- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Do you have the world's best boss? Enter them to win two tickets to Sandals!
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
How to Create a Market Research Plan

Table of Contents
While having a great idea is an important part of establishing a business, you’ll only get so far without laying the proper groundwork. To help your business take off, not only do you need to size up the competition, but you also need to identify who will buy your product, how much it will cost, the best approach to selling it and how many people will demand it.
To get answers to these questions, you’ll need a market research plan, which you can create yourself or pay a specialist to create for you. Market research plans define an existing problem and/or outline an opportunity. From there, the marketing strategy is broken down task by task. Your plan should include objectives and the methods that you’ll use to achieve those objectives, along with a time frame for completing the work.
What should a market research plan include?
A market research plan should provide a thorough examination of how your product or service will fare in a defined area. It should include:
- An examination of the current marketplace and an analysis of the need for your product or service: To know where you fit in the market, it’s important to have a broad understanding of your industry — covering everything from its annual revenue to the industry standards to the total number of businesses operating within it. Start by gathering statistical data from sources like the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics and BMI Research and consider the industry’s market size, potential customer base and how external factors such as laws, technology, world events and socioeconomic changes impact it.
- An assessment of the competition: By analyzing your competitors, you can discover strategies to fill market gaps. This involves identifying well-known competitors and noting trends they employ successfully, scrutinizing customer feedback about businesses in your sector, such as through online reviews, and understanding competitors’ product or service offerings. This knowledge can then guide the refinement of your own products or services to differentiate them from others in the market.
- Data about customers: Identify which segment of potential customers in your industry you can effectively target, considering their demographics — such as age, ethnicity, income and location and psychographics, including beliefs, values and lifestyle. Learn about the challenges your customers face in their daily lives and determine how the features and benefits of your offerings address their needs.
- The direction for your marketing in the upcoming year: Your plan should provide a clear roadmap for your marketing strategies for the next year, focusing on approaches to distinguish your brand from competitors. Develop marketing messages that resonate with and display empathy toward your target market and find ways to address customers’ needs and demonstrate value.
- Goals to be met: Outline goals your business would like to achieve and make these goals clear to all employees on your team. Create goals that are realistic and attainable while also making a meaningful impact on the business’s growth. Consider factors including your target number of products or services, the expected number of units to sell based on market size, target market behavior, pricing for each item and the cost of production and advertising.
How to create your market research plan
Doing business without having a marketing plan is like driving without directions. You may eventually reach your destination, but there will be many costly and time-consuming mistakes made along the way.
Many entrepreneurs mistakenly believe there is a big demand for their service or product but, in reality, there may not be, your prices may be too high or too low or you may be going into a business with so many restrictions that it’s almost impossible to be successful. A market research plan will help you uncover significant issues or roadblocks.
Step 1. Conduct a comprehensive situation analysis.
One of the first steps in constructing your marketing plan is to create a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis , which is used to identify your competition, to know how they operate and then to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
When developing a market research plan, it is essential that you do your homework to determine your possible customer base, to gain knowledge about the competition and to have a solid foundation for your marketing strategy.
Step 2: Develop clear marketing objectives.
In this section, describe the desired outcome for your marketing plan with realistic and attainable objectives, the targets and a clear and concise time frame. The most common way to approach this is with marketing objectives, which may include the total number of customers and the retention rate, the average volume of purchases, total market share and the proportion of your potential market that makes purchases.
Step 3: Make a financial plan.
A financial plan is essentia l for creating a solid marketing plan. The financial plan answers a range of questions that are critical components of your business, such as how much you intend to sell, what will you charge, how much will it cost to deliver your services or produce your products, how much will it cost for your basic operating expenses and how much financing will you need to operate your business.
In your business plan, be sure to describe who you are, what your business will be about, your business goals and what your inspiration was to buy, begin or grow your business.
Step 4: Determine your target audience.
Once you know what makes you stand out from your competitors and how you’ll market yourself, you should decide who to target with all this information. That’s why your market research plan should delineate your target audience. What are their demographics and how will these qualities affect your plan? How do your company’s current products and services affect which consumers you can realistically make customers? Will that change in the future? All of these questions should be answered in your plan.
Step 5: List your research methods.
Rarely does one research avenue make for a comprehensive market research plan. Instead, your plan should indicate several methods that will be used to determine the market share you can realistically obtain. This way, you get as much information as possible from as many sources as possible. The result is a more robust path toward establishing the exact footprint you desire for your company.
A good market research plan involves using more than one type of research to obtain the information you need.
Step 6: Establish a timeline.
With your plan in place, you’ll need to figure out how long your market research process will take. Project management charts are often helpful in this regard as they divide tasks and personnel over a timeframe that you have set. No matter which type of project management chart you use, try to build some flexibility into your timeframe. A two-week buffer toward the home stretch comes in handy when a process scheduled for one week takes two — that buffer will keep you on deadline.
Step 7: Acknowledge ethical concerns.
Market research always presents opportunities for ethical missteps. After all, you’ll need to obtain competitor information and sensitive financial data that may not always be readily available. Your market research plan should thus encourage your team to not take any dicey steps to obtain this information. It may be better to state, “we could not obtain this competitor information,” than to spy on the competitor or pressure their current employees for knowledge. Plus, there’s nothing wrong with simply feeling better about the final state of your plan and how you got it there.
Using a market research firm
If the thought of trying to create your own market research plan seems daunting or too time-consuming, there are plenty of other people willing to do the work for you.
You don’t need to pay thousands of dollars for assistance crafting a market research plan. University business schools often provide free resources that can assist you.
Pros of using a market research firm
As an objective third party, businesses can benefit from a market research firm’s impartial perspective and guidance, helping to shape impactful brand strategies and marketing campaigns. These firms, which can help businesses with everything from their marketing campaigns to brand launches, deliver precise results, drawing on their expertise and experience to provide in-depth insights and solutions tailored specifically to your company’s needs.
Even more, working with a market research firm can elevate a brand above the competition, as they provide credible and unique research that is highly valued by the media, enhancing brand credibility and potentially increasing website traffic, social media shares and online visibility.
Cons of using a market research firm
Although hiring a firm can provide businesses with tremendous results, certain downsides can lead a business toward the do-it-yourself route. Most notably, market research firms can be a costly expense that some businesses can’t afford. However, businesses that can allocate the funds will likely see a positive return on investment, as they are paying for the expertise and proficiency of seasoned professionals in the field.
Additionally, finding the right market research firm for your business’s needs can take some time — and even longer, ranging from weeks to months, for a market research firm to complete a plan. This lack of immediate results can be detrimental for businesses that don’t have the time to wait.
Market research firms can charge into the thousands of dollars for a market research plan, but there are ways to get help more affordably, including:
- Outline your plans carefully and spell out objectives.
- Examine as many sources as possible.
- Before paying for any information, check with librarians, small business development centers or market research professors to see if they can help you access market research data for free.
- You may think you’ll need to spend a hefty sum to create a market research plan, but there are plenty of free and low-cost sources available, especially through university business schools that will guide you through the process.
Miranda Fraraccio contributed to this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
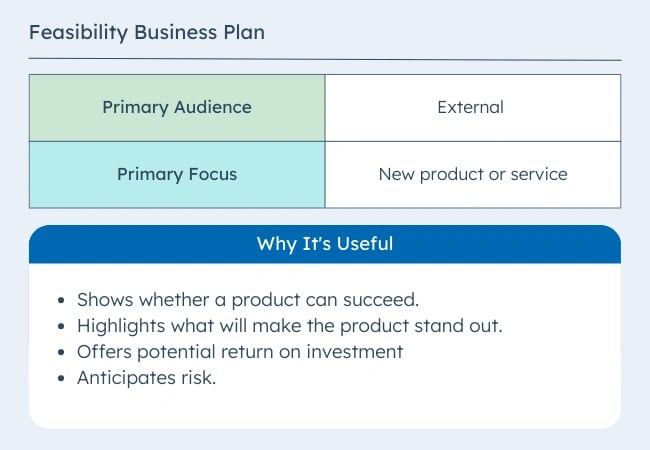
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![business plan meaning in research How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

19 Best Sample Business Plans & Examples to Help You Write Your Own

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![business plan meaning in research 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![business plan meaning in research The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Market Research for a Business Plan: How to Do It in a Day

Whether it’s your first time using market research for a business plan or this isn’t exactly your first rodeo: a quick refresh on the topic can do no harm.
If anything, it’s the smart route to take. Particularly when you consider modern-day market research data can be obtained quicker than ever – when the right tools are used.
Today, I’m going to explain exactly how to conduct market research for a business plan, and how to access that key data and juicy intel without hassle.
The importance of market research in business planning
They say knowledge is power, and where your rivals and your market are concerned, there’s nothing quite like it. By looking at things like consumer behavior, the competitive landscape , market size, and the digital strategies of others; companies at any stage in their lifecycle can stay relevant, maintain a competitive edge, set strategic direction, and experience growth. Doing periodic market research also helps businesses develop a deeper, more informed understanding of a market, its audience, and key players. If you’re seeking financial backing, doing market research is essential to show credibility and build confidence in your plans.

How to conduct market research for a business plan
Good market research for a business plan should be contextualized with information about your company, its goals, products, pricing, and financials. Sounds like a lot of work, right? Read on to learn how to conduct all the market research for a business plan you’re going to need – quickly, using the most up-to-date data there is. I’ll show you how to:
- Understand your audience
- Identify target personas
- Size your market
- Research the competition
- Discover your unique sales proposition
- Define marketing priorities
Before you start, make sure your business planning document includes the following 10 headings:

This format is considered best practice, so I’ve indicated the specific sections that each element of your market research fits into.
Sound good? Then let’s get started.
1. Understand your audience
What it is – A target audience is a social segment of people who are likely to be interested in your products or services. It’s a snapshot of your target customer base, sorted by certain characteristics. It’s also known as audience demographics and can contain data like age, gender, location, values, attitudes, behaviors, and more.
Where to use this market research in a business plan – Demographical data can help determine the size of your market, which slots into the executive summary, marketing plan, market sizing, and financial sections of the plan. What’s more, when you use it to identify groups of people to target, it can also be used in the products and services, competitive research tools , and SWOT analysis sections.
Bonus: Audience demographics can also help you develop stronger branding by choosing imagery that appeals most to your ideal customers.
How to do a quick audience analysis
Similarweb Research Intelligence gives you the ability to view almost any industry in a few seconds; you can also create a custom industry based on specific players in your market. Here’s how to see relevant audience demographics in a market. For this example, I chose the airline industry.
View typical audience relevant to your sector with gender and age distribution, along with geographical data . You can see which companies are experiencing growth and at what rate. Audience loyalty is also key to understanding how people behave, if they tend to shop around and what search terms they use to discover sites in any niche.
Read more: Learn more about how to do a demographic analysis of your market’s audience .
2. Identify target personas
What it is – An audience or target persona is a typical customer profile. It starts with audience demographics, and then zooms into a much deeper level. Most organizations develop multiple target personas, based on things like pain points, location, gender, background, occupation, influential factors, decision-making, likes, dislikes, goals, ideals, and more.

Pro Tip: If you’re in B2B, your target personas are based on the people who make purchasing decisions, not the business itself.
Where to use this market research in a business plan – Creating target personas for your business shows you know whom you’re targeting, and how to market to them. This information will help you complete market sizing, product or service overview, marketing plan, and could fit into the competitive research section too.
How to create a buyer persona in five steps
Guesswork does not equal less work – there’s no place for shortcuts here. Your success depends on developing the most accurate representation of who your customers are, and what they care about.
1. Research: If you’re already in business, use market research surveys as a tool to collect information about your customers. If you’re a startup or pre-startup, you can use a platform like Similarweb to establish a typical customer profile for your market. Don’t forget to use mobile app intelligence and website analytics in tandem to build a complete picture of your audience.
Pro Tip: Secondary market research is another good source of intel for startups. You might be able to find published surveys that relate to your products or market to learn more.
2. Analysis: Here, you’re looking to answer key questions to fill in the blanks and build a complete picture of your ideal customer. Tools like Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence, Google Analytics, and competitors’ social media channels can help you find this out. Typical questions include:
- Where is your audience coming from?
- What channels do they use to find your site?
- Do they favor access via mobile site, app, or desktop?
- What are their demographics? Think age, job, salary, location, and gender.
3. Competitive market research: This shows you what marketing channels, referral partners, and keywords are sending traffic to businesses similar to yours When you combine this data with what you learned in sections 1 + 2, you are ready to build your personas.
4. Fill in a buyer persona template: We’ve done the hard work for you. Download a pre-made template below .
Further reading: The complete guide to creating buyer personas
3. Size your market
What it is – Market sizing is a way to determine the potential size of a target market using informed estimation. This is how you find out the potential revenue and market volume applicable to your business . There are three key metrics: total addressable market (TAM), service addressable market (SAM), and service obtainable market (SOM).
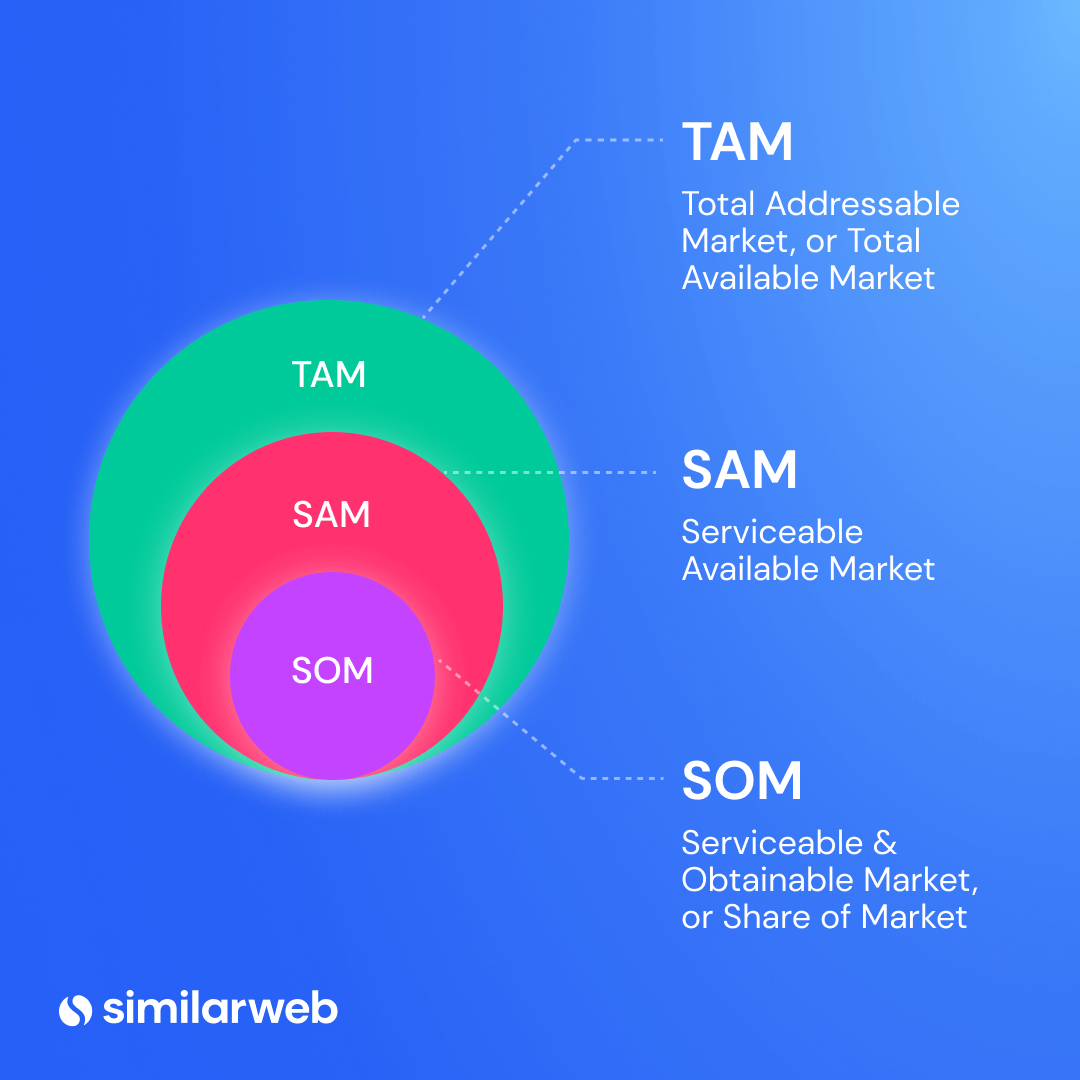
Where to use this market research in a business plan – Knowing how big the slice of the pie you’re going after is crucial. It can inform any goal setting and help with forecasting too. This data can be used in your executive summary, marketing plan, competitive research, SWOT analysis, market sizing, operations, and financial sections.
Further reading: How to do market sizing shows you how to calculate the TAM, SAM, and SOM for your business.
4. Research the competition
What it is – Competitive landscaping shows who you’re up against and how your offering stacks up vs others in your space. By evaluating rivals in-depth and looking at things like features, pricing, support, content, and additional products, you can form a detailed picture of the competition.
Where to use this market research in a business plan – The information you gain from performing a competitive analysis can transform what you offer and how you go to market. In business planning, this market research supports the executive summary, product or service overview, marketing plan, competitive research, SWOT analysis, and operation sections.
How to do competitive landscaping
Using the industry overview section of Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence, competitor research is made quick and easy. Access key metrics on an industry or specific players, then download raw data in a workable excel file or get a PNG image of charts in an instant. Most data can be downloaded via excel or as an image and included in the resource section of your plan.
Here, you can see a summary of a market, yearly growth, and top sites. A quick click to industry leaders shows you market leaders and rising stars. Select any name for a complete picture of their digital presence – use this to spot potential opportunities to gain a competitive advantage.
Read more: See how to do a competitive analysis and get a free template to help you get started.
5. Discover your unique sales proposition

What it is – Not all businesses have them, and that’s OK. A unique selling proposition (USP) is something distinctive your business offers but your rivals don’t . It can be anything that’s unique to a product, service, pricing model, or other.
Why it’s useful – Having a compelling USP helps your company stand out in a market. It can make your business more valuable to a customer vs the competition, and ultimately help you win and retain more customers.
Where to use this market research in a business plan – Your USP should be highlighted in the executive summary, the product and service overview, and the SWOT analysis.
How to find your USP
Unless you’ve developed a unique product or service, or you’re planning to sell to the market at a lower-than-average price point, you’re going to have to look for some kind of service differentiator that’ll help you stand out. In my experience, the quickest way to discover this is through competitive benchmarking. Here, I’m talking about evaluating your closest rivals to uncover things they’re not doing, or looking for gaps that your business can capitalize on.
A competitive review of their site should look at things like:
- Customer support: do they have live chat, email support, telephone support, etc.?
- Content: do they produce additional content that offers value, free resources, etc.?
- Offers: what promotions or offers do they run?
- Loyalty or referral programs: do they reward loyalty or referrals?
- Service level agreements: what commitments do they make to their customers?
- Operations: consider delivery methods, lead times, returns policy etc.
- Price promises: what satisfaction or price promises do they offer, if at all?
Go easy on yourself and create a basic template that details each point. Once complete, look for opportunities to provide something unique that nobody else currently offers.
6. Define marketing priorities
What it is – A detailed plan showing how you position and market your products or service. It should define realistic, clear, and measurable goals that articulate tactics, customer profiles, and the position of your products in the market.
Where to use this market research in a business plan – Relevant intel you uncover should inform the marketing plan first and foremost. However, it can also be used in the SWOT analysis, operation, and financial sections.
How to do it – with a market research example
Using the marketing channels within Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence, you can short-cut the lengthy (and often costly) process of trial and error when trying to decide which channels and activities work best.
Let me show you how.
Using Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence, I can hone in on any site I like, and look at key marketing intel to uncover the strategies they’re using, along with insights into what’s driving traffic, and traffic opportunities.
In less than 60 seconds, I can see easyJet’s complete online presence; its marketing and social channels, and a snapshot of every metric that matters, like referrals, organic and paid ads, keywords, and more. Expand any section to get granular data, and view insights that show exactly where key losses, gains, and opportunities exist.
You can take this a step further and add other sites into the mix. Compare sites side-by-side to see who is winning, and how they’re doing it. While this snapshot shows a comparison of a single competitor, you can compare five at any one time. What’s more, I can see industry leaders, rising players, and any relevant mobile app intelligence stats, should a company or its rivals have an app as part of their offering.
Best practice for market research data in business plans
When doing any type of market research , it’s important to use the most up-to-date data you can get your hands on. There are two key factors for data are timeliness and trustworthiness.
For any market, look for data that applies to any period over the last 12 months. With how fast markets evolve and how quickly consumer behaviors change, being able to view dynamic data is key. What’s more, the source of any data matters just as much as its age.
To emphasize the importance of using the right type of data in a business plan, here’s some timely advice from SBA commercial lending expert and VP of Commerce National Bank and Trust, Steve Fulmer. As someone who, in the past 15 years, has approved approximately $150 million in loans to SMBs; his advice is worth paying attention to.
“ For anybody doing market research for a business plan, they must cite sources. Most new or small businesses lack historical performance data, which removes substantial confidence in their plans. As a lender, we cannot support assumptions in their business plan or their projections if their data hasn’t come from a trustworthy source.”

Wrapping up…
Now you know the six ways to do market research for a business plan, it’s time to knuckle down and get started. With Similarweb, you’ve got access to all the market intel you’re going to need to conduct timely, accurate, and reliable market research. What’s more, you can return to the platform anytime to benchmark your performance , get fresh insights, and adapt your strategies to focus on growth – helping you build a sustainable business that can withstand the test of time.
How do I do market research for a business plan?
By using Digital Research Intelligence tools like Similarweb, you can quickly conduct audience research, company research, market analysis, and benchmarking from a single place. Another method is secondary market research, but this takes more time and data isn’t always up to date.
Why does a business plan need market research?
Doing market research for a business plan is the quickest and easiest way to validate a business idea and establish a clear view of the market and competitive landscape. When done right, it can show you opportunities for growth, strategies to avoid, and effective ways to market your business.
What is market research in a business plan?
Market research in business planning is one of the most powerful tools you can use to flesh out and validate your company or its products. It can tell you whether there’s a market for your product, and how big that market is – it also helps you discover industry trends, and examine the strategies of the rising stars and industry leaders in detail.
Related Posts

The Future of UK Finance: Top Trends to Watch in 2024

From AI to Buy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Retail
How to Conduct a Social Media Competitor Analysis: 5 Quick Steps

Industry Research: The Data-Backed Approach
How to Do a Competitive Analysis: A Complete Guide
How to Check Website Traffic: Analyzing the Digital Data
Wondering what similarweb can do for you.
Here are two ways you can get started with Similarweb today!

- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Business Research: Methods, Types & Examples

Content Index
Business research: Definition
Quantitative research methods, qualitative research methods, advantages of business research, disadvantages of business research, importance of business research.
Business research is a process of acquiring detailed information on all the areas of business and using such information to maximize the sales and profit of the business. Such a study helps companies determine which product/service is most profitable or in demand. In simple words, it can be stated as the acquisition of information or knowledge for professional or commercial purposes to determine opportunities and goals for a business.
Business research can be done for anything and everything. In general, when people speak about business research design , it means asking research questions to know where the money can be spent to increase sales, profits, or market share. Such research is critical to make wise and informed decisions.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
For example: A mobile company wants to launch a new model in the market. But they are not aware of what are the dimensions of a mobile that are in most demand. Hence, the company conducts business research using various methods to gather information, and the same is then evaluated, and conclusions are drawn as to what dimensions are most in demand.
This will enable the researcher to make wise decisions to position his phone at the right price in the market and hence acquire a larger market share.
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
Business research: Types and methodologies
Business research is a part of the business intelligence process. It is usually conducted to determine whether a company can succeed in a new region, to understand its competitors, or simply select a marketing approach for a product. This research can be carried out using steps in qualitative research methods or quantitative research methods.
Quantitative research methods are research methods that deal with numbers. It is a systematic empirical investigation using statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques . Such methods usually start with data collection and then proceed to statistical analysis using various methods. The following are some of the research methods used to carry out business research.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Management Framework
Survey research
Survey research is one of the most widely used methods to gather data, especially for conducting business research. Surveys involve asking various survey questions to a set of audiences through various types like online polls, online surveys, questionnaires, etc. Nowadays, most of the major corporations use this method to gather data and use it to understand the market and make appropriate business decisions.
Various types of surveys, like cross-sectional studies , which need to collect data from a set of audiences at a given point of time, or longitudinal surveys which are needed to collect data from a set of audiences across various time durations in order to understand changes in the respondents’ behavior are used to conduct survey research. With the advancement in technology, surveys can now be sent online through email or social media .
For example: A company wants to know the NPS score for their website i.e. how satisfied are people who are visiting their website. An increase in traffic to their website or the audience spending more time on a website can result in higher rankings on search engines which will enable the company to get more leads as well as increase its visibility.
Hence, the company can ask people who visit their website a few questions through an online survey to understand their opinions or gain feedback and hence make appropriate changes to the website to increase satisfaction.
Learn More: Business Survey Template
Correlational research
Correlational research is conducted to understand the relationship between two entities and what impact each one of them has on the other. Using mathematical analysis methods, correlational research enables the researcher to correlate two or more variables .
Such research can help understand patterns, relationships, trends, etc. Manipulation of one variable is possible to get the desired results as well. Generally, a conclusion cannot be drawn only on the basis of correlational research.
For example: Research can be conducted to understand the relationship between colors and gender-based audiences. Using such research and identifying the target audience, a company can choose the production of particular color products to be released in the market. This can enable the company to understand the supply and demand requirements of its products.
Causal-Comparative research
Causal-comparative research is a method based on the comparison. It is used to deduce the cause-effect relationship between variables. Sometimes also known as quasi-experimental research, it involves establishing an independent variable and analyzing the effects on the dependent variable.
In such research, data manipulation is not done; however, changes are observed in the variables or groups under the influence of the same changes. Drawing conclusions through such research is a little tricky as independent and dependent variables will always exist in a group. Hence all other parameters have to be taken into consideration before drawing any inferences from the research.
LEARN ABOUT: Causal Research
For example: Research can be conducted to analyze the effect of good educational facilities in rural areas. Such a study can be done to analyze the changes in the group of people from rural areas when they are provided with good educational facilities and before that.
Another example can be to analyze the effect of having dams and how it will affect the farmers or the production of crops in that area.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research trends
Experimental research
Experimental research is based on trying to prove a theory. Such research may be useful in business research as it can let the product company know some behavioral traits of its consumers, which can lead to more revenue. In this method, an experiment is carried out on a set of audiences to observe and later analyze their behavior when impacted by certain parameters.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
For example: Experimental research was conducted recently to understand if particular colors have an effect on consumers’ hunger. A set of the audience was then exposed to those particular colors while they were eating, and the subjects were observed. It was seen that certain colors like red or yellow increase hunger.
Hence, such research was a boon to the hospitality industry. You can see many food chains like Mcdonalds, KFC, etc., using such colors in their interiors, brands, as well as packaging.
Another example of inferences drawn from experimental research, which is used widely by most bars/pubs across the world, is that loud music in the workplace or anywhere makes a person drink more in less time. This was proven through experimental research and was a key finding for many business owners across the globe.
Online research / Literature research
Literature research is one of the oldest methods available. It is very economical, and a lot of information can be gathered using such research. Online research or literature research involves gathering information from existing documents and studies, which can be available at Libraries, annual reports, etc.
Nowadays, with the advancement in technology, such research has become even more simple and accessible to everyone. An individual can directly research online for any information that is needed, which will give him in-depth information about the topic or the organization.
Such research is used mostly by marketing and salespeople in the business sector to understand the market or their customers. Such research is carried out using existing information that is available from various sources. However, care has to be taken to validate the sources from where the information is going to be collected.
For example , a salesperson has heard a particular firm is looking for some solution that their company provides. Hence, the salesperson will first search for a decision maker from the company, investigate what department he is from, and understand what the target company is looking for and what they are into.
Using this research, he can cater his solution to be spot on when he pitches it to this client. He can also reach out to the customer directly by finding a means to communicate with him by researching online.’
LEARN ABOUT: 12 Best Tools for Researchers
Qualitative research is a method that has a high importance in business research. Qualitative research involves obtaining data through open-ended conversational means of communication. Such research enables the researcher to not only understand what the audience thinks but also why he thinks it.
In such research, in-depth information can be gathered from the subjects depending on their responses. There are various types of qualitative research methods, such as interviews, focus groups, ethnographic research, content analysis, and case study research, that are widely used.
Such methods are of very high importance in business research as they enable the researcher to understand the consumer. What motivates the consumer to buy and what does not is what will lead to higher sales, and that is the prime objective for any business.
Following are a few methods that are widely used in today’s world by most businesses.
Interviews are somewhat similar to surveys, like sometimes they may have the same types of questions used. The difference is that the respondent can answer these open-ended questions at length, and the direction of the conversation or the questions being asked can be changed depending on the response of the subject.
Such a method usually gives the researcher detailed information about the perspective or opinions of its subject. Carrying out interviews with subject matter experts can also give important information critical to some businesses.
For example: An interview was conducted by a telecom manufacturer with a group of women to understand why they have less number of female customers. After interviewing them, the researcher understood that there were fewer feminine colors in some of the models, and females preferred not to purchase them.
Such information can be critical to a business such as a telecom manufacturer and hence it can be used to increase its market share by targeting women customers by launching some feminine colors in the market.
Another example would be to interview a subject matter expert in social media marketing. Such an interview can enable a researcher to understand why certain types of social media advertising strategies work for a company and why some of them don’t.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
Focus groups
Focus groups are a set of individuals selected specifically to understand their opinions and behaviors. It is usually a small set of a group that is selected keeping in mind the parameters for their target market audience to discuss a particular product or service. Such a method enables a researcher with a larger sample than the interview or a case study while taking advantage of conversational communication.
Focus group is also one of the best examples of qualitative data in education . Nowadays, focus groups can be sent online surveys as well to collect data and answer why, what, and how questions. Such a method is very crucial to test new concepts or products before they are launched in the market.
For example: Research is conducted with a focus group to understand what dimension of screen size is preferred most by the current target market. Such a method can enable a researcher to dig deeper if the target market focuses more on the screen size, features, or colors of the phone. Using this data, a company can make wise decisions about its product line and secure a higher market share.
Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research is one of the most challenging research but can give extremely precise results. Such research is used quite rarely, as it is time-consuming and can be expensive as well. It involves the researcher adapting to the natural environment and observing its target audience to collect data. Such a method is generally used to understand cultures, challenges, or other things that can occur in that particular setting.
For example: The world-renowned show “Undercover Boss” would be an apt example of how ethnographic research can be used in businesses. In this show, the senior management of a large organization works in his own company as a regular employee to understand what improvements can be made, what is the culture in the organization, and to identify hard-working employees and reward them.
It can be seen that the researcher had to spend a good amount of time in the natural setting of the employees and adapt to their ways and processes. While observing in this setting, the researcher could find out the information he needed firsthand without losing any information or any bias and improve certain things that would impact his business.
LEARN ABOUT: Workforce Planning Model
Case study research
Case study research is one of the most important in business research. It is also used as marketing collateral by most businesses to land up more clients. Case study research is conducted to assess customer satisfaction and document the challenges that were faced and the solutions that the firm gave them.
These inferences are made to point out the benefits that the customer enjoyed for choosing their specific firm. Such research is widely used in other fields like education, social sciences, and similar. Case studies are provided by businesses to new clients to showcase their capabilities, and hence such research plays a crucial role in the business sector.
For example: A services company has provided a testing solution to one of its clients. A case study research is conducted to find out what were the challenges faced during the project, what was the scope of their work, what objective was to be achieved, and what solutions were given to tackle the challenges.
The study can end with the benefits that the company provided through its solutions, like reduced time to test batches, easy implementation or integration of the system, or even cost reduction. Such a study showcases the capability of the company, and hence it can be stated as empirical evidence of the new prospect.
Website visitor profiling/research
Website intercept surveys or website visitor profiling/research is something new that has come up and is quite helpful in the business sector. It is an innovative approach to collect direct feedback from your website visitors using surveys. In recent times a lot of business generation happens online, and hence it is important to understand the visitors of your website as they are your potential customers.
Collecting feedback is critical to any business, as without understanding a customer, no business can be successful. A company has to keep its customers satisfied and try to make them loyal customers in order to stay on top.
A website intercept survey is an online survey that allows you to target visitors to understand their intent and collect feedback to evaluate the customers’ online experience. Information like visitor intention, behavior path, and satisfaction with the overall website can be collected using this.
Depending on what information a company is looking for, multiple forms of website intercept surveys can be used to gather responses. Some of the popular ones are Pop-ups, also called Modal boxes, and on-page surveys.
For example: A prospective customer is looking for a particular product that a company is selling. Once he is directed to the website, an intercept survey will start noting his intent and path. Once the transaction has been made, a pop-up or an on-page survey is provided to the customer to rate the website.
Such research enables the researcher to put this data to good use and hence understand the customers’ intent and path and improve any parts of the website depending on the responses, which in turn would lead to satisfied customers and hence, higher revenues and market share.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Research Questions and Questionnaires
- Business research helps to identify opportunities and threats.
- It helps identify research problems , and using this information, wise decisions can be made to tackle the issue appropriately.
- It helps to understand customers better and hence can be useful to communicate better with the customers or stakeholders.
- Risks and uncertainties can be minimized by conducting business research in advance.
- Financial outcomes and investments that will be needed can be planned effectively using business research.
- Such research can help track competition in the business sector.
- Business research can enable a company to make wise decisions as to where to spend and how much.
- Business research can enable a company to stay up-to-date with the market and its trends, and appropriate innovations can be made to stay ahead in the game.
- Business research helps to measure reputation management
- Business research can be a high-cost affair
- Most of the time, business research is based on assumptions
- Business research can be time-consuming
- Business research can sometimes give you inaccurate information because of a biased population or a small focus group.
- Business research results can quickly become obsolete because of the fast-changing markets
Business research is one of the most effective ways to understand customers, the market, and competitors. Such research helps companies to understand the demand and supply of the market. Using such research will help businesses reduce costs and create solutions or products that are targeted to the demand in the market and the correct audience.
In-house business research can enable senior management to build an effective team or train or mentor when needed. Business research enables the company to track its competitors and hence can give you the upper hand to stay ahead of them.
Failures can be avoided by conducting such research as it can give the researcher an idea if the time is right to launch its product/solution and also if the audience is right. It will help understand the brand value and measure customer satisfaction which is essential to continuously innovate and meet customer demands.
This will help the company grow its revenue and market share. Business research also helps recruit ideal candidates for various roles in the company. By conducting such research, a company can carry out a SWOT analysis , i.e. understand the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. With the help of this information, wise decisions can be made to ensure business success.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research industry
Business research is the first step that any business owner needs to set up his business to survive or to excel in the market. The main reason why such research is of utmost importance is that it helps businesses to grow in terms of revenue, market share, and brand value.
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 13 A/B Testing Software for Optimizing Your Website
Apr 12, 2024

21 Best Contact Center Experience Software in 2024

Government Customer Experience: Impact on Government Service
Apr 11, 2024

Employee Engagement App: Top 11 For Workforce Improvement
Apr 10, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
There’s general research planning; then there’s an official, well-executed research plan. Whatever data-driven research project you’re gearing up for, the research plan will be your framework for execution. The plan should also be detailed and thorough, with a diligent set of criteria to formulate your research efforts. Not including these key elements in your plan can be just as harmful as having no plan at all.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project.
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement, devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes, demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:
Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews: this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies: this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting: participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups: use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies: ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys: get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing: tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing: ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project. Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty. But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings

Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
A Roadmap to Business Research
- First Online: 15 March 2023
Cite this chapter

- Merwe Oberholzer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7180-8865 3 &
- Pieter W. Buys ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5345-3594 3
482 Accesses
This chapter seeks to constitute a roadmap or framework to guide business researchers in contextualizing and planning their research efforts. A literature study was conducted to investigate the research concept, the boundary of research, and the research process’ conceptual framework. This chapter summarized research as a systematic investigation to reveal new knowledge. In guiding industry-orientated business research, it is acknowledged that management action may solve some business problems. In contrast, higher levels of organizational issues and critical reflection of business issues may require actual research .
The framework for business research is divided into four parts: the research problem, research design, empirical evidence, and conclusion. The central part of the map is the design section that organizes the philosophic approach (theoretical foundation, research philosophy, and assumptions) on the one side and the applied research methods and techniques on the other side, with the research methodology acting as a bridge between the sides. The framework constitutes a guide when embarking on the journey to solve industry-orientated business research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
AS illustrated later, it must be noted not every business problem needs to be solved by scientific research.
Note that although conceptually four distinct elements, in actuality these ProDEC elements are highly integrated.
Note that the theoretical foundation may not be of equal importance in all paradigms, e.g., the pragmatist and design sciences paradigms where a pragmatic problem solution or artifact is the primary objective.
Abutabenjeh, S., & Jaradat, R. (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36 (3), 237–258.
Article Google Scholar
Babbie, E. (2004). The practice of social research . Thomson/ Wadsworth.
Google Scholar
Brierley, J. A. (2017). The role of a pragmatist paradigm when adopting mixed methods in behavioural accounting research. International Journal of Behavioural Accounting and Finance, 6 (2), 140–154.
Collins. (2021). Definition of research . https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/research Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. (2018). Designing and conducting mixed method research . Sage.
Davis, C., & Fisher, M. (2018). Understanding Research Paradigms. JARNA, 21 (3), 21–25.
Delen, D., & Zolbanin, H. M. (2018). The analytics paradigm in business research. Journal of Business Research, 90 , 186–195.
Department of Education and Training, Western Sydney University. 2020. Research services. https://www.westernsydney.edu.au/research/researchers/preparing_a_grant_application/dest_definition_of_research . Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Elsayed, N., & Elbardan, H. (2018). Investigating the associations between executive compensation and firm performance: Agency theory or tournament theory. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 19 (2), 245–270.
FindAPhD.com. (2021). What are the criteria for a PhD? https://www.findaphd.com/advice/finding/criteria-for-phd.aspx Date of access: 18 August 2021.
Goldkuhl, G. (2011). Design research in search for a paradigm: Pragmatism is the answer. European Design Science Symposium (pp. 84–95). Springer.
Goldkuhl, G. (2020). Design Science Epistemology: A pragmatist inquiry. Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems, 32 (1), 39–79.
Hesse-Biber, S. N., & Leavy, P. (2011). The practice of qualitative research . Sage.
Henderson, K. A. (2011). Post-positivism and the pragmatics of leisure research. Leisure Sciences, 33 (4), 341–346.
Hevner, A.R., March, S.T., Park, J. & Ram, S. (2004). Design science in information systems research. MIS quarterly : 75–105.
Kessler, E. H. (Ed.). (2013). Encyclopedia of management theory . Sage.
Kankam, P. K. (2019). The use of paradigms in information research. Library & Information Science Research, 41 (2), 85–92.
Kekeya, J. (2019, November). The commonalities and differences between research paradigms. Contemporary PNG Studies: DWU Research Journal, 31 , 26–36.
Kivunja, C. (2018). Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework: A systematic review of lessons from the field. International Journal of Higher Education, 7 (6), 44–53.
Kivunja, C., & Kuyini, A. B. (2017). Understanding and applying research paradigms in educational contexts. International Journal for Higher Education, 6 (5), 26–41.
Jansen, J. D. (2020a). What is a research question and why is it important? In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 2–14.
Jansen, J. D. (2020b). Introduction to the language of research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 16–24.
Lexico.com. (2021). Oxford English and Spanish dictionary, synonyms, and Spanish to English translator . https://www.lexico.com/definition/research Date of access: 22 July 2021.
Lincoln, Y. S., Lynham, S. A., & Guba, E. G. (2011). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences, revisited. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 97–128). Sage.
Myers, M. D. (2020). Qualitative research in business & management . Sage.
Mouton, J. (1996). Understanding social research . Van Schaik.
Mouton, J. (2011). How to succeed in your master’s & doctoral studies: A South African guide and resource book. Van Schaik.
Nieuwenhuis, J. (2020). Introducing qualitative research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 56–76.
Pandey, P. & Pandey, M. M. (2015). Research methodology: Tools and techniques . Bridge Center: Buzau.
Pietersen, J. & Maree, K. (2020). Statistical analysis II: Inferential statistics. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 242–258.
Rahi, S. (2017). Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms, sampling issues and instrument development. International Journal of Economics & Management Sciences, 6 (2), 1000403.
Rehman, A. A., & Alharthi, K. (2016). An introduction to research paradigms. International Journal of Educational Investigations, 3 (8), 51–59.
Saunders, M. N. K., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research methods for business students . Pearson.
Sein, M. K., Henfridsson, O., Purao, S., Rossi, M., & Lindgren, R. (2011). Action Design Research. MIS Quarterly, 35 (1), 37–56.
Tubey, R. J., Rotich, J. K., & Bengat, J. K. (2015). Research paradigms: Theory and practice. Research on Humanities and Social Sciences, 5 (5), 224–228.
Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (2020). Introduction to Design Science Research. In: Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (eds.), Design Science Research. Cases. Progress in IS. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46781-4_1 Date of access: 21 October 2021.
Voxco. (2022). Business research: Definition, types, and methods. https://www.voxco.com/blog/business-research-definition-types-and-methods/ Date of access: 23 May 2022.
Wilson, J. (2013). Essentials of business research: A guide to doing your research project. Sage. https://www.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-binaries/59838_Wilson_ch1.pdf Date of access: 3 June 2021.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Management Cybernetics Research Entity, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Merwe Oberholzer & Pieter W. Buys
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pieter W. Buys .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pieter W. Buys
Merwe Oberholzer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Oberholzer, M., Buys, P.W. (2023). A Roadmap to Business Research. In: Buys, P.W., Oberholzer, M. (eds) Business Research . Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Published : 15 March 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-9478-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-9479-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Business plans
- Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurial business strategy
- Entrepreneurial exit strategy
- Entrepreneurial finance
- Entrepreneurial financing
Crossing the River
- Lynda M. Applegate
- March 07, 2011
Working with Your In-Laws Isn't Always a Terrible Idea
- Rob Lachenauer
- June 16, 2014
Adapt to the Market
- Scott D. Anthony
Secure Your Plan with the Right Team
- Heide Abelli
- June 22, 2015

Startups Need Relationships Before They Ask for Money
- March 03, 2016

Why the Best CEOs Are Already Thinking About Their Exits
- Stanislav Shekshnia
- October 31, 2019
Planning for Success
- Prashant Pundrik
Is "Google Will Buy Us" a Solid Business Plan?
- David S. Evans
- April 18, 2007
Keeping Your Business Plan Flexible
- September 02, 2010

When Your Business Needs a Second Growth Engine
- James Allen
- From the May–June 2022 Issue

How to Write a Great Business Plan
- William A. Sahlman
- From the July–August 1997 Issue
Gearing Up at REI
- Dennis Madsen
- Gardiner Morse
- From the May 2003 Issue
How to Write a Winning Business Plan
- Stanley R. Rich
- David E. Gumpert
- From the May 1985 Issue
Business Plans and Other Works of Fiction
- November 06, 2013
Introduction to Business Plan Development
- Harvard Business Publishing
- Steven S. Rogers
- March 12, 2014
Preparing for the Perfect Product Launch
- James P. Hackett
- From the April 2007 Issue

Forget Business Plans; Here’s How to Really Size Up a Startup
- Jim Dougherty
- October 17, 2013

When It's Time to Pivot, What's Your Story?
- Rory McDonald
- Robert Bremner
- From the September–October 2020 Issue
Build a Flexible Business Plan
- Anthony K. Tjan
- February 28, 2012
Experiment to Learn About Your Market
- Robyn Bolton
- June 25, 2015

Vitalia Franchise
- Regina E. Herzlinger
- Beatriz Munoz-Seca
- August 24, 2010
Wild Herbs Grow Tall: Mastering Structural Change in Lusatia - Lusiza (B)
- Jens Weinmann
- Martin Kupp
- Hans Ruediger Lange
- May 19, 2020
For the Love of Laundry: Comparing Organizational Forms to Scale a Social Enterprise
- Kent Walker
- Ian Stecher
- Francine Schlosser
- Megain O'Neil-Renaud
- January 19, 2018
Lease Accounting and Analysis
- David F. Hawkins
- December 02, 1999
Pemex (A): In a Free Fall?
- Noel Maurer
- Aldo Musacchio
- December 04, 2012
Mawlyngot's Tea Growers' Cooperative
- Teidorlang Lyngdoh
- Gopalakrishnan Narayanamurthy
- Sridhar Guda
- March 23, 2017
Briscola-Pizza Society: Scaling Affordable Luxury
- Gary P. Pisano
- Federica Gabrieli
- September 17, 2020
Walnut Venture Associates (A): RBS Group Investment Memorandum
- Michael J. Roberts
- September 21, 1998
Sy Friedland and JF&CS
- Jesseca Timmons
- April 01, 2017
Kapila Krishi Udyog Limited
- Kunwar Milind Singh
- Sukhpal Singh
- May 30, 2021
Growing Up in China: The Financing of BabyCare Ltd.
- Mihir A. Desai
- Mark F. Veblen
- September 22, 2003
Eli Lilly: The Evista Project
- Steven C. Wheelwright
- Matthew C. Verlinden
- March 09, 1999
The Curious Case of Dell (B)
- Marshall Sonenshine
- March 07, 2014
Slalom to the Finish: Carlyle's Exit from Moncler
- Vikas A. Aggarwal
- Michael Prahl
- Claudia Zeisberger
- June 24, 2013
J. Perez Foods (A)
- John A. Davis
- Kacie Lachapelle
- November 01, 2000
Horizon Quantum Computing
- Paul A. Gompers
- February 14, 2024
Anthology: Pivoting the Business Model
- Shikhar Ghosh
- Christopher Payton
- November 14, 2016
China's State-Owned Enterprise Reforms: Then and Now
- Rainny Shuyan Xie
- Jun Jie Yang
- Geraldine Chen
- June 07, 2017
Be Our Guest, Inc.
- Dwight B. Crane
- Penny Joseph
- April 05, 1999

How to Write a Great Business Plan (Harvard Business Review Classics)
- March 01, 2008

Wild Herbs Grow Tall: Mastering Structural Change in Lusatia - Interview with Christina Graetz (A)
Wild herbs grow tall: mastering structural change in lusatia - nagola re (a) and lusiza (b), teaching note.

Investment Management, Staged Financing, and Exits
- Geoffrey Gregson
- December 16, 2014
The Early Game: From Discovery to Development
- Robert Cooper
- May 24, 2001
Getting Started on Discovering Your Plan B--Some Guiding Principles for Your Journey to a New and Better Business Model
- John Mullins
- Randy Komisar
- September 08, 2009
Summary and Future Trends
Popular topics, partner center.
Research And Development Business Plan Template & Guidebook
Are you interested in starting your own research and development company but unsure of where to start? We can help with our sample and how-to manual for business plans for research and development. You can simply construct a business plan that details every facet of your enterprise, from market analysis and financial predictions to marketing plans and operational tactics, with the help of our comprehensive template and professional advice. Our step-by-step process makes it simple to start a prosperous research and development company, enabling you to realize your dream. With the help of our tried-and-true template and direction, you can confidently start the process of creating a successful research and development company. Start now to join the ranks of prosperous R&D business owners!

Get worry-free services and support to launch your business starting at $0 plus state fees.
- How to Start a Profitable Research And Development Business [11 Steps]
- 25 Catchy Research And Development Business Names:
- List of the Best Marketing Ideas For Your Research And Development Business:
How to Write a Research And Development Business Plan in 7 Steps:
1. describe the purpose of your research and development business..
The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your research and development business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind thinking about the customers’ problems. It also helps you identify what makes your business different from others in its industry.
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
Here is an example of a purpose mission statement for a research and development business:
Our mission at the Research and Development company is to drive innovation and advance the state of the art in our field. We are committed to conducting rigorous and cutting-edge research, and to developing new technologies and products that have the potential to make a positive impact on the world. We strive to foster a collaborative and creative environment where our researchers can thrive and make meaningful contributions. We are dedicated to responsible and ethical practices, and to sharing our knowledge and findings with the broader scientific community. Through our passion for discovery and our pursuit of excellence, we aim to be a leader in research and development.

2. Products & Services Offered by Your Research And Development Business.
The next step is to outline your products and services for your research and development business.
When you think about the products and services that you offer, it's helpful to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is my business?
- What are the products and/or services that I offer?
- Why am I offering these particular products and/or services?
- How do I differentiate myself from competitors with similar offerings?
- How will I market my products and services?
You may want to do a comparison of your business plan against those of other competitors in the area, or even with online reviews. This way, you can find out what people like about them and what they don’t like, so that you can either improve upon their offerings or avoid doing so altogether.

3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
If you don't have a marketing plan for your research and development business, it's time to write one. Your marketing plan should be part of your business plan and be a roadmap to your goals.
A good marketing plan for your research and development business includes the following elements:
Target market
- Who is your target market?
- What do these customers have in common?
- How many of them are there?
- How can you best reach them with your message or product?
Customer base
- Who are your current customers?
- Where did they come from (i.e., referrals)?
- How can their experience with your research and development business help make them repeat customers, consumers, visitors, subscribers, or advocates for other people in their network or industry who might also benefit from using this service, product, or brand?
Product or service description
- How does it work, what features does it have, and what are its benefits?
- Can anyone use this product or service regardless of age or gender?
- Can anyone visually see themselves using this product or service?
- How will they feel when they do so? If so, how long will the feeling last after purchasing (or trying) the product/service for the first time?
Competitive analysis
- Which companies are competing with yours today (and why)?
- Which ones may enter into competition with yours tomorrow if they find out about it now through word-of-mouth advertising; social media networks; friends' recommendations; etc.)
- What specific advantages does each competitor offer over yours currently?
Marketing channels
- Which marketing channel do you intend to leverage to attract new customers?
- What is your estimated marketing budget needed?
- What is the projected cost to acquire a new customer?
- How many of your customers do you instead will return?
Form an LLC in your state!

4. Write Your Operational Plan.
Next, you'll need to build your operational plan. This section describes the type of business you'll be running, and includes the steps involved in your operations.
In it, you should list:
- The equipment and facilities needed
- Who will be involved in the business (employees, contractors)
- Financial requirements for each step
- Milestones & KPIs
- Location of your business
- Zoning & permits required for the business
What equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a research and development business?
Research and development businesses provide services to help organizations create, develop, and improve products, processes, and systems. The equipment and supplies needed to run a research and development business can vary depending on the specific services offered and the preferences of the business, but may include:
- Laboratory equipment, such as microscopes, centrifuges, and beakers, to conduct experiments and tests
- Computer equipment, such as computers, laptops, and tablets, to manage data and communicate with clients
- Software, such as data analysis and modeling programs, to analyze and interpret results
- Protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats, to protect against potential hazards
- Supplies, such as chemicals, reagents, and consumables, to conduct experiments and tests
In addition to the equipment and supplies needed to run a research and development business, it is important to obtain any necessary permits and licenses that may be required by local regulations. These permits and licenses may vary depending on the location of the business and the specific services offered.
In summary, the equipment, supplies, and permits needed to run a research and development business can include laboratory equipment, computer equipment, software, protective equipment, and supplies, as well as any necessary licenses and permits.
5. Management & Organization of Your Research And Development Business.
The second part of your research and development business plan is to develop a management and organization section.
This section will cover all of the following:
- How many employees you need in order to run your research and development business. This should include the roles they will play (for example, one person may be responsible for managing administrative duties while another might be in charge of customer service).
- The structure of your management team. The higher-ups like yourself should be able to delegate tasks through lower-level managers who are directly responsible for their given department (inventory and sales, etc.).
- How you’re going to make sure that everyone on board is doing their job well. You’ll want check-ins with employees regularly so they have time to ask questions or voice concerns if needed; this also gives you time to offer support where necessary while staying informed on how things are going within individual departments too!
6. Research And Development Business Startup Expenses & Captial Needed.
This section should be broken down by month and year. If you are still in the planning stage of your business, it may be helpful to estimate how much money will be needed each month until you reach profitability.
Typically, expenses for your business can be broken into a few basic categories:
Startup Costs
Startup costs are typically the first expenses you will incur when beginning an enterprise. These include legal fees, accounting expenses, and other costs associated with getting your business off the ground. The amount of money needed to start a research and development business varies based on many different variables, but below are a few different types of startup costs for a research and development business.
Running & Operating Costs
Running costs refer to ongoing expenses related directly with operating your business over time like electricity bills or salaries paid out each month. These types of expenses will vary greatly depending on multiple variables such as location, team size, utility costs, etc.
Marketing & Sales Expenses
You should include any costs associated with marketing and sales, such as advertising and promotions, website design or maintenance. Also, consider any additional expenses that may be incurred if you decide to launch a new product or service line. For example, if your research and development business has an existing website that needs an upgrade in order to sell more products or services, then this should be listed here.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
A financial plan is an important part of any business plan, as it outlines how the business will generate revenue and profit, and how it will use that profit to grow and sustain itself. To devise a financial plan for your research and development business, you will need to consider a number of factors, including your start-up costs, operating costs, projected revenue, and expenses.
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your research and development business plan:
- Determine your start-up costs: This will include the cost of purchasing or leasing the space where you will operate your business, as well as the cost of buying or leasing any equipment or supplies that you need to start the business.
- Estimate your operating costs: Operating costs will include utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water, as well as labor costs for employees, if any, and the cost of purchasing any materials or supplies that you will need to run your business.
- Project your revenue: To project your revenue, you will need to consider the number of customers you expect to have and the average amount they will spend on each visit. You can use this information to estimate how much money you will make from selling your products or services.
- Estimate your expenses: In addition to your operating costs, you will need to consider other expenses, such as insurance, marketing, and maintenance. You will also need to set aside money for taxes and other fees.
- Create a budget: Once you have estimated your start-up costs, operating costs, revenue, and expenses, you can use this information to create a budget for your business. This will help you to see how much money you will need to start the business, and how much profit you can expect to make.
- Develop a plan for using your profit: Finally, you will need to decide how you will use your profit to grow and sustain your business. This might include investing in new equipment, expanding the business, or saving for a rainy day.
Frequently Asked Questions About Research And Development Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a research and development business.
A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve those goals. It is important to have a business plan for your research and development business because it helps to focus the efforts of the company, communicate the business's goals and objectives to potential investors, and provide a roadmap for the business to follow. Additionally, a business plan can be used to help secure funding from investors or lenders, who will want to see that the business has a solid plan in place before they provide funding.
How to write a business plan for your research and development business?)
To build a business plan for your research and development business, start by researching your industry, competitors, and target market. Use this information to define your business's goals and objectives, as well as the strategies and tactics that you will use to achieve those goals. Next, create a financial plan that outlines your projected income, expenses, and profit. This should include a projected income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. Once you have all of this information, you can use it to create a comprehensive business plan that outlines the goals and objectives of your business, as well as the strategies and tactics that you will use to achieve those goals. A well-written research and development business plan contains the following sections: Purpose, Products & Services, Marketing Plan (including Marketing Strategy), Operations/Management Plan (including Operations/Management Strategy), Financial Plan (including Financial Forecasts), and Appendixes.
Can you write a research and development business plan yourself?
Yes, you can write a research and development business plan yourself. Writing a business plan is a valuable exercise that can help you clarify your business idea, identify potential challenges and opportunities, and develop a roadmap for success. While there are many resources and templates available to help you write a business plan, the process of creating one is ultimately up to you.
Related Business Plans

Home Inventory Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Inspection Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Decor Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Health And Wellness Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hauling Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hardware Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handyman Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hair Extension Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handbag Business Plan Template & Guidebook
I'm Nick, co-founder of newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
Through meticulous research and firsthand experience, I uncover the essential steps, software, tools, and costs associated with launching and maintaining a successful business. By demystifying the complexities of entrepreneurship, I provide the guidance and support needed for others to embark on their journey with confidence.
From assessing market viability and formulating business plans to selecting the right technology and navigating the financial landscape, I am dedicated to helping fellow entrepreneurs overcome challenges and unlock their full potential. As a steadfast advocate for small business success, my mission is to pave the way for a new generation of innovative and driven entrepreneurs who are ready to make their mark on the world.
- UNIVERSITY HOME
- Archives & Special Collections
- Art Collection
- Center for English Language Studies
- University Learning Center

Business Plan Research
- Company Research
- Industry Research
Sample Business Plans
- Business Case Studies This link opens in a new window
- Additional Resources
- Copyright & Fair Use This link opens in a new window
- LIBRARY RESOURCES
- OTHER RESOURCES
- Business Plans Handbook Actual business plans compiled by, and aimed at, entrepreneurs seeking funding for small businesses. Presents sample plans taken from businesses in the manufacturing, retail and service industries which serve as examples of how to approach, structure and compose business plans.
- ProQuest Central This link opens in a new window ProQuest Central brings together many of our most used databases to create the most comprehensive, diverse, and relevant multidisciplinary research database available. It provides access to databases across all major subject areas, including business, health and medical, social sciences, arts and humanities, education, science and technology, and religion. The collection includes thousands of full-text scholarly journals, newspapers, magazines, dissertations, working papers, and market reports all together on a powerful, user-friendly platform.
- BEOnline - Business Plans and Forms This provides you with resources regarding all aspects of business planning.
- BRS Assists This resource provides you with sources to build your business plan and it was created by staff of the Business Reference Section.
- A Guide to Writing Your First Business Plan
- How to Write the Perfect Business Plan A Useful Step-by-Step Guide for the Perfect Business Plan. Provided by BusinessStudent.com.
- << Previous: Industry Research
- Next: Business Case Studies >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 9:26 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.newschool.edu/businessplanresearch
Libraries, Collections, & Academic Services
- Archives & Special Collections
University Resources
- MyNewSchool
- Course Catalog
- Resources and Services A-Z
- Academic Calendar
- Libraries and Archives
- Faculty and Staff Directory
- Your Right to Know
- Harrassment, Discrimination & Title IX
- Shop The New Store
- Working at The New School
- Parsons School of Design
- Eugene Lang College of Liberal Arts
- College of Performing Arts
- The New School for Social Research
- Schools of Public Engagement
- Parsons Paris
- Continuing and Professional Education
Copyright © 2023 The New School
- Privacy Notice
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
8 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
A business plan template can be an excellent tool to simplify the creation of your business plan.
The pre-set structure helps you organize ideas, covers all critical business information, and saves you time and effort on formatting.
The only issue? There are SO many free business plan templates out there.
So, which ones are actually worth using?
To help remove the guesswork, I’ve rounded up some of the best business plan templates you can access right now.
These are listed in no particular order, and each has its benefits and drawbacks.
What to look for in a business plan template
Not all business plan templates are created equal. As you weigh your options and decide which template(s) you’ll use, be sure to review them with the following criteria in mind:
- Easy to edit: A template should save you time. That won’t be the case if you have to fuss around figuring out how to edit the document, or even worse, it doesn’t allow you to edit at all.
- Contains the right sections: A good template should cover all essential sections of a business plan , including the executive summary, product/service description, market/competitive analysis, marketing and sales plan, operations, milestones, and financial projections.
- Provides guidance: You should be able to trust that the information in a template is accurate. That means the organization or person who created the template is highly credible, known for producing useful resources, and ideally has some entrepreneurial experience.
- Software compatibility: Lastly, you want any template to be compatible with the software platforms you use. More than likely, this means it’s available in Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PDF format at a minimum.
1. Bplans — A plan with expert guidance

Since you’re already on Bplans, I have to first mention the templates that we have available.
Our traditional and one-page templates were created by entrepreneurs and business owners with over 80 years of collective planning experience. We revisit and update them annually to ensure they are approachable, thorough, and aligned with our team’s evolving best practices.
The templates, available in Word, PDF, or Google Doc formats, include in-depth guidance on what to include in each section, expert tips, and links to additional resources.
Plus, we have over 550 real-world sample business plans you can use for guidance when filling out your template.
Download: Traditional lender-ready business plan template or a simple one-page plan template .
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. SBA — Introduction to business plans

The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two different business plan templates along with a short planning guide.
While not incredibly in-depth, it’s enough to help you understand how traditional and lean plans are structured and what information needs to be covered. The templates themselves are more like examples, providing you with a finished product to reference as you write your plan.
The key benefit of using these templates is that they were created by the SBA. While they may provide less guidance, you can be assured that the information and structure meet their expectations.
Explore: The SBA’s planning guide and free templates
3. SCORE — Planning workbook

SCORE’s template is more like a workbook. It includes exercises after each section to help you get your ideas down and turn them into a structured plan.
The market research worksheets are especially useful. They provide a clear framework for identifying your target market and analyzing competitors from multiple angles. Plus, they give you an easy way to document all the information you’re collecting.
You will likely have to remove the exercises in this template to make it investor-ready. But it can be worth it if you’re struggling to get past a blank page and want a more interactive planning method.
Download: SCORE’s business plan template
4. PandaDoc — A template with fillable forms

PandaDoc’s library offers a variety of industry-specific business plan templates that feature a modern design flair and concise instructions.
These templates are designed for sharing. They include fillable fields and sections for non-disclosure agreements, which may be necessary when sending a plan to investors.
But the real benefit is their compatibility with PandaDoc’s platform. Yes, they are free, but if you’re a PandaDoc subscriber, you’ll have far more customization options.
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry.
Explore: PandaDoc’s business plan template library
5. Canva — Pitch with your plan

Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool. It offers a diverse array of templates built by their in-house team and the larger creative community, meaning the number of options constantly grows.
You will need to verify that the information in the template you choose matches the standard structure of a traditional business plan.
You should do this with any template, but it’s especially important with any tool that accepts community submissions. While they are likely reviewed and approved, there may still be errors.
Remember, you can only edit these templates within Canva. Luckily, you only need a free subscription, and you may just miss out on some of the visual assets being used.
To get the most value, it may be best to create a more traditional planning document and transfer that information into Canva.
Explore: Canva’s business plan gallery
6. ClickUp — The collaborative template

Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp’s is the most approachable.
Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
There’s also a completed sample plan (structured like an expanded one-page plan) for you to reference and see how the more traditional document can connect to the product management features. You can set goals, target dates, leave comments, and even assign tasks to someone else on your team.
These features are limited to the ClickUp platform and will not be useful for everyone. They will likely get in the way of writing a plan you can easily share with lenders or investors.
But this is a great option if you’re looking for a template that makes internal collaboration more fluid and keeps all your information in one place.
Sign Up: Get a free trial of ClickUp and explore their template library
7. Smartsheet — A wide variety of templates

I’m including Smartsheet’s library of templates on this list because of the sheer number of options they provide.
They have a simple business plan template, a one-page plan, a fill-in-the-blank template, a plan outline, a plan grading rubric, and even an Excel-built project plan. All are perfectly usable and vary in visual style, depth of instructions, and the available format.
Honestly, the only drawback (which is also the core benefit) is that the amount of templates can be overwhelming. If you’re already uncertain which plan option is right for you, the lengthy list they provide may not provide much clarity.
At the same time, it can be a great resource if you want a one-stop shop to view multiple plan types.
Explore: Smartsheet’s business plan template library
8. ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan

I’m adding ReferralRock’s template to this list due to its specificity.
It’s not your standard business plan template. The plan is tailored with specific sections and guidance around launching an affiliate marketing business.
Most of the template is dedicated to defining how to choose affiliates, set commissions, create legal agreements, and track performance.
So, if you plan on starting an affiliate marketing business or program, this template will provide more specific guidance. Just know that you will likely need to reference additional resources when writing the non-industry sections of your plan.
Download: ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan template
Does it matter what business plan template you use?
The short answer is no. As long as the structure is correct, it saves you time, and it helps you write your business plan , then any template will work.
What it ultimately comes down to, is what sort of value you hope to get from the template.
- Do you need more guidance?
- A simple way to structure your plan?
- An option that works with a specific tool?
- A way to make your plan more visually interesting?
Hopefully, this list has helped you hone in on an option that meets one (or several) of these needs. Still, it may be worth downloading a few of these templates to determine the right fit.
And really, what matters most is that you spend time writing a business plan . It will help you avoid early mistakes, determine if you have a viable business, and fully consider what it will take to get up and running.
If you need additional guidance, check out our library of planning resources . We cover everything from plan formats , to how to write a business plan, and even how to use it as a management tool .
If you don’t want to waste time researching other templates, you can download our one-page or traditional business plan template and jump right into the planning process.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Qualities of a good template
- ReferralRock
- Does the template matter?
Related Articles

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

10 Min. Read
14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

6 Min. Read
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained

When Should You Write a Business Plan?
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It may not be as specific to your market as the big-budget stuff, but it can get you the information you need to work out a solid understanding of your market. First Steps: Market-Research ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
A market research plan will help you uncover significant issues or roadblocks. Step 1. Conduct a comprehensive situation analysis. One of the first steps in constructing your marketing plan is to create a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis, which is used to identify your competition, to know how they operate and ...
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement.
Think age, job, salary, location, and gender. 3. Competitive market research: This shows you what marketing channels, referral partners, and keywords are sending traffic to businesses similar to yours When you combine this data with what you learned in sections 1 + 2, you are ready to build your personas. 4.
Business research: Definition. Business research is a process of acquiring detailed information on all the areas of business and using such information to maximize the sales and profit of the business. Such a study helps companies determine which product/service is most profitable or in demand. In simple words, it can be stated as the acquisition of information or knowledge for professional or ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Plan several rounds of edits or have someone else review it. Keep everything in the context of your business. Make sure all the statistics and data you use in your market analysis relate back to your business. Your focus should be on how you are uniquely positioned to meet the needs of the target market.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Start by defining your project's purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language. Thinking about the project's purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities.
Business research refers to the process of conducting research to assist with the launch or operation of a company. Business research involves gathering data and using it to make business predictions, plans or decisions. It may involve analyzing market trends, collecting consumer information or comparing competitors within the industry.
The business plan should clearly and concisely define the mission, val-ues, strategy, measurable objectives, and key results the owner expects. It is important to set aside enough time to formulate the plan. Experts recommend starting the planning pro-cess at least 6 months before initiating a new business.
Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed. Summary. When asked about an opponent's plan for their impending fight, former world heavyweight champion Mike Tyson ...
Abstract. This chapter seeks to constitute a roadmap or framework to guide business researchers in contextualizing and planning their research efforts. A literature study was conducted to investigate the research concept, the boundary of research, and the research process' conceptual framework. This chapter summarized research as a systematic ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Business plans Magazine Article. Stanley R. Rich. David E. Gumpert. The business plan admits the entrepreneur to the investment process. Without a plan furnished in advance, many investor groups ...
How to Write a Research And Development Business Plan in 7 Steps: 1. Describe the Purpose of Your Research And Development Business. The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your research and development business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will ...
Sample Business Plans. Actual business plans compiled by, and aimed at, entrepreneurs seeking funding for small businesses. Presents sample plans taken from businesses in the manufacturing, retail and service industries which serve as examples of how to approach, structure and compose business plans. The ABI/INFORM Collection features thousands ...
Clawback. v. t. e. A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it ...
Introduction. Theoretical aspects and modern trends of the enterprise business planning are considered in the article. The role of the enterprise business planning and the business plan is defined.
Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp's is the most approachable. Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
management and its main functions, with the aim of contextualizing the use of business plans. One of the most common definitions of management is the following: Management is the process of ...