

The Correct Way to Write an Article Title in a Paper
It is a cardinal rule to cite scholarly sources when writing a paper. Most professors will specify the approximate number of sources for a paper, essay, or assignment. A well-written academic paper is objective and has references or works cited page where you list the references used. However, how do you write the title of an article when writing a paper?
When you mention an online or magazine article in your essay, do not just do it as you please. There is a formula you need to follow depending on the referencing style. This post looks at how to title an article in an essay following the APA, Harvard, MLA, and Chicago.
Let’s commence.
How to Title an Article in APA
APA stands for American Psychological Association. The association published the first APA stylebook in the late 1920s. Over the years, the stylebook has been widely adopted beyond psychology. It has also been updated many times. The stylebook meticulously describes how to format every aspect of your essay.
Whenever you mention the name of a source in an APA essay, there are rules you need to follow. This is true for all sources, including articles, books, webpages, reports, chapters, etc.
The rules you need to follow depend on the type of source (standalone source or part of a greater thing). For some sources, you simply capitalize and italicize the main words; for others, you have to capitalize the main words and put them in double quotation marks.
You need to italicize and capitalize their names when you mention standalone sources. Standalone sources include a podcast, a TV series, a dissertation, a movie, and an e-book.
Examples showing how to write larger works in APA
- Morbid: A True Crime Podcast (podcast title)
- The Last of Us (TV series title)
- Canadian Legal System Versus US Legal System: A Comparative Study (dissertation title)
- The Pirates of the Caribbean (movie title)
- For a Dollar and a Dream: State Lotteries in Modern America (e-book title)
On the other hand, when you mention sources that are part of a greater work, you need to capitalize them and put them in double quotation marks. Examples of these sources include a magazine article, a newspaper article, a blog post, and a journal article. This means mentioning any article must capitalize its title and put it in double quotations.
Examples showing how to write article titles in APA
- “Study of Correlation between Criminality and Population” (journal article title)
- “Effective Active Ingredients Obtained through Biotechnology” (journal article title)
- “Doping in Cycling: Everything You Need to Know” (magazine article title)
- “Do you know what is in Your Cosmetics?” (newspaper article title)
- “35 Best Ways to Make Money Online in 2023” (blog post title)
Titling an article in a Harvard Style Format Paper or Essay
The Harvard referencing system was invented late in the nineteenth century by a Harvard University professor. The system has been widely adopted beyond the lecture halls of Harvard. It is popularly used to reference various works in the following fields: philosophy, behavioral sciences, and humanities.
When you name or mention an article in a Harvard essay, there are rules you must follow. There are rules you need to follow when you mention any work in a Harvard essay.
The rules you need to follow depend mainly on the size of the work. The titles of large works are formatted differently compared to the titles of small works.
Large works include books and journals. When you mention a book or journal in a Harvard essay, you must italicize the entire title and capitalize the major words.
Examples showing how to write large works in Harvard
- The Lucifer Effect (book title)
- Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us (book title)
- Games People Play (book title)
- Comparative Studies in Society and History (journal title)
- Journal of American History (journal title)
The titles of smaller works are written differently in contrast to the title of large works. They are written by putting them inside single quotation marks.
Smaller works include journal articles, blog posts, web pages, web articles, etc. Whenever you mention these things in your essay, you must put them inside quotes.
Examples showing how to write smaller works in Harvard
- ‘Sex, Military Brothels, and Gender Violence during the Italian Campaign in the USSR, 1941-3’ (journal article title)
- ‘Hitler’s Worldview and the Interwar Kulturkamf’ (journal article title)
- ’10 POC-Owned Advisory Businesses With Insanely Great Marketing’ (blog post title)
- ‘How to Use Instagram for Your Financial Planning Business’ (blog post title)
- ‘These 9 Decorative Accessory Trends Are About to Pop Off in Your Group Text’ (web page title)
How to Title an Article in MLA
MLA is an acronym for Modern Language Association. The association started in 1883 to promote the study of modern languages and literature. It published the first stylebook in 1953 and has made major updates to it a number of times. The MLA style is widely used in the following fields: cultural studies, comparative literature, literary criticism, foreign languages, and English studies. It is also used in humanities disciplines.
When you mention an article or any other source in MLA, there are rules you need to follow. The rules largely depend on the type of source you mention.
When you mention a large standalone work (a book, a film, a journal, a website, a magazine, or a movie), you must italicize it and then capitalize all major words. (You should capitalize articles in the middle of the title, prepositions, and coordinating conjunctions.
Examples showing how to write large works in MLA
- Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies (book title)
- Literary Theory: An Introduction (book title)
- Fast Company (magazine title)
- Library Philosophy and Practice (journal title)
- Teens Dealing with Death; When Someone Dies: Understanding Grief (movie title)
When you mention a singular article (journal or otherwise) or any other smaller work, you must put it in double quotation marks. No italicizing as in the case of larger works. Examples of smaller works that need to be put in quotes include journal articles, web articles, news articles, book chapters, songs, short stories, TV episodes, magazine articles, and poems.
Examples showing how to write smaller works in MLA
- “Collaborative writing among young EFL learners in a school context: product and process” (journal article title)
- “Investigating cohort effects of early foreign language learning” (journal article title)
- “Studying French is easy: 10 tips to learn French fast” (web article title)
- “ChatGPT Gets Dartmouth Talking” (news article title)
- “Do not go gentle into that good night” (poem title)
How to Title an Article in a Chicago Format Essay/Paper
Chicago format is an American English formatting style invented by the University of Chicago in 1906. It is widely used in many academic disciplines (fine arts, history, and business) and book publishing.
When writing an essay according to the Chicago stylebook, you must follow everything recommended in it. How you are supposed to write the title of a journal or a book is not the same way you are supposed to write the title of a journal article or a book chapter.
The Chicago Manual of Style requires you to italicize the title of all standalone works you mention in your essay. Standalone works that you must italicize include journals, books, plays, and so on.
Examples showing how to write the titles of standalone works in Chicago
- Internal Journal of Art & Design Education (journal-title title)
- Studies in Art Education (journal title)
- Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion (book title)
- Rich Dad Poor Dad (book title)
- Long Day’s Journey Into Night (play title)
The Chicago Manual requires you to enclose the title of short works in double quotation marks. Examples of short works that need to be enclosed include journal articles, magazine articles, news articles, book chapters, etc.
- “Frank Gehry’s non-trivial drawings as gestures” drawdlings and kinaesthetic approach to architecture” (journal article title)
- “The Saka ‘Animal Style’ in Context: Material, Technology, Form and Use” (journal article title)
- “An Abandoned, Industrial Ruin Bursts With New Life in Delaware” (magazine article title)
- “The Unfinished Business of International Business Tax Reform” (news article title)
- “The Technologies Behind Bitcoin” (book chapter title)
On a Final Note!
You now know how to format standalone and shorter works in APA, MLA, Harvard, and Chicago. Therefore, when asked to write an essay following any of these formatting styles, you should be able to correctly mention or talk about any article or larger work in your essay.
Try our paper editing service if you need help editing your essay to conform to APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago standards. We offer essay editing services at affordable rates. We can edit any work to meet any academic requirements. Check out our other writing and homework help services .
Contact us today for fast and professional assistance.

Gradecrest is a professional writing service that provides original model papers. We offer personalized services along with research materials for assistance purposes only. All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. See our Terms of Use Page for proper details.

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Introduce a Journal Article in an Essay
Last Updated: February 9, 2024
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. This article has been viewed 33,816 times.
Using a journal article in your essay can add to your credibility and make your points more persuasive. When you introduce an article to your readers, you help them understand why you're using it as a source. We've gathered a number of different ways you can introduce the journal article and transition between your thoughts and those of the other author. Pick the one that works best for you and your personal writing style.
List the title and the author.

- For example, you might write: "Albus Dumbledore describes the origin of the four Hogwarts houses in his article 'Separating Hogwarts Fact and Fiction.'"
- Put the title of the article in double-quotation marks in your text. [1] X Research source
- If you're quoting directly from the source, include the author's full name the first time you quote them. [2] X Research source
Summarize the article.

- For example, you might write: "The history of Hogwarts makes clear that the houses were never intended to be seen as 'good' or 'evil.' Rather, each house emphasizes and nurtures specific traits students have—how they use those traits is up to them."
- Paraphrasing from the article is similar to summarizing. However, when you summarize, you're covering the entire article in a sentence or two. A paraphrase typically only covers a small portion of the article.
Provide any necessary background.

- For example, you might write: "Professor Slughorn was one of the longest-serving teachers at Hogwarts, schooling generations of students in potions until his retirement."
- You might also include some background if the author of the article is controversial or the article's conclusions have been seriously questioned. If you're doing this, go on to explain why you're using the article in your essay.
Explain the purpose of the source in your essay.

- For example, you might write: "Although this essay doesn't discuss defenses against the dark arts, Gilderoy Lockhart's article provides an example of how you can't learn anything by plagiarizing the work of others."
Frame the source in the context of your own essay.

- For example, you might write: "This article demonstrates broad support for the idea that Hogwarts should continue to sort students into four houses."
Add a signal phrase to distinguish ideas from the source.

- For example, you might write: "McGonagall argues that Slytherin House should be disbanded after the Battle of Hogwarts."
Discuss the source's limitations.

- For example, you might write: "While McGonagall makes a compelling argument that Slytherin House should be disbanded, she was biased by her experiences. In this essay, I will show that the personality traits emphasized by Slytherin are positive traits that can be used for good."
Expert Q&A
- Remember to include an in-text citation for the source if required by your citation guide. You'll also need an entry for the source in your reference list at the end of your paper. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- In an academic essay, you typically introduce a journal article in the first sentence of a paragraph. Then, use the sentences that follow to show how the material from the article relates to the rest of your essay. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://rasmussen.libanswers.com/faq/32501
- ↑ https://www.ursinus.edu/live/files/1160-integrating-quotespdf
- ↑ https://www.una.edu/writingcenter/docs/Writing-Resources/Source%20Integration.pdf
- ↑ https://www.stetson.edu/other/writing-center/media/Handout%20-%20Incorporating%20Sources%20Effectively.pdf
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Food & Dining
- Coronavirus
- Real Estate
- Seattle History
- PNW Politics
Correct Way to Write an Article Title in a Paper
- College & Higher Education
Related Articles
How are the titles of longer works written in mla style, the disadvantages of apa, how to acknowledge poetry in apa references.
- How to Cite USGS Maps Using the MLA Format
- How to Find Good Resources for Writing an Essay
Citing scholarly sources in your writing can help you to support your argument or to tackle counterarguments. Not only do you have to create a page of works cited, but you also have to properly cite those sources in your text by following formatting guides. Modern Language Association and American Psychological Association guidelines are the most-used formatting styles in academic writing, and both have the same rules regarding how to write an article title in a paper: Put quote marks around the title and capitalize the first and last words in the title as well as all other words except articles and prepositions shorter than four letters.
Title Rules
All shorter works such as articles, book chapters, essays and even songs should be in quotation marks when cited in a paper in MLA and APA styles. An example would be: "Article Discussing Effects of Climate Change on Monkeys." If you must include the book or journal where the article is found in your paper, italicize it in both styles. In-text citations are also necessary when listing an article in your paper. For MLA style, an in-text citation includes the author's last name and the page number in parentheses, such as (Bedford 4). For APA style, the in-text citation includes the author's last name, year of publication and page number also in parentheses, such as (Bedford, 1990, p. 4).
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: MLA In-Text Citations: The Basics
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: In-Text Citations: The Basics
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Reference List: Articles in Periodicals
- Carson-Newman University: Punctuating Titles: When to Use Italics, Underlining, and Quotation Marks
- American Psychological Association: How to Capitalize and Format Reference Titles in APA Style
Maria Magher has been working as a professional writer since 2001. She has worked as an ESL teacher, a freshman composition teacher and an education reporter, writing for regional newspapers and online publications. She has written about parenting for Pampers and other websites. She has a Master's degree in English and creative writing.
How to Complain About an Incompetent Professor
Basic guidelines for writing research papers apa style, apa style vs. chicago, how to cite an article within a book, what should be included with an in-text citation in apa formatting, how to cite the retrieval date for apa format, how to cite a source with multiple publication dates, what does it mean to cite specific examples, what are the essential parts of a college essay, most popular.
- 1 How to Complain About an Incompetent Professor
- 2 Basic Guidelines for Writing Research Papers APA Style
- 3 APA Style Vs. Chicago
- 4 How to Cite an Article Within a Book
How do I actually write the names of the article and the journal/magazine in my paper?
To write the name of a journal/magazine title in the body of your paper:
- The title of the journal should be in italics - Example: Journal of the American Medical Association
- Capitalize all of the major words.
To write the the name of an article title in the body of your paper:
- The title of the article should be in quotation marks - E xample: "Tiger Woman on Wall Street"
For more information, please see the following pages on the APA Style Blog :
- Title Case Capitalization
- Use of Italics
- Use of Quotation Marks
Thank you for using ASK US. For more information, please contact your Baker librarians .
- Last Updated May 05, 2023
- Views 533466
- Answered By Baker Librarians
FAQ Actions
- Share on Facebook
Comments (8)
- Do articles contain address? by Danny on Mar 20, 2017
- On the APA References page add Retrieved from and the website address at the end of the citation. See the APA Help page for examples-https://guides.baker.edu/apahelp by ASK US on Mar 20, 2017
- Is this information the same for scientific research journals and articles (still within APA)? by Haley on Apr 03, 2017
- Yes, it is. See the APA Help guide for examples. guides.baker.edu/apahelp by ASK US on Apr 03, 2017
- Do I have to put the name of the author of the article or website the article was from? by Hailee on May 01, 2017
- The answer given was for the body of your paper. Here's how to cite an article both on the References page and in-text: Author Last Name, First & Middle Initials. (Date). Title of article: Subtitle of article. Title of Source, Volume(Issue), Page numbers. Retrieved from... In-text: Paraphrase: (Author Last Name, Year). Quotation: (Author Last Name, Year, p. Page Number). by ASK US on May 02, 2017
- Do I put the title of essay in single quotation marks if I write in UK English (APA)? by joseph on Mar 25, 2019
- See the APA Style Blog's post on How to Capitalize and Format Reference Titles in APA Style: https://blog.apastyle.org/apastyle/2012/03/how-to-capitalize-and-format-reference-titles-in-apa-style.html by Patrick Mullane on Mar 25, 2019
We'll answer you within 3 hours M - F 8:00 am - 4:00 pm.
Write articles in minutes
Write faster with 70+ templates
Do your work 3x faster
Make images with AI
Support & live chat with customers
Build better customer relationships
Give 24/7 self-service support
Write content fluently in 30+ languages
10 Proven Ways to Mention an Article in an Essay - Ultimate Guide 2024

Here are 10 important statistics about mentioning an article in an essay:
- Over 80% of students struggle with properly citing articles in their essays.
- Using proper citations can significantly improve the credibility of your essay.
- Approximately 70% of teachers consider proper citation as a crucial aspect of academic writing.
- Failure to mention an article correctly can result in plagiarism, which can lead to severe consequences.
- More than 50% of students admit to not knowing how to properly mention an article in their essays.
- Using the correct citation format can enhance the overall structure and flow of your essay.
- Properly mentioning an article can help you avoid accusations of intellectual theft.
- Around 90% of college professors expect students to cite their sources accurately.
- Knowing how to mention an article in an essay can save you time and effort in the long run.
- Using the right techniques to mention an article can impress your instructors and boost your grades.
1. Why is it important to mention an article in an essay?

Mentioning an article in an essay is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it adds credibility to your work by acknowledging the sources of information you have used. Secondly, it allows readers to verify the information and conduct further research if desired. Lastly, proper citation demonstrates your understanding of academic integrity and ethical writing practices.
1.1 The importance of academic integrity
Academic integrity is the foundation of scholarly work. By mentioning an article in your essay, you show respect for the original author's ideas and give credit where it is due. This not only upholds ethical standards but also helps you avoid plagiarism, which can have serious consequences on your academic and professional future.
2. How to mention an article in an essay using APA format

APA (American Psychological Association) is one of the most commonly used citation styles in academic writing. To mention an article in an essay using APA format, follow these steps:
2.1 In-text citations
In APA format, in-text citations are used to acknowledge the source of information within the body of your essay. When mentioning an article, include the author's last name and the publication year in parentheses. For example: (Smith, 2022).
3. How to mention an article in an essay using MLA format
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Whitepaper-629d14ebcf3248cebc5230517d1ed7d6.jpg)
MLA (Modern Language Association) is another widely used citation style, particularly in the humanities. To mention an article in an essay using MLA format, follow these guidelines:
3.1 In-text citations
In MLA format, in-text citations typically include the author's last name and the page number where the information was found. For example: (Smith 45).
4. How to mention an article in an essay using Chicago style

The Chicago Manual of Style is commonly used in history, literature, and the arts. To mention an article in an essay using Chicago style, follow these steps:
4.1 Footnotes or endnotes
In Chicago style, footnotes or endnotes are used to cite sources. When mentioning an article, include the author's name, the article title, the publication title, the publication date, and the page number. For example: 1 Smith, John. "The Importance of Mentioning Articles." Journal of Academic Writing 45, no. 2 (2022): 123-145.
5. How to mention an article in an essay using Harvard referencing style

Harvard referencing style is commonly used in the social sciences. To mention an article in an essay using Harvard referencing style, follow these guidelines:
5.1 In-text citations
In Harvard referencing style, in-text citations typically include the author's last name and the publication year in parentheses. For example: (Smith, 2022).
6. How to mention an article in an essay using Vancouver style

Vancouver style is commonly used in the medical and scientific fields. To mention an article in an essay using Vancouver style, follow these steps:
6.1 Numeric system
In Vancouver style, a numeric system is used for in-text citations. Each source is assigned a number, which is then used in the text to refer to the corresponding reference. For example: [1].
7. How to mention an article in an essay without an author

Sometimes, you may come across articles without a clearly identified author. In such cases, follow these guidelines to mention the article in your essay:
7.1 Use the title
If the article does not have an author, use the title of the article in place of the author's name in your citation. For example: ("The Importance of Mentioning Articles," 2022).
8. How to mention an online article in an essay

With the increasing availability of online articles, it is important to know how to properly mention them in your essay. Follow these steps to mention an online article:
8.1 Include the URL
When mentioning an online article, include the URL or the web address of the article in your citation. For example: (Smith, 2022, https://www.example.com/article).
9. How to mention a scholarly journal article in an essay
Scholarly journal articles are often used as sources in academic writing. To mention a scholarly journal article in your essay, follow these guidelines:
9.1 Include the journal title
When mentioning a scholarly journal article, include the title of the journal in your citation. For example: (Smith, 2022, Journal of Academic Writing).
10. How to mention multiple articles in an essay
When referencing multiple articles in your essay, it is important to provide clear and concise citations for each source. Follow these guidelines to mention multiple articles:
10.1 Use semicolons
When mentioning multiple articles in the same sentence, use semicolons to separate the citations. For example: (Smith, 2022; Johnson, 2021; Brown, 2020).
10.2 Use alphabetical order
When listing multiple articles in your essay, arrange them in alphabetical order based on the authors' last names. For example: (Brown, 2020; Johnson, 2021; Smith, 2022).
Over 15,763 SEO agencies and brands are using AtOnce to rank higher on Google.
It lets you write hundreds of articles on any topic, giving you more clicks to your site.
Get more traffic and sales — without wasting months of your time.
How do I mention an article in an essay?
To mention an article in an essay, you should include the author's name, the title of the article in quotation marks, the title of the journal or website in italics, the volume and issue number (if applicable), the publication date, and the page numbers.
What is the correct way to cite an article in an essay?
The correct way to cite an article in an essay is to use the appropriate citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago. Each style has its own specific format for citing articles, so it's important to consult the style guide for the correct citation format.
Can I use a direct quote from an article in my essay?
Yes, you can use a direct quote from an article in your essay. However, it's important to properly cite the quote using the appropriate citation style. In addition, you should only use direct quotes when they are necessary and relevant to your essay.

Asim Akhtar
Asim is the CEO & founder of AtOnce. After 5 years of marketing & customer service experience, he's now using Artificial Intelligence to save people time.
APA In-Text Citations and Sample Essay 7th Edition
This handout focuses on how to format in-text citations in APA.
Proper citation of sources is a two-part process . You must first cite each source in the body of your essay; these citations within the essay are called in-text citations . You MUST cite all quoted, paraphrased, or summarized words, ideas, and facts from sources. Without in-text citations, you are technically in danger of plagiarism, even if you have listed your sources at the end of the essay.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources’ information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided.
More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Citation Rules
Direct quotation with the author named in the text.
Heinze and Lu (2017) stated, “The NFL shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly as the field itself evolved” (p. 509).
Note: The year of publication is listed in parenthesis after the names of the authors, and the page number is listed in parenthesis at the end of the quote.
Direct Quotation without the Author Named in the Text
As the NFL developed as an organization, it “shifted its responses to institutional change around concussions significantly” (Heinze & Lu, 2017, p. 509).
Note: At the end of the quote, the names of the authors, year of publication, and page number are listed in parenthesis.
Paraphrase with 1-2 Authors
As the NFL developed as an organization, its reactions toward concussions also transformed (Heinze & Lu, 2017).
Note: For paraphrases, page numbers are encouraged but not required.
Paraphrase with 3 or More Authors
To work toward solving the issue of violence in prisons begins with determining aspects that might connect with prisoners' violent conduct (Thomson et al., 2019).
Direct Quotation without an Author
The findings were astonishing "in a recent study of parent and adult child relationships" ("Parents and Their Children," 2007, p. 2).
Note: Since the author of the text is not stated, a shortened version of the title is used instead.
Secondary Sources
When using secondary sources, use the phrase "as cited in" and cite the secondary source on the References page.
In 1936, Keynes said, “governments should run deficits when the economy is slow to avoid unemployment” (as cited in Richardson, 2008, p. 257).
Long (Block) Quotations
When using direct quotations of 40 or more words, indent five spaces from the left margin without using quotation marks. The final period should come before the parenthetical citation.
At Meramec, an English department policy states:
To honor and protect their own work and that of others, all students must give credit to proprietary sources that are used for course work. It is assumed that any information that is not documented is either common knowledge in that field or the original work of that student. (St. Louis Community College, 2001, p. 1)
Website Citations
If citing a specific web document without a page number, include the name of the author, date, title of the section, and paragraph number in parentheses:
In America, “Two out of five deaths among U.S. teens are the result of a motor vehicle crash” (National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, 2004, Overview section, para. 1).
Here is a print-friendly version of this content.
Learn more about the APA References page by reviewing this handout .
For information on STLCC's academic integrity policy, check out this webpage .
For additional information on APA, check out STLCC's LibGuide on APA .
Sample Essay
A sample APA essay is available at this link .
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Harvard Referencing / Harvard Referencing Style Examples / How to reference an article in Harvard referencing style
How to reference an article in Harvard referencing style
What is an article.
Almost all writers and academics reference other people’s writing in their works. Referencing demonstrates that you have researched your topic, are well versed in its arguments and theories, and it also helps avoid charges of plagiarism.
The Harvard citation system is just one of many referencing styles – and which style you choose is normally guided by the institution or publication you are writing for.
In this article, you will learn how to use the Harvard citation system to reference the following types of articles:
- journal article
- newspaper article
- magazine article
Properly citing article details in the reference list will help the readers to locate your source material if they wish to read more about a particular area or topic.
Information you need:
- Author name
- (Year published)
- ‘Article title’
- Journal/newspaper/magazine name
- Day and month published, if available
- Volume number, if available
- (Issue) number, if available
- Page number(s), if available
If accessed online:
- Available at: URL or DOI
- (Accessed: date).
Journal articles
Academic or scholarly journals are periodical publications about a specific discipline. No matter what your field is, if you are writing an academic paper, you will inevitably have to cite a journal article in your research. Journal articles often have multiple authors, so make sure you know when to use et al. in Harvard style . The method for referencing a journal article in the reference list is as follows:
Reference list (print) structure:
Last name, F. (Year published) ‘Article title’, Journal name , Volume(Issue), Page(s).
Shepherd, V. (2020) ‘An exploration around peer support for secondary pupils in Scotland with experience of self-harm’, Educational Psychology in Practice, 36(3), pp. 297-312.
Note that the article title uses sentence case. However, the title of the journal uses title case. Additionally, the volume number comes immediately after the journal title followed by the issue number in round brackets.
If the original material you are referencing was accessed online, then the method for citing it in the reference list will be the same as that in print, but with an additional line at the end.
Reference list (online) structure:
Last name, F. (Year published) ‘Article title’, Journal Name , Volume(Issue), Page(s). Available at: URL or DOI (Accessed: date).
Shepherd, V. (2020) ‘An exploration around peer support for secondary pupils in Scotland with experience of self-harm’, Educational Psychology in Practice, 36(3), pp. 297-312. Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02667363.2020.1772726 (Accessed: 08 October 2020).
In-text citation (print or online) structure:
In-text citations are written within round brackets and start with the last name of the author followed by the year published, both separated by a comma.
You can also mention the author within the text and only include the publication year in round brackets.
Examples:
In this article (Shepherd, 2020) deals with…
According to Shepherd (2020), when peer support is available…
Talking about the secondary education system, Shepherd (2020, p.299) suggests that…
Newspaper articles
Even if you are referring to an incident which is public knowledge, you still need to cite the source.
The name of the author in a newspaper article is referred to as a byline. Below are examples for citing an article both with and without a byline.
Reference list (print) structure:
Last name, F. (Year published). ‘Article title’, Newspaper name , Day Month, Page(s).
Hamilton, J. (2018). ‘Massive fire at local department store’, The Daily Local, 10 August, p. 1.
Last name, F. (Year published). ‘Article title’, Newspaper name , Day Month, Page(s). Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year).
Gambino, L. (2020) ‘Kamala Harris and Mike Pence clash over coronavirus response in vice-presidential debate,’ The Guardian, 8 October. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2020/oct/07/debate-kamala-harris-mike-pence-latest-news (Accessed: 8 October 2020).
Reference list structure, no byline:
The basic reference list structure for the reference is the same for both print and online articles. If information isn’t available, simply omit it from the reference.
Newspaper name (Year published) ‘Article Title’, Day Month, Page(s). Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year).
The Chronicler (2016) ‘Local man wins lottery jackpot twice in one year’, 30 May, p. 14. Available at: https://thechroniclerpaper.com/local-man-wins-lottery-twice (Accessed: 1 October 2020).
In-text citation structure (print or online):
The last name of the author and date are written in round brackets, separated by a comma. The method is similar to referencing journal articles in in-text citations.
(Hamilton, 2018)
In his paper, Gambino (2020) mentioned that…
For articles accessed online which do not have an author, the name of the publication is mentioned in place of the author’s name and is italicized.
( The Chronicler , 2016)
Magazine articles
The structure of magazine articles is similar to that of a journal article.
Last name, F. (Year published) ‘Article title’, Magazine Name , Volume(Issue), Page(s).
Ornes, S. (2020). “To save Appalachia’s endangered mussels, scientists hatched a bold plan”, ScienceNews, (198), p.2.
Last name, F. (Year published) ‘Article title’, Magazine name , Volume(Issue), Page(s). Available at: URL (Accessed: Date).
Ornes, S. (2020) ‘To save Appalachia’s endangered mussels, scientists hatched a bold plan’, ScienceNews, (198), p.2. Available at: https://www.sciencenews.org/article/endangered-mussels-appalachia-rivers-biologists-conservation-plan (Accessed: 3 October 2020).
In-text citation (print or online) structure:
(Author last name, Year published)
(Ornes, 2020)
Published October 29, 2020.
Harvard Formatting Guide
Harvard Formatting
- et al Usage
- Direct Quotes
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Page Numbers
- Writing an Outline
- View Harvard Guide
Reference Examples
- View all Harvard Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Harvard Referencing Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
How to Write an Academic Essay with References and Citations
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
If you're wondering how to write an academic essay with references, look no further. In this article, we'll discuss how to use in-text citations and references, including how to cite a website, how to cite a book, and how to cite a Tweet, according to various style guides.

You might need to cite sources when writing a paper that references other sources. For example, when writing an essay, you may use information from other works, such as books, articles, or websites. You must then inform readers where this information came from. Failure to do so, even accidentally, is plagiarism—passing off another person's work as your own.
You can avoid plagiarism and show readers where to find information by using citations and references.
Citations tell readers where a piece of information came from. They take the form of footnotes, endnotes, or parenthetical elements, depending on your style guide. In-text citations are usually placed at the end of a sentence containing the relevant information.
A reference list , bibliography, or works cited list at the end of a text provides additional details about these cited sources. This list includes enough publication information allowing readers to look up these sources themselves.
Referencing is important for more than simply avoiding plagiarism. Referring to a trustworthy source shows that the information is reliable. Referring to reliable information can also support your major points and back up your argument.
Learning how to write an academic essay with references and how to use in-text citations will allow you to cite authors who have made similar arguments. This helps show that your argument is objective and not entirely based on personal biases.
How Do You Determine Which Style Guide to Use?

Often, a professor will assign a style guide. The purpose of a style guide is to provide writers with formatting instructions. If your professor has not assigned a style guide, they should still be able to recommend one.
If you are entirely free to choose, pick one that aligns with your field (for example, APA is frequently used for scientific writing).
Some of the most common style guides are as follows:
AP style for journalism
Chicago style for publishing
APA style for scholarly writing (commonly used in scientific fields)
MLA style for scholarly citations (commonly used in English literature fields)
Some journals have their own style guides, so if you plan to publish, check which guide your target journal uses. You can do this by locating your target journal's website and searching for author guidelines.
How Do You Pick Your Sources?
When learning how to write an academic essay with references, you must identify reliable sources that support your argument.
As you read, think critically and evaluate sources for:
Objectivity
Keep detailed notes on the sources so that you can easily find them again, if needed.
Tip: Record these notes in the format of your style guide—your reference list will then be ready to go.
How to Use In-Text Citations in MLA
An in-text citation in MLA includes the author's last name and the relevant page number:
(Author 123)
How to Cite a Website in MLA

Here's how to cite a website in MLA:
Author's last name, First name. "Title of page."
Website. Website Publisher, date. Web. Date
retrieved. <URL>
With information from a real website, this looks like:
Morris, Nancy. "How to Cite a Tweet in APA,
Chicago, and MLA." Scribendi. Scribendi
Inc., n.d. Web. 22 Dec. 2021.
<https://www.scribendi.com/academy/articles/how_to_cite_a_website.en.html>
How Do You Cite a Tweet in MLA ?
MLA uses the full text of a short Tweet (under 140 characters) as its title. Longer Tweets can be shortened using ellipses.
MLA Tweet references should be formatted as follows:
@twitterhandle (Author Name). "Text of Tweet." Twitter, Date Month, Year, time of
publication, URL.
With information from an actual Tweet, this looks like:
@neiltyson (Neil deGrasse Tyson). "You can't use reason to convince anyone out of an
argument that they didn't use reason to get into." Twitter, 29 Sept. 2020, 10:15 p.m.,
https://twitter.com/neiltyson/status/1311127369785192449 .
How to Cite a Book in MLA
Here's how to cite a book in MLA:
Author's last name, First name. Book Title. Publisher, Year.
With publication information from a real book, this looks like:
Montgomery, L.M. Rainbow Valley. Frederick A. Stokes Company, 1919.
How to Cite a Chapter in a Book in MLA
Author's last name, First name. "Title of Chapter." Book Title , edited by Editor Name,
Publisher, Year, pp. page range.
With publication information from an actual book, this looks like:
Ezell, Margaret J.M. "The Social Author: Manuscript Culture, Writers, and Readers." The
Broadview Reader in Book History , edited by Michelle Levy and Tom Mole, Broadview
Press, 2015,pp. 375–394.

How to Cite a Paraphrase in MLA
You can cite a paraphrase in MLA exactly the same way as you would cite a direct quotation.
Make sure to include the author's name (either in the text or in the parenthetical citation) and the relevant page number.
How to Use In-Text Citations in APA
In APA, in-text citations include the author's last name and the year of publication; a page number is included only if a direct quotation is used:
(Author, 2021, p. 123)
How to Cite a Website in APA
Here's how to cite a website in APA:
Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Year, Month. date of publication). Title of page. https://URL
Morris, N. (n.d.). How to cite a Tweet in APA, Chicago, and MLA.
https://www.scribendi.com/academy/articles/how_to_cite_a_website.en.html
Tip: Learn more about how to write an academic essay with references to websites .
How Do You Cite a Tweet in APA ?
APA refers to Tweets using their first 20 words.
Tweet references should be formatted as follows:
Author, A. A. [@twitterhandle). (Year, Month. date of publication). First 20 words of the
Tweet. [Tweet] Twitter. URL
When we input information from a real Tweet, this looks like:
deGrasse Tyson, N. [@neiltyson]. (2020, Sept. 29). You can't use reason to convince anyone
out of an argument that they didn't use reason to get into. [Tweet] Twitter.
https://twitter.com/neiltyson/status/1311127369785192449

How to Cite a Book in APA
Here's how to cite a book in APA:
Author, A. A. (Year). Book title. Publisher.
For a real book, this looks like:
Montgomery, L. M. (1919). Rainbow valley.
Frederick A. Stokes Company.
How to Cite a Chapter in a Book in APA
Author, A. A. (Year). Chapter title. In Editor Name (Ed.), Book Title (pp. page range).
With information from a real book, this looks like:
Ezell, M. J. M. (2014). The social author: Manuscript culture, writers, and readers. In
Michelle Levy and Tom Mole (Eds.), The Broadview Reader in Book History (pp. 375–
394). Broadview Press.
Knowing how to cite a book and how to cite a chapter in a book correctly will take you a long way in creating an effective reference list.

How to Cite a Paraphrase in APA
You can cite a paraphrase in APA the same way as you would cite a direct quotation, including the author's name and year of publication.
In APA, you may also choose to pinpoint the page from which the information is taken.
Referencing is an essential part of academic integrity. Learning how to write an academic essay with references and how to use in-text citations shows readers that you did your research and helps them locate your sources.
Learning how to cite a website, how to cite a book, and how to cite a paraphrase can also help you avoid plagiarism —an academic offense with serious consequences for your education or professional reputation.
Scribendi can help format your citations or review your whole paper with our Academic Editing services .
Take Your Essay from Good to Great
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample, about the author.

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing transformed into a great one. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained numerous degrees. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

APA Style and APA Formatting

How to Research a Term Paper

MLA Formatting and MLA Style: An Introduction
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

Essay Writing: In-Text Citations
- Essay Writing Basics
- Purdue OWL Page on Writing Your Thesis This link opens in a new window
- Paragraphs and Transitions
- How to Tell if a Website is Legitimate This link opens in a new window
- Formatting Your References Page
- Cite a Website
- Common Grammatical and Mechanical Errors
- Additional Resources
- Proofread Before You Submit Your Paper
- Structuring the 5-Paragraph Essay
Using In-text Citations
Narrative vs Parenthetical In-text citations:
A narrative citation gives the author name as part of the sentence .
- Narrative citation: According to Edwards (2017) , a lthough Smith and Carlos's protest at the 1968 Olympics initially drew widespread criticism, it also led to fundamental reforms in the organizational structure of American amateur athletics.
A parenthetical citation gives the source information in parentheses - first or last - but not as part of the narrative flow.
- Parenthetical citation: Although Tommie Smith and John Carlos paid a heavy price in the immediate aftermath of the protests, they were later vindicated by society at large (Edwards, 2017) .
Full citation for this source:
Edwards, H. (2017). The Revolt of the Black Athlete: 50th Anniversary Edition. University of Illinois Press.
Sample In-text Citations
Note: This example is a direct quote. It is an exact quotation directly from the text of the article. All direct quotes should appear in quotation marks: "...."
Try keeping direct quotes to a minimum in your writing. You need to show your understanding of the source material by being able to paraphrase or summarize it.
List the author’s last name only (no initials) and the year the information was published, like this:
(Dodge, 2008 ). ( Author , Date).
IF you use a direct quote, add the page number to your citation, like this:
( Dodge , 2008 , p. 125 ).
( Author , Date , page number )
What is Plagiarism?
Avoid plagiarism cite your sources .
Using in-text citations:
- shows the reader that you have done your research
- shows that you know how to credit the sources of your information.
- points your reader to the full citation on your References page for more information.
Defining and Understanding Plagiarism:
important in the research and writing process.

From the Plagiarism.org Website:
According to the Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary, to "plagiarize" means
- to steal and pass off (the ideas or words of another) as one's own
- to use (another's production) without crediting the source
- to commit literary theft
- to present as new and original an idea or product derived from an existing source
In other words, plagiarism is an act of fraud . It involves both stealing someone else's work and lying about it afterward .
ALL these are considered plagiarism:
- turning in someone else's work as your own
- copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit
- failing to put a quotation in quotation marks
- giving incorrect information about the source of a quotation
- changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit
- copying so many words or ideas from a source that it makes up the majority of your work, whether you give credit or not (see our section on "fair use" rules)
Quick Sheet: APA 7 Citations
Quick help with apa 7 citations.
- Quick Sheet - Citing Journal Articles, Websites & Videos, and Creating In-Text Citations A quick guide to the most frequently-used types of APA 7 citations.
In-text Citation Tutorial
- Formatting In-text Citations, Full Citations, and Block Quotes In APA 7 Style This presentation will help you understand when, why, and how to use in-text citations in your APA style paper.
Download the In-text Citations presentation (above) for an in-depth look at how to correctly cite your sources in the text of your paper.
SIgnal Phrase Activity
Paraphrasing activity from the excelsior owl, in-text citation quiz.
- << Previous: Formatting Your References Page
- Next: Cite a Website >>
- Last Updated: Jan 24, 2024 11:23 AM
- URL: https://monroecollege.libguides.com/essaywriting
- Research Guides |
- Databases |
How to Add an Article Title Into the Text Using APA Format
Catherine bowers.

Including an article title in the text of your writing serves a different purpose than including it in the Works Cited section of a paper. You may want to include the title of an article in your paper when it is the main subject you’re writing about, a subject you’re discussing that you’re referring to simply as an example, or if the research for your writing isn’t extensive enough to require a citation page. The American Psychological Association (APA) has specific guidelines on how to include an article title in the text of your writing.
Consider section 4.21 of the APA Publication Manual "Use of Italics;" according to it, italics should be used for titles of books, periodicals, films, videos, television shows, and microfilm. Make an exception if words in the title are usually italicized and set them in normal type instead; this is called reverse italicization.
Consider section 4.07 of the APA Publication Manual, “Quotation Marks;” according to it, quotes should be used to set off the title of books, articles, and chapters when you are including it in the text.
Check your writing to make sure you’re following the previous two guidelines; the article you mention in your text should be formatted as follows:
Ms. Bond published her controversial piece, “Housebreaking the Habit” in (italics)Dogfancy(/italics) magazine in June of 2010.
- 1 “Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 6th ed.”; American Psychological Association; 2010
About the Author
In 1998 Catherine Bowers began writing articles for newspapers, including "The Daily Collegian" at Pennsylvania State University. She also edited a Spanish-language journal and wrote product and patent descriptions for inventors. Bowers assists with the Gutenberg Project and graduated from Pennsylvania State with a Bachelor of Arts in English.
Related Articles

How to Reference an Appendix Using the APA Format

APA Style For Quoting More Than 40 Words

How to Insert Dialogue Into an MLA Paper

How Do I Cite Previous Work Written by Myself & Reference...

How to Write Book Titles in an Essay

How to: Heading for a College Admissions Essay

How Do I Check My Paper for Plagiarism?

How to Write the Title of a News Article in a Paper

Miss Manners' Etiquette for Addressing Envelopes

How to Format a Research Paper's Appendix in ASA

How to Write a Textual Analysis

How to Write a Summary Paper in MLA Format

How to Insert an Image on an APA-Style Paper

How to Choose a Title for Your Research Paper

What Fonts to Use for APA

How to Make Italics on Tumblr

How to Properly Write Book Titles in a Report

Different Types of Plagiarism

How to Write a Title Page for a Report

How to Develop an Outline About Plagiarism
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
- Western Libraries
- Ask Us! Answer Service
Q. How do I refer to a book by title in-text in APA format?
- Research & Writing Studio
- 21 Accounts
- 14 Acquisitions
- 4 Anthropology
- 71 APA citations and formatting
- 35 Archives
- 31 Archives & Special Collections
- 36 Articles
- 14 Business resources
- 11 Center for Pacific Northwest Studies
- 3 Chemistry
- 8 Chicago citations and formatting
- 85 Circulation Services (check out/return/renew items)
- 42 Citations and style guides
- 43 Collections
- 50 Community services
- 1 Computer science
- 38 Computers
- 47 Copyright
- 79 Databases
- 22 Digital collections
- 87 Directions
- 7 Education (studies)
- 3 Engineering
- 2 English literature
- 7 Environmental studies/sciences
- 23 Equipment
- 42 Faculty services
- 3 Fairhaven
- 9 Fines and fees
- 12 Fun facts
- 21 Government information
- 5 Graduate students
- 2 Grant writing
- 1 Guest services
- 5 Human Services
- 50 Inter-library loan
- 17 Journals
- 29 Learning Commons
- 8 Library instruction
- 78 Library services
- 13 MLA citations and formatting
- 29 Multimedia
- 6 Newspapers
- 55 OneSearch
- 4 Online Learning
- 64 Outreach and Continuing Education
- 29 Policies
- 2 Political science
- 29 Primary sources
- 30 Printing related
- 3 Psychology
- 2 Rehabilitation Counseling
- 86 Research
- 17 Research & Writing Studio
- 37 Reserves
- 6 Scholarly communication
- 3 Sociology
- 10 Special Collections
- 1 Streaming video
- 44 Student services
- 28 Student Technology Center
- 1 Teaching and Learning Academy
- 16 Technology
- 3 Troubleshooting
- 4 Tutoring Center
- 5 Undergraduate Research Award
- 5 Undergraduate Students
- 18 Video tutorial
- 11 Western CEDAR
- 1 Women's Studies
- 37 Writing related
- 93 WWU general info
Answered By: Gabe Gossett Last Updated: Jun 22, 2023 Views: 614573
The basic format for an in-text citation is: Title of the Book (Author Last Name, year).
One author: Where the Wild Things Are (Sendak, 1963) is a depiction of a child coping with his anger towards his mom.
Two authors (cite both names every time): Brabant and Mooney (1986) have used the comic strip to examine evidence of sex role stereotyping. OR The comic strip has been used to examine evidence of sex role stereotyping (Brabant & Mooney, 1986).
Three or more authors (cite the first author plus et al.): Tales from the Shadowhunter Academy (Clare et al., 2016) depicts a young man's experience at the Shadowhunter Academy, a place where being a former vampire is looked down upon.OR Clare et al. (2016) have crafted a unique story about a young man's journey to find himself.
No author: Cite the first few words of the reference entry (usually the title) and the year. Use double quotation marks around the title of an article or chapter, and italicize the title of a periodical, book, brochure, or report. Examples: From the book Study Guide (2000) ... or ("Reading," 1999).
Note: Titles of periodicals, books, brochures, or reports should be in italics and use normal title capitalization rules.
If you are citing multiple sources by multiple authors in-text, you can list all of them by the author's last name and year of publication within the same set of parentheses, separated by semicolons.
Example: (Adams, 1999; Jones & James, 2000; Miller, 1999)
For more information on how to cite books in-text and as a reference entry, see the APA Publication Manual (7th edition) Section 10.2 on pages 321-325 .
Links & Files
- APA Workshop
- Citation Quick Guides and Style Manuals
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 106 No 85
Comments (13)
- This was very useful for me! I was having a really hard time finding information on how to mention an article title AND the author in text in APA so this was very helpful!!! by Ryan Waddell on Jun 27, 2019
- If I just mention that I used a book to teach a topic do I have to include it in the reference list? by Franw on Oct 17, 2019
- @Franw, if it is a source that informs your paper in any way, or if your reader would have reason to look it up, then you should include a full reference list entry for the book. by Gabe [Research & Writing Studio] on Oct 18, 2019
- Maybe I'm misunderstanding the question, but I think the OP is asking how to refer to a book title, not how to cite one. I believe APA uses quotation marks around book titles and MLA uses italics. by AB on Dec 12, 2019
- @AB: The first sentence has been tweaked to clarify title of book usage, reflecting the examples given. For APA style you should use italics for book titles. It would be quotation marks. by Gabe [Research & Writing Studio] on Dec 12, 2019
- Hi, can any one help me with in-text-citation of this, how can i cite it in the text Panel, I. L. (2002). Digital transformation: A framework for ICT literacy. Educational Testing Service, 1-53. by Milad on Aug 20, 2021
- @Milad: In that case it would be (Panel, 2002). If you are quoting, or otherwise choosing to include page numbers, put a comma after the year, then p. and the page number(s). by Gabe Gossett on Aug 20, 2021
- Hey, I'm a little bit curious, what if I'm mentioning a book and paraphrasing it but still want to give credit. Would I put the information into parenthesis instead? Like: Paraphrased info. ("Title in Italics" Author, year) by Kai on Sep 14, 2023
- @Kai: Apologies for not seeing your question sooner! (Our academic year has not started yet). If I am understanding your question correctly, what I suggest is referring to the book title in the narrative of your writing, rather than in the in-text citation. I do not see an examples of using a book title in an in-text citation except for rare circumstances including citing a classic religious text or using the title when there is no author information because it is the start of your reference list entry. Basically, APA's in-text convention is supposed to make it easy for your reader to locate the source being cited in the reference list. So the first part of the in-text citation, usually authors, comes first to locate it alphabetically. Putting the book title first when you have an author name can throw that off. by Gabe Gossett on Sep 21, 2023
- Perhaps this is along the lines of the response to Kai - Can you reference a book title as a common point of social understanding to demonstrate a common concept? Is official citing required if you use widely known titles such as "Where's Waldo" and "Who Moved My Cheese?" to make a point of illustration? by Chez Renee on Sep 30, 2023
- @Chez: Aside from some classical religious texts, if it is a published book, I'd try to make sure that it is appropriately cited for APA style. That said, I think I understand where it gets tricky with things like Where's Waldo, since that is a series of books and stating "Where's Waldo" is a cultural reference many people would understand, though you can't reasonably cite the entire series. I don't believe that APA gives guidance for this particular issue. If it is being referred to in order to back up a claim, it would help to cite a particular book. If not, then it might work to use a statement such as, "Hanford's Where's Waldo series . . ." by Gabe Gossett on Oct 02, 2023
- How to cite a dissertation thesis in apa form? by Elizabeth on Feb 05, 2024
- @Elizabeth: For citing a dissertation or thesis you can check out our page answering that here https://askus.library.wwu.edu/faq/153308 by Gabe Gossett on Feb 05, 2024
- Find the librarian for your subject area
Related Topics
- APA citations and formatting
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
Published on March 5, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024.
To cite a page from a website, you need a short in-text citation and a corresponding reference stating the author’s name, the date of publication, the title of the page, the website name, and the URL.
This information is presented differently in different citation styles. APA , MLA , and Chicago are the most commonly used styles.
Use the interactive example generator below to explore APA and MLA website citations.
Note that the format is slightly different for citing YouTube and other online video platforms, or for citing an image .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a website in mla style, citing a website in apa style, citing a website in chicago style, frequently asked questions about citations.
An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author’s name , the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL.
The in-text citation usually just lists the author’s name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to locate the specific passage. Don’t use paragraph numbers unless they’re specifically numbered on the page.
The same format is used for blog posts and online articles from newspapers and magazines.
You can also use our free MLA Citation Generator to generate your website citations.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Citing a whole website.
When you cite an entire website rather than a specific page, include the author if one can be identified for the whole site (e.g. for a single-authored blog). Otherwise, just start with the site name.
List the copyright date displayed on the site; if there isn’t one, provide an access date after the URL.
Webpages with no author or date
When no author is listed, cite the organization as author only if it differs from the website name.
If the organization name is also the website name, start the Works Cited entry with the title instead, and use a shortened version of the title in the in-text citation.
When no publication date is listed, leave it out and include an access date at the end instead.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

An APA reference for a webpage lists the author’s last name and initials, the full date of publication, the title of the page (in italics), the website name (in plain text), and the URL.
The in-text citation lists the author’s last name and the year. If it’s a long page, you may include a locator to identify the quote or paraphrase (e.g. a paragraph number and/or section title).
Note that a general reference to an entire website doesn’t require a citation in APA Style; just include the URL in parentheses after you mention the site.
You can also use our free APA Citation Generator to create your webpage citations. Search for a URL to retrieve the details.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Blog posts and online articles.
Blog posts follow a slightly different format: the title of the post is not italicized, and the name of the blog is.
The same format is used for online newspaper and magazine articles—but not for articles from news sites like Reuters and BBC News (see the previous example).
When a page has no author specified, list the name of the organization that created it instead (and omit it later if it’s the same as the website name).
When it doesn’t list a date of publication, use “n.d.” in place of the date. You can also include an access date if the page seems likely to change over time.
In Chicago notes and bibliography style, footnotes are used to cite sources. They refer to a bibliography at the end that lists all your sources in full.
A Chicago bibliography entry for a website lists the author’s name, the page title (in quotation marks), the website name, the publication date, and the URL.
Chicago also has an alternative author-date citation style . Examples of website citations in this style can be found here .
For blog posts and online articles from newspapers, the name of the publication is italicized. For a blog post, you should also add the word “blog” in parentheses, unless it’s already part of the blog’s name.
When a web source doesn’t list an author , you can usually begin your bibliography entry and short note with the name of the organization responsible. Don’t repeat it later if it’s also the name of the website. A full note should begin with the title instead.
When no publication or revision date is shown, include an access date instead in your bibliography entry.
The main elements included in website citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the date of publication, the page title, the website name, and the URL. The information is presented differently in each style.
In APA , MLA , and Chicago style citations for sources that don’t list a specific author (e.g. many websites ), you can usually list the organization responsible for the source as the author.
If the organization is the same as the website or publisher, you shouldn’t repeat it twice in your reference:
- In APA and Chicago, omit the website or publisher name later in the reference.
- In MLA, omit the author element at the start of the reference, and cite the source title instead.
If there’s no appropriate organization to list as author, you will usually have to begin the citation and reference entry with the title of the source instead.
When you want to cite a specific passage in a source without page numbers (e.g. an e-book or website ), all the main citation styles recommend using an alternate locator in your in-text citation . You might use a heading or chapter number, e.g. (Smith, 2016, ch. 1)
In APA Style , you can count the paragraph numbers in a text to identify a location by paragraph number. MLA and Chicago recommend that you only use paragraph numbers if they’re explicitly marked in the text.
For audiovisual sources (e.g. videos ), all styles recommend using a timestamp to show a specific point in the video when relevant.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, January 17). How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/cite-a-website/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite an image | photographs, figures, diagrams, how to cite a lecture | apa, mla & chicago examples, how to cite a youtube video | mla, apa & chicago, what is your plagiarism score.

Weather forecasts have become much more accurate; we now need to make them available to everyone
A four-day forecast today is as accurate as a one-day forecast 30 years ago..
Weather forecasts are often seen as just a nice thing to have. Useful when planning a Sunday barbecue, or when we want to know if we’ll need an umbrella for the day. But in many ways weather forecasts are absolutely crucial: they can be a matter of life and death.
Accurate forecasts can save lives by giving early warnings of storms, heat waves, and disasters. Farmers use them for agricultural management, which can make the difference between a lost harvest or a harvest of plenty. Grid operators rely on accurate forecasts of temperatures for heating and cooling demand, and how much energy they’ll get from wind and solar farms. Pilots and sailors need them to carry people across oceans safely. Accurate information about future weather is often absolutely vital.
In this article, I look at improvements over time and the global inequalities that need to be closed to protect lives and livelihoods around the world.
Weather forecasts have improved a lot
Weather forecasting has come a long way. In 650 B.C. the Babylonians would try to predict weather patterns based on cloud patterns and movements. Three centuries later, Aristotle wrote Meteorologica , discussing how phenomena such as rain, hail, hurricanes, and lightning formed. Much of it turned out to be wrong, but it represents one of the first attempts to explain how the weather works in detail.
It wasn’t until 1859 that the UK’s Meteorological Service (the Met Office) issued its first weather forecast for shipping. Two years later, it broadcasted its first public weather forecast. While meteorological measurements improved over time, the massive step-change in predictions came with the use of computerized numerical modeling. This didn’t start until a century later, in the 1960s.
Forecasts have improved a lot since then. We can see this across a range of measurements, and different national meteorological organizations.
The Met Office says its four-day forecasts are now as accurate as its one-day forecasts were 30 years ago.
Predictions have gotten much better in the United States, too. We can see this in some of the most important forecasts: the prediction of hurricanes.
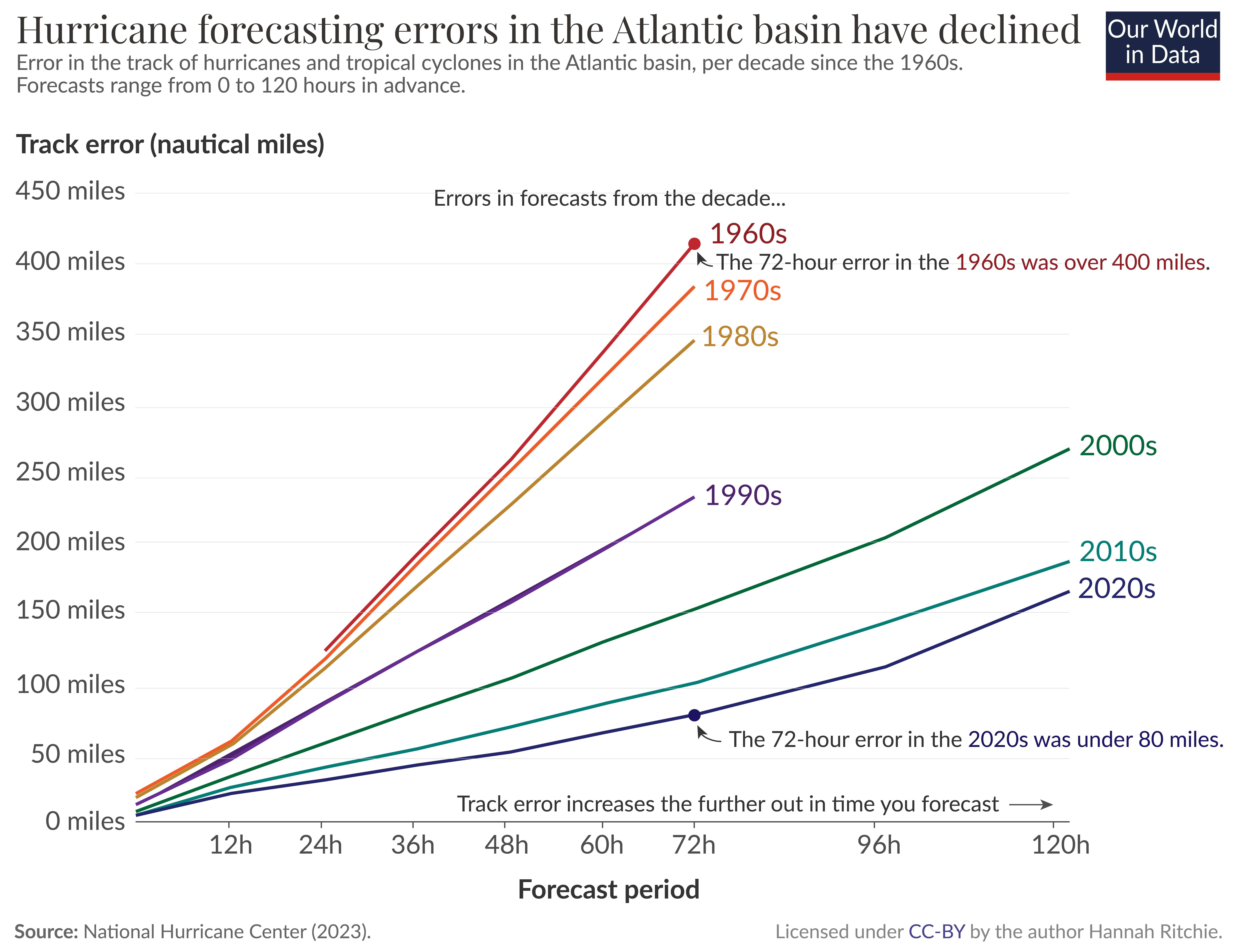
The National Hurricane Center publishes data on the “track error” of hurricanes and cyclones — the error in where the hurricane hits. This is shown in the chart below, from the 1960s onwards.
Each line represents the error of forecasts for different time periods in advance. For example, 12 hours before it hits, all the way up to 120 hours (or 5 days) before.
We can see that this track error — especially for longer-term forecasts — has decreased a lot over time. In the 1970s, a 48-hour forecast had an error between 200 and 400 nautical miles; today this is around 50 nautical miles.
We can show the same data another way. In the chart below, each line represents the average error for each decade. On the horizontal axis we have the forecast period, again extending from 0 to 120 hours.
The 72-hour error in the 1960s and 70s was over 400 nautical miles. Today, it’s less than 80 miles.
Meteorologists can now make pretty accurate predictions of where a hurricane will hit three or four days in advance, which lets cities and communities prepare while preventing unnecessary evacuations that might have been implemented in the past.
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) produces global numerical weather models. While national weather agencies use much higher-resolution processing to get local forecasts, these global models provide a crucial input into these systems.
The ECMWF publishes analyses of its errors over time. This is shown in the chart below. 1 It shows the difference between the forecast and the actual weather outcome for forecasts 3, 5, 7, and 10 days in advance. The metric used here is the “ 500 hPa geopotential height ”, a commonly used meteorological measure of air pressure (which dictates weather patterns).
The solid line is for the Northern Hemisphere, and the dashed line is for the Southern.
Three-day forecasts — shown in blue — have been pretty accurate since the 1980s, and have still gotten a lot better over time. Today the accuracy is around 97%.
The biggest improvements we’ve seen are for longer timeframes. By the early 2000s, 5-day forecasts were “highly accurate” and 7-day forecasts are reaching that threshold today. 10-day forecasts aren’t quite there yet but are getting better.
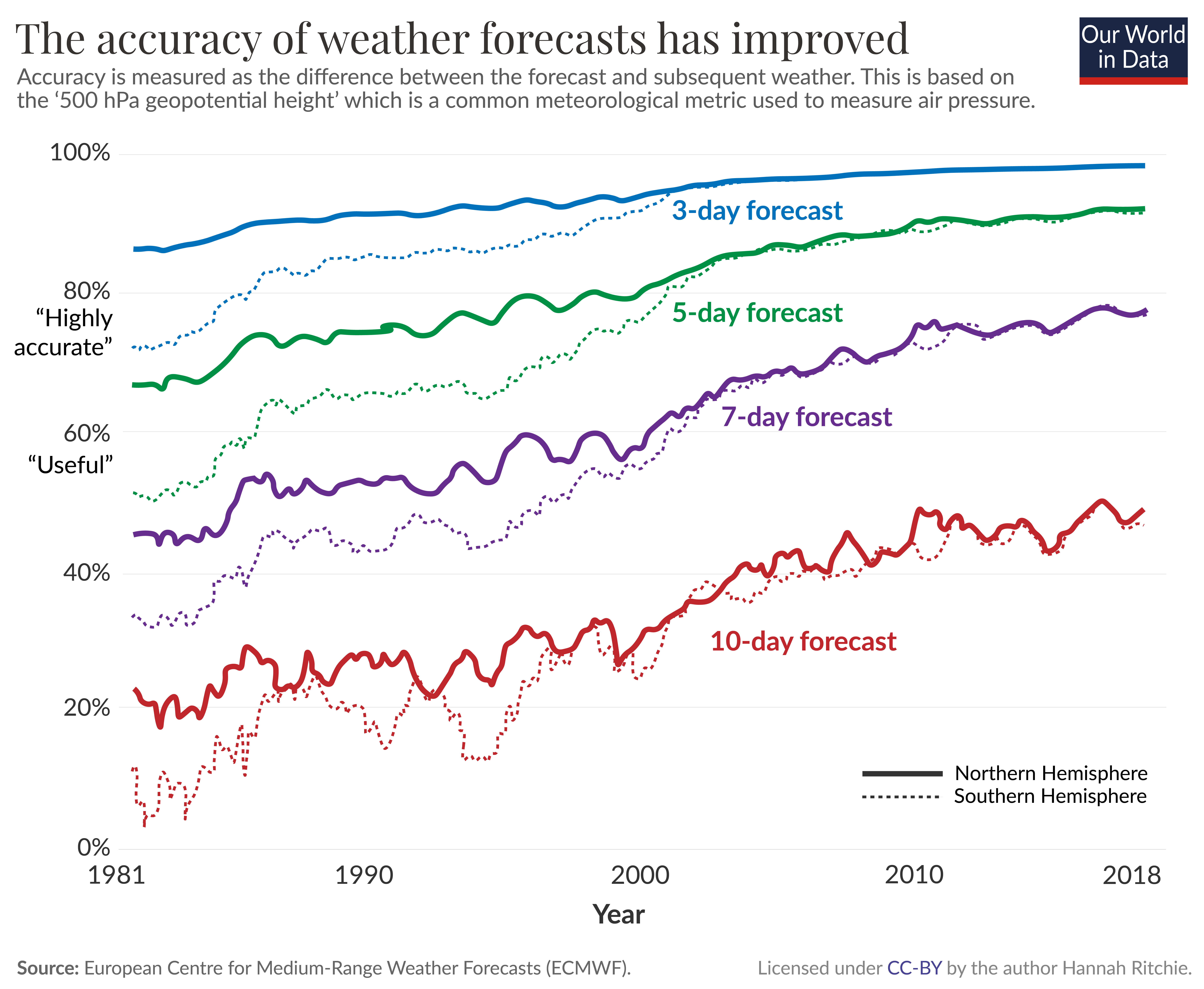
Why have weather forecasts improved?
A few key developments explain these improvements . 2
The first big change is that the data has improved. More extensive and higher-resolution observations can be used as inputs into the weather models. This is because we have more and better satellite data, and because land-based stations are covering many more areas around the globe, and at a higher density. The precision of these instruments has improved, too.
These observations are then fed into numerical prediction models to forecast the weather. That brings us to the next two developments. The computers on which these models are run have gotten much faster. Faster speeds are crucial: the Met Office now chunks the world into grids of smaller and smaller squares. While they once modeled the world in 90-kilometer-wide squares, they are now down to a grid of 1.5-kilometer squares. That means many more calculations need to be run to get this high-resolution map. The methods to turn the observations into model outputs have also improved. We’ve gone from very simple visions of the world to methods that can capture the complexity of these systems in detail.
The final crucial factor is how these forecasts are communicated. Not long ago, you could only get daily updates in the daily newspaper. With the rise of radio and TV, you could get a few notices per day. Now, we can get minute-by-minute updates online or on our smartphones.
Low-income countries have much worse forecasts, and often no early warning systems
At home in Scotland, I can open an app on my phone and get a pretty accurate 5-day forecast within seconds. Unfortunately, this quality of information isn’t available to everyone. There are large differences in weather forecasts across the world, with a large gap between rich and poor.
As the researchers Manuel Linsenmeier and Jeffrey Shrader report in a recent paper , a 7-day forecast in a rich country can be more accurate than a one-day forecast in some low-income ones. 3
While national forecasts have improved over time across all income levels, the quality gap today is almost as wide as it was in the 1980s.
There are a few reasons for this. First, far fewer land-based instruments and radiosondes measure meteorological data in poorer countries. Second, the frequency of reporting is much lower.
This is unsurprising when we look at the amount of money spent on weather and climate information. In a paper published in Science , Lucian Georgeson, Mark Maslin, and Martyn Poessinouw looked at differences in spending across income groups. 4 This includes private and public spending on commercial products that fall within the definition of “weather and climate information services”.
This is shown as the spending per person , and the spending as a share of gross domestic product (GDP) in the chart below.
Low-income countries spend 15 to 20 times less per person than high-income countries. But given the size of their economies, they actually spend more as a share of GDP.
This gap is a problem. 60% of workers in low-income countries are employed in agriculture , arguably the most weather-dependent sector. Most are small-scale farmers , who are often extremely poor.
Having accurate weather forecasts can help farmers make better decisions. They can get information on the best time to plant their crops. They know in advance when irrigation will be most needed, or when fertilizers might be at risk of being washed away. They can receive alerts about pest and disease outbreaks so they can either protect their crops when an attack is coming or save pesticides when the risk is low. That means they can use precious resources most efficiently if they have access to accurate weather forecasts. Good weather forecasts are most crucial for the poorest people in the world.
They’re also crucial for protecting against cyclones, heat waves, flooding, and storm surges. Having accurate forecasts several days in advance allows cities and communities to prepare. Housing can be protected, and emergency services can be on standby to help with the recovery.
But accurate forecasts alone don’t solve the problem: they’re only useful if they are disseminated to people so they can respond. Many of the deadliest disasters over the last few decades were accurately forecasted ahead of time. The common failure was poor communication. 5
Improving forecasts is the foundation. But these also need to be incorporated into effective early warning systems. The World Meteorological Organization estimates that around one-third of the world — predominantly the poorest countries — do not have them.
Improving forecasts — especially in low-income countries — is underrated
After the big progress in recent decades, we take good weather forecasting and dissemination for granted in large parts of the world. Making this available to everyone would make a difference.
This will be even more important as climate change increases the risks of weather-related disasters. It is ultimately the poorest, who are the more vulnerable, who will suffer the worst consequences. Better forecasts are key to good climate change adaptation.
Proper investment and financial support will be essential to close the gaps.
There also emerging technologies that could accelerate this. A recent paper published in Nature documented a new artificial intelligence (AI) system — Pangu-Weather — that can perform forecasts as accurately (or better) than leading meteorological agencies up to 10,000 times faster. 6 It was trained on 39 years of historical data. The speed of these forecasts would make them much cheaper to run and could provide much better results for countries with limited budgets.
Faster and more efficient technologies can also fill the gaps where land-based weather stations aren’t available. Sensor-carrying drones can run surveys over specific areas to build higher-resolution maps. With lower-cost and more efficient ways of turning that into forecasts, mobile technologies can disseminate this information quickly. Some companies are already sending messages to farmers in low-income countries to advise them on the best time to plant their crops.
This innovation is crucial to making countries more resilient to weather today. But it’s also essential in a world where weather is likely to get more extreme.
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to Max Roser and Edouard Mathieu for their valuable feedback and comments on this article.
These charts are sourced from the following sources: Alley, R. B., Emanuel, K. A., & Zhang, F. (2019). Advances in weather prediction. Science, 363(6425), 342-344.
The Economist (2023). The high-tech race to improve weather forecasting.
Alley, R. B., Emanuel, K. A., & Zhang, F. (2019). Advances in weather prediction. Science, 363(6425), 342-344.
Linsenmeier, Manuel & Shrader, Jeffrey G., 2023. "Global inequalities in weather forecasts," SocArXiv 7e2jf, Center for Open Science.
You might wonder how this can be true when the ECMWF forecasts have so quickly improved in both the Northern and Southern Hemisphere. This is because most countries need to develop their own forecasts to get more high-resolution predictions.
Georgeson, L., Maslin, M., & Poessinouw, M. (2017). Global disparity in the supply of commercial weather and climate information services. Science Advances, 3(5), e1602632.
De Perez, E. C., Berse, K. B., Depante, L. A. C., Easton-Calabria, E., Evidente, E. P. R., Ezike, T., ... & Van Sant, C. (2022). Learning from the past in moving to the future: Invest in communication and response to weather early warnings to reduce death and damage. Climate Risk Management, 38, 100461.
Bi, K., Xie, L., Zhang, H. et al. Accurate medium-range global weather forecasting with 3D neural networks. Nature 619, 533–538 (2023).
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Works Cited: Electronic Sources (Web Publications)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9 th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
The MLA Handbook highlights principles over prescriptive practices. Essentially, a writer will need to take note of primary elements in every source, such as author, title, etc. and then assort them in a general format. Thus, by using this methodology, a writer will be able to cite any source regardless of whether it’s included in this list.
However, this guide will highlight a few concerns when citing digital sources in MLA style.
Best Practices for Managing Online Sources
Because online information can change or disappear, it is always a good idea to keep personal copies of important electronic information whenever possible. Downloading or even printing key documents ensures you have a stable backup. You can also use the Bookmark function in your web browser in order to build an easy-to-access reference for all of your project's sources (though this will not help you if the information is changed or deleted).
It is also wise to keep a record of when you first consult with each online source. MLA uses the phrase, “Accessed” to denote which date you accessed the web page when available or necessary. It is not required to do so, but it is encouraged (especially when there is no copyright date listed on a website).
Important Note on the Use of URLs in MLA
Include a URL or web address to help readers locate your sources. Because web addresses are not static (i.e., they change often) and because documents sometimes appear in multiple places on the web (e.g., on multiple databases), MLA encourages the use of citing containers such as Youtube, JSTOR, Spotify, or Netflix in order to easily access and verify sources. However, MLA only requires the www. address, so eliminate all https:// when citing URLs.
Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL.
Online newspapers and magazines sometimes include a “permalink,” which is a shortened, stable version of a URL. Look for a “share” or “cite this” button to see if a source includes a permalink. If you can find a permalink, use that instead of a URL.
Abbreviations Commonly Used with Electronic Sources
If page numbers are not available, use par. or pars. to denote paragraph numbers. Use these in place of the p. or pp. abbreviation. Par. would be used for a single paragraph, while pars. would be used for a span of two or more paragraphs.
Basic Style for Citations of Electronic Sources (Including Online Databases)
Here are some common features you should try to find before citing electronic sources in MLA style. Not every web page will provide all of the following information. However, collect as much of the following information as possible:
- Author and/or editor names (if available); last names first.
- "Article name in quotation marks."
- Title of the website, project, or book in italics.
- Any version numbers available, including editions (ed.), revisions, posting dates, volumes (vol.), or issue numbers (no.).
- Publisher information, including the publisher name and publishing date.
- Take note of any page numbers (p. or pp.) or paragraph numbers (par. or pars.).
- DOI (if available, precede it with "https://doi.org/"), otherwise a URL (without the https://) or permalink.
- Date you accessed the material (Date Accessed). While not required, saving this information it is highly recommended, especially when dealing with pages that change frequently or do not have a visible copyright date.
Use the following format:
Author. "Title." Title of container (self contained if book) , Other contributors (translators or editors), Version (edition), Number (vol. and/or no.), Publisher, Publication Date, Location (pages, paragraphs and/or URL, DOI or permalink). 2 nd container’s title , Other contributors, Version, Number, Publisher, Publication date, Location, Date of Access (if applicable).
Citing an Entire Web Site
When citing an entire website, follow the same format as listed above, but include a compiler name if no single author is available.
Author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site. Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), DOI (preferred), otherwise include a URL or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
Editor, author, or compiler name (if available). Name of Site . Version number, Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), date of resource creation (if available), URL, DOI or permalink. Date of access (if applicable).
The Purdue OWL Family of Sites . The Writing Lab and OWL at Purdue and Purdue U, 2008, owl.english.purdue.edu/owl. Accessed 23 Apr. 2008.
Felluga, Dino. Guide to Literary and Critical Theory . Purdue U, 28 Nov. 2003, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/theory/. Accessed 10 May 2006.
Course or Department Websites
Give the instructor name. Then list the title of the course (or the school catalog designation for the course) in italics. Give appropriate department and school names as well, following the course title.
Felluga, Dino. Survey of the Literature of England . Purdue U, Aug. 2006, web.ics.purdue.edu/~felluga/241/241/Home.html. Accessed 31 May 2007.
English Department . Purdue U, 20 Apr. 2009, www.cla.purdue.edu/english/. Accessed 31 May 2015.
A Page on a Web Site
For an individual page on a Web site, list the author or alias if known, followed by an indication of the specific page or article being referenced. Usually, the title of the page or article appears in a header at the top of the page. Follow this with the information covered above for entire Web sites. If the publisher is the same as the website name, only list it once.
Lundman, Susan. “How to Make Vegetarian Chili.” eHow , www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html. Accessed 6 July 2015.
“ Athlete's Foot - Topic Overview. ” WebMD , 25 Sept. 2014, www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/tc/athletes-foot-topic-overview.
Citations for e-books closely resemble those for physical books. Simply indicate that the book in question is an e-book by putting the term "e-book" in the "version" slot of the MLA template (i.e., after the author, the title of the source, the title of the container, and the names of any other contributors).
Silva, Paul J. How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing. E-book, American Psychological Association, 2007.
If the e-book is formatted for a specific reader device or service, you can indicate this by treating this information the same way you would treat a physical book's edition number. Often, this will mean replacing "e-book" with "[App/Service] ed."
Machiavelli, Niccolo. The Prince , translated by W. K. Marriott, Kindle ed., Library of Alexandria, 2018.
Note: The MLA considers the term "e-book" to refer to publications formatted specifically for reading with an e-book reader device (e.g., a Kindle) or a corresponding web application. These e-books will not have URLs or DOIs. If you are citing book content from an ordinary webpage with a URL, use the "A Page on a Web Site" format above.
An Image (Including a Painting, Sculpture, or Photograph)
Provide the artist's name, the work of art italicized, the date of creation, the institution and city where the work is housed. Follow this initial entry with the name of the Website in italics, and the date of access.
Goya, Francisco. The Family of Charles IV . 1800. Museo Nacional del Prado, Madrid. Museo Nacional del Prado , www.museodelprado.es/en/the-collection/art-work/the-family-of-carlos-iv/f47898fc-aa1c-48f6-a779-71759e417e74. Accessed 22 May 2006.
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine . 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive , www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
If the work cited is available on the web only, then provide the name of the artist, the title of the work, and then follow the citation format for a website. If the work is posted via a username, use that username for the author.
Adams, Clifton R. “People Relax Beside a Swimming Pool at a Country Estate Near Phoenix, Arizona, 1928.” Found, National Geographic Creative, 2 June 2016, natgeofound.tumblr.com/.
An Article in a Web Magazine
Provide the author name, article name in quotation marks, title of the web magazine in italics, publisher name, publication date, URL, and the date of access.
Bernstein, Mark. “ 10 Tips on Writing the Living Web. ” A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites , 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
An Article in an Online Scholarly Journal
For all online scholarly journals, provide the author(s) name(s), the name of the article in quotation marks, the title of the publication in italics, all volume and issue numbers, and the year of publication. Include a DOI if available, otherwise provide a URL or permalink to help readers locate the source.
Article in an Online-only Scholarly Journal
MLA requires a page range for articles that appear in Scholarly Journals. If the journal you are citing appears exclusively in an online format (i.e. there is no corresponding print publication) that does not make use of page numbers, indicate the URL or other location information.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Article in an Online Scholarly Journal That Also Appears in Print
Cite articles in online scholarly journals that also appear in print as you would a scholarly journal in print, including the page range of the article . Provide the URL and the date of access.
Wheelis, Mark. “ Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention. ” Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
An Article from an Online Database (or Other Electronic Subscription Service)
Cite online databases (e.g. LexisNexis, ProQuest, JSTOR, ScienceDirect) and other subscription services as containers. Thus, provide the title of the database italicized before the DOI or URL. If a DOI is not provided, use the URL instead. Provide the date of access if you wish.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. “ Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates. ” Environmental Toxicology, vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library , https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20155. Accessed 26 May 2009.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal, vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest , https://doi.org/10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
E-mail (including E-mail Interviews)
Give the author of the message, followed by the subject line in quotation marks. State to whom the message was sent with the phrase, “Received by” and the recipient’s name. Include the date the message was sent. Use standard capitalization.
Kunka, Andrew. “ Re: Modernist Literature. ” Received by John Watts, 15 Nov. 2000.
Neyhart, David. “ Re: Online Tutoring. ” Received by Joe Barbato, 1 Dec. 2016.
A Listserv, Discussion Group, or Blog Posting
Cite web postings as you would a standard web entry. Provide the author of the work, the title of the posting in quotation marks, the web site name in italics, the publisher, and the posting date. Follow with the date of access. Include screen names as author names when author name is not known. If both names are known, place the author’s name in brackets.
Author or compiler name (if available). “Posting Title.” Name of Site , Version number (if available), Name of institution/organization affiliated with the site (sponsor or publisher), URL. Date of access.
Salmar1515 [Sal Hernandez]. “Re: Best Strategy: Fenced Pastures vs. Max Number of Rooms?” BoardGameGeek , 29 Sept. 2008, boardgamegeek.com/thread/343929/best-strategy-fenced-pastures-vs-max-number-rooms. Accessed 5 Apr. 2009.
Begin with the user's Twitter handle in place of the author’s name. Next, place the tweet in its entirety in quotations, inserting a period after the tweet within the quotations. Include the date and time of posting, using the reader's time zone; separate the date and time with a comma and end with a period. Include the date accessed if you deem necessary.
@tombrokaw. “ SC demonstrated why all the debates are the engines of this campaign. ” Twitter, 22 Jan. 2012, 3:06 a.m., twitter.com/tombrokaw/status/160996868971704320.
@PurdueWLab. “ Spring break is around the corner, and all our locations will be open next week. ” Twitter , 5 Mar. 2012, 12:58 p.m., twitter.com/PurdueWLab/status/176728308736737282.
A YouTube Video
Video and audio sources need to be documented using the same basic guidelines for citing print sources in MLA style. Include as much descriptive information as necessary to help readers understand the type and nature of the source you are citing. If the author’s name is the same as the uploader, only cite the author once. If the author is different from the uploader, cite the author’s name before the title.
McGonigal, Jane. “Gaming and Productivity.” YouTube , uploaded by Big Think, 3 July 2012, www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkdzy9bWW3E.
“8 Hot Dog Gadgets put to the Test.” YouTube, uploaded by Crazy Russian Hacker, 6 June 2016, www.youtube.com/watch?v=WBlpjSEtELs.
A Comment on a Website or Article
List the username as the author. Use the phrase, Comment on, before the title. Use quotation marks around the article title. Name the publisher, date, time (listed on near the comment), and the URL.
Not Omniscient Enough. Comment on “ Flight Attendant Tells Passenger to ‘Shut Up’ After Argument Over Pasta. ” ABC News, 9 Jun 2016, 4:00 p.m., abcnews.go.com/US/flight-attendant-tells-passenger-shut-argument-pasta/story?id=39704050.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
There’s No Such Thing as an American Bible

By Esau McCaulley
Contributing Opinion Writer
The presumptive Republican nominee for president of the United States, who weeks ago started selling shoes , is now peddling Bibles. During Holy Week.
What’s special about this Bible? So many things. For example, according to a promotional website, it’s the only Bible endorsed by Donald Trump. It’s also the only one endorsed by the country singer Lee Greenwood. Admittedly, the translation isn’t distinctive — it’s your standard King James Version — but the features are unique. This Bible includes the Constitution, the Bill of Rights, the Declaration of Independence, the Pledge of Allegiance and part of the lyrics of Mr. Greenwood’s song “God Bless the USA.” Perhaps most striking, the cover of the Bible does not include a cross or any symbol of the Christian tradition; instead, it is emblazoned with the American flag.
While part of me wants to laugh at the absurdity of it — and marvel at the sheer audacity — I find the messaging unsettling and deeply wrong. This God Bless the USA Bible, as it’s officially named, focuses on God’s blessing of one particular people. That is both its danger and, no doubt for some, its appeal.
Whether this Bible is an example of Christian nationalism I will leave to others. It is at least an example of Christian syncretism, a linking of certain myths about American exceptionalism and the Christian faith. This is the American church’s consistent folly: thinking that we are the protagonists in a story that began long before us and whose main character is in fact the Almighty.
Holy Week is the most sacred portion of the Christian calendar, a time when the church recounts the central events of our faith’s narrative, climaxing in the death and resurrection of Jesus. That story, unlike the parochial God Bless the USA Bible, does not belong to any culture.
Holy Week is celebrated on every continent and in too many languages to number. Some of the immigrants Mr. Trump declared were “ poisoning the blood” of America will probably shout “Christ is risen!” this Easter. Many of them come from the largely Christian regions of Latin America and the Caribbean. They may have entered the country with Bibles in their native tongues nestled securely among their other belongings.
One of the beauties of the Christian faith is that it leaps over the lines dividing countries, leading the faithful to call fellow believers from very different cultures brothers and sisters. Most of the members of this international community consist of the poor living in Africa, Asia and Latin America. There are more Spanish-speaking Christians than English- speaking ones .
If there are central messages that emerge from the variety of services that take place during Holy Week, for many Christians they are the setting aside of power to serve, the supremacy of love, the offer of divine forgiveness and the vulnerability of a crucified God.
This is not the stuff of moneymaking schemes or American presidential campaigns.
It was Pontius Pilate , standing in as the representative of the Roman Empire, who sentenced Jesus to death. The Easter story reminds believers that empires are more than willing to sacrifice the innocent if it allows rulers to stay in power. The church sees Christ’s resurrection as liberating the believer from the power of sin. The story challenges imperial modes of thinking, supplanting the endless pursuit of power with the primacy of love and service.
Easter, using the language of St. Augustine, represents the victory of the City of God over the City of Man. It declares the limits of the moral reasoning of nation-states and has fortified Christians who’ve resisted evil regimes such as fascists in South America, Nazis in Germany, apartheid in South Africa and segregation in the United States.
For any politician to suppose that a nation’s founding documents and a country music song can stand side by side with biblical texts fails at a theological and a moral level. I can’t imagine people in other countries going for anything like it. It is hard to picture a modern “God Bless England” Bible with elements of British common law appended to Christianity’s most sacred texts.
I am glad for the freedoms that we share as Americans. But the idea of a Bible explicitly made for one nation displays a misunderstanding of the story the Bible attempts to tell. The Christian narrative culminates in the creation of the Kingdom (and family) of God, a transnational community united by faith and mutual love.
Roman Catholics , Anglicans and Orthodox Christians, who together claim around 1.5 billion members, describe the Bible as a final authority in matters of faith. Evangelicals, who have overwhelmingly supported Mr. Trump over the course of three election cycles, are known for their focus on Scripture, too. None of these traditions cite or refer to any American political documents in their doctrinal statements — and for good reason.
This Bible may be unique in its form, but the agenda it pursues has recurred throughout history. Christianity is often either co-opted or suppressed; it is rarely given the space to be itself. African American Christians have long struggled to disentangle biblical texts from their misuse in the United States. There is a reason that the abolitionist Frederick Douglass said that between the Christianity of this land (America) and the Christianity of Christ, he recognized the “widest possible difference.”
And while Christianity was used to give theological cover to North American race-based chattel slavery, it was violently attacked in places like El Salvador and Uganda, when leaders including the archbishops Oscar Romero and Janani Luwum spoke out against political corruption.
The work of the church is to remain constantly vigilant to maintain its independence and the credibility of its witness. In the case of this particular Bible, discerning what is happening is not difficult. Christians are being played. Rather than being an appropriate time to debut a patriotic Bible, Easter season is an opportune moment for the church to recover the testimony of the supremacy of the cross over any flag, especially one on the cover of a Bible.
Esau McCaulley ( @esaumccaulley ) is a contributing Opinion writer, the author of “ How Far to the Promised Land: One Black Family’s Story of Hope and Survival in the American South ” and an associate professor of New Testament at Wheaton College.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow The New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When you mention a large standalone work (a book, a film, a journal, a website, a magazine, or a movie), you must italicize it and then capitalize all major words. (You should capitalize articles in the middle of the title, prepositions, and coordinating conjunctions. Examples showing how to write large works in MLA.
The author's name might be unknown. If it's the case, use the first several words from the article's title but omit "A," "An," or "The" at the beginning. It can be written in quotes or italics, depending on how it's written in your list of references. The number of words you pick to use depends on the title.
In an academic essay, you typically introduce a journal article in the first sentence of a paragraph. Then, use the sentences that follow to show how the material from the article relates to the rest of your essay. Submit a Tip. All tip submissions are carefully reviewed before being published. Submit.
If you must include the book or journal where the article is found in your paper, italicize it in both styles. In-text citations are also necessary when listing an article in your paper. For MLA style, an in-text citation includes the author's last name and the page number in parentheses, such as (Bedford 4). For APA style, the in-text citation ...
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
Answer. To write the name of a journal/magazine title in the body of your paper: The title of the journal should be in italics - Example: Journal of the American Medical Association. Capitalize all of the major words. To write the the name of an article title in the body of your paper: The title of the article should be in quotation marks - E ...
To mention an article in an essay using MLA format, follow these guidelines: 3.1 In-text citations. In MLA format, in-text citations typically include the author's last name and the page number where the information was found. For example: (Smith 45). 4. How to mention an article in an essay using Chicago style
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
In-text citations point the reader to the sources' information on the references page. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the year of publication. If you use a direct quote, the page number is also provided. More information can be found on p. 253 of the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American ...
The name of the author in a newspaper article is referred to as a byline. Below are examples for citing an article both with and without a byline. Reference list (print) structure: Last name, F. (Year published). 'Article title', Newspaper name, Day Month, Page (s). Example: Hamilton, J. (2018).
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
When learning how to write an academic essay with references, you must identify reliable sources that support your argument. As you read, think critically and evaluate sources for: Accuracy. Objectivity. Currency. Authority. Keep detailed notes on the sources so that you can easily find them again, if needed.
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
Summary: APA (American Psychological Association) style is most commonly used to cite sources within the social sciences. This resource, revised according to the 6 th edition, second printing of the APA manual, offers examples for the general format of APA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the reference page. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual ...
A bibliography entry for a journal article lists the title of the article in quotation marks and the journal name in italics—both in title case. List up to 10 authors in full; use "et al." for 11 or more. In the footnote, use "et al." for four or more authors. Chicago format. Author last name, First name.
General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Author/Authors How to refer to authors in-text, including single and multiple authors, unknown authors, organizations, etc. Reference List. Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats
Using in-text citations: shows the reader that you have done your research. shows that you know how to credit the sources of your information. points your reader to the full citation on your References page for more information. Defining and Understanding Plagiarism: important in the research and writing process.
Including an article title in the text of your writing serves a different purpose than including it in the Works Cited section of a paper. You may want to include the title of an article in your paper when it is the main subject you're writing about, a subject you're discussing that you're referring to ...
Capitalize the first and final word of the title. Capitalize nouns, pronouns, verbs, helping verbs, adjectives and adverbs within the title. Capitalize the first word that follows a colon when using title case. Do not capitalize articles located between the first and final words, such as "the," "a" and "an."
Use double quotation marks around the title of an article or chapter, and italicize the title of a periodical, book, brochure, or report. Examples: From the book Study Guide (2000) ... or ("Reading," 1999). Note: Titles of periodicals, books, brochures, or reports should be in italics and use normal title capitalization rules.
Citing a website in MLA Style. An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL. The in-text citation usually just lists the author's name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to ...
Periodicals include magazines, newspapers, and scholarly journals. Works cited entries for periodical sources include three main elements—the author of the article, the title of the article, and information about the magazine, newspaper, or journal. MLA uses the generic term "container" to refer to any print or digital venue (a website or ...
In this article, I look at improvements over time and the global inequalities that need to be closed to protect lives and livelihoods around the world. Weather forecasts have improved a lot. Weather forecasting has come a long way. In 650 B.C. the Babylonians would try to predict weather patterns based on cloud patterns and movements.
This essay tries to look at the way in which Kālidāsa approaches towns in his three kāvyas: Meghadūta, Kumārasaṁbhava and Raghuvaṁśa. ... Cite article COPY CITATION . OR. Download to reference manager. If you have citation software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice.
However, MLA only requires the www. address, so eliminate all https:// when citing URLs. Many scholarly journal articles found in databases include a DOI (digital object identifier). If a DOI is available, cite the DOI number instead of the URL. Online newspapers and magazines sometimes include a "permalink," which is a shortened, stable ...
Guest Essay. There's No Such Thing as an American Bible. March 31, 2024. ... None of these traditions cite or refer to any American political documents in their doctrinal statements — and for ...