How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write a powerful thesis introduction.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.

Elements of a fantastic thesis introduction
Open with a (personal) story, begin with a problem, define a clear research gap, describe the scientific relevance of the thesis, describe the societal relevance of the thesis, write down the thesis’ core claim in 1-2 sentences, support your argument with sufficient evidence, consider possible objections, address the empirical research context, give a taste of the thesis’ empirical analysis, hint at the practical implications of the research, provide a reading guide, briefly summarise all chapters to come, design a figure illustrating the thesis structure.
An introductory chapter plays an integral part in every thesis. The first chapter has to include quite a lot of information to contextualise the research. At the same time, a good thesis introduction is not too long, but clear and to the point.
A powerful thesis introduction does the following:
- It captures the reader’s attention.
- It presents a clear research gap and emphasises the thesis’ relevance.
- It provides a compelling argument.
- It previews the research findings.
- It explains the structure of the thesis.
In addition, a powerful thesis introduction is well-written, logically structured, and free of grammar and spelling errors. Reputable thesis editors can elevate the quality of your introduction to the next level. If you are in search of a trustworthy thesis or dissertation editor who upholds high-quality standards and offers efficient turnaround times, I recommend the professional thesis and dissertation editing service provided by Editage .
This list can feel quite overwhelming. However, with some easy tips and tricks, you can accomplish all these goals in your thesis introduction. (And if you struggle with finding the right wording, have a look at academic key phrases for introductions .)
Ways to capture the reader’s attention
A powerful thesis introduction should spark the reader’s interest on the first pages. A reader should be enticed to continue reading! There are three common ways to capture the reader’s attention.
An established way to capture the reader’s attention in a thesis introduction is by starting with a story. Regardless of how abstract and ‘scientific’ the actual thesis content is, it can be useful to ease the reader into the topic with a short story.
This story can be, for instance, based on one of your study participants. It can also be a very personal account of one of your own experiences, which drew you to study the thesis topic in the first place.
Start by providing data or statistics
Data and statistics are another established way to immediately draw in your reader. Especially surprising or shocking numbers can highlight the importance of a thesis topic in the first few sentences!
So if your thesis topic lends itself to being kick-started with data or statistics, you are in for a quick and easy way to write a memorable thesis introduction.
The third established way to capture the reader’s attention is by starting with the problem that underlies your thesis. It is advisable to keep the problem simple. A few sentences at the start of the chapter should suffice.
Usually, at a later stage in the introductory chapter, it is common to go more in-depth, describing the research problem (and its scientific and societal relevance) in more detail.
You may also like: Minimalist writing for a better thesis
Emphasising the thesis’ relevance
A good thesis is a relevant thesis. No one wants to read about a concept that has already been explored hundreds of times, or that no one cares about.
Of course, a thesis heavily relies on the work of other scholars. However, each thesis is – and should be – unique. If you want to write a fantastic thesis introduction, your job is to point out this uniqueness!
In academic research, a research gap signifies a research area or research question that has not been explored yet, that has been insufficiently explored, or whose insights and findings are outdated.
Every thesis needs a crystal-clear research gap. Spell it out instead of letting your reader figure out why your thesis is relevant.
* This example has been taken from an actual academic paper on toxic behaviour in online games: Liu, J. and Agur, C. (2022). “After All, They Don’t Know Me” Exploring the Psychological Mechanisms of Toxic Behavior in Online Games. Games and Culture 1–24, DOI: 10.1177/15554120221115397
The scientific relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your work in terms of advancing theoretical insights on a topic. You can think of this part as your contribution to the (international) academic literature.
Scientific relevance comes in different forms. For instance, you can critically assess a prominent theory explaining a specific phenomenon. Maybe something is missing? Or you can develop a novel framework that combines different frameworks used by other scholars. Or you can draw attention to the context-specific nature of a phenomenon that is discussed in the international literature.
The societal relevance of a thesis highlights the importance of your research in more practical terms. You can think of this part as your contribution beyond theoretical insights and academic publications.
Why are your insights useful? Who can benefit from your insights? How can your insights improve existing practices?

Formulating a compelling argument
Arguments are sets of reasons supporting an idea, which – in academia – often integrate theoretical and empirical insights. Think of an argument as an umbrella statement, or core claim. It should be no longer than one or two sentences.
Including an argument in the introduction of your thesis may seem counterintuitive. After all, the reader will be introduced to your core claim before reading all the chapters of your thesis that led you to this claim in the first place.
But rest assured: A clear argument at the start of your thesis introduction is a sign of a good thesis. It works like a movie teaser to generate interest. And it helps the reader to follow your subsequent line of argumentation.
The core claim of your thesis should be accompanied by sufficient evidence. This does not mean that you have to write 10 pages about your results at this point.
However, you do need to show the reader that your claim is credible and legitimate because of the work you have done.
A good argument already anticipates possible objections. Not everyone will agree with your core claim. Therefore, it is smart to think ahead. What criticism can you expect?
Think about reasons or opposing positions that people can come up with to disagree with your claim. Then, try to address them head-on.
Providing a captivating preview of findings
Similar to presenting a compelling argument, a fantastic thesis introduction also previews some of the findings. When reading an introduction, the reader wants to learn a bit more about the research context. Furthermore, a reader should get a taste of the type of analysis that will be conducted. And lastly, a hint at the practical implications of the findings encourages the reader to read until the end.
If you focus on a specific empirical context, make sure to provide some information about it. The empirical context could be, for instance, a country, an island, a school or city. Make sure the reader understands why you chose this context for your research, and why it fits to your research objective.
If you did all your research in a lab, this section is obviously irrelevant. However, in that case you should explain the setup of your experiment, etcetera.
The empirical part of your thesis centers around the collection and analysis of information. What information, and what evidence, did you generate? And what are some of the key findings?
For instance, you can provide a short summary of the different research methods that you used to collect data. Followed by a short overview of how you analysed this data, and some of the key findings. The reader needs to understand why your empirical analysis is worth reading.
You already highlighted the practical relevance of your thesis in the introductory chapter. However, you should also provide a preview of some of the practical implications that you will develop in your thesis based on your findings.
Presenting a crystal clear thesis structure
A fantastic thesis introduction helps the reader to understand the structure and logic of your whole thesis. This is probably the easiest part to write in a thesis introduction. However, this part can be best written at the very end, once everything else is ready.
A reading guide is an essential part in a thesis introduction! Usually, the reading guide can be found toward the end of the introductory chapter.
The reading guide basically tells the reader what to expect in the chapters to come.
In a longer thesis, such as a PhD thesis, it can be smart to provide a summary of each chapter to come. Think of a paragraph for each chapter, almost in the form of an abstract.
For shorter theses, which also have a shorter introduction, this step is not necessary.
Especially for longer theses, it tends to be a good idea to design a simple figure that illustrates the structure of your thesis. It helps the reader to better grasp the logic of your thesis.
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox!
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The most useful academic social networking sites for PhD students
10 reasons not to do a master's degree, related articles.

5 inspiring PhD thesis acknowledgement examples

The top 10 thesis defense questions (+ how to prepare strong answers)

Left your dissertation too late? Ways to take action now

Theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: Simple definitions and an overview of key differences
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
How to Write a Thesis Introduction
What types of information should you include in your introduction .
In the introduction of your thesis, you’ll be trying to do three main things, which are called Moves :
- Move 1 establish your territory (say what the topic is about)
- Move 2 establish a niche (show why there needs to be further research on your topic)
- Move 3 introduce the current research (make hypotheses; state the research questions)
Each Move has a number of stages. Depending on what you need to say in your introduction, you might use one or more stages. Table 1 provides you with a list of the most commonly occurring stages of introductions in Honours theses (colour-coded to show the Moves ). You will also find examples of Introductions, divided into stages with sample sentence extracts. Once you’ve looked at Examples 1 and 2, try the exercise that follows.
Most thesis introductions include SOME (but not all) of the stages listed below. There are variations between different Schools and between different theses, depending on the purpose of the thesis.
Stages in a thesis introduction
- state the general topic and give some background
- provide a review of the literature related to the topic
- define the terms and scope of the topic
- outline the current situation
- evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap
- identify the importance of the proposed research
- state the research problem/ questions
- state the research aims and/or research objectives
- state the hypotheses
- outline the order of information in the thesis
- outline the methodology
Example 1: Evaluation of Boron Solid Source Diffusion for High-Efficiency Silicon Solar Cells (School of Photovoltaic and Renewable Energy Engineering)
Example 2: Methods for Measuring Hepatitis C Viral Complexity (School of Biotechnology and Biological Sciences)
Note: this introduction includes the literature review.
Now that you have read example 1 and 2, what are the differences?
Example 3: The IMO Severe-Weather Criterion Applied to High-Speed Monohulls (School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering)
Example 4: The Steiner Tree Problem (School of Computer Science and Engineering)
Introduction exercise
Example 5.1 (extract 1): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.2 (extract 2): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.3
Example 5.4 (extract 4): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.5 (extract 5): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Example 5.6 (extract 6): The effects of Fluoride on the reproduction of three native Australian plant Species (School of Geography)
Well, firstly, there are many choices that you can make. You will notice that there are variations not only between the different Schools in your faculty, but also between individual theses, depending on the type of information that is being communicated. However, there are a few elements that a good Introduction should include, at the very minimum:
- Either Statement of general topic Or Background information about the topic;
- Either Identification of disadvantages of current situation Or Identification of the gap in current research;
- Identification of importance of proposed research
- Either Statement of aims Or Statement of objectives
- An Outline of the order of information in the thesis
Engineering & science
- Report writing
- Technical writing
- Writing lab reports
- Introductions
- Literature review
- Writing up results
- Discussions
- Conclusions
- Writing tools
- Case study report in (engineering)
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 7 Feb – 10 Apr 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 – 23 May 2024
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to structure a thesis
A typical thesis structure
1. abstract, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 6. discussion, 7. conclusion, 8. reference list, frequently asked questions about structuring a thesis, related articles.
Starting a thesis can be daunting. There are so many questions in the beginning:
- How do you actually start your thesis?
- How do you structure it?
- What information should the individual chapters contain?
Each educational program has different demands on your thesis structure, which is why asking directly for the requirements of your program should be a first step. However, there is not much flexibility when it comes to structuring your thesis.
Abstract : a brief overview of your entire thesis.
Literature review : an evaluation of previous research on your topic that includes a discussion of gaps in the research and how your work may fill them.
Methods : outlines the methodology that you are using in your research.
Thesis : a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis “at a glance” so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
Tip: Consider writing your abstract last, after you’ve written everything else.
The introduction to your thesis gives an overview of its basics or main points. It should answer the following questions:
- Why is the topic being studied?
- How is the topic being studied?
- What is being studied?
In answering the first question, you should know what your personal interest in this topic is and why it is relevant. Why does it matter?
To answer the "how", you should briefly explain how you are going to reach your research goal. Some prefer to answer that question in the methods chapter, but you can give a quick overview here.
And finally, you should explain "what" you are studying. You can also give background information here.
You should rewrite the introduction one last time when the writing is done to make sure it connects with your conclusion. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our thesis introduction guide .
A literature review is often part of the introduction, but it can be a separate section. It is an evaluation of previous research on the topic showing that there are gaps that your research will attempt to fill. A few tips for your literature review:
- Use a wide array of sources
- Show both sides of the coin
- Make sure to cover the classics in your field
- Present everything in a clear and structured manner
For more insights on lit reviews, take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review .
The methodology chapter outlines which methods you choose to gather data, how the data is analyzed and justifies why you chose that methodology . It shows how your choice of design and research methods is suited to answering your research question.
Make sure to also explain what the pitfalls of your approach are and how you have tried to mitigate them. Discussing where your study might come up short can give you more credibility, since it shows the reader that you are aware of its limitations.
Tip: Use graphs and tables, where appropriate, to visualize your results.
The results chapter outlines what you found out in relation to your research questions or hypotheses. It generally contains the facts of your research and does not include a lot of analysis, because that happens mostly in the discussion chapter.
Clearly visualize your results, using tables and graphs, especially when summarizing, and be consistent in your way of reporting. This means sticking to one format to help the reader evaluate and compare the data.
The discussion chapter includes your own analysis and interpretation of the data you gathered , comments on your results and explains what they mean. This is your opportunity to show that you have understood your findings and their significance.
Point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
This is probably your most important chapter. This is where you highlight that your research objectives have been achieved. You can also reiterate any limitations to your study and make suggestions for future research.
Remember to check if you have really answered all your research questions and hypotheses in this chapter. Your thesis should be tied up nicely in the conclusion and show clearly what you did, what results you got, and what you learned. Discover how to write a good conclusion in our thesis conclusion guide .
At the end of your thesis, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX:
🔲 Introduction
🔲 Literature review
🔲 Discussion
🔲 Conclusion
🔲 Reference list
The basic elements of a thesis are: Abstract, Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, and Reference List.
It's recommended to start a thesis by writing the literature review first. This way you learn more about the sources, before jumping to the discussion or any other element.
It's recommended to write the abstract of a thesis last, once everything else is done. This way you will be able to provide a complete overview of your work.
Usually, the discussion is the longest part of a thesis. In this part you are supposed to point out the limitations of your study, provide explanations for unexpected results, and note any questions that remain unanswered.
The order of the basic elements of a thesis are: 1. Abstract, 2. Introduction, 3. Literature Review, 4. Methods, 5. Results, 6. Discussion, 7. Conclusion, and 8. Reference List.

What’s Included: Introduction Template
This template covers all the core components required in the introduction chapter/section of a typical dissertation or thesis, including:
- The opening section
- Background of the research topic
- Statement of the problem
- Rationale (including the research aims, objectives, and questions)
- Scope of the study
- Significance of the study
- Structure of the document
The purpose of each section is clearly explained, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. We’ve also included practical examples to help you understand exactly what’s required, along with links to additional free resources (articles, videos, etc.) to help you along your research journey.
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
PS – if you’d like a high-level template for the entire thesis, you can we’ve got that too .
Thesis Introduction FAQS
What types of dissertations/theses can this template be used for.
The template follows the standard format for academic research projects, which means it will be suitable for the vast majority of dissertations and theses (especially those within the sciences), whether they are qualitative or quantitative in terms of design.
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the introduction chapter/section will vary between universities and degree programs. These are typically minor, but it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalize your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a dissertation, thesis or research project at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the introduction chapter to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same.
Can I share this template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, we kindly request that you reference this page as your source.
What format is the template (DOC, PDF, PPT, etc.)?
The dissertation introduction chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What is the core purpose of this chapter?
The introduction chapter of a dissertation or thesis serves to introduce the research topic, clearly state the research problem, and outline the main research questions. It justifies the significance of the study, delineates its scope, and provides a roadmap of the dissertation’s structure.
In a nutshell, the introduction chapter sets the academic tone and context, laying the foundation for the subsequent analysis and discussion.

How long should the introduction chapter be?
This depends on the level of study (undergrad, Master or Doctoral), as well as your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, introduction chapters for Masters-level projects are usually 1,500 – 2,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects can reach multiples of this.
How specific should the research objectives be in the introduction chapter?
In this chapter, your research objectives should be specific enough to clearly define the scope and direction of your study, but broad enough to encompass its overall aims.
Make sure that each objective can be realistically accomplished within the scope of your study and that each objective is directly related to and supports your research question(s).
As a rule of thumb, you should leave in-depth explanations for later chapters; the introduction should just provide a concise overview.
Can I mention the research results in the introduction?
How do i link the introduction to the literature review.
To transition smoothly from the introduction chapter to the literature review chapter in a thesis, it’s a good idea to:
- Conclude the introduction by summarising the main points, such as the research problem, objectives, and significance of your study.
- Explicitly state that the following chapter (literature review) will explore existing research and theoretical frameworks related to your topic.
- Emphasise how the literature review will address gaps or issues identified in the introduction, setting the stage for your research question or hypothesis.
- Use a sentence that acts as a bridge between the two chapters. For example, “To further understand this issue, the next chapter will critically examine the existing literature on [your topic].”
This approach will help form a logical flow and prepare the reader for the depth and context provided in the literature review.
Do you have templates for the other chapters?
Yes, we do. We are constantly developing our collection of free resources to help students complete their dissertations and theses. You can view all of our template resources here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my dissertation/thesis?
Yes, you’re welcome to get in touch with us to discuss our private coaching services .


Creating an Outline for Your Master’s Thesis
1. introduction.
Your master’s thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master’s thesis is the longest document that they’ve ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. The purpose of this CommKit is to cover a key element of writing your thesis: the outline.
2. Criteria for Success
The most important criterion for success is that you’ve shown an outline with your chapter breakdown to your advisor. Your advisor is the one that formally signs off on your thesis as completed, so their feedback is the most important.
Every master’s thesis will have the following elements.
- Introduction – Familiarize the reader with the topic and what gap exists in the field.
- Literature Review – Provide a detailed analysis of similar work in the field and how your work is unique. Master’s thesis literature reviews typically have at least 60 citations throughout the entire document
- Methods – Explain how you produced your results
- Results – Show your results and comment on their significance and implications.
- Conclusion – Summarize the methodology you used to generate results, your key findings, and any future areas of work.
Having an outline for your master’s thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different experiments or results that you completed. Furthermore, an outline for your master’s thesis can help break down the larger task of writing the entire thesis into smaller, more manageable chapter-sized subtasks.
4. Analyze Your Audience
The most important audience member for your master’s thesis is your advisor, as they are ultimately the person that signs off on whether or not your thesis is sufficient enough to graduate. The needs of any other audience members are secondary.
Ideally, a good master’s thesis is accessible to people that work in your field. In some cases, master’s theses are passed on to newer students so that that research can continue. In these cases, the thesis is used as a guide to introduce newer students to the research area. If you intend for your thesis to be used as a guide for new students, you may spend more time explaining the state of the field in your introduction and literature review. Additionally, your thesis will be posted publicly on DSpace , MIT’s digital repository for all theses.
5. Best Practices
5.1. identify your claims.
A key element to figuring out the unique structure to your master’s thesis is identifying the claims of your work. A claim is an answer to a research question or gap. Your thesis can have both a higher level claim and also lower level claims that motivate the research projects that you worked on. Identifying your claims will help you spot the key objectives which you want to highlight in the thesis. This will keep your writing on topic.
Some examples are shown below:
Gap/Question : There are no field-portable microplastic sensing technologies to measure their distribution in the environment.
→ Claim : Impedance spectroscopy can be used in a microfluidic device to rapidly distinguish organic matter from polymers.
Gap/Question: How effective are convolutional neural networks for pose estimation during in-space assembly?
→ Claim : Convolutional neural networks can be used to estimate the pose of satellites, but struggle with oversaturated images and images with multiple satellites.
5.2. Support Your Claims
Once you have identified your claim, the next step is to identify evidence that will support it. The structure of your paper will be very dependent on the claim that you make. Figure 1 and 2 demonstrate two different structures to support a claim. In one outline, the claim is best supported by a linear structure that describes the building, testing, and validation of a model. In another outline, the claim is best supported by a trifold structure, where three independent methods are discussed. Depending on the extent of the evidence, you could break this trifold structure into 3 separate chapters, or they could all be discussed in a singular chapter. The value of identifying claims and evidence is that it helps you organize your paper coherently at a high level. The number of chapters that are output as a result of your claim identification is up to you and what you think would be sufficient discussion for a chapter within your thesis.
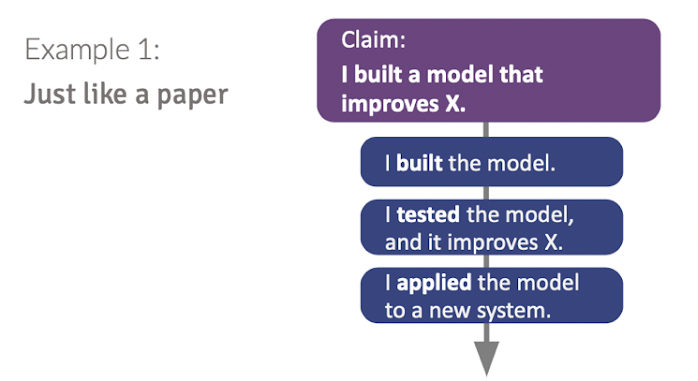
5.3. Connect the Evidence to Your Claims with Reasoning
One common mistake that students make when writing their thesis is treating each chapter as an isolated piece of writing. While it is helpful to break down the actual task of thesis writing into chapter-size pieces, these chapters should have some connection to one another. For your outline, it is ideal to identify what these connections were. Perhaps what made you start on one project was that you realized the weaknesses in your prior work and you wanted to make improvements. For readers who were not doing the research with you, describing the connections between your work in different chapters can help them understand the motivation and value of why you pursued each component.
5.4. Combine Your Claims, Evidence, and Reasoning to Produce Your Outline
Once you have identified your claims, the evidence you have surrounding each claim, and the reasoning that connects each piece of your work, you can now create your full outline, putting the pieces together like a jigsaw puzzle. An example outline is provided as an annotated example.
There are no requirements for minimum or maximum number of chapters that your master’s thesis can have. Therefore, when translating your outline to a literal chapter breakdown, you should feel free to use as many chapters as needed. If your methods section for a claim is extremely long, it may make more sense to have it be a standalone chapter, as shown in the attached annotated pdf.
6. Additional Resources
Every IAP, the Comm Lab hosts a workshop on how to write your master’s thesis. This workshop provides tips for writing each of these sections, and steps you through the process of creating an outline.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Example 1. structure diagram and table of contents, example 2. table of contents.
- Structuring your thesis
- Information and services
- Higher Degree by Research
- HDR candidature support
- How to write a thesis
The best structure for your HDR thesis will depend on your discipline and the research you aim to communicate.
Before you begin writing your thesis, make sure you've read our advice on thesis preparation for information on the requirements you'll need to meet.
Once you've done this, you can begin to think about how to structure your thesis. To help you get started, we've outlined a basic structure below, but the requirements for your discipline may be different .
If you need help determining a suitable structure:
- read other theses in your discipline – you can search for UQ theses on the Library website. For prime examples, search for theses that received commendations from their examiners
- check with your advisor.
A basic thesis structure includes the following sections:
Introduction and literature review
Results or findings.
An abstract is a summary of your entire thesis and should provide a complete overview of the thesis, including your key results and findings.
An abstract is different to your introduction, and shouldn't be used to advertise your thesis — it should provide enough information to allow readers to understand what they'll learn by reading the thesis.
Your abstract should answer the following questions:
- What did you do?
- How did you do it?
- Why was it worth doing?
- What were the key results?
- What are the implications or significance of the results?
As your abstract will have a word limit, you may be unable to answer every question in detail. If you find yourself running out of words, make sure you include your key findings before other information.
All theses require introductions and literature reviews, but the structure and location of these can vary.
In some cases, your literature review will be incorporated into the introduction. You may also review literature in other parts of your thesis, such as in the methods section.
Other options for structuring an introduction and literature review include:
- a brief introductory chapter with a longer, separate literature review chapter
- a long introductory chapter with a brief introductory section followed by literature review sections
- a brief introductory chapter with detailed literature reviews relevant to the topic of each chapter provided separately in each chapter — this is common in a thesis comprised of publications.
If you have a separate introduction and literature review, they should complement, not repeat, each other.
The introduction should outline the background and significance of the broad area of study, as well as your:
- general aims – what you intend to contribute to the understanding of a topic
- specific objectives – which particular aspects of that topic you'll be investigating
- the rationale for proceeding in the way that you did
- your motivation or the justification for your research – the level of detail can vary depending on how much detail you will be including in a literature review.
The literature review should provide a more detailed analysis of research in the field, and present more specific aims or hypotheses for your research. What's expected for a literature review varies depending on your:
- program – a PhD thesis requires a more extensive literature review than an MPhil thesis
- discipline – analyse well-written examples from your discipline to learn the conventions for content and structure.
To get some ideas about how to structure and integrate your literature review, look at how to write a literature review and an example analysis of a literature review , or talk to your advisor.
A possible structure for your methods section is to include an introduction that provides a justification and explanation of the methodological approach you chose, followed by relevant sub-sections. Some standard sub-sections of a methods chapter include:
- Participants
- Procedures.
How the methods section is structured can depend on your discipline, so review other theses from your discipline for ideas for structure.
Regardless of structure, the methods section should explain:
- how you collected and analysed your data – you only need to include enough detail that another expert in the field could repeat what you've done (you don't have to detail field standard techniques or tests)
- why you chose to collect specific data
- how this data will help you to answer your research questions
- why you chose the approach you went with.
You may want to present your results separately to your discussion. If so, use the results section to:
- specify the data you collected and how it was were prepared for analysis
- describe the data analysis (e.g. define the type of statistical test that was applied to the data)
- describe the outcome of the analysis
- present a summary and descriptive statistics in a table or graph.
Use tables and figures effectively
Reports usually include tables, graphs and other graphics to present data and supplement the text. To learn how to design and use these elements effectively, see our guides to:
- incorporating tables, figures, statistics and equations (PDF, 1.2MB)
- graphic presentation (PDF, 2.9MB) .
Use the discussion section to:
- comment on your results and explain what they mean
- compare, contrast and relate your results back to theory or the findings of other studies
- identify and explain any unexpected results
- identify any limitations to your research and any questions that your research was unable to answer
- discuss the significance or implications of your results.
If you find that your research ends up in a different direction to what you intended, it can help to explicitly acknowledge this and explain why in this section.
Use the conclusion section to:
- emphasise that you've met your research aims
- summarise the main findings of your research
- restate the limitations of your research and make suggestions for further research.
In some cases, the discussion and conclusion sections can be combined. Check with your advisor if you want to combine these sections.
- Thesis writing tips
Learning Advisers
Our advisers can help undergraduate and postgraduate students in all programs clarify ideas from workshops, help you develop skills and give feedback on assignments.
How a Learning Adviser can help
Further support
Writing a clear and engaging research paper Thesis and dissertation writing: an examination of published advice and actual practice Scientific writing
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
The thesis introduction, usually chapter 1, is one of the most important chapters of a thesis. It sets the scene. It previews key arguments and findings. And it helps the reader to understand the structure of the thesis. In short, a lot is riding on this first chapter. With the following tips, you can write
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
Stages in a thesis introduction. state the general topic and give some background. provide a review of the literature related to the topic. define the terms and scope of the topic. outline the current situation. evaluate the current situation (advantages/ disadvantages) and identify the gap. identify the importance of the proposed research.
2. Hook the reader and grab their attention. 3. Provide relevant background. 4. Give the reader a sense of what the paper is about. 5. Preview key points and lead into your thesis statement. Frequently Asked Questions about writing a good thesis introduction.
Not sure where to start with your Introduction chapter? Don't worry, you soon will!
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
The introduction should describe and clarify the context of the research question, existing knowledge/previous research and the thesis research question. A delimitation of the area of study is an important part of the introduction. Describe the field / context in which the thesis' research question unfolds: You may picture the
2.2. Structure of the thesis The structure of a thesis mainly depends on the topic of choice and whether it is theoretical or empirical. However, these parts are generally included. Title/cover page Acknowledgements (optional) Index Introduction Chapter 1: Literature review Chapter 2: Methodology and research method (for an empirical thesis)
Answer: Generally, the chapter titles in a thesis are formatted as follows: Chapter X: Name of the chapter. You can choose to name the first chapter "Introduction" or something more imaginative if you feel like, depending on what is the norm in your field. However, if you choose to use more creative names, make sure they are not very informal.
A typical thesis structure. 1. Abstract. The abstract is the overview of your thesis and generally very short. This section should highlight the main contents of your thesis "at a glance" so that someone who is curious about your work can get the gist quickly. Take a look at our guide on how to write an abstract for more info.
To put your results into context and reach conclusions. Formulate conclusions and interpret them in the light of known information. Generalize conclusions into what is it we learned. Make sure that what you have learned is indeed an answer to the question posed in the introduction. Thoughts on applied relevance/the future.
It's helpful to start here by going over the structure of a master's thesis. The precise way that different master's theses are structured is largely going to depend on the discipline area. But most of the time, empirical dissertations follow a format including: Abstract; Table of contents; List of tables/figures; Introduction; Literature ...
This template covers all the core components required in the introduction chapter/section of a typical dissertation or thesis, including: The opening section. Background of the research topic. Statement of the problem. Rationale (including the research aims, objectives, and questions) Scope of the study. Significance of the study.
In engineering, although research article and master's thesis introductions show similarities in structure, the master's theses (Fig. 1) can require two additional elements: Move 3 (Proposing a New Approach) and Move 4-3 (Thesis Scope). Master's Introduction Chapters in Engineering (MICE) MOVE 1 CURRENT SITUATION (compulsory)
Introduction. Your master's thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master's thesis is the longest document that they've ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. ... The structure of your paper will be very dependent on the claim that ...
Structuring your thesis. The best structure for your HDR thesis will depend on your discipline and the research you aim to communicate. Before you begin writing your thesis, make sure you've read our advice on thesis preparation for information on the requirements you'll need to meet. Once you've done this, you can begin to think about how to ...
My question is not about the structure of an entire thesis, but just about the Introduction chapter. At the moment, it consists of the following sections: Objective [where I briefly introduce the aim of my thesis] Area of Research [where my thesis collocates in a more general pipeline] Conclusion [where I very briefly summarize the content of ...
Step 1: Start with a question. You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis, early in the writing process. As soon as you've decided on your essay topic, you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.