

Class 12 Maths: Case Study of Chapter 4 Determinants PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: 12 board / Class 12
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 4 Determinants Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Maths Determinants to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 12 Maths Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Determinants Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 4 Determinants
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
(i) What is the award money for Honesty?
Answer: (b) Rs.300
(ii) What is the award money for Punctuality?
Answer: (d) Rs.500
(iii) What is the award money for Hard work?
Answer: (b) Rs.400
(iv) If a matrix P is both symmetric and skew-symmetric, then IPI is equal to
Answer: (c) 0
(v) If P and Q are two matrices such that PQ = Q and QP = P, then IQ 2 1 is equal to
Answer: (a) IQI
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Determinants Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Class 12 maths: case study of chapter 9 differential equations pdf download, mcq class 12 english journey to the end of the earth questions with answers english chapter 3, poets and pancakes summary class 12 english pdf, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths PDF
The passage-based questions are commonly known as case study questions. Students looking for Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths can use this page to download the PDF file.
The case study questions on Determinants are based on the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus, and therefore, referring to the Determinants case study questions enable students to gain the appropriate knowledge and prepare better for the Class 12 Maths board examination. Continue reading to know how should students answer it and why it is essential to solve it, etc.
Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths with Solutions in PDF
Our experts have also kept in mind the challenges students may face while solving the case study on Determinants, therefore, they prepared a set of solutions along with the case study questions on Determinants.
The case study on Determinants Class 12 Maths with solutions in PDF helps students tackle questions that appear confusing or difficult to answer. The answers to the Determinants case study questions are very easy to grasp from the PDF - download links are given on this page.
Why Solve Determinants Case Study Questions on Class 12 Maths?
There are three major reasons why one should solve Determinants case study questions on Class 12 Maths - all those major reasons are discussed below:
- To Prepare for the Board Examination: For many years CBSE board is asking case-based questions to the Class 12 Maths students, therefore, it is important to solve Determinants Case study questions as it will help better prepare for the Class 12 board exam preparation.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Class 12 Maths Determinants case study questions require students to analyze a given situation, identify the key issues, and apply relevant concepts to find out a solution. This can help CBSE Class 12 students develop their problem-solving skills, which are essential for success in any profession rather than Class 12 board exam preparation.
- Understand Real-Life Applications: Several Determinants Class 12 Maths Case Study questions are linked with real-life applications, therefore, solving them enables students to gain the theoretical knowledge of Determinants as well as real-life implications of those learnings too.
How to Answer Case Study Questions on Determinants?
Students can choose their own way to answer Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths, however, we believe following these three steps would help a lot in answering Class 12 Maths Determinants Case Study questions.
- Read Question Properly: Many make mistakes in the first step which is not reading the questions properly, therefore, it is important to read the question properly and answer questions accordingly.
- Highlight Important Points Discussed in the Clause: While reading the paragraph, highlight the important points discussed as it will help you save your time and answer Determinants questions quickly.
- Go Through Each Question One-By-One: Ideally, going through each question gradually is advised so, that a sync between each question and the answer can be maintained. When you are solving Determinants Class 12 Maths case study questions make sure you are approaching each question in a step-wise manner.
What to Know to Solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Determinants?
A few essential things to know to solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Determinants are -
- Basic Formulas of Determinants: One of the most important things to know to solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Determinants is to learn about the basic formulas or revise them before solving the case-based questions on Determinants.
- To Think Analytically: Analytical thinkers have the ability to detect patterns and that is why it is an essential skill to learn to solve the CBSE Class 12 Maths Determinants case study questions.
- Strong Command of Calculations: Another important thing to do is to build a strong command of calculations especially, mental Maths calculations.
Where to Find Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths?
Use Selfstudys.com to find Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths. For ease, here is a step-wise procedure to download the Determinants Case Study for Class 12 Maths in PDF for free of cost.
Since you are already on this page, you can scroll to the top section of this page to get access to the Case Study on Determinants. To help others reach this page let them know these steps:
- Open Selfstudys.com on your computer/laptop or Smartphone
- Once the website gets loaded, click on the navigation button
- Find CBSE from the given menu
- Click on Case Study
- Choose Class 12
- Search Maths and then navigate to the Determinants Class 12 Maths Case Study
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Class 12 Maths Case...
Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Class 12 Maths question paper will have 1-2 Case Study Questions. These questions will carry 5 MCQs and students will attempt any four of them. As all of these are only MCQs, it is easy to score good marks with a little practice. Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions are available on the myCBSEguide App and Student Dashboard .
Why Case Studies in CBSE Syllabus?
CBSE has introduced case study questions in the CBSE curriculum recently. The purpose was to make students ready to face real-life challenges with the knowledge acquired in their classrooms. It means, there was a need to connect theories with practicals. Whatsoever the students are learning, they must know how to apply it in their day-to-day life. That’s why CBSE is emphasizing case studies and competency-based education .
Case Study Questions in Maths
Let’s have a look over the class 12 Mathematics sample question paper issued by CBSE, New Delhi. Question numbers 17 and 18 are case study questions.
Focus on concepts
If you go through each MCQ there, you will find that the theme/case study is common but the questions are based on different concepts related to the theme. It means, that if you have done ample practice on the various concepts, you can solve all these MCQs in minutes.
Easy Questions with a Practical Approach
The difficulty level of the questions is average or say easy in some cases. On the other hand, you get four options to choose from. So, you get two levels of support to get full marks with very little effort.
Practice Questions Regularly
Most of the time we feel that it’s easy and neglect it. But in the end, we have to pay for this negligence. This may happen here too. Although it’s easy to score good marks on the case study questions if you don’t practice such questions, you may lose your marks. So, we suggest students should practice at least 30-40 such questions before writing the board exam.
12 Maths Case-Based Questions
We are giving you some examples of case study questions here. We have arranged hundreds of such questions chapter-wise on the myCBSEguide App. It is the complete guide for CBSE students. You can download the myCBSEguide App and get more case study questions there.
Case Study Question – 1
- A is a diagonal matrix
- A is a scalar matrix
- A is a zero matrix
- A is a square matrix
- If A and B are two matrices such that AB = B and BA = A, then B 2 is equal to
Case Study Question – 2
- 4(x 3 – 24x 2 + 144x)
- 4(x 3 – 34x 2 + 244x)
- x 3 – 24x 2 + 144x
- 4x 3 – 24x 2 + 144x
- Local maxima at x = c 1
- Local minima at x = c 1
- Neither maxima nor minima at x = c 1
- None of these
Case Study Questions Matrices -1
Answer Key:
Case Study Questions Matrices – 2
Read the case study carefully and answer any four out of the following questions: Once a mathematics teacher drew a triangle ABC on the blackboard. Now he asked Jose,” If I increase AB by 11 cm and decrease the side BC by 11 cm, then what type of triangle it would be?” Jose said, “It will become an equilateral triangle.”
Again teacher asked Suraj,” If I multiply the side AB by 4 then what will be the relation of this with side AC?” Suraj said it will be 10 cm more than the three times AC.
Find the sides of the triangle using the matrix method and answer the following questions:
- (a) 3 × 3
Case Study Questions Determinants – 01
DETERMINANTS: A determinant is a square array of numbers (written within a pair of vertical lines) that represents a certain sum of products. We can solve a system of equations using determinants, but it becomes very tedious for large systems. We will only do 2 × 2 and 3 × 3 systems using determinants. Using the properties of determinants solve the problem given below and answer the questions that follow:
Three shopkeepers Ram Lal, Shyam Lal, and Ghansham are using polythene bags, handmade bags (prepared by prisoners), and newspaper envelopes as carrying bags. It is found that the shopkeepers Ram Lal, Shyam Lal, and Ghansham are using (20,30,40), (30,40,20), and (40,20,30) polythene bags, handmade bags, and newspapers envelopes respectively. The shopkeeper’s Ram Lal, Shyam Lal, and Ghansham spent ₹250, ₹270, and ₹200 on these carry bags respectively.
- (b) Shyam Lal
- (a) Ram Lal
Case Study Questions Determinants – 02
Case study questions application of derivatives.
- R(x) = -x 2 + 200x + 150000
- R(x) = x 2 – 200x – 140000
- R(x) = 200x 2 + x + 150000
- R(x) = -x 2 + 100 x + 100000
- R'(x) > 0
- R'(x) < 0
- R”(x) = 0
- (a) -x 2 + 200x + 150000
- (a) R'(x) = 0
- (c) 257, -63
Case Study Questions Vector Algebra
- tan−1(5/12)
- tan−1(12/3)
- (b) 130 m/s
- (a) tan−1(5/12)
- (b) 170 m/s
More Case Study Questions
These are only some samples. If you wish to get more case study questions for CBSE class 12 maths, install the myCBSEguide App. It has class 12 Maths chapter-wise case studies with solutions.
12 Maths Exam pattern
Question Paper Design of CBSE class 12 maths is as below. It clearly shows that 20% weightage will be given to HOTS questions. Whereas 55% of questions will be easy to solve.
- No. chapter-wise weightage. Care to be taken to cover all the chapters
- Suitable internal variations may be made for generating various templates keeping the overall weightage to different forms of questions and typology of questions the same.
Choice(s): There will be no overall choice in the question paper. However, 33% of internal choices will be given in all the sections
12 Maths Prescribed Books
- Mathematics Part I – Textbook for Class XII, NCERT Publication
- Mathematics Part II – Textbook for Class XII, NCERT Publication
- Mathematics Exemplar Problem for Class XII, Published by NCERT
- Mathematics Lab Manual class XII, published by NCERT
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Reduced Syllabus Class 10 (2020-21)
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2020-21
- Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
1 thought on “Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions”
plz provide solutions too
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Case Based Questions (MCQ)
- Miscellaneous
- Properties of Determinant
Question 3 - Case Based Questions (MCQ) - Chapter 4 Class 12 Determinants
Last updated at April 2, 2024 by Teachoo
Two schools Oxford and Navdeep want to award their selected students on the values of sincerity, truthfulness and helpfulness. Oxford wants to award ₹ x each, ₹ y each and ₹ z each for the three respective values to 3, 2 and 1 students respectively with a total award money of ₹ 1600. Navdeep wants to spend ₹ 2300 to award its 4, 1 and 3 students on the respective values (by giving the same amount to the three values as before). The total amount of the award for one prize on each is ₹ 900.

(i) x + y + z = _______.
(a) 800 , (b) 900 , (c) 1000 .

(ii) 4x + y + 3z = _______.
(a) 1600 , (c) 900 .

The value of y is _______.
(a) 200 , (c) 300 .

The value of 2x + 3y is _______.
(a) 1000 , (c) 1200 .

y – x = _______.
(a) 100 .

Question Two schools Oxford and Navdeep want to award their selected students on the values of sincerity, truthfulness and helpfulness. Oxford wants to award ₹ x each, ₹ y each and ₹ z each for the three respective values to 3, 2 and 1 students respectively with a total award money of ₹ 1600. Navdeep wants to spend ₹ 2300 to award its 4, 1 and 3 students on the respective values (by giving the same amount to the three values as before). The total amount of the award for one prize on each is ₹ 900. Given that Value of award for sincerity = Rs x Value of award for truthfulness = Rs y Value of award for helpfulness = Rs z Given that Total amount of the award for one prize on each is ₹ 900 x + y + z = 900 Also, Oxford wants to award ₹ x each, ₹ y each and ₹ z each for the three respective values to 3, 2 and 1 students respectively with a total award money of ₹ 1600 3x + 2y + z = 1600 And, Navdeep wants to spend ₹ 2300 to award its 4, 1 and 3 students on the respective values. 4x + y + 3z = 2300 Question 1 (i) x + y + z = _______. (a) 800 (b) 900 (c) 1000 (d) 1200 From (1) x + y + z = 900 So, the correct answer is (B) Question 2 (ii) 4x + y + 3z = _______. (a) 1600 (b) 2300 (c) 900 (d) 1200 From (3) 4x + y + 3z = 2300 So, the correct answer is (B) Question 3 The value of y is _______. (a) 200 (b) 250 (c) 300 (d) 350 Now, our equations are x + y + z = 900 3x + 2y + z = 1600 4x + y + 3z = 2300 Writing equation as AX = B [■8(1&1&1@3&2&1@4&1&3)] [■8(𝑥@𝑦@𝑧)] = [■8(900@1600@2300)] Hence A = [■8(1&1&1@3&2&1@4&1&3)], X = [■8(𝑥@𝑦@𝑧)] & B = [■8(900@1600@2300)] Calculating |A| |A| = |■8(1&1&1@3&2&1@4&1&3)| = 1 |■8(2&1@1&3)| – 1 |■8(3&1@4&3)| + 1 |■8(3&2@4&1)| = 1(6 − 1) − 1 (9 − 4) + 1 (3 − 8) = 1 (5) − 1 (5) + 1 (–5) = 5 − 5 − 5 = −5 Thus, |A| ≠ 0 ∴ The system of equation is consistent & has a unique solution Now, AX = B X = A-1 B Calculating A-1 A-1 = 1/(|A|) adj (A) adj (A) = [■8(A_11&A_12&A_13@A_21&A_22&A_23@A_31&A_32&A_33 )]^′ = [■8(A_11&A_21&A_31@A_12&A_22&A_23@A_13&A_32&A_33 )] And, A = [■8(1&1&1@3&2&1@4&1&3)] M11 = [■8(2&1@1&3)] = 6 − 1 = 5 M12 = [■8(3&1@4&3)] = 9 − 4 = 5 M13 = [■8(3&2@4&1)] = 3 − 8 = −5 M21 = [■8(1&1@1&3)] = 3 − 1 = 2 M22 = [■8(1&1@4&3)] = 3 − 4 = −1 M23 = [■8(1&1@4&1)] = 1 − 4 = −3 M31 = [■8(1&1@2&1)] = 1 − 2 = −1 M32 = [■8(1&1@3&1)] = 1 − 3 = −2 M33 = [■8(1&1@3&2)] = 2 − 3 = −1 Now, A11 = (–1)1+1 . M11 = (–1)2 . (5) = 5 A12 = (–1)1+2 . M12 = (–1)3 . (5) = −5 A13 = (–1)1+3 . M13 = (–1)4 . (−5) = −5 A21 = (–1)2+1 . M21 = (–1)3 . (2) = −2 A22 = (–1)2+2 . M22 = (–1)4 . (−1) = −1 A23 = (–1)2+3 . M23 = (–1)5 . (−3) = 3 A31 = (–1)3+1 . M31 = (–1)4 . (−1) = −1 A32 = (–1)3+2 . M32 = (–1)5 . (−2) = 2 A33 = (–1)3+3 . M33 = (–1)6 . (−1) = −1 Thus, adj (A) =[■8(5&−2&−1@−5&−1&2@−5&3&−1)] Now, A-1 = 1/(|A|) adj A Putting values = 1/(−5) [■8(5&−2&−1@−5&−1&2@−5&3&−1)] = 1/5 [■8(−5&2&1@5&1&−2@5&−3&1)] Also, X = A-1 B Putting values [█(■8(𝑥@𝑦)@𝑧)] = 1/5 [■8(−5&2&1@5&1&−2@5&−3&1)][■8(900@1600@2300)] [█(■8(𝑥@𝑦)@𝑧)] = 1/5 [■8(−5(900)+2(1600)+1(2300)@5(900)+1(1600)+(−2)(2300)@5(900)+(−3)(1600)+1(2300) )] [█(■8(𝑥@𝑦)@𝑧)] = 1/5 [■8(−4500+3200+2300@4500+1600−4600@4500−4800+2300)] = 1/5 [█(■8(1000@1500)@2000)] [█(■8(𝑥@𝑦)@𝑧)] = [█(■8(200@300)@400)] Hence, x = 200, y = 300 & z = 400 Since y = 300 So, the correct answer is (C) Question 4 The value of 2x + 3y is _______. (a) 1000 (b) 1100 (c) 1200 (d) 1300 Since, x = 200, y = 300 & z = 400 Thus, 2x + 3y = 2(200) + 3(300) = 400 + 900 = 1300 So, the correct answer is (d) Question 5 y – x = _______. (a) 100 (b) 200 (c) 300 (d) 400 Since, x = 200, y = 300 & z = 400 Thus, y − x = 300 − 200 = 100 So, the correct answer is (A)

Davneet Singh
Davneet Singh has done his B.Tech from Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. He has been teaching from the past 13 years. He provides courses for Maths, Science, Social Science, Physics, Chemistry, Computer Science at Teachoo.
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Mathematics
- Determinants
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
12th Class Mathematics Determinants Question Bank
Done case based (mcqs) - determinants total questions - 15.

A) x - y = 50, 2x - y = 550 done clear
B) x - y = 50, 2x + y = 550 done clear
C) x + y = 50, 2x + y = 550 done clear
D) x + y = 50, 2x + y = 550. done clear
question_answer 2) Which of the following matrix equation is represented by the given information?
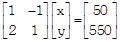
question_answer 3) The value of x (length of rectangular field) is
A) 150 m done clear
B) 400 m done clear
C) 200 m done clear
D) 320 m done clear
question_answer 4) The value of y (breadth of rectangular field) is
B) 200 m done clear
C) 430m done clear
D) 350m done clear
question_answer 5) How much is the area of rectangular field?
A) 60000 Sq.m. done clear
B) 30000 Sq.m. done clear
C) 30000 m done clear
D) 3000 m. done clear
A) 700 done clear
B) 7,000 done clear
C) 6,125 done clear
D) 7875 done clear
question_answer 7) What is the total amount of money (in Rs) collected by schools CVS and KVS?
A) 14,000 done clear
B) 15,725 done clear
C) 21,000 done clear
D) 13,125 done clear
question_answer 8) What is the total amount of money collected by all three schools DPS, CVS and KVS
A) Rs 15,775 done clear
B) Rs 14,000 done clear
C) Rs 21,000 done clear
D) Rs 17,125 done clear
question_answer 9) If the number of handmade fans and plates are interchanged for all the schools, then what is the total money collected by all schools?
A) Rs 18,000 done clear
B) Rs 6,750 done clear
C) Rs 5,000 done clear
D) Rs 21,250. done clear
question_answer 10) How many articles (in total) are sold by three schools?
A) 230 done clear
B) 130 done clear
C) 430 done clear
D) 330 done clear
A) \[5x-4y=40,\text{ }5x-8y=-80\] done clear
B) \[5x-4y=40,\text{ }5x-8y=80\] done clear
C) \[5x-4y=40,\text{ }5x+8y=-80\] done clear
D) \[5x+4y=40,\text{ }5x-8y=-80\] done clear
question_answer 12) Which of the following matrix equations represent the information given above?
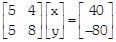
question_answer 13) The number of children who were given some money by Seema, is
A) 30 done clear
B) 40 done clear
C) 23 done clear
D) 32 done clear
question_answer 14) How much amount is given to each child by Seema?
A) Rs 32 done clear
B) Rs 30 done clear
C) Rs 62 done clear
D) Rs 26 done clear
question_answer 15) How much amount Seema spends in distributing the money to all the students of the orphanage?
A) Rs 609 done clear
B) Rs 960 done clear
C) Rs 906 done clear
D) Rs 690 done clear
Study Package

Case Based (MCQs) - Determinants
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.4: Applications of the Determinant
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 20006

- Ken Kuttler
- Brigham Young University via Lyryx
- Use determinants to determine whether a matrix has an inverse, and evaluate the inverse using cofactors.
- Apply Cramer’s Rule to solve a \(2\times 2\) or a \(3\times 3\) linear system.
- Given data points, find an appropriate interpolating polynomial and use it to estimate points.
A Formula for the Inverse
The determinant of a matrix also provides a way to find the inverse of a matrix. Recall the definition of the inverse of a matrix in Definition 2.6.1 . We say that \(A^{-1}\) , an \(n \times n\) matrix, is the inverse of \(A\) , also \(n \times n\) , if \(AA^{-1} = I\) and \(A^{-1}A=I\) .
We now define a new matrix called the cofactor matrix of \(A\) . The cofactor matrix of \(A\) is the matrix whose \(ij^{th}\) entry is the \(ij^{th}\) cofactor of \(A\) . The formal definition is as follows.
Definition \(\PageIndex{1}\): The Cofactor Matrix
Let \(A=\left[ a_{ij}\right]\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix. Then the cofactor matrix of \(A\) , denoted \(\mathrm{cof}\left( A\right)\) , is defined by \(\mathrm{cof}\left( A\right) =\left[ \mathrm{cof}\left(A\right)_{ij}\right]\) where \(\mathrm{cof}\left(A\right)_{ij}\) is the \(ij^{th}\) cofactor of \(A\) .
Note that \(\mathrm{cof}\left(A\right)_{ij}\) denotes the \(ij^{th}\) entry of the cofactor matrix.
We will use the cofactor matrix to create a formula for the inverse of \(A\) . First, we define the adjugate of \(A\) to be the transpose of the cofactor matrix. We can also call this matrix the classical adjoint of \(A\) , and we denote it by \(adj \left(A\right)\) .
In the specific case where \(A\) is a \(2 \times 2\) matrix given by \[A = \left[ \begin{array}{rr} a & b \\ c & d \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] then \({adj}\left(A\right)\) is given by \[{adj}\left(A\right) = \left[ \begin{array}{rr} d & -b \\ -c & a \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
In general, \({adj}\left(A\right)\) can always be found by taking the transpose of the cofactor matrix of \(A\) . The following theorem provides a formula for \(A^{-1}\) using the determinant and adjugate of \(A\) .
Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\): The Inverse and the Determinant
Let \(A\) be an \(n\times n\) matrix. Then \[A \; {adj}\left(A\right) = {adj}\left(A\right)A = {\det \left(A\right)} I\nonumber \]
Moreover \(A\) is invertible if and only if \(\det \left(A\right) \neq 0\) . In this case we have: \[A^{-1} = \frac{1}{\det \left(A\right)} {adj}\left(A\right)\nonumber \]
Notice that the first formula holds for any \(n \times n\) matrix \(A\) , and in the case \(A\) is invertible we actually have a formula for \(A^{-1}\) .
Consider the following example.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Find Inverse Using the Determinant
Find the inverse of the matrix \[A=\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & 1 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] using the formula in Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) .
According to Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) , \[A^{-1} = \frac{1}{\det \left(A\right)} {adj}\left(A\right)\nonumber \]
First we will find the determinant of this matrix. Using Theorems 3.2.1 , 3.2.2 , and 3.2.4 , we can first simplify the matrix through row operations. First, add \(-3\) times the first row to the second row. Then add \(-1\) times the first row to the third row to obtain \[B = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 0 & -6 & -8 \\ 0 & 0 & -2 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] By Theorem 3.2.4 , \(\det \left(A\right) = \det \left(B\right)\) . By Theorem 3.1.2 , \(\det \left(B\right) = 1 \times -6 \times -2 = 12\) . Hence, \(\det \left(A\right) = 12\) .
Now, we need to find \({adj} \left(A\right)\) . To do so, first we will find the cofactor matrix of \(A\) . This is given by \[\mathrm{cof}\left( A\right) = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} -2 & -2 & 6 \\ 4 & -2 & 0 \\ 2 & 8 & -6 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] Here, the \(ij^{th}\) entry is the \(ij^{th}\) cofactor of the original matrix \(A\) which you can verify. Therefore, from Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) , the inverse of \(A\) is given by \[A^{-1} = \frac{1}{12}\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} -2 & -2 & 6 \\ 4 & -2 & 0 \\ 2 & 8 & -6 \end{array} \right] ^{T}= \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} & \frac{1}{6} \\ -\frac{1}{6} & -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{2}{3} \\ \frac{1}{2} & 0 & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Remember that we can always verify our answer for \(A^{-1}\) . Compute the product \(AA^{-1}\) and \(A^{-1}A\) and make sure each product is equal to \(I\) .
Compute \(A^{-1}A\) as follows \[A^{-1}A = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} & \frac{1}{6} \\ -\frac{1}{6} & -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{2}{3} \\ \frac{1}{2} & 0 & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & 1 \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right] = I\nonumber \] You can verify that \(AA^{-1} = I\) and hence our answer is correct.
We will look at another example of how to use this formula to find \(A^{-1}\) .
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\): Find the Inverse From a Formula
Find the inverse of the matrix \[A=\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} \frac{1}{2} & 0 & \frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} & - \frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{5}{6} & \frac{2}{3} & - \frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] using the formula given in Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) .
First we need to find \(\det \left(A\right)\) . This step is left as an exercise and you should verify that \(\det \left(A\right) = \frac{1}{6}.\) The inverse is therefore equal to \[A^{-1} = \frac{1}{(1/6)}\; {adj} \left(A\right) = 6\; {adj} \left(A\right)\nonumber \]
We continue to calculate as follows. Here we show the \(2 \times 2\) determinants needed to find the cofactors. \[A^{-1} = 6\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} \left| \begin{array}{rr} \frac{1}{3} & -\frac{1}{2} \\ \frac{2}{3} & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right| & -\left| \begin{array}{rr} -\frac{1}{6} & -\frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{5}{6} & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right| & \left| \begin{array}{rr} -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} \\ -\frac{5}{6} & \frac{2}{3} \end{array} \right| \\ -\left| \begin{array}{rr} 0 & \frac{1}{2} \\ \frac{2}{3} & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right| & \left| \begin{array}{rr} \frac{1}{2} & \frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{5}{6} & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right| & -\left| \begin{array}{rr} \frac{1}{2} & 0 \\ -\frac{5}{6} & \frac{2}{3} \end{array} \right| \\ \left| \begin{array}{rr} 0 & \frac{1}{2} \\ \frac{1}{3} & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right| & -\left| \begin{array}{rr} \frac{1}{2} & \frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{1}{6} & -\frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right| & \left| \begin{array}{rr} \frac{1}{2} & 0 \\ -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} \end{array} \right| \end{array} \right] ^{T}\nonumber \]
Expanding all the \(2\times 2\) determinants, this yields \[A^{-1} = 6\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} \frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} & \frac{1}{6} \\ \frac{1}{3} & \frac{1}{6} & -\frac{1}{3} \\ -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{6} \end{array} \right] ^{T}= \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & -1 \\ 2 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & -2 & 1 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Again, you can always check your work by multiplying \(A^{-1}A\) and \(AA^{-1}\) and ensuring these products equal \(I\) . \[A^{-1}A = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & -1 \\ 2 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & -2 & 1 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} \frac{1}{2} & 0 & \frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{1}{6} & \frac{1}{3} & - \frac{1}{2} \\ -\frac{5}{6} & \frac{2}{3} & - \frac{1}{2} \end{array} \right] = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] This tells us that our calculation for \(A^{-1}\) is correct. It is left to the reader to verify that \(AA^{-1} = I\) .
The verification step is very important, as it is a simple way to check your work! If you multiply \(A^{-1}A\) and \(AA^{-1}\) and these products are not both equal to \(I\) , be sure to go back and double check each step. One common error is to forget to take the transpose of the cofactor matrix, so be sure to complete this step.
We will now prove Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) .
(of Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) ) Recall that the \((i,j)\) -entry of \({adj}(A)\) is equal to \(\mathrm{cof}(A)_{ji}\) . Thus the \((i,j)\) -entry of \(B=A\cdot {adj}(A)\) is : \[B_{ij}=\sum_{k=1}^n a_{ik} {adj} (A)_{kj}= \sum_{k=1}^n a_{ik} \mathrm{cof} (A)_{jk}\nonumber \] By the cofactor expansion theorem, we see that this expression for \(B_{ij}\) is equal to the determinant of the matrix obtained from \(A\) by replacing its \(j\) th row by \(a_{i1}, a_{i2}, \dots a_{in}\) — i.e., its \(i\) th row.
If \(i=j\) then this matrix is \(A\) itself and therefore \(B_{ii}=\det A\) . If on the other hand \(i\neq j\) , then this matrix has its \(i\) th row equal to its \(j\) th row, and therefore \(B_{ij}=0\) in his case. Thus we obtain: \[A \; {adj}\left(A\right) = {\det \left(A\right)} I\nonumber \] Similarly we can verify that: \[{adj}\left(A\right)A = {\det \left(A\right)} I\nonumber \] And this proves the first part of the theorem.
Further if \(A\) is invertible, then by Theorem 3.2.5 we have: \[1 = \det \left( I \right) = \det \left( A A^{-1} \right) = \det \left( A \right) \det \left( A^{-1} \right)\nonumber \] and thus \(\det \left( A \right) \neq 0\) . Equivalently, if \(\det \left( A \right) = 0\) , then \(A\) is not invertible.
Finally if \(\det \left( A \right) \neq 0\) , then the above formula shows that \(A\) is invertible and that: \[A^{-1} = \frac{1}{\det \left(A\right)} {adj}\left(A\right)\nonumber \]
This completes the proof.
This method for finding the inverse of \(A\) is useful in many contexts. In particular, it is useful with complicated matrices where the entries are functions, rather than numbers.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\): Inverse for Non-Constant Matrix
Suppose \[A\left( t\right) =\left[ \begin{array}{ccc} e^{t} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \cos t & \sin t \\ 0 & -\sin t & \cos t \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] Show that \(A\left( t\right) ^{-1}\) exists and then find it.
First note \(\det \left( A\left( t\right) \right) = e^{t}(\cos^2 t + \sin^2 t) = e^{t}\neq 0\) so \(A\left( t\right) ^{-1}\) exists.
The cofactor matrix is \[C\left( t\right) =\left[ \begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{t}\cos t & e^{t}\sin t \\ 0 & -e^{t}\sin t & e^{t}\cos t \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] and so the inverse is \[\frac{1}{e^{t}}\left[ \begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{t}\cos t & e^{t}\sin t \\ 0 & -e^{t}\sin t & e^{t}\cos t \end{array} \right] ^{T}= \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} e^{-t} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \cos t & -\sin t \\ 0 & \sin t & \cos t \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Cramer’s Rule
Another context in which the formula given in Theorem \(\PageIndex{1}\) is important is Cramer’s Rule . Recall that we can represent a system of linear equations in the form \(AX=B\) , where the solutions to this system are given by \(X\) . Cramer’s Rule gives a formula for the solutions \(X\) in the special case that \(A\) is a square invertible matrix. Note this rule does not apply if you have a system of equations in which there is a different number of equations than variables (in other words, when \(A\) is not square), or when \(A\) is not invertible.
Suppose we have a system of equations given by \(AX=B\) , and we want to find solutions \(X\) which satisfy this system. Then recall that if \(A^{-1}\) exists, \[\begin{aligned} AX&=B \\ A^{-1}\left(AX\right)&=A^{-1}B \\ \left(A^{-1}A\right)X&=A^{-1}B \\ IX&=A^{-1}B\\ X &= A^{-1}B\end{aligned}\] Hence, the solutions \(X\) to the system are given by \(X=A^{-1}B\) . Since we assume that \(A^{-1}\) exists, we can use the formula for \(A^{-1}\) given above. Substituting this formula into the equation for \(X\) , we have \[X=A^{-1}B=\frac{1}{\det \left( A\right) }{adj}\left( A\right)B\nonumber \] Let \(x_i\) be the \(i^{th}\) entry of \(X\) and \(b_j\) be the \(j^{th}\) entry of \(B\) . Then this equation becomes \[x_i = \sum_{j=1}^{n}\left[ a_{ij}\right]^{-1}b_{j}=\sum_{j=1}^{n}\frac{1} {\det \left( A\right) } {adj}\left( A\right) _{ij}b_{j}\nonumber \] where \({adj}\left(A\right)_{ij}\) is the \(ij^{th}\) entry of \({adj}\left(A\right)\) .
By the formula for the expansion of a determinant along a column, \[x_{i}=\frac{1}{\det \left( A\right) }\det \left[ \begin{array}{ccccc} \ast & \cdots & b_{1} & \cdots & \ast \\ \vdots & & \vdots & & \vdots \\ \ast & \cdots & b_{n} & \cdots & \ast \end{array} \right]\nonumber \] where here the \(i^{th}\) column of \(A\) is replaced with the column vector \(\left[ b_{1}\cdots \cdot ,b_{n}\right] ^{T}\) . The determinant of this modified matrix is taken and divided by \(\det \left( A\right)\) . This formula is known as Cramer’s rule.
We formally define this method now.
Procedure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Using Cramer’s Rule
Suppose \(A\) is an \(n\times n\) invertible matrix and we wish to solve the system \(AX=B\) for \(X =\left[ x_{1},\cdots ,x_{n}\right] ^{T}.\) Then Cramer’s rule says \[x_{i}= \frac{\det \left(A_{i}\right)}{\det \left(A\right)}\nonumber \] where \(A_{i}\) is the matrix obtained by replacing the \(i^{th}\) column of \(A\) with the column matrix \[B = \left[ \begin{array}{c} b_1 \\ \vdots \\ b_n \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
We illustrate this procedure in the following example.
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\): Using Cramer's Rule
Find \(x,y,z\) if \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & -3 & 2 \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} x \\ y \\ z \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{r} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
We will use method outlined in Procedure \(\PageIndex{1}\) to find the values for \(x,y,z\) which give the solution to this system. Let \[B = \left[ \begin{array}{r} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{array} \right]\nonumber\]
In order to find \(x\) , we calculate \[x = \frac{\det \left(A_{1}\right)}{\det \left(A\right)}\nonumber \] where \(A_1\) is the matrix obtained from replacing the first column of \(A\) with \(B\) .
Hence, \(A_1\) is given by \[A_1 = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & -3 & 2 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Therefore, \[x= \frac{\det \left(A_{1}\right)}{\det \left(A\right)} = \frac{\left| \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & -3 & 2 \end{array} \right| }{\left| \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & -3 & 2 \end{array} \right| }=\frac{1}{2}\nonumber \]
Similarly, to find \(y\) we construct \(A_2\) by replacing the second column of \(A\) with \(B\) . Hence, \(A_2\) is given by \[A_2 = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 & 2 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Therefore, \[y=\frac{\det \left(A_{2}\right)}{\det \left(A\right)} = \frac{\left| \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 & 2 \end{array} \right| }{\left| \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & -3 & 2 \end{array} \right| }=-\frac{1}{7}\nonumber \]
Similarly, \(A_3\) is constructed by replacing the third column of \(A\) with \(B\) . Then, \(A_3\) is given by \[A_3 = \left[ \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 2 \\ 2 & -3 & 3 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Therefore, \(z\) is calculated as follows.
\[z= \frac{\det \left(A_{3}\right)}{\det \left(A\right)} = \frac{\left| \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 2 \\ 2 & -3 & 3 \end{array} \right| }{\left| \begin{array}{rrr} 1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & -3 & 2 \end{array} \right| }=\frac{11}{14}\nonumber \]
Cramer’s Rule gives you another tool to consider when solving a system of linear equations.
We can also use Cramer’s Rule for systems of non linear equations. Consider the following system where the matrix \(A\) has functions rather than numbers for entries.
Using Cramer’s Rule
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\): Use Cramer's Rule for Non-Constant Matrix
Solve for \(z\) if \[\left[ \begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{t}\cos t & e^{t}\sin t \\ 0 & -e^{t}\sin t & e^{t}\cos t \end{array} \right] \left[ \begin{array}{c} x \\ y \\ z \end{array} \right] =\left[ \begin{array}{c} 1 \\ t \\ {0.05in}t^{2} \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
We are asked to find the value of \(z\) in the solution. We will solve using Cramer’s rule. Thus \[z={.05in} \frac{\left| \begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & e^{t}\cos t & t \\ 0 & -e^{t}\sin t & t^{2} \end{array} \right| }{\left| \begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & e^{t}\cos t & e^{t}\sin t \\ 0 & -e^{t}\sin t & e^{t}\cos t \end{array} \right| }= t\left( \left( \cos t\right) t+\sin t\right) e^{-t}\nonumber \]
Polynomial Interpolation
In studying a set of data that relates variables \(x\) and \(y\) , it may be the case that we can use a polynomial to “fit” to the data. If such a polynomial can be established, it can be used to estimate values of \(x\) and \(y\) which have not been provided.
Example \(\PageIndex{6}\): Polynomial Interpolation
Given data points \((1,4), (2,9), (3,12)\) , find an interpolating polynomial \(p(x)\) of degree at most \(2\) and then estimate the value corresponding to \(x = \frac{1}{2}\) .
We want to find a polynomial given by \[p(x) = r_0 + r_1x_1 + r_2x_2^2\nonumber \] such that \(p(1)=4, p(2)=9\) and \(p(3)=12\) . To find this polynomial, substitute the known values in for \(x\) and solve for \(r_0, r_1\) , and \(r_2\) . \[\begin{aligned} p(1) &= r_0 + r_1 + r_2 = 4\\ p(2) &= r_0 + 2r_1 + 4r_2 = 9\\ p(3) &= r_0 + 3r_1 + 9r_2 = 12\end{aligned}\]
Writing the augmented matrix, we have \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr|r} 1 & 1 & 1 & 4 \\ 1 & 2 & 4 & 9 \\ 1 & 3 & 9 & 12 \end{array} \right]\nonumber\]
After row operations, the resulting matrix is \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrr|r} 1 & 0 & 0 & -3 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 8 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & -1 \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
Therefore the solution to the system is \(r_0 = -3, r_1 = 8, r_2 = -1\) and the required interpolating polynomial is \[p(x) = -3 + 8x - x^2\nonumber \]
To estimate the value for \(x = \frac{1}{2}\) , we calculate \(p(\frac{1}{2})\) : \[\begin{aligned} p(\frac{1}{2}) &= -3 + 8(\frac{1}{2}) - (\frac{1}{2})^2\\ &= -3 + 4 - \frac{1}{4} \\ &= \frac{3}{4}\end{aligned}\]
This procedure can be used for any number of data points, and any degree of polynomial. The steps are outlined below.
Procedure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Finding an Interpolation Polynomial
Suppose that values of \(x\) and corresponding values of \(y\) are given, such that the actual relationship between \(x\) and \(y\) is unknown. Then, values of \(y\) can be estimated using an interpolating polynomial \(p(x)\) . If given \(x_1, ..., x_n\) and the corresponding \(y_1, ..., y_n\) , the procedure to find \(p(x)\) is as follows:
- The desired polynomial \(p(x)\) is given by \[p(x) = r_0 + r_1 x + r_2 x^2 + ... + r_{n-1}x^{n-1}\nonumber \]
- \(p(x_i) = y_i\) for all \(i = 1, 2, ...,n\) so that \[\begin{array}{c} r_0 + r_1x_1 + r_2 x_1^2 + ... + r_{n-1}x_1^{n-1} = y_1 \\ r_0 + r_1x_2 + r_2 x_2^2 + ... + r_{n-1}x_2^{n-1} = y_2 \\ \vdots \\ r_0 + r_1x_n + r_2 x_n^2 + ... + r_{n-1}x_n^{n-1} = y_n \end{array}\nonumber \]
- Set up the augmented matrix of this system of equations \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrrrr|r} 1 & x_1 & x_1^2 & \cdots & x_1^{n-1} & y_1 \\ 1 & x_2 & x_2^2 & \cdots & x_2^{n-1} & y_2 \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & &\vdots & \vdots \\ 1 & x_n & x_n^2 & \cdots & x_n^{n-1} & y_n \\ \end{array} \right]\nonumber \]
- Solving this system will result in a unique solution \(r_0, r_1, \cdots, r_{n-1}\) . Use these values to construct \(p(x)\) , and estimate the value of \(p(a)\) for any \(x=a\) .
This procedure motivates the following theorem.
Theorem \(\PageIndex{2}\): Polynomial Interpolation
Given \(n\) data points \((x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), \cdots, (x_n, y_n)\) with the \(x_i\) distinct, there is a unique polynomial \(p(x) = r_0 + r_1x + r_2x^2 + \cdots + r_{n-1}x^{n-1}\) such that \(p(x_i) = y_i\) for \(i=1,2,\cdots, n\) . The resulting polynomial \(p(x)\) is called the interpolating polynomial for the data points.
We conclude this section with another example.
Example \(\PageIndex{7}\): Polynomial Interpolation
Consider the data points \((0,1), (1,2), (3,22), (5,66)\) . Find an interpolating polynomial \(p(x)\) of degree at most three, and estimate the value of \(p(2)\) .
The desired polynomial \(p(x)\) is given by: \[p(x) = r_0 + r_1 x + r_2x^2 + r_3x^3\nonumber \]
Using the given points, the system of equations is \[\begin{aligned} p(0) &= r_0 = 1 \\ p(1) &= r_0 + r_1 + r_2 + r_3 = 2 \\ p(3) &= r_0 + 3r_1 + 9r_2 + 27r_3 = 22 \\ p(5) &= r_0 + 5r_1 + 25r_2 + 125r_3 = 66\end{aligned}\]
The augmented matrix is given by: \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrrr|r} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 3 & 9 & 27 & 22 \\ 1 & 5 & 25 & 125 & 66 \end{array} \right]\nonumber\]
The resulting matrix is \[\left[ \begin{array}{rrrr|r} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & -2 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 3 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array} \right]\nonumber\]
Therefore, \(r_0 = 1, r_1 = -2, r_2 = 3, r_3 = 0\) and \(p(x) = 1 -2x + 3x^2\) . To estimate the value of \(p(2)\) , we compute \(p(2) = 1 -2(2) + 3(2^2) = 1 - 4 + 12 = 9\) .

CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Determinants Case Study Questions With Solutions 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
12th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Case Study Questions
Let \(\begin{equation} A=\left[\begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 2 & 1 \end{array}\right] \end{equation}\) , and U 1 U 2 are first and second columns respectively of a 2 x 2 matrix U. Also, let the column matrices U I and U 2 satisfying \(\begin{equation} A U_{1}=\left[\begin{array}{l} 1 \\ 0 \end{array}\right] \end{equation}\) and \(\begin{equation} A U_{2}=\left[\begin{array}{l} 2 \\ 3 \end{array}\right] \end{equation}\) Based on the above information, answer the following questions (i) The matrix U 1 + U 2 is equal to
(ii) The value of IUI is
(iii) If \(\begin{equation} X=\left[\begin{array}{ll} 3 & 2 \end{array}\right] U\left[\begin{array}{l} 3 \\ 2 \end{array}\right] \end{equation}\) ,then the value of IXI =
(iv) The minor of element at the position a 22 in U is
(v) If \(\begin{equation} U=\left[a_{i j}\right]_{2 \times 2} \end{equation}\) , then the value of a 11 A 11 + a 12 A l2 where A ij denotes the cofactor of a ij is
(ii) What is the award money for Punctuality?
(iii) What is the award money for Hard work?
(iv) If a matrix P is both symmetric and skew-symmetric, then IPI is equal to
(v) If P and Q are two matrices such that PQ = Q and QP = P, then IQ 2 1 is equal to
(ii) What is the cost of one handmade bag?
(iii) What is the cost of one newspaper envelope
(iv) Keeping in mind the social conditions, which shopkeeper is better?
(v) Keeping in mind the environmental conditions, which shopkeeper is better?
Minor of an element aij of a determinant is the determinant obtained by deleting its ith row and /h column in a ij lies and is denoted by M ij . Cofactor of an element a ij' denoted by A ij ,is defined by \(\begin{equation} A_{i j}=(-1)^{i+j} M_{i j} \end{equation}\) , where M ij is minor of a ij. Also, the determinant of a square matrix A is the sum of the products of the elements of any row (or column with their corresponding cofactors. For example if \(\begin{equation} A=\left[a_{i j}\right]_{3 \times 3}, \text { then }|A|=a_{11} A_{11}+a_{12} A_{12}+a_{13} A_{13} \end{equation}\) . Based on the above information, answer the following questions (i) Find the sum of the cofactors of all the elements of \(\begin{equation} \left|\begin{array}{cc} 1 & -2 \\ 4 & 3 \end{array}\right| \end{equation}\)
(ii) Find the minor of a 21 of \(\begin{equation} \left|\begin{array}{ccc} 5 & 6 & -3 \\ -4 & 3 & 2 \\ -4 & -7 & 3 \end{array}\right| \end{equation}\)
(iii) In the determinant \(\begin{equation} \left|\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & -3 & 5 \\ 6 & 0 & 4 \\ 1 & 5 & -7 \end{array}\right| \end{equation}\) find the value of a 32 ·A 32
(iv) If \(\begin{equation} \Delta=\left|\begin{array}{lll} 5 & 3 & 8 \\ 2 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \end{array}\right| \end{equation}\) , find the value of a 32 ·A 32 .
(v) If \(\begin{equation} \Delta=\left|\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & -3 & 5 \\ 6 & 0 & 4 \\ 1 & 5 & -7 \end{array}\right| \end{equation}\) , then find the value of \(\begin{equation} |\Delta| \end{equation}\) .
(ii) What is the cost of one pen and one bag?
(iii) What is the cost of one pen and one instrument box?
(iv) Which of the following is correct?
(v) From the matrix equation AB = AC, it can be concluded that B = C provided
*****************************************
Related 12th standard cbse maths materials, other 12th standard cbse materials.

CBSE 12th Physics Wave Optics Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 12th physics ray optics and optical instruments chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics nuclei chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics moving charges and magnetism chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics electromagnetic induction chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics atoms chapter case study question with answers, 12th physics alternating current chapter case study question with answers cbse.

12th Chemistry The d and f Block Elements Chapter Case Study Question with Answers CBSE
12th chemistry haloalkanes and haloarenes chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry coordination compounds chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry chemical kinetics chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry biomolecules chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry amines chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th aldehydes ketones and carboxylic acids chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry alcohols phenols and ethers chapter case study question with answers cbse, tamilnadu stateboard 12th standard cbse study materials.

Tamilnadu Stateboard 12th Standard CBSE Subjects

CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Determinants Class 12 Mathematics Important Questions
Students can read the important questions given below for Determinants Class 12 Mathematics. All Determinants Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 12 Mathematics Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Mathematics Question Bank Class 12 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Determinants Class 12
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. If A is an invertible matrix of order 3 and |A| = 5, then find |Adj A|. Answer.
Question. If A is a non-singular matrix of order 3 and |Adj A| = |A| K , then write the value of K. Answer.

Question. If A is a square matrix of order 3 and |3A| = K|A|, then write the value of K. Answer.
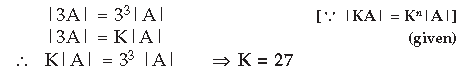
Question. A is a square matrix of order 3 and |A| = 7. Write the value of |adj. A|. Answer. |adj. A|= |A| n–1 = |A| 3 – 1 = (7) 2 = 49
Question. If |A| = 2, where A is a 2 × 2 matrix, find |adj A|. Answer. |adj A|= |A| n – 1 = (2) 2 –1 = 2
Question. What is the value of the determinant
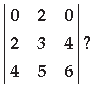
Answer. Expanding along R1 = – 2(12 – 16) = – 2(– 4) = 8
Question. Find the minor of the element of second row and third column (a 23 ) in the following determinant :
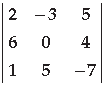
Question. What positive value of x makes the following pair of determinants equal?
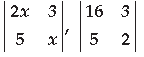
Question. Write the adjoint of the following matrix :
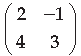
Question. A matrix A of order 3 × 3 is such that |A| = 4. Find the value of |2A|. Answer. |2A| = 2n|A| = 23(4) = 32
Question. If A is an invertible matrix of order 3 and |A| = 5, then find the value of |adj A|. Answer. |adj A|= |A| n – 1 = (5) 3–1 = (5) 2 = 25

⇒ x2 – x = 6 – 4 ⇒ x 2 – x = 2 ⇒ x 2 – x – 2 = 0 ⇒ x 2 – 2x + x – 2 = 0 ⇒ x(x – 2) + 1(x – 2) = 0 ⇒ (x – 2) (x + 1) = 0 ⇒ x = 2 or x = – 1 ∴ The positive value of x is 2.
Question. Let A be a square matrix of order 3 × 3. Write the value of |2A|, where |A| = 4. Answer. |2A| = 2 3 |A| = 8(4) = 32
Question. The value of the determinant of a matrix A of order 3 × 3 is 4. Find the value of |5A|. Answer. |A| = 4 |5A| = 5 3 |A| = 125 (4) = 500
Question. If the determinant of a matrix A of order 3 × 3 is of value 4, write the value of |3A|. Answer. |A| = 4 ⇒ |3A| = 3 3 |A| = 27(4) = 108

Question. If A is a square matrix of order 3 such that |adj A| = 64, find |A|. Answer. |adj A| = 64 |A| 2 = 64 [ ∵ |adj A| = |A| n–1 , Here n= 3] ∴ |A| = ± 8
Question. If A is an invertible square matrix of order 3 and |A| = 5, then find the value of |adj A|. Answer. |adjA|= |A| n–1 = (5) 3–1 = 5 2 = 25 [Here |A| = 5, n = 3
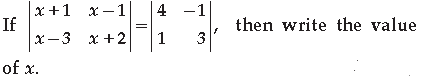
Answer. (x + 1) (x + 2) – (x – 1) (x – 3) = 12 + 1 ⇒ (x 2 + 2x + x + 2) – (x 2 – 3x – x + 3) = 13 ⇒ 3x + 2 + 4x – 3 = 13 ⇒7x – 1 = 13 ⇒ 7x = 14
Question. If A ij i s the cofactor of the element a ij of the
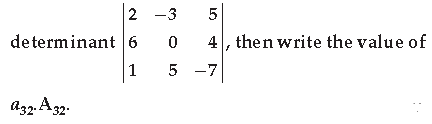
Question. Find the inverse of the matrix
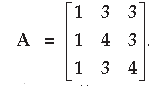
Question. Find the maximum value of
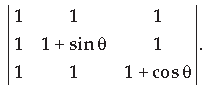
Question. If A is a square matrix of order 2 and |adj A| = 9, find |A|. Answer. |adj A|= 9 …(given) |A| n – 1 = 9, (order, adj, n = 2) |A| 2 – 1 = 9 |A| = 9
Question. If for any 2 × 2 square matrix A,
Question. If A is an invertible matrix of order 2 and det (A) = 4, then write the value of det (A –1 ). Answer.
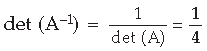
Question. If A is a 3 × 3 invertible matrix, then what will be the value of k if det(A –1 ) = (det A) k Answer.
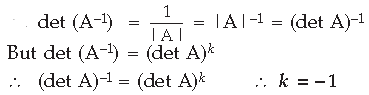
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. If A is a skew-symmetric matrix of order 3, then prove that det A = 0. (All India) Answer. A is a skew-symmetric matrix A t = – A ⇒ |A t | = |– A| ⇒ |A t | = (– 1) n |A| ⇒ |A t | = (– 1) 3 |A| …( ∵ = 3) ⇒ |A| = – |A| ( ∵ |A t | = |A|) ⇒ |A| + |A| = 0 ⇒ 2|A| = 0 ∴ |A| = 0
Short Answer Type Questions-II
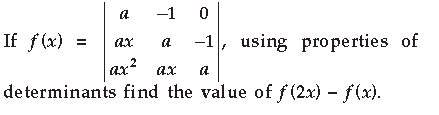
Answer. To find : f (2x) – f (x) 1 st method :

Question. Using properties of determinants, prove the following :
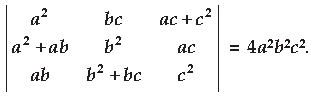
Expanding along C 1 , we have = – 2abc 2 . 1(– ab – ab) = – 2abc 2 (– 2ab) = 4a 2 b 2 c 2 = R.H.S.

Question. Using properties of determinants, solve for x :
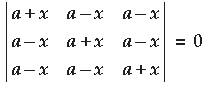
Question. Two schools A and B decided to award prizes to their students for three values, team spirit, truthfulness and tolerance at the rate of ₹ x, ₹y and ₹ z per student respectively. School A, decided to award a total of ₹ 1,100 for the three values to 3, 1 and 2 students respectively while school B decided to award ₹ 1,400 for the three values to 1, 2 and 3 students respectively. If one prize for all the three values together amount to ₹ 600 then (i) Represent the above situation by a matrix equation after forming linear equations. (ii) Is it possible to solve the system of equations so obtained using matrices? Answer.
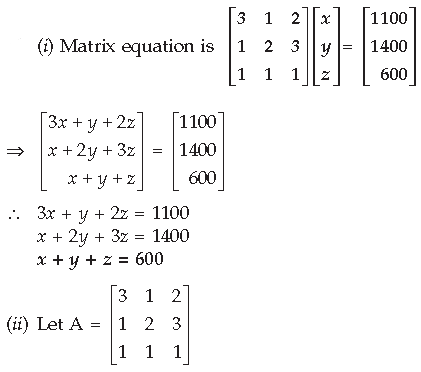
⇒ |A| = 3(2 – 3) – 1(1 – 3) + 2(1 – 2) = – 3 + 2 – 2 = – 3 ≠ 0 A –1 exists, so equations have a unique solution. Hence system of equations can be solved.
Question. Using properties of determinants, prove that
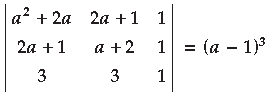
Answer. Given : CD – AB = 0 DC = AB ⇒ D = C –1 AB …(i) |C| = 16 – 15 = 1 ≠ 0;
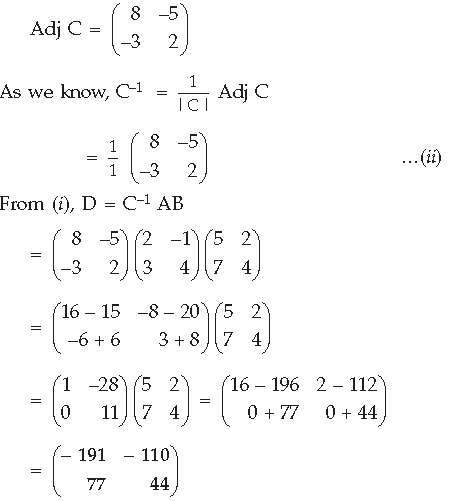
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Using matrices, solve the following system of equations : x + y + z = 1;x – 2y + 3z = 2; x – 3y + 5z = 3 Answer. Given equations can be written as

Question. Using properties of determinants, show the following :
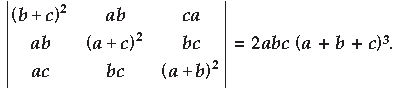
Answer. Part I :
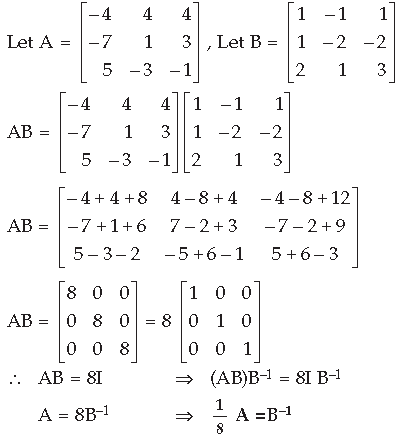
Part II : Given system of equations can be written in matrix form
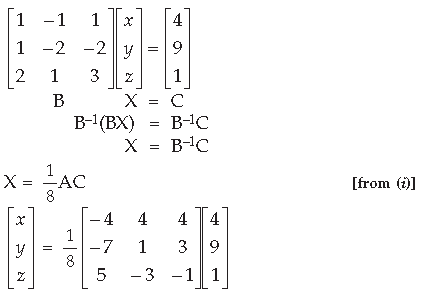
AB. Use this to solve the following system of equations : x – y = 3, 2x + 3y + 4z = 17, y + 2z = 7 Answer. Part I :
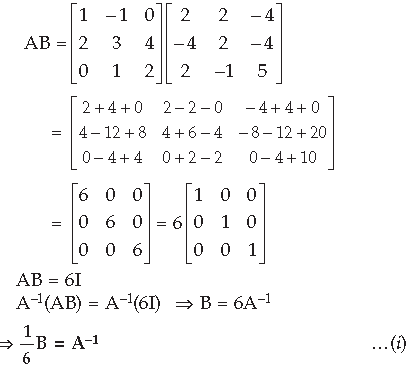
Related Posts

Meeting Life Challenges Class 12 Psychology Important Questions

Secondary Activities Class 12 Geography Important Questions

Water Resources Class 12 Geography Important Questions
Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants MCQs
Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants MCQs are available here to help the students of Class 12 score good marks in the CBSE board exam 2022-2023. Here, we provided multiple objective type questions that will help the students to practise for the exams. These multiple-choice questions form a useful source to prepare for exams as they are given as per the new CBSE guidelines for the academic year 2022-23. All the topics and subtopics of Chapter 4 Determinants of NCERT textbook are covered here in MCQs.
Get access to Class 12 Maths MCQs for all the chapters here at BYJU’S.
MCQs for Chapter 4 Determinants Class 12
Students can access several MCQs on matrices of Class 12 that cover various topics such as fundamentals of matrix and matrix algebra, i.e. mathematical operations on matrices.
Also, check:
- Determinants for Class 12 Notes
- Important Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants
Students must practise more MCQs to understand how to apply the concepts to solve problems in th exam. As we know, the chapter 4 determinants of Class 12 contain several topics and subtopics. They include finding the determinants up to order three only with real entries. Various properties of determinants, minors, cofactors and applications of determinants in finding the triangle area are included.
Download PDF – Chapter 4 Determinants MCQs
Besides, finding the adjoint and inverse of a square matrix, consistency and inconsistency of system of linear equations and solution of linear equations in two or three variables using the inverse of a matrix are included. All these topics are very important from the examination point of view. So, practising MCQs given below will help you get thorough with the formulas and applications of determinants.
MCQs for Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants with Solutions
Correct option: (c) ±6
So, (2x)(x) – (5)(8) = (6)(3) – (-2)(7)
2x 2 – 40 = 18 + 14
2x 2 = 32 + 40
x = √36 = ±6
Correct option: (c) ±4
Given that matrix A is singular.
Thus, the determinant of A is 0.
k(2k) – 8(4) = 0
2k 2 – 32 = 0
3. If A is a square matrix of order 3 and |A| = 5, then the value of |2A′| is
Correct option: (d) 40
According to the property of transpose of a matrix,
(kA′) = kA′
Also, from the property of determinant of a matrix,
and |kA| = k n |A|, where n is the order of matrix A.
Thus, |2A′| = 2 3 |A| {since A is a square matrix of order 3}
4. The area of a triangle with vertices (–3, 0), (3, 0) and (0, k) is 9 sq. units. The value of k will be
Correct option: (b) 3
The formula of area of the triangle with vertices (x 1 , y 1 ), (x 2 , y 2 ), (x 3 , y 3 ) is given by:
Thus, the area of a triangle with vertices (–3, 0), (3, 0) and (0, k) is:
⇒ -3(0 – k) – 0+ 1(3k – 0) = 18
⇒ 3k + 3k = 18
5. Given that A is a square matrix of order 3 and |A| = -4, then |adj A| is equal to
Correct option: (d) 16
Given that A is a square matrix of order 3 and |A| = -4.
We know that |adj A| = |A| n−1 , where n is the order of matrix A.
So, |adj A| = (−4) 3-1 = (-4) 2 = 16
(c) λ ≠ – 2
(d) None of these
Correct option: (d) None of these
The inverse of a matrix exists if its determinant is not equal to 0.
⇒ |A| = 2 (6 – 5) – λ (0 – 5) + (-3) (0 – 2) ≠ 0
⇒ 2 + 5λ + 6 ≠ 0
⇒ 5λ + 8 ≠ 0
Therefore, A-1 exists if and only if λ ≠ -8/5.
= (3)(2) – (-1)(1)
14A -1 = 14[adj A/ |A|] = (14/7) adj A
8. Which of the following is correct?
(a) Determinant is a square matrix.
(b) Determinant is a number associated with a matrix.
(c) Determinant is a number associated with a square matrix.
Correct option: (c) Determinant is a number associated with a square matrix.
We know that we can calculate determinant values only for square matrices.
Therefore, the determinant is a number associated with a square matrix.
9. Given that A = [a ij ] is a square matrix of order 3×3 and |A| = -7, then the value of ∑ i=1 3 a i2 A i2 , where A ij denotes the cofactor of element a ij is
Correct option: (b) -7
Order of matrix A is 3×3.
Now, ∑ i=1 3 a i2 A i2 = a 12 A 12 + a 22 A 22 + a 32 A 32
10. If A is an invertible matrix of order 2, then det (A –1 ) is equal to
(a) det (A)
(b) 1/det (A)
Correct option: (b) 1/det (A)
Given that the A is an invertible matrix of order 2.
If the matrix is invertible, then its determinant is not equal to 0.
We know that,
AA -1 = I, where I is the identity matrix
Taking determinant on both sides,
|AA -1 | = |I|
|A| |A -1 | = 1
|A -1 | = 1/|A| {since A is non-singular, |A| ≠ 0}
det(A -1 ) = 1/det(A)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

CBSE Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths Determinants Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths Determinants in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Assertion Reason Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!
I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Assertion Reason Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
Checkout our Assertion Reason Questions for other chapters
- Chapter 2 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Assertion Reason Questions
- Chapter 3 Matrices Assertion Reason Questions
- Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Assertion Reason Questions
- Chapter 6 Applications of Derivatives Assertion Reason Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Determinants Case Study Questions With Solutions 2021. Two schools A and B want to award their selected students on the values of Honesty, Hard work and Punctuality. The school A wants to award Rs. x each, Rs. y each and Rs.z each for the three respective values to its 3, 2 and 1 students respectivefy with a ...
Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 12 Maths Determinants in order to fully complete your preparation.They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!. I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams.
Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Chapter 4 Determinants Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Maths Determinants to know their preparation level. Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various ...
Case study questions are a type of question that is commonly used in academic and professional settings to evaluate a person's ability to analyze, interpret, and solve problems based on a given scenario or case study. Typically, a case study question presents a real-world situation or problem that requires the individual to apply their ...
Students looking for Case Study on Determinants Class 12 Maths can use this page to download the PDF file. The case study questions on Determinants are based on the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus, and therefore, referring to the Determinants case study questions enable students to gain the appropriate knowledge and prepare better for the Class 12 ...
That's why CBSE is emphasizing case studies and competency-based education. Case Study Questions in Maths. Let's have a look over the class 12 Mathematics sample question paper issued by CBSE, New Delhi. Question numbers 17 and 18 are case study questions. ... Case Study Questions Determinants - 02. Matrices/Determinants: ...
Transcript. Question Two schools Oxford and Navdeep want to award their selected students on the values of sincerity, truthfulness and helpfulness. Oxford wants to award ₹ x each, ₹ y each and ₹ z each for the three respective values to 3, 2 and 1 students respectively with a total award money of ₹ 1600. Navdeep wants to spend ₹ 2300 ...
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams - Complete list of 12th Standard CBSE question papers, syllabus, exam tips, study material, previous year exam question papers, centum ...
Directions: (1 - 5) Manjit wants to donate a rectangular plot of land for a school in his village. When he was asked to give dimensions of the plot, he told that if its length is decreased by 50 cm and breadth is increased by 50 m, then its area will remain same, but if length is decreased by 10 m and breadth is decreased by 20 m, then its area will decrease by \[5300\text{ }{{m}^{2}}\].
Class 12 Mathematics - Case Study Questions on the Topic DeterminantsThis video discusses a case study on the topic of Determinants for Class 12 MathematicsP...
First we will find the determinant of this matrix. Using Theorems 3.2.1, 3.2.2, and 3.2.4, we can first simplify the matrix through row operations. First, add − 3 times the first row to the second row. Then add − 1 times the first row to the third row to obtain B = [1 2 3 0 − 6 − 8 0 0 − 2] By Theorem 3.2.4, det (A) = det (B).
MCQ & Case Study based Question I Chapter 4 Determinants I Part 1 I Class 12 Maths I Session 2021-22. MCQ & Case Study based Question I Chapter 4 Determinants I Part 1 I Class 12 Maths I Session ...
CBSE 12th Standard Maths Subject Determinants Case Study Questions With Solutions 2021. Two schools A and B want to award their selected students on the values of Honesty, Hard work and Punctuality. The school A wants to award Rs. x each, Rs. y each and Rs.z each for the three respective values to its 3, 2 and 1 students respectivefy with a ...
CBSE Exam, class 12
Sep-08 , 2022. QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Maths Subject - Determinants, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks. QB365 Mobile App For Practice Question Papers.
Important Questions of Determinants Class 12. Question. If A is an invertible matrix of order 3 and |A| = 5, then find |Adj A|. Answer. Question. If A is a non-singular matrix of order 3 and |Adj A| = |A|K, then write the value of K. Answer. Question. If A is a square matrix of order 3 and |3A| = K|A|, then write the value of K.
In this case study for Chapter 3, it is shown how determinants may be used to answer certain geometrical questions and to find equations for geometrical objects. For this work one must consider determinants of matrices whose entries are variables or algebraic expressions. In this case the determinant will itself be an algebraic expression. For
Case Study Questions On Matrix & Determinants ( Code VMSIR ) Jun 6, 2021 • 147 views. 1:00:45. EN Mathematics. Case Study Questions On Matrix & Determinants ( Code VMSIR ) Vishal Mahajan. 48K followers • Mathematics. Watch now Download Class PDF. Jun 6, 2021 • 1h • 147 views.
Shivang Maths Academy App :https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=co.mark.zkeraTelegram link : https://t.me/Shivangmathsacademy1Insta I'd- Shivanggupt...
Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinants MCQs are available here to help the students of Class 12 score good marks in the CBSE board exam 2022-2023. Here, we provided multiple objective type questions that will help the students to practise for the exams. These multiple-choice questions form a useful source to prepare for exams as they are given ...
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions. Level UP. Level UP. After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS. These Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths Determinants are latest, comprehensive, confidence inspiring, with easy to understand ...