

Starting Tomato Farming Business Plan (PDF)

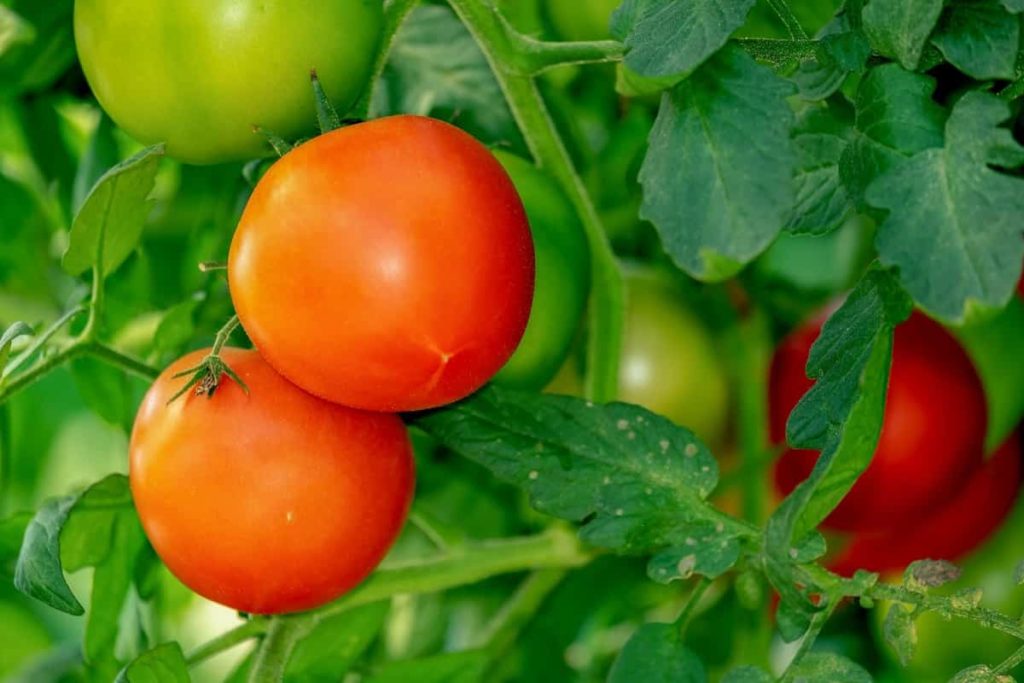
Tomatoes have exceptional nutritional value. They are acclaimed for being beneficial to heart, eye, digestive, and skin health. Tomato farming is one of the most profitable agriculture business ideas. Tomatoes are widely consumed – they can be consumed in diverse ways including raw, as an ingredient in many dishes and sauces and also in drinks. Tomatoes are also used by food processors. Processing of tomatoes consists of canning, freezing, dehydration and juice production. Tomatoes are processed into tomato sauce, whole pealed, tomato and onion bruises, paste, shredded, puree and paste concentrate. This article will outline how to start the tomato farming business, and the tomato farming business plan – PDF, Word and Excel.
Tomato farming is a lucrative business, providing income for millions of people, but there are some essential decisions you need make before you venture into the tomato farming business. You have to make a decision on how many hectares you want to farm, which type of tomatoes you will farm, which season you are going to plant your tomatoes, and your target market. These choices will be affected by the amount of capital you have, and your target market needs. If you do not have a lot of capital, you can always start small and grow your tomato farming business overtime. You also need to carry out market research (Who are you going to sell the tomatoes to? At what price?) and write a tomato business plan before you venture into the business.
Land for Tomato Farming Business
Good tomato production starts with good land selection. The soil type has a huge bearing on the quality and taste of tomatoes you produce. Tomatoes can grow on a wide array of soil textures depending on the variety of the tomato, from light, sandy soils to heavy, clay soils. Sand soils are the most ideal for quick and early maturation tomato varieties. Tomatoes thrive best in loamy soil with is rich in organic material. In not, incorporate compost or animal waste into the soil. The soil should have good drainage. The optimum pH lies between 5.0 and 7.0. If that is not so, add sulphur (if above upper limit) or lime (if below lower limit). The soil for tomato farming must permit adequate root growth to support the plant and supply water, oxygen and mineral nutrients and must be free of toxic elements. It is important that before you start farming tomatoes on your farm, you check whether the soil is suitable for tomato farming. Your tomato production business plan should take into account the cost of purchasing or leasing the land.
Space And Sunlight Exposure
When doing open field tomato farming you must take note of sunlight exposure. Your chosen land must allow for uninterrupted sunlight exposure for at least 8 hours daily. The actual land space you need will be informed by the number of tomato plants. Following recommended spacing is important for the tomato to grow optimally. There must be adequate inter-row and in-row spacing to optimize aeration, sunlight exposure, and curb possible disease outbreaks.
Machinery and Equipment
Machinery and equipment which are required for your tomato farming business will depend on the scale of your operations. Machinery and equipment needed include tractors, harvesters, boom sprayers, fertilizer spreader equipment, irrigation equipment, spray equipment, diggers, scales, ridgers, bins etc. Most farmers usually hire big machinery like tractors when they want to use them, rather than purchasing them as they are expensive. There may also be need of grid hydroelectricity energy for the irrigation systems, standby diesel generators for use during power outages, or solar powered irrigation systems. Farmers especially in the rural areas who do not have the modern farming equipment use animal drawn equipment in tomato farming. The higher the level of mechanization at your tomato farm, the higher the efficiency of your operations, and the profitability of your tomato farming business. The tomato farming business plan should include the costs of acquiring and hiring the various machinery and equipment.
Tomato Seeds/Seedlings
The tomato farming can be started using tomato seeds or seedlings. Tomato varieties can be classified into 3 broad categories which are determinate, semi-determinate and inter-determinate tomatoes. Your choice of which tomato variety to use will depend on variety of factors: time to maturity, yield, availability of seeds, target market preference, season, fruit quality adaptability, disease resistance among other factors. It is important that you purchase your tomato seeds from certified tomato seed suppliers. If you opt for seedlings, then source them from reputable nurseries. The costs of purchasing tomato seeds or seedlings should be accounted for in your commercial tomato farming business plan. If you buy poor quality tomato seeds, your tomatoes will not grow to their full potential and you will have poor yields. Tomatoes can be propagated from seeds or seedlings. In choosing tomato varieties you must understand the core classifications. Aside the classifications below, there are hybrid and heirloom tomato varieties. These usually have superior qualities such as disease resistance, high yields, firmness, long shelf life, and big fruit size.
There three broad tomato types namely, determinate, semi-determinate and indeterminate. Determinate tomatoes are typically bush-like and produce one large harvest of tomatoes and then stop. Indeterminate tomatoes are vine-like and continuously produce tomatoes as long as conditions allow. Semi-determinate tomatoes are in between those 2 characteristics.
Time To Mature
In tomato farming, there are 3 classifications that take maturation period into account. There is early season, mid-season and late season tomatoes. Early season tomatoes take at most 60 days to reach maturity. Mid-season tomatoes mature in between 60 and 80 days. Late season tomatoes need more than 80 days to reach maturity.
Fruit Size Or Type
The colour or taste of tomatoes also constitutes another classification in tomato farming. For example, there are cherry, plum, round, and beefsteak tomatoes, amongst others. This classification is particularly important when factoring in the intended use of the tomatoes when harvested.
Tomato Farming Inputs
You require various farming inputs when doing tomato farming. Fertilizers are required to support the efficient growth of your tomatoes, by providing all the nutrients needed by tomatoes to grow to their full potential. Essential nutrients needed for the growth of tomatoes include nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Organic matter is also important in tomato farming. This can be in the form of compost, decayed leaves, animal manure etc. Organic matter is a good source of plant nutrients. Organic matter also increases the capacity of the soil to retain water and nutrients. It’s a soil conditioner.
Other farming inputs required for tomato farming business include herbicides, for effective weed control at your farm. Pesticides and fungicides are required for protecting your tomato plants against insects and fungi. Trellising and training of tomatoes is very important to some tomato cultivars and varieties. This involves supporting the tomato plants on poles and wires or specialised trellising material. The benefits of training tomatoes include improved spraying to control diseases and pests, better air circulation around the plant and less fruit rotting. The costs of acquiring all these inputs should be included in your tomato farming business plan.
Pest And Disease Management
Some of the common pests in tomato farming are aphids, nematodes, cutworms, and whiteflies. Common diseases that can affect tomatoes are moulds, blights (early or late), and fusarium wilt. Prevention or protection of tomatoes from these can be achieved through integrated approaches. Almost all of them have a dual effect in that they address both pest and disease issues.
Keeping Tomatoes Safe From Pests And Diseases
It all starts with seeing to it that your tomatoes get all they need. These are things such as healthy soil and adequate water. In watering avoid scenarios where leaves get muddied. Drip irrigation is most ideal when farming tomatoes. You must also practice hygiene e.g. cleaning farming implements or machinery after every use. Always remove weeds and dispose them rather than leaving them lying next to the tomatoes. By all means ensure there is no water logging or general wetness – this promotes pests and diseases. As a rule of thumb, practise crop rotation to stop or disrupt pest life cycles.
Harvesting And Storage Of Tomatoes
You can start harvesting tomatoes roughly 60 to 90 days from when you planted the seedlings. This is not cast in stone; remember there are 3 different maturation times (early, mid and late). Determinate tomatoes tend to ripen almost at once – within about 14 days. Indeterminate tomatoes ripen successively over an extended period of time. When you are harvesting tomatoes, ensure that you do not inflict physical damage on them. Physical damage compromises their quality, make them susceptible to pests and diseases, and reduces their shelf live.
Often time the colour of the tomatoes is what guides on when to pick. For instance, some tomato fruits might have fully or partially turned red. The leaves or stem yellowing or drying are also indicators of readiness to harvest. You can also check the fruit skin – you must harvest whilst it still has a rich, smooth, wax-like texture. Ripe tomatoes will tend to be easy to remove by gently twisting off from the vine.
Before storage the tomatoes must be washed, cleaned, sorted, and graded. For long term storage you can freeze, can, or dry your tomatoes. Generally, tomatoes can be stored at room temperature. If it is outside the place must be away from direct sunlight. When it comes to cold storage there are things to consider. Temperatures below 13ºC are not idea for tomato storage. Tomatoes that have ripened partially must not be refrigerated. Refrigerating tomatoes that have ripened tends to compromise their taste.
Farm Workers
When doing tomato farming business, you will need to hire part time farm workers as and when necessary. The duties which they will do include planting tomato seeds, transplanting tomato seedlings; applying fertilizers; trellising tomatoes, ploughing; harvesting, herbiciding and pesticiding. The part time farm workers will be paid according to the number of days worked. You also require supervisors, farm manager, finance & accounting staff, and logistics staff depending on the scale of your tomato farming business. The wages and salaries of your workers should be included in your tomato farming business plan.
Capital for Tomato Farming Business
The amount of capital required for tomato farming business depends on the scale of the project. You can get a loan from the bank, or funding from investors, to use as capital to start your tomato farming business. If you plan to raise capital from investors and a loan from the bank, you need a good tomato farming business plan. If you don’t have access to investors and bank loan, you can use your personal savings and start small, and grow your business overtime. Tomato farming is very profitable, so if you reinvest the profits you get, you can quickly grow. Even if you are not planning to get a loan, you should still get a tomato farming business plan to guide you in starting and operating the business. It is essential for you to have a tomato farming business plan before you venture into the tomato farming business, so that you know all the costs involved and you make an informed decision.
The market for tomatoes is very huge and is ever increasing. The annual global demand of tomatoes is more than 180 million tonnes. That’s a lot! You can supply your tomatoes to individual households, schools, restaurants, food processors, hotels, companies, supermarkets, organizations, events etc. The tomato business plan ought to include a proper marketing plan to use in your tomato farming business.

Advantages Of Tomato Farming Business
Tomato farming is usually a high yields and wide profit margins business venture. Tomatoes are nutrient-rich and have numerous household and commercial uses. This is why there is an inexhaustible market for tomatoes. There are also vast opportunities in the export markets for tomatoes; offering higher profitability. There are limitless value addition options when it comes to tomatoes. Tomatoes generally mature fast which makes the turnaround time relatively short. Tomatoes can be propagated either indoors or outdoors. This makes it possible for almost anyone and anywhere to do tomato farming.
If you are looking to start a lucrative vegetable farming business, seriously consider a tomato farming business. Engage agronomists to find out the latest on the best tomato varieties to grow. It is important that you also do a thorough market research and have a good tomato farming business plan. The timing of your tomato farming must be such that when the tomatoes mature they have customers waiting for them. Post-harvest losses in tomato farming are common so be wary of that.
Pre-Written Tomato Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel): Comprehensive Version, Short Funding/Bank Loan Version and Automated Financial Statements
For an in-depth analysis of the tomato farming business, we encourage you to purchase our well-researched and comprehensive tomato farming business plan. We introduced the business plans after discovering that many were venturing into the tomato production business without enough knowledge and understanding of how to run the tomato farming business, how to farm the tomatoes, lack of understanding of the financial side of the business, lack of understanding of : the industry, the risks involved , costs and profitability of the business; which often leads to disastrous losses.
The StartupBiz Global tomato farming business plan will make it easier for you to launch and run your tomato farming business successfully, fully knowing what you are going into, and what’s needed to succeed in the business. It will be easier to plan and budget as you will be aware of all the costs involved in setting up and running the tomato business.
Uses of the Tomato Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
The tomato business plan can be used for many purposes including:
- Raising capital from investors/friends/relatives
- Applying for a bank loan
- Start-up guide to launch your tomato farming business
- As a tomato farming business proposal
- Assessing profitability of the tomato farming business
- Finding a business partner
- Assessing the initial start-up costs so that you know how much to save
- Manual for current business owners to help in business and strategy formulation
Contents of the Tomato Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
The tomato farming business plan include, but not limited to:
- Marketing Strategy
- Financial Statements (monthly cash flow projections, income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, break even analysis, payback period analysis, start-up costs, financial graphs, revenue and expenses, Bank Loan Amortization)
- Risk Analysis
- Industry Analysis
- Market Analysis
- SWOT & PEST Analysis
- Operational Requirements (Including technical aspects of how to farm the tomatoes, fertilizer requirements etc)
- Operational Strategy
- Why some people in tomato farming business fail, so that you can avoid their mistakes
- Ways to raise capital to start your tomato farming business
The Pre-written tomato farming business plan package consist of 4 files
- Tomato Farming Business Plan – PDF file (Comprehensive Version – 84 Pages)
- Tomato Farming Business Plan – Editable Word File (Comprehensive Version – 84 Pages)
- Tomato Farming Business Plan Funding/Bank Loan Version- Editable Word File (Short version for applying for a loan/funding – 39 pages)
- Tomato Farming Business Plan Automated Financial Statements – (Editable Excel File)
The business plan can be used in any country and can be easily edited. The financial statements are automated. This implies that you can change eg the number of hectares, selling price of the tomatoes etc, and all the other financial statements will automatically adjust to reflect the change.
Click below to download the Contents Page of the Tomato Farming Business Plan (PDF)

Testimonial 1
StartupBiz Global provided a very professional and comprehensive business plan which I used for my business. The business plan was easy to edit, and I was able to get the funding which I wanted. I highly recommend their business plans.
Testimonial 8
Just wanted to say I am very happy with the business plan and I will gladly recommend your products, thank you very much and have a great day.
Testimonial 7
I found Startupbiz Global online when I was in desperate need of a business plan. I was overwhelmed by the quality of the business plan, it’s comprehensive and well researched! I did not have to wait to get the business plan, I got it instantly after payment. I highly recommend Startupbiz Global, and would happily use them again in the future.
Testimonial 6
I purchased a business plan from you, and I’m glad to inform you that I was able to get my loan, and I’m starting my poultry farming business on the 1 st of July. This was made possible because of your business plan. Thank you very much, you made my dream come true.
Testimonial 3
I was extremely lucky to come across StartupBiz Global. Their business plan exceeded my expectations, and most importantly I was able to secure a loan from my bank. Thank you guys, now my dreams are coming true!
Testimonial 4
The business plan which I purchased from your website saved me TIME and MONEY! The layout of the business plan was excellent. The financial statements were detailed and easy for me to edit. I will come back to purchase another business plan soon.
Testimonial 5
I was able to understand the business side of farming because of your business plan. You did extensive research; the business plan was well prepared and fully detailed. It made everything clear, and I have somewhere to start now. I am confident that I am going to succeed in my business because of the guidance from your business plan.
Testimonial 2
Many thanks for your incredibly efficient service and thorough business plan. I am very impressed with the business plan. Before I bought the business plan, I tried to do my own business plan – it was such a nightmare and it turned out badly, also not to mention the stress it caused me. I wish I knew about your website earlier!
Get the Tomato Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
Click Buy Now below to purchase using Paypal, Credit Card, or Debit Card. After you have purchased, you will immediately see the download link for the business plan package on the screen. You will also immediately get an email with the business plan download link. The Pre-written business plan package (PDF, Word, and Excel) costs $30 only!

If you want to purchase multiple business plans at once then click here: Business Plans Store.
The business plan package is a zipped compressed file containing the PDF, Word and Excel documents. To open the package after downloading it, just right click, and select Extract All. If you have any problems in downloading and opening the files, email us on [email protected] and we will assist you.
We wish you the best in your tomato farming business! Check out our collection of business plans , and more business ideas .
Related Posts

Starting Free Range Chicken Farming Business Plan (PDF)

How To Start A Web Hosting Business

Top 6 Non Profit Business Ideas

Starting Honey Beekeeping Business Plan (PDF)

Join our mailing list to receive the latest posts and updates from our website.
You have Successfully Subscribed!

How To Write a Business Plan for Tomato Processing Business in 9 Steps: Checklist
By henry sheykin, resources on tomato processing.
- Financial Model
- Business Plan
- Value Proposition
- One-Page Business Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Model
- Marketing Plan
Are you considering starting a tomato processing business? With the increasing demand for processed tomatoes and the potential for long-term storage, this could be an excellent opportunity for you. In this blog post, we will guide you through the process of writing a business plan for your tomato processing business in 9 easy steps. But before we dive in, let's take a look at some fascinating statistics about the industry and its growth.
The tomato processing industry has seen significant growth in recent years. According to the latest data, the global tomato processing market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth can be attributed to the increasing demand for processed tomatoes in various food products, including sauces, soups, and ketchups. As more consumers seek convenient and ready-to-use tomato products, the demand for processed tomatoes is only expected to rise.
Now that you understand the potential of the tomato processing industry, let's proceed with the essential steps you need to follow to write a business plan for your tomato processing business.
- Conduct market research and identify target customers
- Define the business goals and objectives
- Evaluate the competition and assess market demand
- Determine the legal and regulatory requirements
- Develop a comprehensive financial plan and budget
- Assess the availability and cost of raw materials
- Analyze production and manufacturing processes
- Create a marketing and sales strategy
- Identify potential risks and develop risk management strategies
By following these steps, you will be well-equipped to write a solid business plan that sets the foundation for your tomato processing business's success. Whether you're looking to supply fresh tomatoes, explore long-term storage options, or offer additional customer solutions, a well-designed business plan will guide your operations and help you meet the increasing demand for processed tomatoes.
Conduct Market Research And Identify Target Customers
Conducting thorough market research is a crucial step in developing a business plan for your tomato processing business. By understanding the market dynamics and identifying your target customers, you can tailor your products and services to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Start by gathering information about the tomato industry, including market trends, consumer preferences, and the demand for processed tomato products. Look for data on the consumption patterns, growth rate, and potential market size. This will help you assess the viability and potential profitability of your business.
Key considerations:
- Identify your target customers: Determine who your primary customers will be, such as grocery stores, supermarkets, restaurants, or individual consumers. Understanding their buying habits, preferences, and needs will enable you to develop products and services that cater to their requirements.
- Segment the market: Divide your target market into distinct segments based on demographic factors such as age, income level, and location. This will allow you to customize your marketing strategies for each segment and better address their specific needs.
- Analyze the competition: Research your competitors in the tomato processing industry. Identify their strengths, weaknesses, and unique selling propositions. This analysis will help you differentiate your business and develop strategies to gain a competitive edge.
Tips for conducting market research:
- Utilize online resources: Explore industry reports, market research databases, and trade publications to gather relevant information about the tomato processing industry.
- Conduct surveys and interviews: Gather insights directly from potential customers through surveys and interviews. Ask about their preferences, purchasing patterns, and opinions on existing tomato products in the market.
- Visit trade shows and exhibitions: Attend industry events to network with suppliers, distributors, and other relevant stakeholders. These events can provide valuable market insights and help establish business connections.
- Stay informed about industry regulations: Stay abreast of any regulations or standards governing the tomato processing industry. Complying with these requirements will ensure the safety and quality of your products.
By conducting in-depth market research and identifying your target customers, you can develop a clear understanding of the demand for processed tomatoes and tailor your business plan to meet those needs.
Define The Business Goals And Objectives
In this step, it is crucial to clearly define the goals and objectives of your tomato processing business. These goals will serve as a roadmap for your business and guide your decision-making process. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Profitability: Determine the level of profitability you aim to achieve. This could include setting sales targets, profit margins, and identifying strategies to increase revenue.
- Market Share: Define the market share you aspire to capture within a specific timeframe. This will help you set realistic targets and measure your business's success.
- Product Quality: Establish standards for the quality of your processed tomatoes. Ensure that your business consistently delivers superior quality products to gain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Sustainability: Consider incorporating sustainability practices into your business objectives, such as reducing waste, optimizing energy consumption, or supporting local farmers.
- Customer Satisfaction: Focus on providing exceptional customer experiences and consider setting goals related to customer feedback, ratings, and loyalty.
- Expansion: Determine if your business goals include expanding into new markets or introducing additional product lines in the future.
Tips for Defining Business Goals and Objectives:
- Set Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals to ensure clarity and accountability.
- Align your goals with the overall mission and vision of your tomato processing business.
- Regularly review and reassess your goals to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Involve key stakeholders, such as employees and investors, in the goal-setting process to gain their support and commitment.
- Seek inspiration and learn from successful businesses in the tomato processing industry.
Evaluate The Competition And Assess Market Demand
When starting a tomato processing business, it is crucial to evaluate the competition and gain a deep understanding of the market demand. This step will help you identify key players in the industry and determine the feasibility of your business idea. Here are some important factors to consider:
1. Identify your competitors: Conduct thorough research to identify other tomato processing businesses in your target market. Look for businesses that offer similar products or services and determine their strengths and weaknesses. This information will help you identify gaps in the market and position your business competitively.
2. Study market demand: Understand the demand for tomatoes and tomato-based products in your target market. Look for trends, consumer preferences, and potential growth opportunities. This will help you determine the potential market size and plan your production and marketing strategies accordingly.
3. Analyze pricing: Study the pricing strategies of your competitors and assess whether your business can offer competitive prices while maintaining profitability. Consider the cost of raw materials, production processes, and overhead expenses when determining your pricing strategy.
- Conduct surveys or interviews with potential customers to gather feedback on their preferences and buying habits. This will provide valuable insights into market demand.
- Attend industry trade shows, conferences, and events to network with other professionals and stay updated on the latest market trends.
- Consider conducting a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis to assess your competitors and identify unique selling points for your business.
By thoroughly evaluating the competition and assessing market demand, you can position your tomato processing business for success. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions, differentiate your business from competitors, and meet the growing demand for processed tomatoes in the market.
Determine The Legal And Regulatory Requirements
When starting a tomato processing business, it is crucial to be aware of the legal and regulatory requirements that govern the industry. Failing to comply with these requirements can result in fines, penalties, or even the closure of your business. Therefore, it is essential to thoroughly research and understand the legal obligations before proceeding.
- Business Registration: Begin by registering your tomato processing business with the appropriate government authorities. This step typically involves choosing a business name, selecting a legal structure (such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation), and obtaining the necessary licenses and permits.
- Food Safety Regulations: The tomato processing industry is subject to stringent food safety regulations to ensure the production of safe and high-quality products. Familiarize yourself with these regulations, which include proper hygiene practices, facility sanitation, storage requirements, and labeling guidelines.
- Product Packaging and Labeling: Packaging and labeling requirements vary depending on the jurisdiction. Ensure that your tomato products are packaged and labeled accurately, including information such as ingredients, nutritional content, allergen warnings, and proper storage instructions.
- Environmental Regulations: Tomato processing businesses may have environmental considerations, especially concerning wastewater management and waste disposal. Familiarize yourself with the relevant environmental regulations and take the necessary steps to comply with them.
- Employment Laws: If you plan to hire employees, familiarize yourself with labor laws and regulations regarding minimum wage, working hours, workplace safety, and employee benefits. Complying with these laws will help you maintain a fair and compliant work environment.
- Consult with a legal professional or regulatory agency to ensure you have a comprehensive understanding of all the legal requirements specific to your tomato processing business.
- Regularly stay updated with any changes in laws and regulations that may affect your business. Compliance is an ongoing process.
- Keep detailed records and documentation to demonstrate your adherence to legal and regulatory requirements. This information may be required during inspections or audits.
Develop A Comprehensive Financial Plan And Budget
Developing a comprehensive financial plan and budget is crucial for the success of your tomato processing business. It helps you determine the financial feasibility of your business idea and provides a roadmap for achieving your goals. Here are some important steps to follow:
- Estimate start-up costs: Start by identifying all the costs involved in setting up your business, including equipment, machinery, infrastructure, permits, licenses, and initial inventory. Research the market to get accurate estimates for each item. Keep in mind that unexpected expenses may arise, so it's advisable to add a buffer in your budget.
- Evaluate ongoing expenses: Consider the recurring costs your business will incur on a regular basis, such as utilities, raw materials, packaging materials, employee salaries, insurance, and marketing expenses. Create a detailed list of these expenses and estimate their monthly or annual costs.
- Forecast revenue: Based on your market research and analysis, develop a revenue forecast that outlines your anticipated sales volumes and pricing strategies. Consider factors such as seasonality, competition, and market demand. Be realistic with your projections to avoid overestimating income.
- Calculate profitability: Use your revenue forecast and expense list to calculate the profitability of your business. Determine your gross profit margin by deducting the cost of goods sold from your total revenue. Then, calculate your net profit margin by subtracting all expenses, including operating costs and taxes, from your gross profit. This analysis will help you understand the financial viability of your business.
- Create a cash flow projection: Cash flow is the lifeblood of any business. Estimate your cash inflows from sales and other sources, and project your cash outflows for expenses. This will give you a clear picture of your business's cash position over time, allowing you to plan for any potential cash shortages and take measures to address them.
- Consult with a financial advisor or accountant to ensure accuracy and reliability in your financial plan.
- Consider conducting sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of changes in key variables, such as sales volume and pricing, on your financial projections.
- Regularly review and update your financial plan and budget as your business evolves and market conditions change.
Remember, a comprehensive financial plan and budget will not only help you secure financing for your business but also serve as a guide to monitor and manage your financial performance. It is a vital tool for staying on track with your goals and making informed decisions to drive the success of your tomato processing business.
Assess The Availability And Cost Of Raw Materials
One of the key factors to consider when setting up a tomato processing business is the availability and cost of raw materials . As a tomato processing business, you will heavily rely on a consistent supply of high-quality tomatoes to meet your production needs. Therefore, it is crucial to assess the availability and cost of raw materials before moving forward with your business plan.
Start by researching local tomato growers and suppliers in your area. Contact them to understand their production capacity and if they can meet the demand of your business. Consider visiting their farms or production facilities to evaluate the quality of their tomatoes and their ability to consistently supply the required quantity.
Additionally, consider the seasonality of tomato production. Fresh tomatoes might be readily available during certain times of the year, but they could become scarce during off-season months. Understanding the seasonal fluctuations will help you plan your production and storage needs accordingly.
When assessing the cost of raw materials, compare prices from different suppliers. Take into account factors such as quality, variety, packaging, and transportation costs. Keep in mind that the cost of tomatoes may vary depending on the region, variety, and market conditions.
Tips for assessing the availability and cost of raw materials:
- Establish long-term contracts with reliable suppliers to secure a consistent supply of tomatoes.
- Consider building relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate the risk of supply disruptions.
- Explore opportunities to directly source tomatoes from local farmers or establish partnerships with agricultural cooperatives.
- Track market prices and industry trends to anticipate potential changes in raw material costs.
- Stay informed about any government policies or regulations that may affect tomato production and procurement.
Analyze Production And Manufacturing Processes
When starting a tomato processing business, it is crucial to analyze and understand the production and manufacturing processes involved. This step will help you determine the resources, equipment, and facilities needed to efficiently process and package tomatoes.
Firstly, you should evaluate the different stages of the processing and manufacturing processes. This includes harvesting, cleaning, sorting, packaging, and delivering the tomatoes. Each stage requires specific equipment and techniques to ensure the quality and safety of the processed tomatoes. It is essential to identify the most efficient and cost-effective methods for each process.
- Consult with experts in the tomato processing industry to understand the best practices and technological advancements in the field.
- Consider visiting existing tomato processing facilities to observe their operations and gain insights into their production processes.
- Conduct a thorough analysis of the required machinery, including their costs, maintenance, and operational requirements.
Next, you need to assess the required facilities and space for your processing operations. Determine whether you will need a central processing plant or smaller production units closer to the tomato farms. Consider the space needed for storage, processing equipment, packaging materials, and finished product inventory.
- Calculate the processing capacity needed based on your target production volume and market demand.
- Investigate the availability and cost of potential production sites or facilities, considering factors such as proximity to tomato farms and transportation logistics.
- Ensure compliance with health and safety regulations, such as proper sanitation practices and environmental considerations.
Lastly, it is important to establish quality control measures throughout the production and manufacturing processes. This includes implementing procedures to ensure the freshness, flavor, and nutritional value of the processed tomatoes. Regular quality checks and inspections should be conducted to maintain consistent product standards.
- Develop a comprehensive quality assurance plan that outlines the procedures and techniques to be followed at each stage of the production process.
- Consider obtaining relevant certifications, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), to demonstrate your commitment to food safety and quality standards.
- Train your employees on the proper handling, processing, and packaging techniques to ensure consistent product quality.
By thoroughly analyzing the production and manufacturing processes, you can optimize efficiency, maintain product quality, and meet the growing demand for processed tomatoes in the market.
Create A Marketing And Sales Strategy
A well-defined marketing and sales strategy is crucial for the success of your tomato processing business. It will help you effectively reach your target customers, promote your products, and ultimately drive sales. Here are some key steps to create an effective marketing and sales strategy:
1. Identify your target customers:
- Research and understand the demographics, preferences, and buying behaviors of your target customers. This will help you tailor your marketing efforts to effectively reach and engage them.
- Create customer personas to visualize and understand your ideal customers. This will guide your marketing and sales strategies.
2. Define your unique selling proposition:
- Determine what sets your tomato processing business apart from competitors.
- Highlight the unique qualities and benefits of your products, such as freshness, quality, and sustainability.
- Communicate your unique selling proposition clearly and consistently in all marketing materials.
3. Develop a multi-channel marketing plan:
- Utilize a mix of online and offline channels to reach your target customers.
- Establish a strong online presence through a professional website, social media platforms, and email marketing campaigns.
- Collaborate with local grocery stores, supermarkets, and other vendors to display and promote your products.
- Consider participating in farmers' markets or hosting tasting events to showcase your tomato products and engage directly with customers.
4. Implement effective pricing and promotion strategies:
- Determine competitive yet profitable pricing for your tomato products.
- Create attractive promotions and discounts to incentivize customers to try your products.
- Offer bundle deals or loyalty programs to encourage repeat purchases.
- Utilize social media to share tomato recipes, cooking tips, and nutritional information. This will position your business as a valuable resource for customers.
- Collaborate with local chefs or food bloggers to create content featuring your tomato products. This can help generate buzz and attract new customers.
- Collect and utilize customer feedback to continuously improve your marketing and sales strategies.
Remember, an effective marketing and sales strategy should be flexible and adaptable. Continuously monitor the results of your efforts and make necessary adjustments to optimize your approach. By understanding your target customers, highlighting your unique selling proposition, and utilizing various marketing channels, you can effectively promote your tomato processing business and drive sales.
Identify Potential Risks And Develop Risk Management Strategies
Identifying potential risks is a crucial step in ensuring the success of your tomato processing business. By being proactive and developing effective risk management strategies, you can mitigate the impact of these risks and protect your business.
Here are some important risks to consider and strategies to manage them:
- 1. Price Volatility: The price of tomatoes can fluctuate due to various factors such as weather conditions, supply and demand fluctuations, and changes in market trends. To manage this risk, it is essential to establish long-term contracts with tomato suppliers or consider diversifying your raw material sources. This can help stabilize prices and ensure a consistent supply.
- 2. Quality Control: Maintaining high quality standards is crucial in the tomato processing business. Any issues with the quality of your processed tomatoes can significantly impact your reputation and customer satisfaction. Implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the entire production process. Regularly monitor and test the tomatoes to ensure they meet the required standards and address any quality issues promptly.
- 3. Supply Chain Disruptions: Any disruptions in the supply chain, such as transportation delays or equipment failures, can disrupt your operations and lead to delays in delivering products to your customers. To minimize the impact of such disruptions, establish backup plans and alternative suppliers. Regularly assess the performance and reliability of your transportation and packaging partners to ensure smooth operations.
- 4. Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring food safety and compliance with regulatory requirements is crucial to maintain consumer trust and avoid legal issues. Develop and implement robust food safety protocols, including proper handling, cleaning, and processing techniques. Stay updated with the latest regulations related to food processing and packaging to ensure compliance at all times.
- 5. Technological Advancements: The tomato processing industry is constantly evolving with new technologies and innovations. Failure to adapt and incorporate these advancements into your business can result in losing competitiveness. Stay informed about emerging technologies, machinery, and processes in the industry. Regularly review and upgrade your equipment and systems to stay efficient and competitive.
- Consider establishing strong relationships with suppliers and customers to foster trust and loyalty, which can help mitigate certain risks.
- Regularly conduct risk assessments and have contingency plans in place to respond promptly to unforeseen events.
- Stay updated with market trends and consumer preferences to make informed decisions and adapt your strategies accordingly.
- Seek professional advice from experts or consultants who specialize in risk management to ensure you have a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and effective strategies to address them.
By identifying potential risks and developing robust risk management strategies, you can protect your tomato processing business and ensure its long-term success in a competitive market.
In conclusion, writing a comprehensive business plan for a tomato processing business is crucial for ensuring its success. By following the nine steps outlined in this checklist, entrepreneurs can develop a solid roadmap for their business and address key aspects such as market research, financial planning, production processes, and marketing strategies. With a clear plan in place, tomato processing businesses can thrive in meeting the increasing demand for processed tomatoes while providing value-added services to customers such as delivery, recipe solutions, and cooking techniques.
$169.00 $99.00 Get Template
Related Blogs
- Starting a Business
- KPI Metrics
- Running Expenses
- Startup Costs
- Pitch Deck Example
- Increasing Profitability
- Sales Strategy
- Rising Capital
- Valuing a Business
- How Much Makes
- Sell a Business
- Business Idea
- How To Avoid Mistakes
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published

How to Start a Tomato Processing Plant – Sample Business Plan Template
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business ideas » Agriculture Industry » Agro Processing & Allied Industry
Do you want to start a tomato processing company from scratch? Or you need a sample tomato processing plant business plan template? If YES, then i advice you read on. Tomatoes are consumed all over the world and it is cheap and affordable to all class of people. Tomato fruits are rich in fiber, they contain healthy vitamins and it has no trace of cholesterol.
Tomatoes also contain disease fighting phyto-chemicals. People consume tomato in its raw state as fruit, or after it has been processed. They are also are used for the preparation of various menus like; salads, drinks, pizza, tomato soup and sauces, et al. If you live in the Americas, Africa or any part of the world where tomatoes are produced in large quantities, then establishing your own tomato processing plant might just be the best business venture you might invest in.
No doubt, you would require huge startup capital to build your own tomato processing plant, but good news is that, the market for processed tomato products is enormous and profitable. The good thing about starting a tomato processing plant is that you could establish your plant in any part of the world where you can easily access tomato farms and cheaper labors and then export your products all of the globe.
The end products from an ideal tomato processing plant are the popular ketchup, tomato juice, diced tomatoes, tomato powder, tomato paste, tomato pulp, strained tomatoes, partially dehydrated tomatoes et al. The following guidelines would direct you on how to establish your own tomato processing plant and build it to a level of profitability within the shortest time frame possible.
Starting a Tomato Processing Plant – Sample Business Plan Template
1. be critical with your feasibility studies.
You stand to gain a lot if you carry out a critical feasibility studies before you pump in your money to build your own tomato processing plant. You are able to know how to access your raw materials, the best ways to cut cost of productions and how to maximize profits.
As a matter of fact, with the reports you get from your feasibility studies you could decide to wait a bit before starting your tomato processing plant or source for more funds.
The good thing about feasibility studies is that if it is properly done, it gives you all the positive and negative options you are likely going to face with your proposed project and it guides you in the long run to take the right decisions. With the information gathered, you can proceed to write a tomato processing plant business plan .
2. Register Your Company and Obtain the Required License
Starting a tomato processing plant is not the kind of business you can start without undergoing all the necessary registration processes. You cannot operate this kind of business as an anonymous company because it has to do with what people eat. You are expected to register your tomato processing plant and also obtain the required operating license from the body that regulates foods and drugs production in your country.
3. Choose a Suitable Location to Build Your Plant
Choosing a suitable location for your tomato processing plant is a very important factor that can determine how successful and profitable the business grows. The factors you need to consider when searching for a location to build your tomato processing plant are nearness to tomato farms/ plantations, nearness to source of cheap labor, as well as proximity to the market. You might also position your tomato processing plant to be close to the Seaport or Rail station so as to cut transportation cost especially when you intend to go into exportation of your processed tomato products.
4. Install All the Required Equipment and Machinery
If you are done with choosing a suitable location and building your tomato plantation to meet all the required safety standards, then the next step would be to install all the required equipment and machinery needed to run you plant.
You would need to buy power generating set (especially if your plant is located in the outskirt of town of a country with epileptic power supply), High Pressure Pumps and Homogenizers, Evaporators, Extractors, Separators, Cross-Flow Membrane Filtration Systems, Spray Dryers, Freeze Dryers, Integrated Belt Dryers, Agglomerators, Clarifiers and Decanters, and Complete tomato powder conveying and Packaging lines. You also need trucks for transporting your raw tomatoes from the farm to the plant and then the processed products from the plant to the Market, Seaport or Rail Station.
5. Hire Competent Hands
If you truly want to build a successful business, then you must ensure you hire competent hands. The good thing about running a tomato processing plant is that about 80% of you workforce doesn’t need high tech skills. As a matter of fact, they are only factory workers and you do not have to pay from your nose to keep them. You would also need to hire few experts that are able to handle all the standard operating processes of a tomato processing plant. Bottom-line is do a blend of experienced hands and rookies.
6. Be Detailed With Your Packaging
There are various packaging styles for processed tomato products. You could choose to use bottles, sachet or even plastics. Whichever choice you choose for any of your products, just ensure that the packing is appealing and unique. Because of the competition you would be facing out there in the market, you just have to be detailed with your choice of packaging so that you can gain market acceptance.
For instance; there is nothing unique about the tomato paste that is sold in Asia and the ones that are sold in Americas. The only difference might just be the packaging. Therefore, you too must plug in on the various branding styles there are.
7. Explore Both Local and International Market
The fact that people eat tomato all over the world makes it easier for you to sell your processed tomato products beyond the shores of your country. You can be rest assured that there are international markets waiting for you to explore.
The truth is that if your products are good and of international standards, then with a little push; you can easily break into the global market. People export processed tomato products to every nook and cranny of the world without restrictions.
These are the steps you need to follow to be able to establish your own tomato processing plant and build your brand to be globally accepted. You can choose to go into the production of all the known processed tomato products or select some of them and create your own unique brand. You sure are guaranteed success if you blend a hardworking spirit with all the tips given earlier.
Related Posts:
- How to Start a Logging Business
- How to Start a Poultry Feed Mill Business
- How to Start a Rice Mill – Sample Business Plan Template
- How to Start a Flour Production Company – Sample Business Plan Template
- How to Start a Coconut Oil Production Company – Sample Business Plan Template
- Agriculture Farming
- Livestock Farming
Project Reports
- Hydroponics
- Best Fertilizers
- Vertical Farming
- Sheep Farming
- Goat Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Fish Farming
- Pig Farming
- Dairy Farming
- Rabbit Farming
- Success Stories of Farmers
- Boost Fruit Yield
- District Wise Crop Production
- Schemes & Subsidies
- Agriculture Colleges
- Farm Insurance
- Disease Control And Management
Agriculture
Aquaculture
Horticulture
Agri Business
Tomato Farming Business Plan: A Production and Cultivation Guide for Beginners
Table of contents, tips to succeed in the tomato farming business, what is the best way to grow tomatoes , machinery and equipment needed for tomato farming business, preparation of land for tomato cultivation, transplantation, weed and pest control, protected cultivation of tomato in shade net, protected cultivation of tomato in polyhouse, protected cultivation of tomatoes in the greenhouse, key activities, farm operator, supply chain, things to consider in the tomato farming business for beginners, step 1: business goals , step 2: market research, step 3: business plan , step 4: business identity , step 5: marketing , tomato yield per hectare.
Tomato is one of the world’s most essential and widely grown food crops. It is a warm-season vegetable. Tomato plants cannot tolerate cold and humidity. Tomato belongs to the Solanaceae family. The Tomato is native to Peru and Mexico. There are about 1000 varieties of Tomatoes in India. China is the leading Tomato producer in the world, followed by India and Turkey. Tomato season in India lasts throughout the year. Tomato season in India is mainly at the beginning and end of the year.
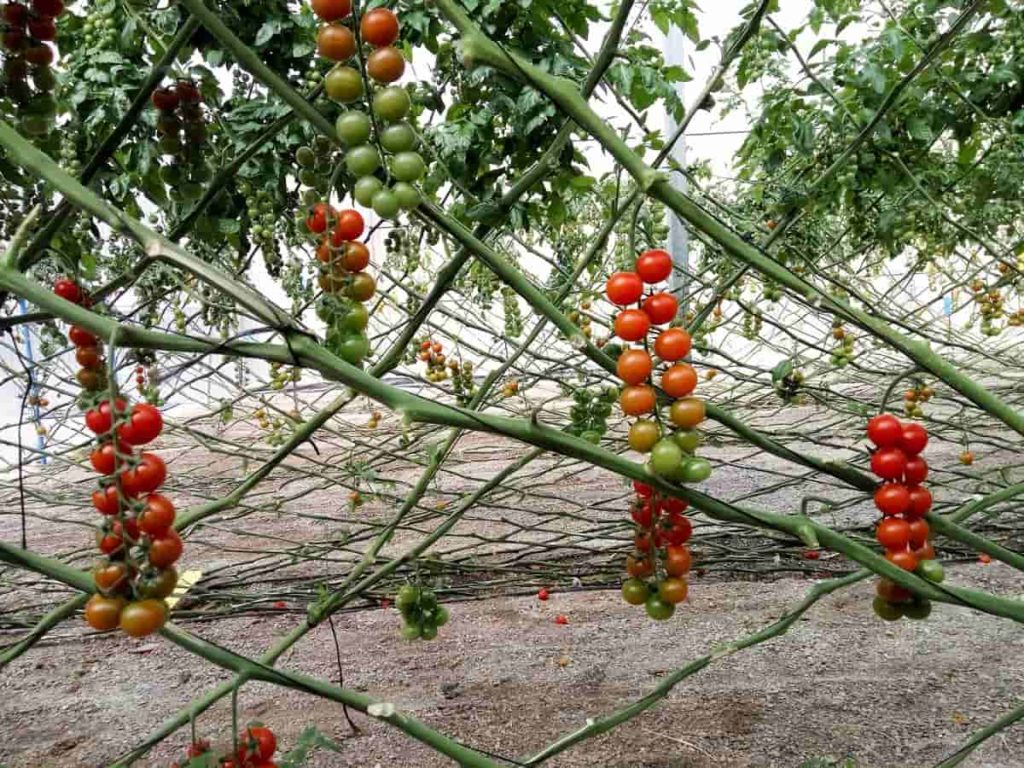

Tomato farming business plan
Most commercial Tomato growers start the crop from seed (hybrid) in an indoor protected environment. While they wait for the young plants to grow and be ready for transplanting (usually 30-50 days), they prepare the field. They till the land and remove the residues of previous cultivation. Some farmers apply black plastic film to the ground. This plastic film not only helps to warm the soil but also controls weeds. Furthermore, Tomato growers design and set up an irrigation system before planting, usually drip irrigation. The most critical success factors are:
- Deep, well-drained soil
- High-yielding and resistant varieties
- Adequate stalking
- Disease control (blights and canker)
Tomatoes are usually cultivated twice a year. One starts in July-August and continues till February-March. The second starts in November-December and continues till June-July. A nursery is made from seeds to start Tomato cultivation. Nursery plants are ready for field planting in about a month. About 15000 plants are planted on one hectare of land. After about 2-3 months of Tomato planting in the field, fruits appear. The growing season of Tomatoes is 9-10 months.
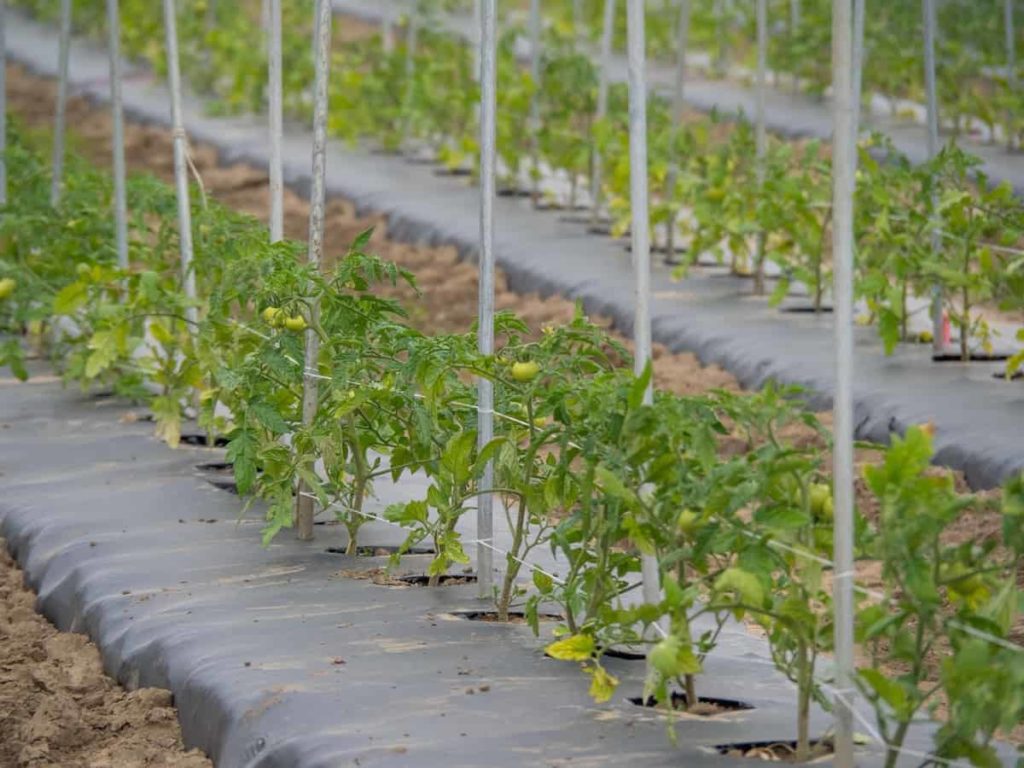
The machinery and equipment required for your Tomato farming business will depend on the scale of your operation. Machinery and equipment required include tractors, harvesters, boom sprayers, fertilizer spreaders, irrigation equipment, diggers, scales, bins, etc. Most farmers usually rent large machinery, such as tractors, when they want to use them instead of buying them as they are expensive.
Irrigation systems may also require grid hydroelectric power, standby diesel generators for use during power outages, or solar-powered irrigation systems. Especially farmers in rural areas who do not have modern farming tools use animal-made tools for Tomato cultivation. The higher the level of mechanization in your Tomato farm, the more efficient your operations will be, and the more profitable your Tomato farming business will be. A Tomato farming business plan should include the cost of acquiring and renting various machinery and equipment.
Farm practices for starting a Tomato farming business
When running a Tomato farming business, you must hire part-time farm workers when needed. Their duties include planting Tomato seeds, planting Tomato plants, fertilizer application, pruning, plowing, pruning, herbicides and pesticides. Part-time farm workers will be paid according to the number of days worked.
It would help if you also had supervisors, farm managers, finance and accounting staff, and logistics staff, depending on the scale of the Tomato business. The wages and salaries of your workers must be included in your Tomato farming business plan.
You should prepare the land for good cultivation by plowing or digging well 2 to 3 times. Finally, add organic manure and 10 kg of carbofuran granules or 200 kg of neem-cake to the soil.
Transplantation is done in small flat beds or shallow furrows, depending on the availability of irrigation. In heavy soil, it is generally transplanted in ridges and is beneficial to plant seedlings during rains.
In case you missed it: How to Start Tomato Farming in the USA: A Step-by-Step Production Guide to Planting to Harvesting
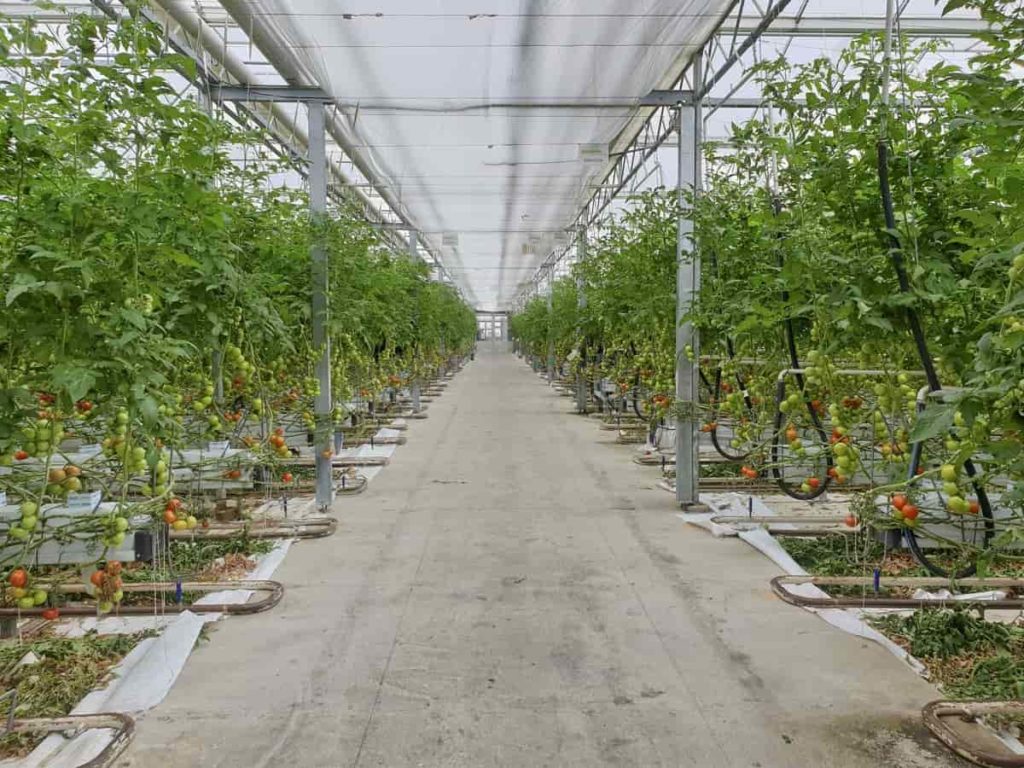

Tomato plants require adequate moisture during their growth. Drip irrigation is most suitable for maintaining a constant supply of moisture. You will need to arrange the first watering immediately after transplanting the plants. Daily irrigation is necessary when the plants are young.
For weed control, you can use intercultural operations like hand-handing, weeding, mulching, and staking as a general system. Weed control can be achieved using herbicides, plastic mulch, and a good crop rotation system. Several pre-plant and post-emergence herbicides are available for Tomatoes, depending on the specific weed problem and the stage of Tomato growth. Early cultivation can help reduce weed problems if infestation levels are light. Insects, especially the Colorado potato beetle, can significantly affect Tomato production.
Early control of adult Colorado potato beetles can prevent crop damage. Aphids, corn earworms, European corn borer, armyworms, thrips, whiteflies, spider mites, and fruit flies can also cause crop damage. Monitoring the pest population with traps or weekly scouting will help determine if you should use an insecticide and how often to spray. Many Tomato diseases can cause crop loss, including bacterial canker, leaf blight, viruses, early blight, anthracnose, and bacterial soft rot.
Several fruit disorders are also caused by excess soil moisture or weather conditions. These include cat face, spot ripening, gray wall, yellow shoulders, sunburn, sun scald, and fruit cracking. Plant diseases and fruit defects can be treated by buying fungicide disease-resistant varieties, maintaining adequate plant nutrition, rotating crops, and growing in well-aerated and well-drained soil. Tomato plants can also be grown organically, but this will require a high level of management and supervision to succeed economically.
Harvesting Tomatoes in the fresh market is labor intensive and requires multiple pickings. Depending on plant variety, maturity, and market value, Tomatoes are harvested four to six times during the growing season. Tomatoes for the wholesale market are picked at the mature green-to-ripe stage to prevent overripe fruit during shipping and handling.
Markets like farmers’ markets, roadside stands, or other live markets will allow you to ripen Tomatoes on the vine before harvesting. After harvest, growers must check Tomatoes for size, color, and defects to ensure the marketing of a high-quality product.
Production methods for Tomato farming under safe cultivation
Tomatoes grow best in well-drained soils with good air and water infiltration rates. Before planting Tomatoes, you should have a soil test done. Tomatoes need a constant supply of moisture throughout the growing season. However, excess water during growth, especially after fruit set, can increase fruit susceptibility to cracking (both l and concentric), reducing fruit quality and yield.
It can be grown in various soils ranging from sandy loam to clay, black clay, and red clay with adequate drainage. Avoid planting in highly acidic soils. Light soils are beneficial for early crops, while clay loam and silt soils are beneficial for heavy production.
During summer, hybrid Tomatoes under a 35% shaded row planting system (80 x 40 x 60 cm – between pairs, rows, and plants) can be grown with a basal application of 50 kg N and K. Apply 250 kg P/ha and 200 kg N and K through straight fertilization.
During the rainy season, indeterminate Tomato hybrids are grown in a medium consisting of FYM: composted coir peat: sand (2:1:1) with 50kg each of the NPK/ hectare is used as a natural fertilizer. 250 kg NPK as water soluble and direct fertilizer by fertigation with black polyethylene mulch (50 microns).
In case you missed it: High Yield Tomato Varieties in India: A Farmer Guide for Good Profits
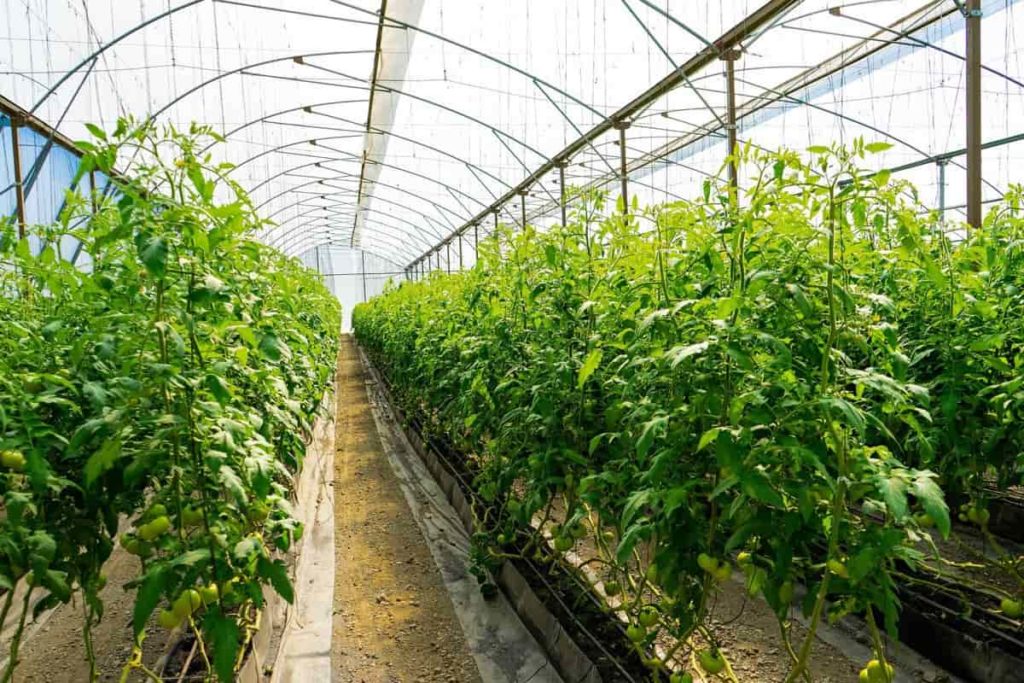

Greenhouse farming is the most efficient way to grow Tomatoes. Tomatoes are grown in greenhouses where water, humidity, temperature, and soil pH are closely monitored. Under this method, Tomato yield is higher than in open field cultivation. The incidence of pests and diseases is also reduced under this method.
Greenhouse production is more expensive than producing the same crop in the open field. The most crucial cost determinants are the depreciation of structures and equipment, labor, energy, and variable costs such as plant material, substrate, and fertilizer. Tomatoes can be grown in any greenhouse, provided it is tall enough to manage and train the plants vertically. High-light transmission is significant and varies between 70% and 81% in modern greenhouses.
The Tomato plant is a short-lived perennial and can be maintained for a year or more in favorable conditions. However, most production schedules allow at least one month between crops for cleaning and pest control. The time chosen to be out of production is usually based on unfavorable prices or environmental conditions.
How to operate a Tomato farm
The critical activities in Tomato cultivation are variety selection, nursery development, transplanting, watering, weeding, pest and disease control, harvesting, and post-harvest handling.
Due to the technical nature of Tomato farming, the farm operator should be assisted by farmers and experts in carrying out critical management practices. Ideally, the operator should have experience in Tomato cultivation.
Buy certified varieties of disease-resistant seeds. Growers should consider Tomatoes’ pest and disease-susceptibility when procuring seeds. Seeds should be procured from certified distributors and agro-dealer shops.
Commercial Tomato farming is a profitable vegetable farming business. However, to ensure maximum profit from production, you should maintain some basics.
- Variety selection plays a significant role in the success of a Tomato farming business.
- You should choose the right one that suits the other climate and soil conditions.
- Planting should be started at the right time of the season.
- You will need to follow proper planting and crop management practices.
- Proper soil condition increases yield per hectare.
- Soil testing and treatment are recommended.
- For Tomato cultivation, you should manage proper irrigation.
- Proper fertilizer and pest management are required.
- Planning is required before marketing. Most importantly – it would help if you prepared a financial plan before starting Tomato farming.
- Tomatoes can be cultivated in many ways. Although open field farming is the most popular, other methods such as polyhouse farming, greenhouse farming, and hydroponics Tomatoes are being explored worldwide. If done correctly, Tomato cultivation has vast opportunities in both domestic and export markets.
A step-by-step guide to starting a Tomato farm business plan for beginners
It is essential to understand that people start businesses for several reasons:
- Following a passion;
- Financial independence;
- Doing something during retirement;
- It has a social impact, etc.
- Take some time to think about starting a Tomato business.
In case you missed it: Top 24 Steps to Boost Tomato Yield: How to Increase Production, Quality, and Size
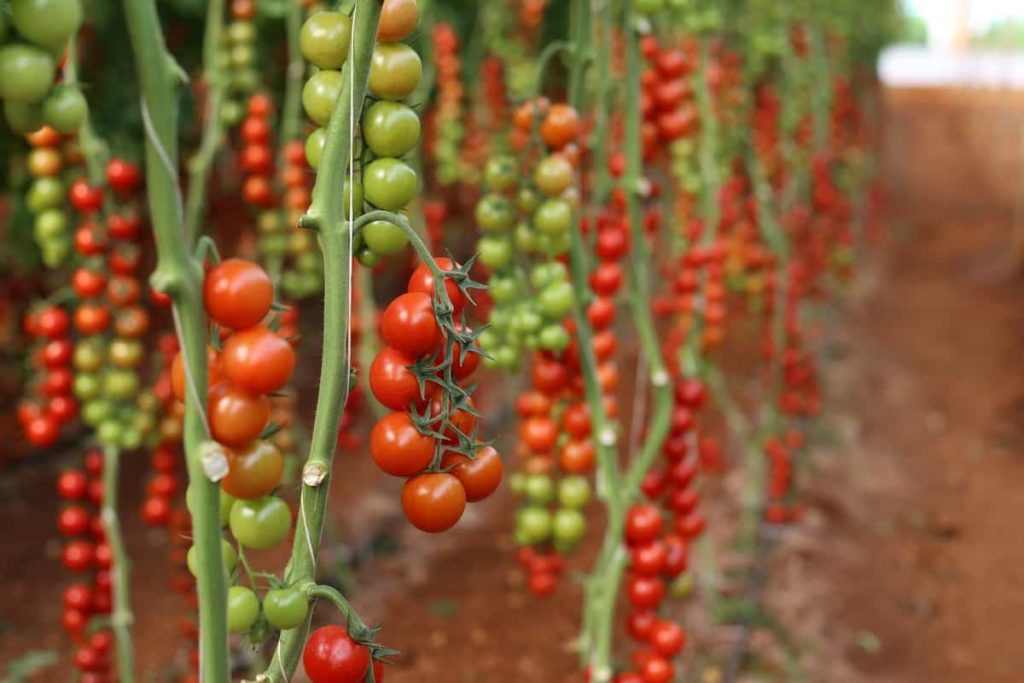

Market research is fundamental for existing business owners to help shape business and strategy; thus, anything you build anywhere will be successful. There are many failed businesses on the continent; opportunities must be aligned with local realities. Assess customer behavior and economic trends to help you improve your business strategy.
Use competitive analysis to determine what is missing in the market and how you can operate your business differently. You can gather competitive information by observing market transactions, conducting surveys, focus groups, and interviewing potential customers. Through careful market research, you will be able to zoom in on your target customers and determine a sales strategy that will be successful.
Writing a business plan should be part of your planning. A properly prepared business plan will increase your confidence in your business idea by answering critical risk and opportunity questions and providing a roadmap for achieving your business goals. But you don’t have to complete a business long or entirely before starting your own. However, it tries to answer who, what and how you plan to make money.
Business Name and Domain : Invest considerable time and care in choosing a business name and domain name (if applicable). These will be key to how customers find and remember you.
Business Structure : Decide which legal structure is best for your business: sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation. This is important because it affects your taxes, personal liability, your ability to get funding, etc. Consider consulting an attorney and accountant to help you make your decision.
Business Location : Location depends on your business; it can make or break your business. You may need to consider issues such as foot traffic, parking, distance from suppliers and customers, ordinances, utilities, crime, convenience, and close competition.
There are some basic marketing alternatives available to the Tomato grower:
- Wholesale markets
- Cooperatives
- Local retailers (grocery stores)
- Roadside stands
- Choose your operations
- Processing firms
In case you missed it: Tomato Farming In Karnataka, Areas, Seasons, Yield

Options are available for processing Tomatoes. In wholesale marketing, you or a shipper can take your crop to market. Shippers usually sell and transport Tomatoes at a predetermined price. Marketing cooperatives typically use daily pooled costs and prices, which spread price fluctuations across all participating producers. Local retailers are another potential market, but you should take the time to contact production managers and provide stores with high-quality Tomatoes when needed.
Roadside stands either own or another grower’s, and do-it-yourself operations offer opportunities to charge higher prices for your Tomatoes than wholesale. There may be additional costs for maintenance and additional costs for providing the service to you. By picking your operations, you save on crop costs, but you must also be willing to accept some waste and the risks of people visiting your farm.
Nitrogen and potassium are fundamental to obtaining high marketable yields. The correct form of nitrogen is essential – ammonium can limit growth and adversely affect quality. Yield per hectare varies greatly with variety and season. The yield of outdoor Tomato cultivation on stalked crops averages 60-100 tons per hectare.
Determinate varieties, however, generally do not yield more than 30–50 tons per hectare due to their short crop cycle. Industrial outdoor Tomatoes from experienced professional growers typically produce 60-80 tons per hectare. These are average yields, and there are impressive deviations in many cases. Tomatoes are collected and classified according to size, shape, and overall condition.
They are then moved to cool but not frozen (13°C) storage areas to avoid possible weight loss. Tomatoes can be stored in excellent conditions (4°C), provided they are collected during their late stages of ripening. If not, the Tomatoes will fail to reach the desired level of maturity. They will probably not achieve intense red color because the production of the substances responsible for giving the fruit its red color stops at low temperatures.
In case you missed it: Tomato Seed Germination, Time Period, and Procedure

The Tomato farming business is one of the most profitable agribusiness ideas. Tomatoes are consumed widely- they can be eaten in various ways, including raw, in many dishes and sauces, and even in drinks. Tomatoes also use a food processor. The Tomato is an herbaceous, sprawling plant with a weak woody stem 1-3 meters tall.
Tomato farming is a profitable business that provides millions of people income. Still, there are some essential things you need to do before you venture into the Tomato farming business. You have to decide how many hectares of land you want to grow, what kind of Tomatoes you will grow, what season you will plant your Tomatoes in, and your target market will be affected by is, and size of your target market.
Types of Pesticides Used in Agriculture: A Beginner’s Guide
Economical aquaculture: a guide to low-budget fish farming, 15 common planting errors that can doom your fruit trees, how to make houseplants bushy: effective tips and ideas, innovative strategies for boosting coconut pollination and yield, pollination strategies for maximum pumpkin yield, the complete guide to chicken fattening: strategies for maximum growth.
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
- Guide to Lotus Cultivation: How to Propagate, Plant, Grow, Care, Cost, and Profit
- Agriculture Drone Subsidy Scheme: Government Kisan Subsidy, License, and How to Apply Online
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Araucana Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Bringing Hydroponics to Classroom: Importance, Benefits of Learning for School Students
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Polish Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Australorp Chickens: Profile, Farming Economics, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Silkie Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Sussex Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet and Care
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf...
Natural solutions for peony leaf and flower problems: 100% effective..., maximizing profits with avocado contract farming in india: a comprehensive..., natural solutions for hydrangea problems: 100% effective remedies for leaf..., the ultimate guide to choosing the perfect foliage friend: bringing..., from sunlight to sustainability: 15 ways to use solar technology..., the ultimate guide to dong tao chicken: exploring from history..., the eco-friendly makeover: how to convert your unused swimming pool..., mastering the art of delaware chicken farming: essentials for healthy..., 20 best homemade fertilizers for money plant: diy recipes and..., brighten your flock: raising easter egger chickens for beauty and..., borewell drilling cost, pump price, and pipe cost, polyhouse subsidy, cost, profit, project report, tractor subsidy, bank loan, eligibility, schemes, process, malabar neem project report details guide, cold storage project report, cost and subsidy, mushroom farming project report, cost and profit analysis.
Farming With Precision!

[Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Tomato Greenhouse Docx
Starting a tomato greenhouse business requires careful planning and strategic implementation. A well-crafted business plan can serve as a roadmap to guide you through the process and increase your chances of success in the competitive agricultural industry.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the key elements to consider when developing a tomato greenhouse business plan. From market analysis and financial projections to production strategies and marketing techniques, we will explore the essential aspects of establishing and operating a profitable tomato greenhouse venture.
[Pdf Sample] Tomato Greenhouse Business Plan Proposal Docx
Table of Contents
To write a business plan, here is a breakdown of how it should be structured and what should be in each category. After this instruction, I will provide you with a sample of one I wrote for my farm, let us go:
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Vegetable Farming Docx

Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a concise overview of your tomato greenhouse business plan . It summarizes the key elements of your venture, including your mission statement, market analysis, competitive advantages, and financial projections. The executive summary serves as a hook to grab the reader’s attention and provide a snapshot of your business idea.
Market Analysis
In the market analysis section, you will delve into the tomato industry, evaluating the demand and trends, competition, and potential market segments. This analysis will help you identify your target market and develop strategies to position your greenhouse business effectively.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan Guide For Strawberry Farming Docx
Target Market and Customers
Understanding your target market and customers is crucial for developing a successful tomato greenhouse business plan. Identify the demographics, preferences, and needs of your potential customers. Determine if you will focus on supplying local restaurants, grocery stores, or direct-to-consumer sales.
Greenhouse Infrastructure
Designing an efficient greenhouse infrastructure is paramount for optimal tomato production. Discuss the layout, size, materials, and technologies you will utilize to create a conducive environment for the growth of healthy and high-yielding tomato plants .
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Bell Pepper Farming Docx
Tomato Cultivation Techniques
This section will outline the cultivation techniques you will employ in your greenhouse. Discuss seed selection, propagation methods , irrigation systems, nutrient management, pest and disease control, and harvesting techniques. Emphasize sustainable and organic practices to attract environmentally conscious customers.

Supply Chain Management
Managing the supply chain effectively is crucial for maintaining the quality and freshness of your tomatoes. Describe your strategies for sourcing inputs, managing inventory, packaging, and distribution. Ensure that your supply chain is streamlined to deliver fresh tomatoes promptly.
Marketing and Sales Strategies
Developing robust marketing and sales strategies will help you create awareness and attract customers to your tomato greenhouse business. Discuss your branding, promotional activities, pricing strategies, and distribution channels. Leverage digital marketing techniques to reach a wider audience and establish an online presence.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Chili Pepper Farming Docx
Financial Projections
The financial projections section presents a comprehensive analysis of the expected costs, revenues, and profitability of your tomato greenhouse business. Include information on initial investments, operational expenses, sales forecasts, and return on investment. Seek professional assistance if needed to ensure accurate financial projections.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Identify potential risks and challenges that may impact your tomato greenhouse business. Assess market risks, natural disasters, pests and diseases, and regulatory changes. Develop contingency plans and mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of these risks.
Operational Plan
The operational plan outlines the day-to-day activities and processes involved in running your tomato greenhouse business. Define your production schedule, quality control measures, equipment maintenance, and record-keeping procedures. Focus on operational efficiency to maximize productivity and minimize costs.
Human Resources Management
Discuss the human resources required for your tomato greenhouse business. Determine the number of staff needed, their roles and responsibilities, and the skills and qualifications required. Outline a recruitment and training plan to ensure a competent and motivated workforce.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Complying with legal and regulatory requirements is essential for operating a tomato greenhouse business. Research the necessary permits, licenses, and certifications required in your locality. Ensure adherence to food safety and environmental regulations to build trust with customers and avoid legal issues.
Sustainability Practices
Integrating sustainable practices into your tomato greenhouse business can attract environmentally conscious consumers and enhance your brand reputation. Explore options such as water conservation , renewable energy sources, waste management, and eco-friendly packaging.
Expansion and Growth Opportunities
As your tomato greenhouse business thrives, consider expansion and growth opportunities. Explore diversification into other crop varieties, regional market expansion, or value-added products. Develop a long-term vision for your business and set goals to guide its growth.
Here Is The Download Link To Business Plan Proposal For Tomato Greenhous Farming By Agrolearner
Business Model: Agrolearners.com’s Tomato Greenhouse Farm
Value proposition:.
Agrolearners.com’s Tomato Greenhouse Farm provides high-quality, organic tomatoes to health-conscious consumers, local grocery stores, restaurants, and food processors in the surrounding region. We offer fresh, flavorful tomatoes grown sustainably without the use of harmful chemicals, ensuring superior quality and nutritional value.
Key Activities:
Tomato cultivation using advanced greenhouse infrastructure and technology-driven techniques.
Supply chain management, including sourcing agricultural inputs, quality control, and distribution.
Marketing and sales strategies to reach and engage the target market.
Continuous research and development to enhance cultivation techniques and improve crop quality.
Customer Segments:
Health-conscious consumers seeking fresh, organic tomatoes .
Local grocery stores, restaurants, and food processors in need of a reliable supplier of premium-quality tomatoes.
Customer Relationships:
Building strong relationships with customers through consistent delivery of high-quality tomatoes.
Engaging with customers through social media, direct sales, and participation in farmers’ markets to gather feedback and understand their evolving needs.
Providing excellent customer service and addressing any concerns promptly.
Revenue Streams:
Direct sales to consumers and businesses.
Wholesale contracts with grocery stores, restaurants, and food processors.
Value-added tomato products, such as sauces and dried tomatoes.
Key Resources:
Greenhouse infrastructure with automated climate control, irrigation systems , and energy management solutions.
Skilled agricultural professionals, farm managers, and greenhouse technicians.
Strategic partnerships with suppliers for seedlings, fertilizers, and other agricultural inputs.
Marketing and sales team to promote and sell products.
Financial resources for investments and operational expenses.
Key Partnerships:
Suppliers of agricultural inputs, ensuring a steady and reliable supply of quality seedlings, fertilizers, and other necessary materials.
Local grocery stores, restaurants, and food processors, establishing long-term partnerships for consistent sales and distribution.
Collaboration with local agricultural research institutions and industry experts to stay up to date with the latest cultivation techniques and market trends.
Online platforms and Agrolearners.com website for product promotion and direct sales.
Social media marketing to reach and engage with target customers.
Direct sales to local businesses, establishing personal relationships and ensuring product quality.
Participation in farmers’ markets and trade shows to showcase products and connect with customers.
Cost Structure:
Greenhouse infrastructure setup and maintenance costs.
Employee salaries and benefits.
Marketing and advertising expenses.
Cost of agricultural inputs, including seedlings, fertilizers, and pest control measures.
Administrative and operational costs, including utilities, packaging, and transportation.
Key Metrics:
Sales revenue and growth rate.
Customer satisfaction and retention rates.
Yield per square meter and production efficiency.
Cost per kilogram of tomatoes.
Market share and customer acquisition rate.
By implementing this business model, Agrolearners.com’s Tomato Greenhouse Farm aims to establish itself as a reliable supplier of premium-quality tomatoes while promoting sustainable agriculture practices . The combination of advanced greenhouse infrastructure, technology-driven cultivation techniques, efficient supply chain management, and a customer-focused approach positions the farm for success in meeting the increasing demand for fresh, organic tomatoes in the local market.
How much capital do I need to start a tomato greenhouse business?
The capital required to start a tomato greenhouse business can vary depending on factors such as the size of the greenhouse, equipment costs, and initial operational expenses. It is recommended to conduct a detailed financial analysis and seek professional advice to determine the exact capital requirements for your specific business.
Are there any specific licenses or permits needed for operating a tomato greenhouse business?
The licenses and permits required for operating a tomato greenhouse business may vary depending on your location. It is important to research and comply with local regulations regarding agricultural operations, food safety, and environmental standards. Consult with local authorities or agricultural extension services to ensure you meet all the necessary requirements.
How can I market my tomatoes effectively?
To market your tomatoes effectively, develop a strong brand identity, create a compelling online presence, and utilize various marketing channels such as social media, local farmers’ markets, and partnerships with local restaurants or grocery stores. Emphasize the quality, freshness, and sustainability of your tomatoes to attract customers who value these attributes.
What are some common challenges faced in tomato greenhouse farming?
Common challenges in tomato greenhouse farming include pest and disease management, maintaining optimal growing conditions, market fluctuations, and competition. It is important to stay updated with the latest agricultural practices , invest in technology and infrastructure, and adapt to changing market dynamics to overcome these challenges successfully.
How can I ensure the quality and freshness of my tomatoes during transportation?
To ensure the quality and freshness of your tomatoes during transportation, use proper packaging that protects the fruits from damage and maintains their freshness. Consider using temperature-controlled vehicles or refrigerated containers to preserve the quality during transit. Efficient supply chain management and prompt delivery are crucial for maintaining the freshness of your tomatoes.
Conclusion:
Agrolearner.com Farm’s tomato greenhouse farming business plan outlines a comprehensive strategy to capture the growing demand for high-quality tomatoes in our target market. With our focus on sustainable practices, advanced cultivation techniques, and efficient supply chain management, we are confident in our ability to deliver superior products while maintaining profitability. We are excited to embark on this journey and contribute to the local agriculture industry while providing consumers with healthy, flavorful tomatoes.
Share this:
Author: Adewebs
You may also like:.

[Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Pig Farming Docx

Starting a Poultry Farm with Limited Resources in Ghana: A Comprehensive Guide for New Farmers

How To Register Agribusiness Company In Kenya (See Full Guide)

Starting a Poultry Farm with Limited Resources in Nigeria: Guide for New Farmers
3 replies to “ [pdf sample] business plan for tomato greenhouse docx ”.
- Pingback: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Cabbage Farming Docx - Agrolearner
Hello. I have read this section about Tomato Greenhouse Business Plan and I wonder if You have this business plan in a PDF file and You may send me to My e-mail? Thank You.
Have a Great Day.
Definitely I have it, drop your email to get a copy of it
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Tomato Processing Plant Business Plan [Sample Template for 2022] (2024)
Are you about starting a tomato processing plant? If YES, here is a complete sample tomato processing business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE . Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a tomato processing business. We also took it further byanalyzing and drafting a sample tomato processing business marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for tomato processing businesses. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
Table of Content
Why Start a Tomato Processing Plant?
1. industry overview, 3. our products and services, 4. our mission and vision statement, 5. job roles and responsibilities, 6. swot analysis, 8. our target market, 9. sales and marketing strategy, 10. sales forecast, 11. publicity and advertising strategy, 12. our pricing strategy, 14. sustainability and expansion strategy.
It is a known fact that tomatoes are used all over the world and it is a cheap and affordable staple for all classes of people. We have been told that tomatoes are rich in fiber, they contain healthy vitamins andhave no trace of cholesterol. Tomatoes are also known to contain disease fighting photo-chemicals. Most people like to consume tomato in its raw state as fruit, or after it have been processed in foods andjuices.
These precious fruits are also used for the preparation of various menu like; salads, drinks, pizza, tomato soups and sauces et al. Residing in a country where tomatoes are produced in large quantities actually means that you can establish your own tomato processing plant and build it to become a worldclassbusiness.
When starting a tomato processing plant, you would require a huge start-up capital, but the good news is that the market for processed tomato products is very huge and profitable. One of the numerous advantages of starting a tomato processing plant is that you can build your plant in any part of the world where you can get tomato plants easily and with cheaper labour and then sell them to the world. Without much waste of time, the sole end products from an ideal tomato processing plant are the popular ketchup, tomato juice, diced tomatoes, tomato powder, tomato paste, tomato pulp, strained tomatoes, partially dehydrated tomatoes et al; which are very much needed in our world.
Here is a sample business plan template for you to go through.
A Sample Tomato Processing Plant Business Plan Template
Just as we stated above, tomato processing plants produce tomato paste, puree, ketchup, juice and sauce. It is important to note that the manufacturing process is made up of the most modern technology of vacuum evaporation through the use of forced circulation evaporators/scrapped surface evaporators.
Also evaporation plants are versatile in nature and can concentrate other juices also. These awesome fruits are used in very huge quantities in the fresh state, as canned tomatoes, and in the form of canned juice, puree, paste, ketchup and sauce. Tomato ketchup and sauce have got a mixed taste of sweet and sour.
They can also be very refreshing and help in increasing appetite. Tomatoes are very good source of vitamin C for our body needs. We all know that the demand for tomato products is increasing day by day. Thisshows a glowing future for new entrepreneurs and as well as existing manufacturers.
2. Executive Summary
First Inland Plants, FIF is a Limited Liability Company based in Fresno, California. It is a business set up with a clear, dedicated and committed vision, to excel and grow into one of the best Agro based industries in California which has taken advantage of the abundant raw materials produced to create goods for export. FIF has its Head office at 3419 Brown Avenue Fresno, a 100 acre site where the proposed plant will be built.
We also have acquired recently a 50,000 hectares plant land in the same region for cultivating of tomato and orange. Our processing plant we believe will be run by a team of experts that include Mr. Jeffery Madeleine as the General Manager. It is also important to note that FIF is registered with an authorized share of 100,000 with a value of $1.67 per share.
We at FIF believe that our plant will have tomato processing capacity of about 1,500 tons per day between the months of October and April of the year 2018. We at FIF plan to make arrangements for skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled manpower, raw materials and plant housing as necessary for the success of our business.
We also believe that our interested partner will provide funding for machinery, skilled manpower, take-off capital, among other things. Our management will jointly organise for marketing of manufactured tomato paste.
This business is the sole dream and arrangement of four friends who have enjoyed immeasurable connection and success in the agro processing industry. These individuals, Jeffrey Madeleine, Constance Kiki, Wilfred Carlos and Steve Cornwall have been friends for at least 23 years and they are bringing their different experiences into this unique business. See Also Reinstalling and patching your Quicken Subscription version after your membership has expired (Quicken for Mac) Quicken Subscription Membership FAQs Reinstalling and patching your Quicken Subscription version after your membership has expired Quicken Review (2023): Features, Pricing & More
We at FIF believe that we will produce quality canned Tomato paste, Tomato Ketchup and orange juice for local consumption and for export. It is our hope at FIF to provide excellent customer service for its customers and suppliers.
FIF will also produce these products, and export 70% of the products directly from the united states, to our neighbouring countries. We believe that the United States will also gain from foreign exchange earnings and added value for its rotten produce which would have gone to waste. Listed below are the products we wish to provide at FIF;
- Tomato Paste
- Tomato Ketchup
- Tomato juice and sauce
- Dried tomatoes
- Tomato powder
- Orange juice
- Our vision at FIF is to become one of the leading ventures in the Agro Processing industry in the whole world, starting from the United States.
- We at FIF have decided to provide a wide variety of processed tomato products to United States citizens. We understand that the customer service we provide is extremely important, because we want each customer to have a pleasant experience with our goods, and it is the intention of our staff to answer questions with expertise and to offer advice when we feel it is needed.
Our Business Structure
FIF has been a long-time dream of our four founding partners, and has been a project in the making for nine years. We at FIF hope that our opening date will be within next year March, and we dream of making our plant the leading figure in the industry. We also plan to focus on providing quality tomato and orange products, which will give nutrients and serve the various needs of our customers, who will cut across different phases of life.
Outlined below are the portfolios we wish to start FIF with:
Chief Executive Officer
HR and administrative Executive
Plant Manager
- Plant worker(s)
- greenhouse worker
Marketing and Sales Manager
Security guard
- His in charge of overseeing all other executives and staff within the organization.
- He is tasked with board of directors and other executives to determine if the company is in accordance with set goals and policies.
- Charged with encouraging business investment.
- He also promotes economic development within communities.
- His in charge of directing the organization’s financial goals, objectives and budgets.
- Implement the organization’s guidelines on a day-to-day basis.
- Preside over quality control.
- In charge of hiring, training, and terminating employees.
- In charge of developing and implementing strategies and set the overall direction of a certain area of the company or organization.
- Provide visionary and strategic leadership for the organization.
- Collaborate with the board of directors to develop the policies and direction of the organization.
- He makes sure that the members of the Board of Directors have the information necessary to perform their fiduciary duties and other governance responsibilities.
- He also provides adequate and timely information to the Board to enable it to effectively execute its oversight role.
- Direct staff, including organizational structure, professional development, motivation, performance evaluation, discipline, compensation, personnel policies, and procedures.
- In charge of overseeing the running of HR and administrative tasks for FIF.
- Monitor office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Stay updated on job knowledge by participating in educational opportunities; reading professional publications; maintaining personal networks; participating in professional organizations.
- Builds the ventures reputation by accepting ownership for accomplishing new and different requests; exploring opportunities to add value to job accomplishments.
- State job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process.
- Organise staff induction for new team members.
- In charge of training, evaluation and assessment of employees.
- In charge of arranging travel, meetings and appointments.
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily office activities.
- In charge of preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization.
- In charge of financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- In charge of developing and managing financial systems and policies.
- In charge of administering payrolls.
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation.
- Handles all financial transactions for the company.
- Serves as internal auditor for the company.
- Will plan, organize, direct and run optimum day-to-day operations to exceed our customers’ expectations.
- Tasked with increasing production, assets capacity and flexibility while minimizing unnecessary costs and maintaining current quality standards.
- In charge of production output, product quality and on-time shipping.
- Allocate resources effectively and fully utilize assets to produce optimal results.
- Will be responsible for implementing strategies in alignment with strategic initiatives and provide a clear sense of direction and focus.
- Will monitor operations and trigger corrective actions.
- Share a trusting relationship with work-group and recruit, manage and develop plant staff.
- Will have to collect and analyse data to find places of waste or overtime.
- Will commit to plant safety procedures.
- In charge of developing systems and processes that track and optimize productivity and standards, metrics and performance targets to ensure effective return on assets.
- Will have to address employees’ issues or grievances and administer collective bargaining agreements.
- Influence and learn from below.
- Stay up to date with latest production management best practices and concepts.
Plant Worker
- Checking and controlling the equipment that make the food.
- Checking instruments, for example temperature gauges, at customary intervals.
- Keeping machines dirt free at all times.
- When problems happen with the production procedure, hewould discontinue the machine and report the fault to a manager or engineer.
- Making sure the production line has a regular supply of raw materials or components.
- Adjusting the momentum of the conveyor belt if required.
Greenhouse Worker
- Graft plants.
- Inspect facilities and equipment for signs of disrepair, and perform necessary maintenance work.
- Negotiate contracts such as those for land leases or tree purchases.
- Position and regulate plant irrigation systems, and program environmental and irrigation control computers.
- Prepare soil for planting, or to transplant seeds, bulbs, and cuttings.
- Provide information to customers on the care of trees, shrubs, flowers, plants, and lawns.
- Assign work schedules and duties to nursery or greenhouse staff, and supervise their work.
- Determine plant growing conditions, such as greenhouses, hydroponics, or natural settings, and set planting and care schedules.
- Determine types and quantities of horticultural plants to be grown, based on budgets, projected sales volumes, and/or executive directives.
- Identify plants as well as problems such as diseases, weeds, and insect pests.
- Manage nurseries that grow horticultural plants for sale to trade or retail customers, for display or exhibition, or for research.
- Select and purchase seeds, plant nutrients, disease control chemicals, and garden and lawn care equipment.
- Tour work areas to observe work being done, to inspect crops, and to evaluate plant and soil conditions.
- Apply pesticides and fertilizers to plants.
- Confer with horticultural personnel in order to plan facility renovations or additions.
- Construct structures and accessories such as greenhouses and benches.
- In charge of identifying, prioritizing, and reaching out to new markets for our agricultural produce, processed food, new partners, and business opportunities within the agro – allied industry.
- In charge of developing, executing and evaluating new plans for expanding sales of all our agriculture produce and processed foods.
- Tasked with documenting all customer contact and information.
- Represents the company in strategic meetings.
- Aids to increase sales and growth for the company.
- In charge of protecting the plant and its environs
- Controls traffic and organize parking
- Tasked with giving security tips when necessary
- Patrols around the plant on a 24 hours basis
- Presents security reports weekly
It is important to note that FIF is a standard Tomato processing plant that was set up to be great and not as a trial and error, which is why conducting a proper SWOT Analysis became a necessity and a must for us at FIF. We actually believe that getting our things right from the start would mean that we have succeeded in layingthe foundation that will help us create a sustainable tomato processing plant.
We at FIF have plans of offering a large number of products and services to the people of California, we have no plans for failure but a well situated plan that will help us to maximize our strength and opportunities and also make our threat and weakness an advantage for us. Properly explained below is a summary of the result of the SWOT analysis for FIF.
According to our SWOT Analysis, the strength of FIF rests on the fact that we have created and built a well based rapport with a handful of major players (agriculture merchants) in the agro – allied industry; both suppliers and buyers within and outside of the United States. Our management have also purchased some of the latest modern machines, tools and equipment that will helps us manage our tomato processing plant. We also have thebest hands for the business in the whole industry. See Also How Do I Manage My Quicken Subscription?
The SWOT Analysis noted that the time it will take to gain customers and boost our brand will be our major weakness at FIF. It explained the unimaginable competitive industry and how industry players are keen on their advertising strategies.
- Opportunities
The opportunities that we at FIF have are the amount of people from the different walks of life that will need our products in their daily lives and activities.
One of the threats that was perceived during the SWOT Analysis is the probability of a global economic downturn that will affect us negatively, bad weather cum natural disasters (droughts, epidemics), unfavourable government policies, a new competitor in our location and faulty machines.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
It’s a known fact in the industry that fresh tomato consumption overall has been stagnant since mid-2000s. But interesting things are happening in the industry, both hothouse and field-grown, across all North American markets. Farms in the United States, Canada and Mexico are getting ready and arranging up their strengths to produce a variety of tomatoes to meet consumer demand for flavour, convenience, interesting colours, sizes and shapes.
It is also important to note that the U.S. per capita consumption of tomatoes increased 5 pounds from 1985 to 2013, which can be accredited to increasing availability of hothouse tomatoes in the industry.
Even though the hothouse tomato industry rose significantly for some time, more recent producers have reported facing market saturation. Hothouse round tomatoes and TOV [tomatoes on the vine] have matured, and all the growth is coming in the snacking category. Estimate in the industry has shown a decline in the total quantity (lbs) of tomatoes sold between 2009 and 2015.
But we believe there have been major changes in the product mix of tomatoes. One specie eating up the revenues of another has been the major story instead of the new varieties causing higher consumption of tomatoes overall. It is also believed that tomato growers may also have opportunities as the food-service industry has been pressured to add more non-animal proteins to their menus. These are round tomatoes which are prized for their firmness and easy slicing attributes.
We at FIF believe that our target market strategy will rest on making our business an attractive choice for residents and retail outlets owners in the city of Fresno, California. We believe that the target markets we are going to be chasing are the residential consumers hoping to use our products for the organization consumption needs. We also believe that the retail stores in the city will be attracted by our competitive prices and a diverse inventory.
We at FIF know that individuals will want to shop at our location because of the superior customer service we hope to provide, and we will love to experience a five to ten percent increase in customers annually, and the profile of our customer consists of the following demographic information:
- Male and Female.
- Married and Single.
- Combined annual income in excess of $50,000.
- Age range of 25 to 80 years, with a median age of 40.
- Retail outlets
- Vegetable export markets
Our competitive advantage
Our strategy at FIF is to profitably and efficiently make use of present and future agricultural technology in the processing of tomatoes. We hope to build a profitable tomato processing plant with all the necessary custom-innovated equipment, that will gain a significant industry advantage. Our other competitive advantages include;
- Efficient production and utilizing greenhouses.
- No existing projects of this magnitude in Fresno, California
- Our founding members have or can boast of a unique experience in the vegetable industry that goes back to 1998.
- Sources of Income
Just like we stated above in the product and service section, we will produce quality canned tomato paste, tomato ketchup and orange juice, for local consumption and for export. We hope to raise substantial income from the sales of products that we produce. FIF will also produce these products, and export 70% of the product directly from the United States, to our neighbouring countries. We believe that the United States will also gain from foreign Exchange earnings. Listed below are the products we wish to gain income from at FIF;
We at FIF expect to have exceptional sales in the first year of operation. We believe that our direct unit costs include the costs for the agricultural supply force who will produce the tomatoes and oranges we process in our plant. These costs we believe are roughly 35% of all direct costs each month. Our sales projections at FIF was analysed from two main revenue streams: the general public, and the retail outlets.
We believe that our sales projections for the second year of operation will be based on a modest growth rate for sales. We at FIF being a new tomato processing plant are projecting a growth rate of 20%, believing our advertising will bring in new customers daily. Outlined below is the sales projections of FIF:
- First Year -: $550,000
- Second Year -: $1,400,000
- Third Year- : $3,000,000
Note : it is worthwhile to note just like we stated above that this forecast was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the believe that none of the threats we mentioned above will be a hindrance or may likely appear.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales strategy
We at FIF will market and supply our unique products to our connected outlets aggressively, focusing at first on local markets, and then on export options. We plan to emphasize the reliable year-round output of our processing plant and hardworking workforce as well as our ability to produce independent tomato products.
We at FIF understand how important marketing is in our industry. We understand the need to reach our prospective customers and leverage all available sources, which is why we will also eventually develop a website and advertise on the internet, although these future marketing avenues are not included in this plan.
We at FIF hope that our marketing strategy will be based on giving the people the products they need for the right price. Our management at FIF plan to maintain an extensive marketing campaign that will ensure maximum visibility for the business in our targeted market. Below is an overview of the publicity and advertising strategies for FIF:
- Establish relationships with landscape contractors within the target market.
- We hope to place adverts on both print (community based newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms; we will also advertise FIF Consultants on financial magazines, real estate and other relevant financial programs on radio and TV.
- FIF will also sponsor relevant community based events/programs.
- We also plan to make use of various online platforms to promote the business. Which will make it easier for people to enter our website with just a click of the mouse. We will take advantage of the internet and social media platforms such as; Instagram, Facebook , twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our brand.
- We also plan to mount our Bill Boards on strategic locations all around Fresno, California.
- We at FIF also plan to engage in road show from time to time.
- We also plan to distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas all around Fresno.
- We plan to make sure that all our workers wear our branded shirts and all our official vehicles are well branded with our company’s logo et al.
Our pricing strategy at FIF will be based on offeringour customers expert service and product knowledge, to build our marketing plan to reach diverse individuals and retailers, while also maximizing profits. FIF believe that to get the right pricing for our products, we need to make sure that we choose a good location for our plant, choose our suppliers wisely, reduce the cost of running our plant to thebarestminimum and make sure we attract buyers to our business, as against taking our products to the market to source for buyers; with this, we would have successfully removed the cost of transporting the goods to the market and other logistics from the equation.
- Payment Options
We at FIF after our extensive research and thorough discussion understand that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them at different times. We plan to make sure that we provide them with payment options that will make their transactions less stressful and very open.
Listed below are the payment options we at FIF plan to make available to our customers;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via bank draft
- Payment via POS
We have also chosen to partner with a known bank in the United States in order to give our customers the best they can ever get in the agricultural sector of the United States.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
We at FIF hope to maintain an average gross margin at or above 50%, generate an average of $1,000 of sales each business day of each month, and realize an annual growth rate of 10% in Year 2. Our unique management believe that these objectives and goals are very much reachable, which is the main reason why we are being very detailed about all information penned down in our business plan. We have also decided on the possible factors to spend our start up capital and they include:
- The price for incorporating our farm in United States of America – $750.
- Our budget for key insurance policies, permits and business license – $4,000
- The cost of acquiring/leasing our facility and land – $55,000
- The budget for preparing our plant– $25,000
- The price for acquiring the required working tools and equipment/machines/tractors et al– $600,000
- The price of launching an official Website – $600
- The budget for paying our workers for 1 year – $500,000
- Other business requirements (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,000
- Miscellaneous – $5,000
From our detailed cost analysis above, we will need $1,192,350 to start FIF and make our processing plant ready to serve the needs of our customers. Here also are the few equipment we believe are necessary in starting FIF :
- TOMATO processing lines
- Equipment for tomato paste production
- Machinery for whole peeled tomatoes production
- Equipment for diced/pulp production
- Machinery for pasta/tomato sauces production
- Equipment for ketchup production
- Machinery for drinkable tomato juice production
- FRUIT processing lines
- VEGETABLES/FRESH CUT/EASYCUBE
- EVAPORATORS
- Twist SPIRAL solutions
- FLUID and SPIRAL FREEZING solutions
- JAM, MARMALADE, CANDYING/ BLENDING and FORMULATING
Generating Funding/Start-up Capital for FIF
We at FIF understand that having the required finance for your business will go a long way to make sure you achieve your desired goal. Our management also understand that funds are basically very crucial factors when it comes to building any business, and building a successful business is not a one day job but a continuous job that requires consistency and hard work.
FIF is a business owned by four partners and they hope to keep it that way with the funding and decision making. Which is why they have decided to leave the means of generating funds for the business in these following ways till further notice.
- Raising part of the start – up capital from personal savings
- Raising part of the start – up capital from family members and friends (soft loans and gifts et al)
- Raising a larger chunk of the start-up capital from banks (loan facility).
FIF, justaswe have stated above will be a partnership of successful businessmen developing a small vision into a highly productive tomato processing plant. We at FIF plan to be growing our own tomatoes in high-tech, multi-span greenhouses. We hope to grow them in 15L bags with a medium used to support the root system. The plants will automatically be fed nutrients through irrigation systems.
The plants will be grown in the best suitable growing conditions which allows each plant to produce the maximum fruit possible. We will also plan to extend its time into a turf . The turf will be irrigated via overhead spray units, using the run-off fertilizer from the multispan tunnels.
This fertilizer is highly effective and will provide all the requirements the instant turf will require. The turf will be cut and sold by the square meter, and is harvested with a sod cutter. We plan to concentrate on the production of tomatoes, but will grow to peppers and cucumbers with time.
Checklist/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts various banks in the United States: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of all form of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Conducting feasibility studies : Completed
- Leasing, renovating and equipping our facility: Completed
- Generating part of the start–up capital from the founder: Completed
- Applications for Loan from our Bankers: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging Marketing/Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed software applications, furniture, office equipment, electronic appliances and facility facelift: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with banks, financial lending institutions, vendors and key players in the industry: In Progress
How long should a business plan be? ›
No matter who you're writing for, your business plan should be short and readable—generally no longer than 15 to 20 pages . If you do have additional documents you think may be valuable to your audience and your goals, consider adding them as appendices.
Tomatoes are used in the preparation of soup, salad, pickles, ketchup, puree, sauces and are also consumed as a vegetable in many other ways. As the raw material is available throughout the country, a small-scale tomato processing unit is a profitable venture in India .
Manufacturing tomato sauce is a profitable business venture if started with proper planning and presentation . India, being one of the largest producers of tomatoes provides a great market for the tomato sauce manufacturing as homemade tomato sauces are gaining great demand from the market.
At their core, business plans have 5 basic pieces of information. They include a description of your business, an analysis of your competitive environment, a marketing plan, a section on HR (people requirements) and key financial information .
- Executive summary. The executive summary is a condensed version of your full business plan. ...
- Company description. Explain the different elements of your business. ...
- Market analysis. ...
- Organization and management. ...
- Service or product line. ...
- Marketing and sales. ...
- Contingency plan.
- Unrealistic Financial Projections. ...
- Not Defining the Target Audience. ...
- Over-Hype. ...
- Bad Research. ...
- No Focus on your Competition. ...
- Hiding Your Weaknesses. ...
- Not Knowing your Distribution Channels. ...
- Including Too Much Information.
Good business plans should include an executive summary and sections on products and services, marketing strategy and analysis, financial planning, and a budget .
✓ A Business Plan is a document in which a business opportunity, or a business already under way, is identified, described and analyzed, examining its technical, economic and financial feasibility .
One of the best ways to promote tomatoes and drive volume is to set an eye-catching price , suggests Procacci's Feighery. “It's all about the right item, at the right time and right price. Also, gauge the promotion currently. Don't run out and don't over-order.
Processing tomatoes are primarily canned, dehydrated, as well as turned into paste, puree, pulp, ketchup, tomato sauce and tomato juice . To preserve the most flavor, processing tomatoes are machine harvested ripe and red. Not all tomato varieties have the unique properties of processing tomatoes.
What is the yield of tomatoes per acre? ›
The farmer can get a total yield of 8 to 12 tonnes/acre . Tomato seed rate for 1 acre is 200 gm, whereas it is about 60 to 80 gms for hybrid varieties. The cost for tomato seeds for 1 acre cultivation is about Rs 300 for good quality seed.
Advertise your tomato sauce on your company website and to local shops . Approach grocery store distributors to inquire about marketing your sauce to the stores they supply. Ask grocery managers to sell your sauce on consignment, which poses little risk to them because you are paid only when your sauce is sold.
Tomato ketchup is a condiment made by mixing concentrated tomato paste with water, sugar, vinegar, salt and seasonings . The tomato paste is typically manufactured using the “Hot Break” method. With this method, pulped tomatoes are heated to 200˚F (90˚C).
Tomato powder is made from select ripe tomatoes . Homemade versions are made by dehydrating tomato wedges and pulverizing them in a food processor. The Spice House's tomato powder is made by freeze drying premium tomato pulp into a perfect, pourable powder.
- Start with a simple brainstorming list. Break down your role in the company into small parts and be sure it's comprehensive. ...
- Prioritize objectives. ...
- Be specific. ...
- Set challenges but be realistic. ...
- Set deadlines. ...
- Share the plan. ...
- Revisit the plan weekly.
- Step 1: Write an Executive Summary. ...
- Step 2: Write a Business Description. ...
- Step 3: Market and Competitive Analysis. ...
- Step 4: Operational Structure. ...
- Step 5: Product Description. ...
- Step 6: Raise Capital. ...
- Step 7: Financial Analysis and Projections. ...
- Step 8: Appendix.
A business plan template is a document that allows you to quickly write a detailed business plan . Among other things, it includes an introduction, executive summary, company description, and marketing plan.
- Executive summary. This is your five-minute elevator pitch. ...
- Business description and structure. This is where you explain why you're in business and what you're selling. ...
- Market research and strategies. ...
- Management and personnel. ...
- Financial documents.
Your restaurant's business plan doesn't need to be hundreds of pages—keep it as short and concise as you can. You'll probably want to include each of these sections: executive summary, company summary, products, market analysis, strategy and implementation, marketing plan, management team, financial plan, and appendix .
- No. 1 - You can predict strong revenue months. Your business plan should determine your strong revenue months, while also finding opportunities for repeat business from customers. ...
- No. 2 - A regular SWOT. ...
- No. 3 - Three month goal. ...
- No. 4 - Insights are important.
What are 5 common mistakes of a business plan? ›
- Ignoring a major section. ...
- Neglecting the research component. ...
- Being vague. ...
- Writing in a closed system. ...
- Boring your reader.
It is a written summary of how the business will organize its resources to meet its goals and how the institution will measure progress . The business plan should be a comprehensive plan, which is the result of in-depth planning by the institution's organizers and management.
The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and highlights what the business plan will cover.
- Write an executive summary. ...
- Detail a mission statement. ...
- Include a SWOT analysis. ...
- Write your goals. ...
- Include business metrics. ...
- Describe your target audience. ...
- Write an industry analysis. ...
- Include a detailed marketing plan.
- Make sure your company has a clear objective.
- Identify your target market.
- Analyze your competition.
- Budget accordingly.
- Identify your goals and financial projections.
- Clearly define the power structure.
- Discuss your marketing plan.
- Keep it short and professional.
Businesses include large organizations such as Coca-Cola, Amazon, Walmart or General Motors . The heart of America, however, remains the small business. Small businesses in your city may include accounting firms, restaurants, local shops, and more.
- Handyman. Image Source. ...
- Woodworker. ...
- Online Dating Consultant. ...
- Sewing and Alteration Specialist. ...
- Freelance Developer. ...
- Personal Trainer. ...
- Freelance Graphic Designer. ...
- Life/ Career Coach.
- Conduct market research. Market research will tell you if there's an opportunity to turn your idea into a successful business. ...
- Write your business plan. ...
- Fund your business. ...
- Pick your business location. ...
- Choose a business structure. ...
- Choose your business name. ...
- Register your business. ...
- Get federal and state tax IDs.
What are 10 small businesses? ›
- Health Care and Virtual Medicine. ...
- Accommodation and Food Services. ...
- Arts, Entertainment, and Crafts. ...
- Personal Trainers (online) ...
- Site building and web design. ...
- Local Auto Repairs. ...
- Secondhand (Online) Stores. ...
- Pet services.
- 1.Consider and analyse the relevant markets. ...
- 2.Note down your ideas and expand them. ...
- 3.Carry out competitive analysis. ...
- 4.Model your business. ...
- 5.Create/design/sketch your mockup and then test it. ...
- 6.Execute a market survey. ...
- 7.Develop your final product.
Author : Edwin Metz
Last Updated : 2024-04-27T09:27:16+07:00
Views : 6178
Rating : 4.8 / 5 (78 voted)
Reviews : 93% of readers found this page helpful
Name : Edwin Metz
Birthday : 1997-04-16
Address : 51593 Leanne Light, Kuphalmouth, DE 50012-5183
Phone : +639107620957
Job : Corporate Banking Technician
Hobby : Reading, scrapbook, role-playing games, Fishing, Fishing, Scuba diving, Beekeeping
Introduction : My name is Edwin Metz, I am a fair, energetic, helpful, brave, outstanding, nice, helpful person who loves writing and wants to share my knowledge and understanding with you.
Without advertising income, we can't keep making this site awesome for you.

Tomato Farm Business Plan (PDF, Excel, Word)

Description
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Products and services
- Operation plan
- Market and industry overview
- Sales & marketing plan
- Financial plan
- Risk management plan
- Potential funding sources
PURCHASE NOW
You may also be interested in.

Market research

Business planning

Sales & Marketing
Upcoming workshops.

Import & Export
Financial analysis.


Business Plan for Solar Processing of Tomatoes
This article presents the business plan of the project "Solar Powered Processing of Tomatoes" by TAMPA (Tigray Agricultural Marketing Promotion Agency) and the Sustainable Land Management Program (GIZ SLMP) in Ethiopia.
- 2.1.1 Tomato Paste
- 2.1.2 Tomato Juice / Tomato Sauce
- 2.1.3 Dried Tomatoes
- 2.1.4 Tomato Powder
- 2.2 Marketing Strategy
- 3.1 Raw Material
- 3.2 Washing
- 3.3 Crushing/Mixing
- 3.4 Sieving
- 3.5 Boiling/Evaporating
- 3.6 Cutting / Chopping
- 3.7 Sun drying
- 3.8 Packaging
- 3.9 Sterilization
- 3.10 Transport
- 3.11 Overheads
- 3.12 Production
- 4.1 Investment costs and depreciation
- 4.2 Variable costs per year
- 4.3 Fix costs
- 4.4 Annual turnover
- 4.5 Net profit
- 5 Management Plan
- 6 Further Information
- 7 Reference
Economic development in remote rural areas in Ethiopia can be enhanced by value adding on farmers’ agricultural raw products. Small scale agro processing must lead to consumable end products, which are food safe, conservable, transportable and marketable. Agro processing depends on availability of electrical power, and this is a critical issue: Actually, in 2014, only 14% from the 90 million Ethiopians have access to grid power, and from the rural population (67 million people) only 2 %.
The use of renewable energy from the sun might be an appropriate alternative in remote areas. Many agro processing steps need both thermic energy (heat) and electrical energy (power), both can be obtained from the sunlight. In Tigray, the availability of solar power is reliable and regular in the dry season, when the weather is not cloudy. This period lasts about 9 months in Tigray, from October to June. The tomato season starts around end of November and ends in the month of June. Then, the processing period will last for 7 months = 210 days.
A room of 16 m2 should be sufficient as processing site. It will be built by the farmers’ men power contribution, stones are available onsite and construction material like cement, metal sheets for the roof and a metal door/window as well as tiles will be supplied by the GIZ SLM Program. The solar panel will be placed on a metal stand, which allows daily cleaning to maintain its power for battery charging and processing work. Also, the stand allows turning around of the panel, by adjusting the direction, an optimal output from the sunlight may be obtained in case of need. Special attention will be given to train the processing team in technical aspects of the photovoltaic power system. This includes the handling of the precious inverter, the regular cleaning of the panel and the maintenance of the acid batteries.
In a first phase, the processing activities are limited to tomato processing activities only. In other phases the commercial activities should be extended to oil seeds processing, animal feed production and agro-products packaging, e.g. appropriate honey packaging.
Tomato processing is the core business activity of this micro enterprise. It should help on the one hand tomato farmers of the area to get rid of their excess production in the peak season in January/February against reasonable payment. On the other hand, tomatoes will be value added to long conservable end products like paste, juice/sauce, tomato powder and dried tomato slices.
Turnover in the first phase arises from annual sale of the following commercial products:
- 3,150 kg of fresh tomatoes are processed to 1,260 kg long conservable tomato paste, packed into 3.150 bags of each 200 gram plus 1,260 bags of 500g
- 1,050 kg of fresh tomatoes are processed to 735 liter of tomato juice, packed in 1,470 bottles (‘Highland’) of each 0.5 liters
- 5,000 kg of fresh tomatoes will be sun-dried to 675 kg dried tomato slices, and 75 kg tomato powder, packed into vacuum-sealed polyethylene bags
Marketing Plan
Tomatoes are easily perishable. If fully ripened, they spoil within one-days-time. Processed tomato products have several advantages, they are….
- conservable without cooling
- value added to ready-made healthy and tasty products through crushing, mixing, sieving, cooking, sterilizing and by adding spices
- daily used in nearly every household in Ethiopia for food preparation
- a value added product from traditionally grown tomatoes, harvested over 9 months a year
- easy to cultivate by the farmers and give high yields, over 10 tons/ha
Farmers must aim on selling most of their production as fresh tomatoes. But in case, the price which they get from wholesale is extremely low, it could be partly processed by a micro business located nearby the cultivation site, so that no considerable losses may occur during transport to the processing unit. This is important because tomatoes that are going to be processed need to be as ripe as possible. The processing site does not have a considerable storage capacity for tomatoes. Tomatoes which are purchased by the enterprise from the farmers must be processed within the following 3 days.
The annual processing capacity is around 10 tons, due to a total of 210 sunny days, allowing the 4 solar cookers to process and sterilize about 20 kg of fresh tomatoes a day. A solar dryer of 10 m² (5 m x 2 m) assures the drying of another 5 tons of fresh tomatoes from which the final product will be 675 kg of dried tomato slices and 75 kg of tomato powder.
Competition
Tomato paste.
There is a modern processing factory (‘MERTI”) in South Ethiopia, producing good quality tomato paste. The paste is sold in cans in many shops, also in Tigray. Actually the sales price is ETB 65 for a can of 850 g content. Tomato paste produced by rural micro enterprise will fill a gap by offering smaller quantities for sale, as it meets the customers’ desire: 200 g and 500 g packed in attractive polyethylene bags (PET-bags). These bags have the advantage that its content is visible for the customer (deep red color); they are strong enough to be transported without damaging and they are easy to open by pulling a prepared part of the plastic.
There is also imported tomato paste for sale in the shops. Cans of 400g content cost ETB 33, and small aluminum packs of 70 grams cost ETB 7, in both cases quality is low.
By summarizing, the micro enterprise is able to offer good quality tomato paste, comparable to the competitive product from MERTI. The offered packages meet the demand of the customers for purchase of smaller quantities and the prizes are much lower in comparison to the competitors. Proven by a food quality laboratory in Germany in August 2014, the locally produced paste is a food safe commercial product, sterile and long conservable without cooling (minimum: 5 months). It will be sold to retailers for ETB 12 (200g package) or ETB 25 (500g package). This prize is extremely cheap and unbeatable by other competitors.
Tomato Juice / Tomato Sauce
The second product is pasteurized tomato juice, sold in 500 ml PET-bottles. It is exactly the same product as the tomato paste except its water content is higher: 70% in comparison to 40%. This means the juice can also serve as ready-made tomato sauce, spices (black pepper and salt) are already added during the processing process. Tomato juice can only be found in supermarkets as imported juice, 1 liter costs ETB 60, and its taste appears artificial in comparison to the natural flavor of the locally produced one.
The juice/sauce is pasteurized and conservable for at least 1 month without cooling. The final sales prize to retailers will be 12 birr per 0.5l-bottle (‘highland’).
Dried Tomatoes
Fresh tomatoes are dried in the sun for 3-4 days to reduce the moisture content to a maximum of 15 %. Dried tomatoes are conservable for about 1 year. They will be offered in polyethylene bags of 200 g net weight, each for 10.5 birr.
Tomato Powder
Tomato powder is obtained, when grinding the above mentioned dried tomatoes by mortar or a hammer mill. They will be packed into small polyethylene bags of 30 gram, each will be offered for 5 birr.
Marketing Strategy
The products should be sold within the woreda Kola Tembien. If necessary, they can be sold also in other woredas of Tigray. As the dried tomatoes are sold at a high prize in Addis-Abeba (60 birr for 100 gram), dried tomatoes from Tigray could be surely competitive, as they are offered for 10.5 birr per 200 gram for retailers.
The enterprise must have a distribution point in the woreda capital Abi Adi. This could be any existing shop from where the products are distributed to retailers. They should be brought regularly once in a week (around 50 bottles of juice, plus 150 packages of tomato paste, plus 200 packages of dried tomatoes and tomato powder) during the production period (December to June) from the production site in the field to the distribution point in the town by public transport. The retailers will provide themselves from this point with the products they need for sale in their shops.
Drinking tomato juice is not yet much common in Ethiopia. For that, most of the juice might be purchased and used for preparation of tomato sauce by adding oil, onions and Berbere before bringing it to boil.
A promotion campaign could be considered to offer the tasty natural tomato juice in the numerous juice shops in towns: It could be sold for ETB 8 per glass of juice (250ml) to final consumers in the already existing juice shops.
Production Plan
Tomatoes will be processed from October to June. Depending on sunny days which are essential for the use of solar energy, in the region of Tigray one can estimate the seven-months-period from November/December to May/June as intensive production period. Thus, the micro enterprise will process during 210 days per year.
2 different value chains are involved, as shown below: The liquid tomato processing value chain and the dry processing value chain. Liquid products are tomato paste and tomato juice or tomato sauce. Dried tomatoes are offered as tomato slices and tomato powder.
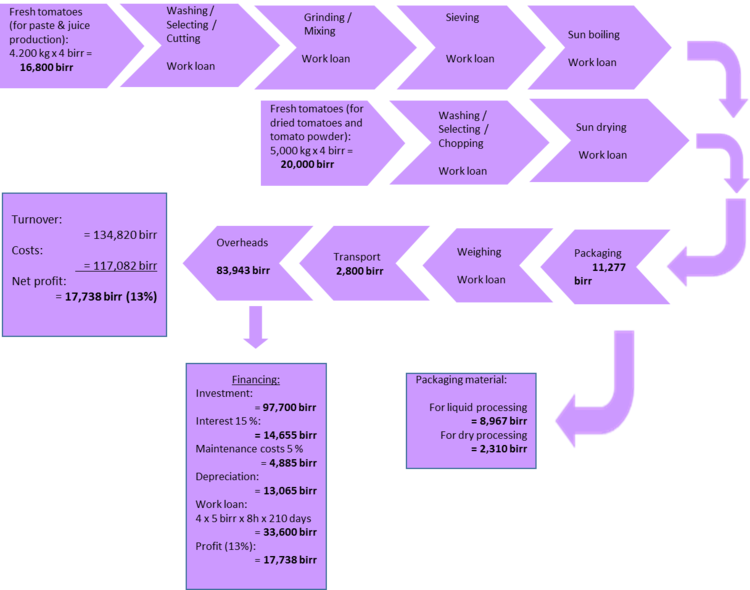
Raw Material
Fresh ripe tomatoes of good quality will be supplied by the surrounding tomato farmers from the village. The enterprise will purchase 44 kg/day for 4 birr/kg starting in December 2014 during 210 days until June. The total amount of 36,800 birr will be paid directly upon delivery to the related tomato farmers
Before being processed, tomatoes will be washed by hand in a water basin with clean water. Cleaned tomatoes will be cut in 2 pieces by knife in order to verify inner quality
Crushing/Mixing
Then filled in an electrical mixer by portions of about 1 kg, crushed and mixed with added spices (salt and pepper).
After spilling the content into a fine metal sieve, the seeds will be separated
Boiling/Evaporating
Around 7 liter of the liquid is spilled in each of 3 black painted cooking pots and brought to boil on 3 solar cookers in a clean and wind protected open site. The boiling process serves to evaporate water: in case of tomato juice/sauce 30 % of water need to be evaporated which takes about 1 hour boiling time. Tomato paste is a more concentrated product: at least 60 % of water need to be evaporated by the force of the sun which takes at least 3 hours per cooking pot of 7 liter content
Cutting / Chopping
Tomatoes which are bound to be dried with the sun dryer are cut in small slices of 0.5 cm each
The slices are exposed to the sun light at an open air sun dryer for around 4 days. The capacity is 100 kg fresh tomatoes, thus around 25 kg/day
Tomato paste will be packed into polyethylene bags and sealed with an electric sealing machine. The bags have 2 different sizes: 200g and 500g content, after filling the bags they are weight in order to determine the net weight allowing exact prize calculation. Tomato juice is filled up to the top into new polyethylene ‘Highland’ bottles of 0.5 liter content at a temperature of at least 60° Celsius, in order to guarantee pasteurization and vacuum packaging. Dried tomatoes are packed as slices in 200g PET-bags and tomato powder in 30 g PET-bags.
Sterilization
One of the 4 solar cookers is permanently boiling water, the tomato paste packages will be sterilized inside for about 30 minutes. This final procedure makes them sterile and long conservable (at least 4 months) without cooling. As the ‘Highland’ bottles are not proved from boiling water, a final bottle sterilization is not possible, which makes them conservable for only 1 month without cooling (3 months by refrigerator cooling, e.g. in juice shops)
The products will be brought to the towns for commercializing by public transport till the distribution point in the woreda capital of Abi Adi. The solid packaging material facilitates transportation on dirt roads without considerable losses
Overheads summarize all fix costs, such like credit/opportunity costs, work loan, maintenance costs, and depreciation and benefit (15%).
During the processing season November to June the total production will be as follows:
Products for commercialization (daily output):
- 20 kg fresh tomatoes for liquid processing = 15 kg for tomato paste + 5 kg for tomato juice. The end products are 6 kg paste + 3.5 litre juice:
= 6 bags of 500g polyethylene bags + 15 bags of 200g polyethylene bags + 7 bottles tomato juice filled into 0.5l new “highland” bottles
- 24 kg of fresh tomatoes for dry processing = 3,240 g dried tomato slices + 360 g tomato powder
= 16 bags of 200g dried tomato slices + 12 bags of 30 g dried tomato powder
Financial plan
Investment costs and depreciation.
The table below shows investment assets, small material, depreciation time and depreciation costs per year.
Variable costs per year
Raw material (fresh tomatoes) : 9,200 kg x 4 birr = 36,800 birr
Packaging costs : 1 role of polyethylene endless tube (Germany), 250 m, 0.6 cm Ø = 420 birr 1 role of polyethylene endless tube (Germany), 250 m, 0.8 cm Ø = 830 birr
30 g package = 0.6 cm Ø x 15 cm = 0.25 birr 200 g package = 0.6 cm Ø x 25 cm = 0.50 birr 500 g package = 0.8 cm Ø x 35 cm = 1.20 birr 1 new polyethylene bottle “Highland”, 0.5 litre = 4 birr
Daily output and packaging material needed: 6 bags of 500 g x 1.2 birr = 7.2 birr (x 210 days = 1,512 birr/year) 15 bags of 200 g x 0.5 birr = 7.5 birr (x 210 days = 1,575 birr/year) 7 bottles of 0.5l juice x 4 birr = 28 birr (x 210 = 5,880 birr/year) Sub-total = 8,967 birr/year
16 bags of 200g dried tomato slices x 0.5 birr = 8 birr (x 210 days = 1,680 birr/year) 12 bags of 30g tomato powder x 0.25 birr = 3.0 birr (x 210 days = 630 birr/year) Sub-total = 2,310 birr/year
Total packaging costs: 11,277 birr/ year
Transport costs : Weekly transport from Tabia Merere to Abi Adi (3 hours by bus) of around 49 bottles of juice (25 kg), plus 150 packages of tomato paste (42 kg), plus 196 packages of dried tomatoes and tomato powder (25 kg) = 92 kg/week x 28 weeks = 2,576 kg/11,760 items. The price for transport of 1 qtl (=100 kg) is around 20 birr. Supposing increased costs for the food items it can be estimated to spend 100 birr for transporting goods of about 100 kg total weight weekly. Transport costs will then be 100 birr x 28 weeks = 2,800 birr per year
Summary variable costs:
Work loan: 4 workers are employed out of the population (landless youth by preference) for 7 months per year. They work daily 8 hours, 5 birr/hour x 210 days (1,200 birr/worker/month). Work loan is considered then as fix cost = 33,600 birr
Credit costs / opportunity costs: As shown in the table above, the investment costs are 97,700 birr. 15% of annual credit costs are considered. Annual credit/opportunity costs are then 14,655 birr
Maintenance costs: 5 % of investment costs = 4,885 birr per year
Depreciation: As shown in the table above = 13,065 birr per year
Profit (net): Net profit (should be around 13 %) = 17,738 birr
Annual turnover
Total turnover = 134,820 birr
17,738 birr (13%)
Management Plan
to be elaborated - only considerations:
Owner of the enterprise could be a cooperative out of the tomato producing farmer households in the tabia (110 households). The micro enterprise is run and managed professionally by 4 employees, by preference landless youth.
All farmers must aim to sell their products as fresh raw products. If the prize per kg drops too low (less than 4 birr/kg), tomatoes should be purchased by the enterprise for processing. But as the processing capacity of the enterprise is limited to around 45 kg per day, the group need to decide on how to share the capacity between the members of the cooperative.
The 4 employees will be trained at start intensively by TAMPA staff for 2 weeks consecutively. During this period of on-the-job-training in (December 2014), the 4 employees get only half of their salary. If farmers do not offer about 40 kg fresh tomatoes because they get better prizes from market sales, the staff needs to be reduced accordingly. The employees are not employed fix, their affordability depends on the daily processing activities.
The cooperative has to provide the running costs for the first month = about 8,500 birr. A bank account is needed as a saving account for depreciation, credit and benefit amounts and other revenues. Petty cash should be available at a save place on the site.
Further Information
- Flyer TAMPA
- Tomato Processing by Solar Energy
- GIZ Sustainable land management, Ethiopia
- Ethiopia Energy Situation
- Energy within Food and Agricultural Value Chains
- PoweringAg Technology Database - Solar Technologies
- Water and Energy for Food (WE4F) portal on energypedia
- German Development Cooperation. Retrieved from www.giz.de
- Financing and Funding
- Productive Use
- Agriculture
- Powering Agriculture
About energypedia
- Introduction
Technologies
- Improved Cooking
Cross Cutting Issues
- Energy Access
- Financing & Funding
- Water & Energy for Food
- Climate Change
- Opportunity
- Publication
- Recent changes
- Browse Help Pages
- Get in Touch With Us
⧼timis-pagehighlighted⧽
Timis-pagehighlighted, ⧼timis-pagenamespaces⧽, ⧼timis-pagetranslate⧽, timis-pagetranslate.
- Enable Google Translate
- View source
Userpage tools
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload File
- Special pages
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- Page information
- Cite this page
- Browse properties
Partners & Networks of energypedia

Sponsors of energypedia

- This page was last edited on 14 July 2020, at 19:11.
- Privacy Policy
- Disclaimers & Terms of Use
Need supply of your products
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Dayoadetiloye.com is a property of Dayo Adetiloye Business Hub committed to connecting entrepreneurs with resources.
We are one stop Business Resource Center where we help you discover, Develop and Fulfil your business potentials.
On this platform, we help you develop business plans and strategies, connect you with funding opportunities and share with your business opportunities.
Facebook Community: https://www.facebook.com/groups/156197005130352/
Twitter: www.twitter.com/dayoadetiloye
Email: [email protected]
Copyright 2024 All Rights Reserved, Dayo Adetiloye
Privacy policy.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A Sample Tomato Processing Plant Business Plan Template. 1. Industry Overview. Just as we stated above, tomato processing plants produce tomato paste, puree, ketchup, juice and sauce. It is important to note that the manufacturing process is made up of the most modern technology of vacuum evaporation through the use of forced circulation ...
Jun 2015 - May 2017. The purpose of Phase 2 is to put our model into action by scaling the nucleus farm, constructing a tomato paste manufacturing facility, and building out the farmer network using the Dami system to provide a constant source of tomatoes for paste. Phase 3: Scale for Growth. Jun 2017 - May 2019.
Processing of tomatoes consists of canning, freezing, dehydration and juice production. Tomatoes are processed into tomato sauce, whole pealed, tomato and onion bruises, paste, shredded, puree and paste concentrate. This article will outline how to start the tomato farming business, and the tomato farming business plan - PDF, Word and Excel.
Tomato farming is an excellent venture for individuals interested in agriculture and seeking a profitable business opportunity. This article aims to provide a comprehensive business plan for tomato farming, covering various aspects from market analysis to production techniques. Whether you are a novice or an experienced farmer, this guide will equip you with the necessary
Analyze production and manufacturing processes. Create a marketing and sales strategy. Identify potential risks and develop risk management strategies. By following these steps, you will be well-equipped to write a solid business plan that sets the foundation for your tomato processing business's success.
3. Our Products and Services. Philip Clinton® Tomato Farms, LLC is a commercial vegetable farm that will be involved in cultivating different species of tomatoes via greenhouse and land farming for both the United States' market and the global market. We are in business to produce tomatoes in commercial quantities.
Starting a Tomato Processing Plant - Sample Business Plan Template. 1. Be Critical With Your Feasibility Studies. You stand to gain a lot if you carry out a critical feasibility studies before you pump in your money to build your own tomato processing plant. You are able to know how to access your raw materials, the best ways to cut cost of ...
TOMATO PROCESSING - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides a business plan for a proposed tomato processing plant in Zambia. It outlines the background of Himuunza Agro Consultancy Company Ltd, which was established in 1975 as a family farm and registered in 1996.
2. Procedure for making tomato powder 2.1 First step: choosing the tomatoes • Select tomatoes that are ripe, red, have a firm texture and are free of disease and mould. 2.2 Second step: washing • Wash the freshly harvested tomatoes in clean water in a large bucket. 2.3 Third step: slicing • Cut tomatoes into slices 0.5 cm thick.
• Procurement of tomatoes. • Firstly, washing of tomatoes and then sort the good quality tomatoes. • After that put the chopped tomato into the twin pulper, which separate seeds, skins, and stems from the pulp. • Cooking & add ingredients: Then the pulp is pumped into cooking tanks or kettles and heated to boiling.
The global tomato processing market reached a volume of around 34 Million Tons in 2016. A number of factors are currently driving the growth of this market. These include changing food habits, rising incomes, urbanisation, emerging markets, growing consumption of fast foods especially by youngsters, etc. Tomato processing in India is still not ...
1 main use of the product (dried, fresh, for direct use or sale) 2 months in which sowing and planting takes place. 3 annual rainfall in mm. 4 the dry months. 5 minimum and maxi mum temperat ures ...
At the optimum soil or growth media temperatures of 20 to 30 ̊C it will take tomato seeds 6 -8 days to germinate. At temperatures ranges of 0-5 ̊C, 40 ̊C and above no germination is expected with seed being dormant. Table 2: The effect of soil temperature on seedling emergence. Soil Temperatures ( ̊C) 0. 5.
A step-by-step guide to starting a Tomato farm business plan for beginners. Step 1: Business goals. Step 2: Market research. Step 3: Business plan. Step 4: Business identity. Step 5: Marketing. Tomato yield per hectare. Conclusion. Tomato is one of the world's most essential and widely grown food crops.
Abstract- The aim of this article is to device strategies for. establishing and managing tomato processing industry, w hich. aims to e nhance t he taste ex periences on different tomato. products ...
The operational plan outlines the day-to-day activities and processes involved in running your tomato greenhouse business. Define your production schedule, quality control measures, equipment maintenance, and record-keeping procedures. Focus on operational efficiency to maximize productivity and minimize costs.
market segments for tomatoes is the open air retail market and a much smaller, but growing, supermarket channel. Given Moldova's history of tomato production and the existing domestic market demand for tomatoes, opportunities for import substitution exist when local growers can offer an improved quality and extend their growing season.
Our budget for key insurance policies, permits and business license - $4,000. The cost of acquiring/leasing our facility and land - $55,000. The budget for preparing our plant- $25,000. The price for acquiring the required working tools and equipment/machines/tractors et al- $600,000.
This business plan provides a blueprint for how to start and manage your Tomato Farm business. Our detailed research and analysis, including interviews with entrepreneurs and stakeholders, will ensure that you plan your future business for success. A business plan is used for various purposes including to (a) Raise funding from investors ...
Tomato Paste Production Business Plan - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Tomato paste production business plan for a factory in Nigeria. The factory will produce double concentrated tomato paste from 500kg/h of fresh tomatoes using a cold break method. Nigeria is currently the largest tomato producer in Africa but imports $1 ...
20 kg fresh tomatoes for liquid processing = 15 kg for tomato paste + 5 kg for tomato juice. The end products are 6 kg paste + 3.5 litre juice: = 6 bags of 500g polyethylene bags + 15 bags of 200g polyethylene bags + 7 bottles tomato juice filled into 0.5l new "highland" bottles. 24 kg of fresh tomatoes for dry processing = 3,240 g dried ...
This survey is conducted in order to investigate business viability and create a detailed business plan to realize our expectations. 1.2 Survey area We chose the Republic of Senegal (hereinafter referred to as "Senegal") for the project. The target area was the northern region of the Senega l River basin.
To achieve net profit of $60,000 in four years. To boost image and awareness by establishing baseline customer satisfaction of 100%. Goal for the Tin Tomato Paste Production Business Plan in Nigeria. To become one of the leading brands in the Tomato farming business in the South West, and also to be amongst the top 5 Tomato Farmers in Nigeria ...