Center for Teaching
Teaching problem solving.
Print Version

Tips and Techniques
Expert vs. novice problem solvers, communicate.
- Have students identify specific problems, difficulties, or confusions . Don’t waste time working through problems that students already understand.
- If students are unable to articulate their concerns, determine where they are having trouble by asking them to identify the specific concepts or principles associated with the problem.
- In a one-on-one tutoring session, ask the student to work his/her problem out loud . This slows down the thinking process, making it more accurate and allowing you to access understanding.
- When working with larger groups you can ask students to provide a written “two-column solution.” Have students write up their solution to a problem by putting all their calculations in one column and all of their reasoning (in complete sentences) in the other column. This helps them to think critically about their own problem solving and helps you to more easily identify where they may be having problems. Two-Column Solution (Math) Two-Column Solution (Physics)
Encourage Independence
- Model the problem solving process rather than just giving students the answer. As you work through the problem, consider how a novice might struggle with the concepts and make your thinking clear
- Have students work through problems on their own. Ask directing questions or give helpful suggestions, but provide only minimal assistance and only when needed to overcome obstacles.
- Don’t fear group work ! Students can frequently help each other, and talking about a problem helps them think more critically about the steps needed to solve the problem. Additionally, group work helps students realize that problems often have multiple solution strategies, some that might be more effective than others
Be sensitive
- Frequently, when working problems, students are unsure of themselves. This lack of confidence may hamper their learning. It is important to recognize this when students come to us for help, and to give each student some feeling of mastery. Do this by providing positive reinforcement to let students know when they have mastered a new concept or skill.
Encourage Thoroughness and Patience
- Try to communicate that the process is more important than the answer so that the student learns that it is OK to not have an instant solution. This is learned through your acceptance of his/her pace of doing things, through your refusal to let anxiety pressure you into giving the right answer, and through your example of problem solving through a step-by step process.
Experts (teachers) in a particular field are often so fluent in solving problems from that field that they can find it difficult to articulate the problem solving principles and strategies they use to novices (students) in their field because these principles and strategies are second nature to the expert. To teach students problem solving skills, a teacher should be aware of principles and strategies of good problem solving in his or her discipline .
The mathematician George Polya captured the problem solving principles and strategies he used in his discipline in the book How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method (Princeton University Press, 1957). The book includes a summary of Polya’s problem solving heuristic as well as advice on the teaching of problem solving.

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules
Teaching Problem-Solving Skills
Many instructors design opportunities for students to solve “problems”. But are their students solving true problems or merely participating in practice exercises? The former stresses critical thinking and decision making skills whereas the latter requires only the application of previously learned procedures.
Problem solving is often broadly defined as "the ability to understand the environment, identify complex problems, review related information to develop, evaluate strategies and implement solutions to build the desired outcome" (Fissore, C. et al, 2021). True problem solving is the process of applying a method – not known in advance – to a problem that is subject to a specific set of conditions and that the problem solver has not seen before, in order to obtain a satisfactory solution.
Below you will find some basic principles for teaching problem solving and one model to implement in your classroom teaching.
Principles for teaching problem solving
- Model a useful problem-solving method . Problem solving can be difficult and sometimes tedious. Show students how to be patient and persistent, and how to follow a structured method, such as Woods’ model described below. Articulate your method as you use it so students see the connections.
- Teach within a specific context . Teach problem-solving skills in the context in which they will be used by students (e.g., mole fraction calculations in a chemistry course). Use real-life problems in explanations, examples, and exams. Do not teach problem solving as an independent, abstract skill.
- Help students understand the problem . In order to solve problems, students need to define the end goal. This step is crucial to successful learning of problem-solving skills. If you succeed at helping students answer the questions “what?” and “why?”, finding the answer to “how?” will be easier.
- Take enough time . When planning a lecture/tutorial, budget enough time for: understanding the problem and defining the goal (both individually and as a class); dealing with questions from you and your students; making, finding, and fixing mistakes; and solving entire problems in a single session.
- Ask questions and make suggestions . Ask students to predict “what would happen if …” or explain why something happened. This will help them to develop analytical and deductive thinking skills. Also, ask questions and make suggestions about strategies to encourage students to reflect on the problem-solving strategies that they use.
- Link errors to misconceptions . Use errors as evidence of misconceptions, not carelessness or random guessing. Make an effort to isolate the misconception and correct it, then teach students to do this by themselves. We can all learn from mistakes.
Woods’ problem-solving model
Define the problem.
- The system . Have students identify the system under study (e.g., a metal bridge subject to certain forces) by interpreting the information provided in the problem statement. Drawing a diagram is a great way to do this.
- Known(s) and concepts . List what is known about the problem, and identify the knowledge needed to understand (and eventually) solve it.
- Unknown(s) . Once you have a list of knowns, identifying the unknown(s) becomes simpler. One unknown is generally the answer to the problem, but there may be other unknowns. Be sure that students understand what they are expected to find.
- Units and symbols . One key aspect in problem solving is teaching students how to select, interpret, and use units and symbols. Emphasize the use of units whenever applicable. Develop a habit of using appropriate units and symbols yourself at all times.
- Constraints . All problems have some stated or implied constraints. Teach students to look for the words "only", "must", "neglect", or "assume" to help identify the constraints.
- Criteria for success . Help students consider, from the beginning, what a logical type of answer would be. What characteristics will it possess? For example, a quantitative problem will require an answer in some form of numerical units (e.g., $/kg product, square cm, etc.) while an optimization problem requires an answer in the form of either a numerical maximum or minimum.
Think about it
- “Let it simmer”. Use this stage to ponder the problem. Ideally, students will develop a mental image of the problem at hand during this stage.
- Identify specific pieces of knowledge . Students need to determine by themselves the required background knowledge from illustrations, examples and problems covered in the course.
- Collect information . Encourage students to collect pertinent information such as conversion factors, constants, and tables needed to solve the problem.
Plan a solution
- Consider possible strategies . Often, the type of solution will be determined by the type of problem. Some common problem-solving strategies are: compute; simplify; use an equation; make a model, diagram, table, or chart; or work backwards.
- Choose the best strategy . Help students to choose the best strategy by reminding them again what they are required to find or calculate.
Carry out the plan
- Be patient . Most problems are not solved quickly or on the first attempt. In other cases, executing the solution may be the easiest step.
- Be persistent . If a plan does not work immediately, do not let students get discouraged. Encourage them to try a different strategy and keep trying.
Encourage students to reflect. Once a solution has been reached, students should ask themselves the following questions:
- Does the answer make sense?
- Does it fit with the criteria established in step 1?
- Did I answer the question(s)?
- What did I learn by doing this?
- Could I have done the problem another way?
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
- Fissore, C., Marchisio, M., Roman, F., & Sacchet, M. (2021). Development of problem solving skills with Maple in higher education. In: Corless, R.M., Gerhard, J., Kotsireas, I.S. (eds) Maple in Mathematics Education and Research. MC 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1414. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81698-8_15
- Foshay, R., & Kirkley, J. (1998). Principles for Teaching Problem Solving. TRO Learning Inc., Edina MN. (PDF) Principles for Teaching Problem Solving (researchgate.net)
- Hayes, J.R. (1989). The Complete Problem Solver. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Woods, D.R., Wright, J.D., Hoffman, T.W., Swartman, R.K., Doig, I.D. (1975). Teaching Problem solving Skills.
- Engineering Education. Vol 1, No. 1. p. 238. Washington, DC: The American Society for Engineering Education.
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
- Learning activities ,
Teaching problem solving: Let students get ‘stuck’ and ‘unstuck’
Subscribe to the center for universal education bulletin, kate mills and km kate mills literacy interventionist - red bank primary school helyn kim helyn kim former brookings expert @helyn_kim.
October 31, 2017
This is the second in a six-part blog series on teaching 21st century skills , including problem solving , metacognition , critical thinking , and collaboration , in classrooms.
In the real world, students encounter problems that are complex, not well defined, and lack a clear solution and approach. They need to be able to identify and apply different strategies to solve these problems. However, problem solving skills do not necessarily develop naturally; they need to be explicitly taught in a way that can be transferred across multiple settings and contexts.
Here’s what Kate Mills, who taught 4 th grade for 10 years at Knollwood School in New Jersey and is now a Literacy Interventionist at Red Bank Primary School, has to say about creating a classroom culture of problem solvers:
Helping my students grow to be people who will be successful outside of the classroom is equally as important as teaching the curriculum. From the first day of school, I intentionally choose language and activities that help to create a classroom culture of problem solvers. I want to produce students who are able to think about achieving a particular goal and manage their mental processes . This is known as metacognition , and research shows that metacognitive skills help students become better problem solvers.
I begin by “normalizing trouble” in the classroom. Peter H. Johnston teaches the importance of normalizing struggle , of naming it, acknowledging it, and calling it what it is: a sign that we’re growing. The goal is for the students to accept challenge and failure as a chance to grow and do better.
I look for every chance to share problems and highlight how the students— not the teachers— worked through those problems. There is, of course, coaching along the way. For example, a science class that is arguing over whose turn it is to build a vehicle will most likely need a teacher to help them find a way to the balance the work in an equitable way. Afterwards, I make it a point to turn it back to the class and say, “Do you see how you …” By naming what it is they did to solve the problem , students can be more independent and productive as they apply and adapt their thinking when engaging in future complex tasks.
After a few weeks, most of the class understands that the teachers aren’t there to solve problems for the students, but to support them in solving the problems themselves. With that important part of our classroom culture established, we can move to focusing on the strategies that students might need.
Here’s one way I do this in the classroom:
I show the broken escalator video to the class. Since my students are fourth graders, they think it’s hilarious and immediately start exclaiming, “Just get off! Walk!”
When the video is over, I say, “Many of us, probably all of us, are like the man in the video yelling for help when we get stuck. When we get stuck, we stop and immediately say ‘Help!’ instead of embracing the challenge and trying new ways to work through it.” I often introduce this lesson during math class, but it can apply to any area of our lives, and I can refer to the experience and conversation we had during any part of our day.
Research shows that just because students know the strategies does not mean they will engage in the appropriate strategies. Therefore, I try to provide opportunities where students can explicitly practice learning how, when, and why to use which strategies effectively so that they can become self-directed learners.
For example, I give students a math problem that will make many of them feel “stuck”. I will say, “Your job is to get yourselves stuck—or to allow yourselves to get stuck on this problem—and then work through it, being mindful of how you’re getting yourselves unstuck.” As students work, I check-in to help them name their process: “How did you get yourself unstuck?” or “What was your first step? What are you doing now? What might you try next?” As students talk about their process, I’ll add to a list of strategies that students are using and, if they are struggling, help students name a specific process. For instance, if a student says he wrote the information from the math problem down and points to a chart, I will say: “Oh that’s interesting. You pulled the important information from the problem out and organized it into a chart.” In this way, I am giving him the language to match what he did, so that he now has a strategy he could use in other times of struggle.
The charts grow with us over time and are something that we refer to when students are stuck or struggling. They become a resource for students and a way for them to talk about their process when they are reflecting on and monitoring what did or did not work.
For me, as a teacher, it is important that I create a classroom environment in which students are problem solvers. This helps tie struggles to strategies so that the students will not only see value in working harder but in working smarter by trying new and different strategies and revising their process. In doing so, they will more successful the next time around.
Related Content
Esther Care, Helyn Kim, Alvin Vista
October 17, 2017
David Owen, Alvin Vista
November 15, 2017
Loren Clarke, Esther Care
December 5, 2017
Global Education K-12 Education
Global Economy and Development
Center for Universal Education
Michael Trucano, Sopiko Beriashvili
April 25, 2024
Online only
9:00 am - 10:00 am EDT
Kelli Bird, Ben Castleman
April 23, 2024
Why Every Educator Needs to Teach Problem-Solving Skills
Strong problem-solving skills will help students be more resilient and will increase their academic and career success .
Want to learn more about how to measure and teach students’ higher-order skills, including problem solving, critical thinking, and written communication?
Problem-solving skills are essential in school, careers, and life.
Problem-solving skills are important for every student to master. They help individuals navigate everyday life and find solutions to complex issues and challenges. These skills are especially valuable in the workplace, where employees are often required to solve problems and make decisions quickly and effectively.
Problem-solving skills are also needed for students’ personal growth and development because they help individuals overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. By developing strong problem-solving skills, students can improve their overall quality of life and become more successful in their personal and professional endeavors.
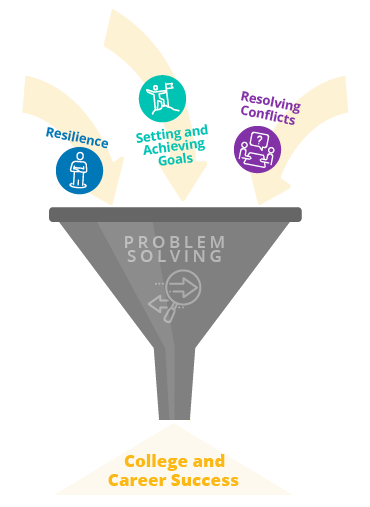
Problem-Solving Skills Help Students…
develop resilience.
Problem-solving skills are an integral part of resilience and the ability to persevere through challenges and adversity. To effectively work through and solve a problem, students must be able to think critically and creatively. Critical and creative thinking help students approach a problem objectively, analyze its components, and determine different ways to go about finding a solution.
This process in turn helps students build self-efficacy . When students are able to analyze and solve a problem, this increases their confidence, and they begin to realize the power they have to advocate for themselves and make meaningful change.
When students gain confidence in their ability to work through problems and attain their goals, they also begin to build a growth mindset . According to leading resilience researcher, Carol Dweck, “in a growth mindset, people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work—brains and talent are just the starting point. This view creates a love of learning and a resilience that is essential for great accomplishment.”
Set and Achieve Goals
Students who possess strong problem-solving skills are better equipped to set and achieve their goals. By learning how to identify problems, think critically, and develop solutions, students can become more self-sufficient and confident in their ability to achieve their goals. Additionally, problem-solving skills are used in virtually all fields, disciplines, and career paths, which makes them important for everyone. Building strong problem-solving skills will help students enhance their academic and career performance and become more competitive as they begin to seek full-time employment after graduation or pursue additional education and training.
Resolve Conflicts
In addition to increased social and emotional skills like self-efficacy and goal-setting, problem-solving skills teach students how to cooperate with others and work through disagreements and conflicts. Problem-solving promotes “thinking outside the box” and approaching a conflict by searching for different solutions. This is a very different (and more effective!) method than a more stagnant approach that focuses on placing blame or getting stuck on elements of a situation that can’t be changed.
While it’s natural to get frustrated or feel stuck when working through a conflict, students with strong problem-solving skills will be able to work through these obstacles, think more rationally, and address the situation with a more solution-oriented approach. These skills will be valuable for students in school, their careers, and throughout their lives.
Achieve Success
We are all faced with problems every day. Problems arise in our personal lives, in school and in our jobs, and in our interactions with others. Employers especially are looking for candidates with strong problem-solving skills. In today’s job market, most jobs require the ability to analyze and effectively resolve complex issues. Students with strong problem-solving skills will stand out from other applicants and will have a more desirable skill set.
In a recent opinion piece published by The Hechinger Report , Virgel Hammonds, Chief Learning Officer at KnowledgeWorks, stated “Our world presents increasingly complex challenges. Education must adapt so that it nurtures problem solvers and critical thinkers.” Yet, the “traditional K–12 education system leaves little room for students to engage in real-world problem-solving scenarios.” This is the reason that a growing number of K–12 school districts and higher education institutions are transforming their instructional approach to personalized and competency-based learning, which encourage students to make decisions, problem solve and think critically as they take ownership of and direct their educational journey.
Problem-Solving Skills Can Be Measured and Taught
Research shows that problem-solving skills can be measured and taught. One effective method is through performance-based assessments which require students to demonstrate or apply their knowledge and higher-order skills to create a response or product or do a task.
What Are Performance-Based Assessments?

With the No Child Left Behind Act (2002), the use of standardized testing became the primary way to measure student learning in the U.S. The legislative requirements of this act shifted the emphasis to standardized testing, and this led to a decline in nontraditional testing methods .
But many educators, policy makers, and parents have concerns with standardized tests. Some of the top issues include that they don’t provide feedback on how students can perform better, they don’t value creativity, they are not representative of diverse populations, and they can be disadvantageous to lower-income students.
While standardized tests are still the norm, U.S. Secretary of Education Miguel Cardona is encouraging states and districts to move away from traditional multiple choice and short response tests and instead use performance-based assessment, competency-based assessments, and other more authentic methods of measuring students abilities and skills rather than rote learning.
Performance-based assessments measure whether students can apply the skills and knowledge learned from a unit of study. Typically, a performance task challenges students to use their higher-order skills to complete a project or process. Tasks can range from an essay to a complex proposal or design.
Preview a Performance-Based Assessment
Want a closer look at how performance-based assessments work? Preview CAE’s K–12 and Higher Education assessments and see how CAE’s tools help students develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and written communication skills.
Performance-Based Assessments Help Students Build and Practice Problem-Solving Skills
In addition to effectively measuring students’ higher-order skills, including their problem-solving skills, performance-based assessments can help students practice and build these skills. Through the assessment process, students are given opportunities to practically apply their knowledge in real-world situations. By demonstrating their understanding of a topic, students are required to put what they’ve learned into practice through activities such as presentations, experiments, and simulations.
This type of problem-solving assessment tool requires students to analyze information and choose how to approach the presented problems. This process enhances their critical thinking skills and creativity, as well as their problem-solving skills. Unlike traditional assessments based on memorization or reciting facts, performance-based assessments focus on the students’ decisions and solutions, and through these tasks students learn to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Performance-based assessments like CAE’s College and Career Readiness Assessment (CRA+) and Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+) provide students with in-depth reports that show them which higher-order skills they are strongest in and which they should continue to develop. This feedback helps students and their teachers plan instruction and supports to deepen their learning and improve their mastery of critical skills.

Explore CAE’s Problem-Solving Assessments
CAE offers performance-based assessments that measure student proficiency in higher-order skills including problem solving, critical thinking, and written communication.
- College and Career Readiness Assessment (CCRA+) for secondary education and
- Collegiate Learning Assessment (CLA+) for higher education.
Our solution also includes instructional materials, practice models, and professional development.
We can help you create a program to build students’ problem-solving skills that includes:
- Measuring students’ problem-solving skills through a performance-based assessment
- Using the problem-solving assessment data to inform instruction and tailor interventions
- Teaching students problem-solving skills and providing practice opportunities in real-life scenarios
- Supporting educators with quality professional development
Get started with our problem-solving assessment tools to measure and build students’ problem-solving skills today! These skills will be invaluable to students now and in the future.

Ready to Get Started?
Learn more about cae’s suite of products and let’s get started measuring and teaching students important higher-order skills like problem solving..
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
- Problem Solving in STEM
Solving problems is a key component of many science, math, and engineering classes. If a goal of a class is for students to emerge with the ability to solve new kinds of problems or to use new problem-solving techniques, then students need numerous opportunities to develop the skills necessary to approach and answer different types of problems. Problem solving during section or class allows students to develop their confidence in these skills under your guidance, better preparing them to succeed on their homework and exams. This page offers advice about strategies for facilitating problem solving during class.
How do I decide which problems to cover in section or class?
In-class problem solving should reinforce the major concepts from the class and provide the opportunity for theoretical concepts to become more concrete. If students have a problem set for homework, then in-class problem solving should prepare students for the types of problems that they will see on their homework. You may wish to include some simpler problems both in the interest of time and to help students gain confidence, but it is ideal if the complexity of at least some of the in-class problems mirrors the level of difficulty of the homework. You may also want to ask your students ahead of time which skills or concepts they find confusing, and include some problems that are directly targeted to their concerns.
You have given your students a problem to solve in class. What are some strategies to work through it?
- Try to give your students a chance to grapple with the problems as much as possible. Offering them the chance to do the problem themselves allows them to learn from their mistakes in the presence of your expertise as their teacher. (If time is limited, they may not be able to get all the way through multi-step problems, in which case it can help to prioritize giving them a chance to tackle the most challenging steps.)
- When you do want to teach by solving the problem yourself at the board, talk through the logic of how you choose to apply certain approaches to solve certain problems. This way you can externalize the type of thinking you hope your students internalize when they solve similar problems themselves.
- Start by setting up the problem on the board (e.g you might write down key variables and equations; draw a figure illustrating the question). Ask students to start solving the problem, either independently or in small groups. As they are working on the problem, walk around to hear what they are saying and see what they are writing down. If several students seem stuck, it might be a good to collect the whole class again to clarify any confusion. After students have made progress, bring the everyone back together and have students guide you as to what to write on the board.
- It can help to first ask students to work on the problem by themselves for a minute, and then get into small groups to work on the problem collaboratively.
- If you have ample board space, have students work in small groups at the board while solving the problem. That way you can monitor their progress by standing back and watching what they put up on the board.
- If you have several problems you would like to have the students practice, but not enough time for everyone to do all of them, you can assign different groups of students to work on different – but related - problems.
When do you want students to work in groups to solve problems?
- Don’t ask students to work in groups for straightforward problems that most students could solve independently in a short amount of time.
- Do have students work in groups for thought-provoking problems, where students will benefit from meaningful collaboration.
- Even in cases where you plan to have students work in groups, it can be useful to give students some time to work on their own before collaborating with others. This ensures that every student engages with the problem and is ready to contribute to a discussion.
What are some benefits of having students work in groups?
- Students bring different strengths, different knowledge, and different ideas for how to solve a problem; collaboration can help students work through problems that are more challenging than they might be able to tackle on their own.
- In working in a group, students might consider multiple ways to approach a problem, thus enriching their repertoire of strategies.
- Students who think they understand the material will gain a deeper understanding by explaining concepts to their peers.
What are some strategies for helping students to form groups?
- Instruct students to work with the person (or people) sitting next to them.
- Count off. (e.g. 1, 2, 3, 4; all the 1’s find each other and form a group, etc)
- Hand out playing cards; students need to find the person with the same number card. (There are many variants to this. For example, you can print pictures of images that go together [rain and umbrella]; each person gets a card and needs to find their partner[s].)
- Based on what you know about the students, assign groups in advance. List the groups on the board.
- Note: Always have students take the time to introduce themselves to each other in a new group.
What should you do while your students are working on problems?
- Walk around and talk to students. Observing their work gives you a sense of what people understand and what they are struggling with. Answer students’ questions, and ask them questions that lead in a productive direction if they are stuck.
- If you discover that many people have the same question—or that someone has a misunderstanding that others might have—you might stop everyone and discuss a key idea with the entire class.
After students work on a problem during class, what are strategies to have them share their answers and their thinking?
- Ask for volunteers to share answers. Depending on the nature of the problem, student might provide answers verbally or by writing on the board. As a variant, for questions where a variety of answers are relevant, ask for at least three volunteers before anyone shares their ideas.
- Use online polling software for students to respond to a multiple-choice question anonymously.
- If students are working in groups, assign reporters ahead of time. For example, the person with the next birthday could be responsible for sharing their group’s work with the class.
- Cold call. To reduce student anxiety about cold calling, it can help to identify students who seem to have the correct answer as you were walking around the class and checking in on their progress solving the assigned problem. You may even want to warn the student ahead of time: "This is a great answer! Do you mind if I call on you when we come back together as a class?"
- Have students write an answer on a notecard that they turn in to you. If your goal is to understand whether students in general solved a problem correctly, the notecards could be submitted anonymously; if you wish to assess individual students’ work, you would want to ask students to put their names on their notecard.
- Use a jigsaw strategy, where you rearrange groups such that each new group is comprised of people who came from different initial groups and had solved different problems. Students now are responsible for teaching the other students in their new group how to solve their problem.
- Have a representative from each group explain their problem to the class.
- Have a representative from each group draw or write the answer on the board.
What happens if a student gives a wrong answer?
- Ask for their reasoning so that you can understand where they went wrong.
- Ask if anyone else has other ideas. You can also ask this sometimes when an answer is right.
- Cultivate an environment where it’s okay to be wrong. Emphasize that you are all learning together, and that you learn through making mistakes.
- Do make sure that you clarify what the correct answer is before moving on.
- Once the correct answer is given, go through some answer-checking techniques that can distinguish between correct and incorrect answers. This can help prepare students to verify their future work.
How can you make your classroom inclusive?
- The goal is that everyone is thinking, talking, and sharing their ideas, and that everyone feels valued and respected. Use a variety of teaching strategies (independent work and group work; allow students to talk to each other before they talk to the class). Create an environment where it is normal to struggle and make mistakes.
- See Kimberly Tanner’s article on strategies to promoste student engagement and cultivate classroom equity.
A few final notes…
- Make sure that you have worked all of the problems and also thought about alternative approaches to solving them.
- Board work matters. You should have a plan beforehand of what you will write on the board, where, when, what needs to be added, and what can be erased when. If students are going to write their answers on the board, you need to also have a plan for making sure that everyone gets to the correct answer. Students will copy what is on the board and use it as their notes for later study, so correct and logical information must be written there.
For more information...
Tipsheet: Problem Solving in STEM Sections
Tanner, K. D. (2013). Structure matters: twenty-one teaching strategies to promote student engagement and cultivate classroom equity . CBE-Life Sciences Education, 12(3), 322-331.
- Designing Your Course
- A Teaching Timeline: From Pre-Term Planning to the Final Exam
- The First Day of Class
- Group Agreements
- Classroom Debate
- Flipped Classrooms
- Leading Discussions
- Polling & Clickers
- Teaching with Cases
- Engaged Scholarship
- Devices in the Classroom
- Beyond the Classroom
- On Professionalism
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
- Faculty & Staff
Teaching problem solving
Strategies for teaching problem solving apply across disciplines and instructional contexts. First, introduce the problem and explain how people in your discipline generally make sense of the given information. Then, explain how to apply these approaches to solve the problem.
Introducing the problem
Explaining how people in your discipline understand and interpret these types of problems can help students develop the skills they need to understand the problem (and find a solution). After introducing how you would go about solving a problem, you could then ask students to:
- frame the problem in their own words
- define key terms and concepts
- determine statements that accurately represent the givens of a problem
- identify analogous problems
- determine what information is needed to solve the problem
Working on solutions
In the solution phase, one develops and then implements a coherent plan for solving the problem. As you help students with this phase, you might ask them to:
- identify the general model or procedure they have in mind for solving the problem
- set sub-goals for solving the problem
- identify necessary operations and steps
- draw conclusions
- carry out necessary operations
You can help students tackle a problem effectively by asking them to:
- systematically explain each step and its rationale
- explain how they would approach solving the problem
- help you solve the problem by posing questions at key points in the process
- work together in small groups (3 to 5 students) to solve the problem and then have the solution presented to the rest of the class (either by you or by a student in the group)
In all cases, the more you get the students to articulate their own understandings of the problem and potential solutions, the more you can help them develop their expertise in approaching problems in your discipline.

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Published 2018
The Problem-solving Classroom
- Visualising
- Working backwards
- Reasoning logically
- Conjecturing
- Working systematically
- Looking for patterns
- Trial and improvement.
- stage of the lesson
- level of thinking
- mathematical skill.
- The length of student response increases (300-700%)
- More responses are supported by logical argument.
- An increased number of speculative responses.
- The number of questions asked by students increases.
- Student - student exchanges increase (volleyball).
- Failures to respond decrease.
- 'Disciplinary moves' decrease.
- The variety of students participating increases. As does the number of unsolicited, but appropriate contributions.
- Student confidence increases.
- conceptual understanding
- procedural fluency
- strategic competence
- adaptive reasoning
- productive disposition

- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How to Teach Kids Problem-Solving Skills
KidStock / Blend Images / Getty Images
- Steps to Follow
- Allow Consequences
Whether your child can't find their math homework or has forgotten their lunch, good problem-solving skills are the key to helping them manage their life.
A 2010 study published in Behaviour Research and Therapy found that kids who lack problem-solving skills may be at a higher risk of depression and suicidality. Additionally, the researchers found that teaching a child problem-solving skills can improve mental health .
You can begin teaching basic problem-solving skills during preschool and help your child sharpen their skills into high school and beyond.
Why Problem-Solving Skills Matter
Kids face a variety of problems every day, ranging from academic difficulties to problems on the sports field. Yet few of them have a formula for solving those problems.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills may avoid taking action when faced with a problem.
Rather than put their energy into solving the problem, they may invest their time in avoiding the issue. That's why many kids fall behind in school or struggle to maintain friendships .
Other kids who lack problem-solving skills spring into action without recognizing their choices. A child may hit a peer who cuts in front of them in line because they are not sure what else to do.
Or, they may walk out of class when they are being teased because they can't think of any other ways to make it stop. Those impulsive choices may create even bigger problems in the long run.
The 5 Steps of Problem-Solving
Kids who feel overwhelmed or hopeless often won't attempt to address a problem. But when you give them a clear formula for solving problems, they'll feel more confident in their ability to try. Here are the steps to problem-solving:
- Identify the problem . Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
- Develop at least five possible solutions . Brainstorm possible ways to solve the problem. Emphasize that all the solutions don't necessarily need to be good ideas (at least not at this point). Help your child develop solutions if they are struggling to come up with ideas. Even a silly answer or far-fetched idea is a possible solution. The key is to help them see that with a little creativity, they can find many different potential solutions.
- Identify the pros and cons of each solution . Help your child identify potential positive and negative consequences for each potential solution they identified.
- Pick a solution. Once your child has evaluated the possible positive and negative outcomes, encourage them to pick a solution.
- Test it out . Tell them to try a solution and see what happens. If it doesn't work out, they can always try another solution from the list that they developed in step two.
Practice Solving Problems
When problems arise, don’t rush to solve your child’s problems for them. Instead, help them walk through the problem-solving steps. Offer guidance when they need assistance, but encourage them to solve problems on their own. If they are unable to come up with a solution, step in and help them think of some. But don't automatically tell them what to do.
When you encounter behavioral issues, use a problem-solving approach. Sit down together and say, "You've been having difficulty getting your homework done lately. Let's problem-solve this together." You might still need to offer a consequence for misbehavior, but make it clear that you're invested in looking for a solution so they can do better next time.
Use a problem-solving approach to help your child become more independent.
If they forgot to pack their soccer cleats for practice, ask, "What can we do to make sure this doesn't happen again?" Let them try to develop some solutions on their own.
Kids often develop creative solutions. So they might say, "I'll write a note and stick it on my door so I'll remember to pack them before I leave," or "I'll pack my bag the night before and I'll keep a checklist to remind me what needs to go in my bag."
Provide plenty of praise when your child practices their problem-solving skills.
Allow for Natural Consequences
Natural consequences may also teach problem-solving skills. So when it's appropriate, allow your child to face the natural consequences of their action. Just make sure it's safe to do so.
For example, let your teenager spend all of their money during the first 10 minutes you're at an amusement park if that's what they want. Then, let them go for the rest of the day without any spending money.
This can lead to a discussion about problem-solving to help them make a better choice next time. Consider these natural consequences as a teachable moment to help work together on problem-solving.
Becker-Weidman EG, Jacobs RH, Reinecke MA, Silva SG, March JS. Social problem-solving among adolescents treated for depression . Behav Res Ther . 2010;48(1):11-18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2009.08.006
Pakarinen E, Kiuru N, Lerkkanen M-K, Poikkeus A-M, Ahonen T, Nurmi J-E. Instructional support predicts childrens task avoidance in kindergarten . Early Child Res Q . 2011;26(3):376-386. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.11.003
Schell A, Albers L, von Kries R, Hillenbrand C, Hennemann T. Preventing behavioral disorders via supporting social and emotional competence at preschool age . Dtsch Arztebl Int . 2015;112(39):647–654. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2015.0647
Cheng SC, She HC, Huang LY. The impact of problem-solving instruction on middle school students’ physical science learning: Interplays of knowledge, reasoning, and problem solving . EJMSTE . 2018;14(3):731-743.
Vlachou A, Stavroussi P. Promoting social inclusion: A structured intervention for enhancing interpersonal problem‐solving skills in children with mild intellectual disabilities . Support Learn . 2016;31(1):27-45. doi:10.1111/1467-9604.12112
Öğülmüş S, Kargı E. The interpersonal cognitive problem solving approach for preschoolers . Turkish J Educ . 2015;4(17347):19-28. doi:10.19128/turje.181093
American Academy of Pediatrics. What's the best way to discipline my child? .
Kashani-Vahid L, Afrooz G, Shokoohi-Yekta M, Kharrazi K, Ghobari B. Can a creative interpersonal problem solving program improve creative thinking in gifted elementary students? . Think Skills Creat . 2017;24:175-185. doi:10.1016/j.tsc.2017.02.011
Shokoohi-Yekta M, Malayeri SA. Effects of advanced parenting training on children's behavioral problems and family problem solving . Procedia Soc Behav Sci . 2015;205:676-680. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.09.106
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
- Try for free
Problem-Solving

Jabberwocky
Problem-solving is the ability to identify and solve problems by applying appropriate skills systematically.
Problem-solving is a process—an ongoing activity in which we take what we know to discover what we don't know. It involves overcoming obstacles by generating hypo-theses, testing those predictions, and arriving at satisfactory solutions.
Problem-solving involves three basic functions:
Seeking information
Generating new knowledge
Making decisions
Problem-solving is, and should be, a very real part of the curriculum. It presupposes that students can take on some of the responsibility for their own learning and can take personal action to solve problems, resolve conflicts, discuss alternatives, and focus on thinking as a vital element of the curriculum. It provides students with opportunities to use their newly acquired knowledge in meaningful, real-life activities and assists them in working at higher levels of thinking (see Levels of Questions ).
Here is a five-stage model that most students can easily memorize and put into action and which has direct applications to many areas of the curriculum as well as everyday life:
Expert Opinion
Here are some techniques that will help students understand the nature of a problem and the conditions that surround it:
- List all related relevant facts.
- Make a list of all the given information.
- Restate the problem in their own words.
- List the conditions that surround a problem.
- Describe related known problems.
It's Elementary
For younger students, illustrations are helpful in organizing data, manipulating information, and outlining the limits of a problem and its possible solution(s). Students can use drawings to help them look at a problem from many different perspectives.
Understand the problem. It's important that students understand the nature of a problem and its related goals. Encourage students to frame a problem in their own words.
Describe any barriers. Students need to be aware of any barriers or constraints that may be preventing them from achieving their goal. In short, what is creating the problem? Encouraging students to verbalize these impediments is always an important step.
Identify various solutions. After the nature and parameters of a problem are understood, students will need to select one or more appropriate strategies to help resolve the problem. Students need to understand that they have many strategies available to them and that no single strategy will work for all problems. Here are some problem-solving possibilities:
Create visual images. Many problem-solvers find it useful to create “mind pictures” of a problem and its potential solutions prior to working on the problem. Mental imaging allows the problem-solvers to map out many dimensions of a problem and “see” it clearly.
Guesstimate. Give students opportunities to engage in some trial-and-error approaches to problem-solving. It should be understood, however, that this is not a singular approach to problem-solving but rather an attempt to gather some preliminary data.
Create a table. A table is an orderly arrangement of data. When students have opportunities to design and create tables of information, they begin to understand that they can group and organize most data relative to a problem.
Use manipulatives. By moving objects around on a table or desk, students can develop patterns and organize elements of a problem into recognizable and visually satisfying components.
Work backward. It's frequently helpful for students to take the data presented at the end of a problem and use a series of computations to arrive at the data presented at the beginning of the problem.
Look for a pattern. Looking for patterns is an important problem-solving strategy because many problems are similar and fall into predictable patterns. A pattern, by definition, is a regular, systematic repetition and may be numerical, visual, or behavioral.
Create a systematic list. Recording information in list form is a process used quite frequently to map out a plan of attack for defining and solving problems. Encourage students to record their ideas in lists to determine regularities, patterns, or similarities between problem elements.
Try out a solution. When working through a strategy or combination of strategies, it will be important for students to …
Keep accurate and up-to-date records of their thoughts, proceedings, and procedures. Recording the data collected, the predictions made, and the strategies used is an important part of the problem solving process.
Try to work through a selected strategy or combination of strategies until it becomes evident that it's not working, it needs to be modified, or it is yielding inappropriate data. As students become more proficient problem-solvers, they should feel comfortable rejecting potential strategies at any time during their quest for solutions.
Monitor with great care the steps undertaken as part of a solution. Although it might be a natural tendency for students to “rush” through a strategy to arrive at a quick answer, encourage them to carefully assess and monitor their progress.
Feel comfortable putting a problem aside for a period of time and tackling it at a later time. For example, scientists rarely come up with a solution the first time they approach a problem. Students should also feel comfortable letting a problem rest for a while and returning to it later.
Evaluate the results. It's vitally important that students have multiple opportunities to assess their own problem-solving skills and the solutions they generate from using those skills. Frequently, students are overly dependent upon teachers to evaluate their performance in the classroom. The process of self-assessment is not easy, however. It involves risk-taking, self-assurance, and a certain level of independence. But it can be effectively promoted by asking students questions such as “How do you feel about your progress so far?” “Are you satisfied with the results you obtained?” and “Why do you believe this is an appropriate response to the problem?”
Featured High School Resources

Related Resources

About the author

TeacherVision Editorial Staff
The TeacherVision editorial team is comprised of teachers, experts, and content professionals dedicated to bringing you the most accurate and relevant information in the teaching space.

Teaching Problem Solving in Math
- Freebies , Math , Planning

Every year my students can be fantastic at math…until they start to see math with words. For some reason, once math gets translated into reading, even my best readers start to panic. There is just something about word problems, or problem-solving, that causes children to think they don’t know how to complete them.
Every year in math, I start off by teaching my students problem-solving skills and strategies. Every year they moan and groan that they know them. Every year – paragraph one above. It was a vicious cycle. I needed something new.

I put together a problem-solving unit that would focus a bit more on strategies and steps in hopes that that would create problem-solving stars.
The Problem Solving Strategies
First, I wanted to make sure my students all learned the different strategies to solve problems, such as guess-and-check, using visuals (draw a picture, act it out, and modeling it), working backward, and organizational methods (tables, charts, and lists). In the past, I had used worksheet pages that would introduce one and provide the students with plenty of problems practicing that one strategy. I did like that because students could focus more on practicing the strategy itself, but I also wanted students to know when to use it, too, so I made sure they had both to practice.
I provided students with plenty of practice of the strategies, such as in this guess-and-check game.

There’s also this visuals strategy wheel practice.
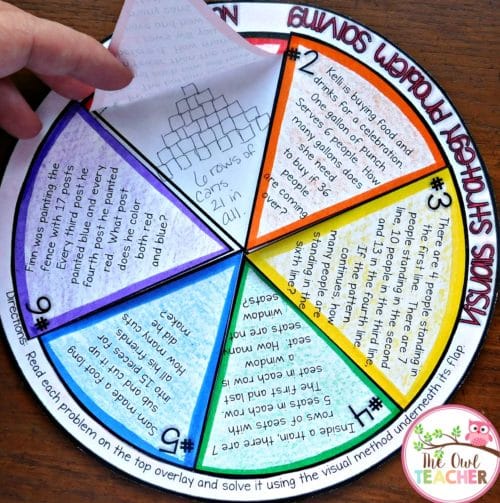

I also provided them with paper dolls and a variety of clothing to create an organized list to determine just how many outfits their “friend” would have.

Then, as I said above, we practiced in a variety of ways to make sure we knew exactly when to use them. I really wanted to make sure they had this down!

Anyway, after I knew they had down the various strategies and when to use them, then we went into the actual problem-solving steps.
The Problem Solving Steps
I wanted students to understand that when they see a story problem, it isn’t scary. Really, it’s just the equation written out in words in a real-life situation. Then, I provided them with the “keys to success.”
S tep 1 – Understand the Problem. To help students understand the problem, I provided them with sample problems, and together we did five important things:
- read the problem carefully
- restated the problem in our own words
- crossed out unimportant information
- circled any important information
- stated the goal or question to be solved
We did this over and over with example problems.

Once I felt the students had it down, we practiced it in a game of problem-solving relay. Students raced one another to see how quickly they could get down to the nitty-gritty of the word problems. We weren’t solving the problems – yet.

Then, we were on to Step 2 – Make a Plan . We talked about how this was where we were going to choose which strategy we were going to use. We also discussed how this was where we were going to figure out what operation to use. I taught the students Sheila Melton’s operation concept map.

We talked about how if you know the total and know if it is equal or not, that will determine what operation you are doing. So, we took an example problem, such as:
Sheldon wants to make a cupcake for each of his 28 classmates. He can make 7 cupcakes with one box of cupcake mix. How many boxes will he need to buy?
We started off by asking ourselves, “Do we know the total?” We know there are a total of 28 classmates. So, yes, we are separating. Then, we ask, “Is it equal?” Yes, he wants to make a cupcake for EACH of his classmates. So, we are dividing: 28 divided by 7 = 4. He will need to buy 4 boxes. (I actually went ahead and solved it here – which is the next step, too.)
Step 3 – Solving the problem . We talked about how solving the problem involves the following:
- taking our time
- working the problem out
- showing all our work
- estimating the answer
- using thinking strategies
We talked specifically about thinking strategies. Just like in reading, there are thinking strategies in math. I wanted students to be aware that sometimes when we are working on a problem, a particular strategy may not be working, and we may need to switch strategies. We also discussed that sometimes we may need to rethink the problem, to think of related content, or to even start over. We discussed these thinking strategies:
- switch strategies or try a different one
- rethink the problem
- think of related content
- decide if you need to make changes
- check your work
- but most important…don’t give up!
To make sure they were getting in practice utilizing these thinking strategies, I gave each group chart paper with a letter from a fellow “student” (not a real student), and they had to give advice on how to help them solve their problem using the thinking strategies above.

Finally, Step 4 – Check It. This is the step that students often miss. I wanted to emphasize just how important it is! I went over it with them, discussing that when they check their problems, they should always look for these things:
- compare your answer to your estimate
- check for reasonableness
- check your calculations
- add the units
- restate the question in the answer
- explain how you solved the problem
Then, I gave students practice cards. I provided them with example cards of “students” who had completed their assignments already, and I wanted them to be the teacher. They needed to check the work and make sure it was completed correctly. If it wasn’t, then they needed to tell what they missed and correct it.

To demonstrate their understanding of the entire unit, we completed an adorable lap book (my first time ever putting together one or even creating one – I was surprised how well it turned out, actually). It was a great way to put everything we discussed in there.

Once we were all done, students were officially Problem Solving S.T.A.R.S. I just reminded students frequently of this acronym.
Stop – Don’t rush with any solution; just take your time and look everything over.
Think – Take your time to think about the problem and solution.
Act – Act on a strategy and try it out.
Review – Look it over and see if you got all the parts.

Wow, you are a true trooper sticking it out in this lengthy post! To sum up the majority of what I have written here, I have some problem-solving bookmarks FREE to help you remember and to help your students!
You can grab these problem-solving bookmarks for FREE by clicking here .
You can do any of these ideas without having to purchase anything. However, if you are looking to save some time and energy, then they are all found in my Math Workshop Problem Solving Unit . The unit is for grade three, but it may work for other grade levels. The practice problems are all for the early third-grade level.
- freebie , Math Workshop , Problem Solving
FIND IT NOW!
Check me out on tpt.

CHECK THESE OUT

Three Types of Rocks and Minerals with Rock Cycle Circle Book
Partitioning Shapes Equal Share Fractions Halves, Thirds, Fourths Math Puzzles
Want to save time?
COPYRIGHT © 2016-2024. The Owl Teacher | Privacy page | Disclosure Page | Shipping | Returns/Refunds
BOGO on EVERYTHING!

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, 5 problem-solving activities for the classroom.

Problem-solving skills are necessary in all areas of life, and classroom problem solving activities can be a great way to get students prepped and ready to solve real problems in real life scenarios. Whether in school, work or in their social relationships, the ability to critically analyze a problem, map out all its elements and then prepare a workable solution is one of the most valuable skills one can acquire in life.
Educating your students about problem solving skills from an early age in school can be facilitated through classroom problem solving activities. Such endeavors encourage cognitive as well as social development, and can equip students with the tools they’ll need to address and solve problems throughout the rest of their lives. Here are five classroom problem solving activities your students are sure to benefit from as well as enjoy doing:
1. Brainstorm bonanza
Having your students create lists related to whatever you are currently studying can be a great way to help them to enrich their understanding of a topic while learning to problem-solve. For example, if you are studying a historical, current or fictional event that did not turn out favorably, have your students brainstorm ways that the protagonist or participants could have created a different, more positive outcome. They can brainstorm on paper individually or on a chalkboard or white board in front of the class.
2. Problem-solving as a group
Have your students create and decorate a medium-sized box with a slot in the top. Label the box “The Problem-Solving Box.” Invite students to anonymously write down and submit any problem or issue they might be having at school or at home, ones that they can’t seem to figure out on their own. Once or twice a week, have a student draw one of the items from the box and read it aloud. Then have the class as a group figure out the ideal way the student can address the issue and hopefully solve it.
3. Clue me in
This fun detective game encourages problem-solving, critical thinking and cognitive development. Collect a number of items that are associated with a specific profession, social trend, place, public figure, historical event, animal, etc. Assemble actual items (or pictures of items) that are commonly associated with the target answer. Place them all in a bag (five-10 clues should be sufficient.) Then have a student reach into the bag and one by one pull out clues. Choose a minimum number of clues they must draw out before making their first guess (two- three). After this, the student must venture a guess after each clue pulled until they guess correctly. See how quickly the student is able to solve the riddle.
4. Survivor scenarios
Create a pretend scenario for students that requires them to think creatively to make it through. An example might be getting stranded on an island, knowing that help will not arrive for three days. The group has a limited amount of food and water and must create shelter from items around the island. Encourage working together as a group and hearing out every child that has an idea about how to make it through the three days as safely and comfortably as possible.
5. Moral dilemma
Create a number of possible moral dilemmas your students might encounter in life, write them down, and place each item folded up in a bowl or bag. Some of the items might include things like, “I saw a good friend of mine shoplifting. What should I do?” or “The cashier gave me an extra $1.50 in change after I bought candy at the store. What should I do?” Have each student draw an item from the bag one by one, read it aloud, then tell the class their answer on the spot as to how they would handle the situation.
Classroom problem solving activities need not be dull and routine. Ideally, the problem solving activities you give your students will engage their senses and be genuinely fun to do. The activities and lessons learned will leave an impression on each child, increasing the likelihood that they will take the lesson forward into their everyday lives.
You may also like to read
- Classroom Activities for Introverted Students
- Activities for Teaching Tolerance in the Classroom
- 5 Problem-Solving Activities for Elementary Classrooms
- 10 Ways to Motivate Students Outside the Classroom
- Motivating Introverted Students to Excel in the Classroom
- How to Engage Gifted and Talented Students in the Classroom
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Assessment Tools , Engaging Activities
- Online & Campus Doctorate (EdD) in Higher Edu...
- Degrees and Certificates for Teachers & Educa...
- Programming Teacher: Job Description and Sala...

How to Teach Problem Solving Skills Like a Pro

Problem solving can be one of the most difficult things to teach children. It isn’t super cut and dry, and often times it can be simple to explain, but challenging for students to put into practice.
Here are the different ways I love to teach problem solving strategies to my students, and will make you a problem solving pro.

Problem Solving Strategies List
- Have a script
- Consistency, consistency, consistency
- Kelso’s Choices
- Realistic & Specific scenarios
Before we jump in- I am going to let you in on a little secret. When I am teaching my students problem-solving skills, I am typically referencing one of two things 1) my problem-solving posters and scenarios or 2) materials from Kelso’s choices. Kelso’s choices is a FANTASTIC, concrete way to give students action steps to take when they are trying to problem-solve.
I highly recommend incorporating Kelso’s choices from the beginning of the school year, and consistently teaching your students how to use it.
1. Have a Script
When you are teaching younger students how to problem solve, it may seem like they should know what to say and when to say it. You ask them, and they can tell you what should happen… and somehow, when that moment comes where there is disagreement…you still are hearing that yelling and screaming that you were hoping to avoid.
Here’s the thing- students need more help with these skills than we think, and that is why I believe it is crucial to have posted scripts for students to use to talk through their problems.

2. Consistency, consistency, consistency
Yup, you guessed it. You can’t just teach problem solving skills once or twice, and expect students to have it perfect. Just like with a new math or reading skill, problem solving takes time. LOTS of time- and lots of practice. Any time you can, have students practice their problem solving skills. Teach whole group and small group lessons on problem solving regularly. Choose one strategy, and teach it as often and consistently as you can.
Also- make sure to catch students working through problems IN THE MOMENT. Talking about it after is helpful, but not as helpful as if you can pull students aside as they are working through a problem, and guide them through it.
Some of the things I tell students before we do a ‘Talk it Out’ is:
-When student A is talking, you will wait to speak. I want you to focus on LISTENING to what they are saying. When Student B is talking, you will stay quiet, and focus on LISTENING.
-Then, I will have student A explain how THEY are feeling (and not what they think the other student did wrong). Then Student B shares their feelings.
-Afterwards, I help the students lead their own discussion on coming up with a solution to the problem.

3. Roleplay
How do actors memorize their lines? They act out their script until they have it memorized. Give your students opportunities to practice solving made up, but realistic, scenarios.
4. Kelso’s Choices
I love Kelso’s Choices . You can access the Kelso’s Choices poster (and other free resources) by clicking here , or, if you are feeling fancy, there is an entire curriculum that can give you some easy, low prep lessons to work on with students.

(If you are someone who prefers to have things ready to go, this is for you. For example, look at this Conflict Management kit! Tell your principal and counselor how awesome it is, and see if they can squeeze it into the budget.)
I introduce Kelso’s Choices at the beginning of the school year. I have the poster hung in the classroom, we look at the wheel, and I play this Kelso’s Choices Rap for students. (It is super silly and engaging.)
Over the first few weeks (or sets of lessons if you don’t see students every day), we really dig into what each choice looks like and means. I also love the motions that this counselor adds to her lessons.
Then, we use scenarios to practice which choice we might choose, and why.
Lastly, we act out those scenarios, so we get lots of practice.
Students know that they need to choose two Kelso’s Choices to try before they come get a teacher to help.

5. Realistic & Specific Scenarios
Last but not least, make your practice scenarios realistic . If you ask a student what they might do if someone has something they want, or they want to join into a game- that is important. But really dig into the specifics of these issues when you practice. Think of every day scenarios, and don’t just practice the original scenario, but what happens NEXT.
What if you ask someone if you can join their game, and they tell you no ? What if you left your homework at home and you already tried to call your grown-up, and they didn’t answer the phone ? If your friend says something mean to you multiple times and you already told them you didn’t like it ? I have a bunch of specific problem-solving scenarios in this product!
Be sure that when you have students practice, your scenarios are realistic and specific.
Overall, when you are teaching problem solving skills to your students, really focus on the specifics, your consistency, and regular practice!

11 of My Favorite Videos to Teach Gratitude

- Our Mission
Problem-Solving in Elementary School
Elementary students practice problem-solving and self-questioning techniques to improve reading and social and emotional learning skills.

In a school district in New Jersey, beginning in kindergarten each child is seen as a future problem solver with creative ideas that can help the world. Vince Caputo, superintendent of the Metuchen School District, explained that what drew him to the position was “a shared value for whole child education.”
Caputo’s first hire as superintendent was Rick Cohen, who works as both the district’s K–12 director of curriculum and principal of Moss Elementary School . Cohen is committed to integrating social and emotional learning (SEL) into academic curriculum and instruction by linking cognitive processes and guided self-talk.
Cohen’s first focus was kindergarten students. “I recommended Moss teachers teach just one problem-solving process to our 6-year-olds across all academic content areas and challenge students to use the same process for social problem-solving,” he explained.
Reading and Social Problem-Solving
Moss Elementary classrooms use a specific process to develop problem-solving skills focused on tending to social and interpersonal relationships. The process also concentrates on building reading skills—specifically, decoding and comprehension.
Stop, Look, and Think. Students define the problem. As they read, they look at the pictures and text for clues, searching for information and asking, “What is important and what is not?” Social problem-solving aspect: Students look for signs of feelings in others’ faces, postures, and tone of voice.
Gather Information . Next, students explore what feelings they’re having and what feelings others may be having. As they read, they look at the beginning sound of a word and ask, “What else sounds like this?” Social problem-solving aspect: Students reflect on questions such as, “What word or words describe the feeling you see or hear in others? What word describes your feeling? How do you know, and how sure are you?”
Brainstorming . Then students seek different solutions. As they read, they wonder, “Does it sound right? Does it make sense? How else could it sound to make more sense? What other sounds do those letters make?” Social problem-solving aspect: Students reflect on questions such as, “How can you solve the problem or make the situation better? What else can you think of? What else can you try? What other ideas do you have?”
Pick the Best One. Next, students evaluate the solution. While reading, they scan for smaller words they know within larger, more difficult words. They read the difficult words the way they think they sound while asking, “Will it make sense to other people?” Social problem-solving aspect: Students reflect on prompts such as, “Pick the solution that you think will be best to solve the problem. Ask yourself, ‘What will happen if I do this—for me, and for others involved?’”
Go . In the next step, students make a plan and act. They do this by rereading the text. Social problem-solving aspect: Students are asked to try out what they will say and how they will say it. They’re asked to pick a good time to do this, when they’re willing to try it.
Check . Finally, students reflect and revise. After they have read, they ponder what exactly was challenging about what they read and, based on this, decide what to do next. Social problem-solving aspect: Students reflect on questions such as, “How did it work out? Did you solve the problem? How did others feel about what happened? What did you learn? What would you do if the same thing happened again?”
You can watch the Moss Elementary Problem Solvers video and see aspects of this process in action.

The Process of Self-Questioning
Moss Elementary students and other students in the district are also taught structured self-questioning. Cohen notes, “We realized that many of our elementary students would struggle to generalize the same steps and thinking skills they previously used to figure out an unknown word in a text or resolve social conflicts to think through complex inquiries and research projects.” The solution? Teach students how to self-question, knowing they can also apply this effective strategy across contexts. The self-questioning process students use looks like this:
Stop and Think. “What’s the question?”
Gather Information. “How do I gather information? What are different sides of the issue?”
Brainstorm and Choose. “How do I select, organize, and choose the information? What are some ways to solve the problem? What’s the best choice?”
Plan and Try. “What does the plan look like? When and how can it happen? Who needs to be involved?”
Check & Revise. “How can I present the information? What did I do well? How can I improve?”
The Benefits
Since using the problem-solving and self-questioning processes, the students at Moss Elementary have had growth in their scores for the last two years on the fifth-grade English language arts PARCC tests . However, as Cohen shares, “More important than preparing our students for the tests on state standards, there is evidence that we are also preparing them for the tests of life.”
Don’t Just Tell Students to Solve Problems. Teach Them How.
The positive impact of an innovative uc san diego problem-solving educational curriculum continues to grow.
- Daniel Kane - [email protected]
Published Date
Share this:, article content.
Problem solving is a critical skill for technical education and technical careers of all types. But what are best practices for teaching problem solving to high school and college students?
The University of California San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering is on the forefront of efforts to improve how problem solving is taught. This UC San Diego approach puts hands-on problem-identification and problem-solving techniques front and center. Over 1,500 students across the San Diego region have already benefited over the last three years from this program. In the 2023-2024 academic year, approximately 1,000 upper-level high school students will be taking the problem solving course in four different school districts in the San Diego region. Based on the positive results with college students, as well as high school juniors and seniors in the San Diego region, the project is getting attention from educators across the state of California, and around the nation and the world.
{/exp:typographee}
In Summer 2023, th e 27 community college students who took the unique problem-solving course developed at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering thrived, according to Alex Phan PhD, the Executive Director of Student Success at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. Phan oversees the project.
Over the course of three weeks, these students from Southwestern College and San Diego City College poured their enthusiasm into problem solving through hands-on team engineering challenges. The students brimmed with positive energy as they worked together.
What was noticeably absent from this laboratory classroom: frustration.
“In school, we often tell students to brainstorm, but they don’t often know where to start. This curriculum gives students direct strategies for brainstorming, for identifying problems, for solving problems,” sai d Jennifer Ogo, a teacher from Kearny High School who taught the problem-solving course in summer 2023 at UC San Diego. Ogo was part of group of educators who took the course themselves last summer.
The curriculum has been created, refined and administered over the last three years through a collaboration between the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering and the UC San Diego Division of Extended Studies. The project kicked off in 2020 with a generous gift from a local philanthropist.
Not getting stuck
One of the overarching goals of this project is to teach both problem-identification and problem-solving skills that help students avoid getting stuck during the learning process. Stuck feelings lead to frustration – and when it’s a Science, Technology, Engineering and Math (STEM) project, that frustration can lead students to feel they don’t belong in a STEM major or a STEM career. Instead, the UC San Diego curriculum is designed to give students the tools that lead to reactions like “this class is hard, but I know I can do this!” – as Ogo, a celebrated high school biomedical sciences and technology teacher, put it.
Three years into the curriculum development effort, the light-hearted energy of the students combined with their intense focus points to success. On the last day of the class, Mourad Mjahed PhD, Director of the MESA Program at Southwestern College’s School of Mathematics, Science and Engineering came to UC San Diego to see the final project presentations made by his 22 MESA students.
“Industry is looking for students who have learned from their failures and who have worked outside of their comfort zones,” said Mjahed. The UC San Diego problem-solving curriculum, Mjahed noted, is an opportunity for students to build the skills and the confidence to learn from their failures and to work outside their comfort zone. “And from there, they see pathways to real careers,” he said.
What does it mean to explicitly teach problem solving?
This approach to teaching problem solving includes a significant focus on learning to identify the problem that actually needs to be solved, in order to avoid solving the wrong problem. The curriculum is organized so that each day is a complete experience. It begins with the teacher introducing the problem-identification or problem-solving strategy of the day. The teacher then presents case studies of that particular strategy in action. Next, the students get introduced to the day’s challenge project. Working in teams, the students compete to win the challenge while integrating the day’s technique. Finally, the class reconvenes to reflect. They discuss what worked and didn't work with their designs as well as how they could have used the day’s problem-identification or problem-solving technique more effectively.
The challenges are designed to be engaging – and over three years, they have been refined to be even more engaging. But the student engagement is about much more than being entertained. Many of the students recognize early on that the problem-identification and problem-solving skills they are learning can be applied not just in the classroom, but in other classes and in life in general.
Gabriel from Southwestern College is one of the students who saw benefits outside the classroom almost immediately. In addition to taking the UC San Diego problem-solving course, Gabriel was concurrently enrolled in an online computer science programming class. He said he immediately started applying the UC San Diego problem-identification and troubleshooting strategies to his coding assignments.
Gabriel noted that he was given a coding-specific troubleshooting strategy in the computer science course, but the more general problem-identification strategies from the UC San Diego class had been extremely helpful. It’s critical to “find the right problem so you can get the right solution. The strategies here,” he said, “they work everywhere.”
Phan echoed this sentiment. “We believe this curriculum can prepare students for the technical workforce. It can prepare students to be impactful for any career path.”
The goal is to be able to offer the course in community colleges for course credit that transfers to the UC, and to possibly offer a version of the course to incoming students at UC San Diego.
As the team continues to work towards integrating the curriculum in both standardized high school courses such as physics, and incorporating the content as a part of the general education curriculum at UC San Diego, the project is expected to impact thousands more students across San Diego annually.
Portrait of the Problem-Solving Curriculum
On a sunny Wednesday in July 2023, an experiential-learning classroom was full of San Diego community college students. They were about half-way through the three-week problem-solving course at UC San Diego, held in the campus’ EnVision Arts and Engineering Maker Studio. On this day, the students were challenged to build a contraption that would propel at least six ping pong balls along a kite string spanning the laboratory. The only propulsive force they could rely on was the air shooting out of a party balloon.
A team of three students from Southwestern College – Valeria, Melissa and Alondra – took an early lead in the classroom competition. They were the first to use a plastic bag instead of disposable cups to hold the ping pong balls. Using a bag, their design got more than half-way to the finish line – better than any other team at the time – but there was more work to do.
As the trio considered what design changes to make next, they returned to the problem-solving theme of the day: unintended consequences. Earlier in the day, all the students had been challenged to consider unintended consequences and ask questions like: When you design to reduce friction, what happens? Do new problems emerge? Did other things improve that you hadn’t anticipated?
Other groups soon followed Valeria, Melissa and Alondra’s lead and began iterating on their own plastic-bag solutions to the day’s challenge. New unintended consequences popped up everywhere. Switching from cups to a bag, for example, reduced friction but sometimes increased wind drag.
Over the course of several iterations, Valeria, Melissa and Alondra made their bag smaller, blew their balloon up bigger, and switched to a different kind of tape to get a better connection with the plastic straw that slid along the kite string, carrying the ping pong balls.
One of the groups on the other side of the room watched the emergence of the plastic-bag solution with great interest.
“We tried everything, then we saw a team using a bag,” said Alexander, a student from City College. His team adopted the plastic-bag strategy as well, and iterated on it like everyone else. They also chose to blow up their balloon with a hand pump after the balloon was already attached to the bag filled with ping pong balls – which was unique.
“I don’t want to be trying to put the balloon in place when it's about to explode,” Alexander explained.
Asked about whether the structured problem solving approaches were useful, Alexander’s teammate Brianna, who is a Southwestern College student, talked about how the problem-solving tools have helped her get over mental blocks. “Sometimes we make the most ridiculous things work,” she said. “It’s a pretty fun class for sure.”
Yoshadara, a City College student who is the third member of this team, described some of the problem solving techniques this way: “It’s about letting yourself be a little absurd.”
Alexander jumped back into the conversation. “The value is in the abstraction. As students, we learn to look at the problem solving that worked and then abstract out the problem solving strategy that can then be applied to other challenges. That’s what mathematicians do all the time,” he said, adding that he is already thinking about how he can apply the process of looking at unintended consequences to improve both how he plays chess and how he goes about solving math problems.
Looking ahead, the goal is to empower as many students as possible in the San Diego area and beyond to learn to problem solve more enjoyably. It’s a concrete way to give students tools that could encourage them to thrive in the growing number of technical careers that require sharp problem-solving skills, whether or not they require a four-year degree.
You May Also Like
Scientists discover a new signaling pathway and design a novel drug for liver fibrosis, foreign-born doctors help serve rural and low-income communities, higher resolution brain mapping tech wins big at research expo, materials scientist awarded schmidt science fellowship, stay in the know.
Keep up with all the latest from UC San Diego. Subscribe to the newsletter today.
You have been successfully subscribed to the UC San Diego Today Newsletter.
Campus & Community
Arts & culture, visual storytelling.
- Media Resources & Contacts
Signup to get the latest UC San Diego newsletters delivered to your inbox.
Award-winning publication highlighting the distinction, prestige and global impact of UC San Diego.
Popular Searches: Covid-19 Ukraine Campus & Community Arts & Culture Voices
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Data Descriptor
- Open access
- Published: 25 April 2024
Students’ performance, attitude, and classroom observation data to assess the effect of problem-based learning approach supplemented by YouTube videos in Ugandan classroom
- Nicholus Gumisirizah 1 ,
- Joseph Nzabahimana 1 &
- Charles M. Muwonge 2
Scientific Data volume 11 , Article number: 428 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Applied physics
In response to global demands, Uganda’s Vision 2040 seeks to transform the country into a modern and prosperous nation by implementing Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 4, focusing on equitable and quality education. The 21st-century workforce requires individuals who can effectively navigate complex workplace challenges. This dataset was gathered from Form-2 Ugandan secondary school students (aged 12 to 15) across 12 schools in the Sheema District. The dataset comprises three types of data: students’ performance in a physics topic (simple machines), their attitudes toward problem-solving and critical thinking when learning physics using Problem-Based Learning (PBL) supplemented by YouTube videos, and classroom observations documented with the reformed teaching observational protocol (RTOP). The intervention of teaching using PBL was executed in 2022, collecting data from 973 lower secondary school students. The intervention involved three approaches: one group (144 students) received PBL along with YouTube videos, another group of 482 students received PBL alone, and a third group (347 students) was taught using the traditional method. This data article explains the study’s data creation, collection, and analysis process. The dataset holds significance for secondary school teachers, policymakers, and researchers, offering insights into the impact of PBL with and without ICT resources on learning physics and students’ attitudes toward these learner-centered approaches.
Background & Summary
Physics education in secondary schools plays a vital role in developing students’ social, physical, leadership, and problem-solving skills. Understanding physics concepts equips learners to know how things work, enabling them to apply this understanding to real-life situations 1 . The physics teaching is structured around activity-based 2 chapters and topics, emphasizing hands-on experiences 3 and practical applicability in everyday life. However, many students find physics challenging, necessitating an active teaching approach. Teaching in physics remains dynamic and interactive, with teachers adopting various strategies to engage students actively. Reciprocal teaching involves dialogues between the teacher and small student groups, while peer collaboration fosters cooperative work on class activities. Problem-Based Learning (PBL) 4 , 5 , 6 is a student-centered approach that encourages group-based learning and teacher facilitation. It has been widely adopted in various educational fields, promoting problem-solving in learning environments. Implementing PBL follows a five-stage process:
Finding a problem
The teacher prepares a task for students to investigate, stimulating problem-solving abilities.
Organizing ideas on the problem
Learners investigate the problem, generate ideas, and receive probing questions from the facilitator to stimulate critical thinking.
The teacher facilitates the distribution of learners into groups, each focusing on solving a particular problem related to the main task. Responsibilities are assigned within each group, promoting cooperation.
Present findings
Learners present solutions to the problem and receive feedback from peers, consolidating their learning outcomes.
Generalizing
Problem-solving leads to the development of skills essential for solving complex, real-world situations. These skills, including problem-solving, creativity, communication, cooperation, and innovation, prepare students to adapt to change and overcome 21st-century challenges.
Integrating YouTube videos as Information and Communication Technology (ICT) tools within a PBL approach offers a multifaceted strategy to enhance physics education 7 , 8 . High-quality videos aligned with curriculum objectives introduce real-world problems and cater to diverse learning styles. Interactive features and accessibility allow continuous learning, and educators can curate playlists to align with curriculum goals. The flipped classroom model 9 combines videos with problem-solving discussions 10 , creating a dynamic learning environment that deepens students’ understanding of physics concepts and their practical applications.
Physics is a subject that holds a significant position in promoting scientific literacy, critical thinking, and essential life skills. However, conventional teaching methods often struggle to engage and empower students in the subject matter effectively. This inadequacy is a pressing concern, as it can hinder students from developing a strong foundation in physics, which is essential for their academic and practical pursuits. This study was critically important due to the existing challenges within physics education in Ugandan secondary schools. Incorporating innovative teaching approaches, such as PBL supplemented by YouTube videos, becomes pivotal in addressing these challenges. These methods can enhance students’ comprehension of physics and nurture vital skills like problem-solving, creativity, communication, cooperation, and innovation. These skills are indispensable for students to thrive in a rapidly evolving, knowledge-driven world.
Sharing the data generated through this study is equally significant. It is a valuable resource for educators, policymakers, curriculum designers, and researchers. By making this data accessible, the study contributes to the ongoing efforts to improve the quality and relevance of secondary education in Uganda. Educators can utilize this data to adopt innovative and effective teaching methods that align with the goals of the educational system, ultimately enhancing students’ performance and fostering lifelong learning. Policymakers and curriculum designers can use the insights derived from this data to conduct essential reviews and make informed decisions about teacher competence and the adoption of innovative teaching methodologies. Furthermore, researchers in similar fields can leverage this data to understand better the impact of PBL and the use of multimedia resources in education. This data identifies gaps and challenges and offers potential solutions and avenues for further research.
This data-sharing article presents insights into the effects of Problem-Based Learning (PBL) supplemented by YouTube videos on students’ comprehension of simple machines in physics within Ugandan lower secondary schools. The research collected data from 973 students, encompassing both public and private schools in the Sheema district of Uganda. Three primary types of data were collected: students’ performance data, attitude data, and classroom observation data.
Performance data was acquired through a Physics Learning Achievement Test (PLAT), involving students from various school types and teaching methods. Attitude data were collected via two surveys, one focusing on problem-solving ability (AAPS) and the other on critical thinking ability (CTMS) under PBL with YouTube videos. The Approaches to Problem-Solving Survey (AAPS) and the Critical Thinking Motivational Scale (CTMS) are measurement tools commonly used in the field of physics. The AAPS assesses various strategies individuals employ when solving problems, while the CTMS evaluates motivational factors influencing critical thinking abilities. The Reformed Teaching Observation Protocol (RTOP) assessed classroom practices and teaching methods.
The dataset, available in raw, filtered, and analyzed formats, offers valuable insights into the impact of innovative teaching methods on student performance, attitudes, and classroom practices. It addresses critical questions about the effectiveness of PBL approaches, with potential implications for science education in Uganda.
This dataset intends to assess the impact of PBL when supplemented with YouTube videos on Ugandan form-2 lower secondary schools in learning simple machines. The following are the research questions:
To what extent do PBL and PBL supplemented with YouTube videos enhance students’ conceptual understanding of simple machines in physics?
What are the problem-solving and critical thinking levels brought by learning with PBL supplemented by YouTube videos?
How is physics teaching reformed when learning simple machines in physics with PBL supplemented by YouTube videos?
Are there differences in students’ academic achievement for school type (government alongside private school)?
Ethics statements
The research project rigorously adhered to ethical standards established by the University of Rwanda College of Education’s (UR-CE) Research and Innovation Unit under the ethical protocol number Ref. 03/DRI-CE/078/EN/gi/2021, dated 30th November 2021. All necessary permissions were obtained systematically and ethically, as outlined in the research project description. Here is a summary of the ethical considerations and recruitment process:
Ethical protocol
The research project adhered to the ethical standards and principles of the UR-CE)‘s Research and Innovation Unit. The protocol number and approval date are explicitly mentioned, demonstrating a formal ethical review.
Permissions from authorities
The Ministry of Education and Sports obtained formal permission to access schools through the Permanent Secretary’s (PS) office. The PS communicated with the Chief Administrative Officer (CAO), District Education Officer (DEO), and Resident District Commissioner (RDC) to secure the necessary support for the study.
Engagement with schools
With the approval from the CAO, the DEO contacted school heads to inform them about the research study. The school heads responded positively and even provided physics teachers with three-day problem-based learning (PBL) training as part of the research. It is worth noting that all participating teachers held teaching qualifications, and as part of the research process, we provided them with a three-day training session specifically focused on implementing PBL interventions. This training aimed to ensure consistent delivery of PBL across treatment classrooms and schools, thereby mitigating variations attributable to individual teaching styles.
Informed consent
Teachers and students, with parental consent, willingly participated in the research study. Informed consent forms were signed, indicating they fully understood the study’s purpose, procedures, potential risks, and benefits. Anonymity was ensured for students by not including their names on the test papers.
The research employed purposive sampling to select 973 students from 12 schools. These schools were divided into three groups, each with a different teaching method: PBL with YouTube videos, PBL alone, and Traditional teaching.
Geographic considerations
Schools were selected from different town councils at extreme ends of the district, sharing similar characteristics suitable for the study. This approach helps ensure that the study’s findings are robust and generalizable.
Research design
The study utilized a non-equivalent comparison group pre/post-test design (Creswell, 2012). The study involves Form 2 students from six Sheema District, Western Uganda schools. Three selected schools were public, while the remaining three were private, offering a diverse representation of school types in the district. The selection of schools was purposeful, aiming to ensure diverse representation and maximize the study’s validity. This approach allowed for the strategic allocation of schools to treatment or control groups based on specific criteria pertinent to the research objectives. Notably, the selection criteria considered factors such as geographical location, school size, academic performance, and availability of resources to ensure a balanced representation of different educational contexts. The traditional method, characterized by conventional lectures supplemented with textbooks and teacher-centered content delivery, was employed in control group schools. Students in this group primarily learned through note-taking with minimal demonstrations. Conversely, four other secondary schools were designated as the first treatment group, where Problem-Based Learning (PBL) was implemented. Four additional schools comprised the second treatment group, which utilized PBL supplemented by educational YouTube videos. These groups collectively engaged in constructing knowledge and enhancing conceptual understanding. The participants in the study were form-2 students, ranging in age from 12 to 15 years, who were already enrolled in the schools.
We provide a performance (achievement) test to all 973 students before and after teaching interventions in all groups. We administered an attitude survey (motivation scale) and observed classes in the group that used PBL and YouTube videos. Table 1 presents the sample size under the teaching intervention of design groups implemented.
The objective of the performance test was to gauge students’ grasp of conceptual understanding acquired through the implementation of a problem-based learning approach following the completion of the topic on simple machines. The test, spanning 25 minutes, consisted of ten questions sourced from practice exercises on simple machines within form-two secondary learners’ physics textbooks. The National Curriculum Development Center and the Ministry of Education and Sports in Uganda approved these textbooks. The examination encompassed themes outlined in the approved lower secondary curriculum physics syllabus, covering concepts like the applications of simple machines, mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency of machines. Specific topics included levers (covering classes and applications), pulley systems (encompassing types, applications, mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency), inclined planes (including applications, mechanical advantage, velocity ratio, and efficiency), wheel and axle (exploring understanding, applications, and velocity ratio), gears (addressing simplification of work, applications, and velocity ratio), and methods of enhancing machine efficiency. The test was validated by four researchers from Mbarara University of Science and Technology (MUST) and the University of Rwanda College of Education (URCE). Test 1 was scored in MS Excel with “IF EXCACT” function, while Test 2 was manually marked, and results were entered in the same software.
Attitude surveys were all adopted from existing literature. Critical Thinking Motivational Scale (CTMS) was used as our Survey 1 and was adapted from Valenzuela et al . 11 , while Attitudes and Approaches to Problem-Solving Survey (AAPS) was used as our Survey 2 and was adapted from Singh and Mason 12 and available at Physport ( https://www.physport.org/assessments/assessment.cfm?A=AAPS ). Problem-solving and critical thinking are integral to effective physics education. They deepen students’ understanding by connecting theoretical concepts to real-world situations 13 , 14 . These skills encourage active engagement and foster analytical abilities, allowing students to break down complex problems. Additionally, they promote creativity, help apply theory to practice, and cultivate logical reasoning. Problem-solving and critical thinking prepare students for future challenges in scientific and engineering fields, encourage collaboration, boost confidence, and instill a mindset for lifelong learning. Incorporating these skills into physics teaching enhances academic performance and equips students with valuable personal and professional growth tools. We adopted all 19 items from CTMS and only 31 items from AAPS to meet our research aim. Thus, the last two items (32 and 33) in AAPS were removed as they were not related to the content delivered in our study. All these surveys were rated on a Likert scale (from strongly disagree to strongly agree). Items 1–4 are related to expectancy, items 5-8 to attainment, items 9-12 to utility, items 13-16 to interest, and items 17-19 to cost.
Classroom observation data was collected with the famous standardized reformed teaching observation protocol (RTOP) from Pibun and Sawada 15 and is available at Pysport ( https://www.physport.org/assessments/assessment.cfm?A=RTOP ). RTOP proved its validity and reliable results across the globe 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 with its potential to reveal reformed teaching while implementing a new teaching method. It comprises 25 statements where each item is evaluated on a 5-scale. It is scored 0 when such practice was not found in a lesson and 4 when a certain practice was very well described or observed in a delivered lesson. During classroom observation, an observer sits in the classroom and observes what the teacher and student do. He/she may take notes on what is happening but wait until the class is over to rate these 25 items.
Data Records
All data described in this descriptor are deposited in figshare ( https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/RTOP_Data_for_the_implementation_of_Problem-based_learning_in_a_Physics_classroom_Uganda/23974902 ) 20
To evaluate the impact of PBL teaching intervention on students’ performance and attitude toward learning physics, we gathered three data types (performance, attitude, and observation) presented in five datasets (two performance tests, two attitude surveys, and one classroom observation).
Students’ performance data
The student performance data comprises two datasets or MS Excel files. The first file contains data for test one titled “Performance data _ Test 1 (Multiple choice) _ 12102022 figshare.” This file contains data from ten multiple-choice questions. The file contains three sheets. The first sheet shows test items (all ten questions), the second presents pretest answer choices, and the third presents post-test answer choices or results. Each results sheet shows the school code (column B), student code (column C), school type (column D), and treatment group (column E) as variables. From column “F” to column “O” we see student answer choices under each test question. From column “Q” to column “Z” we marked the test (one score for each correct question). Column “AB” shows the percent score. Row “3” shows the expected correct answer, while row “4” shows variables and the number of test items.
The second file contains data for test two titled “Performance data _ Test 2 (Problem solving) _ 12102022 figshare.” This file contains data from ten-word problem kinds of questions. The file contains three sheets. The first sheet shows test items (all ten questions), the second presents pretest scores, and the third presents post-test scores or results. Each results sheet shows the school code (column C), student code (column D), school type (column E), and treatment group (column F) as variables. From column “G” to column “P” we see student scores under each test question. Column “R” shows the total score, while column “S” shows percent score. Row “3” shows the assigned score when each question’s expected correct answer was provided. Row “4” shows variables and several test items.
Students’ attitude data
The student attitude data comprises two datasets or MS Excel files. The first file contains data for the first survey titled “Motivation data _ Survey 1 (Critical thinking ability) _ 12102022 figshare.” This file contains data from 19 items of critical thinking ability survey. The file contains two sheets. The first sheet shows the pre-test results, while the second shows the post-test results. Each sheet shows the school code (column C), student code (column D), school type (column E), and treatment group (column F) as variables. From column “F” to column “O” we see student answer choices under each test question. From column “G” to column “Y” we see student answers or agreement (1: STRONGLY DISAGREE, 2: DISAGREE, 3,: NEUTRAL, 4: AGREE, AND 5: STRONGLY AGREE) to each item of the survey. Row “2” shows the survey title, while row “4” shows the variables and number of survey items.
The second file contains data for the second survey titled “Attitude data _ Survey 2 (Problem solving ability) _ 12102022 figshare.” This file contains data from 31 items related to problem-solving ability in learning physics. The file contains two sheets. The first sheet shows the pre-test results, while the second shows post-test results. Each sheet shows the school code (column C), student code (column D), school type (column E), and treatment group (column F) as variables. From column “G” to column “AK” we see student answers or agreement (1: STRONGLY DISAGREE, 2: DISAGREE, 3,: NEUTRAL, 4: AGREE, AND 5: STRONGLY AGREE) to each item of the survey. Row “2” shows the survey title, while row “4” shows the variables and number of survey items.
Classroom observation data
The file for classroom observation data is titled “Classroom observation data _ RTOP for video & pbl group _ 12102022 figshare” and contains only one sheet. From column “B” to column “C” we see RTOP while the following columns (D-AA) present data. Row “10” shows school codes, while row “5” shows several observations and frequencies under each school supplied with PBL and YouTube videos teaching intervention. The data range from 0 (never occurred) to 4 (very descriptive).
Technical Validation
Initially, we had 20 problem-solving questions, but evaluators rated 10 as valid, which were included in the final administration. We also initially had 15 multiple-choice questions, and evaluators rated 10 as appropriate and aligned with the study objectives. A pilot study was conducted with 90 students to evaluate the face validity and reliability of the questions. We assessed the reliability of these items using a split-half method and obtained a high reliability (r = 0.87) for multiple-choice items and a medium reliability (r = 0.68) measured by the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient for problem-solving items. The split-half reliability assumes that the two halves of the test are equivalent in difficulty and content 21 .
CTMS and AAPS
During our pilot phase, the internal consistency of CTMS, assessed using Cronbach’s alpha, was found to be high (0.793) for all 19 items, medium (0.428) for expectancy, (0.411) for attainment, (0.686) for utility, (0.574) for interest, and (0.594) for cost. The AAPS exhibited an internal consistency reliability of Cronbach’s alpha = 0.685. It is important to note that the AAPS contains nine items formulated negatively. Therefore, for a positive attitude, students were required to respond with ‘Disagree’ or ‘Strongly disagree’ to these items (1, 3, 5, 8, 11, 12, 16, 23, and 30). Consequently, the reliability of the 22 positively formulated items was 0.601, while that of the negatively formulated items was 0.480.
Before observing actual classes, we underwent a 2-hour training session and watched and coded a YouTube classroom video on physics. The inter-rater agreement between the first author and the assistant exceeded 80% on two occasions, indicating the reliability of the data.
Scope and potential limitations
In our study, we recognized the significance of investigating potential bias in the results obtained from students in both private and public schools. To ensure the credibility and robustness of our findings, we conducted a comparative analysis to determine whether any notable disparities existed between these two groups. Our data collection process was comprehensive, encompassing a diverse range of schools, including both private and public institutions. This approach allowed us to capture a broad spectrum of socioeconomic backgrounds and educational settings. The study itself involved Form-2 students who were enrolled in schools situated in different town councils at opposite ends of the district. Despite their geographical diversity, these schools shared pertinent characteristics relevant to our research objectives. To facilitate our investigation, we categorized these schools into distinct treatment groups, comprising PBL alone and PBL with videos, along with a control group following traditional teaching methods. Importantly, we deliberately chose to maintain the existing class arrangements in these schools. Our commitment to preserving each school’s established class organization and cultural norms guided this decision.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations inherent in the research design. One notable limitation is the observation of attitudes, which was limited to the student group exposed to the PBL with the video teaching method. This restriction may impact the generalizability of the findings, as attitudes toward learning may vary among students exposed to different instructional methods. Future research endeavors could consider incorporating measures to assess attitudes across all treatment groups to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the intervention’s effects.
The current data files do not contain information on individual teachers due to the scope and focus of the study. These variables could include educators’ teaching experience, pedagogical approach, content knowledge, and instructional effectiveness. Since we recognize the significance of teacher impact, we would consider incorporating such variables in future research projects to provide a more comprehensive analysis of instructional effectiveness and its associated factors.
Regarding the decision to maintain existing class arrangements in schools, particularly considering cultural norms, it is crucial to recognize its potential influence on the study outcomes. The intervention’s impact may have been influenced by preserving the existing class structures, including student composition and dynamics. For instance, certain class arrangements may foster greater collaboration and engagement, while others may present challenges in implementing collaborative learning approaches such as PBL. Therefore, future studies could explore the relationship between class arrangements and instructional effectiveness to provide insights into optimizing learning environments.
Usage Notes
Value of the data.
The data presented is valuable and beneficial to science education in Uganda as it elucidates the status of students’ content knowledge and their perceptions about learning simple machines with PBL approaches.
Policymakers and curriculum designers have the opportunity to conduct essential reviews that highlight the competence of teachers. This process can pave the way for advocating innovative and relevant teaching methodologies, subsequently informing the identification of professional development requirements for educators.
Researchers in similar fields can re-use these data to measure the effect of PBL intervention on student achievement, identify gaps, and predict possible remedies. Thus, data can be analyzed using various variables such as teaching intervention and school type.
Code availability
No custom code was used.
Putri, I. E. & Sinaga, P. Collaborative problem-solving: how to implement and measure it in science teaching and learning. in International conference on mathematics and science education (ICMSCE) 2020 vol 1806 (IOP PUBLISHING LTD, 2021).
Sokoloff, D. R. Active Learning of Introductory Optics: Interactive Lecture Demonstrations and Optics Magic Tricks. in ducation and Training in Optics and Photonics, OSA Technical Digest Series (Optical Society of America, 2007) . https://doi.org/10.1364/ETOP.2007.EWA2 (2007).
Dohn, N. B., Fago, A., Overgaard, J., Madsen, P. T. & Malte, H. Students’ motivation toward laboratory work in physiology teaching. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 40 , 313–318 (2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Nguyen, D.-H., Gire, E. & Rebello, N. S. Facilitating Strategies for Solving Work-Energy Problems in Graphical and Equational Representations. in 2010 PHYSICS EDUCATION RESEARCH CONFERENCE (reds Singh, C., Sabella, M. & Rebello, S.) vol 1289 241–244 (AMER INST PHYSICS, 2010).
Seltpuk, G. S. & Tarak, M. Physics Teaching in Problem-Based Learning Physics Teaching in Problem-Based Learning. 844 , 1–2 (2017).
Bilgin, I. & Erdal, Ş. The Effects of Problem-Based Learning Instruction on University Students’ Performance of Conceptual and Quantitative Problems in Gas Concepts. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 5 , 153–164 (2009).
Article Google Scholar
Susilawati, S., Rahmana, F. & Kosim, K. Practicality of problem-based physics learning tools with video assistance to improve problem-solving ability of students. J. Sci. Sci. Educ. 3 , 55–59 (2022).
Nasbey, H. & Raihanati, R. Developing a video education on the topic of Modern Physics based on problem-based learning (PBL) assisted PhET online learning. in Journal of Physics: Conference Series (reds F.C., W. et al .) vol 2377 (Institute of Physics, 2022).
Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, K. & Shen, D. A Topic-based Computer Aided Instruction System for Programming Practice Courses. in Proceedings of the 2015 international conference on social science, education management and sports education (red Chen, L.) vol 39 1342–1345 (ATLANTIS PRESS, 2015).
Becerra-Labra, C., Gras-Martí, A. & Martínez Torregrosa, J. Effects of a problem-based structure of physics contents on conceptual learning and the ability to solve problems. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 34 , 1235–1253 (2012).
Valenzuela, J., Nieto, A. M. & Saiz, C. Critical Thinking Motivational Scale (CTMS): una aportación para el estudio de la relación entre el pensamiento crítico y la motivación. Electron. J. Res. Educ. Psychol. 9 , 823–848 (2011).
Singh, C. & Mason, A. Physics graduate students’ attitudes and approaches to problem solving. AIP Conf. Proc. 1179 , 273–276 (2009).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Ukobizaba, F., Ndihokubwayo, K., Mukuka, A. & Uwamahoro, J. Insights of teachers and students on mathematics teaching and learning in selected Rwandan secondary schools. African J. Educ. Stud. Math. Sci. 15 , 93–106 (2019).
Dorimana, A., Uworwabayeho, A. & Nizeyimana, G. Enhancing Upper Secondary Learners’ Problem - solving Abilities using Problem-based Learning in Mathematics. Int. J. Learn. Teach. Educ. Res. 21 , 235–252 (2022).
Piburn, M. et al . Reformed teaching observation protocol (RTOP) Training Guide . doi:ED419696 (Tempe, Arizona: Arizona Collaborative for Excellence in the Preparation of Teachers, 2000).
Ndihokubwayo, K., Uwamahoro, J. & Ndayambaje, I. Implementation of the Competence-Based Learning in Rwandan Physics Classrooms: First Assessment Based on the Reformed Teaching Observation Protocol. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 16 , 1–8 (2020).
Ndihokubwayo, K., Uwamahoro, J. & Ndayambaje, I. Classroom observation data collected to document the implementation of physics competence-based curriculum in Rwanda. Data Br. 36 , 107055 (2021).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Park, S., Jang, J. Y., Chen, Y. C. & Jung, J. Is Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK) Necessary for Reformed Science Teaching?: Evidence from an Empirical Study. Res. Sci. Educ. 41 , 245–260 (2010).
MacIsaac, D., Sawada, D. & Falconer, K. Using the Reformed Teaching Observation Protocol (RTOP) as a Catalyst for Self- Reflective Change in Secondary Science Teaching. (2001).
Gumisirizah, N., Nzabahimana, J. & Muwonge, C. M. Students’ academic achievement test, Survey and RTOP data for the implementation of problem-based learning method supplemented by YouTube videos, Uganda. Figshare https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.23974902.v2 (2023).
Adalikwu, S. & Iorkpilgh, I. The Influence of Instructional Materials on Academic Performance of Senior Secondary School Students in Chemistry in Cross River State. Glob. J. Educ. Res. 12 , 39–45 (2013).
Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the African Center for Excellence for Innovative Teaching and Learning Mathematics and Science (ACEITLMS) for funding this study and the authors of the research tools we used to free them to use. All study participants, teachers, and school headteachers are also well acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
African Center of Excellence for Innovative Teaching and Learning Mathematics and Science (ACEITLMS), University of Rwanda College of Education (URCE), Kayonza, P.O Box 55, Rwamagana, Rwanda
Nicholus Gumisirizah & Joseph Nzabahimana
Mbarara Science and Technology (MUST), Mbarara, Uganda
Charles M. Muwonge
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Nicholus Gumisirizah: Conceptualization, Methodology, Visualization, Data curation, Software, Writing- Original draft preparation. Joseph Nzabahimana, Charles M. Muwonge: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing- Reviewing and Editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nicholus Gumisirizah .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gumisirizah, N., Nzabahimana, J. & Muwonge, C.M. Students’ performance, attitude, and classroom observation data to assess the effect of problem-based learning approach supplemented by YouTube videos in Ugandan classroom. Sci Data 11 , 428 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03206-2
Download citation
Received : 04 November 2023
Accepted : 02 April 2024
Published : 25 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03206-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
How to Train Your Problem-Solving Skills
From the hiccups that disrupt your morning routines to the hurdles that define your professional paths, there is always a problem to be solved.
The good news is that every obstacle is an opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and become the best version of yourself. That’s right: It turns out you can get better at problem-solving, which will help you increase success in daily life and long-term goals.
Read on to learn how to improve your problem-solving abilities through scientific research and practical strategies.
Understanding Problem-Solving Skills
You may be surprised to learn that your problem-solving skills go beyond just trying to find a solution. Problem-solving skills involve cognitive abilities such as analytical thinking, creativity, decision-making, logical reasoning, and memory.
Strong problem-solving skills boost critical thinking, spark creativity, and hone decision-making abilities. For you or anyone looking to improve their mental fitness , these skills are necessary for career advancement, personal growth, and positive interpersonal relationships.
Core Components of Problem-Solving Skills Training
To effectively train your problem-solving skills, it’s important to practice all of the steps required to solve the problem. Think of it this way: Before attempting to solve a problem, your brain has already been hard at work evaluating the situation and picking the best action plan. After you’ve worked hard preparing, you’ll need to implement your plan and assess the outcome by following these steps:
- Identify and define problems: Recognizing and clearly articulating issues is the foundational step in solving them.
- Generate solutions: Employing brainstorming techniques helps you develop multiple potential solutions.
- Evaluate and select solutions: Using specific criteria to assess solutions helps you choose the most effective one.
- Implement solutions: Developing and executing action plans, including preparing for potential obstacles, guides you to positive outcomes.
- Review and learn from outcomes: Assessing the success of solutions and learning from the results for future improvement facilitates future success.
Strategies for Developing Problem-Solving Skills
There are many practical exercises and activities that can improve problem-solving abilities.
Cultivate a Problem-Solving Mindset
- Adopt a growth mindset: A growth mindset involves transforming phrases like “I can’t” into “I can’t yet.” Believing in the capacity to improve your skills through effort and perseverance can lead to greater success in problem-solving.
- Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness can enhance cognitive flexibility , allowing you to view problems from multiple perspectives and find creative solutions.
Enhance Core Cognitive Skills
- Strengthen your memory: Engage in activities that challenge your memory since accurately recalling information is crucial in problem-solving. Techniques such as mnemonic devices or memory palaces can be particularly effective.
- Build your critical thinking: Regularly question assumptions, evaluate arguments, and engage in activities that require reasoning, such as strategy games or debates.
Apply Structured Problem-Solving Techniques
- Use the STOP method: This stands for Stop , Think , Observe , and Plan . It's a simple yet effective way to approach any problem methodically, ensuring you consider all aspects before taking action.
- Try reverse engineering: Start with the desired outcome and work backward to understand the steps needed to achieve that result. This approach can be particularly useful for complex problems with unclear starting points.
Incorporate Technology into Your Training
- Engage with online courses and workshops: Many platforms offer courses specifically designed to enhance problem-solving skills, ranging from critical thinking to creative problem-solving techniques.
- Use cognitive training apps: Apps like Elevate provide targeted, research-backed games and workouts to improve cognitive skills including attention, processing speed, and more.
Practice with Real-World Applications and Learn from Experience
- Tackle daily challenges: Use everyday issues as opportunities to practice problem-solving. Whether figuring out a new recipe or managing a tight budget, applying your skills in real-world situations can reinforce learning.
- Keep a problem-solving journal: Record the challenges you face, the strategies you employ, and the outcomes you achieve. Reflecting on your problem-solving process over time can provide insights into your strengths and areas for improvement.
Embracing Problem-Solving as a Lifelong Journey
Since problems arise daily, it’s important to feel confident in solving them.
And you can do just that by downloading the Elevate brain training app. Elevate offers 40+ games and activities designed to improve problem-solving, communication, and other cognitive skills in a personalized way that’s backed by science. Pretty cool, right?
Consider downloading the Elevate app on Android or iOS now—it’ll be the easiest problem you solve all day.
Related Articles
How Problem-Solving Games Can Boost Your Brain
- Discover why problem-solving games are fun and effective ways to train your brain.
Improving Your Problem-Solving Skills
- Discover how to improve your problem-solving skills and make logical, informed decisions.
Best Ways to Boost Your Mental Fitness
- Mental fitness refers to your ability to sustain your overall well-being. Learn tips to improve yours.

Morning Carpool
“Stop Coddling Your Grown Child”: 21 Essential Life Skills That You Should Be Teaching Your Child Before They Leave for College
Posted: February 22, 2024 | Last updated: February 22, 2024

As your child prepares to leave the nest for college, there are certain life skills they need to master to thrive on their own. From learning how to do laundry to budgeting and cooking, these essential skills seem obvious, but many young adults are sent off to college without them.

Doing Laundry
Learning how to do laundry is a crucial skill for any college student. Start by teaching them how to separate colors and fabrics and the right temperature to use for each. Explain the importance of cleaning the lint trap in dryers and how to use laundry detergent properly.

Basic Cooking
Knowing basic cooking skills can save your child from a diet of instant noodles. Teach them how to cook simple, healthy meals like pasta, stir-fries, and salads. Emphasize kitchen safety, including handling knives and managing the stove.

Budgeting is key to managing college expenses. Show them how to track their income and expenses and the importance of saving. Discuss the dangers of credit card debt and impulsive purchases.

Time Management
Time management skills are vital for balancing study, work, and social life. Teach them how to prioritize tasks and use a planner or digital calendar. Stress the importance of setting aside time for studying and relaxation. Good time management can be the difference between success and burnout.

Cleaning and Housekeeping
A clean living space is essential for health and well-being. Teach them basic cleaning skills like dusting, vacuuming, and disinfecting surfaces. Show them how to maintain a clean bathroom and kitchen. Cleanliness plays a big role in making a good impression on roommates and friends.

Grocery Shopping
Teach them how to make a grocery list based on planned meals, compare prices, and select fresh produce. Explain the benefits of buying in bulk and choosing store brands to save money. Show them how to read nutrition labels to make healthier choices. “Grocery shopping on my own was a reality check on adulting,” shared an online commenter.

Public Transportation
Understanding how to navigate public transportation is essential in many college towns. Teach them how to read transit maps, use apps for schedules, and understand fare systems. Discuss the importance of being aware of their surroundings and personal safety while commuting.

Basic First Aid
Basic first aid knowledge can be a lifesaver in minor emergencies. Teach them how to treat cuts, burns, and sprains and when to seek professional medical help. Show them how to create and maintain a basic first aid kit. This skill is not just for them, but for helping others too.

Personal Hygiene
Good personal hygiene is crucial for health and social interactions. Discuss the importance of regular bathing, oral hygiene, and clean clothes. Teach them about skincare and the need for regular haircuts. As a commenter says, “Good hygiene goes a long way in making a good first impression.”

Communication Skills
Effective communication is key in both personal and professional life. Teach teens how to communicate respectfully and assertively, both in person and online. Discuss the importance of active listening and empathy in building relationships.

Basic Sewing
Knowing how to sew a button or fix a minor tear can save time and money. Teach them basic sewing skills and how to use a sewing kit. This is not just practical but also a great way to be self-reliant. Plus, it’s a useful skill for costume parties!

Dealing with Emergencies
Teach them how to respond to various emergencies, like power outages, fire alarms, and severe weather. Discuss the importance of knowing emergency contacts and evacuation routes. “Being prepared for emergencies gave me peace of mind when I lived on my own,” says an online commenter.

Understanding Insurance
Understanding basic insurance concepts like health, auto, and renter’s insurance is important. Teach them how to read and understand an insurance policy and the importance of keeping documents safe. This knowledge is crucial for protecting themselves and their belongings.

Networking and Socializing
Teach teens how to network and the importance of socializing in a healthy, balanced way. Discuss how to approach professors, join clubs, and attend campus events. Networking can lead to friendships, mentorships, and even job opportunities.

Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are essential in and out of the classroom. Encourage them to think independently, question assumptions, and approach problems logically. These skills will help them navigate complex situations and make informed decisions.

Digital Literacy
Teach teens about online safety, using search engines effectively, and managing digital files. Discuss the importance of a professional online presence. As one commenter said, “Digital literacy is as important as reading and writing.”

Personal Safety
Personal safety is paramount. Teach teens about situational awareness, trusting their instincts, and basic self-defense. Discuss the importance of staying safe in social situations and understanding consent.

Stress Management
College can be stressful, so knowing how to manage stress is key. Teach them relaxation techniques, the importance of exercise, and healthy coping mechanisms. Discuss the value of seeking help when needed. Managing stress effectively can enhance their college experience.

Laundry Etiquette
In shared laundry facilities, etiquette is essential. Teach teens about respecting others’ laundry, not leaving clothes unattended, and cleaning up after themselves, which will keep the peace and foster a sense of community responsibility.

Cooking for Special Diets
Knowing how to cook for special diets is helpful if they or their friends have dietary restrictions. Teach them about vegetarian, vegan, gluten-free, and allergy-friendly cooking. This skill is not only considerate but also expands their culinary horizons.

Voting and Civic Engagement
Understanding the importance of voting and civic engagement is crucial. Discuss how to register to vote, the basics of local and national politics, and the importance of staying informed. “Voting for the first time made me feel like a true adult,” shared a commenter.
More for You
Megan Fox Signs With UTA
Here’s Why There Are 10 Hot Dogs in a Pack, But Only 8 Buns
Jason Kelce shares update about his ‘stolen’ Super Bowl ring

Netflix hit watched more than 21 million times in its first three days
I’m a Bank Teller: 3 Times You Should Never Ask For $100 Bills at the Bank
The most expensive state to live in isn't California or New York, based on data. Here are the top 10.
'10-foot-tall people' discovered by archaeologists in Nevada cave
‘We’re in trouble’: Pollster reacts to his discussion with young voters
Culver's Vs Five Guys: Which Burger Chain Is Better?
Why You Should Think Twice Before Pouring Boiling Water Over Ant Hills In Your Yard
19 Safety Features That Are The Opposite Of Safe
I Did a 21-Day Water Fast and Lost 31lbs
Scientists have discovered the maximum age a human can live to
Crumbl Is Finally Selling Smaller Cookies After Hearing Our Pleas
NYPD responds to AOC, says officers 'have to teach' anti-Israel mobs the 'consequences of their actions'
Blood pressure is best lowered by 2 exercises, study finds
30 food items that you might not know are banned in America
10 most ‘overpriced’ tourist attractions in the world – and three are in the US
At 43, I’ve finally learned how to love my size 16 curves
Carbine vs Rifle: What Exactly Is the Difference?
Shady Side Academy Middle School robotics team teaches skills to youngsters at Fox Chapel library

Shady Side Academy Middle School Blue robotics team members helped Fox Chapel Area youths learn more about robots through a new program at Cooper-Siegel Community Library.
The Lego League competitors taught the young builders and coders the benefits of teamwork and problem solving via three classes this year with the help of their coach, University of Pittsburgh professor Jun Yang.
The first one was in January and focused on construction. The second was in February with a focus on programming. The third and final class showcased the culmination of the junior engineers’ efforts April 20.
“It’s really exciting having all of them learning a lot,” said SSA sixth grader Vivian Zhang on the final day. “It’s been fun watching them learn from this. I think they are really bright, and I enjoy teaching them.”
The coach said Vivian and her fellow team members earned first place in robot design and robotics performance in this year’s Western Region of the PA state FIRST — For Inspiration and Recognition in Science and Technology — Lego League Robotics Championship.
Parents Cliff Yang and Ning Li hope that championship knowledge will rub off on their son, Alan Yang, 11.
“My son participated in a competition a year ago,” the father said. “I think this is a very good chance for (him) to evolve into science and engineering and have some experience. It’s very good.”
Li said they are very supportive of Alan’s activities, and he is passionate about robots.
Alan completed his robot fairly quickly and began working on attachments while other program participants were still on laptops and iPads programming their bots.
“It’s interesting to code, especially when you’re doing a mission,” Alan said. “After you master Lego (kits), you can actually use real robotics, which I’m planning on doing. These are small robots. The Shady Side (students) were pretty good teaching us new mechanisms.”
Vivian said the secret to robotic success is to have a very strong bot with not a lot of extra pieces.
“It has to do just what you want to do,” she said. “It can have stuff that makes it look pretty, but you want to make it very effective.”
Yang brought some of her own robot kits as well as some from the academy to the library. Pieces included various sizes of wheels, planks, motors and Bluetooth devices.
She said the program fits in with the Lego competition’s core values.
“It is the team’s effort to teach little kids and introduce this activity so that it can involve more kids,” Yang said. “We initiated it and can teach them from building to coding. This program is for fifth through eighth grade, but a fourth grader can join if they are advanced enough. All these kids (here) are from fifth grade. I think the kids love it and parents are interested.”
The coach said she plans to bring back the free program to the Fox Chapel library next year.
It was offered at Sharpsburg Community Library in previous years.
Michael DiVittorio is a TribLive reporter covering general news in Western Pennsylvania, with a penchant for festivals and food. He can be reached at [email protected] .
Remove the ads from your TribLIVE reading experience but still support the journalists who create the content with TribLIVE Ad-Free.
Get Ad-Free >
TribLIVE's Daily and Weekly email newsletters deliver the news you want and information you need, right to your inbox.
News Spotlight
Kennywood admission cost is similar to other amusement parks, but there are ways to save.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To teach students problem solving skills, a teacher should be aware of principles and strategies of good problem solving in his or her discipline. The mathematician George Polya captured the problem solving principles and strategies he used in his discipline in the book How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method (Princeton University ...
Teach within a specific context. Teach problem-solving skills in the context in which they will be used by students (e.g., mole fraction calculations in a chemistry course). Use real-life problems in explanations, examples, and exams. Do not teach problem solving as an independent, abstract skill. Help students understand the problem. In order ...
Problem solving is a necessary skill in all disciplines and one that the Sheridan Center is focusing on as part of the Brown Learning Collaborative, which provides students the opportunity to achieve new levels of excellence in six key skills traditionally honed in a liberal arts education - critical reading, writing, research, data ...
Teaching problem solving: Let students get 'stuck' and 'unstuck'. This is the second in a six-part blog series on teaching 21st century skills, including problem solving , metacognition ...
Problem-solving skills are also needed for students' personal growth and development because they help individuals overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. By developing strong problem-solving skills, students can improve their overall quality of life and become more successful in their personal and professional endeavors.
1. Link problem-solving to reading. When we can remind students that they already have many comprehension skills and strategies they can easily use in math problem-solving, it can ease the anxiety surrounding the math problem. For example, providing them with strategies to practice, such as visualizing, acting out the problem with math tools ...
Problem Solving in STEM. Solving problems is a key component of many science, math, and engineering classes. If a goal of a class is for students to emerge with the ability to solve new kinds of problems or to use new problem-solving techniques, then students need numerous opportunities to develop the skills necessary to approach and answer ...
Working on solutions. In the solution phase, one develops and then implements a coherent plan for solving the problem. As you help students with this phase, you might ask them to: identify the general model or procedure they have in mind for solving the problem. set sub-goals for solving the problem. identify necessary operations and steps.
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
NRICH defines 'problem-solving skills' as those skills which children use once they have got going on a task and are working on the challenge itself. ... (1989) describes a three-pronged approach to teaching and learning mathematics (Exploration, Codification, Consolidation) which contrasts with the more 'traditional' model of demonstration ...
"Most formal definitions characterize critical thinking as the intentional application of rational, higher order thinking skills, such as analysis, synthesis, problem recognition and problem solving, inference, and evaluation" (Angelo, 1995, p. 6). "Critical thinking is thinking that assesses itself" (Center for Critical Thinking, 1996b).
Here are the steps to problem-solving: . Identify the problem. Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
Problem-solving is the ability to identify and solve problems by applying appropriate skills systematically. Problem-solving is a process—an ongoing activity in which we take what we know to discover what we don't know. It involves overcoming obstacles by generating hypo-theses, testing those predictions, and arriving at satisfactory solutions.
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field ...
Step 1 - Understand the Problem. To help students understand the problem, I provided them with sample problems, and together we did five important things: read the problem carefully. restated the problem in our own words. crossed out unimportant information. circled any important information.
This study presents a three-stage, context-. based, problem-solving, learning activity that involves watching detective films, constructing a context-simulation activity, and introducing a project ...
Like so many things we need to find a way to make time for this. If students lack life skills, I believe they will also lack academic skills because both involve problem-solving. When kids are in preschool and kindergarten they learn through play and manipulatives. I believe that we need to teach students problem-solving skills with hands-on tasks.
2. Problem-solving as a group. Have your students create and decorate a medium-sized box with a slot in the top. Label the box "The Problem-Solving Box.". Invite students to anonymously write down and submit any problem or issue they might be having at school or at home, ones that they can't seem to figure out on their own.
When I am teaching my students problem-solving skills, I am typically referencing one of two things 1) my problem-solving posters and scenarios or 2) materials from Kelso's choices. Kelso's choices is a FANTASTIC, concrete way to give students action steps to take when they are trying to problem-solve.
Reading and Social Problem-Solving. Moss Elementary classrooms use a specific process to develop problem-solving skills focused on tending to social and interpersonal relationships. The process also concentrates on building reading skills—specifically, decoding and comprehension. Stop, Look, and Think. Students define the problem.
The UC San Diego problem-solving curriculum, Mjahed noted, is an opportunity for students to build the skills and the confidence to learn from their failures and to work outside their comfort zone. "And from there, they see pathways to real careers," he said. Jennifer Ogo, a teacher from Kearny High School, taught the problem-solving course ...
Learning problem-solving techniques is a must for working professionals in any field. No matter your title or job description, the ability to find the root cause of a difficult problem and formulate viable solutions is a skill that employers value. Learning the soft skills and critical thinking techniques that good problem solvers use can help ...
Here are some of my tips for teaching problem solving skills to students in speech therapy. Tip #1 for Teaching Problem Solving. Understand the process. Successful problem solving is a process that begins with identifying that there is a problem, thinking through possible solutions, and then selecting and implementing the best solution to that ...
Teaching is a dynamic profession that often requires quick thinking and effective problem-solving skills. Whether you're dealing with classroom management issues, differentiating instruction, or ...
Everyday Speech provides valuable examples of role-play and discussion activities to teach problem-solving skills to students with special needs. One example is a group activity in which students pick a common problem ("such as forgetting their lunch or missing the school bus"), discuss it, and come up with possible solutions.
These skills, including problem-solving, creativity, communication, cooperation, and innovation, prepare students to adapt to change and overcome 21st-century challenges.
The idea of a Delta COA helps institutionalize creative problem-solving. It makes creative problem-solving a well-traveled path when seeking solutions. This is instrumental to success in creative problem-solving because the institutional environment plays an important role in shaping creative activities (Ford, 1996).
To effectively train your problem-solving skills, it's important to practice all of the steps required to solve the problem. Think of it this way: Before attempting to solve a problem, your brain has already been hard at work evaluating the situation and picking the best action plan. After you've worked hard preparing, you'll need to ...
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills are essential in and out of the classroom. Encourage them to think independently, question assumptions, and approach problems logically.
The Lego League competitors taught the young builders and coders the benefits of teamwork and problem solving via three classes this year with the ... robotics team teach skills in new program at ...