- STEM Ambassadors
- School trusts
- ITE and governors
- Invest in schools
- STEM careers inspiration
- Benefits and impact
- Our supporters
- Become a STEM Ambassador
- Request a STEM Ambassador
- Employer information
- Training and support
- STEM Ambassadors Partners
- Working with community groups
- Search icon
- Join the STEM Community

Problem Solving
A selection of resources containing a wide range of open-ended tasks, practical tasks, investigations and real life problems, to support investigative work and problem solving in primary mathematics.
Problem Solving in Primary Maths - the Session
Quality Assured Category: Mathematics Publisher: Teachers TV
In this programme shows a group of four upper Key Stage Two children working on a challenging problem; looking at the interior and exterior angles of polygons and how they relate to the number of sides. The problem requires the children to listen to each other and to work together co-operatively. The two boys and two girls are closely observed as they consider how to tackle the problem, make mistakes, get stuck and arrive at the "eureka" moment. They organise the data they collect and are then able to spot patterns and relate them to the original problem to find a formula to work out the exterior angle of any polygon. At the end of the session the children report back to Mark, explaining how they arrived at the solution, an important part of the problem solving process.
In a second video two maths experts discuss some of the challenges of teaching problem solving. This includes how and at what stage to introduce problem solving strategies and the appropriate moment to intervene when children find tasks difficult. They also discuss how problem solving in the curriculum also helps to develop life skills.
Cards for Cubes: Problem Solving Activities for Young Children
Quality Assured Category: Mathematics Publisher: Claire Publications
This book provides a series of problem solving activities involving cubes. The tasks start simply and progress to more complicated activities so could be used for different ages within Key Stages One and Two depending on ability. The first task is a challenge to create a camel with 50 cubes that doesn't fall over. Different characters are introduced throughout the book and challenges set to create various animals, monsters and structures using different numbers of cubes. Problems are set to incorporate different areas of mathematical problem solving they are: using maths, number, algebra and measure.

Problem solving with EYFS, Key Stage One and Key Stage Two children
Quality Assured Category: Computing Publisher: Department for Education
These three resources, from the National Strategies, focus on solving problems.
Logic problems and puzzles identifies the strategies children may use and the learning approaches teachers can plan to teach problem solving. There are two lessons for each age group.
Finding all possibilities focuses on one particular strategy, finding all possibilities. Other resources that would enhance the problem solving process are listed, these include practical apparatus, the use of ICT and in particular Interactive Teaching Programs .
Finding rules and describing patterns focuses on problems that fall into the category 'patterns and relationships'. There are seven activities across the year groups. Each activity includes objectives, learning outcomes, resources, vocabulary and prior knowledge required. Each lesson is structured with a main teaching activity, drawing together and a plenary, including probing questions.

Primary mathematics classroom resources
Quality Assured Collection Category: Mathematics Publisher: Association of Teachers of Mathematics
This selection of 5 resources is a mixture of problem-solving tasks, open-ended tasks, games and puzzles designed to develop students' understanding and application of mathematics.
Thinking for Ourselves: These activities, from the Association of Teachers of Mathematics (ATM) publication 'Thinking for Ourselves’, provide a variety of contexts in which students are encouraged to think for themselves. Activity 1: In the bag – More or less requires students to record how many more or less cubes in total...
8 Days a Week: The resource consists of eight questions, one for each day of the week and one extra. The questions explore odd numbers, sequences, prime numbers, fractions, multiplication and division.
Number Picnic: The problems make ideal starter activities
Matchstick Problems: Contains two activities concentrating upon the process of counting and spotting patterns. Uses id eas about the properties of number and the use of knowledge and reasoning to work out the rules.
Colours: Use logic, thinking skills and organisational skills to decide which information is useful and which is irrelevant in order to find the solution.

GAIM Activities: Practical Problems
Quality Assured Category: Mathematics Publisher: Nelson Thornes
Designed for secondary learners, but could also be used to enrich the learning of upper primary children, looking for a challenge. These are open-ended tasks encourage children to apply and develop mathematical knowledge, skills and understanding and to integrate these in order to make decisions and draw conclusions.
Examples include:
*Every Second Counts - Using transport timetables, maps and knowledge of speeds to plan a route leading as far away from school as possible in one hour.
*Beach Guest House - Booking guests into appropriate rooms in a hotel.
*Cemetery Maths - Collecting relevant data from a visit to a local graveyard or a cemetery for testing a hypothesis.
*Design a Table - Involving diagrams, measurements, scale.

Go Further with Investigations
Quality Assured Category: Mathematics Publisher: Collins Educational
A collection of 40 investigations designed for use with the whole class or smaller groups. It is aimed at upper KS2 but some activities may be adapted for use with more able children in lower KS2. It covers different curriculum areas of mathematics.

Starting Investigations
The forty student investigations in this book are non-sequential and focus mainly on the mathematical topics of addition, subtraction, number, shape and colour patterns, and money.
The apparatus required for each investigation is given on the student sheets and generally include items such as dice, counters, number cards and rods. The sheets are written using as few words as possible in order to enable students to begin working with the minimum of reading.
NRICH Primary Activities
Explore the NRICH primary tasks which aim to enrich the mathematical experiences of all learners. Lots of whole class open ended investigations and problem solving tasks. These tasks really get children thinking!
Mathematical reasoning: activities for developing thinking skills
Quality Assured Category: Mathematics Publisher: SMILE

Problem Solving 2
Reasoning about numbers, with challenges and simplifications.
Quality Assured Category: Mathematics Publisher: Department for Education
Maths Tutoring Built for Schools
"This is one of the most effective interventions I have come across in my 27 years of teaching."
Hundreds of FREE online maths resources
Daily activities, ready-to-go lesson slides, SATs revision packs, video CPD and more!

Goal Free Problems And Focused Thinking: How I Wish I’d Taught Primary Maths (3)
Clare Sealy
Clare Sealy looks at the benefits that focused thinking and goal free problems (also known as open ended maths investigations), can have when used in a KS2 classroom.
This article is part of a series published to help primary school teachers and leaders implement some of the insights and teaching techniques derived from Craig Barton’s bestselling book How I Wish I’d Taught Maths . Links to the other 5 articles appear at the end.
In the introduction to this series, I outlined how Craig Barton in his book How I Wish I’d Taught Maths described how he had changed his teaching. This was as the result of reading research around cognitive load theory in the classroom , and in particular, realising how easy it was to inadvertently prevent learning by overwhelming working memory through cognitive overload.
In order to avoid this, Craig now plans his teaching with cognitive science considerations at the forefront of his thinking. By making relatively straightforward changes to the presentation of information and instructional design, unhelpful cognitive load (called ‘extraneous’ cognitive load in the research literature) is removed.
Craig’s preferred technique for this is through direct instruction and worked examples, and as a result of these teaching strategies , working memory is freed up to think about what needs to be thought about.

Crib Sheet for How I Wish I'd Taught Primary Maths
Download the key findings from research; share with your staff, your SLT, and at your next job interview!
Results from the research: Cognitive overload can affect pupils’ working memory
Cognitive overload is the enemy of learning. This is because if the capacity of working memory is exceeded, the stuff you actually want children to remember may not make it from the working memory to the long-term memory.
Since learning involves change in the long-term memory, if nothing has changed in the long-term memory, nothing has been learned. Sweller et al, 1998 suggest that teachers should take care to design instruction so that working memories are not overwhelmed. Fortunately, there is a simple way you can do this…
What are goal free problems?
While goal specific questions have an exact answer, goal free questions do not. They are a form of open ended maths investigation and an questioning in the classroom technique, and they are a great way to help prevent cognitive overload among pupils.
Goal free questions are the longer two or three-part reasoning questions that appear in maths, not simple calculations, and they are best used once you have taught the children something and now want them to apply it in a problem-solving context.
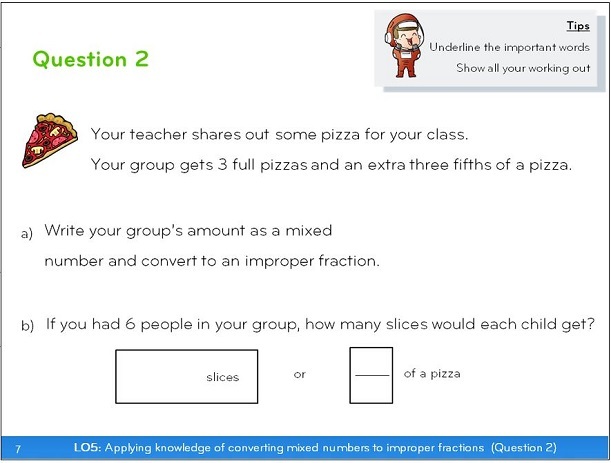
They are not intended to be used at the very start of teaching something .
These are ‘application’ questions, once the initial stage of how to do something has been taught and reinforced through deliberate practice in the short term, and retrieval practice across the school year.
If these open ended maths investigations are introduced before a topic has been fully grasped by pupils, this can result in confusion.
The difference between a goal specific and goal free question
The following examples are all from the KS2 2017 Maths SATs Paper 2 :

This is a goal specific question with a specific answer.
A goal free question would look like this:

So why are goal free questions better?
The reason why the second kind of question is better than the first is that in the second, the pupil can use metacognitive skills to work on parts of the question one at a time, rather than being overwhelmed trying to solve every part at once.
You can find out more about the sorts of thinking skills pupils might use from our blog on metacognition in the classroom .
Thanks to the open ended nature of these maths problems, pupils can focus on one singular part of the problem that they feel is important, and confidently solve this before moving on.
For example:
They would probably decide to work out how much 12 individual stickers cost. They would also not have any niggling, intrusive thoughts about what they need to do next competing for attention in their working memory. Therefore, all of their attention would be devoted to calculating 12x99p.
Having done that, they would probably then realise that buying individual stickers was a rip off! They might also work out other things, for example:
• If Jack had £11, how many individual stickers could he buy? • Or what is the cheapest amount you could pay to get 16 stickers?
But whatever they decided to work out, they were thinking about that and that alone.
Why the traditional method of asking questions can hinder pupils’ learning
With a conventional problem, concerns about the final goal can intrude upon their thinking. The pupil’s attention is split between thinking about the first step and thinking about the other steps that they need to take next.
Therefore, even if they successfully answer the question, they may not have learnt anything generally that could be transferred to new kinds of problems.
Their attention has not been focused enough.
Goal free questions are a great way to help pupils solve the problem in front of them
Once you have given the children the goal free version of the question and various things have been worked out, at that point you can, if you wish, share the goal specific question. You should then realise the hard work of answering the question has already been done and a final tweak might be all that is now needed.
Consider this example, adapted to be open ended and goal free:
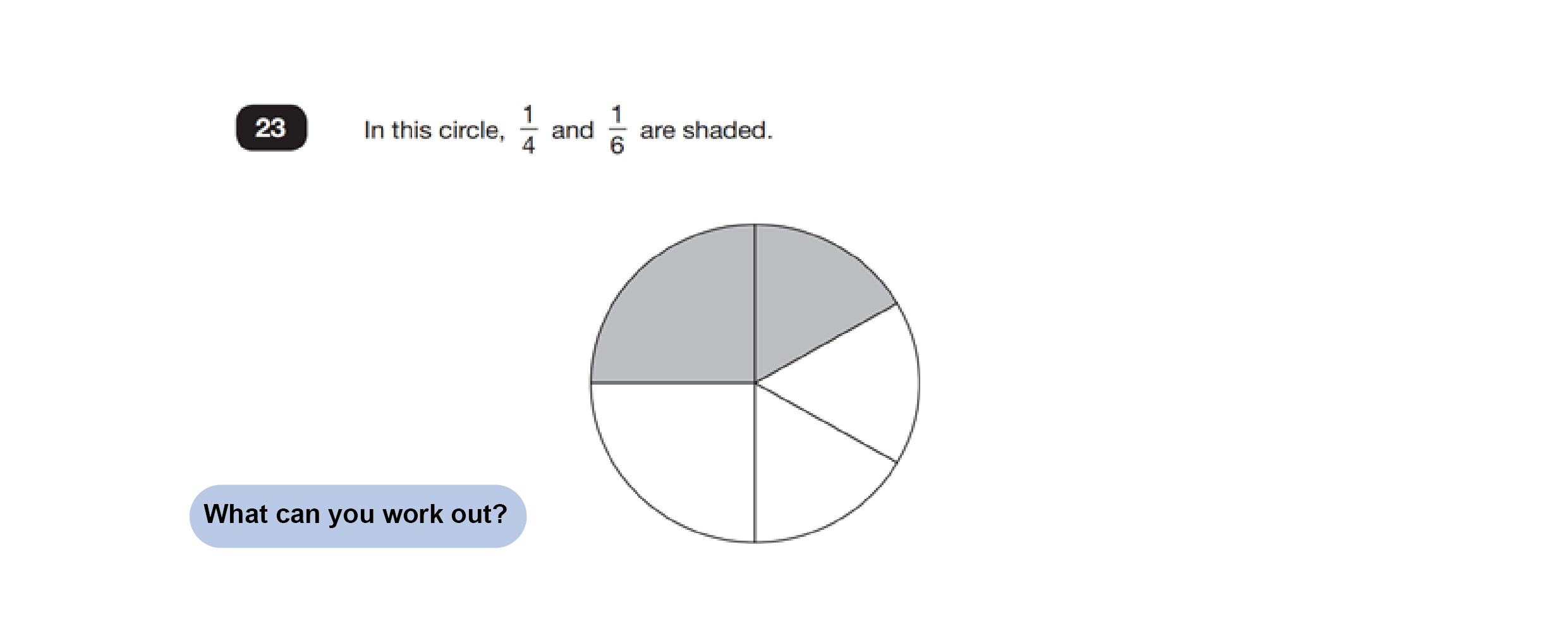
Without a goal specific question looming over them, children will probably quickly be able to identify the size of the individual unshaded parts. Then they might decide to work out what fraction is shaded. Then when the goal specific question is revealed…

…answering it is very easy. Even if they only initially worked out the size of the individual unshaded parts, they are still ahead of the game having done so.
Best practice for open ended, goal free questions
Using goal free questions works particularly well with graphs and geometry questions, with the pupil asking themselves: “What can I work out first?” before worrying (or being told) about what the question actually says.
Doing it this way in a test situation, the pupil is more likely to answer the actual question than if they had tried to solve it from the off. This is because they know that their initial goal free musing is a prelude to the final step of telling the examiner the actual thing that will get them marks.
So, for example, teach pupils to hide the question and first of all annotate the graph to show what it tells them.
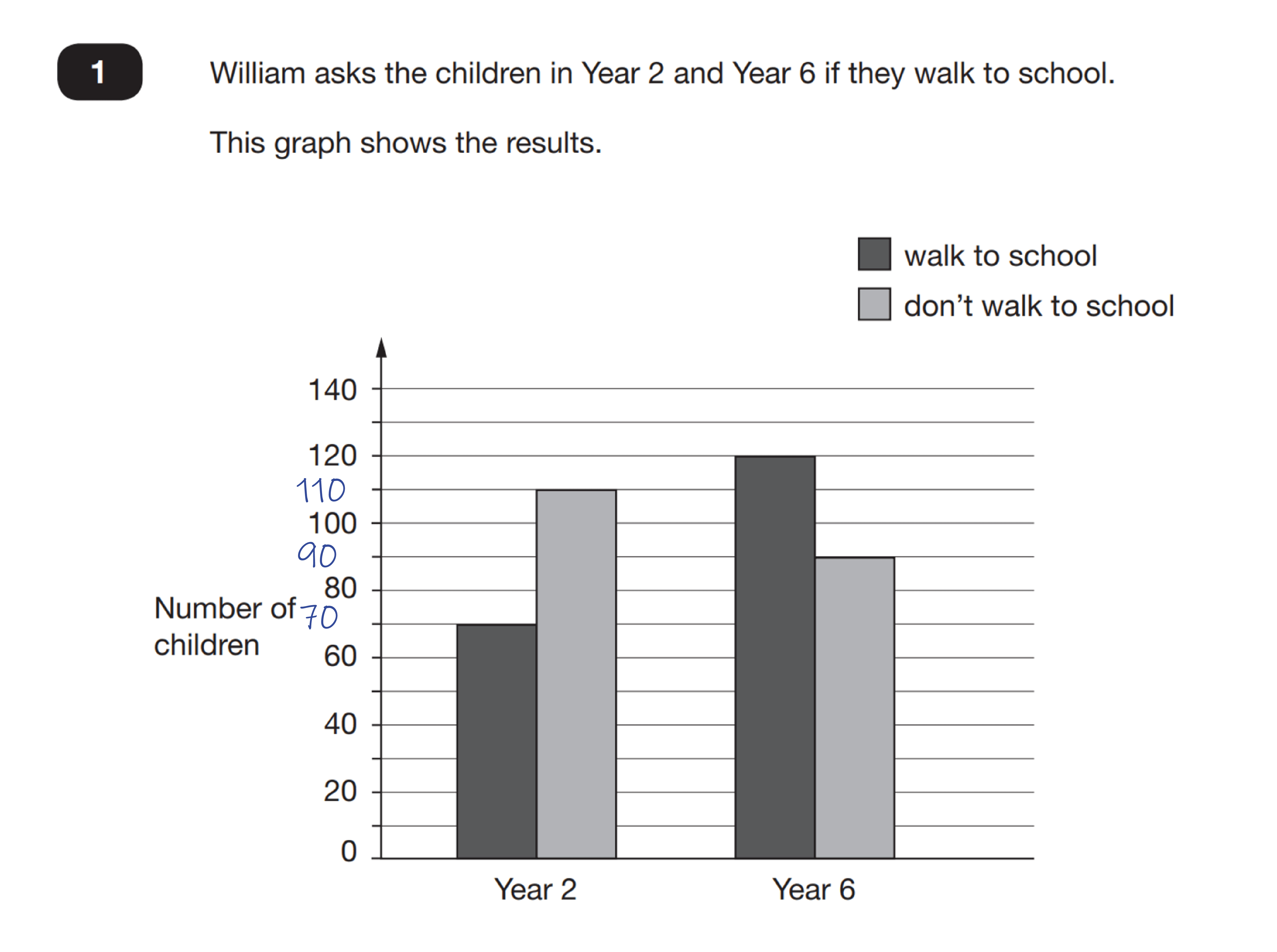
As well as annotating the axes, the child also annotates their paper with the following.
Difference yr 2 – 110-70=40
Difference yr 5 – 120-90=30
Walk – 70+120=190
Don’t walk – 110+90=200
Then when the final specific question is revealed…

…The solution is already worked out. However, by not having to worry about the final question during the initial annotation stage, their attention is much better focused as they explore the graph to find answers to their own question.
It is not necessary to always share the ‘final’ question, especially during the early knowledge-acquisition phase. Goal free, open ended questions are particularly useful the first time you want pupils to apply a skill you have just taught. Goal free questions with an eventual goal specific big reveal are useful when revising in readiness for a test.
3 tips for bringing focused thinking and goal free learning into your classroom
1. Prepare a dedicated selection of open-ended maths investigations for your class in the form of problems, activities or worksheets
2. Present existing questions to students in the manner seen above, asking them what they can take from the question before the final request is revealed
3. Use goal free questions as a way to further cement knowledge, using them after you have taught pupils a principle. This will encourage focused thinking within the classroom
I hope that the theories about goal free, open ended maths investigations and focused thinking presented in this blog prove useful in your classroom.
Sources of inspiration
Sweller, J., Merriënboer, J.J.G. and Pass, F.G.W.C. (1998) ‘Cognitive architecture and instructional design’, Educational Psychology Review 10 (3) pp.251-296
This is the third blog in a series of 6 adapting the book How I Wish I’d Taught Maths for a primary audience. If you wish to read the remaining blogs in the series, check them out below:
- 20 maths strategies that we use in our teaching to guarantee success for any pupil.
- Quality First Teaching Checklist: The 10 Most Effective Strategies For Primary Schools
- Differentiation In The Classroom: The 8 Strategies That Will Support Every Pupil To Reach A Good Standard
- Learning and Memory In The Classroom: What Teachers Should Know About Summer Learning Loss – And How To Fix It
- Teaching ‘Lower Ability’ Students Maths: “Are We Bottom Set?”
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Every week Third Space Learning’s specialist school tutors support thousands of students across hundreds of schools with weekly online 1 to 1 maths lessons designed to plug gaps and boost progress.
Since 2013 these personalised one to one lessons have helped over 150,000 primary and secondary students become more confident, able mathematicians.
Learn how the tutoring integrates with your SEF and Ofsted planning or request a personalised quote for your school to speak to us about your school’s needs and how we can help.
Related articles

A Teacher’s Guide To Spaced Repetition And Creating An Effective Spaced Repetition Schedule

Retrieval Practice: A Foolproof Method To Improve Student Retention and Recall

A Practical Guide To Rosenshine’s Principles of Instruction: How To Apply Them to Maths Lessons

Cognitive Load Theory: A Practical Guide And Tips For Teachers
FREE Guide to Hands on Manipulatives
Download our free guide to manipulatives that you can use in the maths classroom.
Includes 15 of the best concrete resources every KS1 and KS2 classroom should have.
Privacy Overview
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

KS2 Maths (Problem Solving)
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
16 January 2019
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

These topic-focused SATs questions at the end of a unit will help to test and extend students’ understanding as well as helping them to prepare for SATs next year. These questions have fully-worked solutions which can be displayed on a whiteboard making feedback with students more efficient. Click 👉 tes.com/…/KS2-Maths-Questions… for similar-style compilations on the other KS2 topics. <hr> This particular compilation is mainly from the ALGEBRA strand and contains questions which require students us problem solving techniques . In the solutions, I have often used algebraic notation to show how an answer has been obtained, but most of the solutions actually use logic rather than formal algebraic methods. <hr> I have designed this compilation to be printed as an A4 or A5 booklet which is in the style of the actual SATs papers and is convenient for use in class or as homework. It can even be given to individual students if a parent is asking for ‘some more work’!
KEY POINTS:
- I have provided full answers, with comments and working where helpful.
- I have maintained the style of the actual SATs questions so that students can become comfortable with the way that SATs questions are presented.
- Most of the questions are from actual SATs papers, but I have also added questions so that this resource matches the requirements the current curriculum better than the older resources that are still in common use (note that many of the older resources of this type contain questions on topics which are no longer examined).
- I have spent a lot of time arranging the questions so that there is a general increase in difficulty as students work through them, and so that they fit on the pages better – this means less wasted space and significant paper-saving when printing 😃 <hr> 👍If you like this resource, then please rate it and/or leave a comment💬. If the rate-resource button on this page doesn’t work, then go to your ratings page by clicking 👉 www.tes.com/…/rate-resources…
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
JKennedy100
Very helpful. Thank you for sharing. :)
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Thank you so much for putting the time and effort into all of your resources - so helpful.
Absolutely fabulous, exactly what I needed to help my son at home now. Thank you sooo much!!
misshewitt721
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.

Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
Resources tagged with: Money
There are 24 NRICH Mathematical resources connected to Money , you may find related items under Measuring and calculating with units .
Fruity Pairs
Which two items of fruit could Kate and Sam choose? Can you order the prices from lowest to highest?
Planning a School Trip
You are organising a school trip and you need to write a letter to parents to let them know about the day. Use the cards to gather all the information you need.
How Much Did it Cost?
Use your logical-thinking skills to deduce how much Dan's crisps and ice-cream cost altogether.
Your school has been left a million pounds in the will of an ex- pupil. What model of investment and spending would you use in order to ensure the best return on the money?
Plenty of Pens
Amy's mum had given her £2.50 to spend. She bought four times as many pens as pencils and was given 40p change. How many of each did she buy?
Ram divided 15 pennies among four small bags. He could then pay any sum of money from 1p to 15p without opening any bag. How many pennies did Ram put in each bag?
Oh for the Mathematics of Yesteryear
A garrison of 600 men has just enough bread ... but, with the news that the enemy was planning an attack... How many ounces of bread a day must each man in the garrison be allowed, to hold out 45 days against the siege of the enemy?
The Puzzling Sweet Shop
There were chews for 2p, mini eggs for 3p, Chocko bars for 5p and lollypops for 7p in the sweet shop. What could each of the children buy with their money?
Buying a Balloon
Lolla bought a balloon at the circus. She gave the clown six coins to pay for it. What could Lolla have paid for the balloon?
Ben has five coins in his pocket. How much money might he have?
Charitable Pennies
Investigate the different ways that fifteen schools could have given money in a charity fundraiser.
Money Line-up
In this game for two players, the aim is to make a row of four coins which total one dollar.
What is the smallest number of coins needed to make up 12 dollars and 83 cents?
2010: A Year of Investigations
This article for teachers suggests ideas for activities built around 10 and 2010.
At the Pumps
How will you find out how much a tank of petrol costs?
Five More Coins
Could Ben have any amount of money between 5p and £2 in his pocket if he has five coins?
The Money Maze
Go through the maze, collecting and losing your money as you go. Which route gives you the highest return? And the lowest?
History of Money
If you would like a new CD you would probably go into a shop and buy one using coins or notes. (You might need to do a bit of saving first!) However, this way of paying for the things you want did not always exist. Find out more ...
Money Problems?
Marion Bond investigates the skills needed in order for children to understand money.
Chocoholics
George and Jim want to buy a chocolate bar. George needs 2p more and Jim need 50p more to buy it. How much is the chocolate bar?
Roasting Old Chestnuts 4
For teachers. Yet more school maths from long ago-interest and percentages.
Here are the prices for 1st and 2nd class mail within the UK. You have an unlimited number of each of these stamps. Which stamps would you need to post a parcel weighing 825g?
Thirty Nine, Seventy Five
We have exactly 100 coins. There are five different values of coins. We have decided to buy a piece of computer software for 39.75. We have the correct money, not a penny more, not a penny less! Can you discover what the five different types of coins are worth and how many of each we have saved?
Christmas Shopping
Vera is shopping at a market with these coins in her purse. Which things could she give exactly the right amount for?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This selection of 5 resources is a mixture of problem-solving tasks, open-ended tasks, games and puzzles designed to develop students' understanding and application of mathematics. Thinking for Ourselves: ... It is aimed at upper KS2 but some activities may be adapted for use with more able children in lower KS2. It covers different curriculum ...
Age 7 to 11. Challenge Level. This group activity will encourage you to share calculation strategies and to think about which strategy might be the most efficient. Table Patterns Go Wild! Live. Age 7 to 11. Challenge Level. Nearly all of us have made table patterns on hundred squares, that is 10 by 10 grids.
Age 7 to 14. Challenge Level. A game for two people, or play online. Given a target number, say 23, and a range of numbers to choose from, say 1-4, players take it in turns to add to the running total to hit their target.
Problem Solving. This feature is somewhat larger than our usual features, but that is because it is packed with resources to help you develop a problem-solving approach to the teaching and learning of mathematics. Read Lynne's article which discusses the place of problem solving in the new curriculum and sets the scene.
The open-ended nature of problem-solving activities means children have more freedom to be creative with how they respond. Problem-solving key stage 2 primary resources for children. We have tons of maths problem-solving activities for kids, and resources available to help your key stage 2 students practice their problem-solving skills.
3. KS2 Maths Investigations Give Early Exposure To SATs Style, Reasoning Questions. Most, if not all, schools will provide their pupils with exposure to reasoning via SATs-style questions, but this often comes hand in hand with exams and assessment. Yet, it is equally important to get pupils reasoning and problem solving in a low stakes ...
These KS2 maths investigations include lots of problem-solving activities for year 3, 4, 5 and 6 pupils. You can find mystery games, challenge cards and more. ... Odd and Even Numbers Using the Four Operations Open-Ended Task Worksheet. 4.8 ... KS2 Circles Maths Problem-Solving Investigations. 4.8 (4 reviews)
Year 6 Maths Mastery Resources: a comprehensive set of teaching materials, perfect for developing your pupils' fluency, reasoning and problem-solving skills. KS2 Maths Investigations: a huge range of worksheets and games, which are perfect for developing your pupils' maths knowledge and skills. KS2 Mystery Games: fun and engaging, these maths ...
A complete guide to maths problem solving at KS2 & the techniques that work. Free download with word problems & problem solving questions to use in class. ... structure, and the use of several techniques for approaching problem solving. Techniques, such as open-ended problem solving, are usually learned by example so we advise you create ...
Age 7 to 11. Challenge Level. Place the numbers from 1 to 9 in the squares below so that the difference between joined squares is odd. How many different ways can you do this?
These open-ended Year 6 maths investigations are a really fun and creative way to get children learning and engaging with different problems from a mathematical perspective. These activities will not only expand children's maths knowledge, but they will also help them improve their problem-solving skills and logical thinking.
These KS2 maths investigations include lots of problem-solving activities for year 3, 4, 5 and 6 pupils. You can find mystery games, challenge cards and more. ... Odd and Even Numbers Using the Four Operations Open-Ended Task Worksheet. 4.8 (4 reviews) Prime Numbers Challenge ... KS2 Circles Maths Problem-Solving Investigations. 4.8 (4 reviews ...
Goal Free Problems And Focused Thinking: How I Wish I'd Taught Primary Maths (3) Clare Sealy looks at the benefits that focused thinking and goal free problems (also known as open ended maths investigations), can have when used in a KS2 classroom. This article is part of a series published to help primary school teachers and leaders implement ...
Our exciting KS2 teaching resources will help introduce your year 3, year 4, year 5, and year 6 students to problem-solving and reasoning topics. Be sure to take a look at our fun and engaging maths word problems, maths investigations, and maths games, which can all be used with the accompanying key stage 2 worksheets and activities. Our fun ...
Area and Perimeter. Age 7 to 11. Challenge Level. What can you say about these shapes? This problem challenges you to create shapes with different areas and perimeters.
These open-ended Year 6 maths investigations are a really fun and creative way to get children learning and engaging with different problems from a mathematical perspective. These activities will not only expand children's maths knowledge, but they will also help them improve their problem-solving skills and logical thinking.
KS2 Maths (Problem Solving) These topic-focused SATs questions at the end of a unit will help to test and extend students' understanding as well as helping them to prepare for SATs next year. These questions have fully-worked solutions which can be displayed on a whiteboard making feedback with students more efficient.
These interactive activity cards are all about getting children to problem solve and present an argument. Designed specifically for Year 5-6 children, they will provide a great challenge by forcing them to think outside the box to come up with an answer. There are 27 individual open-ended maths activities included. Each is teacher-made, saving you time on lesson planning while ensuring that ...
next year including some open ended problems. Please keep a look out for our work. If you have not seen our schemes and assessments for primary then please take a look at our website www.whiterosemathshub.co.uk doing and the materials that we are releasing. Thank you for taking an interest in our work. The White Rose Maths Hub Team
Fractions in a Box. Age 7 to 11. Challenge Level. The discs for this game are kept in a flat square box with a square hole for each. Use the information to find out how many discs of each colour there are in the box.
These interactive investigation cards are all about getting children to problem-solve and present an argument. Designed specifically for Year 5-6 children, they will provide a great challenge by forcing them to think outside the box to come up with an answer. There are 27 individual open-ended Maths activities included. Each is teacher-made, saving you time on lesson planning while ensuring ...
Planning a School Trip. You are organising a school trip and you need to write a letter to parents to let them know about the day. Use the cards to gather all the information you need.
These interactive investigation cards are all about getting children to problem solve and present an argument. Designed specifically for Year 5-6 children, they will provide a great challenge by forcing them to think outside the box to come up with an answer. There are 27 individual open-ended maths activities included. Each is teacher-made, saving you time on lesson planning while ensuring ...