

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles
Ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 10 circles| pdf download.

- Exercise 10.1 Chapter Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 10.2 Chapter Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 10.3 Chapter Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 10.4 Chapter Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 10.5 Chapter Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 10.6 Chapter Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapters:
How many exercises in chapter 10 circles, the diameter of circle is 3.8 cm. find the length of its radius., what is an arc, what is a diameter, contact form.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles are provided here. Our NCERT Maths solutions contain all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully. Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines. CBSE Class 9 Students who wish to score good marks in the maths exam must practice these questions regularly.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions
Below we have provided the solutions of each exercise of the chapter. Go through the links to access the solutions of exercises you want. You should also check out our NCERT Class 9 Solutions for other subjects to score good marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.1

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.2

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.3

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.4

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.6
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 – Topic Discussion
Below we have listed the topics that have been discussed in this chapter.
- Circles and the related terms
- Angle Subtended by a Chord at a Point
- Perpendicular from the Centre to a Chord
- Circle through Three Points
- Equal Chords and Their Distances from the Centre
- Angle Subtended by an Arc of a Circle
- Cyclic Quadrilaterals
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Maths Notes Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- RD Sharma Solutions Class 9
- Maths Formulas Class 9
- Class 9 Syllabus
- Class 9 Revision Notes
- Physics Notes Class 9
- Chemistry Notes Class 9
- Biology Notes Class 9
- History Notes class 9
- Geography Notes class 9
- Social science Notes class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Triangles
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Constructions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 14 Statistics
- Angle Sum Property of a Quadrilateral
- Euclidean Geometry
- Class 9 NCERT Solutions - Chapter 2 Polynomials - Exercise 2.3
- Triangle Inequality
- Class 9 NCERT Solutions - Chapter 1 Number System - Exercise 1.6
- Transversal Lines
- Class 9 NCERT Solutions - Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry - Exercise 3.3
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles is a curated article by professionals at GFG, to help students solve problems related to circles with ease. All the solutions provided here are factually correct and
The NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles covered a variety of issues, including how to determine the separation between equal chords from the centre and the angles that a chord at a location subtended. There are also studies of cyclic quadrilaterals and their properties, as well as the angles that a circle’s arc subtends.
- Introduction to Circle
- Center of Circle
- Circumference
- Circle Theorems
- Cyclic Quadrilaterals
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Exercise 10.1
Question 1: fill in the blanks.
(i) The centre of a circle lies in ____________ of the circle. (exterior/ interior)
Answer: Interior.
(ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies in ______________ of the circle. (exterior/ interior)
Answer: Exterior.
(iii) The longest chord of a circle is a ______________ of the circle.
Answer: Diameter.
(iv) An arc is a _____________ when its ends are the ends of a diameter.
Answer: Semicircle.
(v) Segment of a circle is the region between an arc and _____________ of the circle.
Answer: Chord.
(vi) A circle divides the plane, on which it lies, in _______________ parts.
Answer: Three.
Problem 2: Write True or False: Give reasons for your answers.
(i) Line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
Answer: True, Any line segment drawn from the centre of the circle to any point on it is called radius of the circle and will be of equal length.
(ii) A circle has only finite number of equal chords.
Answer: False, There can be infinite number of equal chords in a circle.
(iii) If a circle is divided into three equal arcs, each is a major arc.
Answer: False, When the arcs are not equal we will have major and minor arc, equal arcs cannot be classified as a major arc or a minor arc.
(iv) A chord of a circle, which is twice as long as its radius, is a diameter of the circle.
Answer: True, Diameter is the longest chord of the circle and the length of the longest chord in a circle is twice the length of radius of the circle.
(v) Sector is the region between the chord and its corresponding arc.
Answer: False, Sector is defined as the region between the arc and 2 radii of the circle.
(vi) A circle is a plane figure
Answer: True, A circle is a 2D figure which can be drawn on a plane.
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Exercise 10.2
Question 1. recall that two circles are congruent if they have the same radii. prove that equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres. .
Given: Two Congruent Circles C1 and C2 AB is the chord of C1 and PQ is the chord of C2 AB = PQ To Prove: Angle subtended by the Chords AB and PQ are equal i.e. ∠AOB = ∠PXQ Proof: In △AOB & △PXQ AO = PX (Radius of congruent circles are equal) BO = QX (Radius of congruent circles are equal) AB = PQ (Given) △AOB ⩭ △PXQ (SSS congruence rule) Therefore, ∠AOB = ∠PXQ (CPCT)
Question 2. Prove that if chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres, then the chords are equal.
Solution:
Given: Two Congruent circles C1 and C2 AB is the chord of C1 and PQ is chord of C2 & ∠AOB = ∠PXQ To prove : In △AOB and △PXQ , AO = PX (Radius of congruent circles are equal) ∠AOB = ∠PXQ (Given) BO = QX (Radius of congruent circles are equal) △AOB ⩭ △PXQ (SAS congruence rule) Therefore, AB = PQ (CPCT)
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Exercise 10.3
Question 1. draw different pairs of circles. how many points does each pair have in common what is the maximum number of common points .
(i) Two points common (ii) One point common (iii) One point common (iv) No point common (v) No point common As we can analyse from above, two circles can cut each other maximum at two points.
Question 2. Suppose you are given a circle. Give a construction to find its centre.
Let the circle be C1 We need to find its centre. Step 1: Take points P, Q, R on the circle Step 2: Join PR and RQ. We know that perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through centre So, we construct perpendicular bisectors of PR and RQ Step 3: Take a compass. With point P as pointy end and R as pencil end of the compass, mark an arc above and below PR. Do same with R as pointy end P as pencil end of the compass. Step 4: Join points intersected by the arcs. The line formed is the perpendicular bisector of PR. Step 5: Take compass, with point R as pointy end and Q as pencil end of the compass mark an arc above and below RQ. Do the same with Q as pointy end and R as pencil end of the compass Step 6: Join the points intersected by the arcs. The line formed is the perpendicular bisector of RQ. Step 7: The point where two perpendicular bisectors intersect is the centre of the circle. Mark it as point O. Thus, O is the centre of the given circle.
Question 3: If two circles intersect at two points, prove that their centres lie on the perpendicular bisector of the common chord.
Given, Let circle C1 have centre O and circle C2 have centre X, PQ is the common chord. To prove: OX is the perpendicular bisector of PQ i.e. 1. PR = RQ 2. ∠PRO = ∠PRX = ∠QRO = ∠QRX = 90° Construction: Join PO, PX, QO, QX Proof: In △POX and △QOX OP = OQ (Radius of circle C1) XP = XQ (Radius of circle C2) OX = OX (Common) ∴ △POX ≅ △QOX (SSS Congruence rule) ∠POX = ∠QOX (CPCT) —-(1) Also, In △POR and △QOR OP = OQ (Radius of circle C1) ∠POR = ∠QOR ( From (1)) OR = OR (Common) ∴ △OPX ≅ △OQX (SAS Congruence Rule) PR = QR (CPCT) & ∠PRO = ∠QRO (CPCT) —-(2) Since PQ is a line ∠PRO + ∠QRO = 180° (Linear Pair) ∠PRO + ∠PRO= 180° ( From (2)) 2∠PRO = 180° ∠PRO = 180° / 2 ∠PRO = 90° Therefore, ∠QRO = ∠PRO = 90° Also, ∠PRX = ∠QRO = 90° (Vertically opposite angles) ∠QRX = ∠PRO = 90° (Vertically opposite angles) Since, ∠PRO = ∠PRX = ∠QRO = ∠QRX = 90° ∴ OX is the perpendicular bisector of PQ
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Exercise 10.4
Question 1. two circles of radii 5cm and 3cm intersect at two points and the distance between their centers is 4 cm. find the length of the common chord..
Given: OP=4cm, AP=3cm, QR=5cm To find: In ∆APO: AO²=5²=25 OP²=4²=16 AP²=3²=9 OP²+AP²=AO² BY converse of Pythagoras theorem ΔAPO: is a right ∠D=P Now, in the bigger circle OP is perpendicular AB AP=½AB —————-(perpendicular from the center of circle to a chord bisect the chord ) 3=½AB 6=AB ∴ Therefore the length of common chord is 6cm.
Question 2. If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the line joining the point of intersection to the center makes equal angles with the chords.
Given: Equal chord AB & CD intersect at P. To find: AP=PD and PB=PC Construction: Draw OM perpendicular AB ,ON perpendicular CD and join OP. Because perpendicular from center bisect the chord ∴ AM=MB=½AB also CN=ND=½CD AM=MB=CN=ND ——————1 Now, In ∆OMP and ∆ONP ANGLE M=ANGLE N [90° both] OP=OP [COMMON] ON=OM [equal chords are equilateral from center] ∴ ∆OMP≅∆ONP Therefore MP=PN (C.P.C.T.) ——————2 i)from 1 and 2 AM+MP=ND+AN AP=PD ii)MB-MP=CN=PN PB=PC
Question 3. If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the line joining the point of intersection to the Centre makes equal angles with the chords.
Given: Equal chords AB and CD intersect at P. To prove: angle1=angle=2 Construction: Draw OM perpendicular AB & ON perpendicular CD. Solution: In ∆OMP & ∆ONP Angle M= Angel N [90 ° each] OP=OP [common] OM=ON —————[ Equal chords are equal distant from center] ∴ ∆OMP≅∆ONP ———-[R.H.S] ∴ ∠1=∠2 ———–[C.P.C.T]
Question 4. If a line intersects two concentric circles (circles with the same centre) with centre O at A, B, C and D, prove that AB = CD (see Figure).
Given : two concentric circle with O. A line intersect them at A, B, C , and D To prove: AB=CD construction: Draw OM ⊥ AD ,In bigger circle AD is chord OM ⊥ AD. ∴AM=MD —————-[⊥ from center of circle of a circle bisects the chord] __________ 1 The smaller circle : BC is chord OM ⊥ BC BM=MC ——————-[⊥ from center of circle of a circle bisects the chord] __________ 2 subtracting 1-2 AM-BM=MD-MC AB=CD
Question 5. Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are playing a game by standing on a circle of radius 5m drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma. If the distance between Reshma and Salma and between Salma and Mandip is 6m each, what is the distance between Reshma and Mandip?
Solution: To find RM=? Let Reshma, Salma and Mandip be R,S,M Construction: Draw OP ⊥ RS join OR and OS. RP=½RS ___________[⊥ from center bisects the chord] RP=½*6=3m In right ΔORP OP²=OR²- PR² OP= √ 5² -3² =√259 =√16 =4 Area of ΔORS=½*RS*OP =½*6*4=12m² —————–1 Now, ∠N=90° Area of ΔORS=½*SO*RN =½*SO*RN ——————-2 Above ,1=2 12=½*5*RN 12/5*2=RN RN=4.8 RM=2*RN _________________[⊥ from center bisects the chord] =2*4.8 9.6m
Question 6. A circular park of radius 20m is situated in a colony. Three boys Ankur, Syed and David are sitting at equal distance on its boundary. Each boy has toy telephone in his hand to talk with each other. Find the length of the string of each phone.
Draw AM⊥SD AS=SD=AD ∴ ASD is the equilateral Δ Let each side of Δ-2xm SM=2x/2=x Now in Δ DMS, by the Pythagoras theorem AM²+SM²=AS² AM²= AS²- SM² AM=√(2x²+x² ) ==√(3x² ) AM =√3x OM=AM-AO OM=√3x-20 Now in right ΔOMS OM²+SM²=SO² (√3x-20)²+2x²+x²=20² 20²+400-40√3x+x^2=400 4x²=40√3x 4xx=40√3x X=(40√3)/4 X=10√3x Length of each string =2x =2*10√3xm
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Exercise 10.5
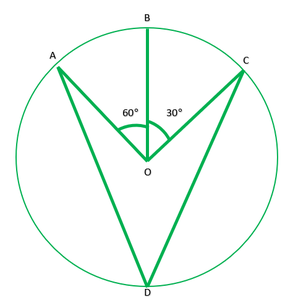
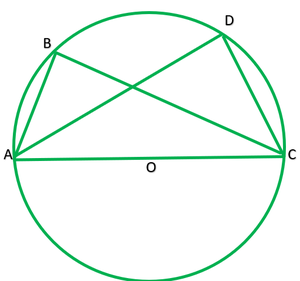
Question 1.in fig. 10.36, a, b , and c are three points on a circle with centre o such that ∠boc=30° and ∠aob=60°. if d is a point on the circle other than the arc abc, find ∠adc..
Given: ∠BOC=30° and ∠AOB=60° To find: ∠ADC Solution: ∠AOC=2∠ADC ———[The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle the angle subtended by it any point on the remaining part of the circle.] ∠AOB+∠BOC=2∠ADC 60°+30°=2∠ADC 90+30=2∠ADC 90/2=∠ADC 45=∠ADC
Question 2. A chord of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. Find the angle subtended by the chord at a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the major arc.
Given: PQ=OP To find: Angle on major arc is ∠A=? Angle on the minor arc is ∠B=? Since, =PO=OQ ∴∠POQ=60° ∠POQ=2∠PAQ [The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it any point on the remaining point of the circle] Reflex ∠POQ=360°-60° Reflex ∠POQ=300° Reflex ∠POQ=2∠POQ 300°=2∠PBQ 300°/2=∠PBQ 150°=∠PBQ
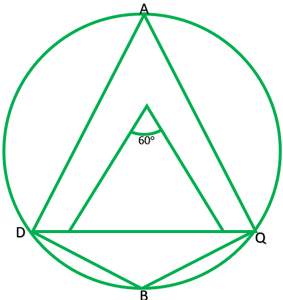
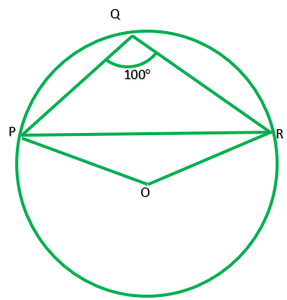
Question 3. In fig. 10.37, ∠PQR=100°,where P, Q and R are the points on a circle with centre O. Find ∠OPR.
Given: ∠PQR=100° To find: ∠OPR=? Reflex ∠POR=2∠PQR ——–[ The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it any point on the remaining point of the circle] Reflex ∠PQR=2*100 =200° ∠POR=360°-200° Now in ∆POR,OP=QR [ Radii of same circle] ∠P=∠R and let each =x. ∴∠P+∠O+∠R=180° [angle sum property of ∆] x+160°+x=180°-160° 2x+160°=180° x=20°/2=10° ∴∠OPR=10°
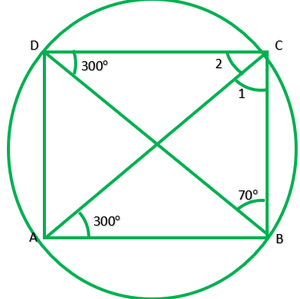
Question 4. In fig. 10.38, ∠ADC=69°,∠ACB=31°,find ∠BDC.
Given: ∠ABC=69°,∠ACB=31° To find: ∠BDC=? Solution: In ∆ABC ∠A+∠B+∠C=180° ———[Angle sum property of ∆] ∠A+69°+31°=180° ∠A=180°-100° ∠A=80° ∠A and ∠D lie on the same segment therefore, ∠D=∠A ∠D=80° ∠BDC=80°
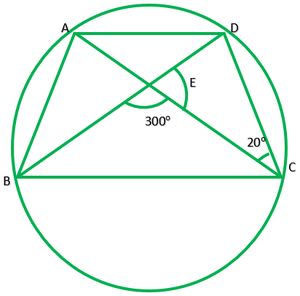
Question 5. In fig., A, B, C and D are four points on a circle.AC and BD intersect at a point E such that ∠BEC=130° and ∠ECD=20°. Find ∠BAC.
Given: ∠BEC=130°,∠ECD=20° To find: ∠BAC? Solution: In ∆EDC ∠E=180°-130° ———[linear pair] ∠E=50° ∠E+∠C+∠D=180° ——[angle sum property of triangle] 50°+20°+∠D=180° 70°+∠D=180° ∠D=180/70=110° Since, ∠A and ∠D line in the same segment ∴∠A=∠D ∠A=110° ∠BAC=110°
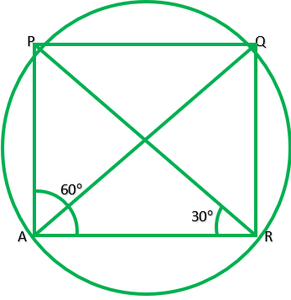
Question 6. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at a point E. If ∠DBC =70°, ∠BAC is 30°, find ∠BCD. Further, if AB=BC, find ∠ECD.
Given: ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral diagonal intersect at E ∠DBC=70°, ∠BAC is 30°. If AB=BC. To find: ∠BCD and ∠ECD ∠BDC=∠BAC=30° ——-[angle in the same segment] In ∆BCD, ∠B+∠C+∠D=180° ——–[angle sum property of triangle] ∠C+100°=180° ∠C=180°-100°=80° ∴∠BCD=80° If AB=BC, Then, ∠BAC=∠BCA 30°=∠BCA Now, ∠BCA+∠ECD=∠BCD 30°+∠ECD=80° ∠ECD=80°-30° ∴∠ECD=50°
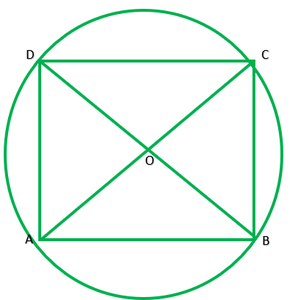
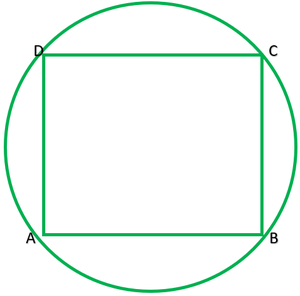
Question 7. If diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral are diameters of the circle through the vertices of the quadrilateral, prove that it is a rectangle.
Given: ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Diagonals of ABCD are also diameters of circle. To prove: ABCD is a rectangle AC=BD ———-[diameters of same circle] OA=OA ———[radii of the same circle] OA=OC=1/2AC ———2 OB=OD=1/2BD ———-2 From I and 2 diagonals are equal and bisect each other ∴ABCD is a rectangle
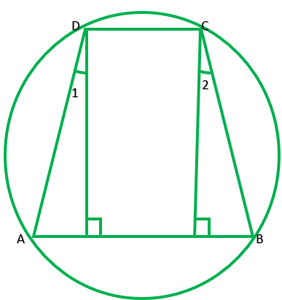
Question 8. If the non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, prove that it is cyclic.
Draw DL perpendicular AB and EF perpendicular AB In ∆DEA and ∆CEB ∠E=∠F ——–[each 90°] AD=BC ——–[given] DE=CF ——–[distance between || lines is same every line] ∴∆DEA≅∆CFB ——–[R.H.S] ∠A=∠B ———[by c.p.c.t.] 1 ∠1=∠2 (from 1) Adding 90° on each sides ∠1+90°=∠2+90° ∠1+∠EDC=∠2+FCD ∠ADC=∠BCD ∠D=∠C 2 Now, ∠A+∠A+∠C+∠C=360° 2∠A+2∠C=360° 2(∠A+∠C)=360° ∠A+∠C=360°/2=190° Because sum of opposite angles is 180°. ABCD is parallelogram.
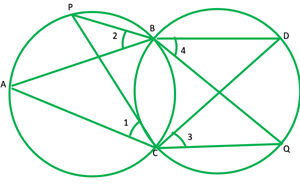
Question 9. Two circles intersect at two points B and C. Through B, two-line segments ABD and PBQ are drawn to intersect the circles at A, D , and P, Q respectively (see fig. 10.40). Prove that ∠ACP=∠QCD.
To prove: ∠ACP=∠QCD or ∠1=∠2 ∠1=∠2 —— [angles in the same segment are equal] 1 ∠ 3=∠ 4 ——- [angles in the same segment are equal] 2 ∠2=∠4 ——- [vertically opposite angles] 3 From 1 2 and 3 ∠1=∠3 ∴∠ACP=∠QCB
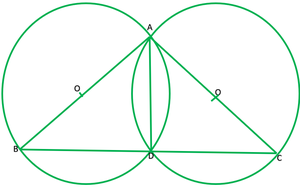
Question 10. If circles are drawn taking two sides of a triangle as diameters, prove that the point of intersection of these circles lie on the third side.
Given: ABC is ∆ and AB and AC are diameters of two circles To prove: Point of intersection is D, lies on the BC. Construction: Join AD ∠ADB=90° ——-[angles in semicircle] 1 ∠ADC=90 ° ——[angles in semicircle] 2 Adding 1 and 2 ∠ADB+∠ADC=90°+90° ∠BDC=180° BDC is a straight line therefore D lies on BC.
Question 11. ABC and ADC are two right triangles with common hypotenuse AC. Prove that ∠CAD=∠CBD.
Given: ABC and ADC are two right angle triangles with common hypotenuse AC. To prove: ∠ADB=∠CBD Solution: ∠ABC=∠ADC=90° Circle drawn by taking AC as diameter passes through B and D. For chord CD ∠CAD=∠CBD ——-[angle in the same segment]
Question 12. Prove that a cyclic parallelogram is rectangle.
Given: ABC is a cyclic ||gm To prove: ABCD is a rectangle. Because ABCD is a cyclic ||gm ∴∠A+∠C=180° ∠A=∠C [opposite angle of ||gm] ∴∠A=∠C=(180°)/2=90° ∠A=90° ∠C=90° Similarly, ∠B+∠D=180° ∴∠B=∠D =(180°)/2=90° ———-[opposite of a ||gm] Each angle of ABCD is 90° ∠B=90° ∠D=90° Thus, ABCD is a rectangle.
NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Exercise 10.6
Question 1. prove that the line of centres of two intersecting circles subtends equal angles at the two points of intersection. .
Given: Two circles with Centre A and B circle intersects at C and D. To prove: ∠ACB=∠ADB Construction: Join AD,BC and BD Proof: In ∆ACB and ∆ADB AC=AD ——–[radii of the same circle] BC=BD ———[radii of the same circle] AB=AB ——–[common] ∴∆ACB≅∆ADB ——— [by S.S.S] ∠ACB=∠ADB ——–[c.p.c.t.]
Question 2. Two chords AB and CD of lengths 5 cm and 11 cm respectively of a circle are parallel to each other and are on opposite sides of its centre. If the distance between AB and CD is 6 cm, find the radius of the circle.
Let O be the centre of circle and be r cm Given: AB=5cm, CD =11cm Construction: Draw OM perpendicular AB and OL perpendicular CD. Because OM perpendicular AB and OL perpendicular CD and AB||CD. ∴Points O,L, and M are collinear, than ∠M=6cm Let OL=x Then OM=6=x Join AO and CO OA=OC =r OL=1/2CD=1/2*11=5.5cm —–[perpendicular from bisects the chord] AM=1/2AB=1/2*5=2.3cm —–[perpendicular from bisects the chord] Now, In right ∆DLC r 2 =(OL) 2 +(CL) 2 r 2 =x 2 +(5.5) 2 r 2 =x 2 +30.25 ———–1 Now in right ∆OMA r 2 =(OM) 2 +(MA) 2 r 2 =(6-x) 2 +(2.5) 2 r 2 =36+x 2 =12x+6.25 r 2 =x 2 -12x+42.25 ———–2 Now equating equation 1 and 2 X 2 +30.25=x 2 -12x+30.25 12x=42.25-30.25 X=12/12=1 Putting value of x in equation 1 r 2 =x 2 +30.25 r 2 =(1) 2 +30.25 r 2 =31.25 r=√31.25=5.6 (approx.) Radius of circle is 5.6cm.
Question 3. The lengths of two parallel chords of a circle are 6 cm and 8 cm. If the smaller chord is at distance 4 cm from the center, what is the distance of the other chord from the centre?
Let AB and CD are|| chord of circle with centre O which AB=6cm and CD=8cm and radius of circle =r cm. Construction: Draw OP perpendicular AB and OM perpendicular CD. Because AB||CD and OP perpendicular AB and OM perpendicular CD therefore. Point O, M and P are collinear. Clearly, OP=4cm ———-[According to question] OM=to find? P is midpoint of AB. ∴AP=1/2 AB=1/2*6=3cm M is midpoint of AB. CM=1/2 CD=1/2*8cm=4cm Join AO and CO Now in Right ∆OPA, r 2 =AP 2 +PO 2 r 2 =3 2 +4 2 r 2 =9+16=25 Now in ∆OMC r 2 =CM 2 +MO 2 25=4 2 +MO 2 25-16=MO 2 9=MO 2 √9=MO 3=MO ∴Therefore distance of the other chord from the centre is 3cm
Question 4. Let the vertex of an angle ABC be located outside a circle and let the sides of the angle intersect equal chords AD and CE with the circle. Prove that ∠ABC is equal to half the difference of the angles subtended by the chords AC and DE at the centre.
Give: Vertex B of ∆ABC lie outside the circle,chord AD=CE To prove: ∠ABC=1/2(∠DOE-∠AOC) Construction: Join AE Solution: Chord DE subtends ∠DOE at the center and ∠DAE at point A on the circle. ∴∠DAE=1/2∠DOE ———-1 chords AC subtends ∠AOC at the centre and ∠AEC at point ∴∠AEC=1/2∠AOC ———2 In ∆ ABE,∠DAE is exterior angle ∠DAE=∠ABC +∠AEC 1/2∠DOE=∠ABC+1/2∠AOC ½(∠DOE-∠AOC)= ∠ABC
Question 5. Prove that the circle drawn with any side of a rhombus as diameter, passes through the point of intersection of its diagonals.
Given: A rhombus ABCD in which O is intersecting point of diagonals AC and BD. A circle is drawn taking CD as diameter. To prove: circle points through O or Lies on the circles. Proof: In rhombus ABCD, ∠DOA=90° ——–[diagonals of rhombus intersect at 90°] 1 In circle: ∠COD=90° ——–[angle made in segment O is right angle] 2 From 1 and 2 O lies on the circle.
Question 6. ABCD is a parallelogram. The circle through A, B and C intersect CD (produced if necessary) at E. Prove that AE = AD.
ABCD is a ||gm. The circle through A,B and C intersect at E. To prove: AE=AD Proof: Here ABCE is a cyclic quadrilateral ∠2+∠4=180° —–[sum of opposite is of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180°] ∠4=180°-∠1 ——-1 Now ∠4+∠6=180°-∠6 ———2 From 1 and 2 180°-∠2=∠180°-∠6 ∠2=∠6 ———–3 Also ∠2=∠5 ———[opposite angles of ||gm are equal] —–4 From 3 and 4 ∠5=∠6 Now, In ∆ADE, ∠5=∠6 ∴AE=AD ——[sides apposite to equal angles in a∆ are equal]
Question 7. AC and BD are chords of a circle which bisect each other. Prove that (i) AC and BD are diameters, (ii) ABCD is a rectangle.
Solution:
Given: Two chords AC and BD bisects each other i.e OA=OC,OB=OD To prove: In ∆AOB and COB AO=CO ——-[given] ∠AOB=∠COD ——[vertically opposite angle] OB=OD ——–[give] ∴∆AOB≅∆COB ——[s.s.s] AB=CD ——[C.P.C.T.] 1 similarly ∆AOD≅∆COB (S.A.S) AD=CD (C.P.C.T.) 2 From 1 and 2 ABCD is a ||gm Since, ABCD is cyclic quadrilateral ∴∠A+∠C=180° ∠B+∠B=180° 2∠B=180° ∠B=180°/2 ∠B=90° ∴ ∠A and ∠B lies in a semicircle → AC and BD are diameter of circle. ii) Since ABCD is a ||gm and ∠A=90° ∴ ABCD is a rectangle.
Question 8. Bisectors of angles A, B and C of a triangle ABC intersect its circumcircle at D, E and F respectively. Prove that the angles of the triangle DEF are 90° – 1 2 A, 90° – 1 2 B and 90° – 1 2 C.
Given:∆ABC and it circum-circle AD,BE and CF are bisectors of ∠A,∠B and ∠C Respectively. To proof:∠ D=90°-1/2∠A , ∠E=90°-1/2∠B , ∠F=90°-1/2∠C Construction: Join AE and AF. Solution: ∠ADE=∠ABE ———-1 [angle in the same segment are equal] ∠ADF=∠ACF ———–2 [angle in the same segment are equal] Adding 1 and 2 ∠ADE+∠ABF=∠ABE+∠ACF ∠D=1/2∠B+1/2∠C ——[BC and CF are bisector of ∠B & ∠c] ∠D=1/2(∠B+∠C) ∠D=1/2(180°-∠A) ∠D=1/2(180°-∠A) ∠D=90°-1/2∠AC
Question 9. Two congruent circles intersect each other at points A and B. Through A any line segment PAQ is drawn so that P, Q lie on the two circles. Prove that BP = BQ.
Given: two congruent circles which intersect at A and B. PAB is a line segment To prove: BA=BQ Construction: join AB Proof: AB is a common chord of both the congruent circle. Segment of both circles will be equal ∠P=∠Q Now, in ∆ BPQ, ∠P=∠Q BP=BQ ——[sides opposite to equal angles are equal]
Question 10. In any triangle ABC, if the angle bisector of ∠A and perpendicular bisector of BC intersect, prove that they intersect on the circumcircle of the triangle ABC.
Given: A ∆ABC, in which AD is angle bisector of ∠A and OD is ⊥ bisector of BC. To prove: D lies on circumcircle. Construction: Join OB and OC Proof: Since BC subtends ∠BAC at A on the remaining of the circle. ∠BOC=2∠BAC ——-1 Now, In ∆BOE and ∆ COE BO=OE ——–(radii of the same circle) BE=CE —–(give) ∴∆BOE≅COE ——-(S.S.S) ∠1=∠2 ——-(c.p.c.t) Now, ∠1+∠2=∠BOC 2∠1=∠BOC 2∠1=2∠BAC ———- (from 1) ∠1=∠BAC ∠BOE=∠BAF ∠BOD=∠BAC ∠BOD=2∠BAD [AD is bisector of ∠BAC] This is possible only if BD is chord of the circle. D lies on the circle.
Important Points to Remember
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 will help students to learn the solution for all the NCERT Problems.
- These solutions are entirely accurate and can be used by students to prepare for their board exams.
- All the solutions provided are in a step-by-step format for better understanding.
Key Takeaways of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10
By utilizing the class 9 questions with solutions on circles, students can reap various advantages that would aid their academic growth. Firstly, these comprehensive resources enable students to improve their scores significantly while simultaneously enhancing their understanding of the subject matter. Moreover, what further adds to their accessibility is the fact that these helpful PDF files are conveniently available free of charge. Therefore, students have the flexibility to choose between a soft copy or a hard copy, based on their personal preference and convenience.
Also Check:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Biology
FAQs – NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles
Q1: why is it important to learn about circles.
It is crucial to understand circles since they are fundamental geometric forms having numerous uses in a variety of industries, including math, physics, engineering, and architecture. Understanding circles enables you to apply ideas like tangents, chords, and sectors to solve issues involving their properties, such as calculating circumference, area, and arc length. In general, understanding circles is crucial for building a solid geometry foundation and for practical applications in a variety of fields.

Q2: What topics are covered in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10- Circles ?
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10- Circles covers circles introduction and related terms and theorems related to circles.
Q3: How can NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10- Circles help me?
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10- Circles can help you solve the NCERT exercise without any limitations. If you are stuck on a problem, you can find its solution in these solutions and free yourself from the frustration of being stuck on some question.
Q4: How many exercises are there in Class 9 Maths Chapter 10-Circles ?
There are 6 exercises in the Class 9 Maths Chapter 10- Circles which covers all the important topics and sub-topics.
Q5: Where can I find NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10-Circles ?
You can find these NCERT Solutions in this article created by our team of experts at GeeksforGeeks.
Q6: How are NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 helpful for Class 9 students?
To excel in CBSE board exams, students often rely on NCERT textbooks as their primary study material. These textbooks are renowned for their comprehensive content, making them an invaluable resource. In order to enhance their understanding of the textbook problems, students can conveniently refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 offered by GeeksforGeeks. These solutions are meticulously prepared by experts, providing precise and accurate methods to solve the problems effectively. By utilizing these solutions, students can significantly boost their proficiency and master the subject in no time.
Please Login to comment...
- Chapterwise-Solutions-Class-9
- Maths-Class-9
- NCERT Solutions Class-9
- Mathematics
- School Learning
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- Otter AI vs Dragon Speech Recognition: Which is the best AI Transcription Tool?
- Google Messages To Let You Send Multiple Photos
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10: Circles - Exercise 10.1
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 (Ex 10.1)
Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.1 (Ex 10.1) and all chapter exercises at one place prepared by expert teacher as per NCERT (CBSE) books guidelines. Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Exercise 10.1 Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks. Register and get all exercise solutions in your emails.

Access NCERT Answers for class 9 Mathematics Chapter 10 – Circles
Exercise 10.1
1. Fill in the blanks
(i) The centre of a circle lies in __________ of the circle. (exterior/interior)
Ans: The centre of a circle lies in the interior of the circle.
(ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies in __________ of the circle. (exterior/interior)
Ans: A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies in the exterior of the circle
(iii) The longest chord of a circle is a __________ of the circle.
Ans: The longest chord of a circle is a diameter of the circle.
(iv) An arc is a __________ when its ends are the ends of a diameter.
Ans: An arc is a semi-circle when its ends are the ends of a diameter.
(v) Segment of a circle is the region between an arc and __________ of the circle.
Ans: Segment of a circle is the region between an arc and chord of the circle.
(vi) A circle divides the plane, on which it lies, in __________ parts.
Ans: A circle divides the plane, on which it lies, in three parts.
2. Write True or False: Give reasons for your answers.
(i) Line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
The radius of the circle is the distance between all points on the circle that are equal distances from the circle's centre.
(ii) A circle has only finite number of equal chords.
Ans: False
A circle has an unlimited number of points.
As a result, an unlimited number of chords of a given length can be drawn.
As a result, there are an endless number of equal chords in a circle.
(iii) If a circle is divided into three equal arcs, each is a major arc.
Ans: False.
Consider the following three arcs: AB, BC, and CA.
It can be shown that CAB is a major arc for minor arc BDC.
As a result, the minor arcs of the circle are AB, BC, and CA.
(iv) A chord of a circle, which is twice as long as its radius, is a diameter of the circle.
Let AB be a chord with a length twice that of its radius.
Our chord will travel through the centre of the circle in this scenario, as can be seen.
As a result, it will be the circle's diameter.
(v) Sector is the region between the chord and its corresponding arc.
The region between an arc and two radii connecting the arc's centre and endpoints is known as a sector.
OAB, for example, is the circle's sector in the illustration.
(vi) A circle is a plane figure.
A circle is a two-dimensional shape that may also be called a planar Shape.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Exercise 10.1
Opting for the NCERT solutions for Ex 10.1 Class 9 Maths is considered as the best option for the CBSE students when it comes to exam preparation. This chapter consists of many exercises. Out of which we have provided the Exercise 10.1 Class 9 Maths NCERT solutions on this page in PDF format. You can download this solution as per your convenience or you can study it directly from our website/ app online.
Vedantu in-house subject matter experts have solved the problems/ questions from the exercise with the utmost care and by following all the guidelines by CBSE. Class 9 students who are thorough with all the concepts from the Subject Circles textbook and quite well-versed with all the problems from the exercises given in it, then any student can easily score the highest possible marks in the final exam. With the help of this Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.1 solutions, students can easily understand the pattern of questions that can be asked in the exam from this chapter and also learn the marks weightage of the chapter. So that they can prepare themselves accordingly for the final exam.
Besides these NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.1, there are plenty of exercises in this chapter which contain innumerable questions as well. All these questions are solved/answered by our in-house subject experts as mentioned earlier. Hence all of these are bound to be of superior quality and anyone can refer to these during the time of exam preparation. In order to score the best possible marks in the class, it is really important to understand all the concepts of the textbooks and solve the problems from the exercises given next to it.
Do not delay any more. Download the NCERT solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.1 from Vedantu website now for better exam preparation. If you have the Vedantu app in your phone, you can download the same through the app as well. The best part of these solutions is these can be accessed both online and offline as well.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10: Circles - Exercise 10.1
1. What is chapter 10 circles exercise 10.1 about?
Exercise 10.1 is about the circle and its related terms. A circle is made up of all the points in a plane that are all at the same set distance from another fixed point in the plane.
2. What is the radius of the circle explained in the ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 10 circles exercise 10.1?
The radius of a circle is the separation between any two points on its circumference. The radius of a circle is also the line segment connecting the center and any point on the circle. In other words, the word "radius" can refer to both the length of a line segment as well as a line segment itself.
3. According to the ncert solutions for class 9 maths chapter 10 circles exercise 10.1 given by vedantu in how many parts a circle is divided?
The plane on which a circle is located is divided into three halves. They are I inside the circle, also known as the circle's interior; (ii) the circle; and (iii) outside the circle, also known as the circle's exterior. The circular region is made up of the circle and its inside.
4. Explain about the diameter and arc used in this exercise?
A diameter is the longest chord and all diameters have the same length, which is equal to two times the radius. The area of a circle that is between two points is known as an arc. The main arc is longer than the minor arc, which is smaller.
5. How can students solve easily through the ncert solutions provided by Vedantu?
Vedantu in-house subject matter experts have solved the questions from exercise 5.2 with the utmost care and by following all the guidelines provided by CBSE. With the help of vedantu one can easily prepare for exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
Cbse study materials for class 9, cbse study materials.
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5 Circles
The NCERT solutions for class 9 maths chapter 10 exercise 10.5 has twelve questions based on the topics and theorems of the angle subtended by an arc of a circle. There are a total of 6 theorems covered under this topic. The first theorem states that the angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the left part of the circle . NCERT solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5 covers all these theorems and concepts along with proofs to help students learn this important topic and its applications.
The concepts associated with the cyclic quadrilateral and the sum of their angles are nicely explained with the help of examples to grasp them easily. It is also better to thoroughly read the notes provided in each section to get a deep understanding of this topic. To download these class 9 maths NCERT solutions chapter 10 exercise 10.5, click on the link given below.
☛ Download NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5
Exercise 10.5 Class 9 Chapter 10 Download PDF
More Exercises in Class 9 Maths Chapter 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Ex 10.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Ex 10.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Ex 10.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Ex 10.5
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Ex 10.6
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5 Tips
The regular practice of questions and sample problems provided in the NCERT solutions class 9 maths chapter 10 exercise 10.5 will benefit students to attain a deep problem-solving approach required to write solutions to each question. This kind of learning is also helpful to obtain high marks in exams.
By following the step-by-step questions present in the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5, students will understand these theorems in-depth. In addition, students should also practice writing the steps of solutions as most of the questions are based on proving the statements. Thus, it will allow them to learn the application of this concept.
Download Cuemath NCERT Solutions PDFs for free and start learning!
Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Video Chapter 10 Exercise 10.5
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Class 9 Mathematics Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 9 Mathematics Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 9 Mathematics . These Assignments for Grade 9 Mathematics cover all important topics which can come in your standard 9 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 9 Mathematics , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 9 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Mathematics Class 9 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Class 9. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics class 9 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 9 Mathematics Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Class 9 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics . Students and teachers can download and save all free Mathematics assignments in Pdf for grade 9th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 9 important questions and answers for Mathematics as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 9 Mathematics and CBSE Assignments for Mathematics Class 9 will be really helpful for standard 9th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 9th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 9 Mathematics Download in Pdf
More assignments for class 9 mathematics.

Advantages of Class 9 Mathematics Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Mathematics assignments for Grade 9, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Mathematics textbooks for Class 9 .
- All Mathematics assignments for Class 9 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 9 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 9 Mathematics question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 9 Mathematics students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Mathematics Class 9 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 9 Mathematics chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Mathematics in Grade 9, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Mathematics Grade 9 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 9 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 9 Mathematics Measures of central Tendency Assignments

Class 9 Malayalam Assignments

Class 9 Social Science Geography Assignments

Chapter 10 – Congruent Triangles
Exercise 10.1, exercise 10.2, exercise 10.3, exercise 10.4, review exercise, multiple choice questions, this post has 3 comments.
Best notes ever
Your notes are very helpful these notes help me veryyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy much and can say that these notes are superb. Great notes great job thanks a lot for such a helpful notes 🙏
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Assignments for Class 9, 10, 11 & 12
Assignments for all Classes and all chapters in PDF format will be available very soon, Revision questions, key points of each chapters and other practice material updated for new academic session 2024-25. Download NCERT Books and offline apps for all class updated for new academic year 2024-25. Assignments for the academic year 2024-25 based on latest CBSE Curriculum will be uploaded very soon.
Chapter wise assignments for class 9 Maths are given below updated for new academic session 2024-25. These assignments will be available in updated form along with new assignments and chapter wise tests with solutions. After the completion of chapters from NCERT Books and Exemplar Books, students should go for Assignments. Visit to Discussion Forum to ask your doubts related to NIOS and CBSE Board. Download NCERT Books and Offline Apps based on latest CBSE Syllabus.
Assignments Chapter 4: 1 2 3 4
Assignments Chapter 8: 1 2 3 4
Assignments Chapter 10: 1 2 3
Assignments Chapter 13: 1 2 3 4 5
Assignments Chapter 14: 1 2 3
Assignments Chapter 15: 1 2
Revision notes are very help full for practice. In the assignments of Chapter 1 and Chapter 2 , a lots of extra questions with answers are given for practice.
- Revision Notes for Chapter 1
- Revision Notes for Chapter 2
- Revision Notes for Chapter 3
- Revision Notes for Chapter 5
- Revision Notes for Chapter 6
- Revision Notes for Chapter 7
- Revision Notes for Chapter 12
We are placing all NCERT solutions in Hindi Medium as well as English Medium for CBSE Board, UP Board, Uttarakhand Board, Bihar Board, Gujrat Board and all other boards who are following NCERT Books 2024-25 for their exams. You can directly go for HINDI MEDIUM or ENGLISH MEDIUM solutions by just clicking on Exercise or Prashnavali as per your requirement. For example, Exercise 1.1 shows English Medium solutions for ex. 1.1 and Prashnavali 1.1 shows Hindi Medium solutions for Exercise 1.1. If you find still some difficulty, please inform us, we will try to rectify as soon as possible. Our only aim is to help the students. You may call us in Hindi or in English or leave message on Whats App, we will call you. You can post your questions through Discussion Forum to get proper answers.
We are here to help you and working as per the requirements of students. We have prepared NCERT Solutions in Hindi Medium only on demand of students. From this session, we will upload so many question papers, assignments, Hand-out sheets and Chapter wise test papers for all chapters divided into three categories – Easy, Average and Difficult. Always provide feedback and give suggestions to improve this website. Your suggestions are valuable for us.
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter-10 Circles
- Active page
NCERT solutions for class 9 maths chapter 10 Circles is prepared by academic team of Physics Wallah. We have prepared NCERT solutions for all exercise of chapter 10. Given below is step by step solutions of all questions given in NCERT textbook for chapter 10. Read chapter 10 theory make sure you have gone through the theory part of chapter 10 from NCERT textbook and you have learned the formula of the given chapter. Physics Wallah prepared a detail notes and additional questions for class 9 maths with short notes of all maths formula of class 9 maths. Do read these contents before moving to solve the exercise of NCERT chapter 10.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.1
Question 1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) The centre of a circle lies in _______________ of the circle.
(ii) A point, whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies in _______________ of the circle.
(iii) The longest chord of a circle is a _______________ of the circle.
(iv) An arc is a _______________ when its ends are the ends of a diameter.
(v) Segment of a circle is the region between an arc and _______________ of the circle.
(vi) A circle divides the plane, on which it lies, in _______________ parts.
Solution: (i) Interior
(ii) Exterior
(iii) diameter
(iv) Semi-circle
Question 2. Write True or False:
(i) Line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
(ii) A circle has only finite number of equal chords.
(iii) If a circle is divided into three equal arcs each is a major arc.
(iv) A chord, which is twice as long as its radius is a diameter of the circle.
(v) Sector is the region between the chord and its corresponding arc.
(vi) A circle is a plane figure.
Solution: (i) True
(iii) False
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.2

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.3

Thus, two circles can have at the most two points in common.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.4
Question 1. Two circles of radii 5 cm and 3 cm intersect at two points and the distance between their centers is 4 cm. Find the length of the common chord.
Solution: Let two circles with centres O and O’ intersect each other at points A and B. On joining A and B, AB is a common chord.

Radius OA = 5 cm, Radius O’A = 3 cm,
Distance between their centers OO’ = 4 cm
In triangle AOO’,
5 2 = 4 2 + 3 2

Hence AOO’ is a right triangle, right angled at O’.
Since, perpendicular drawn from the center of the circle bisects the chord.
Hence O’ is the mid-point of the chord AB. Also O’ is the centre of the circle II.
Therefore length of chord AB = Diameter of circle II

Question 2. If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the segments of one chord are equal to corresponding segments of the other chord.
Solution: Given: Let AB and CD are two equal chords of a circle of centers O intersecting each other at point E within the circle.

To prove: (a) AE = CE
(b) BE = DE

Proof: In right triangles OME and ONE,

[Equal chords are equidistance from the centre]
OE = OE [Common]
[Perpendicular from the centre bisects the chord] …..(ii)
Similarly, NC = CD ……….(iii)
But AB = CD [Given]
From eq. (ii) and (iii), AM = NC ……….(iv)
Also MB = DN …….…(v)
Adding (i) and (iv), we get,
AM + ME = NC + NE
Now AB = CD [Given]
AE = CE [Proved]
Question 3. If two equal chords of a circle intersect within the circle, prove that the line joining the point of intersection to the centre makes equal angles with the chord.
Solution: Given: AB and CD be two equal chords of a circle with centre O intersecting each other with in the circle at point E. OE is joined.

Proof: In right angled triangles OME and ONE,
OM = ON [Equal chords are equidistant from the centre]

Question 4. If a line intersects two concentric circles (circles with the same centre) with centre O at A, B, C and D, prove that AB = CD. (See figure)

To prove: AB = CD

Now, BC is a chord of inner circle and
Subtracting (ii) from (i), we get,
AL – BL = LD – LC
Question 5. Three girls Reshma, Salma and Mandip are standing on a circle of radius 5 m drawn in a park. Reshma throws a ball to Salma, Salma to Mandip, Mandip to Reshma. If the distance between Reshma and Salma and between Salma and Mandip is 6 m each, what is the distance between Reshma and Mandip?
Solution: Let Reshma, Salma and Mandip takes the position C, A and B on the circle. Since AB = AC

Let M be the point of intersection of BC and OA.
Again, since AB = AC and AM bisects

From right angled triangle OMB,
OB 2 = OM 2 + MB 2

Again, in right angled triangle AMB,
AB 2 = AM 2 + MB 2

Equating the value of MB2 from eq. (i) and (ii),

Hence, from eq. (i),

Question 6. A circular park of radius 20 m is situated in a colony. Three boys Ankur, Syed and David are sitting at equal distance on its boundary each having a toy telephone in his hands to talk each other. Find the length of the string of each phone.
Solution: Let position of three boys Ankur, Syed and David are denoted by the points A, B and C respectively.

Since equal sides of equilateral triangle are as equal chords and perpendicular distances of equal chords of a circle are equidistant from the centre.

Join OA, OB and OC.

Now in right angled triangle BEO,
OE 2 + BE 2 = OB 2 [Using Pythagoras theorem]

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.5

Question 2. A chord of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. Find the angle subtended by the chord on a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the major arc.
Solution: Let AB be the minor arc of circle.

D is a point in the minor arc.
Now in isosceles triangle OPR,

Solution: In triangle ABC,

Since, A and D are the points in the same segment of the circle.

[Angles subtended by the same arc at any points in the alternate segment of a circle are equal]

Solution: For chord CD

Question 7. If diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral are diameters of the circle through the vertices of the quadrilateral, prove that it is a rectangle.
Solution: Let ABCD a cyclic quadrilateral having diagonals as BD and AC intersecting each other at point O.

(Considering AC as a chord)

Question 8. If the non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, prove that it is cyclic.

To prove: The points A, B, C, D are concyclic.

Now AD = BC and DA = DE

Hence, ABCD is a cyclic trapezium.

Solution: ; In triangles ACD and QCP,
Hence proved.
Question 10. If circles are drawn taking two sides of a triangle as diameters, prove that the point of intersection of these circles lie on the third side.
Solution: Given: Two circles intersect each other at points A and B. AP and AQ be their respective diameters.
To prove: Point B lies on the third side PQ.
Construction : Join A and B.
Proof: AP is a diameter.

[Angle in semicircle]
AlsoAQ is a diameter.

Thus point B. i.e. point of intersection of these circles lies on the third side i.e., on PQ.
Solution: We have ABC and ADC two right triangles, right angled at B and D respectively.

If we draw a circle with AC (the common hypotenuse) as diameter, this circle will definitely passes through of an arc AC, Because B and D are the points in the alternate segment of an arc AC.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.6

Question 7. AC and BD are chords of a circle which bisect each other. Prove that:
(i) AC and BD are diameters.
(ii) ABCD is a rectangle.
Solution: Given: AC and BD of a circle bisect each other at O.
Then OA = OC and OB = OD
To prove: (i) AC and BD are the diameters. In other words, O is the centre of the circle.
Proof: (i) In triangles AOD and BOC,

AO = OC [given]

OD = OB [given]

(ii) Ac is the diameter. [Proved in (i)]

Similarly BD is the diameter.
Now diameters AC = BD

Similarly AB = DC ….(iv)
Hence ABCD is a rectangle.

Since the angles in the same segment of a circle are equal.

Adding both equations,

In triangle DEF,

Similarly, we can prove that

Question 9. Two congruent circles intersect each other at points A and B. Through A any line segment PAQ is drawn so that P, Q lie on the two circles. Prove that BP = BQ.
Solution: Given: Two equal circles intersect in A and B.
A straight line through A meets the circles in P and Q.

To prove: BP = BQ
Construction: Join A and B.
Proof: AB is a common chord and the circles are equal.

Since equal arcs of two equal circles subtend equal angles at any point on the remaining part of the circle, then we have,
In triangle PBQ,
Then we have, BP = BQ

Solution: Given: ABC is a triangle and a circle passes through its vertices.

To prove: Circumcircle of triangle ABC also passes through point P.
Proof: Since any point on the perpendicular bisector is equidistant from the end points of the corresponding side,

Physics Wallah team developed an additional resource material for all aspirents who are preparing for entrance exam like NEET, JEE,RMO & Olmpiads, if you are preparing for all these exam you need additional theory and questions apart from NCERT books so just click on the following chapter and get the additional theory , notes, question bank, online chapter wise test and many more !
Additional Resource and Notes for class 9 Maths
1. Probability
2. Surface Areas and Volumes
3. Coordinate Geometry
4. Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
5. Line and angle
6 Number system
7. Mensuration
8. consutration
9. circle
10. Areas of parallelograms
11. Polynomial
12. Quadrilaterial
13. Triangle
14. Statistics
15. euclid geometry
Related Chapters
- chapter-1 Number Systems
- chapter-2 Polynomials
- chapter-3 Coordinate Geometry
- chapter-4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- chapter-5 Introduction to Euclid Geometry
- chapter-6 Lines And Angles
- chapter-7 Triangles
- chapter-8 Quadrilaterals
- chapter-9 Areas Of Parallelograms And Triangles
- Chapter-10 Circles
- chapter-11 Constructions
- chapter-12 Herons Formula
- chapter 13-Surface Areas And Volumes
- chapter-14 Statistics
- chapter-15 Probability

Recent Concepts
Talk to our counsellor.

- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 9
- NCERT 9 Maths
- Chapter 10: Circles
- Exercise 10.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.5 Chapter 10 Circles
* According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 – Circles Exercise 10.5 is provided here, in downloadable PDF format. Click on the specified link given below to download it. These solutions have been designed by our Maths experts, to make each student understand the concepts in a better way. The answers given for each question in NCERT solutions for 9th Maths subject are as per the NCERT syllabus and guidelines. No other out-of-syllabus question has been included in this. Solving the problems, and taking these solutions as reference material, will help students to score well in the board exam.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 – Circles Exercise 10.5
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Other Exercise Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 – Circles
Exercise 10.1 Solutions 2 Question (2 Short) Exercise 10.2 Solutions 2 Question (2 long) Exercise 10.3 Solutions 3 Question (3 long) Exercise 10.4 Solutions 6 Question (6 long) Exercise 10.6 Solutions 10 Questions (10 long)
Access Answers to NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 – Circles Exercise 10.5
1. In Fig. 10.36, A,B and C are three points on a circle with centre O such that ∠ BOC = 30° and ∠ AOB = 60°. If D is a point on the circle other than the arc ABC, find ∠ ADC.

It is given that,
∠ AOC = ∠ AOB+ ∠ BOC
So, ∠ AOC = 60°+30°
∴ ∠ AOC = 90°
It is known that an angle which is subtended by an arc at the centre of the circle is double the angle subtended by that arc at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
∠ ADC = (½) ∠ AOC
= (½)× 90° = 45°
2. A chord of a circle is equal to the radius of the circle. Find the angle subtended by the chord at a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the major arc.

Here, the chord AB is equal to the radius of the circle. In the above diagram, OA and OB are the two radii of the circle.
Now, consider ΔOAB. Here,
AB = OA = OB = radius of the circle.
So, it can be said that ΔOAB has all equal sides and thus, it is an equilateral triangle.
∴ ∠ AOC = 60°
And, ∠ ACB = ½ ∠ AOB
So, ∠ ACB = ½ × 60° = 30°
Now, since ACBD is a cyclic quadrilateral,
∠ ADB + ∠ ACB = 180° (Since they are the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral)
So, ∠ ADB = 180°-30° = 150°
So, the angles subtended by the chord at a point on the minor arc and also at a point on the major arc are 150° and 30°, respectively.
3. In Fig. 10.37, ∠ PQR = 100°, where P, Q and R are points on a circle with centre O. Find ∠ OPR.

The angle which is subtended by an arc at the centre of the circle is double the angle subtended by that arc at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
So, the reflex ∠ POR = 2× ∠ PQR
We know the values of angle PQR as 100°
So, ∠ POR = 2×100° = 200°
∴ ∠ POR = 360°-200° = 160°
Now, in ΔOPR,
OP and OR are the radii of the circle
So, OP = OR
Also, ∠ OPR = ∠ ORP
Now, we know the sum of the angles in a triangle is equal to 180 degrees
∠ POR+ ∠ OPR+ ∠ ORP = 180°
∠ OPR+ ∠ OPR = 180°-160°
As ∠ OPR = ∠ ORP
2 ∠ OPR = 20°
Thus, ∠ OPR = 10°
4. In Fig. 10.38, ∠ ABC = 69°, ∠ ACB = 31°, find ∠ BDC.

We know that angles in the segment of the circle are equal, so,
∠BAC = ∠BDC
Now in the ΔABC, the sum of all the interior angles will be 180°
So, ∠ABC+∠BAC+∠ACB = 180°
Now, by putting the values,
∠BAC = 180°-69°-31°
So, ∠BAC = 80°
∴ ∠BDC = 80°
5. In Fig. 10.39, A, B, C and D are four points on a circle. AC and BD intersect at a point E such that ∠ BEC = 130° and ∠ ECD = 20°. Find BAC.

We know that the angles in the segment of the circle are equal.
∠ BAC = ∠ CDE
Now, by using the exterior angles property of the triangle
In ΔCDE we get,
∠ CEB = ∠ CDE+∠ DCE
We know that ∠ DCE is equal to 20°
So, ∠ CDE = 110°
∠ BAC and ∠ CDE are equal
∴ ∠ BAC = 110°
6. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral whose diagonals intersect at a point E. If ∠ DBC = 70°, ∠ BAC is 30°, find ∠ BCD. Further, if AB = BC, find ∠ ECD.
Consider the following diagram.

Consider the chord CD,
We know that angles in the same segment are equal.
So, ∠ CBD = ∠ CAD
∴ ∠ CAD = 70°
Now, ∠ BAD will be equal to the sum of angles BAC and CAD.
So, ∠ BAD = ∠ BAC+∠ CAD
∴ ∠ BAD = 100°
We know that the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral sum up to 180 degrees.
∠ BCD+∠ BAD = 180°
It is known that ∠ BAD = 100°
So, ∠ BCD = 80°
Now consider the ΔABC.
Here, it is given that AB = BC
Also, ∠ BCA = ∠ CAB (They are the angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle)
∠ BCA = 30°
also, ∠ BCD = 80°
∠ BCA +∠ ACD = 80°
Thus, ∠ ACD = 50° and ∠ ECD = 50°
7. If diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral are diameters of the circle through the vertices of the quadrilateral, prove that it is a rectangle.
Draw a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD inside a circle with centre O such that its diagonal AC and BD are two diameters of the circle.

We know that the angles in the semi-circle are equal.
So, ∠ ABC = ∠ BCD = ∠ CDA = ∠ DAB = 90°
So, as each internal angle is 90°, it can be said that the quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle.
8. If the non-parallel sides of a trapezium are equal, prove that it is cyclic.

9. Two circles intersect at two points B and C. Through B, two line segments ABD and PBQ are drawn to intersect the circles at A, D and P, Q respectively (see Fig. 10.40). Prove that ∠ ACP = ∠ QCD.

Construction:
Join the chords AP and DQ.
For chord AP, we know that angles in the same segment are equal.
So, ∠ PBA = ∠ ACP — (i)
Similarly, for chord DQ,
∠ DBQ = ∠ QCD — (ii)
It is known that ABD and PBQ are two line segments which intersect at B.
At B, the vertically opposite angles will be equal.
∴ ∠ PBA = ∠ DBQ — (iii)
From equation (i), equation (ii) and equation (iii) we get,
∠ ACP = ∠ QCD
10. If circles are drawn taking two sides of a triangle as diameters, prove that the point of intersection of these circles lie on the third side.
First, draw a triangle ABC and then two circles having diameters AB and AC, respectively.
We will have to prove now that D lies on BC and BDC is a straight line.

We know that angles in the semi-circle are equal
So, ∠ ADB = ∠ ADC = 90°
Hence, ∠ ADB+∠ ADC = 180°
∴ ∠ BDC is straight line.
So, it can be said that D lies on the line BC.
11. ABC and ADC are two right triangles with common hypotenuse AC. Prove that ∠ CAD = ∠CBD.
We know that AC is the common hypotenuse and ∠ B = ∠ D = 90°.
Now, it has to be proven that ∠ CAD = ∠ CBD

Since ∠ ABC and ∠ ADC are 90°, it can be said that they lie in the semi-circle.
So, triangles ABC and ADC are in the semi-circle, and the points A, B, C and D are concyclic.
Hence, CD is the chord of the circle with centre O.
We know that the angles which are in the same segment of the circle are equal.
∴ ∠ CAD = ∠ CBD
12. Prove that a cyclic parallelogram is a rectangle.
It is given that ABCD is a cyclic parallelogram, and we will have to prove that ABCD is a rectangle.

Thus, ABCD is a rectangle.
Exercise 10.5 has twelve questions based on the topics and theorems given below.
Angle Subtended by an Arc of a Circle Theorem 1: The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the left part of the circle. Theorem 2: Chords which are equal in distance from the centre of a circle are also equal in length. Theorem 3 : Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal. Theorem 4: If a line segment joining two points subtends equal angles at two other points lying on the same side of the line containing the line segment, the four points lie on a circle.
Cyclic Quadrilaterals Theorem 1: The sum of both pairs of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180º. Theorem 2: If the sum of a pair of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is 180º, the quadrilateral is cyclic.
The questions in this exercise have long answers based on constructions and proofs. Solve each exercise problems for chapter 10 of Maths Class 9 here with detailed answers. Also, get our advanced learning materials, such as notes and tips and tricks, to prepare for CBSE exams. For all the classes from 6 to 12, NCERT solutions are provided here, chapter-wise and exercise-wise, in PDFs. Download and learn offline as well.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Byjus app is our best app for learning
Very great solution
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Search This Blog
Cbse mathematics.
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12. A complete resource centre of mathematics for students and teachers
Featured Posts
Maths assignment class viii | quadrilateral, class ix maths formulas | basics | assignments.

RESOURCE CENTRE MATHEMATICS

CHAPTER WISE EXPLANATION
Case study based questions class ix: click here, chapter 1: number system (algebra), chapter 2: polynomials, chapter 3: coordinate geometry, chapter 4: linear equations in two variables, chapter 5: euclid's geometry, chapter 6: lines and angles (geometry), chapter 7: triangles (geometry) , chapter 8: quadrilaterals (geometry), chapter 9: area related to quadrilaterals, chapter 10: circles (geometry), chapter 11: constructions (geometry), chapter 12 heron's formula (area of triangles), chapter 13: surface area and volumes, chapter 14: statistics (mean, mode, median), chapter 15: probability (tossing of coins & dice), post a comment, breaking news, popular post on this blog, lesson plan maths class 10 | for mathematics teacher.

Lesson Plan Math Class 10 (Ch-1) | Real Numbers

Lesson Plan Maths Class XII | For Maths Teacher

- Assignment 10 15
- Assignment 11 12
- Assignment 12 14
- Assignment 8 8
- Assignment 9 5
- Lesson plan 10 15
- Lesson Plan 12 13
- Lesson Plan 8 10
- Maths 10 20
- Maths 11 21
- Maths 12 17
SUBSCRIBE FOR NEW POSTS
Get new posts by email:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
*According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 9. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles are provided here in PDF format, which can be downloaded for free. The NCERT Solutions for the chapter Circles are included as per the latest update of the CBSE curriculum (2023-24) and have been designed by our expert teachers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.4. Ex 10.4 Class 9 Maths Question 1. Two circles of radii 5 cm and 3 cm intersect at two points and the distance between their centres is 4 cm. Find the length of the common chord. We have two intersecting circles with centres at O and O' respectively.
Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Ex 10.6 - 10 Questions (Optional) ☛ Download Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 NCERT Book Topics Covered: The main topics covered in class 9 maths NCERT solutions chapter 10 are the introduction to circles, related terms, the angle subtended by a chord at a point, equal chords and their respective distances from the center ...
Here you will get Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths that are updated as per the latest marking scheme and syllabus prescribed by CBSE. Also you can Download PDF of Chapter 10 Circles NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths to practice in a better way. There are variety of concepts given in this Chapter 10 Class 9 Maths textbook that ...
Our NCERT Maths solutions contain all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully. Here you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 all exercises Exercise in one place. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts and as per the latest NCERT syllabus and guidelines.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 let the students know that, if all the vertices of a quadrilateral lie in Circle, then it is called the cyclic quadrilateral. Exercise 10.5 with 12 Long answer questions. Exercise 10.6 with 10 questions.
6 exercises are included in the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 which are Exercise 1.1 to 1.6. Most of the questions are application based and a few are memory-based questions to test students' application skills and cognizance. Chapter 1 - Number System Exercises in PDF Format. Exercise 1.1.
Exercise 10.1 Chapter 10 Class 9 Maths : NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Ex 10.1 can be checked from here. Students can also download the solutions in PDF format for free.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles is a curated article by professionals at GFG, to help students solve problems related to circles with ease. All the solutions provided here are factually correct and . The NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles covered a variety of issues, including how to determine the separation between equal chords from the centre and the angles that a ...
Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Exercise 10.1 (Ex 10.1) and all chapter exercises at one place prepared by expert teacher as per NCERT (CBSE) books guidelines. Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles Exercise 10.1 Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks. Register and get all exercise solutions in your emails.
NCERT Maths Class 9 Textbook Solutions is solved by expert teachers provide you a strong foundation in the subject Maths. The 9th CBSE Maths Solutions are solved keeping various parameters in mind such as stepwise marks, formulas, mark distribution, etc., This in turn, helps you not to lose even a single mark.
These NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths solutions are designed by our subject experts with respect to the CBSE syllabus (2023-2024) for Chapter 10 based on the topics given below: Circles and their related terms like arc, sector, chords, semicircle, segments, etc. The angle subtended by chords of a circle at a point and theorems based on it.
The NCERT solutions for class 9 maths chapter 10 exercise 10.5 has twelve questions based on the topics and theorems of the angle subtended by an arc of a circle. There are a total of 6 theorems covered under this topic. The first theorem states that the angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on ...
Mathematics Assignment Class 10 Chapter 9. Application of Trigonometry. Question 1. From the window 15 m high above the ground in a street, the angles of elevation and depression of the top and foot of another house on the opposite side of the street are 30o and 45o respectively. Find the height of the opposite house.
All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Class 9. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Mathematics class 9 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 9 Mathematics Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
This Post Has 3 Comments. Download Class 9 Maths, Chapter 10 Notes, Congruent Triangles that contains Solutions of All Exercises, Review Exercises, MCQ's in PDF for free.
Get here the updated NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Math Chapter 10 Heron's Formula Exercise 10.1 in Hindi and English Language format. Question Answers are given given below and these are updated for new academic year 2023-24. UP Board Students can also use these solutions for there board exams.
Chapter wise assignments for class 9 Maths are given below updated for new academic session 2023-24. These assignments will be available in updated form along with new assignments and chapter wise tests with solutions. After the completion of chapters from NCERT Books and Exemplar Books, students should go for Assignments. ...
Topics Covered in Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles: Through examples, arrive at definitions of circle-related concepts, radius, circumference, diameter, chord, arc, and subtended angle. 1. (Prove) Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre and (motivate) its converse. 2. (Motivate) The perpendicular from the centre of a circle ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Exercise 10.4. Question 1. Two circles of radii 5 cm and 3 cm intersect at two points and the distance between their centers is 4 cm. Find the length of the common chord. Solution: Let two circles with centres O and O' intersect each other at points A and B. On joining A and B, AB is a common chord.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 - Circles Exercise 10.5 is provided here, in downloadable PDF format. Click on the specified link given below to download it. These solutions have been designed by our Maths experts, to make each student understand the concepts in a better way. The answers given for each question in NCERT solutions ...
Basic concepts, definitions and formulas of mathematics, mathematics assignments for 9th standard to 10+2 standard, maths study material for 8th, 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th classes, Mathematics lesson plan for classes 8th,10th and 12th standard, Interesting maths riddles and maths magic, Class-wise mathematics study material for students from 8th to 12.