- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing

How to Cite an Online Article
Last Updated: April 4, 2024 References
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been viewed 253,365 times.
When conducting research for a paper or other project, you may use articles you found online as sources. Include a full citation for the online article in the bibliography or Works Cited at the end of your paper. When you paraphrase or quote information from the online article in your paper, use an in-text citation that points to that full citation. While the citation includes essentially the same information, the format will differ depending on whether you're using the Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA), or Chicago citation style.
Sample Citations

- Example: Bernstein, Mark.

- Example: Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web."

- Example: Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites ,

- Example: Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002,
Leave out any information that isn't provided on the website. You don't have to include any abbreviations to indicate that information is not available. For example, if there is no date on the article, simply leave that information out. You don't have to include an abbreviation such as "n.d." for "no date."

- Example: Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving.

- Example: Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.

- Example: (Bernstein).
If there was no author, use the title of the article in your parenthetical citation.

- Example: American Nurses Association. [9] X Trustworthy Source APA Style Definitive source for current APA style writing and citation guidelines Go to source
If no author is listed for the article, start your full citation with the title of the article. There's no need to note that no author was listed.

- Example: American Nurses Association. (2015).

- Example: American Nurses Association. (2015). Academic progression to meet the needs of the registered nurse, the health care consumer, and the U.S. health care system [Position statement].
If the article has no author, the title of the article appears in your citation before the date. There is no need to repeat it again.

- Example: American Nurses Association. (2015). Academic progression to meet the needs of the registered nurse, the health care consumer, and the U.S. health care system [Position statement]. http://nursingworld.org/MainMenuCategories/Policy-Advocacy/Positions-and-Resolutions/ANAPositionStatements/Position-Statements-Alphabetically/Academic-Progression-to-Meet-Needs-of-RN.html

- Example: (American Nurses Association, 2015).
- If you have multiple articles with the same author and year of publication, place a lower-case letter after the year to distinguish them in your in-text citations. Make sure the same lower-case letter is reflected in your reference list.
If you're quoting the source directly, place a comma after the year, then provide the page number where the quoted information appears after the abbreviation "p." Use the abbreviation "n.p." if the article doesn't have page numbers.

- Individual author example: Nunley, Kathie.
- Organizational author example: United Nations Platform for Action Committee.
If the article has no author, skip this part of the citation. Instead, start the citation with the title of the article.

- Individual author example: Nunley, Kathie. "The Caffeine Craze."
- Organizational author example: United Nations Platform for Action Committee. "Globalization and Clothes."

- Individual author example: Nunley, Kathie. "The Caffeine Craze." Layered Curriculum .
- Organizational author example: United Nations Platform for Action Committee. "Globalization and Clothes." Women and the Economy .

- Individual author example: Nunley, Kathie. "The Caffeine Craze." Layered Curriculum . Accessed July 28, 2018.
- Organizational author example: United Nations Platform for Action Committee. "Globalization and Clothes." Women and the Economy . Last modified March 2011.

- Individual author example: Nunley, Kathie. "The Caffeine Craze." Layered Curriculum . Accessed July 28, 2018. http://help4teachers.com/caffeine.htm.
- Organizational author example: United Nations Platform for Action Committee. "Globalization and Clothes." Women and the Economy . Last modified March 2011. http://unpac.ca/economy/g_clothes.html.

- Individual author example: Kathie Nunley, "The Caffeine Craze," Layered Curriculum , accessed July 28, 2018, http://help4teachers.com/caffeine.htm.
- Organizational author example: United Nations Platform for Action Committee, "Globalization and Clothes," Women and the Economy , last modified March 2011, http://unpac.ca/economy/g_clothes.html.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://blog.apastyle.org/apastyle/2016/11/writing-website-in-text-citations-and-references.html
- ↑ http://www.apastyle.org/learn/faqs/web-page-no-author.aspx
- ↑ http://libanswers.snhu.edu/faq/48009
About This Article

To cite an online article using APA style, start with the author's last name and first initial of their first name, followed by a period. Next, include the year of publication in parentheses and end with a period. Then, type out the full title in italics, end with a period, and follow that up with the publication name and volume number, if appropriate. Finally, close the citation with the direct URL. To learn how to cite an article using Chicago or MLA style, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Kathleen Filer
Nov 29, 2017
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Works-Cited-List Entries
How to cite an online work.
To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an online work, list the author, the title of the work, the title of the website as the title of the container, and the publication details. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of work (e.g., book, scholarly article, blog post) and how you accessed it (e.g., from a journal website, from a database). Below are sample entries for online works along with links to posts containing many other examples.
Article on a website
Deresiewicz, William. “The Death of the Artist—and the Birth of the Creative Entrepreneur.” The Atlantic , 28 Dec. 2014, theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2015/01/ the-death-of-the-artist-and-the-birth-of-thecreative-entrepreneur/383497/.
Book on a website
Poe, Edgar Allan. “The Masque of the Red Death.” The Complete Works of Edgar Allan Poe , edited by James A. Harrison, vol. 4, Thomas Y. Crowell, 1902, pp. 250-58. HathiTrust Digital Library , hdl.handle.net/2027/coo.31924079574368.
Journal Article in a Database
Goldman, Anne. “Questions of Transport: Reading Primo Levi Reading Dante.” The Georgia Review , vol. 64, no. 1, spring 2010, pp. 69-88. JSTOR , www.jstor.org/stable/41403188.
More Examples
Digital Sources
Government Publications
Journal Articles
Reference Works
Social Media
- Previous Example
- Next Example
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
How to Cite a Website and Online/Electronic Resources
The pages outlines examples of how to cite websites and media sources using the Harvard Referencing method .
What are electronic sources?
An electronic source is any information source in digital format. The library subscribes to many electronic information resources in order to provide access for students. Electronic sources can include: full-text journals, newspapers, company information, e-books, dictionaries, encyclopaedias, economic data, digital images, industry profiles, market research, etc.
Should I include extra information when I cite electronic sources?
Referencing electronic or online sources can be confusing—it's difficult to know which information to include or where to find it. As a rule, provide as much information as possible concerning authorship, location and availability.
Electronic or online sources require much of the same information as print sources (author, year of publication, title, publisher). However, in some cases extra information may be required:
- the page, paragraph or section number—what you cite will depend on the information available as many electronic or online sources don’t have pages.
- identify the format of the source accessed, for example, E-book, podcast etc.
- provide an accurate access date for online sources, that is, identify when a source was viewed or downloaded.
- provide the location of an online source, for example, a database or web address.
In-text citations
Cite the name of the author/ organisation responsible for the site and the date created or last revised (use the most recent date):
(Department of Social Services 2020)
According to the Department of Social Services (2020) ...
List of References
Include information in the following order:
- author (the person or organisation responsible for the site
- year (date created or revised)
- site name (in italics)
- name of sponsor of site (if available)
- accessed day month year (the date you viewed the site)
- URL or Internet address (between pointed brackets). If possible, ensure that the URL is included without a line-break.
Department of Social Services 2020, Department of social services website , Australian government, accessed 20 February 2020, <https: //www .dss.gov.au/>.
Specific pages or documents within a website
Information should include author/authoring body name(s) and the date created or last revised:
(Li 2004) or:
(World Health Organisation 2013)
- author (the person or organisation responsible for the site)
- year (date created or last updated)
- page title (in italics)
- name of sponsor of site (if available)
- accessed day month year (the day you viewed the site)
- URL or Internet address (pointed brackets).
One author:
Li, L 2014, Chinese scroll painting H533 , Australian Museum, accessed 20 February 2016, <https: // australianmuseum.net.au/chinese-scroll-painting-h533>.
Organisation as author:
World Health Organisation 2013, Financial crisis and global health , The United Nations, accessed 1 August 2013, <http: //www .who.int/topics/financial_crisis/en/>.
Webpages with no author or date
If the author's name is unknown, cite the website/page title and date:
( Land for sale on moon 2007)
Land for sale on moon 2007, accessed 19 June 2007, <http: // www . moonlandrealestate.com>.
If there is not date on the page, use the abbreviation n.d. (no date):
(ArtsNSW n.d.)
List if References
ArtsNSW n.d., New South Wales Premier’s Literary Awards , NSW Department of the Arts, Sport and Recreation, accessed 19 June 2007, <http: // www . arts.nsw.gov.au/awards/ LiteraryAwards/litawards.htm>.
Kim, M n.d., Chinese New Year pictures and propaganda posters , Museum of Applied Arts and Sciences, accessed 12 April 2016, <https: // collection.maas.museum/set/6274>.
Media articles (print)
If there is no author, list the name of the newspaper, the date, year and page number:
( The Independent 2013, p. 36)
If there is an author, cite as you would for a journal article:
(Donaghy 1994, p. 3)
Articles can also be mentioned in the running text:
University rankings were examined in a Sydney Morning Herald report by Williamson (1998, p. 21), where it was evident that ...
- year of publication
- article title (between single quotation marks)
- publication title (in italics with maximum capitalisation)
- date of article (day, month)
- page number
Williamson, S 1998, ‘UNSW gains top ranking from quality team’, Sydney Morning Herald , 30 February, p.21.
Donaghy, B 1994, ‘National meeting set to review tertiary admissions’, Campus News , 3-9 March, p. 3.
An unattributed newspaper article:
If there is no named author, list the article title first:
- Article title, between single quotation marks,
- Publication title (in italics with maximum capitalisation)
- Date published (date, month, year)
- Page number (if available)
‘Baby tapir wins hearts at zoo’, The Independent , 9 August 2013, p. 36
Online media articles
A news article from an electronic database:
If the article has a named author:
(Pianin 2001)
- author (if available)
- newspaper title (in italics)
- date of article (day, month, page number—if given—and any additional information available)
- accessed day month year (the date you accessed the items)
- from name of database
- item number (if given).
Pianin, E 2001, 'As coal's fortunes climb, mountains tremble in W.Va; energy policy is transforming lives', The Washington Post, 25 February, p. A03, accessed March 2001 from Electric Library Australasia.
A news article without a named author:
No named author:
( New York Daily Times 1830)
The article can also be discussed in the body of the paragraph:
An account of the popularity of the baby tapir in The Independent (2013) stated that ...
If there is no named author, list the article title first.
'Amending the Constitution', New York Daily Times , 16 October 1851, p. 2, accessed 15 July 2007 from ProQuest Historical Newspapers database.
'Baby tapir wins hearts at zoo', The Independent , 9 August 2013, Accessed 25 January 2014, <http: // www . independent.ie/world-news/and-finally/baby-tapir-wins-hearts-at-zoo-30495570.html>.
An online news article:
Cite the author name and year:
(Coorey 2007)
Coorey, P 2007, ‘Costello hints at green safety net’, Sydney Morning Herald , 10 May, accessed 14 May 2012, <http: // www . smh.com.au/news/business/costello-hints-at-green-safety-net/2007/05/09/1178390393875.html>.
While a URL for the article should be included, if it is very long (more than two lines) or unfixed (from a search engine), only include the publication URL:
Holmes, L 2017, 'The woman making a living out of pretending to be Kylie Minogue', The Daily Telegraph , 23 April, accessed 22 May 2017, <http: // www . dailytelegraph.com.au>.
Media releases
Cite the author (the person responsible for the release) and date:
Prime Minister Howard (2007) announced plans for further welfare reform...
- author name or authoring organisation name
- title of release (in italics)
- accessed day month year
- URL (between pointed brackets)
Office of the Prime Minister 2007, Welfare Payments Reform , media release, accessed 25 July 2007, <http: // www . pm.gov.au/media/Release/2007/Media_Release24432.cfm>.
How to cite broadcast materials and communications
Harvard referencing
- How to cite different sources
- How to cite references
- How to cite online/electronic sources
- Broadcast and other sources
- Citing images and tables
- FAQs and troubleshooting
- About this guide
- ^ More support
- TutorHome |
- IntranetHome |
- Contact the OU Contact the OU Contact the OU |
- Accessibility Accessibility
- StudentHome
- Help Centre
You are here
Help and support.
- Referencing and plagiarism
Quick guide to Harvard referencing (Cite Them Right)
- Site Accessibility: Library Services

Print this page
There are different versions of the Harvard referencing style. This guide is a quick introduction to the commonly-used Cite Them Right version. You will find further guidance available through the OU Library on the Cite Them Right Database .
For help and support with referencing and the full Cite Them Right guide, have a look at the Library’s page on referencing and plagiarism . If you need guidance referencing OU module material you can check out which sections of Cite Them Right are recommended when referencing physical and online module material .
This guide does not apply to OU Law undergraduate students . If you are studying a module beginning with W1xx, W2xx or W3xx, you should refer to the Quick guide to Cite Them Right referencing for Law modules .
Table of contents
In-text citations and full references.
- Secondary referencing
- Page numbers
- Citing multiple sources published in the same year by the same author
Full reference examples
Referencing consists of two elements:
- in-text citations, which are inserted in the body of your text and are included in the word count. An in-text citation gives the author(s) and publication date of a source you are referring to. If the publication date is not given, the phrase 'no date' is used instead of a date. If using direct quotations or you refer to a specific section in the source you also need the page number/s if available, or paragraph number for web pages.
- full references, which are given in alphabetical order in reference list at the end of your work and are not included in the word count. Full references give full bibliographical information for all the sources you have referred to in the body of your text.
To see a reference list and intext citations check out this example assignment on Cite Them Right .
Difference between reference list and bibliography
a reference list only includes sources you have referred to in the body of your text
a bibliography includes sources you have referred to in the body of your text AND sources that were part of your background reading that you did not use in your assignment
Back to top
Examples of in-text citations
You need to include an in-text citation wherever you quote or paraphrase from a source. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author(s), the year of publication, and a page number if relevant. There are a number of ways of incorporating in-text citations into your work - some examples are provided below. Alternatively you can see examples of setting out in-text citations in Cite Them Right .
Note: When referencing a chapter of an edited book, your in-text citation should give the author(s) of the chapter.
Online module materials
(Includes written online module activities, audio-visual material such as online tutorials, recordings or videos).
When referencing material from module websites, the date of publication is the year you started studying the module.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication/presentation) 'Title of item'. Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
OR, if there is no named author:
The Open University (Year of publication/presentation) 'Title of item'. Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
Rietdorf, K. and Bootman, M. (2022) 'Topic 3: Rare diseases'. S290: Investigating human health and disease . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1967195 (Accessed: 24 January 2023).
The Open University (2022) ‘3.1 The purposes of childhood and youth research’. EK313: Issues in research with children and young people . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1949633§ion=1.3 (Accessed: 24 January 2023).
You can also use this template to reference videos and audio that are hosted on your module website:
The Open University (2022) ‘Video 2.7 An example of a Frith-Happé animation’. SK298: Brain, mind and mental health . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=2013014§ion=4.9.6 (Accessed: 22 November 2022).
The Open University (2022) ‘Audio 2 Interview with Richard Sorabji (Part 2)’. A113: Revolutions . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=1960941§ion=5.6 (Accessed: 22 November 2022).
Note: if a complete journal article has been uploaded to a module website, or if you have seen an article referred to on the website and then accessed the original version, reference the original journal article, and do not mention the module materials. If only an extract from an article is included in your module materials that you want to reference, you should use secondary referencing, with the module materials as the 'cited in' source, as described above.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of message', Title of discussion board , in Module code: Module title . Available at: URL of VLE (Accessed: date).
Fitzpatrick, M. (2022) ‘A215 - presentation of TMAs', Tutor group discussion & Workbook activities , in A215: Creative writing . Available at: https://learn2.open.ac.uk/mod/forumng/discuss.php?d=4209566 (Accessed: 24 January 2022).
Note: When an ebook looks like a printed book, with publication details and pagination, reference as a printed book.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title . Edition if later than first. Place of publication: publisher. Series and volume number if relevant.
For ebooks that do not contain print publication details
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title of book . Available at: DOI or URL (Accessed: date).
Example with one author:
Bell, J. (2014) Doing your research project . Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Adams, D. (1979) The hitchhiker's guide to the galaxy . Available at: http://www.amazon.co.uk/kindle-ebooks (Accessed: 23 June 2021).
Example with two or three authors:
Goddard, J. and Barrett, S. (2015) The health needs of young people leaving care . Norwich: University of East Anglia, School of Social Work and Psychosocial Studies.
Example with four or more authors:
Young, H.D. et al. (2015) Sears and Zemansky's university physics . San Francisco, CA: Addison-Wesley.
Note: You can choose one or other method to reference four or more authors (unless your School requires you to name all authors in your reference list) and your approach should be consistent.
Note: Books that have an editor, or editors, where each chapter is written by a different author or authors.
Surname of chapter author, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of chapter or section', in Initial. Surname of book editor (ed.) Title of book . Place of publication: publisher, Page reference.
Franklin, A.W. (2012) 'Management of the problem', in S.M. Smith (ed.) The maltreatment of children . Lancaster: MTP, pp. 83–95.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference.
If accessed online:
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference. Available at: DOI or URL (if required) (Accessed: date).
Shirazi, T. (2010) 'Successful teaching placements in secondary schools: achieving QTS practical handbooks', European Journal of Teacher Education , 33(3), pp. 323–326.
Shirazi, T. (2010) 'Successful teaching placements in secondary schools: achieving QTS practical handbooks', European Journal of Teacher Education , 33(3), pp. 323–326. Available at: https://libezproxy.open.ac.uk/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/log... (Accessed: 27 January 2023).
Barke, M. and Mowl, G. (2016) 'Málaga – a failed resort of the early twentieth century?', Journal of Tourism History , 2(3), pp. 187–212. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/1755182X.2010.523145
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference.
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) 'Title of article', Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference if available. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Mansell, W. and Bloom, A. (2012) ‘£10,000 carrot to tempt physics experts’, The Guardian , 20 June, p. 5.
Roberts, D. and Ackerman, S. (2013) 'US draft resolution allows Obama 90 days for military action against Syria', The Guardian , 4 September. Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/world/2013/sep/04/syria-strikes-draft-resolut... (Accessed: 9 September 2015).
Surname, Initial. (Year that the site was published/last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Organisation (Year that the page was last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Robinson, J. (2007) Social variation across the UK . Available at: https://www.bl.uk/british-accents-and-dialects/articles/social-variation... (Accessed: 21 November 2021).
The British Psychological Society (2018) Code of Ethics and Conduct . Available at: https://www.bps.org.uk/news-and-policy/bps-code-ethics-and-conduct (Accessed: 22 March 2019).
Note: Cite Them Right Online offers guidance for referencing webpages that do not include authors' names and dates. However, be extra vigilant about the suitability of such webpages.
Surname, Initial. (Year) Title of photograph . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Kitton, J. (2013) Golden sunset . Available at: https://www.jameskittophotography.co.uk/photo_8692150.html (Accessed: 21 November 2021).
stanitsa_dance (2021) Cossack dance ensemble . Available at: https://www.instagram.com/p/COI_slphWJ_/ (Accessed: 13 June 2023).
Note: If no title can be found then replace it with a short description.
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Getting started with the online library
- Disabled user support
- Finding resources for your assignment
- Finding ejournals and articles
- Access eresources using Google Scholar
- Help with online resources
- Finding and using books and theses
- Finding information on your research topic
- Canllaw Cyflym i Gyfeirnodi Harvard (Cite Them Right)
- Quick guide to Cite Them Right referencing for Law modules
- The Classical Studies guide to referencing
- Bibliographic management
- What if I cannot find the reference type I need in my referencing guide?
- I have found a web page with no author, date or publisher - how do I reference it?
- Training and skills
- Study materials
- Using other libraries and SCONUL Access
- Borrowing at the Walton Hall Library
- OU Glossary
- Contacting the helpdesk
Smarter searching with library databases
Thursday, 9 May, 2024 - 20:30
Learn how to access library databases, take advantage of the functionality they offer, and devise a proper search technique.

Library Helpdesk
Chat to a Librarian - Available 24/7
Other ways to contact the Library Helpdesk
The Open University
- Study with us
- Supported distance learning
- Funding your studies
- International students
- Global reputation
- Apprenticeships
- Develop your workforce
- News & media
- Contact the OU
Undergraduate
- Arts and Humanities
- Art History
- Business and Management
- Combined Studies
- Computing and IT
- Counselling
- Creative Writing
- Criminology
- Early Years
- Electronic Engineering
- Engineering
- Environment
- Film and Media
- Health and Social Care
- Health and Wellbeing
- Health Sciences
- International Studies
- Mathematics
- Mental Health
- Nursing and Healthcare
- Religious Studies
- Social Sciences
- Social Work
- Software Engineering
- Sport and Fitness
Postgraduate
- Postgraduate study
- Research degrees
- Masters in Art History (MA)
- Masters in Computing (MSc)
- Masters in Creative Writing (MA)
- Masters degree in Education
- Masters in Engineering (MSc)
- Masters in English Literature (MA)
- Masters in History (MA)
- Master of Laws (LLM)
- Masters in Mathematics (MSc)
- Masters in Psychology (MSc)
- A to Z of Masters degrees
- Accessibility statement
- Conditions of use
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Manage cookie preferences
- Modern slavery act (pdf 149kb)
Follow us on Social media
- Student Policies and Regulations
- Student Charter
- System Status
- Contact the OU Contact the OU
- Modern Slavery Act (pdf 149kb)
© . . .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing

A Quick Guide to Referencing | Cite Your Sources Correctly
Referencing means acknowledging the sources you have used in your writing. Including references helps you support your claims and ensures that you avoid plagiarism .
There are many referencing styles, but they usually consist of two things:
- A citation wherever you refer to a source in your text.
- A reference list or bibliography at the end listing full details of all your sources.
The most common method of referencing in UK universities is Harvard style , which uses author-date citations in the text. Our free Harvard Reference Generator automatically creates accurate references in this style.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Referencing styles, citing your sources with in-text citations, creating your reference list or bibliography, harvard referencing examples, frequently asked questions about referencing.
Each referencing style has different rules for presenting source information. For in-text citations, some use footnotes or endnotes , while others include the author’s surname and date of publication in brackets in the text.
The reference list or bibliography is presented differently in each style, with different rules for things like capitalisation, italics, and quotation marks in references.
Your university will usually tell you which referencing style to use; they may even have their own unique style. Always follow your university’s guidelines, and ask your tutor if you are unsure. The most common styles are summarised below.
Harvard referencing, the most commonly used style at UK universities, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical bibliography or reference list at the end.
Harvard Referencing Guide
Vancouver referencing, used in biomedicine and other sciences, uses reference numbers in the text corresponding to a numbered reference list at the end.
Vancouver Referencing Guide
APA referencing, used in the social and behavioural sciences, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical reference list at the end.
APA Referencing Guide APA Reference Generator
MHRA referencing, used in the humanities, uses footnotes in the text with source information, in addition to an alphabetised bibliography at the end.
MHRA Referencing Guide
OSCOLA referencing, used in law, uses footnotes in the text with source information, and an alphabetical bibliography at the end in longer texts.
OSCOLA Referencing Guide
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
In-text citations should be used whenever you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source (e.g. a book, article, image, website, or video).
Quoting and paraphrasing
Quoting is when you directly copy some text from a source and enclose it in quotation marks to indicate that it is not your own writing.
Paraphrasing is when you rephrase the original source into your own words. In this case, you don’t use quotation marks, but you still need to include a citation.
In most referencing styles, page numbers are included when you’re quoting or paraphrasing a particular passage. If you are referring to the text as a whole, no page number is needed.
In-text citations
In-text citations are quick references to your sources. In Harvard referencing, you use the author’s surname and the date of publication in brackets.
Up to three authors are included in a Harvard in-text citation. If the source has more than three authors, include the first author followed by ‘ et al. ‘
The point of these citations is to direct your reader to the alphabetised reference list, where you give full information about each source. For example, to find the source cited above, the reader would look under ‘J’ in your reference list to find the title and publication details of the source.
Placement of in-text citations
In-text citations should be placed directly after the quotation or information they refer to, usually before a comma or full stop. If a sentence is supported by multiple sources, you can combine them in one set of brackets, separated by a semicolon.
If you mention the author’s name in the text already, you don’t include it in the citation, and you can place the citation immediately after the name.
- Another researcher warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’ (Singh, 2018, p. 13) .
- Previous research has frequently illustrated the pitfalls of this method (Singh, 2018; Jones, 2016) .
- Singh (2018, p. 13) warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’.
The terms ‘bibliography’ and ‘reference list’ are sometimes used interchangeably. Both refer to a list that contains full information on all the sources cited in your text. Sometimes ‘bibliography’ is used to mean a more extensive list, also containing sources that you consulted but did not cite in the text.
A reference list or bibliography is usually mandatory, since in-text citations typically don’t provide full source information. For styles that already include full source information in footnotes (e.g. OSCOLA and Chicago Style ), the bibliography is optional, although your university may still require you to include one.
Format of the reference list
Reference lists are usually alphabetised by authors’ last names. Each entry in the list appears on a new line, and a hanging indent is applied if an entry extends onto multiple lines.

Different source information is included for different source types. Each style provides detailed guidelines for exactly what information should be included and how it should be presented.
Below are some examples of reference list entries for common source types in Harvard style.
- Chapter of a book
- Journal article
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Your university should tell you which referencing style to follow. If you’re unsure, check with a supervisor. Commonly used styles include:
- Harvard referencing , the most commonly used style in UK universities.
- MHRA , used in humanities subjects.
- APA , used in the social sciences.
- Vancouver , used in biomedicine.
- OSCOLA , used in law.
Your university may have its own referencing style guide.
If you are allowed to choose which style to follow, we recommend Harvard referencing, as it is a straightforward and widely used style.
References should be included in your text whenever you use words, ideas, or information from a source. A source can be anything from a book or journal article to a website or YouTube video.
If you don’t acknowledge your sources, you can get in trouble for plagiarism .
To avoid plagiarism , always include a reference when you use words, ideas or information from a source. This shows that you are not trying to pass the work of others off as your own.
You must also properly quote or paraphrase the source. If you’re not sure whether you’ve done this correctly, you can use the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker to find and correct any mistakes.
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- A Quick Guide to Harvard Referencing | Citation Examples
- APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
How to Avoid Plagiarism | Tips on Citing Sources
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to OSCOLA Referencing | Rules & Examples
- Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples
- Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
- MHRA Referencing | A Quick Guide & Citation Examples
- Reference a Website in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Referencing Books in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Vancouver Referencing | A Quick Guide & Reference Examples
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

Penn State University Libraries
Apa quick citation guide.
- In-text Citation
- Citing Generative AI
- Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Citing Articles
- Citing Books
- Citing Business Reports
- Other Formats
- APA Style Quiz
Using In-text Citation
Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list.
APA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the year of publication, for example: (Field, 2005). For direct quotations, include the page number as well, for example: (Field, 2005, p. 14). For sources such as websites and e-books that have no page numbers , use a paragraph number, for example: (Field, 2005, para. 1). More information on direct quotation of sources without pagination is given on the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines web page.
Example paragraph with in-text citation
A few researchers in the linguistics field have developed training programs designed to improve native speakers' ability to understand accented speech (Derwing et al., 2002; Thomas, 2004). Their training techniques are based on the research described above indicating that comprehension improves with exposure to non-native speech. Derwing et al. (2002) conducted their training with students preparing to be social workers, but note that other professionals who work with non-native speakers could benefit from a similar program.
Derwing, T. M., Rossiter, M. J., & Munro, M. J. (2002). Teaching native speakers to listen to foreign-accented speech. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development , 23 (4), 245-259.
Thomas, H. K. (2004). Training strategies for improving listeners' comprehension of foreign-accented speech (Doctoral dissertation). University of Colorado, Boulder.
Citing Web Pages In Text
Cite web pages in text as you would any other source, using the author and date if known. Keep in mind that the author may be an organization rather than a person. For sources with no author, use the title in place of an author.
For sources with no date use n.d. (for no date) in place of the year: (Smith, n.d.). For more information on citations for sources with no date or other missing information see the page on missing reference information on the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines web page.
Below are examples of using in-text citation with web pages.
Web page with author:
In-text citation
Heavy social media use can be linked to depression and other mental disorders in teens (Asmelash, 2019).
Reference entry
Asmelash, L. (2019, August 14). Social media use may harm teens' mental health by disrupting positive activities, study says . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2019/08/13/health/social-media-mental-health-trnd/index.html
Web page with organizational author:
More than 300 million people worldwide are affected by depression (World Health Organization, 2018).
World Health Organization. (2018, March 22). Depression . https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
Web page with no date:
Establishing regular routines, such as exercise, can help survivors of disasters recover from trauma (American Psychological Association [APA], n.d.).
American Psychological Association. (n.d.). Recovering emotionally from disaste r. http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/recovering-disasters.aspx
General Guidelines
In-text references should immediately follow the title, word, or phrase to which they are directly relevant, rather than appearing at the end of long clauses or sentences. In-text references should always precede punctuation marks. Below are examples of using in-text citation.
Author's name in parentheses:
One study found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (Gass & Varonis, 1984).
Author's name part of narrative:
Gass and Varonis (1984) found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic.
Group as author: First citation: (American Psychological Association [APA], 2015) Subsequent citation: (APA, 2015)
Multiple works: (separate each work with semi-colons)
Research shows that listening to a particular accent improves comprehension of accented speech in general (Gass & Varonis, 1984; Krech Thomas, 2004).
Direct quote: (include page number and place quotation marks around the direct quote)
One study found that “the listener's familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (Gass & Varonis, 1984, p. 85).
Gass and Varonis (1984) found that “the listener’s familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (p. 85).
Note: For direct quotations of more than 40 words , display the quote as an indented block of text without quotation marks and include the authors’ names, year, and page number in parentheses at the end of the quote. For example:
This suggests that familiarity with nonnative speech in general, although it is clearly not as important a variable as topic familiarity, may indeed have some effect. That is, prior experience with nonnative speech, such as that gained by listening to the reading, facilitates comprehension. (Gass & Varonis, 1984, p. 77)
Works by Multiple Authors
APA style has specific rules for citing works by multiple authors. Use the following guidelines to determine how to correctly cite works by multiple authors in text. For more information on citing works by multiple authors see the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines page on in-text citation .
Note: When using multiple authors' names as part of your narrative, rather than in parentheses, always spell out the word and. For multiple authors' names within a parenthetic citation, use &.
One author: (Field, 2005)
Two authors: (Gass & Varonis, 1984)
Three or more authors: (Tremblay et al., 2010)
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Citing Generative AI >>
- Last Updated: Jul 19, 2023 2:50 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited Page: Periodicals

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (8 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Periodicals include magazines, newspapers, and scholarly journals. Works cited entries for periodical sources include three main elements—the author of the article, the title of the article, and information about the magazine, newspaper, or journal. MLA uses the generic term “container” to refer to any print or digital venue (a website or print journal, for example) in which an essay or article may be included.
Below is the generic citation for periodicals using the MLA style. Use this as guidance if you are trying to cite a type of source not described on this page, omitting any information that does not apply:
Author. Title. Title of container (self contained if book), Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publisher Date, Location (pp.). 2nd container’s title, Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Pub date, Location (pp.).
Article in a Magazine
Cite by listing the article's author, putting the title of the article in quotations marks, and italicizing the periodical title. Follow with the date of publication. Remember to abbreviate the month. The basic format is as follows:
Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Periodical , Day Month Year, pages.
Poniewozik, James. "TV Makes a Too-Close Call." Time, 20 Nov. 2000, pp. 70-71.
Buchman, Dana. "A Special Education." Good Housekeeping, Mar. 2006, pp. 143-48.
Article in a Newspaper
Cite a newspaper article as you would a magazine article, but note the different pagination in most newspapers. If there is more than one edition available for that date (as in an early and late edition of a newspaper), identify the edition after the newspaper title.
Brubaker, Bill. "New Health Center Targets County's Uninsured Patients." Washington Post, 24 May 2007, p. LZ01.
Krugman, Andrew. "Fear of Eating." New York Times, late ed., 21 May 2007, p. A1.
If the newspaper is a less well-known or local publication, include the city name in brackets after the title of the newspaper.
Behre, Robert. "Presidential Hopefuls Get Final Crack at Core of S.C. Democrats." Post and Courier [Charleston, SC],29 Apr. 2007, p. A11.
Trembacki, Paul. "Brees Hopes to Win Heisman for Team." Purdue Exponent [West Lafayette, IN], 5 Dec. 2000, p. 20.
To cite a review, include the title of the review (if available), then the phrase, “Review of” and provide the title of the work (in italics for books, plays, and films; in quotation marks for articles, poems, and short stories). Finally, provide performance and/or publication information.
Review Author. "Title of Review (if there is one)." Review of Performance Title, by Author/Director/Artist. Title of Periodical, Day Month Year, page.
Seitz, Matt Zoller. "Life in the Sprawling Suburbs, If You Can Really Call It Living." Review of Radiant City , directed by Gary Burns and Jim Brown. New York Times, 30 May 2007, p. E1.
Weiller, K. H. Review of Sport, Rhetoric, and Gender: Historical Perspectives and Media Representations , edited by Linda K. Fuller. Choice, Apr. 2007, p. 1377.
An Editorial & Letter to the Editor
Cite as you would any article in a periodical, but include the designators "Editorial" or "Letter" to identify the type of work it is.
"Of Mines and Men." Editorial. Wall Street Journal, eastern edition, 24 Oct. 2003, p. A14.
Hamer, John. Letter. American Journalism Review, Dec. 2006/Jan. 2007, p. 7.
Anonymous Articles
Cite the article’s title first, then finish the citation as you would any other for that kind of periodical.
"Business: Global Warming's Boom Town; Tourism in Greenland." The Economist , 26 May 2007, p. 82.
"Aging; Women Expect to Care for Aging Parents but Seldom Prepare." Women's Health Weekly, 10 May 2007, p. 18.
An Article in a Scholarly Journal
A scholarly journal can be thought of as a container, as are collections of short stories or poems, a television series, or even a website. A container can be thought of as anything that contains other pieces of work. In this case, cite the author and title of article as you normally would. Then, put the title of the journal in italics. Include the volume number (“vol.”) and issue number (“no.”) when possible, separated by commas. Finally, add the year and page numbers.
Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Journal , Volume, Issue, Year, pages.
Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu ." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature, vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly , vol. 50, no. 3, 1994, pp. 127-53.
An Article in a Special Issue of a Scholarly Journal
When an article appears in a special issue of a journal, cite the name of the special issue in the entry’s title space, in italics. Add the descriptor “special issue of” and include the name of the journal, also in italics, followed by the rest of the information required for a standard scholarly journal citation.
Web entries should follow a similar format, and should include a DOI (if available), otherwise include a URL or permalink.
Burgess, Anthony. "Politics in the Novels of Graham Greene." Literature and Society, special issue of Journal of Contemporary History, vol. 2, no. 2, 1967, pp. 93-99.
Case, Sue-Ellen. “Eve's Apple, or Women's Narrative Bytes.” Technocriticism and Hypernarrative, special issue of Modern Fiction Studies, vol. 43, no. 3, 1997, pp. 631-50. Project Muse , doi:10.1353/mfs.1997.0056.
Gig workers are writing essays for AI to learn from
- Companies are hiring highly educated gig workers to write training content for AI models .
- The shift toward more sophisticated trainers comes as tech giants scramble for new data sources.
- AI could run out of data to learn from by 2026, one research institute has warned.

As artificial intelligence models run out of data to train themselves on, AI companies are increasingly turning to actual humans to write training content.
For years, companies have used gig workers to help train AI models on simple tasks like photo identification , data annotation, and labelling. But the rapidly advancing technology now requires more advanced people to train it.
Companies such as Scale AI and Surge AI are hiring part-timers with graduate degrees to write essays and creative prompts for the bots to gobble up, The New York Times reported . Scale AI, for example, posted a job last year looking for people with Master's degrees or PhDs, who are fluent in either English, Hindi, or Japanese and have professional writing experience in fields like poetry, journalism, and publishing.
Related stories
Their mission? To help AI bots "become better writers," Scale AI wrote in the posting.
And an army of workers are needed to do this kind of work. Scale AI has as many as tens of thousands of contractors working on its platform at a time, per the Times.
"What really makes the A.I. useful to its users is the human layer of data, and that really needs to be done by smart humans and skilled humans and humans with a particular degree of expertise and a creative bent," Willow Primack, the vice president of data operations at Scale AI, told the New York Times. "We have been focusing on contractors, particularly within North America, as a result."
The shift toward more sophisticated gig trainers comes as tech giants scramble to find new data to train their technology on. That's because the programs learn so incredibly fast that they're already running out of available resources to learn from. The vast trove of online information — everything from scientific papers to news articles to Wikipedia pages — is drying up.
Epoch, an AI research institute, has warned that AI could run out of data by 2026.
So, companies are finding more and more creative ways to make sure their systems never stop learning. Google has considered accessing its customers' data in Google Docs , Sheets, and Slides while Meta even thought about buying publishing house Simon & Schuster to harvest its book collection, Business Insider previously reported.
Watch: Nearly 50,000 tech workers have been laid off — but there's a hack to avoid layoffs
- Main content
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on April 8, 2022 by Courtney Gahan and Jack Caulfield. Revised on June 1, 2023.
Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning.
Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone’s exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it’s usually better to integrate sources by paraphrasing instead of quoting. It shows that you have understood the source, reads more smoothly, and keeps your own voice front and center.
Every time you paraphrase, it’s important to cite the source . Also take care not to use wording that is too similar to the original. Otherwise, you could be at risk of committing plagiarism .
What is your plagiarism score?
Compare your paper with 99.3 billion webpages and 8 million publications.
- Best plagiarism checker of 2021
- Plagiarism report & percentage
- Largest plagiarism database
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
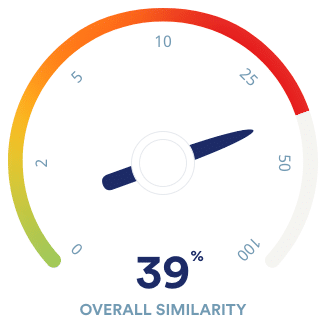
Table of contents
How to paraphrase in five easy steps, how to paraphrase correctly, examples of paraphrasing, how to cite a paraphrase, paraphrasing vs. quoting, paraphrasing vs. summarizing, avoiding plagiarism when you paraphrase, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about paraphrasing.
If you’re struggling to get to grips with the process of paraphrasing, check out our easy step-by-step guide in the video below.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Putting an idea into your own words can be easier said than done. Let’s say you want to paraphrase the text below, about population decline in a particular species of sea snails.
Incorrect paraphrasing
You might make a first attempt to paraphrase it by swapping out a few words for synonyms .
Like other sea creatures inhabiting the vicinity of highly populated coasts, horse conchs have lost substantial territory to advancement and contamination , including preferred breeding grounds along mud flats and seagrass beds. Their Gulf home is also heating up due to global warming , which scientists think further puts pressure on the creatures , predicated upon the harmful effects extra warmth has on other large mollusks (Barnett, 2022).
This attempt at paraphrasing doesn’t change the sentence structure or order of information, only some of the word choices. And the synonyms chosen are poor:
- “Advancement and contamination” doesn’t really convey the same meaning as “development and pollution.”
- Sometimes the changes make the tone less academic: “home” for “habitat” and “sea creatures” for “marine animals.”
- Adding phrases like “inhabiting the vicinity of” and “puts pressure on” makes the text needlessly long-winded.
- Global warming is related to climate change, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing.
Because of this, the text reads awkwardly, is longer than it needs to be, and remains too close to the original phrasing. This means you risk being accused of plagiarism .
Correct paraphrasing
Let’s look at a more effective way of paraphrasing the same text.
Here, we’ve:
- Only included the information that’s relevant to our argument (note that the paraphrase is shorter than the original)
- Introduced the information with the signal phrase “Scientists believe that …”
- Retained key terms like “development and pollution,” since changing them could alter the meaning
- Structured sentences in our own way instead of copying the structure of the original
- Started from a different point, presenting information in a different order
Because of this, we’re able to clearly convey the relevant information from the source without sticking too close to the original phrasing.
Explore the tabs below to see examples of paraphrasing in action.
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
Once you have your perfectly paraphrased text, you need to ensure you credit the original author. You’ll always paraphrase sources in the same way, but you’ll have to use a different type of in-text citation depending on what citation style you follow.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Scribbr citation checker new.
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

It’s a good idea to paraphrase instead of quoting in most cases because:
- Paraphrasing shows that you fully understand the meaning of a text
- Your own voice remains dominant throughout your paper
- Quotes reduce the readability of your text
But that doesn’t mean you should never quote. Quotes are appropriate when:
- Giving a precise definition
- Saying something about the author’s language or style (e.g., in a literary analysis paper)
- Providing evidence in support of an argument
- Critiquing or analyzing a specific claim
A paraphrase puts a specific passage into your own words. It’s typically a similar length to the original text, or slightly shorter.
When you boil a longer piece of writing down to the key points, so that the result is a lot shorter than the original, this is called summarizing .
Paraphrasing and quoting are important tools for presenting specific information from sources. But if the information you want to include is more general (e.g., the overarching argument of a whole article), summarizing is more appropriate.
When paraphrasing, you have to be careful to avoid accidental plagiarism .
This can happen if the paraphrase is too similar to the original quote, with phrases or whole sentences that are identical (and should therefore be in quotation marks). It can also happen if you fail to properly cite the source.
Paraphrasing tools are widely used by students, and can be especially useful for non-native speakers who may find academic writing particularly challenging. While these can be helpful for a bit of extra inspiration, use these tools sparingly, keeping academic integrity in mind.
To make sure you’ve properly paraphrased and cited all your sources, you could elect to run a plagiarism check before submitting your paper. And of course, always be sure to read your source material yourself and take the first stab at paraphrasing on your own.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Critical thinking
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly cite the source . This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style .
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly cite the source .
Try our services
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. & Caulfield, J. (2023, June 01). How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-paraphrase/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, how to write a summary | guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA website citation includes the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the website (in italics), the publication date, and the URL (without "https://"). If the author is unknown, start with the title of the page instead. If the publication date is unknown, or if the content is ...
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
An Article in an Online Scholarly Journal. For all online scholarly journals, provide the author(s) name(s), the name of the article in quotation marks, the title of the publication in italics, all volume and issue numbers, and the year of publication. Include a DOI if available, otherwise provide a URL or permalink to help readers locate the ...
1. Start your full citation with the name of the author. If the article has an identified author, provide their last name followed by a comma, then their first name. Place a period after the author's name. If no author is identified, start your citation with the title. [1] Example: Bernstein, Mark.
How to Cite an Online Work. To create a basic works-cited-list entry for an online work, list the author, the title of the work, the title of the website as the title of the container, and the publication details. You may need to include other elements depending on the type of work (e.g., book, scholarly article, blog post) and how you accessed ...
To reference a website in Harvard style, include the name of the author or organization, the year of publication, the title of the page, the URL, and the date on which you accessed the website. In-text citation example. (Google, 2020) Reference template. Author surname, initial. ( Year) Page Title.
the page, paragraph or section number—what you cite will depend on the information available as many electronic or online sources don't have pages. identify the format of the source accessed, for example, E-book, podcast etc. provide an accurate access date for online sources, that is, identify when a source was viewed or downloaded.
The name of the author in a newspaper article is referred to as a byline. Below are examples for citing an article both with and without a byline. Reference list (print) structure: Last name, F. (Year published). 'Article title', Newspaper name, Day Month, Page (s). Example: Hamilton, J. (2018).
The author's name might be unknown. If it's the case, use the first several words from the article's title but omit "A," "An," or "The" at the beginning. It can be written in quotes or italics, depending on how it's written in your list of references. The number of words you pick to use depends on the title.
There are different versions of the Harvard referencing style. This guide is a quick introduction to the commonly-used Cite Them Right version. You will find further guidance available through the OU Library on the Cite Them Right Database. For help and support with referencing and the full Cite Them Right guide, have a look at the Library's ...
In Harvard style, citations appear in brackets in the text. An in-text citation consists of the last name of the author, the year of publication, and a page number if relevant. Up to three authors are included in Harvard in-text citations. If there are four or more authors, the citation is shortened with et al. Harvard in-text citation examples.
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
In-text citations are quick references to your sources. In Harvard referencing, you use the author's surname and the date of publication in brackets. Up to three authors are included in a Harvard in-text citation. If the source has more than three authors, include the first author followed by ' et al. '.
Using In-text Citation. Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list. APA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the year of publication, for example: (Field, 2005).
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
Quotes should always be cited (and indicated with quotation marks), and you should include a page number indicating where in the source the quote can be found. Example: Quote with APA Style in-text citation. Evolution is a gradual process that "can act only by very short and slow steps" (Darwin, 1859, p. 510).
Morgan (Citation 2010, 249) suggests that travel to new places can provide opportunity for a 'disorientating dilemma', which marks the beginning of the transformative learning process.The gap between the usual and the new place can provide '"distance" … in an experiential or existential sense as well as … geographical' (Morgan Citation 2010, 249).
Periodicals include magazines, newspapers, and scholarly journals. Works cited entries for periodical sources include three main elements—the author of the article, the title of the article, and information about the magazine, newspaper, or journal. MLA uses the generic term "container" to refer to any print or digital venue (a website or ...
The vast trove of online information — everything from scientific papers to news articles to Wikipedia pages — is drying up. Epoch, an AI research institute, has warned that AI could run out ...
In an MLA Works Cited entry for a journal article, the article title appears in quotation marks, the name of the journal in italics—both in title case. List up to two authors in both the in-text citation and the Works Cited entry. For three or more, use "et al.". MLA format. Author last name, First name.
Paraphrasing means putting someone else's ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning. Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone's exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it's usually better to integrate sources by ...