- Applying to Uni
- Apprenticeships
- Health & Relationships
- Money & Finance
Personal Statements
- Postgraduate
- U.S Universities
University Interviews
- Vocational Qualifications
- Accommodation
- Budgeting, Money & Finance
- Health & Relationships
- Jobs & Careers
- Socialising
Studying Abroad
- Studying & Revision
- Technology
- University & College Admissions
Guide to GCSE Results Day
Finding a job after school or college
Retaking GCSEs

In this section
Choosing GCSE Subjects
Post-GCSE Options
GCSE Work Experience
GCSE Revision Tips
Why take an Apprenticeship?
Applying for an Apprenticeship
Apprenticeships Interviews
Apprenticeship Wage
Engineering Apprenticeships
What is an Apprenticeship?
Choosing an Apprenticeship
Real Life Apprentices
Degree Apprenticeships
Higher Apprenticeships
A Level Results Day 2024
AS Levels 2024
Clearing Guide 2024
Applying to University
SQA Results Day Guide 2024
BTEC Results Day Guide
Vocational Qualifications Guide
Sixth Form or College
International Baccalaureate
Post 18 options
Finding a Job
Should I take a Gap Year?
Travel Planning
Volunteering
Gap Year Guide
Gap Year Blogs
Applying to Oxbridge
Applying to US Universities
Choosing a Degree
Choosing a University or College
Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
Guide to Freshers' Week
Student Guides
Student Cooking
Student Blogs
- Top Rated Personal Statements
Personal Statement Examples
Writing Your Personal Statement
- Postgraduate Personal Statements
- International Student Personal Statements
- Gap Year Personal Statements
Personal Statement Length Checker
Personal Statement Examples By University
Personal Statement Changes 2025
Personal Statement Template
Job Interviews
Types of Postgraduate Course
Writing a Postgraduate Personal Statement
Postgraduate Funding
Postgraduate Study
Internships
Choosing A College
Ivy League Universities
Common App Essay Examples
Universal College Application Guide
How To Write A College Admissions Essay
College Rankings
Admissions Tests
Fees & Funding
Scholarships
Budgeting For College
Online Degree
Platinum Express Editing and Review Service
Gold Editing and Review Service
Silver Express Editing and Review Service
UCAS Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
Oxbridge Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
Postgraduate Personal Statement Editing and Review Service
You are here
- Mature Student Personal Statements
- Personal Statements By University
- Accountancy and Finance Personal Statements
- Actuarial Science Personal Statements
- American Studies Personal Statements
- Anthropology Personal Statements
- Archaeology Personal Statements
- Architecture Personal Statements
- Art and Design Personal Statements
- Biochemistry Personal Statements
- Bioengineering Personal Statements
- Biology Personal Statements
- Biomedical Science Personal Statements
- Biotechnology Personal Statements
- Business Management Personal Statement Examples
- Business Personal Statements
- Catering and Food Personal Statements
- Chemistry Personal Statements
- Classics Personal Statements
- Computer Science Personal Statements
- Computing and IT Personal Statements
- Criminology Personal Statements
- Dance Personal Statements
- Dentistry Personal Statements
- Design Personal Statements
- Dietetics Personal Statements
- Drama Personal Statements
- Economics Personal Statement Examples
- Education Personal Statements
- Engineering Personal Statement Examples
- English Personal Statements
- Environment Personal Statements
- Environmental Science Personal Statements
- Event Management Personal Statements
- Fashion Personal Statements
- Film Personal Statements
- Finance Personal Statements
- Forensic Science Personal Statements
- Geography Personal Statements
- Geology Personal Statements
- Health Sciences Personal Statements
- History Personal Statements
- History of Art Personal Statements
- Hotel Management Personal Statements
- International Relations Personal Statements
- International Studies Personal Statements
- Islamic Studies Personal Statements
- Japanese Studies Personal Statements
- Journalism Personal Statements
- Land Economy Personal Statements
- Languages Personal Statements
- Law Personal Statement Examples
- Linguistics Personal Statements
- Management Personal Statements
- Marketing Personal Statements
- Mathematics Personal Statements
- Media Personal Statements
- Medicine Personal Statement Examples
- Midwifery Personal Statements
- Music Personal Statements
- Music Technology Personal Statements
- Natural Sciences Personal Statements
- Neuroscience Personal Statements
- Nursing Personal Statements
- Occupational Therapy Personal Statements
- Osteopathy Personal Statements
- Oxbridge Personal Statements
- Pharmacy Personal Statements
- Philosophy Personal Statements
- Photography Personal Statements
- Physics Personal Statements
- Physiology Personal Statements
- Physiotherapy Personal Statements
- Politics Personal Statements
- Psychology Personal Statement Examples
- Radiography Personal Statements
- Religious Studies Personal Statements
- Social Work Personal Statements
- Sociology Personal Statements
- Sports & Leisure Personal Statements
- Sports Science Personal Statements
- Surveying Personal Statements
- Teacher Training Personal Statements
- Theology Personal Statements
- Travel and Tourism Personal Statements
- Urban Planning Personal Statements
- Veterinary Science Personal Statements
- Zoology Personal Statements
- Personal Statement Editing Service
- Personal Statement Writing Guide
- Submit Your Personal Statement
- Personal Statement Questions 2025
- Personal Statement Changes 2024
Art and Design Personal Statement Examples

Related resources
Personal statement mistakes.

Find out more
Choosing A Student Bank Account


Guidance from our top admission experts — for free!

- Admit Finder
Discover Past Admits, Gauge Your Chances!
- Shortlist Builder
Personalized University Picks, Just a Click Away.
- Course Finder
Navigate Global Courses Tailored for You
- Scholarship Finder
Unlock Funding Opportunities Worldwide.

Get tailored study abroad advice.

Sign in for exclusive content!

Love what you're reading?

Sign in to dive deeper with exclusive content, expert advice, and personalized tips that enhance your study abroad knowledge.

29 September 2023
6 minutes read
Artist Statement of Purpose Examples: Crafting Your Fine Art Personal Statement
When it comes to pursuing a career in fine art, a well-crafted artist statement of purpose can be your ticket to success. Whether you’re applying for an MFA, BFA, or a position in the art world, your personal statement holds the key to showcasing your passion, creativity, and dedication.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dive deep into artist statement of purpose examples, helping you understand how to articulate your love for art effectively and create a compelling personal statement.

Start Your University Applications with Ambitio Pro!
Get Ambitio Pro!
Begin your journey to top universities with Ambitio Pro. Our premium platform offers you the tools and support needed to craft standout applications.
Unlock Advanced Features for a More Comprehensive Application Experience!

Start your Journey today
- The Importance of a Personal Statement
Your personal statement, often interchangeably referred to as a statement of purpose (SOP), is your opportunity to tell your unique story as an artist. It allows admissions committees or potential employers to get to know you beyond your portfolio or resume.
Your personal statement should convey your artistic journey, influences, experiences, and future aspirations. It’s a chance to make a lasting impression and demonstrate why you are a perfect fit for your chosen fine art program or career in the art world.
- Crafting a Captivating Introduction
Personal Statement
Your personal statement should begin with a captivating introduction that immediately grabs the reader’s attention. Think of it as the opening scene in a captivating movie. Here’s an example:
“Art has always been my muse, guiding my life’s path towards creative expression. From the moment I held a paintbrush, I knew that art was more than just colors on a canvas; it was a form of storytelling, a means to connect with the world and express the deepest facets of my being.”
Expressing Your Love for Fine Art
Your introduction should convey your deep-seated love for fine art. You can talk about when and how your passion for art first ignited. Maybe it was a childhood memory of visiting an art museum, or perhaps you had an inspiring art teacher who encouraged your creativity. Sharing this personal connection with art can draw readers into your narrative.
Defining Your Artistic Identity
In the introduction, you should also touch upon what makes your artistic identity unique. What sets you apart as an artist? Do you have a signature style, technique, or theme that defines your work? This is the time to provide a glimpse into what makes your art special.
- Sharing Concrete Examples of Your Work and Experiences
Statement Examples
Once you’ve captured your reader’s attention with a compelling introduction, it’s time to delve into the heart of your personal statement by sharing concrete examples of your work and experiences. This section should showcase your artistic journey and demonstrate your dedication to your craft.
Highlighting Artistic Milestones
In this section, you can mention significant milestones in your artistic journey. These could include exhibitions, awards, or collaborations that have shaped your development as an artist. For instance:
“Over the years, I have had the privilege of showcasing my work in prestigious galleries and museums, such as the Tate Modern in London. These opportunities not only exposed my art to a wider audience but also pushed me to constantly evolve as an artist.”
By highlighting these achievements, you demonstrate your commitment to your art and your ability to thrive in the competitive art world.
Discussing Artistic Influences
Artists are often inspired by the work of others. Share the artists or artworks that have influenced your creative process. You might mention famous painters, sculptors, or contemporary artists whose work resonates with you. Explaining how these influences have shaped your artistic perspective can provide insight into your unique approach to art.
Detailing Your Educational Background
If you’ve pursued formal education in fine art, whether it’s an undergraduate degree, a BFA, or an MFA, this is the place to discuss it. Talk about your academic journey, the courses that had a profound impact on you, and any mentors who guided your artistic growth. Be sure to convey how your education has contributed to your development as an artist.
- Exploring Specific Interests and Influences
Art and Design Personal Statement
Art is a vast and diverse field, and this section allows you to explore your specific interests and influences in greater detail. Whether you’re passionate about painting, sculpture, graphic design, or any other art form, here’s where you can delve into the heart of your creative focus.
Passion for a Specific Art Form
Share your deep-seated passion for your chosen art form. Explain why you are drawn to it and how it allows you to express yourself. For example:
“My fascination with seascapes and the fragility of nature has been a recurring theme in my work. It’s a subject that allows me to explore the vastness and immensity of the natural world while conveying its fragility.”
Artistic Inspirations
Discuss the artists or movements that have had a profound impact on your work within your chosen art form. Whether it’s the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock or the precision of Renaissance art, detailing these influences adds depth to your personal statement.
Your Creative Process
Take the reader on a journey through your creative process. How do you approach your work? Do you start with sketches, embrace spontaneity, or meticulously plan each piece? Sharing your process can provide insight into your artistic mindset.
- Articulating Your Goals and Aspirations
Fine Art Personal Statement
Your personal statement should not only reflect on your past but also look to the future. What are your artistic goals and aspirations? Where do you see yourself in the art world? This section allows you to articulate your vision and ambition as an artist.
Short-Term Goals
Discuss your immediate goals within the art world. Whether it’s participating in specific exhibitions, collaborating with fellow artists, or mastering a new technique, these short-term objectives reveal your drive and commitment.
Long-Term Aspirations
Take a broader view and share your long-term aspirations. Do you dream of curating your own gallery, teaching art to the next generation, or becoming an internationally recognized artist? Expressing these ambitions paints a vivid picture of your future in the art world.
Why This Program or Career?
If you’re applying to a specific program, be it an MFA or a job opportunity, explain why it’s the perfect fit for your artistic journey. Mention how the program’s curriculum, faculty, or mission align with your goals.
- Tailoring Your Statement for MFA and BFA Applications
MFA and BFA
Depending on whether you’re applying for a Master of Fine Arts (MFA) or a Bachelor of Fine Arts (BFA) program, there are specific elements to emphasize in your personal statement.
MFA Program Emphasis
For MFA applicants, emphasize your commitment to furthering your craft and the advanced level of artistry you bring to the table. Discuss your readiness for the intensive program and your eagerness to engage in critical discourse with fellow artists.
“Enrolling in the MFA program at [University Name] is a natural step in my journey to become a professional artist. I am ready to immerse myself in a community of dedicated artists, engage in rigorous critiques, and push the boundaries of my creative practice.”
BFA Program Emphasis
Similarly, BFA applicants should convey their passion and readiness to embark on their educational journey. Highlight your enthusiasm for learning and your willingness to explore various aspects of fine art.
“I am eager to embark on the BFA program, where I can continue to refine my graphic design and photography skills. This program’s focus on nurturing emerging artists aligns perfectly with my goals of honing my craft and exploring new artistic horizons.”
- Showcasing Your Love for Art History
Art History
For those with a passion for art history, your personal statement should reflect your deep love for the subject and your desire to explore its intricacies.
Unearthing Art Historical Insights
Share your favorite periods, artists, or art movements within the scope of art history. Discuss why you find these aspects particularly fascinating and how they have influenced your perspective.
“Art history has been my guiding light in understanding the evolution of artistic expression. I am particularly captivated by the Romantic period and its emphasis on emotion, individualism, and nature, as seen in the works of artists like Caspar David Friedrich.”
Academic Pursuits
If you’re applying for graduate studies in art history, discuss your academic interests and the areas of art history you wish to explore further. Mention any research projects, papers, or presentations that showcase your dedication to the field.
“ During my undergraduate studies, I delved into the complexities of American art history. My thesis on the impact of Abstract Expressionism on post-war American society was a testament to my commitment to scholarly pursuits in this field .”
- Conclusion: Crafting Your Artistic Narrative
Crafting a compelling artist statement of purpose is an art form in itself. By drawing inspiration from these examples and infusing your personal experiences, you can create a statement that reflects your passion for fine art.
Remember, your personal statement is your opportunity to shine and convey why you are a perfect fit for your chosen fine art program or career in the art world.
In closing, let your personal statement be a testament to your love for art and your unwavering commitment to the world of creativity. Use it as a canvas to paint your story, one brushstroke at a time, and let your passion shine through every word. Your artistic journey begins with your statement of purpose, so make it a masterpiece.
With this comprehensive guide, you now have the tools and inspiration to craft a personal statement that leaves a lasting impression and sets you on a path toward success in the world of fine art. Embrace your creativity, share your story, and let your love for art guide you on this incredible artistic journey.
What should I include in my artist statement of purpose?
Your statement should cover your artistic journey, influences, experiences, and future aspirations. Use concrete examples to illustrate your passion for fine art.
How long should my personal statement be?
Aim for a concise statement, typically around 500-800 words. Be sure to follow any specific word limit guidelines provided by the institution or program.
Can I use samples of my work in my statement?
Absolutely! Including images or descriptions of your work can add depth to your statement and showcase your artistic abilities.
Should I mention specific artists or artworks that inspire me?
Yes, mentioning artists or artworks that have influenced you can provide insight into your artistic perspective and passion.
How important is the artist statement in the application process?
Your personal statement is a crucial component of your application. It allows admissions committees to understand your unique voice, passion, and suitability for their program.
Spread the Word!
Share across your social media if you found it helpful

Table of Contents
- • The Importance of a Personal Statement
- • Crafting a Captivating Introduction
- • Sharing Concrete Examples of Your Work and Experiences
- • Exploring Specific Interests and Influences
- • Articulating Your Goals and Aspirations
- • Tailoring Your Statement for MFA and BFA Applications
- • Showcasing Your Love for Art History
- • Conclusion: Crafting Your Artistic Narrative

Recent Blogs

How to Write a Successful Statement of Purpose: A Comprehensive Guide

How to Write a Statement of Purpose for Early Childhood Education

Crafting Your Economics Personal Statement: Expert Tips from the Student Room with a Focus on Cambridge and LSE
Let us make sure you get into the best.
Phone Number
eg. Fall 2024
- 2024 Winter
- 2024 Spring
- 2024 Summer
Enter verification code
Code was sent to
Resend OTP (30s)

- Our Experts
Connect with us on our social media
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
Unique & Better Art Foundation Personal Statement Example
Table of Contents
When considering a career in the arts, it’s essential to have a well-crafted personal statement to show off your talent and passion. A strong personal statement can set you apart from other applicants and increase your chances of acceptance into your coveted art school. Creating a personal statement that stands out takes time and effort. But a well-written art foundation personal statement example can help organize your thoughts and get you on the right track.
This article will list practical tips to help you write a compelling personal statement and provide an example for inspiration.
What Is an Art Foundation Personal Statement?
An art foundation personal statement is a writing sample that demonstrates your creative and intellectual potential in the field of visual arts. Other personal statements focus on extracurricular experiences or academic achievements. But an art foundation personal statement highlights your aptitude for making and responding to artwork.
Besides showcasing your critical thinking skills and artistic inclinations, a successful statement reflects your interest in the particular program to which you are applying. As such, it is important to research each school’s curriculum before beginning work on your essay.
How to Write a Great Art Foundation Personal Statement
When writing an art foundation personal statement , be sure to keep the following in mind:
- Start by introducing yourself and your art practice. Write a brief description of your artistic inspirations.
- Outline why you’re interested in studying art foundation . Explain what you hope to gain from it and how it will help you achieve your artistic goals.
- Demonstrate your creative skills . Explain how they have developed over time through specific examples of past artwork or projects related to the art foundation studies field.
- Discuss any significant achievements or awards you may have earned related to your art practice. Mention any other noteworthy experiences or encounters that have influenced your work as an artist/designer.
- Finish with a strong statement about why you believe that an art foundation course is the right next step for you. Stress all of the reasons why attending this particular program is essential for achieving your future artistic aspirations.

Art Foundation Personal Statement Example
Here’s an art foundation personal statement example to use as inspiration when writing one for your own. This example has been generated by the amazing AI-powered Hey INK tool.
Art and Design Personal Statement Example
As long as I can remember, art has been a critical part of my life. From the crayon drawings that adorned our refrigerator to the elaborate paintings and sculptures that lined our home, art was always around me. It wasn’t until high school that I was first introduced to design principles. I had the first formal art class, where I truly began to appreciate creation in all its forms.
Since then, I’ve made it a point not just to consume but also to create artwork myself. Whether it’s through painting portraits or composing music compositions, photography or film-making, apparel design or architecture—I love diving into any creative endeavor headfirst. What excites me most about these mediums is how they’re constantly evolving and provide seemingly infinite possibilities for exploration.
One of the things that initially drew me towards studying graphic design specifically is how this field marries creativity with functionality. There’s something so inherently gratifying about solving problems through visual communication. To be able to take something from an idea in my mind and see it manifested physically on paper (or screen) is incredibly fulfilling. And being surrounded by like-minded people who share this passion makes San Francisco State feel like a home away from home.
With my background and passion for art, I feel well-equipped to study Fine Arts at the university level. Moreover, I believe that my skill set goes beyond mere artistic talent. I am confident that I possess key qualities such as creativity, dedication, and perseverance – qualities that are essential for any successful artist or designer.
A strong Art Foundation personal statement is the key to cracking your dream university. Those brave few who succeeded in getting into the prestigious institution of their choice have one thing in common: a stellar personal statement. Use the tips in this post and the personal statement example to write a compelling statement that secures a position in a competitive institution.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Write Personal Statement Articles
How to draft meaningful length of law school personal statement.
Are you confused on how to write a law school personal statement? One of the essential elements of your application…
- Write Personal Statement
Effective History and International Relations Personal Statement to Try
Are you considering studying history and international relations? Or you may be curious about what a degree in this field…
Guide to Quality Global Management Personal Statement
Are you applying for a global management program and want to stand out from the crowd? A well-written personal statement…
How to Draft Better Examples of Personal Statements for Residency
Achieving a residency can be a massive accomplishment for any aspiring medical professional. To secure your spot in one of…
Tips for Drafting a Free Example of Personal History Statement
A personal history statement can be crucial to many applications, from university admissions to job search processes. This blog will…
Writing Compelling Dietetic Internship Personal Statement
Applying for a dietetic internship is a rigorous process and requires submitting a personal statement, which is an essential part…
How to Write a Personal Statement for a Foundation Art Course
When applying for a foundation art course, writing a personal statement is an important part of your application. This statement is your opportunity to showcase your creativity and passion for art, as well as demonstrate why you are a suitable candidate for the course. Since foundation courses often lead on to University, this is a great opportunity to fine tune your personal statement writing skills, it can also help identify areas of art you may need more training in.
In this post, we will provide 6 tips and guidelines on how to write a personal statement that will help you stand out and increase your chances of being accepted into a Foundation Art course.
6 tips for writing a personal statement - for an Art Foundation course
Understand the purpose of a personal statement, research the course and school, be specific, show your commitment to art.
- Be unique
Proofread and edit
A personal statement is a written document that highlights your experiences, achievements, and goals - both academic and extra-curricular. It is a perfect opportunity for you to demonstrate to the course provider why you are a good fit for the program and how you will contribute to the school's artistic community. Your personal statement should be unique and reflect your personality and interests.
Ideally, your personal statement will be around 70% on why you would be a good student for the school to take on and why you want to study Foundation Art. The remaining 30% should focus on who you are and what you have done outside of school and academia, such as community art projects.
Before you start writing your personal statement, spend some time researching the Foundation Art course and the school you are applying to. It's easy for admissions staff to spot who has researched and who hasn't, so spend a healthy amount of time on this.
Ensure you have a deep understanding of the course curriculum, the school's mission and values, and the type of students they are looking for. This information will help you tailor your personal statement and identify which of your achievements and qualifications will be best to mention in your personal statement.
When writing your personal statement for a foundation art course, it's important to be specific and avoid generic phrases. Specifics will make you more memorable to the admissions committee and showcase your genuine passion for the subject.
To demonstrate your commitment to art, try to include specific examples of your experiences and achievements. For example, if you have taken art classes or workshops, discuss the specific techniques you learned and how they impacted your artistic style.
Highlighting your unique qualities and experiences will make your personal statement stand out and show the school why you would be a valuable student to have onboard. Additionally, you should consider including your portfolio and any awards or exhibitions you have participated to further demonstrate your dedication to art.
The school wants to see that you are committed to the subject and have a genuine passion for art. Be sure to show them how you have pursued your interests outside the classroom. For example, if you have a portfolio of your artwork, mention it and describe the process of creating your pieces. If you have won any art competitions or have been featured in any exhibitions, mention them as well. This will demonstrate your dedication and commitment to the subject and show the admissions team that you have a deep understanding and passion for art.
Your personal statement should be a reflection of who you are as an individual and an artist, as well as how you want to grow as an artist. Avoid using generic phrases or clichés, focus on showcasing your unique qualities and experiences. Use your specific skills to tell the school why you are the best candidate for an Art Foundation diploma.
Being unique and genuine will make your personal statement stand out, making you more memorable to the school admissions team.
Read, read and read again.
You may be thinking “this is an Art course, why is writing important” but not checking your work for spelling or grammar errors massively reflects on your attention to care, and this will be noticed by the admissions team.
Before submitting your personal statement, spend some time proofreading and editing. Check for spelling and grammatical errors, and make sure your statement is clear and concise. It's important to include relevant information, but try not to bore the reader.
It's also a good idea to have a friend or family member read over it to get a second opinion. Your statement should be polished and professional, as it is a representation of your abilities as an artist and potential student.
Writing a personal statement for a Foundation Art course is an important aspect of the application process, and provides you valuable experience for the future. It provides the admissions committee with a glimpse into your passion and dedication to art, and allows you to showcase your unique qualities and experiences.
Remember, your personal statement should reflect who you are and where you want to go. It should showcase your passion and commitment for art and, if possible, include your real world artistic experiences.
A well-written personal statement can massively increase your chances of being accepted into the course of your choice and continue down the path towards your dream artistic career.
Writing a strong personal statement requires time and effort, but it is well worth it. Following our tips, will help you write a personal statement that stand-out, making you a competitive candidate for a Foundation Art course.
Get your Foundation Art Diploma with OCAD
Study Foundation Art with the Online College of Art and Design (OCAD) and delve into the artistic world.
Our Foundation Art course opens the door to top universities and top employment. With a variety of project pathways you can explore the art disciplines which most suit you and your skills.
Get in touch today!
Newer Post >
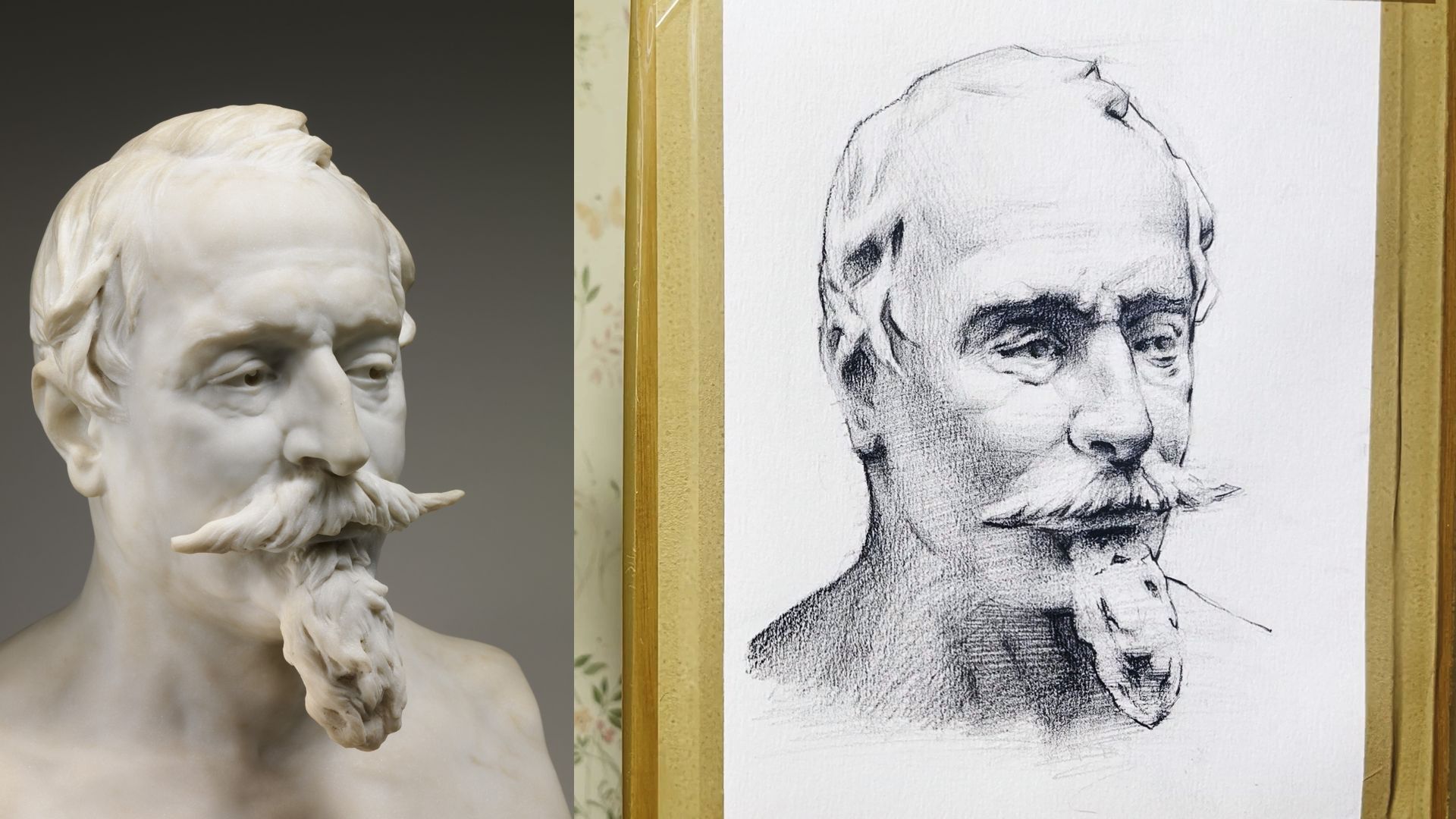

Detailed Study of a Portrait Sculpture in Pencil
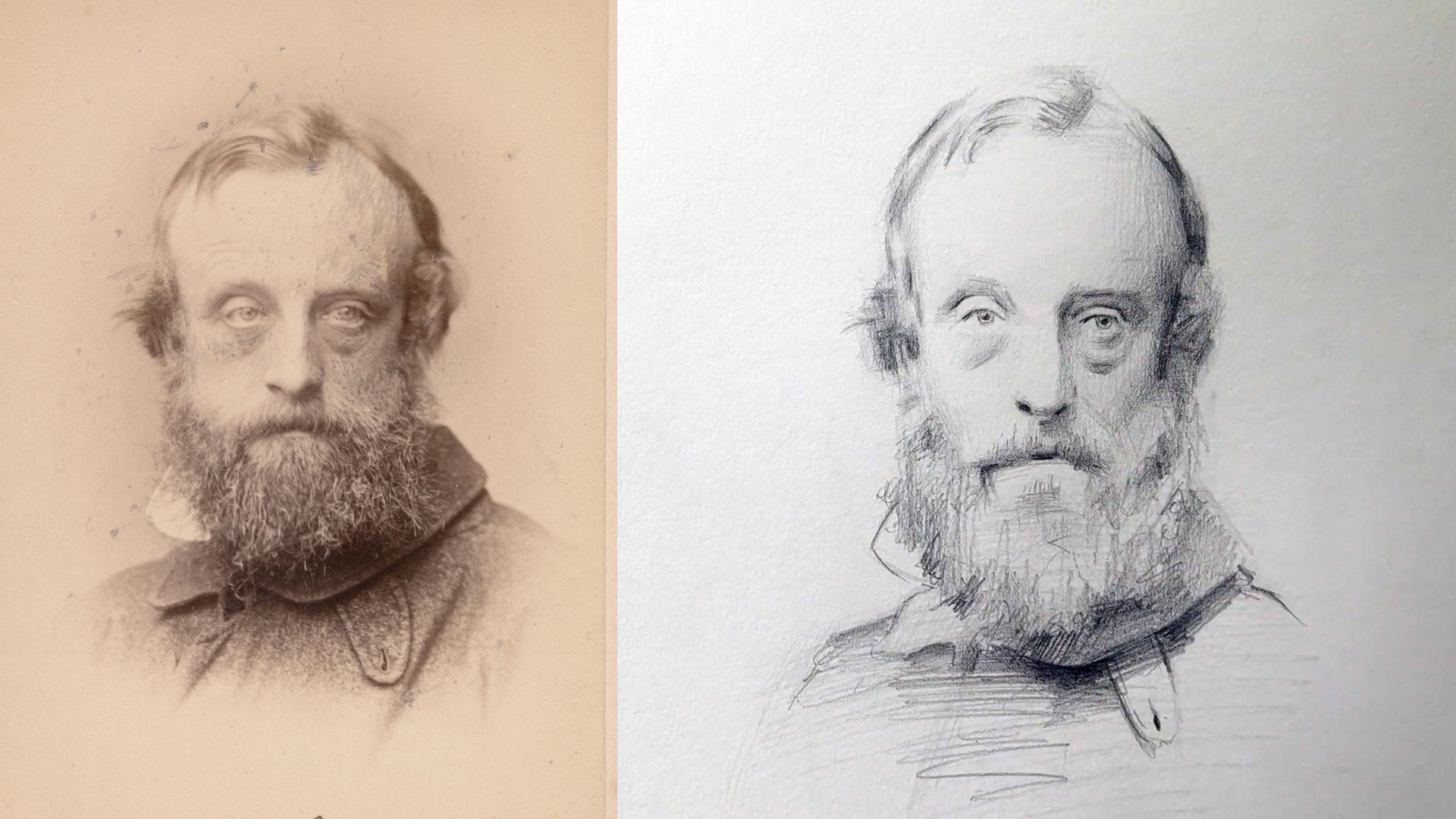

Portrait Sketching in Pencil

Student Work Portfolios: Sketchbooks from Level 2 Certificate (GCSE EQV) in Art and Design
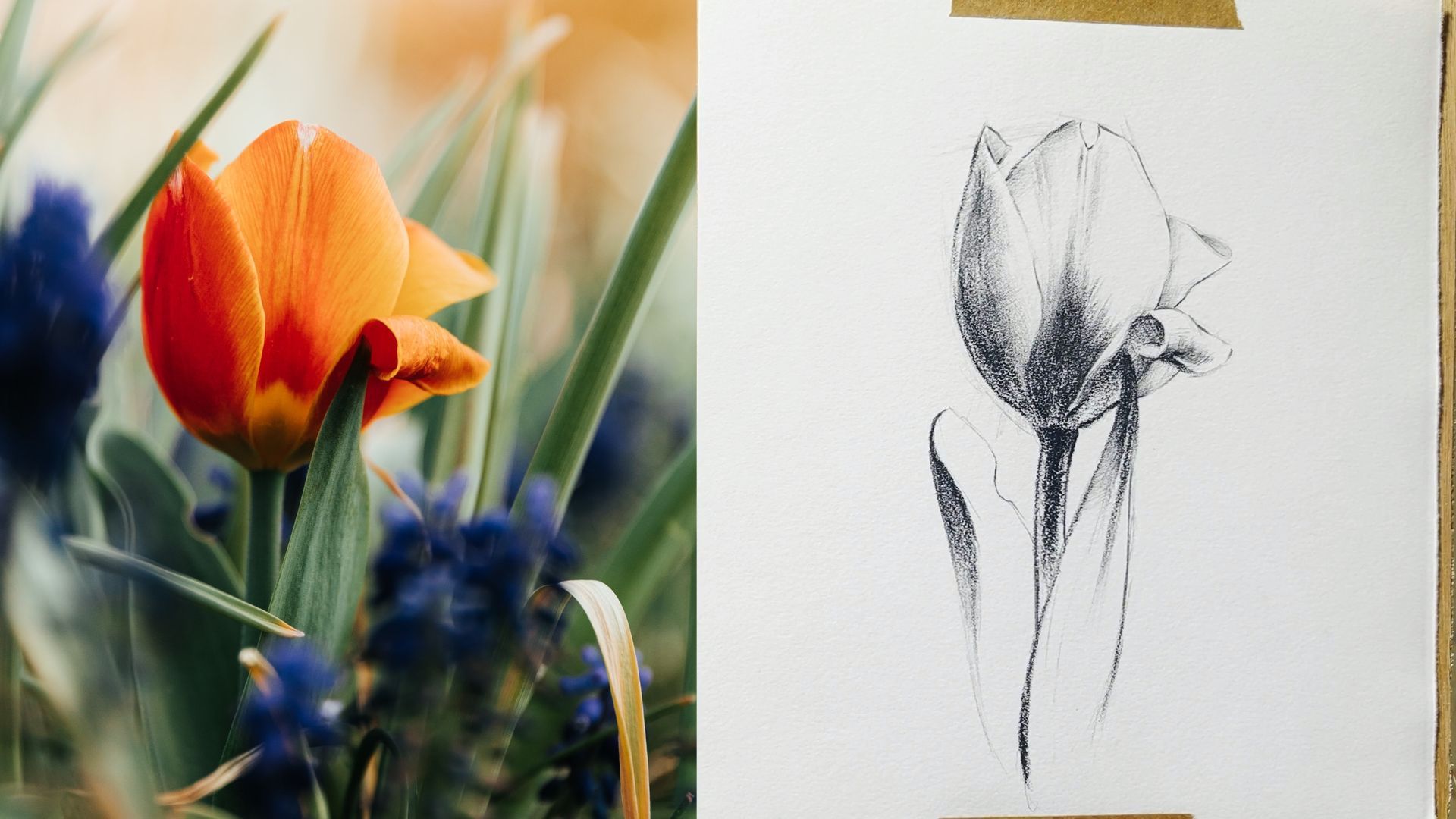

How to Sketch a Tulip

Careers for Visual Artists, Passionate About Working in the Film Industry
Learning To See! Lesson Demo - Task 1 - Level 2 Certificate in Art and Design

STUDENT PORTFOLIO - Level 2 Art and Design - Task 07 Portraiture
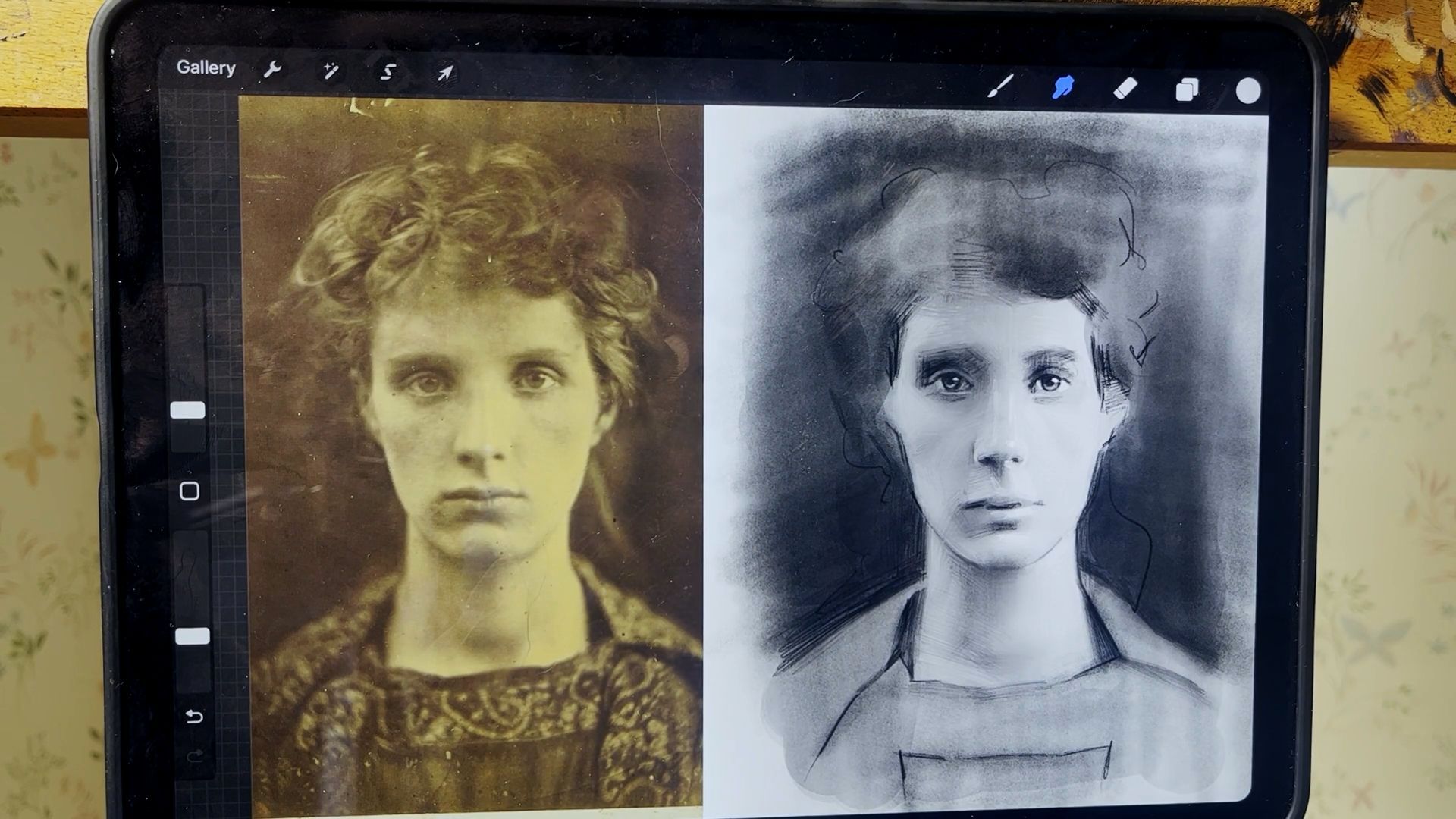

Portrait Sketching with an iPad: Part 1

OCAD LECTURE SERIES with Tim Edgar

STUDENT PORTFOLIO - Level 2 Art and Design - Task 05 - Observational Drawing: METAL
Fill in our short form ➝
Visit the contact page ➝
Check our 5 Star independent Student/Parent Reviews ➝
Find a Centre
Find an OCAD Centre Near You ➝
OCAD is part of the Cambridge Online Education Group - Company number 06594953
Registered UK Learning Provider 10033485
Cambridge Online Education Ltd
Terms of use | Privacy policy
Website by Cotswold Web.
Writing the A2 Art Personal Study: examples, help and guidance
Last Updated on April 2, 2023
This article has been written for CIE A Level Art students who are working on their A2 Art Personal Study . It focuses purely on how to write the text of the Study; a previous article outlines how to come up with a good topic ; a future article will address the illustrations and presentation methods.
The Personal Study is an area of uncertainty for many A Level Art students. It differs from projects that are usually completed within high school Art programmes, as it involves a substantial written component (maximum 3,500 words) – something which can intimidate students, especially if they are unfamiliar with how to critically analyse an artwork, make informed judgements and write personal evaluations. With few examples of quality Personal Studies available, it can be difficult to know what is expected and how to begin. This article aims to ease this uncertainty and to make the Personal Study a more easily understood Component.
READ NEXT: How to make an artist website (and why you need one)

1. Research thoroughly
The Personal Study should be comprised of informed personal views – that is, views that are supported and shaped by an in-depth understanding of the issues discussed. Before starting the project, students should conduct thorough background research, selecting and recording information from second-hand sources (such as books, websites and other publications) and first-hand sources (interviews with artists, studio visits / gallery visits etc). Interviews with artists should be planned thoroughly, after preliminary second-hand research has been completed (as findings from research will suggest important issues to discuss with the artist).
Students are often uncertain about how to phrase questions, so sample questions have been included below (the exact questions asked will depend on the topic and focus of the study):
- Please talk me through the process you follow when designing your paintings. Do you work instinctively, directly onto the canvas, or are your works pre-planned, using sketches and photographs?
- What influences your choice of colour? I am interested particularly in the colours used in [insert name of painting/s]. Could you explain your thought process behind the use of colour in this work, particularly the [give example]?
- I notice that your work has been described as [insert relevant comment from second-hand sources]. Do you agree with this statement? How do you respond to this?
- I notice that [insert an aesthetic feature of their artwork i.e. ‘angular line’ or ‘organic form’] is a dominant feature of your work. Is this strongly connected to the ideas that you are exploring? Have you used these elements deliberately?
- Can you show me work in progress or semi-complete artwork? I would love to understand the process you go through and how you apply media at different stages.
- Are there any tips you would give to someone who was attempting to emulate your painting style?
- Which artists have influenced your work? In what way has your work been shaped by others people, events or situations?
2. Evaluate and interpret research findings
Conducting research is critical for creating an excellent Personal Study, however, it should be noted that submitting research on its own will not gain a student any marks. Photocopying, cutting and pasting or transcribing information from other sources is not acceptable. Examiners do not want to read long lists of facts or chronological sequences of events. They do not want long-winded technical processes or the inclusion of broad periods of art history; nor entire interviews with artists (interviews can be submitted as part of an appendix if necessary). Students should not include an extensive artist biography (only brief and relevant details are needed) nor include vast passages of text that have been regurgitated from other sources.
Instead, students must select the information which is relevant and analyse this in detail, evaluating and interpreting findings in relation to the focus of their study . Research should be used to help form intelligent, knowledgeable, personal responses : to explain, justify or support the viewpoints, judgements and conclusions that are presented.
Evidence of research might be demonstrated, for example, through the use of carefully chosen quotes (to support or contrast the student’s own ideas) or through the inclusion of correct terminology and background knowledge to communicate an in-depth understanding of relevant issues. Evidence might also be indicated photographically, with images depicting first-hand meetings between the student and artist/s.
This Personal Study by CIE A2 Level Art and Design student Alice Ham, from ACG Parnell College , shows a cleverly selected quote alongside images by New Zealand charcoal artist Liam Gerrard . Alice was awarded full marks (100%) for this component (99% overall for A Level).

3. Structure the Personal Study in a logical and clear manner
Before writing the Personal Study, students should plan the content, order and structure of their study thoroughly (often in conjunction with planning the layout of their project – this will discussed in more detail in a subsequent post). This should include headings and subheadings of material discussed and rough diagrams indicating how this will be supported by images. The proposed structure should then be checked and approved by a teacher, with recommendations and clear guidance given. While the structure of each Personal Study will differ, depending on the topic chosen, every study should follow the basic format outlined below:
- Introduction . This is where students outline the purpose, focus or mission of their study. This may include question/s they are going to answer; themes they are going to explore; issues they hope to address etc. It should set the scene for the project and may include reasons for selecting a topic and an indication of how / why the topic is of personal relevance or interest to the student. It is important that the intentions of the project are clearly set out in this section, so that the remainder of the project can be structured accordingly.
- Body . This is the main part of the Personal Study and will need careful thought. It is usually organised into separate sections (which may be formal chapters, or simply different areas of a visual study), usually with individual headings and sometimes sub-headings. (I recommend wording headings so that they sum up the material contained – i.e. ‘ Analysis of Composition: [artwork title] ’ rather than ‘ Chapter 3 ’. This means that the examiner is able to see immediately that the student has covered a range of appropriate areas). The sections should be ordered logically and address the focus of the project; they should NOT ramble haphazardly from one issue to the next. High school Art students have a tendency to write without any preconceived order or structure, discussing issues spontaneously as they think of them. While this can be a suitable approach for more creative writing tasks – and can pulled off by certain students – this strategy runs the risk of creating a muddled and incoherent Personal Study.
- Conclusion . This is where students summarise key points from the project, arrive at final conclusions and make considered personal judgements about what has been learnt.
This is one of the concluding paragraphs in a Personal Study by Nikau Hindin (who achieved 98% for CIE A Level Art while studying at ACG Parnell College), entitled ‘ Identity, Consumerism & Popular Culture: How composition conveys a message ‘. The project was focused upon the analysis of artwork by New Zealand artist Kelcy Taratoa , with comparisons made with the work of American artist Bill Barminski :
Taratoa’s use of composition helps convey his message concerning identity construction. The arrangement of elements is symbolic of an unconscious hierarchy within his paintings that forces the viewer to question and analyse them. The contents of the paintings can be identified, as they reflect New Zealand society. Taratoa’s use of colour is vibrant and modern, echoing the technological era we live in. Barminski has a more dynamic and humorous approach to conveying his message. He mocks consumerism with his witty and blunt slogans and replications of consumer products. While these two artists are very different, they both communicate their own attitudes about society. Making a political statement through your paintings forces an audience to engage. Ultimately we want our art to be remembered and admired and I think if the message of a painting is clear then the viewer is more likely to go away and think about it. Paintings are a powerful tool to communicate a meaning that is deeper than the 2mm of paint on a canvas. Paintings are an artist’s voice.
- Bibliography / References / Acknowledgements . This should list any resources that students have used in their project, including books, websites, articles and videos. It might also include sources of first-hand information, such as museums, galleries or websites, as well as acknowledgements, thanking the artist for their time.

4. Write clearly and coherently
While examiners are sympathetic towards a student whose first language is not English, a similar sympathy does not extend towards those who submit sloppy, poorly edited material.
Just as it is expected that a Coursework project should contain beautiful well-composed artwork, a Personal Study is expected to contain well-structured, well-edited material. Even if a student has chosen to produce a largely visual project, submitting a sequence of annotated images, the text should communicate with intention and the writing quality should match that achieved by an A Level English student. Poor grammar, spelling errors and ‘txt’ speak are inexcusable.
As with any important written project, drafts should be rewritten and refined several times: chapters re-arranged; paragraphs and annotation reorganised; repetitive material, waffle and unnecessary regurgitation eliminated. Teachers, parents and friends can all be recruited to read through drafts, highlighting spelling errors and identifying areas where the writing is muddled. While the work must of course remain entirely that of the student, feedback from a fresh set of eyes is invaluable.
5. Use subject-specific vocabulary
A Personal Study should include an appropriate range of Art related terms and vocabulary. While the exact words used will be dependent upon the nature and focus of the study, there are a number of general Art-specific terms which students should be familiar with (these will be listed, with their definitions, in an upcoming article). Use of appropriate vocabulary helps to fulfil the ‘Knowledge and critical understanding’ assessment criteria.
6. Make it PERSONAL
As the title indicates, a Personal Study must communicate distinctly personal opinions, insights, judgements and responses, demonstrating a clear engagement with the artwork studied.
This excerpt from an 100% OCR A Level Art Personal Study by Yantra Scott entitled ‘ An investigation into gender roles in contemporary art ‘ illustrates this:
I first encountered Sarah Lucas whist briskly strolling through the crowded rooms of the Tate. Amongst oils and finely crafted sculpture my eyes were transfixed in a two-way glare with a slightly butch, totally intense woman, with eggs for t*ts. Ever since then I’ve been hooked.
It is evident that Yantra not only visited and viewed artwork in the flesh, but had a strong personal reaction to it. It could never be assumed that this segment had been reworded from a textbook: it is absolutely the words of a passionate high school Art student. Although Yantra uses coarse language within her study (something which should be emulated with caution) this project is an exceptional example of an intelligent and personal response to a topic. (More of Yantra’s work, as well as the entire text of her study, can be read in full on the great Julia Stubbs’ website ).
Similarly, this quote from an 88% OCR A2 Art Personal Study (one of the examples given in the OCR A2 Art Exemplar Work – Personal Study document ) shows a personal response integrated within the analysis of Damien Hurst ’s work, illustrated below.
The glass is thick, so thick that it is intimidating. It is as if it is holding something terrible back. It makes you question the formaldehyde and query, what if the tank did break? The formaldehyde is not clear as I expected but is quite strongly coloured by a blue and green pigment. This colour is very clinical and has the connotations of a hospital…
The musings about the tank breaking and the formaldehyde differing from expectations are clearly the individual thoughts of a high school art student.

7. Understand ‘cultural context’
Within the Personal Study, students must demonstrate an understanding of cultural context – an understanding that an artist does not create work in isolation, but rather creates work that is shaped and influenced by the circumstance/s they finds themselves in. This might mean that discussion of the influence of natural, social, political or cultural environments is appropriate, or that – as is more common – the influence of other artists is discussed, with comparisons made between artwork that has been created in similar or differing contexts.
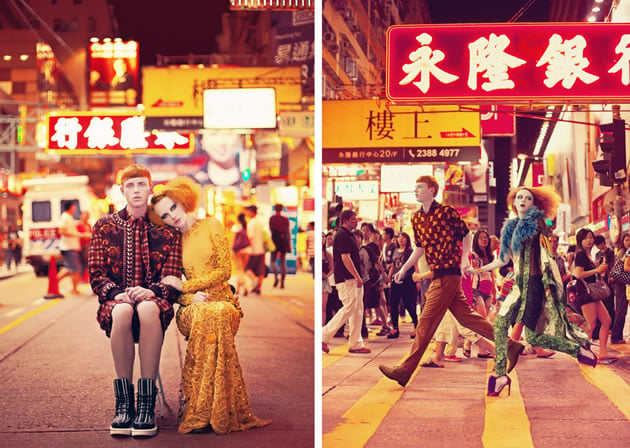

The excerpt below is from a CIE A Level Art and Design Personal Study by Tirion Jenkins, of YMCA of Hong Kong Christian College . Titled ‘Alternative Fashion Photography’, her Personal Study was awarded Best in Hong Kong (2012) and includes analysis of ‘One night in Mong Kok’ by photographer Akif Hakan Celebi . Tirion demonstrates a clear understanding of the interrelationship between a photographer’s work and the setting in which it was created.
The setting itself creates an intoxicating atmosphere with the rows of fluorescent light bulbs and layers of luminous signs that form an endless maze of gaudy colours. However, the setting does not overwhelm the two models who draw my eyes despite the signs above them. They create the focal point of the image through the use of the rule of thirds as they are placed off-centre and through their quirky appearance which magnetises the eye towards them. They seem to belong to a different world to the passersby behind them with their flare of red hair and audacious choice of feathered flittered clothes. Akif has further crafted the image through the use of makeup as their chalk white faces further segregates and emphasises their surreal doll-like appearances. …Akif’s pictures are reminiscent of Japanese cinema which he says he is so influenced by. “I like…its writhed and crazy stories; I feel very close to that way of looking at the world.” This photograph is particularly mystical due to the vibrant and decorative bokeh of Hong Kong’s street lights in the background.
8. Critically analyse artworks
The core of the A2 Art Personal Study is the in-depth analysis of selected artist works. Some of these artworks must be viewed in person, however it is common (and completely acceptable) for students to analyse work from a combination of primary and secondary sources. In the best studies, artworks are chosen specifically to facilitate the discussion of issues which are relevant to the study.
The advice in this section is particularly important and should be read closely by students who are hoping to achieve a high grade for their Personal Study.
When analysing artwork, it is helpful to analyse the work in terms of composition, format, structure and visual elements (such as shape, line, texture, colour, space, tone) . Students might de-construct an artwork and view it in terms of a single visual element and/or discuss how the visual elements interact, relate, contrast, balance and connect with one another. Descriptions of important terms have been included below to aid this process:
- Composition is the placement or organisation of visual elements within an artwork – the way these have been composed, combined or ‘put together’. Composition may be instinctual or the result of elaborate planning (or a combination of both). A ‘compositional device’ is an aspect of a composition which has a certain effect (such as the use of frames within frames, which might help create a sense of distance or space within an artwork).
- Format is the overall shape, size and orientation (portrait or landscape) of an artwork, i.e. whether a work is painted on a long, horizontal oblong canvas, or upon a vertically orientated A4 portrait board. Format can be influenced by practical considerations (i.e. the nature and shape of the object or scene depicted) as well as being an active decision by the artist to help communicate a particular meaning or idea.
- The structure of an artwork is the organisation of basic forms within a composition (this will be illustrated in more detail in the subsequent post focusing on imagery).
- Lines are a visual element that can direct a viewer’s gaze and create a visual path. These can direct attention to a focal point and create depth through perspective or horizon lines. Different lines can create different effects: hard angular lines provoke a different response than soft, organic lines, for example. Repetition of lines can create a sense of movement or rhythm.
- Shape is a visual element that is created by the junction of lines or changes in tone: the perceived boundaries of form. Larger shapes can become dominant focal points within an artwork; similar shapes can be repeated to create balance and create unity / visual harmony. Shapes can be symbolic, i.e. they can represent more complex forms and carry meaning. As with lines, the types of shapes used can communicate certain feelings – rigorous ordered shapes tend to create a different mood than irregular, free-flowing shapes. Shapes might also be used to create borders / frames and boundaries that connect, overlap or intersect, perhaps helping to draw viewers from the foreground / middle-ground to background.
- Space – the absence of form – is an often overlooked visual element. Described as being either positive (the space contained within the boundary of an object) or negative (the background space in and around an object), space can determine how busy and cluttered a painting is. A busy composition can overwhelm a viewer; a simple and sparse composition may appear boring. Careful integration of space is fundamental to any artwork.
- Form is a visual element that is usually discussed more easily in relation to three dimensional objects (as three-dimensional forms are usually described within two dimensional works in terms of shape, tone and line).
- Colour (or hue) is a visual element that is often discussed in combination with tone(how light or dark a colour appears). Colour can affect the mood of an artwork due to colour associations – i.e. blue might indicate sadness. Tone can help to communicate a sense of distance (items that are further away generally appear lighter – due to ‘atmospheric perspective’). Both tone and colour can be used to create contrast within an artwork, attracting the viewer’s attention and helping to create focal areas. Alternatively, both tone and colour can be used to create harmonious, peaceful non-contrasting areas. Use of light and shadow or warm and cool might also be an important area to discuss.
- Texture can be real (the result of brush strokes, irregularities in materials, and the application of a range of materials) or implied…i.e. a surface that is made to looktextured. As with the other visual elements, texture should be integrated so that it balances and becomes an aesthetically pleasing addition to an artwork. Surface qualities – along with other detailed areas and intricate patterns – are only able to be appreciated fully when viewed in person.
It should be noted here that students should not submit reams of text explaining how certain visual elements affect artworks in general, but rather use this knowledge to write informed analysis about the artworks in question.
Here is another example by Nikau Hindin, discussing the use of line in paintings by Kelcy Taratoa. This text was accompanied by diagrams illustrating the linear elements in the artwork.
…Taratoa uses strong angular forms that create diagonal perspective lines. These lines are called ‘leading lines’ and direct us to the focal point of this painting, which is a portrait of Taratoa. They also lead our eyes past him and make us look at the background. This helps to convey Taratoa’s message that one’s identity is linked to social circumstance, upbringing (background) and popular culture. Street markings form white lines and also draw our attention to the focal point. Street markings represent paths and therefore they may be paths to finding and constructing ones identity. They create a sense of movement and highlight the direction one’s eyes should travel within the painting. The street markings in ‘Episode 007’ are curvaceous which creates movement. The curvy lines mirror the organic forms of the superhero’s muscular body, creating a visual link. In ‘Episode 0010’ the repetition of line of the zebra crossing creates a sense of rhythm and leads us to the portrait of Taratoa in the left corner. Horizontal lines are repeated in the background of the painting to unite separate parts of the painting.
As well as the aesthetic qualities discussed above, most students also include sections where they analyse artwork in terms of materials, processes, stylistic influences, techniques (use of media) . For some, this is the primary focus of the Personal Study. This might include analysis of the way an artist has applied paint to a canvas (mark-making, brush strokes), the sequence of building up layers of paint over a prepared ground, or the sequence of events involved in creating a graphic design: from conceptual sketches, development of ideas, construction in Photoshop, through to proofing, paper selection and final printing. It might involve discussion about the way a composition is planned and designed and then the various processes that are undertaken in its completion. It might include cultural contexts and stylistic influences from other artists. In any sections of the Personal Study which are dedicated to process and technique, it is important to note (as mentioned above) that the examiners do not want the regurgitation of long, technical processes, but rather would like to see personal observations about how processes effect and influence the artwork that has been created.
In all analysis of artwork, whether this involves discussion of composition, aesthetic qualities, cultural contexts, use of media, or approach to a theme, it is important that students move beyond simple observations and add perceptive, personal insight. For example, if a student notices that colour has been used to create strong contrast in certain areas of an artwork, they might follow this with a detailed and thoughtful assumption about why this is the case: for example, perhaps the contrast was created deliberately to draw attention to a focal point in the artwork, helping the artist to help convey thematic ideas. These personal insights could be backed up by earlier research, confirmed or suggested by the artist, or might be educated assumptions made by the student, based upon their own responses and personal interaction with the artwork.
Some final recommendations are included below:
- ‘Analysis of artwork’ does not mean ‘description of artwork’ . Analysis means taking an artwork apart (thinking about it in terms of individual elements, such as line, or colour or technique), analysing these individually and/or in terms of how they relate to one another, and making personal observations and judgements, connecting this to the theme or focus of the assignment.
- Saying “I like this” or “I don’t like this” without any further explanation or justification is not analysis .
- Writing should be carefully integrated with the images , so that it is clear which text relates to which images (this will be discussed more in the subsequent post).
Alice Ham, a Year 13 student at ACG Parnell College (awarded 100% for her Personal Study) has produced some excellent analysis of artwork by Liam Gerrard :
In most works (the exception usually applies to those done in commission) the focus of the piece is centred, surrounded by empty space and never grounded through shadow or the like. This is another way in which Gerrard plays with commonly held opinions. Typically, a most aesthetically pleasing composition will follow the rule of thirds – a well known ‘rule’ that correlates to the focus of artworks being offset within the composition, and the entire image being visually divided into 3 sections. Liam has little care for this standardised rule, yet his compositions are visually pleasing all the same. I believe this could be because of the negative space, there is no overcrowding and it allows the viewer to focus on the subject. I also think this space is played upon in the display of the artwork. Galleries in general will have white or very light coloured walls so as not to distract from what is on display. By placing these white canvases on the white walls, hung without obvious framing, the artwork is allowed to ‘flow’ into the viewer’s world, there is no line of separation. This forces the viewer to study Gerrard’s pieces, and perhaps consider the personal message they address for the viewer in everyday life.

Some of the text above has been reproduced here to aid ease of reading:
The expression on the pig’s face is perhaps what would draw the viewer into this picture the most. It directly contradicts the gruesome depiction of decapitation and appears almost to be laughing. This work like most of Gerrard’s others is a single object centred on a stark white background. The amount of empty space in this picture is very eye catching and directs the viewer’s vision inwards, there is no chance of distraction by details in a menial part of the work. Once again Gerrard uses charcoal in his personal style, leaving the artwork in black and white. This lack of colour is cold, it presents the reality of the grisly scene without the embellishment of colours. This does not allow the audience to be caught up in what is ‘pretty’ but forces them to take in every details in it’s highly realistic, and perhaps disturbing, state. The shock factor of this piece is emphasised ten- fold by the sheer size. It cannot be realised until you view this piece in reality, but being dwarfed looking up into a pig’s head captured mid laugh brings upon you a bizarre sense of fascination.
9. Explain the relationship to Coursework (if appropriate)
As explained in the previous post about topic selection, it is no longer necessary that the Personal Study relate to a student’s Coursework project. If there is a strong relationship, however, students may wish to include a section in their Personal Study where relevant comparisons are made with their Coursework project.
10. Don’t exceed the word count
The maximum word count for CIE Art & Design Personal Studies is 3,500 words. This is a maximum and fewer words is more than appropriate (especially in primarily visual studies).
If a student is slightly over the word count, this is unlikely to be an issue (it is rare that examiners would know your exact word count, as no-one is likely to count every word in a project from start to finish); however, if a student is significantly over the word limit, this is obvious and a problem, running the risk that the examiners will run out of time (or enthusiasm) to read your project in its entirety. Almost all cases of word count breaches come from students who have attempted to bulk up their study with unnecessary information from second-hand sources. If you are encroaching the word limit, you should immediately ensure that you have not included supplementary research material or unnecessary information summarised from textbooks. If you are still battling with the word count and inclusion of material from second-hand sources is not an issue, you should re-edit your project, eliminating waffle, and ensuring you communicate succinctly.
Final Notes
I encourage teachers to locate and print the excerpts from Personal Studies that are included in the 9704 Standards booklet on the CIE Teachers’ password protected site , which can be downloaded as a PDF document from the A Level Art & Design page. This document is invaluable.
Finally, we are actively looking for more examples of high achieving Personal Studies to share on the Student Art Guide. If you or someone you know someone who excelled in this Component, please read our submission guidelines for more information.
If you found this information helpful, you may wish to read the previous article in this series: How to select a great A2 Art Personal Study Topic or our overview of the CIE A Level Art: Personal Study .

Amiria has been an Art & Design teacher and a Curriculum Co-ordinator for seven years, responsible for the course design and assessment of student work in two high-achieving Auckland schools. She has a Bachelor of Architectural Studies, Bachelor of Architecture (First Class Honours) and a Graduate Diploma of Teaching. Amiria is a CIE Accredited Art & Design Coursework Assessor.
JOIN OVER 21,000 PEOPLE WHO RECEIVE OUR FREE NEWSLETTER
You will be notified first when free resources are available: Art project ideas, teaching handouts, printable lesson plans, tips and advice from experienced teachers. What are you waiting for?
Email Address*
We send emails monthly. And don’t worry, we hate spam too! Unsubscribe at any time.

- Colleges and Institutes
- Accessibility --> Accessibility tools
- --> Subjects -->