- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
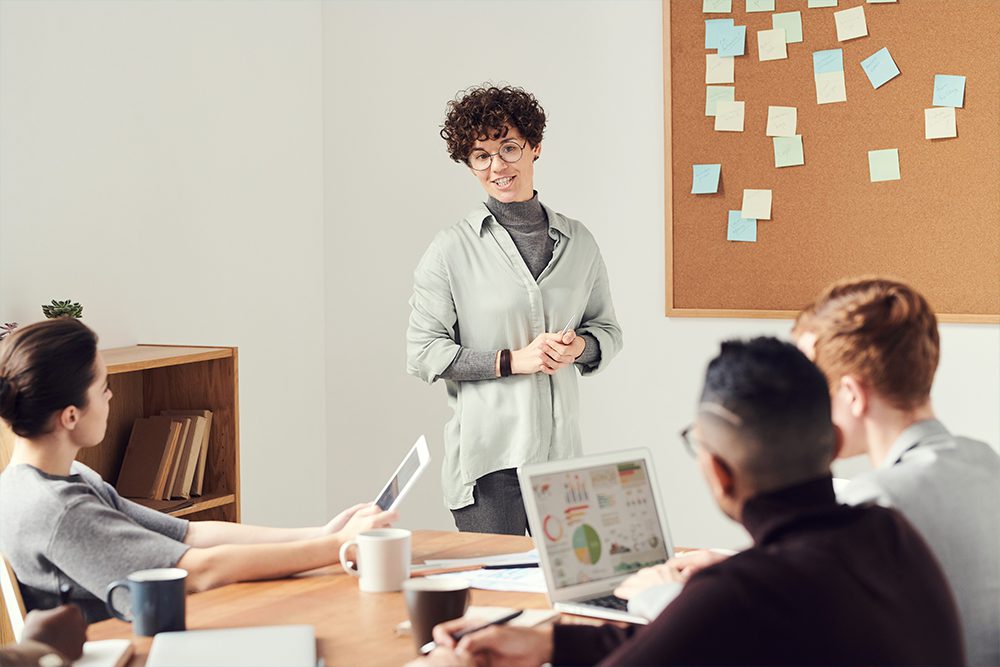
How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips

- 01 Mar 2022
The importance of creativity in the workplace—particularly when problem-solving—is undeniable. Business leaders can’t approach new problems with old solutions and expect the same result.
This is where innovation-based processes need to guide problem-solving. Here’s an overview of what creative problem-solving is, along with tips on how to use it in conjunction with design thinking.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Encountering problems with no clear cause can be frustrating. This occurs when there’s disagreement around a defined problem or research yields unclear results. In such situations, creative problem-solving helps develop solutions, despite a lack of clarity.
While creative problem-solving is less structured than other forms of innovation, it encourages exploring open-ended ideas and shifting perspectives—thereby fostering innovation and easier adaptation in the workplace. It also works best when paired with other innovation-based processes, such as design thinking .
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Design thinking is a solutions-based mentality that encourages innovation and problem-solving. It’s guided by an iterative process that Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar outlines in four stages in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation :

- Clarify: This stage involves researching a problem through empathic observation and insights.
- Ideate: This stage focuses on generating ideas and asking open-ended questions based on observations made during the clarification stage.
- Develop: The development stage involves exploring possible solutions based on the ideas you generate. Experimentation and prototyping are both encouraged.
- Implement: The final stage is a culmination of the previous three. It involves finalizing a solution’s development and communicating its value to stakeholders.
Although user research is an essential first step in the design thinking process, there are times when it can’t identify a problem’s root cause. Creative problem-solving addresses this challenge by promoting the development of new perspectives.
Leveraging tools like design thinking and creativity at work can further your problem-solving abilities. Here are eight tips for doing so.

8 Creative Problem-Solving Tips
1. empathize with your audience.
A fundamental practice of design thinking’s clarify stage is empathy. Understanding your target audience can help you find creative and relevant solutions for their pain points through observing them and asking questions.
Practice empathy by paying attention to others’ needs and avoiding personal comparisons. The more you understand your audience, the more effective your solutions will be.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
If a problem is difficult to define, reframe it as a question rather than a statement. For example, instead of saying, "The problem is," try framing around a question like, "How might we?" Think creatively by shifting your focus from the problem to potential solutions.
Consider this hypothetical case study: You’re the owner of a local coffee shop trying to fill your tip jar. Approaching the situation with a problem-focused mindset frames this as: "We need to find a way to get customers to tip more." If you reframe this as a question, however, you can explore: "How might we make it easier for customers to tip?" When you shift your focus from the shop to the customer, you empathize with your audience. You can take this train of thought one step further and consider questions such as: "How might we provide a tipping method for customers who don't carry cash?"
Whether you work at a coffee shop, a startup, or a Fortune 500 company, reframing can help surface creative solutions to problems that are difficult to define.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
If you encounter an idea that seems outlandish or unreasonable, a natural response would be to reject it. This instant judgment impedes creativity. Even if ideas seem implausible, they can play a huge part in ideation. It's important to permit the exploration of original ideas.
While judgment can be perceived as negative, it’s crucial to avoid accepting ideas too quickly. If you love an idea, don’t immediately pursue it. Give equal consideration to each proposal and build on different concepts instead of acting on them immediately.
4. Overcome Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind that prevents you from recognizing a situation’s alternative solutions or interpretations instead of considering every situation through the lens of past experiences.
Although it's efficient in the short-term, cognitive fixedness interferes with creative thinking because it prevents you from approaching situations unbiased. It's important to be aware of this tendency so you can avoid it.
5. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
One of the key principles of creative problem-solving is the balance of divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking is the process of brainstorming multiple ideas without limitation; open-ended creativity is encouraged. It’s an effective tool for generating ideas, but not every idea can be explored. Divergent thinking eventually needs to be grounded in reality.
Convergent thinking, on the other hand, is the process of narrowing ideas down into a few options. While converging ideas too quickly stifles creativity, it’s an important step that bridges the gap between ideation and development. It's important to strike a healthy balance between both to allow for the ideation and exploration of creative ideas.
6. Use Creative Tools
Using creative tools is another way to foster innovation. Without a clear cause for a problem, such tools can help you avoid cognitive fixedness and abrupt decision-making. Here are several examples:
Problem Stories
Creating a problem story requires identifying undesired phenomena (UDP) and taking note of events that precede and result from them. The goal is to reframe the situations to visualize their cause and effect.
To start, identify a UDP. Then, discover what events led to it. Observe and ask questions of your consumer base to determine the UDP’s cause.
Next, identify why the UDP is a problem. What effect does the UDP have that necessitates changing the status quo? It's helpful to visualize each event in boxes adjacent to one another when answering such questions.
The problem story can be extended in either direction, as long as there are additional cause-and-effect relationships. Once complete, focus on breaking the chains connecting two subsequent events by disrupting the cause-and-effect relationship between them.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool encourages you to consider how people from different backgrounds would approach similar situations. For instance, how would someone in hospitality versus manufacturing approach the same problem? This tool isn't intended to instantly solve problems but, rather, to encourage idea generation and creativity.
7. Use Positive Language
It's vital to maintain a positive mindset when problem-solving and avoid negative words that interfere with creativity. Positive language prevents quick judgments and overcomes cognitive fixedness. Instead of "no, but," use words like "yes, and."
Positive language makes others feel heard and valued rather than shut down. This practice doesn’t necessitate agreeing with every idea but instead approaching each from a positive perspective.
Using “yes, and” as a tool for further idea exploration is also effective. If someone presents an idea, build upon it using “yes, and.” What additional features could improve it? How could it benefit consumers beyond its intended purpose?
While it may not seem essential, this small adjustment can make a big difference in encouraging creativity.
8. Practice Design Thinking
Practicing design thinking can make you a more creative problem-solver. While commonly associated with the workplace, adopting a design thinking mentality can also improve your everyday life. Here are several ways you can practice design thinking:
- Learn from others: There are many examples of design thinking in business . Review case studies to learn from others’ successes, research problems companies haven't addressed, and consider alternative solutions using the design thinking process.
- Approach everyday problems with a design thinking mentality: One of the best ways to practice design thinking is to apply it to your daily life. Approach everyday problems using design thinking’s four-stage framework to uncover what solutions it yields.
- Study design thinking: While learning design thinking independently is a great place to start, taking an online course can offer more insight and practical experience. The right course can teach you important skills , increase your marketability, and provide valuable networking opportunities.

Ready to Become a Creative Problem-Solver?
Though creativity comes naturally to some, it's an acquired skill for many. Regardless of which category you're in, improving your ability to innovate is a valuable endeavor. Whether you want to bolster your creativity or expand your professional skill set, taking an innovation-based course can enhance your problem-solving.
If you're ready to become a more creative problem-solver, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses . If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Creative Problem Solving
Finding innovative solutions to challenges.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Imagine that you're vacuuming your house in a hurry because you've got friends coming over. Frustratingly, you're working hard but you're not getting very far. You kneel down, open up the vacuum cleaner, and pull out the bag. In a cloud of dust, you realize that it's full... again. Coughing, you empty it and wonder why vacuum cleaners with bags still exist!
James Dyson, inventor and founder of Dyson® vacuum cleaners, had exactly the same problem, and he used creative problem solving to find the answer. While many companies focused on developing a better vacuum cleaner filter, he realized that he had to think differently and find a more creative solution. So, he devised a revolutionary way to separate the dirt from the air, and invented the world's first bagless vacuum cleaner. [1]
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
In this article, we'll explore what CPS is, and we'll look at its key principles. We'll also provide a model that you can use to generate creative solutions.
About Creative Problem Solving
Alex Osborn, founder of the Creative Education Foundation, first developed creative problem solving in the 1940s, along with the term "brainstorming." And, together with Sid Parnes, he developed the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving Process. Despite its age, this model remains a valuable approach to problem solving. [2]
The early Osborn-Parnes model inspired a number of other tools. One of these is the 2011 CPS Learner's Model, also from the Creative Education Foundation, developed by Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Marie Mance, and co-workers. In this article, we'll use this modern four-step model to explore how you can use CPS to generate innovative, effective solutions.
Why Use Creative Problem Solving?
Dealing with obstacles and challenges is a regular part of working life, and overcoming them isn't always easy. To improve your products, services, communications, and interpersonal skills, and for you and your organization to excel, you need to encourage creative thinking and find innovative solutions that work.
CPS asks you to separate your "divergent" and "convergent" thinking as a way to do this. Divergent thinking is the process of generating lots of potential solutions and possibilities, otherwise known as brainstorming. And convergent thinking involves evaluating those options and choosing the most promising one. Often, we use a combination of the two to develop new ideas or solutions. However, using them simultaneously can result in unbalanced or biased decisions, and can stifle idea generation.
For more on divergent and convergent thinking, and for a useful diagram, see the book "Facilitator's Guide to Participatory Decision-Making." [3]
Core Principles of Creative Problem Solving
CPS has four core principles. Let's explore each one in more detail:
- Divergent and convergent thinking must be balanced. The key to creativity is learning how to identify and balance divergent and convergent thinking (done separately), and knowing when to practice each one.
- Ask problems as questions. When you rephrase problems and challenges as open-ended questions with multiple possibilities, it's easier to come up with solutions. Asking these types of questions generates lots of rich information, while asking closed questions tends to elicit short answers, such as confirmations or disagreements. Problem statements tend to generate limited responses, or none at all.
- Defer or suspend judgment. As Alex Osborn learned from his work on brainstorming, judging solutions early on tends to shut down idea generation. Instead, there's an appropriate and necessary time to judge ideas during the convergence stage.
- Focus on "Yes, and," rather than "No, but." Language matters when you're generating information and ideas. "Yes, and" encourages people to expand their thoughts, which is necessary during certain stages of CPS. Using the word "but" – preceded by "yes" or "no" – ends conversation, and often negates what's come before it.
How to Use the Tool
Let's explore how you can use each of the four steps of the CPS Learner's Model (shown in figure 1, below) to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Figure 1 – CPS Learner's Model
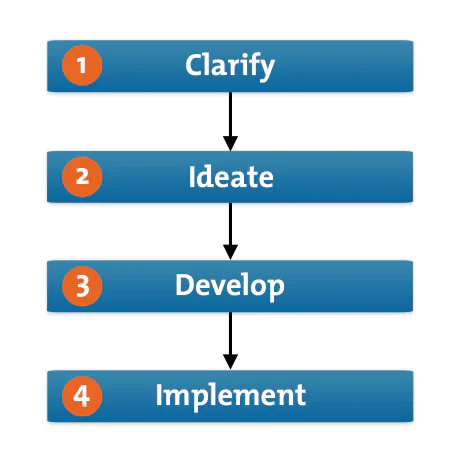
Explore the Vision
Identify your goal, desire or challenge. This is a crucial first step because it's easy to assume, incorrectly, that you know what the problem is. However, you may have missed something or have failed to understand the issue fully, and defining your objective can provide clarity. Read our article, 5 Whys , for more on getting to the root of a problem quickly.
Gather Data
Once you've identified and understood the problem, you can collect information about it and develop a clear understanding of it. Make a note of details such as who and what is involved, all the relevant facts, and everyone's feelings and opinions.
Formulate Questions
When you've increased your awareness of the challenge or problem you've identified, ask questions that will generate solutions. Think about the obstacles you might face and the opportunities they could present.
Explore Ideas
Generate ideas that answer the challenge questions you identified in step 1. It can be tempting to consider solutions that you've tried before, as our minds tend to return to habitual thinking patterns that stop us from producing new ideas. However, this is a chance to use your creativity .
Brainstorming and Mind Maps are great ways to explore ideas during this divergent stage of CPS. And our articles, Encouraging Team Creativity , Problem Solving , Rolestorming , Hurson's Productive Thinking Model , and The Four-Step Innovation Process , can also help boost your creativity.
See our Brainstorming resources within our Creativity section for more on this.
Formulate Solutions
This is the convergent stage of CPS, where you begin to focus on evaluating all of your possible options and come up with solutions. Analyze whether potential solutions meet your needs and criteria, and decide whether you can implement them successfully. Next, consider how you can strengthen them and determine which ones are the best "fit." Our articles, Critical Thinking and ORAPAPA , are useful here.
4. Implement
Formulate a plan.
Once you've chosen the best solution, it's time to develop a plan of action. Start by identifying resources and actions that will allow you to implement your chosen solution. Next, communicate your plan and make sure that everyone involved understands and accepts it.
There have been many adaptations of CPS since its inception, because nobody owns the idea.
For example, Scott Isaksen and Donald Treffinger formed The Creative Problem Solving Group Inc . and the Center for Creative Learning , and their model has evolved over many versions. Blair Miller, Jonathan Vehar and Roger L. Firestien also created their own version, and Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Mary C. Murdock, and Marie Mance developed CPS: The Thinking Skills Model. [4] Tim Hurson created The Productive Thinking Model , and Paul Reali developed CPS: Competencies Model. [5]
Sid Parnes continued to adapt the CPS model by adding concepts such as imagery and visualization , and he founded the Creative Studies Project to teach CPS. For more information on the evolution and development of the CPS process, see Creative Problem Solving Version 6.1 by Donald J. Treffinger, Scott G. Isaksen, and K. Brian Dorval. [6]
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) Infographic
See our infographic on Creative Problem Solving .

Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
There have been many adaptations of the original Osborn-Parnes model, but they all involve a clear structure of identifying the problem, generating new ideas, evaluating the options, and then formulating a plan for successful implementation.
[1] Entrepreneur (2012). James Dyson on Using Failure to Drive Success [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 27, 2022.]
[2] Creative Education Foundation (2015). The CPS Process [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022.]
[3] Kaner, S. et al. (2014). 'Facilitator′s Guide to Participatory Decision–Making,' San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
[4] Puccio, G., Mance, M., and Murdock, M. (2011). 'Creative Leadership: Skils That Drive Change' (2nd Ed.), Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
[5] OmniSkills (2013). Creative Problem Solving [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022].
[6] Treffinger, G., Isaksen, S., and Dorval, B. (2010). Creative Problem Solving (CPS Version 6.1). Center for Creative Learning, Inc. & Creative Problem Solving Group, Inc. Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
What is problem solving.
Book Insights
The Back of the Napkin: Solving Problems and Selling Ideas With Pictures
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

How to Build a Strong Culture in a Distributed Team
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Top tips for delegating.
Delegate work to your team members effectively with these top tips
Ten Dos and Don'ts of Change Conversations
Tips for tackling discussions about change
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Heart, smarts, guts, and luck.
Expert Interviews
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

Effective Problem-Solving Techniques in Business

January 20, 2023
Purdue Online
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Dr. Amy David , clinical associate professor of management for supply chain and operations management, spoke about business problem-solving methods and how the Purdue University Online MBA program prepares students to be business decision-makers.
Why Are Problem-Solving Skills Essential in Leadership Roles?
Every business will face challenges at some point. Those that are successful will have people in place who can identify and solve problems before the damage is done.
“The business world is constantly changing, and companies need to be able to adapt well in order to produce good results and meet the needs of their customers,” David says. “They also need to keep in mind the triple bottom line of ‘people, profit and planet.’ And these priorities are constantly evolving.”
To that end, David says people in management or leadership need to be able to handle new situations, something that may be outside the scope of their everyday work.
“The name of the game these days is change—and the speed of change—and that means solving new problems on a daily basis,” she says.
The pace of information and technology has also empowered the customer in a new way that provides challenges—or opportunities—for businesses to respond.
“Our customers have a lot more information and a lot more power,” she says. “If you think about somebody having an unhappy experience and tweeting about it, that’s very different from maybe 15 years ago. Back then, if you had a bad experience with a product, you might grumble about it to one or two people.”
David says that this reality changes how quickly organizations need to react and respond to their customers. And taking prompt and decisive action requires solid problem-solving skills.
What Are Some of the Most Effective Problem-Solving Methods?
David says there are a few things to consider when encountering a challenge in business.
“When faced with a problem, are we talking about something that is broad and affects a lot of people? Or is it something that affects a select few? Depending on the issue and situation, you’ll need to use different types of problem-solving strategies,” she says.
Using Techniques
There are a number of techniques that businesses use to problem solve. These can include:
- Five Whys : This approach is helpful when the problem at hand is clear but the underlying causes are less so. By asking “Why?” five times, the final answer should get at the potential root of the problem and perhaps yield a solution.
- Gap Analysis : Companies use gap analyses to compare current performance with expected or desired performance, which will help a company determine how to use its resources differently or adjust expectations.
- Gemba Walk : The name, which is derived from a Japanese word meaning “the real place,” refers to a commonly used technique that allows managers to see what works (and what doesn’t) from the ground up. This is an opportunity for managers to focus on the fundamental elements of the process, identify where the value stream is and determine areas that could use improvement.
- Porter’s Five Forces : Developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter, applying the Five Forces is a way for companies to identify competitors for their business or services, and determine how the organization can adjust to stay ahead of the game.
- Six Thinking Hats : In his book of the same name, Dr. Edward de Bono details this method that encourages parallel thinking and attempting to solve a problem by trying on different “thinking hats.” Each color hat signifies a different approach that can be utilized in the problem-solving process, ranging from logic to feelings to creativity and beyond. This method allows organizations to view problems from different angles and perspectives.
- SWOT Analysis : This common strategic planning and management tool helps businesses identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT).
“We have a lot of these different tools,” David says. “Which one to use when is going to be dependent on the problem itself, the level of the stakeholders, the number of different stakeholder groups and so on.”
Each of the techniques outlined above uses the same core steps of problem solving:
- Identify and define the problem
- Consider possible solutions
- Evaluate options
- Choose the best solution
- Implement the solution
- Evaluate the outcome
Data drives a lot of daily decisions in business and beyond. Analytics have also been deployed to problem solve.
“We have specific classes around storytelling with data and how you convince your audience to understand what the data is,” David says. “Your audience has to trust the data, and only then can you use it for real decision-making.”
Data can be a powerful tool for identifying larger trends and making informed decisions when it’s clearly understood and communicated. It’s also vital for performance monitoring and optimization.
How Is Problem Solving Prioritized in Purdue’s Online MBA?
The courses in the Purdue Online MBA program teach problem-solving methods to students, keeping them up to date with the latest techniques and allowing them to apply their knowledge to business-related scenarios.
“I can give you a model or a tool, but most of the time, a real-world situation is going to be a lot messier and more valuable than what we’ve seen in a textbook,” David says. “Asking students to take what they know and apply it to a case where there’s not one single correct answer is a big part of the learning experience.”
Make Your Own Decision to Further Your Career
An online MBA from Purdue University can help advance your career by teaching you problem-solving skills, decision-making strategies and more. Reach out today to learn more about earning an online MBA with Purdue University .
About the Author
- Communication
- Health Sciences
- Student Advice
What is creative problem-solving?
Table of Contents
An introduction to creative problem-solving.
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming . It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh perspectives becomes invaluable for individuals, businesses, and communities alike.
Importance of divergent and convergent thinking
At the heart of creative problem-solving lies the balance between divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking encourages free-flowing, unrestricted ideation, leading to a plethora of potential solutions. Convergent thinking, on the other hand, is about narrowing down those options to find the most viable solution. This dual approach ensures both breadth and depth in the problem-solving process.
Emphasis on collaboration and diverse perspectives
No single perspective has a monopoly on insight. Collaborating with individuals from different backgrounds, experiences, and areas of expertise offers a richer tapestry of ideas. Embracing diverse perspectives not only broadens the pool of solutions but also ensures more holistic and well-rounded outcomes.
Nurturing a risk-taking and experimental mindset
The fear of failure can be the most significant barrier to any undertaking. It's essential to foster an environment where risk-taking and experimentation are celebrated. This involves viewing failures not as setbacks but as invaluable learning experiences that pave the way for eventual success.
The role of intuition and lateral thinking
Sometimes, the path to a solution is not linear. Lateral thinking and intuition allow for making connections between seemingly unrelated elements. These 'eureka' moments often lead to breakthrough solutions that conventional methods might overlook.
Stages of the creative problem-solving process
The creative problem-solving process is typically broken down into several stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in understanding, addressing, and resolving challenges in innovative ways.
Clarifying: Understanding the real problem or challenge
Before diving into solutions, one must first understand the problem at its core. This involves asking probing questions, gathering data, and viewing the challenge from various angles. A clear comprehension of the problem ensures that effort and resources are channeled correctly.
Ideating: Generating diverse and multiple solutions
Once the problem is clarified, the focus shifts to generating as many solutions as possible. This stage champions quantity over quality, as the aim is to explore the breadth of possibilities without immediately passing judgment.
Developing: Refining and honing promising solutions
With a list of potential solutions in hand, it's time to refine and develop the most promising ones. This involves evaluating each idea's feasibility, potential impact, and any associated risks, then enhancing or combining solutions to maximize effectiveness.
Implementing: Acting on the best solutions
Once a solution has been honed, it's time to put it into action. This involves planning, allocating resources, and monitoring the results to ensure the solution is effectively addressing the problem.
Techniques for creative problem-solving
Solving complex problems in a fresh way can be a daunting task to start on. Here are a few techniques that can help kickstart the process:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a widely-used technique that involves generating as many ideas as possible within a set timeframe. Variants like brainwriting (where ideas are written down rather than spoken) and reverse brainstorming (thinking of ways to cause the problem) can offer fresh perspectives and ensure broader participation.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps structure information, making connections between disparate pieces of data. It is particularly useful in organizing thoughts, visualizing relationships, and ensuring a comprehensive approach to a problem.
SCAMPER technique
SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. This technique prompts individuals to look at existing products, services, or processes in new ways, leading to innovative solutions.
Benefits of creative problem-solving
Creative problem-solving offers numerous benefits, both at the individual and organizational levels. Some of the most prominent advantages include:
Finding novel solutions to old problems
Traditional problems that have resisted conventional solutions often succumb to creative approaches. By looking at challenges from fresh angles and blending different techniques, we can unlock novel solutions previously deemed impossible.
Enhanced adaptability in changing environments
In our rapidly evolving world, the ability to adapt is critical. Creative problem-solving equips individuals and organizations with the agility to pivot and adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring resilience and longevity.
Building collaborative and innovative teams
Teams that embrace creative problem-solving tend to be more collaborative and innovative. They value diversity of thought, are open to experimentation, and are more likely to challenge the status quo, leading to groundbreaking results.
Fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement
Creative problem-solving is not just about finding solutions; it's also about continuous learning and improvement. By encouraging an environment of curiosity and exploration, organizations can ensure that they are always at the cutting edge, ready to tackle future challenges head-on.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Learn Creative Problem Solving Techniques to Stimulate Innovation in Your Organization
By Kate Eby | October 20, 2017 (updated August 27, 2021)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations need processes in place to make strong, well-informed, and innovative decisions. Problem solving - in particular creative problem solving (CPS) - is a key skill in learning how to accurately identify problems and their causes, generate potential solutions, and evaluate all the possibilities to arrive at a strong corrective course of action. Every team in any organization, regardless of department or industry, needs to be effective, creative, and quick when solving problems.
In this article, we’ll discuss traditional and creative problem solving, and define the steps, best practices, and common barriers associated. After that, we’ll provide helpful methods and tools to identify the cause(s) of problematic situations, so you can get to the root of the issue and start to generate solutions. Then, we offer nearly 20 creative problem solving techniques to implement at your organization, or even in your personal life. Along the way, experts weigh in on the importance of problem solving, and offer tips and tricks.
What Is Problem Solving and Decision Making?
Problem solving is the process of working through every aspect of an issue or challenge to reach a solution. Decision making is choosing one of multiple proposed solutions — therefore, this process also includes defining and evaluating all potential options. Decision making is often one step of the problem solving process, but the two concepts are distinct.
Collective problem solving is problem solving that includes many different parties and bridges the knowledge of different groups. Collective problem solving is common in business problem solving because workplace decisions typically affect more than one person.
Problem solving, especially in business, is a complicated science. Not only are business conflicts multifaceted, but they often involve different personalities, levels of authority, and group dynamics. In recent years, however, there has been a rise in psychology-driven problem solving techniques, especially for the workplace. In fact, the psychology of how people solve problems is now studied formally in academic disciplines such as psychology and cognitive science.

Joe Carella is the Assistant Dean for Executive Education at the University of Arizona . Joe has over 20 years of experience in helping executives and corporations in managing change and developing successful business strategies. His doctoral research and executive education engagements have seen him focus on corporate strategy, decision making and business performance with a variety of corporate clients including Hershey’s, Chevron, Fender Musical Instruments Corporation, Intel, DP World, Essilor, BBVA Compass Bank.
He explains some of the basic psychology behind problem solving: “When our brain is engaged in the process of solving problems, it is engaged in a series of steps where it processes and organizes the information it receives while developing new knowledge it uses in future steps. Creativity is embedded in this process by incorporating diverse inputs and/or new ways of organizing the information received.”

Laura MacLeod is a Professor of Social Group Work at City University of New York, and the creator of From The Inside Out Project® , a program that coaches managers in team leadership for a variety of workplaces. She has a background in social work and over two decades of experience as a union worker, and currently leads talks on conflict resolution, problem solving, and listening skills at conferences across the country.
MacLeod thinks of problem solving as an integral practice of successful organizations. “Problem solving is a collaborative process — all voices are heard and connected, and resolution is reached by the group,” she says. “Problems and conflicts occur in all groups and teams in the workplace, but if leaders involve everyone in working through, they will foster cohesion, engagement, and buy in. Everybody wins.”
10 tips that will make you more productive.

Uncover the top three factors that are killing your productivity and 10 tips to help you overcome them.
Download the free e-book to overcome my productivity killers
Project Management Guide
Your one-stop shop for everything project management

Ready to get more out of your project management efforts? Visit our comprehensive project management guide for tips, best practices, and free resources to manage your work more effectively.
View the guide
What Is the First Step in Solving a Problem?
Although problem solving techniques vary procedurally, experts agree that the first step in solving a problem is defining the problem. Without a clear articulation of the problem at stake, it is impossible to analyze all the key factors and actors, generate possible solutions, and then evaluate them to pick the best option.

Dr. Elliott Jaffa is a behavioral and management psychologist with over 25 years of problem solving training and management experience. “Start with defining the problem you want to solve,” he says, “And then define where you want to be, what you want to come away with.” He emphasizes these are the first steps in creating an actionable, clear solution.

Bryan Mattimore is Co-Founder of Growth Engine, an 18-year old innovation agency based in Norwalk, CT. Bryan has facilitated over 1,000 ideation sessions and managed over 200 successful innovation projects leading to over $3 billion in new sales. His newest book is 21 Days to a Big Idea . When asked about the first critical component to successful problem solving, Mattimore says, “Defining the challenge correctly, or ‘solving the right problem’ … The three creative techniques we use to help our clients ‘identify the right problem to be solved’ are questioning assumptions, 20 questions, and problem redefinition. A good example of this was a new product challenge from a client to help them ‘invent a new iron. We got them to redefine the challenge as first: a) inventing new anti-wrinkle devices, and then b) inventing new garment care devices.”

What Are Problem Solving Skills?
To understand the necessary skills in problem solving, you should first understand the types of thinking often associated with strong decision making. Most problem solving techniques look for a balance between the following binaries:
- Convergent vs. Divergent Thinking: Convergent thinking is bringing together disparate information or ideas to determine a single best answer or solution. This thinking style values logic, speed, and accuracy, and leaves no chance for ambiguity. Divergent thinking is focused on generating new ideas to identify and evaluate multiple possible solutions, often uniting ideas in unexpected combinations. Divergent thinking is characterized by creativity, complexity, curiosity, flexibility, originality, and risk-taking.
- Pragmatics vs. Semantics: Pragmatics refer to the logic of the problem at hand, and semantics is how you interpret the problem to solve it. Both are important to yield the best possible solution.
- Mathematical vs. Personal Problem Solving: Mathematical problem solving involves logic (usually leading to a single correct answer), and is useful for problems that involve numbers or require an objective, clear-cut solution. However, many workplace problems also require personal problem solving, which includes interpersonal, collaborative, and emotional intuition and skills.
The following basic methods are fundamental problem solving concepts. Implement them to help balance the above thinking models.
- Reproductive Thinking: Reproductive thinking uses past experience to solve a problem. However, be careful not to rely too heavily on past solutions, and to evaluate current problems individually, with their own factors and parameters.
- Idea Generation: The process of generating many possible courses of action to identify a solution. This is most commonly a team exercise because putting everyone’s ideas on the table will yield the greatest number of potential solutions.
However, many of the most critical problem solving skills are “soft” skills: personal and interpersonal understanding, intuitiveness, and strong listening.
Mattimore expands on this idea: “The seven key skills to be an effective creative problem solver that I detail in my book Idea Stormers: How to Lead and Inspire Creative Breakthroughs are: 1) curiosity 2) openness 3) a willingness to embrace ambiguity 4) the ability to identify and transfer principles across categories and disciplines 5) the desire to search for integrity in ideas, 6) the ability to trust and exercise “knowingness” and 7) the ability to envision new worlds (think Dr. Seuss, Star Wars, Hunger Games, Harry Potter, etc.).”
“As an individual contributor to problem solving it is important to exercise our curiosity, questioning, and visioning abilities,” advises Carella. “As a facilitator it is essential to allow for diverse ideas to emerge, be able to synthesize and ‘translate’ other people’s thinking, and build an extensive network of available resources.”
MacLeod says the following interpersonal skills are necessary to effectively facilitate group problem solving: “The abilities to invite participation (hear all voices, encourage silent members), not take sides, manage dynamics between the monopolizer, the scapegoat, and the bully, and deal with conflict (not avoiding it or shutting down).”
Furthermore, Jaffa explains that the skills of a strong problem solver aren’t measurable. The best way to become a creative problem solver, he says, is to do regular creative exercises that keep you sharp and force you to think outside the box. Carella echoes this sentiment: “Neuroscience tells us that creativity comes from creating novel neural paths. Allow a few minutes each day to exercise your brain with novel techniques and brain ‘tricks’ – read something new, drive to work via a different route, count backwards, smell a new fragrance, etc.”
What Is Creative Problem Solving? History, Evolution, and Core Principles
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a method of problem solving in which you approach a problem or challenge in an imaginative, innovative way. The goal of CPS is to come up with innovative solutions, make a decision, and take action quickly. Sidney Parnes and Alex Osborn are credited with developing the creative problem solving process in the 1950s. The concept was further studied and developed at SUNY Buffalo State and the Creative Education Foundation.
The core principles of CPS include the following:
- Balance divergent and convergent thinking
- Ask problems as questions
- Defer or suspend judgement
- Focus on “Yes, and…” rather than “No, but…”
According to Carella, “Creative problem solving is the mental process used for generating innovative and imaginative ideas as a solution to a problem or a challenge. Creative problem solving techniques can be pursued by individuals or groups.”
When asked to define CPS, Jaffa explains that it is, by nature, difficult to create boundaries for. “Creative problem solving is not cut and dry,” he says, “If you ask 100 different people the definition of creative problem solving, you’ll get 100 different responses - it’s a non-entity.”
Business presents a unique need for creative problem solving. Especially in today’s competitive landscape, organizations need to iterate quickly, innovate with intention, and constantly be at the cutting-edge of creativity and new ideas to succeed. Developing CPS skills among your workforce not only enables you to make faster, stronger in-the-moment decisions, but also inspires a culture of collaborative work and knowledge sharing. When people work together to generate multiple novel ideas and evaluate solutions, they are also more likely to arrive at an effective decision, which will improve business processes and reduce waste over time. In fact, CPS is so important that some companies now list creative problem solving skills as a job criteria.
MacLeod reiterates the vitality of creative problem solving in the workplace. “Problem solving is crucial for all groups and teams,” she says. “Leaders need to know how to guide the process, hear all voices and involve all members - it’s not easy.”
“This mental process [of CPS] is especially helpful in work environments where individuals and teams continuously struggle with new problems and challenges posed by their continuously changing environment,” adds Carella.
Problem Solving Best Practices
By nature, creative problem solving does not have a clear-cut set of do’s and don’ts. Rather, creating a culture of strong creative problem solvers requires flexibility, adaptation, and interpersonal skills. However, there are a several best practices that you should incorporate:
- Use a Systematic Approach: Regardless of the technique you use, choose a systematic method that satisfies your workplace conditions and constraints (time, resources, budget, etc.). Although you want to preserve creativity and openness to new ideas, maintaining a structured approach to the process will help you stay organized and focused.
- View Problems as Opportunities: Rather than focusing on the negatives or giving up when you encounter barriers, treat problems as opportunities to enact positive change on the situation. In fact, some experts even recommend defining problems as opportunities, to remain proactive and positive.
- Change Perspective: Remember that there are multiple ways to solve any problem. If you feel stuck, changing perspective can help generate fresh ideas. A perspective change might entail seeking advice of a mentor or expert, understanding the context of a situation, or taking a break and returning to the problem later. “A sterile or familiar environment can stifle new thinking and new perspectives,” says Carella. “Make sure you get out to draw inspiration from spaces and people out of your usual reach.”
- Break Down Silos: To invite the greatest possible number of perspectives to any problem, encourage teams to work cross-departmentally. This not only combines diverse expertise, but also creates a more trusting and collaborative environment, which is essential to effective CPS. According to Carella, “Big challenges are always best tackled by a group of people rather than left to a single individual. Make sure you create a space where the team can concentrate and convene.”
- Employ Strong Leadership or a Facilitator: Some companies choose to hire an external facilitator that teaches problem solving techniques, best practices, and practicums to stimulate creative problem solving. But, internal managers and staff can also oversee these activities. Regardless of whether the facilitator is internal or external, choose a strong leader who will value others’ ideas and make space for creative solutions. Mattimore has specific advice regarding the role of a facilitator: “When facilitating, get the group to name a promising idea (it will crystalize the idea and make it more memorable), and facilitate deeper rather than broader. Push for not only ideas, but how an idea might specifically work, some of its possible benefits, who and when would be interested in an idea, etc. This fleshing-out process with a group will generate fewer ideas, but at the end of the day will yield more useful concepts that might be profitably pursued.” Additionally, Carella says that “Executives and managers don’t necessarily have to be creative problem solvers, but need to make sure that their teams are equipped with the right tools and resources to make this happen. Also they need to be able to foster an environment where failing fast is accepted and celebrated.”
- Evaluate Your Current Processes: This practice can help you unlock bottlenecks, and also identify gaps in your data and information management, both of which are common roots of business problems.
MacLeod offers the following additional advice, “Always get the facts. Don’t jump too quickly to a solution – working through [problems] takes time and patience.”
Mattimore also stresses that how you introduce creative problem solving is important. “Do not start by introducing a new company-wide innovation process,” he says. “Instead, encourage smaller teams to pursue specific creative projects, and then build a process from the ground up by emulating these smaller teams’ successful approaches. We say: ‘You don’t innovate by changing the culture, you change the culture by innovating.’”
Barriers to Effective Problem Solving
Learning how to effectively solve problems is difficult and takes time and continual adaptation. There are several common barriers to successful CPS, including:
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to only search for or interpret information that confirms a person’s existing ideas. People misinterpret or disregard data that doesn’t align with their beliefs.
- Mental Set: People’s inclination to solve problems using the same tactics they have used to solve problems in the past. While this can sometimes be a useful strategy (see Analogical Thinking in a later section), it often limits inventiveness and creativity.
- Functional Fixedness: This is another form of narrow thinking, where people become “stuck” thinking in a certain way and are unable to be flexible or change perspective.
- Unnecessary Constraints: When people are overwhelmed with a problem, they can invent and impose additional limits on solution avenues. To avoid doing this, maintain a structured, level-headed approach to evaluating causes, effects, and potential solutions.
- Groupthink: Be wary of the tendency for group members to agree with each other — this might be out of conflict avoidance, path of least resistance, or fear of speaking up. While this agreeableness might make meetings run smoothly, it can actually stunt creativity and idea generation, therefore limiting the success of your chosen solution.
- Irrelevant Information: The tendency to pile on multiple problems and factors that may not even be related to the challenge at hand. This can cloud the team’s ability to find direct, targeted solutions.
- Paradigm Blindness: This is found in people who are unwilling to adapt or change their worldview, outlook on a particular problem, or typical way of processing information. This can erode the effectiveness of problem solving techniques because they are not aware of the narrowness of their thinking, and therefore cannot think or act outside of their comfort zone.
According to Jaffa, the primary barrier of effective problem solving is rigidity. “The most common things people say are, ‘We’ve never done it before,’ or ‘We’ve always done it this way.’” While these feelings are natural, Jaffa explains that this rigid thinking actually precludes teams from identifying creative, inventive solutions that result in the greatest benefit.
“The biggest barrier to creative problem solving is a lack of awareness – and commitment to – training employees in state-of-the-art creative problem-solving techniques,” Mattimore explains. “We teach our clients how to use ideation techniques (as many as two-dozen different creative thinking techniques) to help them generate more and better ideas. Ideation techniques use specific and customized stimuli, or ‘thought triggers’ to inspire new thinking and new ideas.”
MacLeod adds that ineffective or rushed leadership is another common culprit. “We're always in a rush to fix quickly,” she says. “Sometimes leaders just solve problems themselves, making unilateral decisions to save time. But the investment is well worth it — leaders will have less on their plates if they can teach and eventually trust the team to resolve. Teams feel empowered and engagement and investment increases.”
Strategies for Problem Cause Identification
As discussed, most experts agree that the first and most crucial step in problem solving is defining the problem. Once you’ve done this, however, it may not be appropriate to move straight to the solution phase. Rather, it is often helpful to identify the cause(s) of the problem: This will better inform your solution planning and execution, and help ensure that you don’t fall victim to the same challenges in the future.
Below are some of the most common strategies for identifying the cause of a problem:
- Root Cause Analysis: This method helps identify the most critical cause of a problem. A factor is considered a root cause if removing it prevents the problem from recurring. Performing a root cause analysis is a 12 step process that includes: define the problem, gather data on the factors contributing to the problem, group the factors based on shared characteristics, and create a cause-and-effect timeline to determine the root cause. After that, you identify and evaluate corrective actions to eliminate the root cause.
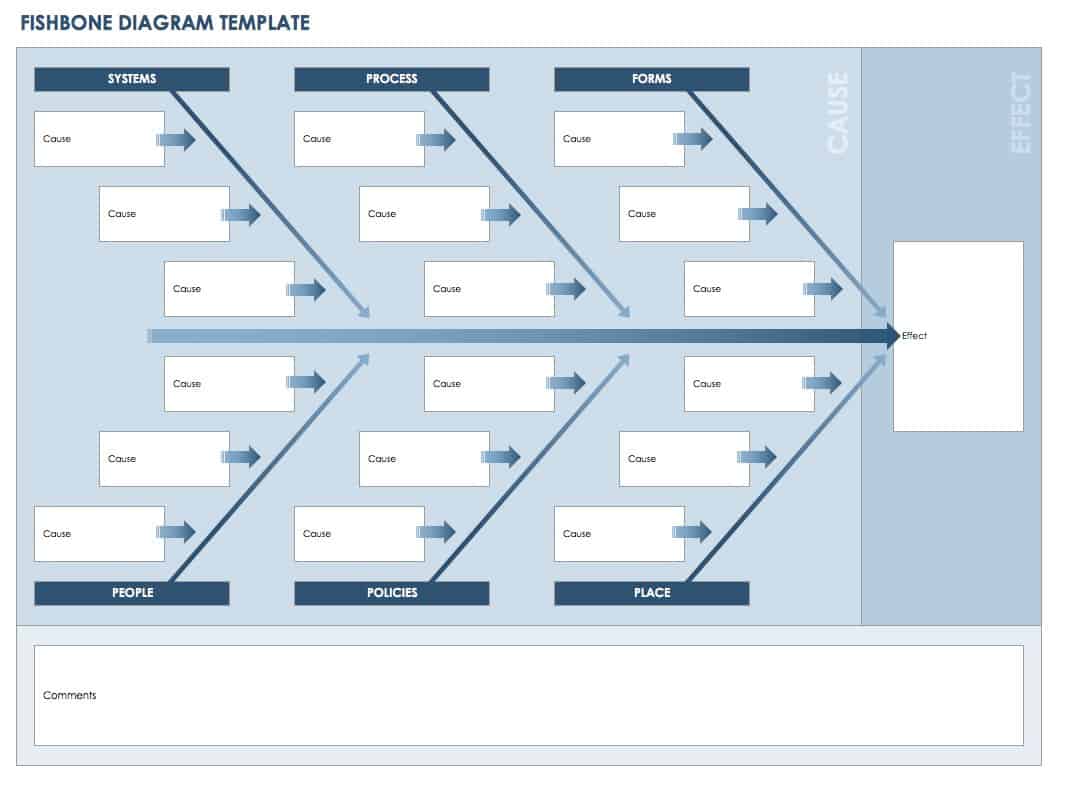
Download Fishbone Diagram Template - Excel
Download 5 Whys Template Excel | Word | PDF
Problem Solving Techniques and Strategies
In this section, we’ll explain several traditional and creative problem solving methods that you can use to identify challenges, create actionable goals, and resolve problems as they arise. Although there is often procedural and objective crossover among techniques, they are grouped by theme so you can identify which method works best for your organization.
Divergent Creative Problem Solving Techniques
Brainstorming: One of the most common methods of divergent thinking, brainstorming works best in an open group setting where everyone is encouraged to share their creative ideas. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible – you analyze, critique, and evaluate the ideas only after the brainstorming session is complete. To learn more specific brainstorming techniques, read this article .
Mind Mapping: This is a visual thinking tool where you graphically depict concepts and their relation to one another. You can use mind mapping to structure the information you have, analyze and synthesize it, and generate solutions and new ideas from there. The goal of a mind map is to simplify complicated problems so you can more clearly identify solutions.
Appreciative Inquiry (AI): The basic assumption of AI is that “an organization is a mystery to be embraced.” Using this principle, AI takes a positive, inquisitive approach to identifying the problem, analyzing the causes, and presenting possible solutions. The five principles of AI emphasize dialogue, deliberate language and outlook, and social bonding.
Lateral Thinking: This is an indirect problem solving approach centered on the momentum of idea generation. As opposed to critical thinking, where people value ideas based on their truth and the absence of errors, lateral thinking values the “movement value” of new ideas: This means that you reward team members for producing a large volume of new ideas rapidly. With this approach, you’ll generate many new ideas before approving or rejecting any.
Problem Solving Techniques to Change Perspective
Constructive Controversy: This is a structured approach to group decision making to preserve critical thinking and disagreement while maintaining order. After defining the problem and presenting multiple courses of action, the group divides into small advocacy teams who research, analyze, and refute a particular option. Once each advocacy team has presented its best-case scenario, the group has a discussion (advocacy teams still defend their presented idea). Arguing and playing devil’s advocate is encouraged to reach an understanding of the pros and cons of each option. Next, advocacy teams abandon their cause and evaluate the options openly until they reach a consensus. All team members formally commit to the decision, regardless of whether they advocated for it at the beginning. You can learn more about the goals and steps in constructive controversy here .
Carella is a fan of this approach. “Create constructive controversy by having two teams argue the pros and cons of a certain idea,” he says. “It forces unconscious biases to surface and gives space for new ideas to formulate.”
Abstraction: In this method, you apply the problem to a fictional model of the current situation. Mapping an issue to an abstract situation can shed extraneous or irrelevant factors, and reveal places where you are overlooking obvious solutions or becoming bogged down by circumstances.
Analogical Thinking: Also called analogical reasoning , this method relies on an analogy: using information from one problem to solve another problem (these separate problems are called domains). It can be difficult for teams to create analogies among unrelated problems, but it is a strong technique to help you identify repeated issues, zoom out and change perspective, and prevent the problems from occurring in the future. .
CATWOE: This framework ensures that you evaluate the perspectives of those whom your decision will impact. The factors and questions to consider include (which combine to make the acronym CATWOE):
- Customers: Who is on the receiving end of your decisions? What problem do they currently have, and how will they react to your proposed solution?
- Actors: Who is acting to bring your solution to fruition? How will they respond and be affected by your decision?
- Transformation Process: What processes will you employ to transform your current situation and meet your goals? What are the inputs and outputs?
- World View: What is the larger context of your proposed solution? What is the larger, big-picture problem you are addressing?
- Owner: Who actually owns the process? How might they influence your proposed solution (positively or negatively), and how can you influence them to help you?
- Environmental Constraints: What are the limits (environmental, resource- and budget-wise, ethical, legal, etc.) on your ideas? How will you revise or work around these constraints?
Complex Problem Solving
Soft Systems Methodology (SSM): For extremely complex problems, SSM can help you identify how factors interact, and determine the best course of action. SSM was borne out of organizational process modeling and general systems theory, which hold that everything is part of a greater, interconnected system: This idea works well for “hard” problems (where logic and a single correct answer are prioritized), and less so for “soft” problems (i.e., human problems where factors such as personality, emotions, and hierarchy come into play). Therefore, SSM defines a seven step process for problem solving:
- Begin with the problem or problematic situation
- Express the problem or situation and build a rich picture of the themes of the problem
- Identify the root causes of the problem (most commonly with CATWOE)
- Build conceptual models of human activity surrounding the problem or situation
- Compare models with real-world happenings
- Identify changes to the situation that are both feasible and desirable
- Take action to implement changes and improve the problematic situation
SSM can be used for any complex soft problem, and is also a useful tool in change management .
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): This method helps teams anticipate potential problems and take steps to mitigate them. Use FMEA when you are designing (redesigning) a complex function, process, product, or service. First, identify the failure modes, which are the possible ways that a project could fail. Then, perform an effects analysis to understand the consequences of each of the potential downfalls. This exercise is useful for internalizing the severity of each potential failure and its effects so you can make adjustments or safeties in your plan.
Download FMEA Template
Problem Solving Based on Data or Logic (Heuristic Methods)
TRIZ: A Russian-developed problem solving technique that values logic, analysis, and forecasting over intuition or soft reasoning. TRIZ (translated to “theory of inventive problem solving” or TIPS in English) is a systematic approach to defining and identifying an inventive solution to difficult problems. The method offers several strategies for arriving at an inventive solution, including a contradictions matrix to assess trade-offs among solutions, a Su-Field analysis which uses formulas to describe a system by its structure, and ARIZ (algorithm of inventive problem solving) which uses algorithms to find inventive solutions.
Inductive Reasoning: A logical method that uses evidence to conclude that a certain answer is probable (this is opposed to deductive reasoning, where the answer is assumed to be true). Inductive reasoning uses a limited number of observations to make useful, logical conclusions (for example, the Scientific Method is an extreme example of inductive reasoning). However, this method doesn’t always map well to human problems in the workplace — in these instances, managers should employ intuitive inductive reasoning , which allows for more automatic, implicit conclusions so that work can progress. This, of course, retains the principle that these intuitive conclusions are not necessarily the one and only correct answer.
Process-Oriented Problem Solving Methods
Plan Do Check Act (PDCA): This is an iterative management technique used to ensure continual improvement of products or processes. First, teams plan (establish objectives to meet desired end results), then do (implement the plan, new processes, or produce the output), then check (compare expected with actual results), and finally act (define how the organization will act in the future, based on the performance and knowledge gained in the previous three steps).
Means-End Analysis (MEA): The MEA strategy is to reduce the difference between the current (problematic) state and the goal state. To do so, teams compile information on the multiple factors that contribute to the disparity between the current and goal states. Then they try to change or eliminate the factors one by one, beginning with the factor responsible for the greatest difference in current and goal state. By systematically tackling the multiple factors that cause disparity between the problem and desired outcome, teams can better focus energy and control each step of the process.
Hurson’s Productive Thinking Model: This technique was developed by Tim Hurson, and is detailed in his 2007 book Think Better: An Innovator’s Guide to Productive Thinking . The model outlines six steps that are meant to give structure while maintaining creativity and critical thinking: 1) Ask “What is going on?” 2) Ask “What is success?” 3) Ask “What is the question?” 4) Generate answers 5) Forge the solution 6) Align resources.
Control Influence Accept (CIA): The basic premise of CIA is that how you respond to problems determines how successful you will be in overcoming them. Therefore, this model is both a problem solving technique and stress-management tool that ensures you aren’t responding to problems in a reactive and unproductive way. The steps in CIA include:
- Control: Identify the aspects of the problem that are within your control.
- Influence: Identify the aspects of the problem that you cannot control, but that you can influence.
- Accept: Identify the aspects of the problem that you can neither control nor influence, and react based on this composite information.
GROW Model: This is a straightforward problem solving method for goal setting that clearly defines your goals and current situation, and then asks you to define the potential solutions and be realistic about your chosen course of action. The steps break down as follows:
- Goal: What do you want?
- Reality: Where are you now?
- Options: What could you do?
- Will: What will you do?
OODA Loop: This acronym stands for observe, orient, decide, and act. This approach is a decision-making cycle that values agility and flexibility over raw human force. It is framed as a loop because of the understanding that any team will continually encounter problems or opponents to success and have to overcome them.
There are also many un-named creative problem solving techniques that follow a sequenced series of steps. While the exact steps vary slightly, they all follow a similar trajectory and aim to accomplish similar goals of problem, cause, and goal identification, idea generation, and active solution implementation.
MacLeod offers her own problem solving procedure, which echoes the above steps:
“1. Recognize the Problem: State what you see. Sometimes the problem is covert. 2. Identify: Get the facts — What exactly happened? What is the issue? 3. and 4. Explore and Connect: Dig deeper and encourage group members to relate their similar experiences. Now you're getting more into the feelings and background [of the situation], not just the facts. 5. Possible Solutions: Consider and brainstorm ideas for resolution. 6. Implement: Choose a solution and try it out — this could be role play and/or a discussion of how the solution would be put in place. 7. Evaluate: Revisit to see if the solution was successful or not.”
Many of these problem solving techniques can be used in concert with one another, or multiple can be appropriate for any given problem. It’s less about facilitating a perfect CPS session, and more about encouraging team members to continually think outside the box and push beyond personal boundaries that inhibit their innovative thinking. So, try out several methods, find those that resonate best with your team, and continue adopting new techniques and adapting your processes along the way.
Improve Problem Solving with Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

Creative Problem Solving And Its Techniques
Entrepreneurs need to script their own journeys, figure out their own things, and solve problems. If you keep running back…

Entrepreneurs need to script their own journeys, figure out their own things, and solve problems. If you keep running back to your mentor at the drop of your hat, you’re not an entrepreneur. A true entrepreneur is a risk-taker, problem-solver, a person who’s willing to face challenges and failures.
– Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw, chairperson, and MD of Biocon
While scripting your own life and career journey, it is imperative to master the skill of creative problem-solving. Successful people and organizations recognize that the solutions to their problems lie within themselves. They try to find them with a creative problem-solving process.
Most professionals face problems at work. It could be meeting a sales target or fixing a technical glitch in a product. Learning how to solve problems efficiently is a key skill for success at work and life in general. Sometimes, you have to think out of the box to solve problems creatively.
What is creative problem-solving?
Have you noticed how some people have a knack for turning a problem into an opportunity? Take the stones people throw at you and use them to build a monument, said former Tata Group chairman Ratan Tata. It was a fantastic way of expressing creative problem-solving at work.
Creative problem-solving involves approaching a problem or a challenge in an inventive way. It is a process that redefines problems and opportunities and helps us come up with innovative solutions.
Generally, the creative problem-solving process involves the following stages:
Identify the problem or the challenge
Generate ideas that may be possible solutions
Solve the problem with the help of generated ideas
Implement the solution plan and move to the next step
A well-planned and strategically executed creative problem-solving process brings team members together. It encourages proactive participation among colleagues.
Let’s look at an example. Seema was not happy with her career in the IT industry. She approached the problem by thinking about various options that appealed to her. Using her creative problem-solving skill, she decided to try her hand at travel blogging given her passion for travel and nose for digital marketing.
Let’s turn to some highly successful techniques of creative problem-solving.
Techniques of creative problem-solving
1. brainstorming.
Brainstorming is one of the most popular techniques of creative problem-solving. It is an individual as well as a group activity. When the city’s municipal corporation needs to come up with measures regarding safety and health, citizens are often asked to brainstorm and suggest innovative ideas. Brainstorming is a blend of creativity and problem-solving.
2. Mind-mapping
Mind-mapping is a useful creative problem-solving process. A mind map is a graphic representation of ideas and concepts. It is a visual tool for creativity and problem-solving. Mind maps help you categorize and structure information. They aid comprehension, analysis, and help generate innovative ideas. Seeing the problem and possible solutions represented in visual form helps many of us see the bigger picture and connect the dots.
3. Counterfactual Thinking
When Rosie has to take a call on a problem, she thinks about all her previous decisions. She thinks of the things that have gone wrong and the opportunities that she missed out on. Such counterfactual thinking helps her face the current problem and find a solution. Counterfactual thinking is one of the smartest examples of creative problem-solving at work. However, it is important not to channel negative emotions while going down the counterfactual thinking route. Use your past experiences to ensure you don’t repeat mistakes, seize opportunities, and measure how far you’ve come. Be present and future-focused, and don’t use counterfactual thoughts to get trapped in the “What ifs” of your past.
4. Abstraction
Abstraction is a great booster for creativity and problem-solving. When a creative director in an advertising agency has to design a campaign for a brand of fruit drinks or evening wear, he uses abstraction. He thinks about the emotions associated with the drink or the evening, such as camaraderie, romance, taste, health, joy, and so on. ( xanax )
You must have noticed many examples of creative problem-solving at work.
Deploying a thought experiment by using comparison or similarity as a tool
Breaking free from assumptions to think originally
Going beyond assigned tasks to experiment
Raising questions and seeking new viewpoints
Reapplying rules that have worked previously
Stepping out of your comfort zone and thinking differently
Go ahead and build a culture of creativity around you. Overcome your mental barriers and let your imagination run free. Navigate obstacles to solve problems and come up with innovative solutions.
Harappa Education’s Unleashing Creativity course teaches you how to generate, test, and refine new ideas. It empowers you with in-depth creativity and problem-solving skills by teaching you concepts such as the Disney Creative Tool framework involving three roles: including dreamers, realists, and critics. Assigning these roles to groups will help organizations brainstorm ideas, create plans, and identify roadblocks. to reach the desired goals successfully. Sign up and begin your creative problem-solving journey.
Explore topics such as Creative Thinking & How to be Creative at Work from our Harappa Diaries blog section and develop your strategic thinking skills .

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Solve Problems
- Laura Amico

To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety.
Teams today aren’t just asked to execute tasks: They’re called upon to solve problems. You’d think that many brains working together would mean better solutions, but the reality is that too often problem-solving teams fall victim to inefficiency, conflict, and cautious conclusions. The two charts below will help your team think about how to collaborate better and come up with the best solutions for the thorniest challenges.
- Laura Amico is a former senior editor at Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center
.webp)
Creative Problem Solving: A Key to Team Building Success

Creative Problem Solving- A Key to Team Building Success
The ability to solve problems in a creative manner is an important skill for any organization. Problem-solving skills are essential for employees and team leaders alike, as it helps to ensure that challenges can be addressed in an effective and timely manner. Team building is also an important component of any successful business, as it helps to ensure that employees are working together in a cohesive manner to achieve the organization’s objectives. Creative problem-solving is a key element of successful team building, as it encourages collaboration and the development of innovative solutions
Importance of creative problem-solving at a workplace
1. encourages innovation.
Creative problem solving encourages innovation in the workplace. When employees are given the opportunity to brainstorm and come up with creative solutions, they are more likely to develop new and innovative ideas that can help the organization grow and succeed
2. Promotes Collaboration
Creative problem solving promotes collaboration among team members. It encourages individuals to work together, share ideas and perspectives, and come up with creative solutions that everyone can contribute to
3. Increases Efficiency
By using creative problem-solving techniques, teams can identify problems and find solutions more quickly and efficiently. This can help to save time, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity
"Efficiency is doing things right; effectiveness is doing the right things." - Peter Drucker
4. Boosts Morale
When employees are given the opportunity to use their creativity and problem-solving skills, it can boost their morale and job satisfaction. This can lead to a more positive work environment and increased employee retention
5. Enhances Decision Making
Creative problem solving involves evaluating different options and making informed decisions based on the available information. By using this approach, teams can make better decisions and avoid potential pitfalls
"Good decision-making is essential to success, and good communication is essential to good decision-making." - Sir Richard Branson
6. Improves Customer Satisfaction
By using creative problem solving to address customer issues and concerns, organizations can improve customer satisfaction. This can lead to increased loyalty, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth referrals
"Customer satisfaction is not just a goal, it's a necessity. Without it, businesses will struggle to survive in today's competitive market." - Shep Hyken
Problems on not using creative problem-solving techniques
1. lack of innovation.
A team that does not use creative problem-solving techniques may struggle to come up with innovative solutions to complex challenges. This can result in a lack of growth and progress for the organization
Innovation is not just a buzzword or a trendy concept. It’s a critical component of success in today’s rapidly changing business environment. Organizations that foster a culture of innovation are more likely to thrive and succeed in the long term.
2. Poor Communication
Without a creative problem-solving approach, team members may struggle to communicate effectively with each other. This can lead to misunderstandings, miscommunications, and conflicts that can hinder progress
3. Reduced Efficiency
Teams that do not use creative problem-solving techniques may take longer to identify and address problems. This can result in reduced efficiency and productivity, which can impact the bottom line
4. Low Morale
When a team is unable to solve problems effectively, it can lead to frustration and low morale among team members. This can impact job satisfaction and lead to high turnover rates
You May Like: 9 Tried And Tested Ways To Boost Your Employee Morale In 2021
5. Decreased Customer Satisfaction
When a team is unable to solve problems effectively, it can lead to decreased customer satisfaction. This can result in lost business and damage to the organization's reputation
It is important for teams to use creative problem-solving techniques to address challenges effectively and avoid these potential problems. By encouraging innovation, effective communication, and increased efficiency, teams can work together to achieve their goals and promote the success of the organization
10 tactics for cultivating practice of creative problem-solving
1. set clear goals.
Set clear goals for problem-solving initiatives. This can help employees to focus their efforts and stay on track
2. Promote Flexibility
Promote flexibility in problem-solving approaches. Encourage employees to try different approaches and be open to new ideas
"Flexibility is the key to stability." - John Wooden
3. Provide Training
Provide training on creative problem-solving techniques and tools. This can help employees to develop their skills and become more effective problem solvers
4. Encourage Diversity
Encourage diversity in the workplace. This can bring a variety of perspectives and ideas to the table, which can lead to more innovative solutions
5. Create a Safe Environment
Create a safe environment where employees feel comfortable sharing their ideas and taking risks. Encourage open communication and a non-judgmental attitude
"Creating a safe and supportive work environment is essential to achieving high levels of engagement and success." - Susan Lucas-Conwell
6. Provide Resources
Provide employees with the resources they need to solve problems creatively. This can include access to technology, research materials, and other tools
7. Encourage Innovation
Encourage employees to think outside the box and come up with unique solutions to problems. Allow them to take risks and experiment with new ideas. Innovation requires a willingness to take risks and try new things. It requires a willingness to fail, learn from those failures, and try again
8. Foster Collaboration
Encourage collaboration among team members. Encourage them to share their ideas and perspectives. Create an environment where everyone feels comfortable contributing
9. Celebrate Success
Celebrate successful problem-solving initiatives. This can help to reinforce the importance of creative problem-solving and encourage future efforts
10. Incorporate Feedback
Incorporate feedback from employees and stakeholders in problem-solving initiatives. This can help to ensure that solutions are effective and meet the needs of all parties involved
You May Like: Employee Feedback: 3 Things You Should Be Doing & Why
By implementing these tips, organizations can cultivate a culture of creative problem-solving and promote innovation, collaboration, and success
Problem-solving is a part of almost every person's daily life at home and in the workplace hence, Creative problem solving helps us understand our environment, identify the things we want or need to change, and find a solution to improve the environment's performance. Creative problem solving is essential for individuals at organizations because it helps us control what's happening in our environment. Humans have learned to observe the environment and identify risks that may lead to specific outcomes in the future. Anticipating is helpful not only for fixing broken things but also for influencing the performance of items. Creative problem solving is not just about fixing broken things; it's about innovating and creating something new. Observing and analysing the environment, we identify opportunities for new ideas that will improve our environment in the future
Continue reading

Juggling Projects: Mastering Multiple Priorities Like a Pro
Manage multiple projects and deadlines with ease. Learn how to juggle like a pro!

10 Awesome Team Building Activities Your Team Won't Hate
These 10 team-building activities help teams learn about one another — how each person works, thinks, solves issues, and has fun.

Boosting Employee Loyalty and Engagement: Best Practices
The success and growth of a company is largely dependent on its employees and how happy or content they are in their roles.
.webp)
Let's team up on social media.
.webp)
Team Outing Places
- Corporate Team Outing Places In Bangalore
- Corporate Team Outing Places In Hyderabad
- Corporate Team Outing Places In Coorg
- Corporate Team Outing Places In Mumbai
- Corporate Team Outing Places In Chennai
Quick Links
- Corporate Team Outing In Bangalore
- Corporate Team Offsite
- One Day Outing Resorts In Hyderabad
- Team building Activities In Bangalore
- One Day Outing In Bangalore
- Privacy policy
- Virtual Activities
- Outbound Activities
- Simulation Training

12 Powerful Creative Problem-Solving Techniques That Work
No one likes the feeling of being stuck.
It creates internal tension. That tension seeks resolution.
Thankfully, there are many creative problem-solving techniques for resolving this tension and revealing new solutions.
In this guide, we’ll explore 12 creative ways to solve problems with a variety of techniques, tools, and methods that be used for personal use and in the workplace.
Let’s dive in…
How to Approach Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
All of the creative problem-solving techniques discussed below work some of the time .
While it’s fine to have a favorite “go-to” creative problem-solving technique, the reality is each problem has some unique elements to it.
The key to is mix and match various techniques and methodologies until you get a workable solution.
When faced with a difficult challenge, try a combination of the problem-solving techniques listed below.
The Power of Divergent Thinking
Creativity is everyone’s birthright.
One study with 1,500 participants, found that 98 percent of children around the age of five qualify as geniuses. 1 George Land and Beth Jarman, Breakpoint and Beyond , 1998.
That is, virtually all children are gifted with divergent thinking— the ability to see many possible answers to a question.
For example, how many uses can you think of for a paper clip?
The average adult might offer 10 to 15 answers. Those skilled in divergent thinking divine closer to 200 answers.
Yet, something happens along the way because by adulthood, how many people score at the genius level? Only 2 percent!
That is, we see a complete inversion: from 98% being geniuses in early childhood to only 2% in adulthood.
What causes this debilitating drop in creativity?
According to creativity researcher Sir Ken Robinson, the answer is our schooling. 2 Sir Ken Robinson, Do schools kill creativity? TED Talk , 2006. Through 13 years of “education” our innate creativity is stripped out of us!
Conditioning Yourself for Creative Solutions
So to improve the efficacy of these creative problem-solving techniques, it helps to re-condition ourselves to use divergent thinking.
The key is to learn how to remove our prior conditioning and restore our natural creative abilities. You’ll notice that many of the creative problem-solving techniques below help us do just that.
Thankfully, divergent thinking is a skill and we can develop it like a muscle. So the more we use divergent thinking, the more second nature it becomes.
For this reason, when you’re presented with personal, professional, or business-related problems, celebrate them as an opportunity to exercise your creative abilities.
12 Powerful Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
Now, we’re going to cover 12 creative problem-solving techniques with examples that you can apply right away to get results.
These creative problem-solving methods are:
- Use “What If” Scenarios
- Focus on Quantity Over Quality
- Switch Roles
- Use the Six Thinking Hats Technique
- Explore Different Contexts
- Take a 30,000-Foot View
- Ask Your Subconscious
- Mind Map Your Problem
- Adopt a Beginner’s Mind
- Alter Your State of Consciousness
- Find Your Center
Then, we’ll quickly review a series of problem-solving tools you can experiment with.
1 – Use “What If” Scenarios
Use “what if?” questions to project different scenarios into the future.
In A Whack on the Side of the Head , Roger Von Oech, says,
“In the imaginative phase, you ask questions such as: What if? Why not? What rules can we break? What assumptions can we drop? How about if we looked at this backwards? Can we borrow a metaphor from another discipline? The motto of the imaginative phase is: Thinking something different.”
Using this creative problem-solving technique challenges you to allow your mind to play out different scenarios without judgment or criticism .
(Judgment always comes after the creative problem-solving process—not before.)
2 – Focus on Quantity Over Quality
Creativity research shows that focusing on generating more ideas or solutions instead of on the quality of the ideas ultimately produces better results. 3 Paulus, Paul & Kohn, Nicholas & ARDITTI, LAUREN. (2011). Effects of Quantity and Quality Instructions on Brainstorming. The Journal of Creative Behavior. 45. 10.1002/j.2162-6057.2011.tb01083.x .
This phenomenon is known as the “Equal-Odds rule.” Nobel laureate Linus Pauling instinctively suggested a similar process: 4 The Evening Sentinel , Priestley Award Winner Says Deployment of ABM’s “Silly”, Start Page 1, Quote Page 6, Column 1, Carlisle, Pennsylvania. March 28, 1969.
I was once asked ‘How do you go about having good ideas?’ and my answer was that you have a lot of ideas and throw away the bad ones.
When I used to facilitate meetings and brainstorming sessions with leadership teams in large organizations, this was an invaluable creative problem-solving technique. By consciously focusing on generating more ideas first instead of evaluating the quality of the ideas, you avoid shifting into a critical mindset that often stops the ideation process.
3 – Switch Roles
Our minds tend to get locked in habitual patterns, leading to what’s called “paradigm blindness.” Another related term is the “curse of knowledge,” a common cognitive bias observed in so-called “experts” in their field. 5 Hinds, Pamela J. (1999). “The curse of expertise: The effects of expertise and debiasing methods on prediction of novice performance”. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. 5 (2): 205–221. doi:10.1037/1076-898X.5.2.205 . S2CID 1081055
This cognitive bias is another illustration of how divergent thinking was conditioned out of us during our formative years.
Switching roles helps us “wear a different hat” where we momentarily shift away from our conditioning.
For example, if you have a marketing-related problem, try putting on an engineer’s hat—or even a gardener’s hat. If you have a problem as an entrepreneur, put yourself in the customer’s mindset. See the world from their point of view.
The idea is to shift your perspective so you can approach the problem from a new angle. Your ability to shift perspectives quickly—without privileging any one perspective—doesn’t only help you solve problems. It also helps you become a stronger leader .
4 – Use the Six Thinking Hats Technique
Speaking of hats, creativity researcher Edward de Bono developed an effective creative problem-solving technique called the Six Thinking Hats.
The Six Thinking Hats provides you and your team with six different perspectives to utilize when tackling a problem. (You can use these six hats on your own too.)
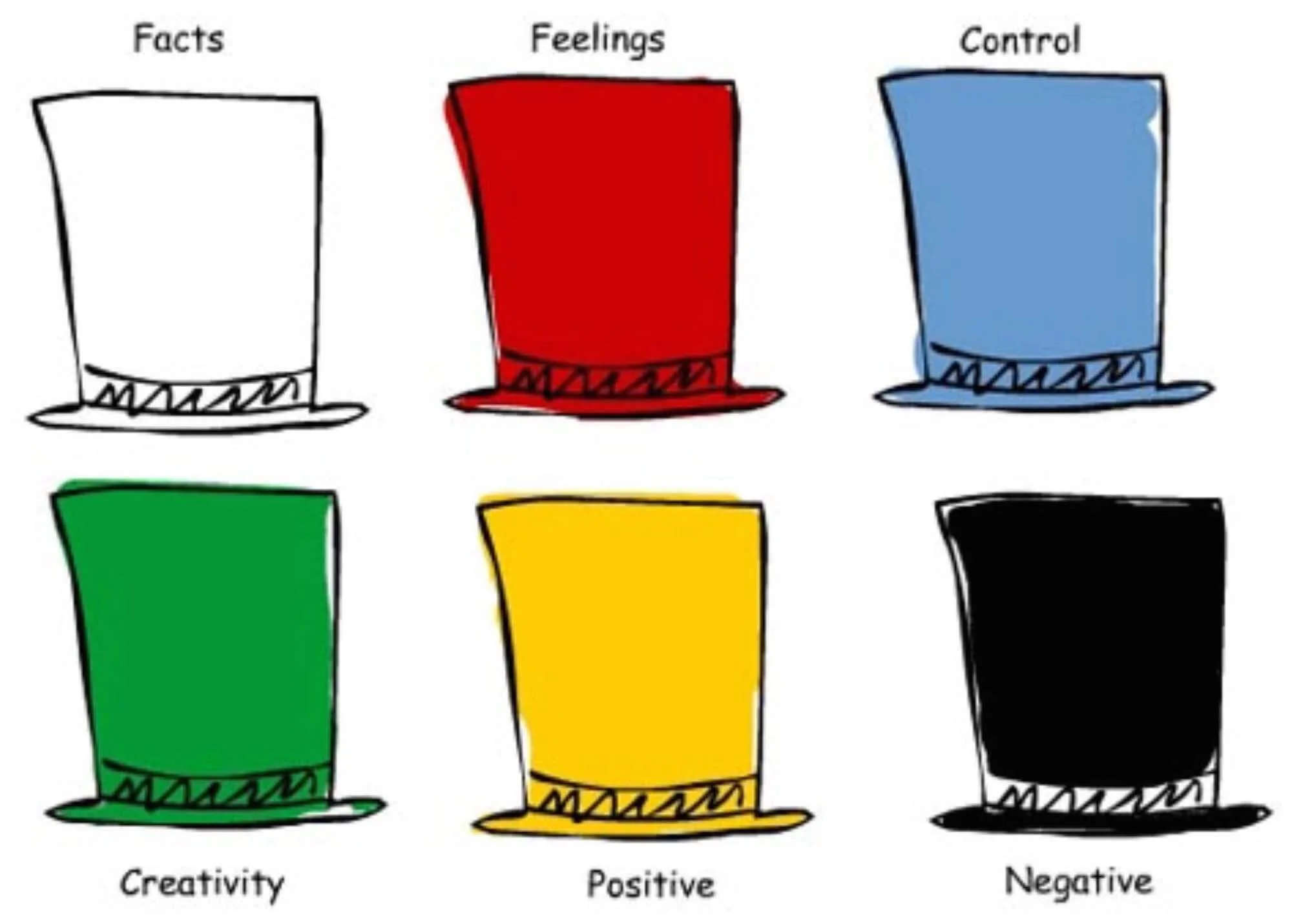
Each hat serves a different function. For creative problem solving, you start with the blue hat to clearly define the problem.
You then move to the white hat where you outline all of the existing and known data regarding the issue. Next, you put on the green hat and generate as many ideas as you can (similar to the “quantity over quality” technique above).
Then, you put on the yellow hat, which represents what de Bono calls “value sensitivity.” The yellow hat is used to build on the ideas generated from the green hat phase. Finally, you put on the black hat to evaluate your solutions and play Devil’s Advocate.
The Six Thinking Hats is an excellent technique for group brainstorming and creative problem-solving.
5 – Explore Different Contexts
Many problems arise because we neglect to zoom out from the problem and examine the larger context.
For example, long-term investments are often based on an “investment thesis.” This thesis might be based on trends in the market, consumer demands, brand recognition, dominant market share, strength in innovation, or a combination of factors. But sometimes the assumptions you base your thesis on are wrong.
So if you’re facing a problem at home or work, examine your assumptions.
If sales are down, for example, instead of revisiting your sales strategy investigate the context of your overall industry:
- Has your industry changed?
- Is your business disconnected from your customer’s needs?
- Is your product or service becoming obsolete?
We can often find creative solutions to our problems by shifting the context.
6 – Take a 30,000-Foot View
Often, when we’re stuck in a problem, it’s because we’re “missing the forest for the trees.”
Zoom out and take a “30,000-foot view” of the situation. See your problem from above with a detached, neutral mindset. Take an expansive viewpoint before narrowing in on the specific problem.
This problem-solving technique is another variation of changing the context.
Sometimes you’ll find this to be a powerful creative problem-solving technique where the right solution spontaneously presents itself. (You’ll think to yourself: Why didn’t I see this before? )

7 – Walk Away
Most often, the best problem-solving technique is to stop trying to solve it —and walk away.
Yet, our minds often don’t like this technique. The mind likes to be in control. And walking away means letting go of control.
I spent five years researching creative geniuses trying to better understand the source of inspiration for a book I was writing years ago. 6 Scott Jeffrey, Creativity Revealed: Discovering the Source of Inspiration , 2008.
In studying dozens of creative geniuses, from Mozart to William Blake, a clear pattern emerged.
Creative geniuses know when to walk away from the problems they are facing. They instinctively access what can be called the Wanderer archetype.
More recent studies show that deliberate “mind-wandering” supports creativity. 7 Henriksen D, Richardson C, Shack K. Mindfulness and creativity: Implications for thinking and learning. Think Skills Creat. 2020 Sep;37:100689. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2020.100689 . Epub 2020 Aug 1. PMID: 32834868; PMCID: PMC7395604. Great ideas come to use when we’re not trying. 8 Kaplan, M. Why great ideas come when you aren’t trying. Nature (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10678
Wandering and reverie are essential to the creative process because they allow us to hear our Muse. The key is knowing when to let go of trying to solve the problem. Creativity problem-solving can, in this way, become an effortless process.
8 – Ask Your Subconscious
When we’re stuck on a problem and we need a creative solution, it means our conscious mind is stuck.
It does not, however, mean that we don’t already know the answer. The creative solution is often known below our conscious awareness in what can be termed our subconscious mind, or our unconscious.
Psychiatrist Carl Jung realized that dreams are a bridge from the wisdom of our unconscious to our conscious minds. As Jungian analyst Marie-Louise von Franz explains, 9 Fraser Boa, The Way of the Dream: Conversations on Jungian Dream Interpretation With Marie-Louise Von Franz , 1994.
Dreams are the letters of the Self that the Self writes us every night.
One of the most powerful creative problem-solving techniques is to ask your subconscious mind to solve the problem you’re facing before you go to sleep. Then, keep a journal and pen on your nightstand and when you awaken, record whatever comes to mind.
This is a powerful technique that will improve with practice. It’s used by many geniuses and inventors.
Another variation of this creative problem-solving technique that doesn’t require sleeping is to ask your inner guide. I provide a step-by-step creative technique to access your inner guide here .
9 – Mind Map Your Problem
Another way to get unstuck in solving problems is to access the visual side of our brain. In left/right hemisphere parlance, the left brain is dominated by logic, reason, and language while the right brain is dominated by images, symbols, and feelings. (I realize that the “science” behind this distinction is now questionable, however, the concept is still useful.)
Our problems arise largely in our “thinking brain” as we tend to favor our thoughts over other modes of processing information. In the language of Jung’s Psychological Types , most of us have a dominant thinking function that rules over our feelings, intuition, and sensing functions.
Mind mapping is a powerful creative problem-solving technique that deploys visual brainstorming.
I learned about mind mapping in the 1990s from Tony Buzan’s The Mind Map Book and used this method for many years.
In the context of problem-solving, you draw the problem in the center of the page and then start ideating and connecting ideas from the center. Think of mind mapping as a visual outline.
You don’t need to be a skilled artist to use mind mapping. Nowadays, there are also numerous apps for mind mapping including Mind Meister and Miro, but I would still recommend using a blank piece of paper and some colored pencils or markers.
10 – Adopt a Beginner’s Mind
Our early “education” conditions us with what psychologists call functional fixedness where we look at problems from a familiar viewpoint.
Numerous creative problem-solving techniques we discussed above—like switching the context, changing our roles, wearing the Six Thinking Hats, and taking a 30,000-foot view—are designed to overcome functional fixedness.
Another technique is found in Zen philosophy called a Beginner’s Mind .
With a beginner’s mind, we empty our minds and forget what we think we know. In doing so, we enter a more playful, childlike state. Instead of being serious and “attacking the problem,” we can tinker and play with different ideas and scenarios without any fears of “getting it wrong.”
It can be a liberating experience. Psychologist Abraham Maslow found that self-actualizing individuals enter a state like the Beginner’s Mind where they get fully absorbed in whatever they are doing.
11 – Alter Your State of Consciousness
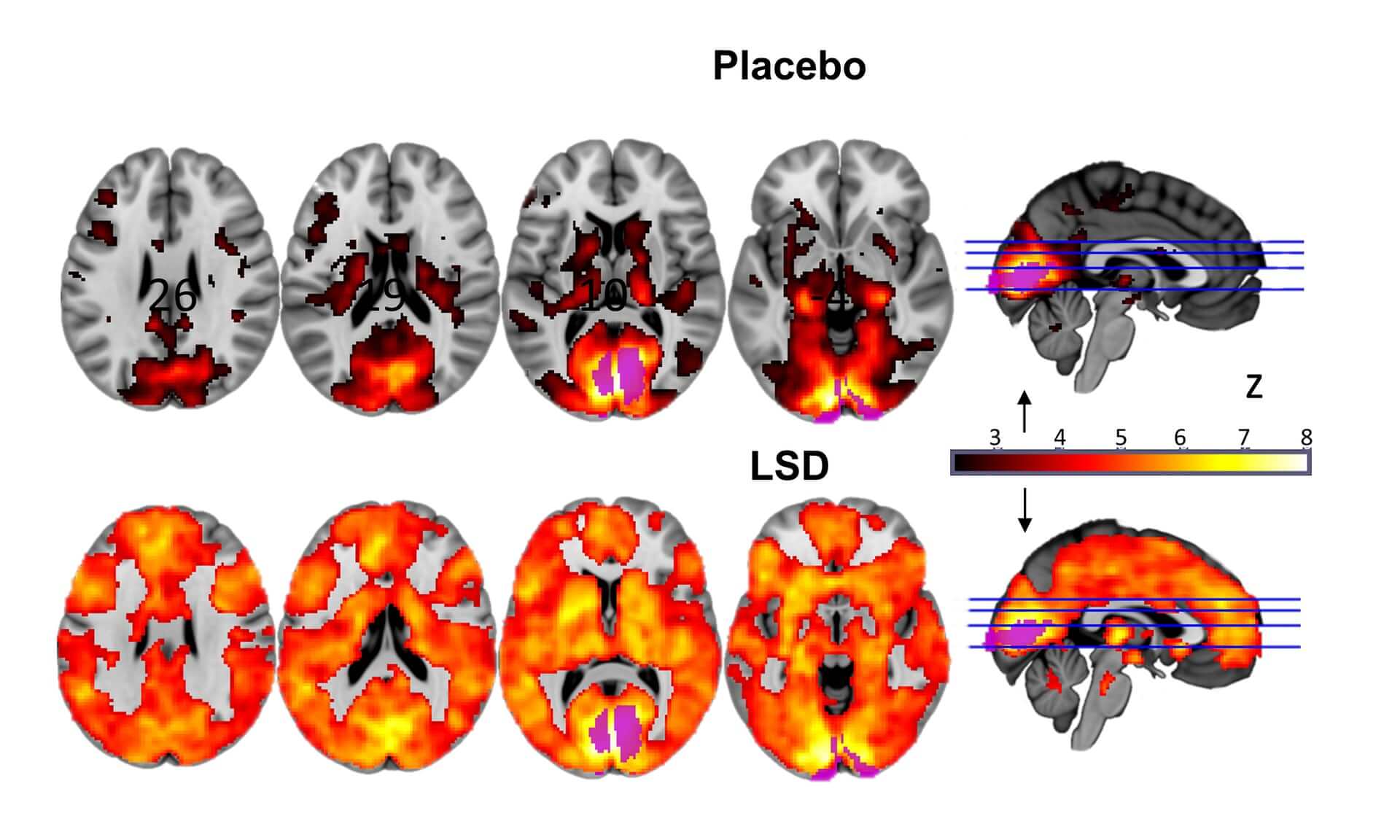
Another thing I noticed in my examination of artists and creative geniuses is that virtually all of them used various substances to alter their state of consciousness when producing creative work and solving intellectual problems .
The substances vary widely including stimulants like coffee and/or cigarettes, alcohol (like absinthe), and all manner of psychedelic substances like LSD, psilocybin mushrooms, and peyote.
I’m not suggesting you should “take drugs” to solve your problems. The point is that it’s incredibly useful to alter your state of consciousness to help find creative solutions.
While using various substances is one way to accomplish this, there are many other methods like:
- Stanislav Grof’s Holotropic Breathing Technique (similar to pranayama breathing)
- The WIM Hof Method (ice cold showers)
- Brainwave entrainment programs (binaural beats and isochronic tones)
- The Silva Method (also uses brainwave entrainment)
- Kasina Mind Media System by Mindplace (light stimulation and binaural beats)
Many of these types of programs shift your brain from a beta-dominant state to an alpha-dominated state which is more conducive for creativity. See, for example, Brain Awake by iAwake Technologies.
12 – Access Your Center
Perhaps the easiest and safest way of altering your state of consciousness is via meditation . Studies show that people experience improved brainstorming and higher creativity after only twenty minutes of meditation—even if they’re inexperienced meditators. 10 Colzato, L.S., Szapora, A., Lippelt, D. et al. Prior Meditation Practice Modulates Performance and Strategy Use in Convergent- and Divergent-Thinking Problems. Mindfulness 8, 10–16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-014-0352-9
When we’re stuck on a problem, or feeling confused about what we should do, we’re usually experiencing internal resistance. Different parts of us called archetypes hijack our minds and give us conflicting wants, beliefs, attitudes, and perspectives. These parts keep us from thinking clearly to find workable solutions.
As such, when you’re stuck, it helps to find your center first . It can also be highly beneficial to ground yourself on the earth . Both of these methods can help you quiet your mind chatter and shift into a more alpha-dominant brain pattern.
Getting in the habit of centering yourself before approaching a problem is perhaps the most powerful creative problem-solving technique. It can greatly assist you in taking a 30,000-foot view of our problem as well.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
We referenced numerous problem-solving tools in the above examples including:
- Roger von Oech’s Creative Whack Pack (a deck of cards with 64 creative strategies)
- Edward de Bono’s Six Thinking Hats method
- Mind mapping (see Tony Buzan’s How to Mind Map or research online)
- Brainwave entrainment (download free samples on iAwake or try your luck online)
- All of the mind-altering methods under “Alter Your State of Consciousness”
If you’re looking for problem-solving tools for a business/group context, in addition to the Six Thinking Hats, you might also try:
SWOT Analysis
Brainwriting.
Let’s have a quick look at each of these tools.
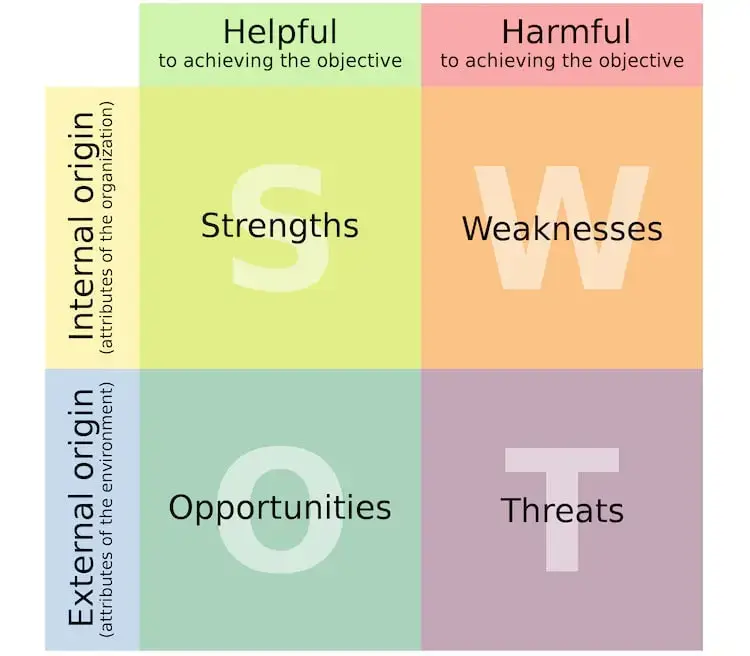
SWOT analysis is an excellent tool for business owners to help them understand their competitive landscape and make important business decisions. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. SWOT analysis is a practical strategic planning tool for businesses and it can be an effective problem-solving tool for your business.
Five Whys sometimes helps identify the root cause of the problem when it’s not clearly understood. You start by stating the problem as you understand it. Then you ask, “Why?” (For example, why is this occurring? ) As the tool’s name implies, you ask Why questions five times in total.
Brainwriting is a form of brainstorming where individuals generate ideas on their own before meeting to discuss them as a group. For a host of psychological reasons, this is often a superior way of approaching problem-solving in the workplace. Combining brainwriting with the Six Thinking Hats method can be even more powerful.
Using These Creative Problem-Solving Tools
All of the techniques and tools above represent creative problem-solving methods.
These examples illustrate that there are numerous pathways to get the answers we seek.
Some pathways, however, are more effective than others. The key is to experiment with various methods to uncover which ones work best for you .
Different methods will be more effective in different contexts.
Here, wisdom and intuition come into play. Over time, your connection with your inner guide improves and creative problem-solving becomes a more spontaneous process.
Recap: Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
Creative problem-solving is a skill based on the development of divergent thinking combined with altering our state of consciousness.
Due to our early conditioning, our “normal” waking state of consciousness is often filled with biases, limitations, blind spots, and negativity. This causes us to perceive problems rigidly.
When we get “stuck” it’s because our minds are fixed on a limited number of options.
To get “unstuck,” we just need to alter our state of consciousness and examine our problems from various perspectives, which is what the above creative problem-solving techniques are designed to do.
The more you play with these techniques, the more they become second nature to you.
You may find that each technique begins to play off the other. Then, the art and subtleties of the discovery process begin to emerge.
Enjoy solving your next problem!
How to Access Your Imagination
Peak Experiences: A Complete Guide
How to Restore Your Circadian Rhythm
About the Author
Scott Jeffrey is the founder of CEOsage, a self-leadership resource publishing in-depth guides read by millions of self-actualizing individuals. He writes about self-development, practical psychology, Eastern philosophy, and integrated practices. For 25 years, Scott was a business coach to high-performing entrepreneurs, CEOs, and best-selling authors. He's the author of four books including Creativity Revealed .
Learn more >
Some great ideas here. I am particularly intrigued by the "walk away" idea fulfilling the wanderer archetype. While counter intuitive, in my experience, walking away lets my mind develop subconcious connections that are sometimes the best. Sort of like letting my brain do the work instead of me! Bravo!
Todd Alexander
Thanks for your comments, Todd. It seems as though he need to train and remind ourselves to "walk away" because the mind thinks it can push its way through the problem.
How many times does it take for us to "absolutely know" that answers answer themselves when we take a break from forceful problem-solving and walk into the creative nature zone?! ;) The solution presents itself when we let go.
Great Post, Scott!
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
- Collaboration |
- Turn your team into skilled problem sol ...
Turn your team into skilled problem solvers with these problem-solving strategies

Picture this, you're handling your daily tasks at work and your boss calls you in and says, "We have a problem."
Unfortunately, we don't live in a world in which problems are instantly resolved with the snap of our fingers. Knowing how to effectively solve problems is an important professional skill to hone. If you have a problem that needs to be solved, what is the right process to use to ensure you get the most effective solution?
In this article we'll break down the problem-solving process and how you can find the most effective solutions for complex problems.
What is problem solving?
Problem solving is the process of finding a resolution for a specific issue or conflict. There are many possible solutions for solving a problem, which is why it's important to go through a problem-solving process to find the best solution. You could use a flathead screwdriver to unscrew a Phillips head screw, but there is a better tool for the situation. Utilizing common problem-solving techniques helps you find the best solution to fit the needs of the specific situation, much like using the right tools.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

4 steps to better problem solving
While it might be tempting to dive into a problem head first, take the time to move step by step. Here’s how you can effectively break down the problem-solving process with your team:
1. Identify the problem that needs to be solved
One of the easiest ways to identify a problem is to ask questions. A good place to start is to ask journalistic questions, like:
Who : Who is involved with this problem? Who caused the problem? Who is most affected by this issue?
What: What is happening? What is the extent of the issue? What does this problem prevent from moving forward?
Where: Where did this problem take place? Does this problem affect anything else in the immediate area?
When: When did this problem happen? When does this problem take effect? Is this an urgent issue that needs to be solved within a certain timeframe?
Why: Why is it happening? Why does it impact workflows?
How: How did this problem occur? How is it affecting workflows and team members from being productive?
Asking journalistic questions can help you define a strong problem statement so you can highlight the current situation objectively, and create a plan around that situation.
Here’s an example of how a design team uses journalistic questions to identify their problem:
Overarching problem: Design requests are being missed
Who: Design team, digital marketing team, web development team
What: Design requests are forgotten, lost, or being created ad hoc.
Where: Email requests, design request spreadsheet
When: Missed requests on January 20th, January 31st, February 4th, February 6th
How : Email request was lost in inbox and the intake spreadsheet was not updated correctly. The digital marketing team had to delay launching ads for a few days while design requests were bottlenecked. Designers had to work extra hours to ensure all requests were completed.
In this example, there are many different aspects of this problem that can be solved. Using journalistic questions can help you identify different issues and who you should involve in the process.
2. Brainstorm multiple solutions
If at all possible, bring in a facilitator who doesn't have a major stake in the solution. Bringing an individual who has little-to-no stake in the matter can help keep your team on track and encourage good problem-solving skills.
Here are a few brainstorming techniques to encourage creative thinking:
Brainstorm alone before hand: Before you come together as a group, provide some context to your team on what exactly the issue is that you're brainstorming. This will give time for you and your teammates to have some ideas ready by the time you meet.
Say yes to everything (at first): When you first start brainstorming, don't say no to any ideas just yet—try to get as many ideas down as possible. Having as many ideas as possible ensures that you’ll get a variety of solutions. Save the trimming for the next step of the strategy.
Talk to team members one-on-one: Some people may be less comfortable sharing their ideas in a group setting. Discuss the issue with team members individually and encourage them to share their opinions without restrictions—you might find some more detailed insights than originally anticipated.
Break out of your routine: If you're used to brainstorming in a conference room or over Zoom calls, do something a little different! Take your brainstorming meeting to a coffee shop or have your Zoom call while you're taking a walk. Getting out of your routine can force your brain out of its usual rut and increase critical thinking.
3. Define the solution
After you brainstorm with team members to get their unique perspectives on a scenario, it's time to look at the different strategies and decide which option is the best solution for the problem at hand. When defining the solution, consider these main two questions: What is the desired outcome of this solution and who stands to benefit from this solution?
Set a deadline for when this decision needs to be made and update stakeholders accordingly. Sometimes there's too many people who need to make a decision. Use your best judgement based on the limitations provided to do great things fast.
4. Implement the solution
To implement your solution, start by working with the individuals who are as closest to the problem. This can help those most affected by the problem get unblocked. Then move farther out to those who are less affected, and so on and so forth. Some solutions are simple enough that you don’t need to work through multiple teams.
After you prioritize implementation with the right teams, assign out the ongoing work that needs to be completed by the rest of the team. This can prevent people from becoming overburdened during the implementation plan . Once your solution is in place, schedule check-ins to see how the solution is working and course-correct if necessary.
Implement common problem-solving strategies
There are a few ways to go about identifying problems (and solutions). Here are some strategies you can try, as well as common ways to apply them:
Trial and error
Trial and error problem solving doesn't usually require a whole team of people to solve. To use trial and error problem solving, identify the cause of the problem, and then rapidly test possible solutions to see if anything changes.
This problem-solving method is often used in tech support teams through troubleshooting.
The 5 whys problem-solving method helps get to the root cause of an issue. You start by asking once, “Why did this issue happen?” After answering the first why, ask again, “Why did that happen?” You'll do this five times until you can attribute the problem to a root cause.
This technique can help you dig in and find the human error that caused something to go wrong. More importantly, it also helps you and your team develop an actionable plan so that you can prevent the issue from happening again.
Here’s an example:
Problem: The email marketing campaign was accidentally sent to the wrong audience.
“Why did this happen?” Because the audience name was not updated in our email platform.
“Why were the audience names not changed?” Because the audience segment was not renamed after editing.
“Why was the audience segment not renamed?” Because everybody has an individual way of creating an audience segment.
“Why does everybody have an individual way of creating an audience segment?” Because there is no standardized process for creating audience segments.
“Why is there no standardized process for creating audience segments?” Because the team hasn't decided on a way to standardize the process as the team introduced new members.
In this example, we can see a few areas that could be optimized to prevent this mistake from happening again. When working through these questions, make sure that everyone who was involved in the situation is present so that you can co-create next steps to avoid the same problem.
A SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis can help you highlight the strengths and weaknesses of a specific solution. SWOT stands for:
Strength: Why is this specific solution a good fit for this problem?
Weaknesses: What are the weak points of this solution? Is there anything that you can do to strengthen those weaknesses?
Opportunities: What other benefits could arise from implementing this solution?
Threats: Is there anything about this decision that can detrimentally impact your team?
As you identify specific solutions, you can highlight the different strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of each solution.
This particular problem-solving strategy is good to use when you're narrowing down the answers and need to compare and contrast the differences between different solutions.
Even more successful problem solving
After you’ve worked through a tough problem, don't forget to celebrate how far you've come. Not only is this important for your team of problem solvers to see their work in action, but this can also help you become a more efficient, effective , and flexible team. The more problems you tackle together, the more you’ll achieve.
Looking for a tool to help solve problems on your team? Track project implementation with a work management tool like Asana .
Related resources

Don’t let your digital tools sabotage the employee experience

12 tips for effective communication in the workplace

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.3: Creative Problem-Solving Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 62756
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the five steps in the creative problem-solving process
- Identify and describe common creative problem-solving tools
Creativity can be an important trait of an entrepreneur. In that discussion, we learned about creativity’s role in innovation . Here, we will look in more depth at creativity’s role in problem-solving . Let’s first formally define creativity as the development of original ideas to solve an issue. The intent of being an entrepreneur is to break away from practical norms and use imagination to embrace quick and effective solutions to an existing problem, usually outside the corporate environment.
The Steps of the Creative Problem-Solving Process
Training oneself to think like an entrepreneur means learning the steps to evaluating a challenge: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate (Figure 3.3.1).

Step 1: Clarify
To clarify is the critical step of recognizing the existence of a gap between the current state and a desired state. This can also be thought of as having need awareness , which occurs when the entrepreneur notes a gap between societal or customer needs and actual circumstances. Clarifying the problem by speaking with clients and developing a detailed description of the problem brings the specifics of a problem to light. Failure to identify the specifics of a problem leaves the entrepreneur with the impossible task of solving a ghost problem, a problem that is fully unknown or unseen. To establish and maintain credibility, an entrepreneur must clarify the problem by focusing on solving the problem itself, rather than solving a symptom of the problem.
For example, a farm could have polluted water, but it would not be enough to solve the problem only on that farm. Clarifying would involve identifying the source of the pollution to adequately tackle the problem. After gaining an understanding of a problem, the entrepreneur should begin to formulate plans for eliminating the gap. A fishbone diagram, as shown in Figure 3.3.2, is a tool that can be used to identify the causes of such a problem.

In the case of our water pollution example, a fishbone diagram exploring the issue might reveal the items shown in Figure 3.3.3.

Step 2: Ideate
To ideate is the step of the creative problem-solving process that involves generating and detailing ideas by the entrepreneur. After collecting all information relevant to the problem, the entrepreneur lists as many causes of the problem as possible. This is the step in which the largest variety of ideas are put forth. Each idea must be evaluated for feasibility and cost as a solution to the problem. If a farm does not have clean water, for example, the entrepreneur must list causes of toxic water and eliminate as many of those causes as possible. The entrepreneur must then move forward investigating solutions to bring the water back to a safe state. If, say, nearby livestock are polluting the water, the livestock should be isolated from the water source.
Step 3: Develop
To develop is the step in which the entrepreneur takes the list of ideas generated and tests each solution for feasibility. The entrepreneur must consider the cost of each idea and the obstacles to implementation. In the preceding example, adding a chemical to the water may not be a feasible solution to the farmer. Not every farmer wants additional chloride or fluoride added to the water due to the effect on both humans and livestock. These tradeoffs should be addressed in the feasibility assessment. The farmer might prefer a filtration system, but the cost of that solution might not be practicable. The entrepreneur should identify and assess alternative solutions to find one that is most cost-effective and feasible to the customer.
Step 4: Implement
To implement is the step in which the solution to the problem is tested and evaluated. The entrepreneur walks through the planned implementation with the client and tests each part of the solution, if a service, or thoroughly tests a developed good. The entrepreneur implements the solution and goes through a structured system of follow-up to ensure the solution remains effective and viable. In the water example, the solution would be reducing runoff from toxic insecticides by adding prairie strips, buffers of grass, and vegetation along banks of streams.
Step 5: Evaluate
To evaluate is the step in which the final solution is assessed. This is a very important step that entrepreneurs often overlook. Any fallacy in the implementation of the product or service is reassessed, and new solutions are implemented. A continual testing process may be needed to find the final solution. The prairie strips, buffers of grass, and vegetation along banks of streams chosen in the farming water example should then be analyzed and tested to ensure the chosen solution changed the content of the water.
ARE YOU READY?
Implementing Creative Problem Solving
Removing waste is a problem, and it can also present an entrepreneurial opportunity. Try to examine ways in which waste products that you usually pay to have hauled away can now generate revenue. Whether it’s recycling aluminum cans or cardboard, or garbage that could be used to feed animals, your task is to come up with solutions to this entrepreneurial-oriented problem.
- Try following the first step of the creative problem-solving process and clearly identify the problem.
- Next, gather data and formulate the challenge.
- Then, explore ideas and come up with solutions.
- Develop a plan of action.
- Finally, note how you would evaluate the effectiveness of your solution.
Using Creativity to Solve Problems
Entrepreneurs are faced with solving many problems as they develop their ideas for filling gaps, whether those opportunities involve establishing a new company or starting a new enterprise within an existing company. Some of these problems include staffing, hiring and managing employees, handling legal compliance, funding, marketing, and paying taxes. Beyond the mundane activities listed, the entrepreneur, or the team that the entrepreneur puts in place, is indispensable in maintaining the ongoing creativity behind the product line or service offered. Innovation and creativity in the business are necessary to expand the product line or develop a groundbreaking service.
It is not necessary for the entrepreneur to feel isolated when it comes to finding creative solutions to a problem. There are societies, tools, and new methods available to spur the creativity of the entrepreneur that will further support the success and expansion of a new enterprise. 14 Learning and using entrepreneurial methods to solve problems alleviates the stress many startup owners feel. The entrepreneur’s creativity will increase using collaborative methodologies. Some entrepreneurial collaborative methodologies include crowdsourcing, brainstorming, storyboarding, conducting quick online surveys to test ideas and concepts, and team creativity activities.
Crowdsourcing
Professor Daren Brabham at the University of Southern California has written books on crowdsourcing and touts its potential in for-profit and not-for-profit business sectors. He defines it simply as “an online, distributed problem-solving and production model.” 15 Crowdsourcing involves teams of amateurs and nonexperts working together to form a solution to a problem. 16 The idea, as cbsnews.com’s Jennifer Alsever has put it, is to “tap into the collective intelligence of the public at large to complete business-related tasks that a company would normally either perform itself or outsource to a third-party provider. Yet free labor is only a narrow part of crowdsourcing's appeal. More importantly, it enables managers to expand the size of their talent pool while also gaining deeper insight into what customers really want. The challenge is to take a cautionary approach to the ‘wisdom of the crowd,’ which can lead to a ‘herd’ mentality.” 17
LINK TO LEARNING
Read this article that discusses what crowdsourcing is, how to use it, and its benefits for more information.
This new business prototype, similar to outsourcing, features an enterprise posting a problem online and asking for volunteers to consider the problem and propose solutions. Volunteers earn a reward, such as prize money, promotional materials like a T-shirt, royalties on creative outlets like photos or designs, and in some cases, compensation for their labor. Before proposing the solution, volunteers learn that the solutions become the intellectual property of the startup posting the problem. The solution is then mass-produced for profit by the startup that posted the problem. 18 The process evolves into the crowdsourcing process after the enterprise mass produces and profits from the labor of the volunteers and the team. Entrepreneurs should consider that untapped masses have solutions for many issues for which agendas do not yet exist. Crowdsourcing can exploit those agendas and add to the tools used to stimulate personal creativity. This type of innovation is planned and strategically implemented for profit.
For example, Bombardier held a crowdsourced innovation contest to solicit input on the future of train interiors, including seat design and coach class interior. A corporate jury judged the submissions, with the top ten receiving computers or cash prizes. Companies are often constrained, however, by internal rules limiting open source or external idea sourcing, as they could be accused of “stealing” an idea. While crowdsourcing outside of software can be problematic, some products such as MakerBot’s 3D printers, 3DR’s drones, and Jibo’s Social Robot have used developer kits and “makers” to help build a community and stimulate innovation from the outside.
WORK IT OUT
A Crowdsourced Potato Chip
In an effort to increase sales among millennials, PepsiCo turned to crowdsourcing to get new flavor ideas for their Lay’s potato chips (called Walker’s in the UK). Their 2012 campaign, “Do Us a Flavor,” was so successful that they received over 14 million submissions. The winner was Cheesy Garlic Bread, which increased their potato chip sales by 8 percent during the first three months after the launch.
- What are some other products that would work well for a crowdsourced campaign contest?
- What items wouldn’t work well?
Amazon’s Mechanical Turk is an online crowdsourcing platform that allows individuals to post tasks for workers to complete. In many instances, these tasks are compensated, but the payment can be less than one dollar per item completed. Mechanical Turk is one of the largest and most well-known crowdsourcing platforms, but there are a number of other more niche ones as well that would apply to smaller markets. In the case of innovation contests and outsourced tasks from corporations, those tasks may be hosted internally by the corporation.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is the generation of ideas in an environment free of judgment or dissension with the goal of creating solutions. Brainstorming is meant to stimulate participants into thinking about problem-solving in a new way. Using a multifunctional group, meaning participants come from different departments and with different skill sets, gives entrepreneurs and support teams a genuine chance to suggest and actualize ideas. The group works together to refine and prototype potential solutions to a problem.
Brainstorming is a highly researched and often practiced technique for the development of innovative solutions. One of the more successful proponents of brainstorming is the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). UNICEF faces unique problems of solving resource problems for mothers and children in underdeveloped nations. See how UNICEF practices brainstorming to solve problems including child survival, gender inclusion, refugee crises, education, and others.
The setting for a brainstorming session should remain as informal and relaxed as possible. The group needs to avoid standard solutions. All ideas are welcome and listed and considered with no censorship and with no regard to administrative restrictions. All team members have an equal voice. The focus of brainstorming is on quantity of ideas rather than on the ideal solution provided in every suggestion. A classic entrepreneurial brainstorming activity, as popularized by business software developer Strategyzer, is known as the “silly cow” exercise. Teams come up with ideas for new business models pertaining to a cow, with the results often outrageous, ranging from sponsored cows to stroking cows for therapeutic release. Participants are asked to identify some aspect of a cow and develop three business models around that concept in a short time period, typically two minutes or fewer. The activity is designed to get creative juices flowing.
Watch this video from ABC’s Nightline that shows how IDEO designed a new shopping cart for an example of a design process that involves brainstorming.
Storyboarding
Storyboarding is the process of presenting an idea in a step-by-step graphic format, as Figure 3.3.4 shows. This tool is useful when the entrepreneur is attempting to visualize a solution to a problem. The steps to the solution of a problem are sketched and hung in graphic format. Once the original graphic is placed, images of steps working toward a solution are added, subtracted, and rearranged on a continual basis, until the ultimate solution emerges in the ultimate graphic format. For many years, entrepreneurs have used this process to create a pre-visual for various media sequences.

Team Creativity
Team creativity is the process whereby an entrepreneur works with a team to create an unexpected solution for an issue or challenge. Teams progress through the same creative problem-solving process described already: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate. The main advantage of team creativity is the collaboration and support members receive from one another. Great teams trust in other team members, have diverse members with diverse points of view, are cohesive, and have chemistry.
Team members should work in a stress-free and relaxing environment. Reinforcement and expansion of ideas in the team environment motivates the team to continually expand horizons toward problem solution. A small idea in a team may spark the imagination of a team member to an original idea. Mark Zuckerberg, co-founder of Facebook, once said, “The most important thing for you as an entrepreneur trying to build something is, you need to build a really good team. And that’s what I spend all my time on.” 19
ENTREPRENEUR IN ACTION
Taaluma Totes 20
Young entrepreneurs Jack DuFour and Alley Heffern began to notice the beautiful fabrics that came from the different countries they visited. The entrepreneurs thought about what could be done with the fabrics to create employment opportunities both in the country from which the fabric originated and in their home base of Virginia. They decided to test producing totes from the fabrics they found and formed Taaluma Totes (Figure 3.3.5). DuFour and Heffern also wanted to promote the production of these fabrics and help underserved populations in countries where the fabric originated maintain a living or follow a dream.

The team continued to test the process and gathered original fabrics, which they sent to Virginia to create totes. They trained individuals with disabilities in Virginia to manufacture the totes, thus serving populations in the United States. The entrepreneurs then decided to take 20 percent of their profits and make microloans to farmers and small business owners in the countries where the fabric originated to create jobs there. Microloans are small loans, below $50,000, which certain lenders offer to enterprising startups. These startups, for various reasons (they are in poor nations, at the poverty level), can’t afford a traditional loan from a major bank. The lenders offer business support to the borrower, which in turn helps the borrower repay the microloan. The microloans from Taaluma are repaid when the borrower is able. Repayments are used to buy more fabric, completing Taaluma’s desire to serve dual populations. If the process proved unsuccessful, the co-owners would revise the process to meet the plan’s requirements.
DuFour and Heffern now have fabrics from dozens of countries from Thailand to Ecuador. The totes are specialized with features to meet individual needs. The product line is innovated regularly and Taaluma Totes serves a dual purpose of employing persons with disabilities in Virginia and creating employment for underserved populations in other countries.

The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible pp 298–313 Cite as
Creative Problem-Solving
- Gerard J. Puccio 2 ,
- Barry Klarman 2 &
- Pamela A. Szalay 2
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2023
115 Accesses
Life and work in the beginning of the twenty-first century has been described as volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous. In this fast changing, innovation-driven environment, Creative Problem-Solving has been identified as a fundamental skill for success. In contrast to routine problem-solving, with straightforward and repeatable solution paths, today’s problems are described as being complex and wicked. To generate the possibilities that can effectively address complex problems, individuals need to draw on the highest level of human thought – creativity. Creative Problem-Solving explicitly draws on, and promotes, effective creative thinking. The purpose of this entry is to describe and distinguish Creative Problem-Solving from other forms of problems-solving. Moreover, as Creative Problem-Solving is a deliberate creativity methodology, this chapter also provides a description of the more specific thinking skills that are embodied by the higher-order skill of creative thinking and are explicitly called on in Creative Problem-Solving. Complex problems require complex thinking, and Creative Problem-Solving provides a structured process that allows individuals to more easily and efficiently deploy their creative thinking skills.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (Eds.). (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives: Complete edition . New York: Longman.
Google Scholar
Basadur, M. (1994). Simplex. Buffalo, NY: The Creative Education Foundation.
Brackett, M. (2019). Permission to feel: Unlocking the power of emotions to help our kids, ourselves, and our society thrive . New York: Celadon Books.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience . New York: HarperPerennial.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996). Creativity: Flow and the psychology of discovery and invention . New York: HarperCollins.
Darwin, C. (2003). The origin of species: By means of natural selection of the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life (p. 252). New York: Signet Classics.
Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional intelligence: Why it can matter more than IQ . New York: Bantam.
Isaksen, S. G., & Treffinger, D. J. (1985). Creative problem solving: The basic course. Buffalo, NY: Bearly Limited.
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B., & Treffinger, D. J. (1994). Creative approaches to problem solving. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt.
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B. & Treffinger, D. J. (2000). Creative approaches to problem solving (2nd ed.). Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing.
Johnson, B. (1996). Polarity management: Identifying and managing unsolvable problem . Amherst: HRD Press.
Miller, J. C. (2004). The transcendent function: Jung’s model of psychological growth through dialogue with the unconscious . Albany: State University of New York Press.
Morriss-Kay, G. M. (2010). The evolution of human artistic creativity. Journal of Anatomy, 216 , 158–176.
Article Google Scholar
Mumford, M. D., Zaccaro, S. J., Harding, F. D., Jacobs, T. O., & Fleishman, E. A. (2000). Leadership skills for a changing world: Solving complex problems. Leadership Quarterly, 11 , 11–35.
Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . New York: Scribner.
Osborn, A. F. (1963). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving (3rd ed.). New York: Scribner.
Otani, A. (2015, January). These are the skills you need if you want to be headhunted. Retrieved on 27 July 2015 from Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . New York: Scribner.
Parnes, S. J. (1967). Creative behavior workbook. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Parnes, S. J. (1988). Visionizing. East Aurora, NY: D.O.K. Publishers.
Parnes, S. J. (1992). Creative problem solving and visionizing. In S.J. Parnes (Ed.), Sourcebook for creative problem solving (pp. 133–154). Buffalo, NY: Creative Education Press.
Parnes, S. J., & Biondi, A. M. (1975). Creative behavior: A delicate balance. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 9 , 149–158.
Puccio, G. J. (2017). From the dawn of humanity to the 21st century: Creativity as an enduring survival skill. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 51 , 330–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.203 .
Puccio, G. J., Murdock, M. C., & Mance, M. (2005). Current developments in creative problem solving for organizations: A focus on thinking skills and styles. The Korean Journal of Thinking & Problem Solving, 15 , 43–76.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., & Murdock, M. (2011). Creative leadership: Skills that drive change (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: SAGE.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., Switalski, B., & Reali, P. (2012). Creativity rising: Creative thinking and problem solving in the 21st century . Buffalo: ICSC Press.
Puccio, G. J., Burnett, C., Acar, S., Yudess, J. A., Holinger, M., & Cabra, J. F. (2018). Creative problem solving in small groups: The effects of creativity training on idea generation, solution creativity, and leadership effectiveness. The Journal of Creative Behavior . Advance online publication. [not sure of order]. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.381 .
Scott, G. M., Leritz, L. E., & Mumford, M. D. (2004). The effectiveness of creativity training: A meta-analysis. Creativity Research Journal, 16 , 361–388.
Stokes, P. D. (2013). Crossing disciplines: A constraint-based model of the creative/innovative process. The Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31 (2), 247–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12093 .
Trilling, B., & Fadel, C. (2009). 21st century skills: Learning for life in our times . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Vehar, J. R., Firestien, R. L., & Miller, B. (1997). Creativity unbound. Williamsville, NY: Innovation Systems Group.
Wagner, T. (2008). The global achievement gap: Why even our best schools don’t teach the new survival skills our children need – And what we can do about it . New York: Basic Books.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
International Center for Studies in Creativity, The State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, USA
Gerard J. Puccio, Barry Klarman & Pamela A. Szalay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gerard J. Puccio .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Vlad Petre Glăveanu
Section Editor information
No affiliation provided
Sergio Agnoli
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Puccio, G.J., Klarman, B., Szalay, P.A. (2022). Creative Problem-Solving. In: Glăveanu, V.P. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_41
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_41
Published : 26 January 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-90912-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-90913-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Psychological safety and the critical role of leadership development
When employees feel comfortable asking for help, sharing suggestions informally, or challenging the status quo without fear of negative social consequences, organizations are more likely to innovate quickly , unlock the benefits of diversity , and adapt well to change —all capabilities that have only grown in importance during the COVID-19 crisis. 1 Jonathan Emmett, Gunnar Schrah, Matt Schrimper, and Alexandra Wood, “ COVID-19 and the employee experience: How leaders can seize the moment ,” June 2020, McKinsey.com; Tera Allas, David Chinn, Pal Erik Sjatil, and Whitney Zimmerman, “ Well-being in Europe: Addressing the high cost of COVID-19 on life satisfaction ,” June 2020, McKinsey.com. Yet a McKinsey Global Survey conducted during the pandemic confirms that only a handful of business leaders often demonstrate the positive behaviors that can instill this climate, termed psychological safety , in their workforce. 2 The online survey was in the field from May 14–29, 2020, and garnered responses from 1,574 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, we analyzed the results of 1,223 participants who said they were a member of a team that they did not lead, where a team is defined as two or more people who work together to achieve a common goal. CEOs were included in the findings if they said that a) their organization had a board of directors and b) they were not the board’s chair, so that they could think of their board when asked questions about their team.
As considerable prior research shows, psychological safety is a precursor to adaptive, innovative performance—which is needed in today’s rapidly changing environment—at the individual, team, and organization levels. 3 Amy C. Edmondson, The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth, first edition, Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, November 2018; Shirley A. Ashauer and Therese Macan, “How can leaders foster team learning? Effects of leader-assigned mastery and performance goals and psychological safety,” Journal of Psychology, November–December 2013, Volume 147, Number 6, pp. 541–61, tandfonline.com; Anne Boon et al., “Team learning beliefs and behaviours in response teams,” European Journal of Training and Development, May 2013, Volume 37, Number 4, pp. 357–79, emerald.com; Daphna Brueller and Abraham Carmeli, “Linking capacities of high-quality relationships to team learning and performance in service organizations,” Human Resource Management, July–August 2011, Volume 50, Number 4, pp. 455–77, wileyonlinelibrary.com; M. Lance Frazier et al., “Psychological safety: A meta-analytic review and extension,” Personnel Psychology, February 2017, Volume 70, Number 1, pp. 113–65, onlinelibrary.wiley.com; Nikos Bozionelos and Konstantinos C. Kostopoulos, “Team exploratory and exploitative learning: Psychological safety, task conflict, and team performance,” Group & Organization Management, June 2011, Volume 36, Number 3, pp. 385–415, journals.sagepub.com; Rosario Ortega et al., “The emotional impact of bullying and cyberbullying on victims: A European cross-national study,” Aggressive Behavior, September–October 2012, Volume 38, Issue 5, pp. 342–56, onlinelibrary.wiley.com; Corinne Post, “Deep-level team composition and innovation: The mediating roles of psychological safety and cooperative learning,” Group & Organizational Management, October 2012, Volume 37, Number 5, pp. 555–88, journals.sagepub.com; Charles Duhigg, “What Google learned from its quest to build the perfect team,” New York Times, February 25, 2016, nytimes.com. Amy Edmondson’s 1999 research previously found—and our survey findings confirm—that higher psychological safety predicts a higher degree of boundary-spanning behavior, which is accessing and coordinating with those outside of an individual’s team to accomplish goals. For example, successfully creating a “ network of teams ”—an agile organizational structure that empowers teams to tackle problems quickly by operating outside of bureaucratic or siloed structures—requires a strong degree of psychological safety.
Fortunately, our newest research suggests how organizations can foster psychological safety. Doing so depends on leaders at all levels learning and demonstrating specific leadership behaviors that help their employees thrive. Investing in and scaling up leadership-development programs can equip leaders to embody these behaviors and consequently cultivate psychological safety across the organization.
A recipe for leadership that promotes psychological safety
Leaders can build psychological safety by creating the right climate, mindsets, and behaviors within their teams. In our experience, those who do this best act as catalysts, empowering and enabling other leaders on the team—even those with no formal authority—to help cultivate psychological safety by role modeling and reinforcing the behaviors they expect from the rest of the team.
Our research finds that a positive team climate—in which team members value one another’s contributions, care about one another’s well-being, and have input into how the team carries out its work—is the most important driver of a team’s psychological safety. 4 Past research by Frazier et al. (2017) found three categories to be the main drivers of psychological safety: positive leader relations, work-design characteristics, and a positive team climate. We conducted multiple regression with relative-importance analysis to understand which category matters most, and our results show that a positive team climate has a significantly stronger direct effect on psychological safety than the other two. Based on these results, we tested a structural-equation model (SEM) in which the frequency with which team leaders displayed four leadership behaviors predicted psychological safety both directly and indirectly via positive team climate. Exploratory analyses were conducted to determine whether the effect of the leadership behaviors affected psychological safety at different levels of team climate. By setting the tone for the team climate through their own actions, team leaders have the strongest influence on a team’s psychological safety. Moreover, creating a positive team climate can pay additional dividends during a time of disruption. Our research finds that a positive team climate has a stronger effect on psychological safety in teams that experienced a greater degree of change in working remotely than in those that experienced less change during the COVID-19 pandemic. Yet just 43 percent of all respondents report a positive climate within their team.
Positive team climate is the most important driver of psychological safety and most likely to occur when leaders demonstrate supportive, consultative behaviors, then begin to challenge their teams.
During the pandemic, we have seen an accelerated shift away from the traditional command-and-control leadership style known as authoritative leadership, one of the four well-established styles of leadership behavior we examined to understand which ones encourage a positive team climate and psychological safety . The survey finds that team leaders’ authoritative-leadership behaviors are detrimental to psychological safety, while consultative- and supportive-leadership behaviors promote psychological safety.
The results also suggest that leaders can further enhance psychological safety by ensuring a positive team climate (Exhibit 1). Both consultative and supportive leadership help create a positive team climate, though to varying degrees and through different types of behaviors.
With consultative leadership, which has a direct and indirect effect on psychological safety, leaders consult their team members, solicit input, and consider the team’s views on issues that affect them. 5 The standardized regression coefficient between consultative leadership and psychological safety was 0.54. The survey measured consultative-leadership behaviors by asking respondents how frequently their team leaders demonstrate the following behaviors: ask the opinions of others before making important decisions, give team members the autonomy to make their own decisions, and try to achieve team consensus on decisions. Supportive leadership has an indirect but still significant effect on psychological safety by helping to create a positive team climate; it involves leaders demonstrating concern and support for team members not only as employees but also as individuals. 6 The survey measured supportive leadership behaviors by asking respondents how frequently their team leaders demonstrate the following behaviors: create a sense of teamwork and mutual support within the team, and demonstrate concern for the welfare of team members. These behaviors also can encourage team members to support one another.
Another set of leadership behaviors can sometimes strengthen psychological safety—but only when a positive team climate is in place. This set of behaviors, known as challenging leadership, encourages employees to do more than they initially think they can. A challenging leader asks team members to reexamine assumptions about their work and how it can be performed in order to exceed expectations and fulfill their potential. Challenging leadership has previously been linked with employees expressing creativity, feeling empowered to make work-related changes, and seeking to learn and improve. 7 Giles Hirst, Helen Shipton, and Qin Zhou, “Context matters: Combined influence of participation and intellectual stimulation on the promotion focus–employee creative relationship,” Journal of Organizational Behavior, October 2012, Volume 33, Number 7, pp. 894–909, onlinelibrary.wiley.com; Le Cong Thuan, “Motivating follower creativity by offering intellectual stimulation,” International Journal of Organizational Analysis, December 2019, Volume 28, Number 4, pp. 817–29, emerald.com; Jie Li et al., “Not all transformational leadership behaviors are equal: The impact of followers’ identification with leader and modernity on taking charge,” Journal of Leadership and Organizational Studies, August 2017, Volume 24, Number 3, pp. 318–34, journals.sagepub.com; Susana Llorens-Gumbau, Marisa Salanova Soria, and Israel Sánchez-Cardona, “Leadership intellectual stimulation and team learning: The mediating role of team positive affect,” Universitas Psychologica, March 2018, Volume 17, Number 1, pp. 1–16, revistas.javeriana.edu.co. However, the survey findings show that the highest likelihood of psychological safety occurs when a team leader first creates a positive team climate, through frequent supportive and consultative actions, and then challenges their team; without a foundation of positive climate, challenging behaviors have no significant effect. And employees’ experiences look very different depending on how their leaders behave, according to Amy Edmondson, the Novartis Professor of Leadership and Management at Harvard Business School (interactive).
What’s more, the survey results show that a climate conducive to psychological safety starts at the very top of an organization. We sought to understand the effects of senior-leader behavior on employees’ sense of safety and found that senior leaders can help create a culture of inclusiveness that promotes positive leadership behaviors throughout an organization by role-modeling these behaviors themselves. Team leaders are more likely to exhibit supportive, consultative, and challenging leadership if senior leaders demonstrate inclusiveness—for example, by seeking out opinions that might differ from their own and by treating others with respect.
The importance of developing leaders at all levels
Our findings show that investing in leadership development across an organization—for all leadership positions—is an effective method for cultivating the combination of leadership behaviors that enhance psychological safety. Employees who report that their organizations invest substantially in leadership development are more likely to also report that their team leaders frequently demonstrate consultative, supportive, and challenging leadership behaviors. They also are 64 percent more likely to rate senior leaders as more inclusive (Exhibit 2). 8 We measured investing in leadership development by asking about agreement with the following statements: “my organization places a great deal of importance on developing its leaders,” and “my organization devotes significant resources to developing its leaders.” However, the results suggest that the effectiveness of these programs varies depending upon the skills they address.
Reorient the skills developed in leadership programs
Organizations often attempt to cover many topics in their leadership-development programs . But our findings suggest that focusing on a handful of specific skills and behaviors in these learning programs can improve the likelihood of positive leadership behaviors that foster psychological safety and, ultimately, of strong team performance. Some of the most commonly taught skills at respondents’ organizations—such as open-dialogue skills, which allow leaders to explore disagreements and talk through tension in a team—are among the ones most associated with positive leadership behaviors. However, several relatively untapped skill areas also yield beneficial results (Exhibit 3).
Two of the less-commonly addressed skills in formal programs are predictive of positive leadership. Training in sponsorship—that is, enabling others’ success ahead of one’s own—supports both consultative- and challenging-leadership behaviors, yet just 26 percent of respondents say their organizations include the skill in development programs. And development of situational humility, which 36 percent of respondents say their organizations address, teaches leaders how to develop a personal-growth mindset and curiosity. Addressing this skill is predictive of leaders displaying consultative behaviors.
Development at the top is equally important
According to the data, fostering psychological safety at scale begins with companies’ most senior leaders developing and embodying the leadership behaviors they want to see across the organization. Many of the same skills that promote positive team-leader behaviors can also be developed among senior leaders to promote inclusiveness. For example, open-dialogue skills and development of social relationships within teams are also important skill sets for senior leaders.
In addition, several skills are more important at the very top of the organization. Situational and cultural awareness, or understanding how beliefs can be developed based on selective observations and the norms in different cultures, are both linked with senior leaders’ inclusiveness.
Looking ahead
Given the quickening pace of change and disruption and the need for creative, adaptive responses from teams at every level, psychological safety is more important than ever. The organizations that develop the leadership skills and positive work environment that help create psychological safety can reap many benefits, from improved innovation, experimentation, and agility to better overall organizational health and performance. 9 We define organizational health as an organization’s ability to align on a clear vision, strategy, and culture; to execute with excellence; and to renew the organization’s focus over time by responding to market trends.
As clear as this call to action may be, “How do we develop psychological safety?” and, more specifically, “Where do we start?” remain the most common questions we are asked. These survey findings show that there is no time to waste in creating and investing in leadership development at scale to help enhance psychological safety. Organizations can start doing so in the following ways:
- Go beyond one-off training programs and deploy an at-scale system of leadership development. Human behaviors aren’t easily shifted overnight. Yet too often we see companies try to do so by using targeted training programs alone. Shifting leadership behaviors within a complex system at the individual, team, and enterprise levels begins with defining a clear strategy aligned to the organization’s overall aspiration and a comprehensive set of capabilities that are required to achieve it. It’s critical to develop a taxonomy of skills (having an open dialogue, for example) that not only supports the realization of the organization’s overall identity but also fosters learning and growth and applies directly to people’s day-to-day work. Practically speaking, while the delivery of learning may be sequenced as a series of trainings—and rapidly codified and scaled for all leaders across a cohort or function of the organization—those trainings will be even more effective when combined with other building blocks of a broader learning system, such as behavioral reinforcements. While learning experiences look much different now than before the COVID-19 pandemic , digital learning provides large companies with more opportunities to break down silos and create new connections across an organization through learning.
- Invest in leadership-development experiences that are emotional, sensory, and create aha moments. Learning experiences that are immersive and engaging are remembered more clearly and for a longer time. Yet a common pitfall of learning programs is an outsize focus on the content—even though it is usually not a lack of knowledge that holds leaders back from realizing their full potential. Therefore, it’s critical that learning programs prompt leaders to engage with and shift their underlying beliefs, assumptions, and emotions to bring about lasting mindset changes. This requires a learning environment that is both conducive to the often vulnerable process of learning and also expertly designed. Companies can begin with facilitated experiences that push learners toward personal introspection through targeted reflection questions and small, intimate breakout conversations. These environments can help leaders achieve increased self-awareness, spark the desire for further growth, and, with the help of reflection and feedback, drive collective growth and performance.
- Build mechanisms to make development a part of leaders’ day-to-day work. Formal learning and skill development serve as springboards in the context of real work; the most successful learning journeys account for the rich learning that happens in day-to-day work and interactions. The use of learning nudges (that is, daily, targeted reminders for individuals) can help learners overcome obstacles and move from retention to application of their knowledge. In parallel, the organization’s most senior leaders need to be the first adopters of putting real work at the core of their development, which requires senior leaders to role model—publicly—their own processes of learning. In this context, the concept of role models has evolved; rather than role models serving as examples of the finished product, they become examples of the work in progress, high on self-belief but low on perfect answers. These examples become strong signals for leaders across the organization that it is safe to be practicing, failing, and developing on the job.
The contributors to the development and analysis of this survey include Aaron De Smet , a senior partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office; Kim Rubenstein, a research-science specialist in the New York office; Gunnar Schrah, a director of research science in the Denver office; Mike Vierow, an associate partner in the Brisbane office; and Amy Edmondson , the Novartis Professor of Leadership and Management at Harvard Business School.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, an associate editor in the Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Psychological safety, emotional intelligence, and leadership in a time of flux

Why rigor is the key ingredient to develop leaders

Diverse employees are struggling the most during COVID-19—here’s how companies can respond

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
8. Practice Design Thinking. Practicing design thinking can make you a more creative problem-solver. While commonly associated with the workplace, adopting a design thinking mentality can also improve your everyday life. Here are several ways you can practice design thinking: Learn from others: There are many examples of design thinking in ...
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues.You may face challenges around growth, design, user engagement, and even team culture and happiness.In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team's skillset.
Key Points. Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming. It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh ...
All episodes. Details. Transcript. December 04, 2018. Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the ...
The creative problem-solving process is a systematic approach that can be seamlessly integrated into any business strategy. It begins with identifying the problem, requiring a clear understanding ...
In today's competitive business landscape, organizations need processes in place to make strong, well-informed, and innovative decisions. Problem solving - in particular creative problem solving (CPS) - is a key skill in learning how to accurately identify problems and their causes, generate potential solutions, and evaluate all the possibilities to arrive at a strong corrective course of ...
2. Mind-mapping. Mind-mapping is a useful creative problem-solving process. A mind map is a graphic representation of ideas and concepts. It is a visual tool for creativity and problem-solving. Mind maps help you categorize and structure information. They aid comprehension, analysis, and help generate innovative ideas.
How to Solve Problems. To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety. Teams today aren't just asked to execute tasks: They're called upon to solve problems. You'd ...
Problems on not using creative problem-solving techniques 1. Lack of Innovation. A team that does not use creative problem-solving techniques may struggle to come up with innovative solutions to complex challenges. This can result in a lack of growth and progress for the organization . Innovation is not just a buzzword or a trendy concept.
Here, wisdom and intuition come into play. Over time, your connection with your inner guide improves and creative problem-solving becomes a more spontaneous process. Recap: Creative Problem-Solving Techniques. Creative problem-solving is a skill based on the development of divergent thinking combined with altering our state of consciousness.
1. Starbursting. A visual brainstorming technique, starbursting should be used once you or your team of brainstormers has homed in on a single idea. To begin starbursting, put an idea on the middle of a whiteboard and draw a six-point star around it. Each point will represent a question:
The simplest form of the creative problem solving process involves four steps: Clarify - define the objectives, the problem, the facts, and the opportunity to achieve. Ideate - brainstorm many possible solutions or approaches. Develop - further develop your ideas by turning them into experiments. Implement - create a plan and move ...
4 steps to better problem solving. While it might be tempting to dive into a problem head first, take the time to move step by step. Here's how you can effectively break down the problem-solving process with your team: 1. Identify the problem that needs to be solved. One of the easiest ways to identify a problem is to ask questions.
That's what we've found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They're terrific problem solvers under any conditions.
1. Use a strategic framework. Creative problem-solving is a framework within itself. It lets you break down issues that are hard to measure with a structured approach. Try these steps: Gather information: During this phase, clarify your goal or your problem. Gather as much information and unbiased input as you can.
The Steps of the Creative Problem-Solving Process. Training oneself to think like an entrepreneur means learning the steps to evaluating a challenge: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate (Figure 3.3.1). Figure 3.3.1 3.3. 1: The process of creativity is not random; it is a specific and logical process that includes evaluation.
cated problem-solving techniques until it captures all that can be learned from the simple ones. The main objective is to uncover problems, ask the right questions, engage everyone in the problem-solving effort, and develop the organization's problem-solving muscles. An effective process for identifying and solving problems involves five ...
2 Foster Curiosity. Curiosity is the engine that powers creative problem solving. You should encourage your team to ask questions and challenge assumptions. Create a culture where it's safe to ...
As the saying goes, work smarter - not harder. Instead of mentally preparing yourself to endure a tough road ahead, start thinking imaginatively and using creativity to your advantage to lighten ...
Humans are innate creative problem-solvers. Since early humans developed the first stone tools to crack open fruit and nuts more than 2 million years ago, the application of creative thinking to solve problems has been a distinct competitive advantage for our species (Puccio 2017).Originally used to solve problems related to survival, the tendency toward the use of creative problem-solving to ...
Reorient the skills developed in leadership programs. Organizations often attempt to cover many topics in their leadership-development programs.But our findings suggest that focusing on a handful of specific skills and behaviors in these learning programs can improve the likelihood of positive leadership behaviors that foster psychological safety and, ultimately, of strong team performance.