How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies


Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table.
We’ll first guide you through the seven step problem solving process you and your team can use to effectively solve complex business challenges. We’ll also look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
What is a problem solving process?
- What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Solving problems is like baking a cake. You can go straight into the kitchen without a recipe or the right ingredients and do your best, but the end result is unlikely to be very tasty!
Using a process to bake a cake allows you to use the best ingredients without waste, collect the right tools, account for allergies, decide whether it is a birthday or wedding cake, and then bake efficiently and on time. The result is a better cake that is fit for purpose, tastes better and has created less mess in the kitchen. Also, it should have chocolate sprinkles. Having a step by step process to solve organizational problems allows you to go through each stage methodically and ensure you are trying to solve the right problems and select the most appropriate, effective solutions.
What are the problem solving steps I need to follow?
All problem solving processes go through a number of steps in order to move from identifying a problem to resolving it.
Depending on your problem solving model and who you ask, there can be anything between four and nine problem solving steps you should follow in order to find the right solution. Whatever framework you and your group use, there are some key items that should be addressed in order to have an effective process.
We’ve looked at problem solving processes from sources such as the American Society for Quality and their four step approach , and Mediate ‘s six step process. By reflecting on those and our own problem solving processes, we’ve come up with a sequence of seven problem solving steps we feel best covers everything you need in order to effectively solve problems.
1. Problem identification
The first stage of any problem solving process is to identify the problem or problems you might want to solve. Effective problem solving strategies always begin by allowing a group scope to articulate what they believe the problem to be and then coming to some consensus over which problem they approach first. Problem solving activities used at this stage often have a focus on creating frank, open discussion so that potential problems can be brought to the surface.
2. Problem analysis
Though this step is not a million miles from problem identification, problem analysis deserves to be considered separately. It can often be an overlooked part of the process and is instrumental when it comes to developing effective solutions.
The process of problem analysis means ensuring that the problem you are seeking to solve is the right problem . As part of this stage, you may look deeper and try to find the root cause of a specific problem at a team or organizational level.
Remember that problem solving strategies should not only be focused on putting out fires in the short term but developing long term solutions that deal with the root cause of organizational challenges.
Whatever your approach, analyzing a problem is crucial in being able to select an appropriate solution and the problem solving skills deployed in this stage are beneficial for the rest of the process and ensuring the solutions you create are fit for purpose.
3. Solution generation
Once your group has nailed down the particulars of the problem you wish to solve, you want to encourage a free flow of ideas connecting to solving that problem. This can take the form of problem solving games that encourage creative thinking or problem solving activities designed to produce working prototypes of possible solutions.
The key to ensuring the success of this stage of the problem solving process is to encourage quick, creative thinking and create an open space where all ideas are considered. The best solutions can come from unlikely places and by using problem solving techniques that celebrate invention, you might come up with solution gold.
4. Solution development
No solution is likely to be perfect right out of the gate. It’s important to discuss and develop the solutions your group has come up with over the course of following the previous problem solving steps in order to arrive at the best possible solution. Problem solving games used in this stage involve lots of critical thinking, measuring potential effort and impact, and looking at possible solutions analytically.
During this stage, you will often ask your team to iterate and improve upon your frontrunning solutions and develop them further. Remember that problem solving strategies always benefit from a multitude of voices and opinions, and not to let ego get involved when it comes to choosing which solutions to develop and take further.
Finding the best solution is the goal of all problem solving workshops and here is the place to ensure that your solution is well thought out, sufficiently robust and fit for purpose.
5. Decision making
Nearly there! Once your group has reached consensus and selected a solution that applies to the problem at hand you have some decisions to make. You will want to work on allocating ownership of the project, figure out who will do what, how the success of the solution will be measured and decide the next course of action.
The decision making stage is a part of the problem solving process that can get missed or taken as for granted. Fail to properly allocate roles and plan out how a solution will actually be implemented and it less likely to be successful in solving the problem.
Have clear accountabilities, actions, timeframes, and follow-ups. Make these decisions and set clear next-steps in the problem solving workshop so that everyone is aligned and you can move forward effectively as a group.
Ensuring that you plan for the roll-out of a solution is one of the most important problem solving steps. Without adequate planning or oversight, it can prove impossible to measure success or iterate further if the problem was not solved.
6. Solution implementation
This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind.
Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully. Only then can you ensure that you are solving the right problem but also that you have developed the correct solution and can then successfully implement and measure the impact of that solution.
Project management and communication skills are key here – your solution may need to adjust when out in the wild or you might discover new challenges along the way.
7. Solution evaluation
So you and your team developed a great solution to a problem and have a gut feeling its been solved. Work done, right? Wrong. All problem solving strategies benefit from evaluation, consideration, and feedback. You might find that the solution does not work for everyone, might create new problems, or is potentially so successful that you will want to roll it out to larger teams or as part of other initiatives.
None of that is possible without taking the time to evaluate the success of the solution you developed in your problem solving model and adjust if necessary.
Remember that the problem solving process is often iterative and it can be common to not solve complex issues on the first try. Even when this is the case, you and your team will have generated learning that will be important for future problem solving workshops or in other parts of the organization.
It’s worth underlining how important record keeping is throughout the problem solving process. If a solution didn’t work, you need to have the data and records to see why that was the case. If you go back to the drawing board, notes from the previous workshop can help save time. Data and insight is invaluable at every stage of the problem solving process and this one is no different.
Problem solving workshops made easy
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.
Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
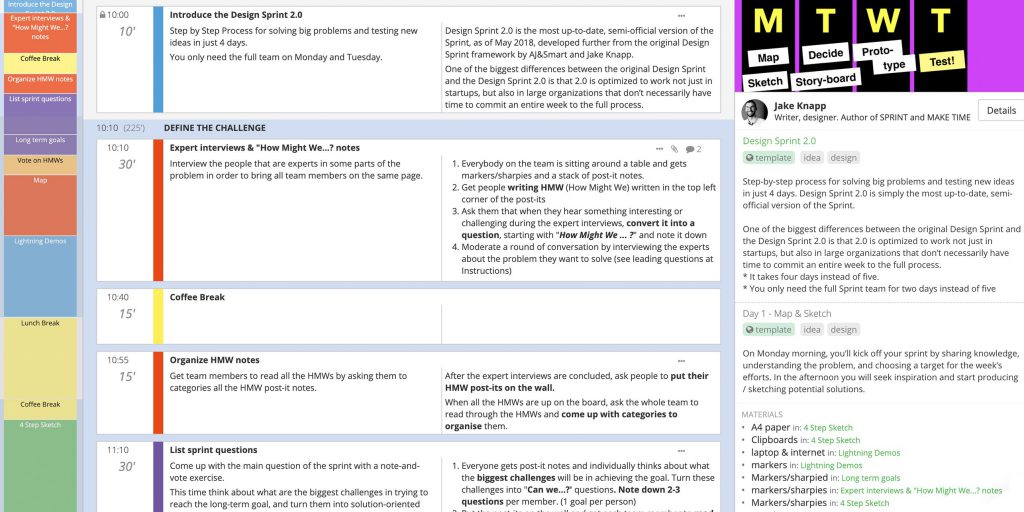
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.
LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Sign up free
10 Problem Solving Training Courses for Better Solutions
Problems are almost always inevitable in your organization. Your team may end up getting into a conflict with co-workers, and customers may have problems with your product or services, among others. Luckily, we’ve listed the best problem solving training courses to help your team come up with better solutions when faced with these problems.

1. Problem Solver by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
At the heart of every problem is the desire of each side to solve the problem together and come up with solutions agreeable to everyone. SC Training (formerly EdApp)’s Problem Solver teaches them how to do precisely that.
This problem solving training course gives your team creative conflict resolution solutions that are structured, reasonable, and data-driven. This program begins with an explanation of the significance of problem-solving and creativity, as well as not being bound by functional fixedness.
It also dives into many concepts and types of collaboration, as well as innovative problem-solving tactics, to better equip your teams for any challenges that may arise during problem discussions. Finally, it covers how to tackle the problem by identifying the main cause to avoid implementing band-aid approaches.
The great thing about taking an SC Training (formerly EdApp) course is that there’ll be a series of quizzes included for better retention. They're presented in game formats, such as matching words, true or false, missing words, the traditional multiple-choice format, and more. These strategies make sure your team will have an enjoyable and engaging learning experience.
- Scope: Creative problem solving, principles of problem-solving, different kinds of problem-solving, kinds of decision making
Created by SC Training (formerly EdApp)

2. Creating a Problem Statement for Your Organization by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
The core mission of a nonprofit organization is to solve societal, environmental, and ethical problems. But as a budding organization, it can be tough to choose which problem you and your team want to address and solve. SC Training (formerly EdApp)’s Creating a Problem Statement for Your Organization can help narrow down your organization’s choices.
This problem solving training course dives into the heart of a problem statement each organization should have. It talks about the importance of narrowing down what your organization aims to solve, which can help your team focus on issues better. It also gives different examples of problem statements to help you and your team identify the strengths and weaknesses of each. This will also give them a better idea of what to use and what not to use for your organization’s problem statement.
- Scope: Importance of a problem statement, how to write a problem statement, creating a problem statement
Created By SC Training (formerly EdApp)

3. Improving Your First Call Resolution (FCR) by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
The first call resolution is a critical indicator in the customer service sector. If your support employees can fix your customers' concerns at the initial point of contact, they’ll be able to build stronger relationships with them and have a more positive experience with your company. Improving Your First Call Resolution by SC Training (formerly EdApp) walks your learners through the process of reaching that goal.
This problem solving training course explains what FCR is and why it is vital for them to get one. It then supplies your team with an understanding of how to determine whether or not a problem was truly handled and how well the client experience was throughout the conversation. Finally, it offers advice on how to enhance and optimize their conversations so that any customer conflicts are handled on the first contact.
- Scope: First call resolution overview, how to calculate FCR, how to improve FCR

4. Handling Irate Customers (Call Center) by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
Handling Irate Customers (Call Center) by SC Training (formerly EdApp) educates your staff on how to handle and resolve client calls. This problem solving training course is ideal for your support workers that are dealing with difficult clients and tough problems. It covers how to listen to upset customers so that they can learn how to give them better solutions to their problems and even build a better relationship with your organization.
This training also includes call resolution suggestions and tactics that your team may use on their next difficult call. At the end of the course, they’ll have the opportunity to practice several mock call conversations and hone their communication skills so they can better implement these approaches in their day-to-day support interactions.
- Scope: Call resolutions, mock call conversations examples

5. Managing Difficult Conversations by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
This SC Training (formerly EdApp) problem solving training teaches your employees the vital information and resources they need to handle challenging and problematic talks. When a problem arises, everyone's voice should be heard. Managing Difficult Conversations teaches them how to actively listen to those they’re speaking with and check that everyone is heard. It covers subjects including prioritizing tough talks, addressing and tackling awkward interactions, offering constructive feedback, and apologizing honestly. It also teaches them how to spot frequent blunders during dispute resolution discussions.
- Scope: Handling difficult conversations, offering negative feedback, delivering authentic apologies
Explore our library including problem solving training courses.

6. Handling Objections with Emotional Intelligence by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
Keeping a cool head can go a long way toward solving problems within and outside your organization. SC Training (formerly EdApp)’s Handling Objections with Emotional Intelligence will teach your team how to do just that.
This problem solving training will teach them how emotional intelligence can help them resolve collective difficulties and arguments professionally and respectfully. It demonstrates how paying attention to another person's body language and attentively listening may help them have more productive conversations. Learners will also get a module on problem resolution and constructive criticism using the appropriate emotional approach.
- Scope: Active listening, body language, resolving conflicts

7. Active Listening by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
Problems can only be solved if your team knows how to actively listen to the people they’re interacting with. SC Training (formerly EdApp)’s Active Listening details the steps and techniques they can take today to improve their active listening skills.
This problem solving training program teaches the principles of active listening to your team, which is great if they lack a basic grasp of this ability. It reviews the important listening strategies that can help people in improving their communication and relationship with one another. The second half of this course is dedicated to avoiding bad listening habits at all costs. These poor behaviors include listening to what isn't being said and speaking without making direct eye contact. It also digs into the difficulties of active listening and suggests ways to overcome them while dealing with conflict and problems.
- Scope: Active listening strategies, bad listening practices

8. Retail Services - Communication by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
Communication is key to being able to smoothly navigate through problematic situations. This is especially true in retail services. That’s why SC Training (formerly EdApp) designed a communication course dedicated to helping your retail teams get out of sticky situations.
In this course, your employees will learn how to actively listen to customers to better understand them and the possible issues they may have. They'll also become acquainted with open and closed-type inquiries, allowing them to select the best question type for various scenarios and interaction goals.
By the end of this training, your retail teams will be more engaged and strategic in their work. Observe how they engage and communicate with clients more effectively and often, resulting in greater sales and happier customers.
- Scope: Active listening, differences betweenopen vs closed questions, how to use open questions

9. Effective Communication in Customer Service by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
SC Training (formerly EdApp)'s Effective Communication in Customer Service course was developed to improve customer service workers' listening abilities for better and faster problem resolution. So, if you manage a team in a similar field, this is an ideal course to consider.
This problem solving program comprises three short sessions that address themes, such as empathy, the function of active listening in developing a great customer connection, and the impediments to successful listening. It walks your team through the process of active listening and presents listening tips and tactics. Some examples are using verbal signals to demonstrate attention while interacting with customers and clarifying by summarizing and asking open-ended questions. There's also a lesson that emphasizes some of the typical issues that will keep your team from actively listening, even if they're using the strategies you've taught them.
- Scope: Active listening, active listening in customer interactions

10. Expectations Setting by SC Training (formerly EdApp)
Knowing how to properly set different people’s expectations can go a long way in solving and avoiding problems in your organization. SC Training (formerly EdApp)’s Expectations Setting will teach your team the tips and tricks for how to appropriately set expectations.
The problem solving course helps your learners avoid the pitfalls of having unreasonable expectations, which typically lead to disappointment, problems, frustration, and broken relationships. They'll learn how to deal with collaborative goal setting so that everyone feels consulted and heard, including outlining expectations for each party.
- Scope: Elements of expectations, avoiding unrealistic expectations
Create better solutions with problem solving training courses
In both a professional and personal setting, problems are almost always unavoidable. People with different opinions, backgrounds, and personalities can clash and create problems and conflicts inside and outside your organization. As a leader, it’s vital to equip your team with the right problem solving skills so they know how to get themselves out of sticky situations and create better solutions for everyone. Read our list of problem solving courses to get started on problem solving skills training today.
Explore more
Explore case studies
Learn how customers like you use EdApp. Their results speak for themselves.
Book a demo
Get a tour of our core products and features with one of our experts.
Take a bootcamp
Instantly access our video library updated weekly with live demonstrations.
Check out G2 reviews
Don't take our word for it. Here’s what our customers have to say.
And the best part? Your team can complete courses anytime, anywhere, on any device.
Learn Problem Solving to Eliminate the Causes for Failures and Overload
Problem solving training for result-driven managers and functional specialists to effectively eliminate the root causes of variability, gaps, defects, frustrations, and stress., cases, when to use:.
- Frustration from never-ending fire-fighting
- Excessive defects, uncontrolled variability
- Stress from unhappy boss, customer, spouse
- Working too hard, too late, risking burnout
Clients, for whom:
- Department managers and team leaders
- Functional specialists, engineers, controllers
- Consultants and improvement champions
- Anyone struggling with too many problems
Process, how it works:
- Online training course with personal coaching
- Apply 5 shifts to successfully address any problem
- Eliminate causes at physical, human, system root
- Learn proven strategies; practical templates included
Benefits, what to gain:
- Status and recognition as expert problem solver
- Become indispensable to the organization
- Free time to spend with family, friends, hobby
- Strategy for better pay and career advancement
Course Content - What You Will Learn
- Systematically solve safety, quality, reliability issues
- Define issue statements based on data, observations
- Learn proven tools and techniques to tackle deviations
- Use basic PDCA and 5-Why analysis for simple issues
- Use Causal Factor Analysis (CFA) for disasters, accidents
- Use Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) for rule-based problems
- Identify cause-effect relationships between factors
- Provide evidence to confirm or reject assumptions
- Drill down causes at the physical, human, latent root
- Develop actions to remove, reduce, control causes
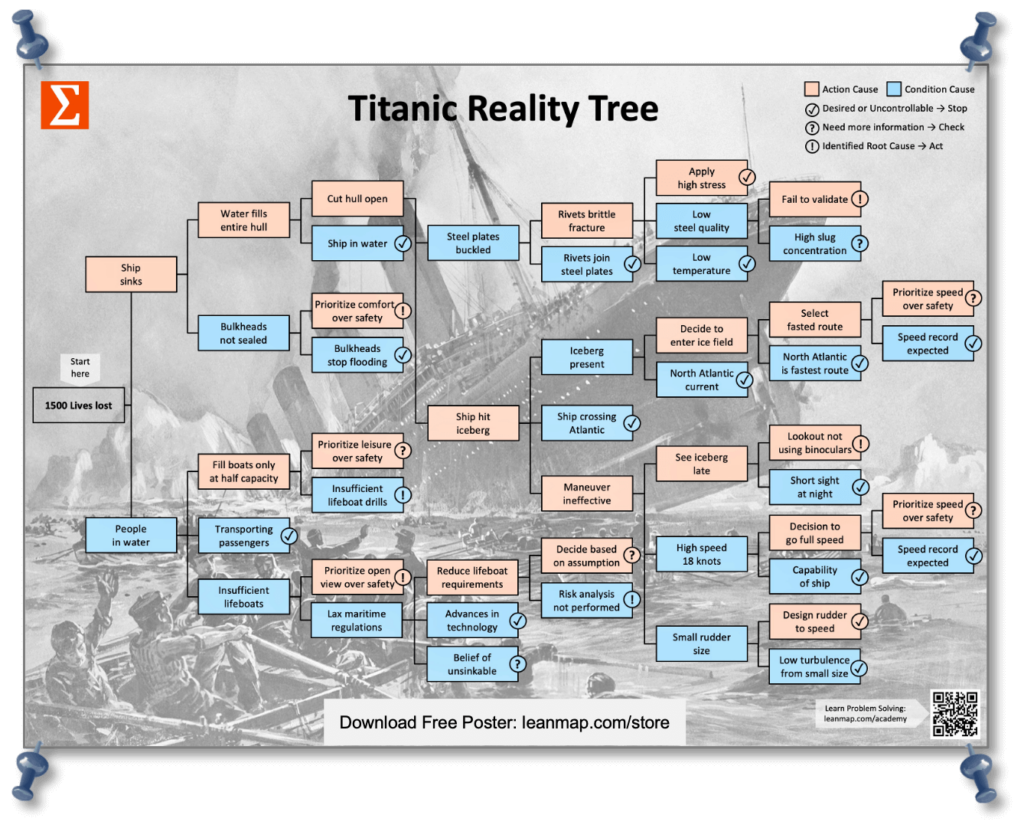
Why Did the Titanic Sink?
The 13 Reasons for Formal Problem Solving
- Undesirable condition
- Deviation, defect, failure
- Safety accident, incident, major risk
- Product failure due to strength, performance, reliability
- Line stop event
- Regulatory non-compliance
- Customer dissatisfaction or request
- Cost overrun
- Equipment breakdown
- Process failure
- Behavioral issue, noncompliant, disengaged
- Repetitive or transferable problem
- Detection failure
Ineffective Trouble Shooting
- Fire fighting
- Going from crisis to crisis
- Stagnant or declining performance
- No time for deeper analysis
- Look for the guilty party: ”Who did that?”
- Jumping from problem into actions
- Generate laundry list of actions to firefight symptoms
- Sub-optimizing one area, spot scope
- Focus on lagging metrics (yield, sales, profits) and hope processes will improve as a result
Effective Problem Solving

- Systems thinking
- Continuous improvement
- Systematic root cause elimination
- Better performance after each problem
- Allocate time to analyze, dialogue, conclude
- Seek deep understanding: “How did that happen?”
- Acting after understanding cause-effect relationships
- Addressing all factors of the failure tree
- Optimizing the value stream, enterprise scope
- Focus on improving processes (capability) that effect actual performance metrics

The Problem Solving Training Gets You Certified
The Beginner Problem Solving Training helps anyone to get started with systematic problem solving. Within a few days, you will learn the basic methods and tools, and apply them to solve a difficult situation in five steps: (1) Describe Gap, (2) Analyze Issues, (3) Identify Causes, (4) Address Causes, (5) Evaluate Results. Quizzes and self-evaluation forms help you to test your skills and evaluate solution the effectiveness of your solutions.
The Advanced Problem Solving Training is for managers, supervisors, and functional specialists to build their their problem-solving skills. The course focuses on systematic root-cause analysis and developing countermeasures to effectively contain, correct, and prevent failures from reoccurring. The advanced course is supported by a coach, helping students through the process, while providing feedback to get the analysis right.
The Expert Problem Solving Training is for engineers, managers, and quality professionals to build expert skills in systematic problem solving. The course covers the deep analysis of event-based problems, rule-based problems and human failures. The expert toolkit allows you tackling deviations and defects at the system level by eliminating, reducing, and controlling the entire set of causes, identified on the logic tree – assisted by an experienced coach.

Problem Solver | Basic Skills
Online course for beginners to build foundational skills to identify, describe, contain, correct, and prevent simple problems from reoccurring.

Problem Solver | Advanced Skills
Coaching-supported advanced course to strengthen problem-solving skills, to deeply analyze and effectively address identified root causes.

Problem Solver | Expert Skills
Coaching-supported expert course to solve complex problems by systematically reducing, eliminating, or controlling direct causes and root causes.
Basic Problem Solver
- 100% online and self-certified, without coaching
- Build basic skills in systematic problem solving
- Ideal for beginners from any function, any level
- Formally analyze and solve a basic problem
- Takes 2-5 days effort during a 1-month period
- Get access to basic videos, templates, toolkit
- Apply multi-5-why to identify root causes
- Formally implement a solution using PDCA
- Create financial benefits; typ. $3k or more
- Get your certificate "Problem Solver"
Advanced Problem Solver
- Coaching sessions for business case and impact
- Build advanced skills in problem-solving
- Ideal for managers, supervisors, specialists
- Solve an advanced problem and get feedback
- Takes 5-10 days effort during a 2-month period
- Get access to advanced videos, templates, tools
- Perform root cause analysis and test robustness
- Formally implement solutions, test effectiveness
- Create financial benefits; typ. $30k or more
- Get your certificate "Advanced Problem Solver"
Expert Problem Solver
- Coaching sessions, expert validation, live support
- Build expert skills in systematic problem solving
- For engineers. managers, quality professionals
- Solve a major problem, supported by a coach
- Takes 10-20 days effort during a 3-month period
- Get access to expert videos, templates, toolkit
- Identify physical, human, and latent causes
- Formally eliminate, reduce, control causes
- Create financial benefits; typ. $60k or more
- Get your certificate "Expert Problem Solver"
Introduction to Problem Solving Skills
What is problem solving and why is it important.
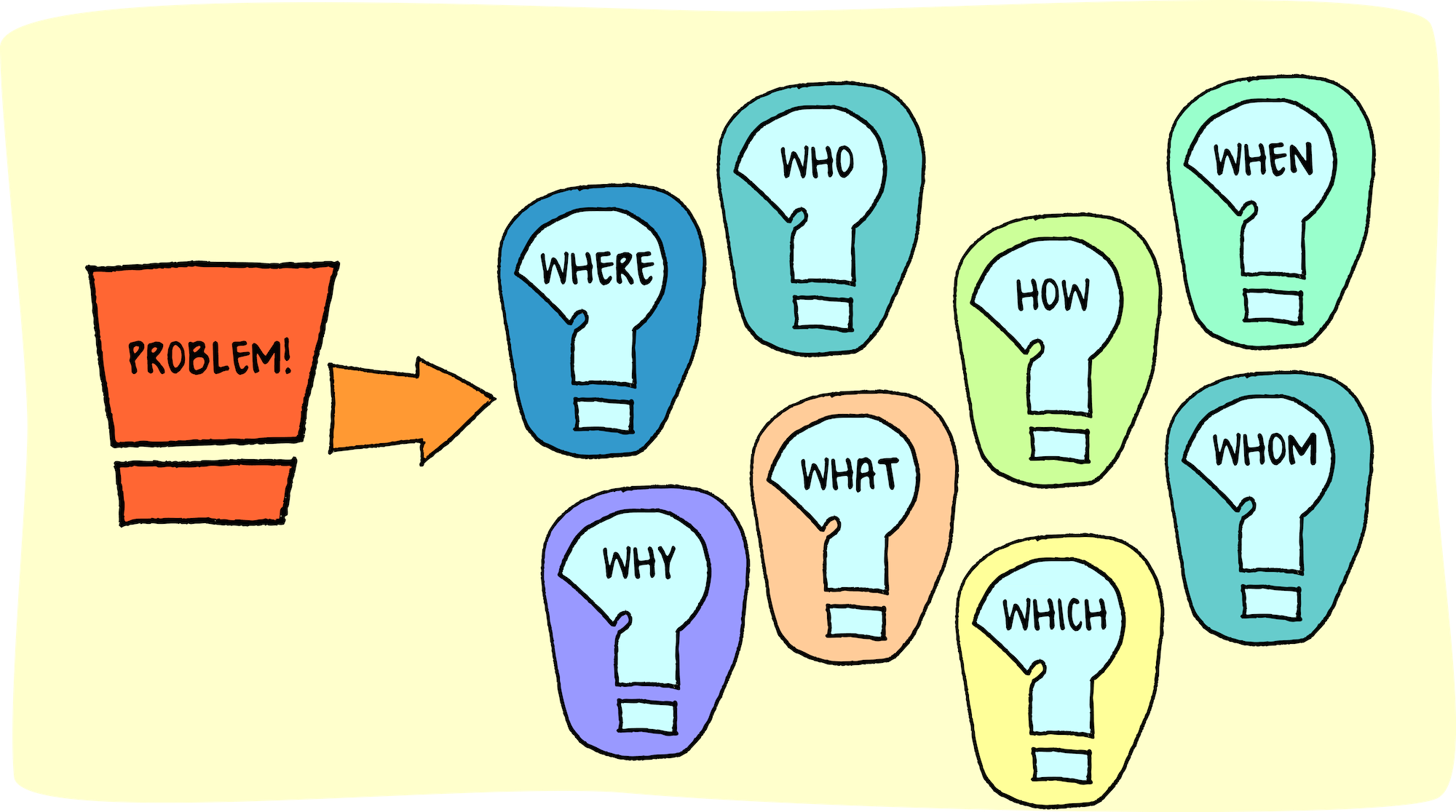
The ability to solve problems is a basic life skill and is essential to our day-to-day lives, at home, at school, and at work. We solve problems every day without really thinking about how we solve them. For example: it’s raining and you need to go to the store. What do you do? There are lots of possible solutions. Take your umbrella and walk. If you don't want to get wet, you can drive, or take the bus. You might decide to call a friend for a ride, or you might decide to go to the store another day. There is no right way to solve this problem and different people will solve it differently.
Problem solving is the process of identifying a problem, developing possible solution paths, and taking the appropriate course of action.
Why is problem solving important? Good problem solving skills empower you not only in your personal life but are critical in your professional life. In the current fast-changing global economy, employers often identify everyday problem solving as crucial to the success of their organizations. For employees, problem solving can be used to develop practical and creative solutions, and to show independence and initiative to employers.
Throughout this case study you will be asked to jot down your thoughts in idea logs. These idea logs are used for reflection on concepts and for answering short questions. When you click on the "Next" button, your responses will be saved for that page. If you happen to close the webpage, you will lose your work on the page you were on, but previous pages will be saved. At the end of the case study, click on the "Finish and Export to PDF" button to acknowledge completion of the case study and receive a PDF document of your idea logs.
What Does Problem Solving Look Like?
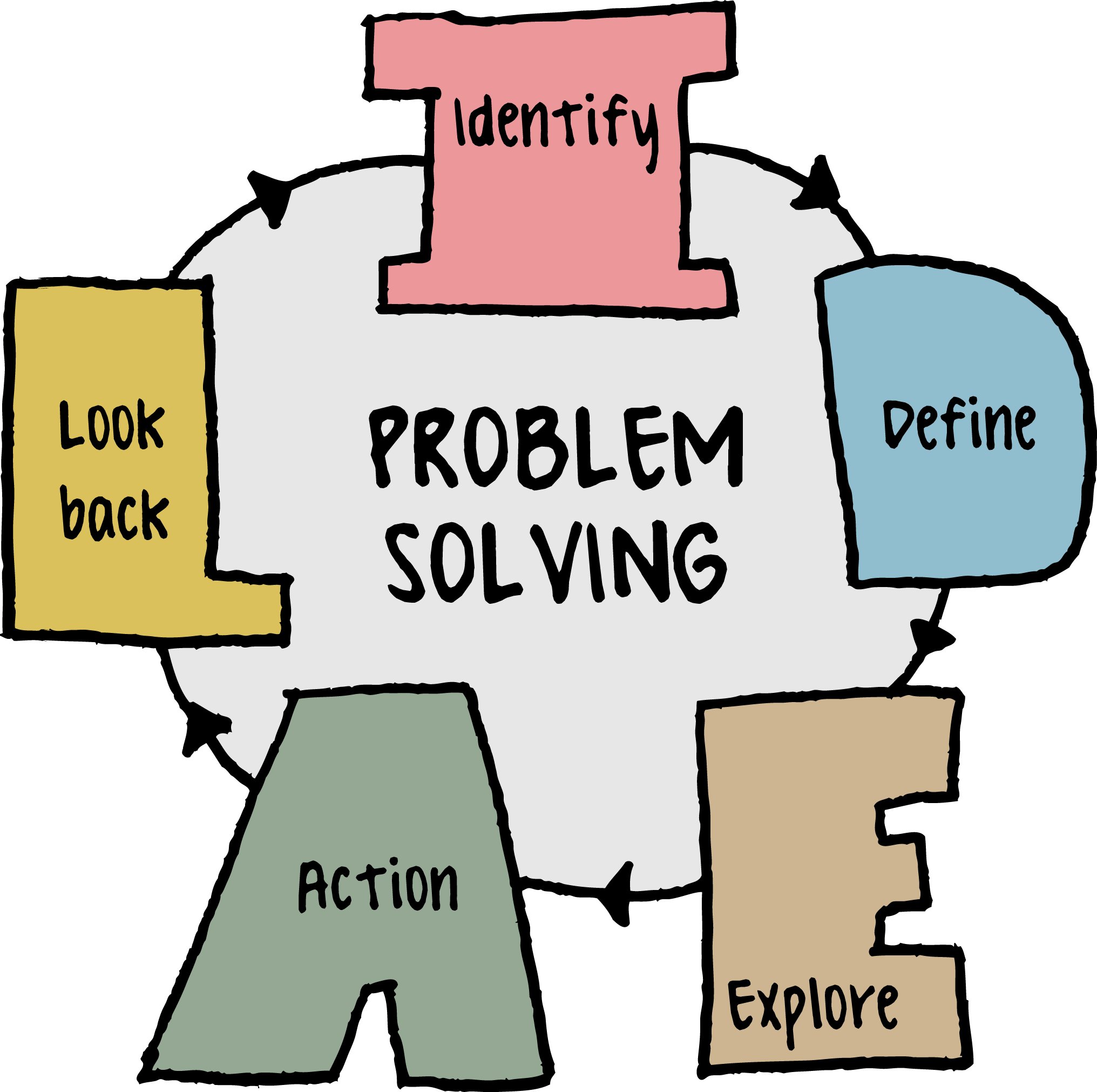
The ability to solve problems is a skill, and just like any other skill, the more you practice, the better you get. So how exactly do you practice problem solving? Learning about different problem solving strategies and when to use them will give you a good start. Problem solving is a process. Most strategies provide steps that help you identify the problem and choose the best solution. There are two basic types of strategies: algorithmic and heuristic.
Algorithmic strategies are traditional step-by-step guides to solving problems. They are great for solving math problems (in algebra: multiply and divide, then add or subtract) or for helping us remember the correct order of things (a mnemonic such as “Spring Forward, Fall Back” to remember which way the clock changes for daylight saving time, or “Righty Tighty, Lefty Loosey” to remember what direction to turn bolts and screws). Algorithms are best when there is a single path to the correct solution.
But what do you do when there is no single solution for your problem? Heuristic methods are general guides used to identify possible solutions. A popular one that is easy to remember is IDEAL [ Bransford & Stein, 1993 ] :
- I dentify the problem
- D efine the context of the problem
- E xplore possible strategies
- A ct on best solution
IDEAL is just one problem solving strategy. Building a toolbox of problem solving strategies will improve your problem solving skills. With practice, you will be able to recognize and use multiple strategies to solve complex problems.
Watch the video
What is the best way to get a peanut out of a tube that cannot be moved? Watch a chimpanzee solve this problem in the video below [ Geert Stienissen, 2010 ].
[PDF transcript]
Describe the series of steps you think the chimpanzee used to solve this problem.
- [Page 2: What does Problem Solving Look Like?] Describe the series of steps you think the chimpanzee used to solve this problem.
Think of an everyday problem you've encountered recently and describe your steps for solving it.
- [Page 2: What does Problem Solving Look Like?] Think of an everyday problem you've encountered recently and describe your steps for solving it.
Developing Problem Solving Processes
Problem solving is a process that uses steps to solve problems. But what does that really mean? Let's break it down and start building our toolbox of problem solving strategies.
What is the first step of solving any problem? The first step is to recognize that there is a problem and identify the right cause of the problem. This may sound obvious, but similar problems can arise from different events, and the real issue may not always be apparent. To really solve the problem, it's important to find out what started it all. This is called identifying the root cause .
Example: You and your classmates have been working long hours on a project in the school's workshop. The next afternoon, you try to use your student ID card to access the workshop, but discover that your magnetic strip has been demagnetized. Since the card was a couple of years old, you chalk it up to wear and tear and get a new ID card. Later that same week you learn that several of your classmates had the same problem! After a little investigation, you discover that a strong magnet was stored underneath a workbench in the workshop. The magnet was the root cause of the demagnetized student ID cards.
The best way to identify the root cause of the problem is to ask questions and gather information. If you have a vague problem, investigating facts is more productive than guessing a solution. Ask yourself questions about the problem. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? When was the last time it worked correctly? What has changed since then? Can you diagram the process into separate steps? Where in the process is the problem occurring? Be curious, ask questions, gather facts, and make logical deductions rather than assumptions.
Watch Adam Savage from Mythbusters, describe his problem solving process [ ForaTv, 2010 ]. As you watch this section of the video, try to identify the questions he asks and the different strategies he uses.
Adam Savage shared many of his problem solving processes. List the ones you think are the five most important. Your list may be different from other people in your class—that's ok!
- [Page 3: Developing Problem Solving Processes] Adam Savage shared many of his problem solving processes. List the ones you think are the five most important.
“The ability to ask the right question is more than half the battle of finding the answer.” — Thomas J. Watson , founder of IBM
Voices From the Field: Solving Problems
In manufacturing facilities and machine shops, everyone on the floor is expected to know how to identify problems and find solutions. Today's employers look for the following skills in new employees: to analyze a problem logically, formulate a solution, and effectively communicate with others.
In this video, industry professionals share their own problem solving processes, the problem solving expectations of their employees, and an example of how a problem was solved.
Meet the Partners:
- Taconic High School in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, is a comprehensive, fully accredited high school with special programs in Health Technology, Manufacturing Technology, and Work-Based Learning.
- Berkshire Community College in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, prepares its students with applied manufacturing technical skills, providing hands-on experience at industrial laboratories and manufacturing facilities, and instructing them in current technologies.
- H.C. Starck in Newton, Massachusetts, specializes in processing and manufacturing technology metals, such as tungsten, niobium, and tantalum. In almost 100 years of experience, they hold over 900 patents, and continue to innovate and develop new products.
- Nypro Healthcare in Devens, Massachusetts, specializes in precision injection-molded healthcare products. They are committed to good manufacturing processes including lean manufacturing and process validation.
Making Decisions
Now that you have a couple problem solving strategies in your toolbox, let's practice. In this exercise, you are given a scenario and you will be asked to decide what steps you would take to identify and solve the problem.
Scenario: You are a new employee and have just finished your training. As your first project, you have been assigned the milling of several additional components for a regular customer. Together, you and your trainer, Bill, set up for the first run. Checking your paperwork, you gather the tools and materials on the list. As you are mounting the materials on the table, you notice that you didn't grab everything and hurriedly grab a few more items from one of the bins. Once the material is secured on the CNC table, you load tools into the tool carousel in the order listed on the tool list and set the fixture offsets.
Bill tells you that since this is a rerun of a job several weeks ago, the CAD/CAM model has already been converted to CNC G-code. Bill helps you download the code to the CNC machine. He gives you the go-ahead and leaves to check on another employee. You decide to start your first run.
What problems did you observe in the video?
- [Page 5: Making Decisions] What problems did you observe in the video?
- What do you do next?
- Try to fix it yourself.
- Ask your trainer for help.
As you are cleaning up, you think about what happened and wonder why it happened. You try to create a mental picture of what happened. You are not exactly sure what the end mill hit, but it looked like it might have hit the dowel pin. You wonder if you grabbed the correct dowel pins from the bins earlier.
You can think of two possible next steps. You can recheck the dowel pin length to make sure it is the correct length, or do a dry run using the CNC single step or single block function with the spindle empty to determine what actually happened.

- Check the dowel pins.
- Use the single step/single block function to determine what happened.
You notice that your trainer, Bill, is still on the floor and decide to ask him for help. You describe the problem to him. Bill asks if you know what the end mill ran into. You explain that you are not sure but you think it was the dowel pin. Bill reminds you that it is important to understand what happened so you can fix the correct problem. He suggests that you start all over again and begin with a dry run using the single step/single block function, with the spindle empty, to determine what it hit. Or, since it happened at the end, he mentions that you can also check the G-code to make sure the Z-axis is raised before returning to the home position.
- Run the single step/single block function.
- Edit the G-code to raise the Z-axis.
You finish cleaning up and check the CNC for any damage. Luckily, everything looks good. You check your paperwork and gather the components and materials again. You look at the dowel pins you used earlier, and discover that they are not the right length. As you go to grab the correct dowel pins, you have to search though several bins. For the first time, you are aware of the mess - it looks like the dowel pins and other items have not been put into the correctly labeled bins. You spend 30 minutes straightening up the bins and looking for the correct dowel pins.
Finally finding them, you finish setting up. You load tools into the tool carousel in the order listed on the tool list and set the fixture offsets. Just to make sure, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do a dry run of the part. Everything looks good! You are ready to create your first part. The first component is done, and, as you admire your success, you notice that the part feels hotter than it should.
You wonder why? You go over the steps of the process to mentally figure out what could be causing the residual heat. You wonder if there is a problem with the CNC's coolant system or if the problem is in the G-code.
- Look at the G-code.
After thinking about the problem, you decide that maybe there's something wrong with the setup. First, you clean up the damaged materials and remove the broken tool. You check the CNC machine carefully for any damage. Luckily, everything looks good. It is time to start over again from the beginning.
You again check your paperwork and gather the tools and materials on the setup sheet. After securing the new materials, you use the CNC single step/single block function with the spindle empty, to do a dry run of the part. You watch carefully to see if you can figure out what happened. It looks to you like the spindle barely misses hitting the dowel pin. You determine that the end mill was broken when it hit the dowel pin while returning to the start position.
After conducting a dry run using the single step/single block function, you determine that the end mill was damaged when it hit the dowel pin on its return to the home position. You discuss your options with Bill. Together, you decide the best thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis before returning to home. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code. Just to make sure, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. You are ready to create your first part. It works. You first part is completed. Only four more to go.
As you are cleaning up, you notice that the components are hotter than you expect and the end mill looks more worn than it should be. It dawns on you that while you were milling the component, the coolant didn't turn on. You wonder if it is a software problem in the G-code or hardware problem with the CNC machine.
It's the end of the day and you decide to finish the rest of the components in the morning.
- You decide to look at the G-code in the morning.
- You leave a note on the machine, just in case.
You decide that the best thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis of the spindle before it returns to home. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code.
While editing the G-code to raise the Z-axis, you notice that the coolant is turned off at the beginning of the code and at the end of the code. The coolant command error caught your attention because your coworker, Mark, mentioned having a similar issue during lunch. You change the coolant command to turn the mist on.
- You decide to talk with your supervisor.
- You discuss what happened with a coworker over lunch.
As you reflect on the residual heat problem, you think about the machining process and the factors that could have caused the issue. You try to think of anything and everything that could be causing the issue. Are you using the correct tool for the specified material? Are you using the specified material? Is it running at the correct speed? Is there enough coolant? Are there chips getting in the way?
Wait, was the coolant turned on? As you replay what happened in your mind, you wonder why the coolant wasn't turned on. You decide to look at the G-code to find out what is going on.
From the milling machine computer, you open the CNC G-code. You notice that there are no coolant commands. You add them in and on the next run, the coolant mist turns on and the residual heat issues is gone. Now, its on to creating the rest of the parts.
Have you ever used brainstorming to solve a problem? Chances are, you've probably have, even if you didn't realize it.
You notice that your trainer, Bill, is on the floor and decide to ask him for help. You describe the problem with the end mill breaking, and how you discovered that items are not being returned to the correctly labeled bins. You think this caused you to grab the incorrect length dowel pins on your first run. You have sorted the bins and hope that the mess problem is fixed. You then go on to tell Bill about the residual heat issue with the completed part.
Together, you go to the milling machine. Bill shows you how to check the oil and coolant levels. Everything looks good at the machine level. Next, on the CNC computer, you open the CNC G-code. While looking at the code, Bill points out that there are no coolant commands. Bill adds them in and when you rerun the program, it works.
Bill is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are the third worker to mention G-code issues over the last week. You noticed the coolant problems in your G-code, John noticed a Z-axis issue in his G-code, and Sam had issues with both the Z-axis and the coolant. Chances are, there is a bigger problem and Bill will need to investigate the root cause .
Talking with Bill, you discuss the best way to fix the problem. Bill suggests editing the G-code to raise the Z-axis of the spindle before it returns to its home position. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code. Following the setup sheet, you re-setup the job and use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. Everything looks good, so you run the job again and create the first part. It works. Since you need four of each component, you move on to creating the rest of them before cleaning up and leaving for the day.
It's a new day and you have new components to create. As you are setting up, you go in search of some short dowel pins. You discover that the bins are a mess and components have not been put away in the correctly labeled bins. You wonder if this was the cause of yesterday's problem. As you reorganize the bins and straighten up the mess, you decide to mention the mess issue to Bill in your afternoon meeting.
You describe the bin mess and using the incorrect length dowels to Bill. He is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are not the first person to mention similar issues with tools and parts not being put away correctly. Chances are there is a bigger safety issue here that needs to be addressed in the next staff meeting.
In any workplace, following proper safety and cleanup procedures is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money.
You now know that the end mill was damaged when it hit the dowel pin. It seems to you that the easiest thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis position of the spindle before it returns to the home position. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code, raising the Z-axis. Starting over, you follow the setup sheet and re-setup the job. This time, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. Everything looks good, so you run the job again and create the first part.
At the end of the day, you are reviewing your progress with your trainer, Bill. After you describe the day's events, he reminds you to always think about safety and the importance of following work procedures. He decides to bring the issue up in the next morning meeting as a reminder to everyone.
In any workplace, following proper procedures (especially those that involve safety) is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money. One tool to improve communication is the morning meeting or huddle.
The next morning, you check the G-code to determine what is wrong with the coolant. You notice that the coolant is turned off at the beginning of the code and also at the end of the code. This is strange. You change the G-code to turn the coolant on at the beginning of the run and off at the end. This works and you create the rest of the parts.
Throughout the day, you keep wondering what caused the G-code error. At lunch, you mention the G-code error to your coworker, John. John is not surprised. He said that he encountered a similar problem earlier this week. You decide to talk with your supervisor the next time you see him.
You are in luck. You see your supervisor by the door getting ready to leave. You hurry over to talk with him. You start off by telling him about how you asked Bill for help. Then you tell him there was a problem and the end mill was damaged. You describe the coolant problem in the G-code. Oh, and by the way, John has seen a similar problem before.
Your supervisor doesn't seem overly concerned, errors happen. He tells you "Good job, I am glad you were able to fix the issue." You are not sure whether your supervisor understood your explanation of what happened or that it had happened before.
The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how to share your ideas and concerns. If you need to tell your supervisor that something is not going well, it is important to remember that timing, preparation, and attitude are extremely important.
It is the end of your shift, but you want to let the next shift know that the coolant didn't turn on. You do not see your trainer or supervisor around. You decide to leave a note for the next shift so they are aware of the possible coolant problem. You write a sticky note and leave it on the monitor of the CNC control system.
How effective do you think this solution was? Did it address the problem?
In this scenario, you discovered several problems with the G-code that need to be addressed. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring and avoid injury to personnel. The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how and when to share your ideas and concerns. If you need to tell your co-workers or supervisor that there is a problem, it is important to remember that timing and the method of communication are extremely important.
You are able to fix the coolant problem in the G-code. While you are glad that the problem is fixed, you are worried about why it happened in the first place. It is important to remember that if a problem keeps reappearing, you may not be fixing the right problem. You may only be addressing the symptoms.
You decide to talk to your trainer. Bill is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are the third worker to mention G-code issues over the last week. You noticed the coolant problems in your G-code, John noticed a Z-axis issue in his G-code, and Sam had issues with both the Z-axis and the coolant. Chances are, there is a bigger problem and Bill will need to investigate the root cause .
Over lunch, you ask your coworkers about the G-code problem and what may be causing the error. Several people mention having similar problems but do not know the cause.
You have now talked to three coworkers who have all experienced similar coolant G-code problems. You make a list of who had the problem, when they had the problem, and what each person told you.
When you see your supervisor later that afternoon, you are ready to talk with him. You describe the problem you had with your component and the damaged bit. You then go on to tell him about talking with Bill and discovering the G-code issue. You show him your notes on your coworkers' coolant issues, and explain that you think there might be a bigger problem.
You supervisor thanks you for your initiative in identifying this problem. It sounds like there is a bigger problem and he will need to investigate the root cause. He decides to call a team huddle to discuss the issue, gather more information, and talk with the team about the importance of communication.
Root Cause Analysis

Root cause analysis ( RCA ) is a method of problem solving that identifies the underlying causes of an issue. Root cause analysis helps people answer the question of why the problem occurred in the first place. RCA uses clear cut steps in its associated tools, like the "5 Whys Analysis" and the "Cause and Effect Diagram," to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
- Determine what happened.
- Determine why it happened.
- Fix the problem so it won’t happen again.
RCA works under the idea that systems and events are connected. An action in one area triggers an action in another, and another, and so on. By tracing back these actions, you can discover where the problem started and how it developed into the problem you're now facing. Root cause analysis can prevent problems from recurring, reduce injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money. There are many different RCA techniques available to determine the root cause of a problem. These are just a few:
- Root Cause Analysis Tools
- 5 Whys Analysis
- Fishbone or Cause and Effect Diagram
- Pareto Analysis

How Huddles Work

Communication is a vital part of any setting where people work together. Effective communication helps employees and managers form efficient teams. It builds trusts between employees and management, and reduces unnecessary competition because each employee knows how their part fits in the larger goal.
One tool that management can use to promote communication in the workplace is the huddle . Just like football players on the field, a huddle is a short meeting where everyone is standing in a circle. A daily team huddle ensures that team members are aware of changes to the schedule, reiterated problems and safety issues, and how their work impacts one another. When done right, huddles create collaboration, communication, and accountability to results. Impromptu huddles can be used to gather information on a specific issue and get each team member's input.
The most important thing to remember about huddles is that they are short, lasting no more than 10 minutes, and their purpose is to communicate and identify. In essence, a huddle’s purpose is to identify priorities, communicate essential information, and discover roadblocks to productivity.
Who uses huddles? Many industries and companies use daily huddles. At first thought, most people probably think of hospitals and their daily patient update meetings, but lots of managers use daily meetings to engage their employees. Here are a few examples:
- Brian Scudamore, CEO of 1-800-Got-Junk? , uses the daily huddle as an operational tool to take the pulse of his employees and as a motivational tool. Watch a morning huddle meeting .
- Fusion OEM, an outsourced manufacturing and production company. What do employees take away from the daily huddle meeting .
- Biz-Group, a performance consulting group. Tips for a successful huddle .
Brainstorming
One tool that can be useful in problem solving is brainstorming . Brainstorming is a creativity technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. The method was first popularized in 1953 by Alex Faickney Osborn in the book Applied Imagination . The goal is to come up with as many ideas as you can in a fixed amount of time. Although brainstorming is best done in a group, it can be done individually. Like most problem solving techniques, brainstorming is a process.
- Define a clear objective.
- Have an agreed a time limit.
- During the brainstorming session, write down everything that comes to mind, even if the idea sounds crazy.
- If one idea leads to another, write down that idea too.
- Combine and refine ideas into categories of solutions.
- Assess and analyze each idea as a potential solution.
When used during problem solving, brainstorming can offer companies new ways of encouraging staff to think creatively and improve production. Brainstorming relies on team members' diverse experiences, adding to the richness of ideas explored. This means that you often find better solutions to the problems. Team members often welcome the opportunity to contribute ideas and can provide buy-in for the solution chosen—after all, they are more likely to be committed to an approach if they were involved in its development. What's more, because brainstorming is fun, it helps team members bond.
- Watch Peggy Morgan Collins, a marketing executive at Power Curve Communications discuss How to Stimulate Effective Brainstorming .
- Watch Kim Obbink, CEO of Filter Digital, a digital content company, and her team share their top five rules for How to Effectively Generate Ideas .
Importance of Good Communication and Problem Description

Communication is one of the most frequent activities we engage in on a day-to-day basis. At some point, we have all felt that we did not effectively communicate an idea as we would have liked. The key to effective communication is preparation. Rather than attempting to haphazardly improvise something, take a few minutes and think about what you want say and how you will say it. If necessary, write yourself a note with the key points or ideas in the order you want to discuss them. The notes can act as a reminder or guide when you talk to your supervisor.
Tips for clear communication of an issue:
- Provide a clear summary of your problem. Start at the beginning, give relevant facts, timelines, and examples.
- Avoid including your opinion or personal attacks in your explanation.
- Avoid using words like "always" or "never," which can give the impression that you are exaggerating the problem.
- If this is an ongoing problem and you have collected documentation, give it to your supervisor once you have finished describing the problem.
- Remember to listen to what's said in return; communication is a two-way process.
Not all communication is spoken. Body language is nonverbal communication that includes your posture, your hands and whether you make eye contact. These gestures can be subtle or overt, but most importantly they communicate meaning beyond what is said. When having a conversation, pay attention to how you stand. A stiff position with arms crossed over your chest may imply that you are being defensive even if your words state otherwise. Shoving your hands in your pockets when speaking could imply that you have something to hide. Be wary of using too many hand gestures because this could distract listeners from your message.
The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how and when to share your ideas or concerns. If you need to tell your supervisor or co-worker about something that is not going well, keep in mind that good timing and good attitude will go a long way toward helping your case.
Like all skills, effective communication needs to be practiced. Toastmasters International is perhaps the best known public speaking organization in the world. Toastmasters is open to anyone who wish to improve their speaking skills and is willing to put in the time and effort to do so. To learn more, visit Toastmasters International .
Methods of Communication
Communication of problems and issues in any workplace is important, particularly when safety is involved. It is therefore crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. As issues and problems arise, they need to be addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important skill because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money.
There are many different ways to communicate: in person, by phone, via email, or written. There is no single method that fits all communication needs, each one has its time and place.
In person: In the workplace, face-to-face meetings should be utilized whenever possible. Being able to see the person you need to speak to face-to-face gives you instant feedback and helps you gauge their response through their body language. Be careful of getting sidetracked in conversation when you need to communicate a problem.
Email: Email has become the communication standard for most businesses. It can be accessed from almost anywhere and is great for things that don’t require an immediate response. Email is a great way to communicate non-urgent items to large amounts of people or just your team members. One thing to remember is that most people's inboxes are flooded with emails every day and unless they are hyper vigilant about checking everything, important items could be missed. For issues that are urgent, especially those around safety, email is not always be the best solution.
Phone: Phone calls are more personal and direct than email. They allow us to communicate in real time with another person, no matter where they are. Not only can talking prevent miscommunication, it promotes a two-way dialogue. You don’t have to worry about your words being altered or the message arriving on time. However, mobile phone use and the workplace don't always mix. In particular, using mobile phones in a manufacturing setting can lead to a variety of problems, cause distractions, and lead to serious injury.
Written: Written communication is appropriate when detailed instructions are required, when something needs to be documented, or when the person is too far away to easily speak with over the phone or in person.
There is no "right" way to communicate, but you should be aware of how and when to use the appropriate form of communication for your situation. When deciding the best way to communicate with a co-worker or manager, put yourself in their shoes, and think about how you would want to learn about the issue. Also, consider what information you would need to know to better understand the issue. Use your good judgment of the situation and be considerate of your listener's viewpoint.
Did you notice any other potential problems in the previous exercise?
- [Page 6:] Did you notice any other potential problems in the previous exercise?
Summary of Strategies
In this exercise, you were given a scenario in which there was a problem with a component you were creating on a CNC machine. You were then asked how you wanted to proceed. Depending on your path through this exercise, you might have found an easy solution and fixed it yourself, asked for help and worked with your trainer, or discovered an ongoing G-code problem that was bigger than you initially thought.
When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money. Although, each path in this exercise ended with a description of a problem solving tool for your toolbox, the first step is always to identify the problem and define the context in which it happened.
There are several strategies that can be used to identify the root cause of a problem. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving that helps people answer the question of why the problem occurred. RCA uses a specific set of steps, with associated tools like the “5 Why Analysis" or the “Cause and Effect Diagram,” to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
Once the underlying cause is identified and the scope of the issue defined, the next step is to explore possible strategies to fix the problem.
If you are not sure how to fix the problem, it is okay to ask for help. Problem solving is a process and a skill that is learned with practice. It is important to remember that everyone makes mistakes and that no one knows everything. Life is about learning. It is okay to ask for help when you don’t have the answer. When you collaborate to solve problems you improve workplace communication and accelerates finding solutions as similar problems arise.
One tool that can be useful for generating possible solutions is brainstorming . Brainstorming is a technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. The method was first popularized in 1953 by Alex Faickney Osborn in the book Applied Imagination. The goal is to come up with as many ideas as you can, in a fixed amount of time. Although brainstorming is best done in a group, it can be done individually.
Depending on your path through the exercise, you may have discovered that a couple of your coworkers had experienced similar problems. This should have been an indicator that there was a larger problem that needed to be addressed.
In any workplace, communication of problems and issues (especially those that involve safety) is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they be addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money.
One strategy for improving communication is the huddle . Just like football players on the field, a huddle is a short meeting with everyone standing in a circle. A daily team huddle is a great way to ensure that team members are aware of changes to the schedule, any problems or safety issues are identified and that team members are aware of how their work impacts one another. When done right, huddles create collaboration, communication, and accountability to results. Impromptu huddles can be used to gather information on a specific issue and get each team member's input.
To learn more about different problem solving strategies, choose an option below. These strategies accompany the outcomes of different decision paths in the problem solving exercise.
- View Problem Solving Strategies Select a strategy below... Root Cause Analysis How Huddles Work Brainstorming Importance of Good Problem Description Methods of Communication
Communication is one of the most frequent activities we engage in on a day-to-day basis. At some point, we have all felt that we did not effectively communicate an idea as we would have liked. The key to effective communication is preparation. Rather than attempting to haphazardly improvise something, take a few minutes and think about what you want say and how you will say it. If necessary, write yourself a note with the key points or ideas in the order you want to discuss them. The notes can act as a reminder or guide during your meeting.
- Provide a clear summary of the problem. Start at the beginning, give relevant facts, timelines, and examples.
In person: In the workplace, face-to-face meetings should be utilized whenever possible. Being able to see the person you need to speak to face-to-face gives you instant feedback and helps you gauge their response in their body language. Be careful of getting sidetracked in conversation when you need to communicate a problem.
There is no "right" way to communicate, but you should be aware of how and when to use the appropriate form of communication for the situation. When deciding the best way to communicate with a co-worker or manager, put yourself in their shoes, and think about how you would want to learn about the issue. Also, consider what information you would need to know to better understand the issue. Use your good judgment of the situation and be considerate of your listener's viewpoint.
"Never try to solve all the problems at once — make them line up for you one-by-one.” — Richard Sloma
Problem Solving: An Important Job Skill
Problem solving improves efficiency and communication on the shop floor. It increases a company's efficiency and profitability, so it's one of the top skills employers look for when hiring new employees. Recent industry surveys show that employers consider soft skills, such as problem solving, as critical to their business’s success.
The 2011 survey, "Boiling Point? The skills gap in U.S. manufacturing ," polled over a thousand manufacturing executives who reported that the number one skill deficiency among their current employees is problem solving, which makes it difficult for their companies to adapt to the changing needs of the industry.
In this video, industry professionals discuss their expectations and present tips for new employees joining the manufacturing workforce.
Quick Summary
- [Quick Summary: Question1] What are two things you learned in this case study?
- What question(s) do you still have about the case study?
- [Quick Summary: Question2] What question(s) do you still have about the case study?
- Is there anything you would like to learn more about with respect to this case study?
- [Quick Summary: Question3] Is there anything you would like to learn more about with respect to this case study?
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Problem-Solving Skills Are Essential for Leaders in Any Industry

- 17 Jan 2023
Any organization offering a product or service is in the business of solving problems.
Whether providing medical care to address health issues or quick convenience to those hungry for dinner, a business’s purpose is to satisfy customer needs .
In addition to solving customers’ problems, you’ll undoubtedly encounter challenges within your organization as it evolves to meet customer needs. You’re likely to experience growing pains in the form of missed targets, unattained goals, and team disagreements.
Yet, the ubiquity of problems doesn’t have to be discouraging; with the right frameworks and tools, you can build the skills to solve consumers' and your organization’s most challenging issues.
Here’s a primer on problem-solving in business, why it’s important, the skills you need, and how to build them.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving is the process of systematically removing barriers that prevent you or others from reaching goals.
Your business removes obstacles in customers’ lives through its products or services, just as you can remove obstacles that keep your team from achieving business goals.
Design Thinking
Design thinking , as described by Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , is a human-centered , solutions-based approach to problem-solving and innovation. Originally created for product design, design thinking’s use case has evolved . It’s now used to solve internal business problems, too.
The design thinking process has four stages :

- Clarify: Clarify a problem through research and feedback from those impacted.
- Ideate: Armed with new insights, generate as many solutions as possible.
- Develop: Combine and cull your ideas into a short list of viable, feasible, and desirable options before building prototypes (if making physical products) and creating a plan of action (if solving an intangible problem).
- Implement: Execute the strongest idea, ensuring clear communication with all stakeholders about its potential value and deliberate reasoning.
Using this framework, you can generate innovative ideas that wouldn’t have surfaced otherwise.
Creative Problem-Solving
Another, less structured approach to challenges is creative problem-solving , which employs a series of exercises to explore open-ended solutions and develop new perspectives. This is especially useful when a problem’s root cause has yet to be defined.
You can use creative problem-solving tools in design thinking’s “ideate” stage, which include:
- Brainstorming: Instruct everyone to develop as many ideas as possible in an allotted time frame without passing judgment.
- Divergent thinking exercises: Rather than arriving at the same conclusion (convergent thinking), instruct everyone to come up with a unique idea for a given prompt (divergent thinking). This type of exercise helps avoid the tendency to agree with others’ ideas without considering alternatives.
- Alternate worlds: Ask your team to consider how various personas would manage the problem. For instance, how would a pilot approach it? What about a young child? What about a seasoned engineer?
It can be tempting to fall back on how problems have been solved before, especially if they worked well. However, if you’re striving for innovation, relying on existing systems can stunt your company’s growth.
Related: How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips
Why Is Problem-Solving Important for Leaders?
While obstacles’ specifics vary between industries, strong problem-solving skills are crucial for leaders in any field.
Whether building a new product or dealing with internal issues, you’re bound to come up against challenges. Having frameworks and tools at your disposal when they arise can turn issues into opportunities.
As a leader, it’s rarely your responsibility to solve a problem single-handedly, so it’s crucial to know how to empower employees to work together to find the best solution.
Your job is to guide them through each step of the framework and set the parameters and prompts within which they can be creative. Then, you can develop a list of ideas together, test the best ones, and implement the chosen solution.
Related: 5 Design Thinking Skills for Business Professionals
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need
1. problem framing.
One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you’re trying to solve.
“Before you begin to generate solutions for your problem, you must always think hard about how you’re going to frame that problem,” Datar says in the course.
For instance, imagine you work for a company that sells children’s sneakers, and sales have plummeted. When framing the problem, consider:
- What is the children’s sneaker market like right now?
- Should we improve the quality of our sneakers?
- Should we assess all children’s footwear?
- Is this a marketing issue for children’s sneakers specifically?
- Is this a bigger issue that impacts how we should market or produce all footwear?
While there’s no one right way to frame a problem, how you do can impact the solutions you generate. It’s imperative to accurately frame problems to align with organizational priorities and ensure your team generates useful ideas for your firm.
To solve a problem, you need to empathize with those impacted by it. Empathy is the ability to understand others’ emotions and experiences. While many believe empathy is a fixed trait, it’s a skill you can strengthen through practice.
When confronted with a problem, consider whom it impacts. Returning to the children’s sneaker example, think of who’s affected:
- Your organization’s employees, because sales are down
- The customers who typically buy your sneakers
- The children who typically wear your sneakers
Empathy is required to get to the problem’s root and consider each group’s perspective. Assuming someone’s perspective often isn’t accurate, so the best way to get that information is by collecting user feedback.
For instance, if you asked customers who typically buy your children’s sneakers why they’ve stopped, they could say, “A new brand of children’s sneakers came onto the market that have soles with more traction. I want my child to be as safe as possible, so I bought those instead.”
When someone shares their feelings and experiences, you have an opportunity to empathize with them. This can yield solutions to their problem that directly address its root and shows you care. In this case, you may design a new line of children’s sneakers with extremely grippy soles for added safety, knowing that’s what your customers care most about.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Breaking Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind in which you examine situations through the lens of past experiences. This locks you into one mindset rather than allowing you to consider alternative possibilities.
For instance, your cognitive fixedness may make you think rubber is the only material for sneaker treads. What else could you use? Is there a grippier alternative you haven’t considered?
Problem-solving is all about overcoming cognitive fixedness. You not only need to foster this skill in yourself but among your team.
4. Creating a Psychologically Safe Environment
As a leader, it’s your job to create an environment conducive to problem-solving. In a psychologically safe environment, all team members feel comfortable bringing ideas to the table, which are likely influenced by their personal opinions and experiences.
If employees are penalized for “bad” ideas or chastised for questioning long-held procedures and systems, innovation has no place to take root.
By employing the design thinking framework and creative problem-solving exercises, you can foster a setting in which your team feels comfortable sharing ideas and new, innovative solutions can grow.

How to Build Problem-Solving Skills
The most obvious answer to how to build your problem-solving skills is perhaps the most intimidating: You must practice.
Again and again, you’ll encounter challenges, use creative problem-solving tools and design thinking frameworks, and assess results to learn what to do differently next time.
While most of your practice will occur within your organization, you can learn in a lower-stakes setting by taking an online course, such as Design Thinking and Innovation . Datar guides you through each tool and framework, presenting real-world business examples to help you envision how you would approach the same types of problems in your organization.
Are you interested in uncovering innovative solutions for your organization’s business problems? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation —one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses —to learn how to leverage proven frameworks and tools to solve challenges. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
The California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare
- Contact the CEBC
- Sign up for The CEBC Connection
- Topic Areas
- Rating Scales
- Implementation-Specific Tools & Resources
- Implementation Guide
- Implementation Examples
Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST)
About this program.
Target Population: 7 to 14 year olds with behavioral problems, particularly children who struggle to handle disappointments, frustrations, or problems calmly
For children/adolescents ages: 7 – 14
Program Overview
PSST is aimed at decreasing inappropriate or disruptive behavior in children. The program teaches that problem behaviors arise because children lack constructive ways to deal with thoughts and feelings and instead resort to dysfunctional ones. It is designed to help children learn to slow down, stop and think, and generate multiple solutions to any given problem. The program uses a cognitive-behavioral approach to teach techniques in managing thoughts and feelings, and interacting appropriately with others. Specific techniques include modeling, role-playing, positive reinforcement of appropriate behavior, and teaching alternative behaviors. Children are typically given homework to help them practice implementing these skills. Most sessions are individual, but parents may be brought in to observe and to learn how to assist in reinforcing new skills.
Program Goals
The goals of Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) are:
- Train the child to think differently about situations and behave differently in diverse situations
- Help the child internalize the problem solving steps so that they are able to use them to evaluate potential solutions to problems occurring outside of therapy
- Learn and generalize problem solving skills and how to apply problem solving skills using self-instruction
- Learn how to generate positive solutions that would enable the child to avoid physical aggression, resolve the conflict, and keep themselves out of trouble
Logic Model
The program representative did not provide information about a Logic Model for Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) .
Essential Components
The essential components of Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) include:
- Sessions that are fun for children as they play various games and have the opportunity to earn prizes as they learn the following:
- The 5 Problem Solving Steps used to handle any problem situation
- How to use these problem solving steps for hypothetical problems
- How to use these problem solving steps for simple problems outside of session
- How to use these steps to solve challenging hypothetical situations
- How to ultimately use these steps to solve problems that come up in their own life
- Individual treatment with one of the staff of certified clinicians who will keep the child's goals in mind throughout the therapy
- A number of sessions with the parent before beginning with the child so that the parents will know how to encourage and maintain the child's growth
Program Delivery
Child/adolescent services.
Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) directly provides services to children/adolescents and addresses the following:
- Oppositional behavior, aggressive behavior, antisocial behavior
Services Involve Family/Support Structures:
This program involves the family or other support systems in the individual's treatment: Parents are involved sporadically during treatment to help support their child in implementing Problem-Solving Skills Training .
Recommended Intensity:
Weekly 50-minute sessions
Recommended Duration:
Approximately 8 to 14 weeks
Delivery Settings
This program is typically conducted in a(n):
- Outpatient Clinic
Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) includes a homework component:
The child is given homework to help them learn to apply problem solving skills to everyday situations. Homework is a natural extension of treatment where learned problem solving skills are applied to real life situations.
Resources Needed to Run Program
The typical resources for implementing the program are:
PSST requires a standard clinical treatment room.
Manuals and Training
Prerequisite/minimum provider qualifications.
PSST providers must be Master's level mental health professionals.
Manual Information
There is not a manual that describes how to deliver this program.
Training Information
There is training available for this program.
Training Contact:
- Bernadette Lecza, MS, CKPMT [email protected]
Training Type/Location:
Training is occasionally available either online or onsite.
Number of days/hours:
Total training time is about 8 hours.
Implementation Information
Pre-implementation materials.
There are no pre-implementation materials to measure organizational or provider readiness for Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) .
Formal Support for Implementation
There is no formal support available for implementation of Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) .
Fidelity Measures
There are no fidelity measures for Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) .
Implementation Guides or Manuals
There are implementation guides or manuals for Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) as listed below:
A comprehensive overview of Problem Solving Skills Training is available. For more information, please contact the program representative who is listed at the bottom of the page.
Research on How to Implement the Program
Research has not been conducted on how to implement Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) .
Relevant Published, Peer-Reviewed Research
Child Welfare Outcome: Child/Family Well-Being
Kazdin, A., Esveldt-Dawson, K., French, N., & Unis, A. (1987). Problem-Solving Skills Training and relationship therapy in the treatment of antisocial child behavior. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 55 (1), 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.55.1.76
Type of Study: Randomized controlled trial Number of Participants: 56
Population:
- Age — 7–13 years
- Race/Ethnicity — 77% White and 23% Black
- Gender — 45 Male and 11 Female
- Status — Participants were inpatients at a psychiatric facility.
Location/Institution: Not specified
Summary: (To include basic study design, measures, results, and notable limitations) The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effects of cognitive-behavioral Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) and nondirective relationship therapy (RT) for the treatment of antisocial child behavior. Participants were randomly assigned to PSST , relationship therapy (RT), or a control group that had therapist contact with no directed focus on the elements of the two treatment conditions. Measures utilized include the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL), Therapist Evaluation Inventory, and the Child Evaluation Inventory . Results indicate that children in the PSST condition had greater decreases in aggression, externalizing behaviors, and overall behavior problems and greater increases in pro-social behavior at follow-up than did the RT and control groups. Limitations include the use of a hospitalized sample and reliance on a small number and type of evaluations.
Length of controlled postintervention follow-up: 1 year.
Kazdin, A. E., Bass, D., Siegel, T., & Thomas, C. (1989). Cognitive-behavioral therapy and relationship therapy in the treatment of children referred for antisocial behavior. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 57 (4), 522–535. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.57.4.522
Type of Study: Randomized controlled trial Number of Participants: 112
- Race/Ethnicity — Not specified
- Gender — 87 Male and 25 Female
- Status — Participants were children receiving inpatient or outpatient treatment at a child conduct clinic.
Summary: (To include basic study design, measures, results, and notable limitations) The purpose of the study was to evaluate alternative treatments for children referred for severe antisocial behavior. Participants were randomized to receive one of two Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) treatment conditions: standard PSST or PSST-P which included a set of planned activities and "homework" to be performed outside of therapeutic sessions, or to a relationship therapy (RT) control condition. Measures utilized include the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL), the School Behavior Checklist, the Parent Daily Report, Interview for Antisocial Behavior, the Children's Action Tendency Scale, and the Self-Esteem Inventory . Results indicate that both PSST groups showed significantly higher improvement in behavior than the RT group. Improvement in PSST-P children's school-related behaviors were shown to be stronger in comparison with standard PSST . Limitations include no direct assessment of the cognitive processes that problem-solving skills training were designed to change and relationship therapy may not have been well or fairly tested.
Kazdin, A. E., Siegel, T. C., & Bass, D. (1992). Cognitive problem-solving skills training and parent management training in the treatment of antisocial behavior in children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60 (5), 733–747. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.60.5.733
Type of Study: Randomized controlled trial Number of Participants: 97
- Race/Ethnicity — 69% White and 31% Black
- Gender — 76 Male and 21 Female
- Status — Participants were children referred for treatment to a psychiatric facility.
Summary: (To include basic study design, measures, results, and notable limitations) The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effects of Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) and parent management training (PMT) on children referred for severe antisocial behavior. Participants were randomly assigned to receive PSST , PMT, or a combination of PSST + PMT. Measures utilized include the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL), the Teacher Report Form (TRF), the Health Resources Inventory, the Interview for Antisocial Behavior, the Children's Action Tendency Scale, the Self-Report Delinquency Checklist, the Parent Daily Report, the Parenting Stress Index (PSI), the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) (mothers), and the Family Environment Scale . Results indicate that children in all conditions showed significant improvement at home and school, which was maintained at follow-up. PSST + PMT had the greatest effects on children's aggressive, delinquent, and antisocial behavior; and was also associated with greater improvements in parental stress and depression. Limitations include lack of an untreated comparison group, large attrition rate, and the small sample size.
Bushman, B. B., & Gimpel Peacock, G. (2010). Does teaching problem-solving skills matter? An evaluation of Problem-Solving Skills Training for the treatment of social and behavioral problems in children. Child & Family Behavior Therapy, 32 (2), 103–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/07317101003776449
Type of Study: Randomized controlled trial Number of Participants: 26
- Age — Mean=8.27 years
- Race/Ethnicity — 23 Caucasian, 1 Asian, and 2 Biracial
- Gender — 17 Male and 9 Female
- Status — Participants were families with children with social and behavioral problems.
Location/Institution: Utah
Summary: (To include basic study design, measures, results, and notable limitations) The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness of Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) for the treatment of social and behavioral problems in children. Participants were randomly assigned to either a PSST treatment group or a nondirective comparison group. Measures utilized include the Skills Rating System (SSRS), the Parent Daily Report (PDR), Child Behavior Checklist for Ages 6-18 (CBCL/6-18), Parenting Stress Index-Short Form (PSI-SF) , and a parent questionnaire at baseline, post-treatment, and at a 6-week follow-up. Results indicate that children in both the treatment and comparison group showed similar improvement, with PSST showing a minor advantage on several PDR and SSRS scales. Limitations include the small sample size and short-term follow-up.
Length of controlled postintervention follow-up: 6 weeks.
Additional References
Kazdin, A. E. (2010). Problem-Solving Skills Training and Parent Management Training for Oppositional Defiant Disorder and Conduct Disorder. In J. R. Weisz & A. E. Kazdin (Eds.). Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (2nd ed., pp. 211-226). Guilford Press.
Kazdin, A. E. (2011). Problem-Solving Skills Training for children and adolescents: Overview. Yale Parenting Center.
Kazdin, A. E. (2017). Parent Management Training and Problem-Solving Skills Training for child and adolescent conduct problems. In J. R. Weisz & A. E. Kazdin (Eds.), Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents (pp.142–158). Guilford Press.
Contact Information
Date Research Evidence Last Reviewed by CEBC: December 2023
Date Program Content Last Reviewed by Program Staff: November 2021
Date Program Originally Loaded onto CEBC: April 2009

Glossary | Sitemap | Limitations & Disclosures
The CEBC is funded by the California Department of Social Services’ (CDSS’) Office of Child Abuse Prevention and is one of their targeted efforts to improve the lives of children and families served within child welfare system.
© copyright 2006-2024 The California Evidence-Based Clearinghouse for Child Welfare www.cebc4cw.org
- Introduction
- Conclusions
- Article Information
GRADE indicates Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations; SMD, standardized mean difference.
a For meta-analysis of parental problem-solving skills, quality of life, pediatric quality of life, and social functioning, the problem-solving skills training (PSST) group was preferable when the effect size was greater than 0, while the value of effect size for other outcomes less than 0 indicated a favor of PSST.
b For meta-analysis of parental posttraumatic stress, quality of life, pediatric mental problems, and parent-child conflict, the values of I 2 were less than 50%, and the inverse variance method was therefore used.
c Downgraded 1 level for serious inconsistency due to statistical heterogeneity.
d Downgraded 1 level for serious risk of bias of included studies.
e Downgraded 1 level for serious inconsistency due to statistical heterogeneity, and downgraded 1 level for serious imprecision due to limited sample size.
f Downgraded 1 level for serious inconsistency due to statistical heterogeneity, and downgraded 2 levels for very serious imprecision due to limited sample size and wide CIs.
g Downgraded 2 levels for very serious imprecision due to limited sample size and data from only 2 studies.
h Downgraded 1 level for serious inconsistency due to statistical heterogeneity and downgraded 1 level for serious imprecision due to wide CIs.
i Downgraded 1 level for serious imprecision due to limited sample size.
j Downgraded 1 level for serious risk of bias of included studies and downgraded 1 level for serious imprecision due to limited sample size.
eTable 1. Study Search Strategies
eTable 2. Intervention Characteristics of Included Studies
eTable 3. Author Judgments of Risk of Bias Across All Included Studies
eTable 4. Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) Evidence Profile
eFigure 1. Forest Plot Meta-Analyses for Different Psychosocial Outcomes
eFigure 2. Subgroup Analyses of Each Outcome According to Children- and Intervention-Level Factors
eFigure 3. Funnel Plot Analyses
eFigure 4. Leave-One-Out Sensitivity Analyses
Data Sharing Statement
- Enhancing the Interpretation of Continuous Outcomes and Subgroup Analyses in Systematic Reviews JAMA Pediatrics Comment & Response April 22, 2024 Jing Wu, PhD; Qi Wang, PhD; Xiaoning He, PhD
See More About
Select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Others Also Liked
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Zhou T , Luo Y , Xiong W , Meng Z , Zhang H , Zhang J. Problem-Solving Skills Training for Parents of Children With Chronic Health Conditions : A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis . JAMA Pediatr. 2024;178(3):226–236. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5753
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Problem-Solving Skills Training for Parents of Children With Chronic Health Conditions : A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1 Xiangya School of Nursing, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 2 Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, China
- Comment & Response Enhancing the Interpretation of Continuous Outcomes and Subgroup Analyses in Systematic Reviews Jing Wu, PhD; Qi Wang, PhD; Xiaoning He, PhD JAMA Pediatrics
Question What is the association between problem-solving skills training (PSST) for parents of children with chronic health conditions and psychosocial outcomes of the parents, their children, and their families?
Findings In this systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 randomized clinical trials including 3141 parents, PSST was associated with improvements in parental problem-solving skills; decreased parental depression, distress, posttraumatic stress, and parenting stress; better quality of life for both parents and children; fewer pediatric mental problems; and less parent-child conflict.
Meaning These findings suggest that PSST should be an active component of and serve as an emerging perspective for psychosocial interventions for parents of children with chronic health conditions.
Importance Problem-solving skills training (PSST) has a demonstrated potential to improve psychosocial well-being for parents of children with chronic health conditions (CHCs), but such evidence has not been fully systematically synthesized.
Objective To evaluate the associations of PSST with parental, pediatric, and family psychosocial outcomes.
Data Sources Six English-language databases (PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library), 3 Chinese-language databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Science and Technology Journal Database, and Wanfang), gray literature, and references were searched from inception to April 30, 2023.
Study Selection Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that performed PSST for parents of children with CHCs and reported at least 1 parental, pediatric, or family psychosocial outcome were included.
Data Extraction and Synthesis Study selection, data extraction, and quality assessment were conducted independently by 2 reviewers. Data were pooled for meta-analysis using the standardized mean difference (SMD) by the inverse variance method or a random-effects model. Subgroup analyses of children- and intervention-level characteristics were conducted.
Main Outcomes and Measures The psychosocial outcomes of the parents, their children, and their families, such as problem-solving skills, negative affectivity, quality of life (QOL), and family adaptation.
Results The systematic review included 23 RCTs involving 3141 parents, and 21 of these trials were eligible for meta-analysis. There was a significant association between PSST and improvements in parental outcomes, including problem-solving skills (SMD, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.27-0.58), depression (SMD, −0.45; 95% CI, −0.66 to −0.23), distress (SMD, −0.61; 95% CI, −0.81 to −0.40), posttraumatic stress (SMD −0.39; 95% CI, −0.48 to −0.31), parenting stress (SMD, −0.62; 95% CI, −1.05 to −0.19), and QOL (SMD, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.15-0.74). For children, PSST was associated with better QOL (SMD, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.04-1.47) and fewer mental problems (SMD, −0.51; 95% CI, −0.68 to −0.34), as well as with less parent-child conflict (SMD, −0.38; 95% CI, −0.60 to −0.16). Subgroup analysis showed that PSST was more efficient for parents of children aged 10 years or younger or who were newly diagnosed with a CHC. Significant improvements in most outcomes were associated with PSST delivered online.
Conclusions and Relevance These findings suggest that PSST for parents of children with CHCs may improve the psychosocial well-being of the parents, their children, and their families. Further high-quality RCTs with longer follow-up times and that explore physical and clinical outcomes are encouraged to generate adequate evidence.
Childhood chronic health conditions (CHCs) include physical, developmental, behavioral, or emotional conditions with an expected duration of more than 3 months or the impossibility of cure. 1 Approximately 37% of children have at least 1 current or lifelong health condition. 2 The diagnosis of a childhood CHC and its prolonged treatments are profoundly unsettling experiences for children and their families, especially their parents. 3 - 5 Compared with parents of healthy children, parents of children with CHCs have reported worse mental health (more depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress), 6 - 8 significant stress and burden, 9 , 10 and a poorer quality of life (QOL). 6 , 11 Considering that parental psychosocial outcomes are strongly associated with children’s health and family adaptation, 12 - 14 interventions to improve parents’ well-being may have synergistic benefits for the whole family. Parental problem-solving skills, which are associated with parents’ well-being, are general coping skills applicable to a variety of difficult situations commonly encountered during the treatment of childhood CHCs. 15 With better problem-solving skills, parents could become more self-assured to address children’s health concerns, fully use resources to cope with stress, and collaborate to address challenges presented by daily care, thereby improving family adaptation and children’s health outcomes. 16 However, nearly one-half of parents lack problem-solving skills, especially the ability to solve daily problems related to their children’s complex treatment processes, 3 which may eventually perpetuate negative outcomes for parental and child well-being. 17 , 18
Problem-solving skills training (PSST) is an effective intervention to improve problem-solving skills and decrease negative affectivity. 19 , 20 Based on the problem-solving therapy approaches of D’Zurilla and colleagues, 20 , 21 PSST includes 2 essential components: establishing a positive problem orientation and mastering the systematic steps to solve problems. The training has long been established as being effective in adults with chronic illness and their caregivers, 22 , 23 which theoretically could have broad outcomes for parents of children with CHCs due to the long-term nature and equally multiple, intensive, and ongoing stressors across childhood CHCs. Problem-solving skills training is a cognitive-behavioral process by which parents can identify and create problem-focused strategies to buffer the outcomes of stressful events and improve coping, thus preventing episodes of negative affectivity by effectively solving various children’s disease-related problems. 15 , 21 These problem-solving strategies, while possibly differing in specifics, are beneficial in helping parents to cope with significant stressors inherent to each CHC. Preliminary studies have shown the efficacy of PSST in enhancing problem-solving skills and alleviating depression symptoms for parents, although the majority of such studies have had small sample sizes. Moreover, these studies only considered improved parental well-being, and most did not show significant changes in pediatric or family adaptation outcomes. 15 , 24 In addition, although previous reviews of PSST have explored the effectiveness of psychosocial interventions for parents of children with CHCs, they had limited specificity. 19 , 25 - 28 To address these gaps, we evaluated the associations between PSST for parents of children with CHCs and parental, pediatric, and family psychosocial outcomes.
The study protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis has been registered with PROSPERO ( CRD42023424077 ). The revised Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) guideline 29 was followed to report the findings.
A systematic search was performed across 6 English-language databases (PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, PsycINFO, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library) and 3 Chinese-language databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Science and Technology Journal Database, and Wanfang) from inception to April 30, 2023. The search strategies applied a combination of Medical Subject Heading terms and keywords, and the following constructs were used: child AND chronic health conditions AND parents AND PSST. The full search string for each database is provided in eTable 1 in Supplement 1 . Gray literature was searched using OpenGrey, Mednar, and the World Health Organization’s search portal. We also screened reference lists of included studies to identify potentially eligible articles.
The population, intervention, comparator, outcomes, and study design framework was used to define the inclusion and exclusion criteria ( Table 1 ). Eligible studies were RCTs that performed PSST for parents of children with CHCs and reported at least 1 psychosocial outcome of parents, children, or their families.
All identified articles were imported into EndNote, version 20.0 (Clarivate Analytics) to eliminate duplications. Title and abstract screening and full-text review were performed independently using the web-based software Rayyan 30 by 2 reviewers (T.Z. and W.X.). Data extraction was conducted in duplicate by the 2 reviewers and checked by another reviewer (Y.L.). Information was extracted using a predesigned worksheet, including publication details, population demographics (pediatric [age, medical condition, and illness duration] and parental [age, sex, race and ethnicity]), intervention and control group details (approach, mode, number of sessions, and duration), and psychosocial outcomes and measures.
We included only the postintervention data in the meta-analysis, as follow-up data were not reported consistently enough to achieve proper homogeneity. When both parents and children reported a psychosocial outcome of children, we prioritized extracting the parent-reported data, as they were more reliable. If multiple records were available for the same trial, we collected all relevant data and analyzed them as a single study. Corresponding authors were contacted via email to retrieve missing data.
The risk of bias for the included studies was assessed independently by 2 reviewers (T.Z. and W.X.) according to the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool, version 2.0, 31 which includes 5 domains: randomization process, deviations from intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported result. We judged the studies to be low risk, of some concern, or high risk. Additionally, the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) 32 framework was applied to assess the certainty of the evidence for all outcomes. The certainty was categorized as high, moderate, low, or very low based on the risk of bias, inconsistency, imprecision, indirectness, and publication bias. 33 , 34 Any disagreements in the study selection, data extraction, and quality assessment processes were resolved through discussion to reach a consensus, and if conflicts persisted, they were arbitrated by a third reviewer (Y.L.).
Statistical analyses were performed using Stata, version 16 software (StataCorp LLC). We conducted a meta-analysis only when 2 or more intervention studies were available with similar participants and outcomes. The psychosocial outcomes included in this review were measured by different scales; therefore, the effect size is presented as the standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% CI. 35 Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using both the χ 2 test and I 2 statistic. 36 The inverse variance method ( P ≥ .10 and I 2 <50%) or a random-effects model ( P < .10 or I 2 ≥50%) was applied based on the P and I 2 values. Subgroup analyses were performed for children’s and intervention characteristics. In addition, we conducted leave-one-out sensitivity analyses to examine the consistent associations between PSST and all identified outcomes. We also used funnel plots and Egger test to evaluate the publication bias for analyses with at least 10 studies. 37 The threshold for statistical significance was set at a 2-sided P < .05. The most recent analysis update was performed between October 10 and 20, 2023.
The initial comprehensive search yielded 2665 publications: 2641 from 9 databases and an additional 24 from gray literature and reference list review. After removing 1195 duplicates and screening 1470 titles and abstracts, 227 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Ultimately, 23 eligible RCTs 38 - 60 were included in the review, and 21 studies 38 - 42 , 44 - 48 , 50 - 60 were included in the meta-analysis ( Figure 1 ). Almost perfect agreement on the study selection was achieved (97%; κ = 0.89). 61
Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of the included 23 RCTs published between 2002 and 2021. Most were conducted in the US (21 studies 38 , 40 - 44 , 46 - 60 ), with 1 study each in Australia 45 and Jamaica. 39 Twenty-one studies 38 - 48 , 50 - 59 used a 2-arm RCT design. In addition, most studies (12 [52%]) 39 , 42 , 45 - 48 , 50 , 53 - 57 reported that a control group received usual care.
A total of 3141 parents were included in this review. Twenty-one studies 38 - 47 , 49 - 58 , 60 reported on parent sex, which totaled 2799 mothers (94%) and 185 fathers (6%), and 6 studies 38 , 39 , 42 , 53 - 55 only recruited mothers. The age of the parents ranged from 20 to 67 years, with an estimated mean (SD) age of 38.3 (9.0) years. Of 2914 parents who reported race and ethnicity, 38 , 41 - 44 , 46 - 60 569 (19%) were Hispanic, 316 (11%) were non-Hispanic Black, 1708 (59%) were non-Hispanic White, and 321 (11%) were of other race or ethnicity. The CHC diagnoses were traumatic brain injury (6 studies), 49 , 51 , 57 - 60 cancer (5 studies), 38 , 52 - 55 sickle cell disease (2 studies), 39 , 40 autism spectrum disorder (2 studies), 41 , 42 epilepsy (2 studies), 46 , 47 mental health problems (1 study), 43 inflammatory bowel disease (1 study), 44 first-episode psychosis (1 study), 45 diabetes (1 study), 48 chronic pain (1 study), 50 and asthma (1 study). 56 The mean (SD) age of the children was 10.0 (5.5) years, with the illness duration ranging from 2 weeks to 8 years.
Problem-solving skills training was confirmed as the primary focus of the intervention across the 23 RCTs, all of which were developed based on problem-solving therapy that emphasized positive problem orientation and covered the 5 core problem-solving steps (eTable 2 in Supplement 1 ). The number of PSST sessions included ranged from 2 to 21, with the duration of PSST varying from 5 weeks to 12 months. Most studies (18 [78%]) 38 - 43 , 45 - 48 , 50 , 52 - 57 , 60 involved interventions that required parents to attend face-to-face sessions, 6 of which integrated telephone-based online support. 40 , 43 , 45 - 48 In the remaining studies, 38 , 44 , 49 , 51 , 52 , 58 - 60 PSST was delivered entirely online, including via telephone sessions, web-based didactic modules, and videoconferences. Three interventions 39 - 41 were group-based, 9 interventions 38 , 42 , 43 , 45 , 50 , 52 - 55 were delivered to individuals 1 on 1, and 11 interventions 44 , 46 - 49 , 51 , 56 - 60 included both parents and children.
The methodological quality assessment resulted in 96% mutual agreement (κ = 0.93). 61 Seven studies (30%) 39 , 42 , 45 , 47 , 50 , 51 , 56 were classified as low risk, 8 studies (35%) 40 , 44 , 46 , 52 , 55 , 57 , 58 , 60 raised some concerns, and 8 studies (35%) 38 , 41 , 43 , 48 , 49 , 53 , 54 , 59 were identified as having a high risk ( Figure 2 ). Two studies 41 , 48 reported neither random sequence generation nor allocation concealment and hence were considered high risk for the randomization process. For 5 trials (22%), 38 , 49 , 53 , 54 , 59 there was a high risk of reporting bias, as the prespecified outcomes were not fully reported (eTable 3 in Supplement 1 ).
Figure 3 illustrates the meta-analysis summary for all outcomes. Forest plots and GRADE ratings are presented in eFigure 1 and eTable 4 in Supplement 1 , respectively.
Overall, PSST had a significant positive effect on problem-solving skills (12 studies including 1887 parents 38 - 42 , 46 , 50 , 52 - 55 , 58 ; SMD, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.27-0.58; I 2 = 64.28%), depression (12 studies including 2036 parents 38 , 39 , 41 , 42 , 50 - 52 , 54 , 55 , 57 , 58 , 60 ; SMD, −0.45; 95% CI, −0.66 to −0.23; I 2 = 85.29%), and distress (12 studies including 2038 parents 38 , 45 , 50 - 55 , 57 - 60 ; SMD, −0.61; 95% CI, −0.81 to −0.40; I 2 = 83.88%), all of which indicated a medium effect size and moderate certainty evidence. The studies also showed that PSST significantly alleviated posttraumatic stress (5 studies including 1469 parents 38 , 50 , 52 , 54 , 55 ; SMD, −0.39; 95% CI, −0.48 to −0.31; I 2 = 44.93%) and parenting stress (5 studies including 391 parents 39 , 41 , 42 , 45 , 50 ; SMD, −0.62; 95% CI, −1.05 to −0.19; I 2 = 76.24%). The levels of evidence for the associations of PSST with lower posttraumatic stress and parenting stress were moderate and low, respectively. The meta-analysis of parental anxiety showed a positive but nonsignificant effect. In addition, 2 studies 45 , 50 including 175 parents indicated a significant improvement in QOL among parents in the PSST group (SMD, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.15-0.74; I 2 = 0.00%), with low-certainty evidence and no heterogeneity ( Figure 3 ).
There was an association between PSST and better pediatric QOL compared with control groups (6 studies including 590 parents 40 , 44 , 47 , 48 , 56 , 60 ; SMD, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.04-1.47; I 2 = 94.90%). Data for 436 parents showed a significant association between PSST and fewer children’s mental problems (6 studies 50 , 51 , 57 - 60 ; SMD −0.51; 95% CI, −0.68 to −0.34; I 2 = 34.54%) ( Figure 3 ). We found that PSST had both medium effect sizes for improving pediatric QOL and mental health, with low- and moderate-certainty evidence, respectively, whereas no association was found for social functioning. Four RCTs 41 , 48 , 51 , 57 including 314 parents provided low-certainty evidence that PSST may reduce parent-child conflict (SMD, −0.38; 95% CI, −0.60 to −0.16), with moderate heterogeneity ( I 2 = 36.98%).
Subgroup analyses were conducted according to child- and intervention-level characteristics (eFigure 2 in Supplement 1 ). Subgroup analysis by child age indicated that PSST was associated with significant changes in parental depression (SMD, −0.39; 95% CI, −0.52 to −0.26), problem-solving skills (SMD, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.24-0.48), posttraumatic stress (SMD, −0.40; 95% CI, −0.49 to −0.31), and parenting stress (SMD, −0.43; 95% CI, −0.72 to −0.13) for the parents of children who were 10 years or younger compared with the parents of older children (>10 years). Regarding changes in parental depression and posttraumatic stress, PSST had no association for parents of children who had not been newly diagnosed with a CHC but was associated with significant changes (reductions) for parents of children with newly diagnosed CHCs (depression: SMD, −0.40 [95% CI, −0.52 to −0.28]; posttraumatic stress: SMD, −0.40 [95% CI, −0.49 to −0.31]). Furthermore, compared with other medical conditions, PSST was associated with significant improvement in all psychosocial outcomes in parents of children diagnosed with cancer.
Overall, PSST delivered online yielded larger effects on all outcomes except for parent-child conflict than only face-to-face PSST. There was a significant improvement in depression (SMD, −0.39; 95% CI, −0.52 to −0.27) and problem-solving skills (SMD, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.24-0.50) among parents who received individual-based PSST. However, the parent-child interventions showed significant changes in pediatric and family psychosocial outcomes. As for intervention duration, PSST for 5 to 8 weeks had stronger effects on reducing parental depression and parenting stress and improving problem-solving skills than PSST with durations exceeding 8 weeks. The number of sessions followed a similar pattern, with significant improvements in depression (SMD, −0.48; 95% CI, −0.67 to −0.28) and problem-solving skills (SMD, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29-0.70) among parents who underwent 8 to 12 sessions.
We assessed the publication bias for outcomes that included more than 10 trials (problem-solving skills, parental depression, and distress). Overall, the funnel plots were mostly symmetrical (eFigure 3 in Supplement 1 ); Egger tests were not significant for problem-solving skills ( z = 1.64, P = .10), depression ( z = −1.21, P = .23), and distress ( z = −0.46, P = .65), thus indicating no publication bias. The leave-one-out sensitivity analyses yielded similar results to those of the primary analyses, indicating the robustness of key outcomes (eFigure 4 in Supplement 1 ).
This systematic review and meta-analysis of 23 RCTs is the first to our knowledge to adequately examine the positive association of PSST with improved parental, pediatric, and family psychosocial outcomes. The findings show that PSST was associated with improved problem-solving skills, less negative affectivity, and better QOL for parents. Positivity and problem-solving throughout PSST is achieved by refining problems and effectively troubleshooting obstacles commonly encountered during the treatment of childhood CHCs, thus contributing to parental well-being. 15 , 41 Additionally, PSST was associated with improvements in pediatric QOL, mental health, and parent-child conflict, in accordance with previous review results that psychological interventions for parents may facilitate their ability to scaffold behavioral and emotional changes in their children and thus reduce conflicts between parents and children. 19 , 27 , 62 Our findings extend this evidence by suggesting that PSST is also associated with better psychosocial outcomes for children and families, showing promise for the use of PSST to increase the well-being of all family members and promote family adaptation.
Problem-solving skills training is an emerging and promising area of research, with 17 (74%) included studies published in 2010 or later. 39 - 47 , 49 - 52 , 55 , 56 , 59 , 60 A total of 3141 patients were included in this review, and there were sufficient sample sizes for most outcomes. Although the included RCTs were conducted in only 3 countries, which may decrease the representativeness of the results in terms of dissemination capability, the ethnic and linguistic diversity of parents across included studies showed equally positive responses to PSST when presented in various contexts. Across all psychosocial outcomes, the certainty of the evidence varied from moderate to very low. Despite the suggested effectiveness of PSST in this review, some heterogeneity remains. On one hand, the included studies used diverse definitions and instruments to measure psychosocial outcomes; on the other hand, the studies included parents of children with 11 different CHCs, all of which may have introduced clinical heterogeneity. However, the diversity may also suggest a better clinical fitness of the evidence in this review. Additionally, the current evidence on the long-term effects of PSST is limited by the small number of follow-up studies. Overall, although our review provides relatively high certainty of evidence, further research on higher-level evidence with sustained follow-up is warranted. Furthermore, it is necessary to expand the range of outcomes (eg, physical and clinical) to fully reflect the effectiveness of PSST, as most relevant studies have only reported psychosocial outcomes.
Our subgroup analysis revealed a significant decrease in negative affectivity among the parents of children aged 10 years or younger and who had been newly diagnosed with CHCs, as younger children are more reliant on their parents for daily life and disease management. 63 These findings are compatible with broader evidence supporting early PSST’s improvement of parental well-being when children are newly diagnosed. 64 A significant decrease in negative emotions was also found among parents of children with cancer compared with the parents of children with other medical conditions, possibly because cancer is a leading cause of death in children 65 and their parents may experience a substantial care burden. 8 , 66 The subgroup analysis according to intervention characteristics indicated that online intervention yielded larger effects on most outcomes than the in-person approach, which may be due to the flexibility and wider dissemination of an online approach. 52 , 67 With the rapid development of internet and mobile technologies in pediatric nursing, 68 future research could combine in-person PSST with enhanced online materials. Additionally, individual-based PSST was preferable for parental well-being, whereas the parent-child intervention favored pediatric and family psychosocial outcomes. The participants had more opportunities to receive personalized feedback in the individual-based interventions that included 1-on-1 activities 69 and to enhance family communication and cohesion in the parent-child intervention. 26 Hence, it may be worthwhile to integrate parent-child interaction when tailoring PSST according to families’ needs. Finally, PSST delivered for 5 to 8 weeks and consisting of 8 to 12 sessions had stronger associations in terms of parental psychosocial outcomes. This finding highlights the importance of shorter periods and less complexity to higher engagement in PSST, as parents’ busy schedules may interfere with long-term interventions. 70
This review had several limitations. First, we limited our search to articles in English and Chinese, which might have led to selection bias and affected the reliability of the results. Second, some of the findings must be interpreted with caution, as they were based on only 2 or 3 studies. Third, the assessment could differ across people due to the methodological subjectivity of the risk-of-bias tool and GRADE. Fourth, the psychosocial outcomes identified in this review were measured using multiple scales, and despite using SMD as recommended, the heterogeneity of most outcomes was high. Hence, the interpretability and application of the results were diminished. Finally, only the postintervention data were analyzed, as follow-up data were not reported consistently and sufficiently, and the long-term outcomes remain unclear.
The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that PSST is associated with improvements in parental psychosocial outcomes (problem-solving skills, depression, distress, posttraumatic stress, parenting stress, and QOL) as well as pediatric (QOL and mental problems) and family psychosocial outcomes (parent-child conflict). Moreover, our findings on children- and intervention-level characteristics may guide the design and delivery of future PSST by presenting information on factors associated with effectiveness. Further high-quality RCTs with longer follow-up times and that explore physical and clinical outcomes are encouraged to generate adequate evidence for PSST. In conclusion, PSST should be an active component of psychosocial interventions for parents of children with CHCs.
Accepted for Publication: October 25, 2023.
Published Online: January 2, 2024. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.5753
Open Access: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License . © 2024 Zhou T et al. JAMA Pediatrics .
Corresponding Author: Yuanhui Luo, PhD, Xiangya School of Nursing, Central South University, No. 172, Tongzipo Rd, Changsha City 410013, Hunan Province, China ( [email protected] ).
Author Contributions: Drs Zhou and Luo had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: Zhou, Luo, J. Zhang.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript: Zhou, Luo, H. Zhang.
Critical review of the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors.
Statistical analysis: Zhou, Xiong, Meng, H. Zhang.
Obtained funding: Luo.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Luo, J. Zhang.
Supervision: Luo, J. Zhang.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported.
Funding/Support: This study was supported by grant CMB-OC-22-462 from the China Medical Board (Dr Luo).
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Data Sharing Statement: See Supplement 2 .
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Problem-solving
Duration 10'
No. of mini-lessons 4
Resources Takeaway Tasks
Course overview
Do you know what the world’s best-selling toy is?
No, it’s not some new-fangled, shiny, or high-tech gadget. It’s actually the humble Rubik’s cube! That colourful 3D puzzle with problem-solving at its core. And despite the amount of competition out there, the Rubik’s cube has stood the test of time.
See, problem-solving is all about using logic and imagination to make sense of a situation and come up with an intelligent solution . And it’s vital in the business world, too.
It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions , so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
What's covered
What does “problem-solving” mean in business
What are the benefits of effective problem-solving
How to demonstrate strategies that can improve your team’s problem-solving skills

Why your teams need this course
This course is for leaders of all levels who want to encourage better problem-solving within their teams. No matter what the problem or need your business may be addressing, creative ideas and fresh approaches can often make the difference between a successful company and one that’s unable to keep up with its competitors.

Accredited by CPD
TalentLibrary is recognized as reaching the standards and benchmarks required by the Continuing Professional Development (CPD) Certification Service.
The CPD Certification Service is the world’s leading and largest independent accreditation organization for professional development courses across all industry sectors.
Other courses in this collection

The 7 Skills of Critical Thinking
Develop your critical thinking skills and keep up with the rapidly changing business world that’s full of problems to be solved.

Creative Thinking
Discover ways to hone your creative thinking skills and apply them to solving problems and addressing challenges at work.

Critical Observation
Discover how sharp critical observation skills can help you spot and prevent workplace issues, and help solve problems that arise.
View collection
Power up your training with TalentLMS & TalentLibrary
Get started
*No credit card required. Upgrade when you’re ready
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Invention Education and STEM: Perspectives and Possibilities
Systematic Review of Invention Education Research Landscape: State of the Discipline and Future Directions Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Saline High School, United States
- 2 Eastern Michigan University, United States
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Invention and innovation education and its associated practices (e.g., problem-finding, problem-defining, learning from failure, iterative problem-solving, innovation-focused curricula, collaboration, and maker spaces) are moving from the periphery to the center of education at an ever-increasing pace. Although the research and literature on invention and innovation education, collectively termed as Invention Education (IvE) in this research, is on the rise, to our knowledge no attempt has been made to systematically review the literature available on the topic. To address this gap, we identify, collect, and systematically review scientific literature on IvE. We conduct Bibliometrix-based and targeted analysis to identify the topics, sources, authors, and articles most cited, as well as prominent countries publishing IvE literature. Another objective of this research is to uncover the intellectual, conceptual, and social structures of IvE. A third objective is to identify the progress made and the challenges being faced in furthering IvE and propose future directions. Our review shows that the field has seen substantial growth, especially in recent years particularly in the USA. Research shows IvE’s importance in nurturing a well-rounded, innovative, and skilled future workforce, emphasizing creativity, critical thinking, collaboration, adaptability, and problem-solving skills. Although with a plethora of curricula and K-20 programs in USA, followed by South Korea, and China, IvE lacks unifying conceptualization, definitions and frameworks. The lack of commonly accepted terms and theoretical bases, and difficulties integrating invention into STEM coursework, are compounded by barriers like resource limitations, curriculum constraints, and the need for teacher training and support. The review underscores the need for IvE to address and dismantle inventor stereotypes and cultivate a diverse and inclusive generation of innovators. It points to the impact of gender and stereotypes on participation in IvE programs and the importance of promoting equity and access to IvE opportunities for all students. The article concludes with a discussion of challenges and future research directions to address them.
Keywords: Invention education, Innovation education, Systematic Literature Review, Bibliometrix, problem-solving
Received: 28 Aug 2023; Accepted: 01 May 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Dalela and Ahmed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Miss. Suhani L. Dalela, Saline High School, Saline, 48176, Michigan, United States
People also looked at
FREE SHIPPING on ALL Training Supplies! Use Coupon Code DELIVERY0424 at checkout! Shop Now >
New 2024 Lifeguarding Program Materials are Here! Buy More, Save More with quantity discounts available! Shop Now >
The 2024 Red Cross Lifeguarding Program updates are here! Learn more >

- 0 Your Cart is Empty < Continue Shopping
Your browser's Javascript functionality is turned off. Please turn it on so that you can experience the full capabilities of this site.
Advanced Life Support Review r.21
The Advanced Life Support (ALS) provides healthcare providers the knowledge and skills necessary to assess recognize and care for adult patients experiencing life threatening medical emergencies. Consistent with the American Red Cross Focused Updates and Guidelines 2020 the ALS course emphasizes providing high-quality care and integrating psychomotor skills with critical thinking and problem solving to achieve the best possible patient outcomes. This is an attenuated review course.
Equipment Terms & Conditions
Local classes held at convenient locations and times Participate in hands-on training Provides full certification Learn from experienced instructors
Classroom / Skills Check
- Local in-person training
- Learn from experienced instructors
- Convenient locations and times for instructor-led skills check
- Satisfies OSHA workplace safety certification requirements
Certification
Red Cross courses offer Digital Certification, an online version of a Red Cross certificate, which provides anytime, anywhere access to student training history and course certificates. Digital certificates can be viewed, printed or shared online and can be accessed anytime through your Red Cross Account. Each certificate includes a unique ID and a QR code which meets employment requirements and allows employers to easily confirm your certificate is valid. There is no need to carry your printed certificate around anymore!
Once training has been successfully completed, students may also request healthcare continuing education credit. The American Red Cross is an accredited provider of continuing education by the Commission on Accreditation for Prehospital Continuing Education. For additional information on receiving continuing education credit go to www.redcross.org/CAPCE .
It is incumbent upon the healthcare professional to verify that the accredited continuing education credit provided by the American Red Cross meets the requirements of specific professional and licensing bodies.

The content of these reviews regarding the quality and value of this course is based on data collected across all American Red Cross classes with this title and does not reflect ratings of any specific instructor or provider.

COMMENTS
Problem-solving is an essential skill in today's fast-paced and ever-changing workplace. It requires a systematic approach that incorporates effective decision-making. Throughout this course, we will learn an overarching process of identifying problems to generate potential solutions, then apply decision-making styles in order to implement and ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Learn Problem Solving or improve your skills online today. Choose from a wide range of Problem Solving courses offered from top universities and industry leaders. Our Problem Solving courses are perfect for individuals or for corporate Problem Solving training to upskill your workforce.
Learning problem-solving techniques is a must for working professionals in any field. No matter your title or job description, the ability to find the root cause of a difficult problem and formulate viable solutions is a skill that employers value. Learning the soft skills and critical thinking techniques that good problem solvers use can help ...
Purpose. PSST is designed to teach the skills involved in effective problem-solving, including skills that address practical problems faced by caregivers. Strategy. See specific description of tasks for each session in PSST provided below. Target Population. PSST was developed to provide PST to parents of children with cancer and other illnesses.
6. Solution implementation. This is what we were waiting for! All problem solving strategies have the end goal of implementing a solution and solving a problem in mind. Remember that in order for any solution to be successful, you need to help your group through all of the previous problem solving steps thoughtfully.
Explore the suite of online courses made available through edX and expand your transferable problem-solving skills. We've added 500+ learning opportunities to create one of the world's most comprehensive free-to-degree online learning platforms. Explore online problem solving courses and more. Develop new skills to advance your career with edX.
Location. Online. Length. 5 weeks. Price. CHF 1,950. Apply. Discover how to solve complex problems in three steps on IMD's Complex Problem Solving course. Boost your critical thinking capabilities and develop much-valued skills.
1. Problem Solver by SC Training (formerly EdApp) At the heart of every problem is the desire of each side to solve the problem together and come up with solutions agreeable to everyone. SC Training (formerly EdApp)'s Problem Solver teaches them how to do precisely that. This problem solving training course gives your team creative conflict ...
The Advanced Problem Solving Training is for managers, supervisors, and functional specialists to build their their problem-solving skills. The course focuses on systematic root-cause analysis and developing countermeasures to effectively contain, correct, and prevent failures from reoccurring.
Course details. You can't solve a problem unless you can get to the cause—and sometimes there's more than one. In this course, learn techniques for identifying the root cause of a problem ...
Training sessions can enhance problem-solving skills by incorporating interactive exercises, case studies, and simulations. Engaging participants in real-life scenarios encourages critical ...
Module 1 • 2 hours to complete. In this module, you will be able to apply a model for solving any problem, large or small, in a creative and collaborative way. You will also be able to identify all aspects of a problem and examine role in the problem. You will be able to reframe a goal oriented question. What's included.
Today's employers look for the following skills in new employees: to analyze a problem logically, formulate a solution, and effectively communicate with others. In this video, industry professionals share their own problem solving processes, the problem solving expectations of their employees, and an example of how a problem was solved.
Problem-solving skills defined. Problem-solving skills are skills that allow individuals to efficiently and effectively find solutions to issues. This attribute is a primary skill that employers look for in job candidates and is essential in a variety of careers. This skill is considered to be a soft skill, or an individual strength, as opposed ...
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
Define the problem. 2. Generate possible solutions. 3. Choose and implement the best solution. 4. Evaluate and follow up. Be the first to add your personal experience. 5.
Problem solving training courses can help save your organization money, time, and resources. Find course listings and member discounts at ASQ.org. ... Problem Solving. Learning how to effectively solve and prevent problems can help you save your organization time, money, and resources.
The goals of Problem-Solving Skills Training (PSST) are: Train the child to think differently about situations and behave differently in diverse situations. Help the child internalize the problem solving steps so that they are able to use them to evaluate potential solutions to problems occurring outside of therapy.
There are 4 modules in this course. This course deals directly with your ability for creativity which is a critical skill in any field. It focuses on divergent thinking, the ability to develop multiple ideas and concepts to solve problems. Through a series of creativity building exercises, short lectures, and readings, learners develop both an ...
Problem-solving skills training is an emerging and promising area of research, with 17 (74%) included studies published in 2010 or later. 39-47,49-52,55,56,59,60 A total of 3141 patients were included in this review, and there were sufficient sample sizes for most outcomes. Although the included RCTs were conducted in only 3 countries, which ...
See, problem-solving is all about using logic and imagination to make sense of a situation and come up with an intelligent solution. And it's vital in the business world, too. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
Invention and innovation education and its associated practices (e.g., problem-finding, problem-defining, learning from failure, iterative problem-solving, innovation-focused curricula, collaboration, and maker spaces) are moving from the periphery to the center of education at an ever-increasing pace. Although the research and literature on invention and innovation education, collectively ...
The critical thinking courses we offer are designed to enhance your analytical and problem-solving abilities, equipping you with essential skills for various professional fields. These courses aim to develop your logical reasoning, decision-making, and creative thinking skills, enabling you to effectively evaluate and analyze complex situations.
The Advanced Life Support (ALS) provides healthcare providers the knowledge and skills necessary to assess recognize and care for adult patients experiencing life threatening medical emergencies. Consistent with the American Red Cross Focused Updates and Guidelines 2020 the ALS course emphasizes providing high-quality care and integrating psychomotor skills with critical thinking and problem ...