Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples

What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples
Published on March 31, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on June 22, 2023.
An observational study is used to answer a research question based purely on what the researcher observes. There is no interference or manipulation of the research subjects, and no control and treatment groups .
These studies are often qualitative in nature and can be used for both exploratory and explanatory research purposes. While quantitative observational studies exist, they are less common.
Observational studies are generally used in hard science, medical, and social science fields. This is often due to ethical or practical concerns that prevent the researcher from conducting a traditional experiment . However, the lack of control and treatment groups means that forming inferences is difficult, and there is a risk of confounding variables and observer bias impacting your analysis.
Table of contents
Types of observation, types of observational studies, observational study example, advantages and disadvantages of observational studies, observational study vs. experiment, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
There are many types of observation, and it can be challenging to tell the difference between them. Here are some of the most common types to help you choose the best one for your observational study.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
There are three main types of observational studies: cohort studies, case–control studies, and cross-sectional studies .
Cohort studies
Cohort studies are more longitudinal in nature, as they follow a group of participants over a period of time. Members of the cohort are selected because of a shared characteristic, such as smoking, and they are often observed over a period of years.
Case–control studies
Case–control studies bring together two groups, a case study group and a control group . The case study group has a particular attribute while the control group does not. The two groups are then compared, to see if the case group exhibits a particular characteristic more than the control group.
For example, if you compared smokers (the case study group) with non-smokers (the control group), you could observe whether the smokers had more instances of lung disease than the non-smokers.
Cross-sectional studies
Cross-sectional studies analyze a population of study at a specific point in time.
This often involves narrowing previously collected data to one point in time to test the prevalence of a theory—for example, analyzing how many people were diagnosed with lung disease in March of a given year. It can also be a one-time observation, such as spending one day in the lung disease wing of a hospital.
Observational studies are usually quite straightforward to design and conduct. Sometimes all you need is a notebook and pen! As you design your study, you can follow these steps.
Step 1: Identify your research topic and objectives
The first step is to determine what you’re interested in observing and why. Observational studies are a great fit if you are unable to do an experiment for practical or ethical reasons , or if your research topic hinges on natural behaviors.
Step 2: Choose your observation type and technique
In terms of technique, there are a few things to consider:
- Are you determining what you want to observe beforehand, or going in open-minded?
- Is there another research method that would make sense in tandem with an observational study?
- If yes, make sure you conduct a covert observation.
- If not, think about whether observing from afar or actively participating in your observation is a better fit.
- How can you preempt confounding variables that could impact your analysis?
- You could observe the children playing at the playground in a naturalistic observation.
- You could spend a month at a day care in your town conducting participant observation, immersing yourself in the day-to-day life of the children.
- You could conduct covert observation behind a wall or glass, where the children can’t see you.
Overall, it is crucial to stay organized. Devise a shorthand for your notes, or perhaps design templates that you can fill in. Since these observations occur in real time, you won’t get a second chance with the same data.
Step 3: Set up your observational study
Before conducting your observations, there are a few things to attend to:
- Plan ahead: If you’re interested in day cares, you’ll need to call a few in your area to plan a visit. They may not all allow observation, or consent from parents may be needed, so give yourself enough time to set everything up.
- Determine your note-taking method: Observational studies often rely on note-taking because other methods, like video or audio recording, run the risk of changing participant behavior.
- Get informed consent from your participants (or their parents) if you want to record: Ultimately, even though it may make your analysis easier, the challenges posed by recording participants often make pen-and-paper a better choice.
Step 4: Conduct your observation
After you’ve chosen a type of observation, decided on your technique, and chosen a time and place, it’s time to conduct your observation.
Here, you can split them into case and control groups. The children with siblings have a characteristic you are interested in (siblings), while the children in the control group do not.
When conducting observational studies, be very careful of confounding or “lurking” variables. In the example above, you observed children as they were dropped off, gauging whether or not they were upset. However, there are a variety of other factors that could be at play here (e.g., illness).
Step 5: Analyze your data
After you finish your observation, immediately record your initial thoughts and impressions, as well as follow-up questions or any issues you perceived during the observation. If you audio- or video-recorded your observations, you can transcribe them.
Your analysis can take an inductive or deductive approach :
- If you conducted your observations in a more open-ended way, an inductive approach allows your data to determine your themes.
- If you had specific hypotheses prior to conducting your observations, a deductive approach analyzes whether your data confirm those themes or ideas you had previously.
Next, you can conduct your thematic or content analysis . Due to the open-ended nature of observational studies, the best fit is likely thematic analysis .
Step 6: Discuss avenues for future research
Observational studies are generally exploratory in nature, and they often aren’t strong enough to yield standalone conclusions due to their very high susceptibility to observer bias and confounding variables. For this reason, observational studies can only show association, not causation .
If you are excited about the preliminary conclusions you’ve drawn and wish to proceed with your topic, you may need to change to a different research method , such as an experiment.
- Observational studies can provide information about difficult-to-analyze topics in a low-cost, efficient manner.
- They allow you to study subjects that cannot be randomized safely, efficiently, or ethically .
- They are often quite straightforward to conduct, since you just observe participant behavior as it happens or utilize preexisting data.
- They’re often invaluable in informing later, larger-scale clinical trials or experimental designs.
Disadvantages
- Observational studies struggle to stand on their own as a reliable research method. There is a high risk of observer bias and undetected confounding variables or omitted variables .
- They lack conclusive results, typically are not externally valid or generalizable, and can usually only form a basis for further research.
- They cannot make statements about the safety or efficacy of the intervention or treatment they study, only observe reactions to it. Therefore, they offer less satisfying results than other methods.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The key difference between observational studies and experiments is that a properly conducted observational study will never attempt to influence responses, while experimental designs by definition have some sort of treatment condition applied to a portion of participants.
However, there may be times when it’s impossible, dangerous, or impractical to influence the behavior of your participants. This can be the case in medical studies, where it is unethical or cruel to withhold potentially life-saving intervention, or in longitudinal analyses where you don’t have the ability to follow your group over the course of their lifetime.
An observational study may be the right fit for your research if random assignment of participants to control and treatment groups is impossible or highly difficult. However, the issues observational studies raise in terms of validity , confounding variables, and conclusiveness can mean that an experiment is more reliable.
If you’re able to randomize your participants safely and your research question is definitely causal in nature, consider using an experiment.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
An observational study is a great choice for you if your research question is based purely on observations. If there are ethical, logistical, or practical concerns that prevent you from conducting a traditional experiment , an observational study may be a good choice. In an observational study, there is no interference or manipulation of the research subjects, as well as no control or treatment groups .
The key difference between observational studies and experimental designs is that a well-done observational study does not influence the responses of participants, while experiments do have some sort of treatment condition applied to at least some participants by random assignment .
A quasi-experiment is a type of research design that attempts to establish a cause-and-effect relationship. The main difference with a true experiment is that the groups are not randomly assigned.
Exploratory research aims to explore the main aspects of an under-researched problem, while explanatory research aims to explain the causes and consequences of a well-defined problem.
Experimental design means planning a set of procedures to investigate a relationship between variables . To design a controlled experiment, you need:
- A testable hypothesis
- At least one independent variable that can be precisely manipulated
- At least one dependent variable that can be precisely measured
When designing the experiment, you decide:
- How you will manipulate the variable(s)
- How you will control for any potential confounding variables
- How many subjects or samples will be included in the study
- How subjects will be assigned to treatment levels
Experimental design is essential to the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, June 22). What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/observational-study/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, naturalistic observation | definition, guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Case Study Observational Research: A Framework for Conducting Case Study Research Where Observation Data Are the Focus
Affiliation.
- 1 1 University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand.
- PMID: 27217290
- DOI: 10.1177/1049732316649160
Case study research is a comprehensive method that incorporates multiple sources of data to provide detailed accounts of complex research phenomena in real-life contexts. However, current models of case study research do not particularly distinguish the unique contribution observation data can make. Observation methods have the potential to reach beyond other methods that rely largely or solely on self-report. This article describes the distinctive characteristics of case study observational research, a modified form of Yin's 2014 model of case study research the authors used in a study exploring interprofessional collaboration in primary care. In this approach, observation data are positioned as the central component of the research design. Case study observational research offers a promising approach for researchers in a wide range of health care settings seeking more complete understandings of complex topics, where contextual influences are of primary concern. Future research is needed to refine and evaluate the approach.
Keywords: New Zealand; appreciative inquiry; case studies; case study observational research; health care; interprofessional collaboration; naturalistic inquiry; observation; primary health care; qualitative; research design.
- Observational Studies as Topic / methods*
- Observational Studies as Topic / standards
- Primary Health Care / organization & administration
- Research Design*
- Self Report / standards

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.6: Observational Research
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 19655

- Rajiv S. Jhangiani, I-Chant A. Chiang, Carrie Cuttler, & Dana C. Leighton
- Kwantlen Polytechnic U., Washington State U., & Texas A&M U.—Texarkana
Learning Objectives
- List the various types of observational research methods and distinguish between each.
- Describe the strengths and weakness of each observational research method.
What Is Observational Research?
The term observational research is used to refer to several different types of non-experimental studies in which behavior is systematically observed and recorded. The goal of observational research is to describe a variable or set of variables. More generally, the goal is to obtain a snapshot of specific characteristics of an individual, group, or setting. As described previously, observational research is non-experimental because nothing is manipulated or controlled, and as such we cannot arrive at causal conclusions using this approach. The data that are collected in observational research studies are often qualitative in nature but they may also be quantitative or both (mixed-methods). There are several different types of observational methods that will be described below.
Naturalistic Observation
Naturalistic observation is an observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. Thus naturalistic observation is a type of field research (as opposed to a type of laboratory research). Jane Goodall’s famous research on chimpanzees is a classic example of naturalistic observation. Dr. Goodall spent three decades observing chimpanzees in their natural environment in East Africa. She examined such things as chimpanzee’s social structure, mating patterns, gender roles, family structure, and care of offspring by observing them in the wild. However, naturalistic observation could more simply involve observing shoppers in a grocery store, children on a school playground, or psychiatric inpatients in their wards. Researchers engaged in naturalistic observation usually make their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied. Such an approach is called disguised naturalistic observation. Ethically, this method is considered to be acceptable if the participants remain anonymous and the behavior occurs in a public setting where people would not normally have an expectation of privacy. Grocery shoppers putting items into their shopping carts, for example, are engaged in public behavior that is easily observable by store employees and other shoppers. For this reason, most researchers would consider it ethically acceptable to observe them for a study. On the other hand, one of the arguments against the ethicality of the naturalistic observation of “bathroom behavior” discussed earlier in the book is that people have a reasonable expectation of privacy even in a public restroom and that this expectation was violated.
In cases where it is not ethical or practical to conduct disguised naturalistic observation, researchers can conduct undisguised naturalistic observation where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior. However, one concern with undisguised naturalistic observation is reactivity. Reactivity refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior. In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, the concern with reactivity is that when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would. This type of reactivity is known as the Hawthorne effect . For instance, you may act much differently in a bar if you know that someone is observing you and recording your behaviors and this would invalidate the study. So disguised observation is less reactive and therefore can have higher validity because people are not aware that their behaviors are being observed and recorded. However, we now know that people often become used to being observed and with time they begin to behave naturally in the researcher’s presence. In other words, over time people habituate to being observed. Think about reality shows like Big Brother or Survivor where people are constantly being observed and recorded. While they may be on their best behavior at first, in a fairly short amount of time they are flirting, having sex, wearing next to nothing, screaming at each other, and occasionally behaving in ways that are embarrassing.
Participant Observation
Another approach to data collection in observational research is participant observation. In participant observation , researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying. Participant observation is very similar to naturalistic observation in that it involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. As with naturalistic observation, the data that are collected can include interviews (usually unstructured), notes based on their observations and interactions, documents, photographs, and other artifacts. The only difference between naturalistic observation and participant observation is that researchers engaged in participant observation become active members of the group or situations they are studying. The basic rationale for participant observation is that there may be important information that is only accessible to, or can be interpreted only by, someone who is an active participant in the group or situation. Like naturalistic observation, participant observation can be either disguised or undisguised. In disguised participant observation, the researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
In a famous example of disguised participant observation, Leon Festinger and his colleagues infiltrated a doomsday cult known as the Seekers, whose members believed that the apocalypse would occur on December 21, 1954. Interested in studying how members of the group would cope psychologically when the prophecy inevitably failed, they carefully recorded the events and reactions of the cult members in the days before and after the supposed end of the world. Unsurprisingly, the cult members did not give up their belief but instead convinced themselves that it was their faith and efforts that saved the world from destruction. Festinger and his colleagues later published a book about this experience, which they used to illustrate the theory of cognitive dissonance (Festinger, Riecken, & Schachter, 1956) [1] .
In contrast with undisguised participant observation, the researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation. Once again there are important ethical issues to consider with disguised participant observation. First no informed consent can be obtained and second deception is being used. The researcher is deceiving the participants by intentionally withholding information about their motivations for being a part of the social group they are studying. But sometimes disguised participation is the only way to access a protective group (like a cult). Further, disguised participant observation is less prone to reactivity than undisguised participant observation.
Rosenhan’s study (1973) [2] of the experience of people in a psychiatric ward would be considered disguised participant observation because Rosenhan and his pseudopatients were admitted into psychiatric hospitals on the pretense of being patients so that they could observe the way that psychiatric patients are treated by staff. The staff and other patients were unaware of their true identities as researchers.
Another example of participant observation comes from a study by sociologist Amy Wilkins on a university-based religious organization that emphasized how happy its members were (Wilkins, 2008) [3] . Wilkins spent 12 months attending and participating in the group’s meetings and social events, and she interviewed several group members. In her study, Wilkins identified several ways in which the group “enforced” happiness—for example, by continually talking about happiness, discouraging the expression of negative emotions, and using happiness as a way to distinguish themselves from other groups.
One of the primary benefits of participant observation is that the researchers are in a much better position to understand the viewpoint and experiences of the people they are studying when they are a part of the social group. The primary limitation with this approach is that the mere presence of the observer could affect the behavior of the people being observed. While this is also a concern with naturalistic observation, additional concerns arise when researchers become active members of the social group they are studying because that they may change the social dynamics and/or influence the behavior of the people they are studying. Similarly, if the researcher acts as a participant observer there can be concerns with biases resulting from developing relationships with the participants. Concretely, the researcher may become less objective resulting in more experimenter bias.
Structured Observation
Another observational method is structured observation . Here the investigator makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation. Often the setting in which the observations are made is not the natural setting. Instead, the researcher may observe people in the laboratory environment. Alternatively, the researcher may observe people in a natural setting (like a classroom setting) that they have structured some way, for instance by introducing some specific task participants are to engage in or by introducing a specific social situation or manipulation.
Structured observation is very similar to naturalistic observation and participant observation in that in all three cases researchers are observing naturally occurring behavior; however, the emphasis in structured observation is on gathering quantitative rather than qualitative data. Researchers using this approach are interested in a limited set of behaviors. This allows them to quantify the behaviors they are observing. In other words, structured observation is less global than naturalistic or participant observation because the researcher engaged in structured observations is interested in a small number of specific behaviors. Therefore, rather than recording everything that happens, the researcher only focuses on very specific behaviors of interest.
Researchers Robert Levine and Ara Norenzayan used structured observation to study differences in the “pace of life” across countries (Levine & Norenzayan, 1999) [4] . One of their measures involved observing pedestrians in a large city to see how long it took them to walk 60 feet. They found that people in some countries walked reliably faster than people in other countries. For example, people in Canada and Sweden covered 60 feet in just under 13 seconds on average, while people in Brazil and Romania took close to 17 seconds. When structured observation takes place in the complex and even chaotic “real world,” the questions of when, where, and under what conditions the observations will be made, and who exactly will be observed are important to consider. Levine and Norenzayan described their sampling process as follows:
“Male and female walking speed over a distance of 60 feet was measured in at least two locations in main downtown areas in each city. Measurements were taken during main business hours on clear summer days. All locations were flat, unobstructed, had broad sidewalks, and were sufficiently uncrowded to allow pedestrians to move at potentially maximum speeds. To control for the effects of socializing, only pedestrians walking alone were used. Children, individuals with obvious physical handicaps, and window-shoppers were not timed. Thirty-five men and 35 women were timed in most cities.” (p. 186).
Precise specification of the sampling process in this way makes data collection manageable for the observers, and it also provides some control over important extraneous variables. For example, by making their observations on clear summer days in all countries, Levine and Norenzayan controlled for effects of the weather on people’s walking speeds. In Levine and Norenzayan’s study, measurement was relatively straightforward. They simply measured out a 60-foot distance along a city sidewalk and then used a stopwatch to time participants as they walked over that distance.
As another example, researchers Robert Kraut and Robert Johnston wanted to study bowlers’ reactions to their shots, both when they were facing the pins and then when they turned toward their companions (Kraut & Johnston, 1979) [5] . But what “reactions” should they observe? Based on previous research and their own pilot testing, Kraut and Johnston created a list of reactions that included “closed smile,” “open smile,” “laugh,” “neutral face,” “look down,” “look away,” and “face cover” (covering one’s face with one’s hands). The observers committed this list to memory and then practiced by coding the reactions of bowlers who had been videotaped. During the actual study, the observers spoke into an audio recorder, describing the reactions they observed. Among the most interesting results of this study was that bowlers rarely smiled while they still faced the pins. They were much more likely to smile after they turned toward their companions, suggesting that smiling is not purely an expression of happiness but also a form of social communication.
In yet another example (this one in a laboratory environment), Dov Cohen and his colleagues had observers rate the emotional reactions of participants who had just been deliberately bumped and insulted by a confederate after they dropped off a completed questionnaire at the end of a hallway. The confederate was posing as someone who worked in the same building and who was frustrated by having to close a file drawer twice in order to permit the participants to walk past them (first to drop off the questionnaire at the end of the hallway and once again on their way back to the room where they believed the study they signed up for was taking place). The two observers were positioned at different ends of the hallway so that they could read the participants’ body language and hear anything they might say. Interestingly, the researchers hypothesized that participants from the southern United States, which is one of several places in the world that has a “culture of honor,” would react with more aggression than participants from the northern United States, a prediction that was in fact supported by the observational data (Cohen, Nisbett, Bowdle, & Schwarz, 1996) [6] .
When the observations require a judgment on the part of the observers—as in the studies by Kraut and Johnston and Cohen and his colleagues—a process referred to as coding is typically required . Coding generally requires clearly defining a set of target behaviors. The observers then categorize participants individually in terms of which behavior they have engaged in and the number of times they engaged in each behavior. The observers might even record the duration of each behavior. The target behaviors must be defined in such a way that guides different observers to code them in the same way. This difficulty with coding illustrates the issue of interrater reliability, as mentioned in Chapter 4. Researchers are expected to demonstrate the interrater reliability of their coding procedure by having multiple raters code the same behaviors independently and then showing that the different observers are in close agreement. Kraut and Johnston, for example, video recorded a subset of their participants’ reactions and had two observers independently code them. The two observers showed that they agreed on the reactions that were exhibited 97% of the time, indicating good interrater reliability.
One of the primary benefits of structured observation is that it is far more efficient than naturalistic and participant observation. Since the researchers are focused on specific behaviors this reduces time and expense. Also, often times the environment is structured to encourage the behaviors of interest which again means that researchers do not have to invest as much time in waiting for the behaviors of interest to naturally occur. Finally, researchers using this approach can clearly exert greater control over the environment. However, when researchers exert more control over the environment it may make the environment less natural which decreases external validity. It is less clear for instance whether structured observations made in a laboratory environment will generalize to a real world environment. Furthermore, since researchers engaged in structured observation are often not disguised there may be more concerns with reactivity.
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth examination of an individual. Sometimes case studies are also completed on social units (e.g., a cult) and events (e.g., a natural disaster). Most commonly in psychology, however, case studies provide a detailed description and analysis of an individual. Often the individual has a rare or unusual condition or disorder or has damage to a specific region of the brain.
Like many observational research methods, case studies tend to be more qualitative in nature. Case study methods involve an in-depth, and often a longitudinal examination of an individual. Depending on the focus of the case study, individuals may or may not be observed in their natural setting. If the natural setting is not what is of interest, then the individual may be brought into a therapist’s office or a researcher’s lab for study. Also, the bulk of the case study report will focus on in-depth descriptions of the person rather than on statistical analyses. With that said some quantitative data may also be included in the write-up of a case study. For instance, an individual’s depression score may be compared to normative scores or their score before and after treatment may be compared. As with other qualitative methods, a variety of different methods and tools can be used to collect information on the case. For instance, interviews, naturalistic observation, structured observation, psychological testing (e.g., IQ test), and/or physiological measurements (e.g., brain scans) may be used to collect information on the individual.
HM is one of the most notorious case studies in psychology. HM suffered from intractable and very severe epilepsy. A surgeon localized HM’s epilepsy to his medial temporal lobe and in 1953 he removed large sections of his hippocampus in an attempt to stop the seizures. The treatment was a success, in that it resolved his epilepsy and his IQ and personality were unaffected. However, the doctors soon realized that HM exhibited a strange form of amnesia, called anterograde amnesia. HM was able to carry out a conversation and he could remember short strings of letters, digits, and words. Basically, his short term memory was preserved. However, HM could not commit new events to memory. He lost the ability to transfer information from his short-term memory to his long term memory, something memory researchers call consolidation. So while he could carry on a conversation with someone, he would completely forget the conversation after it ended. This was an extremely important case study for memory researchers because it suggested that there’s a dissociation between short-term memory and long-term memory, it suggested that these were two different abilities sub-served by different areas of the brain. It also suggested that the temporal lobes are particularly important for consolidating new information (i.e., for transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory),
The history of psychology is filled with influential cases studies, such as Sigmund Freud’s description of “Anna O.” (see Note 6.1 “The Case of “Anna O.””) and John Watson and Rosalie Rayner’s description of Little Albert (Watson & Rayner, 1920) [7] , who allegedly learned to fear a white rat—along with other furry objects—when the researchers repeatedly made a loud noise every time the rat approached him.
The Case of “Anna O.”
Sigmund Freud used the case of a young woman he called “Anna O.” to illustrate many principles of his theory of psychoanalysis (Freud, 1961) [8] . (Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim, and she was an early feminist who went on to make important contributions to the field of social work.) Anna had come to Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer around 1880 with a variety of odd physical and psychological symptoms. One of them was that for several weeks she was unable to drink any fluids. According to Freud,
She would take up the glass of water that she longed for, but as soon as it touched her lips she would push it away like someone suffering from hydrophobia.…She lived only on fruit, such as melons, etc., so as to lessen her tormenting thirst. (p. 9)
But according to Freud, a breakthrough came one day while Anna was under hypnosis.
[S]he grumbled about her English “lady-companion,” whom she did not care for, and went on to describe, with every sign of disgust, how she had once gone into this lady’s room and how her little dog—horrid creature!—had drunk out of a glass there. The patient had said nothing, as she had wanted to be polite. After giving further energetic expression to the anger she had held back, she asked for something to drink, drank a large quantity of water without any difficulty, and awoke from her hypnosis with the glass at her lips; and thereupon the disturbance vanished, never to return. (p.9)
Freud’s interpretation was that Anna had repressed the memory of this incident along with the emotion that it triggered and that this was what had caused her inability to drink. Furthermore, he believed that her recollection of the incident, along with her expression of the emotion she had repressed, caused the symptom to go away.
As an illustration of Freud’s theory, the case study of Anna O. is quite effective. As evidence for the theory, however, it is essentially worthless. The description provides no way of knowing whether Anna had really repressed the memory of the dog drinking from the glass, whether this repression had caused her inability to drink, or whether recalling this “trauma” relieved the symptom. It is also unclear from this case study how typical or atypical Anna’s experience was.

Case studies are useful because they provide a level of detailed analysis not found in many other research methods and greater insights may be gained from this more detailed analysis. As a result of the case study, the researcher may gain a sharpened understanding of what might become important to look at more extensively in future more controlled research. Case studies are also often the only way to study rare conditions because it may be impossible to find a large enough sample of individuals with the condition to use quantitative methods. Although at first glance a case study of a rare individual might seem to tell us little about ourselves, they often do provide insights into normal behavior. The case of HM provided important insights into the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation.
However, it is important to note that while case studies can provide insights into certain areas and variables to study, and can be useful in helping develop theories, they should never be used as evidence for theories. In other words, case studies can be used as inspiration to formulate theories and hypotheses, but those hypotheses and theories then need to be formally tested using more rigorous quantitative methods. The reason case studies shouldn’t be used to provide support for theories is that they suffer from problems with both internal and external validity. Case studies lack the proper controls that true experiments contain. As such, they suffer from problems with internal validity, so they cannot be used to determine causation. For instance, during HM’s surgery, the surgeon may have accidentally lesioned another area of HM’s brain (a possibility suggested by the dissection of HM’s brain following his death) and that lesion may have contributed to his inability to consolidate new information. The fact is, with case studies we cannot rule out these sorts of alternative explanations. So, as with all observational methods, case studies do not permit determination of causation. In addition, because case studies are often of a single individual, and typically an abnormal individual, researchers cannot generalize their conclusions to other individuals. Recall that with most research designs there is a trade-off between internal and external validity. With case studies, however, there are problems with both internal validity and external validity. So there are limits both to the ability to determine causation and to generalize the results. A final limitation of case studies is that ample opportunity exists for the theoretical biases of the researcher to color or bias the case description. Indeed, there have been accusations that the woman who studied HM destroyed a lot of her data that were not published and she has been called into question for destroying contradictory data that didn’t support her theory about how memories are consolidated. There is a fascinating New York Times article that describes some of the controversies that ensued after HM’s death and analysis of his brain that can be found at: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/08/07/magazine/the-brain-that-couldnt-remember.html?_r=0
Archival Research
Another approach that is often considered observational research involves analyzing archival data that have already been collected for some other purpose. An example is a study by Brett Pelham and his colleagues on “implicit egotism”—the tendency for people to prefer people, places, and things that are similar to themselves (Pelham, Carvallo, & Jones, 2005) [9] . In one study, they examined Social Security records to show that women with the names Virginia, Georgia, Louise, and Florence were especially likely to have moved to the states of Virginia, Georgia, Louisiana, and Florida, respectively.
As with naturalistic observation, measurement can be more or less straightforward when working with archival data. For example, counting the number of people named Virginia who live in various states based on Social Security records is relatively straightforward. But consider a study by Christopher Peterson and his colleagues on the relationship between optimism and health using data that had been collected many years before for a study on adult development (Peterson, Seligman, & Vaillant, 1988) [10] . In the 1940s, healthy male college students had completed an open-ended questionnaire about difficult wartime experiences. In the late 1980s, Peterson and his colleagues reviewed the men’s questionnaire responses to obtain a measure of explanatory style—their habitual ways of explaining bad events that happen to them. More pessimistic people tend to blame themselves and expect long-term negative consequences that affect many aspects of their lives, while more optimistic people tend to blame outside forces and expect limited negative consequences. To obtain a measure of explanatory style for each participant, the researchers used a procedure in which all negative events mentioned in the questionnaire responses, and any causal explanations for them were identified and written on index cards. These were given to a separate group of raters who rated each explanation in terms of three separate dimensions of optimism-pessimism. These ratings were then averaged to produce an explanatory style score for each participant. The researchers then assessed the statistical relationship between the men’s explanatory style as undergraduate students and archival measures of their health at approximately 60 years of age. The primary result was that the more optimistic the men were as undergraduate students, the healthier they were as older men. Pearson’s r was +.25.
This method is an example of content analysis —a family of systematic approaches to measurement using complex archival data. Just as structured observation requires specifying the behaviors of interest and then noting them as they occur, content analysis requires specifying keywords, phrases, or ideas and then finding all occurrences of them in the data. These occurrences can then be counted, timed (e.g., the amount of time devoted to entertainment topics on the nightly news show), or analyzed in a variety of other ways.
- Festinger, L., Riecken, H., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails: A social and psychological study of a modern group that predicted the destruction of the world. University of Minnesota Press. ↵
- Rosenhan, D. L. (1973). On being sane in insane places. Science, 179 , 250–258. ↵
- Wilkins, A. (2008). “Happier than Non-Christians”: Collective emotions and symbolic boundaries among evangelical Christians. Social Psychology Quarterly, 71 , 281–301. ↵
- Levine, R. V., & Norenzayan, A. (1999). The pace of life in 31 countries. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 30 , 178–205. ↵
- Kraut, R. E., & Johnston, R. E. (1979). Social and emotional messages of smiling: An ethological approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 , 1539–1553. ↵
- Cohen, D., Nisbett, R. E., Bowdle, B. F., & Schwarz, N. (1996). Insult, aggression, and the southern culture of honor: An "experimental ethnography." Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70 (5), 945-960. ↵
- Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 3 , 1–14. ↵
- Freud, S. (1961). Five lectures on psycho-analysis . New York, NY: Norton. ↵
- Pelham, B. W., Carvallo, M., & Jones, J. T. (2005). Implicit egotism. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14 , 106–110. ↵
- Peterson, C., Seligman, M. E. P., & Vaillant, G. E. (1988). Pessimistic explanatory style is a risk factor for physical illness: A thirty-five year longitudinal study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 23–27. ↵

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Non-Experimental Research
32 Observational Research
Learning objectives.
- List the various types of observational research methods and distinguish between each.
- Describe the strengths and weakness of each observational research method.
What Is Observational Research?
The term observational research is used to refer to several different types of non-experimental studies in which behavior is systematically observed and recorded. The goal of observational research is to describe a variable or set of variables. More generally, the goal is to obtain a snapshot of specific characteristics of an individual, group, or setting. As described previously, observational research is non-experimental because nothing is manipulated or controlled, and as such we cannot arrive at causal conclusions using this approach. The data that are collected in observational research studies are often qualitative in nature but they may also be quantitative or both (mixed-methods). There are several different types of observational methods that will be described below.
Naturalistic Observation
Naturalistic observation is an observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. Thus naturalistic observation is a type of field research (as opposed to a type of laboratory research). Jane Goodall’s famous research on chimpanzees is a classic example of naturalistic observation. Dr. Goodall spent three decades observing chimpanzees in their natural environment in East Africa. She examined such things as chimpanzee’s social structure, mating patterns, gender roles, family structure, and care of offspring by observing them in the wild. However, naturalistic observation could more simply involve observing shoppers in a grocery store, children on a school playground, or psychiatric inpatients in their wards. Researchers engaged in naturalistic observation usually make their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied. Such an approach is called disguised naturalistic observation . Ethically, this method is considered to be acceptable if the participants remain anonymous and the behavior occurs in a public setting where people would not normally have an expectation of privacy. Grocery shoppers putting items into their shopping carts, for example, are engaged in public behavior that is easily observable by store employees and other shoppers. For this reason, most researchers would consider it ethically acceptable to observe them for a study. On the other hand, one of the arguments against the ethicality of the naturalistic observation of “bathroom behavior” discussed earlier in the book is that people have a reasonable expectation of privacy even in a public restroom and that this expectation was violated.
In cases where it is not ethical or practical to conduct disguised naturalistic observation, researchers can conduct undisguised naturalistic observation where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior. However, one concern with undisguised naturalistic observation is reactivity. Reactivity refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior. In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, the concern with reactivity is that when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would. This type of reactivity is known as the Hawthorne effect . For instance, you may act much differently in a bar if you know that someone is observing you and recording your behaviors and this would invalidate the study. So disguised observation is less reactive and therefore can have higher validity because people are not aware that their behaviors are being observed and recorded. However, we now know that people often become used to being observed and with time they begin to behave naturally in the researcher’s presence. In other words, over time people habituate to being observed. Think about reality shows like Big Brother or Survivor where people are constantly being observed and recorded. While they may be on their best behavior at first, in a fairly short amount of time they are flirting, having sex, wearing next to nothing, screaming at each other, and occasionally behaving in ways that are embarrassing.
Participant Observation
Another approach to data collection in observational research is participant observation. In participant observation , researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying. Participant observation is very similar to naturalistic observation in that it involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs. As with naturalistic observation, the data that are collected can include interviews (usually unstructured), notes based on their observations and interactions, documents, photographs, and other artifacts. The only difference between naturalistic observation and participant observation is that researchers engaged in participant observation become active members of the group or situations they are studying. The basic rationale for participant observation is that there may be important information that is only accessible to, or can be interpreted only by, someone who is an active participant in the group or situation. Like naturalistic observation, participant observation can be either disguised or undisguised. In disguised participant observation , the researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
In a famous example of disguised participant observation, Leon Festinger and his colleagues infiltrated a doomsday cult known as the Seekers, whose members believed that the apocalypse would occur on December 21, 1954. Interested in studying how members of the group would cope psychologically when the prophecy inevitably failed, they carefully recorded the events and reactions of the cult members in the days before and after the supposed end of the world. Unsurprisingly, the cult members did not give up their belief but instead convinced themselves that it was their faith and efforts that saved the world from destruction. Festinger and his colleagues later published a book about this experience, which they used to illustrate the theory of cognitive dissonance (Festinger, Riecken, & Schachter, 1956) [1] .
In contrast with undisguised participant observation , the researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation. Once again there are important ethical issues to consider with disguised participant observation. First no informed consent can be obtained and second deception is being used. The researcher is deceiving the participants by intentionally withholding information about their motivations for being a part of the social group they are studying. But sometimes disguised participation is the only way to access a protective group (like a cult). Further, disguised participant observation is less prone to reactivity than undisguised participant observation.
Rosenhan’s study (1973) [2] of the experience of people in a psychiatric ward would be considered disguised participant observation because Rosenhan and his pseudopatients were admitted into psychiatric hospitals on the pretense of being patients so that they could observe the way that psychiatric patients are treated by staff. The staff and other patients were unaware of their true identities as researchers.
Another example of participant observation comes from a study by sociologist Amy Wilkins on a university-based religious organization that emphasized how happy its members were (Wilkins, 2008) [3] . Wilkins spent 12 months attending and participating in the group’s meetings and social events, and she interviewed several group members. In her study, Wilkins identified several ways in which the group “enforced” happiness—for example, by continually talking about happiness, discouraging the expression of negative emotions, and using happiness as a way to distinguish themselves from other groups.
One of the primary benefits of participant observation is that the researchers are in a much better position to understand the viewpoint and experiences of the people they are studying when they are a part of the social group. The primary limitation with this approach is that the mere presence of the observer could affect the behavior of the people being observed. While this is also a concern with naturalistic observation, additional concerns arise when researchers become active members of the social group they are studying because that they may change the social dynamics and/or influence the behavior of the people they are studying. Similarly, if the researcher acts as a participant observer there can be concerns with biases resulting from developing relationships with the participants. Concretely, the researcher may become less objective resulting in more experimenter bias.
Structured Observation
Another observational method is structured observation . Here the investigator makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation. Often the setting in which the observations are made is not the natural setting. Instead, the researcher may observe people in the laboratory environment. Alternatively, the researcher may observe people in a natural setting (like a classroom setting) that they have structured some way, for instance by introducing some specific task participants are to engage in or by introducing a specific social situation or manipulation.
Structured observation is very similar to naturalistic observation and participant observation in that in all three cases researchers are observing naturally occurring behavior; however, the emphasis in structured observation is on gathering quantitative rather than qualitative data. Researchers using this approach are interested in a limited set of behaviors. This allows them to quantify the behaviors they are observing. In other words, structured observation is less global than naturalistic or participant observation because the researcher engaged in structured observations is interested in a small number of specific behaviors. Therefore, rather than recording everything that happens, the researcher only focuses on very specific behaviors of interest.
Researchers Robert Levine and Ara Norenzayan used structured observation to study differences in the “pace of life” across countries (Levine & Norenzayan, 1999) [4] . One of their measures involved observing pedestrians in a large city to see how long it took them to walk 60 feet. They found that people in some countries walked reliably faster than people in other countries. For example, people in Canada and Sweden covered 60 feet in just under 13 seconds on average, while people in Brazil and Romania took close to 17 seconds. When structured observation takes place in the complex and even chaotic “real world,” the questions of when, where, and under what conditions the observations will be made, and who exactly will be observed are important to consider. Levine and Norenzayan described their sampling process as follows:
“Male and female walking speed over a distance of 60 feet was measured in at least two locations in main downtown areas in each city. Measurements were taken during main business hours on clear summer days. All locations were flat, unobstructed, had broad sidewalks, and were sufficiently uncrowded to allow pedestrians to move at potentially maximum speeds. To control for the effects of socializing, only pedestrians walking alone were used. Children, individuals with obvious physical handicaps, and window-shoppers were not timed. Thirty-five men and 35 women were timed in most cities.” (p. 186).
Precise specification of the sampling process in this way makes data collection manageable for the observers, and it also provides some control over important extraneous variables. For example, by making their observations on clear summer days in all countries, Levine and Norenzayan controlled for effects of the weather on people’s walking speeds. In Levine and Norenzayan’s study, measurement was relatively straightforward. They simply measured out a 60-foot distance along a city sidewalk and then used a stopwatch to time participants as they walked over that distance.
As another example, researchers Robert Kraut and Robert Johnston wanted to study bowlers’ reactions to their shots, both when they were facing the pins and then when they turned toward their companions (Kraut & Johnston, 1979) [5] . But what “reactions” should they observe? Based on previous research and their own pilot testing, Kraut and Johnston created a list of reactions that included “closed smile,” “open smile,” “laugh,” “neutral face,” “look down,” “look away,” and “face cover” (covering one’s face with one’s hands). The observers committed this list to memory and then practiced by coding the reactions of bowlers who had been videotaped. During the actual study, the observers spoke into an audio recorder, describing the reactions they observed. Among the most interesting results of this study was that bowlers rarely smiled while they still faced the pins. They were much more likely to smile after they turned toward their companions, suggesting that smiling is not purely an expression of happiness but also a form of social communication.
In yet another example (this one in a laboratory environment), Dov Cohen and his colleagues had observers rate the emotional reactions of participants who had just been deliberately bumped and insulted by a confederate after they dropped off a completed questionnaire at the end of a hallway. The confederate was posing as someone who worked in the same building and who was frustrated by having to close a file drawer twice in order to permit the participants to walk past them (first to drop off the questionnaire at the end of the hallway and once again on their way back to the room where they believed the study they signed up for was taking place). The two observers were positioned at different ends of the hallway so that they could read the participants’ body language and hear anything they might say. Interestingly, the researchers hypothesized that participants from the southern United States, which is one of several places in the world that has a “culture of honor,” would react with more aggression than participants from the northern United States, a prediction that was in fact supported by the observational data (Cohen, Nisbett, Bowdle, & Schwarz, 1996) [6] .
When the observations require a judgment on the part of the observers—as in the studies by Kraut and Johnston and Cohen and his colleagues—a process referred to as coding is typically required . Coding generally requires clearly defining a set of target behaviors. The observers then categorize participants individually in terms of which behavior they have engaged in and the number of times they engaged in each behavior. The observers might even record the duration of each behavior. The target behaviors must be defined in such a way that guides different observers to code them in the same way. This difficulty with coding illustrates the issue of interrater reliability, as mentioned in Chapter 4. Researchers are expected to demonstrate the interrater reliability of their coding procedure by having multiple raters code the same behaviors independently and then showing that the different observers are in close agreement. Kraut and Johnston, for example, video recorded a subset of their participants’ reactions and had two observers independently code them. The two observers showed that they agreed on the reactions that were exhibited 97% of the time, indicating good interrater reliability.
One of the primary benefits of structured observation is that it is far more efficient than naturalistic and participant observation. Since the researchers are focused on specific behaviors this reduces time and expense. Also, often times the environment is structured to encourage the behaviors of interest which again means that researchers do not have to invest as much time in waiting for the behaviors of interest to naturally occur. Finally, researchers using this approach can clearly exert greater control over the environment. However, when researchers exert more control over the environment it may make the environment less natural which decreases external validity. It is less clear for instance whether structured observations made in a laboratory environment will generalize to a real world environment. Furthermore, since researchers engaged in structured observation are often not disguised there may be more concerns with reactivity.
Case Studies
A case study is an in-depth examination of an individual. Sometimes case studies are also completed on social units (e.g., a cult) and events (e.g., a natural disaster). Most commonly in psychology, however, case studies provide a detailed description and analysis of an individual. Often the individual has a rare or unusual condition or disorder or has damage to a specific region of the brain.
Like many observational research methods, case studies tend to be more qualitative in nature. Case study methods involve an in-depth, and often a longitudinal examination of an individual. Depending on the focus of the case study, individuals may or may not be observed in their natural setting. If the natural setting is not what is of interest, then the individual may be brought into a therapist’s office or a researcher’s lab for study. Also, the bulk of the case study report will focus on in-depth descriptions of the person rather than on statistical analyses. With that said some quantitative data may also be included in the write-up of a case study. For instance, an individual’s depression score may be compared to normative scores or their score before and after treatment may be compared. As with other qualitative methods, a variety of different methods and tools can be used to collect information on the case. For instance, interviews, naturalistic observation, structured observation, psychological testing (e.g., IQ test), and/or physiological measurements (e.g., brain scans) may be used to collect information on the individual.
HM is one of the most notorious case studies in psychology. HM suffered from intractable and very severe epilepsy. A surgeon localized HM’s epilepsy to his medial temporal lobe and in 1953 he removed large sections of his hippocampus in an attempt to stop the seizures. The treatment was a success, in that it resolved his epilepsy and his IQ and personality were unaffected. However, the doctors soon realized that HM exhibited a strange form of amnesia, called anterograde amnesia. HM was able to carry out a conversation and he could remember short strings of letters, digits, and words. Basically, his short term memory was preserved. However, HM could not commit new events to memory. He lost the ability to transfer information from his short-term memory to his long term memory, something memory researchers call consolidation. So while he could carry on a conversation with someone, he would completely forget the conversation after it ended. This was an extremely important case study for memory researchers because it suggested that there’s a dissociation between short-term memory and long-term memory, it suggested that these were two different abilities sub-served by different areas of the brain. It also suggested that the temporal lobes are particularly important for consolidating new information (i.e., for transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory).

The history of psychology is filled with influential cases studies, such as Sigmund Freud’s description of “Anna O.” (see Note 6.1 “The Case of “Anna O.””) and John Watson and Rosalie Rayner’s description of Little Albert (Watson & Rayner, 1920) [7] , who allegedly learned to fear a white rat—along with other furry objects—when the researchers repeatedly made a loud noise every time the rat approached him.
The Case of “Anna O.”
Sigmund Freud used the case of a young woman he called “Anna O.” to illustrate many principles of his theory of psychoanalysis (Freud, 1961) [8] . (Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim, and she was an early feminist who went on to make important contributions to the field of social work.) Anna had come to Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer around 1880 with a variety of odd physical and psychological symptoms. One of them was that for several weeks she was unable to drink any fluids. According to Freud,
She would take up the glass of water that she longed for, but as soon as it touched her lips she would push it away like someone suffering from hydrophobia.…She lived only on fruit, such as melons, etc., so as to lessen her tormenting thirst. (p. 9)
But according to Freud, a breakthrough came one day while Anna was under hypnosis.
[S]he grumbled about her English “lady-companion,” whom she did not care for, and went on to describe, with every sign of disgust, how she had once gone into this lady’s room and how her little dog—horrid creature!—had drunk out of a glass there. The patient had said nothing, as she had wanted to be polite. After giving further energetic expression to the anger she had held back, she asked for something to drink, drank a large quantity of water without any difficulty, and awoke from her hypnosis with the glass at her lips; and thereupon the disturbance vanished, never to return. (p.9)
Freud’s interpretation was that Anna had repressed the memory of this incident along with the emotion that it triggered and that this was what had caused her inability to drink. Furthermore, he believed that her recollection of the incident, along with her expression of the emotion she had repressed, caused the symptom to go away.
As an illustration of Freud’s theory, the case study of Anna O. is quite effective. As evidence for the theory, however, it is essentially worthless. The description provides no way of knowing whether Anna had really repressed the memory of the dog drinking from the glass, whether this repression had caused her inability to drink, or whether recalling this “trauma” relieved the symptom. It is also unclear from this case study how typical or atypical Anna’s experience was.

Case studies are useful because they provide a level of detailed analysis not found in many other research methods and greater insights may be gained from this more detailed analysis. As a result of the case study, the researcher may gain a sharpened understanding of what might become important to look at more extensively in future more controlled research. Case studies are also often the only way to study rare conditions because it may be impossible to find a large enough sample of individuals with the condition to use quantitative methods. Although at first glance a case study of a rare individual might seem to tell us little about ourselves, they often do provide insights into normal behavior. The case of HM provided important insights into the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation.
However, it is important to note that while case studies can provide insights into certain areas and variables to study, and can be useful in helping develop theories, they should never be used as evidence for theories. In other words, case studies can be used as inspiration to formulate theories and hypotheses, but those hypotheses and theories then need to be formally tested using more rigorous quantitative methods. The reason case studies shouldn’t be used to provide support for theories is that they suffer from problems with both internal and external validity. Case studies lack the proper controls that true experiments contain. As such, they suffer from problems with internal validity, so they cannot be used to determine causation. For instance, during HM’s surgery, the surgeon may have accidentally lesioned another area of HM’s brain (a possibility suggested by the dissection of HM’s brain following his death) and that lesion may have contributed to his inability to consolidate new information. The fact is, with case studies we cannot rule out these sorts of alternative explanations. So, as with all observational methods, case studies do not permit determination of causation. In addition, because case studies are often of a single individual, and typically an abnormal individual, researchers cannot generalize their conclusions to other individuals. Recall that with most research designs there is a trade-off between internal and external validity. With case studies, however, there are problems with both internal validity and external validity. So there are limits both to the ability to determine causation and to generalize the results. A final limitation of case studies is that ample opportunity exists for the theoretical biases of the researcher to color or bias the case description. Indeed, there have been accusations that the woman who studied HM destroyed a lot of her data that were not published and she has been called into question for destroying contradictory data that didn’t support her theory about how memories are consolidated. There is a fascinating New York Times article that describes some of the controversies that ensued after HM’s death and analysis of his brain that can be found at: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/08/07/magazine/the-brain-that-couldnt-remember.html?_r=0
Archival Research
Another approach that is often considered observational research involves analyzing archival data that have already been collected for some other purpose. An example is a study by Brett Pelham and his colleagues on “implicit egotism”—the tendency for people to prefer people, places, and things that are similar to themselves (Pelham, Carvallo, & Jones, 2005) [9] . In one study, they examined Social Security records to show that women with the names Virginia, Georgia, Louise, and Florence were especially likely to have moved to the states of Virginia, Georgia, Louisiana, and Florida, respectively.
As with naturalistic observation, measurement can be more or less straightforward when working with archival data. For example, counting the number of people named Virginia who live in various states based on Social Security records is relatively straightforward. But consider a study by Christopher Peterson and his colleagues on the relationship between optimism and health using data that had been collected many years before for a study on adult development (Peterson, Seligman, & Vaillant, 1988) [10] . In the 1940s, healthy male college students had completed an open-ended questionnaire about difficult wartime experiences. In the late 1980s, Peterson and his colleagues reviewed the men’s questionnaire responses to obtain a measure of explanatory style—their habitual ways of explaining bad events that happen to them. More pessimistic people tend to blame themselves and expect long-term negative consequences that affect many aspects of their lives, while more optimistic people tend to blame outside forces and expect limited negative consequences. To obtain a measure of explanatory style for each participant, the researchers used a procedure in which all negative events mentioned in the questionnaire responses, and any causal explanations for them were identified and written on index cards. These were given to a separate group of raters who rated each explanation in terms of three separate dimensions of optimism-pessimism. These ratings were then averaged to produce an explanatory style score for each participant. The researchers then assessed the statistical relationship between the men’s explanatory style as undergraduate students and archival measures of their health at approximately 60 years of age. The primary result was that the more optimistic the men were as undergraduate students, the healthier they were as older men. Pearson’s r was +.25.
This method is an example of content analysis —a family of systematic approaches to measurement using complex archival data. Just as structured observation requires specifying the behaviors of interest and then noting them as they occur, content analysis requires specifying keywords, phrases, or ideas and then finding all occurrences of them in the data. These occurrences can then be counted, timed (e.g., the amount of time devoted to entertainment topics on the nightly news show), or analyzed in a variety of other ways.
Media Attributions
- What happens when you remove the hippocampus? – Sam Kean by TED-Ed licensed under a standard YouTube License
- Pappenheim 1882 by unknown is in the Public Domain .
- Festinger, L., Riecken, H., & Schachter, S. (1956). When prophecy fails: A social and psychological study of a modern group that predicted the destruction of the world. University of Minnesota Press. ↵
- Rosenhan, D. L. (1973). On being sane in insane places. Science, 179 , 250–258. ↵
- Wilkins, A. (2008). “Happier than Non-Christians”: Collective emotions and symbolic boundaries among evangelical Christians. Social Psychology Quarterly, 71 , 281–301. ↵
- Levine, R. V., & Norenzayan, A. (1999). The pace of life in 31 countries. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 30 , 178–205. ↵
- Kraut, R. E., & Johnston, R. E. (1979). Social and emotional messages of smiling: An ethological approach. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 , 1539–1553. ↵
- Cohen, D., Nisbett, R. E., Bowdle, B. F., & Schwarz, N. (1996). Insult, aggression, and the southern culture of honor: An "experimental ethnography." Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70 (5), 945-960. ↵
- Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 3 , 1–14. ↵
- Freud, S. (1961). Five lectures on psycho-analysis . New York, NY: Norton. ↵
- Pelham, B. W., Carvallo, M., & Jones, J. T. (2005). Implicit egotism. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14 , 106–110. ↵
- Peterson, C., Seligman, M. E. P., & Vaillant, G. E. (1988). Pessimistic explanatory style is a risk factor for physical illness: A thirty-five year longitudinal study. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 23–27. ↵
Research that is non-experimental because it focuses on recording systemic observations of behavior in a natural or laboratory setting without manipulating anything.
An observational method that involves observing people’s behavior in the environment in which it typically occurs.
When researchers engage in naturalistic observation by making their observations as unobtrusively as possible so that participants are not aware that they are being studied.
Where the participants are made aware of the researcher presence and monitoring of their behavior.
Refers to when a measure changes participants’ behavior.
In the case of undisguised naturalistic observation, it is a type of reactivity when people know they are being observed and studied, they may act differently than they normally would.
Researchers become active participants in the group or situation they are studying.
Researchers pretend to be members of the social group they are observing and conceal their true identity as researchers.
Researchers become a part of the group they are studying and they disclose their true identity as researchers to the group under investigation.
When a researcher makes careful observations of one or more specific behaviors in a particular setting that is more structured than the settings used in naturalistic or participant observation.
A part of structured observation whereby the observers use a clearly defined set of guidelines to "code" behaviors—assigning specific behaviors they are observing to a category—and count the number of times or the duration that the behavior occurs.
An in-depth examination of an individual.
A family of systematic approaches to measurement using qualitative methods to analyze complex archival data.
Research Methods in Psychology Copyright © 2019 by Rajiv S. Jhangiani, I-Chant A. Chiang, Carrie Cuttler, & Dana C. Leighton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.

Design Science Methodology for Information Systems and Software Engineering pp 225–245 Cite as
Observational Case Studies
- Roel J. Wieringa 2
- First Online: 01 January 2014
9620 Accesses
1 Citations
An observational case study is a study of a real-world case without performing an intervention. Measurement may influence the measured phenomena, but as in all forms of research, the researcher tries to restrict this to a minimum.
- Requirement Engineering
- Population Predicate
- Knowledge Question
- Analytical Induction
- Abductive Inference
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
D. Damian, J. Chisan, An empirical study of the complex relationships between requirements engineering processes and other processes that lead to payoffs in productivity, quality and risk management. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 32 (7), 433–453 (2006)
Article Google Scholar
M. Denscombe, The Good Research Guide For Small-Scale Social Research Projects , 4th edn. (Open University Press, Maidenhead, 2010)
Google Scholar
K.M. Eisenhardt, Building theories from case study research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 14 (4), 532–550 (1989)
B. Flyvberg, Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qual. Inq. 12 (2), 219–245 (2006)
R.L. Glass, Pilot studies: What, why, and how. J. Syst. Softw. 36 , 85–97 (1997)
M.M. Kennedy, Generalizing from single case studies. Eval. Q. 3 (4), 661–678 (1979)
B. Kitchenham, L. Pickard, S.L. Pfleeger, Case studies for method and tool evaluation. IEEE Softw. 12 (4), 52–62 (1995)
C. Robson, Real World Research , 2nd edn. (Blackwell, Oxford, 2002)
P. Runeson, M. Höst, A. Rainer, B. Regnell, Case Study Research in Software Engineering: Guidelines and Examples (Wiley, Hoboken, 2012)
Book Google Scholar
J.M. Verner, J. Sampson, V. Tosic, N.A.A. Bakar, B.A. Kitchenham, Guidelines for industrially-based multiple case studies in software engineering, in Research Challenges in Information Science, 2009. RCIS 2009. Third International Conference on , 2009, pp. 313–324
L. Warne, D. Hart, The impact of organizational politics on information systems project failure-a case study, in Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences , vol. 4, 1996, pp. 191–201
R.J. Wieringa, Towards a unified checklist for empirical research in software engineering: first proposal, in 16th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering (EASE 2012) , ed. by T. Baldaresse, M. Genero, E. Mendes, M. Piattini (IET, Ciudad Real, 2012), pp. 161–165
R.J. Wieringa, A unified checklist for observational and experimental research in software engineering (version 1). Technical Report TR-CTIT-12-07, Centre for Telematics and Information Technology University of Twente (2012)
R.K. Yin, Case Study research: Design and Methods (Sage, Thousand Oaks, 1984)
R.K. Yin, Case Study research: Design and Methods , 3rd edn. (Sage, Thousand Oaks, 2003)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands
Roel J. Wieringa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Wieringa, R.J. (2014). Observational Case Studies. In: Design Science Methodology for Information Systems and Software Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43839-8_17
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-43839-8_17
Published : 20 August 2014
Publisher Name : Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN : 978-3-662-43838-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-662-43839-8
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Designing and Conducting Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.
Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.
Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Becker, Bronwyn, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, & Mike Palmquist. (2005). Case Studies. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=60
Observation Method in Psychology: Naturalistic, Participant and Controlled
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
The observation method in psychology involves directly and systematically witnessing and recording measurable behaviors, actions, and responses in natural or contrived settings without attempting to intervene or manipulate what is being observed.
Used to describe phenomena, generate hypotheses, or validate self-reports, psychological observation can be either controlled or naturalistic with varying degrees of structure imposed by the researcher.
There are different types of observational methods, and distinctions need to be made between:
1. Controlled Observations 2. Naturalistic Observations 3. Participant Observations
In addition to the above categories, observations can also be either overt/disclosed (the participants know they are being studied) or covert/undisclosed (the researcher keeps their real identity a secret from the research subjects, acting as a genuine member of the group).
In general, conducting observational research is relatively inexpensive, but it remains highly time-consuming and resource-intensive in data processing and analysis.
The considerable investments needed in terms of coder time commitments for training, maintaining reliability, preventing drift, and coding complex dynamic interactions place practical barriers on observers with limited resources.
Controlled Observation
Controlled observation is a research method for studying behavior in a carefully controlled and structured environment.
The researcher sets specific conditions, variables, and procedures to systematically observe and measure behavior, allowing for greater control and comparison of different conditions or groups.
The researcher decides where the observation will occur, at what time, with which participants, and in what circumstances, and uses a standardized procedure. Participants are randomly allocated to each independent variable group.
Rather than writing a detailed description of all behavior observed, it is often easier to code behavior according to a previously agreed scale using a behavior schedule (i.e., conducting a structured observation).
The researcher systematically classifies the behavior they observe into distinct categories. Coding might involve numbers or letters to describe a characteristic or the use of a scale to measure behavior intensity.
The categories on the schedule are coded so that the data collected can be easily counted and turned into statistics.
For example, Mary Ainsworth used a behavior schedule to study how infants responded to brief periods of separation from their mothers. During the Strange Situation procedure, the infant’s interaction behaviors directed toward the mother were measured, e.g.,
- Proximity and contact-seeking
- Contact maintaining
- Avoidance of proximity and contact
- Resistance to contact and comforting
The observer noted down the behavior displayed during 15-second intervals and scored the behavior for intensity on a scale of 1 to 7.
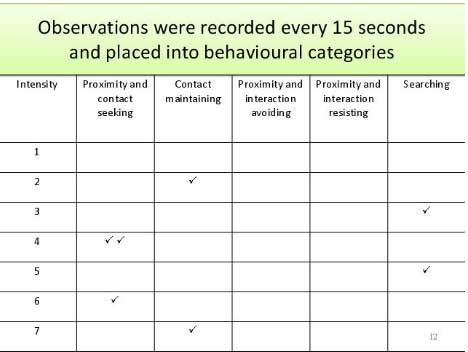
Sometimes participants’ behavior is observed through a two-way mirror, or they are secretly filmed. Albert Bandura used this method to study aggression in children (the Bobo doll studies ).
A lot of research has been carried out in sleep laboratories as well. Here, electrodes are attached to the scalp of participants. What is observed are the changes in electrical activity in the brain during sleep ( the machine is called an EEG ).
Controlled observations are usually overt as the researcher explains the research aim to the group so the participants know they are being observed.
Controlled observations are also usually non-participant as the researcher avoids direct contact with the group and keeps a distance (e.g., observing behind a two-way mirror).
- Controlled observations can be easily replicated by other researchers by using the same observation schedule. This means it is easy to test for reliability .
- The data obtained from structured observations is easier and quicker to analyze as it is quantitative (i.e., numerical) – making this a less time-consuming method compared to naturalistic observations.
- Controlled observations are fairly quick to conduct which means that many observations can take place within a short amount of time. This means a large sample can be obtained, resulting in the findings being representative and having the ability to be generalized to a large population.
Limitations
- Controlled observations can lack validity due to the Hawthorne effect /demand characteristics. When participants know they are being watched, they may act differently.
Naturalistic Observation
Naturalistic observation is a research method in which the researcher studies behavior in its natural setting without intervention or manipulation.
It involves observing and recording behavior as it naturally occurs, providing insights into real-life behaviors and interactions in their natural context.
Naturalistic observation is a research method commonly used by psychologists and other social scientists.
This technique involves observing and studying the spontaneous behavior of participants in natural surroundings. The researcher simply records what they see in whatever way they can.
In unstructured observations, the researcher records all relevant behavior with a coding system. There may be too much to record, and the behaviors recorded may not necessarily be the most important, so the approach is usually used as a pilot study to see what type of behaviors would be recorded.
Compared with controlled observations, it is like the difference between studying wild animals in a zoo and studying them in their natural habitat.
With regard to human subjects, Margaret Mead used this method to research the way of life of different tribes living on islands in the South Pacific. Kathy Sylva used it to study children at play by observing their behavior in a playgroup in Oxfordshire.
Collecting Naturalistic Behavioral Data
Technological advances are enabling new, unobtrusive ways of collecting naturalistic behavioral data.
The Electronically Activated Recorder (EAR) is a digital recording device participants can wear to periodically sample ambient sounds, allowing representative sampling of daily experiences (Mehl et al., 2012).
Studies program EARs to record 30-50 second sound snippets multiple times per hour. Although coding the recordings requires extensive resources, EARs can capture spontaneous behaviors like arguments or laughter.
EARs minimize participant reactivity since sampling occurs outside of awareness. This reduces the Hawthorne effect, where people change behavior when observed.
The SenseCam is another wearable device that passively captures images documenting daily activities. Though primarily used in memory research currently (Smith et al., 2014), systematic sampling of environments and behaviors via the SenseCam could enable innovative psychological studies in the future.
- By being able to observe the flow of behavior in its own setting, studies have greater ecological validity.
- Like case studies , naturalistic observation is often used to generate new ideas. Because it gives the researcher the opportunity to study the total situation, it often suggests avenues of inquiry not thought of before.
- The ability to capture actual behaviors as they unfold in real-time, analyze sequential patterns of interactions, measure base rates of behaviors, and examine socially undesirable or complex behaviors that people may not self-report accurately.
- These observations are often conducted on a micro (small) scale and may lack a representative sample (biased in relation to age, gender, social class, or ethnicity). This may result in the findings lacking the ability to generalize to wider society.
- Natural observations are less reliable as other variables cannot be controlled. This makes it difficult for another researcher to repeat the study in exactly the same way.
- Highly time-consuming and resource-intensive during the data coding phase (e.g., training coders, maintaining inter-rater reliability, preventing judgment drift).
- With observations, we do not have manipulations of variables (or control over extraneous variables), meaning cause-and-effect relationships cannot be established.
Participant Observation
Participant observation is a variant of the above (natural observations) but here, the researcher joins in and becomes part of the group they are studying to get a deeper insight into their lives.
If it were research on animals , we would now not only be studying them in their natural habitat but be living alongside them as well!
Leon Festinger used this approach in a famous study into a religious cult that believed that the end of the world was about to occur. He joined the cult and studied how they reacted when the prophecy did not come true.
Participant observations can be either covert or overt. Covert is where the study is carried out “undercover.” The researcher’s real identity and purpose are kept concealed from the group being studied.
The researcher takes a false identity and role, usually posing as a genuine member of the group.
On the other hand, overt is where the researcher reveals his or her true identity and purpose to the group and asks permission to observe.
- It can be difficult to get time/privacy for recording. For example, researchers can’t take notes openly with covert observations as this would blow their cover. This means they must wait until they are alone and rely on their memory. This is a problem as they may forget details and are unlikely to remember direct quotations.
- If the researcher becomes too involved, they may lose objectivity and become biased. There is always the danger that we will “see” what we expect (or want) to see. This problem is because they could selectively report information instead of noting everything they observe. Thus reducing the validity of their data.

Recording of Data
With controlled/structured observation studies, an important decision the researcher has to make is how to classify and record the data. Usually, this will involve a method of sampling.
In most coding systems, codes or ratings are made either per behavioral event or per specified time interval (Bakeman & Quera, 2011).
The three main sampling methods are:
Event-based coding involves identifying and segmenting interactions into meaningful events rather than timed units.
For example, parent-child interactions may be segmented into control or teaching events to code. Interval recording involves dividing interactions into fixed time intervals (e.g., 6-15 seconds) and coding behaviors within each interval (Bakeman & Quera, 2011).
Event recording allows counting event frequency and sequencing while also potentially capturing event duration through timed-event recording. This provides information on time spent on behaviors.
Coding Systems
The coding system should focus on behaviors, patterns, individual characteristics, or relationship qualities that are relevant to the theory guiding the study (Wampler & Harper, 2014).
Codes vary in how much inference is required, from concrete observable behaviors like frequency of eye contact to more abstract concepts like degree of rapport between a therapist and client (Hill & Lambert, 2004). More inference may reduce reliability.
Macroanalytic coding systems
Macroanalytic coding systems involve rating or summarizing behaviors using larger coding units and broader categories that reflect patterns across longer periods of interaction rather than coding small or discrete behavioral acts.
For example, a macroanalytic coding system may rate the overall degree of therapist warmth or level of client engagement globally for an entire therapy session, requiring the coders to summarize and infer these constructs across the interaction rather than coding smaller behavioral units.
These systems require observers to make more inferences (more time-consuming) but can better capture contextual factors, stability over time, and the interdependent nature of behaviors (Carlson & Grotevant, 1987).
Microanalytic coding systems
Microanalytic coding systems involve rating behaviors using smaller, more discrete coding units and categories.
For example, a microanalytic system may code each instance of eye contact or head nodding during a therapy session. These systems code specific, molecular behaviors as they occur moment-to-moment rather than summarizing actions over longer periods.
Microanalytic systems require less inference from coders and allow for analysis of behavioral contingencies and sequential interactions between therapist and client. However, they are more time-consuming and expensive to implement than macroanalytic approaches.
Mesoanalytic coding systems
Mesoanalytic coding systems attempt to balance macro- and micro-analytic approaches.
In contrast to macroanalytic systems that summarize behaviors in larger chunks, mesoanalytic systems use medium-sized coding units that target more specific behaviors or interaction sequences (Bakeman & Quera, 2017).
For example, a mesoanalytic system may code each instance of a particular type of therapist statement or client emotional expression. However, mesoanalytic systems still use larger units than microanalytic approaches coding every speech onset/offset.
The goal of balancing specificity and feasibility makes mesoanalytic systems well-suited for many research questions (Morris et al., 2014). Mesoanalytic codes can preserve some sequential information while remaining efficient enough for studies with adequate but limited resources.
For instance, a mesoanalytic couple interaction coding system could target key behavior patterns like validation sequences without coding turn-by-turn speech.
In this way, mesoanalytic coding allows reasonable reliability and specificity without requiring extensive training or observation. The mid-level focus offers a pragmatic compromise between depth and breadth in analyzing interactions.
Preventing Coder Drift
Coder drift results in a measurement error caused by gradual shifts in how observations get rated according to operational definitions, especially when behavioral codes are not clearly specified.
This type of error creeps in when coders fail to regularly review what precise observations constitute or do not constitute the behaviors being measured.
Preventing drift refers to taking active steps to maintain consistency and minimize changes or deviations in how coders rate or evaluate behaviors over time. Specifically, some key ways to prevent coder drift include:
- Operationalize codes : It is essential that code definitions unambiguously distinguish what interactions represent instances of each coded behavior.
- Ongoing training : Returning to those operational definitions through ongoing training serves to recalibrate coder interpretations and reinforce accurate recognition. Having regular “check-in” sessions where coders practice coding the same interactions allows monitoring that they continue applying codes reliably without gradual shifts in interpretation.
- Using reference videos : Coders periodically coding the same “gold standard” reference videos anchors their judgments and calibrate against original training. Without periodic anchoring to original specifications, coder decisions tend to drift from initial measurement reliability.
- Assessing inter-rater reliability : Statistical tracking that coders maintain high levels of agreement over the course of a study, not just at the start, flags any declines indicating drift. Sustaining inter-rater agreement requires mitigating this common tendency for observer judgment change during intensive, long-term coding tasks.
- Recalibrating through discussion : Having meetings for coders to discuss disagreements openly explores reasons judgment shifts may be occurring over time. Consensus on the application of codes is restored.
- Adjusting unclear codes : If reliability issues persist, revisiting and refining ambiguous code definitions or anchors can eliminate inconsistencies arising from coder confusion.
Essentially, the goal of preventing coder drift is maintaining standardization and minimizing unintentional biases that may slowly alter how observational data gets rated over periods of extensive coding.
Through the upkeep of skills, continuing calibration to benchmarks, and monitoring consistency, researchers can notice and correct for any creeping changes in coder decision-making over time.
Reducing Observer Bias
Observational research is prone to observer biases resulting from coders’ subjective perspectives shaping the interpretation of complex interactions (Burghardt et al., 2012). When coding, personal expectations may unconsciously influence judgments. However, rigorous methods exist to reduce such bias.
Coding Manual
A detailed coding manual minimizes subjectivity by clearly defining what behaviors and interaction dynamics observers should code (Bakeman & Quera, 2011).
High-quality manuals have strong theoretical and empirical grounding, laying out explicit coding procedures and providing rich behavioral examples to anchor code definitions (Lindahl, 2001).
Clear delineation of the frequency, intensity, duration, and type of behaviors constituting each code facilitates reliable judgments and reduces ambiguity for coders. Application risks inconsistency across raters without clarity on how codes translate to observable interaction.
Coder Training
Competent coders require both interpersonal perceptiveness and scientific rigor (Wampler & Harper, 2014). Training thoroughly reviews the theoretical basis for coded constructs and teaches the coding system itself.
Multiple “gold standard” criterion videos demonstrate code ranges that trainees independently apply. Coders then meet weekly to establish reliability of 80% or higher agreement both among themselves and with master criterion coding (Hill & Lambert, 2004).
Ongoing training manages coder drift over time. Revisions to unclear codes may also improve reliability. Both careful selection and investment in rigorous training increase quality control.
Blind Methods
To prevent bias, coders should remain unaware of specific study predictions or participant details (Burghardt et al., 2012). Separate data gathering versus coding teams helps maintain blinding.
Coders should be unaware of study details or participant identities that could bias coding (Burghardt et al., 2012).
Separate teams collecting data versus coding data can reduce bias.
In addition, scheduling procedures can prevent coders from rating data collected directly from participants with whom they have had personal contact. Maintaining coder independence and blinding enhances objectivity.

Bakeman, R., & Quera, V. (2017). Sequential analysis and observational methods for the behavioral sciences. Cambridge University Press.
Burghardt, G. M., Bartmess-LeVasseur, J. N., Browning, S. A., Morrison, K. E., Stec, C. L., Zachau, C. E., & Freeberg, T. M. (2012). Minimizing observer bias in behavioral studies: A review and recommendations. Ethology, 118 (6), 511-517.
Hill, C. E., & Lambert, M. J. (2004). Methodological issues in studying psychotherapy processes and outcomes. In M. J. Lambert (Ed.), Bergin and Garfield’s handbook of psychotherapy and behavior change (5th ed., pp. 84–135). Wiley.
Lindahl, K. M. (2001). Methodological issues in family observational research. In P. K. Kerig & K. M. Lindahl (Eds.), Family observational coding systems: Resources for systemic research (pp. 23–32). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Mehl, M. R., Robbins, M. L., & Deters, F. G. (2012). Naturalistic observation of health-relevant social processes: The electronically activated recorder methodology in psychosomatics. Psychosomatic Medicine, 74 (4), 410–417.
Morris, A. S., Robinson, L. R., & Eisenberg, N. (2014). Applying a multimethod perspective to the study of developmental psychology. In H. T. Reis & C. M. Judd (Eds.), Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology (2nd ed., pp. 103–123). Cambridge University Press.
Smith, J. A., Maxwell, S. D., & Johnson, G. (2014). The microstructure of everyday life: Analyzing the complex choreography of daily routines through the automatic capture and processing of wearable sensor data. In B. K. Wiederhold & G. Riva (Eds.), Annual Review of Cybertherapy and Telemedicine 2014: Positive Change with Technology (Vol. 199, pp. 62-64). IOS Press.
Traniello, J. F., & Bakker, T. C. (2015). The integrative study of behavioral interactions across the sciences. In T. K. Shackelford & R. D. Hansen (Eds.), The evolution of sexuality (pp. 119-147). Springer.
Wampler, K. S., & Harper, A. (2014). Observational methods in couple and family assessment. In H. T. Reis & C. M. Judd (Eds.), Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology (2nd ed., pp. 490–502). Cambridge University Press.

- Research Process
What is Observational Study Design and Types
- 4 minute read
- 107.1K views
Table of Contents
Most people think of a traditional experimental design when they consider research and published research papers. There is, however, a type of research that is more observational in nature, and it is appropriately referred to as “observational studies.”
There are many valuable reasons to utilize an observational study design. But, just as in research experimental design, different methods can be used when you’re considering this type of study. In this article, we’ll look at the advantages and disadvantages of an observational study design, as well as the 3 types of observational studies.
What is Observational Study Design?
An observational study is when researchers are looking at the effect of some type of intervention, risk, a diagnostic test or treatment, without trying to manipulate who is, or who isn’t, exposed to it.
This differs from an experimental study, where the scientists are manipulating who is exposed to the treatment, intervention, etc., by having a control group, or those who are not exposed, and an experimental group, or those who are exposed to the intervention, treatment, etc. In the best studies, the groups are randomized, or chosen by chance.
Any evidence derived from systematic reviews is considered the best in the hierarchy of evidence, which considers which studies are deemed the most reliable. Next would be any evidence that comes from randomized controlled trials. Cohort studies and case studies follow, in that order.
Cohort studies and case studies are considered observational in design, whereas the randomized controlled trial would be an experimental study.
Let’s take a closer look at the different types of observational study design.
The 3 types of Observational Studies
The different types of observational studies are used for different reasons. Selecting the best type for your research is critical to a successful outcome. One of the main reasons observational studies are used is when a randomized experiment would be considered unethical. For example, a life-saving medication used in a public health emergency. They are also used when looking at aetiology, or the cause of a condition or disease, as well as the treatment of rare conditions.
Case Control Observational Study
Researchers in case control studies identify individuals with an existing health issue or condition, or “cases,” along with a similar group without the condition, or “controls.” These two groups are then compared to identify predictors and outcomes. This type of study is helpful to generate a hypothesis that can then be researched.
Cohort Observational Study
This type of observational study is often used to help understand cause and effect. A cohort observational study looks at causes, incidence and prognosis, for example. A cohort is a group of people who are linked in a particular way, for example, a birth cohort would include people who were born within a specific period of time. Scientists might compare what happens to the members of the cohort who have been exposed to some variable to what occurs with members of the cohort who haven’t been exposed.
Cross Sectional Observational Study
Unlike a cohort observational study, a cross sectional observational study does not explore cause and effect, but instead looks at prevalence. Here you would look at data from a particular group at one very specific period of time. Researchers would simply observe and record information about something present in the population, without manipulating any variables or interventions. These types of studies are commonly used in psychology, education and social science.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Observational Study Design
Observational study designs have the distinct advantage of allowing researchers to explore answers to questions where a randomized controlled trial, or RCT, would be unethical. Additionally, if the study is focused on a rare condition, studying existing cases as compared to non-affected individuals might be the most effective way to identify possible causes of the condition. Likewise, if very little is known about a condition or circumstance, a cohort study would be a good study design choice.
A primary advantage to the observational study design is that they can generally be completed quickly and inexpensively. A RCT can take years before the data is compiled and available. RCTs are more complex and involved, requiring many more logistics and details to iron out, whereas an observational study can be more easily designed and completed.
The main disadvantage of observational study designs is that they’re more open to dispute than an RCT. Of particular concern would be confounding biases. This is when a cohort might share other characteristics that affect the outcome versus the outcome stated in the study. An example would be that people who practice good sleeping habits have less heart disease. But, maybe those who practice effective sleeping habits also, in general, eat better and exercise more.
Language Editing Plus Service
Need help with your research writing? With our Language Editing Plus service , we’ll help you improve the flow and writing of your paper, including UNLIMITED editing support. Use the simulator below to check the price for your manuscript, using the total number of words of the document.

Clinical Questions: PICO and PEO Research

Paper Retraction: Meaning and Main Reasons
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
2.2 Approaches to Research
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different research methods used by psychologists
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, surveys, and archival research
- Compare longitudinal and cross-sectional approaches to research
- Compare and contrast correlation and causation
There are many research methods available to psychologists in their efforts to understand, describe, and explain behavior and the cognitive and biological processes that underlie it. Some methods rely on observational techniques. Other approaches involve interactions between the researcher and the individuals who are being studied—ranging from a series of simple questions to extensive, in-depth interviews—to well-controlled experiments.
Each of these research methods has unique strengths and weaknesses, and each method may only be appropriate for certain types of research questions. For example, studies that rely primarily on observation produce incredible amounts of information, but the ability to apply this information to the larger population is somewhat limited because of small sample sizes. Survey research, on the other hand, allows researchers to easily collect data from relatively large samples. While this allows for results to be generalized to the larger population more easily, the information that can be collected on any given survey is somewhat limited and subject to problems associated with any type of self-reported data. Some researchers conduct archival research by using existing records. While this can be a fairly inexpensive way to collect data that can provide insight into a number of research questions, researchers using this approach have no control on how or what kind of data was collected. All of the methods described thus far are correlational in nature. This means that researchers can speak to important relationships that might exist between two or more variables of interest. However, correlational data cannot be used to make claims about cause-and-effect relationships.
Correlational research can find a relationship between two variables, but the only way a researcher can claim that the relationship between the variables is cause and effect is to perform an experiment. In experimental research, which will be discussed later in this chapter, there is a tremendous amount of control over variables of interest. While this is a powerful approach, experiments are often conducted in artificial settings. This calls into question the validity of experimental findings with regard to how they would apply in real-world settings. In addition, many of the questions that psychologists would like to answer cannot be pursued through experimental research because of ethical concerns.
Clinical or Case Studies
In 2011, the New York Times published a feature story on Krista and Tatiana Hogan, Canadian twin girls. These particular twins are unique because Krista and Tatiana are conjoined twins, connected at the head. There is evidence that the two girls are connected in a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is a major sensory relay center. Most incoming sensory information is sent through the thalamus before reaching higher regions of the cerebral cortex for processing.
Link to Learning
Watch this CBC video about Krista's and Tatiana's lives to learn more.
The implications of this potential connection mean that it might be possible for one twin to experience the sensations of the other twin. For instance, if Krista is watching a particularly funny television program, Tatiana might smile or laugh even if she is not watching the program. This particular possibility has piqued the interest of many neuroscientists who seek to understand how the brain uses sensory information.
These twins represent an enormous resource in the study of the brain, and since their condition is very rare, it is likely that as long as their family agrees, scientists will follow these girls very closely throughout their lives to gain as much information as possible (Dominus, 2011).
Over time, it has become clear that while Krista and Tatiana share some sensory experiences and motor control, they remain two distinct individuals, which provides invaluable insight for researchers interested in the mind and the brain (Egnor, 2017).
In observational research, scientists are conducting a clinical or case study when they focus on one person or just a few individuals. Indeed, some scientists spend their entire careers studying just 10–20 individuals. Why would they do this? Obviously, when they focus their attention on a very small number of people, they can gain a precious amount of insight into those cases. The richness of information that is collected in clinical or case studies is unmatched by any other single research method. This allows the researcher to have a very deep understanding of the individuals and the particular phenomenon being studied.
If clinical or case studies provide so much information, why are they not more frequent among researchers? As it turns out, the major benefit of this particular approach is also a weakness. As mentioned earlier, this approach is often used when studying individuals who are interesting to researchers because they have a rare characteristic. Therefore, the individuals who serve as the focus of case studies are not like most other people. If scientists ultimately want to explain all behavior, focusing attention on such a special group of people can make it difficult to generalize any observations to the larger population as a whole. Generalizing refers to the ability to apply the findings of a particular research project to larger segments of society. Again, case studies provide enormous amounts of information, but since the cases are so specific, the potential to apply what’s learned to the average person may be very limited.
Naturalistic Observation
If you want to understand how behavior occurs, one of the best ways to gain information is to simply observe the behavior in its natural context. However, people might change their behavior in unexpected ways if they know they are being observed. How do researchers obtain accurate information when people tend to hide their natural behavior? As an example, imagine that your professor asks everyone in your class to raise their hand if they always wash their hands after using the restroom. Chances are that almost everyone in the classroom will raise their hand, but do you think hand washing after every trip to the restroom is really that universal?
This is very similar to the phenomenon mentioned earlier in this chapter: many individuals do not feel comfortable answering a question honestly. But if we are committed to finding out the facts about hand washing, we have other options available to us.
Suppose we send a classmate into the restroom to actually watch whether everyone washes their hands after using the restroom. Will our observer blend into the restroom environment by wearing a white lab coat, sitting with a clipboard, and staring at the sinks? We want our researcher to be inconspicuous—perhaps standing at one of the sinks pretending to put in contact lenses while secretly recording the relevant information. This type of observational study is called naturalistic observation : observing behavior in its natural setting. To better understand peer exclusion, Suzanne Fanger collaborated with colleagues at the University of Texas to observe the behavior of preschool children on a playground. How did the observers remain inconspicuous over the duration of the study? They equipped a few of the children with wireless microphones (which the children quickly forgot about) and observed while taking notes from a distance. Also, the children in that particular preschool (a “laboratory preschool”) were accustomed to having observers on the playground (Fanger, Frankel, & Hazen, 2012).
It is critical that the observer be as unobtrusive and as inconspicuous as possible: when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to behave naturally. If you have any doubt about this, ask yourself how your driving behavior might differ in two situations: In the first situation, you are driving down a deserted highway during the middle of the day; in the second situation, you are being followed by a police car down the same deserted highway ( Figure 2.7 ).
It should be pointed out that naturalistic observation is not limited to research involving humans. Indeed, some of the best-known examples of naturalistic observation involve researchers going into the field to observe various kinds of animals in their own environments. As with human studies, the researchers maintain their distance and avoid interfering with the animal subjects so as not to influence their natural behaviors. Scientists have used this technique to study social hierarchies and interactions among animals ranging from ground squirrels to gorillas. The information provided by these studies is invaluable in understanding how those animals organize socially and communicate with one another. The anthropologist Jane Goodall , for example, spent nearly five decades observing the behavior of chimpanzees in Africa ( Figure 2.8 ). As an illustration of the types of concerns that a researcher might encounter in naturalistic observation, some scientists criticized Goodall for giving the chimps names instead of referring to them by numbers—using names was thought to undermine the emotional detachment required for the objectivity of the study (McKie, 2010).
The greatest benefit of naturalistic observation is the validity , or accuracy, of information collected unobtrusively in a natural setting. Having individuals behave as they normally would in a given situation means that we have a higher degree of ecological validity, or realism, than we might achieve with other research approaches. Therefore, our ability to generalize the findings of the research to real-world situations is enhanced. If done correctly, we need not worry about people or animals modifying their behavior simply because they are being observed. Sometimes, people may assume that reality programs give us a glimpse into authentic human behavior. However, the principle of inconspicuous observation is violated as reality stars are followed by camera crews and are interviewed on camera for personal confessionals. Given that environment, we must doubt how natural and realistic their behaviors are.
The major downside of naturalistic observation is that they are often difficult to set up and control. In our restroom study, what if you stood in the restroom all day prepared to record people’s hand washing behavior and no one came in? Or, what if you have been closely observing a troop of gorillas for weeks only to find that they migrated to a new place while you were sleeping in your tent? The benefit of realistic data comes at a cost. As a researcher you have no control of when (or if) you have behavior to observe. In addition, this type of observational research often requires significant investments of time, money, and a good dose of luck.
Sometimes studies involve structured observation. In these cases, people are observed while engaging in set, specific tasks. An excellent example of structured observation comes from Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth (you will read more about this in the chapter on lifespan development). The Strange Situation is a procedure used to evaluate attachment styles that exist between an infant and caregiver. In this scenario, caregivers bring their infants into a room filled with toys. The Strange Situation involves a number of phases, including a stranger coming into the room, the caregiver leaving the room, and the caregiver’s return to the room. The infant’s behavior is closely monitored at each phase, but it is the behavior of the infant upon being reunited with the caregiver that is most telling in terms of characterizing the infant’s attachment style with the caregiver.
Another potential problem in observational research is observer bias . Generally, people who act as observers are closely involved in the research project and may unconsciously skew their observations to fit their research goals or expectations. To protect against this type of bias, researchers should have clear criteria established for the types of behaviors recorded and how those behaviors should be classified. In addition, researchers often compare observations of the same event by multiple observers, in order to test inter-rater reliability : a measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of observations by different observers.
Often, psychologists develop surveys as a means of gathering data. Surveys are lists of questions to be answered by research participants, and can be delivered as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally ( Figure 2.9 ). Generally, the survey itself can be completed in a short time, and the ease of administering a survey makes it easy to collect data from a large number of people.
Surveys allow researchers to gather data from larger samples than may be afforded by other research methods . A sample is a subset of individuals selected from a population , which is the overall group of individuals that the researchers are interested in. Researchers study the sample and seek to generalize their findings to the population. Generally, researchers will begin this process by calculating various measures of central tendency from the data they have collected. These measures provide an overall summary of what a typical response looks like. There are three measures of central tendency: mode, median, and mean. The mode is the most frequently occurring response, the median lies at the middle of a given data set, and the mean is the arithmetic average of all data points. Means tend to be most useful in conducting additional analyses like those described below; however, means are very sensitive to the effects of outliers, and so one must be aware of those effects when making assessments of what measures of central tendency tell us about a data set in question.
There is both strength and weakness of the survey in comparison to case studies. By using surveys, we can collect information from a larger sample of people. A larger sample is better able to reflect the actual diversity of the population, thus allowing better generalizability. Therefore, if our sample is sufficiently large and diverse, we can assume that the data we collect from the survey can be generalized to the larger population with more certainty than the information collected through a case study. However, given the greater number of people involved, we are not able to collect the same depth of information on each person that would be collected in a case study.
Another potential weakness of surveys is something we touched on earlier in this chapter: People don't always give accurate responses. They may lie, misremember, or answer questions in a way that they think makes them look good. For example, people may report drinking less alcohol than is actually the case.
Any number of research questions can be answered through the use of surveys. One real-world example is the research conducted by Jenkins, Ruppel, Kizer, Yehl, and Griffin (2012) about the backlash against the US Arab-American community following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Jenkins and colleagues wanted to determine to what extent these negative attitudes toward Arab-Americans still existed nearly a decade after the attacks occurred. In one study, 140 research participants filled out a survey with 10 questions, including questions asking directly about the participant’s overt prejudicial attitudes toward people of various ethnicities. The survey also asked indirect questions about how likely the participant would be to interact with a person of a given ethnicity in a variety of settings (such as, “How likely do you think it is that you would introduce yourself to a person of Arab-American descent?”). The results of the research suggested that participants were unwilling to report prejudicial attitudes toward any ethnic group. However, there were significant differences between their pattern of responses to questions about social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to other ethnic groups: they indicated less willingness for social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to the other ethnic groups. This suggested that the participants harbored subtle forms of prejudice against Arab-Americans, despite their assertions that this was not the case (Jenkins et al., 2012).
Archival Research
Some researchers gain access to large amounts of data without interacting with a single research participant. Instead, they use existing records to answer various research questions. This type of research approach is known as archival research . Archival research relies on looking at past records or data sets to look for interesting patterns or relationships.
For example, a researcher might access the academic records of all individuals who enrolled in college within the past ten years and calculate how long it took them to complete their degrees, as well as course loads, grades, and extracurricular involvement. Archival research could provide important information about who is most likely to complete their education, and it could help identify important risk factors for struggling students ( Figure 2.10 ).
In comparing archival research to other research methods, there are several important distinctions. For one, the researcher employing archival research never directly interacts with research participants. Therefore, the investment of time and money to collect data is considerably less with archival research. Additionally, researchers have no control over what information was originally collected. Therefore, research questions have to be tailored so they can be answered within the structure of the existing data sets. There is also no guarantee of consistency between the records from one source to another, which might make comparing and contrasting different data sets problematic.
Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Research
Sometimes we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. When we test the same group of individuals repeatedly over an extended period of time, we are conducting longitudinal research. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time. For example, we may survey a group of individuals about their dietary habits at age 20, retest them a decade later at age 30, and then again at age 40.
Another approach is cross-sectional research. In cross-sectional research , a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time. Using the dietary habits example above, the researcher might directly compare different groups of people by age. Instead of studying a group of people for 20 years to see how their dietary habits changed from decade to decade, the researcher would study a group of 20-year-old individuals and compare them to a group of 30-year-old individuals and a group of 40-year-old individuals. While cross-sectional research requires a shorter-term investment, it is also limited by differences that exist between the different generations (or cohorts) that have nothing to do with age per se, but rather reflect the social and cultural experiences of different generations of individuals that make them different from one another.
To illustrate this concept, consider the following survey findings. In recent years there has been significant growth in the popular support of same-sex marriage. Many studies on this topic break down survey participants into different age groups. In general, younger people are more supportive of same-sex marriage than are those who are older (Jones, 2013). Does this mean that as we age we become less open to the idea of same-sex marriage, or does this mean that older individuals have different perspectives because of the social climates in which they grew up? Longitudinal research is a powerful approach because the same individuals are involved in the research project over time, which means that the researchers need to be less concerned with differences among cohorts affecting the results of their study.
Often longitudinal studies are employed when researching various diseases in an effort to understand particular risk factors. Such studies often involve tens of thousands of individuals who are followed for several decades. Given the enormous number of people involved in these studies, researchers can feel confident that their findings can be generalized to the larger population. The Cancer Prevention Study-3 (CPS-3) is one of a series of longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society aimed at determining predictive risk factors associated with cancer. When participants enter the study, they complete a survey about their lives and family histories, providing information on factors that might cause or prevent the development of cancer. Then every few years the participants receive additional surveys to complete. In the end, hundreds of thousands of participants will be tracked over 20 years to determine which of them develop cancer and which do not.
Clearly, this type of research is important and potentially very informative. For instance, earlier longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society provided some of the first scientific demonstrations of the now well-established links between increased rates of cancer and smoking (American Cancer Society, n.d.) ( Figure 2.11 ).
As with any research strategy, longitudinal research is not without limitations. For one, these studies require an incredible time investment by the researcher and research participants. Given that some longitudinal studies take years, if not decades, to complete, the results will not be known for a considerable period of time. In addition to the time demands, these studies also require a substantial financial investment. Many researchers are unable to commit the resources necessary to see a longitudinal project through to the end.
Research participants must also be willing to continue their participation for an extended period of time, and this can be problematic. People move, get married and take new names, get ill, and eventually die. Even without significant life changes, some people may simply choose to discontinue their participation in the project. As a result, the attrition rates, or reduction in the number of research participants due to dropouts, in longitudinal studies are quite high and increase over the course of a project. For this reason, researchers using this approach typically recruit many participants fully expecting that a substantial number will drop out before the end. As the study progresses, they continually check whether the sample still represents the larger population, and make adjustments as necessary.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-2-approaches-to-research
© Jan 6, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Biochem Med (Zagreb)
- v.24(2); 2014 Jun
Observational and interventional study design types; an overview
The appropriate choice in study design is essential for the successful execution of biomedical and public health research. There are many study designs to choose from within two broad categories of observational and interventional studies. Each design has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the need to understand these limitations is necessary to arrive at correct study conclusions.
Observational study designs, also called epidemiologic study designs, are often retrospective and are used to assess potential causation in exposure-outcome relationships and therefore influence preventive methods. Observational study designs include ecological designs, cross sectional, case-control, case-crossover, retrospective and prospective cohorts. An important subset of observational studies is diagnostic study designs, which evaluate the accuracy of diagnostic procedures and tests as compared to other diagnostic measures. These include diagnostic accuracy designs, diagnostic cohort designs, and diagnostic randomized controlled trials.
Interventional studies are often prospective and are specifically tailored to evaluate direct impacts of treatment or preventive measures on disease. Each study design has specific outcome measures that rely on the type and quality of data utilized. Additionally, each study design has potential limitations that are more severe and need to be addressed in the design phase of the study. This manuscript is meant to provide an overview of study design types, strengths and weaknesses of common observational and interventional study designs.
Introduction
Study design plays an important role in the quality, execution, and interpretation of biomedical and public health research ( 1 – 12 ). Each study design has their own inherent strengths and weaknesses, and there can be a general hierarchy in study designs, however, any hierarchy cannot be applied uniformly across study design types ( 3 , 5 , 6 , 9 ). Epidemiological and interventional research studies include three elements; 1) definition and measure of exposure in two or more groups, 2) measure of health outcome(s) in these same groups, and 3) statistical comparison made between groups to assess potential relationships between the exposure and outcome, all of which are defined by the researcher ( 1 – 4 , 8 , 13 ). The measure of exposure in epidemiologic studies may be tobacco use (“Yes” vs . “No”) to define the two groups and may be the treatment (Active drug vs . placebo) in interventional studies. Health outcome(s) can be the development of a disease or symptom (e.g. lung cancer) or curing a disease or symptom (e.g. reduction of pain). Descriptive studies, which are not epidemiological or interventional, lack one or more of these elements and have limited application. High quality epidemiological and interventional studies contain detailed information on the design, execution and interpretation of results, with methodology clearly written and able to be reproduced by other researchers.
Research is generally considered as primary or secondary research. Primary research relies upon data gathered from original research expressly for that purpose ( 1 , 3 , 5 ). Secondary research focuses on single or multiple data sources that are not collected for a single research purpose ( 14 , 15 ). Secondary research includes meta-analyses and best practice guidelines for treatments. This paper will focus on the study designs and their strengths, weaknesses, and common statistical outcomes of primary research.
The choice of a study design hinges on many factors, including prior research, availability of study participants, funding, and time constraints. One common decision point is the desire to suggest causation. The most common causation criteria are proposed by Hill ( 16 ). Of these, demonstrating temporality is the only mandatory criterion for suggesting temporality. Therefore, prospective studies that follow study participants forward through time, including prospective cohort studies and interventional studies, are best suited for suggesting causation. Causal conclusions cannot be proven from an observational study. Additionally, causation between an exposure and an outcome cannot be proven by one study alone; multiple studies across different populations should be considered when making causation assessments ( 17 ).
Primary research has been categorized in different ways. Common categorization schema include temporal nature of the study design (retrospective or prospective), usability of the study results (basic or applied), investigative purpose (descriptive or analytical), purpose (prevention, diagnosis or treatment), or role of the investigator (observational or interventional). This manuscript categorizes study designs by observational and interventional criteria, however, other categorization methods are described as well.
Observational and interventional studies
Within primary research there are observational studies and interventional studies. Observational studies, also called epidemiological studies, are those where the investigator is not acting upon study participants, but instead observing natural relationships between factors and outcomes. Diagnostic studies are classified as observational studies, but are a unique category and will be discussed independently. Interventional studies, also called experimental studies, are those where the researcher intercedes as part of the study design. Additionally, study designs may be classified by the role that time plays in the data collection, either retrospective or prospective. Retrospective studies are those where data are collected from the past, either through records created at that time or by asking participants to remember their exposures or outcomes. Retrospective studies cannot demonstrate temporality as easily and are more prone to different biases, particularly recall bias. Prospective studies follow participants forward through time, collecting data in the process. Prospective studies are less prone to some types of bias and can more easily demonstrate that the exposure preceded the disease, thereby more strongly suggesting causation. Table 1 describes the broad categories of observational studies: the disease measures applicable to each, the appropriate measures of risk, and temporality of each study design. Epidemiologic measures include point prevalence, the proportion of participants with disease at a given point in time, period prevalence, the proportion of participants with disease within a specified time frame, and incidence, the accumulation of new cases over time. Measures of risk are generally categorized into two categories: those that only demonstrate an association, such as an odds ratio (and some other measures), and those that demonstrate temporality and therefore suggest causation, such as hazard ratio. Table 2 outlines the strengths and weaknesses of each observational study design.
Observational study design measures of disease, measures of risk, and temporality.
Observational study design strengths and weaknesses.
Observational studies
Ecological study design.
The most basic observational study is an ecological study. This study design compares clusters of people, usually grouped based on their geographical location or temporal associations ( 1 , 2 , 6 , 9 ). Ecological studies assign one exposure level for each distinct group and can provide a rough estimation of prevalence of disease within a population. Ecological studies are generally retrospective. An example of an ecological study is the comparison of the prevalence of obesity in the United States and France. The geographic area is considered the exposure and the outcome is obesity. There are inherent potential weaknesses with this approach, including loss of data resolution and potential misclassification ( 10 , 11 , 13 , 18 , 19 ). This type of study design also has additional weaknesses. Typically these studies derive their data from large databases that are created for purposes other than research, which may introduce error or misclassification ( 10 , 11 ). Quantification of both the number of cases and the total population can be difficult, leading to error or bias. Lastly, due to the limited amount of data available, it is difficult to control for other factors that may mask or falsely suggest a relationship between the exposure and the outcome. However, ecological studies are generally very cost effective and are a starting point for hypothesis generation.
Proportional mortality ratio study design
Proportional mortality ratio studies (PMR) utilize the defined well recorded outcome of death and subsequent records that are maintained regarding the decedent ( 1 , 6 , 8 , 20 ). By using records, this study design is able to identify potential relationships between exposures, such as geographic location, occupation, or age and cause of death. The epidemiological outcomes of this study design are proportional mortality ratio and standardized mortality ratio. In general these are the ratio of the proportion of cause-specific deaths out of all deaths between exposure categories ( 20 ). As an example, these studies can address questions about higher proportion of cardiovascular deaths among different ethnic and racial groups ( 21 ). A significant drawback to the PMR study design is that these studies are limited to death as an outcome ( 3 , 5 , 22 ). Additionally, the reliance on death records makes it difficult to control for individual confounding factors, variables that either conceal or falsely demonstrate associations between the exposure and outcome. An example of a confounder is tobacco use confounding the relationship between coffee intake and cardiovascular disease. Historically people often smoked and drank coffee while on coffee breaks. If researchers ignore smoking they would inaccurately find a strong relationship between coffee use and cardiovascular disease, where some of the risk is actually due to smoking. There are also concerns regarding the accuracy of death certificate data. Strengths of the study design include the well-defined outcome of death, the relative ease and low cost of obtaining data, and the uniformity of collection of these data across different geographical areas.
Cross-sectional study design
Cross-sectional studies are also called prevalence studies because one of the main measures available is study population prevalence ( 1 – 12 ). These studies consist of assessing a population, as represented by the study sample, at a single point in time. A common cross-sectional study type is the diagnostic accuracy study, which is discussed later. Cross-sectional study samples are selected based on their exposure status, without regard for their outcome status. Outcome status is obtained after participants are enrolled. Ideally, a wider distribution of exposure will allow for a higher likelihood of finding an association between the exposure and outcome if one exists ( 1 – 3 , 5 , 8 ). Cross-sectional studies are retrospective in nature. An example of a cross-sectional study would be enrolling participants who are either current smokers or never smokers, and assessing whether or not they have respiratory deficiencies. Random sampling of the population being assessed is more important in cross-sectional studies as compared to other observational study designs. Selection bias from non-random sampling may result in flawed measure of prevalence and calculation of risk. The study sample is assessed for both exposure and outcome at a single point in time. Because both exposure and outcome are assessed at the same time, temporality cannot be demonstrated, i.e. it cannot be demonstrated that the exposure preceded the disease ( 1 – 3 , 5 , 8 ). Point prevalence and period prevalence can be calculated in cross-sectional studies. Measures of risk for the exposure-outcome relationship that can be calculated in cross-sectional study design are odds ratio, prevalence odds ratio, prevalence ratio, and prevalence difference. Cross-sectional studies are relatively inexpensive and have data collected on an individual which allows for more complete control for confounding. Additionally, cross-sectional studies allow for multiple outcomes to be assessed simultaneously.
Case-control study design
Case-control studies were traditionally referred to as retrospective studies, due to the nature of the study design and execution ( 1 – 12 , 23 , 24 ). In this study design, researchers identify study participants based on their case status, i.e. diseased or not diseased. Quantification of the number of individuals among the cases and the controls who are exposed allow for statistical associations between exposure and outcomes to be established ( 1 – 3 , 5 , 8 ). An example of a case control study is analysing the relationship between obesity and knee replacement surgery. Cases are participants who have had knee surgery, and controls are a random sampling of those who have not, and the comparison is the relative odds of being obese if you have knee surgery as compared to those that do not. Matching on one or more potential confounders allows for minimization of those factors as potential confounders in the exposure-outcome relationship ( 1 – 3 , 5 , 8 ). Additionally, case-control studies are at increased risk for bias, particularly recall bias, due to the known case status of study participants ( 1 – 3 , 5 , 8 ). Other points of consideration that have specific weight in case-control studies include the appropriate selection of controls that balance generalizability and minimize bias, the minimization of survivor bias, and the potential for length time bias ( 25 ). The largest strength of case-control studies is that this study design is the most efficient study design for rare diseases. Additional strengths include low cost, relatively fast execution compared to cohort studies, the ability to collect individual participant specific data, the ability to control for multiple confounders, and the ability to assess multiple exposures of interest. The measure of risk that is calculated in case-control studies is the odds ratio, which are the odds of having the exposure if you have the disease. Other measures of risk are not applicable to case-control studies. Any measure of prevalence and associated measures, such as prevalence odds ratio, in a case-control study is artificial because the researcher arbitrarily sets the proportion of cases to non-cases in this study design. Temporality can be suggested, however, it is rarely definitively demonstrated because it is unknown if the development of the disease truly preceded the exposure. It should be noted that for certain outcomes, particularly death, the criteria for demonstrating temporality in that specific exposure-outcome relationship are met and the use of relative risk as a measure of risk may be justified.
Case-crossover study design
A case-crossover study relies upon an individual to act as their own control for comparison issues, thereby minimizing some potential confounders ( 1 , 5 , 12 ). This study design should not be confused with a crossover study design which is an interventional study type and is described below. For case-crossover studies, cases are assessed for their exposure status immediately prior to the time they became a case, and then compared to their own exposure at a prior point where they didn’t become a case. The selection of the prior point for comparison issues is often chosen at random or relies upon a mean measure of exposure over time. Case-crossover studies are always retrospective. An example of a case-crossover study would be evaluating the exposure of talking on a cell phone and being involved in an automobile crash. Cases are drivers involved in a crash and the comparison is that same driver at a random timeframe where they were not involved in a crash. These types of studies are particularly good for exposure-outcome relationships where the outcome is acute and well defined, e.g. electrocutions, lacerations, automobile crashes, etc. ( 1 , 5 ). Exposure-outcome relationships that are assessed using case-crossover designs should have health outcomes that do not have a subclinical or undiagnosed period prior to becoming a “case” in the study ( 12 ). The exposure is cell phone use during the exposure periods, both before the crash and during the control period. Additionally, the reliance upon prior exposure time requires that the exposure not have an additive or cumulative effect over time ( 1 , 5 ). Case-crossover study designs are at higher risk for having recall bias as compared with other study designs ( 12 ). Study participants are more likely to remember an exposure prior to becoming a case, as compared to not becoming a case.
Retrospective and prospective cohort study design
Cohort studies involve identifying study participants based on their exposure status and either following them through time to identify which participants develop the outcome(s) of interest, or look back at data that were created in the past, prior to the development of the outcome. Prospective cohort studies are considered the gold standard of observational research ( 1 – 3 , 5 , 8 , 10 , 11 ). These studies begin with a cross-sectional study to categorize exposure and identify cases at baseline. Disease-free participants are then followed and cases are measured as they develop. Retrospective cohort studies also begin with a cross-sectional study to categorize exposure and identify cases. Exposures are then measured based on records created at that time. Additionally, in an ideal retrospective cohort, case status is also tracked using historical data that were created at that point in time. Occupational groups, particularly those that have regular surveillance or certifications such as Commercial Truck Drivers, are particularly well positioned for retrospective cohort studies because records of both exposure and outcome are created as part of commercial and regulatory purposes ( 8 ). These types of studies have the ability to demonstrate temporality and therefore identify true risk factors, not associated factors, as can be done in other types of studies.
Cohort studies are the only observational study that can calculate incidence, both cumulative incidence and an incidence rate ( 1 , 3 , 5 , 6 , 10 , 11 ). Also, because the inception of a cohort study is identical to a cross-sectional study, both point prevalence and period prevalence can be calculated. There are many measures of risk that can be calculated from cohort study data. Again, the measures of risk for the exposure-outcome relationship that can be calculated in cross-sectional study design of odds ratio, prevalence odds ratio, prevalence ratio, and prevalence difference can be calculated in cohort studies as well. Measures of risk that leverage a cohort study’s ability to calculate incidence include incidence rate ratio, relative risk, risk ratio, and hazard ratio. These measures that demonstrate temporality are considered stronger measures for demonstrating causation and identification of risk factors.
Diagnostic testing and evaluation study designs
A specific study design is the diagnostic accuracy study, which is often used as part of the clinical decision making process. Diagnostic accuracy study designs are those that compare a new diagnostic method with the current “gold standard” diagnostic procedure in a cross-section of both diseased and healthy study participants. Gold standard diagnostic procedures are the current best-practice for diagnosing a disease. An example is comparing a new rapid test for a cancer with the gold standard method of biopsy. There are many intricacies to diagnostic testing study designs that should be considered. The proper selection of the gold standard evaluation is important for defining the true measures of accuracy for the new diagnostic procedure. Evaluations of diagnostic test results should be blinded to the case status of the participant. Similar to the intention-to-treat concept discussed later in interventional studies, diagnostic tests have a procedure of analyses called intention to diagnose (ITD), where participants are analysed in the diagnostic category they were assigned, regardless of the process in which a diagnosis was obtained. Performing analyses according to an a priori defined protocol, called per protocol analyses (PP or PPA), is another potential strength to diagnostic study testing. Many measures of the new diagnostic procedure, including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, and diagnostic odds ratio can be calculated. These measures of the diagnostic test allow for comparison with other diagnostic tests and aid the clinician in determining which test to utilize.
Interventional study designs
Interventional study designs, also called experimental study designs, are those where the researcher intervenes at some point throughout the study. The most common and strongest interventional study design is a randomized controlled trial, however, there are other interventional study designs, including pre-post study design, non-randomized controlled trials, and quasi-experiments ( 1 , 5 , 13 ). Experimental studies are used to evaluate study questions related to either therapeutic agents or prevention. Therapeutic agents can include prophylactic agents, treatments, surgical approaches, or diagnostic tests. Prevention can include changes to protective equipment, engineering controls, management, policy or any element that should be evaluated as to a potential cause of disease or injury.
Pre-post study design
A pre-post study measures the occurrence of an outcome before and again after a particular intervention is implemented. A good example is comparing deaths from motor vehicle crashes before and after the enforcement of a seat-belt law. Pre-post studies may be single arm, one group measured before the intervention and again after the intervention, or multiple arms, where there is a comparison between groups. Often there is an arm where there is no intervention. The no-intervention arm acts as the control group in a multi-arm pre-post study. These studies have the strength of temporality to be able to suggest that the outcome is impacted by the intervention, however, pre-post studies do not have control over other elements that are also changing at the same time as the intervention is implemented. Therefore, changes in disease occurrence during the study period cannot be fully attributed to the specific intervention. Outcomes measured for pre-post intervention studies may be binary health outcomes such as incidence or prevalence, or mean values of a continuous outcome such as systolic blood pressure may also be used. The analytic methods of pre-post studies depend on the outcome being measured. If there are multiple treatment arms, it is also likely that the difference from beginning to end within each treatment arm are analysed.
Non-randomized trial study design
Non-randomized trials are interventional study designs that compare a group where an intervention was performed with a group where there was no intervention. These are convenient study designs that are most often performed prospectively and can suggest possible relationships between the intervention and the outcome. However, these study designs are often subject to many types of bias and error and are not considered a strong study design.
Randomized controlled trial study design
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are the most common type of interventional study, and can have many modifications ( 26 – 28 ). These trials take a homogenous group of study participants and randomly divide them into two separate groups. If the randomization is successful then these two groups should be the same in all respects, both measured confounders and unmeasured factors. The intervention is then implemented in one group and not the other and comparisons of intervention efficacy between the two groups are analysed. Theoretically, the only difference between the two groups through the entire study is the intervention. An excellent example is the intervention of a new medication to treat a specific disease among a group of patients. This randomization process is arguably the largest strength of an RCT ( 26 – 28 ). Additional methodological elements are utilized among RCTs to further strengthen the causal implication of the intervention’s impact. These include allocation concealment, blinding, measuring compliance, controlling for co-interventions, measuring dropout, analysing results by intention to treat, and assessing each treatment arm at the same time point in the same manner.
Crossover randomized controlled trial study design
A crossover RCT is a type of interventional study design where study participants intentionally “crossover” to the other treatment arm. This should not be confused with the observational case-crossover design. A crossover RCT begins the same as a traditional RCT, however, after the end of the first treatment phase, each participant is re-allocated to the other treatment arm. There is often a wash-out period in between treatment periods. This design has many strengths, including demonstrating reversibility, compensating for unsuccessful randomization, and improving study efficiency by not using time to recruit subjects.
Allocation concealment theoretically guarantees that the implementation of the randomization is free from bias. This is done by ensuring that the randomization scheme is concealed from all individuals involved ( 26 – 30 ). A third party who is not involved in the treatment or assessment of the trial creates the randomization schema and study participants are randomized according to that schema. By concealing the schema, there is a minimization of potential deviation from that randomization, either consciously or otherwise by the participant, researcher, provider, or assessor. The traditional method of allocation concealment relies upon sequentially numbered opaque envelopes with the treatment allocation inside. These envelopes are generated before the study begins using the selected randomization scheme. Participants are then allocated to the specific intervention arm in the pre-determined order dictated by the schema. If allocation concealment is not utilized, there is the possibility of selective enrolment into an intervention arm, potentially with the outcome of biased results.
Blinding in an RCT is withholding the treatment arm from individuals involved in the study. This can be done through use of placebo pills, deactivated treatment modalities, or sham therapy. Sham therapy is a comparison procedure or treatment which is identical to the investigational intervention except it omits a key therapeutic element, thus rendering the treatment ineffective. An example is a sham cortisone injection, where saline solution of the same volume is injected instead of cortisone. This helps ensure that patients do not know if they are receiving the active or control treatment. The process of blinding is utilized to help ensure equal treatment of the different groups, therefore continuing to isolate the difference in outcome between groups to only the intervention being administered ( 28 – 31 ). Blinding within an RCT includes patient blinding, provider blinding, or assessor blinding. In some situations it is difficult or impossible to blind one or more of the parties involved, but an ideal study would have all parties blinded until the end of the study ( 26 – 28 , 31 , 32 ).
Compliance is the degree of how well study participants adhere to the prescribed intervention. Compliance or non-compliance to the intervention can have a significant impact on the results of the study ( 26 – 29 ). If there is a differentiation in the compliance between intervention arms, that differential can mask true differences, or erroneously conclude that there are differences between the groups when one does not exist. The measurement of compliance in studies addresses the potential for differences observed in intervention arms due to intervention adherence, and can allow for partial control of differences either through post hoc stratification or statistical adjustment.
Co-interventions, interventions that impact the outcome other than the primary intervention of the study, can also allow for erroneous conclusions in clinical trials ( 26 – 28 ). If there are differences between treatment arms in the amount or type of additional therapeutic elements then the study conclusions may be incorrect ( 29 ). For example, if a placebo treatment arm utilizes more over-the-counter medication than the experimental treatment arm, both treatment arms may have the same therapeutic improvement and show no effect of the experimental treatment. However, the placebo arm improvement is due to the over-the-counter medication and if that was prohibited, there may be a therapeutic difference between the two treatment arms. The exclusion or tracking and statistical adjustment of co-interventions serves to strengthen an RCT by minimizing this potential effect.
Participants drop out of a study for multiple reasons, but if there are differential dropout rates between intervention arms or high overall dropout rates, there may be biased data or erroneous study conclusions ( 26 – 28 ). A commonly accepted dropout rate is 20% however, studies with dropout rates below 20% may have erroneous conclusions ( 29 ). Common methods for minimizing dropout include incentivizing study participation or short study duration, however, these may also lead to lack of generalizability or validity.
Intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis is a method of analysis that quantitatively addresses deviations from random allocation ( 26 – 28 ). This method analyses individuals based on their allocated intervention, regardless of whether or not that intervention was actually received due to protocol deviations, compliance concerns or subsequent withdrawal. By maintaining individuals in their allocated intervention for analyses, the benefits of randomization will be captured ( 18 , 26 – 29 ). If analysis of actual treatment is solely relied upon, then some of the theoretical benefits of randomization may be lost. This analysis method relies on complete data. There are different approaches regarding the handling of missing data and no consensus has been put forth in the literature. Common approaches are imputation or carrying forward the last observed data from individuals to address issues of missing data ( 18 , 19 ).
Assessment timing can play an important role in the impact of interventions, particularly if intervention effects are acute and short lived ( 26 – 29 , 33 ). The specific timing of assessments are unique to each intervention, however, studies that allow for meaningfully different timing of assessments are subject to erroneous results. For example, if assessments occur differentially after an injection of a particularly fast acting, short-lived medication the difference observed between intervention arms may be due to a higher proportion of participants in one intervention arm being assessed hours after the intervention instead of minutes. By tracking differences in assessment times, researchers can address the potential scope of this problem, and try to address it using statistical or other methods ( 26 – 28 , 33 ).
Randomized controlled trials are the principle method for improving treatment of disease, and there are some standardized methods for grading RCTs, and subsequently creating best practice guidelines ( 29 , 34 – 36 ). Much of the current practice of medicine lacks moderate or high quality RCTs to address what treatment methods have demonstrated efficacy and much of the best practice guidelines remains based on consensus from experts ( 28 , 37 ). The reliance on high quality methodology in all types of studies will allow for continued improvement in the assessment of causal factors for health outcomes and the treatment of diseases.
Standards of research and reporting
There are many published standards for the design, execution and reporting of biomedical research, which can be found in Table 3 . The purpose and content of these standards and guidelines are to improve the quality of biomedical research which will result in providing sound conclusions to base medical decision making upon. There are published standards for categories of study designs such as observational studies (e.g. STROBE), interventional studies (e.g. CONSORT), diagnostic studies (e.g. STARD, QUADAS), systematic reviews and meta-analyses (e.g. PRISMA ), as well as others. The aim of these standards and guideline are to systematize and elevate the quality of biomedical research design, execution, and reporting.
Published standard for study design and reporting.
- Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials (CONSORT, www.consort-statement.org ) are interventional study standards, a 25 item checklist and flowchart specifically designed for RCTs to standardize reporting of key elements including design, analysis and interpretation of the RCT.
- Strengthening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE, www.strobe-statement.org ) is a collection of guidelines specifically for standardization and improvement of the reporting of observational epidemiological research. There are specific subsets of the STROBE statement including molecular epidemiology (STROBE-ME), infectious diseases (STROBE-ID) and genetic association studies (STREGA).
- Standards for Reporting Studies of Diagnos tic Accuracy (STARD, www.stard-statement.org ) is a 25 element checklist and flow diagram specifically designed for the reporting of diagnostic accuracy studies.
- Quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies (QUADAS, www.bris.ac.uk/quadas ) is a quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies.
- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA, www.prisma-statement.org ) is a 27 element checklist and multiphase flow diagram to improve quality of reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses. It replaces the QUOROM statement.
- Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) is a 32 element checklist designed for reporting of qualitative data from interviews and focus groups.
- Statistical Analyses and Methods in the Published Literature (SAMPL) is a guideline for statistical methods and analyses of all types of biomedical research.
- Consensus-based Clinical Case Reporting Guideline Development (CARE, www.carestatement.org ) is a checklist comprised of 13 elements and is designed only for case reports.
- Standards for Quality Improvement Reporting Excellence (SQUIRE, www.squire-statement.org ) are publication guidelines comprised of 19 elements, for authors aimed at quality improvement in health care reporting.
- Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS) is a 24 element checklist of reporting practices for economic evaluations of interventional studies.
- Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research (ENTREQ) is a guideline specifically for standardizing and improving the reporting of qualitative biomedical research.
When designing or evaluating a study it may be helpful to review the applicable standards prior to executing and publishing the study. All published standards and guidelines are available on the web, and are updated based on current best practices as biomedical research evolves. Additionally, there is a network called “Enhancing the quality and transparency of health research” (EQUATOR, www.equator-network.org ) , which has guidelines and checklists for all standards reported in Table 3 and is continually updated with new study design or specialty specific standards.
The appropriate selection of a study design is only one element in successful research. The selection of a study design should incorporate consideration of costs, access to cases, identification of the exposure, the epidemiologic measures that are required, and the level of evidence that is currently published regarding the specific exposure-outcome relationship that is being assessed. Reviewing appropriate published standards when designing a study can substantially strengthen the execution and interpretation of study results.
Potential conflict of interest
None declared.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Ch 2: Psychological Research Methods

Have you ever wondered whether the violence you see on television affects your behavior? Are you more likely to behave aggressively in real life after watching people behave violently in dramatic situations on the screen? Or, could seeing fictional violence actually get aggression out of your system, causing you to be more peaceful? How are children influenced by the media they are exposed to? A psychologist interested in the relationship between behavior and exposure to violent images might ask these very questions.
The topic of violence in the media today is contentious. Since ancient times, humans have been concerned about the effects of new technologies on our behaviors and thinking processes. The Greek philosopher Socrates, for example, worried that writing—a new technology at that time—would diminish people’s ability to remember because they could rely on written records rather than committing information to memory. In our world of quickly changing technologies, questions about the effects of media continue to emerge. Is it okay to talk on a cell phone while driving? Are headphones good to use in a car? What impact does text messaging have on reaction time while driving? These are types of questions that psychologist David Strayer asks in his lab.
Watch this short video to see how Strayer utilizes the scientific method to reach important conclusions regarding technology and driving safety.
You can view the transcript for “Understanding driver distraction” here (opens in new window) .
How can we go about finding answers that are supported not by mere opinion, but by evidence that we can all agree on? The findings of psychological research can help us navigate issues like this.
Introduction to the Scientific Method
Learning objectives.
- Explain the steps of the scientific method
- Describe why the scientific method is important to psychology
- Summarize the processes of informed consent and debriefing
- Explain how research involving humans or animals is regulated

Scientists are engaged in explaining and understanding how the world around them works, and they are able to do so by coming up with theories that generate hypotheses that are testable and falsifiable. Theories that stand up to their tests are retained and refined, while those that do not are discarded or modified. In this way, research enables scientists to separate fact from simple opinion. Having good information generated from research aids in making wise decisions both in public policy and in our personal lives. In this section, you’ll see how psychologists use the scientific method to study and understand behavior.
The Scientific Process
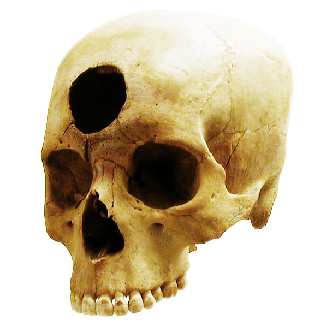
The goal of all scientists is to better understand the world around them. Psychologists focus their attention on understanding behavior, as well as the cognitive (mental) and physiological (body) processes that underlie behavior. In contrast to other methods that people use to understand the behavior of others, such as intuition and personal experience, the hallmark of scientific research is that there is evidence to support a claim. Scientific knowledge is empirical : It is grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless of who is observing.
While behavior is observable, the mind is not. If someone is crying, we can see the behavior. However, the reason for the behavior is more difficult to determine. Is the person crying due to being sad, in pain, or happy? Sometimes we can learn the reason for someone’s behavior by simply asking a question, like “Why are you crying?” However, there are situations in which an individual is either uncomfortable or unwilling to answer the question honestly, or is incapable of answering. For example, infants would not be able to explain why they are crying. In such circumstances, the psychologist must be creative in finding ways to better understand behavior. This module explores how scientific knowledge is generated, and how important that knowledge is in forming decisions in our personal lives and in the public domain.
Process of Scientific Research
Scientific knowledge is advanced through a process known as the scientific method. Basically, ideas (in the form of theories and hypotheses) are tested against the real world (in the form of empirical observations), and those empirical observations lead to more ideas that are tested against the real world, and so on.
The basic steps in the scientific method are:
- Observe a natural phenomenon and define a question about it
- Make a hypothesis, or potential solution to the question
- Test the hypothesis
- If the hypothesis is true, find more evidence or find counter-evidence
- If the hypothesis is false, create a new hypothesis or try again
- Draw conclusions and repeat–the scientific method is never-ending, and no result is ever considered perfect
In order to ask an important question that may improve our understanding of the world, a researcher must first observe natural phenomena. By making observations, a researcher can define a useful question. After finding a question to answer, the researcher can then make a prediction (a hypothesis) about what he or she thinks the answer will be. This prediction is usually a statement about the relationship between two or more variables. After making a hypothesis, the researcher will then design an experiment to test his or her hypothesis and evaluate the data gathered. These data will either support or refute the hypothesis. Based on the conclusions drawn from the data, the researcher will then find more evidence to support the hypothesis, look for counter-evidence to further strengthen the hypothesis, revise the hypothesis and create a new experiment, or continue to incorporate the information gathered to answer the research question.
Basic Principles of the Scientific Method
Two key concepts in the scientific approach are theory and hypothesis. A theory is a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena that can be used to make predictions about future observations. A hypothesis is a testable prediction that is arrived at logically from a theory. It is often worded as an if-then statement (e.g., if I study all night, I will get a passing grade on the test). The hypothesis is extremely important because it bridges the gap between the realm of ideas and the real world. As specific hypotheses are tested, theories are modified and refined to reflect and incorporate the result of these tests.
Other key components in following the scientific method include verifiability, predictability, falsifiability, and fairness. Verifiability means that an experiment must be replicable by another researcher. To achieve verifiability, researchers must make sure to document their methods and clearly explain how their experiment is structured and why it produces certain results.
Predictability in a scientific theory implies that the theory should enable us to make predictions about future events. The precision of these predictions is a measure of the strength of the theory.
Falsifiability refers to whether a hypothesis can be disproved. For a hypothesis to be falsifiable, it must be logically possible to make an observation or do a physical experiment that would show that there is no support for the hypothesis. Even when a hypothesis cannot be shown to be false, that does not necessarily mean it is not valid. Future testing may disprove the hypothesis. This does not mean that a hypothesis has to be shown to be false, just that it can be tested.
To determine whether a hypothesis is supported or not supported, psychological researchers must conduct hypothesis testing using statistics. Hypothesis testing is a type of statistics that determines the probability of a hypothesis being true or false. If hypothesis testing reveals that results were “statistically significant,” this means that there was support for the hypothesis and that the researchers can be reasonably confident that their result was not due to random chance. If the results are not statistically significant, this means that the researchers’ hypothesis was not supported.
Fairness implies that all data must be considered when evaluating a hypothesis. A researcher cannot pick and choose what data to keep and what to discard or focus specifically on data that support or do not support a particular hypothesis. All data must be accounted for, even if they invalidate the hypothesis.
Applying the Scientific Method
To see how this process works, let’s consider a specific theory and a hypothesis that might be generated from that theory. As you’ll learn in a later module, the James-Lange theory of emotion asserts that emotional experience relies on the physiological arousal associated with the emotional state. If you walked out of your home and discovered a very aggressive snake waiting on your doorstep, your heart would begin to race and your stomach churn. According to the James-Lange theory, these physiological changes would result in your feeling of fear. A hypothesis that could be derived from this theory might be that a person who is unaware of the physiological arousal that the sight of the snake elicits will not feel fear.
Remember that a good scientific hypothesis is falsifiable, or capable of being shown to be incorrect. Recall from the introductory module that Sigmund Freud had lots of interesting ideas to explain various human behaviors (Figure 5). However, a major criticism of Freud’s theories is that many of his ideas are not falsifiable; for example, it is impossible to imagine empirical observations that would disprove the existence of the id, the ego, and the superego—the three elements of personality described in Freud’s theories. Despite this, Freud’s theories are widely taught in introductory psychology texts because of their historical significance for personality psychology and psychotherapy, and these remain the root of all modern forms of therapy.
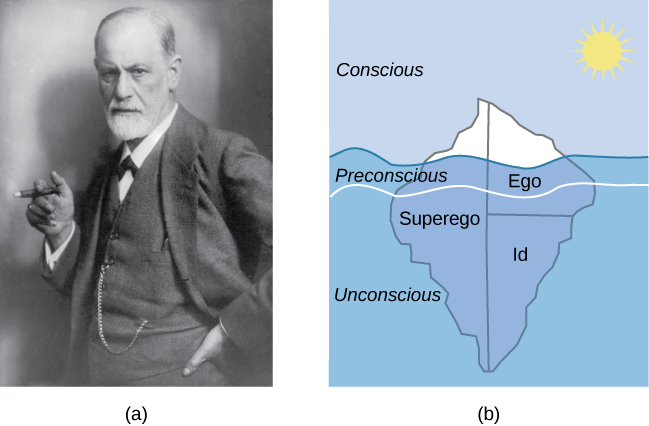
In contrast, the James-Lange theory does generate falsifiable hypotheses, such as the one described above. Some individuals who suffer significant injuries to their spinal columns are unable to feel the bodily changes that often accompany emotional experiences. Therefore, we could test the hypothesis by determining how emotional experiences differ between individuals who have the ability to detect these changes in their physiological arousal and those who do not. In fact, this research has been conducted and while the emotional experiences of people deprived of an awareness of their physiological arousal may be less intense, they still experience emotion (Chwalisz, Diener, & Gallagher, 1988).
Link to Learning
Why the scientific method is important for psychology.
The use of the scientific method is one of the main features that separates modern psychology from earlier philosophical inquiries about the mind. Compared to chemistry, physics, and other “natural sciences,” psychology has long been considered one of the “social sciences” because of the subjective nature of the things it seeks to study. Many of the concepts that psychologists are interested in—such as aspects of the human mind, behavior, and emotions—are subjective and cannot be directly measured. Psychologists often rely instead on behavioral observations and self-reported data, which are considered by some to be illegitimate or lacking in methodological rigor. Applying the scientific method to psychology, therefore, helps to standardize the approach to understanding its very different types of information.
The scientific method allows psychological data to be replicated and confirmed in many instances, under different circumstances, and by a variety of researchers. Through replication of experiments, new generations of psychologists can reduce errors and broaden the applicability of theories. It also allows theories to be tested and validated instead of simply being conjectures that could never be verified or falsified. All of this allows psychologists to gain a stronger understanding of how the human mind works.
Scientific articles published in journals and psychology papers written in the style of the American Psychological Association (i.e., in “APA style”) are structured around the scientific method. These papers include an Introduction, which introduces the background information and outlines the hypotheses; a Methods section, which outlines the specifics of how the experiment was conducted to test the hypothesis; a Results section, which includes the statistics that tested the hypothesis and state whether it was supported or not supported, and a Discussion and Conclusion, which state the implications of finding support for, or no support for, the hypothesis. Writing articles and papers that adhere to the scientific method makes it easy for future researchers to repeat the study and attempt to replicate the results.
Ethics in Research
Today, scientists agree that good research is ethical in nature and is guided by a basic respect for human dignity and safety. However, as you will read in the Tuskegee Syphilis Study, this has not always been the case. Modern researchers must demonstrate that the research they perform is ethically sound. This section presents how ethical considerations affect the design and implementation of research conducted today.
Research Involving Human Participants
Any experiment involving the participation of human subjects is governed by extensive, strict guidelines designed to ensure that the experiment does not result in harm. Any research institution that receives federal support for research involving human participants must have access to an institutional review board (IRB) . The IRB is a committee of individuals often made up of members of the institution’s administration, scientists, and community members (Figure 6). The purpose of the IRB is to review proposals for research that involves human participants. The IRB reviews these proposals with the principles mentioned above in mind, and generally, approval from the IRB is required in order for the experiment to proceed.

An institution’s IRB requires several components in any experiment it approves. For one, each participant must sign an informed consent form before they can participate in the experiment. An informed consent form provides a written description of what participants can expect during the experiment, including potential risks and implications of the research. It also lets participants know that their involvement is completely voluntary and can be discontinued without penalty at any time. Furthermore, the informed consent guarantees that any data collected in the experiment will remain completely confidential. In cases where research participants are under the age of 18, the parents or legal guardians are required to sign the informed consent form.
While the informed consent form should be as honest as possible in describing exactly what participants will be doing, sometimes deception is necessary to prevent participants’ knowledge of the exact research question from affecting the results of the study. Deception involves purposely misleading experiment participants in order to maintain the integrity of the experiment, but not to the point where the deception could be considered harmful. For example, if we are interested in how our opinion of someone is affected by their attire, we might use deception in describing the experiment to prevent that knowledge from affecting participants’ responses. In cases where deception is involved, participants must receive a full debriefing upon conclusion of the study—complete, honest information about the purpose of the experiment, how the data collected will be used, the reasons why deception was necessary, and information about how to obtain additional information about the study.
Dig Deeper: Ethics and the Tuskegee Syphilis Study
Unfortunately, the ethical guidelines that exist for research today were not always applied in the past. In 1932, poor, rural, black, male sharecroppers from Tuskegee, Alabama, were recruited to participate in an experiment conducted by the U.S. Public Health Service, with the aim of studying syphilis in black men (Figure 7). In exchange for free medical care, meals, and burial insurance, 600 men agreed to participate in the study. A little more than half of the men tested positive for syphilis, and they served as the experimental group (given that the researchers could not randomly assign participants to groups, this represents a quasi-experiment). The remaining syphilis-free individuals served as the control group. However, those individuals that tested positive for syphilis were never informed that they had the disease.
While there was no treatment for syphilis when the study began, by 1947 penicillin was recognized as an effective treatment for the disease. Despite this, no penicillin was administered to the participants in this study, and the participants were not allowed to seek treatment at any other facilities if they continued in the study. Over the course of 40 years, many of the participants unknowingly spread syphilis to their wives (and subsequently their children born from their wives) and eventually died because they never received treatment for the disease. This study was discontinued in 1972 when the experiment was discovered by the national press (Tuskegee University, n.d.). The resulting outrage over the experiment led directly to the National Research Act of 1974 and the strict ethical guidelines for research on humans described in this chapter. Why is this study unethical? How were the men who participated and their families harmed as a function of this research?

Learn more about the Tuskegee Syphilis Study on the CDC website .
Research Involving Animal Subjects

This does not mean that animal researchers are immune to ethical concerns. Indeed, the humane and ethical treatment of animal research subjects is a critical aspect of this type of research. Researchers must design their experiments to minimize any pain or distress experienced by animals serving as research subjects.
Whereas IRBs review research proposals that involve human participants, animal experimental proposals are reviewed by an Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) . An IACUC consists of institutional administrators, scientists, veterinarians, and community members. This committee is charged with ensuring that all experimental proposals require the humane treatment of animal research subjects. It also conducts semi-annual inspections of all animal facilities to ensure that the research protocols are being followed. No animal research project can proceed without the committee’s approval.
Introduction to Approaches to Research
- Differentiate between descriptive, correlational, and experimental research
- Explain the strengths and weaknesses of case studies, naturalistic observation, and surveys
- Describe the strength and weaknesses of archival research
- Compare longitudinal and cross-sectional approaches to research
- Explain what a correlation coefficient tells us about the relationship between variables
- Describe why correlation does not mean causation
- Describe the experimental process, including ways to control for bias
- Identify and differentiate between independent and dependent variables

Psychologists use descriptive, experimental, and correlational methods to conduct research. Descriptive, or qualitative, methods include the case study, naturalistic observation, surveys, archival research, longitudinal research, and cross-sectional research.
Experiments are conducted in order to determine cause-and-effect relationships. In ideal experimental design, the only difference between the experimental and control groups is whether participants are exposed to the experimental manipulation. Each group goes through all phases of the experiment, but each group will experience a different level of the independent variable: the experimental group is exposed to the experimental manipulation, and the control group is not exposed to the experimental manipulation. The researcher then measures the changes that are produced in the dependent variable in each group. Once data is collected from both groups, it is analyzed statistically to determine if there are meaningful differences between the groups.
When scientists passively observe and measure phenomena it is called correlational research. Here, psychologists do not intervene and change behavior, as they do in experiments. In correlational research, they identify patterns of relationships, but usually cannot infer what causes what. Importantly, with correlational research, you can examine only two variables at a time, no more and no less.
Watch It: More on Research
If you enjoy learning through lectures and want an interesting and comprehensive summary of this section, then click on the Youtube link to watch a lecture given by MIT Professor John Gabrieli . Start at the 30:45 minute mark and watch through the end to hear examples of actual psychological studies and how they were analyzed. Listen for references to independent and dependent variables, experimenter bias, and double-blind studies. In the lecture, you’ll learn about breaking social norms, “WEIRD” research, why expectations matter, how a warm cup of coffee might make you nicer, why you should change your answer on a multiple choice test, and why praise for intelligence won’t make you any smarter.
You can view the transcript for “Lec 2 | MIT 9.00SC Introduction to Psychology, Spring 2011” here (opens in new window) .
Descriptive Research
There are many research methods available to psychologists in their efforts to understand, describe, and explain behavior and the cognitive and biological processes that underlie it. Some methods rely on observational techniques. Other approaches involve interactions between the researcher and the individuals who are being studied—ranging from a series of simple questions to extensive, in-depth interviews—to well-controlled experiments.
The three main categories of psychological research are descriptive, correlational, and experimental research. Research studies that do not test specific relationships between variables are called descriptive, or qualitative, studies . These studies are used to describe general or specific behaviors and attributes that are observed and measured. In the early stages of research it might be difficult to form a hypothesis, especially when there is not any existing literature in the area. In these situations designing an experiment would be premature, as the question of interest is not yet clearly defined as a hypothesis. Often a researcher will begin with a non-experimental approach, such as a descriptive study, to gather more information about the topic before designing an experiment or correlational study to address a specific hypothesis. Descriptive research is distinct from correlational research , in which psychologists formally test whether a relationship exists between two or more variables. Experimental research goes a step further beyond descriptive and correlational research and randomly assigns people to different conditions, using hypothesis testing to make inferences about how these conditions affect behavior. It aims to determine if one variable directly impacts and causes another. Correlational and experimental research both typically use hypothesis testing, whereas descriptive research does not.
Each of these research methods has unique strengths and weaknesses, and each method may only be appropriate for certain types of research questions. For example, studies that rely primarily on observation produce incredible amounts of information, but the ability to apply this information to the larger population is somewhat limited because of small sample sizes. Survey research, on the other hand, allows researchers to easily collect data from relatively large samples. While this allows for results to be generalized to the larger population more easily, the information that can be collected on any given survey is somewhat limited and subject to problems associated with any type of self-reported data. Some researchers conduct archival research by using existing records. While this can be a fairly inexpensive way to collect data that can provide insight into a number of research questions, researchers using this approach have no control on how or what kind of data was collected.
Correlational research can find a relationship between two variables, but the only way a researcher can claim that the relationship between the variables is cause and effect is to perform an experiment. In experimental research, which will be discussed later in the text, there is a tremendous amount of control over variables of interest. While this is a powerful approach, experiments are often conducted in very artificial settings. This calls into question the validity of experimental findings with regard to how they would apply in real-world settings. In addition, many of the questions that psychologists would like to answer cannot be pursued through experimental research because of ethical concerns.
The three main types of descriptive studies are, naturalistic observation, case studies, and surveys.
Naturalistic Observation
If you want to understand how behavior occurs, one of the best ways to gain information is to simply observe the behavior in its natural context. However, people might change their behavior in unexpected ways if they know they are being observed. How do researchers obtain accurate information when people tend to hide their natural behavior? As an example, imagine that your professor asks everyone in your class to raise their hand if they always wash their hands after using the restroom. Chances are that almost everyone in the classroom will raise their hand, but do you think hand washing after every trip to the restroom is really that universal?
This is very similar to the phenomenon mentioned earlier in this module: many individuals do not feel comfortable answering a question honestly. But if we are committed to finding out the facts about hand washing, we have other options available to us.
Suppose we send a classmate into the restroom to actually watch whether everyone washes their hands after using the restroom. Will our observer blend into the restroom environment by wearing a white lab coat, sitting with a clipboard, and staring at the sinks? We want our researcher to be inconspicuous—perhaps standing at one of the sinks pretending to put in contact lenses while secretly recording the relevant information. This type of observational study is called naturalistic observation : observing behavior in its natural setting. To better understand peer exclusion, Suzanne Fanger collaborated with colleagues at the University of Texas to observe the behavior of preschool children on a playground. How did the observers remain inconspicuous over the duration of the study? They equipped a few of the children with wireless microphones (which the children quickly forgot about) and observed while taking notes from a distance. Also, the children in that particular preschool (a “laboratory preschool”) were accustomed to having observers on the playground (Fanger, Frankel, & Hazen, 2012).

It is critical that the observer be as unobtrusive and as inconspicuous as possible: when people know they are being watched, they are less likely to behave naturally. If you have any doubt about this, ask yourself how your driving behavior might differ in two situations: In the first situation, you are driving down a deserted highway during the middle of the day; in the second situation, you are being followed by a police car down the same deserted highway (Figure 9).
It should be pointed out that naturalistic observation is not limited to research involving humans. Indeed, some of the best-known examples of naturalistic observation involve researchers going into the field to observe various kinds of animals in their own environments. As with human studies, the researchers maintain their distance and avoid interfering with the animal subjects so as not to influence their natural behaviors. Scientists have used this technique to study social hierarchies and interactions among animals ranging from ground squirrels to gorillas. The information provided by these studies is invaluable in understanding how those animals organize socially and communicate with one another. The anthropologist Jane Goodall, for example, spent nearly five decades observing the behavior of chimpanzees in Africa (Figure 10). As an illustration of the types of concerns that a researcher might encounter in naturalistic observation, some scientists criticized Goodall for giving the chimps names instead of referring to them by numbers—using names was thought to undermine the emotional detachment required for the objectivity of the study (McKie, 2010).

The greatest benefit of naturalistic observation is the validity, or accuracy, of information collected unobtrusively in a natural setting. Having individuals behave as they normally would in a given situation means that we have a higher degree of ecological validity, or realism, than we might achieve with other research approaches. Therefore, our ability to generalize the findings of the research to real-world situations is enhanced. If done correctly, we need not worry about people or animals modifying their behavior simply because they are being observed. Sometimes, people may assume that reality programs give us a glimpse into authentic human behavior. However, the principle of inconspicuous observation is violated as reality stars are followed by camera crews and are interviewed on camera for personal confessionals. Given that environment, we must doubt how natural and realistic their behaviors are.
The major downside of naturalistic observation is that they are often difficult to set up and control. In our restroom study, what if you stood in the restroom all day prepared to record people’s hand washing behavior and no one came in? Or, what if you have been closely observing a troop of gorillas for weeks only to find that they migrated to a new place while you were sleeping in your tent? The benefit of realistic data comes at a cost. As a researcher you have no control of when (or if) you have behavior to observe. In addition, this type of observational research often requires significant investments of time, money, and a good dose of luck.
Sometimes studies involve structured observation. In these cases, people are observed while engaging in set, specific tasks. An excellent example of structured observation comes from Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth (you will read more about this in the module on lifespan development). The Strange Situation is a procedure used to evaluate attachment styles that exist between an infant and caregiver. In this scenario, caregivers bring their infants into a room filled with toys. The Strange Situation involves a number of phases, including a stranger coming into the room, the caregiver leaving the room, and the caregiver’s return to the room. The infant’s behavior is closely monitored at each phase, but it is the behavior of the infant upon being reunited with the caregiver that is most telling in terms of characterizing the infant’s attachment style with the caregiver.
Another potential problem in observational research is observer bias . Generally, people who act as observers are closely involved in the research project and may unconsciously skew their observations to fit their research goals or expectations. To protect against this type of bias, researchers should have clear criteria established for the types of behaviors recorded and how those behaviors should be classified. In addition, researchers often compare observations of the same event by multiple observers, in order to test inter-rater reliability : a measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of observations by different observers.
Case Studies
In 2011, the New York Times published a feature story on Krista and Tatiana Hogan, Canadian twin girls. These particular twins are unique because Krista and Tatiana are conjoined twins, connected at the head. There is evidence that the two girls are connected in a part of the brain called the thalamus, which is a major sensory relay center. Most incoming sensory information is sent through the thalamus before reaching higher regions of the cerebral cortex for processing.
The implications of this potential connection mean that it might be possible for one twin to experience the sensations of the other twin. For instance, if Krista is watching a particularly funny television program, Tatiana might smile or laugh even if she is not watching the program. This particular possibility has piqued the interest of many neuroscientists who seek to understand how the brain uses sensory information.
These twins represent an enormous resource in the study of the brain, and since their condition is very rare, it is likely that as long as their family agrees, scientists will follow these girls very closely throughout their lives to gain as much information as possible (Dominus, 2011).
In observational research, scientists are conducting a clinical or case study when they focus on one person or just a few individuals. Indeed, some scientists spend their entire careers studying just 10–20 individuals. Why would they do this? Obviously, when they focus their attention on a very small number of people, they can gain a tremendous amount of insight into those cases. The richness of information that is collected in clinical or case studies is unmatched by any other single research method. This allows the researcher to have a very deep understanding of the individuals and the particular phenomenon being studied.
If clinical or case studies provide so much information, why are they not more frequent among researchers? As it turns out, the major benefit of this particular approach is also a weakness. As mentioned earlier, this approach is often used when studying individuals who are interesting to researchers because they have a rare characteristic. Therefore, the individuals who serve as the focus of case studies are not like most other people. If scientists ultimately want to explain all behavior, focusing attention on such a special group of people can make it difficult to generalize any observations to the larger population as a whole. Generalizing refers to the ability to apply the findings of a particular research project to larger segments of society. Again, case studies provide enormous amounts of information, but since the cases are so specific, the potential to apply what’s learned to the average person may be very limited.
Often, psychologists develop surveys as a means of gathering data. Surveys are lists of questions to be answered by research participants, and can be delivered as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally (Figure 11). Generally, the survey itself can be completed in a short time, and the ease of administering a survey makes it easy to collect data from a large number of people.
Surveys allow researchers to gather data from larger samples than may be afforded by other research methods . A sample is a subset of individuals selected from a population , which is the overall group of individuals that the researchers are interested in. Researchers study the sample and seek to generalize their findings to the population.

There is both strength and weakness of the survey in comparison to case studies. By using surveys, we can collect information from a larger sample of people. A larger sample is better able to reflect the actual diversity of the population, thus allowing better generalizability. Therefore, if our sample is sufficiently large and diverse, we can assume that the data we collect from the survey can be generalized to the larger population with more certainty than the information collected through a case study. However, given the greater number of people involved, we are not able to collect the same depth of information on each person that would be collected in a case study.
Another potential weakness of surveys is something we touched on earlier in this chapter: people don’t always give accurate responses. They may lie, misremember, or answer questions in a way that they think makes them look good. For example, people may report drinking less alcohol than is actually the case.
Any number of research questions can be answered through the use of surveys. One real-world example is the research conducted by Jenkins, Ruppel, Kizer, Yehl, and Griffin (2012) about the backlash against the US Arab-American community following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Jenkins and colleagues wanted to determine to what extent these negative attitudes toward Arab-Americans still existed nearly a decade after the attacks occurred. In one study, 140 research participants filled out a survey with 10 questions, including questions asking directly about the participant’s overt prejudicial attitudes toward people of various ethnicities. The survey also asked indirect questions about how likely the participant would be to interact with a person of a given ethnicity in a variety of settings (such as, “How likely do you think it is that you would introduce yourself to a person of Arab-American descent?”). The results of the research suggested that participants were unwilling to report prejudicial attitudes toward any ethnic group. However, there were significant differences between their pattern of responses to questions about social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to other ethnic groups: they indicated less willingness for social interaction with Arab-Americans compared to the other ethnic groups. This suggested that the participants harbored subtle forms of prejudice against Arab-Americans, despite their assertions that this was not the case (Jenkins et al., 2012).
Think It Over
Archival research.

In comparing archival research to other research methods, there are several important distinctions. For one, the researcher employing archival research never directly interacts with research participants. Therefore, the investment of time and money to collect data is considerably less with archival research. Additionally, researchers have no control over what information was originally collected. Therefore, research questions have to be tailored so they can be answered within the structure of the existing data sets. There is also no guarantee of consistency between the records from one source to another, which might make comparing and contrasting different data sets problematic.
Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Research
Sometimes we want to see how people change over time, as in studies of human development and lifespan. When we test the same group of individuals repeatedly over an extended period of time, we are conducting longitudinal research. Longitudinal research is a research design in which data-gathering is administered repeatedly over an extended period of time. For example, we may survey a group of individuals about their dietary habits at age 20, retest them a decade later at age 30, and then again at age 40.
Another approach is cross-sectional research . In cross-sectional research, a researcher compares multiple segments of the population at the same time. Using the dietary habits example above, the researcher might directly compare different groups of people by age. Instead of observing a group of people for 20 years to see how their dietary habits changed from decade to decade, the researcher would study a group of 20-year-old individuals and compare them to a group of 30-year-old individuals and a group of 40-year-old individuals. While cross-sectional research requires a shorter-term investment, it is also limited by differences that exist between the different generations (or cohorts) that have nothing to do with age per se, but rather reflect the social and cultural experiences of different generations of individuals make them different from one another.
To illustrate this concept, consider the following survey findings. In recent years there has been significant growth in the popular support of same-sex marriage. Many studies on this topic break down survey participants into different age groups. In general, younger people are more supportive of same-sex marriage than are those who are older (Jones, 2013). Does this mean that as we age we become less open to the idea of same-sex marriage, or does this mean that older individuals have different perspectives because of the social climates in which they grew up? Longitudinal research is a powerful approach because the same individuals are involved in the research project over time, which means that the researchers need to be less concerned with differences among cohorts affecting the results of their study.
Often longitudinal studies are employed when researching various diseases in an effort to understand particular risk factors. Such studies often involve tens of thousands of individuals who are followed for several decades. Given the enormous number of people involved in these studies, researchers can feel confident that their findings can be generalized to the larger population. The Cancer Prevention Study-3 (CPS-3) is one of a series of longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society aimed at determining predictive risk factors associated with cancer. When participants enter the study, they complete a survey about their lives and family histories, providing information on factors that might cause or prevent the development of cancer. Then every few years the participants receive additional surveys to complete. In the end, hundreds of thousands of participants will be tracked over 20 years to determine which of them develop cancer and which do not.
Clearly, this type of research is important and potentially very informative. For instance, earlier longitudinal studies sponsored by the American Cancer Society provided some of the first scientific demonstrations of the now well-established links between increased rates of cancer and smoking (American Cancer Society, n.d.) (Figure 13).

As with any research strategy, longitudinal research is not without limitations. For one, these studies require an incredible time investment by the researcher and research participants. Given that some longitudinal studies take years, if not decades, to complete, the results will not be known for a considerable period of time. In addition to the time demands, these studies also require a substantial financial investment. Many researchers are unable to commit the resources necessary to see a longitudinal project through to the end.
Research participants must also be willing to continue their participation for an extended period of time, and this can be problematic. People move, get married and take new names, get ill, and eventually die. Even without significant life changes, some people may simply choose to discontinue their participation in the project. As a result, the attrition rates, or reduction in the number of research participants due to dropouts, in longitudinal studies are quite high and increases over the course of a project. For this reason, researchers using this approach typically recruit many participants fully expecting that a substantial number will drop out before the end. As the study progresses, they continually check whether the sample still represents the larger population, and make adjustments as necessary.
Correlational Research
Did you know that as sales in ice cream increase, so does the overall rate of crime? Is it possible that indulging in your favorite flavor of ice cream could send you on a crime spree? Or, after committing crime do you think you might decide to treat yourself to a cone? There is no question that a relationship exists between ice cream and crime (e.g., Harper, 2013), but it would be pretty foolish to decide that one thing actually caused the other to occur.
It is much more likely that both ice cream sales and crime rates are related to the temperature outside. When the temperature is warm, there are lots of people out of their houses, interacting with each other, getting annoyed with one another, and sometimes committing crimes. Also, when it is warm outside, we are more likely to seek a cool treat like ice cream. How do we determine if there is indeed a relationship between two things? And when there is a relationship, how can we discern whether it is attributable to coincidence or causation?
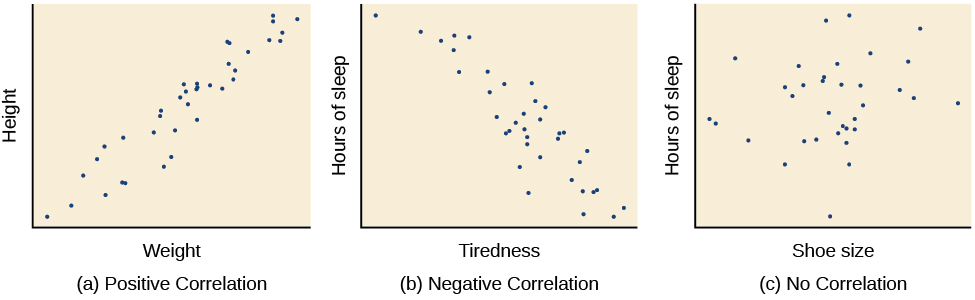
Correlation Does Not Indicate Causation
Correlational research is useful because it allows us to discover the strength and direction of relationships that exist between two variables. However, correlation is limited because establishing the existence of a relationship tells us little about cause and effect . While variables are sometimes correlated because one does cause the other, it could also be that some other factor, a confounding variable , is actually causing the systematic movement in our variables of interest. In the ice cream/crime rate example mentioned earlier, temperature is a confounding variable that could account for the relationship between the two variables.
Even when we cannot point to clear confounding variables, we should not assume that a correlation between two variables implies that one variable causes changes in another. This can be frustrating when a cause-and-effect relationship seems clear and intuitive. Think back to our discussion of the research done by the American Cancer Society and how their research projects were some of the first demonstrations of the link between smoking and cancer. It seems reasonable to assume that smoking causes cancer, but if we were limited to correlational research , we would be overstepping our bounds by making this assumption.

Unfortunately, people mistakenly make claims of causation as a function of correlations all the time. Such claims are especially common in advertisements and news stories. For example, recent research found that people who eat cereal on a regular basis achieve healthier weights than those who rarely eat cereal (Frantzen, Treviño, Echon, Garcia-Dominic, & DiMarco, 2013; Barton et al., 2005). Guess how the cereal companies report this finding. Does eating cereal really cause an individual to maintain a healthy weight, or are there other possible explanations, such as, someone at a healthy weight is more likely to regularly eat a healthy breakfast than someone who is obese or someone who avoids meals in an attempt to diet (Figure 15)? While correlational research is invaluable in identifying relationships among variables, a major limitation is the inability to establish causality. Psychologists want to make statements about cause and effect, but the only way to do that is to conduct an experiment to answer a research question. The next section describes how scientific experiments incorporate methods that eliminate, or control for, alternative explanations, which allow researchers to explore how changes in one variable cause changes in another variable.
Watch this clip from Freakonomics for an example of how correlation does not indicate causation.
You can view the transcript for “Correlation vs. Causality: Freakonomics Movie” here (opens in new window) .
Illusory Correlations
The temptation to make erroneous cause-and-effect statements based on correlational research is not the only way we tend to misinterpret data. We also tend to make the mistake of illusory correlations, especially with unsystematic observations. Illusory correlations , or false correlations, occur when people believe that relationships exist between two things when no such relationship exists. One well-known illusory correlation is the supposed effect that the moon’s phases have on human behavior. Many people passionately assert that human behavior is affected by the phase of the moon, and specifically, that people act strangely when the moon is full (Figure 16).

There is no denying that the moon exerts a powerful influence on our planet. The ebb and flow of the ocean’s tides are tightly tied to the gravitational forces of the moon. Many people believe, therefore, that it is logical that we are affected by the moon as well. After all, our bodies are largely made up of water. A meta-analysis of nearly 40 studies consistently demonstrated, however, that the relationship between the moon and our behavior does not exist (Rotton & Kelly, 1985). While we may pay more attention to odd behavior during the full phase of the moon, the rates of odd behavior remain constant throughout the lunar cycle.
Why are we so apt to believe in illusory correlations like this? Often we read or hear about them and simply accept the information as valid. Or, we have a hunch about how something works and then look for evidence to support that hunch, ignoring evidence that would tell us our hunch is false; this is known as confirmation bias . Other times, we find illusory correlations based on the information that comes most easily to mind, even if that information is severely limited. And while we may feel confident that we can use these relationships to better understand and predict the world around us, illusory correlations can have significant drawbacks. For example, research suggests that illusory correlations—in which certain behaviors are inaccurately attributed to certain groups—are involved in the formation of prejudicial attitudes that can ultimately lead to discriminatory behavior (Fiedler, 2004).
We all have a tendency to make illusory correlations from time to time. Try to think of an illusory correlation that is held by you, a family member, or a close friend. How do you think this illusory correlation came about and what can be done in the future to combat them?
Experiments
Causality: conducting experiments and using the data, experimental hypothesis.
In order to conduct an experiment, a researcher must have a specific hypothesis to be tested. As you’ve learned, hypotheses can be formulated either through direct observation of the real world or after careful review of previous research. For example, if you think that children should not be allowed to watch violent programming on television because doing so would cause them to behave more violently, then you have basically formulated a hypothesis—namely, that watching violent television programs causes children to behave more violently. How might you have arrived at this particular hypothesis? You may have younger relatives who watch cartoons featuring characters using martial arts to save the world from evildoers, with an impressive array of punching, kicking, and defensive postures. You notice that after watching these programs for a while, your young relatives mimic the fighting behavior of the characters portrayed in the cartoon (Figure 17).

These sorts of personal observations are what often lead us to formulate a specific hypothesis, but we cannot use limited personal observations and anecdotal evidence to rigorously test our hypothesis. Instead, to find out if real-world data supports our hypothesis, we have to conduct an experiment.
Designing an Experiment
The most basic experimental design involves two groups: the experimental group and the control group. The two groups are designed to be the same except for one difference— experimental manipulation. The experimental group gets the experimental manipulation—that is, the treatment or variable being tested (in this case, violent TV images)—and the control group does not. Since experimental manipulation is the only difference between the experimental and control groups, we can be sure that any differences between the two are due to experimental manipulation rather than chance.
In our example of how violent television programming might affect violent behavior in children, we have the experimental group view violent television programming for a specified time and then measure their violent behavior. We measure the violent behavior in our control group after they watch nonviolent television programming for the same amount of time. It is important for the control group to be treated similarly to the experimental group, with the exception that the control group does not receive the experimental manipulation. Therefore, we have the control group watch non-violent television programming for the same amount of time as the experimental group.
We also need to precisely define, or operationalize, what is considered violent and nonviolent. An operational definition is a description of how we will measure our variables, and it is important in allowing others understand exactly how and what a researcher measures in a particular experiment. In operationalizing violent behavior, we might choose to count only physical acts like kicking or punching as instances of this behavior, or we also may choose to include angry verbal exchanges. Whatever we determine, it is important that we operationalize violent behavior in such a way that anyone who hears about our study for the first time knows exactly what we mean by violence. This aids peoples’ ability to interpret our data as well as their capacity to repeat our experiment should they choose to do so.
Once we have operationalized what is considered violent television programming and what is considered violent behavior from our experiment participants, we need to establish how we will run our experiment. In this case, we might have participants watch a 30-minute television program (either violent or nonviolent, depending on their group membership) before sending them out to a playground for an hour where their behavior is observed and the number and type of violent acts is recorded.
Ideally, the people who observe and record the children’s behavior are unaware of who was assigned to the experimental or control group, in order to control for experimenter bias. Experimenter bias refers to the possibility that a researcher’s expectations might skew the results of the study. Remember, conducting an experiment requires a lot of planning, and the people involved in the research project have a vested interest in supporting their hypotheses. If the observers knew which child was in which group, it might influence how much attention they paid to each child’s behavior as well as how they interpreted that behavior. By being blind to which child is in which group, we protect against those biases. This situation is a single-blind study , meaning that one of the groups (participants) are unaware as to which group they are in (experiment or control group) while the researcher who developed the experiment knows which participants are in each group.
In a double-blind study , both the researchers and the participants are blind to group assignments. Why would a researcher want to run a study where no one knows who is in which group? Because by doing so, we can control for both experimenter and participant expectations. If you are familiar with the phrase placebo effect, you already have some idea as to why this is an important consideration. The placebo effect occurs when people’s expectations or beliefs influence or determine their experience in a given situation. In other words, simply expecting something to happen can actually make it happen.
The placebo effect is commonly described in terms of testing the effectiveness of a new medication. Imagine that you work in a pharmaceutical company, and you think you have a new drug that is effective in treating depression. To demonstrate that your medication is effective, you run an experiment with two groups: The experimental group receives the medication, and the control group does not. But you don’t want participants to know whether they received the drug or not.
Why is that? Imagine that you are a participant in this study, and you have just taken a pill that you think will improve your mood. Because you expect the pill to have an effect, you might feel better simply because you took the pill and not because of any drug actually contained in the pill—this is the placebo effect.
To make sure that any effects on mood are due to the drug and not due to expectations, the control group receives a placebo (in this case a sugar pill). Now everyone gets a pill, and once again neither the researcher nor the experimental participants know who got the drug and who got the sugar pill. Any differences in mood between the experimental and control groups can now be attributed to the drug itself rather than to experimenter bias or participant expectations (Figure 18).
Independent and Dependent Variables
In a research experiment, we strive to study whether changes in one thing cause changes in another. To achieve this, we must pay attention to two important variables, or things that can be changed, in any experimental study: the independent variable and the dependent variable. An independent variable is manipulated or controlled by the experimenter. In a well-designed experimental study, the independent variable is the only important difference between the experimental and control groups. In our example of how violent television programs affect children’s display of violent behavior, the independent variable is the type of program—violent or nonviolent—viewed by participants in the study (Figure 19). A dependent variable is what the researcher measures to see how much effect the independent variable had. In our example, the dependent variable is the number of violent acts displayed by the experimental participants.
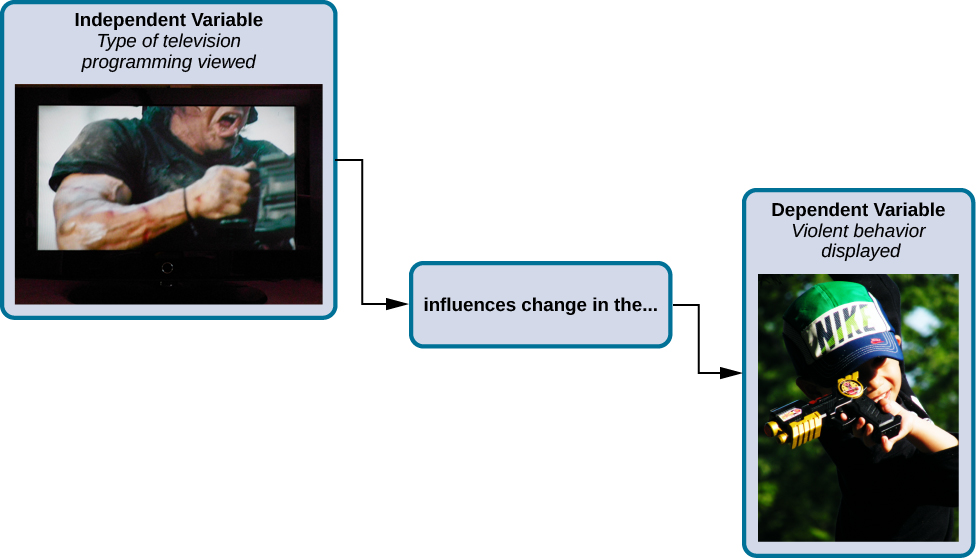
We expect that the dependent variable will change as a function of the independent variable. In other words, the dependent variable depends on the independent variable. A good way to think about the relationship between the independent and dependent variables is with this question: What effect does the independent variable have on the dependent variable? Returning to our example, what effect does watching a half hour of violent television programming or nonviolent television programming have on the number of incidents of physical aggression displayed on the playground?
Selecting and Assigning Experimental Participants
Now that our study is designed, we need to obtain a sample of individuals to include in our experiment. Our study involves human participants so we need to determine who to include. Participants are the subjects of psychological research, and as the name implies, individuals who are involved in psychological research actively participate in the process. Often, psychological research projects rely on college students to serve as participants. In fact, the vast majority of research in psychology subfields has historically involved students as research participants (Sears, 1986; Arnett, 2008). But are college students truly representative of the general population? College students tend to be younger, more educated, more liberal, and less diverse than the general population. Although using students as test subjects is an accepted practice, relying on such a limited pool of research participants can be problematic because it is difficult to generalize findings to the larger population.
Our hypothetical experiment involves children, and we must first generate a sample of child participants. Samples are used because populations are usually too large to reasonably involve every member in our particular experiment (Figure 20). If possible, we should use a random sample (there are other types of samples, but for the purposes of this section, we will focus on random samples). A random sample is a subset of a larger population in which every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Random samples are preferred because if the sample is large enough we can be reasonably sure that the participating individuals are representative of the larger population. This means that the percentages of characteristics in the sample—sex, ethnicity, socioeconomic level, and any other characteristics that might affect the results—are close to those percentages in the larger population.
In our example, let’s say we decide our population of interest is fourth graders. But all fourth graders is a very large population, so we need to be more specific; instead we might say our population of interest is all fourth graders in a particular city. We should include students from various income brackets, family situations, races, ethnicities, religions, and geographic areas of town. With this more manageable population, we can work with the local schools in selecting a random sample of around 200 fourth graders who we want to participate in our experiment.
In summary, because we cannot test all of the fourth graders in a city, we want to find a group of about 200 that reflects the composition of that city. With a representative group, we can generalize our findings to the larger population without fear of our sample being biased in some way.

Now that we have a sample, the next step of the experimental process is to split the participants into experimental and control groups through random assignment. With random assignment , all participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either group. There is statistical software that will randomly assign each of the fourth graders in the sample to either the experimental or the control group.
Random assignment is critical for sound experimental design. With sufficiently large samples, random assignment makes it unlikely that there are systematic differences between the groups. So, for instance, it would be very unlikely that we would get one group composed entirely of males, a given ethnic identity, or a given religious ideology. This is important because if the groups were systematically different before the experiment began, we would not know the origin of any differences we find between the groups: Were the differences preexisting, or were they caused by manipulation of the independent variable? Random assignment allows us to assume that any differences observed between experimental and control groups result from the manipulation of the independent variable.
Issues to Consider
While experiments allow scientists to make cause-and-effect claims, they are not without problems. True experiments require the experimenter to manipulate an independent variable, and that can complicate many questions that psychologists might want to address. For instance, imagine that you want to know what effect sex (the independent variable) has on spatial memory (the dependent variable). Although you can certainly look for differences between males and females on a task that taps into spatial memory, you cannot directly control a person’s sex. We categorize this type of research approach as quasi-experimental and recognize that we cannot make cause-and-effect claims in these circumstances.
Experimenters are also limited by ethical constraints. For instance, you would not be able to conduct an experiment designed to determine if experiencing abuse as a child leads to lower levels of self-esteem among adults. To conduct such an experiment, you would need to randomly assign some experimental participants to a group that receives abuse, and that experiment would be unethical.
Introduction to Statistical Thinking
Psychologists use statistics to assist them in analyzing data, and also to give more precise measurements to describe whether something is statistically significant. Analyzing data using statistics enables researchers to find patterns, make claims, and share their results with others. In this section, you’ll learn about some of the tools that psychologists use in statistical analysis.
- Define reliability and validity
- Describe the importance of distributional thinking and the role of p-values in statistical inference
- Describe the role of random sampling and random assignment in drawing cause-and-effect conclusions
- Describe the basic structure of a psychological research article
Interpreting Experimental Findings
Once data is collected from both the experimental and the control groups, a statistical analysis is conducted to find out if there are meaningful differences between the two groups. A statistical analysis determines how likely any difference found is due to chance (and thus not meaningful). In psychology, group differences are considered meaningful, or significant, if the odds that these differences occurred by chance alone are 5 percent or less. Stated another way, if we repeated this experiment 100 times, we would expect to find the same results at least 95 times out of 100.
The greatest strength of experiments is the ability to assert that any significant differences in the findings are caused by the independent variable. This occurs because random selection, random assignment, and a design that limits the effects of both experimenter bias and participant expectancy should create groups that are similar in composition and treatment. Therefore, any difference between the groups is attributable to the independent variable, and now we can finally make a causal statement. If we find that watching a violent television program results in more violent behavior than watching a nonviolent program, we can safely say that watching violent television programs causes an increase in the display of violent behavior.
Reporting Research
When psychologists complete a research project, they generally want to share their findings with other scientists. The American Psychological Association (APA) publishes a manual detailing how to write a paper for submission to scientific journals. Unlike an article that might be published in a magazine like Psychology Today, which targets a general audience with an interest in psychology, scientific journals generally publish peer-reviewed journal articles aimed at an audience of professionals and scholars who are actively involved in research themselves.
A peer-reviewed journal article is read by several other scientists (generally anonymously) with expertise in the subject matter. These peer reviewers provide feedback—to both the author and the journal editor—regarding the quality of the draft. Peer reviewers look for a strong rationale for the research being described, a clear description of how the research was conducted, and evidence that the research was conducted in an ethical manner. They also look for flaws in the study’s design, methods, and statistical analyses. They check that the conclusions drawn by the authors seem reasonable given the observations made during the research. Peer reviewers also comment on how valuable the research is in advancing the discipline’s knowledge. This helps prevent unnecessary duplication of research findings in the scientific literature and, to some extent, ensures that each research article provides new information. Ultimately, the journal editor will compile all of the peer reviewer feedback and determine whether the article will be published in its current state (a rare occurrence), published with revisions, or not accepted for publication.
Peer review provides some degree of quality control for psychological research. Poorly conceived or executed studies can be weeded out, and even well-designed research can be improved by the revisions suggested. Peer review also ensures that the research is described clearly enough to allow other scientists to replicate it, meaning they can repeat the experiment using different samples to determine reliability. Sometimes replications involve additional measures that expand on the original finding. In any case, each replication serves to provide more evidence to support the original research findings. Successful replications of published research make scientists more apt to adopt those findings, while repeated failures tend to cast doubt on the legitimacy of the original article and lead scientists to look elsewhere. For example, it would be a major advancement in the medical field if a published study indicated that taking a new drug helped individuals achieve a healthy weight without changing their diet. But if other scientists could not replicate the results, the original study’s claims would be questioned.
Dig Deeper: The Vaccine-Autism Myth and the Retraction of Published Studies
Some scientists have claimed that routine childhood vaccines cause some children to develop autism, and, in fact, several peer-reviewed publications published research making these claims. Since the initial reports, large-scale epidemiological research has suggested that vaccinations are not responsible for causing autism and that it is much safer to have your child vaccinated than not. Furthermore, several of the original studies making this claim have since been retracted.
A published piece of work can be rescinded when data is called into question because of falsification, fabrication, or serious research design problems. Once rescinded, the scientific community is informed that there are serious problems with the original publication. Retractions can be initiated by the researcher who led the study, by research collaborators, by the institution that employed the researcher, or by the editorial board of the journal in which the article was originally published. In the vaccine-autism case, the retraction was made because of a significant conflict of interest in which the leading researcher had a financial interest in establishing a link between childhood vaccines and autism (Offit, 2008). Unfortunately, the initial studies received so much media attention that many parents around the world became hesitant to have their children vaccinated (Figure 21). For more information about how the vaccine/autism story unfolded, as well as the repercussions of this story, take a look at Paul Offit’s book, Autism’s False Prophets: Bad Science, Risky Medicine, and the Search for a Cure.
Reliability and Validity
Dig deeper: everyday connection: how valid is the sat.
Standardized tests like the SAT are supposed to measure an individual’s aptitude for a college education, but how reliable and valid are such tests? Research conducted by the College Board suggests that scores on the SAT have high predictive validity for first-year college students’ GPA (Kobrin, Patterson, Shaw, Mattern, & Barbuti, 2008). In this context, predictive validity refers to the test’s ability to effectively predict the GPA of college freshmen. Given that many institutions of higher education require the SAT for admission, this high degree of predictive validity might be comforting.
However, the emphasis placed on SAT scores in college admissions has generated some controversy on a number of fronts. For one, some researchers assert that the SAT is a biased test that places minority students at a disadvantage and unfairly reduces the likelihood of being admitted into a college (Santelices & Wilson, 2010). Additionally, some research has suggested that the predictive validity of the SAT is grossly exaggerated in how well it is able to predict the GPA of first-year college students. In fact, it has been suggested that the SAT’s predictive validity may be overestimated by as much as 150% (Rothstein, 2004). Many institutions of higher education are beginning to consider de-emphasizing the significance of SAT scores in making admission decisions (Rimer, 2008).
In 2014, College Board president David Coleman expressed his awareness of these problems, recognizing that college success is more accurately predicted by high school grades than by SAT scores. To address these concerns, he has called for significant changes to the SAT exam (Lewin, 2014).
Statistical Significance

Does drinking coffee actually increase your life expectancy? A recent study (Freedman, Park, Abnet, Hollenbeck, & Sinha, 2012) found that men who drank at least six cups of coffee a day also had a 10% lower chance of dying (women’s chances were 15% lower) than those who drank none. Does this mean you should pick up or increase your own coffee habit? We will explore these results in more depth in the next section about drawing conclusions from statistics. Modern society has become awash in studies such as this; you can read about several such studies in the news every day.
Conducting such a study well, and interpreting the results of such studies requires understanding basic ideas of statistics , the science of gaining insight from data. Key components to a statistical investigation are:
- Planning the study: Start by asking a testable research question and deciding how to collect data. For example, how long was the study period of the coffee study? How many people were recruited for the study, how were they recruited, and from where? How old were they? What other variables were recorded about the individuals? Were changes made to the participants’ coffee habits during the course of the study?
- Examining the data: What are appropriate ways to examine the data? What graphs are relevant, and what do they reveal? What descriptive statistics can be calculated to summarize relevant aspects of the data, and what do they reveal? What patterns do you see in the data? Are there any individual observations that deviate from the overall pattern, and what do they reveal? For example, in the coffee study, did the proportions differ when we compared the smokers to the non-smokers?
- Inferring from the data: What are valid statistical methods for drawing inferences “beyond” the data you collected? In the coffee study, is the 10%–15% reduction in risk of death something that could have happened just by chance?
- Drawing conclusions: Based on what you learned from your data, what conclusions can you draw? Who do you think these conclusions apply to? (Were the people in the coffee study older? Healthy? Living in cities?) Can you draw a cause-and-effect conclusion about your treatments? (Are scientists now saying that the coffee drinking is the cause of the decreased risk of death?)
Notice that the numerical analysis (“crunching numbers” on the computer) comprises only a small part of overall statistical investigation. In this section, you will see how we can answer some of these questions and what questions you should be asking about any statistical investigation you read about.
Distributional Thinking
When data are collected to address a particular question, an important first step is to think of meaningful ways to organize and examine the data. Let’s take a look at an example.
Example 1 : Researchers investigated whether cancer pamphlets are written at an appropriate level to be read and understood by cancer patients (Short, Moriarty, & Cooley, 1995). Tests of reading ability were given to 63 patients. In addition, readability level was determined for a sample of 30 pamphlets, based on characteristics such as the lengths of words and sentences in the pamphlet. The results, reported in terms of grade levels, are displayed in Figure 23.
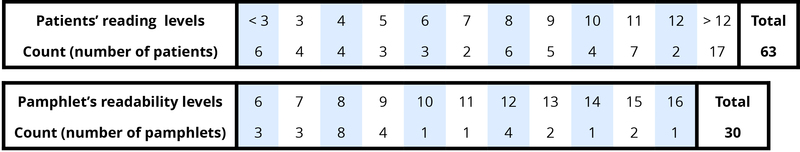
- Data vary . More specifically, values of a variable (such as reading level of a cancer patient or readability level of a cancer pamphlet) vary.
- Analyzing the pattern of variation, called the distribution of the variable, often reveals insights.
Addressing the research question of whether the cancer pamphlets are written at appropriate levels for the cancer patients requires comparing the two distributions. A naïve comparison might focus only on the centers of the distributions. Both medians turn out to be ninth grade, but considering only medians ignores the variability and the overall distributions of these data. A more illuminating approach is to compare the entire distributions, for example with a graph, as in Figure 24.
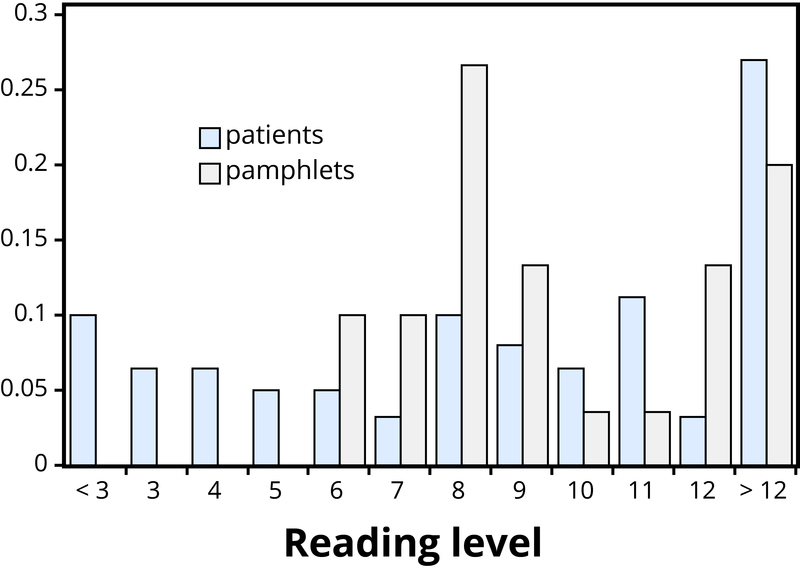
Figure 24 makes clear that the two distributions are not well aligned at all. The most glaring discrepancy is that many patients (17/63, or 27%, to be precise) have a reading level below that of the most readable pamphlet. These patients will need help to understand the information provided in the cancer pamphlets. Notice that this conclusion follows from considering the distributions as a whole, not simply measures of center or variability, and that the graph contrasts those distributions more immediately than the frequency tables.
Finding Significance in Data
Even when we find patterns in data, often there is still uncertainty in various aspects of the data. For example, there may be potential for measurement errors (even your own body temperature can fluctuate by almost 1°F over the course of the day). Or we may only have a “snapshot” of observations from a more long-term process or only a small subset of individuals from the population of interest. In such cases, how can we determine whether patterns we see in our small set of data is convincing evidence of a systematic phenomenon in the larger process or population? Let’s take a look at another example.
Example 2 : In a study reported in the November 2007 issue of Nature , researchers investigated whether pre-verbal infants take into account an individual’s actions toward others in evaluating that individual as appealing or aversive (Hamlin, Wynn, & Bloom, 2007). In one component of the study, 10-month-old infants were shown a “climber” character (a piece of wood with “googly” eyes glued onto it) that could not make it up a hill in two tries. Then the infants were shown two scenarios for the climber’s next try, one where the climber was pushed to the top of the hill by another character (“helper”), and one where the climber was pushed back down the hill by another character (“hinderer”). The infant was alternately shown these two scenarios several times. Then the infant was presented with two pieces of wood (representing the helper and the hinderer characters) and asked to pick one to play with.
The researchers found that of the 16 infants who made a clear choice, 14 chose to play with the helper toy. One possible explanation for this clear majority result is that the helping behavior of the one toy increases the infants’ likelihood of choosing that toy. But are there other possible explanations? What about the color of the toy? Well, prior to collecting the data, the researchers arranged so that each color and shape (red square and blue circle) would be seen by the same number of infants. Or maybe the infants had right-handed tendencies and so picked whichever toy was closer to their right hand?
Well, prior to collecting the data, the researchers arranged it so half the infants saw the helper toy on the right and half on the left. Or, maybe the shapes of these wooden characters (square, triangle, circle) had an effect? Perhaps, but again, the researchers controlled for this by rotating which shape was the helper toy, the hinderer toy, and the climber. When designing experiments, it is important to control for as many variables as might affect the responses as possible. It is beginning to appear that the researchers accounted for all the other plausible explanations. But there is one more important consideration that cannot be controlled—if we did the study again with these 16 infants, they might not make the same choices. In other words, there is some randomness inherent in their selection process.
Maybe each infant had no genuine preference at all, and it was simply “random luck” that led to 14 infants picking the helper toy. Although this random component cannot be controlled, we can apply a probability model to investigate the pattern of results that would occur in the long run if random chance were the only factor.
If the infants were equally likely to pick between the two toys, then each infant had a 50% chance of picking the helper toy. It’s like each infant tossed a coin, and if it landed heads, the infant picked the helper toy. So if we tossed a coin 16 times, could it land heads 14 times? Sure, it’s possible, but it turns out to be very unlikely. Getting 14 (or more) heads in 16 tosses is about as likely as tossing a coin and getting 9 heads in a row. This probability is referred to as a p-value . The p-value represents the likelihood that experimental results happened by chance. Within psychology, the most common standard for p-values is “p < .05”. What this means is that there is less than a 5% probability that the results happened just by random chance, and therefore a 95% probability that the results reflect a meaningful pattern in human psychology. We call this statistical significance .
So, in the study above, if we assume that each infant was choosing equally, then the probability that 14 or more out of 16 infants would choose the helper toy is found to be 0.0021. We have only two logical possibilities: either the infants have a genuine preference for the helper toy, or the infants have no preference (50/50) and an outcome that would occur only 2 times in 1,000 iterations happened in this study. Because this p-value of 0.0021 is quite small, we conclude that the study provides very strong evidence that these infants have a genuine preference for the helper toy.
If we compare the p-value to some cut-off value, like 0.05, we see that the p=value is smaller. Because the p-value is smaller than that cut-off value, then we reject the hypothesis that only random chance was at play here. In this case, these researchers would conclude that significantly more than half of the infants in the study chose the helper toy, giving strong evidence of a genuine preference for the toy with the helping behavior.
Drawing Conclusions from Statistics
Generalizability.

One limitation to the study mentioned previously about the babies choosing the “helper” toy is that the conclusion only applies to the 16 infants in the study. We don’t know much about how those 16 infants were selected. Suppose we want to select a subset of individuals (a sample ) from a much larger group of individuals (the population ) in such a way that conclusions from the sample can be generalized to the larger population. This is the question faced by pollsters every day.
Example 3 : The General Social Survey (GSS) is a survey on societal trends conducted every other year in the United States. Based on a sample of about 2,000 adult Americans, researchers make claims about what percentage of the U.S. population consider themselves to be “liberal,” what percentage consider themselves “happy,” what percentage feel “rushed” in their daily lives, and many other issues. The key to making these claims about the larger population of all American adults lies in how the sample is selected. The goal is to select a sample that is representative of the population, and a common way to achieve this goal is to select a r andom sample that gives every member of the population an equal chance of being selected for the sample. In its simplest form, random sampling involves numbering every member of the population and then using a computer to randomly select the subset to be surveyed. Most polls don’t operate exactly like this, but they do use probability-based sampling methods to select individuals from nationally representative panels.
In 2004, the GSS reported that 817 of 977 respondents (or 83.6%) indicated that they always or sometimes feel rushed. This is a clear majority, but we again need to consider variation due to random sampling . Fortunately, we can use the same probability model we did in the previous example to investigate the probable size of this error. (Note, we can use the coin-tossing model when the actual population size is much, much larger than the sample size, as then we can still consider the probability to be the same for every individual in the sample.) This probability model predicts that the sample result will be within 3 percentage points of the population value (roughly 1 over the square root of the sample size, the margin of error. A statistician would conclude, with 95% confidence, that between 80.6% and 86.6% of all adult Americans in 2004 would have responded that they sometimes or always feel rushed.
The key to the margin of error is that when we use a probability sampling method, we can make claims about how often (in the long run, with repeated random sampling) the sample result would fall within a certain distance from the unknown population value by chance (meaning by random sampling variation) alone. Conversely, non-random samples are often suspect to bias, meaning the sampling method systematically over-represents some segments of the population and under-represents others. We also still need to consider other sources of bias, such as individuals not responding honestly. These sources of error are not measured by the margin of error.
Cause and Effect
In many research studies, the primary question of interest concerns differences between groups. Then the question becomes how were the groups formed (e.g., selecting people who already drink coffee vs. those who don’t). In some studies, the researchers actively form the groups themselves. But then we have a similar question—could any differences we observe in the groups be an artifact of that group-formation process? Or maybe the difference we observe in the groups is so large that we can discount a “fluke” in the group-formation process as a reasonable explanation for what we find?
Example 4 : A psychology study investigated whether people tend to display more creativity when they are thinking about intrinsic (internal) or extrinsic (external) motivations (Ramsey & Schafer, 2002, based on a study by Amabile, 1985). The subjects were 47 people with extensive experience with creative writing. Subjects began by answering survey questions about either intrinsic motivations for writing (such as the pleasure of self-expression) or extrinsic motivations (such as public recognition). Then all subjects were instructed to write a haiku, and those poems were evaluated for creativity by a panel of judges. The researchers conjectured beforehand that subjects who were thinking about intrinsic motivations would display more creativity than subjects who were thinking about extrinsic motivations. The creativity scores from the 47 subjects in this study are displayed in Figure 26, where higher scores indicate more creativity.
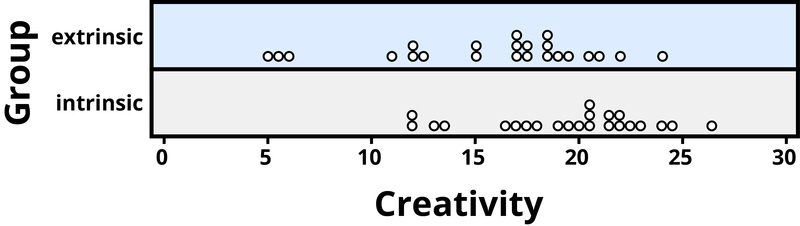
In this example, the key question is whether the type of motivation affects creativity scores. In particular, do subjects who were asked about intrinsic motivations tend to have higher creativity scores than subjects who were asked about extrinsic motivations?
Figure 26 reveals that both motivation groups saw considerable variability in creativity scores, and these scores have considerable overlap between the groups. In other words, it’s certainly not always the case that those with extrinsic motivations have higher creativity than those with intrinsic motivations, but there may still be a statistical tendency in this direction. (Psychologist Keith Stanovich (2013) refers to people’s difficulties with thinking about such probabilistic tendencies as “the Achilles heel of human cognition.”)
The mean creativity score is 19.88 for the intrinsic group, compared to 15.74 for the extrinsic group, which supports the researchers’ conjecture. Yet comparing only the means of the two groups fails to consider the variability of creativity scores in the groups. We can measure variability with statistics using, for instance, the standard deviation: 5.25 for the extrinsic group and 4.40 for the intrinsic group. The standard deviations tell us that most of the creativity scores are within about 5 points of the mean score in each group. We see that the mean score for the intrinsic group lies within one standard deviation of the mean score for extrinsic group. So, although there is a tendency for the creativity scores to be higher in the intrinsic group, on average, the difference is not extremely large.
We again want to consider possible explanations for this difference. The study only involved individuals with extensive creative writing experience. Although this limits the population to which we can generalize, it does not explain why the mean creativity score was a bit larger for the intrinsic group than for the extrinsic group. Maybe women tend to receive higher creativity scores? Here is where we need to focus on how the individuals were assigned to the motivation groups. If only women were in the intrinsic motivation group and only men in the extrinsic group, then this would present a problem because we wouldn’t know if the intrinsic group did better because of the different type of motivation or because they were women. However, the researchers guarded against such a problem by randomly assigning the individuals to the motivation groups. Like flipping a coin, each individual was just as likely to be assigned to either type of motivation. Why is this helpful? Because this random assignment tends to balance out all the variables related to creativity we can think of, and even those we don’t think of in advance, between the two groups. So we should have a similar male/female split between the two groups; we should have a similar age distribution between the two groups; we should have a similar distribution of educational background between the two groups; and so on. Random assignment should produce groups that are as similar as possible except for the type of motivation, which presumably eliminates all those other variables as possible explanations for the observed tendency for higher scores in the intrinsic group.
But does this always work? No, so by “luck of the draw” the groups may be a little different prior to answering the motivation survey. So then the question is, is it possible that an unlucky random assignment is responsible for the observed difference in creativity scores between the groups? In other words, suppose each individual’s poem was going to get the same creativity score no matter which group they were assigned to, that the type of motivation in no way impacted their score. Then how often would the random-assignment process alone lead to a difference in mean creativity scores as large (or larger) than 19.88 – 15.74 = 4.14 points?
We again want to apply to a probability model to approximate a p-value , but this time the model will be a bit different. Think of writing everyone’s creativity scores on an index card, shuffling up the index cards, and then dealing out 23 to the extrinsic motivation group and 24 to the intrinsic motivation group, and finding the difference in the group means. We (better yet, the computer) can repeat this process over and over to see how often, when the scores don’t change, random assignment leads to a difference in means at least as large as 4.41. Figure 27 shows the results from 1,000 such hypothetical random assignments for these scores.
Only 2 of the 1,000 simulated random assignments produced a difference in group means of 4.41 or larger. In other words, the approximate p-value is 2/1000 = 0.002. This small p-value indicates that it would be very surprising for the random assignment process alone to produce such a large difference in group means. Therefore, as with Example 2, we have strong evidence that focusing on intrinsic motivations tends to increase creativity scores, as compared to thinking about extrinsic motivations.
Notice that the previous statement implies a cause-and-effect relationship between motivation and creativity score; is such a strong conclusion justified? Yes, because of the random assignment used in the study. That should have balanced out any other variables between the two groups, so now that the small p-value convinces us that the higher mean in the intrinsic group wasn’t just a coincidence, the only reasonable explanation left is the difference in the type of motivation. Can we generalize this conclusion to everyone? Not necessarily—we could cautiously generalize this conclusion to individuals with extensive experience in creative writing similar the individuals in this study, but we would still want to know more about how these individuals were selected to participate.

Statistical thinking involves the careful design of a study to collect meaningful data to answer a focused research question, detailed analysis of patterns in the data, and drawing conclusions that go beyond the observed data. Random sampling is paramount to generalizing results from our sample to a larger population, and random assignment is key to drawing cause-and-effect conclusions. With both kinds of randomness, probability models help us assess how much random variation we can expect in our results, in order to determine whether our results could happen by chance alone and to estimate a margin of error.
So where does this leave us with regard to the coffee study mentioned previously (the Freedman, Park, Abnet, Hollenbeck, & Sinha, 2012 found that men who drank at least six cups of coffee a day had a 10% lower chance of dying (women 15% lower) than those who drank none)? We can answer many of the questions:
- This was a 14-year study conducted by researchers at the National Cancer Institute.
- The results were published in the June issue of the New England Journal of Medicine , a respected, peer-reviewed journal.
- The study reviewed coffee habits of more than 402,000 people ages 50 to 71 from six states and two metropolitan areas. Those with cancer, heart disease, and stroke were excluded at the start of the study. Coffee consumption was assessed once at the start of the study.
- About 52,000 people died during the course of the study.
- People who drank between two and five cups of coffee daily showed a lower risk as well, but the amount of reduction increased for those drinking six or more cups.
- The sample sizes were fairly large and so the p-values are quite small, even though percent reduction in risk was not extremely large (dropping from a 12% chance to about 10%–11%).
- Whether coffee was caffeinated or decaffeinated did not appear to affect the results.
- This was an observational study, so no cause-and-effect conclusions can be drawn between coffee drinking and increased longevity, contrary to the impression conveyed by many news headlines about this study. In particular, it’s possible that those with chronic diseases don’t tend to drink coffee.
This study needs to be reviewed in the larger context of similar studies and consistency of results across studies, with the constant caution that this was not a randomized experiment. Whereas a statistical analysis can still “adjust” for other potential confounding variables, we are not yet convinced that researchers have identified them all or completely isolated why this decrease in death risk is evident. Researchers can now take the findings of this study and develop more focused studies that address new questions.
Explore these outside resources to learn more about applied statistics:
- Video about p-values: P-Value Extravaganza
- Interactive web applets for teaching and learning statistics
- Inter-university Consortium for Political and Social Research where you can find and analyze data.
- The Consortium for the Advancement of Undergraduate Statistics
- Find a recent research article in your field and answer the following: What was the primary research question? How were individuals selected to participate in the study? Were summary results provided? How strong is the evidence presented in favor or against the research question? Was random assignment used? Summarize the main conclusions from the study, addressing the issues of statistical significance, statistical confidence, generalizability, and cause and effect. Do you agree with the conclusions drawn from this study, based on the study design and the results presented?
- Is it reasonable to use a random sample of 1,000 individuals to draw conclusions about all U.S. adults? Explain why or why not.
How to Read Research
In this course and throughout your academic career, you’ll be reading journal articles (meaning they were published by experts in a peer-reviewed journal) and reports that explain psychological research. It’s important to understand the format of these articles so that you can read them strategically and understand the information presented. Scientific articles vary in content or structure, depending on the type of journal to which they will be submitted. Psychological articles and many papers in the social sciences follow the writing guidelines and format dictated by the American Psychological Association (APA). In general, the structure follows: abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and references.
- Abstract : the abstract is the concise summary of the article. It summarizes the most important features of the manuscript, providing the reader with a global first impression on the article. It is generally just one paragraph that explains the experiment as well as a short synopsis of the results.
- Introduction : this section provides background information about the origin and purpose of performing the experiment or study. It reviews previous research and presents existing theories on the topic.
- Method : this section covers the methodologies used to investigate the research question, including the identification of participants , procedures , and materials as well as a description of the actual procedure . It should be sufficiently detailed to allow for replication.
- Results : the results section presents key findings of the research, including reference to indicators of statistical significance.
- Discussion : this section provides an interpretation of the findings, states their significance for current research, and derives implications for theory and practice. Alternative interpretations for findings are also provided, particularly when it is not possible to conclude for the directionality of the effects. In the discussion, authors also acknowledge the strengths and limitations/weaknesses of the study and offer concrete directions about for future research.
Watch this 3-minute video for an explanation on how to read scholarly articles. Look closely at the example article shared just before the two minute mark.
https://digitalcommons.coastal.edu/kimbel-library-instructional-videos/9/
Practice identifying these key components in the following experiment: Food-Induced Emotional Resonance Improves Emotion Recognition.
In this chapter, you learned to
- define and apply the scientific method to psychology
- describe the strengths and weaknesses of descriptive, experimental, and correlational research
- define the basic elements of a statistical investigation
Putting It Together: Psychological Research
Psychologists use the scientific method to examine human behavior and mental processes. Some of the methods you learned about include descriptive, experimental, and correlational research designs.
Watch the CrashCourse video to review the material you learned, then read through the following examples and see if you can come up with your own design for each type of study.
You can view the transcript for “Psychological Research: Crash Course Psychology #2” here (opens in new window).
Case Study: a detailed analysis of a particular person, group, business, event, etc. This approach is commonly used to to learn more about rare examples with the goal of describing that particular thing.
- Ted Bundy was one of America’s most notorious serial killers who murdered at least 30 women and was executed in 1989. Dr. Al Carlisle evaluated Bundy when he was first arrested and conducted a psychological analysis of Bundy’s development of his sexual fantasies merging into reality (Ramsland, 2012). Carlisle believes that there was a gradual evolution of three processes that guided his actions: fantasy, dissociation, and compartmentalization (Ramsland, 2012). Read Imagining Ted Bundy (http://goo.gl/rGqcUv) for more information on this case study.
Naturalistic Observation : a researcher unobtrusively collects information without the participant’s awareness.
- Drain and Engelhardt (2013) observed six nonverbal children with autism’s evoked and spontaneous communicative acts. Each of the children attended a school for children with autism and were in different classes. They were observed for 30 minutes of each school day. By observing these children without them knowing, they were able to see true communicative acts without any external influences.
Survey : participants are asked to provide information or responses to questions on a survey or structure assessment.
- Educational psychologists can ask students to report their grade point average and what, if anything, they eat for breakfast on an average day. A healthy breakfast has been associated with better academic performance (Digangi’s 1999).
- Anderson (1987) tried to find the relationship between uncomfortably hot temperatures and aggressive behavior, which was then looked at with two studies done on violent and nonviolent crime. Based on previous research that had been done by Anderson and Anderson (1984), it was predicted that violent crimes would be more prevalent during the hotter time of year and the years in which it was hotter weather in general. The study confirmed this prediction.
Longitudinal Study: researchers recruit a sample of participants and track them for an extended period of time.
- In a study of a representative sample of 856 children Eron and his colleagues (1972) found that a boy’s exposure to media violence at age eight was significantly related to his aggressive behavior ten years later, after he graduated from high school.
Cross-Sectional Study: researchers gather participants from different groups (commonly different ages) and look for differences between the groups.
- In 1996, Russell surveyed people of varying age groups and found that people in their 20s tend to report being more lonely than people in their 70s.
Correlational Design: two different variables are measured to determine whether there is a relationship between them.
- Thornhill et al. (2003) had people rate how physically attractive they found other people to be. They then had them separately smell t-shirts those people had worn (without knowing which clothes belonged to whom) and rate how good or bad their body oder was. They found that the more attractive someone was the more pleasant their body order was rated to be.
- Clinical psychologists can test a new pharmaceutical treatment for depression by giving some patients the new pill and others an already-tested one to see which is the more effective treatment.
American Cancer Society. (n.d.). History of the cancer prevention studies. Retrieved from http://www.cancer.org/research/researchtopreventcancer/history-cancer-prevention-study
American Psychological Association. (2009). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
American Psychological Association. (n.d.). Research with animals in psychology. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/research/responsible/research-animals.pdf
Arnett, J. (2008). The neglected 95%: Why American psychology needs to become less American. American Psychologist, 63(7), 602–614.
Barton, B. A., Eldridge, A. L., Thompson, D., Affenito, S. G., Striegel-Moore, R. H., Franko, D. L., . . . Crockett, S. J. (2005). The relationship of breakfast and cereal consumption to nutrient intake and body mass index: The national heart, lung, and blood institute growth and health study. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 105(9), 1383–1389. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2005.06.003
Chwalisz, K., Diener, E., & Gallagher, D. (1988). Autonomic arousal feedback and emotional experience: Evidence from the spinal cord injured. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 820–828.
Dominus, S. (2011, May 25). Could conjoined twins share a mind? New York Times Sunday Magazine. Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2011/05/29/magazine/could-conjoined-twins-share-a-mind.html?_r=5&hp&
Fanger, S. M., Frankel, L. A., & Hazen, N. (2012). Peer exclusion in preschool children’s play: Naturalistic observations in a playground setting. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 58, 224–254.
Fiedler, K. (2004). Illusory correlation. In R. F. Pohl (Ed.), Cognitive illusions: A handbook on fallacies and biases in thinking, judgment and memory (pp. 97–114). New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Frantzen, L. B., Treviño, R. P., Echon, R. M., Garcia-Dominic, O., & DiMarco, N. (2013). Association between frequency of ready-to-eat cereal consumption, nutrient intakes, and body mass index in fourth- to sixth-grade low-income minority children. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 113(4), 511–519.
Harper, J. (2013, July 5). Ice cream and crime: Where cold cuisine and hot disputes intersect. The Times-Picaune. Retrieved from http://www.nola.com/crime/index.ssf/2013/07/ice_cream_and_crime_where_hot.html
Jenkins, W. J., Ruppel, S. E., Kizer, J. B., Yehl, J. L., & Griffin, J. L. (2012). An examination of post 9-11 attitudes towards Arab Americans. North American Journal of Psychology, 14, 77–84.
Jones, J. M. (2013, May 13). Same-sex marriage support solidifies above 50% in U.S. Gallup Politics. Retrieved from http://www.gallup.com/poll/162398/sex-marriage-support-solidifies-above.aspx
Kobrin, J. L., Patterson, B. F., Shaw, E. J., Mattern, K. D., & Barbuti, S. M. (2008). Validity of the SAT for predicting first-year college grade point average (Research Report No. 2008-5). Retrieved from https://research.collegeboard.org/sites/default/files/publications/2012/7/researchreport-2008-5-validity-sat-predicting-first-year-college-grade-point-average.pdf
Lewin, T. (2014, March 5). A new SAT aims to realign with schoolwork. New York Times. Retreived from http://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/06/education/major-changes-in-sat-announced-by-college-board.html.
Lowry, M., Dean, K., & Manders, K. (2010). The link between sleep quantity and academic performance for the college student. Sentience: The University of Minnesota Undergraduate Journal of Psychology, 3(Spring), 16–19. Retrieved from http://www.psych.umn.edu/sentience/files/SENTIENCE_Vol3.pdf
McKie, R. (2010, June 26). Chimps with everything: Jane Goodall’s 50 years in the jungle. The Guardian. Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/science/2010/jun/27/jane-goodall-chimps-africa-interview
Offit, P. (2008). Autism’s false prophets: Bad science, risky medicine, and the search for a cure. New York: Columbia University Press.
Perkins, H. W., Haines, M. P., & Rice, R. (2005). Misperceiving the college drinking norm and related problems: A nationwide study of exposure to prevention information, perceived norms and student alcohol misuse. J. Stud. Alcohol, 66(4), 470–478.
Rimer, S. (2008, September 21). College panel calls for less focus on SATs. The New York Times. Retrieved from http://www.nytimes.com/2008/09/22/education/22admissions.html?_r=0
Rothstein, J. M. (2004). College performance predictions and the SAT. Journal of Econometrics, 121, 297–317.
Rotton, J., & Kelly, I. W. (1985). Much ado about the full moon: A meta-analysis of lunar-lunacy research. Psychological Bulletin, 97(2), 286–306. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.97.2.286
Santelices, M. V., & Wilson, M. (2010). Unfair treatment? The case of Freedle, the SAT, and the standardization approach to differential item functioning. Harvard Education Review, 80, 106–134.
Sears, D. O. (1986). College sophomores in the laboratory: Influences of a narrow data base on social psychology’s view of human nature. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 515–530.
Tuskegee University. (n.d.). About the USPHS Syphilis Study. Retrieved from http://www.tuskegee.edu/about_us/centers_of_excellence/bioethics_center/about_the_usphs_syphilis_study.aspx.
CC licensed content, Original
- Psychological Research Methods. Provided by : Karenna Malavanti. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution ShareAlike
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Psychological Research. Provided by : OpenStax College. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-introduction .
- Why It Matters: Psychological Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/introduction-15/
- Introduction to The Scientific Method. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/outcome-the-scientific-method/
- Research picture. Authored by : Mediterranean Center of Medical Sciences. Provided by : Flickr. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/mcmscience/17664002728 .
- The Scientific Process. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution ShareAlike Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/reading-the-scientific-process/
- Ethics in Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/ethics/
- Ethics. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-4-ethics . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction .
- Introduction to Approaches to Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/outcome-approaches-to-research/
- Lec 2 | MIT 9.00SC Introduction to Psychology, Spring 2011. Authored by : John Gabrieli. Provided by : MIT OpenCourseWare. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=syXplPKQb_o .
- Paragraph on correlation. Authored by : Christie Napa Scollon. Provided by : Singapore Management University. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike Located at : http://nobaproject.com/modules/research-designs?r=MTc0ODYsMjMzNjQ%3D . Project : The Noba Project.
- Descriptive Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution ShareAlike Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/reading-clinical-or-case-studies/
- Approaches to Research. Authored by : OpenStax College. License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-2-approaches-to-research
- Analyzing Findings. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-3-analyzing-findings . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction.
- Experiments. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/reading-conducting-experiments/
- Research Review. Authored by : Jessica Traylor for Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/reading-conducting-experiments/
- Introduction to Statistics. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/outcome-statistical-thinking/
- histogram. Authored by : Fisher’s Iris flower data set. Provided by : Wikipedia.
- License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Meetup/DC/Statistics_Edit-a-thon#/media/File:Fisher_iris_versicolor_sepalwidth.svg .
- Statistical Thinking. Authored by : Beth Chance and Allan Rossman . Provided by : California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo.
- License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommerci al-S hareAlike . License Terms : http://nobaproject.com/license-agreement Located at : http://nobaproject.com/modules/statistical-thinking . Project : The Noba Project.
- Drawing Conclusions from Statistics. Authored by: Pat Carroll and Lumen Learning. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/reading-drawing-conclusions-from-statistics/
- Statistical Thinking. Authored by : Beth Chance and Allan Rossman, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo. Provided by : Noba. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike Located at : http://nobaproject.com/modules/statistical-thinking .
- The Replication Crisis. Authored by : Colin Thomas William. Provided by : Ivy Tech Community College. License: CC BY: Attribution
- How to Read Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/how-to-read-research/
- What is a Scholarly Article? Kimbel Library First Year Experience Instructional Videos. 9. Authored by: Joshua Vossler, John Watts, and Tim Hodge. Provided by : Coastal Carolina University License : CC BY NC ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives Located at : https://digitalcommons.coastal.edu/kimbel-library-instructional-videos/9/
- Putting It Together: Psychological Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at: https://pressbooks.online.ucf.edu/lumenpsychology/chapter/putting-it-together-psychological-research/
- Research. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution Located at:
All rights reserved content
- Understanding Driver Distraction. Provided by : American Psychological Association. License : Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XToWVxS_9lA&list=PLxf85IzktYWJ9MrXwt5GGX3W-16XgrwPW&index=9 .
- Correlation vs. Causality: Freakonomics Movie. License : Other. License Terms : Standard YouTube License Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lbODqslc4Tg.
- Psychological Research – Crash Course Psychology #2. Authored by : Hank Green. Provided by : Crash Course. License : Other. License Terms : Standard YouTube License Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hFV71QPvX2I .
Public domain content
- Researchers review documents. Authored by : National Cancer Institute. Provided by : Wikimedia. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Researchers_review_documents.jpg . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless of who is observing
well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena
(plural: hypotheses) tentative and testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables
an experiment must be replicable by another researcher
implies that a theory should enable us to make predictions about future events
able to be disproven by experimental results
implies that all data must be considered when evaluating a hypothesis
committee of administrators, scientists, and community members that reviews proposals for research involving human participants
process of informing a research participant about what to expect during an experiment, any risks involved, and the implications of the research, and then obtaining the person’s consent to participate
purposely misleading experiment participants in order to maintain the integrity of the experiment
when an experiment involved deception, participants are told complete and truthful information about the experiment at its conclusion
committee of administrators, scientists, veterinarians, and community members that reviews proposals for research involving non-human animals
research studies that do not test specific relationships between variables
research investigating the relationship between two or more variables
research method that uses hypothesis testing to make inferences about how one variable impacts and causes another
observation of behavior in its natural setting
inferring that the results for a sample apply to the larger population
when observations may be skewed to align with observer expectations
measure of agreement among observers on how they record and classify a particular event
observational research study focusing on one or a few people
list of questions to be answered by research participants—given as paper-and-pencil questionnaires, administered electronically, or conducted verbally—allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of people
subset of individuals selected from the larger population
overall group of individuals that the researchers are interested in
method of research using past records or data sets to answer various research questions, or to search for interesting patterns or relationships
studies in which the same group of individuals is surveyed or measured repeatedly over an extended period of time
compares multiple segments of a population at a single time
reduction in number of research participants as some drop out of the study over time
relationship between two or more variables; when two variables are correlated, one variable changes as the other does
number from -1 to +1, indicating the strength and direction of the relationship between variables, and usually represented by r
two variables change in the same direction, both becoming either larger or smaller
two variables change in different directions, with one becoming larger as the other becomes smaller; a negative correlation is not the same thing as no correlation
changes in one variable cause the changes in the other variable; can be determined only through an experimental research design
unanticipated outside factor that affects both variables of interest, often giving the false impression that changes in one variable causes changes in the other variable, when, in actuality, the outside factor causes changes in both variables
seeing relationships between two things when in reality no such relationship exists
tendency to ignore evidence that disproves ideas or beliefs
group designed to answer the research question; experimental manipulation is the only difference between the experimental and control groups, so any differences between the two are due to experimental manipulation rather than chance
serves as a basis for comparison and controls for chance factors that might influence the results of the study—by holding such factors constant across groups so that the experimental manipulation is the only difference between groups
description of what actions and operations will be used to measure the dependent variables and manipulate the independent variables
researcher expectations skew the results of the study
experiment in which the researcher knows which participants are in the experimental group and which are in the control group
experiment in which both the researchers and the participants are blind to group assignments
people's expectations or beliefs influencing or determining their experience in a given situation
variable that is influenced or controlled by the experimenter; in a sound experimental study, the independent variable is the only important difference between the experimental and control group
variable that the researcher measures to see how much effect the independent variable had
subjects of psychological research
subset of a larger population in which every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected
method of experimental group assignment in which all participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either group
consistency and reproducibility of a given result
accuracy of a given result in measuring what it is designed to measure
determines how likely any difference between experimental groups is due to chance
statistical probability that represents the likelihood that experimental results happened by chance
Psychological Science is the scientific study of mind, brain, and behavior. We will explore what it means to be human in this class. It has never been more important for us to understand what makes people tick, how to evaluate information critically, and the importance of history. Psychology can also help you in your future career; indeed, there are very little jobs out there with no human interaction!
Because psychology is a science, we analyze human behavior through the scientific method. There are several ways to investigate human phenomena, such as observation, experiments, and more. We will discuss the basics, pros and cons of each! We will also dig deeper into the important ethical guidelines that psychologists must follow in order to do research. Lastly, we will briefly introduce ourselves to statistics, the language of scientific research. While reading the content in these chapters, try to find examples of material that can fit with the themes of the course.
To get us started:
- The study of the mind moved away Introspection to reaction time studies as we learned more about empiricism
- Psychologists work in careers outside of the typical "clinician" role. We advise in human factors, education, policy, and more!
- While completing an observation study, psychologists will work to aggregate common themes to explain the behavior of the group (sample) as a whole. In doing so, we still allow for normal variation from the group!
- The IRB and IACUC are important in ensuring ethics are maintained for both human and animal subjects
Psychological Science: Understanding Human Behavior Copyright © by Karenna Malavanti is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An observational study is used to answer a research question based purely on what the researcher observes. There is no interference or manipulation of the research subjects, and no control and treatment groups. These studies are often qualitative in nature and can be used for both exploratory and explanatory research purposes.
characteristics of case study observational research, a modified form of Yin's 2014 model of case study research the authors used in a study exploring interprofessional collaboration in primary care. In this approach, observation data are positioned as the central component of the research design.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Observation methods have the potential to reach beyond other methods that rely largely or solely on self-report. This article describes the distinctive characteristics of case study observational research, a modified form of Yin's 2014 model of case study research the authors used in a study exploring interprofessional collaboration in primary ...
Case study research is a comprehensive method that incorporates multiple sources of data to provide detailed accounts of complex research phenomena in real-life contexts. However, current models of case study research do not particularly distinguish the unique contribution observation data can make.
A case study is an in-depth examination of an individual. Sometimes case studies are also completed on social units (e.g., a cult) and events (e.g., a natural disaster). ... So, as with all observational methods, case studies do not permit determination of causation. In addition, because case studies are often of a single individual, and ...
Case Studies. A case study is an in-depth examination of an individual. Sometimes case studies are also completed on social units (e.g., a cult) and events (e.g., a natural disaster). ... Like many observational research methods, case studies tend to be more qualitative in nature. Case study methods involve an in-depth, and often a longitudinal ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
Download chapter PDF. An observational case study is a study of a real-world case without performing an intervention. Measurement may influence the measured phenomena, but as in all forms of research, the researcher tries to restrict this to a minimum. The researcher may study a sample of two or even more cases, but the goal of case study ...
A case study is an in-depth analysis of one individual or group. Learn more about how to write a case study, including tips and examples, and its importance in psychology. ... Direct observation: This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting. While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize ...
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a real-life phenomenon or situation. Learn how to write a case study for your social sciences research assignments with this helpful guide from USC Library. Find out how to define the case, select the data sources, analyze the evidence, and report the results.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process. Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study. Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina ...
Case-control study. A case-control study is an observational analytic retrospective study design [].It starts with the outcome of interest (referred to as cases) and looks back in time for exposures that likely caused the outcome of interest [13, 20].This design compares two groups of participants - those with the outcome of interest and the matched control [].
Like case studies, naturalistic observation is often used to generate new ideas. Because it gives the researcher the opportunity to study the total situation, it often suggests avenues of inquiry not thought of before. The ability to capture actual behaviors as they unfold in real-time, analyze sequential patterns of interactions, measure base ...
Case Control Observational Study. Researchers in case control studies identify individuals with an existing health issue or condition, or "cases," along with a similar group without the condition, or "controls." These two groups are then compared to identify predictors and outcomes. This type of study is helpful to generate a hypothesis ...
Again, case studies provide enormous amounts of information, but since the cases are so specific, the potential to apply what's learned to the average person may be very limited. Naturalistic Observation. ... This type of observational study is called naturalistic observation: observing behavior in its natural setting. To better understand ...
Cohort studies and case-control studies are two primary types of observational studies that aid in evaluating associations between diseases and exposures. In this review article, we describe these study designs, methodological issues, and provide examples from the plastic surgery literature. Keywords: observational studies, case-control study ...
Observational study designs include ecological designs, cross sectional, case-control, case-crossover, retrospective and prospective cohorts. An important subset of observational studies is diagnostic study designs, which evaluate the accuracy of diagnostic procedures and tests as compared to other diagnostic measures.
The three main types of descriptive studies are, naturalistic observation, case studies, and surveys. Try It. Naturalistic Observation. If you want to understand how behavior occurs, one of the best ways to gain information is to simply observe the behavior in its natural context. However, people might change their behavior in unexpected ways ...
Accurate and reliable precipitation data are important for analyzing regional precipitation distribution, water resource management, and ecological environment construction. Due to the scarcity of meteorological stations in the Turpan-Hami region, precipitation observation conditions are limited, and it is difficult to obtain precipitation data. Firstly, the applicability of TRMM 3B43v7, GPM ...
Current methods mainly rely on differential digital elevation models and displacement tracking, which are limited by observation conditions and imaging geometry, resulting in low accuracy of three-dimensional deformation and reducing the applicability of the mass conservation method. ... a case study in Gongjue County, Tibet. China. Remote ...