

The Author’s Purpose for students and teachers
What Is The Author’s Purpose?

When discussing the author’s purpose, we refer to the ‘why’ behind their writing. What motivated the author to produce their work? What is their intent, and what do they hope to achieve?
The author’s purpose is the reason they decided to write about something in the first place.
There are many reasons a writer puts pen to paper, and students must possess the necessary tools to identify these reasons and intents to react and respond appropriately.
Understanding why authors write is essential for students to navigate the complex landscape of texts effectively. The concept of author’s purpose encompasses the motivations behind a writer’s choice of words, style, and structure. By teaching students to discern these purposes, educators empower them to engage critically with various forms of literature and non-fiction.
Author’s Purpose Definition
The author’s purpose is his or her motivation for writing a text and their intent to Persuade, Inform, Entertain, Explain or Describe something to an audience.
Author’s Purpose Examples and Types
It is universally accepted there are three base categories of the Author’s Purpose: To Persuade, To Inform , and To Entertain . These can easily be remembered with the PIE acronym and should be the starting point on this topic. However, you may also encounter other subcategories depending on who you ask.
This table provides many author’s purpose examples, and we will cover the first five in detail in this article.
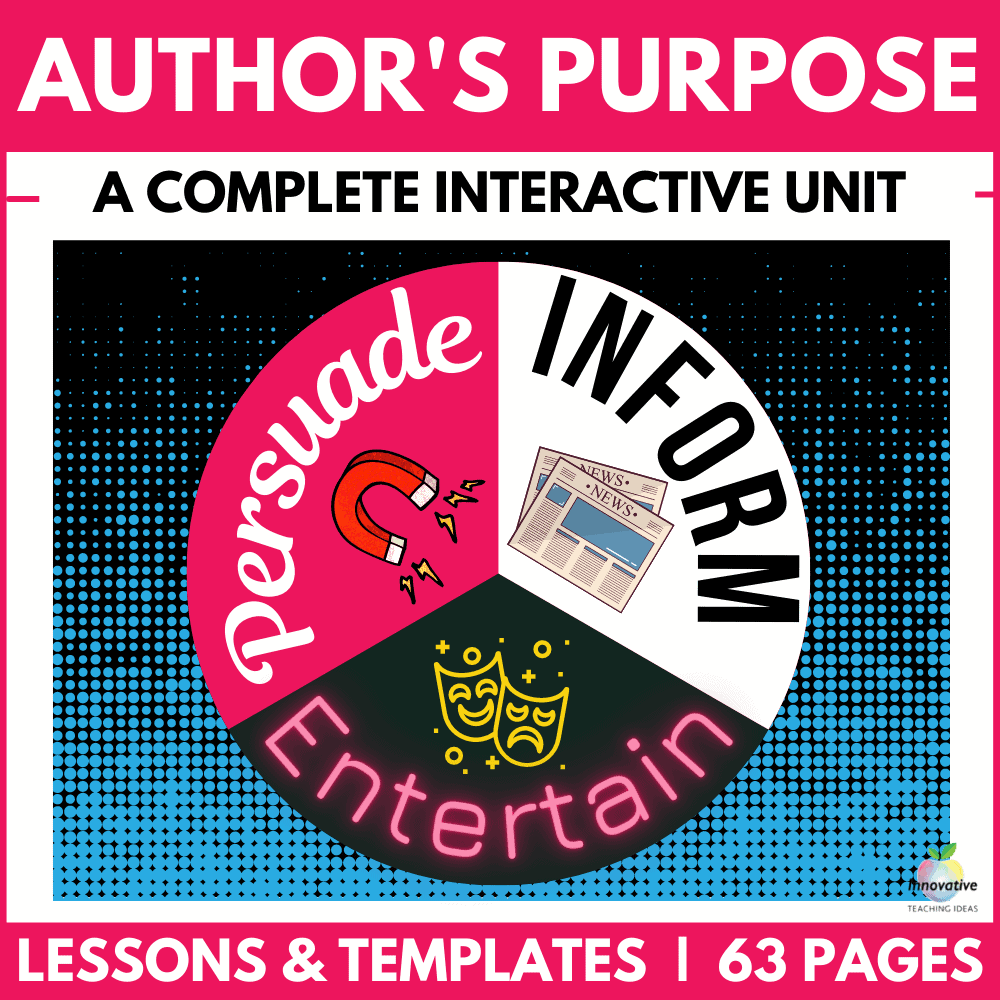
Author’s Purpose Teaching Unit
Teach your students ALL ASPECTS of the Author’s Purpose with this fully EDITABLE 63-page Teaching Unit.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ ( 42 reviews )

Author’s Purpose 1: To Persuade

Definition: This is a prevalent purpose of writing, particularly in nonfiction. When a text is written to persuade, it aims to convince the reader of the merits of a particular point of view . In this type of writing, the author attempts to persuade the reader to agree with this point of view and/or subsequently take a particular course of action.
Examples: This purpose can be found in all kinds of writing. It can even be in fiction writing when the author has an agenda, consciously or unconsciously. However, it is most commonly the motivation behind essays, advertisements, and political writing, such as speech and propaganda.
Persuasion is commonly also found in…
- A political speech urges voters to support a particular candidate by presenting arguments for their suitability for the position, policies, and record of achievements.
- An advertisement for a new product that emphasizes its unique features and benefits over competing products, attempting to convince consumers to choose it over alternatives.
- A letter to the editor of a newspaper expressing a strong opinion on a controversial issue and attempting to persuade others to adopt a similar position by presenting compelling evidence and arguments.
How to Identify: To identify when the author’s purpose is to persuade, students should ask themselves if they feel the writer is trying to get them to believe something or take a specific action. They should learn to identify the various tactics and strategies used in persuasive writing, such as repetition, multiple types of supporting evidence, hyperbole, attacking opposing viewpoints, forceful phrases, emotive imagery, and photographs.
We have a complete persuasive writing guide if you want to learn more.
Strategies for being a more PERSUASIVE writer
To become a persuasive writer, students can employ several strategies to convey their arguments and influence their readers effectively. Here are five strategies for persuasive writing:
- Understand Your Audience: Know your target audience and tailor your persuasive arguments to appeal to their interests, values, and beliefs. Consider their potential objections and address them in your writing. Understanding your audience helps you create a more compelling and persuasive piece.
- Use Strong Evidence and Examples: Support your claims with credible evidence, statistics, and real-life examples. Persuasive writing relies on logic and facts to support your arguments. Conduct research to find reliable sources that strengthen your case and make your writing more convincing.
- Craft a Persuasive Structure: Organize your writing clearly and persuasively. Start with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader’s attention and states your main argument. Use body paragraphs to present evidence and supporting points logically. Finish with a strong conclusion that reinforces your main message and calls the reader to take action or adopt your viewpoint.
- Appeal to Emotions: Persuasive writing is not just about logic; emotions are crucial in influencing readers. Use emotional appeals to connect with your audience and evoke empathy, sympathy, or excitement. Be careful not to manipulate emotions but use them to reinforce your argument authentically.
- Anticipate Counterarguments: Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to show that you have considered different perspectives. By addressing opposing viewpoints, you demonstrate that you have thoroughly thought about the issue and strengthen your credibility as a persuasive writer.
Bonus Tip: Use Persuasive Language: Pay attention to your choice of words and language. Use compelling language that evokes a sense of urgency or importance. Employ rhetorical devices, such as repetition, analogy, and rhetorical questions, to make your writing more persuasive and memorable.
Please encourage students to practice these strategies in their writing in formal essays and everyday persuasive situations. By mastering persuasive writing techniques, students can effectively advocate for their ideas, inspire change, and have a greater impact with their words.
Author’s Purpose 2: To Inform
Definition: When an author aims to inform, they usually wish to enlighten their readership about a real-world topic. Often, they will do this by providing lots of facts. Informational texts impart information to the reader to educate them on a given topic.
Examples: Many types of school books are written with the express purpose of informing the reader, such as encyclopedias, recipe books, newspapers and informative texts…
- A news article reporting on a recent event or development provides factual details about what happened, who was involved, and where and when it occurred.
- A scientific journal article describes a research study’s findings, explaining the methodology, results, and implications for further analysis or practical application.
- A travel guidebook that provides detailed information about a particular destination, including its history, culture, attractions, accommodation options, and practical advice for visitors.
How to Identify: In the process of informing the reader, the author will use facts, which is one surefire way to spot the intent to inform.
However, when the author’s purpose is persuasion, they will also likely provide the reader with some facts to convince them of the merits of their particular case. The main difference between the two ways facts are employed is that when the intention is to inform, facts are presented only to teach the reader. When the author aims to persuade, they commonly mask their opinions amid the facts.
Students must become adept at recognizing ‘hidden’ opinions through practice. Teach your students to beware of persuasion masquerading as information!
Please read our complete guide to learn more about writing an information report.
Strategies for being a more INFORMATIVE writer
To become an informative writer, students can employ several strategies to effectively convey information and knowledge clearly and engagingly. Here are five strategies for informative writing:
- Conduct Thorough Research: Before writing, gather information from credible sources such as books, academic journals, reputable websites, and expert interviews. Use reliable data and evidence to support your points. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your information is essential in informative writing.
- Organize Information Logically: Structure your writing clearly and logically. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to organize information into easily digestible chunks. A well-structured piece helps readers understand complex topics more quickly.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Aim for clarity and avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language that might confuse your readers. Use simple and concise sentences to deliver information effectively. Make sure to define any technical terms or concepts unfamiliar to your audience.
- Provide Real-Life Examples: Illustrate your points with real-life examples, case studies, or anecdotes. Concrete examples make abstract concepts more understandable and relatable. They also help to keep the reader engaged throughout the piece.
- Incorporate Visual Aids: Whenever possible, use visual aids such as charts, graphs, diagrams, and images to complement your text. Visual elements enhance understanding and retention of information. Be sure to explain the significance of each visual aid in your writing.
Bonus Tip: Practice Summarization: After completing informative writing, practice summarizing the main points. Being able to summarize your work concisely reinforces your understanding of the topic and helps you identify any gaps in your information.
Encourage students to practice these strategies in various writing tasks, such as research papers, reports, and explanatory essays. By mastering informative writing techniques, students can effectively educate their readers, share knowledge, and contribute meaningfully to their academic and professional pursuits.
Author’s Purpose 3: To Entertain
Definition: When an author’s chief purpose is to entertain the reader, they will endeavour to keep things as interesting as possible. Things happen in books written to entertain, whether in an action-packed plot , inventive characterizations, or sharp dialogue.

Examples: Not surprisingly, much fiction is written to entertain, especially genre fiction. For example, we find entertaining examples in science fiction, romance, and fantasy.
Here are some more entertaining texts to consider.
- A novel that tells a compelling story engages the reader’s emotions and imagination through vivid characters, evocative settings, and unexpected twists and turns.
- A comedy television script that uses humour and wit to amuse the audience, often by poking fun at everyday situations or societal norms.
- A stand-up comedy routine that relies on the comedian’s storytelling ability and comedic timing to entertain the audience, often by commenting on current events or personal experiences.
How to Identify: When writers attempt to entertain or amuse the reader, they use various techniques to engage their attention. They may employ cliffhangers at the end of a chapter, for example. They may weave humour into their story or even have characters tell jokes. In the case of a thriller, an action-packed scene may follow an action-packed scene as the drama builds to a crescendo. Think of the melodrama of a soap opera here rather than the subtle touch of an arthouse masterpiece.
Strategies for being a more ENTERTAINING writer
To become an entertaining writer, students can use several strategies to captivate their readers and keep them engaged. Here are five effective techniques:
- Use Humor: Inject humour to tickle the reader’s funny bone. Incorporate witty remarks, funny anecdotes, or clever wordplay. Humour lightens the tone of your writing and makes it enjoyable to read. However, be mindful of your audience and ensure your humour is appropriate and relevant to the topic.
- Create Engaging Characters: Whether you’re writing a story, essay, or any other type of content, develop compelling and relatable characters. Readers love connecting with well-developed characters with distinct personalities, flaws, and strengths. Use descriptive language to bring them to life and make them memorable.
- Craft Intriguing Beginnings: Grab your reader’s attention from the very first sentence. Start with a compelling hook that sparks curiosity or creates intrigue. An exciting beginning sets the tone for the rest of the piece and encourages the reader to continue reading.
- Build Suspense and Surprise: Incorporate twists, turns, and surprises into your writing to keep readers on their toes. Building suspense creates anticipation and makes readers eager to discover what happens next. Surprise them with unexpected plot developments or revelations to keep them engaged throughout the piece.
- Use Imagery and Vivid Descriptions : Paint vivid pictures with your words to immerse readers in your writing. Use sensory language and descriptive imagery to transport them to different places, evoke emotions, and create a multisensory experience. Readers love to feel like they’re part of the story, and vivid descriptions help achieve that.
Bonus Tip: Read Widely and Analyze: To become an entertaining writer, read a variety of books, articles, and pieces from different genres and authors. Pay attention to the elements that make their writing engaging and entertaining. Analyze their use of humour, character development, suspense, and descriptions. Learning from the work of accomplished writers can inspire and improve your own writing.
By using these strategies and practising regularly, students can become more entertaining writers, captivating their audience and making their writing a joy to read. Remember, the key to entertaining writing is engaging your readers and leaving them with a positive and memorable experience.
Author’s Purpose 4: To Explain

Definition: When writers write to explain, they want to tell the reader how to do something or reveal how something works. This type of writing is about communicating a method or a process.
Examples: Writing to explain can be found in instructions, step-by-step guides, procedural outlines, and recipes such as these…
- A user manual explaining how to operate a piece of machinery or a technical device provides step-by-step instructions and diagrams to help users understand the process.
- A textbook chapter that explains a complex scientific or mathematical concept breaks it into simpler components and provides examples and illustrations to aid comprehension.
- A how-to guide that explains how to complete a specific task or achieve a particular outcome, such as cooking a recipe, gardening, or home repair. It provides a list of materials, step-by-step instructions, and tips to ensure success.
How to Identify: Often, this writing is organized into bulleted or numbered points. As it focuses on telling the reader how to do something, often lots of imperatives will be used within the writing. Diagrams and illustrations are often used to reinforce the text explanations too.
Read our complete guide to explanatory texts here.
Strategies for being a more EXPLANATORY WRITER
To become a more explanatory writer, students can employ several strategies to effectively clarify complex ideas and concepts for their readers. Here are five strategies for explanatory writing:
- Define Technical Terms: When writing about a specialized or technical topic, ensure that you define any relevant terms or jargon that might be unfamiliar to your readers. A clear and concise definition helps readers grasp the meaning of these terms and facilitates better understanding of the content.
- Use Analogies and Comparisons: Use analogies and comparisons to relate complex ideas to more familiar concepts. This technique makes abstract or difficult concepts more relatable and easier to understand. Analogies provide a frame of reference that helps readers connect new information to something they already know.
- Provide Step-by-Step Explanations: Break down complex processes or procedures into step-by-step explanations. This approach helps readers follow the sequence of events or actions and understand the logic behind each step. Use numbered lists or bullet points to make the process visually clear.
- Include Visuals and Diagrams: Supplement your explanatory writing with visual aids such as diagrams, flowcharts, or illustrations. Visuals can enhance understanding and retention of information by visually representing the concepts being discussed.
- Address “Why” and “How”: In explanatory writing, go beyond simply stating “what” happened or what a concept is. Focus on explaining “why” something occurs and “how” it works. Providing the underlying reasons and mechanisms helps readers better understand the subject matter.
Bonus Tip: Review and Revise: After completing your explanatory writing, review your work and assess whether the explanations are clear and comprehensive. Consider seeking feedback from peers or teachers to identify areas needing further clarification or expansion.
Please encourage students to practice these strategies in writing across different subjects and topics. By mastering explanatory writing techniques, students can effectively communicate complex ideas, promote better understanding, and excel academically and professionally.
Author’s Purpose 5: To Describe

Definition: Writers often use words to describe something in more detail than conveyed in a photograph alone. After all, they say a picture paints a thousand words, and text can help get us beyond the one-dimensional appearance of things.
Examples: We can find lots of descriptive writing in obvious places like short stories, novels and other forms of fiction where the writer wishes to paint a picture in the reader’s imagination. We can also find lots of writing with the purpose of description in nonfiction too – in product descriptions, descriptive essays or these text types…
- A travelogue that describes a particular place, highlighting its natural beauty, cultural attractions, and unique characteristics. The author uses sensory language to create a vivid mental picture in the reader’s mind.
- A painting analysis that describes the colors, shapes, textures, and overall impression of a particular artwork. The author uses descriptive language to evoke the emotions and ideas conveyed by the painting.
- A product review that describes the features, benefits, and drawbacks of a particular item. The author uses descriptive language to give the reader a clear sense of the product and whether it might suit their needs.
How to Identify: In the case of fiction writing which describes, the reader will notice the writer using lots of sensory details in the text. Our senses are how we perceive the world, and to describe their imaginary world, writers will draw heavily on language that appeals to these senses. In both fiction and nonfiction, readers will notice that the writer relies heavily on adjectives.
Strategies for being a more descriptive writer
Becoming a descriptive writer is a valuable skill that allows students to paint vivid pictures with words and immerse readers in their stories. Here are five strategies for students to enhance their descriptive writing:
- Sensory Language: Engage the reader’s senses by incorporating sensory language into your writing. Use descriptive adjectives, adverbs, and strong verbs to create a sensory experience for your audience. For example, instead of saying “the flower was pretty,” describe it as “the delicate, fragrant blossom with hues of vibrant pink and a velvety texture.”
- Show, Don’t Tell: Use the “show, don’t tell” technique to make your writing more descriptive and immersive. Rather than stating emotions or characteristics directly, use descriptive details and actions to show them. For instance, instead of saying “she was scared,” describe how “her heart raced, and her hands trembled as she peeked around the dark corner.”
- Use Metaphors and Similes: Integrate metaphors and similes to add depth and creativity to your descriptions. Compare two unrelated things to create a powerful visual image. For example, “the sun dipped below the horizon like a golden coin slipping into a piggy bank.”
- Focus on Setting: Pay attention to the setting of your story or narrative. Describe the environment, atmosphere, and surroundings in detail. Take the reader on a journey by clearly depicting the location. Let your words bring the setting to life, whether it’s a lush forest, a bustling city street, or a mystical castle.
- Practice Observation: Practice keen observation skills in your daily life. Take note of the world around you—the sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and textures. Observe people, places, and objects with a writer’s eye. By developing a habit of keen observation, you’ll have a rich bank of sensory details to draw from when you write.
Bonus Tip: Revise and Edit: Good descriptive writing often comes through revision and editing. After writing a draft, go back and read your work critically. Look for opportunities to add more descriptive elements, eliminate unnecessary adjectives or cliches, and refine your language to make it more engaging.
By applying these strategies and continually honing your descriptive writing skills, you’ll be able to transport readers to new worlds, evoke emotions, and make your writing more captivating and memorable.
Free Author’s Purpose Anchor Charts & Posters

Author’s Purpose Teaching Activities

The Author’s Purpose Task 1. The Author’s Purpose Anchor Chart
Whether introducing the general idea of the author’s purpose or working on identifying the specifics of a single purpose, a pie author’s purpose anchor chart can be an excellent resource for students when working independently. Compiling the anchor chart collaboratively with the students can be an effective way for them to reconstruct and reinforce their learning.
The Author’s Purpose Task 2. Gather Real-Life Examples
Challenging students to identify and collect real-life examples of the various types of writing as homework can be a great way to get some hands-on practice. Encourage your students to gather various forms of text together indiscriminately. They then sift through them to categorize them appropriately according to their purpose. The students will soon begin to see that all writing has a purpose. You may also like to make a classroom display of the gathered texts to serve as examples.
The Author’s Purpose Task 3. DIY
One of the most effective ways for students to recognize the authorial intent behind a piece of writing is to gain experience producing writing for various purposes. Design writing tasks with this in mind. For example, if you are focused on writing to persuade, you could challenge the students to produce a script for a radio advertisement. If the focus is entertaining, you could ask the students to write a funny story.
The Author’s Purpose Task 4. Classroom Discussion
When teaching author’s purpose, organize the students into small discussion groups of, say, 4 to 5. Provide each group with copies of sample texts written for various purposes. Students should have some time to read through the texts by themselves. They then work to identify the author’s purpose, making notes as they go. Students can discuss their findings as a group.
Remember: the various purposes are not mutually exclusive; sometimes, a text has more than one purpose. It is possible to be both entertaining and informative, for example. It is essential students recognize this fact. A careful selection of texts can ensure the students can discover this for themselves.
Students need to understand that regardless of the text they are engaged with, every piece of writing has some purpose behind it. It’s important that they work towards recognizing the various features of different types of writing that reveal to the reader just what that purpose is.
Initially, the process of learning to identify the different types of writing and their purposes will require conscious focus on the part of the student. Plenty of opportunities should be created to allow this necessary classroom practice.
However, this practice doesn’t have to be exclusively in the form of discrete lessons on the author’s purpose. Simply asking students what they think the author’s purpose is when reading any text in any context can be a great way to get the ‘reps’ in quickly and frequently.
Eventually, students will begin to recognize the author’s purpose quickly and unconsciously in the writing of others.
Ultimately, this improved comprehension of writing, in general, will benefit students in their own independent writing.
This video is an excellent introductory guide for students looking for a simple visual breakdown of the author’s purpose and how it can impact their approach to writing and assessment.
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO THE AUTHOR’S PURPOSE
Teaching Cause and Effect in Reading and Writing

The Writing Process

Elements of Literature
Teaching The 5 Story Elements: A Complete Guide for Teachers & Students

Understanding Author’s Purpose: Why It Matters in Writing

Share This Article
Welcome to our exploration of author’s purpose in writing! Have you ever wondered why authors write what they do?
Understanding an author’s purpose is like deciphering the code behind their words. It’s about uncovering the intentions and motivations that drive their writing. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the significance of author’s purpose, its impact on the reader, and why it’s essential for both writers and readers to grasp.
So, let’s embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of author’s purpose in writing.

Now, let’s explore why authors write the way they do, and why it’s crucial for both writers and readers to understand this concept.
The purpose behind a piece of writing is like the North Star guiding a ship through the vast ocean of words. Every word, every sentence, every paragraph crafted by an author serves a purpose beyond mere communication. Whether it’s to inform, persuade, entertain, or provoke thought, the author’s purpose shapes the entire composition, influencing the tone, style, and content.
Consider a persuasive essay advocating for environmental conservation. The author’s purpose is to convince readers of the urgency to protect the planet. They employ rhetorical strategies, emotional appeals, and factual evidence to sway the audience towards their viewpoint. Understanding this purpose allows readers to engage critically with the text, evaluating the effectiveness of the author’s arguments and forming informed opinions.

Similarly, in a work of fiction, the author’s purpose might be to transport readers to a different world, evoke emotions, or convey universal truths about the human experience. By recognizing the underlying purpose, readers can immerse themselves more fully in the narrative, empathizing with characters, and grasping the deeper themes woven into the story.
For writers, clarity of purpose is paramount. Before putting pen to paper or fingers to keyboard, authors must ask themselves: What do I hope to achieve with this piece? Whether it’s to entertain, educate, inspire, or provoke change, a clear understanding of their purpose guides every decision—from choosing the right words to structuring the narrative.
Moreover, understanding author’s purpose fosters critical thinking skills essential in today’s information-saturated world. When readers approach a text with an awareness of the author’s intentions, they become active participants in the dialogue, questioning, analyzing, and interpreting the content more effectively.
What Is Authors Purpose?
The author’s purpose refers to the reason behind why a writer creates a particular piece of writing. It encompasses the goals, intentions, or objectives that drive the author to communicate their message to the audience. Understanding the author’s purpose is crucial for readers as it helps them comprehend the text better, evaluate its effectiveness, and engage critically with the content.
What are the different types of authors’ purpose?
There are several different types of author’s purposes, each serving a distinct function in communication. Here are the primary categories:
- To Inform : The author aims to impart knowledge, facts, or information to the audience. This purpose is prevalent in textbooks, news articles, research papers, and instructional manuals. The author seeks to educate the reader about a specific topic, event, or concept.
- To Persuade : In persuasive writing, the author endeavors to sway the audience’s beliefs, opinions, or actions. This could involve presenting arguments, making appeals to emotions or logic, and advocating for a particular viewpoint or course of action. Examples include opinion pieces, advertisements, political speeches, and editorials.
- To Entertain : Authors may write primarily to amuse, entertain, or engage the audience. Fictional works such as novels, short stories, poetry, and plays often serve this purpose. Through storytelling, humor, drama, or suspense, the author seeks to captivate readers and provide enjoyment.
- To Express : Sometimes, authors write to express themselves, their thoughts, feelings, or experiences. This purpose is common in personal narratives, journals, memoirs, and reflective essays. The author may use writing as a form of self-expression, catharsis, or exploration of identity.
- To Instruct : Writing with the intention to instruct involves providing guidance, directions, or step-by-step procedures to help readers learn or accomplish something. This purpose is evident in how-to guides, recipes, manuals, and tutorials. The author aims to facilitate understanding and skill acquisition in the audience.
- To Describe : Authors may write to describe a person, place, object, or event in vivid detail, appealing to the reader’s senses and imagination. Descriptive writing is often found in travelogues, nature writing, and creative non-fiction. The author aims to paint a rich, sensory picture for the reader.
- To Convey Emotion : Some authors write with the primary goal of evoking emotions in the reader. This purpose is prevalent in poetry, lyrical prose, and personal essays. Through the use of imagery, metaphor, and language, the author seeks to elicit feelings of joy, sadness, nostalgia, or empathy.
Understanding these different types of author’s purposes allows readers to engage more deeply with a variety of texts, discerning the intentions behind the writing and interpreting the messages effectively.

What are the key words for author’s purpose?
Key words for identifying the author’s purpose in a text vary depending on the specific purpose. Here are some key words associated with each purpose:
- To Inform : inform, explain, describe, report, detail, educate, illustrate, clarify
- To Persuade : persuade, convince, argue, advocate, influence, convince, sway, urge, recommend
- To Entertain : entertain, amuse, delight, captivate, engage, charm, entertain, divert, thrill
- To Express : express, share, reveal, convey, articulate, narrate, recount, reflect, disclose
- To Instruct : instruct, guide, teach, demonstrate, show, explain, clarify, direct, advise
- To Describe : describe, depict, portray, characterize, illustrate, paint, evoke, capture, depict
- To Convey Emotion : evoke, express, convey, evoke, stir, elicit, provoke, arouse, communicate
What are the characteristics of the author’s purpose?
- Clarity : The purpose should be clear and evident throughout the text.
- Consistency : The content should align with the stated purpose.
- Tone : The tone of the writing often reflects the author’s purpose (e.g., formal for informing, persuasive for persuading, emotive for conveying emotion).
- Content : The type of information, arguments, or storytelling techniques used correspond to the purpose.
- Audience Engagement : The author aims to engage the audience according to their purpose (e.g., providing information, sparking emotions, guiding actions).
Why does purpose matter in writing?
Understanding the purpose of writing is paramount because it serves as the guiding force behind every word, sentence, and paragraph. Here’s why purpose matters in writing:
- Clarity of Communication : Identifying the purpose helps writers articulate their message clearly and effectively. Whether the goal is to inform, persuade, entertain, or express, knowing the purpose ensures that the content is tailored to achieve that objective.
- Audience Engagement : Purpose-driven writing resonates with the intended audience, capturing their attention and maintaining their interest. By aligning the content with the audience’s expectations and needs, writers can create meaningful connections and foster engagement.
- Effectiveness of Communication : Understanding the purpose allows writers to choose the most appropriate language, tone, and style to convey their message. This enhances the effectiveness of communication, ensuring that the intended message is conveyed accurately and convincingly.
- Achieving Goals : Writing with a clear purpose helps writers achieve their goals, whether it’s to inform, persuade, entertain, or inspire action. By keeping the purpose in mind throughout the writing process, writers can stay focused and effectively achieve their objectives.
- Impact on Readers : Purposeful writing has a significant impact on readers, influencing their perceptions, beliefs, and actions. Whether the goal is to educate, motivate, or entertain, purpose-driven writing can inspire readers, provoke thought, and evoke emotions, leaving a lasting impression.
Overall, purpose serves as the compass that guides writers through the writing process, ensuring that their message is clear, engaging, and impactful.
What is a top priority for all proposal writers?
For proposal writers, a top priority is to clearly articulate the purpose and objectives of the proposal. Here’s why:
- Clarity of Intent : Clearly stating the purpose of the proposal helps stakeholders understand the goals, objectives, and desired outcomes. This ensures alignment and clarity of intent, reducing ambiguity and misinterpretation.
- Audience Engagement : Clearly defining the purpose of the proposal captures the attention of stakeholders and engages them in the proposed initiative or project. It communicates the relevance and importance of the proposal, motivating stakeholders to invest time and resources in its success.
- Alignment of Strategies : A clearly defined purpose enables proposal writers to develop strategies and action plans that align with the intended objectives. It provides a framework for decision-making and prioritization, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Measurable Outcomes : Defining the purpose of the proposal allows for the establishment of measurable outcomes and success criteria. This enables stakeholders to assess the effectiveness and impact of the proposed initiative, facilitating accountability and evaluation.
Overall, clearly articulating the purpose of the proposal is essential for gaining stakeholder buy-in, guiding decision-making, and ultimately achieving the desired results.

In conclusion, understanding the purpose of writing is fundamental to effective communication. Whether informing, persuading, entertaining, or expressing, the purpose serves as the driving force behind every word penned by the author. It guides the tone, style, and content of the writing, ensuring clarity, engagement, and impact on the audience.
Recognizing the writer’s purpose and tone empowers readers to interpret and evaluate the content critically, fostering deeper engagement and meaningful dialogue. For proposal writers, clearly articulating the purpose of the proposal is paramount for gaining stakeholder buy-in, guiding decision-making, and ultimately achieving success.
In essence, purpose matters in writing because it provides direction, relevance, and significance to the text. By understanding the purpose behind the words, both writers and readers can navigate the complexities of communication with clarity, purpose, and effectiveness.
About Sara Cook
Hi, I am Sara! I am the founder of TheWritersHQ! I have loved writing and reading since I was a little kid! Stephen King has my heart! I started this site to share my knowledge and build on my passion!
Thewritershq
REVIEW GUIDELINES
THEWritershq 2023 ©
When You Write
What is the Author’s Purpose & Why Does it Matter?
There’s always a reason a writer decides to produce their work. We rarely think about it, but there’s always a motivating factor behind intent and goals they hope to achieve.
This “why” behind the author’s writing is what we call the author’s purpose, and it is the reason the author decided to write about something.
There are billions—maybe more—of reasons a writer decides to write something and when you understand the why behind the words, you can effectively and accurately evaluate their writing.
When you understand the why, you can apprehend what the author is trying to say, grasp the writer’s message, and the intent of a particular piece of literary work.
Without further ado, let me explain what the author’s purpose is and how you can identify it.
What is Author’s Purpose?
Just as I introduced the term, an author’s purpose is the author’s reason for or intent in writing.
In both fiction and non-fiction, the author selects the genre, writing format, and language to suit the author’s purpose.
The writing formats, genres, and vernacular are chosen to communicate a key message to the reader, to entertain the reader, to sway the reader’s opinion, et cetera.
The way an author writes about a topic fulfills their purpose; for example, if they intend to amuse, the writing will have a couple of jokes or anecdotal sections. The author’s purpose is also reflected in the way they title their works, write prefaces, and in their background.
In general, the purposes fall into three main categories, namely persuade, inform, and entertain. The three types of author’s purpose make the acronym PIE.
But, there are many reasons to write, the PIE just represents the three main classes of the author’s purpose .
In the next section, I’m going to elaborate on the various forms of the author’s purpose including the three broader categories that I have introduced.
How useful is the Author’s Purpose?
Understanding the author’s purpose helps readers understand and analyze writing. This analytical advantage helps the reader have an educated point of view. Titles or opening passages act as the text’s signposts, and we can assume what type of text we’re about to read.
If you can identify the author’s purpose, it becomes easier to recognize the proficiencies used to achieve that particular purpose. So, once you identify the author’s purpose, you can recognize the style, tone, word, and content used by the author to communicate their message.
You also get to explore other people’s attitudes, beliefs, or perspectives.
Why does the Author’s Purpose Matter for the Writer?
The intent and manner in which a body of text is written determine how one perceives the information one reads.
Perception is especially important if the author aims to inform, educate, or explain something to the reader. For instance, an author writing an informative piece should provide relevant or reliable information and clearly explain his concepts; otherwise, the reader will think they are trying to be deceptive.
The readers—particularly those reading informative or persuasive pieces—expect authors to support their arguments and demonstrate validity by using autonomous sources as references for their writing.
Likewise, readers expect to be thoroughly entertained by works of fiction.
Types of Author’s Purpose
Mostly, reasons for writing are condensed into 5 broad categories, and here they are:
1. to Persuade
Using this form of author’s purpose, the author tries to sway the reader and make them agree with their opinion, declaration, or stance. The goal is to convince the reader and make them act in a specific way.
To convince a reader to believe a concept or to take a specific course of action, the author backs the idea with facts, proof, and examples.
Authors also have to be creative with their persuasive writing . For instance, apart from form complementary facts and examples, the author has to borrow some forms of entertaining elements and amuse their readers. This makes their writing enjoyable and relatable to some extent, increasing the likelihood of persuading people to take the required course of action.
2. to Inform
When the author’s purpose is to inform or teach the reader, they use expository writing. The author attempts to teach objectively by showing or explaining facts.
When you look at informative writing and persuasive writing, you can identify a common theme: the use of facts. However, the two forms of the author’s purpose use these facts differently. Unlike persuasive writing, which uses facts to convince the reader, informative writing uses facts to educate the reader about a particular subject. With persuasive writing, it’s like there’s a catch: the call to action. But, informative writing only uses facts to educate the reader, not to convince them to take a specific course of action.
Informative writing only seeks to “expose” factual information about a topic for enlightenment.
3. to Entertain
Most fiction books are written to entertain the reader—and, yes, including horror. On the other hand, non-fiction works combine an entertaining element with informative writing.
To entertain, the author tries to keep things as interesting as possible by coming up with fascinating characters , exciting plots, thrilling storylines, and sharp dialogue.
Most narratives, poetry, and plays are written to entertain. Be that as it may, these works of fiction can also be persuasive or informative, but if we fuse values and ideas, changing the reader’s perspective becomes an easier task.
Nonetheless, the entertaining purpose has to dominate, or else, readers are going to lose interest quickly and the informative purpose will be defeated.
4. to Explain
When the author’s purpose is to explain, they write with the intent of telling the reader how to do something or giving details on how something works.
This type of writing is about teaching a method or a process and the text contains explanations that teach readers how a particular process works or the procedure required to do or create something.
5. to Describe
When describing is the author’s purpose, the author uses words to complement images in describing something. This type of writing attempts to give a more detailed description of something, a bit more detail than the “thousand words that a picture paints.”
The writer uses adjectives and images to make the reader feel as though it were their own sensory experience.
Main elements and examples of Author’s Purpose
A great way to identify the author’s purpose is to analyze the whole piece of literature. The first step would be to ask “What is the point of this piece?” One can also look at why it was written, who it was written for, and what effect they wanted it to have on readers.
Another method is to break down the text into different categories of purpose. For example, if someone wants their writing to persuade, they would use rhetorical devices (i.e., logical appeals).
Below are the types of publications dominated by each purpose and the things to look for when identifying the author’s purpose.
Persuasive Purpose
Persuasion is usually found in non-fiction, but countless other fiction books have also been used to persuade the reader.
Propaganda works are top of the list when it comes to persuasion in writing. But we also have other works including:
- Political speeches
- Advertisements
- Infomercial scripts and news editorials meant to persuade the reader
- Fiction writing whose author has an agenda
How to Identify Persuasive Purpose
When trying to identify persuasion in writing, you should ask yourself if the author is attempting to convince the reader to take a specific course of action.
If the author is trying to persuade their readers, they employ several tactics and schemes including hyperboles, forceful phrases, repetition, supporting evidence, imagery, and photographs, and they attack opposing ideas or proponents.
Informative Purpose
Although some works of fiction are also informative, informative writing is commonly found on non-fiction shelves and dominates academic works.
Many types of academic textbooks are written with the primary purpose of informing the reader.
Informative writing is generally found in the following:
- Textbooks
- Encyclopedias
- Recipe books
How to identify Informative Purpose
Just like in persuasive writing, the writer will attempt to inform the reader by feeding them facts.
So, how can you spot a pure intent to inform?
The difference between the two is that an author whose purpose is persuasion is likely going to provide the reader with some facts in an attempt with the primary goal of convincing the reader of the worthwhileness or valuableness of a particular idea, item, situation, et cetera.
On the other hand, in informative writing, facts are used to inform and are not sugar-coated by the author’s opinion, like is the case when the author’s purpose is to persuade.
Entertaining Purpose
The entertaining purpose dominates fiction writing—there’s a huge emphasis placed on entertaining the reader in almost every fiction book.
In almost every type of fiction (be it science fiction, romance, or fantasy), the writer works on an exciting story that will leave his readers craving for more.
The only issue with this purpose is that the adjective ‘entertaining’ is subjective and what entertains one reader may not be so riveting for another.
For example, the type of ‘entertainment’ one gets from romance novels is different from the amusement another gets from reading science fiction.
Although entertainment in writing is mostly used in fiction, non-fiction works also use storytelling—now and then—to keep the reader engaged and drive home a specific point.
How to identify Entertaining Purpose
Identifying works meant to entertain is fairly easy: When an author intends to entertain or amuse the reader, they use a variety of schemes aimed at getting the readers engaged.
The author may insert some humor into their narrative or use dialogue to weave in some jokes.
The writer may also use cliffhangers at the end of a page or chapter to keep the reader interested in the story.
Explaining Purpose
Authors also write to explain a topic or concept, especially in the non-fiction category. Fiction writers also write to explain things, usually not for the sole purpose of explaining that topic, but to help readers understand the plot, an event, a setting, or a character.
This type of purpose is dominant in How-to books, texts with recipes, DIY books, company or school books for orientation, and others.
How to identify Explaining Purpose
Texts with explaining purpose typically have a list of points (using a numbered or bulleted format), use infographics, diagrams, or illustrations.
Explaining purpose also contains a lot of verbs that try to convey directions, instructions, or guidelines.
Every author’s purpose or motive should be more than just entertaining the reader, it should be about more than just telling a good story.
A lot of authors tell stories to accomplish different objectives – some want to teach, provoke thought and debate, or show people that they’re not alone in their struggles. Others—like yours truly—write an article about the different types of Author’s purpose and hope it changes your writing style accordingly.
Authors must take their audience’s needs and interests into account, as well as their purposes for writing when writing something they intend to publish.
The author should find a way to make a piece that both generates interest as well as provides value to their reader.
Recommended Reading...
4 things that will improve your writing imagination, how to write an affirmation, best cities for writers to live and write in, list of interesting places to write that evoke inspiration.
Keep in mind that we may receive commissions when you click our links and make purchases. However, this does not impact our reviews and comparisons. We try our best to keep things fair and balanced, in order to help you make the best choice for you.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
© 2024 When You Write
What is The Author's Purpose?
- Test Prep Strategies
- Study Skills
- SAT Test Prep
- ACT Test Prep
- GRE Test Prep
- LSAT Test Prep
- Certifications
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/kr01-56a946be5f9b58b7d0f9d8d0.jpg)
- B.A., English, University of Michigan
Here's your heads up for the day: most standardized tests have a reading comprehension section. I'm fairly certain you knew that, but in case you didn't, you're welcome. What you may not have known is that in most reading comprehension sections, you will be called upon to answer questions about the author's purpose, along with other concepts like main idea , vocabulary in context , inferences and more. If you have no idea what author's purpose means you're going to have a hard time finding it, huh? I thought so. Take a peek below to read a little more about this reading skill and how you can find it in those long reading passages on standardized tests.
Author's Purpose Practice
Author's Purpose Basics
The author's purpose is basically the reason he or she chose to act in a particular way, whether that's writing the passage, selecting a phrase, using a word, etc. It differs from the main idea in that author's purpose not the point you're supposed to get or understand; rather, it's the why behind why the author picked up a pen or selected those words in the first place. It can be difficult to determine because, after all, you may not be inside the mind if the writer. You may not actually know why she or he chose to include a particular phrase or idea. The good news? The majority of author's purpose questions will come in multiple choice format. So you won't have to come up with the reason for an author's behavior. You'll just need to select the best choice.
If you're trying to determine the author's purpose on a standardized test, your question may look a little something like this:
1. The author most likely mentions the Depression in lines 33 - 34 to: A. identify the primary purpose for Social Security. B. criticize FDR's adoption of a program that would run out of money. C. contrast the effectiveness of the Social Security Program with that of family care. D. list another factor that contributed to the need for the Social Security Program.
Author's Purpose Key Words
There are a few key words associated with the author's purpose. Often times, you can narrow down what an author was trying to accomplish by looking at the language he or she used while writing. Take a look at the words below. The bold word will be used in the answer choices. The phrase following the bold words is an explanation of what it really means when you see it. If you click on the "How to Find the Author's Purpose" below, you'll see each of these phrases explained thoroughly so you can understand how to determine when each is being used in context.
- Compare: Author wanted to show similarities between ideas
- Contrast: Author wanted to show differences between ideas
- Criticize: Author wanted to give a negative opinion of an idea
- Describe/Illustrate: Author wanted to paint a picture of an idea
- Explain: Author wanted to break down an idea into simpler terms
- Identify/List: Author wanted to tell the reader about an idea or series of ideas
- Intensify: Author wanted to make an idea greater
- Suggest: Author wanted to propose an idea
If you can master these bad boys, then you'll have a much easier time answering those reading comprehension questions on your next standardized test, mostly because these key words are often used so very often in those questions! Bonus!
How to Find The Author's Purpose
Sometimes, reading for the author's purpose is as simple as just that; you read, and you figure out that the writer really hated the Red Sox and wanted to criticize the whole franchise. Other times, it isn't so simple, so it's good to have a technique to guide you when you're looking!
- Finding the Author's Purpose
- Worksheet 1: Author's Purpose
- Reading Comprehension Practice Questions
- How to Find the Main Idea
- What Is Author's Tone?
- Understanding Vocabulary Words in Context
- High School Vocabulary in Context Worksheets
- Worksheet 2: Author's Purpose
- Top 5 ACT Reading Strategies
- Inference: A Critical Assumption
- LSAT Sections: What's on the LSAT?
- How to Boost Reading Comprehension With Reciprocal Teaching
- 3 Tricks to Figure out the Author's Tone
- Third Grade Reading Comprehension Books
- How to Find the Main Idea - Worksheet
- How to Find the Implied Main Idea

A Guide To The Author’s Purpose

Table of Contents
What does persuasion mean, some examples of persuasion in writing:, clues to look for persuasive purpose:, what does inform mean, some examples of information in writing:, clues to look for informative purpose:, what does entertain mean, some examples of entertainment in writing:, clues to look for entertaining purpose:, what does explain mean, some examples of explanation in writing:, clues to look for explaining purpose:, what does describe mean, some examples of description in writing:, clues to look for descriptive purpose:.
An essential concept in mastering reading is understanding the why behind the words. What is the author trying to say? What is the motivation, the message, the intent of the literary work?
The reason why the author writes a particular piece of fiction or non-fiction is called the author’s purpose. Authors choose the genre, writing format, and language based on the author’s purpose. Therefore, a student cannot assume the purpose because the text falls in a specific genre category or because it’s a story and not a textbook.
What is authors purpose and how does the reader identify the author’s purpose?
The 5 Types of Author’s Purpose
To persuade.
This is an extremely common form of writing where the author attempts to convince the reader to agree with them or for the reader to act in a specific way. Persuasive writing is easily recognized by a call to action in the text or the author sharing their opinion backed with facts, proof, and examples to help convince the reader.
While it’s commonly found in non-fiction, many well-written fiction books are also attempting to persuade the reader.
- Propaganda pieces that influence people to think or act in a certain way
- Speeches that attempts to convince the reader to agree with the speaker’s opinion
- Advertisements that persuade a person to buy the product or service
- Commercial and news editorials that inform and persuade the reader
- The author’s purpose is in the motivation behind an essay.
- Fiction writing where the author has an agenda intentionally or unintentionally.
- Is the author attempting to convince the reader to take a specific action or believe something specific?
- Does the author make use of hyperbole?
- Does the author use forceful phrases?
- Does the author attack viewpoints that oppose theirs?
- Is the writing filled with imagery and graphics to extract specific types of emotions from the reader?
When the author’s purpose is to inform, they write objectively and use facts. Although both informative writing and persuasive writing use facts, the goals are different. Persuasive writing uses facts to support an opinion; it’s part of the process to convince the reader and present itself as “informative.” Informative writing, however, uses facts to educate the reader about a certain topic. There is no hidden goal; the author presents informative facts to teach the reader and is not interested in convincing the reader to believe or act in a certain way.
You’ll often find a liberal dose of text features in an text when an author’s purpose is to inform.
Informative writing is generally found in non-fiction writing. Fiction may also present information throughout the text.
- School textbooks are written for the primary purpose of teaching students about a subject.
- Recipe books provide the ingredients and methods of how to cook a specific dish.
- Newspapers inform the public about current events and news happening locally, nationally, or internationally.
- Encyclopedias and dictionaries define, explain, and inform about a word or subject.
- Does the author use facts to inform and educate without wanting to persuade the reader?
- Is the content objective where the author does not give their opinion to convince the student in a specific way?
- Does the text contain hidden opinions that are not informative but persuasive?
- Did the reader learn something when reading the text?
To Entertain
The author’s purpose in fiction books is generally to entertain the reader. Non-fiction texts, however, may also be entertaining while informing the reader too. Fiction writers use fascinating characters, sharp dialogue, an exciting storyline, or an action-packed plot to keep readers interested and engaged. Readers may prefer reading genres that they find more enjoyable than others.
Although entertainment in writing is generally found in fiction, non-fiction writers also may use storytelling to engage the reader and accentuate a point.
- Genre fiction authors write for readers who enjoy reading the type of stories typical to that genre. Readers could be picky with the genres they prefer. For example, science fiction readers may not find romance novels as entertaining, and romance lovers may not enjoy suspense that much.
- The author tells an entertaining story that the reader wants to read.
- Does the writer use techniques to keep the reader engaged?
- Do chapters end with cliffhangers or in such a way that all the questions aren’t answered entice the reader to read the next chapter to find out what happened next?
- Does the story or text contain humor, funny incidents, or characters telling jokes?
- Do action-packed scenes build on each other to increase suspense?
- Does the reader identify with a character or circumstances that invite them to read further?
Authors write explanatory text when they want to bring across a particular method or process. The text contains explanations to help the reader understand how the process works or what the procedure requires to do, create, or complete something.
Authors who write to explain a topic generally write non-fiction books. An author may also explain a topic in a novel, for example, how a drone works, to better understand the situation or character better.
- How-to books explain to the reader how to do something or how something works.
- A book with recipes is a classic example of explaining a method to the reader. The reader follows the instructions to cook that specific dish.
- Step-by-step guides like DIY methods instruct the reader through each step by explaining what to do to complete that step.
- Companies may use procedural outlines in orientation or training outlining the steps and the order the actions should take place.
- Does the writing contain a list of points in numbered or bullet format?
- Are there infographics, diagrams, or illustrations that reinforce the written explanation?
- Is the writing action orientated with lots of verbs that portray commands, orders, or instructions?
- Does the text focus on telling the reader how to do something?
To Describe
If describing is the author’s purpose, then the text may contain adjectives and images to illustrate something in detail. The writer may write with such detail that the reader experiences the imagery through their sense as if it were real.
Fiction authors use descriptions in their writing to engage and entertain the reader. Non-fiction may also use detailed reports expanding on a point.
- Novels and short stories contain descriptions to paint a picture drawing the reader into the story.
- Businesses use product descriptions to show potential customer what they will buy.
- Descriptive essays and other non-fiction writing use descriptions to help the reader understand the point, product, or service.
- Does the writer use adjectives to describe something?
- Does the author use language that appeals to the reader’s senses?
Retha Groenewald is a professional writer working for FractusLearning. When not working with Fractus, she is web copywriter for the Christian market. Her writing is featured at Christian Web Copywriter and at Writing That Breathes Life.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

13 Author’s Purpose
Authors and audiences both have a wide range of purposes for communicating. The importance of purpose in rhetorical situations cannot be overstated. It is the varied purposes of a rhetorical situation that determine how an author communicates a text and how audiences receive a text. Rhetorical situations rarely have only one purpose. Authors and audiences tend to bring their own purposes (and often multiple purposes each) to a rhetorical situation, and these purposes may conflict or complement each other depending on the efforts of both authors and audiences.
UTHORS’ PURPOSES
In the textbook Writing Today , Johnson-Sheehan and Paine discuss purpose more specifically in terms of the author of a text. They suggest that most texts written in college or in the workplace often fill one of two broader purposes: to be informative or to be persuasive. Under each of these two broad purposes, they identify a host of more specific purposes. The following table is not exhaustive; authors could easily have purposes that are not listed on this table.
Table: Author Purposes
The Reading Handbook Copyright © 2019 by Grace Richardson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Evaluating a Text
Main idea, purpose, & audience.

Text evaluation and analysis usually start with the core elements of that text: main idea, purpose, and audience. An author needs to consider all three of these elements before writing, as they help determine the author’s content and language. As a reader, it’s important to ascertain these aspects of a text which exist as a foundation for the author’s content and language.
Always start with the main idea. Main ideas may be stated directly in the text or implied; you need to read a text carefully in order to determine the main idea. Put the main idea into your own words, so that it’s expressed in a way that makes sense to you. Then ask and answer the following basic questions about that main idea:
- Is the main idea reasonable/believable to most readers?
- Is the main idea clear and if not, why do you think the author embedded it?
- Is the main idea the author’s opinion, or is it something that the author asserts about an issue?
Asking and answering these questions should help you get a sense of the author’s intention in the text, and lead into considering the author’s purpose.
Main idea and purpose are intricately linked. There are a few basic purposes for texts; figuring out the basic purpose leads to more nuanced text analysis based on its purpose. Basic purposes of a text include:
- to inform – to describe, explain, or teach something to your audience
- to persuade/argue – to get your audience to do something, to take a particular action, or to think in a certain way
- to entertain – to provide your audience with insight into a different reality, distraction, and/or enjoyment
The following video more fully explains these different purposes of a text, and adds a fourth, to share insights or feelings.
Main Idea & Purpose Determine Analysis
The author’s main idea and purpose in writing a text determine whether you need to analyze and evaluate the text. They also determine the pieces of the text you should analyze—content or language or both.
If the purpose is to persuade or argue
You always need to analyze the text to see if the main idea is justified. Do the supporting ideas relate to and develop the main idea? Is the supporting evidence taken from recognized, valid sources? Is the author arguing via language instead of evidence or facts? Persuasion and argument need to present logically valid information to make the reader agree intellectually (not emotionally) with the main idea.
If the purpose is to inform
You usually need to analyze the text, since the text needs to present valid information in as objective a way as possible, in order to meet its purpose of explaining concepts so a reader understands.
If the purpose is to entertain
You may or may not need to analyze the text. Writing that entertains does not necessarily have to be either logical or complete in order to accomplish its purpose. You may want to analyze the text for language, though, to see how the author manipulates language to accomplish their purpose.

Who are the author’s intended readers? Figuring out this will help you understand an author’s approach to providing the main idea with a particular purpose. Does the audience know little or nothing about the topic, or are they already knowledgeable? Is the audience’s knowledge at beginner or expert level, somewhere in between, or mixed? Does the audience include people who may be skeptical of the author’s ideas? Does the audience include people who outright oppose the author’s ideas? As you can see, asking and answering questions about audience can help an author determine the type and amount of content to include in a text. As a reader, it’s important to figure out the author’s intended audience, to help you analyze the type, amount, and appropriateness of the text’s information.
The following video presents the concept of audience from a writer’s perspective, but the concepts are applicable to you as a reader who needs to consider audience as a foundation for evaluating a text.
You may also want to link to one of Purdue’s Online Writing Lab’s page on Author and Audience to get a sense of the wide array of variables that can influence an author’s purpose, and that an author may consider about an audience.
Read the article “ Forget Shorter Showers ” by Derrick Jensen.
Note that most of the Try It exercises in this section of the text will be based on this article, so you should read carefully, annotate, take notes, and apply appropriate strategies for reading to understand a text.
Then answer the following questions about the article’s main idea, purpose, and audience.
Which selection best represents the author’s main idea?
- We have it in our power and right to take action to stop the industrial economy over-using and wasting our natural resources.
- We are victims of a campaign of misdirection, being told and accepting that our personal use of natural resources is both the cause of scarcity and the solution to preservation.
- Because we have accepted our identities as consumers, we reduce our forms of political existence to consuming and not consuming.
- Simple living is better for the planet than over-consumption.
Sentence 1 is the best answer. Although sentences 2 and 3 extract main ideas from the text, they are key supporting points that help lead to the author’s conclusion and main idea.
Which selection best represents the author’s purpose?
- to inform readers about the actual use of resources by individuals vs. the industrial economy
- to persuade readers to consider taking action against an unjust situation that assigns blame to individuals instead of big business in regard to the depletion of natural resources
- to persuade readers to re-think their personal attempts to live more simply and more “green”
- to entertain readers interested in nature with accusations against the industrial economy
Selection 2 best represents the author’s purpose. The author’s purpose is to get readers thinking about conservation of resources in order to spur them to action against a system that, in his opinion, exploits those resources as well as individuals. His purpose is both to inform and persuade, but persuasion seems to take precedence, as he both starts and ends with a reminder about historically justified instances of activism.
Who comprises the author’s audience and what cues can you use to determine that audience?
The author is writing to an audience of readers who are interested in nature and conservation. If you look on the Orion website and read the “About” section on Mission and History, you’ll see that this publication started as a magazine about nature and grew from there. Based on reading the text, the author’s intended audience has the following characteristics:
- Educated – The author assumes that readers know about WWII, the Civil Rights Act of 1974, and other historic events. The author also uses language such as “systematic misdirection,” “solar photovoltaics,” and even “consensus” (instead of agreement).
- Concerned about the environment – because they are reading this magazine in the first place
- Willing to entertain the idea of taking action to improve quality of life and preserve resources
- Comfortable enough (with themselves? with their social status? with their personal philosophies?) to feel that their voices might make a difference if they choose to protest the current use of natural resources
- Purpose & Audience. Authored by : Susan Oaks. Project : Introduction to College Reading & Writing. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- video The Author's Purpose. Authored by : Marc Franco. Provided by : Snap Language. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z6H2NLPqWtI . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video Audience: Introduction & Overview. Authored by : Gracemarie Mike and Daniel Liddle. Provided by : The Purdue Online Writing Lab. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4_ypxLRYsrE . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- image of woman with a stack of books instead of a head, facing shelves of books. Authored by : Gerd Altmann. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/books-question-mark-student-stack-4158244/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- image of the word Evaluation. Authored by : Gerd Altmann. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/illustrations/district-evaluation-assessment-1264717/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved

Privacy Policy

Reading Skills
Analyzing author’s purpose and point of view.
- The Albert Team
- Last Updated On: June 16, 2023

Introduction
Do you ever wonder why writers write the way they do? Why they pick certain words or tell a story in a specific way? The reason behind this is called the author’s purpose and point of view. It’s like a secret code that helps you understand what they really mean.
In this blog post, we’ll learn about this secret code. You’ll learn to figure out what an author is trying to say, and how they see the world. This will help you understand books, articles, and even posts on social media even better!

What is the Author’s Point of View?
When you read a text, it’s important to think about the author’s point of view. The author’s point of view refers to their unique perspective, opinions, beliefs, and biases that shape how they present information or tell a story. They might see things in a way that’s different from you because of their own experiences, beliefs, and backgrounds.
Understanding an author’s point of view allows us to dig deeper into the underlying motivations and intentions behind their words. It can also help you find hidden messages in the text. So, how do we figure out an author’s point of view? Let’s talk about some ways to do this.

How to Determine the Author’s Point of View

You might think figuring out an author’s point of view is hard, but it can be fun, like solving a mystery! Here are some tips to help you do it:
- Look at the Words : Notice the words the author uses. Are they showing strong feelings or opinions? The way they write can give you hints about what they think and feel.
- Learn About the Author : Knowing more about the author can help you understand their point of view. What kind of job do they have? Where are they from? What are some important things that have happened to them?
- Think About Why the Author Wrote the Text: Why do you think the author wrote this? Do they want to teach you something, make you think, or make you laugh? Knowing this can help you understand what they’re trying to say.
- Notice Patterns: Look for ideas that come up again and again. These can tell you a lot about what the author thinks is important.
- Think About Who the Author is Writing For: Authors often write for specific groups of people. The way they write can tell you a lot about who they are trying to talk to.
Remember, figuring out an author’s point of view is about understanding the text better, not about deciding if they are right or wrong.
Why is the Author’s Point of View Important?

Why should we care about the author’s point of view? Here are some good reasons:
- Contextual Understanding : The author’s point of view helps us make sense of the text. It shows us why they chose to write the way they did and what they want us to learn.
- Uncovering Bias: No author can be totally unbiased. By understanding their point of view, we can see their own opinions in the text. This helps us think critically about what we’re reading.
- Evaluating Objectivity: Knowing the author’s point of view helps us see if the text is objective (without personal feelings) or subjective (based on personal feelings). This can help us decide if we can trust the information in the text.
- Enhancing Interpretation: Understanding the author’s point of view helps us understand what the text really means. We can see what arguments the author is making and think more deeply about the text.
- Encouraging Empathy and Perspective: By seeing things from the author’s point of view, we can better understand people who are different from us. This helps us be more understanding and open-minded.
As you can see, knowing the author’s point of view helps us understand and think about what we read in a deeper way. It makes us better readers and thinkers!
How to Determine the Author’s Purpose

In addition to analyzing the author’s point of view, it is also key to examine the author’s purpose. Here are some tips to help you figure out the author’s purpose:
- Check the Type of Text: Look at what kind of text it is. Is it a story, a news article, or maybe an essay? This can give you clues about why the author wrote it.
- Look at the Words and Tone: Pay attention to the words the author uses and how they write. If they use a lot of emotion, they might be trying to persuade you. If they give a lot of facts, they’re probably trying to inform you.
- Think About Who It’s Written For: Who is the author writing for? For example, a text for experts might be trying to give new information, while a text for kids might be trying to teach something in a fun way.
- Look for Main Ideas: What are the big ideas in the text? What is the author trying to say? This can give you a hint about why they wrote it.
- Check for Facts or Stories: Does the author use a lot of facts and data? Or do they tell stories? This can also help you figure out the author’s purpose.
- Think About the Time and Place: When and where was the text written? Sometimes, this can tell you a lot about why the author wrote the text.
Remember, you might not always see the author’s purpose right away. But if you look closely, you can usually find clues that will help you figure it out.
How Text Structure Contributes to the Author’s Purpose

Text structure, or the way a text is put together, plays a significant role in conveying the author’s purpose and shaping the overall message of a written piece. The way a text is organized and structured can greatly influence how the information is presented and how the reader engages with it. Here are some ways that text structure contributes to the author’s purpose
- Order of Ideas: Authors choose how to order their ideas for a reason. They might use a time order, cause and effect, or compare and contrast to help get their point across.
- Important Points Stand Out: Authors use things like headings or bullet points to show important ideas. This can tell us what the author thinks is most important.
- Storytelling Techniques: In stories, authors might play with the order of events, use flashbacks, or tell the story from different viewpoints. This can make the story more interesting or help make a point.
- Persuasion Techniques: If the author is trying to convince you of something, they will present their arguments in a careful order. They might present a problem, then give evidence, then propose a solution.
- Easy to Follow: A well-organized text is easier to understand. The way the author organizes the text can help you follow their ideas and understand what they want to say.
By looking at how a text is structured, you can get a better idea of what the author’s purpose is. So, next time you read something, pay attention to how it’s put together!
Classroom Application: What is the Author’s Purpose in this Passage?

Analyzing the author’s purpose becomes more engaging and relatable when you can apply your skills to historical speeches. One exemplary text for this exercise is Abraham Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address. Use this step-by-step guide to analyze the author’s purpose in this significant piece of writing:
Step 1: Background Research:
First, start by gathering some background information about Abraham Lincoln, his presidency, and the context of the Second Inaugural Address. Learn about the Civil War and how it impacted the nation during that time.
Step 2: Reading and Annotation:
Next, read the Second Inaugural Address carefully, highlighting or underlining key statements and phrases. Take note of any repeated themes or arguments and mark moments where Lincoln’s perspective or tone seems particularly important.
Step 3: Identifying the Type of Text:
Consider the type of text you are analyzing, which is a presidential inauguration speech. Think about the common purposes associated with such speeches, like inspiring unity, expressing gratitude, or outlining a vision for the nation.
Step 4: Analyzing Language and Tone:
Pay close attention to Lincoln’s choice of language and tone throughout the address. Look for emotional or persuasive language and note instances of unity, humility, or calls for reconciliation. Consider how these choices contribute to Lincoln’s purpose.
Step 5: Reflecting on Historical Context:
Think about the historical context surrounding the Second Inaugural Address. For example, you could reflect on the divided nation during the Civil War and how it affected Lincoln’s presidency. Then, connect these historical events to Lincoln’s purpose in addressing the nation during such a critical time.
Step 6: Identifying Key Statements and Arguments:
Identify the central statements and arguments made by Lincoln in the address. Consider how these statements reflect his purpose and the message he wanted to convey. Think critically about the implications of these arguments.
Step 7: Considering the Audience:
Reflect on the intended audience of the Second Inaugural Address, which includes both supporters and opponents of Lincoln. Analyze how Lincoln’s purpose might have been influenced by this diverse audience and how he aimed to unite the nation through his words.
Step 8: Drawing Conclusions:
Based on the evidence you gathered from the text analysis and understanding of the historical context, draw conclusions about Lincoln’s purpose in delivering the Second Inaugural Address. Make sure to support your conclusions with evidence from the text.
Step 9: Classroom Discussion and Reflection:
Finally, wrap up by participating in a classroom discussion, where you can share your analysis and engage in thoughtful reflection. Compare and contrast interpretations with your classmates to deepen your understanding of the author’s purpose and the complexities of historical texts.
By following these steps to analyze Lincoln’s Second Inaugural Address, you’ll develop critical thinking skills, gain historical understanding, and appreciate the power of language in shaping significant historical events. This assignment will enhance your ability to analyze texts and provide you with a deeper insight into the intentions of historical figures like Abraham Lincoln.
Analyzing an author’s purpose and point of view is a skill that empowers you to unlock the hidden meanings within texts. By understanding why authors write the way they do and recognizing their unique perspectives, you can gain valuable insights into the world of written communication.
Practice Makes Perfect
Albert provides engaging practice questions for key skills like analyzing the author’s purpose as well as a wide range of texts for students to analyze and interpret. For more practice with the skills covered in this post, check out our Author’s Purpose questions in our Short Readings course, which uses short passages to reinforce fundamental reading skills. Readers at all ability levels may enjoy our Leveled Readings course, which offers Lexile® leveled passages focused on a unifying essential question that keeps all students on the same page regardless of reading level. Learn more about the Lexile Framework here !
With our easy-to-use interface and informative feedback, Albert.io is the perfect tool for learning how to determine the author’s purpose and point of view and helping students develop a deeper understanding of the texts they encounter.
Interested in a school license?
Popular posts.

AP® Score Calculators
Simulate how different MCQ and FRQ scores translate into AP® scores

AP® Review Guides
The ultimate review guides for AP® subjects to help you plan and structure your prep.

Core Subject Review Guides
Review the most important topics in Physics and Algebra 1 .

SAT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall SAT® score

ACT® Score Calculator
See how scores on each section impacts your overall ACT® score


Grammar Review Hub
Comprehensive review of grammar skills

AP® Posters
Download updated posters summarizing the main topics and structure for each AP® exam.
21 Author’s Purpose Examples

The author’s purpose of a text refers to why they wrote the text .
It;s important to know the author’s purpose for a range of reasons, including:
- Media Literacy : We want to make sure we’re not tricked by the author. When reading an article online, for example, we want to figure out what the author’s purpose is in order to determine whether they’re going to write with a particular political bias.
- Determining Meaning: We might also want to know the author’s purpose in order to infer and predict what the underlying message might be. If an author’s job is to inform, we can read the text closely in order to examine its logic; but if the purpose is to entertain, we can consume the text with less of a critical lens.
- Understand Genre Convention : If we know the author’s purpose, we can predict and develop expectations about how the piece will be written. For example, persuasive texts should cite sources, while in reflective texts, we should expect first-person language and more intimate language.
Below are a range of possible purposes that authors may have when writing texts.
Author’s Purpose Examples
1. to inform.
Common Text Genres: News articles, Research papers, Textbooks, Biographies, Manuals.
Texts designed to inform tend to seek an objective stance, where the author presents facts, data, or truths to the reader with the sole intention of educating or delivering important information to the reader. It is common, for example, in news articles, where journalists must adhere to journalistic ethics and ensure the information is entirely factual. This is also often the purpose of non-fiction books, academic writing, scientific articles, and of course, this very website you’re reading right now.
Example of an Informative Text A National Geographic article on climate change informs readers about the state of the planet, providing facts and figures about global warming, melting ice caps, and so on.
2. To Entertain
Common Text Genres: Novels, Short stories, Poetry, Plays, Comics
This type of writing is meant to captivate the reader’s imagination and provide enjoyment. Here, the content needs to be delivered in a way that doesn’t bore and keeps the reader compelled to keep reading. To do this, the writing might be humorous, suspenseful, mysterious, or touching, depending on the genre. The author may also create characters, plot, and settings to keep the reader engaged and entertained, as with novels.
Example of an Entertaining Text A well-known example is J.K. Rowling’s “Harry Potter” series, which was written with the primary goal of entertaining readers with its magical world and captivating story.
3. To Persuade
Common Text Genres: Advertisements, Speeches, Opinion columns, Cover letters, Product reviews
In persuasive texts, the author’s main purpose is to convince the reader to accept a particular point of view or to take a specific action. This involves the use of arguments, logic, evidence, and emotional appeals. Persuasive writing can be found in speeches, advertisements, and opinion editorials. To examine some key techniques and strategies authors use to persuade, consult my article on the thirty types of persuasion in literature .
Example of a Persuasive Text A classic example is Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech, in which he persuasively argues for the end of racial discrimination in the United States.
4. To Describe
Common Text Genres: Travelogues, Food reviews, Personal essays, Descriptive poetry, Nature writing
Descriptive texts aim to paint a vivid picture in the reader’s mind. These sorts of texts can take us away to a different place and draw us into a complex world created by the author. For example, the author uses detailed and evocative descriptions to convey a scene, object, person, or feeling. The goal is to make the reader see, hear, smell, taste, or feel what is being described. This can be seen in many forms of writing, but is most evident in fiction, poetry, and travel writing, and can be paired with other author purposes, such as entertainment.
Example of a Descriptive Text An example of descriptive writing is F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby”, especially in its portrayal of the extravagant lifestyle of Jay Gatsby.
5. To Explain
Common Text Genres: How-to articles, Technical manuals, FAQs, Cookbooks, Explanatory journalism
In this type of writing, the author seeks to make the reader understand a process, concept, or idea. The writing breaks down complex subjects into simpler, more digestible parts. The author provides step-by-step explanations, examples, and definitions to aid understanding. This can be seen in how-to guides, tutorials, and expository essays . Of course, this purpose overlaps significantly with to inform , but tends to be more step-by-step or strips complex ideas into clear-to-understand chunks of information .
Example of an Explanatory Text A real-world example is Stephen Hawking’s “A Brief History of Time”, in which complex topics such as the Big Bang, black holes, and light cones are explained in a manner accessible to non-scientists.
6. To Analyze
Common Text Genres: Critical essays, Business reports, Scientific research papers, Market research, Literary analysis
Authors who write to analyze seek to break down a complex concept, event, or piece of work into smaller parts in order to better understand it. Analytical writing looks closely at all the components of a topic and how they work together. It’s about making connections and recognizing patterns. It could, for example, aim to identify flaws in a topic, or draw connections, similarities and differences, between multiple different concepts. You’ll commonly find these types of texts in professional contexts, such as reports provided to a company to give them guidance that helps them make better business decisions.
Example of an Analytical Text “The Art of War” by Sun Tzu offers a comprehensive analysis of warfare strategies, breaking down the complexities of warfare into key principles.
7. To Teach
Common Text Genres: Textbooks, How-to guides, Cookbooks, Self-help books
The author aims to impart knowledge or skills to the reader. These texts often provide step-by-step instructions or delve deep into a topic to ensure understanding. The goal is not only to inform but to enable the reader to perform a task or understand a concept independently. Examples of texts like this can include self-help books and textbooks, which might also contain ‘tasks’, ‘homework’ or ‘revision quizzes’ at the end of each chapter.
Example of an Educational Text “On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft” by Stephen King teaches readers about the art of writing and the life of a writer.
8. To Argue
Common Text Genres: Opinion editorials, Political speeches, Legal briefs, Persuasive essays
For these sorts of texts, the author’s purpose is to persuade the reader to accept a particular perspective, worldview, or ideology, often presenting a thesis and supporting it with evidence and logical reasoning. The goal is to make a case and convince the reader of its validity. Authors could use pathos , meaning emotion , to argue a point (e.g. appealing to a person’s emotional side), or logos , meaning logic (e.g. setting out a clear and logical explanation of why the author’s perspective is correct).
Example of an Argumentative Text A famous example is “A Vindication of the Rights of Woman” by Mary Wollstonecraft, where she argues for women’s rights and equality.
9. To Inspire
Common Text Genres: Motivational speeches, Inspirational books, Success stories, Motivational posters
Authors with this purpose want to stimulate their readers to act or create a change, instill hope, or provoke a sense of awe. These writings often share success stories, motivational thoughts, or beautiful descriptions of nature or humanity. A wide range of texts aim to inspire, from novels about amazing journeys, biographies about great people from history, and even people writing sales copy for brands.
Example of an Inspirational Text “I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings” by Maya Angelou is a work meant to inspire readers through its tale of overcoming adversity.
10. To Reflect
Common Text Genres: Diaries or journals, Vlogs and blogs, Retirement speeches, Reflective essays
In a reflective piece, the aim of the author is to share personal experiences, thoughts, or insights in an introspective manner. The goal is to convey the author’s personal journey or internal thought process. These texts often give readers a window into the author’s mind, and they may invite readers to reflect on their own experiences as well. Sometimes, the author will write the piece as a tool for self-improvement , such as to identify where they made mistakes or weaknesses in their processes, so they don’t make those mistakes next time.
Example of a Reflective Text “Meditations” by Marcus Aurelius is a series of personal writings, reflecting the author’s stoic philosophy and ideas on life.
11. To Share
Common Text Genres: Personal Blogs, Social Media Posts, Personal Essays, Anecdotes , Letters.
In this type of writing, the author aims to share personal experiences, thoughts, ideas, or information with the reader. The writer may offer insights into their lives, discuss their passions, or recount an event that happened to them. We might see this, for example, for someone who writes detailed reflections on their travels in their travel blog, or even a personal email back to friends and family each week.
Example of a Text designed to Share Elizabeth Gilbert’s “Eat, Pray, Love” is a memoir where the author shares her journey of self-discovery as she travels through Italy, India, and Indonesia.
12. To Record
Common Text Genres: Historical Accounts, Diaries, Journals, Biographies, Documentaries.
When writing to record, the author aims to create a detailed and factual account of events or experiences, either for personal reflection or to inform future generations. This type of writing can also serve to preserve personal or historical memories. We see this, for example, in historians’ writing as well as in some journalistic work, such as in the New York Times, which has become known as the paper of record for its longevity in recording important moments in US history.
Example of a Text of Record Anne Frank’s “The Diary of a Young Girl” is a historical record of her experiences hiding during the Nazi occupation of the Netherlands.
13. To Provoke Thought
Common Text Genres: Philosophical Works, Thought-Provoking Novels, Reflective Essays, Social Commentaries.
Authors who write to provoke thought aim to challenge their readers, pushing them to think more deeply about certain topics or to see things from a different perspective. They may raise complex questions, explore ambiguities, or critique societal norms. Such authors might be even aiming to get the reader upset, animated, or otherwise achieving cognitive dissonance in order to shift their thinking in some way.
Example of a Thought-Provoking Text George Orwell’s “1984” provokes thought about totalitarianism, surveillance, and individual freedom.
14. To Criticize
Common Text Genres: Reviews, Critical Essays, Satire, Polemics, Critiques .
When authors write to criticize, their aim is to express disapproval, dissent, or disagreement. They may critique a person, an idea, a societal trend, a piece of work, etc. They typically present their criticisms in a structured, reasoned manner, often supported by evidence. We see this regularly, for example, in ‘letters to the editor’ in newspapers, where everyday people can write into a newspaper in order to share their thoughts or rants for everyone to read.
Example of a Critical Text In his essay “Self-Reliance,” Ralph Waldo Emerson criticizes societal conformity and advocates for individualism.
15. To Predict
Common Text Genres: Speculative Fiction, Futurism Articles, Predictive Analytics Reports, Science Fiction.
Authors who write to predict aim to forecast future events or trends. These predictions could be based on current data, societal trends, scientific understanding, or simply imaginative speculation. This can be anything from a piece written by an economist or political scientist who’s predicting social trends that are upcoming, to a sci-fi novel that attempts to predict a dystopian future where AI has taken over the world!
Example of a Predictive Text In Aldous Huxley’s “Brave New World,” the author predicts a future society characterized by technological advancements, consumerism, and a lack of individual freedom.
16. To Express Emotion
Common Text Genres: Poetry, Personal Essays, Novels, Letters, Memoirs.
When authors write to express emotion, their main goal is to convey their feelings, or the feelings of someone else, to the reader. They might explore their emotional reaction to events, or evoke emotion in the reader. This is a common purpose of poetry and song lyrics, which have long genre-histories of evoking emotions in audiences, especially when the lyrics are read or sung to a live audience.
Example of an Emotional Text Sylvia Plath’s poetry, such as in her collection “Ariel,” often expresses deep personal emotions, particularly her struggles with depression.
17. To Explore
Common Text Genres: Adventure Novels, Travel Writing, Scientific Papers, Experimental Poetry, Philosophy Books.
Authors who write to explore aim to delve deeply into a topic, concept, or place. This might involve exploring physical environments, such as in travel writing, or abstract concepts , as in philosophical or scientific texts. Exploratory writing may start without a clear end-goal, and can ramble its way to an unknown conclusion.
Example of an Exploratory Text Charles Darwin’s “On the Origin of Species” explores the concept of natural selection and evolution.
18. To Satirize
Common Text Genres: Satirical Novels, Political Cartoons, Satirical Essays, Parodies.
Satirical writing uses humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people’s stupidity or vices, particularly in the context of contemporary politics and other societal issues. It could, for example, be a satirical novel which tries to undermine or make a joke out of other famous texts or genres. This, obviously, overlaps with the author purpose of to entertain but may also have elements of social commentary.
Example of a Satirical Text Jonathan Swift’s “Gulliver’s Travels” satirizes human nature and the “travelers’ tales” literary subgenre.
19. To Commemorate
Common Text Genres: Eulogies, Obituaries, Commemorative Speeches, Historical Fiction.
Writing to commemorate aims to honor or remember a person, event, or idea. It often involves highlighting the subject’s significance or impact. For example, a person might write a piece that commemorates veterans on Vetertan’s Day. Similarly, an obituary commemorates a person’s life and attempts to sum up their achievements and the things that were of great importance to them.
Example of a Commemorative Text The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln was a speech to commemorate the lives lost during the Civil War and to reaffirm the principles of liberty and equality.
20. To Plead
Common Text Genres: Petitions, Open Letters, Advocacy Articles, Speeches.
When authors write to plead, they aim to make an urgent appeal or request for something. This could be a plea for action, support, change, etc. These texts commonly ask for social change or a change in perspective from the reader. The author may be pleading for themselves and their family (e.g. a refugee who pleads their case in a newspaper op-ed) or for the less advantaged (e.g. an activist pleading for people to donate to children in poverty).
Example of a Text that Pleads a Case In “Letter from Birmingham Jail,” Martin Luther King Jr. pleads for an end to racial segregation and appeals for justice and equality.
21. To Celebrate
Common Text Genres: Commendatory Speeches, Reviews, Praises, Tributes.
Authors who write to celebrate aim to acknowledge, praise, or express gratitude for someone or something. They might celebrate a person, a culture, a historical event, an achievement, or a simple joy of life. A celebratory text, for example, might be a speech someone gives at a graduation ceremony, with the intention of celebrating the graduates’ successes in finally completing their degree.
Example of a Celebratory Text Maya Angelou’s poem “Still I Rise” celebrates the resilience and strength of African American women.
See Also: Examples of Text Types
Texts are written for a range of reasons. By determining the intentions of the author, we can begin to infer genre expectations, whether there will be much bias, or indeed, whether we can simply read for entertainment and throw caution to the wind! Similarly, if you want to be a writer, it’s worth examining other author’s texts that have similar purposes, and take notes on their style and turns-of-phrase to learn from them.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Authors and audiences both have a wide range of purposes for communicating. The importance of purpose in rhetorical situations cannot be overstated. It is the varied purposes of a rhetorical situation that determine how an author communicates a text and how audiences receive a text. Rhetorical situations rarely have only one purpose. Authors and audiences tend to bring their own purposes (and often multiple purposes each) to a rhetorical situation, and these purposes may conflict or complement each other depending on the efforts of both authors and audiences.
Authors’ purposes
In the textbook Writing Today , Johnson-Sheehan and Paine discuss purpose more specifically in terms of the author of a text. They suggest that most texts written in college or in the workplace often fill one of two broader purposes: to be informative or to be persuasive. Under each of these two broad purposes, they identify a host of more specific purposes. The following table is not exhaustive; authors could easily have purposes that are not listed on this table.
Table: Author Purposes
(Johnson-Sheehan & Paine 17)
Audiences’ purposes
Authors’ purposes tend to be almost exclusive active if only because authors conscientiously create texts for specific audiences. But audiences’ purposes may range from more passive purpose to more active purposes.
Table: Audience Purposes
The Role of Purposes
Authors’ and audiences’ purposes in communicating determine the basic rationale behind other decisions both authors and audiences make (such as what to write or speak about, or whom to listen to, or what medium to use, or what setting to read in, among others). An author’s purpose in communicating could be to instruct, persuade, inform, entertain, educate, startle, excite, sadden, enlighten, punish, console, or many, many others. Like authors, audiences have varied purposes for reading, listening to, or otherwise appreciating pieces of communication. Audiences may seek to be instructed, persuaded, informed, entertained, educated, startled, excited, saddened, enlightened, punished, consoled, or many, many others. Authors’ and audiences’ purposes are only limited to what authors and audiences want to accomplish in their moments of communication. There are as many purposes for communicating as there are words to describe those purposes.
Attitude is related to purpose and is a much-overlooked element of rhetorical situations. But attitude affects a great deal of how a rhetorical situation unfolds. Consider if an author communicates with a flippant attitude as opposed to a serious attitude, or with drama as opposed to comedy, or calmly as opposed to excitedly. Depending on authors’ purposes, audiences’ specific qualities, the nature of the context, and other factors, any of these attitudes could either help or hinder authors in their efforts to communicate depending on the other factors in any given rhetorical situation. Like authors, audiences bring diverse attitudes to how they appreciate different pieces of communication. The audience’s attitude while reading, listening, observing, or whatnot affects how they receive and process the communication they receive.

Teaching Author’s Purpose in Speech

Author’s Purpose is a reading strategy that is commonly taught in elementary schools across the country. According to the Common Core State Standards, beginning in second grade, students need to be able to determine why an author has written a passage.
Additionally, as students advance, they are expected to be able to use text evidence to show what the author’s purpose is, distinguish between different author’s purposes in texts with the same topic, and identify changes in author’s purposes within the same text or in different sections of a newspaper.
Whew! All of this requires the students to have some really good language skills. Students need to comprehend a text, need vocab of the text and the different purposes, and also recognize keywords in the question to know what is expected. This can be really difficult for students with speech and language deficits. But the good news is that there are some concrete ways that we can help our speech and language students with this skill. As SLPs, we are always trying to incorporate our students’ general education curriculum into our speech time, so these are perfect steps to take in order to help with that.
What is Author’s Purpose?
First, students need to understand that everyone writes for a reason. Authors of textbooks, newspaper journalists, and other writers don't just write for no reason! As teachers, we teach students that those reasons are:
- to teach the reader about something
- to make the reader want to do something
- or just for fun!
Some of the most common examples of these types of writing that your students may see on a daily basis are textbooks to inform, novels or picture books to entertain, and something like a poster encouraging hand-washing to persuade.
How Does Understanding Author’s Purpose Help With Comprehension?
With all of the reading skills and strategies that students have to learn, why is author’s purpose one of them? Why should students (or we!) care why somebody wrote something? To answer this, let’s think about the statement “The floor is wet.” If we just read that statement without any context, and without understanding why the author wrote it, we have no idea what to make of that statement.
If the statement “The floor is wet” is written in an informational context, we know that the author is simply telling us that the floor is wet. If that statement is prefaced by the word “Stop!”, we know that this is a warning and that the author is trying to persuade us to stop or slow down. And if the statement is written in the context of a comedy for entertainment purposes, we can make a prediction that a character might slip on the floor upon reading that statement. It’s important for students to know in what context things are written in order to gain a greater understanding of the text.
What Difficulties Might a Speech Student Face in Learning Author’s Purpose?
Author’s purpose can be especially difficult for students with receptive language and nonverbal learning disabilities, especially if the text is being presented as a read-aloud. Determining author’s purpose involves putting yourself in someone else’s (the author’s) shoes and making a determination as to why they wrote what they wrote. They may also miss tone and infection that helps determine the author's purpose.
How Can SLPs Help?
Fortunately, there are some really concrete ways that we can help students recognize the nuances needed to determine the author's purpose. These can include the following:
- Reviewing and role–playing what it means to inform, entertain, and persuade. For example, you can model what it would sound like for you to persuade someone to do something, and then let the student role-play the same thing back. You can also use body language and gestures to help get your point across.
- Determining the type of text. A good indicator of author’s purpose is the type of text that the student is reading. For example, fiction books are mostly to entertain. Textbooks are mostly to inform. By determining the type of text, the student will get a better idea of what the author’s purpose is.
- Giving word clues. Specific words can provide clues as to what the author’s purpose is. For example, the word “should” is used frequently in persuasive essays. Things like units of measure and dates are used frequently in informative text, and adjectives are used a lot in a text to entertain. Students can highlight words they think may be clue words, and match them to a list of clue words that you provide.
- Do a sort. Students can read short passages and then either cut and paste or drag and drop the passages into the correct category.
If the last idea sounds interesting to you, then check out this Author’s Purpose activity ! It’s available as a printable OR in a Boom Card version. Check out the preview to see a sample activity.

Another option is to join my membership program, SLP Elevate , which is chock-full of monthly, minimal-prep activities older speech students love, including Author’s Purpose activities!

You’re all set to teach author’s purpose! Your students will be identifying the purpose of all sorts of texts in no time.
Related Posts

- Privacy Policy
- Book A Live Event
- SLP Elevate
- Speech Retreat
- Ella Bella Book
Snap Language
Getting Smarter through Language

Advanced Reading Course
Please support Snap Language by white-listing this site.
Interpreting What You Read | Part 2
Previously, you saw the importance to advance beyond simply understanding words and sentences in a paragraph. You learned that writers use transition words to show the relationships between ideas and that they often use figures of speech to express their ideas clearly. It is up to you, the reader, to identify these elements of writing so that you can interpret what the writer wants to communicate.
Other parts of the message are important for readers to interpret are
- the author’s purpose,
- the author’s point of view, and
- the author’s tone.
Understanding the author’s purpose for writing a passage, point of view, and tone will help you get deeper into the writer’s thinking and, therefore, understand what you read more deeply.
The Author’s Purpose
When you write, you have a purpose in mind. That purpose is not always stated directly in the passage, but it changes how the writer approaches the topic. As the reader, it is important for you identify the writer’s purpose so you can interpret the message.

Isaque Pereira | Pexels
Here, you will learn to identify when the author’s purpose is to inform, persuade, entertain, and share insights or feelings; which publications are likely to have each purpose; and what you should do as the reader to interpret the writer’s message written for each of these purposes.
Video Activity 12

Watch a video to learn about the author’s purpose and how recognizing the writer’s purpose helps you read more effectively. Take good study notes.
The Author’s Point of View
In this section, you will learn how to interpret the author’s point of view. Writers’ viewpoints color their perceptions and affect what they say and how they say it. Understanding the author’s viewpoint helps you evaluate the information the writers present and question what the author may be choosing to include or exclude from the passage.
Video Activity 13

Watch a video to learn about the author’s point of view and how recognizing the writer’s point of view improves your reading comprehension. Take good study notes.
The Author’s Tone
How writers state something (that is, the tone they use when stating it), often tells you more about the information than what is actually being presented.
Writers have their own points of view and feelings toward the topics they write about. Through word choice, they can use words that convey the tone that expresses their ideas exactly. In this section, you will learn about the author’s tone in writing, which you must detect and interpret to improve your reading comprehension.
Video Activity 14

Watch a video to learn about the author’s tone and how detecting the writer’s tone helps you read more effectively. Take good study notes.
Up Next: Interpreting What Your Read | Part 3
Continue the lesson to learn about detecting and interpreting irony.
Teaching Tidbits and More
Teaching Author’s Purpose

How to Teach About the Author’s Purpose
An important part of reading is learning about the author’s purpose . When an author writes something, they are most likely going to have a purpose of some sort. Don’t worry, that purpose is not narrowed down in one reason. Sometimes the author’s purpose may be to persuade the reader. Other times it may be to inform the reader. Let’s talk about how to teach author’s purpose.
General Purpose
It’s safe to say that an author can have many purposes in mind whenever they are writing something. I want to narrow down the four main purposes.
- Persuasive – An author’s purpose may be a persuasive one. The author might be trying to convince you of something.
- Inform/Expository – This may be a more confusing one for someone to understand, but it can still be an author’s purpose. If you plan on teaching or informing the reader, then this is the approach you want to take.
- Descriptive – When an author wants to explain what something looks like or feels like, then they may use a descriptive approach.
- Entertain/Narrative – Another author’s purpose approach, but this purpose is to tell a story or recount events.
A good way to help teach about the author’s purpose is this: Let’s say that the author is trying to convince you to eat ice cream for breakfast, they will make several persuasive points trying to get you to see their side.
Activities for Teaching the Author’s Purpose
If you’re going to spend time teaching about the author’s purpose, then I have a few fun teaching methods for you.
Ask Questions
One of my favorite things to do, when teaching about the author’s purpose is to ask why. Take the time to ask your students WHY. A good and solid question you can ask is why did the author write this writing piece?

Let Your Students Write
As you know, doing is one of the best things ways you can teach a student anything. Give your student’s a chance to write and their writing to have an author’s purpose. Allow them to bounce ideas off of you!

Practice Makes Perfect
If you follow my blog, then you know I’m all about practice. Grab my learning packet that teaches about the author’s purpose. Your student will be able to go through this packet learning more about the author’s purpose and how it works in text. This resource includes nonfiction text features too. This resource is part of a bundle that helps focus on particular reading standards. You can find more information about the bundle by clicking here.

Have a Conversation
Hear me out for a second. When students are able to study the text and the author, then they are able to understand the author’s purpose even more. If there is a non-fiction text an author has written, allow your students to pull out information on that author. Allow your students to spend time learning about the author and draw conclusions about why they might have written the text.
Teaching about the author’s purpose may be a lot easier than you thought possible. Now, which activity will you use to teach this important concept used in reading and writing?
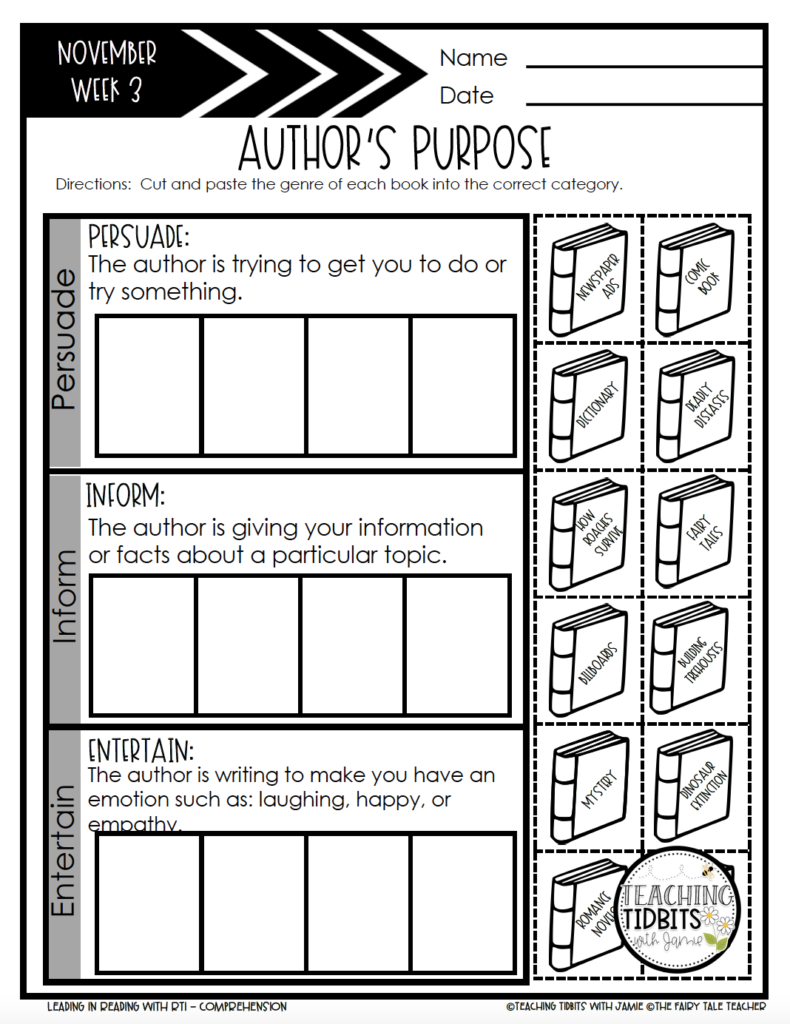
If you are interested in this resource you can check it out here on this blog or in my Teachers Pay Teachers shop .
If you are wanting to make sure that you are hitting all your reading standards, especially with your small group. Be sure to check out the year long bundle . Get everything you need for the year at a discounted price. You can find the bundle here on this website or in my Teachers Pay Teachers shop .

Thank you for stopping by and taking a peek! If you have any fun ideas for teaching author’s purpose I would love to hear from you.
Latest on Pinterest

Latest on Facebook

There are Super Bowl $1 deals happening right now on TpT. Plus, you can find half off BUNDLES. I have several items on sale. Here are links to each of my deals: March Stem Challenges: www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/touchdown2024-Science-Experiments-Stem-Activities-March-Scien... Multi Step Math Word Problems (Addition and Subtraction w/Regrouping): www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/touchdown2024-Word-Problems-Addition-and-Subtraction-Addition... Leading in Reading (RTI Bundle): www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/HALFOFFHALFTIME-RTI-for-ELA-Response-to-Intervention-Small-Gr... Year Long Fluency Bundle Set: www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/HALFOFFHALFTIME-luency-Passages-Reading-Fluency-Passages-for-... ... See More See Less

- Comments: 0
0 Comments Comment on Facebook
Looking for fun book ideas and treats to share with your classroom? I have you covered. Below are some of my favorite books for the classroom and easy treats to hand out. Click the link for more: www.amazon.com/shop/teachingtidbitswithjamie/list/2E0NJIEALE7E4?ref_=aipsflist_aipsfteachingtidbi... ... See More See Less

I work with the best team! ❤️ ... See More See Less

It starts at home! ... See More See Less
This content isn't available right now
- likes love 6
- Comments: 2
2 Comments Comment on Facebook
Teachers, if you aren’t already knee-deep in bulletin board borders, you’re probably at least drawing up plans for your seating chart. It’s that time again, and we want to make it the best year ever. This is exactly why a group of teacher friends and I got together to select some of our best resources for this school year and we are offering them for only $1. On Monday, September 5th + Tuesday, September 6th, search #laboroflove on TpT to find hundreds of products marked down to only $1. That’s right---$1 deals for our #1 teacher (that’s you!) You can check out the products included in this sale here >>>> bit.ly/3D0u8Ty I have two of my best resources in this sale. You can find the links here: Community Resource: www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/laboroflove-Communities-Urban-Suburban-Rural-Social-Studies-C... October Stem: www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/laboroflove-STEM-Activities-and-Challenges-STEM-Activities-Ha... ... See More See Less
Latest on Instagram

Get in touch with us
Are you sure you want to logout?
Please select your grade.
- Earth and space

Author Purpose
What is author’s purpose .
Author Purpose is all that –
- Are you engaged while reading a book?
- Sometimes they are so interesting that we read them continuously. Ever wondered how an author can engage their audience? That is through a concept called Author’s Purpose.

Let’s learn more about it:
An author’s purpose is his reason for or intent in writing.
An author’s purpose may be:
- To amuse the reader
- To persuade the reader
- To inform the reader, or
- To satirize a condition
An author’s purpose is seen in the way he writes about a topic.
For example:
If he wants create amusement in the minds of reader, he uses jokes or anecdotes in his writing.

Why does the Author write the story?
Persuade: The author tries to make you believe what he is saying or do something.
Inform: The author presents information about a topic.
Entertain: The author tells us a story for us to enjoy.

Related topics

Exploring the World of Adjectives: Types, Usage, and Examples
What are Parts of Speech? Parts of speech determine words’ grammatical and semantic position in a sentence. Activity time The parts of speech are nouns, adverbs, conjunctions, pronouns, interjections, adjectives, articles, prepositions, and verbs. Identify the parts of speech of the underlined words in the following sentences. White- Adjective Big- Adjective Exciting- Adjectives New- […]

Memoir Writing: Basic Elements, Structures, and Types
Memoir: A memoir is a narrative written from an author’s perspective about a particular facet of his/her own life. ‘Memoir’ word comes from the French word ‘memoire’, which means ‘memory’ or ‘reminiscence’. Example Night: Elie Wiesel gives an account of how he survived his teenage years at Auschwitz and Buchenwald concentration camps during World War […]
Identification of Main Idea in Fiction and Non-fiction
Every story or paragraph or non-fictional text has at least one main idea. The MAIN IDEA is what the text is mostly about. (It is backed up or supported by SUPPORTING DETAILS) Before discussing how to find the main idea, we shall first look at TOPIC. Can you define a topic? A topic can be […]

Writing an Article: Structure and Essential Tips
What is an article? Structure of Article Writing : Title : Draw the attention of readers with an attractive title and indicate the main topic of the article Introduction : Attract the reader’s attention with a sentence that gives a general presentation of the topic. Main Body : Between these sentences, the body should do […]

Other topics
How to Find the Area of Rectangle?

How to Solve Right Triangles?

Ways to Simplify Algebraic Expressions

Freeland's new federal budget hikes taxes on the rich to cover billions in new spending
With interest rates running high, cost to service the national debt surpasses federal health care spending.

Social Sharing
HIGHLIGHTS:
- Ottawa to spend $52.9 billion more than planned over the next five years.
- Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland projects Ottawa will post a $40 billion deficit this fiscal year.
- The budget includes $8.5 billion in new spending for housing.
- Other major budget items include a $6 billion Canada Disability Benefit, a $1 billion national school food program and a $500-million fund for youth mental health.
- Freeland will hike capital gain taxes paid by the rich and corporations to collect an estimated $19 billion in new revenue.
- The cost to service the growing national debt has increased substantially — it's now about $2 billion more than it was projected to be just a few months ago.
- The government will spend more on servicing its debt than on health care this year.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland's fourth budget delivers a big-ticket housing program for millennials and Generation Z voters — a multi-billion dollar commitment to be paid for in part with a tax hike on the rich and corporate Canada.
Freeland's document calls for about $52.9 billion in new spending over the next five years — a significant jump over what Ottawa had said it would spend in the fall economic statement released just a few months ago.
To offset some of that new spending, Freeland is pitching policy changes the government says will generate roughly $21.9 billion in new revenue. That money is to come in part from higher capital gains taxes and a hike to excise taxes on cigarettes and vaping products.
"We are making Canada's tax system more fair by ensuring that the very wealthiest pay their fair share," Freeland said Tuesday after tabling her budget in Parliament.
"We are doing this because a fair chance to build a good, middle class life — to do as well as your parents, and grandparents, or better — has always been the promise of Canada."
- 2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes
- Are you renting with no plans to buy? Here's what the federal budget has for you
- Updated Federal budget's funding boost for defence spread out over multiple years
The result is a projected budget deficit of about $40 billion in the 2024-25 fiscal year — roughly what Freeland had predicted.
While the government is spending more overall, it says that better-than-expected economic growth and higher taxes will keep the deficit under control.
The Liberal government's preferred "fiscal anchor" — the budget benchmark that guides its decisions — has long been to keep the net debt-to-GDP ratio on a declining trend, with debt levels closely tracking the overall size of the economy.
The budget document says the government must meet that benchmark in the years ahead to retain Canada's triple-A credit rating.
Debt charges soar
Deficits eventually roll over into long-term debt. The cost to finance Canada's growing debt pile — which has more than doubled over the last nine years to $1.4 trillion — is eating up more and more taxpayer dollars as the government is forced to refinance its borrowing at higher rates.
Public debt charges will cost $2 billion more this year than the forecast in November as the Bank of Canada keeps rates relatively high to tame inflation — which has shown signs of slowing down.
- Liberals pledge $9B in new money for Indigenous communities in 2024 budget
With interest rates at a 20-year high, Ottawa's cost to borrow has spiked from $20.3 billion in 2020-21 to $54.1 billion in 2024-25.
That means Ottawa will spend more to service its debt than it will on health care this year — and the debt charges will march even higher in the years ahead.
Carrying the debt is expected to cost the federal treasury $64.3 billion in 2028-29 — more than double what Ottawa sends to the provinces through equalization payments.
"The interest rates are hurting the government just as much as they're hurting us consumers," said Sahir Khan, a former deputy parliamentary budget officer and the executive vice-president of the uOttawa Institute of Fiscal Studies and Democracy.
"It's now a meaningful amount relative to other spending pressures and it's going to start squeezing other programs. The government built up a stock of debt subject to prevailing interest rates and that creates a risk."
Billions more for housing
The budget allocates $8.5 billion more to housing to help alleviate a crisis that has locked a generation of young people out of the dream of home ownership. The government maintains its housing measures will drive the creation of roughly four million more homes by 2031.
New investment to lead 'housing revolution in Canada,' Freeland says
Freeland has freed up money to send more cash to municipalities through the Housing Accelerator Fund, build more homes on underused public lands and at Canada Post outlets, cut cheques for new water and solid waste infrastructure in growing communities , offer tens of billions of dollars in loans to spur new rental construction and secondary suites, and help non-profits acquire existing rental homes and keep them affordable.
"We are moving with purpose to help build more homes, faster. We are making life cost less," Freeland said. "Millennial and Gen Z Canadians, we want them to look forward to the future with a sense of anticipation, not angst."

The government also has committed to maintaining the already well-subscribed tax-free savings account , extending mortgage amortization terms and increasing the RRSP withdrawal limit for some first-home buyers, among other measures.
The housing program is a "home run," said Armine Yalnizyan, a progressive economist and the Atkinson Fellow on the Future of Workers.
Yalnizyan said Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre's early focus on housing hurt the Liberals' standing among some millennial voters.
Now, the Liberals are trying to reclaim some of those votes with an ambitious program which, if it's carried out as planned, will meaningfully increase the country's housing supply, she said.
"It's really an attempt to stop the Conservatives from eating their lunch," she said.
A tax hike on the rich
As Ottawa moves to remake the housing landscape, roll out a national dental care program and launch pharmacare , Freeland's budget includes a number of targeted tax hikes that it says will yield some $21.9 billion in new revenue over the next five years.
The biggest windfall will come from an increase to the capital gains inclusion rate.
Under the current regime, only 50 per cent of capital gains are taxable. If a taxpayer sells an asset like a cottage, an investment property, a stock or mutual fund for $100,000 more than they paid, they are taxed only on $50,000 of that profit.
With this new budget, the "inclusion rate" will increase from one-half to two-thirds on capital gains above $250,000 per year for individuals, and on all capital gains realized by corporations and trusts.
The move is likely to be seen by business-friendly groups as an attack on the people and businesses that create jobs.
Freeland said she anticipates some blowback.
"I know there will be many voices raised in protest. No one likes paying more tax, even — or perhaps particularly — those who can afford it the most," she said.
"Tax policy is not only, or chiefly, the province of accountants or economists. It belongs to all of us because it is how we decide what kind of country we want to live in and what kind of country we want to build."
The NDP — the government's partner in the supply-and-confidence agreement — likely will welcome the change; party leader Jagmeet Singh has said the wealthy and big corporations should shoulder more of the country's tax burden.
"We are asking the wealthiest Canadians to contribute a bit more, so that we can make investments to ensure a fair chance for every generation," the budget document says. "Canada's tax system can be more fair."
The change will not apply to any capital gains from the sale of a primary residence. Investment income earned in an RRSP or TFSA, including capital gains, also will not be taxed.
According to government data, only 0.13 per cent of Canadians — people with an average income of about $1.4 million a year — are expected to pay more in personal income tax on their capital gains as a result of this change.
Jimmy Jean, an economist at Desjardins who tracks Ottawa's spending, said the federal government's goal of collecting about $19 billion from the capital gains measure may be difficult to achieve.
"The jury's out on whether they can get that much," Jean said.
"Targeting the income and wealth of the wealthy — it's difficult because it's more mobile, they can move it around. I'm skeptical."
Other new revenue-generating measures in the budget include a promise to crack down on bankruptcy fraud and tackle "aggressive tax planning schemes."
Beyond housing, there's also a promise to top up the incentives for zero-emission vehicles, deliver a new carbon tax rebate for small businesses, stand up an $800-million energy efficiency retrofit program, increase student grants, create a $500-million fund for youth mental health , launch a $6 billion Canada Disability Benefit, fund a $1 billion national school food program and deliver a $900-million top-up to the Indigenous infrastructure program .
CBC/Radio-Canada will get a one-off $42 million budget boost for news and entertainment programming — a cash injection that will help the company avoid some of the previously announced layoffs .
VIA Rail Canada stands to gain about $400 million over the next few years to turn the dream of high-frequency rail in central Canada into a reality.

What's in the new federal budget?
Poilievre blasts budget, singh stays noncommittal.
Poilievre pilloried the budget and said his party would vote against it.
Speaking in the House of Commons, the Conservative leader said the Liberal government has never presented a balanced budget in all the years it's been in office and the promised $40 billion in new spending will drive inflation higher.
"This is the ninth deficit. The ninth deficit after the prime minister promised the budget would balance itself and what did he do with the money? Everything he spent it on has become more expensive," Poilievre said.
"This is like a pyromaniac spraying gas on the inflationary fire that he lit. It is getting too hot and too expensive for Canadians and that's why we need a carbon tax election to replace him with a common sense Conservative government."
Conservative leader rises in House of Commons to reject Liberal budget
Singh, meanwhile, said it's too early to say if his party will support the budget.
While he praised some measures he said his party forced the government to include, such as dental care, pharmacare and a national school food program, Singh said he wants to meet with Trudeau to raise some other "concerns" before making a final decision.
Singh said he's not onside with a plan to cut about 5,000 public servants through attrition — the federal bureaucracy has grown to about 357,247 workers under Trudeau — and he said there's inadequate funding for Indigenous peoples.
Liberals 'ignored opportunity' in budget to tackle corporate greed, NDP says
If Singh and his NDP MPs withhold their votes, the minority government could lose the confidence of the House of Commons, tipping the country into an early election.
While the capital gains tax increase will cost the country's big businesses billions more than what they pay now, Singh said "the Liberals ignored the opportunity to take on corporate greed."
Singh said the companies he blames for inflation — grocery store chains, telecommunications companies and "housing and corporate landlords" — should have faced tax hikes.
Green Party Leader Elizabeth May said her caucus will vote against Freeland's budget.
She said the government's planned disability benefit, which amounts to about $200 a month for eligible Canadians, is too low.
May also said there's not enough money earmarked for social housing — just more loans for developers to build more affordable homes.
"The budget falls far short of our hopes," May said. "It's not meeting the moment. We need dramatic, transformative changes to our society to be able to afford the things we need."
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Senior reporter
J.P. Tasker is a journalist in CBC's parliamentary bureau who reports for digital, radio and television. He is also a regular panellist on CBC News Network's Power & Politics. He covers the Conservative Party, Canada-U.S. relations, Crown-Indigenous affairs, climate change, health policy and the Senate. You can send story ideas and tips to J.P. at [email protected].
- Follow J.P. on X
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Digital SAT Reading and Writing
Course: digital sat reading and writing > unit 2, text structure and purpose | lesson.
- Part-to-whole relationships | Lesson
- Text Structure and Purpose — Worked example
- Text Structure and Purpose — Quick example
- Text structure and purpose: foundations
What are "text structure and purpose" questions?
- (Choice A) The speaker provides examples of an admirable way of approaching nature and then challenges that approach. A The speaker provides examples of an admirable way of approaching nature and then challenges that approach.
- (Choice B) The speaker describes attempts to control nature and then offers a reminder that not all nature is controllable. B The speaker describes attempts to control nature and then offers a reminder that not all nature is controllable.
- (Choice C) The speaker argues against interfering with nature and then gives evidence supporting this interference. C The speaker argues against interfering with nature and then gives evidence supporting this interference.
- (Choice D) The speaker presents an account of efforts to dominate nature and then cautions that such efforts are only temporary. D The speaker presents an account of efforts to dominate nature and then cautions that such efforts are only temporary.
Despite the fact that we can control and shape the land...
We can't control the sea.
Despite the fact that we can control and shape the land, we can't control the sea.
Choice A says the speaker is focused on whether an approach to nature is "admirable", but the poem doesn't focus on good or bad. Instead, it focuses on possible or impossible. We can eliminate this choice.
Choice C says the speaker argues against interfering with nature, but the poem doesn't say that it's bad to interfere with nature. Also, notice that the second half of the poem doesn't "[give] evidence supporting" interference with nature; the second half of the poem argues that interfering with the sea is impossible. We can eliminate this choice.
Choice D is tempting. The first half of the poem does indeed "[present] an account of efforts to dominate nature". However, the second half of the poem doesn't say those efforts are "temporary". Instead, it argues that in some cases it's simply impossible to dominate nature. We can eliminate this choice.
While some nature can be controlled, some nature can't.
How should we think about text structure and purpose questions?
- to explain ______
- to illustrate ______
- to criticize ______
- to argue ______
- to introduce ______
How to approach text structure and purpose questions
Step 1: Identify the task
Step 2: Summarize the text
Step 3: Test the choices
Stay specific
- Choice A introduces the word "admirable", which makes a judgment about whether these attempts to control nature are good or bad. But the poem doesn't discuss whether things are good or bad. We can eliminate this choice.
- Choice D describes the first part of the text pretty well. The first four lines of the poem do discuss "efforts to dominate nature". However, the second half of choice D disqualifies the whole choice; the poem never claims that anything is "temporary". We can eliminate this choice.
Lean on transitions
The text uses the subordinating conjunction "no matter" to link the first half of the poem to the second half. "No matter" is very similar to "despite" or "regardless", and it very clearly signals that there will be a contrast between the first half of the poem and the second half. This contrast is reflected in the correct answer.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

- Australia edition
- International edition
- Europe edition

Trump thought Ukraine ‘must be part of Russia’ during presidency, book says
Ex-president ‘could not get his head around the idea that Ukraine was an independent state’, former adviser Fiona Hill tells author
As president, Donald Trump “made it very clear” that he thought Ukraine “must be part of Russia”, his former adviser Fiona Hill says in a new book about US national security under threat from Russia and China.
“Trump made it very clear that he thought, you know, that Ukraine, and certainly Crimea, must be part of Russia,” Hill, senior director for European and Russian affairs on the US national security council between 2017 and 2019, tells David Sanger, a New York Times reporter and author of New Cold Wars: China’s Rise, Russia’s Invasion, and America’s Struggle to Defend the West .
“He really could not get his head around the idea that Ukraine was an independent state.”
This, Sanger writes, meant Trump’s view of Ukraine was “essentially identical” to that of Vladimir Putin , the Russian president who would order an invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, a year after Trump left office.
Before triggering the invasion, Putin said in a speech : “Ukraine is an inalienable part of our own history, culture and spiritual space.”
Last month, in a speech marking 10 years since the annexation of Crimea, Putin declared that parts of occupied Ukraine were part of a “New Russia”.
New Cold Wars will be published in the US on Tuesday. The Guardian obtained a copy.
The book appears with the Ukraine war grinding into its third year but with $60bn of new US military aid to Kyiv blocked by far-right Republicans in the US House, acting in accordance with Trump’s wishes as he runs to defeat Joe Biden in a presidential election rematch and return to power.
The House speaker, Mike Johnson, has indicated he wants to pass Ukraine aid but he faces strong opposition, not least from Trump, with whom Johnson is due to appear in Florida on Friday. Biden has strongly condemned Republicans’ hold on Ukraine aid, as have lawmakers from both parties . Biden and other senior figures have also condemned Trump’s words in support of Putin, including a stunning promise to “encourage Russia to do what the hell they want” to US Nato allies he deems financially delinquent.
On Thursday, Alexander Vindman , formerly the top Ukraine aide on Trump’s national security council, told CNN that without new US aid, Ukraine’s position had become “quite precarious”.
Like Hill, Vindman was a key witness in Trump’s first impeachment trial, over his attempts to blackmail Ukraine by withholding military support, in an attempt to extract political dirt on rivals including Biden.
Vindman was fired , after Senate Republicans loyal to Trump assured the president’s acquittal at trial. Hill left office on her own terms.
Vindman was born in Ukraine. Hill was born in Britain. Now a fellow at the Brookings Institution in Washington DC and chancellor of Durham University in the UK, Hill’s thoughts on Trump, Russia and Putin remain eagerly sought, particularly given her co-authorship of Mr Putin: Operative in the Kremlin , a well-regarded biography.
after newsletter promotion
In Washington in February, Hill told a conference staged by anti-Trump conservatives that Trump “idolises” Putin for his autocratic leadership and longevity in power.
That view, Hill said, contributed to Trump’s furious rejection of intelligence agencies’ conclusion that Russia intervened in the 2016 election to help Trump win.
She also said she had spoken to European leaders at the Munich security conference, finding them nervously preparing for a possible second Trump administration .
“The prime ministers and presidents and foreign ministers and others … all know how capricious Trump is,” Hill said. “And that’s really what they’re worried about, because it doesn’t matter how many people that they know who become secretary of state or secretary of defense, it comes down to Trump himself and the unpredictability of his personality.”
Hill’s words to Sanger about Trump’s view of Ukraine, though brief, seem guaranteed only to add to such worries.
The result of growing qualms about Trump, his attitude to Russia and other idiosyncrasies, Hill said in February, “is that [European leaders] have started to lose faith in the United States. And it’s very distressing to hear.”
- Donald Trump
- Vladimir Putin
- US politics
- Trump administration
- Politics books
Most viewed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
a phrase 'Author's purpose' functions as a noun and refers to the reason or intent an author has for writing a particular piece. It's the main goal the author wants to achieve, whether it's to inform, entertain, persuade, or some other objective. as a noun phrase, 'author's purpose' can serve as the subject, object, or complement in a sentence.
The author's purpose is to provide step-by-step guidance or directions to the reader. Examples include manuals, how-to guides, and recipes. To Describe: The author uses vivid language to paint a picture in the reader's mind. This can be found in travel writing, descriptive essays, or literature.
The author's biography can contain hints to the author's purpose. Author information may be available in the book, on the author's website, in a biography, or in an encyclopedia . Relevant points ...
The author aims to facilitate understanding and skill acquisition in the audience. To Describe: Authors may write to describe a person, place, object, or event in vivid detail, appealing to the reader's senses and imagination. Descriptive writing is often found in travelogues, nature writing, and creative non-fiction.
1. to Persuade. Using this form of author's purpose, the author tries to sway the reader and make them agree with their opinion, declaration, or stance. The goal is to convince the reader and make them act in a specific way. To convince a reader to believe a concept or to take a specific course of action, the author backs the idea with facts ...
Today we are going on a dangerous journey inside the mind of the author. (ominous music) Every piece of text is written for a purpose, and especially in informational text, every author structures their texts, words, and their ideas with that purpose in mind. And sometimes that purpose will be harder to see. As readers, our job is to consider ...
Authors often use the connotation of words to reveal their purpose in texts. The connotation of a word is how it makes us feel. A rainstorm described as "dreary" has a negative connotation, while a rainstorm described as "refreshing" has a positive connotation. Tone: The tone of a text reflects the author's attitude towards the subject ...
Author's Purpose Basics. The author's purpose is basically the reason he or she chose to act in a particular way, whether that's writing the passage, selecting a phrase, using a word, etc. It differs from the main idea in that author's purpose not the point you're supposed to get or understand; rather, it's the why behind why the author picked ...
When the author's purpose is to inform, they write objectively and use facts. Although both informative writing and persuasive writing use facts, the goals are different. Persuasive writing uses facts to support an opinion; it's part of the process to convince the reader and present itself as "informative.". Informative writing, however ...
Purposes. Authors and audiences both have a wide range of purposes for communicating. The importance of purpose in rhetorical situations cannot be overstated. It is the varied purposes of a rhetorical situation that determine how an author communicates a text and how audiences receive a text. Rhetorical situations rarely have only one purpose.
Main Idea, Purpose, & Audience. Text evaluation and analysis usually start with the core elements of that text: main idea, purpose, and audience. An author needs to consider all three of these elements before writing, as they help determine the author's content and language. As a reader, it's important to ascertain these aspects of a text ...
Analyzing the author's purpose becomes more engaging and relatable when you can apply your skills to historical speeches. One exemplary text for this exercise is Abraham Lincoln's Second Inaugural Address. Use this step-by-step guide to analyze the author's purpose in this significant piece of writing: Step 1: Background Research:
Author's purpose. Sketch from Penny Illustrated Paper illustrating scenes from the play Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde, performed at the Lyceum Theatre in London in 1888. Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde is a thrilling book that explores the nature of humans. Author Robert Louis Stevenson creates two identities within a single individual, one ...
The author's purpose of a text refers to why they wrote the text.. It;s important to know the author's purpose for a range of reasons, including: Media Literacy: We want to make sure we're not tricked by the author.When reading an article online, for example, we want to figure out what the author's purpose is in order to determine whether they're going to write with a particular ...
Authors and audiences both have a wide range of purposes for communicating. The importance of purpose in rhetorical situations cannot be overstated. It is the varied purposes of a rhetorical situation that determine how an author communicates a text and how audiences receive a text. Rhetorical situations rarely have only one purpose.
Author's Purpose is a reading strategy that is commonly taught in elementary schools across the country. According to the Common Core State Standards, beginning in second grade, students need to be able to determine why an author has written a passage. Additionally, as students advance, they are expected to be able to use text evidence to ...
Adjectives. Persuade. The author is trying to convince the reader to do something or to think a certain way. Entertain. the author wants to give the reader something to enjoy reading. Explain. The author instructs or tells how to do something such as give directions. Perspective. the way the author views the topic of the text.
Other parts of the message are important for readers to interpret are. the author's purpose, the author's point of view, and. the author's tone. Understanding the author's purpose for writing a passage, point of view, and tone will help you get deeper into the writer's thinking and, therefore, understand what you read more deeply.
How to Teach About the Author's Purpose . An important part of reading is learning about the author's purpose. When an author writes something, they are most likely going to have a purpose of some sort. Don't worry, that purpose is not narrowed down in one reason. Sometimes the author's purpose may be to persuade the reader.
An author's purpose can be divided into three: 1. To Inform-. To provide information about a topic. Authors with this goal want to present facts that will help readers understand or learn anything. Example: Pain is a natural aspect of the human body that alerts us when something is amiss. 2.
An author's purpose is his/her reason or intent with which they write. An author's purpose may be any of the following: To amuse the reader. To persuade the reader. To inform the reader. To describe a condition. To explain something. An author's purpose is seen in the way he writes about a topic. For example, if he/she wants to amuse the ...
An author's purpose is seen in the way he writes about a topic. To amuse the reader.. An author purpose is his reason for or intent in writing. An author's purpose is seen in the way he writes about a topic. ... What are Parts of Speech? Parts of speech determine words' grammatical and semantic position in a sentence. Activity time The ...
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland's fourth budget delivers a big-ticket housing program for millennials and Generation Z voters — a multi-billion dollar commitment to be paid for in part with ...
While structure and purpose are closely linked, you may find it helpful to read the passage while focusing on just the one the question asks about. Step 2: Summarize the text. Read the passage closely and summarize the ideas you encounter. Try to boil the whole text down to one or two simple points.
The current study is part of a l... Purpose:The study purpose was to compare the practice patterns captured by self-reported logbook data and those recorded by a computerized home program application. ... AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SPEECH-LANGUAGE PATHOLOGY (AJSLP) JOURNAL OF SPEECH, LANGUAGE, AND HEARING RESEARCH (JSLHR) LANGUAGE, SPEECH, AND HEARING ...
Last month, in a speech marking 10 years since the annexation of Crimea, Putin declared that parts of occupied Ukraine were part of a "New Russia". New Cold Wars will be published in the US on ...