graham, 1992a) and during adolescence (Applebee, 1984; Langer & Applebee, 1987).
A problem-solving system that can be used in a variety of curriculum areas and with a variety of problems is called IDEAL (Bransford & Steen, 1984). IDEAL involves five stages of problem-solving:
- Identify the problem. Learners must know what the problem is before they can solve it. During this stage of problem-solving, learners ask themselves whether they understand what the problem is and whether they have stated it clearly.
- Define terms. During this stage, learners check whether they understand what each word in the problem statement means.
- Explore strategies. At this stage, learners compile relevant information and try out strategies to solve the problem. This can involve drawing diagrams, working backward to solve a mathematical or reading comprehension problem, or breaking complex problems into manageable units.
- Act on the strategy. Once learners have explored a variety of strategies, they select one and now use it.
- Look at the effects. During the final stage of the IDEAL method, learners ask themselves whether they have come up with an acceptable solution.
Video 5.4.2. The Problem Solving Model explains the process involved in solving problems. These steps can be explicitly taught to enhance problem-solving skills.
Candela Citations
- Problem-Solving. Authored by : Nicole Arduini-Van Hoose. Provided by : Hudson Valley Community College. Retrieved from : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/edpsy/chapter/problemsolving. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Educational Psychology. Authored by : Kelvin Seifert and Rosemary Sutton. Provided by : The Saylor Foundation. Retrieved from : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/educationalpsychology. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Educational Psychology. Authored by : Bohlin. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Problem Solving. Authored by : Carole Yue. Provided by : Khan Academy. Retrieved from : https://youtu.be/J3GGx9wy07w. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- The Problem Solving Model. Provided by : Gregg Learning. Retrieved from : https://youtu.be/CDk_BD1LXiI. License : All Rights Reserved
Educational Psychology Copyright © 2020 by Nicole Arduini-Van Hoose is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
The Stages of the Problem Solving Cycle in Cognitive Psychology – Understanding, Planning, Execution, Evaluation, and Reflection
- Post author By bicycle-u
- Post date 08.12.2023
Problem solving is a fundamental aspect of human cognition. It involves the ability to identify and define a problem, generate potential solutions, evaluate those solutions, and select the most appropriate one. The problem solving cycle is a key concept in cognitive psychology that helps us understand how individuals approach and solve problems.
In the problem solving cycle , individuals first must recognize and define the problem they are facing. This involves identifying the specific issue or obstacle that needs to be overcome. Once the problem is clearly defined, individuals can then move on to the next stage of the cycle.
Next, individuals engage in the process of generating potential solutions . This may involve brainstorming ideas, seeking out information or advice, or experimenting with different approaches. The goal is to come up with as many possible solutions as possible, without judgment or evaluation.
Once a range of potential solutions has been generated, individuals then evaluate these solutions based on their feasibility and effectiveness . This involves assessing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution and considering the potential outcomes of implementing them. It may also involve consulting others or seeking additional information to inform the evaluation process.
Finally, individuals select the most appropriate solution from the evaluated options. This decision-making process takes into account various factors such as the individual’s goals, resources, and constraints. Once a solution has been selected, individuals can then implement and evaluate its effectiveness, closing the problem solving cycle.
The problem solving cycle is a dynamic and iterative process that can be applied to a wide range of problems and situations. It provides a framework for understanding how individuals approach and solve problems, and it can be useful in both personal and professional settings. By understanding the various stages of the problem solving cycle, individuals can become more effective problem solvers and make better decisions.
Understanding the Problem Solving Process
In cognitive psychology, the problem solving process is a key concept in understanding how individuals navigate and overcome challenges. Problem solving is a cyclical process that involves identifying a problem, developing a strategy to solve it, implementing the strategy, and then evaluating the results.
Identifying the problem: The first step in the problem solving cycle is identifying the problem at hand. This may involve defining the problem, gathering information and relevant data, and understanding the desired outcome.
Developing a strategy: Once the problem is identified, individuals must develop a strategy or plan of action to solve it. This may involve brainstorming ideas, evaluating potential solutions, and selecting the best approach.
Implementing the strategy: After a strategy is developed, it must be put into action. This may involve executing specific steps, utilizing resources, and adjusting the strategy as needed.
Evaluating the results: The final step in the problem solving cycle is evaluating the results of the implemented strategy. This may involve assessing the effectiveness of the solution, determining if the desired outcome was achieved, and making any necessary adjustments or improvements.
The Role of Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology plays a crucial role in understanding the problem solving process. It focuses on how individuals perceive, think, and reason about problems, as well as the various strategies and mental processes involved in solving them.
Research in cognitive psychology has shown that problem solving is not purely a linear process, but rather a dynamic and iterative cycle. Individuals may iterate through the different stages of the problem solving cycle multiple times as they encounter new information or face unexpected challenges.
The study of problem solving in cognitive psychology has led to the development of various theories and models, such as the Gestalt theory, which emphasizes the importance of insight and reorganizing information, and the information processing model, which highlights the role of attention, memory, and decision-making in problem solving.
The Importance of Problem Solving Skills
Problem solving is a key concept in cognitive psychology. It is a process that involves identifying, analyzing, and coming up with solutions to problems. Problem solving skills are essential in various aspects of life, including personal and professional contexts.
Mastering problem solving skills enables individuals to tackle challenges and overcome obstacles effectively. It helps in critical thinking, decision making, and finding innovative solutions. Problem solving skills are also important in the field of psychology, as they are often used to understand and address complex psychological issues.
Enhancing Cognitive Abilities
Problem solving activities stimulate and enhance cognitive abilities. They require individuals to think critically, analyze information, and use logical reasoning. By engaging in problem solving, individuals improve their cognitive processes, such as memory, attention, and problem representation.
Building Resilience
Developing problem solving skills also helps in building resilience. It teaches individuals to approach challenges with a proactive mindset and seek solutions rather than giving up. This resilience can be applied in various aspects of life, including personal relationships, work, and education.
In conclusion, problem solving skills play a crucial role in cognitive psychology and various aspects of life. They enhance cognitive abilities, promote critical thinking, and build resilience. Developing and honing problem solving skills is essential for personal growth and success in today’s complex world.
The Four Stages of Problem Solving
Problem solving is a cognitive process that involves the use of mental processes to find a solution to a problem. It is a cycle that is often studied in cognitive psychology. The problem solving cycle consists of four stages, which are:
1. Understanding the Problem
In this stage, the individual must first understand and define the problem. This involves gathering information, analyzing the problem, and identifying the key elements that need to be addressed. It is important to have a clear understanding of the problem before moving on to the next stage.
2. Generating Potential Solutions
Once the problem is understood, the next stage involves generating potential solutions. This requires using both logical and creative thinking to come up with possible ways to solve the problem. It is important to consider different perspectives and explore a variety of options.
3. Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
After generating potential solutions, the individual must evaluate and select the most appropriate solution. This involves weighing the pros and cons of each potential solution and considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and practicality. The goal is to select a solution that is likely to lead to the desired outcome.
4. Implementing and Evaluating the Solution
Once a solution has been selected, the final stage involves implementing the solution and evaluating its effectiveness. This may involve taking action, making changes, and monitoring the results. It is important to assess whether the solution has solved the problem and to make adjustments if needed.
In conclusion, problem solving is a cognitive process that involves four stages: understanding the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating and selecting solutions, and implementing and evaluating the solution. By following this problem solving cycle, individuals can effectively approach and solve a wide range of problems.
Identifying the Problem
The first step in the problem solving cycle is identifying the problem. In cognitive psychology, this step involves recognizing that there is a problem to be solved and understanding what it entails.
When identifying a problem, it is important to clearly define and articulate what the issue is. This can involve breaking the problem down into smaller components or examining the factors that contribute to the problem.
Factors to consider when identifying a problem:
- What is the desired outcome or goal?
- What are the obstacles or challenges that need to be overcome?
- What are the potential causes or explanations for the problem?
Identifying the problem involves gathering information and analyzing it to gain a better understanding of the situation. This can include conducting research, gathering data, or seeking input from others who may have expertise or experience in the area.
Once the problem has been clearly identified, it can then be approached using the problem solving cycle. By breaking down the problem into smaller steps and systematically working through each one, individuals can increase their chances of finding an effective solution.
Defining the Problem
Defining the problem is a crucial step in the problem-solving cycle. In the context of cognitive psychology, a problem can be defined as a situation or task that requires a solution. This could be a complex mathematical equation, a riddle, or a real-life challenge. The process of defining the problem involves clarifying the specific requirements or constraints of the situation and understanding what needs to be solved. By clearly defining the problem, it becomes easier to identify potential strategies and solutions.
When defining a problem, it is important to consider both the immediate and underlying issues. Often, the surface-level problem may not be the root cause, and addressing only the symptoms may not lead to a satisfactory solution. Therefore, it is essential to dig deeper and identify the underlying factors that contribute to the problem.
Clarifying the requirements
One aspect of defining the problem is clarifying the specific requirements or constraints that need to be considered. These requirements can include the desired outcome, the available resources, the time frame, and any limitations or restrictions. By understanding these requirements, it becomes easier to focus on finding a solution that meets the given criteria.
Understanding the problem space
Another important aspect of defining the problem is understanding the problem space. The problem space refers to the set of all possible solutions and strategies that can be explored to solve the problem. By understanding the problem space, individuals can develop a clearer understanding of the scope of the problem and the potential avenues for finding a solution.
Generating Solution Options
In cognitive psychology, problem solving is a key concept that explores how individuals go about finding solutions to problems. One important aspect of the problem solving cycle is generating solution options.
When faced with a problem, individuals engage in cognitive processes to come up with potential solutions. This often involves brainstorming, where individuals generate a list of possible options.
There are various strategies that individuals can use to generate solution options. One common approach is divergent thinking, which involves thinking creatively and generating a large number of potential solutions. This can be done by considering different perspectives, exploring alternative possibilities, and challenging assumptions.
Another strategy is convergent thinking, which involves evaluating and narrowing down the potential solutions. This can be done by considering the feasibility and practicality of each option, as well as weighing the potential risks and benefits.
It is important for individuals to consider a wide range of solution options, as this increases the likelihood of finding an effective solution. This can be achieved by using techniques such as mind mapping, where individuals visually organize their thoughts and ideas to generate new connections and possibilities.
By generating a variety of solution options, individuals can increase their chances of finding the most suitable and effective solution to a problem. This stage of the problem solving cycle is crucial in the overall problem solving process.
Evaluating and Selecting the Best Solution
Once you have gone through the problem solving cycle and generated potential solutions, the next step is to evaluate and select the best solution. This is an essential part of the problem solving process, as it involves critically analyzing each potential solution and determining which one is the most effective and feasible.
When evaluating potential solutions, it is important to consider various factors. One key factor is the effectiveness of each solution in actually solving the problem at hand. Will the solution address the root cause of the problem, or just temporarily alleviate the symptoms?
In addition to effectiveness, it is also important to consider the feasibility of each solution. Is the solution realistic and practical to implement? Does it require significant resources or time that may not be available? These are all important considerations to take into account when evaluating potential solutions.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the potential consequences of each solution. Will the solution create any new problems or unintended side effects? Will it have any negative impacts on other areas or stakeholders? These potential consequences must be carefully considered before making a final decision.
Finally, it is important to approach the evaluation process with an open and flexible mindset. It is not uncommon for new information or perspectives to emerge during the evaluation process, which may alter the assessment of potential solutions. Remaining open to new information and being willing to adapt the evaluation criteria is crucial in selecting the best solution.
By carefully evaluating each potential solution and considering factors such as effectiveness, feasibility, and potential consequences, you can effectively select the best solution to the problem at hand. This is an essential step in the problem solving cycle, as it moves you closer to a successful resolution.
Implementing the Solution
Once the problem-solving cycle has been completed in cognitive psychology, the next step is to implement the solution. This phase involves taking the proposed solution and putting it into action.
Before implementation, it is crucial to evaluate the solution thoroughly. This evaluation helps ensure that the proposed solution is practical and feasible.
Evaluating the Solution
The evaluation process involves considering possible obstacles and risks that could hinder the successful implementation of the solution. By identifying these potential challenges, steps can be taken to mitigate them.
In addition, evaluating the solution also involves conducting a cost-benefit analysis. This analysis takes into account the potential costs and benefits associated with implementing the solution. It helps determine whether the solution is worth pursuing.
Putting the Solution into Action
Once the solution has been thoroughly evaluated, it is time to put it into action. This requires careful planning and coordination.
During the implementation phase, it is important to closely monitor the progress and make any necessary adjustments. This ensures that the solution is effectively addressing the problem at hand.
Furthermore, clear communication is vital during implementation. All relevant stakeholders should be informed and involved in the process to ensure everyone is working towards a common goal.
By implementing the solution effectively, the problem-solving cycle in cognitive psychology can come to a successful conclusion.
Monitoring and Evaluating the Outcome
Monitoring and evaluating the outcome is a crucial step in the problem-solving process in cognitive psychology. After identifying and implementing a solution, it is important to assess whether the problem has been effectively solved and whether the desired outcome has been achieved.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Solution
One way to monitor and evaluate the outcome is to assess the effectiveness of the solution. This involves determining whether the chosen solution has successfully addressed the problem and whether it has led to the desired result. Cognitive psychologists often use various measures and metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of problem-solving strategies. These may include objective measures such as test scores or subjective measures such as self-report questionnaires.
By evaluating the effectiveness of the solution, cognitive psychologists can determine whether further adjustments or modifications are necessary. If the outcome is not satisfactory, they can go back to the problem-solving cycle and repeat the steps to find a more suitable solution.
Reflecting on the Process
In addition to evaluating the effectiveness of the solution, it is also important to reflect on the problem-solving process itself. This involves considering the strategies and techniques used, as well as identifying any obstacles or challenges encountered. By reflecting on the process, cognitive psychologists can gain valuable insights into how they approached the problem and how they can improve their problem-solving skills in the future.
Reflection can be done through self-reflection or by seeking feedback from others, such as colleagues or experts in the field. This feedback can provide alternative perspectives and help identify areas for improvement.
In conclusion, monitoring and evaluating the outcome is a critical aspect of the problem-solving cycle in cognitive psychology. By assessing the effectiveness of the solution and reflecting on the process, cognitive psychologists can continually improve their problem-solving skills and contribute to the development of this field.
The Role of Cognitive Processes in Problem Solving
In the field of cognitive psychology, problem solving is a fundamental aspect of human thinking. It involves the use of various cognitive processes to analyze a problem, develop possible solutions, and determine the best course of action.
One key cognitive process involved in problem solving is perception. This process allows individuals to perceive and understand the problem at hand, by gathering information from the environment and organizing it into meaningful patterns. Perception helps identify the relevant aspects of a problem and guides the problem-solving process.
Another important cognitive process in problem solving is reasoning. Reasoning involves logical thinking and the ability to draw conclusions based on available information. It helps individuals make sense of the problem and generate possible solutions. Reasoning also helps evaluate the potential outcomes of each solution and select the most appropriate one.
Memory plays a crucial role in problem solving as well. It allows individuals to recall relevant information from past experiences and apply it to the current problem. Memory aids in recognizing patterns, generating hypotheses, and retrieving information necessary for problem solving. Without memory, it would be challenging to solve problems efficiently.
Moreover, attention and concentration are essential cognitive processes in problem solving. They help individuals focus on the relevant aspects of a problem and block out distractions. Attention allows individuals to allocate cognitive resources effectively and process information in a systematic manner. Concentration enables individuals to stay engaged in problem solving and persevere until a solution is found.
The role of cognitive processes in problem solving is vital as they provide the framework for effective problem-solving strategies. Understanding how perception, reasoning, memory, attention, and concentration contribute to problem solving helps researchers and practitioners develop interventions and techniques to improve problem-solving skills.
In conclusion, cognitive processes are crucial in problem solving. Perception, reasoning, memory, attention, and concentration work together to help individuals analyze problems, generate solutions, and make informed decisions. By studying and understanding these cognitive processes, researchers can enhance problem-solving abilities, ultimately leading to more effective problem-solving strategies in various fields of study and practice.

How Cognitive Biases can Impact Problem Solving
Cognitive biases are inherent tendencies in human thinking that can lead to errors or deviations from rationality. These biases can have a significant impact on problem solving, as they can influence the way individuals perceive, interpret, and evaluate information.
Confirmation Bias
One common cognitive bias that can affect problem solving is confirmation bias. This bias leads individuals to favor information that confirms their existing beliefs or hypotheses while disregarding or downplaying information that contradicts them. In problem-solving scenarios, confirmation bias can prevent individuals from considering alternative solutions or exploring different perspectives, potentially leading to a less effective problem-solving process.
Availability Heuristic
The availability heuristic is another cognitive bias that can impact problem solving. This bias involves relying on easily accessible information or examples when making judgments or decisions. In problem-solving situations, this bias can lead individuals to overlook less accessible information or fail to consider all relevant factors. This can limit the effectiveness of problem solving by restricting the range of potential solutions or failing to consider alternative approaches.
- Overcoming cognitive biases in problem solving
Recognizing and overcoming cognitive biases is crucial for effective problem solving. Strategies such as actively seeking out diverse perspectives, questioning assumptions, and considering alternative explanations can help mitigate the impact of cognitive biases. Additionally, fostering an environment that encourages open-mindedness, critical thinking, and intellectual humility can also support more effective problem-solving processes.
By understanding how cognitive biases can impact problem solving, psychologists and individuals alike can work towards improving their problem-solving skills and decision-making processes. By recognizing and addressing these biases, individuals can enhance their ability to approach problems with greater objectivity, flexibility, and creativity.
The Relationship Between Problem Solving and Decision Making
Problem solving and decision making are closely interconnected in cognitive psychology. When faced with a problem, individuals engage in a cognitive process known as problem solving, which involves identifying and evaluating possible solutions in order to reach a desired goal or outcome. Decision making, on the other hand, refers to the act of choosing one particular solution from the options generated during the problem-solving process.
The problem-solving cycle, a key concept in cognitive psychology, highlights the iterative nature of problem solving and decision making. This cycle consists of several steps, including problem identification, problem analysis, solution generation, solution evaluation, and solution implementation. During the problem identification phase, individuals recognize and define the problem they are facing. Problem analysis involves gathering information and analyzing the underlying causes and factors contributing to the problem. Once a thorough analysis is conducted, individuals can generate potential solutions through creative thinking and brainstorming.
After generating potential solutions, individuals must evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of each option. This involves considering the potential consequences and weighing the pros and cons of each alternative. By carefully assessing each solution, individuals can make an informed decision and choose the most suitable course of action. Finally, the chosen solution is implemented, and individuals monitor the outcomes to determine whether the problem has been effectively resolved.
It is important to note that problem solving and decision making are not linear processes, but rather they involve feedback loops and revisions as new information becomes available or as the initial solution proves to be ineffective. Successful problem solving and decision making require flexibility, critical thinking, and adaptability to changing circumstances.
In summary, problem solving and decision making are intertwined cognitive processes within the problem-solving cycle. Problem solving involves identifying and evaluating possible solutions, while decision making involves choosing the most appropriate solution. By understanding the relationship between problem solving and decision making, individuals can enhance their problem-solving skills and make more effective decisions in various aspects of life and work.
The Effect of Expertise on Problem Solving
In the cognitive psychology field, the problem solving cycle is a key concept that involves several stages: understanding the problem, devising a plan, executing the plan, and evaluating the solution. An important factor that can influence problem solving abilities is expertise.
Experts, who have extensive knowledge and experience in a specific domain, often exhibit superior problem solving skills compared to novices. This is because experts have a large mental database of problem-solving strategies and a deep understanding of the underlying concepts. They can quickly recognize patterns and make accurate decisions based on their knowledge.
Research has shown that experts are able to solve problems more efficiently and effectively than novices. They are able to quickly identify the relevant information and ignore irrelevant details, which allows them to focus on the core of the problem. Experts also have a better ability to generate and evaluate multiple potential solutions, leading to more creative problem solving.
Furthermore, experts are more likely to use metacognitive strategies, such as self-monitoring and self-regulation, during the problem solving process. They are able to reflect on their own thinking and adjust their strategies as needed. This metacognitive awareness helps experts to overcome obstacles and adapt their problem solving approach as necessary.
However, it is important to note that expertise is domain-specific. An individual may be an expert in one area but not in another. For example, a chess grandmaster may struggle with solving complex math problems. Therefore, expertise does not guarantee proficiency in all problem-solving domains.
In conclusion, expertise plays a significant role in problem solving. Experts have a deeper understanding of the problem domain, possess a larger repertoire of strategies, and exhibit metacognitive awareness. These factors contribute to their more efficient and effective problem solving abilities compared to novices.
Developing Problem Solving Skills through Practice
In the field of psychology, problem solving is considered an essential cognitive skill that helps individuals navigate through various challenges and obstacles. The problem solving cycle, a key concept in cognitive psychology, emphasizes the importance of practice in developing and honing problem solving skills.
Practice plays a crucial role in problem solving as it helps individuals familiarize themselves with different problem-solving techniques and strategies. By engaging in regular practice, individuals can strengthen their analytical thinking, creative problem solving, and decision-making abilities.
Through practice, individuals learn to approach problems systematically, breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps. This systematic approach allows individuals to identify the root causes of a problem, generate potential solutions, and evaluate the effectiveness of each solution.
In addition to improving analytical thinking, practice also helps individuals develop their creative problem solving skills. By repeatedly facing various problems, individuals become more comfortable with thinking outside the box and exploring unconventional solutions. This creative thinking enables individuals to come up with innovative and effective solutions to complex problems.
Moreover, practice enhances individuals’ decision-making abilities. As individuals engage in problem solving practice, they become more skilled at assessing different options, weighing the pros and cons, and making informed decisions. This ability to make sound decisions is crucial in both personal and professional contexts.
In conclusion, developing problem solving skills requires consistent practice. By engaging in regular problem solving practice, individuals can improve their analytical thinking, creative problem solving, and decision-making abilities. The problem solving cycle emphasizes the importance of practice in developing these skills, and individuals who actively engage in practice are more likely to become adept problem solvers.
Teaching Problem Solving Skills in Education
Problem solving skills are an essential component of education, as they enable students to analyze and tackle complex issues across various subject areas. By teaching problem solving skills, educators help students develop critical thinking abilities and cognitive strategies that can be applied in real-life situations.
The Problem Solving Cycle
One effective approach to teaching problem solving skills is through the use of the problem solving cycle. The problem solving cycle is a key concept in cognitive psychology, which involves a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems.
First, students are introduced to a problem or a question that requires analysis and solution. They are encouraged to define the problem clearly and understand its scope. This initial step helps students develop problem awareness and identify potential barriers or constraints that may affect the problem-solving process.
Next, students engage in information gathering and analysis. They gather relevant data, facts, and evidence, and apply critical thinking skills to evaluate and interpret the information. This step helps students develop analytical skills and generate possible solutions.
Once students have gathered and analyzed the information, they move on to the generation of potential solutions. This involves brainstorming and exploring different approaches to the problem, encouraging creativity and flexibility in thinking. Students are encouraged to think outside the box and consider multiple perspectives.
After generating potential solutions, students evaluate each option based on effectiveness, feasibility, and potential consequences. They consider the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, weighing the pros and cons. This step helps students develop decision-making skills and enhances their ability to critically evaluate potential solutions.
Finally, students select the most appropriate solution and implement it. They develop an action plan, outlining the steps needed to solve the problem. This requires effective communication skills, as students may need to collaborate and communicate their ideas with others.
Benefits of Teaching Problem Solving Skills
Teaching problem solving skills in education offers numerous benefits to students. Firstly, it enhances their cognitive abilities, allowing them to think critically and logically. This helps students become more independent learners and problem solvers.
Additionally, teaching problem solving skills improves students’ creativity and innovation. By encouraging them to think outside the box and explore different solutions, educators foster a mindset of curiosity and exploration.
Moreover, problem solving skills are transferable to various contexts, both within and outside of the classroom. Students can apply these skills to academic subjects, as well as to real-life situations, such as social issues, personal challenges, and future career paths.
In conclusion, teaching problem solving skills in education is crucial for students’ cognitive development and future success. By implementing the problem solving cycle and fostering critical thinking abilities, educators empower students with the skills necessary to navigate complex challenges and become lifelong learners.
Real-World Applications of the Problem Solving Cycle
The problem solving cycle is a fundamental concept in cognitive psychology that has numerous applications in real-world situations. This cycle involves a series of steps that individuals go through in order to identify, analyze, and solve problems.
1. Business
In the business world, problem solving is essential for success. From identifying market trends and determining customer needs to finding solutions to production issues or administrative challenges, the problem solving cycle is used to tackle a variety of business-related problems.
2. Education
The problem solving cycle is also highly applicable in education. Teachers often use this approach to help students develop critical thinking skills and solve complex problems. By following this cycle, students learn to break down problems, gather relevant information, analyze various options, and come up with effective solutions.
3. Medicine
Medical professionals frequently employ the problem solving cycle when diagnosing and treating patients. By systematically gathering patient history, evaluating symptoms, conducting tests, and analyzing data, doctors are able to identify the underlying problem and develop appropriate treatment plans.
4. Engineering
In the field of engineering, the problem solving cycle is crucial for designing and implementing solutions. Engineers use this approach to identify and address technical challenges, improve existing systems, and develop innovative technologies. By following this cycle, engineers can efficiently solve complex problems and ensure the success of their projects.
5. Everyday Life
Lastly, the problem solving cycle is applicable to everyday life. Whether it’s figuring out the best route to work, resolving conflicts in relationships, or making important decisions, individuals use this cycle to identify issues, explore possible solutions, and make informed choices.
The problem solving cycle is a versatile concept that finds widespread applications in various domains. From business and education to medicine and engineering, this approach facilitates effective problem solving and decision making. By following the steps of the cycle, individuals and organizations can overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
The Future of Problem Solving Research
In the field of cognitive psychology, research on problem solving is an ongoing and dynamic area of study. As technology continues to advance and our understanding of the cognitive processes involved in problem solving deepens, the future of problem solving research looks promising.
Advancements in Technology
Advancements in technology have already had a significant impact on problem solving research. The use of computer simulations and virtual environments has allowed researchers to create realistic problem-solving scenarios and collect data in a controlled environment. This technology has also allowed for the development of intelligent tutoring systems that can provide personalized feedback and guidance to individuals as they work through various problem-solving tasks.
In the future, we can expect even more sophisticated technologies to be developed, which will enhance our ability to study problem solving. For example, virtual reality technology may allow researchers to create immersive problem-solving environments that closely mimic real-life situations. This could provide researchers with valuable insights into how individuals approach and solve complex problems in a realistic setting.
Integration of Cognitive Processes
As our understanding of cognitive processes continues to grow, future research on problem solving will likely focus on the integration of various cognitive processes. Problem solving is a complex task that involves numerous cognitive processes, such as attention, memory, decision-making, and reasoning. Understanding how these processes interact and influence problem-solving performance will be crucial in developing effective strategies for problem solving.
Researchers may also explore the role of emotions in problem solving. Emotions can have a significant impact on cognitive processes and decision-making. Understanding how emotions influence problem-solving performance may provide valuable insights into how individuals can improve their problem-solving abilities.
Collaborative Problem Solving
Collaborative problem solving, or problem solving in a group setting, is another area that holds great potential for future research. Many real-world problems require collaboration and teamwork to solve effectively. Research on collaborative problem solving can provide valuable insights into how individuals interact and communicate with each other during problem-solving tasks, and how team dynamics impact problem-solving performance.
Furthermore, advancements in communication technology have made it easier than ever for individuals to collaborate remotely. Studying how individuals solve problems in virtual teams or online communities can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of collaborative problem solving in today’s interconnected world.
Continued Development of the Problem Solving Cycle
The problem solving cycle, which involves the stages of problem identification, solution generation, solution implementation, and solution evaluation, will continue to be a key concept in problem solving research. Researchers will seek to understand how individuals move through these stages, the strategies they employ at each stage, and how their problem-solving performance can be optimized.
By understanding the cognitive processes involved in each stage of the problem solving cycle, researchers can develop interventions and strategies to help individuals become more effective problem solvers.
In conclusion, the future of problem solving research in cognitive psychology looks promising. Advancements in technology, a deeper understanding of cognitive processes, the study of collaborative problem solving, and the continued development of the problem solving cycle will all contribute to our understanding of problem solving and help individuals become more effective in solving complex problems.
Questions and answers:
What is the problem-solving cycle.
The problem-solving cycle is a key concept in cognitive psychology that refers to the sequence of steps or processes involved in solving a problem.
What are the stages of the problem-solving cycle?
The problem-solving cycle typically consists of four stages: problem identification, problem definition, strategy selection, and solution implementation.
How does problem identification occur in the problem-solving cycle?
Problem identification involves recognizing that there is a problem or a discrepancy between a desired state and the current state.
What is problem definition in the problem-solving cycle?
Problem definition involves clearly specifying or defining the problem in a way that allows for a focused approach to finding a solution.
What is strategy selection in the problem-solving cycle?
Strategy selection involves choosing an appropriate approach or method to solve the problem, such as using a specific algorithm or heuristic.
What is the problem-solving cycle in cognitive psychology?
The problem-solving cycle is a concept in cognitive psychology that outlines the steps individuals go through when tackling a problem. It involves identifying the problem, gathering information, generating possible solutions, evaluating the solutions, and implementing the best one.
How does the problem-solving cycle help in problem-solving?
The problem-solving cycle provides a structured approach to problem-solving by breaking it down into manageable steps. By following this cycle, individuals can better understand the problem, explore various solutions, evaluate their effectiveness, and ultimately make an informed decision on how to solve the problem.
Related posts:
- A Comprehensive Guide to the Problem Solving Cycle in Psychology – Strategies, Techniques, and Applications
- The Importance of Implementing the Problem Solving Cycle in Education to Foster Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills in Students
- The Step-by-Step Problem Solving Cycle for Effective Solutions
- The Comprehensive Guide to the Problem Solving Cycle in PDF Format
- The Importance of the Problem Solving Cycle in Business Studies – Strategies for Success
- A Comprehensive Guide on the Problem Solving Cycle – Step-by-Step Approach with Real-Life Example
- The Seven Essential Steps of the Problem Solving Cycle
- Exploring the Problem Solving Cycle in Computer Science – Strategies, Techniques, and Tools

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
IResearchNet
Problem Solving
Problem solving, a fundamental cognitive process deeply rooted in psychology, plays a pivotal role in various aspects of human existence, especially within educational contexts. This article delves into the nature of problem solving, exploring its theoretical underpinnings, the cognitive and psychological processes that underlie it, and the application of problem-solving skills within educational settings and the broader real world. With a focus on both theory and practice, this article underscores the significance of cultivating problem-solving abilities as a cornerstone of cognitive development and innovation, shedding light on its applications in fields ranging from education to clinical psychology and beyond, thereby paving the way for future research and intervention in this critical domain of human cognition.
Introduction
Problem solving, a quintessential cognitive process deeply embedded in the domains of psychology and education, serves as a linchpin for human intellectual development and adaptation to the ever-evolving challenges of the world. The fundamental capacity to identify, analyze, and surmount obstacles is intrinsic to human nature and has been a subject of profound interest for psychologists, educators, and researchers alike. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of problem solving, investigating its theoretical foundations, cognitive intricacies, and practical applications in educational contexts. With a clear understanding of its multifaceted nature, we will elucidate the pivotal role that problem solving plays in enhancing learning, fostering creativity, and promoting cognitive growth, setting the stage for a detailed examination of its significance in both psychology and education. In the continuum of psychological research and educational practice, problem solving stands as a cornerstone, enabling individuals to navigate the complexities of their world. This article’s thesis asserts that problem solving is not merely a cognitive skill but a dynamic process with profound implications for intellectual growth and application in diverse real-world contexts.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, the nature of problem solving.
Problem solving, within the realm of psychology, refers to the cognitive process through which individuals identify, analyze, and resolve challenges or obstacles to achieve a desired goal. It encompasses a range of mental activities, such as perception, memory, reasoning, and decision-making, aimed at devising effective solutions in the face of uncertainty or complexity.
Problem solving as a subject of inquiry has drawn from various theoretical perspectives, each offering unique insights into its nature. Among the seminal theories, Gestalt psychology has highlighted the role of insight and restructuring in problem solving, emphasizing that individuals often reorganize their mental representations to attain solutions. Information processing theories, inspired by computer models, emphasize the systematic and step-by-step nature of problem solving, likening it to information retrieval and manipulation. Furthermore, cognitive psychology has provided a comprehensive framework for understanding problem solving by examining the underlying cognitive processes involved, such as attention, memory, and decision-making. These theoretical foundations collectively offer a richer comprehension of how humans engage in and approach problem-solving tasks.
Problem solving is not a monolithic process but a series of interrelated stages that individuals progress through. These stages are integral to the overall problem-solving process, and they include:
- Problem Representation: At the outset, individuals must clearly define and represent the problem they face. This involves grasping the nature of the problem, identifying its constraints, and understanding the relationships between various elements.
- Goal Setting: Setting a clear and attainable goal is essential for effective problem solving. This step involves specifying the desired outcome or solution and establishing criteria for success.
- Solution Generation: In this stage, individuals generate potential solutions to the problem. This often involves brainstorming, creative thinking, and the exploration of different strategies to overcome the obstacles presented by the problem.
- Solution Evaluation: After generating potential solutions, individuals must evaluate these alternatives to determine their feasibility and effectiveness. This involves comparing solutions, considering potential consequences, and making choices based on the criteria established in the goal-setting phase.
These components collectively form the roadmap for navigating the terrain of problem solving and provide a structured approach to addressing challenges effectively. Understanding these stages is crucial for both researchers studying problem solving and educators aiming to foster problem-solving skills in learners.
Cognitive and Psychological Aspects of Problem Solving
Problem solving is intricately tied to a range of cognitive processes, each contributing to the effectiveness of the problem-solving endeavor.
- Perception: Perception serves as the initial gateway in problem solving. It involves the gathering and interpretation of sensory information from the environment. Effective perception allows individuals to identify relevant cues and patterns within a problem, aiding in problem representation and understanding.
- Memory: Memory is crucial in problem solving as it enables the retrieval of relevant information from past experiences, learned strategies, and knowledge. Working memory, in particular, helps individuals maintain and manipulate information while navigating through the various stages of problem solving.
- Reasoning: Reasoning encompasses logical and critical thinking processes that guide the generation and evaluation of potential solutions. Deductive and inductive reasoning, as well as analogical reasoning, play vital roles in identifying relationships and formulating hypotheses.
While problem solving is a universal cognitive function, individuals differ in their problem-solving skills due to various factors.
- Intelligence: Intelligence, as measured by IQ or related assessments, significantly influences problem-solving abilities. Higher levels of intelligence are often associated with better problem-solving performance, as individuals with greater cognitive resources can process information more efficiently and effectively.
- Creativity: Creativity is a crucial factor in problem solving, especially in situations that require innovative solutions. Creative individuals tend to approach problems with fresh perspectives, making novel connections and generating unconventional solutions.
- Expertise: Expertise in a specific domain enhances problem-solving abilities within that domain. Experts possess a wealth of knowledge and experience, allowing them to recognize patterns and solutions more readily. However, expertise can sometimes lead to domain-specific biases or difficulties in adapting to new problem types.
Despite the cognitive processes and individual differences that contribute to effective problem solving, individuals often encounter barriers that impede their progress. Recognizing and overcoming these barriers is crucial for successful problem solving.
- Functional Fixedness: Functional fixedness is a cognitive bias that limits problem solving by causing individuals to perceive objects or concepts only in their traditional or “fixed” roles. Overcoming functional fixedness requires the ability to see alternative uses and functions for objects or ideas.
- Confirmation Bias: Confirmation bias is the tendency to seek, interpret, and remember information that confirms preexisting beliefs or hypotheses. This bias can hinder objective evaluation of potential solutions, as individuals may favor information that aligns with their initial perspectives.
- Mental Sets: Mental sets are cognitive frameworks or problem-solving strategies that individuals habitually use. While mental sets can be helpful in certain contexts, they can also limit creativity and flexibility when faced with new problems. Recognizing and breaking out of mental sets is essential for overcoming this barrier.
Understanding these cognitive processes, individual differences, and common obstacles provides valuable insights into the intricacies of problem solving and offers a foundation for improving problem-solving skills and strategies in both educational and practical settings.
Problem Solving in Educational Settings
Problem solving holds a central position in educational psychology, as it is a fundamental skill that empowers students to navigate the complexities of the learning process and prepares them for real-world challenges. It goes beyond rote memorization and standardized testing, allowing students to apply critical thinking, creativity, and analytical skills to authentic problems. Problem-solving tasks in educational settings range from solving mathematical equations to tackling complex issues in subjects like science, history, and literature. These tasks not only bolster subject-specific knowledge but also cultivate transferable skills that extend beyond the classroom.
Problem-solving skills offer numerous advantages to both educators and students. For teachers, integrating problem-solving tasks into the curriculum allows for more engaging and dynamic instruction, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter. Additionally, it provides educators with insights into students’ thought processes and areas where additional support may be needed. Students, on the other hand, benefit from the development of critical thinking, analytical reasoning, and creativity. These skills are transferable to various life situations, enhancing students’ abilities to solve complex real-world problems and adapt to a rapidly changing society.
Teaching problem-solving skills is a dynamic process that requires effective pedagogical approaches. In K-12 education, educators often use methods such as the problem-based learning (PBL) approach, where students work on open-ended, real-world problems, fostering self-directed learning and collaboration. Higher education institutions, on the other hand, employ strategies like case-based learning, simulations, and design thinking to promote problem solving within specialized disciplines. Additionally, educators use scaffolding techniques to provide support and guidance as students develop their problem-solving abilities. In both K-12 and higher education, a key component is metacognition, which helps students become aware of their thought processes and adapt their problem-solving strategies as needed.
Assessing problem-solving abilities in educational settings involves a combination of formative and summative assessments. Formative assessments, including classroom discussions, peer evaluations, and self-assessments, provide ongoing feedback and opportunities for improvement. Summative assessments may include standardized tests designed to evaluate problem-solving skills within a particular subject area. Performance-based assessments, such as essays, projects, and presentations, offer a holistic view of students’ problem-solving capabilities. Rubrics and scoring guides are often used to ensure consistency in assessment, allowing educators to measure not only the correctness of answers but also the quality of the problem-solving process. The evolving field of educational technology has also introduced computer-based simulations and adaptive learning platforms, enabling precise measurement and tailored feedback on students’ problem-solving performance.
Understanding the pivotal role of problem solving in educational psychology, the diverse pedagogical strategies for teaching it, and the methods for assessing and measuring problem-solving abilities equips educators and students with the tools necessary to thrive in educational environments and beyond. Problem solving remains a cornerstone of 21st-century education, preparing students to meet the complex challenges of a rapidly changing world.
Applications and Practical Implications
Problem solving is not confined to the classroom; it extends its influence to various real-world contexts, showcasing its relevance and impact. In business, problem solving is the driving force behind product development, process improvement, and conflict resolution. For instance, companies often use problem-solving methodologies like Six Sigma to identify and rectify issues in manufacturing. In healthcare, medical professionals employ problem-solving skills to diagnose complex illnesses and devise treatment plans. Additionally, technology advancements frequently stem from creative problem solving, as engineers and developers tackle challenges in software, hardware, and systems design. Real-world problem solving transcends specific domains, as individuals in diverse fields address multifaceted issues by drawing upon their cognitive abilities and creative problem-solving strategies.
Clinical psychology recognizes the profound therapeutic potential of problem-solving techniques. Problem-solving therapy (PST) is an evidence-based approach that focuses on helping individuals develop effective strategies for coping with emotional and interpersonal challenges. PST equips individuals with the skills to define problems, set realistic goals, generate solutions, and evaluate their effectiveness. This approach has shown efficacy in treating conditions like depression, anxiety, and stress, emphasizing the role of problem-solving abilities in enhancing emotional well-being. Furthermore, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) incorporates problem-solving elements to help individuals challenge and modify dysfunctional thought patterns, reinforcing the importance of cognitive processes in addressing psychological distress.
Problem solving is the bedrock of innovation and creativity in various fields. Innovators and creative thinkers use problem-solving skills to identify unmet needs, devise novel solutions, and overcome obstacles. Design thinking, a problem-solving approach, is instrumental in product design, architecture, and user experience design, fostering innovative solutions grounded in human needs. Moreover, creative industries like art, literature, and music rely on problem-solving abilities to transcend conventional boundaries and produce groundbreaking works. By exploring alternative perspectives, making connections, and persistently seeking solutions, creative individuals harness problem-solving processes to ignite innovation and drive progress in all facets of human endeavor.
Understanding the practical applications of problem solving in business, healthcare, technology, and its therapeutic significance in clinical psychology, as well as its indispensable role in nurturing innovation and creativity, underscores its universal value. Problem solving is not only a cognitive skill but also a dynamic force that shapes and improves the world we inhabit, enhancing the quality of life and promoting progress and discovery.
In summary, problem solving stands as an indispensable cornerstone within the domains of psychology and education. This article has explored the multifaceted nature of problem solving, from its theoretical foundations rooted in Gestalt psychology, information processing theories, and cognitive psychology to its integral components of problem representation, goal setting, solution generation, and solution evaluation. It has delved into the cognitive processes underpinning effective problem solving, including perception, memory, and reasoning, as well as the impact of individual differences such as intelligence, creativity, and expertise. Common barriers to problem solving, including functional fixedness, confirmation bias, and mental sets, have been examined in-depth.
The significance of problem solving in educational settings was elucidated, underscoring its pivotal role in fostering critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability. Pedagogical approaches and assessment methods were discussed, providing educators with insights into effective strategies for teaching and evaluating problem-solving skills in K-12 and higher education.
Furthermore, the practical implications of problem solving were demonstrated in the real world, where it serves as the driving force behind advancements in business, healthcare, and technology. In clinical psychology, problem-solving therapies offer effective interventions for emotional and psychological well-being. The symbiotic relationship between problem solving and innovation and creativity was explored, highlighting the role of this cognitive process in pushing the boundaries of human accomplishment.
As we conclude, it is evident that problem solving is not merely a skill but a dynamic process with profound implications. It enables individuals to navigate the complexities of their environment, fostering intellectual growth, adaptability, and innovation. Future research in the field of problem solving should continue to explore the intricate cognitive processes involved, individual differences that influence problem-solving abilities, and innovative teaching methods in educational settings. In practice, educators and clinicians should continue to incorporate problem-solving strategies to empower individuals with the tools necessary for success in education, personal development, and the ever-evolving challenges of the real world. Problem solving remains a steadfast ally in the pursuit of knowledge, progress, and the enhancement of human potential.
References:
- Anderson, J. R. (1995). Cognitive psychology and its implications. W. H. Freeman.
- Atkinson, R. C., & Shiffrin, R. M. (1968). Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In The psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 2, pp. 89-195). Academic Press.
- Duncker, K. (1945). On problem-solving. Psychological Monographs, 58(5), i-113.
- Gick, M. L., & Holyoak, K. J. (1980). Analogical problem solving. Cognitive Psychology, 12(3), 306-355.
- Jonassen, D. H., & Hung, W. (2008). All problems are not equal: Implications for problem-based learning. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 2(2), 6.
- Kitchener, K. S., & King, P. M. (1981). Reflective judgment: Concepts of justification and their relation to age and education. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 2(2), 89-116.
- Luchins, A. S. (1942). Mechanization in problem solving: The effect of Einstellung. Psychological Monographs, 54(6), i-95.
- Mayer, R. E. (1992). Thinking, problem solving, cognition. W. H. Freeman.
- Newell, A., & Simon, H. A. (1972). Human problem solving (Vol. 104). Prentice-Hall Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem solving (3rd ed.). Charles Scribner’s Sons.
- Polya, G. (1945). How to solve it: A new aspect of mathematical method. Princeton University Press.
- Sternberg, R. J. (2003). Wisdom, intelligence, and creativity synthesized. Cambridge University Press.

A Crash Course in Critical Thinking
What you need to know—and read—about one of the essential skills needed today..
Posted April 8, 2024 | Reviewed by Michelle Quirk
- In research for "A More Beautiful Question," I did a deep dive into the current crisis in critical thinking.
- Many people may think of themselves as critical thinkers, but they actually are not.
- Here is a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you are thinking critically.
Conspiracy theories. Inability to distinguish facts from falsehoods. Widespread confusion about who and what to believe.
These are some of the hallmarks of the current crisis in critical thinking—which just might be the issue of our times. Because if people aren’t willing or able to think critically as they choose potential leaders, they’re apt to choose bad ones. And if they can’t judge whether the information they’re receiving is sound, they may follow faulty advice while ignoring recommendations that are science-based and solid (and perhaps life-saving).
Moreover, as a society, if we can’t think critically about the many serious challenges we face, it becomes more difficult to agree on what those challenges are—much less solve them.
On a personal level, critical thinking can enable you to make better everyday decisions. It can help you make sense of an increasingly complex and confusing world.
In the new expanded edition of my book A More Beautiful Question ( AMBQ ), I took a deep dive into critical thinking. Here are a few key things I learned.
First off, before you can get better at critical thinking, you should understand what it is. It’s not just about being a skeptic. When thinking critically, we are thoughtfully reasoning, evaluating, and making decisions based on evidence and logic. And—perhaps most important—while doing this, a critical thinker always strives to be open-minded and fair-minded . That’s not easy: It demands that you constantly question your assumptions and biases and that you always remain open to considering opposing views.
In today’s polarized environment, many people think of themselves as critical thinkers simply because they ask skeptical questions—often directed at, say, certain government policies or ideas espoused by those on the “other side” of the political divide. The problem is, they may not be asking these questions with an open mind or a willingness to fairly consider opposing views.
When people do this, they’re engaging in “weak-sense critical thinking”—a term popularized by the late Richard Paul, a co-founder of The Foundation for Critical Thinking . “Weak-sense critical thinking” means applying the tools and practices of critical thinking—questioning, investigating, evaluating—but with the sole purpose of confirming one’s own bias or serving an agenda.
In AMBQ , I lay out a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you’re thinking critically. Here are some of the questions to consider:
- Why do I believe what I believe?
- Are my views based on evidence?
- Have I fairly and thoughtfully considered differing viewpoints?
- Am I truly open to changing my mind?
Of course, becoming a better critical thinker is not as simple as just asking yourself a few questions. Critical thinking is a habit of mind that must be developed and strengthened over time. In effect, you must train yourself to think in a manner that is more effortful, aware, grounded, and balanced.
For those interested in giving themselves a crash course in critical thinking—something I did myself, as I was working on my book—I thought it might be helpful to share a list of some of the books that have shaped my own thinking on this subject. As a self-interested author, I naturally would suggest that you start with the new 10th-anniversary edition of A More Beautiful Question , but beyond that, here are the top eight critical-thinking books I’d recommend.
The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark , by Carl Sagan
This book simply must top the list, because the late scientist and author Carl Sagan continues to be such a bright shining light in the critical thinking universe. Chapter 12 includes the details on Sagan’s famous “baloney detection kit,” a collection of lessons and tips on how to deal with bogus arguments and logical fallacies.

Clear Thinking: Turning Ordinary Moments Into Extraordinary Results , by Shane Parrish
The creator of the Farnham Street website and host of the “Knowledge Project” podcast explains how to contend with biases and unconscious reactions so you can make better everyday decisions. It contains insights from many of the brilliant thinkers Shane has studied.
Good Thinking: Why Flawed Logic Puts Us All at Risk and How Critical Thinking Can Save the World , by David Robert Grimes
A brilliant, comprehensive 2021 book on critical thinking that, to my mind, hasn’t received nearly enough attention . The scientist Grimes dissects bad thinking, shows why it persists, and offers the tools to defeat it.
Think Again: The Power of Knowing What You Don't Know , by Adam Grant
Intellectual humility—being willing to admit that you might be wrong—is what this book is primarily about. But Adam, the renowned Wharton psychology professor and bestselling author, takes the reader on a mind-opening journey with colorful stories and characters.
Think Like a Detective: A Kid's Guide to Critical Thinking , by David Pakman
The popular YouTuber and podcast host Pakman—normally known for talking politics —has written a terrific primer on critical thinking for children. The illustrated book presents critical thinking as a “superpower” that enables kids to unlock mysteries and dig for truth. (I also recommend Pakman’s second kids’ book called Think Like a Scientist .)
Rationality: What It Is, Why It Seems Scarce, Why It Matters , by Steven Pinker
The Harvard psychology professor Pinker tackles conspiracy theories head-on but also explores concepts involving risk/reward, probability and randomness, and correlation/causation. And if that strikes you as daunting, be assured that Pinker makes it lively and accessible.
How Minds Change: The Surprising Science of Belief, Opinion and Persuasion , by David McRaney
David is a science writer who hosts the popular podcast “You Are Not So Smart” (and his ideas are featured in A More Beautiful Question ). His well-written book looks at ways you can actually get through to people who see the world very differently than you (hint: bludgeoning them with facts definitely won’t work).
A Healthy Democracy's Best Hope: Building the Critical Thinking Habit , by M Neil Browne and Chelsea Kulhanek
Neil Browne, author of the seminal Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking, has been a pioneer in presenting critical thinking as a question-based approach to making sense of the world around us. His newest book, co-authored with Chelsea Kulhanek, breaks down critical thinking into “11 explosive questions”—including the “priors question” (which challenges us to question assumptions), the “evidence question” (focusing on how to evaluate and weigh evidence), and the “humility question” (which reminds us that a critical thinker must be humble enough to consider the possibility of being wrong).

Warren Berger is a longtime journalist and author of A More Beautiful Question .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Chapter 7: Thinking and Intelligence
Solving problems.
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem-solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
Video 1. Problem Solving explains strategies used for solving problems.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them. For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve the desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backward is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C., and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backward heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Video 2. What problem-solving method could you use to solve Einstein’s famous riddle?
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Everyday Connections: Solving Puzzles
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (Figure 1) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
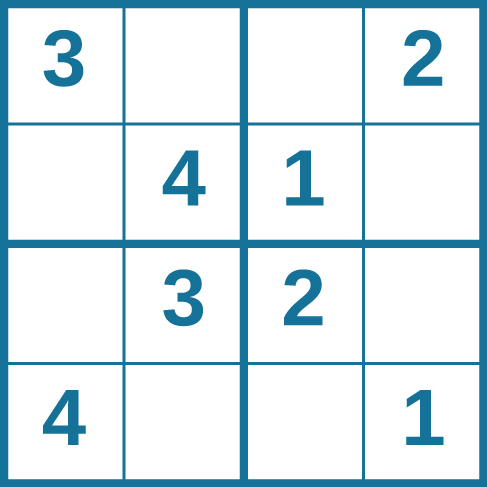
Figure 1 . How long did it take you to solve this sudoku puzzle? (You can see the answer at the end of this section.)
Here is another popular type of puzzle that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
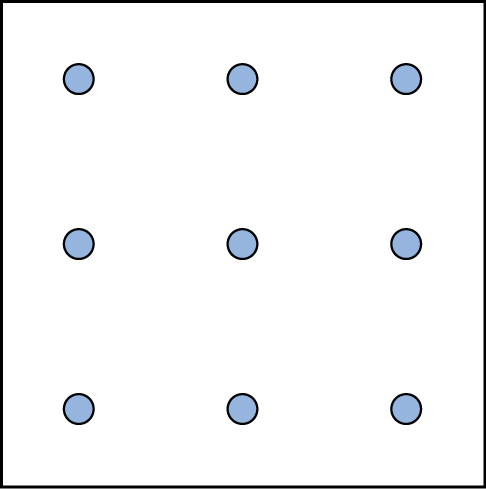
Figure 2. Did you figure it out? (The answer is at the end of this section.) Once you understand how to crack this puzzle, you won’t forget.
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below (Figure 3). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
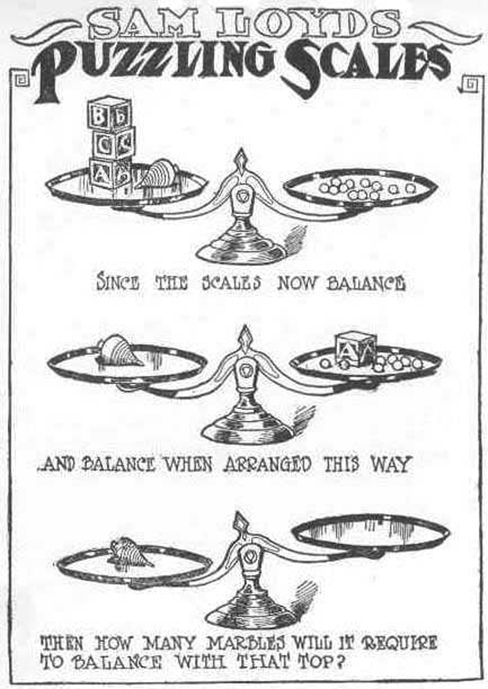
Figure 3 . The puzzle reads, “Since the scales now balance…and balance when arranged this way, then how many marbles will it require to balance with that top?
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in the Puzzling Scales? You need nine. Were you able to solve the other problems above? Here are the answers:
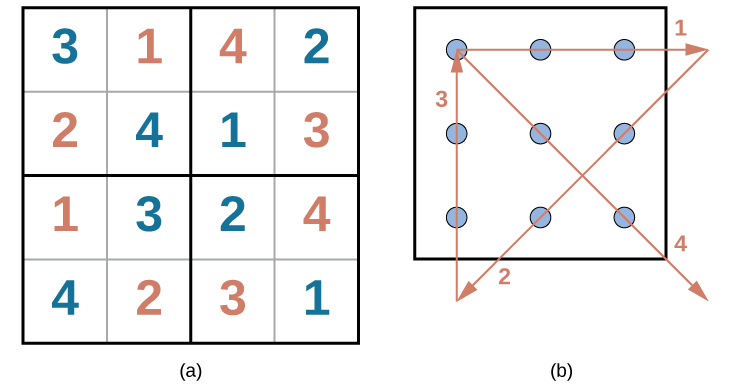
Pitfalls to Problem-Solving
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem?
Video 3. Cognitive Biases: What They Are , Why They’re Important provides an introduction to the many cognitive biases that prevent us from always thinking clearly and rationally.
Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now. Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Link to Learning
Check out this Apollo 13 scene where a group of NASA engineers is given the task of overcoming functional fixedness.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
Confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. This bias proves that first impressions do matter and that we tend to look for information to confirm our initial judgments of others.
Video 4. Watch this video from the Big Think to learn more about confirmation bias.
Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . To use a common example, would you guess there are more murders or more suicides in America each year? When asked, most people would guess there are more murders. In truth, there are twice as many suicides as there are murders each year. However, murders seem more common because we hear a lot more about murders on an average day. Unless someone we know or someone famous takes their own life, it does not make the news. Murders, on the other hand, we see in the news every day. This leads to the erroneous assumption that the easier it is to think of instances of something, the more often that thing occurs.
Video 5. Watch the following video for an example of the availability heuristic.
Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in Table 2 below.
Learn more about heuristics and common biases through the article, “ 8 Common Thinking Mistakes Our Brains Make Every Day and How to Prevent Them ” by Belle Beth Cooper.
You can also watch this clever music video explaining these and other cognitive biases.
- Modification and adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Psychology in Real Life: Choice Blindness. Authored by : Patrick Carroll for Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Problem-Solving. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:Lk3YnvuC@6/Problem-Solving . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/content/col11629/latest/.
- Actors Headshots . Authored by : Vanity Studios. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/149481436@N03/34277183806/in/photostream/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of man. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/en/boy-portrait-outdoors-facial-men-s-3566903/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- https://pixabay.com/en/boy-portrait-outdoors-facial-men-s-3566903/. Authored by : Simon Robben. Provided by : Pexels. Located at : https://www.pexels.com/photo/face-facial-hair-fine-looking-guy-614810/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- image of businessman. Authored by : RoyalAnwar. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/en/model-businessman-corporate-2911332/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- man in black shirt. Authored by : songjayjay. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/en/face-men-s-asia-shirts-blacj-young-1391628/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- woman headshot. Authored by : Richard Ha. Provided by : Flickr. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/richardha101/31951459743/in/photolist-QFrzNX-V9Amf2-UM2ZU5-HMQxnd-WmpZx1-5ztiGT-ovm92d-28C1Eyi-qhwZzM-8szjMV-YRsM5B-LCTNFR-LtgVC9-LCUgd8-8gRLbQ-REArrY-WQNThG-ph52sx-2bC2DwH-qE61yp-28NspiC-21h8cj4-RVoBBc-29GiNJ3-21QEU6M-M1YTcp-PePwTJ-LALKtr-RVoBtg-Ry1bpy-FVr9BB-282GDDG-V7zSQJ-NwmdK9-29bSs5N-29mSb5G-272dN8p-26brtas-28tTQWf-RS1osg-WHoUSc-25uETMH-D7crwK-28m9fEh-25taZPB-JCwqE7-241e8Xp-265Ce4A-22V7VVo-25N7i4q . License : CC BY: Attribution
- businesswoman headshot. Authored by : Richard Rives. Provided by : Flickr. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/richpat2/38251159285/in/photostream/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Can you solve Einsteinu2019s Riddle? . Authored by : Dan Van der Vieren. Provided by : Ted-Ed. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1rDVz_Fb6HQ&index=3&list=PLUmyCeox8XCwB8FrEfDQtQZmCc2qYMS5a . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- BBC Choice Blindness. Authored by : BBC. Provided by : ChoiceBlindnessLab. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wRqyw-EwgTk . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Using Choice Blindness to Shift Political Attitudes and Voter Intentions. Provided by : ChoiceBlindnessLab. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_htNx0eWmgs . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Privacy Policy
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Thinking and Intelligence
Problem Solving
OpenStaxCollege
[latexpage]
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGIES
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( [link] ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( [link] ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
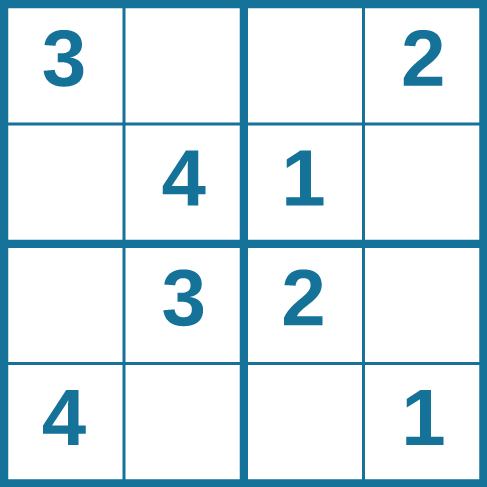
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( [link] ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
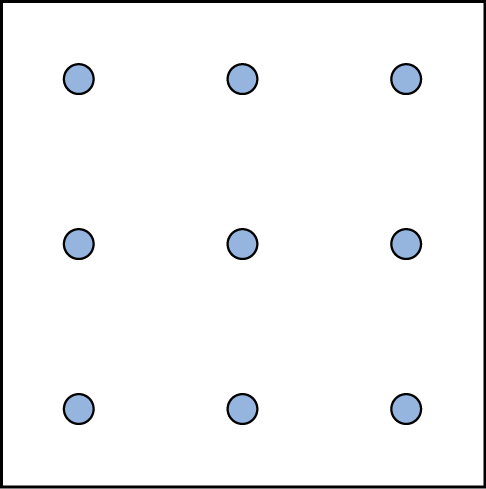
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( [link] ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
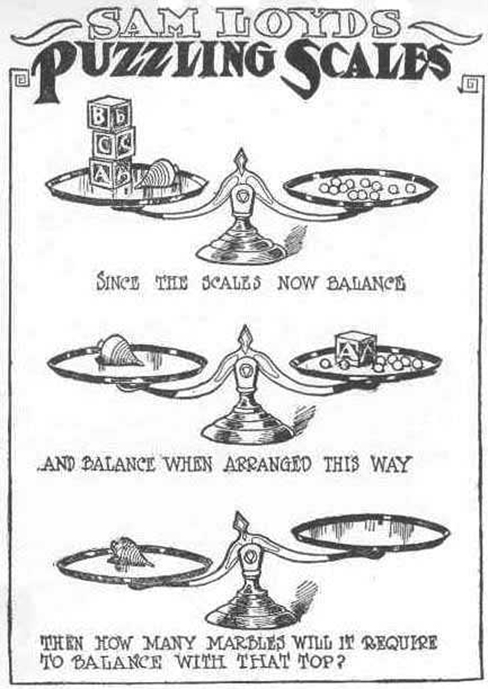
PITFALLS TO PROBLEM SOLVING
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.

Check out this Apollo 13 scene where the group of NASA engineers are given the task of overcoming functional fixedness.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in [link] .
Please visit this site to see a clever music video that a high school teacher made to explain these and other cognitive biases to his AP psychology students.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in [link] ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in [link] and [link] ? Here are the answers ( [link] ).
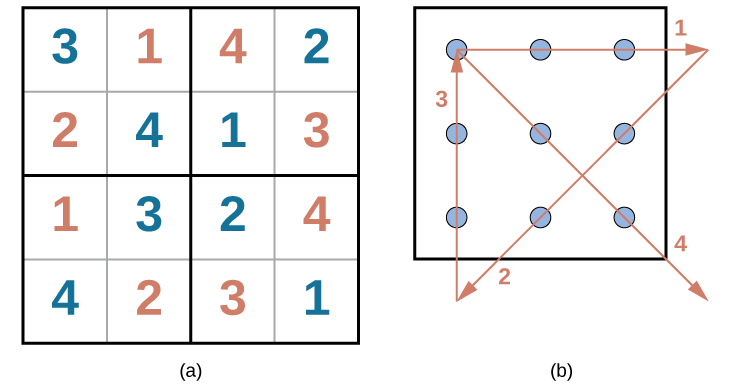
Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
Review Questions
A specific formula for solving a problem is called ________.
- an algorithm
- a heuristic
- a mental set
- trial and error
A mental shortcut in the form of a general problem-solving framework is called ________.
Which type of bias involves becoming fixated on a single trait of a problem?
- anchoring bias
- confirmation bias
- representative bias
- availability bias
Which type of bias involves relying on a false stereotype to make a decision?
Critical Thinking Questions
What is functional fixedness and how can overcoming it help you solve problems?
Functional fixedness occurs when you cannot see a use for an object other than the use for which it was intended. For example, if you need something to hold up a tarp in the rain, but only have a pitchfork, you must overcome your expectation that a pitchfork can only be used for garden chores before you realize that you could stick it in the ground and drape the tarp on top of it to hold it up.
How does an algorithm save you time and energy when solving a problem?
An algorithm is a proven formula for achieving a desired outcome. It saves time because if you follow it exactly, you will solve the problem without having to figure out how to solve the problem. It is a bit like not reinventing the wheel.
Personal Application Question
Which type of bias do you recognize in your own decision making processes? How has this bias affected how you’ve made decisions in the past and how can you use your awareness of it to improve your decisions making skills in the future?
Problem Solving Copyright © 2014 by OpenStaxCollege is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

8 Effective Problem-Solving Strategies
Categories Cognition

Sharing is caring!
If you need to solve a problem, there are a number of different problem-solving strategies that can help you come up with an accurate decision. Sometimes the best choice is to use a step-by-step approach that leads to the right solution, but other problems may require a trial-and-error approach.
Some helpful problem-solving strategies include: Brainstorming Step-by-step algorithms Trial-and-error Working backward Heuristics Insight Writing it down Getting some sleep
Table of Contents
Why Use Problem-Solving Strategies
While you can always make a wild guess or pick at random, that certainly isn’t the most accurate way to come up with a solution. Using a more structured approach allows you to:
- Understand the nature of the problem
- Determine how you will solve it
- Research different options
- Take steps to solve the problem and resolve the issue
There are many tools and strategies that can be used to solve problems, and some problems may require more than one of these methods in order to come up with a solution.
Problem-Solving Strategies
The problem-solving strategy that works best depends on the nature of the problem and how much time you have available to make a choice. Here are eight different techniques that can help you solve whatever type of problem you might face.
Brainstorming
Coming up with a lot of potential solutions can be beneficial, particularly early on in the process. You might brainstorm on your own, or enlist the help of others to get input that you might not have otherwise considered.
Step-by-Step
Also known as an algorithm, this approach involves following a predetermined formula that is guaranteed to produce the correct result. While this can be useful in some situations—such as solving a math problem—it is not always practical in every situation.
On the plus side, algorithms can be very accurate and reliable. Unfortunately, they can also be time-consuming.
And in some situations, you cannot follow this approach because you simply don’t have access to all of the information you would need to do so.
Trial-and-Error
This problem-solving strategy involves trying a number of different solutions in order to figure out which one works best. This requires testing steps or more options to solve the problem or pick the right solution.
For example, if you are trying to perfect a recipe, you might have to experiment with varying amounts of a certain ingredient before you figure out which one you prefer.
On the plus side, trial-and-error can be a great problem-solving strategy in situations that require an individualized solution. However, this approach can be very time-consuming and costly.
Working Backward
This problem-solving strategy involves looking at the end result and working your way back through the chain of events. It can be a useful tool when you are trying to figure out what might have led to a particular outcome.
It can also be a beneficial way to play out how you will complete a task. For example, if you know you need to have a project done by a certain date, working backward can help you figure out the steps you’ll need to complete in order to successfully finish the project.
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that allow you to come up with solutions quite quickly. They are often based on past experiences that are then applied to other situations. They are, essentially, a handy rule of thumb.
For example, imagine a student is trying to pick classes for the next term. While they aren’t sure which classes they’ll enjoy the most, they know that they tend to prefer subjects that involve a lot of creativity. They utilize this heuristic to pick classes that involve art and creative writing.
The benefit of a heuristic is that it is a fast way to make fairly accurate decisions. The trade-off is that you give up some accuracy in order to gain speed and efficiency.
Sometimes, the solution to a problem seems to come out of nowhere. You might suddenly envision a solution after struggling with the problem for a while. Or you might abruptly recognize the correct solution that you hadn’t seen before.
No matter the source, insight-based problem-solving relies on following your gut instincts. While this may not be as objective or accurate as some other problem-solving strategies, it can be a great way to come up with creative, novel solutions.
Write It Down
Sometimes putting the problem and possible solutions down in paper can be a useful way to visualize solutions. Jot down whatever might help you envision your options. Draw a picture, create a mind map, or just write some notes to clarify your thoughts.
Get Some Sleep
If you’re facing a big problem or trying to make an important decision, try getting a good night’s sleep before making a choice. Sleep plays an essential role in memory consolidation, so getting some rest may help you access the information or insight you need to make the best choice.
Other Considerations
Even with an arsenal of problem-solving strategies at your disposal, coming up with solutions isn’t always easy. Certain challenges can make the process more difficult. A few issues that might emerge include:
- Mental set : When people form a mental set, they only rely on things that have worked in the last. Sometimes this can be useful, but in other cases, it can severely hinder the problem-solving process.
- Cognitive biases : Unconscious cognitive biases can make it difficult to see situations clearly and objectively. As a result, you may not consider all of your options or ignore relevant information.
- Misinformation : Poorly sourced clues and irrelevant details can add more complications. Being able to sort out what’s relevant and what’s not is essential for solving problems accurately.
- Functional fixedness : Functional fixedness happens when people only think of customary solutions to problems. It can hinder out-of-the-box thinking and prevents insightful, creative solutions.
Important Problem-Solving Skills
Becoming a good problem solver can be useful in a variety of domains, from school to work to interpersonal relationships. Important problem-solving skills encompass being able to identify problems, coming up with effective solutions, and then implementing these solutions.
According to a 2023 survey by the National Association of Colleges and Employers, 61.4% of employers look for problem-solving skills on applicant resumes.
Some essential problem-solving skills include:
- Research skills
- Analytical abilities
- Decision-making skills
- Critical thinking
- Communication
- Time management
- Emotional intelligence
Solving a problem is complex and requires the ability to recognize the issue, collect and analyze relevant data, and make decisions about the best course of action. It can also involve asking others for input, communicating goals, and providing direction to others.
How to Become a Better Problem-Solver
If you’re ready to strengthen your problem-solving abilities, here are some steps you can take:
Identify the Problem
Before you can practice your problem-solving skills, you need to be able to recognize that there is a problem. When you spot a potential issue, ask questions about when it started and what caused it.
Do Your Research
Instead of jumping right in to finding solutions, do research to make sure you fully understand the problem and have all the background information you need. This helps ensure you don’t miss important details.
Hone Your Skills
Consider signing up for a class or workshop focused on problem-solving skill development. There are also books that focus on different methods and approaches.
The best way to strengthen problem-solving strategies is to give yourself plenty of opportunities to practice. Look for new challenges that allow you to think critically, analytically, and creatively.
Final Thoughts
If you have a problem to solve, there are plenty of strategies that can help you make the right choice. The key is to pick the right one, but also stay flexible and willing to shift gears.
In many cases, you might find that you need more than one strategy to make the choices that are right for your life.
Brunet, J. F., McNeil, J., Doucet, É., & Forest, G. (2020). The association between REM sleep and decision-making: Supporting evidences. Physiology & Behavior , 225, 113109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113109
Chrysikou, E. G, Motyka, K., Nigro, C., Yang, S. I. , & Thompson-Schill, S. L. (2016). Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality. Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts , 10(4):425‐435. https://doi.org/10.1037/aca0000050
Sarathy, V. (2018). Real world problem-solving. Front Hum Neurosci , 12:261. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261

Looking for a Therapist?
Finding and engaging the right therapist for you if paramount to a successful and fruitful therapy. We have curated a directory of psychology and counselling practices in various countries to serve the local communities.
Are you a Therapist in Asia? Join our Free Directory or Premium Listing starting from $13.75/mth Today.
- New Zealand
- Philippines
- South Korea
- Mood Disorders
- Bipolar Disorder I or II
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Impulse-Control Disorders
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- Conduct Disorder
- Intermittent Explosive Disorder (IED)
- Oppositional-Defiant Disorder
- Substance Use Disorders
- Alcohol Abuse
- Alcohol Dependence
- Drug Dependence
- Anxiety Disorders
- Agoraphobia
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Panic Disorder
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Separation Anxiety Disorder
- Social Phobia
- Specific Phobia
Common Mental Disorders
Psychology news.
Look at latest news on mental health
Mental Health Articles
Read latest articles contributed by Mental Health Professionals
- 16 Apr 2024 Singapore Emotion-Focused Therapy Module 2
- 02 May 2024 Online Helping Children and Adolescents through Grief and Loss
- 07 May 2024 Online Certificate in Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
- 23 May 2024 Online The Essentials of Motivational Interviewing

Psychology Articles
Problem-solving with teens: steps, introduction: the complex terrain of teenage years.
Navigating the teenage years can be a rollercoaster of emotions for both teens and parents alike. In this blog post, we'll explore effective problem-solving strategies to address common teenage problems and solutions . By understanding the steps and tips involved, parents can foster open communication and support their teens in building essential life skills.
1.Understanding Teenage Challenges
Setting the stage for our exploration, this section delves into the unique challenges that teenagers often face. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the complexities of adolescence to approach problem-solving with empathy and insight.
2.The Power of Open Communication
Introducing the cornerstone of effective problem-solving , this section emphasizes the power of open communication. It discusses how fostering a supportive and non-judgmental environment encourages teens to share their concerns and actively engage in finding solutions.
3.Identifying Teenage Problems: A Compassionate Approach
Delving into the heart of the matter, this section explores the process of identifying teenage problems with a compassionate approach. It discusses the significance of active listening and empathy in gaining insights into a teen's perspective.
4.Common Teenage Problems and Solutions
Transitioning into specific examples, this section addresses common teenage problems and provides practical solutions. It covers areas such as academic stress, peer relationships , time management, and self-esteem, offering actionable tips for parents to support their teens.
5.Teaching Problem-Solving Skills: A Lifelong Gift
Exploring the importance of imparting problem-solving skills, this section discusses how teaching teens to navigate challenges is a lifelong gift. It emphasizes the role of parents in guiding their teens towards independent problem-solving and decision-making.
6.Steps in Problem-Solving with Teens
Breaking down the steps involved, this section introduces a structured approach to problem-solving with teens. It covers steps such as defining the problem, brainstorming solutions, evaluating options, and implementing the chosen solution.
7.Tips for Effective Problem-Solving Sessions
Offering practical tips, this section provides insights into conducting effective problem-solving sessions with teens. It discusses the significance of creating a safe space, encouraging creativity, and maintaining a collaborative mindset throughout the process.
8.Encouraging Responsibility and Accountability
Discussing the long-term impact of problem-solving, this section explores how encouraging responsibility and accountability fosters a sense of independence in teens. It emphasizes the importance of teens taking an active role in implementing and evaluating the effectiveness of solutions.
9.Cultivating Resilience in Teens
Addressing the broader goal of cultivating resilience, this section discusses how the problem-solving process contributes to building resilience in teens. It emphasizes the role of setbacks as learning opportunities and the importance of adapting to change.
10.Celebrating Success: Reinforcing Positive Outcomes
Incorporating a positive note, this section emphasizes the importance of celebrating success. It discusses how acknowledging and reinforcing positive outcomes in the problem-solving process enhances a teen's confidence and self-efficacy.
11.Conclusion: Nurturing Growth and Connection
In conclusion, this section summarizes the key takeaways from the blog post. It emphasizes that problem-solving with teens goes beyond immediate solutions; it is a journey of nurturing growth, fostering resilience, and strengthening the connection between parents and their adolescents. As parents embrace these steps and tips, they contribute to a supportive environment that empowers teens to face challenges with confidence and resilience.
Category(s):Adjusting to Change / Life Transitions
Related articles.
Written by:
Most popular articles.
Demystifying the process of change in Counselling- How you get better
Introduction to Animal Assisted Therapy (AAT)
Clear Signs There Is Serious Chemistry Between You and Your Partner
Why Do People Lash Out?
Why do I feel like I am suffocating around my parents?
Our monthly newsletter keeps you up to date with new psychology articles and events around Asia.
Enter your email and click on "Add Me" to subscribe and "Remove Me" to unsubscribe
Find a Therapist in
Australia Bangladesh Brunei Cambodia China Hong Kong India Indonesia Israel Japan Laos
Macau Malaysia Myanmar New Zealand Pakistan Philippines Singapore South Korea Sri Lanka Taiwan Thailand Vietnam
User Management
Register a User Account
Reset Account Password
Resend Activation Email
Reactivate Locked Account
About Psychology Matters Asia
Psychology Matters Asia is an online resource built to provide useful information to both mental health professionals and those seeking therapy for mental health problems in Asia
Premium Listing
Register my practice, advertise with us, contact pm.a, terms & conditions.
7.3 Problem Solving
Learning objectives.
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( Table 7.2 ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Everyday Connection
Solving puzzles.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( Figure 7.8 ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( Figure 7.9 ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( Figure 7.10 ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
Pitfalls to Problem Solving
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Link to Learning
Check out this Apollo 13 scene where the group of NASA engineers are given the task of overcoming functional fixedness.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in Table 7.3 .
Please visit this site to see a clever music video that a high school teacher made to explain these and other cognitive biases to his AP psychology students.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure 7.10 ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in Figure 7.8 and Figure 7.9 ? Here are the answers ( Figure 7.11 ).
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, Kathryn Dumper, William Jenkins, Arlene Lacombe, Marilyn Lovett, Marion Perlmutter
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology
- Publication date: Dec 8, 2014
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/7-3-problem-solving
© Feb 9, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Do You Understand the Problem You’re Trying to Solve?
To solve tough problems at work, first ask these questions.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem without taking time to really understand the dilemma we face, according to Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg , an expert in innovation and the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for just one root cause can be misleading.
Key episode topics include: leadership, decision making and problem solving, power and influence, business management.
HBR On Leadership curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock the best in those around you. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR IdeaCast episode: The Secret to Better Problem Solving (2016)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR on Leadership , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock the best in those around you.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem – without taking time to really understand what we’re facing.
He’s an expert in innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems, by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for one root cause can be misleading. And you’ll learn how to use experimentation and rapid prototyping as problem-solving tools.
This episode originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in December 2016. Here it is.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Sarah Green Carmichael.
Problem solving is popular. People put it on their resumes. Managers believe they excel at it. Companies count it as a key proficiency. We solve customers’ problems.
The problem is we often solve the wrong problems. Albert Einstein and Peter Drucker alike have discussed the difficulty of effective diagnosis. There are great frameworks for getting teams to attack true problems, but they’re often hard to do daily and on the fly. That’s where our guest comes in.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg is a consultant who helps companies and managers reframe their problems so they can come up with an effective solution faster. He asks the question “Are You Solving The Right Problems?” in the January-February 2017 issue of Harvard Business Review. Thomas, thank you so much for coming on the HBR IdeaCast .
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thanks for inviting me.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I thought maybe we could start by talking about the problem of talking about problem reframing. What is that exactly?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Basically, when people face a problem, they tend to jump into solution mode to rapidly, and very often that means that they don’t really understand, necessarily, the problem they’re trying to solve. And so, reframing is really a– at heart, it’s a method that helps you avoid that by taking a second to go in and ask two questions, basically saying, first of all, wait. What is the problem we’re trying to solve? And then crucially asking, is there a different way to think about what the problem actually is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I feel like so often when this comes up in meetings, you know, someone says that, and maybe they throw out the Einstein quote about you spend an hour of problem solving, you spend 55 minutes to find the problem. And then everyone else in the room kind of gets irritated. So, maybe just give us an example of maybe how this would work in practice in a way that would not, sort of, set people’s teeth on edge, like oh, here Sarah goes again, reframing the whole problem instead of just solving it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I mean, you’re bringing up something that’s, I think is crucial, which is to create legitimacy for the method. So, one of the reasons why I put out the article is to give people a tool to say actually, this thing is still important, and we need to do it. But I think the really critical thing in order to make this work in a meeting is actually to learn how to do it fast, because if you have the idea that you need to spend 30 minutes in a meeting delving deeply into the problem, I mean, that’s going to be uphill for most problems. So, the critical thing here is really to try to make it a practice you can implement very, very rapidly.
There’s an example that I would suggest memorizing. This is the example that I use to explain very rapidly what it is. And it’s basically, I call it the slow elevator problem. You imagine that you are the owner of an office building, and that your tenants are complaining that the elevator’s slow.
Now, if you take that problem framing for granted, you’re going to start thinking creatively around how do we make the elevator faster. Do we install a new motor? Do we have to buy a new lift somewhere?
The thing is, though, if you ask people who actually work with facilities management, well, they’re going to have a different solution for you, which is put up a mirror next to the elevator. That’s what happens is, of course, that people go oh, I’m busy. I’m busy. I’m– oh, a mirror. Oh, that’s beautiful.
And then they forget time. What’s interesting about that example is that the idea with a mirror is actually a solution to a different problem than the one you first proposed. And so, the whole idea here is once you get good at using reframing, you can quickly identify other aspects of the problem that might be much better to try to solve than the original one you found. It’s not necessarily that the first one is wrong. It’s just that there might be better problems out there to attack that we can, means we can do things much faster, cheaper, or better.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, in that example, I can understand how A, it’s probably expensive to make the elevator faster, so it’s much cheaper just to put up a mirror. And B, maybe the real problem people are actually feeling, even though they’re not articulating it right, is like, I hate waiting for the elevator. But if you let them sort of fix their hair or check their teeth, they’re suddenly distracted and don’t notice.
But if you have, this is sort of a pedestrian example, but say you have a roommate or a spouse who doesn’t clean up the kitchen. Facing that problem and not having your elegant solution already there to highlight the contrast between the perceived problem and the real problem, how would you take a problem like that and attack it using this method so that you can see what some of the other options might be?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right. So, I mean, let’s say it’s you who have that problem. I would go in and say, first of all, what would you say the problem is? Like, if you were to describe your view of the problem, what would that be?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I hate cleaning the kitchen, and I want someone else to clean it up.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: OK. So, my first observation, you know, that somebody else might not necessarily be your spouse. So, already there, there’s an inbuilt assumption in your question around oh, it has to be my husband who does the cleaning. So, it might actually be worth, already there to say, is that really the only problem you have? That you hate cleaning the kitchen, and you want to avoid it? Or might there be something around, as well, getting a better relationship in terms of how you solve problems in general or establishing a better way to handle small problems when dealing with your spouse?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Or maybe, now that I’m thinking that, maybe the problem is that you just can’t find the stuff in the kitchen when you need to find it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right, and so that’s an example of a reframing, that actually why is it a problem that the kitchen is not clean? Is it only because you hate the act of cleaning, or does it actually mean that it just takes you a lot longer and gets a lot messier to actually use the kitchen, which is a different problem. The way you describe this problem now, is there anything that’s missing from that description?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That is a really good question.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Other, basically asking other factors that we are not talking about right now, and I say those because people tend to, when given a problem, they tend to delve deeper into the detail. What often is missing is actually an element outside of the initial description of the problem that might be really relevant to what’s going on. Like, why does the kitchen get messy in the first place? Is it something about the way you use it or your cooking habits? Is it because the neighbor’s kids, kind of, use it all the time?
There might, very often, there might be issues that you’re not really thinking about when you first describe the problem that actually has a big effect on it.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I think at this point it would be helpful to maybe get another business example, and I’m wondering if you could tell us the story of the dog adoption problem.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Yeah. This is a big problem in the US. If you work in the shelter industry, basically because dogs are so popular, more than 3 million dogs every year enter a shelter, and currently only about half of those actually find a new home and get adopted. And so, this is a problem that has persisted. It’s been, like, a structural problem for decades in this space. In the last three years, where people found new ways to address it.
So a woman called Lori Weise who runs a rescue organization in South LA, and she actually went in and challenged the very idea of what we were trying to do. She said, no, no. The problem we’re trying to solve is not about how to get more people to adopt dogs. It is about keeping the dogs with their first family so they never enter the shelter system in the first place.
In 2013, she started what’s called a Shelter Intervention Program that basically works like this. If a family comes and wants to hand over their dog, these are called owner surrenders. It’s about 30% of all dogs that come into a shelter. All they would do is go up and ask, if you could, would you like to keep your animal? And if they said yes, they would try to fix whatever helped them fix the problem, but that made them turn over this.
And sometimes that might be that they moved into a new building. The landlord required a deposit, and they simply didn’t have the money to put down a deposit. Or the dog might need a $10 rabies shot, but they didn’t know how to get access to a vet.
And so, by instigating that program, just in the first year, she took her, basically the amount of dollars they spent per animal they helped went from something like $85 down to around $60. Just an immediate impact, and her program now is being rolled out, is being supported by the ASPCA, which is one of the big animal welfare stations, and it’s being rolled out to various other places.
And I think what really struck me with that example was this was not dependent on having the internet. This was not, oh, we needed to have everybody mobile before we could come up with this. This, conceivably, we could have done 20 years ago. Only, it only happened when somebody, like in this case Lori, went in and actually rethought what the problem they were trying to solve was in the first place.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, what I also think is so interesting about that example is that when you talk about it, it doesn’t sound like the kind of thing that would have been thought of through other kinds of problem solving methods. There wasn’t necessarily an After Action Review or a 5 Whys exercise or a Six Sigma type intervention. I don’t want to throw those other methods under the bus, but how can you get such powerful results with such a very simple way of thinking about something?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That was something that struck me as well. This, in a way, reframing and the idea of the problem diagnosis is important is something we’ve known for a long, long time. And we’ve actually have built some tools to help out. If you worked with us professionally, you are familiar with, like, Six Sigma, TRIZ, and so on. You mentioned 5 Whys. A root cause analysis is another one that a lot of people are familiar with.
Those are our good tools, and they’re definitely better than nothing. But what I notice when I work with the companies applying those was those tools tend to make you dig deeper into the first understanding of the problem we have. If it’s the elevator example, people start asking, well, is that the cable strength, or is the capacity of the elevator? That they kind of get caught by the details.
That, in a way, is a bad way to work on problems because it really assumes that there’s like a, you can almost hear it, a root cause. That you have to dig down and find the one true problem, and everything else was just symptoms. That’s a bad way to think about problems because problems tend to be multicausal.
There tend to be lots of causes or levers you can potentially press to address a problem. And if you think there’s only one, if that’s the right problem, that’s actually a dangerous way. And so I think that’s why, that this is a method I’ve worked with over the last five years, trying to basically refine how to make people better at this, and the key tends to be this thing about shifting out and saying, is there a totally different way of thinking about the problem versus getting too caught up in the mechanistic details of what happens.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: What about experimentation? Because that’s another method that’s become really popular with the rise of Lean Startup and lots of other innovation methodologies. Why wouldn’t it have worked to, say, experiment with many different types of fixing the dog adoption problem, and then just pick the one that works the best?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: You could say in the dog space, that’s what’s been going on. I mean, there is, in this industry and a lot of, it’s largely volunteer driven. People have experimented, and they found different ways of trying to cope. And that has definitely made the problem better. So, I wouldn’t say that experimentation is bad, quite the contrary. Rapid prototyping, quickly putting something out into the world and learning from it, that’s a fantastic way to learn more and to move forward.
My point is, though, that I feel we’ve come to rely too much on that. There’s like, if you look at the start up space, the wisdom is now just to put something quickly into the market, and then if it doesn’t work, pivot and just do more stuff. What reframing really is, I think of it as the cognitive counterpoint to prototyping. So, this is really a way of seeing very quickly, like not just working on the solution, but also working on our understanding of the problem and trying to see is there a different way to think about that.
If you only stick with experimentation, again, you tend to sometimes stay too much in the same space trying minute variations of something instead of taking a step back and saying, wait a minute. What is this telling us about what the real issue is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, to go back to something that we touched on earlier, when we were talking about the completely hypothetical example of a spouse who does not clean the kitchen–
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Completely, completely hypothetical.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Yes. For the record, my husband is a great kitchen cleaner.
You started asking me some questions that I could see immediately were helping me rethink that problem. Is that kind of the key, just having a checklist of questions to ask yourself? How do you really start to put this into practice?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I think there are two steps in that. The first one is just to make yourself better at the method. Yes, you should kind of work with a checklist. In the article, I kind of outlined seven practices that you can use to do this.
But importantly, I would say you have to consider that as, basically, a set of training wheels. I think there’s a big, big danger in getting caught in a checklist. This is something I work with.
My co-author Paddy Miller, it’s one of his insights. That if you start giving people a checklist for things like this, they start following it. And that’s actually a problem, because what you really want them to do is start challenging their thinking.
So the way to handle this is to get some practice using it. Do use the checklist initially, but then try to step away from it and try to see if you can organically make– it’s almost a habit of mind. When you run into a colleague in the hallway and she has a problem and you have five minutes, like, delving in and just starting asking some of those questions and using your intuition to say, wait, how is she talking about this problem? And is there a question or two I can ask her about the problem that can help her rethink it?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, that is also just a very different approach, because I think in that situation, most of us can’t go 30 seconds without jumping in and offering solutions.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Very true. The drive toward solutions is very strong. And to be clear, I mean, there’s nothing wrong with that if the solutions work. So, many problems are just solved by oh, you know, oh, here’s the way to do that. Great.
But this is really a powerful method for those problems where either it’s something we’ve been banging our heads against tons of times without making progress, or when you need to come up with a really creative solution. When you’re facing a competitor with a much bigger budget, and you know, if you solve the same problem later, you’re not going to win. So, that basic idea of taking that approach to problems can often help you move forward in a different way than just like, oh, I have a solution.
I would say there’s also, there’s some interesting psychological stuff going on, right? Where you may have tried this, but if somebody tries to serve up a solution to a problem I have, I’m often resistant towards them. Kind if like, no, no, no, no, no, no. That solution is not going to work in my world. Whereas if you get them to discuss and analyze what the problem really is, you might actually dig something up.
Let’s go back to the kitchen example. One powerful question is just to say, what’s your own part in creating this problem? It’s very often, like, people, they describe problems as if it’s something that’s inflicted upon them from the external world, and they are innocent bystanders in that.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Right, or crazy customers with unreasonable demands.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Exactly, right. I don’t think I’ve ever met an agency or consultancy that didn’t, like, gossip about their customers. Oh, my god, they’re horrible. That, you know, classic thing, why don’t they want to take more risk? Well, risk is bad.
It’s their business that’s on the line, not the consultancy’s, right? So, absolutely, that’s one of the things when you step into a different mindset and kind of, wait. Oh yeah, maybe I actually am part of creating this problem in a sense, as well. That tends to open some new doors for you to move forward, in a way, with stuff that you may have been struggling with for years.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, we’ve surfaced a couple of questions that are useful. I’m curious to know, what are some of the other questions that you find yourself asking in these situations, given that you have made this sort of mental habit that you do? What are the questions that people seem to find really useful?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: One easy one is just to ask if there are any positive exceptions to the problem. So, was there day where your kitchen was actually spotlessly clean? And then asking, what was different about that day? Like, what happened there that didn’t happen the other days? That can very often point people towards a factor that they hadn’t considered previously.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: We got take-out.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: S,o that is your solution. Take-out from [INAUDIBLE]. That might have other problems.
Another good question, and this is a little bit more high level. It’s actually more making an observation about labeling how that person thinks about the problem. And what I mean with that is, we have problem categories in our head. So, if I say, let’s say that you describe a problem to me and say, well, we have a really great product and are, it’s much better than our previous product, but people aren’t buying it. I think we need to put more marketing dollars into this.
Now you can go in and say, that’s interesting. This sounds like you’re thinking of this as a communications problem. Is there a different way of thinking about that? Because you can almost tell how, when the second you say communications, there are some ideas about how do you solve a communications problem. Typically with more communication.
And what you might do is go in and suggest, well, have you considered that it might be, say, an incentive problem? Are there incentives on behalf of the purchasing manager at your clients that are obstructing you? Might there be incentive issues with your own sales force that makes them want to sell the old product instead of the new one?
So literally, just identifying what type of problem does this person think about, and is there different potential way of thinking about it? Might it be an emotional problem, a timing problem, an expectations management problem? Thinking about what label of what type of problem that person is kind of thinking as it of.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That’s really interesting, too, because I think so many of us get requests for advice that we’re really not qualified to give. So, maybe the next time that happens, instead of muddying my way through, I will just ask some of those questions that we talked about instead.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That sounds like a good idea.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, Thomas, this has really helped me reframe the way I think about a couple of problems in my own life, and I’m just wondering. I know you do this professionally, but is there a problem in your life that thinking this way has helped you solve?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I’ve, of course, I’ve been swallowing my own medicine on this, too, and I think I have, well, maybe two different examples, and in one case somebody else did the reframing for me. But in one case, when I was younger, I often kind of struggled a little bit. I mean, this is my teenage years, kind of hanging out with my parents. I thought they were pretty annoying people. That’s not really fair, because they’re quite wonderful, but that’s what life is when you’re a teenager.
And one of the things that struck me, suddenly, and this was kind of the positive exception was, there was actually an evening where we really had a good time, and there wasn’t a conflict. And the core thing was, I wasn’t just seeing them in their old house where I grew up. It was, actually, we were at a restaurant. And it suddenly struck me that so much of the sometimes, kind of, a little bit, you love them but they’re annoying kind of dynamic, is tied to the place, is tied to the setting you are in.
And of course, if– you know, I live abroad now, if I visit my parents and I stay in my old bedroom, you know, my mother comes in and wants to wake me up in the morning. Stuff like that, right? And it just struck me so, so clearly that it’s– when I change this setting, if I go out and have dinner with them at a different place, that the dynamic, just that dynamic disappears.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, Thomas, this has been really, really helpful. Thank you for talking with me today.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thank you, Sarah.
HANNAH BATES: That was Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg in conversation with Sarah Green Carmichael on the HBR IdeaCast. He’s an expert in problem solving and innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about leadership from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
We’re a production of Harvard Business Review. If you want more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, find it all at HBR dot org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Music by Coma Media. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener.
See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about leadership.
- Decision making and problem solving
- Power and influence
- Business management
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Here are the steps involved in problem solving, approved by expert psychologists. 1. Identifying the Problem. Identifying the problem seems like the obvious first stem, but it's not exactly as simple as it sounds. People might identify the wrong source of a problem, which will render the steps thus carried on useless.
Steps for solving the Tower of Hanoi in the minimum number of moves when there are 3 disks. With 3 disks, the puzzle can be solved in 7 moves. The ... GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY AND PROBLEM SOLVING. As you may recall from the sensation and perception chapter, Gestalt psychology describes whole patterns, forms and configurations of perception and ...
Problem Solving is the process of identifying, analyzing, and finding effective solutions to complex issues or challenges. Key Steps in Problem Solving: Identification of the problem: Recognizing and clearly defining the issue that needs to be resolved. Analysis and research: Gathering relevant information, data, and facts to understand the ...
In general, effective problem-solving strategies include the following steps: Define the problem. Come up with alternative solutions. Decide on a solution. Implement the solution. Problem-solving ...
Cognitive—Problem solving occurs within the problem solver's cognitive system and can only be inferred indirectly from the problem solver's behavior (including biological changes, introspections, and actions during problem solving).. Process—Problem solving involves mental computations in which some operation is applied to a mental representation, sometimes resulting in the creation of ...
The findings from this second experiment showed that people tend to go through two different stages when solving a series of problems. People begin their problem-solving process in a generative manner during which they explore various tactics — some successful and some not. Then they use their experience to narrow down their choices of ...
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A "rule of thumb" is an example of a heuristic.
The Psychology of Problem Solving organizes in one volume much of what psychologists know about problem solving and the factors that contribute to its success or failure. There are chapters by leading experts in this field, including Miriam Bassok, Randall Engle, Anders Ericsson, Arthur Graesser, Keith Stanovich, Norbert Schwarz, and Barry ...
Problem-solving is one technique used on the behavioral side of cognitive-behavioral therapy. The problem-solving technique is an iterative, five-step process that requires one to identify the ...
Problem-Solving. Somewhat less open-ended than creative thinking is problem-solving, the analysis and solution of tasks or situations that are complex or ambiguous and that pose difficulties or obstacles of some kind (Mayer & Wittrock, 2006). Problem-solving is needed, for example, when a physician analyzes a chest X-ray: a photograph of the ...
The problem-solving cycle is a concept in cognitive psychology that outlines the steps individuals go through when tackling a problem. It involves identifying the problem, gathering information, generating possible solutions, evaluating the solutions, and implementing the best one.
Problem Solving Theory (in Psychology) In this theory, problems are defined as difficulties that cause a person to ask questions that enrich their knowledge (Dostál, 2015). There are four basic steps to problem-solving according to this theory. 1. Awareness of the problem.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
The Nature of Problem Solving. Problem solving, within the realm of psychology, refers to the cognitive process through which individuals identify, analyze, and resolve challenges or obstacles to achieve a desired goal. It encompasses a range of mental activities, such as perception, memory, reasoning, and decision-making, aimed at devising ...
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Here is a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you are thinking critically. Conspiracy theories. Inability to distinguish facts from falsehoods. Widespread confusion ...
Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (Figure 1) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4.
Solving Puzzles. Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( [link]) is a 4×4 grid.
Critical thinking. Leadership. Communication. Time management. Emotional intelligence. Solving a problem is complex and requires the ability to recognize the issue, collect and analyze relevant data, and make decisions about the best course of action.
5.Teaching Problem-Solving Skills: A Lifelong Gift. Exploring the importance of imparting problem-solving skills, this section discusses how teaching teens to navigate challenges is a lifelong gift. It emphasizes the role of parents in guiding their teens towards independent problem-solving and decision-making. 6.Steps in Problem-Solving with Teens
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed.
To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve. In this episode, you'll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that ...