Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Leeds University Business School
- Research degrees
Writing a research proposal
When applying for a research degree you will need to produce a document that outlines your proposed research topic and programme of research.
Watch our step-by-step guide on how to write your research proposal.
Viewing this page in China? Watch on Bilibili .
Getting your PhD proposal right is a critical part of the application process. It is important that you communicate the right messages about why your research is important and why you are the person to carry it out. Quality rather than quantity is key to a good proposal. Below is an outline of the elements a research proposal might typically contain.
Step 1: Create your title
A clear and succinct description of your research to use as a working title. Include relevant keywords that relate to your research and ensure your title goes beyond just describing the topic. It should give a clear indication of your approach and research questions.
Step 2: Write your introduction
Explain your research problem and outline why the research is of value and where its originality lies. You should clearly explain how your research will address a real-world problem and how it will meaningfully contribute to the area of research. You’ll need to clearly define your aim and objectives, using concepts, theories and empirics. Remember, you cannot cover everything on the topic within a PhD so be specific about what you are seeking to explore. Typically, an overarching aim and 3 or 4 objectives works well, then use these to justify the major approaches you will take. Keep this between 250 and 350 words.
Step 3: Write your literature review
Demonstrate your knowledge of current literature surrounding your topic, and your ability to critically reflect on and select it. Ensure you identify existing research gaps or problems, and highlight how your research will contribute to it. You’ll need to provide a clear statement of your research question and thoroughly examine key recent academic contributions within your research areas. It’s crucial that you make your contribution clear. Your literature review should be between 1,200 and 1,400 words.
Step 4: Outline your research method
A well-developed methodology section is crucial. Clearly describe and justify your methodology and overall approach, to help you and potential supervisors determine the viability of your research. You’ll need to include data collection and analysis methods and techniques. Justify your approach and rationalise your choices by engaging with the literature on the pros and cons of your specific methodological choices. Keep it between 1,200 and 1,400 words.
Step 5: Complete your references
Any literature cited in the proposal should be listed at the end of the document. Use of the Harvard referencing style is preferred. Also include a clear timeline for completing key activities (literature review, analysis, writing up etc.).
Step 6: Proofread your research proposal
This is your opportunity to show how you can present information accurately, coherently and concisely.
Vedran Lesic talks about his experience of studying a research degree at Leeds University Business School
Whilst there is no right or wrong way to produce a research proposal you may find our hints and tips useful.
Don’t produce a proposal for ‘mass consumption’ .
If you are applying to multiple institutions make sure you understand and tailor your proposal to the relevant research being undertaken there. Research the department you are applying to, its staff and the research they are undertaking related to your topic. Readers can easily spot if a proposal has been produced for mass consumption.
Keep things short and simple
As a general rule, keep things concise. Use sentences that are 8-10 words long and avoid long, rambling paragraphs. You are trying to sell the importance of the study to potential supervisors, so be specific and don’t meander off topic.
Avoid plagiarism
This one should be obvious. Make sure that all of your work is your own, written in your own words. You need to ensure that the literature review and the way the contribution is defined and developed, as well as all other elements, are correctly cited using appropriate references and that they are written by you. If not, your application will not succeed.
Let your passion for the topic shine through
By constructing a clear and well-written proposal, your interest in the topic should be clear. Demonstrate your interest in the topic and what the study aims to achieve – this should include contributions to theory, but might also have practical applications such as recommendations for policy and/or practice.

Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
12 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
kindly assist me in writing the proposal in psychology education
Please,Kindly assist my in my phd thesis writing on personal and socio cultural factors as determinate of family planning adoption
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
8 Research Proposal Examples & Template to Use

Written by: Raja Mandal

So you have a groundbreaking research idea you've spent months or even years developing, and now you're ready to take the next step.
How do you get funding for your research, and how should you approach potential funders? The answer is to create a convincing research proposal.
Unfortunately, most research proposals often get rejected. According to the European Research Council, the success rate for repeat proposal applications was only 14.8% in 2023 .
Pitching a novel research concept isn’t enough. To increase your chances of securing funding, your research proposal must check the right boxes in terms of clarity, feasibility, aesthetic appeal and other factors.
If you’re looking for inspiration to create a persuasive and feasible proposal, you’re in the right place. In this article, we have compiled a list of research proposal examples to help you create yours.
These examples will help you understand how to organize your proposal, what information to include and how to present it in a way that encourages others to support your project.
Let's dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a research proposal, what to include in a research proposal, 8 research proposal examples & templates, research proposal faqs.
- A research proposal is a document that outlines your proposed research project, explaining what you plan to study, why it's important and how you will conduct your research.
- A well-structured research proposal includes a title page, abstract and table of contents, introduction, literature review, research design and methodology, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, timeline and budget.
- Visme's research proposal examples and templates offer a great starting point for creating engaging and well-structured proposals.
- Choose a template from Visme's research proposal examples and customize it to fit your needs.
- With Visme’s proposal maker , you can create a research proposal that stands out. Access a drag-and-drop editor and advanced features like AI tools , collaboration features, brand wizard and more.
A research proposal is a structured document that outlines the core idea of your research, the methods you intend to use, the required resources and the expected results.
Think of it as a sales pitch for your research. It answers some big questions: What are you planning to explore? Why is it important to conduct the research? What are your research objectives and the methods you’ll use to achieve them? What are the potential outcomes or contributions of this research to the field?
A research proposal serves two primary purposes. First, it convinces funding bodies or academic committees to support your research project expected to bring new ideas and insights. Second, it provides a roadmap for your research journey, helping you stay focused, organized and on track.
Now, we'll discuss what to include in a research proposal. You'll learn about the important parts of a research proposal template and how they help present your research idea clearly.
Here’s an infographic that you can use to understand the elements of a research proposal quickly.

1. Title Page
Start your research proposal with a title page that clearly states your research. The title page is like a book cover, giving the first impression of your project. Therefore, you must ensure the design is engaging enough to attract your audience at first glance.
Include the following details on your title page:
- Title of your research
- Contact Details
- Name of the department or organization
- Date of submission

2. Abstract and Table of Contents
After the title page comes the abstract and the table of contents.
The abstract is a concise summary of your project that briefly outlines your research question, the reasons behind the study and the methods you intend to use. It is a quick way for readers to understand your proposal without reading the entire document.
The table of contents is a detailed list of the sections and subsections in your proposal, with page numbers. It helps readers navigate through your document and quickly locate different parts they're interested in.

3. Introduction
The introduction of your research proposal sets the tone for the rest of the document. It should grab the reader's attention and make them want to learn more. It's your chance to make a strong case for why your research is worth investigating and how it can fill a gap in current knowledge or solve a specific problem.
Make sure that your introduction covers the following:
- Background Information: Set the stage with a brief snapshot of existing research and why your topic is relevant.
- Research Problem: Identify the specific problem or knowledge gap that your study will address.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: Present the central question or hypothesis that guides your research focus.
- Aims and Objectives: Outline your research's main goal and the steps you'll take to achieve it.
- Significance and Contribution: Explain how your research will add value to the field and what impact it could have.
4. Literature Review
A literature review is a list of the scholarly works you used to conduct your research. It helps you demonstrate your current knowledge about the topic.
Here's how this part works:
- Summary of Sources: Talk about the main ideas or findings from your research materials and explain how they connect to your research questions.
- Finding Gaps: Show where the current research falls short or doesn't give the full picture—this is where your research comes in!
- Key Theories: Tell the readers about any theories or ways of thinking that help shape your research.
- Learning from Methods: Discuss what previous researchers worked on and how their methods might guide your research.
- Recognizing Authors and Studies: Honor the pioneers whose work has had a major influence on your topic.
5. Research Design and Methodology
This section outlines your plan for answering your research question. It explains how you intend to gather and analyze information, providing a clear roadmap of the investigation process.
Here are the key components:
Population and Sample
Describe the entire group you're interested in (the population). This could be all teachers in a specific state or all social media platform users. After that, you will need to explain how you will choose a smaller group, known as a sample, to study directly. This sample should be selected to accurately represent the larger population you are interested in studying.
To choose the right sampling method, you need to assess your population properly. For instance, to obtain general insights, you can use random sampling to select individuals without bias. If the population consists of different categories, such as professionals and students, you can use stratified sampling to ensure that each category is represented in the sample.
Other popular sampling methods include systematic, convenience, purposive, cluster, and probability sampling techniques.
Research Approach
There are three main approaches for the research: qualitative (focusing on experiences and themes), quantitative (using numbers and statistics), or mixed methods (combining both). Your choice will depend on your research question and the kind of data you need.
Data Collection
This section details the specific methods you'll use to gather information. Will you distribute surveys online or in person? Conduct interviews? Perhaps you'll use existing data sets. Here, you'll also explain how you'll ensure the data collection process is reliable and ethical.
Data Analysis
Once you have collected your data, the next step is to analyze it to obtain meaningful insights. The method you choose depends on the available data type.
If you have quantitative data, you can employ statistical tests to analyze it. And if you're dealing with qualitative data, coding techniques can help you spot patterns and themes in your collected data.

6. Contribution to Knowledge
In this section, you need to explain how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge in your field. You should describe whether your study will fill a knowledge gap, challenge conventional ideas or beliefs or offer a fresh perspective on a topic.
Clearly outline how your work will advance your field of study and why this new knowledge is essential.
7. Research Schedule and Timeline
Create a timeline with important milestones, such as finishing your literature review, completing data collection and finalizing your analysis.
This shows that you've carefully considered the scope of your project and can manage your time effectively. Furthermore, account for possible delays and be prepared to adapt your schedule accordingly.
To create this timeline, consider using a visual tool like a Gantt chart or a simple spreadsheet. These tools will help you organize individual tasks, assign deadlines, and visualize the project's overall progress.
Choose a Gantt chart template from Visme's library and customize it to create your timeline quickly. Here's an example template:

The budget section is your opportunity to show them that you've carefully considered all necessary expenses and that your funding request is justified.
Here's how you can approach this part:
- Understand the Rules: Before making calculations, thoroughly review the funding agency's guidelines. Pay attention to what types of expenses are allowed or excluded and whether there are any budget caps.
- Personnel: Salaries and benefits for yourself, research assistants, or collaborators.
- Equipment: Specialized tools, software, or lab supplies.
- Travel: Transportation, lodging and meals if data collection requires travel.
- Dissemination: Costs for publishing results or presenting at conferences.
- Provide Justifications: Don't just list a cost. Briefly explain why each expense is crucial for completing your research.
- Be Thorough and Realistic: Research prices for specific items using quotes or online comparisons. Don't underestimate expenses, as this can raise troubles about the project's feasibility.
- Don't Forget Contingencies: Include a small buffer (around 5% of your total budget) for unexpected costs that might arise.

Using these research proposal examples and templates, you can create a winning proposal in no time. You will find templates for various topics and customize every aspect of them to make them your own.
Visme’s drag-and-drop editor, advanced features and a vast library of templates help organizations and individuals worldwide create engaging documents.
Here’s what a research student who uses Visme to create award-winning presentations has to say about the tool:
Chantelle Clarke
Research Student
Now, let’s dive into the research proposal examples.
1. Research Proposal Presentation Template

This research proposal presentation template is a powerful tool for presenting your research plan to stakeholders. The slides include specific sections to help you outline your research, including the research background, questions, objectives, methodology and expected results.
The slides create a coherent narrative, highlighting the importance and significance of your research. Overall, the template has a calming and professional blue color scheme with text that enables your audience to grasp the key points.
If you need help creating your presentation slides in a fraction of the time, check out Visme's AI presentation maker . Enter your requirements using text prompts, and the AI tool will generate a complete presentation with engaging visuals, text and clear structure. You can further customize the template completely to your needs.
2. Sales Research Proposal Template

Sales research gives you a deeper understanding of their target audience. It also helps you identify gaps in the market and develop effective sales strategies that drive revenue growth. With this research proposal template, you can secure funding for your next research project.
It features a sleek and professional grayscale color palette with a classic and modern vibe. The high-quality images in the template are strategically placed to reinforce the message without overwhelming the reader. Furthermore, the template includes a vertical bar graph that effectively represents budget allocations, enabling the reader to quickly grasp the information.
Use Visme's interactive elements and animations to add a dynamic layer to your research proposals. You can animate any object and add pop-ups or link pages for a more immersive experience. Use these functionalities to highlight key findings, demonstrate trends or guide readers through your proposal, making the content engaging and interactive.
3. General Funding Research Proposal Template

This proposal template is a great tool for securing funding for any type of research project. It begins with a captivating title page that grabs attention. The beautiful design elements and vector icons enhance the aesthetic and aid visual communication.
This template revolves around how a specific user group adopts cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. The goal is to assess awareness, gauge interest and understand key factors affecting cryptocurrency adoption.
The project methodology includes survey design, data collection, and market research. The expected impact is to enhance customer engagement and position the company as a customer-centric brand.
Do you need additional help crafting the perfect text for your proposal? Visme's AI writer can quickly generate content outlines, summaries and even entire sections. Just explain your requirements to the tool using a text prompt, and the tool will generate it for you.
4. Product Research Proposal Template

Creating a product that delights users begins with detailed product research. With this modern proposal template, you can secure buy-in and funding for your next research.
It starts with a background that explains why the research is important. Next, it highlights what the research is set to achieve, how the research will be conducted, how much it will cost, the timeline and the expected outcomes. With a striking color scheme combining black, yellow, and gray, the template grabs attention and maintains it until the last page.
What we love about this template is the smart use of visuals. You'll find a flowchart explaining the methodology, a bar graph for the budget, and a timeline for the project. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg regarding the visual elements you’ll find in Visme.
Visme offers data visualization tools with 30+ data widgets, such as radial gauges, population arrays, progress bars and more. These tools can help you turn complex data into engaging visuals for your research proposal or any other document.
For larger data sets, you can choose from 20+ types of charts and graphs , including bar graphs , bubble charts , Venn diagrams and more.
5. Tech Research Proposal Template

If you’re a tech researcher, we’ve got the perfect template for you. This research proposal example is about predictive analytics in e-commerce. However, you can customize it for any other type of research proposal.
It highlights the project's objectives, including the effectiveness of predictive analysis, the impact of product recommendations and supply chain optimization. The methods proposed for achieving these objectives involve A/B testing and data analysis, a comprehensive budget and a 12-month timeline for clear project planning.
The title page has a unique triptych-style layout that immediately catches the reader's attention. It has plenty of white space that enhances readability, allowing your audience to focus on the critical points.
Submitting to different funding agencies? You don’t have to manually make changes to your document. Visme's dynamic fields can help save time and eliminate repetitive data entry.
Create custom fields like project names, addresses, contact information and more. Any changes made to these fields will automatically populate throughout the document.
6. Marketing Research Proposal Template

Artificial intelligence (AI) is taking the world by storm and the marketing niche isn’t left out. With this eye-catching template, you can attract attention to your proposed marketing research project for an AI-driven platform.
The main goal of the research is to evaluate the platform's feasibility and marketing potential. To achieve this goal, the scope of work includes a comprehensive analysis of the market and competitors and pilot testing. The proposal also contains a budget overview that clearly outlines the allocation of funds, ensuring a well-planned and transparent approach.
Using Visme's Brand Design Tool , you can easily customize this template to suit your branding with just one click. Simply enter your URL into the brand wizard, and the tool will automatically extract your company logo, brand colors, and brand fonts . Once saved, you or your team members can apply the branding elements to any document. It's that simple!
7. Environmental Research Proposal Template

The environmental research proposal example focuses on carbon emissions, identifies their contributing factors, and suggests sustainable practices to address them. It uses an appropriate sample size and data collection techniques to gather and evaluate data and provide sustainable recommendations to reduce industrial carbon footprints and waste.
From a design standpoint, the green and white color combination matches the theme of nature and environmental friendliness. In addition to its aesthetic appeal, the proposal includes relevant images that support ecological advocacy, making it informative and visually aligned with its purpose.
A key feature of this template is its detailed breakdown of the project's timeline. It uses a Gantt chart to clearly present stages, milestones and deadlines.
Collaborate with your team members to customize these research proposal templates using Visme’s collaborative design features . These features allow you to leave feedback, draw annotations and even make live edits. Invite your teammates via email or a shareable link and allow them to work together on projects.
8. General Approval Research Proposal Template

This research proposal template is a total game-changer - you can use it for any research proposal and customize it however you want. It features a modern and refreshing color scheme that immediately makes it stand out, providing a contemporary look that can adapt to any project's needs.
The template's layout is thoughtfully designed with primary fields that users can easily personalize by changing text, adjusting colors, or swapping images. No matter the research topic, you can tailor the template to fit your specific needs.
Once you're done customizing your research proposal template on Visme, you can download, share and publish it in different ways. For offline usage, you may download the proposal in PDF, PNG, or JPG format. To share it online, you can use a private or public link or generate a code snippet that you can embed anywhere on the web.
Want to create other types of proposals? Here are 29 proposal templates that you can easily customize in Visme.
Q. What Are the Five Steps of Writing a Research Proposal?
Follow these steps to write a solid research proposal:
- Choose a topic within your field of study that can be explored and investigated.
- Research existing literature and studies to build a foundational understanding and prepare your research question.
- Outline your research proposal: introduction, literature review, proposed methodology, budget and timeline.
- Conduct more detailed studies to strengthen your proposition, refine your research question and justify your methodology.
- Follow your outline to write a clear and organized proposal, then review and edit for accuracy before submitting.
If you want to learn more about creating an expert research proposal , we highly recommend checking out our in-depth guide.
Q. How Long Is a Research Proposal?
Research proposals can range from 1,000 to 5,000 words. For smaller projects or when specific requirements aren't provided, aim for a concise and informative proposal that effectively outlines your research plan.
However, the ideal length depends on these factors:
- Projects with complex methodologies or multiple phases may require longer proposals to explain the scope and procedures in detail.
- Universities, academic institutions and funding agencies often have guidelines of a specific length. Always check their requirements beforehand.
- When writing a proposal, adjust the level of study based on the audience. Academic proposals may require comprehensive explanations, while business or non-profit proposals require a more streamlined approach.
Q. How Long Does It Take to Write a Research Proposal?
The time it takes to write a research proposal depends on a few factors:
- Complex research with extensive data collection or analysis will naturally take longer to plan and write about.
- If you're new to writing research proposals, expect to spend more time learning the format and best practices.
- If you've already conducted some research or a thorough literature review, the writing process might go faster.
- Funding applications often have strict deadlines that will dictate your timeline.
Set aside several weeks to a couple of months for researching, writing, and revising your proposal. Start early to avoid stress and produce your best work.
Q. What Not to Do for a Research Proposal?
There are several factors that can make a research proposal weak. Here are some of the most common errors that you should avoid while preparing your research proposal:
- Don’t choose a topic that’s too broad. Focus on a specific area you can thoroughly explore within your proposal’s limits.
- Don’t ignore the rules for formatting and submitting your proposal. Always adhere to the requirements set by your institution or funding body.
- Don’t forget to conduct a thorough literature review. It's crucial to show your grasp of existing research related to your topic.
- Don't be vague about your methods. Ensure they're clearly defined and suitable for answering your research question.
- Don't overlook errors in grammar, typos or structure. A well-proofread proposal reflects professionalism, so review it carefully before submitting it.
Craft Professional & Engaging Proposals with Visme
Writing a compelling research proposal takes effort, but with the right tools, the process becomes a breeze. Use the research proposal examples and templates in this article as a launching point to write your own proposal.
The best part? Visme provides easy-to-use tools with a vast collection of customizable templates, design elements and powerful features.
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a student, Visme has the resources to help you create visually appealing and well-structured research proposals. In addition to research proposals, Visme helps you create many other document types, such as presentations , infographics , reports and more.
Ready to create your own research proposal? Check out Visme's proposal maker and start crafting professional and engaging proposals in minutes!
Create professional research proposals with Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Raja Antony Mandal is a Content Writer at Visme. He can quickly adapt to different writing styles, possess strong research skills, and know SEO fundamentals. Raja wants to share valuable information with his audience by telling captivating stories in his articles. He wants to travel and party a lot on the weekends, but his guitar, drum set, and volleyball court don’t let him.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a research proposal

What is a research proposal?
What is the purpose of a research proposal , how long should a research proposal be, what should be included in a research proposal, 1. the title page, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 4. research design, 5. implications, 6. reference list, frequently asked questions about writing a research proposal, related articles.
If you’re in higher education, the term “research proposal” is something you’re likely to be familiar with. But what is it, exactly? You’ll normally come across the need to prepare a research proposal when you’re looking to secure Ph.D. funding.
When you’re trying to find someone to fund your Ph.D. research, a research proposal is essentially your “pitch.”
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research.
You’ll need to set out the issues that are central to the topic area and how you intend to address them with your research. To do this, you’ll need to give the following:
- an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls
- an overview of how much is currently known about the topic
- a literature review that covers the recent scholarly debate or conversation around the topic
➡️ What is a literature review? Learn more in our guide.
Essentially, you are trying to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into.
It is the opportunity for you to demonstrate that you have the aptitude for this level of research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas:
It also helps you to find the right supervisor to oversee your research. When you’re writing your research proposal, you should always have this in the back of your mind.
This is the document that potential supervisors will use in determining the legitimacy of your research and, consequently, whether they will invest in you or not. It is therefore incredibly important that you spend some time on getting it right.
Tip: While there may not always be length requirements for research proposals, you should strive to cover everything you need to in a concise way.
If your research proposal is for a bachelor’s or master’s degree, it may only be a few pages long. For a Ph.D., a proposal could be a pretty long document that spans a few dozen pages.
➡️ Research proposals are similar to grant proposals. Learn how to write a grant proposal in our guide.
When you’re writing your proposal, keep in mind its purpose and why you’re writing it. It, therefore, needs to clearly explain the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. You need to then explain what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
Generally, your structure should look something like this:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Research Design
- Implications
If you follow this structure, you’ll have a comprehensive and coherent proposal that looks and feels professional, without missing out on anything important. We’ll take a deep dive into each of these areas one by one next.
The title page might vary slightly per your area of study but, as a general point, your title page should contain the following:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- The name of your institution and your particular department
Tip: Keep in mind any departmental or institutional guidelines for a research proposal title page. Also, your supervisor may ask for specific details to be added to the page.
The introduction is crucial to your research proposal as it is your first opportunity to hook the reader in. A good introduction section will introduce your project and its relevance to the field of study.
You’ll want to use this space to demonstrate that you have carefully thought about how to present your project as interesting, original, and important research. A good place to start is by introducing the context of your research problem.
Think about answering these questions:
- What is it you want to research and why?
- How does this research relate to the respective field?
- How much is already known about this area?
- Who might find this research interesting?
- What are the key questions you aim to answer with your research?
- What will the findings of this project add to the topic area?
Your introduction aims to set yourself off on a great footing and illustrate to the reader that you are an expert in your field and that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge and theory.
The literature review section answers the question who else is talking about your proposed research topic.
You want to demonstrate that your research will contribute to conversations around the topic and that it will sit happily amongst experts in the field.
➡️ Read more about how to write a literature review .
There are lots of ways you can find relevant information for your literature review, including:
- Research relevant academic sources such as books and journals to find similar conversations around the topic.
- Read through abstracts and bibliographies of your academic sources to look for relevance and further additional resources without delving too deep into articles that are possibly not relevant to you.
- Watch out for heavily-cited works . This should help you to identify authoritative work that you need to read and document.
- Look for any research gaps , trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions.
- Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal.
This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal. It should be a discussion about the overall approach you plan on taking, and the practical steps you’ll follow in answering the research questions you’ve posed.
So what should you discuss here? Some of the key things you will need to discuss at this point are:
- What form will your research take? Is it qualitative/quantitative/mixed? Will your research be primary or secondary?
- What sources will you use? Who or what will you be studying as part of your research.
- Document your research method. How are you practically going to carry out your research? What tools will you need? What procedures will you use?
- Any practicality issues you foresee. Do you think there will be any obstacles to your anticipated timescale? What resources will you require in carrying out your research?
Your research design should also discuss the potential implications of your research. For example, are you looking to confirm an existing theory or develop a new one?
If you intend to create a basis for further research, you should describe this here.
It is important to explain fully what you want the outcome of your research to look like and what you want to achieve by it. This will help those reading your research proposal to decide if it’s something the field needs and wants, and ultimately whether they will support you with it.
When you reach the end of your research proposal, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX.
Your project may also require you to have a timeline, depending on the budget you are requesting. If you need one, you should include it here and explain both the timeline and the budget you need, documenting what should be done at each stage of the research and how much of the budget this will use.
This is the final step, but not one to be missed. You should make sure that you edit and proofread your document so that you can be sure there are no mistakes.
A good idea is to have another person proofread the document for you so that you get a fresh pair of eyes on it. You can even have a professional proofreader do this for you.
This is an important document and you don’t want spelling or grammatical mistakes to get in the way of you and your reader.
➡️ Working on a research proposal for a thesis? Take a look at our guide on how to come up with a topic for your thesis .
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. Generally, your research proposal will have a title page, introduction, literature review section, a section about research design and explaining the implications of your research, and a reference list.
A good research proposal is concise and coherent. It has a clear purpose, clearly explains the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. A good research proposal explains what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
You need a research proposal to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into. It is your opportunity to demonstrate your aptitude for this level or research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas clearly, concisely, and critically.
A research proposal is essentially your "pitch" when you're trying to find someone to fund your PhD. It is a clear and concise summary of your proposed research. It gives an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls, it elaborates how much is currently known about the topic, and it highlights any recent debate or conversation around the topic by other academics.
The general answer is: as long as it needs to be to cover everything. The length of your research proposal depends on the requirements from the institution that you are applying to. Make sure to carefully read all the instructions given, and if this specific information is not provided, you can always ask.

- Sample Research
FREE 10+ Business Research Proposal Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word

A business or organization with proper research has an excellent chance of winning the market. Research is a strategy that helps businesses discover new ideas and factors that will help them in improving business operations, generating concrete action plans, securing a healthy financial status, and more. Hence, it is essential to execute it well. Thus, the purpose of having a business research proposal. In this article, you will learn the importance of writing one. Scroll down below.
Business Research Proposal
Free 10+ business research proposal samples & templates in pdf | ms word, 1. business research proposal sample pdf, 2. business research proposal, what are the types of business research, 1. exploratory research:, 2. descriptive research:, 3. causal research:, 4. correlational research:, 5. cross-sectional research:, 6. longitudinal research:, 7. quantitative research:, 8. qualitative research:, 9. action research:, 10. case study research:, 11. cross-functional research:, 12. market research:, 13. social media research:, 3. business research proposal example, 4. business proposal research, 5. business research proposal sample, how to make a business research proposal, 1. start with a title and an overview, 2. write a clear introduction, 3. present the data gathering procedure, 4. provide and organize the research questionnaire, 5. state a brief conclusion, 6. make the content simple and organized, 6. research proposal about business, 7. business administration research proposal pdf, advantages and disadvantages of business research, 8. research proposal on business management pdf, 9. business research examples pdf, 10. simple research proposal template, 11. research proposal outline sample, what is a business research proposal, what are the types of research proposal, what should a research proposal include, how do you start a business research proposal, what is the role of business research, what is ethics in business research.
In this article, we have provided business research proposal samples and templates that are accessible anytime. These sample templates come with professionally written content and are preformatted in PDF and MS Word file formats for your convenience. Check them out now!

Size: 17 KB
Size: 165 KB
Business research is a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting information related to a business problem or opportunity. There are several types of business research, each serving different purposes. Here are some common types:
- Aimed at exploring a new area or gaining insights into a phenomenon.
- Helps in understanding the basic nature of a problem.
- Focuses on providing an accurate description of a situation or phenomenon.
- Involves gathering data to characterize and define the subject of study.
- Investigates cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
- Aims to establish a cause-and-effect connection between two or more variables.
- Examines the statistical association between two or more variables.
- Does not imply causation but identifies relationships between variables.
- Involves collecting data from participants at a single point in time.
- Provides a snapshot of the situation or phenomenon.
- Involves collecting data from the same group of participants over an extended period.
- Helps to track changes or developments over time.
- Focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis.
- Involves the use of surveys, experiments, and structured observations.
- Emphasizes understanding and interpreting non-numerical data.
- Involves methods such as interviews, focus groups, and case studies.
- Conducted by practitioners within an organization to solve specific problems.
- Involves a cyclical process of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
- In-depth analysis of a specific case or situation.
- Often used to gain a deep understanding of a particular phenomenon.
- Involves collaboration between different functional areas of a business.
- Aims to address complex issues that require input from multiple perspectives.
- Focuses on understanding market trends, customer preferences, and competition.
- Helps businesses make informed decisions about their products or services.
- Involves analyzing data from social media platforms to understand consumer sentiment, trends, and feedback.
These types of business research can be used individually or in combination, depending on the nature of the research question and the goals of the study.

Size: 104 KB

Size: 184 KB

Size: 23 KB
A business research proposal serves a vital role in research related to business. That is why it is only imperative to ensure that it follows the accurate procedure and should contain the relevant information. Using this allows you to outline the things to be done to gather the right data to be presented in a research report . So, if you are writing a research proposal for your business and you don’t know-how, then you are on the right page. Below are simple yet useful tips on how to make an informative and effective business research proposal. Read below.
Begin writing your business research proposal by providing the business research title and a brief yet informative research overview. The title should be concise and triggers the curiosity of the management. As for the research overview, it should present the highlight of the research.
The next thing you need to put in your business research proposal is a precise and clear introduction. This section should identify what the research is all about, its scope, and its importance to the business. The introduction should also provide the objectives and sub-objectives of the business study that needs to be achieved.
After the introduction, the next thing you need to do is to present the data gathering procedure. In this section, you have to outline the activities that should be done for the process. And to this, you have to identify the appropriate data gathering methods, whether qualitative or quantitative research . There are different methods and strategies that you can use. However, you should have to choose the appropriate methodology that will work on your business process.
The next thing you have to include in your business research proposal is the research questionnaire. The list of questions will help you collect relevant and useful data that will complete the research process. In presenting this information, you may use bullet points to make it organized and understandable.
Finalize your business research proposal by writing a brief conclusion that summarizes the whole idea of your proposals’ content. In this section, you have to emphasize the importance and purpose of research for your business. Also, provide a statement of the several benefits and advantages that the company will gain from the research.
Having an informative business research proposal is not useful if the people who will read it are not able to grasp the idea the proposal is providing. That is why it is essential to use only simple words and terms that are readable and understandable by your readers. The organization of thoughts is also important. It presents the right structure of information accordingly.

Size: 929 KB

Size: 94 KB
| 1. Provides a basis for making informed and strategic business decisions. | 1. Conducting research can be expensive, especially for small businesses with limited resources. |
| 2. Helps in understanding market trends, customer preferences, and competition. | 2. Research processes can be time-intensive, leading to delays in decision implementation. |
| 3. Enables businesses to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with new ventures or strategies. | 3. The research process can be complex, requiring expertise and specialized skills. |
| 4. Fosters innovation by identifying new opportunities and areas for improvement. | 4. Findings may not always be completely accurate, and there could be uncertainties in data interpretation. |
| 5. Provides a competitive edge by staying ahead of market changes and customer preferences. | 5. Research outcomes may be influenced by researcher bias or subjective interpretations. |
| 6. Helps in understanding customer needs and improving products or services to enhance customer satisfaction. | 6. Ethical issues such as invasion of privacy may arise during data collection. |
| 7. Aids in effective allocation of resources by identifying areas of high potential return on investment. | 7. Findings may not always be applicable universally due to specific contextual factors. |
| 8. Supports the development of long-term business strategies and goals. | 8. Business environments are dynamic, and research findings may become outdated quickly. |
| 9. Provides a basis for measuring the success of implemented strategies or changes. | 9. Employees and stakeholders may resist changes based on research findings. |
| 10. Builds confidence among stakeholders, investors, and customers through evidence-based decision-making. | 10. Obtaining accurate and relevant data can be challenging, especially in diverse markets. |
This table highlights some key aspects of both the advantages and disadvantages of business research. Keep in mind that the impact of these factors can vary depending on the specific context and industry.

Size: 441 KB

Size: 133 KB

Size: 55 KB

Size: 57 KB
Researches that are related to businesses are essential for sustainability and success. According to an article from Medium, research is a critical component for businesses, specifically market research . Hence, business owners should put enough effort into researching to secure a permanent and high spot in the market. And this is where a business research proposal comes useful—the first thing that management should have before research.
A business research proposal is a written document used by management for either marketing research, accounting research, etc. The business research proposal presents and justifies the purpose of the study to be conducted. This also outlines the ways on how business research should be conducted. The standard length for the business research proposal is two to three pages. Nonetheless, it should be informative and well-written.
There are two types of research proposals that are useful for businesses, organizations, as well as in academic, approval proposals and funding proposals. Approval proposals refer to a written document that is written before doing the actual research. On the other hand, a funding proposal refers to a written document that seeks research funds.
A research proposal must present the idea of what the research is about and its importance. Thus, it should include a clear research title, a research overview, an introduction, the questionnaire, data gathering methods, and a research timeline. These components are commonly used in business and academic research.
Begin a business research proposal with a concise introduction outlining the research problem, its significance, and the proposed methodology. Clearly state the objectives and expected outcomes to provide a solid foundation for the study.
Business research plays a crucial role in informing strategic decisions by gathering, analyzing, and interpreting relevant data. It guides organizations in understanding market trends, consumer behavior, and industry dynamics for informed decision-making and sustainable growth.
Ethics in business research involves adhering to principles of integrity, honesty, and fairness. It ensures researchers conduct studies responsibly, respect participants’ rights, and maintain confidentiality, fostering trust and credibility.
Business research is one of the most important components of a sustainable and successful business. With this, businesses or organizations will be able to grasp new ideas that they can use to enhance their operations and improve marketing strategies . Hence, making sure that business research follows the standard format and obtains the necessary information. Thus, the use of a business research proposal to make the process comprehensive and effective.

Related Posts
Free 10+ construct validity samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ code of human research ethics samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ biography research report samples and templates in pdf, free 10+ system documentation samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ process document samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ action research samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ longitudinal research samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ causal research samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ client discovery samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ null hypothesis samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 9+ product knowledge samples & templates in pdf, free 10+ software documentation samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ exploratory research samples & templates in pdf | ms word, free 10+ experimental research samples & templates in ms word | pdf, free 10+ descriptive research samples & templates in pdf, free 15+ investment proposal templates in pdf ms word ..., free 9+ one-page proposal samples in pdf ms word, 9+ free sample restaurant proposals - pdf, how to create a music business proposal [5+ samples].
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
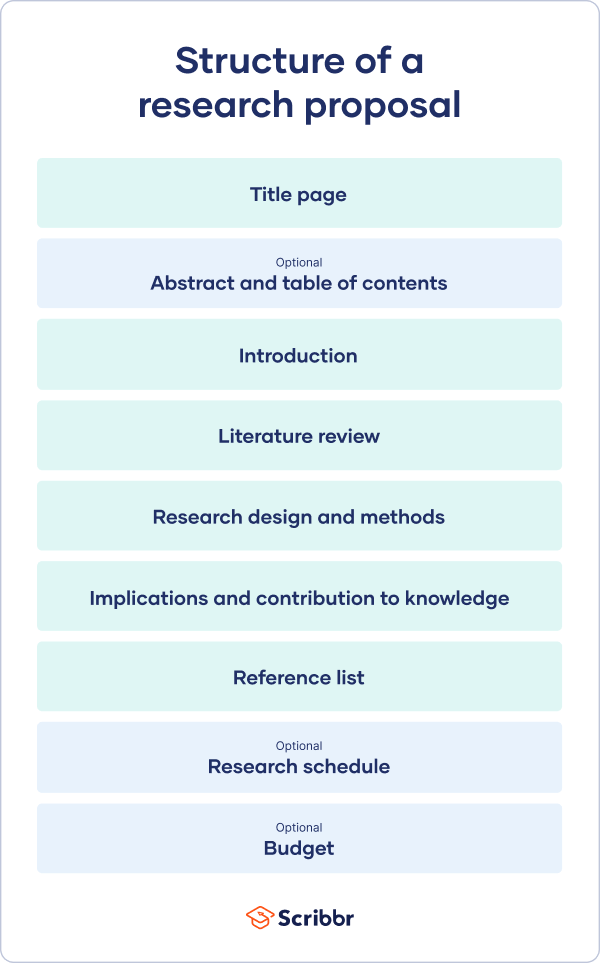
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
PhD Assistance
Writing a research proposal for business management.
A research design is a thorough plan that helps a research project achieves its goals. Business research is a scientific examination that entails a series of highly interconnected operations, each of which might have negative consequences for subsequent activities if completed incorrectly (Greener, 2021). The steps of the business research proposal process are explained in this blog.

Fig1. Writing a Research Proposal
- Identifying the Problem
The determination of the topics that need to be explored is the first step in the research process. In the case of fundamental research undertaken by academics, a topic of interest or a new field of inquiry is found.
2. Collection of basic literatures
Following the identification of the problem , the following stage is to gather preliminary data/literature that can aid in developing a basic grasp of the problem; in the case of business difficulties consulting, this can aid in understanding the scenario (Saeed et al., 2021).
3. Problem Statement
Although other writers may not have included this step as an explicit step, I believe it is critical to explicitly express the problem. Clearly defining the problem with a statement can give significant benefits. It can assist in generating a clear knowledge of the issue that needs to be handled, as well as clearly spelling out the objectives that must be met in order to solve the problem.
4. Detailed Literature Review
Literature review is an important aspect of academic research since it acts as the heart of the study. It expands research horizons, aids in the development of focus, gives direction, and minimises ambiguity. A literature review entails searching the body of knowledge for relevant literature that will aid in not only identifying but also determining the direction of relationships between variables, as well as in the formulation of hypotheses. It will also be useful in discussions later on in the research (Pereira et al., 2021).
5. Research Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a well-informed estimate; it’s called such since it’s founded on the conceptual framework established in the literature study and theoretical framework . Predictable and testable hypotheses are essential.
6. Methodology
The researcher decides how the research will be carried out at this stage. It is critical that this part provide adequate information to the reader so that he or she may easily reproduce the research in their own situations (Wickert et al., 2021).
Step 7: Collecting data
After deciding on a study approach, the following step is to gather data . Telephonic interviews, individually delivered surveys, postal questionnaires, face-to-face interviews, and observation are all examples of data collection methods.
Step 8: Data Entry and Screening & Cleansing of Data
The first step is to enter the information into any statistical programme that can aid in rapid data analysis . It is critical to review and cleaning of data for any irregularities once it has been submitted; failing to do so will result in inaccurate results.
Step 9: Data Analysis with statistical techniques
The next stage is to conduct proper statistical study based on the study hypothesis after the data has been input and cleaned. To examine the data, a variety of procedures are employed.
Step 10: Interpretation/Presentation of Results
After the data has been processed and the findings have been displayed on the screen, the following step is to analyse the data before presenting it. Contact PhD Assistance for any of your PhD requirements as we offer PhD Dissertation Writing UK, Content Quality of Dissertation Proposal UK. The interpretation of the results is one of the most important challenges that most studies encounter. The researcher must assess whether the findings are important, whether the hypothesis is correct, and then report the findings in a clear and understandable manner (Johnson et al., 2021).
Step 11: Discussion
The Discussion chapter is the most significant portion of the article and the culmination of the study, but it is often overlooked. The majority of newcomers to research just interpret the findings without discussing them. Reviewing the research findings in light of previous research is part of the discussion. This part entails comparing and contrasting the study findings with those of earlier studies to evaluate if the findings are comparable or conflicting. If they are in conflict, the researcher must determine what is causing the change.
Step 12: Conclusion
A conclusion is the last phase of a research project. It gives a high-level summary of the thesis while highlighting the key areas of debate. This section presents the study findings in a logical order (Nair et al., 2021). When the conclusions agree with the findings of other studies, they might cite references.
Bell, Bryman, and H. (2018). Formulating a research proposal .
Greener, S. L. (2021). Non-supervisory support for doctoral students in business and management: A critical friend. The International Journal of Management Education , 19 (2), 100463.
Hejase, H. J. (2022). Faculty of Business Administration Guidelines on Writing the MBA Research Project / Thesis Faculty of Business Administration Guidelines on Writing the MBA Research Project / Thesis Applicable to most business emphases Accounting Economics Finance Hospita . February .
Johnson, C. D., Bauer, B. C., & Niederman, F. (2021). The Automation of Management and Business Science. Academy of Management Perspectives , 35 (2), 292–309.
Nair, R., Arshad, R., Abd Aziz, A. Z., & Muda, R. (2021). A critical reading of impression management in times of financial crisis and implications for business writing. Journal of Education for Business , 96 (4), 230–236.
Pereira, L., Santos, R., Sempiterno, M., Costa, R. L. da, Dias, Á., & António, N. (2021). Pereira Problem Solving: Business Research Methodology to Explore Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity , 7 (1), 84.
Peterson, M. (2021). Teaching the Online Marketing Research Course for MBA Students. Journal of Marketing Education , 43 (3), 371–385.
Saeed, M. A., Mohammed H. Al-Ahdal, A. A., & Al Qunayeer, H. S. (2021). Integrating research proposal writing into a postgraduate research method course: what does it tell us? International Journal of Research & Method in Education , 44 (3), 303–318 .
Shao, H., Zhang, Z., & Wang, B. (2021). Research on accounting information security management based on blockchain. Mobile Information Systems , 2021 .
Wickert, C., Post, C., Doh, J. P., Prescott, J. E., & Prencipe, A. (2021). Management Research that Makes a Difference: Broadening the Meaning of Impact. Journal of Management Studies , 58 (2), 297–320.
- Business and management research proposal help
- Business and management research proposal service
- Business and management thesis writing help
- Business and management thesis writing service
- PhD Research Proposal Help

Quick Contact

- Adversial Attacks
- Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and ML ( Machine Learning )
- Big Data Analysis
- Business and Management
- Categories of Research methodology – PhDAssistance
- Category of Research Proposal Services
- coding & algorithm
- Computer Data Science
- Category of Machine Learning – PhDassistance
- Computer Science/Research writing/Manuscript
- Course Work Service
- Data Analytics
- Data Processing
- Deep Networks
- Dissertation Statistics
- economics dissertation
- Editing Services
- Electrical Engineering Category
- Engineering & Technology
- finance dissertation writing
- Gap Identification
- Healthcare Dissertation Writing
- Intrusion-detection-system
- journals publishing
- Life Science Dissertation writing services
- literature review service
- Machine Learning
- medical thesis writing
- Peer review
- PhD Computer Programming
- PhD Dissertation
- PhD dissertation Writing
- Phd Journal Manuscript
- Annotated Bibliography
- PhD Publication Support
- Phd thesis writing services
- Phd Topic Selection
- Categories of PhdAssistance Dissertation
- Power Safety
- problem identification
- Quantitative Analysis
- quantitative research
- Recent Trends
- Referencing and Formatting
- Research Gap
- research journals
- Research Methodology
- research paper
- Research Proposal Service
- secondary Data collection
- Statistical Consulting Services
- Uncategorized
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

How to Write a PhD Research Proposal

Starting on PhD research is a big step in a researcher’s academic journey, and submitting a research proposal is a significant part of it. Indeed, many PhD scholars seek guidance on how to write a PhD research proposal , which is the foundational document that outlines the scope, objectives, and methodology of their prospective doctoral study. This article takes a look at the essential elements of a PhD research proposal and discuss practical steps to help develop an effective and strong document.
What is a PhD Research Proposal ?
Think of a PhD research proposal as a blueprint for your research. It lays out the main questions you want to seek answers to in your study, and presents an overview of the field you are planning to dive into. The PhD research proposal is not just about summarizing what is already available in the public domain. It is a critical document that demonstrates the feasibility, significance, and originality of the proposed research, and therefore, plays a crucial role in influencing admission decisions and securing funding opportunities. It also explains how your research is different and new and underscores the unique angles, perspectives and originality of your area of study.[ 1]
Why is a PhD Research Proposal Needed?
Even though your research proposal focuses on what you plan to do in the future, supervisors and funders also want to see what you have already achieved academically. Their interest lies in how well you understand the existing research, including recent studies and discussions in your academic field.
Therefore, it is essential to showcase your awareness about gaps in current knowledge and how your research will develop new knowledge and perspectives. Presenting a clear and detailed picture of this background is critical.[ 2]
How to Structure Your PhD Research Proposal ?
Research proposals can vary based on the institution you wish to send the proposal to or your subject of study, but there is a broad structure that needs to be followed.[ 3][4][5] A good PhD research proposal structure should highlight what makes your idea unique, feasible, and significant.
Follow these proven tips to structure a PhD research proposal and make it stand out:
- Provisional Title: The title should not only describe the subject matter but also hint at your approach or main question.
- Key Question: The key question is crucial for defining the scope and purpose of the research, making sure everything stays clear and organized.
- Topic Description: This section serves to introduce readers to the topic being studied, outlines its key focus areas, and helps establish a clear context for the study.
- Existing Knowledge: Here, researchers are required to provide a brief outline of existing knowledge drawn from seminal works, recent research findings, and ongoing debates and highlight gaps in the literature, demonstrating their awareness of existing scholarship.
- Detailed Bibliography: A detailed bibliography not only reflects the thoroughness of the literature review but also provides credibility to the proposed study. It allows reviewers to assess the quality and relevance of sources and enables them to gauge the scholarly merit of the PhD proposal.
- Research Methodology: Details of a comprehensive plan outlining the methodology, procedures, and techniques that will be employed to address the research objectives are included here. Methodology includes information on any special facilities, resources, or equipment required for data collection, analysis, or experimentation.
- Research Plan: This section provides a structured outline of the tasks and activities to be undertaken, along with their respective deadlines or milestones. It includes key phases such as literature review, data collection, analysis, and writing up the findings.
How Long Should a PhD Research Proposal be?
A research proposal typically spans approximately 2,500 words, although there is flexibility in the length as there is no strict upper or lower limit. However, the length may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or funding agency.
Tips for Writing Your PhD Research Proposal
Now that you understand the structure of a PhD research proposal , here are some tips to help you craft a compelling document: [7]
- Start early: Begin drafting your research proposal well in advance to allow yourself ample time for revisions and refinement.
- Be specific: Provide clear and detailed explanations of your objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Seek feedback: Share your proposal with peers or advisors to receive constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Write clearly and concisely: Use clear and concise language to convey your ideas effectively, avoiding unnecessary jargon or technical terms.
- Be ethical: Address any ethical considerations related to your research, such as participant consent or data privacy.
- Revise and proofread: Take time to revise, proofread and proofread again. Best to weed out any inconsistencies and errors for a favourable impression and to clearly communicate your ideas.
- Be passionate: Clearly convey your enthusiasm for the research topic and potential impact of your proposed study. Let your passion for your research topic shine through your proposal.
References:
- How to write a PhD research proposal – University of Liverpool
- How to write a successful research proposal – Prospects
- How to write a good PhD proposal – The University of Queensland
- Writing a research proposal – Sociological Studies – The University of Sheffield
- Writing a Good PhD Research Proposal – Researchgate
- Guidelines to Writing a Research Proposal – University of Oxford
- Top tips for writing your research proposal – University of Birmingham
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
- Research Funding Basics: What Should a Grant Proposal Include?
APA format: Basic Guide for Researchers
How to choose a dissertation topic, best wordtune alternative: detailed review and comparison, you may also like, how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements, how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of....
- Privacy Policy

Home » Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide
Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Proposal is a formal document or presentation that outlines a plan, idea, or project and seeks to persuade others to support or adopt it. Proposals are commonly used in business, academia, and various other fields to propose new initiatives, solutions to problems, research studies, or business ventures.
Proposal Layout
While the specific layout of a proposal may vary depending on the requirements or guidelines provided by the recipient, there are some common sections that are typically included in a standard proposal. Here’s a typical layout for a proposal:
- The title of the proposal.
- Your name or the name of your organization.
- Date of submission.
- A list of sections or headings with corresponding page numbers for easy navigation.
- An overview of the proposal, highlighting its key points and benefits.
- Summarize the problem or opportunity.
- Outline the proposed solution or project.
- Mention the expected outcomes or deliverables.
- Keep it concise and compelling.
- Provide background information about the issue or context.
- Explain the purpose and objectives of the proposal.
- Clarify the problem statement or opportunity that the proposal aims to address.
- Describe in detail the methodology , approach , or plan to achieve the objectives.
- Outline the steps or tasks involved in implementing the proposal.
- Explain how the proposed solution or project will be executed.
- Include a timeline or schedule to demonstrate the project’s timeline.
- Define the specific activities, tasks, or services to be provided.
- Clarify the deliverables and expected outcomes.
- Mention any limitations or exclusions, if applicable.
- Provide a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with the proposal.
- Include itemized expenses such as personnel, materials, equipment, and any other relevant costs.
- If applicable, include a justification for each cost.
- Introduce the individuals or team members involved in the proposal.
- Highlight their qualifications, expertise, and experience relevant to the project.
- Include their roles and responsibilities.
- Specify how the success of the proposal will be measured.
- Define evaluation criteria and metrics to assess the outcomes.
- Explain how progress will be tracked and reported.
- Recap the main points of the proposal.
- Reiterate the benefits and advantages of the proposed solution.
- Emphasize the value and importance of supporting or adopting the proposal.
- Include any additional documents, references, charts, graphs, or data that support your proposal.
- These can include resumes, letters of support, financial projections, or relevant research materials.
Types of Types of Proposals
When it comes to proposals, there are various types depending on the context and purpose. Here are some common types of proposals:
Business Proposal
This type of proposal is used in the business world to present a plan, idea, or project to potential clients, investors, or partners. It typically includes an executive summary, problem statement, proposed solution, timeline, budget, and anticipated outcomes.
Project Proposal
A project proposal is a detailed document that outlines the objectives, scope, methodology, deliverables, and budget of a specific project. It is used to seek approval and funding from stakeholders or clients.
Research Proposal
Research proposals are commonly used in academic or scientific settings. They outline the research objectives, methodology, timeline, expected outcomes, and potential significance of a research study. These proposals are submitted to funding agencies, universities, or research institutions.
Grant Proposal
Non-profit organizations, researchers, or individuals seeking funding for a project or program often write grant proposals. These proposals provide a detailed plan of the project, including goals, methods, budget, and expected outcomes, to convince grant-making bodies to provide financial support.
Sales Proposal
Sales proposals are used by businesses to pitch their products or services to potential customers. They typically include information about the product/service, pricing, features, benefits, and a persuasive argument to encourage the recipient to make a purchase.
Sponsorship Proposal
When seeking sponsorship for an event, sports team, or individual, a sponsorship proposal is created. It outlines the benefits for the sponsor, the exposure they will receive, and the financial or in-kind support required.
Marketing Proposal
A marketing proposal is developed by marketing agencies or professionals to present their strategies and tactics to potential clients. It includes an analysis of the target market, proposed marketing activities, budget, and expected results.
Policy Proposal
In the realm of government or public policy, individuals or organizations may create policy proposals to suggest new laws, regulations, or changes to existing policies. These proposals typically provide an overview of the issue, the proposed solution, supporting evidence, and potential impacts.
Training Proposal
Organizations often create training proposals to propose a training program for their employees. These proposals outline the training objectives, topics to be covered, training methods, resources required, and anticipated outcomes.
Partnership Proposal
When two or more organizations or individuals wish to collaborate or form a partnership, a partnership proposal is used to present the benefits, shared goals, responsibilities, and terms of the proposed partnership.
Event Proposal
Event planners or individuals organizing an event, such as a conference, concert, or wedding, may create an event proposal. It includes details about the event concept, venue, logistics, budget, marketing plan, and anticipated attendee experience.
Technology Proposal
Technology proposals are used to present new technological solutions, system upgrades, or IT projects to stakeholders or decision-makers. These proposals outline the technology requirements, implementation plan, costs, and anticipated benefits.
Construction Proposal
Contractors or construction companies create construction proposals to bid on construction projects. These proposals include project specifications, cost estimates, timelines, materials, and construction methodologies.
Book Proposal
Authors or aspiring authors create book proposals to pitch their book ideas to literary agents or publishers. These proposals include a synopsis of the book, target audience, marketing plan, author’s credentials, and sample chapters.
Social Media Proposal
Social media professionals or agencies create social media proposals to present their strategies for managing social media accounts, creating content, and growing online presence. These proposals include an analysis of the current social media presence, proposed tactics, metrics for success, and pricing.
Training and Development Proposal
Similar to training proposals, these proposals focus on the overall development and growth of employees within an organization. They may include plans for leadership development, skill enhancement, or professional certification programs.
Consulting Proposal
Consultants create consulting proposals to present their services and expertise to potential clients. These proposals outline the problem statement, proposed approach, scope of work, timeline, deliverables, and fees.
Policy Advocacy Proposal
Organizations or individuals seeking to influence public policy or advocate for a particular cause create policy advocacy proposals. These proposals present research, evidence, and arguments to support a specific policy change or reform.
Website Design Proposal
Web designers or agencies create website design proposals to pitch their services to clients. These proposals outline the project scope, design concepts, development process, timeline, and pricing.
Environmental Proposal
Environmental proposals are created to address environmental issues or propose conservation initiatives. These proposals may include strategies for renewable energy, waste management, biodiversity preservation, or sustainable practices.
Health and Wellness Proposal
Proposals related to health and wellness can cover a range of topics, such as wellness programs, community health initiatives, healthcare system improvements, or health education campaigns.
Human Resources (HR) Proposal
HR professionals may create HR proposals to introduce new policies, employee benefits programs, performance evaluation systems, or employee training initiatives within an organization.
Nonprofit Program Proposal
Nonprofit organizations seeking funding or support for a specific program or project create nonprofit program proposals. These proposals outline the program’s objectives, activities, target beneficiaries, budget, and expected outcomes.
Government Contract Proposal
When bidding for government contracts, businesses or contractors create government contract proposals. These proposals include details about the project, compliance with regulations, cost estimates, and qualifications.
Product Development Proposal
Businesses or individuals seeking to develop and launch a new product present product development proposals. These proposals outline the product concept, market analysis, development process, production costs, and marketing strategies.
Feasibility Study Proposal
Feasibility study proposals are used to assess the viability and potential success of a project or business idea. These proposals include market research, financial analysis, risk assessment, and recommendations for implementation.
Educational Program Proposal
Educational institutions or organizations create educational program proposals to introduce new courses, curricula, or educational initiatives. These proposals outline the program objectives, learning outcomes, curriculum design, and resource requirements.
Social Service Proposal
Organizations involved in social services, such as healthcare, community development, or social welfare, create social service proposals to seek funding, support, or partnerships. These proposals outline the social issue, proposed interventions, anticipated impacts, and sustainability plans.
Proposal Writing Guide
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with proposal writing:
- Understand the Requirements: Before you begin writing your proposal, carefully review any guidelines, instructions, or requirements provided by the recipient or organization. This will ensure that you meet their expectations and include all necessary information.
- Research and Gather Information: Conduct thorough research on the topic or project you are proposing. Collect relevant data, statistics, case studies, and any supporting evidence that strengthens your proposal. This will demonstrate your knowledge and credibility.
- Define the Problem or Opportunity: Clearly identify and articulate the problem or opportunity that your proposal aims to address. Provide a concise and compelling explanation of why it is important and relevant.
- State Your Objectives: Outline the specific objectives or goals of your proposal. What do you hope to achieve? Make sure your objectives are clear, measurable, and aligned with the needs of the recipient.
- Present Your Solution: Propose your solution or approach to the problem. Describe how your solution is unique, innovative, and effective. Provide a step-by-step plan or methodology, highlighting key activities, deliverables, and timelines.
- Demonstrate Benefits and Impact: Clearly outline the benefits and impact of your proposal. Explain how it will add value, solve the problem, or create positive change. Use evidence and examples to support your claims.
- Develop a Budget: If applicable, include a detailed budget that outlines the costs associated with implementing your proposal. Be transparent and realistic about expenses, and clearly explain how the funding will be allocated.
- Address Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies: Identify any potential risks, challenges, or obstacles that may arise during the implementation of your proposal. Offer strategies or contingency plans to mitigate these risks and ensure the success of your project.
- Provide Supporting Documentation: Include any supporting documents that add credibility to your proposal. This may include resumes or bios of key team members, letters of support or partnership, relevant certifications, or past success stories.
- Write Clearly and Concisely: Use clear and concise language to communicate your ideas effectively. Avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse or alienate the reader. Structure your proposal with headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance readability.
- Proofread and Edit: Carefully review your proposal for grammar, spelling, and formatting errors. Ensure that it is well-organized, coherent, and flows logically. Consider asking someone else to review it for feedback and suggestions.
- Include a Professional Cover Letter: If appropriate, attach a cover letter introducing your proposal. This letter should summarize the key points, express your enthusiasm, and provide contact information for further discussion.
- Follow Submission Instructions: Follow the specific instructions for submitting your proposal. This may include submitting it electronically, mailing it, or delivering it in person. Pay attention to submission deadlines and any additional requirements.
- Follow Up: After submitting your proposal, consider following up with the recipient to ensure they received it and address any questions or concerns they may have. This shows your commitment and professionalism.
Purpose of Proposal
The purpose of a proposal is to present a plan, idea, project, or solution to a specific audience in a persuasive and compelling manner. Proposals are typically written documents that aim to:
- Convince and Persuade: The primary purpose of a proposal is to convince the recipient or decision-makers to accept and support the proposed plan or idea. It is important to present a strong case, providing evidence, logical reasoning, and clear benefits to demonstrate why the proposal should be approved.
- Seek Approval or Funding: Proposals often seek approval or funding for a project, program, research study, business venture, or initiative. The purpose is to secure the necessary resources, whether financial, human, or technical, to implement the proposed endeavor.
- Solve Problems or Address Opportunities: Proposals are often developed in response to a problem, challenge, or opportunity. The purpose is to provide a well-thought-out solution or approach that effectively addresses the issue or leverages the opportunity for positive outcomes.
- Present a Comprehensive Plan : Proposals outline a comprehensive plan, including objectives, strategies, methodologies, timelines, budgets, and anticipated outcomes. The purpose is to demonstrate the feasibility, practicality, and potential success of the proposed plan.
- Inform and Educate: Proposals provide detailed information and analysis to educate the audience about the subject matter. They offer a thorough understanding of the problem or opportunity, the proposed solution, and the potential impact.
- Establish Credibility: Proposals aim to establish the credibility and expertise of the individual or organization presenting the proposal. They demonstrate the knowledge, experience, qualifications, and track record that make the proposer capable of successfully executing the proposed plan.
- I nitiate Collaboration or Partnerships: Proposals may serve as a means to initiate collaboration, partnerships, or contractual agreements. They present an opportunity for individuals, organizations, or entities to work together towards a common goal or project.
- Provide a Basis for Decision-Making: Proposals offer the information and analysis necessary for decision-makers to evaluate the merits and feasibility of the proposed plan. They provide a framework for informed decision-making, allowing stakeholders to assess the risks, benefits, and potential outcomes.
When to write a Proposal
Proposals are typically written in various situations when you need to present a plan, idea, or project to a specific audience. Here are some common scenarios when you may need to write a proposal:
- Business Opportunities: When you identify a business opportunity, such as a potential client or partnership, you may write a proposal to pitch your products, services, or collaboration ideas.
- Funding or Grants: If you require financial support for a project, research study, non-profit program, or any initiative, you may need to write a proposal to seek funding from government agencies, foundations, or philanthropic organizations.
- Project Planning: When you plan to undertake a project, whether it’s a construction project, software development, event organization, or any other endeavor, writing a project proposal helps outline the objectives, deliverables, timelines, and resource requirements.
- Research Studies: In academic or scientific settings, researchers write research proposals to present their study objectives, research questions, methodology, anticipated outcomes, and potential significance to funding bodies, universities, or research institutions.
- Business Development: If you’re expanding your business, launching a new product or service, or entering a new market, writing a business proposal helps outline your plans, strategies, market analysis, and financial projections to potential investors or partners.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: When seeking partnerships, collaborations, or joint ventures with other organizations or individuals, writing a partnership proposal helps communicate the benefits, shared goals, responsibilities, and terms of the proposed partnership.
- Policy or Advocacy Initiatives: When advocating for a particular cause, addressing public policy issues, or proposing policy changes, writing a policy proposal helps outline the problem, proposed solutions, supporting evidence, and potential impacts.
- Contract Bidding: If you’re bidding for contracts, whether in government or private sectors, writing a proposal is necessary to present your capabilities, expertise, resources, and pricing to potential clients or procurement departments.
- Consulting or Service Contracts: If you offer consulting services, professional expertise, or specialized services, writing a proposal helps outline your approach, deliverables, fees, and timeline to potential clients.
Importance of Proposal
Proposals play a significant role in numerous areas and have several important benefits. Here are some key reasons why proposals are important:
- Communication and Clarity: Proposals serve as a formal means of communication, allowing you to clearly articulate your plan, idea, or project to others. By presenting your proposal in a structured format, you ensure that your message is conveyed effectively, minimizing misunderstandings and confusion.
- Decision-Making Tool: Proposals provide decision-makers with the necessary information and analysis to make informed choices. They offer a comprehensive overview of the proposal, including objectives, strategies, timelines, budgets, and anticipated outcomes. This enables stakeholders to evaluate the proposal’s feasibility, alignment with goals, and potential return on investment.
- Accountability and Documentation: Proposals serve as a written record of commitments, responsibilities, and expectations. Once a proposal is approved, it becomes a reference point for all parties involved, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and accountable for their roles and obligations.
- Planning and Organization: Writing a proposal requires thorough planning and organization. It compels you to define objectives, outline strategies, consider potential risks, and create a timeline. This process helps you think critically about the proposal, identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas that require further refinement.
- Persuasion and Influence: Proposals are persuasive documents that aim to convince others to support or approve your plan. By presenting a well-constructed proposal, supported by evidence, logical reasoning, and benefits, you enhance your ability to influence decision-makers and stakeholders.
- Resource Allocation and Funding: Many proposals are written to secure resources, whether financial, human, or technical. A compelling proposal can increase the likelihood of obtaining funding, grants, or other resources needed to execute a project or initiative successfully.
- Partnership and Collaboration Opportunities: Proposals enable you to seek partnerships, collaborations, or joint ventures with other organizations or individuals. By presenting a clear proposal that outlines the benefits, shared goals, responsibilities, and terms, you increase the likelihood of forming mutually beneficial relationships.
- Professionalism and Credibility: A well-written proposal demonstrates professionalism, expertise, and credibility. It showcases your ability to analyze complex issues, develop effective strategies, and present ideas in a concise and persuasive manner. This can enhance your reputation and increase trust among stakeholders.
- Continual Improvement: The process of writing proposals encourages you to refine your ideas, explore alternatives, and seek feedback. It provides an opportunity for reflection and refinement, ultimately leading to continuous improvement in your plans and approaches.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide
Von der Leyen vows to increase EU research spending in new term
As Ursula von der Leyen is re-elected as president of the European Commission, she promises to expand the ERC and the EIC

Commission president Ursula von der Leyen giving her speech before the European Parliament in Strasbourg ahead of her re-election. Photo credits: Christophe Licoppe / European Union
Ursula von der Leyen promised to put research and innovation “at the centre of our economy” as she laid out her plans for the next five years, before the European Parliament voted to confirm her second term as president of the European Commission.
A total of 401 MEPs voted in favour of von der Leyen’s re-election this afternoon, and 284 voted against, making for a more comfortable majority than her first vote in 2019.
There was no mention of research in her speech to MEPs before the vote, but in her political guidelines published this morning, von der Leyen pledges to increase the EU’s research spending, and “expand” the European Research Council (ERC) and the European Innovation Council (EIC).
The ERC delivers grants to support primarily early-stage research, with a budget of more than €16 billion under Horizon Europe. French president Emmanuel Macron has called for the ERC to be reinforced , and ERC president Maria Leptin recently urged grant holders to lobby politicians for more funding.
The EIC supports researchers and innovators with grants and equity investments. Its €10.1 billion budget until 2027 makes it one of the biggest deep tech investors in the world, but its president has stressed the need for additional funding.
Meanwhile MEPs and the research community have been calling for the Horizon Europe budget to be doubled to €200 billion in the next framework programme, as member states continue to show no signs of spending 3% of GDP on R&D, targets which were proposed back in 2003.
Von der Leyen also wants to launch new public-private partnerships, propose a European biotech act next year as part of a wider life sciences strategy, and strengthen the university alliances designed to deepen cross-border links between institutions.
Leptin said von der Leyen’s appointment would provide much-needed continuity, and she is “very pleased” with the commitment to increase research spending with a focus on fundamental research, scientific excellence, and disruptive innovation, and to expand the ERC.
“In the ERC competitions, we can now only fund 60% of excellent proposals; increased funds would certainly help to close this gap and further curb the brain drain from Europe,” Leptin said. “What’s more, there is a need to increase the funding given to ERC grantees as the grant sizes have not changed since the creation of the ERC in 2007, despite inflation.”
Eszter Lakos, newly elected Hungarian MEP who previously worked as a science and technology diplomat in Brussels and represented Hungary in the Council of the EU during negotiations for Horizon Europe, told Science|Business that she welcomes von der Leyen’s call to increase the R&I budget.
However, “numbers are important,” she said, recalling that the current Horizon Europe budget is far short of what it would have taken to fund all the excellent research proposals it received.
Also, according to Lakos, one question to be clarified is how much research will remain at the heart of the framework programme.
“The research side is not to be forgotten because it is at the root and upstream of innovation,” Lakos said.
Good news for research
Von der Leyen’s appointment is “good news for research in Europe,” said Christian Ehler MEP, who was a co-rapporteur for Horizon Europe. The support for the ERC and EIC and the pledge to increase R&I investments bode well for the next framework programme, FP10, he said.
“I believe her commitments to provide the circumstances for researchers to thrive, to create new public-private partnerships and to focus on strategic priorities indicate that FP10 can be different of nature than Horizon Europe by being more focussed and less complex,” Ehler told Science|Business.
“The only issue I would like to be emphasised more in the mission letter to the new Commissioner is European values in research, particularly the protection of the freedom of scientific research and our commitment to supporting researchers at risk.”
Sovereignty fund?
Addressing the European Parliament this morning ahead of the decisive vote, von der Leyen promised to make prosperity and competitiveness her top priority. “This mandate has to be the time of investment,” she said.
Central to that strategy is the proposal for a European Competitiveness Fund to be included in the EU’s next long-term budget, to invest in strategic technologies such as artificial intelligence, space, clean tech and biotech.
It is a similar concept to the EU sovereignty fund von der Leyen first pitched last year, before member states refused to hand over fresh money. A reinforced budget for the 2028-2034 period could allow that idea to finally come to fruition, although negotiations will not be easy. The fund will focus on cross-border projects, and will support the Important Projects of Common European Interest (IPCEIs), which von der Leyen wants to make simpler and faster.
“The fundamentals of the global economy are changing, those who stand still will fall behind, those who are not competitive will be dependent,” she told MEPs.
According to von der Leyen, the European Single Market needs to ease bureaucracy and increase public and private investment “from farming to industry, from digital to strategic technologies but also more investment in people and their skills”.
The strategy puts at its centre European start-ups and SMEs, for which von der Leyen proposed to introduce a revamped SME and competitiveness check to get rid of burdensome micromanagement and give companies better incentives.
She proposed to ask each commissioner to work on this, appointing a vice-president to report on progress to the Parliament once a year.
Von der Leyen's strategy echoes that proposed by former prime minister Enrico Letta in his high-profile report released in mid-April.
As Letta set out, the current fragmentation of the single market hinders SMEs in numerous ways, including administrative burdens like business law and the taxation system. Reducing these obstacles and harmonising state aid rules would boost SMEs’ access to support and improve European R&I, he said.
In her speech, von der Leyen addressed the innovation race against US and Asia. She said the EU should boost its liquid capital market and adopt a competition policy that can support start-ups to scale up, without pushing companies to look for funding abroad to finance their expansion. “Europe must be the home of opportunity and innovation,” she said.
As well as completing the Captital Markets Union, von der Leyen wants to deliver Letta’s idea of a European Savings and Investments Union. “Every year, €300 billion of European family savings go from Europe to foreign markets because our capital markets are too fragmented. This money is often used to buy European innovative companies from abroad and the companies leave. This has to change,” she said.
Clean Industrial Deal
A new Clean Industrial Deal to decarbonise and bring down energy prices will also be put forward in the first 100 days of the mandate. The initiative is designated to channel investment in infrastructure and industry, in particular for energy-intensive sectors, von der Leyen said.
“This will help create lead markets in everything from clean steel to clean tech and it will speed up planning, tendering, and permitting,” and enable the EU to “break free from dirty Russian fossil fuels,” she said.
This will also involve enshrining the target of reducing carbon emissions by 90% by 2040 into law. The initiative represents a renewed commitment to the Green Deal, but a shift in focus towards implementation and investment.
CERN for AI
In her political guidelines, von der Leyen is also pledging to step up investment in cutting-edge technologies, “in particular supercomputing, semiconductors, the Internet of Things, genomics, quantum computing, space tech and beyond”.
When it comes to artificial intelligence, the guidelines mark a shift from regulation to innovation. The new commission will develop an “apply AI strategy” alongside member states, industry and civil society to support industrial and public service applications of AI.
The president will propose setting up an AI Research Council to pool resources, picking up the idea of a CERN for AI, a concept that recently received the backing of the Commission’s scientific advisors.
“It’s great to see this proposal is now gaining traction,” said Nicole Grobert, chair of the group of chief scientific advisers. “We need to make sure that we think carefully about how an AI institute is designed, because it really matters. It should provide fair access to massive high-performing computational power, a sustainable cloud infrastructure, funding for research with AI and AI training programmes for researchers in all disciplines to explore and adopt AI in their sciences.”
Defence union
The most rousing section of von der Leyen’s speech was when she reaffirmed the EU’s support for Ukraine, and the need to invest more in Europe’s security and defence. “I do believe it is now time to build a veritable defence union,” she told MEPs, urging support for common European projects such as a “complete air defence system”.
She goes further in the political guidelines, promising to appoint a Commissioner for Defence, and to present a white paper on the future of European Defence in the first 100 days of the mandate to set out the new approach and identify investment needs.
In the document she pledges to reinforce the European Defence Industry Programme , designed to incentivise common procurement, and the European Defence Fund (EDF), which supports cross-border innovation projects.
Paulius Saudargas, a newly-elected Lithuanian MEP in von der Leyen’s EPP group with a PhD in biophysics, welcomed the outcome of the vote and the president’s R&I agenda. “I agree that research and innovation must be put at the core of our economy. It is the recipe for the competitive and prosperous EU,” he told Science|Business.
Saudargas believes special attention should be paid to security and defence, including support for collaborative R&I projects in defence technologies, and he was pleased to note the mention of a European Defence Union and a single market for defence.
Related news

Von der Leyen commits to Green Deal, reassuring EU clean tech industry
Industry welcomed Commission President Ursula von der Leyen’s plans for more climate investments, but environmental groups are not convinced
Never miss an update from Science|Business: Newsletter sign-up
Related News

Get the Science|Business newsletters
Sign up for the Funding Newswire
Sign up for the Policy Bulletin
Sign up for The Widening
Funding Newswire subscription

Follow where the public and private R&I money is going and which collaborative opportunities you can pursue.
Subscribe today
Find out more about the Science|Business Network

Why join?
Become a member
- Funding Newswire
- The Widening
- R&D Policy
- Why subscribe?
- Testimonials
- Become a member
- Network news
- Strategic advice
- Sponsorships
- EU Projects
- Enquire today

- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Budget 2024
- Olympics 2024
- Partner Content
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
Budget 2024: Proposals for critical minerals to help achieve net-zero goals
In her budget speech on tuesday, finance minister nirmala sitharaman announced a slew of measures for sectors, including infrastructure, manufacturing and healthcare.
)
Rs 10,000 crore fund for solar infrastructure development, including solar parks and grid integration, is a pivotal step towards achieving renewable energy targets. | Photo: Bloomberg
Listen to This Article
More from this section, opposition mps stage walkout to protest union budget 2024 in parliament, research, infra allocation will boost innovation in steel sector: isa, angel tax was on investments, such inflows should not be taxed: dpiit secy, union budget 2024-25 significant milestone for country, says sicci, budget 2024: what is the 'purvodaya' scheme announced by fm sitharaman.
(Only the headline and picture of this report may have been reworked by the Business Standard staff; the rest of the content is auto-generated from a syndicated feed.)
Parliament LIVE news: No state ignored in Union Budget, says FM Sitharaman; INDIA bloc MPs walk out
Dpiit to create timelines for govt agencies for clearance of fdi proposals, india needs to monetise assets to support spending, says jpmorgan, pvt sector needs to step up, match govt's efforts: anand mahindra, congress cms to boycott niti aayog meet over 'discriminatory' 2024 budget.
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Jul 24 2024 | 2:44 PM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Budget 2024 Budget 2024 Live Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)

Times of San Diego
Local News and Opinion for San Diego
Higher Vacancies, Lower Rates Seen in Annual Survey of Regional Rental Market

Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)

The Southern California Rental Housing Association announced Thursday that its annual Vacancy and Rental Rate Survey found increased availability and a decrease in rents compared to last year.
“The 2024 annual Survey indicates what industry members have been experiencing; higher vacancies and lower asking rents,” said Alan Pentico, executive director of the SCRHA, in a statement. “While we still face a housing shortage in California, this change in the local market is good news for renters.”
The vacancy rate went up to 6.36% in spring 2024, up from 3.9% from last spring. The city of San Diego experienced a rise in vacancy rates within the region to 4.22% compared to 2.64% last year.
The increase in vacancies can be linked to new properties on the market and higher rates in older properties.
Throughout San Diego County, the average rent decreased to $2,170, compared to $2,338 from 2023, a drop slightly over 7%. In the City of San Diego, the average rent fell from $2,266 last spring to $2,189 this spring, a decline over 3%.
The data was collected through surveys mailed to approximately 6,000 San Diego County rental property owners and managers in March 2024, with responses representing about 11,400 units. Participants provided information on rates, number of bedrooms, square footage, property age, location, and occupancy status.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that your research is suitable (for the requirements of the degree program) and manageable (given the time and resource constraints you will face). The most important word here is "convince" - in other words, your ...
Below is an outline of the elements a research proposal might typically contain. Step 1: Create your title . A clear and succinct description of your research to use as a working title. Include relevant keywords that relate to your research and ensure your title goes beyond just describing the topic.
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
Key Takeaways. Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the ...
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
A well-structured research proposal includes a title page, abstract and table of contents, introduction, literature review, research design and methodology, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, timeline and budget. Visme's research proposal examples and templates offer a great starting point for creating engaging and well-structured ...
Develop an Outline. Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content. Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution. Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers ...
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
Look for any research gaps, trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions. Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal. 4. Research Design. This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal.
Style: If space allows, provide a clear project title. Structure your text - if allowed use section headings. Present the information in short paragraphs rather than a solid block of text. Write short sentences. If allowed, provide images/charts/diagrams to help break up the text.
Begin writing your business research proposal by providing the business research title and a brief yet informative research overview. The title should be concise and triggers the curiosity of the management. As for the research overview, it should present the highlight of the research. 2. Write a Clear Introduction.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Academic Research Proposal. This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, and expected outcomes.
A good research proposal is the key to successful research. Any research--whether in the area of Public Health examining the impact of passive smoking, or industrial pollution of in the area of social change investigating the impact of new agricultural technology on a rural society--must begin with a clearly focused research proposal. In
A research design is a thorough plan that helps a research project achieves its goals. Business research is a scientific examination that entails a series of highly interconnected operations, each of which might have negative consequences for subsequent activities if completed incorrectly (Greener, 2021). The steps of the business research proposal process are explained in+ Read More
In a research proposal you pitch your research idea. You pitch a research problem, your approach to developing a solution and why it matters. This pitch needs to be credible and convincing. You need to sell your research idea. A research proposal describes your planned research. It presents your research topic and describes why this topic is ...
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
Starting on PhD research is a big step in a researcher's academic journey, and submitting a research proposal is a significant part of it. Indeed, many PhD scholars seek guidance on how to write a PhD research proposal, which is the foundational document that outlines the scope, objectives, and methodology of their prospective doctoral study.This article takes a look at the essential ...
Proposal. Definition: Proposal is a formal document or presentation that outlines a plan, idea, or project and seeks to persuade others to support or adopt it. Proposals are commonly used in business, academia, and various other fields to propose new initiatives, solutions to problems, research studies, or business ventures.
Business Innovation Research (SBIR/STTR) Program award. A similar certification will be used to ensure continued compliance with specific program requirements during the life of the funding agreement. The definitions for the terms used in this certification are set forth in the Small Business Act, SBA regulations (13 C.F.R. Part
E. J. Ourso College of Business . Summer Research Funding Proposal Guidelines. Revised, April 29, 2022. To request summer funding to support research from foundation accounts (chairs, professorships, departmental development funds, etc.), the following proposal guidelines have been established. 1.
Ursula von der Leyen promised to put research and innovation "at the centre of our economy" as she laid out her plans for the next five years, before the European Parliament voted to confirm her second term as president of the European Commission. A total of 401 MEPs voted in favour of von der Leyen's re-election this afternoon, and 284 voted against, making for a more comfortable ...
The Budget announcements related to critical minerals and green transition will not only make India self reliant in resources but also help in meeting net-zero goals, energy industry players said. In her Budget speech on Tuesday, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a slew of measures for ...
EDMONTON, Alberta, July 25, 2024 - PRESS RELEASE - Aurora Cannabis Inc., a leading Canadian-based global medical cannabis company, has been granted two licenses by the Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) under Germany's new Medical Cannabis Act (MedCan-G).Aurora's license grants the company continued domestic cultivation, which has been underway for two years now.
The vacancy rate went up to 6.36% in spring 2024, up from 3.9% from last spring. The city of San Diego experienced a rise in vacancy rates within the region to 4.22% compared to 2.64% last year.