Assignment Biography: Student Criteria and Rubric for Writing
Researching an Individual Aligned to Common Core Writing Standards
- Tips & Strategies
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Teaching Resources
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.A., English, Western Connecticut State University
- B.S., Education, Southern Connecticut State University
The genre of biography can also be categorized in the sub-genre of narrative nonfiction/historical nonfiction. When a teacher assigns a biography as a writing assignment, the purpose is to have a student utilize multiple research tools to gather and to synthesize information that may be used as evidence in a written report about an individual. The evidence gained from research can include a person’s words, actions, journals, reactions, related books, interviews with friends, relatives, associates, and enemies. The historical context is equally important. Since there are people who have influenced every academic discipline, assigning a biography can be a cross-disciplinary or inter-disciplinary writing assignment.
Middle and high school teachers should allow students to have a choice in selecting the subject for a biography. Providing student choice, particularly for students in grades 7-12, increases their engagement and their motivation especially if students select individuals they care about. Students would find it difficult to write about a person they do not like. Such an attitude compromises the process of researching and writing the biography.
According to by Judith L. Irvin, Julie Meltzer and Melinda S. Dukes in their book Taking Action on Adolescent Literacy:
"As humans, we are motivated to engage when we are interested or have real purpose for doing so. So motivation to engage [students] is the first step on the road to improving literacy habits and skills" (Chapter 1).
Students should find at least three different sources (if possible) to make sure the biography is accurate. A good biography is well-balanced and objective. That means if there is disagreement between sources, the student can use the evidence to state that there is a conflict. Students should know that a good biography is more than a timeline of events in a person's life.
The context of a person's life is important. Students should include information about the historical time period in which a subject lived and did her/his work.
In addition, the student should have a purpose for researching another person's life. For example, the purpose for a student to research and write a biography can be in a response to the prompt:
"How does this writing this biography help me to understand the influence of this person on history, and quite possibly, this person's impact on me?"
The following standards-based criteria and scoring rubrics can be used to grade a student-selected biography. Both criteria and rubrics should be given to students before they begin their work.

Criteria for a Student Biography aligned to Common Core State Standards
A General Outline for Biography Details
- Birthdate /Birthplace
- Death (if applicable).
- Family Members.
- Miscellaneous (religion, titles, etc).
Education/Influences
- Schooling.Training.
- Work Experiences.
- Contemporaries/Relationships.
Accomplishments/ Significance
- Evidence of major accomplishments.
- Evidence of minor accomplishments (if relevant).
- The analysis that supports why the individual was worthy of note in their field of expertise during his or her life.
- Analysis why this individual is worthy of note in their field of expertise today.
Quotes/Publications
- Statements made.
- Works published.
Biography Organization using the CCSS Anchor Writing Standards
- Transitions are effective in assisting the reader to understand shifts.
- Ideas within each paragraph are fully developed.
- Each point is supported by evidence.
- All evidence is relevant.
- Important terms are explained to the reader.
- Purpose of each paragraph (introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion) is clear.
- Clear relationship between topic sentence(s) and paragraph(s) that came before is evident.
Grading Rubric: Holistic Standards with Letter Grade Conversions
(based on extended response Smarter Balanced Assessment writing rubric)
Score: 4 or Letter Grade: A
Student response is a thorough elaboration of the support/evidence on the topic (individual) including the effective use of source material. The response clearly and effectively develops ideas, using precise language:
- Comprehensive evidence (facts and details) from source materials are integrated.
- Relevant, and specific clear citations or attribution to source materials.
- Effective use of a variety of elaborative techniques.
- Vocabulary is clearly appropriate for the audience and purpose.
- Effective, appropriate style enhances content.
Score: 3 Letter Grade: B
Student response is an adequate elaboration of the support/evidence in the biography that includes the use of source materials. The student response adequately develops ideas, employing a mix of precise and more general language:
- Adequate evidence (facts and details) from the source materials is integrated and relevant, yet the evidence and explanation may be general.
- Adequate use of citations or attribution to the source material.
- Adequate use of some elaborative techniques.
- Vocabulary is generally appropriate for the audience and purpose.
- The style is generally appropriate for the audience and purpose.
Score: 2 Letter Grade: C
Student response is uneven with a cursory elaboration of the support/evidence in the biography that includes the uneven or limited use of source material. The student response develops ideas unevenly, using simplistic language:
- Some evidence (facts and details) from the source materials may be weakly integrated, imprecise, repetitive, vague, and/or copied.
- Weak use of citations or attribution to source materials.
- Weak or uneven use of elaborative techniques.
- Development may consist primarily of source summaries.
- Vocabulary use is uneven or somewhat ineffective for the audience and purpose.
- Inconsistent or weak attempt to create the appropriate style.
Score: 1 Letter Grade: D
Student response provides a minimal elaboration of the support/evidence in the biography that includes little or no use of source material. The student response is vague, lacks clarity, or is confusing:
- Evidence (facts and details) from the source material is minimal, irrelevant, absent, incorrectly used.
- Insufficient use of citations or attribution to the source material.
- Minimal, if any, use of elaborative techniques.
- Vocabulary is limited or ineffective for the audience and purpose.
- Little or no evidence of appropriate style.
- Insufficient or plagiarized (copied without credit) text.
- Off-topic.
- Off-purpose.
- Pros and Cons to Flexible Grouping in Middle and High School
- Grading for Proficiency in the World of 4.0 GPAs
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography?
- How to Write an Interesting Biography
- T.E.S.T. Season for Grades 7-12
- Topics for a Lesson Plan Template
- The Whys and How-tos for Group Writing in All Content Areas
- How to Create a Rubric in 6 Steps
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
- What Is Plagiarism?
- 10 Test Question Terms and What They Ask Students to Do
- Higher Level Thinking: Synthesis in Bloom's Taxonomy
- What Is a Rubric?
- Writing Prompt (Composition)
- Rubrics - Quick Guide for all Content Areas

How to Write a Biography
Biographies are big business. Whether in book form or Hollywood biopics, the lives of the famous and sometimes not-so-famous fascinate us.
While it’s true that most biographies are about people who are in the public eye, sometimes the subject is less well-known. Primarily, though, famous or not, the person who is written about has led an incredible life.
In this article, we will explain biography writing in detail for teachers and students so they can create their own.
While your students will most likely have a basic understanding of a biography, it’s worth taking a little time before they put pen to paper to tease out a crystal-clear definition of one.

What Is a Biography?

A biography is an account of someone’s life written by someone else . While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction.
Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject’s life from the earliest days of childhood to the present day or, if the subject is deceased, their death.
The job of a biography is more than just to outline the bare facts of a person’s life.
Rather than just listing the basic details of their upbringing, hobbies, education, work, relationships, and death, a well-written biography should also paint a picture of the subject’s personality and experience of life.

Full Biographies
Teaching unit.
Teach your students everything they need to know about writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY and a BIOGRAPHY.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ ( 26 reviews )
Features of a Biography
Before students begin writing a biography, they’ll need to have a firm grasp of the main features of a Biography. An excellent way to determine how well they understand these essential elements is to ask them to compile a checklist like the one-blow
Their checklists should contain the items below at a minimum. Be sure to help them fill in any gaps before moving on to the writing process.
The purpose of a biography is to provide an account of someone’s life.
Biography structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Open your biography with a strong hook to grab the reader’s attention
SEQUENCING: In most cases, biographies are written in chronological order unless you are a very competent writer consciously trying to break from this trend.
COVER: childhood, upbringing, education, influences, accomplishments, relationships, etc. – everything that helps the reader to understand the person.
CONCLUSION: Wrap your biography up with some details about what the subject is doing now if they are still alive. If they have passed away, make mention of what impact they have made and what their legacy is or will be.
BIOGRAPHY FEATURES
LANGUAGE Use descriptive and figurative language that will paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read. Use time connectives to link events.
PERSPECTIVE Biographies are written from the third person’s perspective.
DETAILS: Give specific details about people, places, events, times, dates, etc. Reflect on how events shaped the subject. You might want to include some relevant photographs with captions. A timeline may also be of use depending upon your subject and what you are trying to convey to your audience.
TENSE Written in the past tense (though ending may shift to the present/future tense)
THE PROCESS OF WRITING A BIOGRAPHY
Like any form of writing, you will find it simple if you have a plan and follow it through. These steps will ensure you cover the essential bases of writing a biography essay.
Firstly, select a subject that inspires you. Someone whose life story resonates with you and whose contribution to society intrigues you. The next step is to conduct thorough research. Engage in extensive reading, explore various sources, watch documentaries, and glean all available information to provide a comprehensive account of the person’s life.
Creating an outline is essential to organize your thoughts and information. The outline should include the person’s early life, education, career, achievements, and any other significant events or contributions. It serves as a map for the writing process, ensuring that all vital information is included.
Your biography should have an engaging introduction that captivates the reader’s attention and provides background information on the person you’re writing about. It should include a thesis statement summarising the biography’s main points.
Writing a biography in chronological order is crucial . You should begin with the person’s early life and move through their career and achievements. This approach clarifies how the person’s life unfolded and how they accomplished their goals.
A biography should be written in a narrative style , capturing the essence of the person’s life through vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes. Avoid dry, factual writing and focus on creating a compelling narrative that engages the reader.
Adding personal insights and opinions can enhance the biography’s overall impact, providing a unique perspective on the person’s achievements, legacy, and impact on society.
Editing and proofreading are vital elements of the writing process. Thoroughly reviewing your biography ensures that the writing is clear, concise, and error-free. You can even request feedback from someone else to ensure that it is engaging and well-written.
Finally, including a bibliography at the end of your biography is essential. It gives credit to the sources that were used during research, such as books, articles, interviews, and websites.
Tips for Writing a Brilliant Biography
Biography writing tip #1: choose your subject wisely.
There are several points for students to reflect on when deciding on a subject for their biography. Let’s take a look at the most essential points to consider when deciding on the subject for a biography:
Interest: To produce a biography will require sustained writing from the student. That’s why students must choose their subject well. After all, a biography is an account of someone’s entire life to date. Students must ensure they choose a subject that will sustain their interest throughout the research, writing, and editing processes.
Merit: Closely related to the previous point, students must consider whether the subject merits the reader’s interest. Aside from pure labors of love, writing should be undertaken with the reader in mind. While producing a biography demands sustained writing from the author, it also demands sustained reading from the reader.
Therefore, students should ask themselves if their chosen subject has had a life worthy of the reader’s interest and the time they’d need to invest in reading their biography.
Information: Is there enough information available on the subject to fuel the writing of an entire biography? While it might be a tempting idea to write about a great-great-grandfather’s experience in the war. There would be enough interest there to sustain the author’s and the reader’s interest, but do you have enough access to information about their early childhood to do the subject justice in the form of a biography?
Biography Writing Tip #2: R esearch ! Research! Research!
While the chances are good that the student already knows quite a bit about the subject they’ve chosen. Chances are 100% that they’ll still need to undertake considerable research to write their biography.
As with many types of writing , research is an essential part of the planning process that shouldn’t be overlooked. If students wish to give as complete an account of their subject’s life as possible, they’ll need to put in the time at the research stage.
An effective way to approach the research process is to:
1. Compile a chronological timeline of the central facts, dates, and events of the subject’s life
2. Compile detailed descriptions of the following personal traits:
- Physical looks
- Character traits
- Values and beliefs
3. Compile some research questions based on different topics to provide a focus for the research:
- Childhood : Where and when were they born? Who were their parents? Who were the other family members? What education did they receive?
- Obstacles: What challenges did they have to overcome? How did these challenges shape them as individuals?
- Legacy: What impact did this person have on the world and/or the people around them?
- Dialogue & Quotes: Dialogue and quotations by and about the subject are a great way to bring color and life to a biography. Students should keep an eagle eye out for the gems that hide amid their sources.
As the student gets deeper into their research, new questions will arise that can further fuel the research process and help to shape the direction the biography will ultimately go in.
Likewise, during the research, themes will often begin to suggest themselves. Exploring these themes is essential to bring depth to biography, but we’ll discuss this later in this article.
Research Skills:
Researching for biography writing is an excellent way for students to hone their research skills in general. Developing good research skills is essential for future academic success. Students will have opportunities to learn how to:
- Gather relevant information
- Evaluate different information sources
- Select suitable information
- Organize information into a text.
Students will have access to print and online information sources, and, in some cases, they may also have access to people who knew or know the subject (e.g. biography of a family member).
These days, much of the research will likely take place online. It’s crucial, therefore, to provide your students with guidance on how to use the internet safely and evaluate online sources for reliability. This is the era of ‘ fake news ’ and misinformation after all!
COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON INTERNET RESEARCH SKILLS USING GOOGLE SEARCH

Teach your students ESSENTIAL SKILLS OF THE INFORMATION ERA to become expert DIGITAL RESEARCHERS.
⭐How to correctly ask questions to search engines on all devices.
⭐ How to filter and refine your results to find exactly what you want every time.
⭐ Essential Research and critical thinking skills for students.
⭐ Plagiarism, Citing and acknowledging other people’s work.
⭐ How to query, synthesize and record your findings logically.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip #3: Find Your Themes In Biography Writing
Though predominantly a nonfiction genre, the story still plays a significant role in good biography writing. The skills of characterization and plot structuring are transferable here. And, just like in fiction, exploring themes in a biographical work helps connect the personal to the universal. Of course, these shouldn’t be forced; this will make the work seem contrived, and the reader may lose faith in the truthfulness of the account. A biographer needs to gain and maintain the trust of the reader.
Fortunately, themes shouldn’t need to be forced. A life well-lived is full of meaning, and the themes the student writer is looking for will emerge effortlessly from the actions and events of the subject’s life. It’s just a case of learning how to spot them.
One way to identify the themes in a life is to look for recurring events or situations in a person’s life. These should be apparent from the research completed previously. The students should seek to identify these patterns that emerge in the subject’s life. For example, perhaps they’ve had to overcome various obstacles throughout different periods of their life. In that case, the theme of overcoming adversity is present and has been identified.
Usually, a biography has several themes running throughout, so be sure your students work to identify more than one theme in their subject’s life.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing
While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person’s life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject’s life is not enough. The student biographer should not be afraid to share their thoughts and feelings with the reader throughout their account of their subject’s life.
The student can weave some of their personality into the fabric of the text by providing commentary and opinion as they relate the events of the person’s life and the wider social context at the time. Unlike the detached and objective approach we’d expect to find in a history textbook, in a biography, student-writers should communicate their enthusiasm for their subject in their writing.
This makes for a more intimate experience for the reader, as they get a sense of getting to know the author and the subject they are writing about.
Biography Examples For Students
- Year 5 Example
- Year 7 Example
- Year 9 Example
“The Rock ‘n’ Roll King: Elvis Presley”
Elvis Aaron Presley, born on January 8, 1935, was an amazing singer and actor known as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Even though he’s been dead for nearly 50 years, I can’t help but be fascinated by his incredible life!
Elvis grew up in Tupelo, Mississippi, in a tiny house with his parents and twin brother. His family didn’t have much money, but they shared a love for music. Little did they know Elvis would become a music legend!
When he was only 11 years old, Elvis got his first guitar. He taught himself to play and loved singing gospel songs. As he got older, he started combining different music styles like country, blues, and gospel to create a whole new sound – that’s Rock ‘n’ Roll!
In 1954, at the age of 19, Elvis recorded his first song, “That’s All Right.” People couldn’t believe how unique and exciting his music was. His famous hip-swinging dance moves also made him a sensation!
Elvis didn’t just rock the music scene; he also starred in movies like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.” But fame came with challenges. Despite facing ups and downs, Elvis kept spreading happiness through his music.

Tragically, Elvis passed away in 1977, but his music and charisma live on. Even today, people worldwide still enjoy his songs like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love.” Elvis Presley’s legacy as the King of Rock ‘n’ Roll will live forever.
Long Live the King: I wish I’d seen him.
Elvis Presley, the Rock ‘n’ Roll legend born on January 8, 1935, is a captivating figure that even a modern-day teen like me can’t help but admire. As I delve into his life, I wish I could have experienced the magic of his live performances.
Growing up in Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis faced challenges but found solace in music. At 11, he got his first guitar, a symbol of his journey into the world of sound. His fusion of gospel, country, and blues into Rock ‘n’ Roll became a cultural phenomenon.
The thought of being in the audience during his early performances, especially when he recorded “That’s All Right” at 19, sends shivers down my spine. Imagining the crowd’s uproar and feeling the revolutionary energy of that moment is a dream I wish I could have lived.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical prodigy; he was a dynamic performer. His dance moves, the embodiment of rebellion, and his roles in films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock” made him a true icon.
After watching him on YouTube, I can’t help but feel a little sad that I’ll never witness the King’s live performances. The idea of swaying to “Hound Dog” or being enchanted by “Can’t Help Falling in Love” in person is a missed opportunity. Elvis may have left us in 1977, but he was the king of rock n’ roll. Long live the King!
Elvis Presley: A Teen’s Take on the Rock ‘n’ Roll Icon”
Elvis Presley, born January 8, 1935, was a revolutionary force in the music world, earning his title as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Exploring his life, even as a 16-year-old today, I’m captivated by the impact he made.
Hailing from Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis grew up in humble beginnings, surrounded by the love of his parents and twin brother. It’s inspiring to think that, despite financial challenges, this young man would redefine the music scene.
At 11, Elvis got his first guitar, sparking a self-taught journey into music. His early gospel influences evolved into a unique fusion of country, blues, and gospel, creating the electrifying genre of Rock ‘n’ Roll. In 1954, at only 19, he recorded “That’s All Right,” marking the birth of a musical legend.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical innovator; he was a cultural phenomenon. His rebellious dance moves and magnetic stage presence challenged the norms. He transitioned seamlessly into acting, starring in iconic films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.”
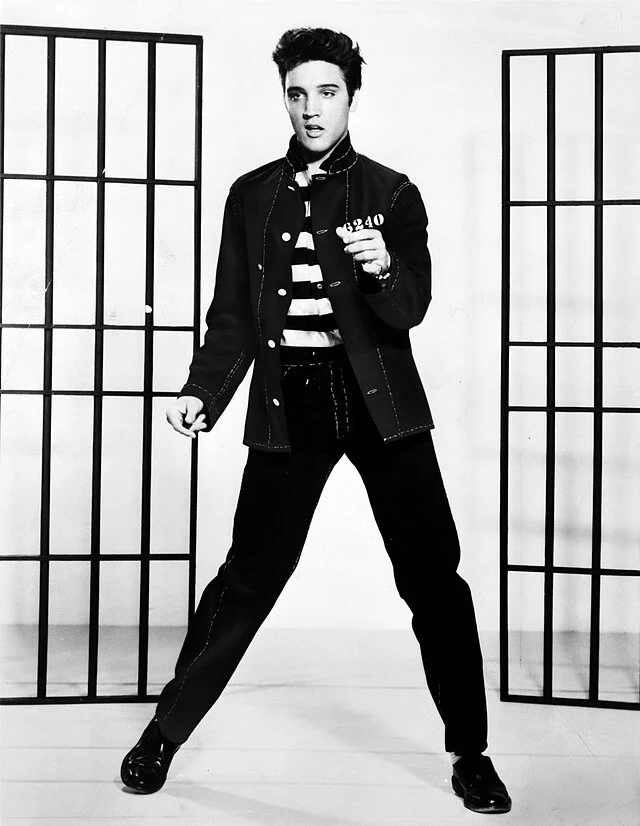

However, fame came at a cost, and Elvis faced personal struggles. Despite the challenges, his music continued to resonate. Even now, classics like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love” transcend generations.
Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is undeniable. He was known for his unique voice, charismatic persona, and electrifying performances. He sold over one billion records worldwide, making him one of the best-selling solo artists in history. He received numerous awards throughout his career, including three Grammy Awards and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Elvis’s influence can still be seen in today’s music. Many contemporary artists, such as Bruno Mars, Lady Gaga, and Justin Timberlake, have cited Elvis as an inspiration. His music continues to be featured in movies, TV shows, and commercials.
Elvis left us in 1977, but his legacy lives on. I appreciate his breaking barriers and fearlessly embracing his artistic vision. Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is timeless, a testament to the enduring power of his artistry. His music has inspired generations and will continue to do so for many years to come.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING TEACHING IDEAS AND LESSONS
We have compiled a sequence of biography-related lessons or teaching ideas that you can follow as you please. They are straightforward enough for most students to follow without further instruction.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 1:
This session aims to give students a broader understanding of what makes a good biography.
Once your students have compiled a comprehensive checklist of the main features of a biography, allow them to use it to assess some biographies from your school library or on the internet using the feature checklist.
When students have assessed a selection of biographies, take some time as a class to discuss them. You can base the discussion around the following prompts:
- Which biographies covered all the criteria from their checklist?
- Which biographies didn’t?
- Which biography was the most readable in terms of structure?
- Which biography do you think was the least well-structured? How would you improve this?
Looking at how other writers have interpreted the form will help students internalize the necessary criteria before attempting to produce a biography. Once students have a clear understanding of the main features of the biography, they’re ready to begin work on writing a biography.
When the time does come to put pen to paper, be sure they’re armed with the following top tips to help ensure they’re as well prepared as possible.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 2:
This session aims to guide students through the process of selecting the perfect biography subject.
Instruct students to draw up a shortlist of three potential subjects for the biography they’ll write.
Using the three criteria mentioned in the writing guide (Interest, Merit, and Information), students award each potential subject a mark out of 5 for each of the criteria. In this manner, students can select the most suitable subject for their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 3:
This session aims to get students into the researching phase, then prioritise and organise events chronologically.
Students begin by making a timeline of their subject’s life, starting with their birth and ending with their death or the present day. If the student has yet to make a final decision on the subject of their biography, a family member will often serve well for this exercise as a practice exercise.
Students should research and gather the key events of the person’s life, covering each period of their life from when they were a baby, through childhood and adolescence, right up to adulthood and old age. They should then organize these onto a timeline. Students can include photographs with captions if they have them.
They can present these to the class when they have finished their timelines.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 4:
Instruct students to look over their timeline, notes, and other research. Challenge them to identify three patterns that repeat throughout the subject’s life and sort all the related events and incidents into specific categories.
Students should then label each category with a single word. This is the thematic concept or the broad general underlying idea. After that, students should write a sentence or two expressing what the subject’s life ‘says’ about that concept.
This is known as the thematic statement . With the thematic concepts and thematic statements identified, the student now has some substantial ideas to explore that will help bring more profound meaning and wider resonance to their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 5:
Instruct students to write a short objective account of an event in their own life. They can write about anyone from their past. It needn’t be more than a couple of paragraphs, but the writing should be strictly factual, focusing only on the objective details of what happened.
Once they have completed this, it’s time to rewrite the paragraph, but they should include some opinion and personal commentary this time.
The student here aims to inject some color and personality into their writing, to transform a detached, factual account into a warm, engaging story.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING BIOGRAPHIES

Teach your students to write AMAZING BIOGRAPHIES & AUTOBIOGRAPHIES using proven RESEARCH SKILLS and WRITING STRATEGIES .
- Understand the purpose of both forms of biography.
- Explore the language and perspective of both.
- Prompts and Challenges to engage students in writing a biography.
- Dedicated lessons for both forms of biography.
- Biographical Projects can expand students’ understanding of reading and writing a biography.
- A COMPLETE 82-PAGE UNIT – NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
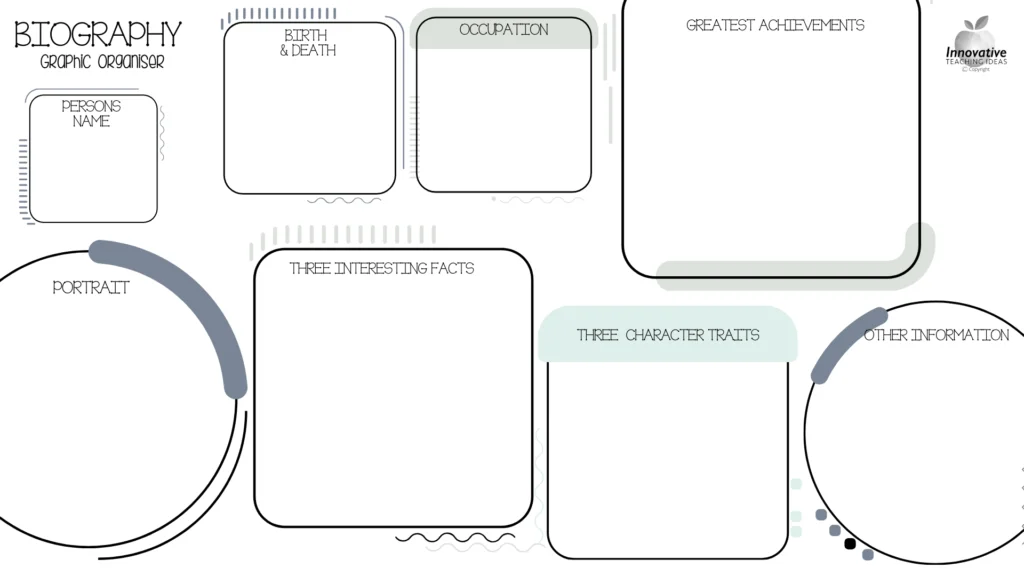
FREE Biography Writing Graphic Organizer
Use this valuable tool in the research and writing phases to keep your students on track and engaged.
WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
To Conclude
By this stage, your students should have an excellent technical overview of a biography’s essential elements.
They should be able to choose their subject in light of how interesting and worthy they are, as well as give consideration to the availability of information out there. They should be able to research effectively and identify emerging themes in their research notes. And finally, they should be able to bring some of their personality and uniqueness into their retelling of the life of another.
Remember that writing a biography is not only a great way to develop a student’s writing skills; it can be used in almost all curriculum areas. For example, to find out more about a historical figure in History, to investigate scientific contributions to Science, or to celebrate a hero from everyday life.
Biography is an excellent genre for students to develop their writing skills and to find inspiration in the lives of others in the world around them.
HOW TO WRITE A BIOGRAPHY TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO BIOGRAPHY WRITING

How to write an Autobiography

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Personal Narrative Writing Guide

How to Write a Professional Biography for a College Student

How to Write a Biography Statement
A professional biography is an asset to help you stand out, and it may even help you land a job or internship. Develop your biography as early in your college career as possible, and then refine it as you pinpoint your goals. Whether the biography is optional or is a mandatory assignment for a class, it’s vital to create a concise, succinct self-portrait that will catch the attention of your intended readers. This is achieved with a combination of good writing and facts about your academic and professional background .
Grammar and Mechanics in a Biography
Good grammar demonstrates your professionalism and your attention to detail. A professional biography is written in the third person. Chris Grant from the University of Rochester recommends you start the first sentence with your full name, and subsequently refer to yourself by last name. Avoid redundancy: Start every other sentence or two with a personal pronoun (“he” or “she”). Vary sentence lengths to create a biography that is both easy to read and interesting. There is usually no word limit to a professional biography, but say as much as you can in one paragraph . The exception is a long biography , which is about one page, according to Grant. Longer biographies may be assigned in class, or required for scholarships. Yale University Law school recommends two paragraphs for its student bios to accommodate an abundance of information.
Balance Academic and Work Experience
An academic biography primarily focuses on your credentials as a college student, including notable research papers, grades and related extracurricular activities. You can include these elements in a professional biography, but you should also discuss current and past jobs, internships and volunteer work. As with a resume, write down the most recent experience and then include past work. For example, start by writing something like:
“John Smith is a student at XYZ University majoring in journalism, where he edits the student newspaper.” Then list other academic and work experience. Longer bios, such as those recommended by Yale Law School, often start in the reverse order.
Incorporate Relevant Personal Facts
Personal information can make a professional biography more engaging, so long as the facts are relevant to your audience and not too personal. You might mention places you’ve traveled or favorite books, but don't discuss significant others or family members.
If you can’t think of anything relevant to a position you’re applying for, describe a few hobbies to make the biography more personable. For example: “When he isn’t busy editing the student paper or studying, Smith enjoys baseball and kayaking.” Add any personal information at the very end of your professional biography.
How to Handle Lack of Experience
Not all students have resumes full of experience. This is especially true for freshmen or students undecided about their majors. Start by stating which school you attend, and discuss one of your most recent assignments.
For example: “John Smith is a student at XYZ University, where he recently completed a research paper on the effects of social media on interpersonal communication.” Then discuss any courses or clubs you have joined to highlight the fact that you’re an ambitious student with leadership skills.
Related Articles

How to Improve a Resume for Graduate School
Objectives for resumes for scholarships.

Letters of Recommendation for High School Student Scholarship Money

How to Write a 200 Word Biography

How to Write a Letter to the President of a College

How to Write an Essay Fast

How to Write an Autobiography for a University

How to Write a High School Recommendation Letter
- University of Alaska Anchorage: Writing an Effective Personal Profile
Kristeen Cherney began writing healthy lifestyle and education articles in 2008. Since then, her work has appeared in various online publications, including Healthline.com, Ideallhealth.com and FindCollegeInfo.com. Cherney holds a Bachelor of Arts in communication from Florida Gulf Coast University and is currently pursuing a Master of Arts in English.
It's My Life: Multimodal Autobiography Project

- Resources & Preparation
- Instructional Plan
- Related Resources
In this unit, students write autobiographies, illustrate them, and set them to music. Music is a powerful tool to evoke emotion, and students will carefully select songs to accompany the stories from their lives. Students brainstorm lists of important events in their lives, along with images and music that represent those events. They then create storyboards in preparation for the final PowerPoint project. After making revisions, they present their final projects to their peers in class. If PowerPoint is unavailable, students might create posters and play soundtracks using cassette or CD players.
Featured Resources
Stapleless Book : Students use this online tool to plan each slide of an autobiographical PowerPoint presentation.
From Theory to Practice
According to William Kist, "students should be able to both read critically and write functionally, no matter what the medium." We have "broadened the concept of literacy" (cf. Kist) to include multimodal projects so that no student will feel isolated, and every student will gain knowledge and understanding from the sharing of ideas. As the NCTE Statement on Multimodal Literacies states, "The use of different modes of expression in student work should be integrated into the overall literacy goals of the curriculum and appropriate for time and resources invested." This lesson plan encourages such integration by asking students to create multimodal presentations. Further Reading
Common Core Standards
This resource has been aligned to the Common Core State Standards for states in which they have been adopted. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, CCSS alignments are forthcoming.
State Standards
This lesson has been aligned to standards in the following states. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, standard alignments are not currently available for that state.
NCTE/IRA National Standards for the English Language Arts
- 4. Students adjust their use of spoken, written, and visual language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- 5. Students employ a wide range of strategies as they write and use different writing process elements appropriately to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes.
- 6. Students apply knowledge of language structure, language conventions (e.g., spelling and punctuation), media techniques, figurative language, and genre to create, critique, and discuss print and nonprint texts.
- 8. Students use a variety of technological and information resources (e.g., libraries, databases, computer networks, video) to gather and synthesize information and to create and communicate knowledge.
- 12. Students use spoken, written, and visual language to accomplish their own purposes (e.g., for learning, enjoyment, persuasion, and the exchange of information).
- It’s My Life Assignment
- Presentation Music and Image Planner
- It’s My Life Project Rubric
- Sample Multimodal Autobiography
- It’s My Life Self-Assessment
Preparation
- Arrange for the use of a computer lab, projector, and CD player.
- Familiarize yourself with PowerPoint. Visit the PowerPoint in the Classroom Website and the PowerPoint tutorials on adding sound and adding music for helpful information and guides. You may also choose to share these Web resources with your students.
- Create a model autobiography presentation for students to view (optional).
- Review fair use and copyright guidelines before having students use copyrighted music and images in their projects.
- Make copies of the Copyright and Fair Use Guidelines for School Projects , It’s My Life Assignment , Presentation Music and Image Planner , Sample Multimodal Autobiography , It’s My Life Self-Assessment , and It’s My Life Project Rubric sheets for your students.
- Test the Stapleless Book on your computers to familiarize yourself with the tool and ensure that you have the Flash plug-in installed. You can download the plug-in from the technical support page .
Student Objectives
Students will
- examine the lyrics to songs and describe how the music and words relate to their life stories.
- organize their thoughts and express their stories by using PowerPoint presentations.
- improve technical skills by familiarizing themselves with PowerPoint.
- evaluate their own work.
Session One
- Present the PowerPoint autobiography assignment to students and explain the required elements. If you have created a model presentation, you can use it to present the concept to students.
- Students will select five important events in their lives. Using written summaries of these events, they will create PowerPoint multimodal autobiographies.
- Students may use recordings from the radio or their personal music collections.
- Students will follow guidelines for fair use of copyrighted images and music. (Explain that this topic will be discussed in detail in the next session.)
- Student will present their slideshows in class. Slideshows are limited to 5–10 minutes in length.
- Students will respond to their peers’ presentations in writing.
- First day of school (e.g., preschool, kindergarten, first grade, middle school, high school)
- A special family trip or vacation
- A family event or milestone
- A personal achievement (e.g., first place in a competition)
- A personal loss
- Explain that in this stage of the writing process, students should write down all of their ideas. If they are working in groups or with the whole class, lay ground rules that encourage all students to share their ideas with the group and that discourage students from critiquing their peers’ responses during this brainstorming stage. Explain that students will have the opportunity to evaluate their lists and select the events that they want to include in their autobiographies in later sessions.
- Have students view the PowerPoint presentation Finding Your Focus: The Writing Process . Discuss the stages of the writing process—including drafting, revising, and editing—and explain that students will go through each of these stages as they work on their autobiographies. The final stage will be the actual publishing of their autobiographies in the form of PowerPoint presentations.
- Ask students to select 8–10 events from their lists and write a brief paragraph summary for each one. Students may also include events that were not included on the lists they created during their brainstorming sessions.
- Have students set aside these summaries to use in a later session. If necessary, have students complete this activity for homework.
Session Two
- Initiate a class discussion by describing a significant event from your own life (i.e., birth of a sibling, parents’ divorce, first car). You can refer to the Sample Multimodal Autobiography for an example.
- Ask a few students to share an event from their own lists, and record each event on the board.
- Have students think about the events described and to connect songs to these events. For example, a student might associate a love song with a family member’s wedding ceremony.
- How does the song make you feel?
- What images come to mind when you think of this event?
- What images come to mind when you think of this song?
- Next play a song or two that you associate with the event from your own life that you’ve described. It doesn’t matter if the songs are not “current” hits; students will understand the feelings behind the music.
- Ask students to discuss how the song fits the event and to suggest other songs they might associate with the same event.
- Have students review the summaries they wrote in Session One.
- From the list of events they described, ask students to select five to include in their autobiographical presentations.
- Pass out the Presentation Music and Image Planner and have students list each of the five events they’ll include.
- Have students use the Presentation Music and Image Planner to write the title of a song and describe an image for each event they will include in their presentations. Students can work with a classmate or in small groups if they are having trouble generating ideas. You may wish to have students begin this activity in class and then complete their planners for homework.
- Be sure to discuss lyrics with students to assure that song selections are classroom-appropriate as determined by teacher and school policy.
- Emphasize that students should avoid using music that involves profanity or derogatory remarks towards any race, gender, and/or religious affiliation. Encourage students to discuss any questionable lyrics with you in advance. Point out you will either approve students’ choice of songs and images or provide suggestions for revision on their planning sheets.
- Have you ever downloaded music or other content from the Internet? What other Internet resources have you used?
- You will need to use music for your presentations. What are some ways you can get the songs you’ll need? From what sources can you download music? Are all of these ways legal?
- Is it OK to use other people’s music in something you are creating?
- Students can use 1–5 images from the same photographer or illustrator without permission.
- Up to 10% of a song can be used in a presentation. That translates to about 30 seconds from one song.
- Students must include a bibliography of any work used in their presentations.
- Before beginning Session Three, review students’ planners to ensure that they understand the assignment and have selected appropriate images and songs. Approve each plan, providing feedback, or make suggestions for revision.
- Meet with students individually to discuss any necessary changes.
Session Three
- Tape sheets of plain paper together along the short edges.
- Divide a large piece of blank paper into equal rectangles.
- Use a blank index card for each PowerPoint slide.
- Use the ReadWriteThink Stapleless Book interactive to plan each slide of their presentation. This tool provides space for students to write the text that will appear on the slide and information about the song they will include, along with space for a simple illustration.
- Before beginning their PowerPoint presentations, students should use the storyboards to lay out their text and images, and to write the titles of the songs and specific lyrics they will use for each slide.
- Have students add the text of the paragraphs they wrote in Session One to their storyboards in this drafting session.
- Remind students of the writing process and explain that they will have the opportunity to revise their text and other elements when they reach the revising stage.
- Allow more than one session of class time to complete this work if required. You can choose to extend this activity to the next class period or have students complete their drafts for homework. Students should also have any CDs or music they want to use available for the next session.
- Provide access to a scanner for students who wish to scan photographs or other images for use in their projects.
- Before moving to the next session, review students’ drafts and provide feedback.
Sessions Four through Six
- PowerPoint in the Classroom
- PowerPoint Tutorial—Adding sound
- Demo: Add music to a presentation
- Once students are comfortable with PowerPoint and have practiced with the software, have them begin creating slides using their drafts/storyboards.
- Remind students of the guidelines for using copyrighted music in their projects.
- Share this adding sounds page from PowerPoint in the Classroom with students, which details how to add portions of a song from a CD to a PowerPoint slide.
- Review students’ progress as they work and provide assistance to students who are having difficulty using PowerPoint.
- Allow additional time as needed for students to work on their projects in or out of class.
Session Seven
- Are slides arranged in an effective way? How are the events in my autobiography arranged? Sequentially? Thematically?
- Can I do a better job of describing each event? Will the reader/viewer understand what I’m trying to communicate?
- Do the images I’ve selected adequately represent the events?
- Does the song reflect my feelings about each event?
- Guide students in working through this stage of the writing process and encourage them to make revisions that will help them more effectively communicate the information included in their autobiographies.
Sessions Eight and Nine
- When students have finished making revisions, have them take turns presenting their PowerPoint autobiographies to the class. Use a projector if you have access to one.
- After all students have completed their presentations, have them respond in writing by completing the It’s My Life Self-Assessment .
- Teach the ReadWriteThink lesson Copyright Infringement or Not? The Debate over Downloading Music to reinforce the concepts of fair use and copyright infringement explored in this lesson.
- Teach the ReadWriteThink lesson The Year I Was Born: An Autobiographical Research Project to have students further explore the autobiography writing genre.
- In place of or in addition to PowerPoint presentations, have students write a typed autobiography, a narrated audio autobiography (set to music) on CD, cassette, or MP3, or a videotaped biography. Students can use the CD/DVD Cover Creator to design and print their covers for their finished presentations.
- Have students use the Profile Publisher to enhance their autobiographies by creating one or more profiles to represent themselves at different times in their lives, with a special focus on the connection between experiences and music.
Student Assessment / Reflections
- Have students reflect on their projects by completing the It’s My Life Self-Assessment .
- Assess students’ PowerPoint projects using the It’s My Life Project Rubric .
- Professional Library
- Strategy Guides
- Student Interactives
- Lesson Plans
The Stapleless Book can be used for taking notes while reading, making picture books, collecting facts, or creating vocabulary booklets . . . the possibilities are endless!
Add new comment
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
How to Write a Biography
Learn how to write a biography with our comprehensive guide.

Last updated on Dec 8th, 2023

When you click on affiliate links on QuillMuse.com and make a purchase, you won’t pay a penny more, but we’ll get a small commission—this helps us keep up with publishing valuable content on QuillMuse. Read More .
Table of Contents
How to write a biography can be a fun challenge as you share someone’s life story with readers. You may need to write a biography for a class or decide to write a biography as a personal project. Once you’ve identified the subject of your biography, do your research to learn as much as you can about them. Then, immerse yourself in writing the biography and revising it until it’s best. What I am going to share with you in today’s post is how to write a biography. If you want to know the rules of how to write a biography correctly then this post of ours is essential for you.
Introduction
While it’s true that most biographies involve people in the public eye, sometimes the subject is less well-known. But most of the time, famous or not, the person we’re talking about has an incredible life. Although your students may have a basic understanding of How to write a biography, you should take some time before putting pen to paper to come up with a very clear definition of biography.
Before knowing how to write a biography, let’s first understand what a biography is. A biography is an account of a person’s life written by someone else. Although there is a genre called fictional biography, by definition biographies are mostly non-fiction. In general, biographies trace the subject’s life from early childhood to the present day or until death if the subject is deceased.
Biography writing is not limited to describing the bare facts of a person’s life. Instead of just listing basic details about their upbringing, interests, education, work, relationships, and deaths, a well-written biography should also paint a picture of a person’s personality as well as that person’s life experiences.
Tips and Tricks For How To Write a Biography
1. ask the subject’s permission to write a biography.
Here are the first tips on how to write a biography. Before starting your research, make sure you get your subject’s consent to write their biography. Ask them if they’re ready to be the subject. Getting their permission will make writing a biography much easier and ensure that they are open to information about their lives.
If the theme does not allow you to write a bio, you can choose another theme. If you decide to publish a profile without the subject’s permission, you may be subject to legal action from the subject.
If the topic no longer exists, you don’t need to ask permission to write about them.
2. Research primary sources on the topic
Primary sources may include books, letters, photographs, diaries, newspaper clippings, magazines, Internet articles, magazines, videos, interviews, existing biographies, or autobiographies on the subject. Find these resources in your local library or online. Read as much as you can about the topic and highlight any important information you come across in your sources.
You can create research questions to help you focus your research on this topic, such as:
What do I find interesting about this topic? Why is this topic important to readers?
3. Conduct interviews with subjects and their relatives
Interviewing people will turn your research into reality: the people you interview will be able to tell you stories you can’t find in history books. Interview the subject as well as people close to them, such as spouses, friends, business associates, family members, co-workers, and friends. Interview in person, over the phone, or via email.
For in-person interviews, record them with a voice recorder or voice recorder on your computer or phone. You may need to interview the subject and others multiple times to get the documents you need.
4. Visit places important to the topic
Whenever you want to know how to write a biography, to understand the history of the subject, spend time in places and areas that are significant to the subject. This may be the subject’s childhood home or neighborhood. You can also visit the subject’s workplace and regular meeting places.
You may also want to visit areas where the subject made important decisions or breakthroughs in their life. Being physically present in the area can give you an idea of what your subjects may have felt and help you write about their experiences more effectively.
5. Research the time and place of the subject’s life
Contextualize your subject’s life by observing what’s going on around them. Consider the period in which they grew up as well as the history of the places they lived. Study the economics, politics, and culture of their time. See current events happening where they live or work.
When you studying how to write a biography, ask yourself about time and place:
What were the social norms of this period?
What happened economically and politically?
How has the political and social environment influenced this topic?
6. Make a timeline of a person’s life
To help you organize your research, create a timeline of a person’s entire life, from birth. Draw a long line on a piece of paper and sketch out as many details about a person’s life as possible. Highlight important events or moments on the timeline. Include important dates, locations, and names.
If you think about how to write a biography You can also include historical events or moments that affect the topic in the timeline. For example, a conflict or civil war may occur during a person’s lifetime and affect their life.
7. Focus on important events and milestones
Major events can include marriage, birth, or death during a person’s lifetime. They may also achieve milestones like their first successful business venture or their first civil rights march. Highlights key moments in a person’s life so readers clearly understand what’s important to that person and how they influence the world around them.
For example, you might focus on one person’s achievements in the civil rights movement. You could write an entire section about their contributions and participation in major civil rights marches in their hometowns.
8. Cite all sources used in biography
Most biographies will include information from sources such as books, journal articles, magazines, and interviews. Remember to cite any sources that you directly quote or paraphrase. You can use citations, footnotes, or endnotes. If the biography is for a course, use MLA, APA, or Chicago Style citations according to your instructor’s preference.
9. Reread the biography
Check the biography for spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Circle all punctuation marks in the text to confirm they are correct. Read the text backward to check for spelling and grammar errors.
Having a biography full of spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors can frustrate readers and lead to poor grades if you submit your work to the class.
10. Show your biography to others to get their feedback
It is a momentous step of how to write a biography. Once you have completed your draft biography, show it to your colleagues, friends, teachers, and mentors to get their feedback. Ask them if they have a good understanding of someone’s life and if the biography is easy to read. Be open to feedback so you can improve the biography and make it error-free. Revise profile based on feedback from others. Don’t be afraid to trim or edit your biography to suit your readers’ needs.
11. Use flashbacks
Flashbacks happen when you move from the present to the past. You can start with the present moment, and then bring in a scene from the person’s past. Or you could have one chapter focusing on the present and one focusing on the past, alternating as you go.
The flashback scene must be as detailed and realistic as the present-day scene. Use your research notes and interviews with subjects to better understand their past to reminisce.
For example, you can move from a person’s death in the present to reminiscing about their favorite childhood memory.
12. Outline Your Story Chronologically
This is another important step in how to write a biography is to write an outline that describes your story in chronological order. An outline is a tool that helps you visualize the structure and key elements of your story. This can help you organize your story into chapters and sections.
You can write your plan in a digital document or draw it with pen and paper. Remember to store your outline in an easily accessible place so you can refer to it throughout the writing process.
What citation style should I use for my biography?
Use MLA, APA, or Chicago Style citations based on your instructor’s preference when citing sources in your biography.
Should I include personal opinions in a biography?
No, a biography should be objective and based on facts. Avoid injecting personal opinions or bias into the narrative.
What’s the difference between a biography and an autobiography?
A biography is written by someone else about a person’s life, while an autobiography is written by the subject themselves about their own life.
Can I write a biography about a living person?
Yes, you can write a biography about a living person with their consent. Ensure you respect their privacy and follow ethical guidelines when writing about them.
Conclusion
Other than creating a sense of closure, there are no set rules about how a biography ends. An author may want to summarize their main points about the subject of their biography. If the person is still alive, the author can inform the reader about their condition or circumstances. If the person has died, inheritance can be discussed. Authors can also remind readers how they can learn from the biographical subject. Sharing a closing quote or about a person can leave the audience with a point to consider or discuss in more detail.
For further insights into writing and to avoid common mistakes, check out our article on Most Common Mistakes in Writing . Additionally, explore the Best Writing Tools for Writers to enhance your writing skills and discover the tools that can assist you. If you’re looking to improve your typing speed and accuracy, our article on How to Type Faster with Accuracy offers valuable tips.
How we've reviewed this article
Our content is thoroughly researched and fact-checked using reputable sources. While we aim for precision, we encourage independent verification for complete confidence.
We keep our articles up-to-date regularly to ensure accuracy and relevance as new information becomes available.
- Current Version
- Dec 8th, 2023
- Oct 22nd, 2023
Share this article
Leave a Comment Login Please login to comment 0 Comments Inline Feedbacks View all comments
Prev Previous Next Next

12 Creative Writing Tips for Beginners to Be Expert
So many people want to be writers. Some of them want to be professional writers. Do you want to be a creative writer? If you have been assigned creative writing, at that point it may be an incredible chance for you to increase your learning and writing skills. Even if

How to Write a Check: A Step-by-Step Guide
Knowing how to write a check is a crucial life skill that everyone should possess. While cash and credit cards are widely used, there are still many situations where you’ll need to use a paper checkbook to pay bills, send money, or settle taxes. If you find yourself in any

How to Write an Essay: A Three-Step Guide with Examples
Is the essay deadline making you nervous? Do you ever look at the flashing line on your computer screen and want to write something, but just can’t think of anything and feel stuck? Fear not, a fellow student or maybe even a writer facing a new challenge! This guide is
Report this article
Let us know if you notice any incorrect information about this article or if it was copied from others. We will take action against this article ASAP.
- Profile Page
- Edit Profile
- Add New Post
Read our Content Writing Guide .

Eat, Sleep, Wander
20+ Student Biography Examples
Welcome to the world of students! We have created an amazing collection of 30 student biography examples to help you write your own.
As a student, you are likely to be writing a variety of biographical pieces. Whether you are writing a personal profile for your CV, a biography for an awards application or a biography for a college admissions essay, it’s important that you construct an interesting and engaging narrative of who you are.

Student Biography Examples
1. Growing up I was always interested in the sciences and technology. In high school, I excelled in math and science classes, which led me to pursue a degree in engineering. I went on to earn my Bachelor’s degree in Engineering and am currently working on my Master’s in Civil Engineering. After I finish my degree, I plan to use my knowledge to help improve infrastructure in developing countries.
2. Since a young age, I have been passionate about helping people in need. During college, I decided to focus my studies on sociology and political science. I used my knowledge to take action and participated in several non-profit organizations to promote social justice. With the help of internships, I have also gained experience in policy development and public relations. I’m currently working on a graduate degree in Social Work and aim to eventually work for the United Nations .
3. As a freshman in high school, I was unsure of what kind of career path I wanted to pursue. After talking with my parents and teachers, I decided to start college as an undeclared major. After two years of exploration, I settled on a double major of business and economics. I’ve been able to take advantage of various opportunities on and off campus and served as an intern in the Human Resources department of a major banking firm. I look forward to earning my degree and using my skills to become a successful business leader.
4. I never thought that I had the ability to become a professional photographer, but my high school photography teacher pushed me to pursue my dreams. I learned how to use a variety of cameras, develop photographs, and post-process my images. I continued my photography studies at college, where I gained additional knowledge in studio lighting and digital editing. I was even able to gain experience in the fashion industry, interning for a well-known photographer . Today, I am working as an event photographer, documenting weddings, reunions, and corporate events.
5. When I was younger I was passionate about art, which prompted me to pursue a bachelor’s degree in Fine Arts. During college, I was able to gain experience as a studio assistant and also learn various digital and traditional art techniques. With the help of a scholarship, I was able to travel to various countries and learn even more about different art styles. After graduation, I started working as a freelance artist and have been able to produce several commissioned artworks and pieces.
6. As a child, I always exhibited an aptitude for mathematics and problem solving. After researching various career paths, I decided to major in Computer Science. I was able to gain valuable experience while interning at a tech startup and also during an internship with the Department of Defense. I am currently working on my master’s degree and plan to focus my studies on artificial intelligence and machine learning.
7. I have been involved in theater since I was a young child. During my high school years, I focused on honing my abilities through various extracurricular activities. I was able to gain valuable experience by participating in multiple productions and I even gained a scholarship for theater. I attended college to study Musical Theater and continued to foster my talent. With help from internships and workshops, I was able to build additional experience and formed a touring theater company with some of my colleagues.
8. From an early age, I was interested in the environment and the outdoors. I spent a lot of time reading environmental books and researching environmental issues. This passion inspired me to major in Environmental Science in college. I’ve gained valuable experience through various internships and part-time jobs. With the help of my degree, I’ve been able to work on several conservation projects and hope to soon work for a non-profit organization focused on sustainability.
9. When I graduated high school I wanted to focus my career on the medical field. After much research, I decided to major in Biomedical Engineering. During my time in college, I was able to gain a valuable experience by interning as a research assistant. I have been able to learn more about medical technology and have been able to contribute to various projects. I’m currently pursuing a master’s degree in Biomedical Engineering and plan to continue my research in the field and eventually work for a healthcare company.
10. I have always had an interest in fashion and design, so when the time came to decide my career path it made sense to pursue design. During college, I was able to study many aspects of fashion and gain experience through various internships. I was also able to travel to other countries to observe trends and learn about different cultures. With my degree, I am currently working as a fashion designer and I plan to continue to use my creative eye to come up with innovative and stylish designs.
More Student Biography Examples on the next page…

It’s Never too Early for Your Students to Write Their Autobiography (Lesson Plan)

Unwrapping the Onion of the Autobiography
Key points of the lesson, tips for writing biographies & autobiographies, project materials, lesson procedures, lesson resources, digital learning skills, follow up activities.
Who are your students?
What do they know about themselves?
What have they done with themselves before they entered your classroom?
These are just a few of the questions that might come up at the beginning of the school year.
It can be said that the most important thing that a student learns how to do during their 13 years of education is to have the skill set to introduce themselves to the world and be able to clearly articulate their identity.
In this lesson plan, we are going to share a great way for students to create an autobiography that has not just one, but several functions throughout the school year.
On the surface, this lesson asks the students to describe all the things that make them unique in this world. However, once you have your students thinking about these subject areas this project takes on a life of its own based on projects that might stem from its completion. (See below for more information)
In this project, students will learn:
- What is a biography & autobiography?
- How to write a personal narrative
- How to peer edit a partner's biography
- How to share your story.
Throughout this lesson, there are several key topics that the student will learn. Each of these types of autobiographies has the potential of opening additional projects during the school year making this the perfect first or second lesson.
- A Biography is a story (in third person) about someone's life and accomplishments.
- They are designed to help tell someone's story and are meant to help provide a clear picture of who someone is personally and professionally.
- A tool that can be leveraged when networking.
- Social Media Profiles
- Presentations / Speeches
- “About Me” Pages
- “Johnny Appleseed is an 8th grade student in Middle School.”
- “Johnny Appleseed is interested in Volleyball and science, and plays the violin.”
- “In 2018, Johnny won his first bowling competition…”
- “When not attending Middle School, Johnny is active in Volleyball.”
- “Johnny Appleseed lives with his mother and 4 siblings”
- Begin writing your bio with your first and last name.
- Showcase what you currently are doing with your life or are interested in.
- Include at least one accomplishment.
- Briefly tell your readers who you are outside of school.
- Consider adding a personal story.
- Google Doc: Introduction Assignment
- Google Doc: Biography Outline
- Google Doc: Write your Autobiography Assignment

Part 1: Write Down Your Thoughts
- Create an assignment using the “ What Do You Remember? ” Google Doc
- Ask your students to write down as many memorable events in their life as they can think of that are meaningful.
- When finished, ask your students to click the TURN IN button in Google Classroom.
Part 2: Biography Outline
- Create an assignment using the “ Who Are You? (Outline) ” Google Doc
- Ask your students to fill in the blanks using details from their backgrounds, history, and accomplishments.
Part 3: Writing the Biography
- Create an assignment using the “ Who Are You? (Template) ” in Google Classroom
- Ask your students to write the first draft of their autobiography using the paragraph guides in the template.
- Video 1: How to Write an Autobiography
- Video 2: How to Write an Autobiography
- Video 3: How to Write YOUR Autobiography
There are several digital learning skills that students will need or will learn when completing this activity.
- Peer-Review
- Capitalization and Punctuation
- Bold / Italics
- Header & Paragraph Styles
As mentioned above, there are several follow-up activities that will nicely complement this lesson. Once a student has written their autobiography, they can then choose someone from history or from a topic that is in the curriculum and write a report to share someone else's story. Another great extension of this lesson would be to put your students in front of a camera and read the autobiography into a camera to create the beginnings of a short video project.
Are you interested in creating dynamic lessons this year to support digital learning skills? Would you be interested in having me work with you or your team of teachers? Please reach out and let me know how I can best support you this year.
- Recent Posts
- FETC 2025 Request For Proposals: Get Ready To Share Your Super Powers! - March 29, 2024
- Maximize Your Podcasting Setup with the Best Microphone Boom Arm - March 16, 2024
- Experience the Solar Eclipse with LEGO® Education - March 14, 2024
Share this:
Listen and subscribe, start typing and press enter to search, discover more from teachercast educational network.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
Consider Using this Student Biography to Highlight Skills
Table of Contents
Talking about yourself can be challenging at times. We don’t always have the right words to express and introduce ourselves to a broad audience. If you’re struggling with a student biography assignment, consider using a student biography example as your basis.

This article explains biographies and their importance.
What are Student Biographies?
A biography is a document that details significant moments in a student’s life . They give a peek into an individual’s life and help readers understand something about their personality and background. Student bios are typically 150 to 200 words long.
Particularly, they help students understand their academic role in light of their social development and learn how they fit into society. Good student biographies help students become great thinkers and hone their writing skills.
The manner in which students paint themselves in their biographies is a small step toward learning how to market themselves in a professional setting. Who knows, you could be someone in the future. You wouldn’t want a poorly-written biography to mar your image.
Why are they Important?
Student biographies are important because they help classmates, friends, and employers understand the individual behind the number . This is useful in getting knowledge from someone who may not have had a chance to participate in extracurricular activities or interviews.
From a professional perspective, academic papers can support information on your resume. Biographies also give an insight into a person’s self-perception and self-image.
Biographies can also detail a writer’s struggles and how they overcame them. They help us look into the psyche of highly successful people and to analyze the way they grapple with challenges and obstacles. Moreover, biographies show readers the inner struggles that a student went through to get to their current position.
Biographies serve as points of reference for understanding an applicant better, and they can also hold wisdom for those who read them. For most people, a student bio must include your career and school accomplishments. Students can use biographies when looking for work.
Tips for Writing a Student Biography
Here are some things to consider when writing a student biography.
Adhere to Format Rules
Remember to write your student and professional bios in the third person and to limit it to one or two paragraphs.
Your bio must start with your name and a brief sentence describing your background. Your background can refer to your educational background, academic focus, and professional and personal interests.
Start with a Background Story
Your bio should read like a formal personal narrative. It should describe the experiences that helped shape you as an individual. The details in your bio must explain details not evident in your resume.
Adding recent events is a great idea because it helps distinguish you from other applicants. It shows your ability to respond to new challenges. This is also a straightforward way to add personality to your bio. Make sure to highlight things and experiences, such as studying abroad or doing volunteer work.
Share Your Interests
It’s important to focus on your career aspirations because this is the heart of your student biography. This will show readers your intended path, and it gives them an idea of your goals. This can be crucial data in the hiring process for jobs and internships.
Make sure to add hobbies that make you happy. This not only makes you more human but also highlights your uniqueness as a candidate.
Emphasize How You Can Add Value
Finally, try to communicate your unique value proposition in your biography. This is a good way to end your document on a high note, and it increases your chances of landing a role.
You want your reader to understand you’re a well-rounded person and that you have a lot of wisdom and knowledge to share. Moreover, don’t forget to include your most relevant skills and traits in your bio.
Student Biography Example
If you need a guide for applying the aforementioned tips, try to browse this list for a student biography example you like.
Bryan Watch is one of the best students in his class. He is currently studying at the Summer Sample Business University. During his college years, Bryan was part of a program that gave students the opportunity to pursue any education they wanted.
Bryan plans to pursue a degree in public policy and follow in the footsteps of his late father. He will begin this new chapter in the next few days to come.
Greg graduated top of his class. He is one of the few young awardees recognized by the state as an honorary member of a major field research group. Greg has written many books for the high school level. He also has a long history of excellent fieldwork. Greg worked with fellow teachers and family members to render service to students as well as out-of-school youth.
Brandon is a resident doctor at the Sacred Heart hospital. He spends his time building birdhouses and creating content for various Medicine-related pages. He prides himself on his ability to gather facts pertinent to any case before making any assumptions. Brandon truly is a master of following the evidence.
Ivan is a Psych major who graduated from the University of Sans Louis. Like his father, he plans to dedicate himself as a guardian of state laws and as an extension of God’s divine justice. He comes from a family of doctors and lawyers.
In college, he was part of the university swim team, where he represented the university in various competitions for three years. He plans to start his law school life next year at the College of Excellent Law Students. He strongly believes in getting schools and colleges to include basic law subjects in their general curriculum.
The Bottom Line
Student biographies describe a student’s background to readers. They help give readers insight into an author’s personality, experiences, and feelings. If you’re struggling to come up with a bio, you can always use a student biography example as a basis. We hope these examples help you understand how to write an effective biography.
Be sure to check out our other guides. They include examples and tips for writing all kinds of biographies.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Personal Bio Generator Articles
Describing someone in a unique way.
We value and care the people in our lives for various reasons. But sometimes it can be challenging to explain…
- Personal Bio Generator
Tips for Writing a Bio for Artists
Your artist bio should connect emotionally with the reader and provide a glimpse into your personality. It allows you to…
Saddest Bios You Can Use for Facebook
Facebook offers many advantages to businesses, whether you have a Facebook page or have sparked a personal page. One of…
Coolest Insta Bios For Software Engineers
It’s a pretty cool to be a software engineer. You have the fun and challenge of writing code for a…
Best Instagram Bios for Singers’ Pages
Writing a singer or musician’s biography can be challenging, especially for press materials and Instagram. Writing a compelling musician bio…
Freshest Instagram Bios for Nature Lovers
Being a lover of nature makes you want to observe the beauty of nature all the time. The various hues…

How to Write a Good Academic Biography (Part 1)
When your journal article gets accepted or you are preparing for a public presentation, you will often be asked for a short academic biography. For many people, these academic bios are more difficult to write than a dissertation. How do you sum up yourself and your work in 3-5 sentences? What do you need to include? What should you leave out?
What You Should Do
- Start with your full name followed by your current position, your general interests, and your current project, keeping them all very brief.
- If you are within a year of receiving a prestigious award, mention that as well.
- Finally, finish with a sentence that’s personal: add a hobby, a pet’s name, the city you live in—whatever you are comfortable with that is personal but not too private.
What You Should Avoid
- Avoid speaking in the first person, i.e., don’t use “I.”
- Don’t divulge details beyond your current position.
- In a longer bio of multiple paragraphs, you may add more awards and information about your master’s and bachelor’s degrees, but not in a short bio. Moreover, don’t add anything that happened before grad school—including your place of birth. For example:
Hi! My name is Scott. I was originally born in Vermont and now I’m a professor at North Yankee University in Fargone, New York (in upstate New York). I study antelopes’ migration patterns and their impact of native grain growth. My interest in antelopes began as a teenager when I first saw one in the wild. I did my undergrad degree in biology at SUNY and my masters and UCLA and my PhD in Forestry at Hunter College.
Related: Finished drafting your academic biography and heading for an international conference? Check out this post now!
The above example is far too casual and Scott’s work and current position are overshadowed by all the other random details. This can be written in a much better way:
Scott Sampson is a professor of Wildlife Biology at North Yankee University. His work focuses specifically on the migration patterns of antelope and their impact on the growth of native grain. His favorite place to do research in his backyard, which opens to the Akron National Forest.
This improvised version is concise, relevant, and makes Scott’s bio appear professional while giving a short description of his personal details.
Longer Bios
For longer bios, follow the same basic rules, but go into a bit more depth about your work, your education, and your future projects or interests. You may also consider adding a line about your immediate family. But as always, leave the personal details for a short and friendly mention at the end of the bio.
Mostly, your bio will be used by someone to introduce you at a conference or public event so if you write your bio using these tips, you will help them give a smooth and accurate introduction. Remember that the bio is the first thing that people know about you so pack it full of the most important things about yourself!
If you would like to know more about different formats of academic biography, read the next article in this series!
Appreciating the dedication you put into your blog and detailed information you provide. It’s good to come across a blog every once in a while that isn’t the same out of date rehashed material. Fantastic read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Greeting from Enago Academy! Thank you for your positive comment. We are glad to know that you found our resources useful. Your feedback is very valuable to us. Happy reading!
Super helpful! Thank you for writing about this.
wow great article. I got lots of new ideas from this post. Thanks a lot.
Thank you! Really a short and precise description of how to write short biographic sentence.
Excellent! Just what I needed; thank you.
Thanks for sharing this post, It is a very helpful article.
Excellent information…
Comparing to my introduction and yours, there is a huge difference and mine is like grade R?. Thank you so much for developing such content and helping disadvantaged students like me, hence holding Honours. Once again thank you
it is good, i learnt something new
Your articles are so much meaningful and informative.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
How to Write a Good Academic Biography (Part 2)
Writing an academic biography is part of many academic activities. Whether your paper is accepted…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- Try for free
Biography Themed Teaching Resources
Our biographies on famous and historical figures will enhance your lessons and students will enjoy studying them. Included are reading warm-ups, poems, discussion guides, and more. These resources are appropriate for a variety of grade levels, from kindergarten through high school.
Printables for Grades K-5
- Nelson Mandela Biography: A Reading Warm-Up
Helen Keller Biography: A Reading Warm-Up
- Walt Disney Biography: A Nonfiction Reading Warm-Up
- Harriet Tubman and the Underground Railroad
Helen Keller
Getting to Know Me
Learn About Susan B. Anthony
- More Popular Biography Printables for Grades K-5
Printables for Grades 6-12
- We Beat the Street Discussion Guide
- Albert Einstein Biography: A Reading Warm-Up
- Albert Einstein, Physicist
- The Peanuts Gang: Charles Schulz
- Leonardo da Vinci
- Fastest Woman in the World: Wilma Rudolph
- More Biography Printables for Grades 6-12
Lesson Plans for Grades K-12
An Autobiographical Poem
- Sunflowers, Van Gogh, and You
- Rachel Carson: The Coming of a Silent Spring
- Martin Luther King Jr, Civil Rights Leader
- Marie Curie's Discovery
- Jackie Robinson and Civil Rights
- The Era of Thomas Jefferson
- More Biography Lesson Plans
Biography Teaching Guides
- Red Scarf Girl Teacher's Guide
- Incidents in the Life of a Slave Girl Teacher's Guide
- A Long Way Gone Teacher's Guide
- The Henry Books: A Teacher's Guide
- Up Close: Jane Goodall Discussion Guide
- Listening Is an Act of Love Teacher's Guide
- Balloons Over Broadway: The True Story of the Puppeteer of the Macy's Day Parade Educator's Guide
- More Biography Teaching Guides
Social Studies Activities
Anne Frank: Diary of a Young Girl Discussion Guide
- Chronology of Conscription in the U.S. -- Colonial Era to 1999
- Benjamin Franklin Little Book
- Abraham Lincoln Biography & Mini-Book
- Ryan White, My Own Story
- Betsy Ross Little Book
- More Biography Activities for Social Studies
Reading & Language Arts Activities
- Babe Ruth Reading Warm-Up: Biography
- Henry Ford Biography: A Reading Warm-Up
- Diary of a Wimpy Kid: Greg Heffley's Journal
Learning About Famous People
- More Biography Activities for Reading & Language Arts
Science Activities
- Learn About Johnny Appleseed
- Science and Social Studies: Benjamin Franklin
- Bio of a Famous Scientist
- Jane Goodall, Ethologist
- The First Man in Space
- Early Astronomers
- More Biography Activities for Science Class
Holidays & Seasonal Resources
- "I Have a Dream" Little Book
- Jackie Robinson Coloring Page
- Rosa Parks Coloring Page
- Learn About Pocahontas
- Nonfiction Reading Warm-Up: Sacagawea Biography
- More Biography Resources for the Holidays
Art & Music Activities
- My Book About Abraham Lincoln
- My Book About George Washington
- George Washington Carver Coloring Page
- My Book About Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Claude Monet Biography: A Reading Warm-Up
I Have a Dream: Drawing Activity
- More Biography Activities for Art & Music
Biographies & Physical Education Connected
- Past Olympic Athletes: Profiles, Biographies, and Activities
Michelle Kwan Reading Warm-Up
- Jesse Owens: Olympic Champion
- Jackie Robinson Mini-Biography
- Jim Thorpe Reading Warm-Up
- Althea Gibson
- More Physical Education Biographies
- Overview of the Presidents: Basic Facts & Figures
- Martin Luther King Jr.'s Life
- Assassinations and Attempts in U.S. Since 1865
- Just Where Was Columbus?
- President Barack Hussein Obama, Jr. Biography
- President George Washington Biography
- President James Monroe Biography
- More Popular Biography References
- Martin Luther King Jr. Quiz
- Notable African-American Women Quiz
- Martin Luther King Jr. Printable Book (Grades 4-8)
- Popular Presidents' Day Printables
Recommended Biographies Resources

Albert Einstein Biography: A Reading Warm-Up (Grades 5 & 6)
Timeline: Conscription in the United States, 1620-Present

Sense and Sensibility
DAILY WARM-UPS
Clara Barton Reading Warm-Up

Theodor Seuss Geisel Biography
Influencing Others in Our World
Spoonerisms Activity
LESSON PLANS
Birthday Buddies

The Life and Accomplishments of Martin Luther King Jr.
Harriet Tubman Writing Activity
Carleton Kendrick Ed.M., LCSW

Homesick: My Own Story
The Anne Frank and Miep Gies Connection

Published In: Brief
How to Write a Biography (Examples & Templates)
A biography is a written account of a person’s life that details their life in chronological order. Another person usually writes this detailed account, and it contains reports of their childhood, career, major life events, relationships, and social impact. It also details their relationships with their family, children, and life accomplishments.
The best way to find out more about a popular figure is through reading their biographies, so you need to make sure you get the correct information. Before writing a biography, you need to do a lot of research and interviews to represent a person’s life accurately.
Types of Biography
A biography is the story of someone’s life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest.
A biography aims to share a person’s story or highlight a part of their life.
There are different types of biographies, depending on the story. Some biographies are written true to the story, while some are written as fictional works. Biographies can give you true understanding of a person on an internal as well as external level along with a lot of life lessons.
Autobiography
An autobiography is different from a biography because it is written by the subject of the story, themselves. The author writes in the first-person narrative, and it flows step-by-step like a story of their life. Autobiographies contain personal accounts of the subject’s life, along with their perspectives and opinions on events in their life.
How To Write a Biography
Pick a subject.
Picking a subject is the first step in writing a biography. You can pick an already famous person or a relatively unknown person with a great life story. If you already have a few in mind, you can start by asking yourself some questions such as;
- What has the subject accomplished that makes them a good subject?
- Have they had an impact on society?
- Is the subject a celebrity or a well-known personality?
- Will the biography appeal to a wide audience?
Get Permission
When you pick a subject, the next thing to do is to get permission from them or their family or rights owners. Although, with some historical figures, there may not be any need for permission. Getting permission from your subject makes it easier for you to get stories to put into your book. You can get the chance to obtain additional personal stories and anecdotes that will make your book more interesting by doing so as well.
Do The Research
Research is the most important part of a biography’s process as the entire content of the book is dependent on it. Irrespective of what you know about the subject, you need to carry out as much research as possible to get the story’s facts precisely.
Biography research comes from various sources, depending on the book’s subject. Firsthand reports from family, friends, or personal accounts from the subjects are primary sources. They are usually the most accurate and reliable, and they are crucial for a biography. Secondary sources come from other sources like magazines or documentaries.
Pick a Format
Biographies come in various formats, with each of them having their pros and cons. A typical biography will start at the beginning, usually with the birth and childhood of the subject. Yet, if the biography’s theme involves a different event in their life, the author may want to explore the flashback option or one with concurrent events from different times.
Usually, biographies have a theme or a general life lesson at the center. The author’s role is to tell the subject’s story leading up to the major event.
Which-ever format you choose should place the theme at the center, with the other events detailing the journey.
Create a Timeline Of The Story
Since a biography takes place in chronological order, there needs to be a timeline of the events in the right order. The timeline should contain the key events in the subject’s life, in the order the author plans on revealing them. A great way to declutter the story and keep it interesting is to use flashbacks . This way, the author can introduce past events and explain later events excluding the element of monotony.
Add In Your Thoughts
The good thing about biographies is that you don’t have to stick to the hard facts only. As the author, you can share your opinions and emotions in writing. The author has the freedom to do this by commenting on a significant action by the subject in a manner that describes why they feel the subject may have done what they did.
The author can also include commentary on events depicted in the biography – how it was influenced society or its impact on the lives around them. Recounting these events through a different perspective can make the biography more relatable and interesting to read.
FAQ’s
Why is a biography template important.
A biography template has an outline that makes the writing easier for the author. Biography templates usually contain a sample timeline, format, and questions that provide more information about the subject. With a great biography template, you can cut your writing time in half and spend less time coming up with an outline.
How are biographies better in comparison to autobiographies
Since a different person writes biographies, they tend to be more objective and somewhat accurate than autobiographies. An autobiography tells things from the author’s perspective, so their views and perspective cloud it. Thus, a biography will likely tell a more factual story.
These are the important steps you need to take to help you write a great biography. Now, to make things easier for you, we have a free customizable autobiography and biography template that you can use to start your first book. Get the template and start writing today
What are some of the most important elements to keep in consideration while writing a biography?
Any author looking to write a biography must consider the factors below. They aren’t the only important factors, but a biography isn’t complete without them. • Date and place of their birth • Academic background • Professional expertise • Death, if deceased • Facts and anecdotes about the person • Main accomplishments • Detailed accounts of their child and adult life
Biographies tell the untold stories of some incredibly relevant people in the world. But biographies are not always strictly accurate. So, every biographer needs to follow the necessary steps to provide a biography with all the requirements.
Related Documents

How to Write an Autobiography Fast

Writing your autobiography is like exploring a treasure trove of memories that make up your life. But starting can feel overwhelming. Where do you begin? How do you turn your experiences into a compelling story? Don't worry – this guide is here to help. Whether you're a seasoned writer or a total beginner, we'll break down the process of how to write your autobiography into easy-to-follow steps. Together, we'll uncover the magic of storytelling and turn your life into a captivating reflective essay that's uniquely yours. Get ready to start this adventure of self-discovery and creativity!
What Is an Autobiography
The autobiography definition explains it is a written account of a person's life penned by the individual who has lived those experiences. It is a personal narrative that chronicles significant events, reflections, and emotions throughout various stages of the author's life. Unlike a biography, which is typically written by someone else, an autobiography provides a firsthand perspective, allowing the author to share their thoughts, memories, and insights. It is a cogent medium for self-expression, enabling students to convey the essence of their unique journey, impart lessons learned, and leave a lasting record of their lives for themselves and others to explore.
Need Help With Writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY?
All you have to do to get professional help is to us send your paper requirements and set the deadline.
Autobiography vs. Biography: What’s the Difference
The key distinction between an autobiography and a biography lies in the authorship and perspective. An autobiography is a personal account of one's own life written by the subject themselves. It offers an intimate insight into the author's experiences, emotions, and reflections. For instance, in "The Diary of a Young Girl," Anne Frank provides a poignant autobiographical account of her life hiding from the Nazis during World War II. On the other hand, a biography is a narrative of someone's life written by another person. It often involves extensive research and interviews to present a comprehensive and objective view. A notable example is "Steve Jobs" by Walter Isaacson, a biography offering an in-depth portrayal of the Apple co-founder, drawing on interviews with Jobs himself and those who knew him. While both genres illuminate lives, the crucial difference lies in the source of the narrative – whether it emanates directly from the subject or is crafted by an external observer.
A biography vs autobiography offers distinct perspectives on individuals' lives, shaping narratives through either personal reflections or external observations. Maya Angelou's "I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings" is a powerful autobiography chronicling her tumultuous childhood and journey toward self-discovery. In contrast, a notable biography like "Leonardo da Vinci" by Walter Isaacson delves into the life of the Renaissance polymath, painting a vivid picture through meticulous research and analysis. Autobiographies often provide a deeply personal lens, as seen in "The Glass Castle" by Jeannette Walls, where Walls recounts her unconventional upbringing. In contrast, biographies such as "Unbroken" by Laura Hillenbrand meticulously document the extraordinary life of Louis Zamperini, offering a comprehensive view shaped by the author's investigative work. These examples underscore the unique storytelling approaches each genre employs, either from the firsthand perspective of the subject or the external perspective of an author.
Autobiography Example
Ready to explore autobiography examples? We've got a cool section coming up where we'll check out two awesome examples. Autobiographies are like personal tours into someone's life, and we'll be looking at the stories of Alex Sterling and Trevor Noah. They've poured their experiences onto the pages, and we're going to see what we can learn from their journeys. Get ready to be inspired and maybe even think about telling your own story down the line. Let's dive in!
.webp)
Example 1: “Wanderer's Odyssey: The Uncharted Life of Alex Sterling”
This autobiography recounts the life of a character born in a bustling city who, driven by a thirst for adventure, leaves behind urban life to explore the open road. The narrative explores the protagonist's experiences of hitchhiking, forming connections, and finding self-discovery in the midst of the unpredictable journey. The story emphasizes the lessons learned from the road, the challenges faced, and the ultimate embrace of authenticity. The epilogue reflects on the character's life as a well-lived odyssey, highlighting themes of resilience, connection, and the pursuit of one's true identity.
Example 2: “Echoes of Eternity: The Memoirs of Amelia Reed”
This autobiography follows a character from a countryside village who harbors expansive dreams of adventure. The narrative unfolds as the protagonist sets out to pursue these dreams, facing trials and triumphs that shape their character and lead to self-discovery. The story emphasizes the transformative power of embracing the unknown, with the epilogue reflecting on a life well-lived, highlighting the legacy of fulfilled dreams and the enduring impact on future generations. In addition to examples, we have samples of narrative essay topics that might be useful for you as well.
Tell your story with EssayPro . Our skilled writers can help you craft an autobiography that truly reflects your journey. Share your unique experiences and life lessons in a way that resonates with readers.

Autobiography Elements Explained
Writing an autobiography provides a personal account of one's experiences, achievements, challenges, and personal growth. While each autobiography is unique, certain common elements are often found in this genre:
Introduction
- Autobiographies typically begin with an introduction where the author sets the stage for their life story.
- It may include background information such as birthplace, family, and early experiences.
Birth and Early Years
- Authors often include details about their birth, childhood, and family background.
- Early influences, relationships, and experiences that shaped the individual may be highlighted.
Significant Life Events
- Autobiographies focus on key events and milestones that have had a significant impact on the author's life.
- This could include achievements, failures, relationships, and other impactful experiences.
Challenges and Obstacles
- Autobiographies explore the challenges and obstacles the author faced throughout their life.
- This can include personal struggles, professional setbacks, or other difficulties.
Personal Growth and Development
- Authors reflect on their personal growth and development over the years.
- This may involve self-discovery, learning from experiences, and evolving perspectives.
Achievements and Milestones
- Autobiographies highlight the author's achievements, whether personal, professional, or both.
- Major milestones and successes are often detailed to showcase the individual's journey.
Influential Relationships
- Autobiographies frequently discuss relationships with family, friends, mentors, and significant others.
- The impact of these relationships on the author's life is explored.
Reflection and Insight
- Authors often reflect on their lives, offering insights into their beliefs, values, and lessons learned.
- This section may also include the author's perspective on the world and society.
Themes and Motifs
- Autobiographies may explore recurring themes or motifs that run throughout the individual's life.
- Common themes include resilience, determination, love, loss, and personal identity.
- Autobiographies typically conclude with a summary or reflection on the author's life.
- The author may share their current perspective and future aspirations.
Writing Style
- The writing style can vary, ranging from a formal tone to a more conversational and reflective approach.
- Authors may use literary devices and storytelling techniques to engage readers.
Remember that autobiographies are highly personal, and the structure and emphasis on different elements can vary widely depending on the author's preferences and purpose for writing.
Autobiographical Essay Structure
Autobiographies typically follow a chronological order, beginning with the author's early life and progressing towards the present or a significant moment. The introduction sets the stage, introducing the author and offering insight into the main themes. As you can see in an autobiography example, the narrative then unfolds, exploring the author's significant life events, challenges faced, and personal growth. Achievements and milestones are highlighted, and the impact of influential relationships is examined. Throughout, recurring themes and motifs add depth to the narrative. In the reflection and insight section, the author shares personal lessons learned and beliefs. The conclusion summarizes the autobiography, reflecting on the author's life and future aspirations.
.webp)
Learning how to start an autobiography involves captivating the reader's attention while providing context. Authors often employ engaging anecdotes, vivid descriptions, or thought-provoking statements related to the overarching theme of their lives. The goal is to draw readers in from the beginning and establish a connection between the author and the audience. In the introduction, authors can introduce themselves to the reader. This can be done by sharing a captivating snapshot of their life or posing a question that intrigues the audience. The autobiography introduction sets the tone for the entire narrative, providing a glimpse into the themes and events that will be explored in the autobiography.
The autobiography conclusion offers the culmination of the author's life story. Here, authors often summarize the key points and experiences shared throughout the narrative. It is a moment of reflection, where the author can offer insights into the significance of their journey and the lessons learned along the way. The conclusion may also touch on the author's current perspective, providing a sense of closure to the narrative while leaving room for future aspirations and growth.
Literary Forms of Autobiography
Autobiographies, while generally a non-fiction genre, can take on various literary forms and styles. Here are some literary forms commonly found in autobiographical works:
Traditional Autobiography
- The straightforward narrative of an individual's life, which is usually written by the person themselves. It follows a chronological order, covering significant events and experiences.
- Similar to an autobiography but often focusing on specific themes, periods, or aspects of the author's life rather than a comprehensive account. Memoirs often delve into personal reflections and emotions.
Diary or Journal Form
- Some autobiographies adopt the form of a diary or journal, presenting the author's life through dated entries. This format provides a more immediate and personal perspective.
Epistolary Autobiography
- Written in the form of letters, an epistolary autobiography may consist of the author addressing themselves or others. This style adds an intimate and conversational tone to the narrative.
Graphic Novel or Comic Memoir
- Autobiographical stories are presented in a graphic novel or comic format. Visual elements complement the written narrative, providing a unique and engaging way to convey personal experiences.
Experimental or Nonlinear Autobiography
- Some authors choose to play with the chronological order, presenting their life story non-linearly. This experimental approach can create a more artistic and challenging reading experience.
Biographical Fiction
- While not entirely autobiographical, some authors write fictionalized versions of their own lives. It allows for creative exploration and artistic liberties while drawing inspiration from real experiences.
Travelogue Autobiography
- Autobiographies that take on the form of a travelogue often focus on the author's journeys, both physical and metaphorical. The narrative is shaped by the places visited and the impact of these experiences on personal growth.
Essayistic Autobiography
- Autobiographies that incorporate elements of essays, exploring themes, ideas, and reflections on the author's life. This form allows for a more contemplative and philosophical approach.
Collaborative Autobiography
- Co-written autobiographies involve collaboration between the autobiographical subject and a professional writer. It is common when the subject may not be a writer but has a compelling story to share.
These literary forms highlight the versatility of autobiographical writing, showcasing how authors can creatively shape their life stories to engage readers in various ways. Are you working on other academic assignments? Use our term paper writing services to put your finger on any pending task at hand quickly and for a reasonable price.
How to Write an Autobiography in 5 Steps
Writing an autobiography can be a rewarding and reflective process. Here's a simplified guide in 5 steps to help you get started:
Step 1: Reflection and Brainstorming
Begin by reflecting on your life, considering important events, challenges, and moments of growth. Make a mental inventory of key experiences and people who have influenced you.
Step 2: Establish a Focus
Choose a central theme or focus for your autobiography. This could be a specific period of your life, a significant achievement, or a recurring theme that ties your experiences together. Having a clear focus will guide your writing.
Step 3: Create a Chronological Outline
Develop a rough chronological outline of your life story, starting from your early years and progressing through significant events to the present or another crucial point. Identify key moments and experiences to include in each section.
Step 4: Write with Detail and Emotion
An important aspect of how to write an autobiography for college is appealing to emotion. As you delve into each body paragraph, share your story with vivid details. Use descriptive language to bring your experiences to life for the reader. Infuse your writing with emotion, allowing readers to connect with the depth of your personal journey.
Step 5: Conclude Reflectively
In the concluding section, summarize the key aspects of your life story. Reflect on the significance of your journey, the lessons you've learned, and how you've grown. Provide insights into your current perspective and aspirations for the future, bringing your autobiography to a thoughtful conclusion.
Writing Techniques to Use in an Autobiography
When you write an autobiography, the process involves employing various techniques to make the narrative engaging, evocative, and compelling. Here are some tips for writing autobiography commonly used in autobiographies:
Descriptive Language
- Use vivid and descriptive language to paint a detailed picture of events, people, and settings. Engage the reader's senses to create a more immersive experience.
- Incorporate dialogue to bring conversations to life. Direct quotes can provide authenticity and convey the personalities of the people involved.
Show, Don't Tell
- Instead of merely stating facts, show the emotions and experiences through actions, reactions, and sensory details.
Flashbacks and Foreshadowing
- Employ flashbacks to delve into past events and foreshadowing to create anticipation about future developments.
Metaphors and Similes
- Use metaphors and similes to enhance descriptions and convey complex emotions. Comparisons can make abstract concepts more relatable.
- Integrate symbols and motifs that hold personal significance. This adds depth to the narrative and can be a thematic thread throughout the autobiography.
Humor and Wit
- Infuse your writing with humor and wit when appropriate.
- Introduce suspense by strategically withholding information or revealing key details at crucial moments.
First-Person Perspective
- Utilize the first-person point of view to offer a direct and personal connection between the author and the reader.
Dramatic Irony
- Introduce dramatic irony by revealing information to the reader that the author may not have known at the time.
Parallelism
- Create parallel structures within the narrative, drawing connections between different periods, events, or themes in your life.
Experimenting with different styles can make your story more engaging and memorable for readers. If you haven’t used these techniques in your paper, simply say, ‘ edit my essay ,’ and our experts will imbue stylistic and creative devices in your document to increase its scholarly value.
Benefits of Writing an Autobiography
Working on an autobiography can be incredibly beneficial on a personal level. When you take the time to reflect on your life and put it into words, you gain a deeper understanding of yourself. It's like a journey of self-discovery where you uncover patterns, values, and beliefs that have shaped who you are. This process not only promotes self-awareness but can also help you grow and bounce back from tough times. Writing about challenging moments can be a therapeutic release, allowing you to confront and make sense of your experiences, leading to emotional healing.
On a broader scale, sharing your life story through an autobiography has its impact. It becomes a piece of history, offering insights into the times you've lived through, the culture around you, and societal changes. Your personal narrative connects you with others, creating empathy and understanding. Autobiographies often inspire people by showing that it's possible to overcome challenges, find purpose, and navigate the ups and downs of life. By sharing your story, you become a part of the larger human experience, contributing to a rich tapestry of diverse stories that help us better understand the shared journey of being human. Order an essay or any other type of task to streamline your educational progress is only a few clicks.
Best Piece of Advice for Making Your Autobiography Spot-on
The most valuable advice on how to write an autobiography is to infuse authenticity into every word. Be genuine, raw, and honest about your experiences, emotions, and growth. Readers connect deeply with authenticity, and it's what makes your story uniquely yours. Don't shy away from expressing vulnerability, as it adds a human touch and makes your narrative relatable. Share the highs and lows, the triumphs and struggles, with sincerity, and let your true self shine through. This honesty not only enhances the impact of your autobiography but also contributes to a more profound connection between you and your readers, creating an authentic and memorable narrative. Here are additional tips for bringing your autobiography assignment up to par:
- Essential Details. Focus on key moments that significantly contribute to your story, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Thematic Cohesion. Introduce and explore recurring themes to add depth and coherence to your narrative.
- Authentic Expression. Embrace your unique voice, personality, and storytelling style to create an authentic connection with readers.
- Dialogue and Monologue. Use genuine dialogue and inner monologue to provide insights into your thoughts and emotions during pivotal moments.
- Symbolic Elements. Incorporate symbolic imagery or metaphors to convey deeper meanings and emotions.
- Strategic Foreshadowing. Use foreshadowing purposefully, providing subtle hints that contribute meaningfully to the overall narrative.
- Reflective Closure. Conclude your autobiography with a reflective summary that offers insights into the broader significance of your journey.
Our essay writers know many more tips regarding all possible types of academic tasks. If you ever find yourself in writer’s block, not knowing how to tackle any particular assignment, let us know!
Final Words
If you want to understand how to write a good autobiography, think of it as painting a vivid picture of your life for others to see. It's about being real, digging deep into your memories, and choosing the moments that really matter. Let your personality shine through in your writing – be yourself because that's what makes your story unique. Weave in themes that tie everything together, and use storytelling techniques like dialogue and symbolism to make your narrative come alive. And as you reach the end, leave your readers with some food for thought – a reflection on the bigger lessons learned from your journey. If you ever need assistance with this or any other college assignment, use our research paper services without hesitation.
Do You Need Some Help With Your AUTOBIOGRAPHY?
Address to out professional writers to get your paper done asap
How to Write an Autobiography?
How to start an autobiography essay, what is the difference between autobiography and biography, related articles.
.webp)
Teachers Workshop
A Duke TIP Blog
Body Biographies: Deepen Character Analysis in English and History Class
September 25, 2018 By Mandy Perret 5 Comments

What is a Body Biography?
How can we get gifted and talented students to deepen their understanding of literary and historical characters? How can we bring together isolated facts and help students visualize and analyze the impact of a person on a story or a time period? A Body Biography is a way students can use images and writing to express that analytical and conceptual understanding of characters. Gifted youth are ready for the rigor of digging deep into concepts, metaphors, and high-level interpretations. This differentiated lesson activity provides a way for gifted students to get to the higher levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
This assessment can be used in multiple classes such as social studies, history, government/civics, English Language Arts, science, and religious studies, to name a few. This task allows groups of students to select key samples of text and use symbolic visuals to show their understanding of the person’s words, feelings, beliefs, and impact. The goal of a body biography is not only to illustrate the literal looks of a person, but to also make a thorough visual representation, using symbols, colors, quotations, and a body outline. As students choose the best words and images to explain the person, they must analyze how to represent the historical or thematic impact of this individual with a symbolic representation of the body.
How do you get gifted students to analyze historical figures or literary characters in depth?
Share with us below!
How do students make a Body Biography?

To create the image outline, students can
- use butcher paper and outline a fellow student
- use a premade outline provided by you, the teacher
- or use digital tools to develop the image.
Each part of the body represents something.
- The spine represents the person’s values and beliefs
- The heart represents what they love or what means a lot to them
- The hands represent what they literally hold or what they hold dear
- Their feet represent where they came from and where they are going
- Their brain represents what they are thinking
- The mouth will speak quotes that represent the person’s typical speech as well as any other spoken aspects that students find important
- A mirror can be included to represent how the person sees themselves or how others see them (a mask can also be used)
- Ears show what others say about them
- Eyes show what they see or want to see
- Text–quotes from historical documents or literary documents–can be integrated in multiple places on the image, and not just presented near the mouth in speech bubbles. They can be integrated throughout the body outline and parts.
- a stomach to represent worries they have or worries others have about their choices
- the front to back to represent what is behind them and what lies in front of them
- literal or figurative objects from the person’s life
- clothing items that are typical of or symbolically representative of the person’s qualities
- any other body parts that help show a detailed understanding of the person and the role they play in history or in the text.
- Students should think about colors and what they represent
What is the person’s role?
This activity has two phases: a Planning Research Sheet , and Image Development, designed to help students understand why this person matters to history or the story. Through research and note-taking, followed by group conversations, gifted youth can get to the “big ideas” of a person’s impact by being selective about the details they share within the image. Gifted youth can develop a thesis, or Essential Understanding, about this individual.
Therefore students do not have to address every item listed above. What is key is ensuring that the details that students do choose are meaningful, cohesive, and connected to a larger understanding of the person’s role in history or in the story. View the first category of the rubric , Quotes: Role in Story or History, to think about the Essential Question students are answering: What is the person’s role in history or the story?
As they answer that driving question, students can gather facts about the person from various textual sources, whether primary or secondary historical sources, or from a literary text or secondary sources/literary criticism about that text. Students should share the research task within a group and each come to the task with a few pieces of evidence to discuss, and then have a discussion using each element of the body outline to see which evidence best fits each element.The combination of analysis of the person from multiple viewpoints as well as evaluating the sources to create words and visuals takes isolated facts and allows students to visualize and analyze the person throughout the story or time period.
How do you set up the assignment?
This project can be used for all students in a regular classroom or a gifted self-contained classroom. Group work or independent work is possible with this assignment. Students who need deeper challenge can research certain themes, impacts, or patterns/trends with their character and use additional body parts or visual and textual elements to render a deeper understanding.
You might assign students their person at the beginning of the unit so they can begin gathering ideas and information. This project works best in groups to develop deeper understanding and to compare/contrast what information each group member provides, in order to choose which words/images the group will use in the final product.
Materials for the Lesson
Here are some materials for assignment set-up.
- Planning Research Sheet . This document gets students researching and brainstorming. Students can complete this individually or in a group.
- Note that there is space for you to set requirements for number of quotes, body parts, and symbols to be included.
- Image Outline . If you don’t have time for students to create their own outline, use this one.
- My teacher resource book, Challenging Common Core Language Arts Lessons Grade 8 , Lesson 2.4 also offers additional resources you can use.

How can it be used as an assessment?
An assessment such as this one can close a unit of literary or historical study unit to evaluate student learning utilizing benchmarks and standards, depending on your location. This assignment can be connected to standards related to citing evidence from primary and secondary sources and evaluate their roles in events. This assessment also highlights the C-3 curriculum concepts of gathering and evaluating sources and communicating and critiquing conclusions. It allows students to use words and images to show their complete evaluative and analytical analysis of their person or character. Rigor is increased with the use of individual resources, extended primary/secondary sources, and the creation of additional body parts or interpretation. It allows students to use creative learning while challenging their higher-order thinking skills. You may wish to use this as a formative assessment as well.
Let’s take a gallery walk
The use of a gallery walk is a great way for students share this information and for the class to ask what the Essential Understanding is about the person and their role in history or the story. Body Biographies can be placed around the room with a number. Students in their groups will spend a few minutes viewing the other body biographies and making notes and creating questions to ask the other groups about their body biographies. (I use note cards for each viewing).
After students have viewed all Body Biographies in a rotation, each group will have a chance to present to the class key details from the image as well as the Essential Understanding. The goal of other students listening can be to help presenters better articulate Essential Understandings, by asking questions. The rubric can be used as a guide for conversation if this task is formative, and it can also be used as the rubric for determining a final evaluation if you choose the task to be summative.
By the close of this assignment, students should see a whole cast of characters or historical individuals who made significant impacts within a narrative, whether fictional or historical.
How do you get gifted students to analyze historical figures or literary characters in depth? Share with us below!

About Mandy Perret
Mandy Perret has taught middle and high school students for 16 years and is a mother of three children. She is the author of Challenging Common Core Language Arts Lessons: Activities and Extensions for Gifted and Advanced Learners in Grade 8. The last 10 years she has served in special education/gifted education. Her role as gifted teacher is to take learning outside the textbook and expand and enrich high school curriculum. She loves teaching the ways history connects with other subjects such as the arts and literature. She follows the philosophy that in order to help one’s students grow, the teacher must continue to learn. She holds three degrees from LSU, including an Education Specialist degree. She enjoys working with gifted students to prepare for their futures. Her motto is the words of Albert Einstein, “It is the supreme art of the teacher to awaken joy of creative expression and knowledge.”
September 26, 2018 at 12:58 am
Absolutely love this and not just for gifted students. I’m going to do it across my KS3 and try with bottom set year 10s for use with understanding the characters from An Inspector Calls. Thank you for the inspiration! Will share with colleagues and promote your book
September 26, 2018 at 9:04 am
Elaine- Thank you so much for your kind words. Having to teach multiple grade levels each year, I love lesson ideas that can be adapted for all grades and interests. I am so excited you have a plan to use the body biographies with your class text.
December 1, 2019 at 5:29 am
Just stumbled across this. I love the idea and think it would be great for both GT and regular ed kids. Looking forward to adding it into an upcoming unit. Thanks!
[…] Body Biography […]
[…] Body Biography, The human body is a wonder of intricacy and excellence, including a wide exhibit of frameworks and organs that work amicably to support life. From the complicated organization of veins to the entrancing brain associations in the cerebrum, the human body has been a subject of interest and investigation for a really long time. In this article, we dive into the spellbinding universe of the body memoir, an exceptional and convincing approach to understanding and portraying the human structure. […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Join the Conversation
- Karrie on Architecture: Discover, Dream, Design
- Kailey on Architecture: Discover, Dream, Design
- Earnestine on 5 Ways to Ignite Gifted Kids’ Curiosity
- From Objective to Assessment: Aligning Your Lesson Plans - TeachEDX on Making a PBL Mystery: Build Those Bones
- Zearlene Roberts on 5 Ways to Ignite Gifted Kids’ Curiosity
Find Your Content
How To Write An Autobiography
Autobiography Examples
11+ Autobiography Examples: A Detailed Guide

People also read
Learn How to Write an Autobiography Step by Step
Basic Types of Autobiography Writing With Examples
Simple Autobiography Format for Students to Follow
Autobiography vs. Biography vs. Memoirs: The Differences & Similarities
Autobiography vs. Memoir - Differences & Similarities
How to Write a Memoir: Everything You Need to Know
Have you ever thought about telling your life story?
An autobiography is like a special book about you – your experiences, ups, downs, and everything in between.
But when it comes to autobiography writing , putting it all into words, it can feel a bit tricky, especially for students like you.
In this blog, we're here to help you understand what an autobiography is all about and make it easier for you to write one with the help of examples.
We'll dive into practical examples and autobiography templates to help you see how it's done.
So, let's dive in!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
- 1. Memoir Vs Autobiography Example
- 2. Autobiography Outline Examples
- 3. How to Write an Autobiography - Examples
- 4. Autobiography Examples for Students
- 5. Personal Autobiography Examples
- 6. Famous Autobiography Examples
Memoir Vs Autobiography Example
Memoirs and autobiographies both delve into personal experiences, but they have their own styles and purposes.
Let’s jump into example to see what is the actual difference between memoir and autobiography:
Memoir Vs Autobiography Example PDf
Autobiography Outline Examples
Any academic or professional writing needs to follow a proper format to organize the information. And an outline is the best way to follow the proper format. It helps you organize your information and structure your data into a proper format.
Here are some autobiography outline examples to help you learn the basics of the autobiography format .
Autobiography Outline for College - Example
Autobiography Sample Outline
How to Write an Autobiography - Examples
As we have mentioned earlier, there are as many stories as there are people on earth. Each of the stories is different from the others; no two of them could be the same.
How you present your ideas really matters. That's why using the right strategies and the correct format is essential to make your writing creative.
It is important to know the difference between autobiography and biography . These examples will help you learn how to start an autobiography that leaves a good impression on the reader’s mind.
Autobiography Sample PDF
Writing an Autobiography - Example
Autobiography Examples for Students
An autobiography is your life story. If your teacher tells you to write one, they just want to hear about your life. Even if you think your story isn't super exciting, following the structure can make it work better.
These autobiography examples for students will help you understand how you can properly format the autobiography.
Autobiography Examples for Kids
School is a time of discovery, and what better way to explore your own journey than through the lens of an autobiography? Here are some great autobiography examples crafted specifically for kids.
Autobiography Examples Ks2
Autobiography Examples For Grade 7
Autobiography Examples For Class 6
Short Autobiography Example for Students
Here is a sample of a short autobiography for you. Give it a good read and learn how to write an excellent short autobiography.
Short Autobiography for Students - Example
High School Autobiography Example
Check out this sample and learn to write an incredible autobiography for high school students.
High School Autobiography - Example
Spiritual Autobiography Example for College Students
Spiritual autobiographies give a glimpse into the spiritual person's life. Have a look at the following sample spiritual autobiography and give it a good read to learn more.
Spiritual Autobiography for College Students - Example
Cultural Autobiography Examples
Here is a sample of a cultural autobiography that contains detailed information on culture. Have a look at the sample to know more about it.
Cultural Autobiography Examples
Funny Autobiography Examples
Autobiographies are thought to be boring and mundane, but that is not the case. You can make an interesting story, as well as funny. Learn to write a funny autobiography by this example.
Funny Autobiography Examples
Educational Autobiography Example
Here is a sample educational autobiography that will help you formulate an effective and inspiring autobiography.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Social Class Autobiography Example
Writing a social class or sociology assignment could be a bit difficult. This sample will help you work on yours easily.
Rambling Autobiography Examples
Rambling autobiographies are like a casual conversation with a friend, where stories unfold in their own unique way.
Let’s jump into some fascinating examples about this type of autobiography:
Personal Autobiography Examples
Personal autobiography or personal narrative essay provides a complete picture of the author’s life story. The following personal autobiography demonstrates how to write a personal narrative autobiography.
Personal Narrative Autobiography - Example
Autobiography Examples for Students About Yourself
Famous Autobiography Examples
Autobiographical essays are usually about famous people or historical figures. Just as a renowned autobiography of Benjamin Franklin tells us about his life, his unfinished records, his accomplishments, etc.
Below are some examples of famous autobiographies for your better understanding:
Famous Literacy Autobiography Example
Famous Autobiography - Sample
All in all, we have explored different examples, like understanding what makes memoirs different from autobiographies and exploring rambling ones. These examples are like guides to help you tell your own story and maybe inspire others on your writing journey.
So, go ahead, give it a try, and have fun telling your unique tale.
And if you need assistance you can always reach out to us!
Our writers can write outstanding autobiography for you! All you have to do is place your " write an essay for me " request and we'll create your custom autobiography in no time!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When a teacher assigns a biography as a writing assignment, the purpose is to have a student utilize multiple research tools to gather and to synthesize information that may be used as evidence in a written report about an individual. The evidence gained from research can include a person's words, actions, journals, reactions, related books ...
Overview. Set the stage for high-interest reading with a purpose through a biography project. Students work together to generate questions they would like to answer about several well-known people, then each student chooses one of these and finds information by reading a biography from the library and doing Internet research.
Biography Examples for Students for Artists and Musicians. Leonardo da Vinci 🎨📚 Renaissance Genius, Accomplished Artist. Frida Kahlo 🎨🌺 Mexican Painter, Symbol of Feminism and Identity. Pablo Picasso 🎨👨🎨 Modernist Painter, Co-founder of Cubism. Vincent van Gogh 🎨🌻 Post-Impressionist Painter, Starry Night.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing. While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person's life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject's life is not enough.
The biography questions listed here are designed to uncover the personal and human side of these figures, providing insights into their daily lives, relationships, and personal philosophies. Students can gain a broader perspective, going beyond the standard facts and dates to truly connect with these individuals on a more personal level.
Balance Academic and Work Experience. An academic biography primarily focuses on your credentials as a college student, including notable research papers, grades and related extracurricular activities. You can include these elements in a professional biography, but you should also discuss current and past jobs, internships and volunteer work. As with a resume, write down the most recent ...
Present the PowerPoint autobiography assignment to students and explain the required elements. If you have created a model presentation, you can use it to present the concept to students. ... In place of or in addition to PowerPoint presentations, have students write a typed autobiography, a narrated audio autobiography (set to music) on CD ...
1. Review the Definitions. Take a moment to review the definition of a biography. You can also use this time to focus on the differences and similarities between a biography and an autobiography. This leads nicely into a short discussion about word parts (auto, bio, and graph). 2. Start with a Mentor Text or Example.
6. Make a timeline of a person's life. To help you organize your research, create a timeline of a person's entire life, from birth. Draw a long line on a piece of paper and sketch out as many details about a person's life as possible. Highlight important events or moments on the timeline.
Cover Page: It's important to review the meaning of the term biography and require students to think critically about who they will research and why. Giving students room to pick the person they will research and write about is what makes this assignment student-centered. Even picking from a list of figures provides students with a sense of choice, helping them take ownership of their learning.
Student Biography Examples. 1. Growing up I was always interested in the sciences and technology. In high school, I excelled in math and science classes, which led me to pursue a degree in engineering. I went on to earn my Bachelor's degree in Engineering and am currently working on my Master's in Civil Engineering.
Teach Students to Write Biography Reports. Author: Jessica Boschen. Social Studies, Writing. Our biography unit is one of my favorite units in our classroom! This is the first time students experience an independent report, use technology, and have to synthesize information from various sources. That can be a difficult task for second graders!
requirements of the student autobiography). Day 2 -Show the class a few different examples of autobiographies and share small portions of them. -Explain that we are going to be writing autobiographies. -Hand out the worksheet "Autobiography Assignment" and discuss with students.
Part 3: Writing the Biography. Step 1: Create an assignment using the "Who Are You? (Template)" in Google Classroom; Step 2: Ask your students to write the first draft of their autobiography using the paragraph guides in the template. Step 3: When finished, ask your students to click the TURN IN button in Google Classroom. Lesson Resources
A biography is a document that details significant moments in a student's life. They give a peek into an individual's life and help readers understand something about their personality and background. Student bios are typically 150 to 200 words long. Particularly, they help students understand their academic role in light of their social ...
What You Should Do. Start with your full name followed by your current position, your general interests, and your current project, keeping them all very brief. If you are within a year of receiving a prestigious award, mention that as well. Finally, finish with a sentence that's personal: add a hobby, a pet's name, the city you live in ...
length of the biography and the number of repetitions. Procedure: 1. Read or orally summarize the biography two or three times, adapting as needed for the students' listening level. Successive summaries need not be exactly the same. 2. Give students a list of key words and phrases from the biography. 3. Ask students to work in pairs or
Our printables will enhance your lessons on reading biographies. Included are warm-ups about well-known people, creating books and auto-biographical information, and more. Use these printables to expand your students' learning about well-known people. Activities include warm-ups, reading passages, fun-fact printables, and much more.
A biography is the story of someone's life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest. A biography aims to share a person's story or highlight a ...
Unlike a biography, which is typically written by someone else, an autobiography provides a firsthand perspective, allowing the author to share their thoughts, memories, and insights. It is a cogent medium for self-expression, enabling students to convey the essence of their unique journey, impart lessons learned, and leave a lasting record of ...
A Body Biography is a way students can use images and writing to express that analytical and conceptual understanding of characters. Gifted youth are ready for the rigor of digging deep into concepts, metaphors, and high-level interpretations. This differentiated lesson activity provides a way for gifted students to get to the higher levels of ...
Famous Autobiography Examples. Autobiographical essays are usually about famous people or historical figures. Just as a renowned autobiography of Benjamin Franklin tells us about his life, his unfinished records, his accomplishments, etc. Below are some examples of famous autobiographies for your better understanding:
Editing 2nd Grade Student Biography Writing. On day 2 of this activity, my students work with dictionaries to look up the underlined/circled words. Any of the words from the previous day should be corrected/checked. Depending on your state, dictionary skills may or may not be something that your students need to possess.