AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

Free Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis , and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup or small business, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
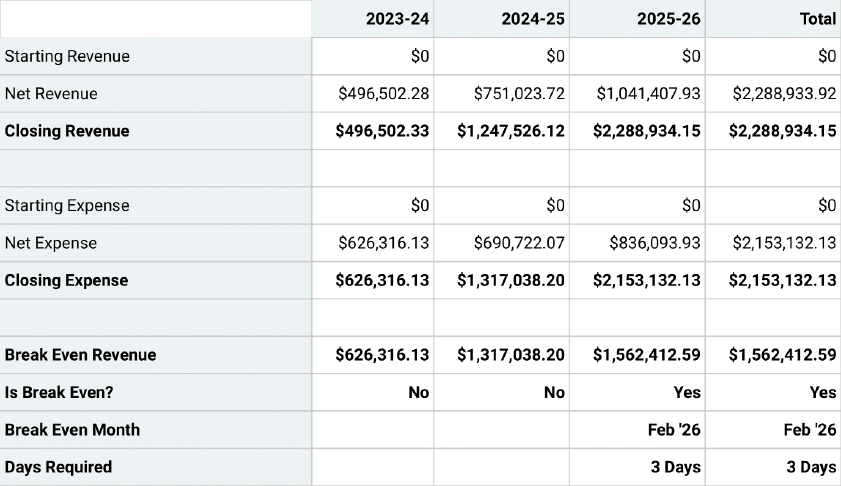
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup or small business.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your small business and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan for your business plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.
6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
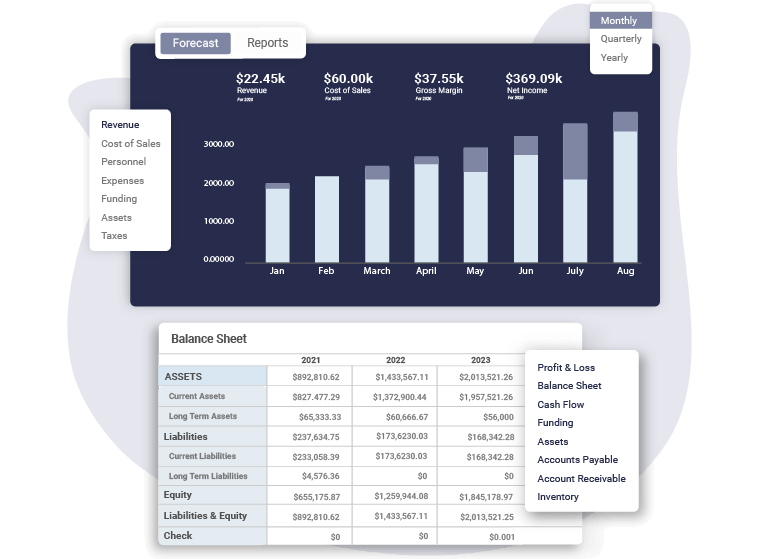
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
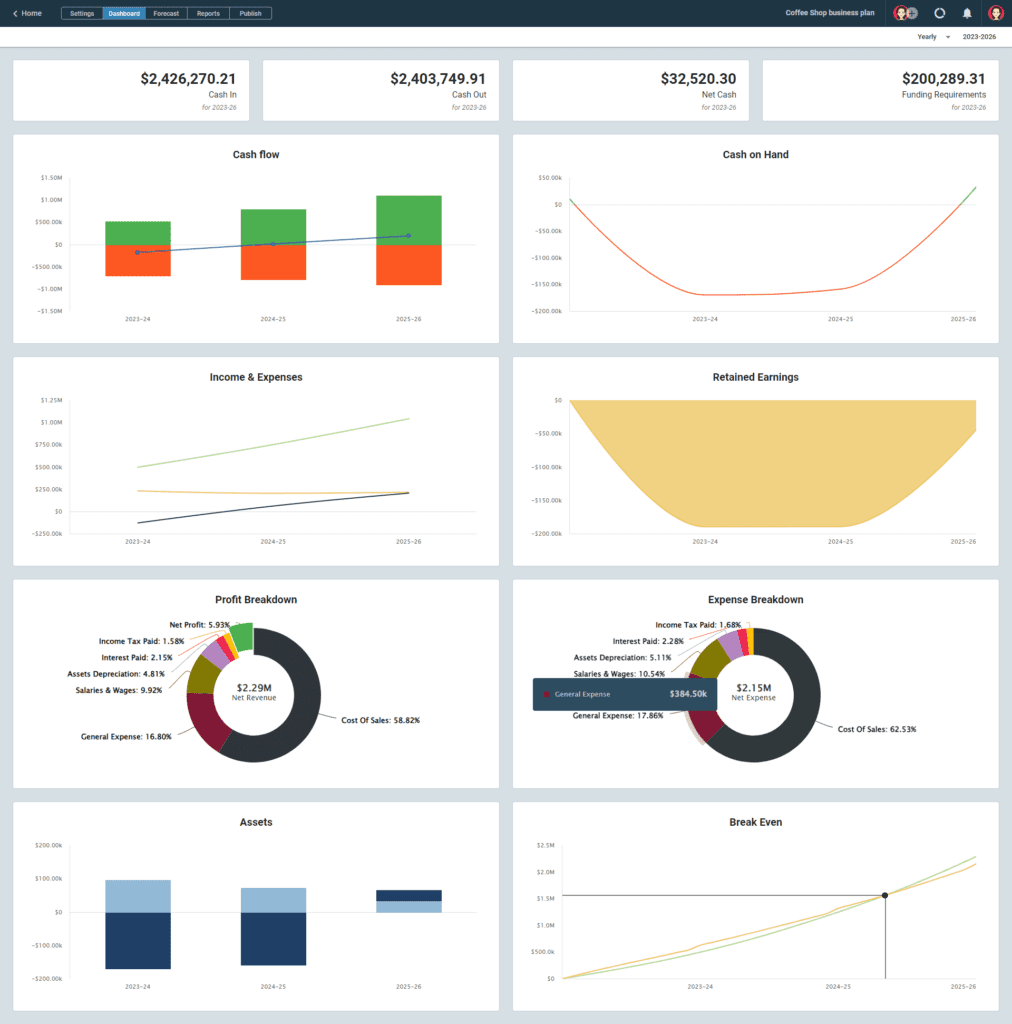
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan for your small business, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
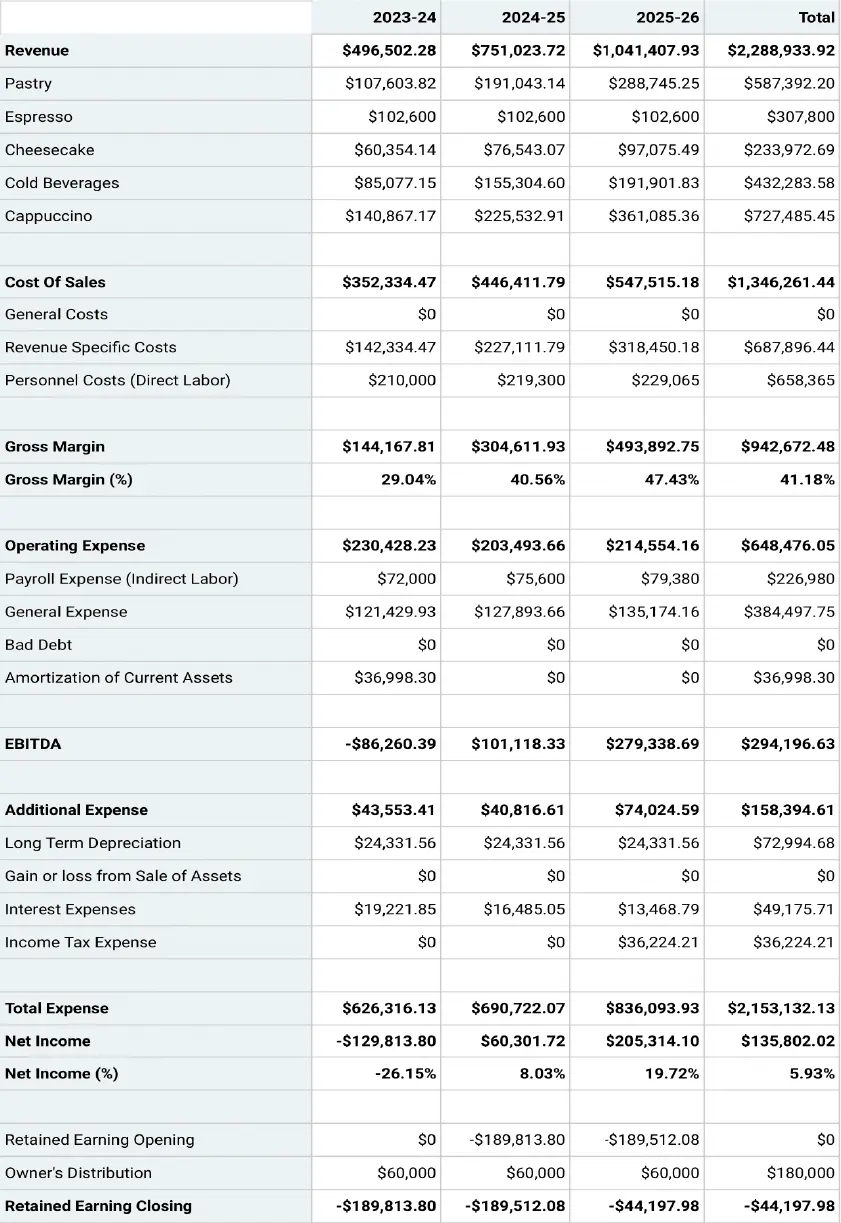
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
Projected Balance Sheet
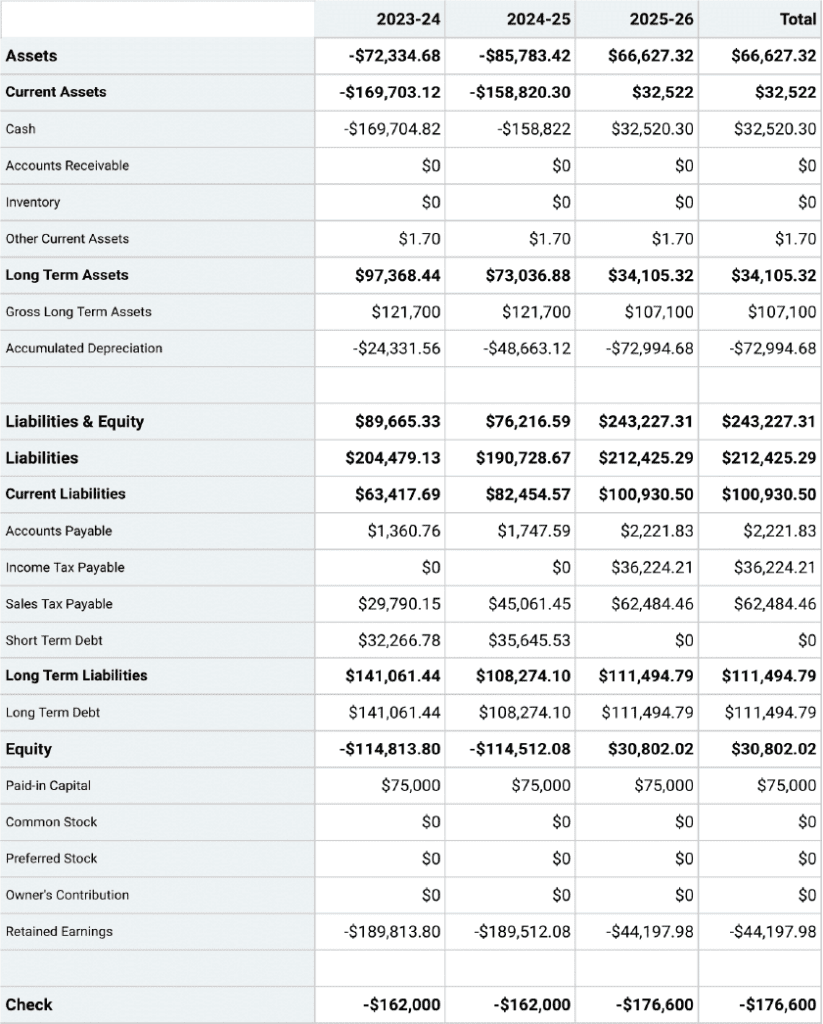
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
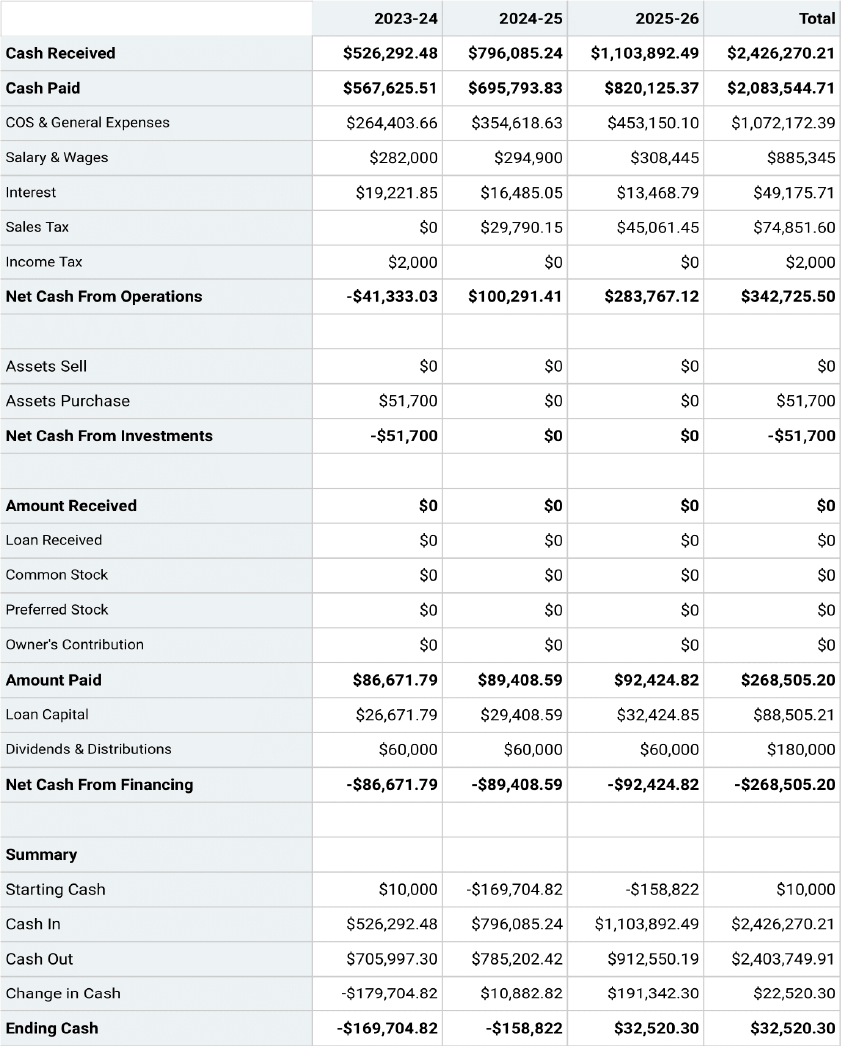
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
Break Even Analysis
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or small businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, business plan financials: 3 statements to include.
The finance section of your business plan is essential to securing investors and determining whether your idea is even viable. Here's what to include.

If your business plan is the blueprint of how to run your company, the financials section is the key to making it happen. The finance section of your business plan is essential to determining whether your idea is even viable in the long term. It’s also necessary to convince investors of this viability and subsequently secure the type and amount of funding you need. Here’s what to include in your business plan financials.
[Read: How to Write a One-Page Business Plan ]
What are business plan financials?
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you’ll need to plan for your business’s future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any funding requests in this part of your business plan.
Business plan financials are vital because they allow you to budget for existing or future expenses, as well as forecast your business’s future finances. A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Sections to include in your business plan financials
Here are the three statements to include in the finance section of your business plan:
Profit and loss statement
A profit and loss statement , also known as an income statement, identifies your business’s revenue (profit) and expenses (loss). This document describes your company’s overall financial health in a given time period. While profit and loss statements are typically prepared quarterly, you will need to do so at least annually before filing your business tax return with the IRS.
Common items to include on a profit and loss statement :
- Revenue: total sales and refunds, including any money gained from selling property or equipment.
- Expenditures: total expenses.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): the cost of making products, including materials and time.
- Gross margin: revenue minus COGS.
- Operational expenditures (OPEX): the cost of running your business, including paying employees, rent, equipment and travel expenses.
- Depreciation: any loss of value over time, such as with equipment.
- Earnings before tax (EBT): revenue minus COGS, OPEX, interest, loan payments and depreciation.
- Profit: revenue minus all of your expenses.
Businesses that have not yet started should provide projected income statements in their financials section. Currently operational businesses should include past and present income statements, in addition to any future projections.
[Read: Top Small Business Planning Strategies ]
A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your company’s finances, allowing you to keep track of earnings and expenses. It includes what your business owns (assets) versus what it owes (liabilities), as well as how much your business is currently worth (equity).
On the assets side of your balance sheet, you will have three subsections: current assets, fixed assets and other assets. Current assets include cash or its equivalent value, while fixed assets refer to long-term investments like equipment or buildings. Any assets that do not fall within these categories, such as patents and copyrights, can be classified as other assets.
On the liabilities side of your balance sheet, include a total of what your business owes. These can be broken down into two parts: current liabilities (amounts to be paid within a year) and long-term liabilities (amounts due for longer than a year, including mortgages and employee benefits).
Once you’ve calculated your assets and liabilities, you can determine your business’s net worth, also known as equity. This can be calculated by subtracting what you owe from what you own, or assets minus liabilities.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement shows the exact amount of money coming into your business (inflow) and going out of it (outflow). Each cost incurred or amount earned should be documented on its own line, and categorized into one of the following three categories: operating activities, investment activities and financing activities. These three categories can all have inflow and outflow activities.
Operating activities involve any ongoing expenses necessary for day-to-day operations; these are likely to make up the majority of your cash flow statement. Investment activities, on the other hand, cover any long-term payments that are needed to start and run your business. Finally, financing activities include the money you’ve used to fund your business venture, including transactions with creditors or funders.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
More tips for your startup
How to choose a legal entity for your startup, 5 steps to use social media to launch your business, 5 alternatives to writing a traditional business plan.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan
By Andy Marker | July 29, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up expert-tested financial templates for your business plan, all of which are free to download in Excel, Google Sheets, and PDF formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find the essential financial statement templates, including income statement templates , cash flow statement templates , and balance sheet templates . Plus, we cover the key elements of the financial section of a business plan .
Financial Plan Templates
Download and prepare these financial plan templates to include in your business plan. Use historical data and future projections to produce an overview of the financial health of your organization to support your business plan and gain buy-in from stakeholders
Business Financial Plan Template
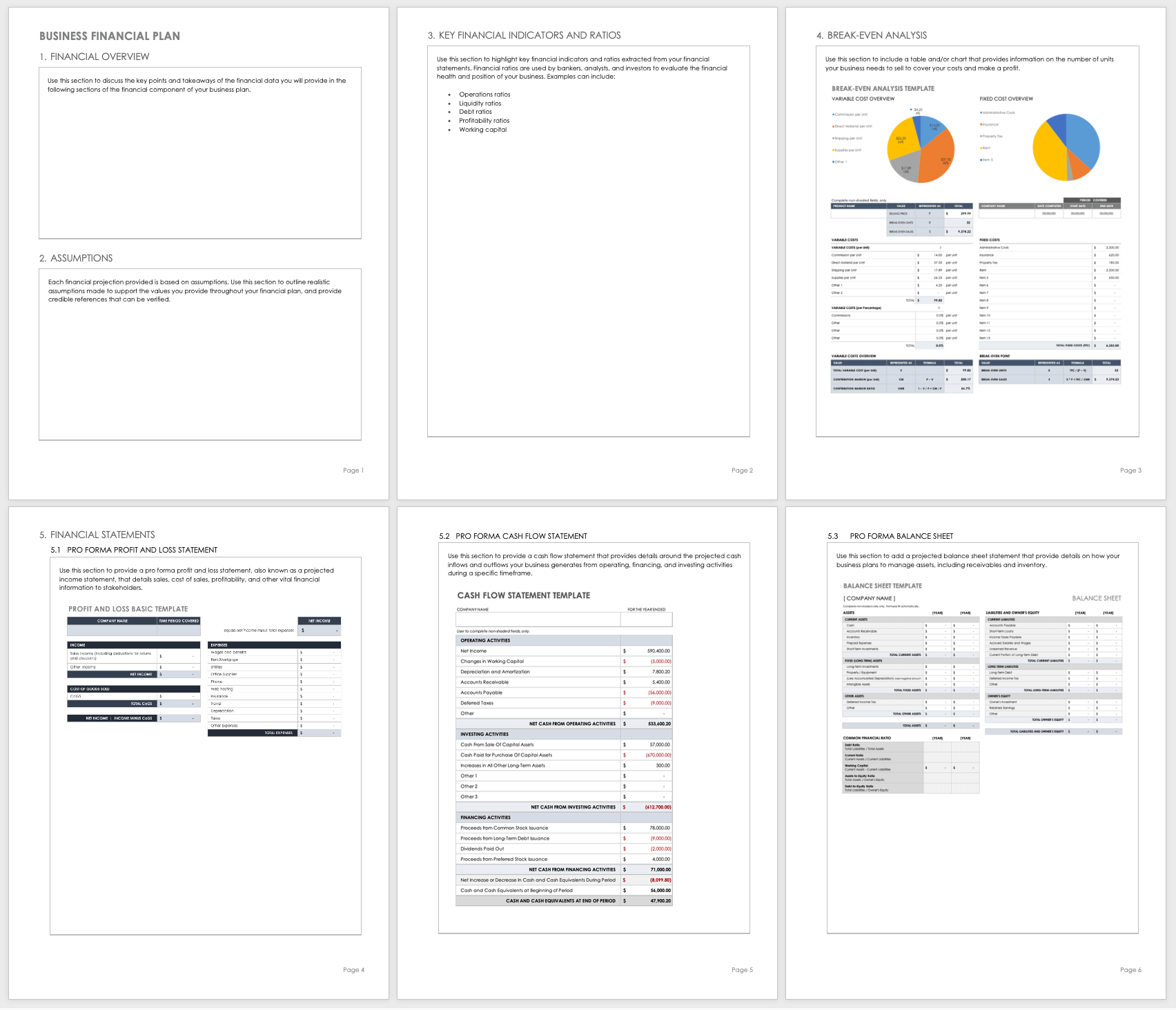
Use this financial plan template to organize and prepare the financial section of your business plan. This customizable template has room to provide a financial overview, any important assumptions, key financial indicators and ratios, a break-even analysis, and pro forma financial statements to share key financial data with potential investors.
Download Financial Plan Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Financial Plan Projections Template for Startups
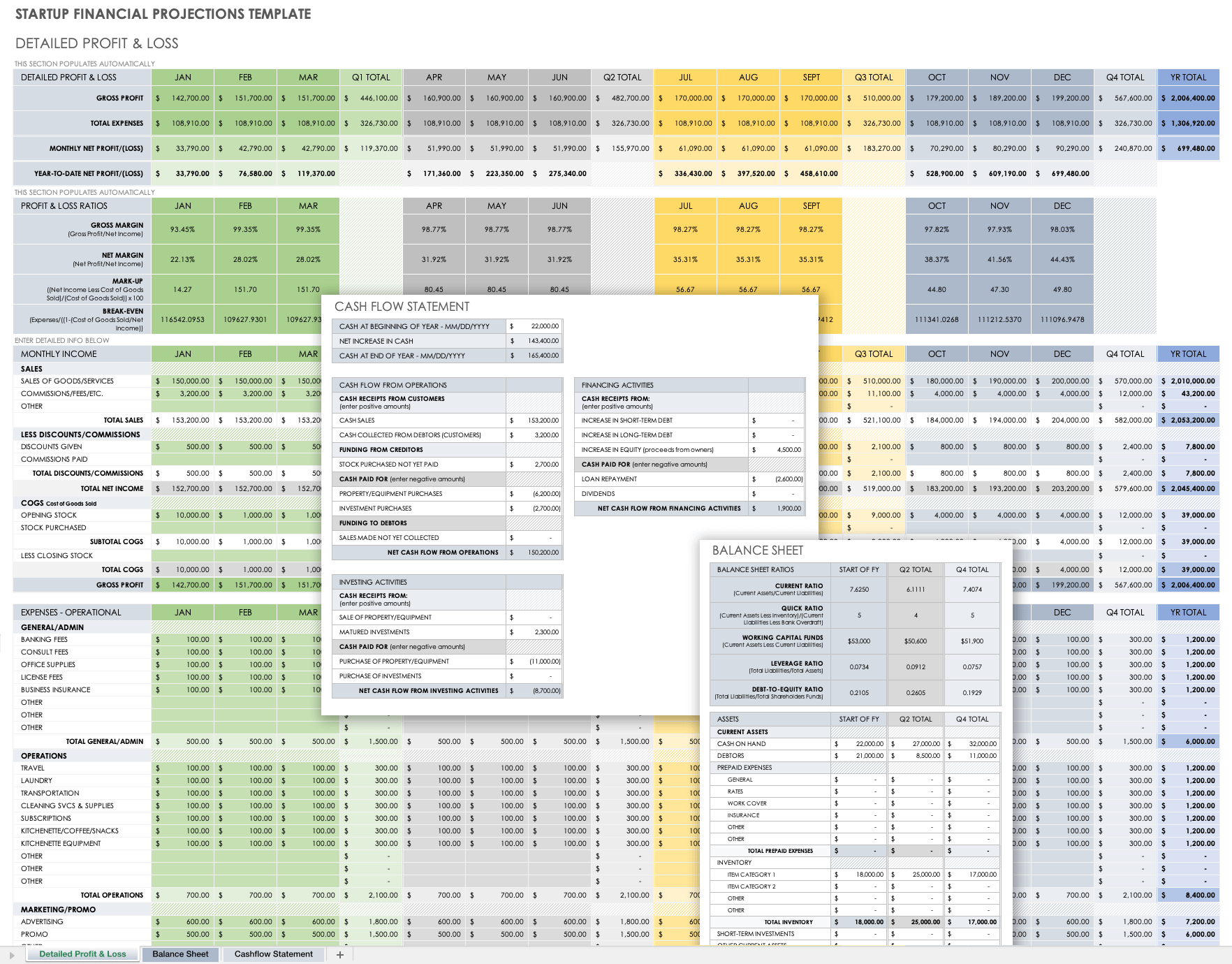
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business.
Download Startup Financial Projections Template
Excel | Smartsheet
Income Statement Templates for Business Plan
Also called profit and loss statements , these income statement templates will empower you to make critical business decisions by providing insight into your company, as well as illustrating the projected profitability associated with business activities. The numbers prepared in your income statement directly influence the cash flow and balance sheet forecasts.
Pro Forma Income Statement/Profit and Loss Sample
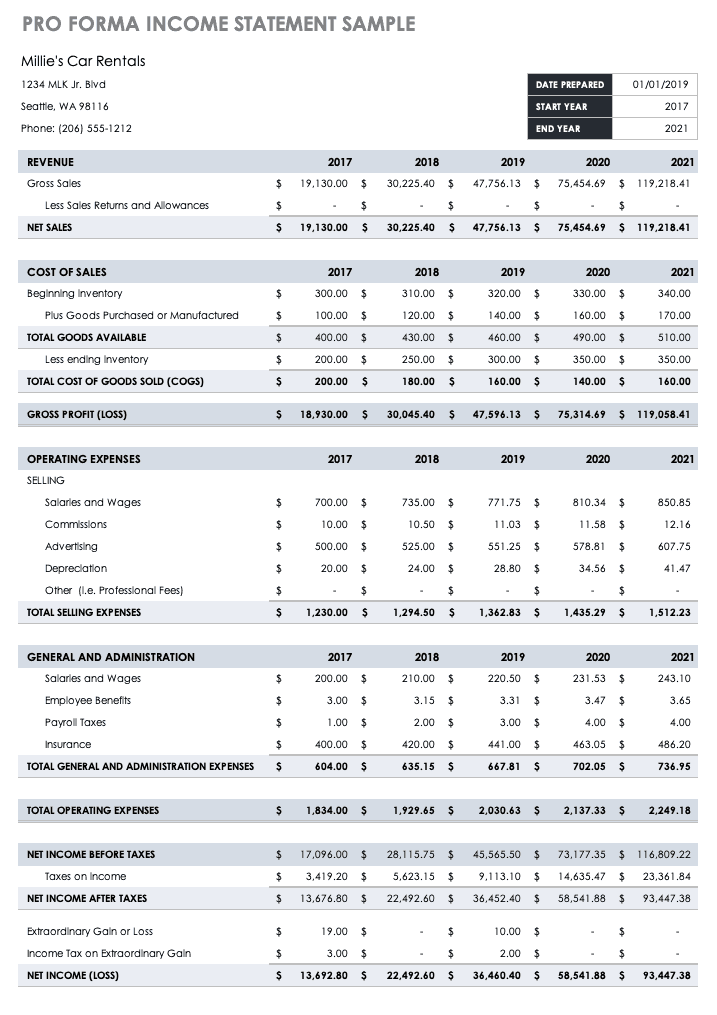
Use this pro forma income statement template to project income and expenses over a three-year time period. Pro forma income statements consider historical or market analysis data to calculate the estimated sales, cost of sales, profits, and more.
Download Pro Forma Income Statement Sample - Excel
Small Business Profit and Loss Statement
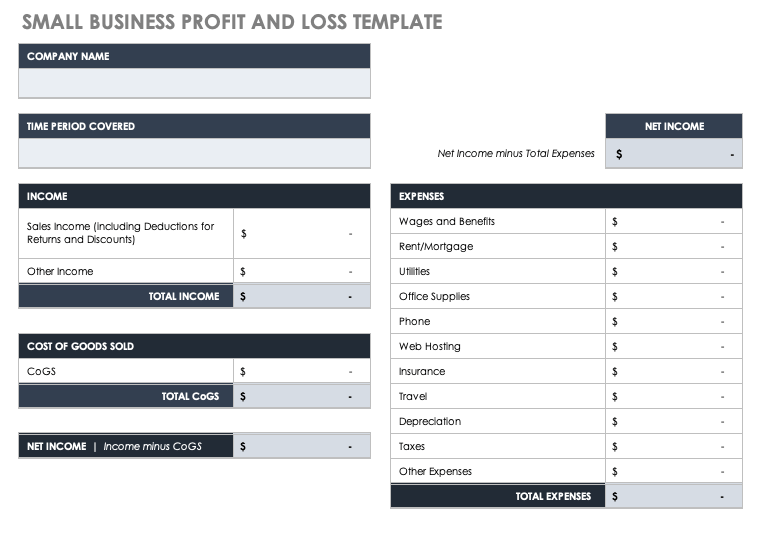
Small businesses can use this simple profit and loss statement template to project income and expenses for a specific time period. Enter expected income, cost of goods sold, and business expenses, and the built-in formulas will automatically calculate the net income.
Download Small Business Profit and Loss Template - Excel
3-Year Income Statement Template
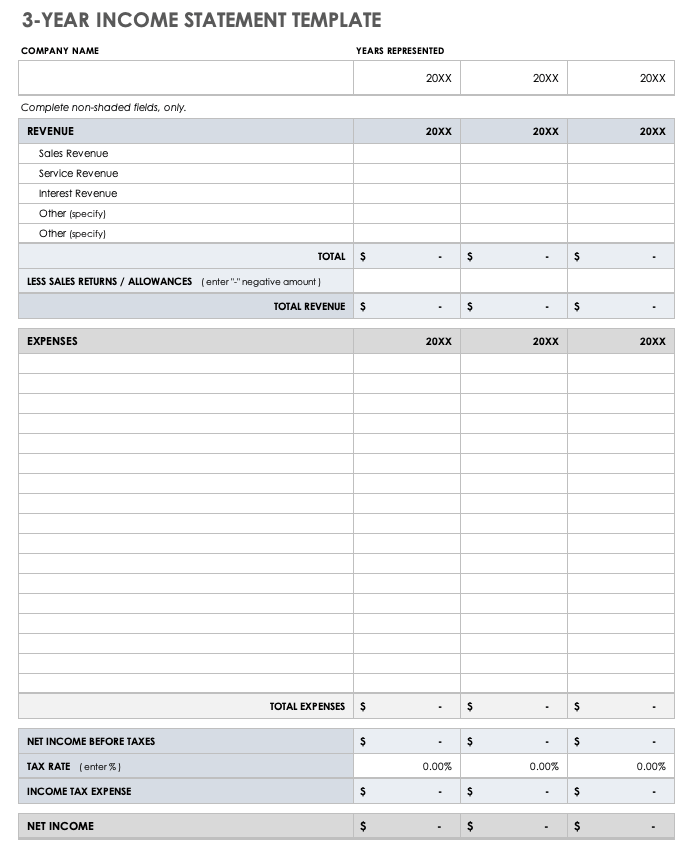
Use this income statement template to calculate and assess the profit and loss generated by your business over three years. This template provides room to enter revenue and expenses associated with operating your business and allows you to track performance over time.
Download 3-Year Income Statement Template
For additional resources, including how to use profit and loss statements, visit “ Download Free Profit and Loss Templates .”
Cash Flow Statement Templates for Business Plan
Use these free cash flow statement templates to convey how efficiently your company manages the inflow and outflow of money. Use a cash flow statement to analyze the availability of liquid assets and your company’s ability to grow and sustain itself long term.
Simple Cash Flow Template

Use this basic cash flow template to compare your business cash flows against different time periods. Enter the beginning balance of cash on hand, and then detail itemized cash receipts, payments, costs of goods sold, and expenses. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate total cash payments, net cash change, and the month ending cash position.
Download Simple Cash Flow Template
12-Month Cash Flow Forecast Template
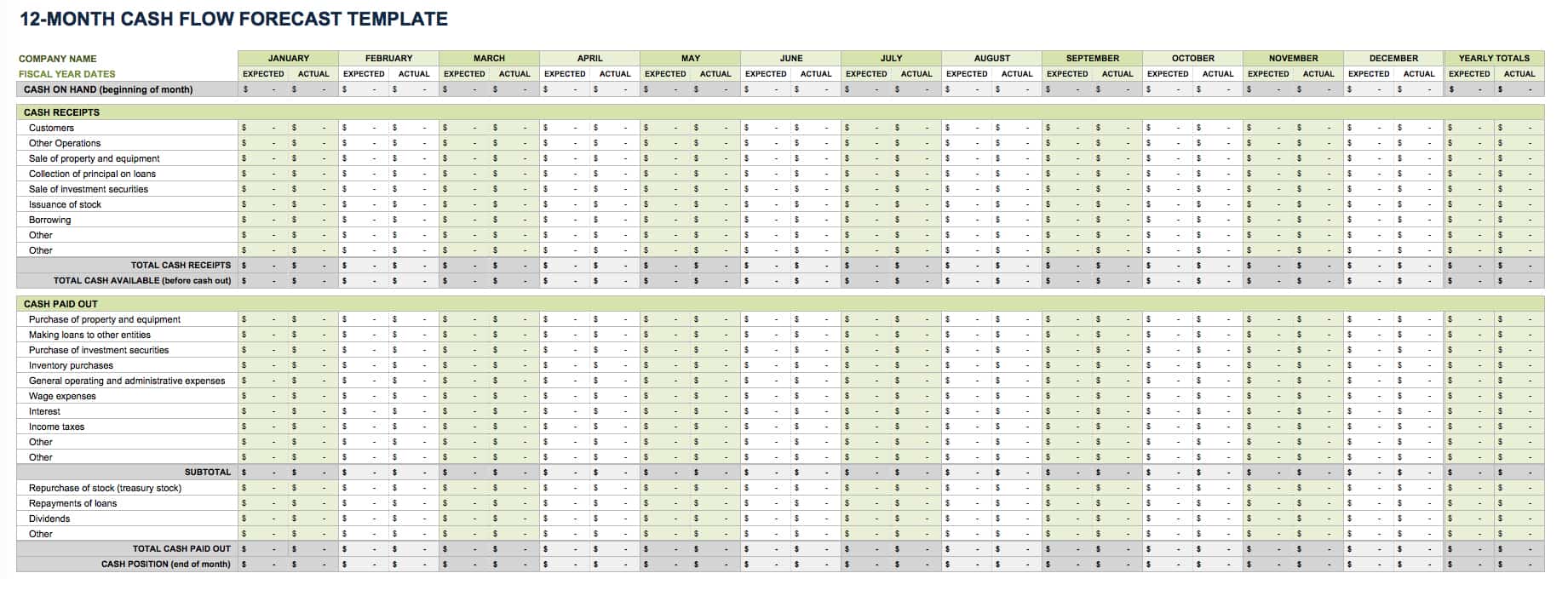
Use this cash flow forecast template, also called a pro forma cash flow template, to track and compare expected and actual cash flow outcomes on a monthly and yearly basis. Enter the cash on hand at the beginning of each month, and then add the cash receipts (from customers, issuance of stock, and other operations). Finally, add the cash paid out (purchases made, wage expenses, and other cash outflow). Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate your cash position for each month with.
Download 12-Month Cash Flow Forecast
3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template Set
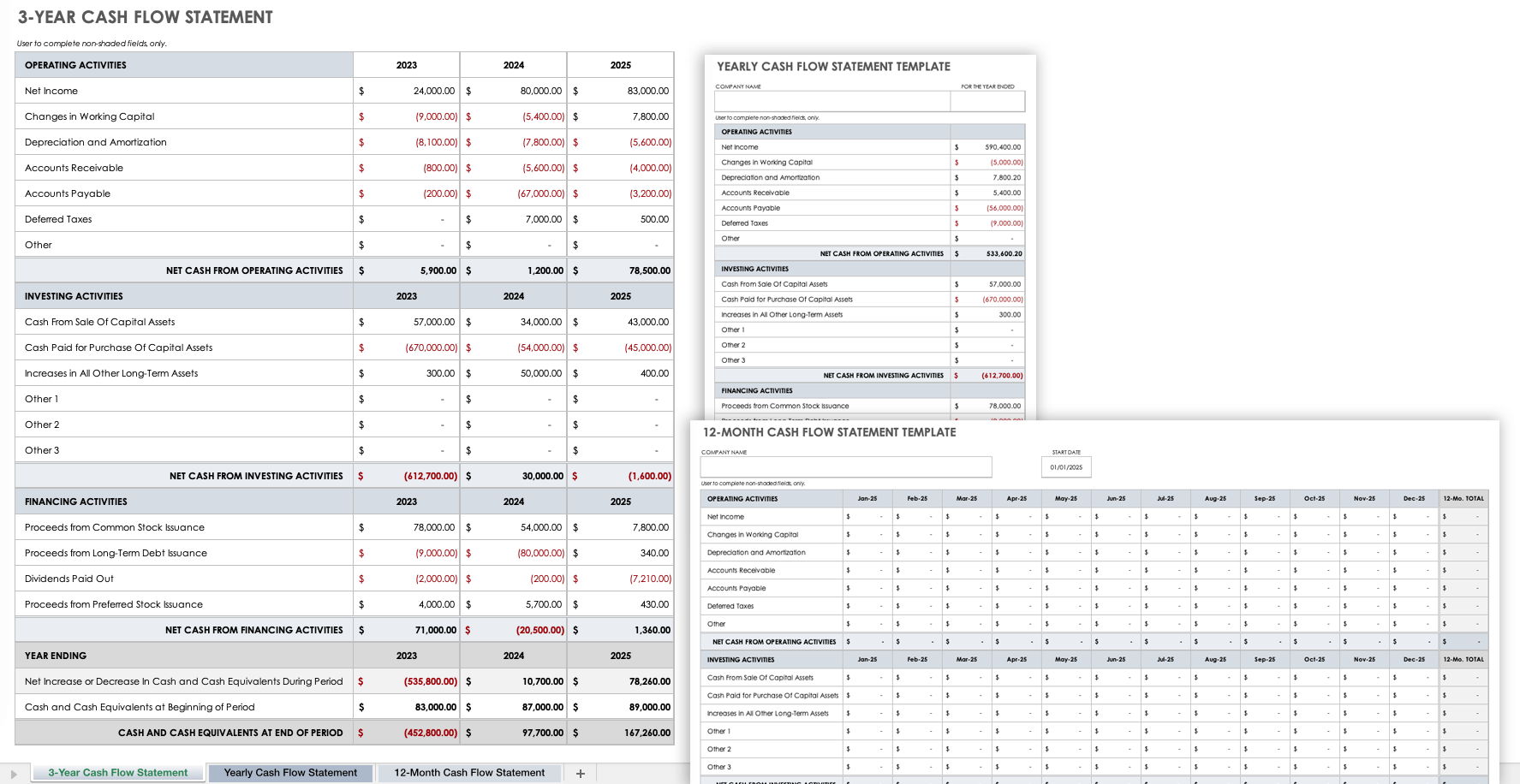
Use this cash flow statement template set to analyze the amount of cash your company has compared to its expenses and liabilities. This template set contains a tab to create a monthly cash flow statement, a yearly cash flow statement, and a three-year cash flow statement to track cash flow for the operating, investing, and financing activities of your business.
Download 3-Year Cash Flow Statement Template
For additional information on managing your cash flow, including how to create a cash flow forecast, visit “ Free Cash Flow Statement Templates .”
Balance Sheet Templates for a Business Plan
Use these free balance sheet templates to convey the financial position of your business during a specific time period to potential investors and stakeholders.
Small Business Pro Forma Balance Sheet
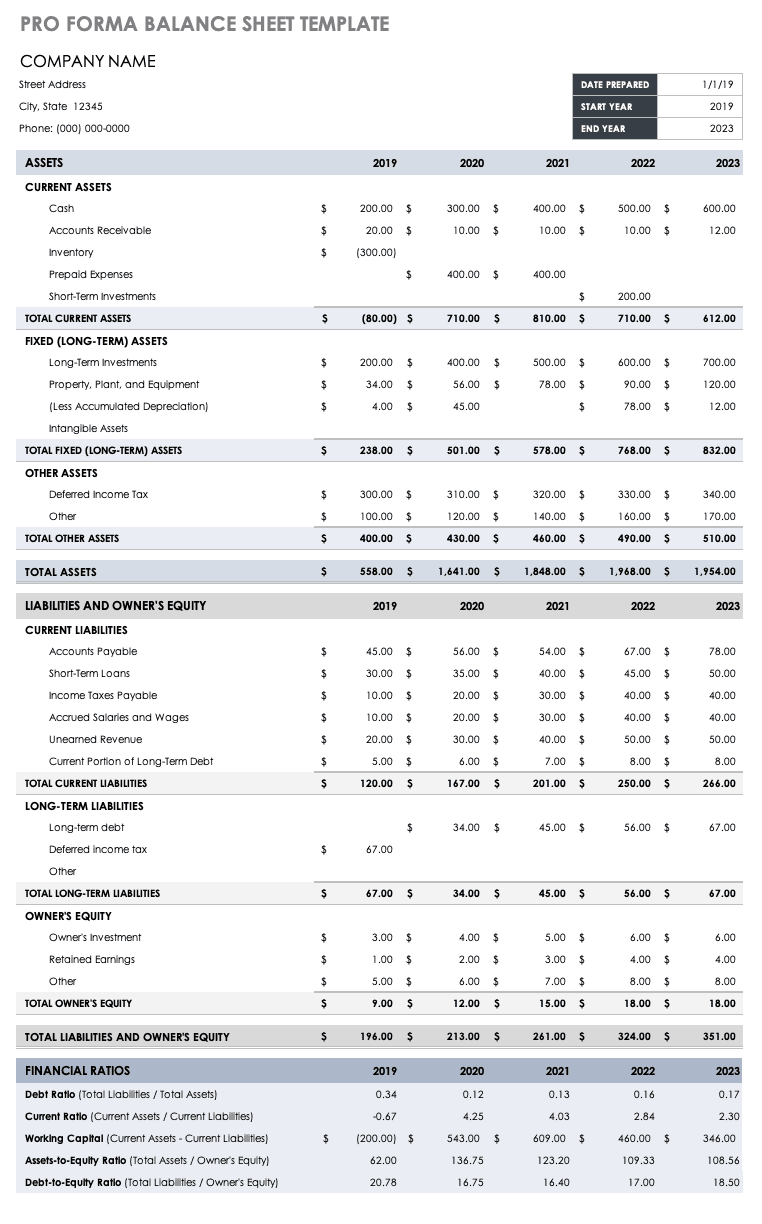
Small businesses can use this pro forma balance sheet template to project account balances for assets, liabilities, and equity for a designated period. Established businesses can use this template (and its built-in formulas) to calculate key financial ratios, including working capital.
Download Pro Forma Balance Sheet Template
Monthly and Quarterly Balance Sheet Template
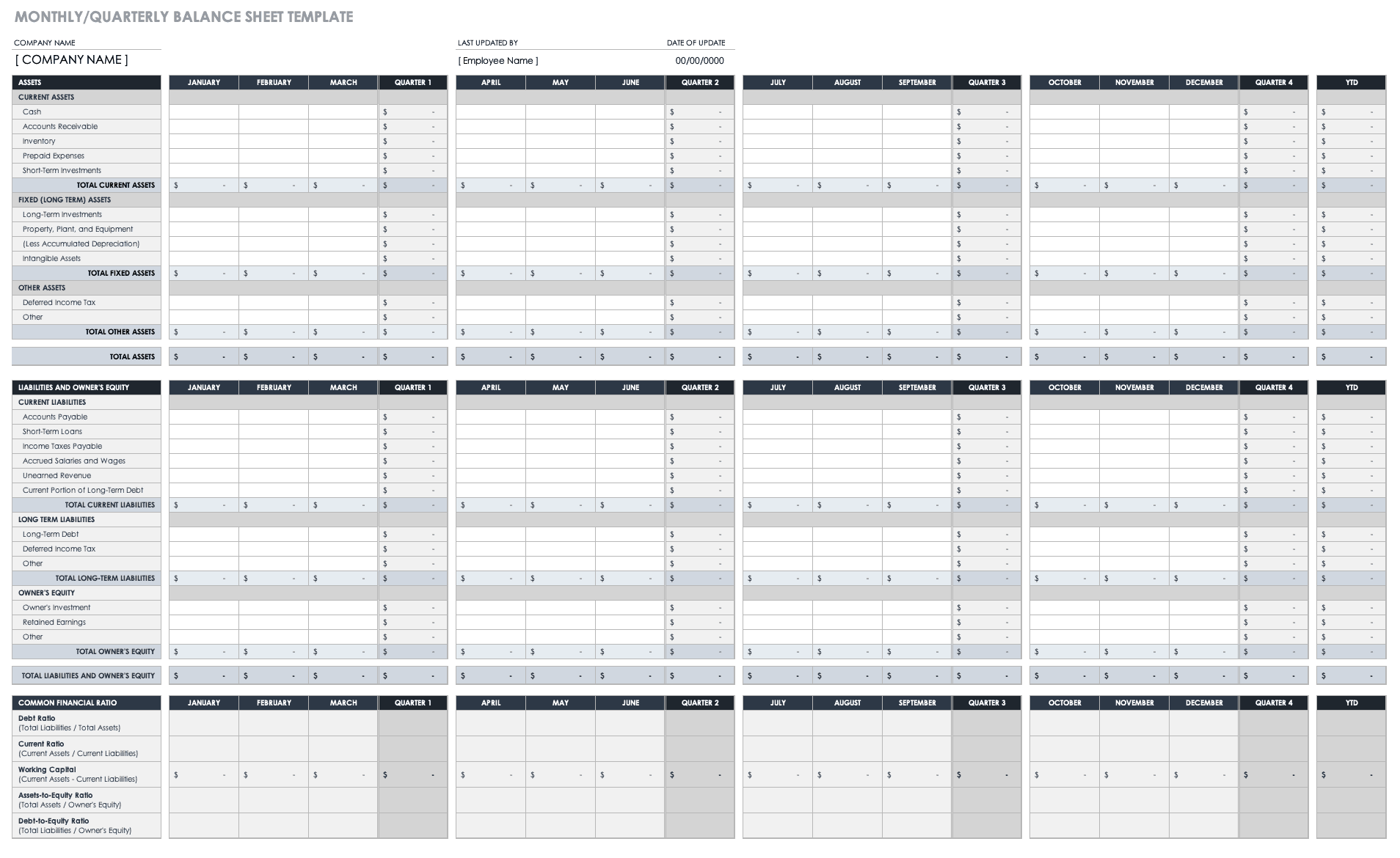
Use this balance sheet template to evaluate your company’s financial health on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. You can also use this template to project your financial position for a specified time in the future. Once you complete the balance sheet, you can compare and analyze your assets, liabilities, and equity on a quarter-over-quarter or year-over-year basis.
Download Monthly/Quarterly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
Yearly Balance Sheet Template
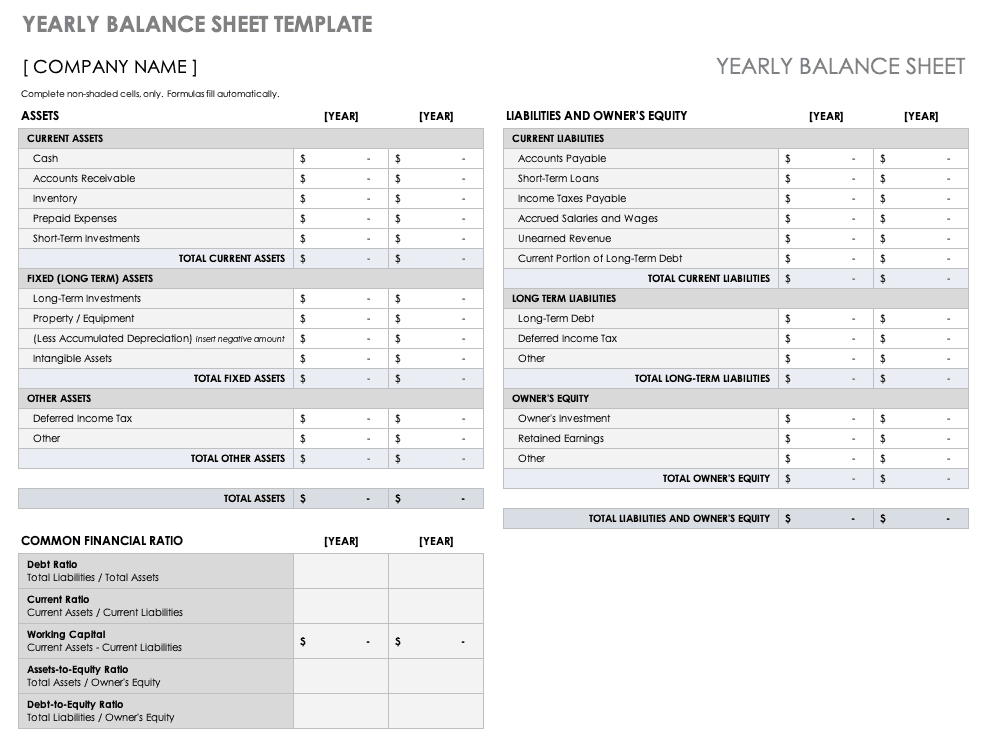
Use this balance sheet template to compare your company’s short and long-term assets, liabilities, and equity year-over-year. This template also provides calculations for common financial ratios with built-in formulas, so you can use it to evaluate account balances annually.
Download Yearly Balance Sheet Template - Excel
For more downloadable resources for a wide range of organizations, visit “ Free Balance Sheet Templates .”
Sales Forecast Templates for Business Plan
Sales projections are a fundamental part of a business plan, and should support all other components of your plan, including your market analysis, product offerings, and marketing plan . Use these sales forecast templates to estimate future sales, and ensure the numbers align with the sales numbers provided in your income statement.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
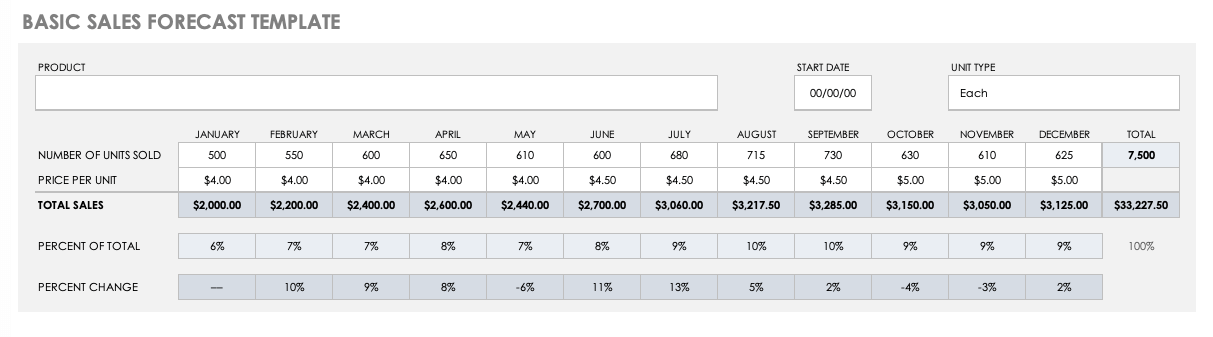
Use this basic forecast template to project the sales of a specific product. Gather historical and industry sales data to generate monthly and yearly estimates of the number of units sold and the price per unit. Then, the pre-built formulas will calculate percentages automatically. You’ll also find details about which months provide the highest sales percentage, and the percentage change in sales month-over-month.
Download Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
12-Month Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
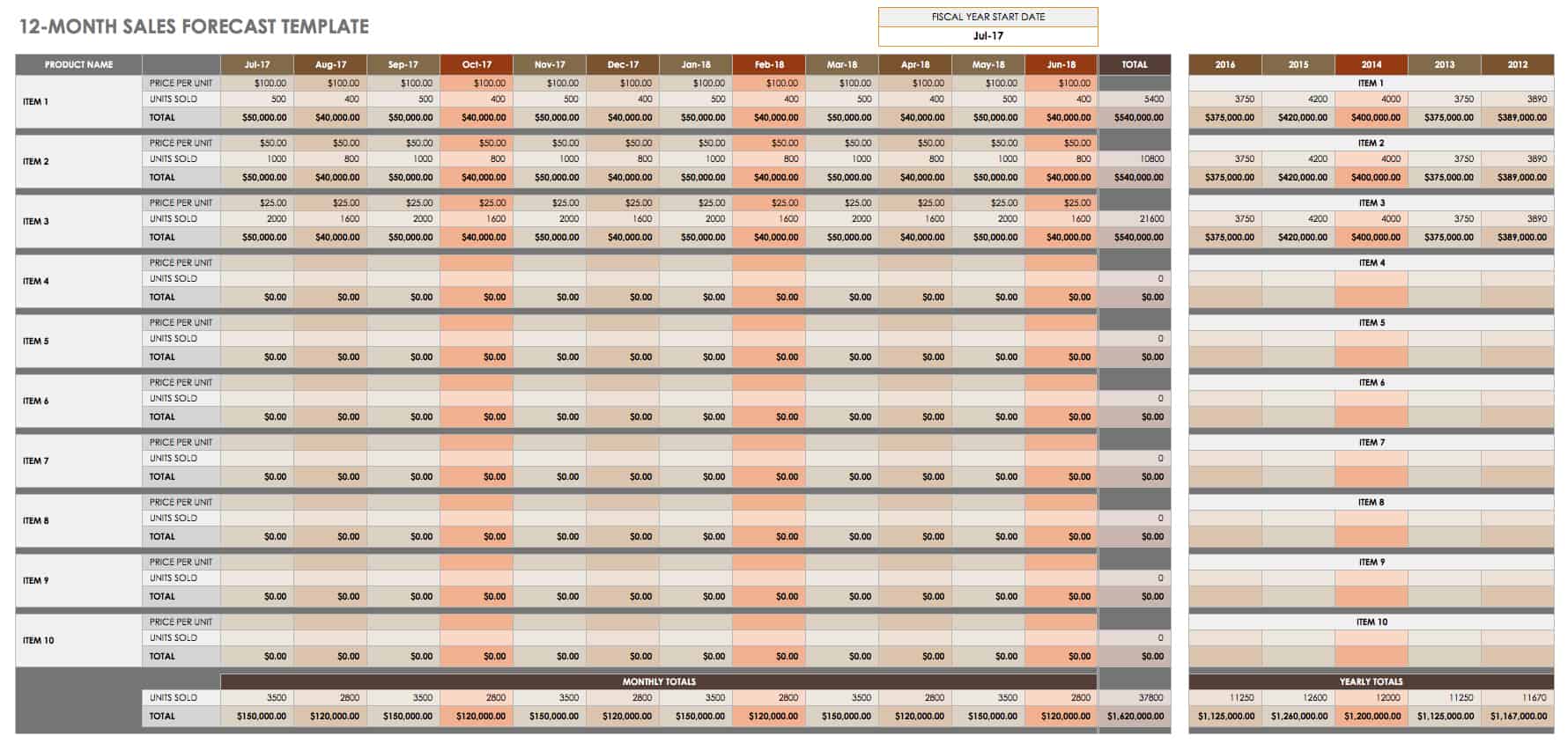
Use this sales forecast template to project the future sales of a business across multiple products or services over the course of a year. Enter your estimated monthly sales, and the built-in formulas will calculate annual totals. There is also space to record and track year-over-year sales, so you can pinpoint sales trends.
Download 12-Month Sales Forecasting Template for Multiple Products
3-Year Sales Forecast Template for Multiple Products
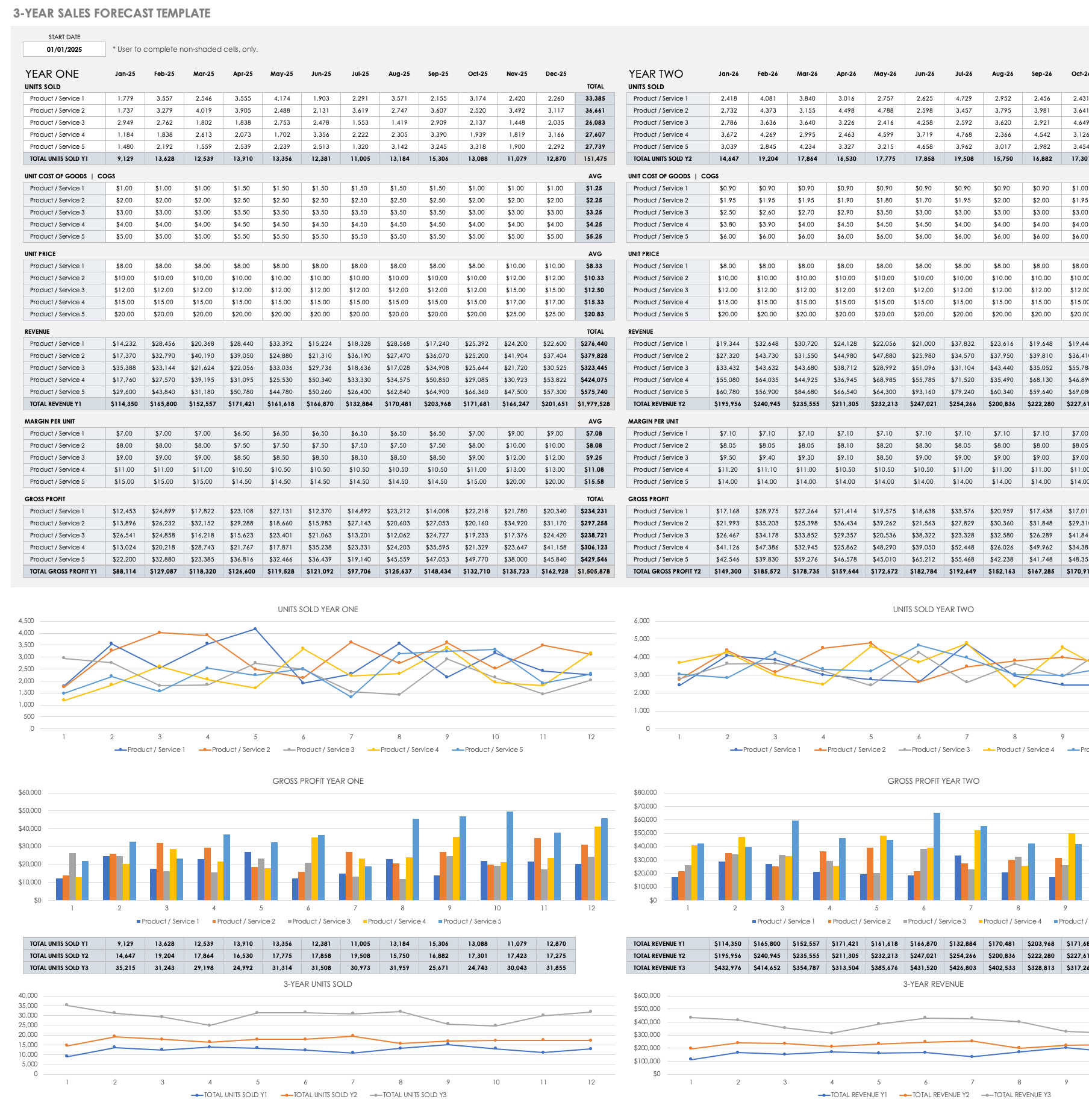
Use this sales forecast template to estimate the monthly and yearly sales for multiple products over a three-year period. Enter the monthly units sold, unit costs, and unit price. Once you enter those values, built-in formulas will automatically calculate revenue, margin per unit, and gross profit. This template also provides bar charts and line graphs to visually display sales and gross profit year over year.
Download 3-Year Sales Forecast Template - Excel
For a wider selection of resources to project your sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Break-Even Analysis Template for Business Plan
A break-even analysis will help you ascertain the point at which a business, product, or service will become profitable. This analysis uses a calculation to pinpoint the number of service or unit sales you need to make to cover costs and make a profit.
Break-Even Analysis Template
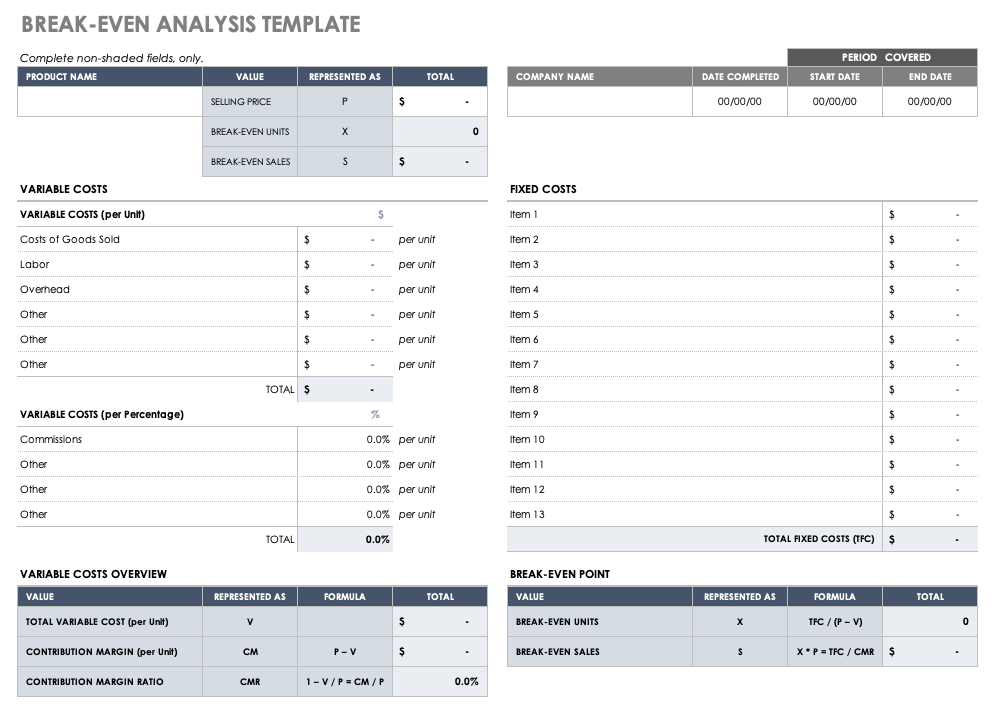
Use this break-even analysis template to calculate the number of sales needed to become profitable. Enter the product's selling price at the top of the template, and then add the fixed and variable costs. Once you enter those values, the built-in formulas will calculate the total variable cost, the contribution margin, and break-even units and sales values.
Download Break-Even Analysis Template
For additional resources, visit, “ Free Financial Planning Templates .”
Business Budget Templates for Business Plan
These business budget templates will help you track costs (e.g., fixed and variable) and expenses (e.g., one-time and recurring) associated with starting and running a business. Having a detailed budget enables you to make sound strategic decisions, and should align with the expense values listed on your income statement.
Startup Budget Template
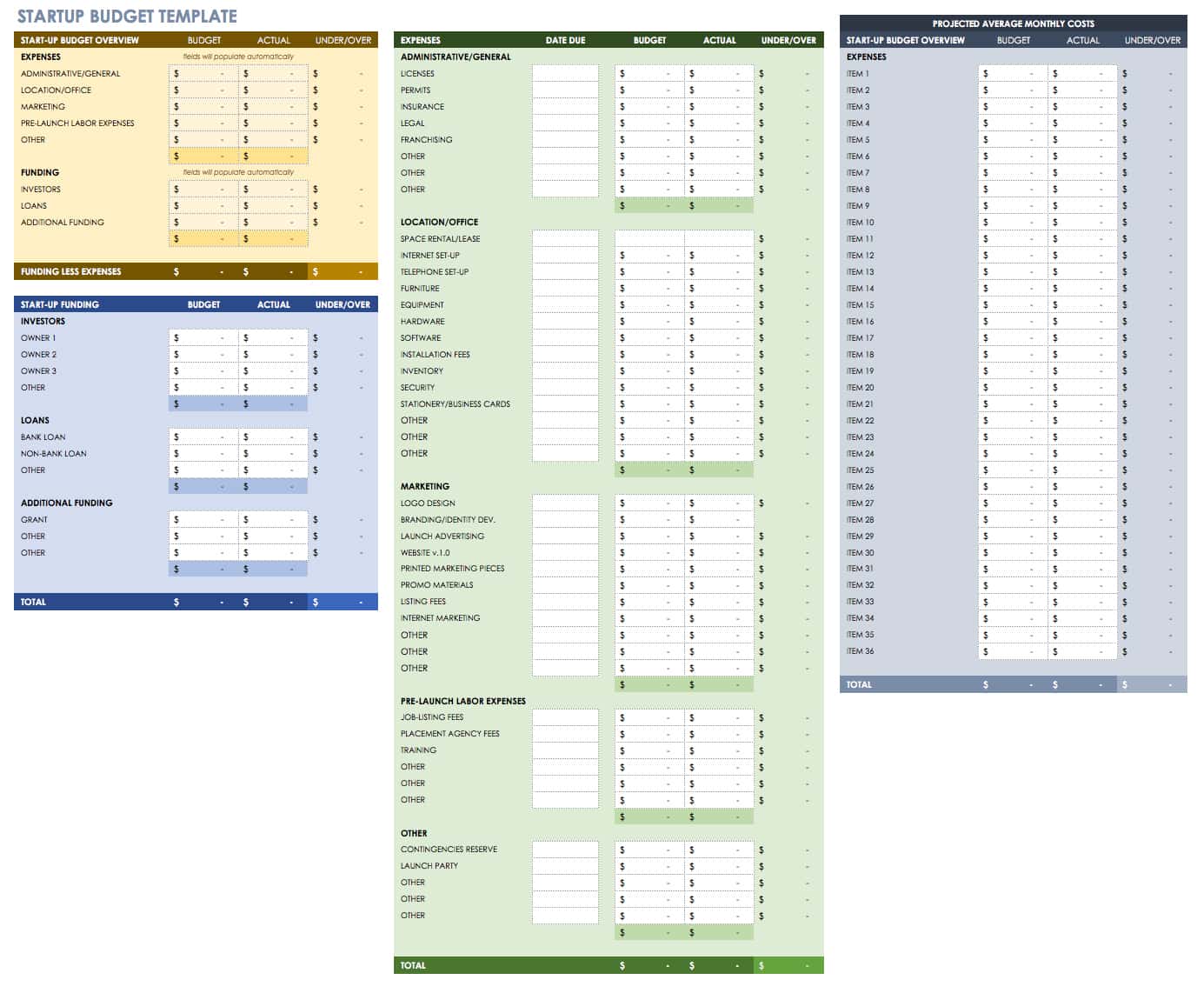
Use this startup budget template to track estimated and actual costs and expenses for various business categories, including administrative, marketing, labor, and other office costs. There is also room to provide funding estimates from investors, banks, and other sources to get a detailed view of the resources you need to start and operate your business.
Download Startup Budget Template
Small Business Budget Template
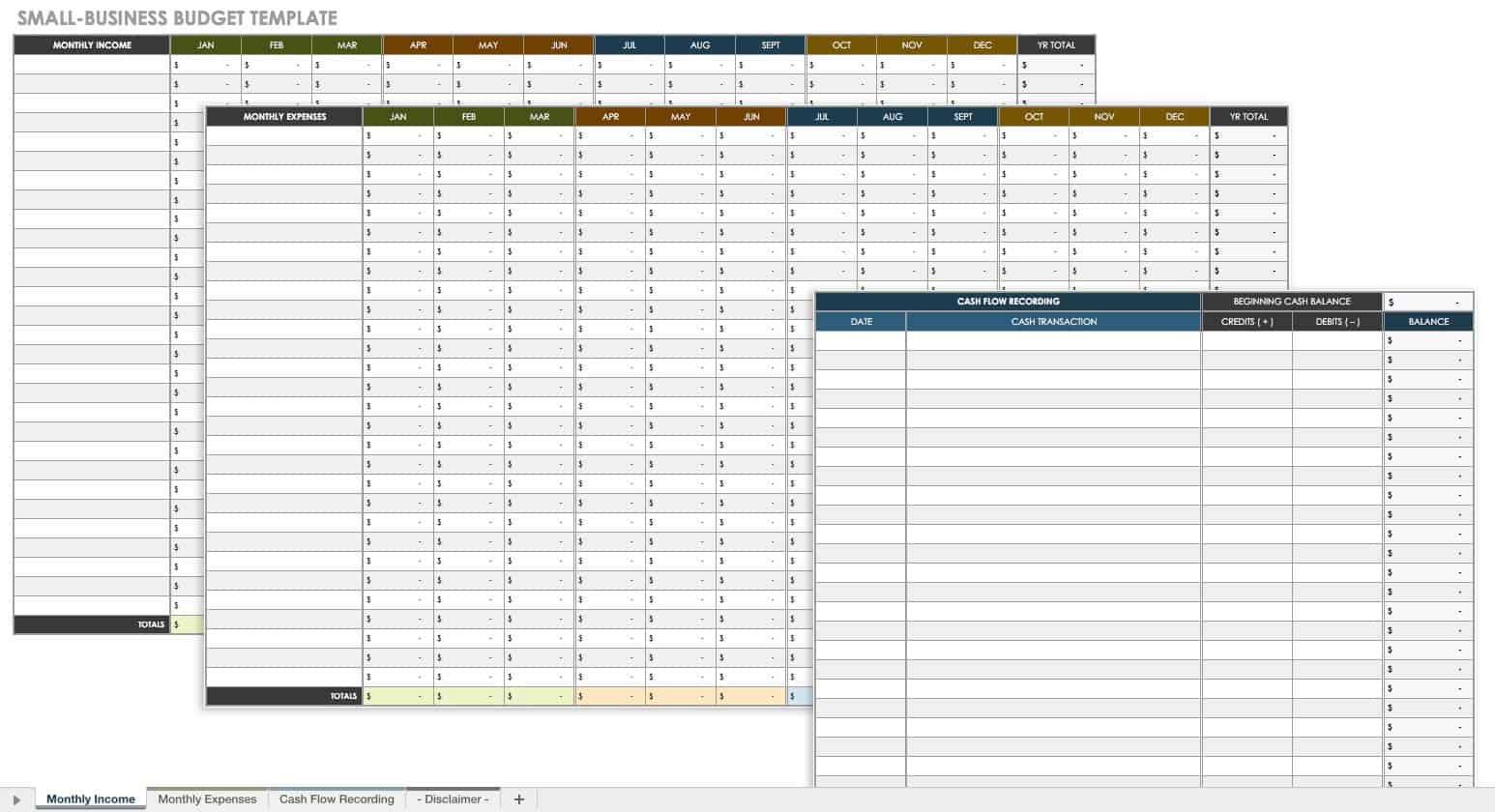
This business budget template is ideal for small businesses that want to record estimated revenue and expenditures on a monthly and yearly basis. This customizable template comes with a tab to list income, expenses, and a cash flow recording to track cash transactions and balances.
Download Small Business Budget Template
Professional Business Budget Template

Established organizations will appreciate this customizable business budget template, which contains a separate tab to track projected business expenses, actual business expenses, variances, and an expense analysis. Once you enter projected and actual expenses, the built-in formulas will automatically calculate expense variances and populate the included visual charts.
Download Professional Business Budget Template
For additional resources to plan and track your business costs and expenses, visit “ Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company .”
Other Financial Templates for Business Plan
In this section, you’ll find additional financial templates that you may want to include as part of your larger business plan.
Startup Funding Requirements Template
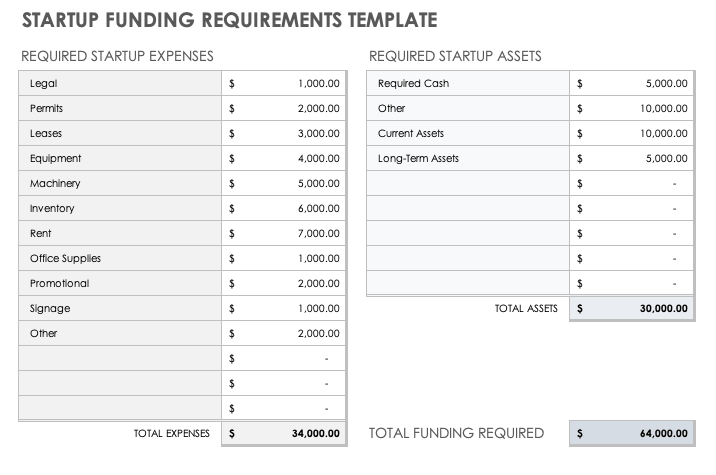
This simple startup funding requirements template is useful for startups and small businesses that require funding to get business off the ground. The numbers generated in this template should align with those in your financial projections, and should detail the allocation of acquired capital to various startup expenses.
Download Startup Funding Requirements Template - Excel
Personnel Plan Template
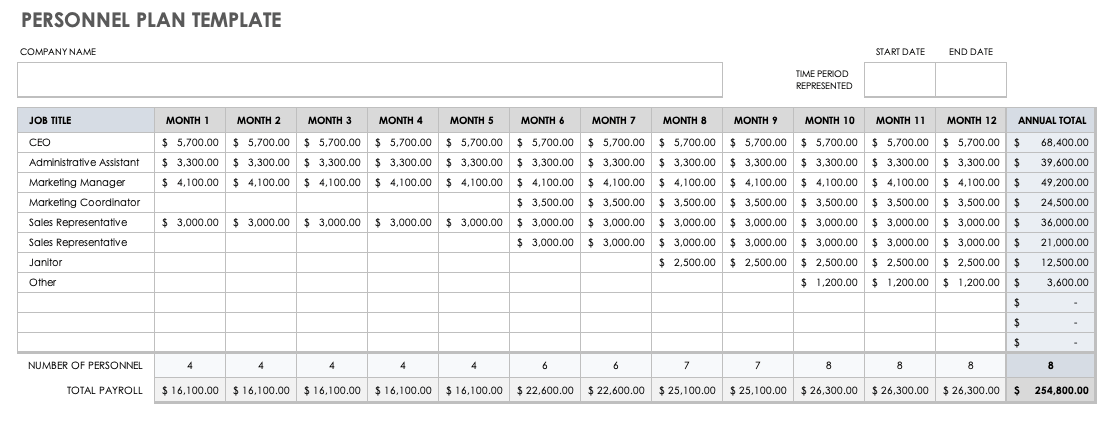
Use this customizable personnel plan template to map out the current and future staff needed to get — and keep — the business running. This information belongs in the personnel section of a business plan, and details the job title, amount of pay, and hiring timeline for each position. This template calculates the monthly and yearly expenses associated with each role using built-in formulas. Additionally, you can add an organizational chart to provide a visual overview of the company’s structure.
Download Personnel Plan Template - Excel
Elements of the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Whether your organization is a startup, a small business, or an enterprise, the financial plan is the cornerstone of any business plan. The financial section should demonstrate the feasibility and profitability of your idea and should support all other aspects of the business plan.
Below, you’ll find a quick overview of the components of a solid financial plan.
- Financial Overview: This section provides a brief summary of the financial section, and includes key takeaways of the financial statements. If you prefer, you can also add a brief description of each statement in the respective statement’s section.
- Key Assumptions: This component details the basis for your financial projections, including tax and interest rates, economic climate, and other critical, underlying factors.
- Break-Even Analysis: This calculation helps establish the selling price of a product or service, and determines when a product or service should become profitable.
- Pro Forma Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement, this section details the sales, cost of sales, profitability, and other vital financial information to stakeholders.
- Pro Forma Cash Flow Statement: This area outlines the projected cash inflows and outflows the business expects to generate from operating, financing, and investing activities during a specific timeframe.
- Pro Forma Balance Sheet: This document conveys how your business plans to manage assets, including receivables and inventory.
- Key Financial Indicators and Ratios: In this section, highlight key financial indicators and ratios extracted from financial statements that bankers, analysts, and investors can use to evaluate the financial health and position of your business.
Need help putting together the rest of your business plan? Check out our free simple business plan templates to get started. You can learn how to write a successful simple business plan here .
Visit this free non-profit business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy. If you are looking for a business plan template by file type, visit our pages dedicated specifically to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates. Read our articles offering startup business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Plan Financials and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to Write a Financial Plan for a Business Plan

Noah Parsons
4 min. read
Updated July 11, 2024

Creating a financial plan for a business plan is often the most intimidating part for small business owners.
It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts.
Here is everything you need to include in your business plan’s financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid , and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan in business plans
A sound financial plan for a business plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, you’ll need to include a few additional pieces of information as part of your business plan’s financial plan example.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios.
While including these metrics in your financial plan for a business plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Key financial terms you should know
It’s not hard. Anybody who can run a business can understand these key financial terms. And every business owner and entrepreneur should know them.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- How to improve your financial plan
Your financial statements are the core part of your business plan’s financial plan that you’ll revisit most often. Instead of worrying about getting it perfect the first time, check out the following resources to learn how to improve your projections over time.
Common mistakes with business forecasts
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with startup financial projections. I read about 100 business plans per year, and I have this list of mistakes.
How to improve your financial projections
Learn how to improve your business financial projections by following these five basic guidelines.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write the Company Overview for a Business Plan
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Partners Hub
- Help Center
- 1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
How to make financial statements for small businesses.

Information is power. As long as you can make sense of that information. As a business owner, you’ll want to track your financial progress to make informed business decisions about your future. And that involves understanding cash flows, operating expenses, and net profit, all found in your financial statements.
Even if you delegate the bookkeeping to a professional, and don’t prepare financial statements yourself, you’ll need to know what your CPA is talking about when they walk you through your balance sheet.
In this article, you’ll learn about the 3 principal financial statements—income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements—and how to interpret them.
Here’s what we’ll cover: Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement) Balance Sheet Difference Between an Income Statement and a Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement Financial Statements Are Fundamental
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
An income statement shows a company’s financial performance by revealing whether it’s made a profit or a loss.
Without an income statement, you’d be in the dark about the profitability of your business. An income statement is also known as a profit and loss statement, profit and loss account, or P&L.
The reporting period for an income statement is typically one fiscal year.

What Goes on an Income Statement?
Let’s now jump to the format of an income statement.
In most cases, it will look something like this:
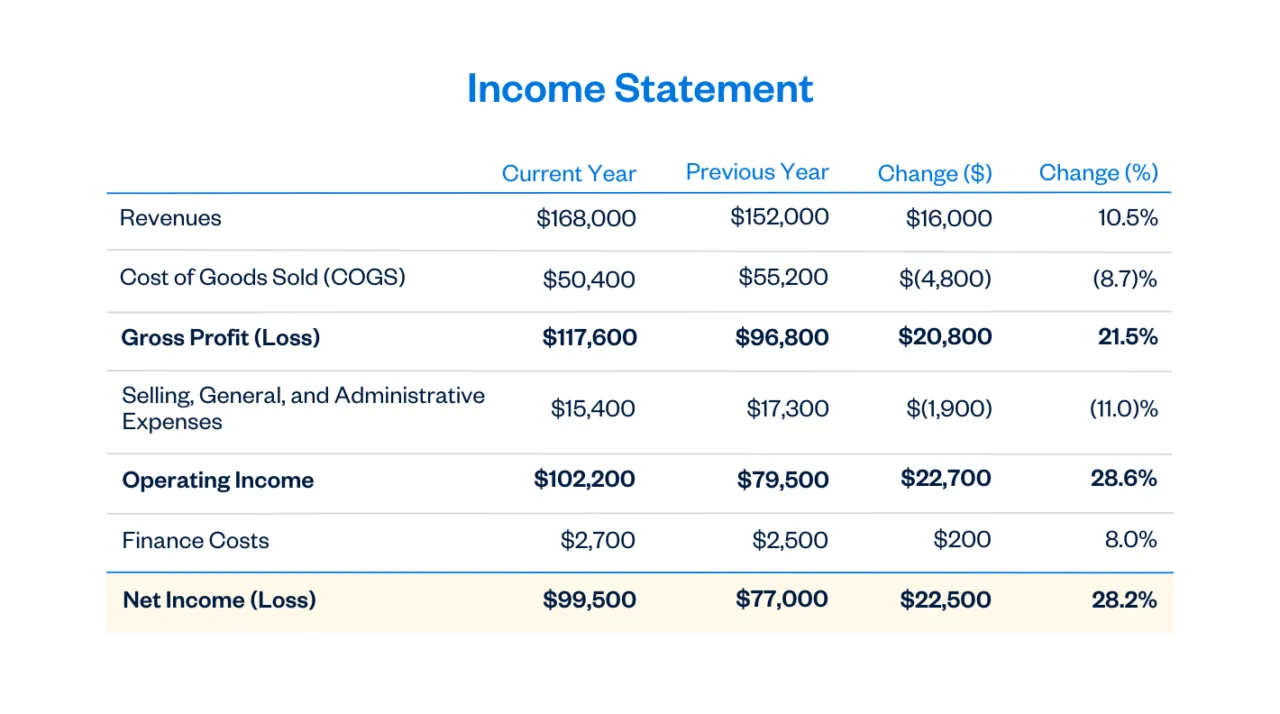
Now, let’s dig into what an income statement covers.
Revenues (or Sales)
This is the top line on your income statement. It’s the total amount for the year of all the things or services you sold. But if you’ve given any discounts, you’ll reduce your sales by the discount amount.
For example, if you sold $100 in t-shirts but offered a 10% discount as a Black Friday incentive, you would record $90 as your net sales amount .
Cost of Goods Sold (or Cost of Sales)
These are the expenses directly related to the sales you’ve made. Suppose you’re selling electronics. The cost of goods sold is the cost of the electronics you sell within a financial year. And this is important. It’s not the cost of the electronics you bought in the year.
In a service-related business, a consultancy, for example, the cost of sales is often termed direct costs. Hence, you’ll include costs directly related to your service.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is the profit that results directly and specifically from the trading activity of buying and selling. You calculate the gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenues.
Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses
All other expenses like salaries, rent, or travel merely facilitate the main trading activity of your business and are often categorized under selling, general, or administrative (SG&A) expenses.
You can have as many categories of SG&A expense as is necessary and helpful for running your business. Some of the common ones are:
- Office supplies
- Salaries and wages
- Marketing and advertising
Operating Income
Next is operating income. As the name implies, it’s the profit your business has earned from its operations when considering all the revenue and expenses necessary to run your business.
Finance Costs
Finance costs represent the costs of financing arrangements, such as interest on bank loans. You’ll want to strip financing costs away from SG&A expenses because they don’t represent the costs necessary for producing the goods or services you sell.
Net Income
After factoring in finance costs, you’re left with net income (or net loss). This is the much-talked-about bottom line. Your net income is how much your company has earned throughout the year.
What About Income Taxes?
You may ask yourself, why didn’t we include taxes? A small business isn’t burdened with income tax unless it’s structured as a C-corporation (which few small businesses are due to their complexity and maintenance costs). Instead, the business profits pass through to the owner and get taxed on the individual Form 1040.
Balance Sheet
Also known as the statement of financial position, the balance is an organization’s most important financial report because it shows the company’s financial health.
A balance sheet reports data for a specific point in time, often the last day of a fiscal year.
What Goes on a Balance Sheet?
Balance sheets contain 3 sections: assets, liabilities, and equity.
These are the resources your company owns that have a current or future economic value. These include cash, equipment (such as computers), and vehicles.
Assets can be broken down into:
- Current assets: This is anything you own that can be converted to cash within one year (e.g., accounts receivable and inventory). Also called short-term assets.
- Non-current assets: These are assets that can’t be quickly converted into cash, like computers, equipment, and vehicles, or intangible assets, like trademarks and copyrights. Also called fixed assets or long-term assets.
2. Business Liabilities
These are amounts your business owes other entities such as banks, employees, and suppliers.
- Current liabilities: Amounts you owe that are due within one year (e.g., accounts payable and payroll liabilities)
- Non-current (long-term) liabilities: Debts that will be repaid in more than one year
3. Owner Equity or Shareholder Equity
This is the value of the owner’s or shareholders’ investment in the business after liabilities are subtracted from assets. It may also be called owner’s or shareholders’ capital.
Purpose of a Balance Sheet
The balance sheet shows anyone what your business is worth. Lenders, investors, partners, and potential buyers will want to review your balance sheet.
The overall worth of your business can be measured or estimated by the total value of its assets, which are recorded and presented on the balance sheet.
But even more important, your balance sheet shows your business’s net worth , which is the owner’s equity (or shareholder’s equity). This is a business’s residual value after removing its liabilities . It’s what ultimately belongs to the business owner.
Format of a Balance Sheet
Balance sheets are prepared based on the accounting equation, which is:
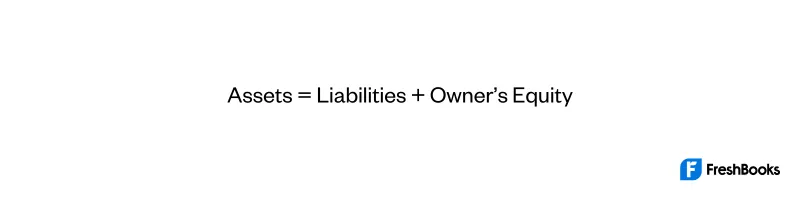
Traditionally, before accounting software was developed and bookkeeping was done with pencil and paper, assets were put on the left side of the balance sheet, while equity and liabilities went to the right side.
Today, however, a balance sheet will almost always look like this:
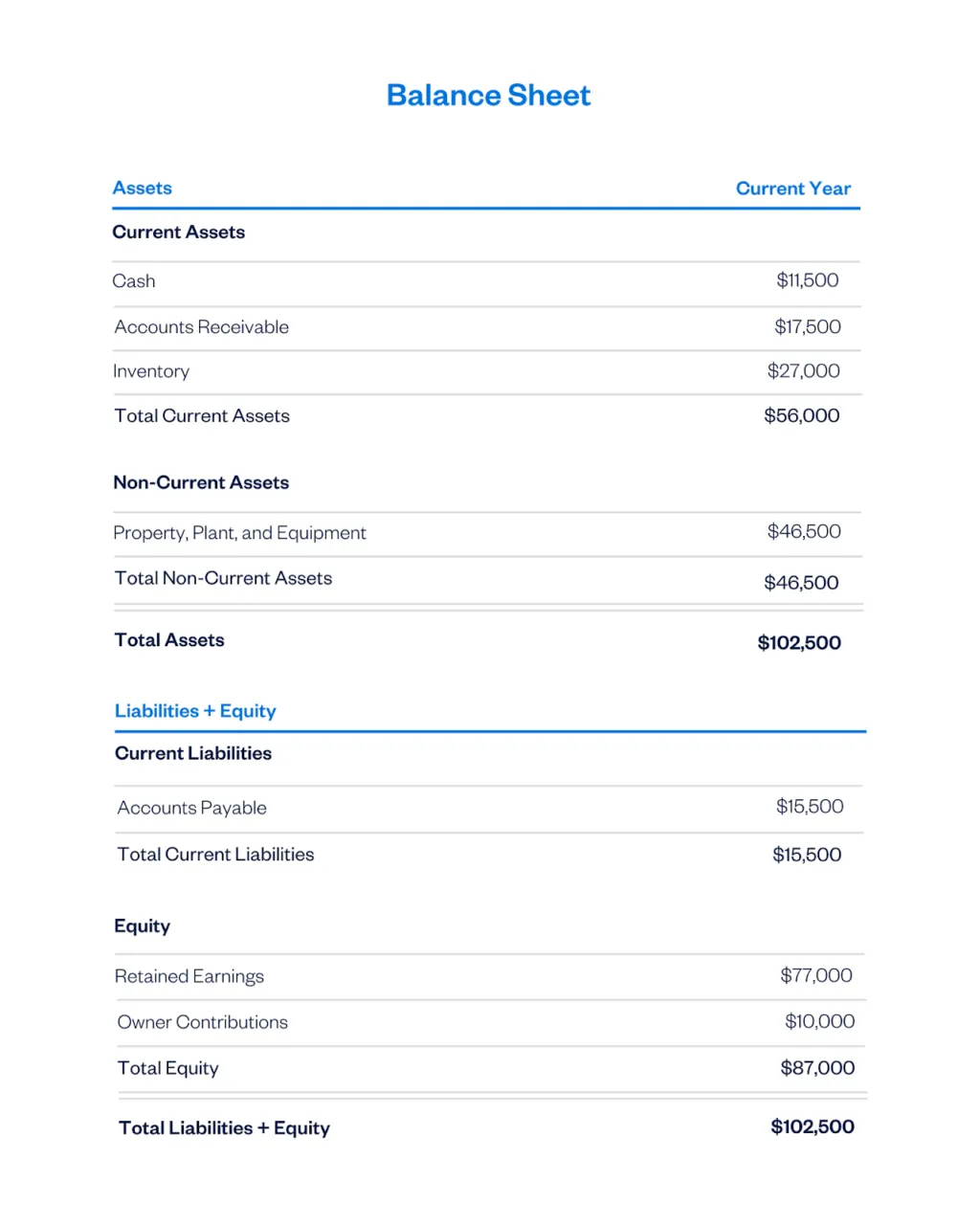
Now here’s something to remember.
The net income (your income statement bottom line) is annually transferred to your balance sheet, where it will appear as retained earnings. So retained earnings are a running total of your company’s profitability from day 1.
Difference Between an Income Statement and a Balance Sheet
If you want to know how your business has performed over a span of time (a year, month, or quarter), you’ll want to refer to your income statement.
On the flip side, if you want to know your business’s financial health, to know its value or worth at a particular point since it was established, the balance sheet is the report you’ll want to refer to.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement shows the movement of cash, the cash inflows and outflows within the business, based on 3 cash sources and cash expenditure categories: operations, investing, and financing.
This is an extremely important financial statement because, ultimately, cash is the best indicator of the financial health of an enterprise.
The reporting period for a cash flow statement is often one fiscal year but could be a quarter, month, or any reporting period that makes sense for your business.
Why Do You Need a Cash Flow Statement?
You already have an income statement that shows you the profits you’ve made. Why do you still need a cash flow statement?
An income statement is prepared based on the accrual method of accounting . This means your sales are recorded when you earn them, not when your business receives the actual cash.
This creates a timing difference. A sales amount of $10,000 on your income statement, for example, doesn’t always mean this amount is in your bank account. It may be an invoice you sent to your customer, and you’re still awaiting payment.
The same goes for expenses. In accrual-basis accounting, expenses are recorded when your business incurs them and not when you pay out the cash.
But what about the cash figure on the balance sheet? While the balance sheet captures the cash balance, which can be meaningful, this balance sheet figure doesn’t tell us the source of the cash.
The cash could be from a windfall, like an insurance claim, which is a one-time event and unsustainable. Or it could be from normal day-to-day business operations, which are more sustainable.
Sections of a Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement has 3 sections:
- Cash from operations (or from operating activities)
- Cash from investing activities
- Cash from financing activities
And this is what a typical cash flow statement looks like:
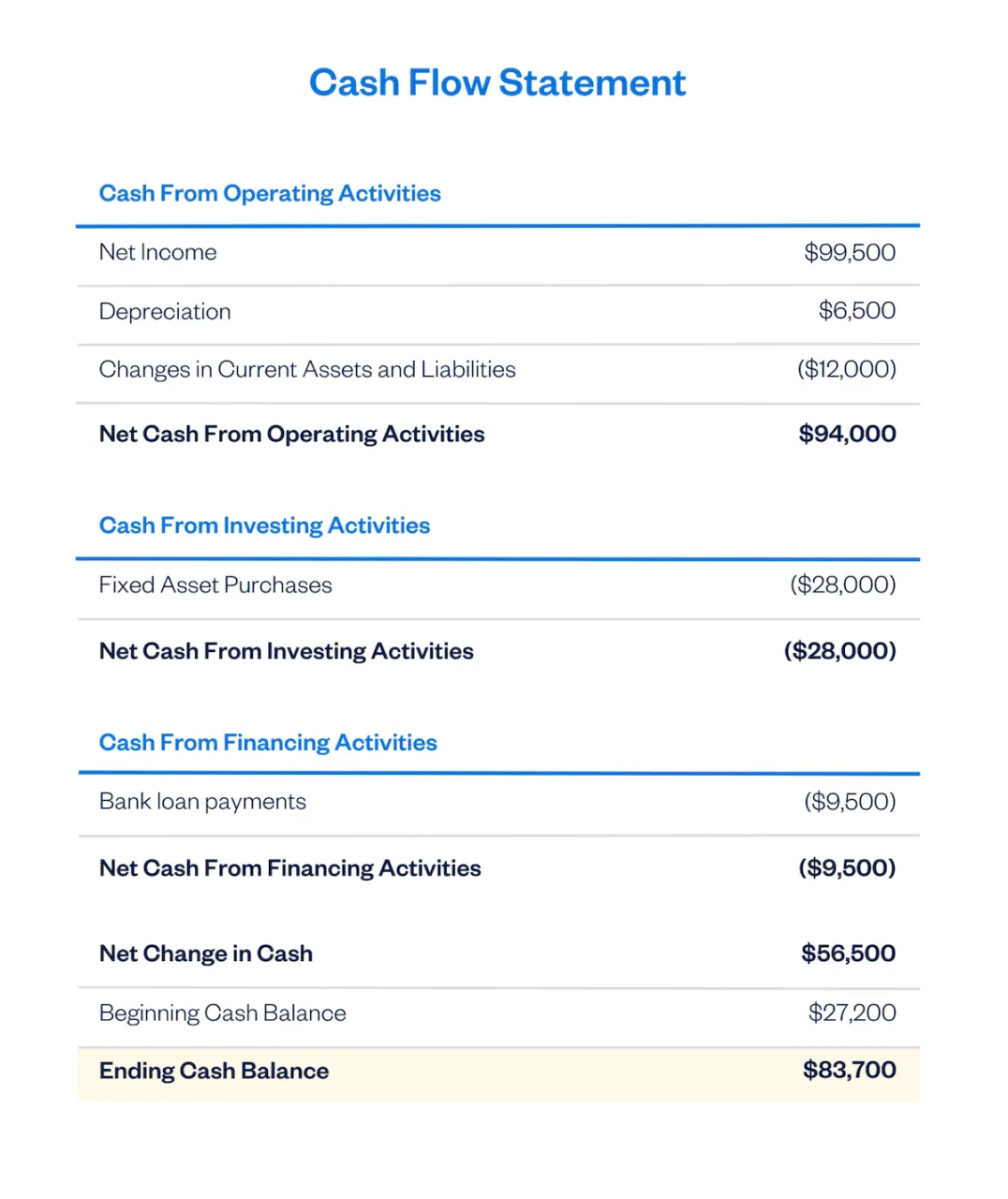
Cash From Operating Activities
Cash from operations is the first section of a cash flow statement, revealing its relative importance in the cash flow statement hierarchy. Cash from operating activities is the most meaningful because this is cash from your day-to-day trading activities.
These include cash received from sales, set off against cash expenses like the cost of goods sold, utility expenses, and rent.
It also takes into account non-cash items, like depreciation , that are included in net income but don’t involve any actual cash movement. And it considers any changes in your assets and liabilities during the time period, like an increase in accounts receivable .
Since operating activities are the mainstay of a business, a company with positive cash flow from operating activities will be more sustainable.
Cash From Investing Activities
The main source and use of cash from investing activities are purchasing and selling fixed assets. Common examples of fixed asset items are things like buildings, vehicles, computer equipment, or machinery.
But other investment items can appear in the investing activity section, such as buying stocks and bonds for investment purposes.
Cash From Financing Activities
All cash inflows and outflows from financing activities will be captured in this last section of cash flow statements.
If you’ve taken out a bank loan to purchase equipment, the cash the bank provided you will show up in this section. And when you begin making loan payments, these will be included here. To learn more about this follow our guide on Loan Repayment Entry , which provide you with the right steps.

Financial Statements Are Fundamental
In Sam Walton’s autobiography Made In America , here’s what Al Johnson, the CEO of Walmart at one time, revealed about Walmart’s owner and founder:
“Every Friday morning for six years, I would take my columnar pad with all the numbers on it into Sam’s office for him to review. Sam would jot them down on his own pad and work through the calculations himself. I always knew I could not just go in there and lay a sheet of numbers in front of him and expect him to just accept it.”
As a small business owner, you should be able to make sense of your financial statements. It will ensure you ask the right questions and follow important clues and cues.
You can make financial statements manually in a spreadsheet, but accounting software automates everything, so it’s faster and easier and leaves less room for error. With all your financial information in one place, you can immediately access your financial data whenever you or your accountant needs it.
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
More From Forbes
Basics of a business plan financials section.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
A good business plan is an entrepreneur’s best friend. It’s an indispensable document, and every section matters, from the executive summary to the market analysis to the appendix; however, no section matters as much as the financials section. You’re in business to make money, after all, and your business plan has to clearly, numerically reflect a lucrative business pursuit, preferably with visuals, especially if you want funding.
The financials section of your business plan tells you and your potential investors, loan providers or partners whether your business idea makes economic sense. Without an impressive financials section, you’re looking at an uphill battle when it comes to scoring capital; underwhelming financials may indicate a need to make some revisions to your approach.
Basic Financials
So, how to build an impressive financials section? As with all things in small business, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach; it varies by business and field. But there are some general guidelines that can give you a clear idea of where to start and what kind of data you’ll need to gather.
You need to include at least three documents in the financials section of your business plan:
1. Income statement: Are you profitable?
2. Cash flow statement: How much cash do you have on hand?
3. Balance sheet: What’s your net worth?
There’s other financial information you can — and often should — add to your business plan, like sales forecasts and personnel plans. But the income statement, cash flow projections and balance sheet are the ones you can’t leave out.
Here's a brief run-down of the three major data sets.
Income Statement
Also called a profit/loss statement, here’s where your reader can see if your business is profitable. If you’re not operating the business yet, this will be a projected income statement, based on a well-informed analysis of your business’s first year.
The income statement is broken down by month and shows revenue (sales), expenses (costs of operating) and the resulting profit or loss for one fiscal year. (Revenue - expenses = profit/loss.)
Cash Flow Statements
Here’s where your reader can see how much money you’re going to need in the first year of operations. If you’re not yet up and running, you’ll only have projections.
For cash flow projections, you’ll predict the cash money that will flow into and out of your business in a particular month. You’ll need a year’s worth of monthly projections. If you’re already operating, also include cash flow statements for past months showing actual numbers.
Cash flow statements have three basic components: cash revenues, cash disbursements and reconciliation of revenues to disbursements. For each month, you start with your previous month’s balance, add revenues and subtract disbursements. The final balance becomes the opening balance for the following month.
Balance Sheet
Here’s where your reader sees your business’s net worth. It breaks down into monthly balance sheets and a final net worth at the end of the fiscal year. There are three parts to a balance sheet:
• Accounts receivable
• Inventory, equipment
• Real estate
2. Liabilities
• Accounts payable
• Loan debts
3. Equity: Total assets minus total liabilities (Assets = liabilities + equity.)
It’s good to offer readers an analysis of the three basic financial statements — how they fit together and what they mean for the future of your business. It doesn’t have to be in depth; focus is good. Just interpret the data from each statement, putting it in context and indicating what the reader should take away from the financials section of your business plan.
Other Financial Documents
These are the basics of your financials, but you’ll need to fill out the section with other data based on the specifics of your business and your capital needs. Other financial information you might provide includes:
• Sales forecast: Estimates of future sales volumes
• Personnel plan: Who you plan to recruit/hire and how much it will cost
• Breakeven analysis: Projected point at which your sales will match your expenses
• Financial history: Summary of your business finances from the start of operations to the present time
Make It Easy
A lot of this can be made easier with business planning software, which can not only guide you through the process and make sure you don’t leave anything else but may also generate graphs, charts and other visuals to accompany the data in your financials section. Those types of visuals are highly recommended because some readers will skim. Anything you can do to convey information in a glance imparts a benefit.
Revisit Monthly
Once in operation, don’t forget to go back into your financials every month to update your projections with actual numbers and then adjust any future projections accordingly. Regular updates will tell you if you’re on track with your predictions and hitting your goals, as well as whether you need to make adjustments. Don’t forget this part — when you’re starting out, planning really is your best friend.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Financial Analysis
The last article in a comprehensive series to help you craft the perfect business plan for your startup.

This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan .
Numbers tell the story. Bottom line results indicate the success or failure of any business.
Financial projections and estimates help entrepreneurs, lenders, and investors or lenders objectively evaluate a company's potential for success. If a business seeks outside funding, providing comprehensive financial reports and analysis is critical.
But most importantly, financial projections tell you whether your business has a chance of being viable--and if not let you know you have more work to do.
Most business plans include at least five basic reports or projections:
- Balance Sheet: Describes the company cash position including assets, liabilities, shareholders, and earnings retained to fund future operations or to serve as funding for expansion and growth. It indicates the financial health of a business.
- Income Statement: Also called a Profit and Loss statement, this report lists projected revenue and expenses. It shows whether a company will be profitable during a given time period.
- Cash Flow Statement: A projection of cash receipts and expense payments. It shows how and when cash will flow through the business; without cash, payments (including salaries) cannot be made.
- Operating Budget: A detailed breakdown of income and expenses; provides a guide for how the company will operate from a "dollars" point of view.
- Break-Even Analysis: A projection of the revenue required to cover all fixed and variable expenses. Shows when, under specific conditions, a business can expect to become profitable.
It's easy to find examples of all of the above. Even the most basic accounting software packages include templates and samples. You can also find templates in Excel and Google Docs. (A quick search like "google docs profit and loss statement" yields plenty of examples.)
Or you can work with an accountant to create the necessary financial projections and documents. Certainly feel free to do so... but I'd first recommend playing around with the reports yourself. While you don't need to be an accountant to run a business, you do need to understand your numbers... and the best way to understand your numbers is usually to actually work with your numbers.
But ultimately the tools you use to develop your numbers are not as important as whether those numbers are as accurate as possible--and whether those numbers help you decide whether to take the next step and put your business plan into action.
Then Financial Analysis can help you answer the most important business question: "Can we make a profit?"
Some business plans include less essential but potentially important information in an Appendix section. You may decide to include, as backup or additional information:
- Resumes of key leaders
- Additional descriptions of products and services
- Legal agreements
- Organizational charts
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Photographs of potential facilities, products, etc
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Additional financial documents or projections
Keep in mind creating an Appendix is usually only necessary if you're seeking financing or hoping to bring in partners or investors. Initially the people reading your business plan don't wish to plow through reams and reams of charts, numbers, and backup information. If one does want to dig deeper, fine--he or she can check out the documents in the Appendix.
That way your business plan can share your story clearly and concisely.
Otherwise, since you created your business plan... you should already have the backup.
And one last thing: always remember the goal of your business plan is to convince you that your idea makes sense--because it's your time, your money, and your effort on the line.
More in this series:
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Key Concepts
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: the Executive Summary
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Overview and Objectives
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Products and Services
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Market Opportunities
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Sales and Marketing
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Competitive Analysis
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Operations
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Management Team
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy
Call Us (877) 968-7147 Login
Most popular blog categories
- Payroll Tips
- Accounting Tips
- Accountant Professional Tips

How to Craft the Financial Section of Business Plan (Hint: It’s All About the Numbers)
Writing a small business plan takes time and effort … especially when you have to dive into the numbers for the financial section. But, working on the financial section of business plan could lead to a big payoff for your business.
Read on to learn what is the financial section of a business plan, why it matters, and how to write one for your company.
What is the financial section of business plan?
Generally, the financial section is one of the last sections in a business plan. It describes a business’s historical financial state (if applicable) and future financial projections. Businesses include supporting documents such as budgets and financial statements, as well as funding requests in this section of the plan.
The financial part of the business plan introduces numbers. It comes after the executive summary, company description , market analysis, organization structure, product information, and marketing and sales strategies.
Businesses that are trying to get financing from lenders or investors use the financial section to make their case. This section also acts as a financial roadmap so you can budget for your business’s future income and expenses.
Why it matters
The financial section of the business plan is critical for moving beyond wordy aspirations and into hard data and the wonderful world of numbers.
Through the financial section, you can:
- Forecast your business’s future finances
- Budget for expenses (e.g., startup costs)
- Get financing from lenders or investors
- Grow your business
- Growth : 64% of businesses with a business plan were able to grow their business, compared to 43% of businesses without a business plan.
- Financing : 36% of businesses with a business plan secured a loan, compared to 18% of businesses without a plan.
So, if you want to possibly double your chances of securing a business loan, consider putting in a little time and effort into your business plan’s financial section.
Writing your financial section
To write the financial section, you first need to gather some information. Keep in mind that the information you gather depends on whether you have historical financial information or if you’re a brand-new startup.
Your financial section should detail:
- Business expenses
Financial projections
Financial statements, break-even point, funding requests, exit strategy, business expenses.
Whether you’ve been in business for one day or 10 years, you have expenses. These expenses might simply be startup costs for new businesses or fixed and variable costs for veteran businesses.
Take a look at some common business expenses you may need to include in the financial section of business plan:
- Licenses and permits
- Cost of goods sold
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Payroll costs (e.g., salaries and taxes)
- Utilities
- Equipment
- Supplies
- Advertising
Write down each type of expense and amount you currently have as well as expenses you predict you’ll have. Use a consistent time period (e.g., monthly costs).
Indicate which expenses are fixed (unchanging month-to-month) and which are variable (subject to changes).
How much do you anticipate earning from sales each month?
If you operate an existing business, you can look at previous monthly revenue to make an educated estimate. Take factors into consideration, like seasonality and economic ups and downs, when basing projections on previous cash flow.
Coming up with your financial projections may be a bit trickier if you are a startup. After all, you have nothing to go off of. Come up with a reasonable monthly goal based on things like your industry, competitors, and the market. Hint : Look at your market analysis section of the business plan for guidance.
A financial statement details your business’s finances. The three main types of financial statements are income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets.
Income statements summarize your business’s income and expenses during a period of time (e.g., a month). This document shows whether your business had a net profit or loss during that time period.
Cash flow statements break down your business’s incoming and outgoing money. This document details whether your company has enough cash on hand to cover expenses.
The balance sheet summarizes your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Balance sheets help with debt management and business growth decisions.
If you run a startup, you can create “pro forma financial statements,” which are statements based on projections.
If you’ve been in business for a bit, you should have financial statements in your records. You can include these in your business plan. And, include forecasted financial statements.

You’re just in luck. Check out our FREE guide, Use Financial Statements to Assess the Health of Your Business , to learn more about the different types of financial statements for your business.
Potential investors want to know when your business will reach its break-even point. The break-even point is when your business’s sales equal its expenses.
Estimate when your company will reach its break-even point and detail it in the financial section of business plan.
If you’re looking for financing, detail your funding request here. Include how much you are looking for, list ideal terms (e.g., 10-year loan or 15% equity), and how long your request will cover.
Remember to discuss why you are requesting money and what you plan on using the money for (e.g., equipment).
Back up your funding request by emphasizing your financial projections.
Last but not least, your financial section should also discuss your business’s exit strategy. An exit strategy is a plan that outlines what you’ll do if you need to sell or close your business, retire, etc.
Investors and lenders want to know how their investment or loan is protected if your business doesn’t make it. The exit strategy does just that. It explains how your business will make ends meet even if it doesn’t make it.
When you’re working on the financial section of business plan, take advantage of your accounting records to make things easier on yourself. For organized books, try Patriot’s online accounting software . Get your free trial now!
Stay up to date on the latest accounting tips and training
You may also be interested in:
Need help with accounting? Easy peasy.
Business owners love Patriot’s accounting software.
But don’t just take our word…

Explore the Demo! Start My Free Trial
Relax—run payroll in just 3 easy steps!
Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support. Try our payroll software in a free, no-obligation 30-day trial.

Relax—pay employees in just 3 steps with Patriot Payroll!
Business owners love Patriot’s award-winning payroll software.

Watch Video Demo!
Watch Video Demo

Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan
We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.
Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
$0.00 | ||||||
$0.00 | ||||||
$0.00 | ||||||
$10.00 (waivable) | ||||||
$0.00 |
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2024 All Rights Reserved.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Running a Business
- Business Finances
How to Write a Financial Statement
Last Updated: December 22, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Kathy Duong . Kathy Duong is a certified accountant who has been working as an accountant for over 25 years. She received her BS in Finance and Accounting from California State University, Los Angeles in 1992. There are 20 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 84% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 188,118 times.
Financial statements are the formal record of a company's financial activity. The main components of a financial statement are the balance sheet, the income statement, and the statement of cash flows. The balance sheet shows the assets, liabilities, and the shareholder's equity at a specific point in time. The income sheet, on the other hand, shows the revenues, expenses, and income or loss for a specific period of time, usually a month, quarter, or year. The statement of cash flows shows the cash balance at the beginning of a period, the inflows and outflows of cash during a specific period, and the ending cash balance. For public companies, what goes on these sheets is regulated by the Securities Exchange Commission in compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). You should hire a professional to make sure you are compliant with those standards if you are unfamiliar with them.
Building a Balance Sheet

- Balance sheets may be constructed using accounting software. Or, you can simply create a spreadsheet or written list with two columns that can be used to total your assets and liabilities by category. [2] X Research source

- Your current assets include the cash you have on hand and what could be liquidated quickly, usually within a year. In this category, you would have things like your accounts receivable (what people owe your company), any securities becoming due with a year such as bonds or savings accounts, and your inventory. It can also include pre-payments or deposits you've made ahead of time, such as insurance for the next year.
- Fixed assets are tangible and known as property, plant, and equipment. These are assets with a useful life in excess of one year.
- There are also intangible assets that may be held on a balance sheet. These include patents, brand recognition, and copyrights, along with other non-physical assets. [4] X Research source
- All of these assets need actual dollar figures in your balance sheet, these can be calculated exactly or estimated based on (and in compliance with) industry convention.

- Current liabilities include things like what you owe on lines of credit and credit cards, as well as anything owed to other companies for goods and supplies. It also includes the income and wages you've paid out to employees and taxes owed, along with unpaid rent and utilities. [6] X Research source
- Long-term liabilities include long-term loans payable, bonds payable, and other liabilities that will be paid out over a time period longer than one year. [7] X Research source

- Have a line for your total assets. Below it, have a line for your total liabilities. Show what the shareholder's equity is when you subtract the second from the first.

- When you've listed these categories out, sum them up to arrive at total shareholder's equity. [9] X Research source
- Compare your total to the difference between assets and liabilities from your earlier calculations. If the figures don't match, either you or the accountant that keeps the company's books has made a mistake somewhere along the way.
- Many balance sheets are organized such that the assets are totaled on the left and liabilities and shareholder's equity are totaled on the right. This provides a more literal representation of the basic accounting equation.
Writing the Income Statement

- Unlike the balance sheet, the income statement covers financial activity throughout the period in question, whether that is a month, a quarter, or a year.
- The income statement is organized as a reduction of net sales by various expenses faced by the company to arrive at net income (also called net profit or the bottom line). [11] X Research source

- Separate these expenses into three major categories: selling, general and administrative expenses. When you've written out the amount of each expense, total them to find total operating expenses.
- Subtract total operating expenses from gross profit to arrive at operating income. [15] X Research source

- Put the net sales on one line. Underneath that, put the cost of sales. Below that, subtract the cost of sales from the net sales to get the gross profit. Skip a line before moving on to operating costs.
- Put the operating costs in general categories underneath the gross profit. Generally, selling, general, and administrative costs are lumped into one, but not always. Underneath that, write the operating income that you derived from subtracting the operating costs from the gross profit. [17] X Research source
- Next, have a line each for the interest and the taxes. You can subtract them separately or together. Separately gives you more precise data.
- The final line should be the net income. [18] X Research source
Writing the Statement of Cash Flows

- The statement of cash flows is split into three pieces: cash flows from operating activities, cash flows from investing activities, and cash flows from financing activities. [20] X Research source

- Amortization is when the company spreads out the cost of something over time for accounting purposes. However, it is not really a cost taking away from cash flow right now. Therefore, you add that expense back in. [22] X Research source
- The same with depreciation. It's a number taken away from the total amount of an asset, as it loses value over time. However, it's not technically a cash flow problem, so that expense is added back in. [23] X Research source
- This method is the indirect method of figuring out cash flow. The direct method involves adding up cash flows from scratch rather than starting with net income. [24] X Research source

- If you have sold fixed assets within the period, such as property, you need to look at whether it was a gain or loss, then add or subtract it from the operating costs.
- You also need to look at changes in accounts receivable. Since accounts receivable is what other people owe the company if it goes down, that means the company has gained cash, and that needs to be added in.
- On the other hand, if the company has bought inventory, that signals a decrease in cash and needs to be subtracted from the cash flow.
- Other items that can affect the cash flow include taxes payable, insurance you've already paid, and salaries payable. [26] X Research source

- This step can include money you've put into new equipment or other capital, such as buildings, which will be subtracted from cash flow. [28] X Research source It can also be equipment you've sold, which would be added to the cash flow.
- This step also includes any money invested in the stock market, what you've bought and sold, and how that affects your overall cash. [29] X Research source

- Loans are added to your overall cash. However, your loan payments for the year are taken out of the overall cash.
- Dividends you pay out to shareholders obviously reduces your cash, while if you issue bonds or common stock, the issue is recorded as an influx of cash. [31] X Research source

- Add in last year's cash. If you have any cash left over from last year or you started out with a deficit, add that or subtract that to this year's cash.
- That will give you the total amount of cash you have on hand, also called your total cash resources. [33] X Research source
Expert Q&A
- If you're still unsure how to prepare a financial statement, considering hiring an accountant to work on your statements with you. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.accountingcoach.com/accounting-equation/explanation
- ↑ https://quickbooks.intuit.com/r/financial-management/creating-financial-statements-how-to-prepare-a-balance-sheet/
- ↑ https://quickbooks.intuit.com/r/bookkeeping/5-simple-ways-create-balance-sheet/
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/intangibleasset.asp
- ↑ https://www.bouffordca.com/FS/SampleFS.pdf
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/balancesheet.asp
- ↑ https://www.accountingcoach.com/balance-sheet/explanation/2
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/n/netsales.asp
- ↑ https://www.accountingcoach.com/income-statement/explanation
- ↑ https://www.accountingcoach.com/income-statement/explanation/4
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cogs.asp
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/g/general-and-administrative-expenses.asp
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/walkthrough/corporate-finance/2/financial-statements/income-statement.aspx
- ↑ https://articles.bplans.com/how-to-read-an-income-statement/
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/articles/04/022504.asp
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/articles/04/033104.asp
- ↑ https://articles.bplans.com/cash-flow-101-building-a-cash-flow-statement/
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/amortization.asp
- ↑ https://www.accountingtools.com/questions-and-answers/how-to-prepare-a-cash-flow-statement.html
- ↑ https://www.zionsbank.com/pdfs/biz_resources_book-4.pdf

About This Article
To write a financial statement, start by putting together a balance sheet with details such as your assets and liabilities. Then, write your income statement showing net sales, gross profits from those sales, and operating and non-operating expenses to figure out your net income. After that, compile your statement of cash flows to show how cash moved in and out of the business throughout the year, and how much was left at the end of the year. To learn more, like how to determine your shareholder’s equity, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Akachukwu Mbata
Oct 4, 2018
Did this article help you?

Sep 14, 2017
Oct 10, 2018
Jun 6, 2016
Joshua Sorinolu
Nov 22, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
6 Small Business Financial Statements for Startup Financing
Financial Statements You'll Need for Your Startup Business Plan
You're ready to start your small business and your're working on a great business plan to take to a bank or other lender. A key part of that plan is the financial statements. These statements will be looked at carefully by the lender, so here are some tips for making these documents SELL your business plan .
Financial Statements You Will Need
You may need several different types of statements, depending on the requirements of your lender and your own technical expertise.
The statements you will certainly need are:
- A startup budget or cash flow statement
- A startup costs worksheet
- A pro forma (projected) profit and loss statement
- A pro forma (projected) balance sheet
Your lender may also want these financial statements:
- Sources and uses of funds statement
- Break-even analysis
Putting these Statements in Order
First, work on your startup budget and your startup costs worksheet. You'll need to do a lot of estimating.
The trick is to underestimate income and overestimate expenses, so you can create a more realistic picture of your business over the first year or two.
Then work on a profit and loss statement for the first year. A lender will definitely want to see this one. And, even though it's not going to be accurate, lenders like to see a startup balance sheet.
Some lenders may ask for a break-even analysis, a cash flow statement, or a sources and uses of funds statement. We'll go over these statements so you can quickly provide them if asked.
Business Startup Budget
A startup budget is like a projected cash flow statement, but with a little more guesswork.
Your lender wants to know your budget - that is, what you expect to bring in and how much to expect to spend each month. Lenders want to know that you can follow a budget and that you will not over-spend.
They also want to see how much you will need to pay your bills while your business is starting out (working capital), and how long it will take you to have a positive cash flow (bring in more money than you are spending).
Include some key information on your budget:
- What products or services you are selling, including prices and estimated volumes
- Key drivers for expenses, like how many employees you'll need and your marketing initiatives
A typical budget worksheet should be carried through three years, so your lender can see how you expect to generate the cash to make your monthly loan payments.
Startup Costs Worksheet
A startup costs worksheet answers the question "What do you need the money for?" In other words, it shows all the purchases you will need to make in order to open your doors for business. This could be called a "Day One" statement because it's everything you will need on your first day of business.
- Facilities costs, like deposits on insurance and utilities
- Office equipment, computers, phones
- Supplies and advertising materials like signs and business cards
- Fees to set up your business website and email
- Legal fees licenses and permits
Profit and Loss Statement/Income Statement
After you have completed the monthly budget and you have gathered some other information, you should be able to complete a Profit and Loss or Income Statement. This statement shows your business activity over a specific period of time, like a month, quarter, or year.
To create this statement, you'll need to list all your sources to get your gross income over that time. Then, list all expenses for the same time.
Because you haven't started yet, this statement is a called a projected P&L, because it projects out your estimates into the future.
This statement gathers up all your sources of income, including shows your profit or loss for the year and how much tax you estimate having to pay.
Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis shows your lender that you know the point at which you will start making a profit or the price that will cover your fixed costs . The break-even analysis is primarily for businesses making or selling products, or to set the right price for a product or service.
It's usually shown as a graph with sales volume on the X axis and revenue on the Y axis. Then fixed an variable costs (those you must pay) are included. The break-even point marks the place where costs are covered.
This analysis can also be useful for service-type businesses to show an overall profit point for specific services. If you include a break-even analysis, be sure you can explain it.
Beginning Balance Sheet
A startup balance sheet is difficult to prepare, even if there isn't much to include. The balance sheet shows the value of the assets you have purchased for startup, how much you owe to lenders and other creditors, and any initial investments you have made to get started. The date for this spreadsheet is the day you open the business.
Sources and Uses of Funds Statement
Large businesses use Sources and Uses of Funds statements in their annual reports, but you can create a slightly different simple statement to show your lender what you need the money for, what sources you have already, and what's left over to be financed.
To create this statement, list all your startup and working capital(on-going cash needs), how much collateral you will be bringing to the business, other sources of funding, and how much you need to borrow.
Optional: A Business Requirements Document
A business requirements document is similar to a proposal document, but for a larger, more complex project or startup. It gives a complete picture of the project or the business plan. It goes into more detail on the project that will be using the financial statements.
Include Financial Statements in Your Business Plan
You will need a complete startup business plan to take to a bank or other business lender. The financial statements are a key part of this plan. Give the main points in the executive summary and include all the statements in the financial section.
Finally, Check for Mistakes!
Before you submit your startup business plan and financial statements, check this list. Don't make these common business plan mistakes !
Check all numbers for accuracy and consistency. Especially make sure the amounts you are requesting are specific and that they are the same throughout all the parts of your business plan.
SCORE.org. " How to Set Up and Maintain a Budget for Your Small Business ." Accessed Sept. 10, 2020.
SCORE.org. " Financial Projections Template ." Accessed Sept. 10, 2020.
Harvard Business Review. " A Quick Guide to Breakeven Analysis ." Accessed Sept. 10, 2020.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
When you are starting a small business or a startup, you will need to make financial projections for your business.
Financial plan in business plan helps understand the chances of your business becoming a financial success. Investors want to see a financial plan to know how much money they’ll invest and what the expected return over investment is for them.
We have briefly discussed the process of writing a financial plan in business plan. One thing that can make or break your financial plan in business plan is your honesty about numbers.
Try not to be over-optimistic. See the growth pattern of similar businesses and project closely to them. Don’t overestimate the effects of your competitive advantage.

Want to write a business plan?
Hire our top business plan writers now!
What is Financial Plan in Business Plan?
A financial plan in business plan is an overview of your business financial projections.
Business plan financial projections include financial reports including Profit & Loss, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
A financial plan will also discuss sales forecast, employees’ salaries and other expenses forecast, business breakeven analysis, and important business rations that help measure growth.
How to Write A Business Plan Financial Section
A business plan financial section is about making simple forecasts and creating a few financial reports. You don’t need to know accounting, nor is it necessary for creating financial projections.
We have outlined and simplified the process of creating a financial plan for business plan. Simply follow the process and take help from our examples and templates to write an excellent financial plan section of a business plan.

Review your Business Goals and Strategic Plan
You have set business goals in your business plan. A strategic plan is how you will navigate to financial success.
Everything in a business plan that contributes toward your business goals. Before writing financial projections, consider these goals and milestones:
- Expansion plans
- Adding more people to your team
- Resources required to meet your business goals
- Cash flow needs of your business in the short and long term
- Financing needs to meet business goals
Create Financial Projections
Financial projections in a business plan will include the following:
- Profit and loss statement
Cash Flow Statement
- Balance Sheet
Sales Forecast
- Personnel Plan
- Business Ratios and Breakeven Analysis
We will explore each in detail in the following section. By the end of the article, you will fully understand how to create financial plan in business plan.
Profit and Loss Statement
A profit and loss statement is the first financial report you will create when writing financial plan in business plan.
A profit and loss statement reports your business income or loss over a certain period of time.
Profit and loss statement is also known by other names including its short form i.e., P & L statement, income statement, and pro forma income statement.
A profit and loss statement includes total revenues, expenses, and costs. A P&L statement is made for different time intervals like quarterly, bi-annual and annual. It shows net income after the cost of goods sold, expenses, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
Before creating a P&L statement for your business, you may need to look for the right format for your business structure. For example, you will need a different format for a profit and loss statement for a sole proprietorship and a different one for an LLC.
Check income statement examples to understand and create one yourself.
Profit and Loss Statement Template
Download our free profit and loss statement templates & examples, and make a professional income statement for financial plan in business plan.
Parts of a Profit and Loss Statement
Every profit and loss statement includes the following elements:
- Total Revenues
- Cost of Sales or Cost of Goods Sold
- Gross Margin
Depending on the business type, a P&L statement may include insurance, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Make sure to include a forecast for all heads in financial plan in business plan.
Calculate Operating Income
Start your profit and loss statement by calculating operating income; use this formula.
Gross Margin – Operating Expenses = Operating Income
Typically, operating income is equal to EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization).
Operating income is also called the gross profit and it does not deduce taxes or other accounting adjustments from the income.
Calculate Net Income
Use this formula to calculate net income.
Operating Income – (Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization Expenses) = Net Income
Access our free sample business plans now!
A cash flow statement is typically prepared every month. You can create monthly and quarterly cash flow statement in financial plan in business plan.
A cash flow statement informs about the cash your business brought income, the cash it paid out, and how much is still available with the bank.
A cash flow statement gives an understanding of your income sources and expenses. When you forecast your financial reports, a cash flow statement will show your expected income sources and expenses.
A cash flow statement will help potential lenders and investors understand how you plan to make money. It provides reliable data about cash in and cash out. Keep it realistic and in line with the industry number for the most part. An exception may be an innovation or a breakthrough you bring to the market.
Your profit and cash flow are not the same. It is possible to have a cashless, profitable business or a business in loss with plenty of cash. A good cash flow helps you keep your business open and turn things around.
A cash flow statement also reflects your behavior with money. It shows if you spend on spur of the moment or think strategically. When creating a cash flow statement in a business plan, you will need to understand two basic concepts of accounting; cash accounting and accrual accounting.
Professional Business Templates for Small Businesses
Check our extensive library of business templates for small businesses and make use of the templates and examples in writing your business plan.
Difference between Cash and Accrual Accounting
The difference between cash and accrual accounting is Accrual accounting records revenues/income and expenses when they occur while cash accounting records income/revenue and expenses when the money actually changes hands.
You will need to decide if you will use cash accounting or accrual accounting. However, the final choice will depend on your business type and product.
For example, you are selling tickets to a show or you are taking preorders for your new product. Under cash accounting, you will record all income now and expenses when you have actually shipped the product or organized the show.
However, with accrual accounting, you will record both income and expenses when you have shipped the product or held the show.
Here, cash accounting will show the months with cash abundance as profitable and the months of spending, like shipping of the products of event organization, as a loss. It is hard to see a pattern and get actionable insight with cash accounting.
It is a good time to decide about the accounting method you will use when you are writing a financial plan in business plan.
Check with your accounting consultant and discuss accrual and cash accounting to select the one most suitable for your business.
Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a summary of the financial position of your business.
A balance sheet includes assets, liabilities, and equity. A balance sheet is based on this formula and it is always equal on both sides of the equation.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Here, Assets include your inventory, cash at hand and bank, property, vehicles, accounts receivables, etc. Liabilities are debts, loans and account payables. Equity includes shares proceeds, retained earnings, and owner’s money.
Download Balance Sheet Template from WiseBusinessPlan and make a balance sheet easy.
A sales forecast is your projection about the sales you will make in a certain time. Investors and lenders will be interested in seeing your sales forecast. They will estimate your chances of meeting the forecast and projections.
Keep your sales forecast consistent with the financial reports like the cash flow statement and profit & loss statement.
How To Make A Sales Forecast For A Business Plan?
First, decide the period for the sales forecast, like one month or a quarter. Then, do the following steps to make a sales forecast for that period.
- List goods or services your business sells
- Forecast sales for each product or service
- Set per unit price for your goods or services
- Find sales volume by multiplying units sold with unit price
- Calculate the cost of goods sold
- Multiply the cost of goods sold by the number of units sold, this is your total cost
- Take the total cost amount from the total sales amount
Need Business Plan Cover Page?
Download our business plan cover page now!
Personnel Plan
A personnel plan shows the costs and value of the employees you will hire.
Very small businesses, startups, or solopreneurs may not need a personnel plan but any business with employees, or plans to hire employees, will need this.
Forecast the cost of each employee and the value they will provide. You don’t need to discuss everything about employees, just do a short cost-benefit analysis for each position or employee.
Breakeven Analysis and Business Ratios
Breakeven analysis tells you the number of sales you need to bring in to cover all of your business expenses.
Use this formula to calculate the breakeven point for your business.
Break-Even Point (units) = Fixed Costs / (Sales price per unit – Variable costs per unit)
Business ratios are like signals for your business. You can quickly spot a growth or fall with a ratio. Some business ratios also help you see business health.
You are not required to include business ratio forecasts however, it is good to know about them when writing a business plan.
Here are some of the most used business ratios.
- Gross margin
- Return on sales
- Return on assets
- Return on investment
- Debt-to-equity
- Current ratio
- Working capital
- gross margin
- return on investment (ROI)
- Debt-to-equity.
Use Financial Plan as a Tool for Business Management
One mistake that most people make is thinking that building a business plan is a one time thing.
Your business plan and your financial projections can help you measure your business growth. You can use these numbers as a yard stick to see if you are meeting your projections or not.
Here is how you can your business plan as a management tool for your business.
Schedule monthly and quarterly business review meetings. Compare your actual data for that period with your forecast data and see how you are moving towards your business goals. Adjust your forecast or projections with the help of actual data to keep your growth trajectory in the right direction.
Hire our professional who can help write a business plan !
Frequently asked questions (faqs).
The financial section of a business plan should include key financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It should also provide details on projected sales, expenses, and profitability, along with any assumptions or financial ratios used.
Forecasting sales and revenue involves analyzing market research, understanding your target audience, and considering factors such as pricing, competition, and marketing strategies. Utilize historical data, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth assumptions to estimate future sales figures.
In addition to sales and revenue projections, the financial section should include projected expenses, such as operational costs, marketing expenses, and overheads. It should also outline anticipated profits, cash flow projections, and return on investment (ROI) calculations.
Yes, including a break-even analysis is important as it helps determine the point at which your business will start generating profits. It identifies the sales volume needed to cover all expenses and provides insights into the viability of your business.
Supporting documents may include historical financial statements, tax returns, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and any other relevant financial records. Additionally, include details about any loans, investments, or funding sources that contribute to the financial projections.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077


- Creating a Small Business Financial Plan

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on September 02, 2023
Are You Retirement Ready?
Table of contents, financial plan overview.
A financial plan is a comprehensive document that charts a business's monetary objectives and the strategies to achieve them. It encapsulates everything from budgeting and forecasting to investments and resource allocation.
For small businesses, a solid financial plan provides direction, helping them navigate economic challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and ensure sustainable growth.
The strength of a financial plan lies in its ability to offer a clear roadmap for businesses.
Especially for small businesses that may not have a vast reserve of resources, prioritizing financial goals and understanding where every dollar goes can be the difference between growth and stagnation.
It lends clarity, ensures informed decision-making, and sets the stage for profitability and success.
Understanding the Basics of Financial Planning for Small Businesses
Role of financial planning in business success.
Financial planning is the backbone of any successful business endeavor. It serves as a compass, guiding businesses toward profitability, stability, and growth.
With proper financial planning, businesses can anticipate potential cash shortfalls, make informed investment decisions, and ensure they have the capital needed to seize new opportunities.
For small businesses, in particular, tight financial planning can mean the difference between thriving and shuttering. Given the limited resources, it's vital to maximize every dollar and anticipate financial challenges.
Through diligent planning, small businesses can position themselves competitively, adapt to market changes, and drive consistent growth.
Core Components of a Financial Plan for Small Businesses
Every financial plan comprises several core components that, together, provide a holistic view of a business's financial health and direction. These include setting clear objectives, estimating costs , preparing financial statements , and considering sources of financing.
Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring a thorough and actionable financial strategy .
For small businesses, these components often need a more granular approach. Given the scale of operations, even minor financial missteps can have significant repercussions.
As such, it's essential to tailor each component, ensuring they address specific challenges and opportunities that small businesses face, from initial startup costs to revenue forecasting and budgetary constraints.
Setting Clear Small Business Financial Objectives
Identifying business's short-term and long-term financial goals.
Every business venture starts with a vision. Translating this vision into actionable financial goals is the essence of effective planning.
Short-term goals could range from securing initial funding and achieving a set monthly revenue to covering startup costs. These targets, usually spanning a year or less, set the immediate direction for the business.
On the other hand, long-term financial goals delve into the broader horizon. They might encompass aspirations like expanding to new locations, diversifying product lines, or achieving a specific market share within a decade.
By segmenting goals into short-term and long-term, businesses can craft a step-by-step strategy, making the larger vision more attainable and manageable.
Understanding the Difference Between Profitability and Cash Flow
Profitability and cash flow, while closely linked, are distinct concepts in the financial realm. Profitability pertains to the ability of a business to generate a surplus after deducting all expenses.
It's a metric of success and indicates the viability of a business model . Simply put, it answers whether a business is making more than it spends.
In contrast, cash flow represents the inflow and outflow of cash within a business. A company might be profitable on paper yet struggle with cash flow if, for instance, clients delay payments or unexpected expenses arise.
For small businesses, maintaining positive cash flow is paramount. It ensures that they can cover operational costs, pay employees, and reinvest in growth, even if they're awaiting payments or navigating financial hiccups.
Estimating Small Business Startup Costs (for New Businesses)
Fixed vs variable costs.
When embarking on a new business venture, understanding costs is paramount. Fixed costs remain consistent regardless of production levels. They include expenses like rent, salaries, and insurance . These are predictable outlays that don't fluctuate with business performance.
Variable costs , conversely, change in direct proportion to production or business activity. Think of costs associated with materials for manufacturing or commission for sales .
For a startup, delineating between fixed and variable costs aids in crafting a more dynamic budget, allowing for adaptability as the business scales and evolves.
One-Time Expenditures vs Ongoing Expenses
Startups often grapple with numerous upfront costs. From purchasing equipment and setting up a workspace to initial marketing campaigns, these one-time expenditures lay the foundation for business operations.
They differ from ongoing expenses like utility bills, raw materials, or employee wages that recur monthly or annually.
For a small business owner, distinguishing between these costs is critical. One-time expenditures often demand a larger chunk of initial capital, while ongoing expenses shape the monthly and annual budget.
By categorizing them separately, businesses can strategize funding needs more effectively, ensuring they're equipped to meet both immediate and recurrent financial obligations.
Funding Sources for Small Businesses
Personal savings.
This is often the most straightforward way to fund a startup. Entrepreneurs tap into their personal savings accounts to jumpstart their business.
While this method has the benefit of not incurring debt or diluting company ownership, it intertwines the individual's personal financial security with the business's fate.
The entrepreneur must be prepared for potential losses, and there's the evident psychological strain of putting one's hard-earned money on the line.
Loans can be sourced from various institutions, from traditional banks to credit unions . They offer a substantial sum of money that can be paid back over time, usually with interest .
The main advantage of taking a loan is that the entrepreneur retains full ownership and control of the business.
However, there's the obligation of monthly repayments, which can strain a business's cash flow, especially in its early days. Additionally, securing a loan often requires collateral and a sound credit history.
Investors, including angel investors and venture capitalists , offer capital in exchange for equity or a stake in the company.
Angel investors are typically high-net-worth individuals who provide funding in the initial stages, while venture capitalists come in when there's proven business potential, often injecting larger sums. The advantage is substantial funding without the immediate pressure of repayments.
However, in exchange for their investment, they often seek a say in business decisions, which might mean compromising on some aspects of the original business vision.
Grants are essentially 'free money' often provided by government programs, non-profit organizations, or corporations to promote innovation and support businesses in specific sectors.
The primary advantage of grants is that they don't need to be repaid, nor do they dilute company ownership. However, they can be highly competitive and might come with stipulations on how the funds should be used.
Moreover, the application process can be lengthy and requires showcasing the business's potential or alignment with the specific goals or missions of the granting institution.

Preparing Key Financial Statements for Small Businesses
Income statement (profit & loss).
An Income Statement , often termed as the Profit & Loss statement , showcases a business's financial performance over a specific time frame. It details revenues , expenses, and ultimately, profits or losses.
By analyzing this statement, business owners can pinpoint revenue drivers, identify exorbitant costs, and understand the net result of their operations.
For small businesses, this document is instrumental in making informed decisions. For instance, if a certain product line is consistently unprofitable, it might be prudent to discontinue it. Conversely, if another segment is thriving, it might warrant further investment.
The Income Statement, thus, serves as a financial mirror, reflecting the outcomes of business strategies and decisions.
Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet offers a snapshot of a company's assets , liabilities , and equity at a specific point in time.
Assets include everything the business owns, from physical items like equipment to intangible assets like patents .
Liabilities, on the other hand, encompass what the company owes, be it bank loans or unpaid bills.
Equity represents the owner's stake in the business, calculated as assets minus liabilities.
This statement is crucial for small businesses as it offers insights into their financial health. A robust asset base, minimal liabilities, and growing equity signify a thriving enterprise.
In contrast, mounting liabilities or dwindling assets could be red flags, signaling the need for intervention and strategy recalibration.
Cash Flow Statement
While the Income Statement reveals profitability, the Cash Flow Statement tracks the actual movement of money.
It categorizes cash flows into operating (day-to-day business), investing (buying/selling assets), and financing (loans or equity transactions) activities. This statement unveils the liquidity of a business, indicating whether it has sufficient cash to meet immediate obligations.
For small businesses, maintaining positive cash flow is often more vital than showcasing profitability.
After all, a business might be profitable on paper yet struggle if clients delay payments or unforeseen expenses emerge.
By regularly reviewing the Cash Flow Statement, small business owners can anticipate cash crunches and strategize accordingly, ensuring seamless operations irrespective of revenue cycles.

Small Business Budgeting and Expense Management
Importance of budgeting for a small business.
Budgeting is the financial blueprint for any business, detailing anticipated revenues and expenses for a forthcoming period. It's a proactive approach, enabling businesses to allocate resources efficiently, plan for investments, and prepare for potential financial challenges.
For small businesses, a meticulous budget is often the linchpin of stability, ensuring they operate within their means and avoid financial pitfalls.
Having a well-defined budget also fosters discipline. It curtails frivolous spending, emphasizes cost-efficiency, and sets clear financial boundaries.
For small businesses, where every dollar counts, a stringent budget is the gateway to financial prudence, ensuring that funds are utilized judiciously, fostering growth, and minimizing wastage.
Strategies for Reducing Costs and Optimizing Expenses
Bulk purchasing.
When businesses buy supplies in large quantities, they often benefit from discounts due to economies of scale . This can significantly reduce per-unit costs.
However, while bulk purchasing leads to immediate savings, businesses must ensure they have adequate storage and that the products won't expire or become obsolete before they're used.
Renegotiating Vendor Contracts
Regularly reviewing and renegotiating contracts with suppliers or service providers can lead to better terms and lower costs. This might involve exploring volume discounts, longer payment terms, or even bartering services.
Building strong relationships with vendors often paves the way for such negotiations.
Adopting Energy-Saving Measures
Simple changes, like switching to LED lighting or investing in energy-efficient appliances, can lead to long-term savings in utility bills. Moreover, energy conservation not only reduces costs but also minimizes the environmental footprint, which can enhance the business's reputation.
Embracing Technology
Modern software and technology can streamline business processes. Automation tools can handle repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs.
Meanwhile, data analytics tools can provide insights into customer preferences and behavior, ensuring that marketing budgets are used effectively and target the right audience.
Streamlining Operations
Regularly reviewing and refining business processes can eliminate redundancies and improve efficiency. This might mean merging roles, cutting down on unnecessary meetings, or simplifying supply chains. A leaner operation often translates to reduced expenses.
Outsourcing Non-core Tasks
Instead of maintaining an in-house team for every function, businesses can outsource tasks that aren't central to their operations.
For instance, functions like accounting , IT support, or digital marketing can be outsourced to specialized agencies, often leading to cost savings and access to expert skills.
Cultivating a Culture of Frugality
Encouraging employees to adopt a cost-conscious mindset can lead to collective savings. This can be fostered through incentives, regular training, or even simple practices like recycling and reusing office supplies.
When everyone in the organization is attuned to the importance of cost savings, the cumulative effect can be substantial.

Forecasting Small Business Revenue and Cash Flow
Techniques for predicting future sales in a small business, past sales data analysis.
Historical sales data is a foundational element in any forecasting effort. By reviewing previous sales figures, businesses can identify patterns, understand seasonal fluctuations, and recognize the effects of past initiatives.
This information offers a baseline upon which to build future projections, accounting for known recurring variables in the business cycle .
Market Research
Understanding the larger market dynamics is crucial for accurate forecasting. This involves tracking industry trends, monitoring shifts in consumer behavior, and being aware of potential market disruptions.
For instance, a sudden technological advancement can change consumer preferences or regulatory changes might impact an industry.
Local Trend Analysis
For small businesses, localized insights can be especially impactful. Observing local competitors, understanding regional consumer preferences, or noting shifts in the local economy can offer precise data points.
These granular details, when integrated into a larger forecasting model, can enhance prediction accuracy.
Customer Feedback
Direct feedback from customers is an invaluable source of insights. Surveys, focus groups, or even informal chats can reveal customer sentiments, preferences, and potential future purchasing behavior.
For instance, if a majority of loyal customers express interest in a new product or service, it can be indicative of future sales potential.
Moving Averages
This technique involves analyzing a series of data points (like monthly sales) by creating averages from different subsets of the full data set.
For yearly forecasting, a 12-month moving average can be used to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical tool used to identify relationships between variables. In sales forecasting, it can help understand how different factors (like marketing spend, seasonal variations, or competitor actions) relate to sales figures.
Once these relationships are understood, businesses can predict future sales based on planned actions or expected external events.

Understanding the Cash Cycle of Business
The cash cycle encompasses the time it takes for a business to convert resource investments, often in the form of inventory, back into cash.
This involves the processes of purchasing inventory, selling it, and subsequently collecting payment. A shorter cycle implies quicker cash turnarounds, which are vital for liquidity.
For small businesses, a firm grasp of the cash cycle can aid in managing cash flow more effectively.
By identifying bottlenecks or delays, businesses can strategize to expedite processes. This might involve renegotiating payment terms with suppliers, offering discounts for prompt customer payments, or optimizing inventory levels to prevent overstocking.
Ultimately, understanding and optimizing the cash cycle ensures that a business remains liquid and agile.
Preparing for Seasonality and Unexpected Changes
Seasonality affects many businesses, from the ice cream vendor witnessing summer surges to the retailer bracing for holiday shopping frenzies.
By analyzing historical data and market trends, businesses can prepare for these cyclical shifts, ensuring they stock up, staff appropriately, and market effectively.
Small businesses, often operating on tighter margins , need to be especially vigilant. Beyond seasonality, they must also brace for unexpected changes – a local construction project obstructing store access, a sudden competitor emergence, or unforeseen regulatory changes.
Building a financial buffer, diversifying product or service lines, and maintaining flexible operational strategies can equip small businesses to weather these unforeseen challenges with resilience.
Securing Small Business Financing and Capital
Role of debt and equity financing.
When businesses seek external funding, they often grapple with the debt vs. equity conundrum. Debt financing involves borrowing money, typically via loans. While it doesn't dilute ownership, it necessitates regular interest payments, potentially impacting cash flow.
Equity financing, on the other hand, entails selling a stake in the business to investors. It might not demand regular repayments, but it dilutes ownership and might influence business decisions.
Small businesses must weigh these options carefully. While loans offer a structured repayment plan and retained control, they might strain finances if the business hits a rough patch.
Equity financing, although relinquishing some control, might bring aboard strategic partners, offering expertise and networks in addition to funds.
The optimal choice hinges on the business's financial health, growth aspirations, and the founder's comfort with sharing control.
Choosing Between Different Types of Loans
A staple in the lending arena, term loans offer businesses a fixed amount of capital that is paid back over a specified period with interest. They're often used for significant one-time expenses, such as purchasing machinery, real estate , or even business expansion.
With predictable monthly payments, businesses can plan their budgets accordingly. However, they might require collateral and a robust credit history for approval.
Lines of Credit
Unlike term loans that provide funds in a lump sum, a line of credit grants businesses access to a pool of funds up to a certain limit.
Businesses can draw from this line as needed, only paying interest on the amount they use. This makes it a versatile tool, especially for managing cash flow fluctuations or unexpected expenses. It serves as a financial safety net, ready for use whenever required.
As the name suggests, microloans are smaller loans designed to cater to businesses that might not need substantial amounts of capital. They're particularly beneficial for startups, businesses with limited credit histories, or those in need of a quick, small financial boost.
Since they are of a smaller denomination, the approval process might be more lenient than traditional loans.
Peer-To-Peer Lending
A contemporary twist to the traditional lending model, peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms connect borrowers directly with individual lenders or investor groups.
This direct model often translates to quicker approvals and competitive interest rates as the overheads of traditional banking structures are removed. With technology at its core, P2P lending can offer a more user-friendly, streamlined process.
However, creditworthiness still plays a pivotal role in determining interest rates and loan amounts.
Crowdfunding and Alternative Financing Options
In an increasingly digital age, crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo have emerged as viable financing avenues.
These platforms enable businesses to raise small amounts from a large number of people, often in exchange for product discounts, early access, or other perks. This not only secures funds but also validates the business idea and fosters a community of supporters.
Other alternatives include invoice financing, where businesses get an advance on pending invoices, or merchant cash advances tailored for businesses with significant credit card sales.
Each financing mode offers unique advantages and constraints. Small businesses must meticulously evaluate their financial landscape, growth trajectories, and risk appetite to harness the most suitable option.
Small Business Tax Planning and Management
Basic tax obligations for small businesses.
Navigating the maze of taxation can be daunting, especially for small businesses. Yet, understanding and fulfilling tax obligations is crucial.
Depending on the business structure—whether sole proprietorship , partnership , LLC , or corporation—different tax rules apply. For instance, while corporations are taxed on their earnings, sole proprietors report business income and expenses on their personal tax returns.
In addition to income taxes, small businesses may also be responsible for employment taxes if they have employees. This covers Social Security , Medicare , federal unemployment, and sometimes state-specific taxes.
There might also be sales taxes, property taxes, or special state-specific levies to consider.
Consistently maintaining accurate financial records, being aware of filing deadlines, and setting aside funds for tax obligations are essential practices to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Advantages of Tax Planning and Potential Deductions
Tax planning is the strategic approach to minimizing tax liability through the best use of available allowances, deductions, exclusions, and breaks.
For small businesses, effective tax planning can lead to significant savings.
This might involve strategies like deferring income to a later tax year, choosing the optimal time to purchase equipment, or taking advantage of specific credits available to businesses in certain sectors or regions.
Several potential deductions can reduce taxable income for small businesses. These include expenses like rent, utilities, business travel, employee wages, and even certain meals.
By keeping abreast of tax law changes and actively seeking out eligible deductions, small businesses can optimize their financial landscape, ensuring they're not paying more in taxes than necessary.
Importance of Hiring a Tax Professional or Accountant
While it's feasible for small business owners to manage their taxes, the intricate nuances of tax laws make it beneficial to consult professionals.
An experienced accountant or tax consultant can not only ensure compliance but can proactively recommend strategies to reduce tax liability.
They can guide businesses on issues like whether to classify someone as an employee or a contractor, how to structure the business for optimal taxation, or when to make certain capital investments.
Beyond just annual tax filing, these professionals offer year-round counsel, helping businesses maintain clean financial records, stay updated on tax law changes, and plan for future financial moves.
The investment in professional advice often pays dividends , saving businesses from costly mistakes, penalties, or missed financial opportunities.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting the Small Business Financial Plan
Setting checkpoints and milestones.
Like any strategic blueprint, a financial plan isn't static. It serves as a guiding framework but should be flexible enough to adapt to evolving business realities.
Setting regular checkpoints— quarterly , half-yearly, or annually—can help businesses assess whether they're on track to meet their financial objectives.
Milestones, such as reaching a specific sales target, launching a new product, or expanding into a new market, offer tangible markers of progress. Celebrating these victories can bolster morale, while any shortfalls can serve as lessons, prompting strategy tweaks. F
or small businesses, where agility is an asset, regularly revisiting the financial plan ensures that the business remains aligned with its overarching financial goals while being responsive to the dynamic marketplace.
Using Financial Ratios to Monitor Business Health
Financial ratios offer a distilled snapshot of a business's health. Ratios like the current ratio ( current assets divided by current liabilities ) can shed light on liquidity, indicating whether a business can meet short-term obligations.
The debt-to-equity ratio , contrasting borrowed funds with owner's equity, offers insights into the business's leverage and potential financial risk.
Profit margin , depicting profitability relative to sales, can highlight operational efficiency. By consistently monitoring these and other pertinent ratios, small businesses can glean actionable insights, understanding their financial strengths and areas needing attention.
In a realm where early intervention can stave off major financial setbacks, these ratios serve as vital diagnostic tools, guiding informed decision-making.
Pivoting Strategies Based on Financial Performance
In the ever-evolving world of business, flexibility is paramount. If financial reviews indicate that certain strategies aren't yielding anticipated results, it might be time to pivot.
This could involve tweaking product offerings, revising pricing strategies, targeting a different customer segment, or even overhauling the business model.
For small businesses, the ability to pivot can be a lifeline. It allows them to respond swiftly to market changes, customer feedback, or internal challenges.
A robust financial plan, while offering direction, should also be pliable, accommodating shifts in strategy based on real-world performance. After all, in the business arena, adaptability often spells the difference between stagnation and growth.

Bottom Line
Financial foresight is integral for the stability and growth of small businesses. Effective revenue and cash flow forecasting, anchored by historical sales data and enhanced by market research, local trends, and customer feedback, ensures businesses are prepared for future demands.
With the unpredictability of the business environment, understanding the cash cycle and preparing for unforeseen challenges is essential.
As businesses contemplate external financing, the decision between debt and equity and the myriad of loan types, should be made judiciously, keeping in mind the business's health, growth aspirations, and risk appetite.
Furthermore, diligent tax planning, with professional guidance, can lead to significant financial benefits. Regular reviews using financial ratios allow businesses to gauge their performance, adapt strategies, and pivot when necessary.
Ultimately, the agility to adapt, guided by a well-structured financial plan, is pivotal for businesses to thrive in a dynamic marketplace.
Creating a Small Business Financial Plan FAQs
What is the importance of a financial plan for small businesses.
A financial plan offers a structured roadmap, guiding businesses in making informed decisions, ensuring growth, and navigating financial challenges.
How do forecasting revenue and understanding cash cycles aid in financial planning?
Forecasting provides insights into expected income, aiding in budget allocation, while understanding cash cycles ensures effective liquidity management.
What are the core components of a financial plan for small businesses?
Core components include setting objectives, estimating startup costs, preparing financial statements, budgeting, forecasting, securing financing, and tax management.
Why is tax planning vital for small businesses?
Tax planning ensures compliance, optimizes tax liabilities through available deductions, and helps businesses save money and avoid penalties.
How often should a small business review its financial plan?
Regular reviews, ideally quarterly or half-yearly, ensure alignment with business goals and allow for strategy adjustments based on real-world performance.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Average Cost of a Certified Financial Planner
- Benefits of Having a Financial Planner
- Cash Flow Management
- Charitable Financial Planning
- Debt Reduction Strategies
- Disadvantages of Not Having a Financial Plan
- Divorce Financial Planning
- Education Planning
- Fee-Only Financial Planning
- Financial Contingency Planning
- Financial Planner Fee Structure
- Financial Planner for Retirement
- Financial Planning Pyramid
- Financial Planning Tips
- Financial Planning Trends
- Financial Planning and Analysis
- Financial Planning and Investment
- Financial Planning for Allied Health Professionals
- Financial Planning for Married Couples
- Financial Planning for Military Families
- Financial Planning for Retirement
- Financial Planning for Startups
- Financial Planning vs Budgeting
- Financial Tips for Young Adults
- How to Build a 5-Year Financial Plan
- Limitations of Financial Planning
- Military Spouse Financial Planning
- The Function of a Financial Planner
- When Do You Need a Financial Planner?
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you, our recommended advisors.

Claudia Valladares
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
To ensure one vote per person, please include the following info, great thank you for voting., get in touch with a financial advisor, submit your info below and someone will get back to you shortly..
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
Better Knowledge. Your Insight Is Sharper
Essential Guide to Understanding Financial Statement Analysis
Updated: August 24, 2024 · Reviewed by: Ahmad Nasrudin

This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we may earn a small commission if you purchase through our links. This helps support our work.
Financial statement analysis is valuable for understanding a company’s financial health and performance. Whether you’re an investor, a lender, or a business owner, knowing how to read and interpret financial statements can help you make informed decisions.
What is Financial Statement Analysis?
Financial statement analysis is the process of evaluating a company’s financial performance and financial position using its financial statements. These statements typically include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Financial statement analysis is a powerful tool that helps you understand a company’s financial health and performance. By examining a company’s income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement, you can gain valuable insights into its profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency.
Why is Financial Statement Analysis Important?
There are several reasons why financial statement analysis is crucial:
- Investment decisions: If you’re an investor, understanding a company’s financial statements can help you decide where to allocate your money. By analyzing a company’s financial performance, you can assess its potential for growth and profitability.
- Credit decisions: Lenders use financial statement analysis to determine a company’s creditworthiness. If a company has a strong financial position, it is more likely to be able to repay its debts.
- Internal management: Companies use financial statement analysis to identify areas for improvement and make informed business decisions. By analyzing their financial performance, companies can identify strengths and weaknesses and make necessary adjustments to their operations.
In summary, financial statement analysis is essential for anyone who wants to understand a company’s financial health and performance. Learning to read and interpret financial statements allows you to make more informed decisions about your investments, loans, and business operations.
What are the Three Main Financial Statements?
Financial statement analysis involves examining a company’s financial performance using three primary statements: the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
The Income Statement
The income statement is a snapshot of a company’s profitability over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It shows the company’s revenue, expenses, and net income.
- Revenue: The total income a company earns from its sales of goods or services.
- Expenses: The costs incurred by the company in generating revenue, such as salaries, rent, and materials.
- Net Income: The profit or loss a company earns after deducting expenses from revenue.
The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Assets: What the company owns, such as cash, inventory, and property.
- Liabilities: What the company owes, such as debts and loans.
- Equity: The residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities.
The Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement shows how a company’s cash inflows and outflows changed over a specific period. It is divided into three sections:
- Operating activities: Cash flows from the company’s core business operations.
- Investing activities: Cash flows from buying and selling long-term assets, such as property and equipment.
- Financing activities: Cash flows from borrowing money, issuing stock, and paying dividends.
How Do I Read and Analyze Financial Statements?
To effectively analyze financial statements, follow these steps:
- Understand the basics: Familiarize yourself with fundamental financial terms and concepts, such as revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Compare to industry standards: Benchmark a company’s performance against industry averages and competitors. This helps you identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Analyze financial ratios: Calculate and interpret various financial ratios to assess a company’s financial health, including profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency.
- Look for trends: Examine how a company’s financial performance has changed over time. This can reveal positive or negative trends in its business.
By understanding and analyzing these three financial statements, you can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health and make informed decisions about investing or lending.
Free Up Your Learning Journey
Note: While those offer many free courses, some might require payment for certificates or additional materials. Please check individual course details.
What are the Key Financial Ratios to Analyze?
Financial statement analysis involves examining a company’s financial performance using various ratios to assess its financial health. Here are some of the key financial ratios to consider:
Profitability ratios
Profitability ratios measure a company’s ability to generate profits. Some common profitability ratios include the following:
- Profit margin: This ratio shows the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after deducting expenses. A higher profit margin indicates better profitability.
- Return on assets (ROA): This ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate profits. A higher ROA indicates that the company generates more profit per dollar of assets.
- Return on equity (ROE): This ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its shareholders’ equity to generate profits. A higher ROE indicates a better return for investors.
Liquidity ratios
Liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Some common liquidity ratios include:
- Current ratio compares a company’s current assets to its current liabilities. A current ratio greater than 1 indicates that the company has enough current assets to cover its current liabilities.
- Quick ratio is similar to the current ratio but excludes inventory from current assets. Thus, it provides a more conservative measure of liquidity.
Solvency ratios
Solvency ratios measure a company’s ability to meet its long-term obligations. Some common solvency ratios include:
- Debt-to-equity ratio compares a company’s total debt to its total equity. A higher debt-to-equity ratio indicates that the company relies more on debt financing.
- Interest coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to cover its interest expenses with earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT). A higher interest coverage ratio indicates a stronger financial position.
Efficiency ratios
Efficiency ratios measure a company’s ability to use its assets efficiently. Some common efficiency ratios include:
- Inventory turnover ratio measures how efficiently a company manages its inventory. A higher ratio indicates that the company sells its inventory quickly.
- Accounts receivable turnover ratio measures how efficiently a company collects customer payments. A higher ratio indicates that the company collects payments promptly.
By analyzing these key financial ratios, you can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health and make informed decisions about investing or lending.
What are the Common Pitfalls in Financial Statement Analysis?
Financial statement analysis is a powerful tool, but knowing its limitations is important. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
Overreliance on past performance
While past performance can provide valuable insights, it does not guarantee future results. Companies can experience significant changes in their financial performance due to various factors, such as economic conditions, industry trends, and management decisions. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider both historical data and future prospects when analyzing financial statements.
Ignoring non-financial factors
Financial statements provide quantitative data, but it’s essential also to consider qualitative factors that can impact a company’s performance. These factors include:
- Management quality: The quality of a company’s management team can significantly influence its success.
- Industry trends: Industry-specific factors, such as technological advancements or regulatory changes, can affect a company’s financial performance.
- Competitive landscape: A company’s position and competitive advantage can also impact its financial results.
Misinterpreting ratios
Financial ratios are valuable tools for analyzing financial statements but should not be interpreted in isolation. They should be considered in conjunction with other financial data and industry benchmarks. For example, a high-profit margin may be positive, but it could also indicate that the company is charging excessively high prices.
Where Can I Learn More?
If you’re interested in learning more about financial statement analysis, there are many resources available:
- Online courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer financial statement analysis courses that can provide a structured learning experience.
- Books: Numerous books on the subject are available, ranging from introductory guides to advanced textbooks. My go-to international financial statement analysis book is Int ernational Financial Statement Analysis by Thomas R. Robinson.
- Financial news and analysis: Websites like The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg, and Investopedia provide articles, news, and analysis on financial statements and their implications.
By understanding these common pitfalls and utilizing the available resources, you can effectively analyze financial statements and make informed decisions about your investments or business ventures.
How Can I Improve My Financial Statement Analysis Skills?
Financial statement analysis is a skill that can be honed through practice and continuous learning. Here are some tips to help you improve your abilities:
- Practice regularly: One of the best ways to improve your financial statement analysis skills is to practice regularly. Analyze financial statements from different industries and companies to gain exposure to various financial situations. This will help you develop your ability to identify patterns, trends, and potential red flags.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback on your analysis from experienced professionals or online communities. This can help you identify areas where you can improve and gain new perspectives. Consider joining online forums or discussion groups dedicated to financial analysis.
- Stay updated: Keep up-to-date with changes in accounting standards and industry trends. Accounting standards can evolve over time, and industry-specific developments can affect financial statements. Staying informed will ensure that your analysis is accurate and relevant.
What is the Difference Between Financial Statement Analysis and Financial Modeling?
Financial statement analysis and financial modeling are related but distinct concepts.
- Financial statement analysis involves examining historical financial data to understand a company’s past performance and financial health. It helps you assess a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency.
- Financial modeling involves creating projections of a company’s future financial performance based on various assumptions and scenarios. It helps you forecast revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
While financial statement analysis provides insights into a company’s past, financial modeling helps you anticipate its future performance.
Can I Use Financial Statement Analysis to Value a Company?
Financial statement analysis can be a valuable tool for valuing a company. Several valuation methods rely on financial statements, including:
- Discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis: This method estimates a company’s future cash flows and discounts them back to their present value.
- Comparable company analysis: This method compares a company’s valuation to similar companies in the same industry.
- Precedent transaction analysis: This method compares a company’s valuation to recent similar company transactions.
Analyzing financial statements and using appropriate valuation methods can help you make informed decisions about investing in or acquiring a company.
How Can I Use Financial Statement Analysis to Make Investment Decisions?
Analyzing a company’s financial statements can help you assess its financial health, growth potential, and risk. This information can also help you make informed investment decisions.
- Assessing financial health: Financial statements can help you assess a company’s overall financial health. By analyzing profitability, liquidity, and solvency ratios, you can determine if a company is generating profits, meeting its short-term and long-term obligations, and using its assets efficiently.
- Evaluating growth potential: Financial statements can also help you evaluate a company’s growth potential. Look for trends in revenue, earnings, and other key financial metrics. A company’s consistently growing revenue and profits may be a good investment opportunity.
- Assessing risk: Financial statement analysis can help you identify potential risks associated with an investment. For example, a company with high debt levels may be more vulnerable to economic downturns.
- Making informed decisions: By combining your analysis of financial statements with other factors, such as industry trends, competitive landscape, and management quality, you can make more informed investment decisions.
What are the Limitations of Financial Statement Analysis?
While financial statement analysis is a valuable tool, it has some limitations:
- Quality of financial reporting: The accuracy and reliability of financial statements depend on the quality of a company’s accounting practices. Some companies may engage in fraudulent or misleading accounting practices, which can distort their financial picture.
- Subjectivity: Some financial ratios and valuation methods involve subjective judgments. For example, when estimating future cash flows, analysts may use different assumptions, which can lead to varying valuations.
- Non-financial factors: Financial statements only provide a quantitative view of a company’s performance. Non-financial factors, such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, or consumer preferences, can also significantly impact a company’s success.
Therefore, it’s important to use financial statement analysis in conjunction with other sources of information and consider both quantitative and qualitative factors when making investment decisions.
Take the first step towards financial freedom. Explore our investing fundamentals.
- Types of Financial Ratios: Their Analysis and Interpretation
- Valuation Ratio: Formula And Its Interpretation
- Efficiency Ratio: Type, Formula, Interpretation
- Cash Flow Ratios: Examples, Formulas, and Interpretations
- Liquidity Ratio: Examples, Formulas, How to Calculate
About Ahmad Nasrudin
Introverted writer with a passion for storytelling. Leveraged analytical skills from financial background (equity research, credit risk) at a leading rating agency to enhance writing with a unique statistical and macroeconomic perspective. Learn more about me
- Business Size: How Business Scale Shapes Success (Importances, Measurement, Classification)
- Values, Attitudes and Lifestyles (VALS): Categories and Why They Matter
- Roles of Business: Satisfying Needs and Wants and Creating Value, Jobs, Income
- Sociocultural Environment: Key Factors Impacting Businesses
- Top-Level Management: Examples, Roles and Responsibilities, Skills
Money blog: House price map shows where they're rising - and where they're falling
The Money blog is a hub for personal finance and consumer news and tips. Today's posts include Zoopla data on where house prices are rising and falling. Leave a comment on any of the stories we're covering in the form below.
Wednesday 28 August 2024 09:50, UK
- Map shows house price change in each region - with most up
- Fuel prices are 6p more than they should be - RAC
- PM tells Britons he'll make 'big asks' of them in budget
Essential reads
- Top chef shares cheap soup recipe - as he picks best budget eats in Kent
- Has the Nike trainer bubble burst?
- Half of young people doing 'big no-no' with holiday money - here's the golden rules
Tips and advice
- Hidden refund option that could save you hundreds of pounds
- Best mortgage rates for first-time buyers right now
- How to spend less on school uniform
Ask a question or make a comment
There's good news for holidaymakers as the boss of Ryanair suggests fares could keep falling through the winter and into next year.
Michael O'Leary told reporters that fares for the budget airline had been predicted to rise by 10% from July to September - but instead will fall 5%.
We reported earlier this month that resorts around Europe have been lowering rates due to lower demand - with the post-COVID boom easing and travellers reluctant to keep paying premium prices.
Mr O'Leary said it was reasonable to expect that fares could stay down by 5% in the six months to the end of the financial year in March.
"More people are flying with us this summer at lower fares," said Mr O'Leary.
"Good news for our passengers, bad news for our shareholders."
The boss of Iceland says a sudden further minimum wage increase could bankrupt the budget supermarket chain.
Richard Walker told The Telegraph that it was right for employees to be paid as much as possible - but any changes should be "bled in slowly".
The minimum wage increased in April to £11.44 for workers aged 21 and over. The rate for 18-20-year-olds now sits at £8.60.
The Labour government has not confirmed any future changes, but deputy prime minister Angela Rayner has championed a proposed overhaul of workers' rights - including increasing the minimum wage, ending zero-hours contracts and ending "fire and rehire" practices.
Mr Walker, a former Tory donor who switched support to Labour in January, said he supported the overhaul but warned there could be a "disastrous" impact if wage changes are not brought in gradually.
"If Labour puts up the minimum wage and brings in day one rights, that's fine, but it needs to be bled in slowly. If they turn around and say 'the minimum wage is £15 now', that would bankrupt us," he said.
"A huge leap in the national minimum wage would be disastrous. Of course, people should be paid as much as we possibly can. So let's keep the ambition and keep pushing, but not have such a shock to business."
Every Wednesday we ask Michelin chefs to pick their favourite budget eats where they live and when they cook at home. This week we speak to Stephen Harris, chef-patron at one-starred gastropub The Sportsman in Whitstable, Kent.
Hi Stephen, can you tell us your favourite places in Kent where you can get a meal for two for less than £40?
I love going to The Refectory in St Dunstan's, Canterbury. I go with my son every Saturday morning on my way to The Goods Shed farmers market. The food is brunch/breakfast but done in that Aussie style whereby it has restaurant standards. I often have eggs benedict or just scrambled egg on toast. The coffee is also top drawer. It is very busy and a queue often builds up, but it is worth the wait.
I also love going to the Harbour Street Tapas in Whitstable. I like to go early in the evening and I always have the Iberico ham. We have been taking my son since he was about three and he has learnt how to go to restaurants through this place. The staff are great and we are lucky to have it at the end of our road.
What is your go-to cheap eat to cook at home when you have a night in?
I love to cook a vegetable stew when I am not at work. I use an unusual method as I put all of the trimmings of the veg in a pan and add aromatics like dried cep, ginger, soy sauce, herbs, tomato puree and make a stock by covering it in water and bringing it to the boil - taking it off after a couple of minutes.
I fry a chopped onion in olive oil, then add the veg according to what is about and add the hardest veg first, eg carrot, celery, chilli, herbs, garlic, peppers, courgettes, tomatoes (freshly chopped) and then either potatoes or beans.
After they have all been softened, I pour over the stock made of trimmings and aromatics and cook it until the stock has reduced and evaporated - you have a nice, thick sauce.
The result is a healthy veg-based meal which tastes really good.
How did you get into cheffing?
I only became a chef at the age of 34 because I wanted to open a restaurant and I like cooking. Before that I was a history teacher and then a financial consultant.
I taught myself to cook but I got a job in a kitchen in London to learn how restaurants operate in preparation for opening my own place. I worked as a commis chef at The Fire Station in Waterloo before moving back to Kent in 1996.
We've spoken to lots of top chefs - check out their Cheap Eats from around the country here...
House prices have risen by 1.4% so far this year and are on track to be 2.5% higher annually by the end of 2024, according to one measure of market conditions.
Zoopla's latest house price index also shows that buyer demand has risen by a fifth compared with this time last year, while the supply of homes for sale is at a seven-year high.
"All key measures of sales market activity are higher than 2023 supported by economic growth and rising consumer confidence," the property portal said.
Annually, the cost of the average home has risen by 0.5% - but the picture differs across the country, as this map shows...
Most areas have seen an improvement, though the South West, South East, East of England and East Midlands have recorded "small falls", Zoopla noted.
Overall, the UK's housing market is "more balanced than at any time in the last five years", it said.
"Lower mortgage rates and an improving economic outlook has bought more sellers and buyers into the market...
"Our view is average mortgage rates will remain above 4%, which is sufficient to support more homes moves and sales," it added.
Fuel retailers are being urged to "do the right thing" and cut prices for motorists as wholesale costs fall.
The RAC has issued an appeal to retailers up and down the country to reflect a "steady drop" in costs, "which began at the start of July and accelerated sharply last week".
What are wholesale costs?
Data from its Fuel Watch service shows the wholesale price of petrol averaged 103p a litre last week, with a retailer margin of 10p. That's 2p more than the long-term average of 8p and should lead to average prices of just under 136p per litre including VAT, the RAC said.
What are costs at the pump?
However, the average price of petrol currently sits at 142p - 6p more. When it comes to diesel, RAC says retailers should be selling the fuel at around 139p per litre - 8p less than the current 147p.
It comes after regulators found last month that fuel prices in the UK remain a rip-off .
RAC head of policy Simon Williams said: "It's all the more outrageous when you factor in the fact we're all meant to be benefitting from a temporary 5p cut in fuel duty, that looks likely to disappear in the coming months.
"Once again, we urge retailers to do the right thing and reflect the lower prices they're paying for wholesale fuel on their forecourts."
Asda has been forced to apologise after an IT glitch meant thousands of customers who ordered from its clothing range were left out of pocket.
It comes after the supermarket upgraded George's online system as part of an £800m IT project. Asda says all orders have now been fulfilled.
River Island has threatened to send back clothing to suppliers over quality and sizing issues.
The Times is reporting that the fashion retailer has requested discounts on goods that it says have not met its standards.
One supplier said River Island had accused it of sending a shipment of tops worth hundreds of thousands of pounds that were "ever so slightly too short in length. They threatened to send the whole lot back if we didn't agree to a discount".
According to Waitrose we are buying more treats , with early signs people are feeling increasingly confident about their finances.
James Bailey, Waitrose's executive director, said the grocer was seeing more sales of its premium products compared to this time last year.
He said that earlier in August, sales of its premium own-brand No.1 range were up about a fifth compared with the same week a year ago, in terms of volume.
Other premium labels, such as its Duchy Organic food and drink products, were also selling better than last year, he added.
Retail sales have dropped for the third month in a row, new data suggests.
The Confederation of British Industry's (CBI) latest Distributive Trades Survey found that sales have been "poor" in August.
The latest report's headline retail sales balance hit -27% for the month, as significantly more retailers witnessed a dip in sales.
However, it did represent an improvement, following a balance of -43% in July.
Martin Sartorius, principal economist at the CBI, struck a hopeful note: "Although households seem to still be feeling the pinch from the cost-of-living crisis, firms should gradually begin to see some tailwinds from consumers' rising real incomes."
By Katie Williams and Brad Young , Money reporters
Half of young people are making the costly error of exchanging pounds for foreign currency at the airport instead of sorting it before their trip, a new survey has found.
Research from Compare the Market found that nearly three in 10 holidaymakers (28%) have opted for a currency exchange just before their flight - including more than half of people aged 16-24 (51%).
Those aged over 55 (12%) were more prepared, with most exchanging currency elsewhere.
Meanwhile, more than one in five people (22%) said they withdrew money from a cashpoint or bank during their last holiday abroad and were charged a fee, rising to 26% of 16 to 24-year-olds and a third of 25 to 34-year-olds.
Guy Anker, money expert at Compare the Market, said buying currency at the airport is a "big no-no".
Earlier this year we spoke with three travel experts to find out when, where and how to pay abroad to make your money goes as far as possible...
CREDIT CARD
"The cheapest way to spend overseas is often on plastic , if you've got the right plastic," said James Jones, head of consumer affairs at Experian.
"Using credit and debit cards can be a great way to get the very best exchange rates."
He said rates offered by currency exchange shops are usually "much less attractive" than those offered on some cards, which were much closer to the rates the banks use themselves.
Fees could wipe out any gains
But it's essential to be aware of things like non-sterling transaction fees, cash withdrawal fees and credit card interest.
So shop around for a card with travel rewards, Mr Jones said - and do this before your trip.
"You probably need to give yourself, ideally, six weeks."
Extra protection
When you book a trip between £100 and £30,000, try and pay for some of it on a credit card to get "extra protection" under Section 75 of the Consumer Credit Act, said Mr Jones.
That means the card provider is jointly responsible with the retailer if something goes wrong, such as arriving at a hotel only to find it has closed down.
If you are using a credit card, make sure you can pay it off in full to avoid interest charges, said Sean Tipton from the Association of British Travel Agents (ABTA).
One trap you must not fall into
An increasingly common trap when paying with card (credit or debit) is being presented with the option to pay in the local currency or in pounds, said Mr Jones and Mr Tipton.
While paying in sterling might "seem like a wonderful convenience" you will ultimately be paying "quite a bit more for the purchase", Mr Jones said.
If you pay in pounds, the local retailer's bank sets the exchange rate, but if you pay in the local currency, your UK bank sets the rate.
DEBIT CARDS
"Some service providers don't apply fees for overseas use on their regular UK debit cards," says Moneyfacts - but you must always check as some incur big fees.
Alternatively, "some service providers offer specialist travel debit cards that don't impose non-sterling transaction fees and cash withdrawal fees".
PREPAID TRAVEL CARDS
If you're looking to avoid a credit check, prepaid cards can be loaded with multiple currencies and work like a debit card, without being connected to your bank.
"Typically, prepaid travel cards will offer competitive or even no charges for foreign usage, which can make them a cheaper alternative to using a normal credit or debit card while on holiday," says MoneyFacts.
One of the most popular prepaid cards, Revolut, uses its own exchange rates, which might not always be the best you can find - and while it is fee free on weekdays, there are charges at weekends, so do your research.
Also be aware - prepaid cards do not offer purchase protection like a credit card and aren't regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority.
"Don't rely solely on a card - it can backfire on you if you do," said Mr Tipton.
Some taxis only take cash, leaving you to face hefty charges withdrawing from an ATM.
In some countries, like Argentina, it can be difficult to get money out of ATMs without a local bank account, Mr Tipton said.
Mr Jones added: "If you're in a very remote part of the world that actually doesn't have many ATMs and maybe where cash is king, then that might dictate what you need to do."
Where and when to get cash
"I'd strongly recommend [to] get some cash out in the UK," said Mr Tipton.
It can be difficult to find a bureau de change in some developing nations, and ATMs have "started introducing quite hefty charges" across the board, he said.
The exceptions are countries with really high inflation rates, where it may make more sense to get cash out when you arrive, he added.
When to exchange currency really depends on the destination, said Laura Plunkett, head of travel money at the Post Office.
"Exchange rates change frequently, so if you have time, do your homework and lock in a rate when it is good."
What is a good exchange rate for Europe?
Some 80% of British holidays abroad take place in the Eurozone, said Mr Tipton.
The rate has remained "fairly stable", but if you see the pound increasing in value that may be the time to buy a larger amount of Euros for a couple of years in advance, he added.
Mr Tipton said 1.2 to the pound is a "pretty healthy" time to buy, but "it is a bit of a lottery".
Every year the pound gets stronger against the South African rand, and the same in Argentina, where the peso is "unbelievably weak", Mr Tipton suggested.
In store or online?
"Most online suppliers will insist on a minimum order value that might be too high for some people, and you'll have to make sure that you're home for when it's delivered," said Ms Plunkett.
"But typically, rates are better online if that's an option for you."
Terry's is hoping to move "beyond" just being known for its famous chocolate orange and is launching a milk chocolate ball.
It will come in the same 20-segment format as its orange counterpart - to enable some "familiarity" to shoppers, Terry's has said.
It will roll into "all major retailers" in September, with full distribution in October. The expected price will be £2, putting it on par with previous versions (although you can usually find them on sale somewhere - they're currently £1 at Asda and £1.50 at Tesco).
It comes after Terry's launched its chocolate mint ball last year, which sold out halfway through the Christmas season (it will also return again this year).
"Terry's is an institution so anything we do needs to respect the love that our customers have for it," said Terry's senior marketing manager Lorène Decam.
"We are always very careful to balance innovation with the brand's core."
It's not the first time the brand has tried to innovate - some slightly less successful predecessors to the famous orange were Terry's chocolate apple (1926) and the Terry's chocolate lemon (1970).
If you're looking to consolidate your credit card debt, you may find that some of the top deals have worsened - with several big banks reducing the amount of interest-free time they allow.
An 0% interest card is actually what it says on the tin - you can put spending/debt on it and you won't pay any interest for a set amount of time. It can be a good option if you are looking to spread out spending on a high-value item, such as a sofa or washing machine.
But once the interest-free period ends, you can quickly rack up interest, with the average rate of APR standing at 35.6%.
While consumers could find offers of up to 30 months (two-and-a-half years) interest-free, these are becoming harder to come by, according to Moneyfactscompare.co.uk .
Tesco Bank, one of the market leaders, has reduced its 0% balance transfer offer from 29 months down to 27 months.
And a month ago, Virgin Money cut its 28-month 0% balance transfer offer to 26 months.
In August 2023, the top offer was 30 months interest-free - today it is 28 months.
If you are shopping around for a new interest-free card, it's worth being aware of exactly when your rate ends, as the interest can quickly stack up.
Set a calendar reminder a month ahead of time, and try and stick to repayments to ensure the debt is cleared in time.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Revenue - Expenses = Profit / Loss. Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best. Your income or P&L statement must list the following: Cost of goods or cost of sale.
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you'll need to plan for your business's future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any ...
Balance Sheet. The balance sheet portion of the financial plan aims to give an idea of what the business will be worth, considering all its assets and liabilities, at a future date. To do this, it uses figures from the income statement and cash flow statement. The essence of a balance sheet is found in the equation: Liabilities + Equity = Assets.
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business. Download Startup Financial Projections Template.
Financial ratios and metrics. With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios. While including these metrics in your financial plan for a business plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall ...
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders ...
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement) An income statement shows a company's financial performance by revealing whether it's made a profit or a loss. Without an income statement, you'd be in the dark about the profitability of your business. An income statement is also known as a profit and loss statement, profit and loss account ...
3. Equity: Total assets minus total liabilities (Assets = liabilities + equity.) Analysis. It's good to offer readers an analysis of the three basic financial statements — how they fit ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Operating Budget: A detailed breakdown of income and expenses; provides a guide for how the company will operate from a "dollars" point of view. Break-Even Analysis: A projection of the revenue ...
The financial section of your business plan should include a sales forecast, expenses budget, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and a profit and loss statement. Be sure to follow the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) set forth by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, a private-sector organization responsible for setting ...
Generally, the financial section is one of the last sections in a business plan. It describes a business's historical financial state (if applicable) and future financial projections. Businesses include supporting documents such as budgets and financial statements, as well as funding requests in this section of the plan. The financial part of ...
The financial analysis section should be based on estimates for new businesses or recent data for established businesses. It should include these elements: Balance sheet: Your assumed and anticipated business financials, including assets, liabilities, and equity. Cash-flow analysis: An overview of the cash you anticipate will be coming into ...
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
How to write a financial statement. Steps on how to write a financial statement include: 1. Write an introduction. Write a brief introduction to the summary that outlines what's contained in the section. Keep your writing simple and concise to aid understanding. If the business plan is to serve a certain purpose, write one to two sentences ...
Here are some steps that you can take to create the financial section of a business plan: 1. Create a sales forecast. The first document to create for the financial section is the sales forecast. This is a document that highlights the sales that you might project the business to achieve over the next three years.
Whether the business is starting from scratch or modifying its plan, the best financial plans include the following elements: Income statement: The income statement reports the business's net profit or loss over a specific period of time, such a month, quarter or year.
6. Lay out your statement of cash flows. Start with the net income at the top, and move down through the three categories. It's best to keep the three categories separate, as then people reading the statement of cash flows can see where expenses are going in and out.
Include Financial Statements in Your Business Plan. You will need a complete startup business plan to take to a bank or other business lender. The financial statements are a key part of this plan. Give the main points in the executive summary and include all the statements in the financial section.
A financial plan in business plan is an overview of your business financial projections. Business plan financial projections include financial reports including Profit & Loss, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. A financial plan will also discuss sales forecast, employees' salaries and other expenses forecast, business breakeven analysis ...
Every financial plan comprises several core components that, together, provide a holistic view of a business's financial health and direction. These include setting clear objectives, estimating costs, preparing financial statements, and considering sources of financing. Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring a thorough and actionable ...
Planning is an essential part of operating a business, but a business plan isn't the only roadmap you need. Cortlon Cofield, CPA and owner of Cofield Advisors, a small business financial planning service, said, "Having a well thought out financial plan for your business is the blueprint to success.". Bradford Daniel Creger, chief economist and lead wealth strategist at TFR Group, a ...
Financial statement analysis involves examining a company's financial performance using three primary statements: the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. The Income Statement The income statement is a snapshot of a company's profitability over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you create a financial plan to help you build each paycheck and investment into a retirement plan you can count on. Step 1: Assess Your Current Financial ...
Welcome to the Money blog, a hub for personal finance and consumer news and tips. Today's posts include a look at the chargeback refund option and the best way to buy holiday money. Let us know ...