Risk Management 101: Process, Examples, Strategies
Emily Villanueva
August 16, 2023
Effective risk management takes a proactive and preventative stance to risk, aiming to identify and then determine the appropriate response to the business and facilitate better decision-making. Many approaches to risk management focus on risk reduction, but it’s important to remember that risk management practices can also be applied to opportunities, assisting the organization with determining if that possibility is right for it.
Risk management as a discipline has evolved to the point that there are now common subsets and branches of risk management programs, from enterprise risk management (ERM) , to cybersecurity risk management, to operational risk management (ORM) , to supply chain risk management (SCRM) . With this evolution, standards organizations around the world, like the US’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the International Standards Organization (ISO) have developed and released their own best practice frameworks and guidance for businesses to apply to their risk management plan.
Companies that adopt and continuously improve their risk management programs can reap the benefits of improved decision-making, a higher probability of reaching goals and business objectives, and an augmented security posture. But, with risks proliferating and the many types of risks that face businesses today, how can an organization establish and optimize its risk management processes? This article will walk you through the fundamentals of risk management and offer some thoughts on how you can apply it to your organization.


What Are Risks?
We’ve been talking about risk management and how it has evolved, but it’s important to clearly define the concept of risk. Simply put, risks are the things that could go wrong with a given initiative, function, process, project, and so on. There are potential risks everywhere — when you get out of bed, there’s a risk that you’ll stub your toe and fall over, potentially injuring yourself (and your pride). Traveling often involves taking on some risks, like the chance that your plane will be delayed or your car runs out of gas and leave you stranded. Nevertheless, we choose to take on those risks, and may benefit from doing so.
Companies should think about risk in a similar way, not seeking simply to avoid risks, but to integrate risk considerations into day-to-day decision-making.
- What are the opportunities available to us?
- What could be gained from those opportunities?
- What is the business’s risk tolerance or risk appetite – that is, how much risk is the company willing to take on?
- How will this relate to or affect the organization’s goals and objectives?
- Are these opportunities aligned with business goals and objectives?
With that in mind, conversations about risks can progress by asking, “What could go wrong?” or “What if?” Within the business environment, identifying risks starts with key stakeholders and management, who first define the organization’s objectives. Then, with a risk management program in place, those objectives can be scrutinized for the risks associated with achieving them. Although many organizations focus their risk analysis around financial risks and risks that can affect a business’s bottom line, there are many types of risks that can affect an organization’s operations, reputation, or other areas.
Remember that risks are hypotheticals — they haven’t occurred or been “realized” yet. When we talk about the impact of risks, we’re always discussing the potential impact. Once a risk has been realized, it usually turns into an incident, problem, or issue that the company must address through their contingency plans and policies. Therefore, many risk management activities focus on risk avoidance, risk mitigation, or risk prevention.
What Different Types of Risks Are There?
There’s a vast landscape of potential risks that face modern organizations. Targeted risk management practices like ORM and SCRM have risen to address emerging areas of risk, with those disciplines focused on mitigating risks associated with operations and the supply chain. Specific risk management strategies designed to address new risks and existing risks have emerged from these facets of risk management, providing organizations and risk professionals with action plans and contingency plans tailored to unique problems and issues.
Common types of risks include: strategic, compliance, financial, operational, reputational, security, and quality risks.
Strategic Risk
Strategic risks are those risks that could have a potential impact on a company’s strategic objectives, business plan, and/or strategy. Adjustments to business objectives and strategy have a trickle-down effect to almost every function in the organization. Some events that could cause strategic risks to be realized are: major technological changes in the company, like switching to a new tech stack; large layoffs or reductions-in-force (RIFs); changes in leadership; competitive pressure; and legal changes.
Compliance Risk
Compliance risks materialize from regulatory and compliance requirements that businesses are subject to, like Sarbanes-Oxley for publicly-traded US companies, or GDPR for companies that handle personal information from the EU. The consequence or impact of noncompliance is generally a fine from the governing body of that regulation. These types of risks are realized when the organization does not maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, whether those requirements are environmental, financial, security-specific, or related to labor and civil laws.
Financial Risk
Financial risks are fairly self-explanatory — they have the possibility of affecting an organization’s profits. These types of risks often receive significant attention due to the potential impact on a company’s bottom line. Financial risks can be realized in many circumstances, like performing a financial transaction, compiling financial statements, developing new partnerships, or making new deals.
Operational Risk
Risks to operations, or operational risks, have the potential to disrupt daily operations involved with running a business. Needless to say, this can be a problematic scenario for organizations with employees unable to do their jobs, and with product delivery possibly delayed. Operational risks can materialize from internal or external sources — employee conduct, retention, technology failures, natural disasters, supply chain breakdowns — and many more.
Reputational Risk
Reputational risks are an interesting category. These risks look at a company’s standing in the public and in the media and identify what could impact its reputation. The advent of social media changed the reputation game quite a bit, giving consumers direct access to brands and businesses. Consumers and investors too are becoming more conscious about the companies they do business with and their impact on the environment, society, and civil rights. Reputational risks are realized when a company receives bad press or experiences a successful cyber attack or security breach; or any situation that causes the public to lose trust in an organization.
Security Risk
Security risks have to do with possible threats to your organization’s physical premises, as well as information systems security. Security breaches, data leaks, and other successful types of cyber attacks threaten the majority of businesses operating today. Security risks have become an area of risk that companies can’t ignore, and must safeguard against.
Quality Risk
Quality risks are specifically associated with the products or services that a company provides. Producing low-quality goods or services can cause an organization to lose customers, ultimately affecting revenue. These risks are realized when product quality drops for any reason — whether that’s technology changes, outages, employee errors, or supply chain disruptions.
Steps in the Risk Management Process
The six risk management process steps that we’ve outlined below will give you and your organization a starting point to implement or improve your risk management practices. In order, the risk management steps are:
- Risk identification
- Risk analysis or assessment
- Controls implementation
- Resource and budget allocation
- Risk mitigation
- Risk monitoring, reviewing, and reporting
If this is your organization’s first time setting up a risk management program, consider having a formal risk assessment completed by an experienced third party, with the goal of producing a risk register and prioritized recommendations on what activities to focus on first. Annual (or more frequent) risk assessments are usually required when pursuing compliance and security certifications, making them a valuable investment.
Step 1: Risk Identification
The first step in the risk management process is risk identification. This step takes into account the organization’s overarching goals and objectives, ideally through conversations with management and leadership. Identifying risks to company goals involves asking, “What could go wrong?” with the plans and activities aimed at meeting those goals. As an organization moves from macro-level risks to more specific function and process-related risks, risk teams should collaborate with critical stakeholders and process owners, gaining their insight into the risks that they foresee.
As risks are identified, they should be captured in formal documentation — most organizations do this through a risk register, which is a database of risks, risk owners, mitigation plans, and risk scores.

Step 2: Risk Analysis or Assessment
Analyzing risks, or assessing risks, involves looking at the likelihood that a risk will be realized, and the potential impact that risk would have on the organization if that risk were realized. By quantifying these on a three- or five-point scale, risk prioritization becomes simpler. Multiplying the risk’s likelihood score with the risk’s impact score generates the risk’s overall risk score. This value can then be compared to other risks for prioritization purposes.
The likelihood that a risk will be realized asks the risk assessor to consider how probable it would be for a risk to actually occur. Lower scores indicate less chances that the risk will materialize. Higher scores indicate more chances that the risk will occur.
Likelihood, on a 5×5 risk matrix, is broken out into:
- Highly Unlikely
- Highly Likely
The potential impact of a risk, should it be realized, asks the risk assessor to consider how the business would be affected if that risk occurred. Lower scores signal less impact to the organization, while higher scores indicate more significant impacts to the company.
Impact, on a 5×5 risk matrix, is broken out into:
- Negligible Impact
- Moderate Impact
- High Impact
- Catastrophic Impact
Risk assessment matrices help visualize the relationship between likelihood and impact, serving as a valuable tool in risk professionals’ arsenals.
Organizations can choose whether to employ a 5×5 risk matrix, as shown above, or a 3×3 risk matrix, which breaks likelihood, impact, and aggregate risk scores into low, moderate, and high categories.
Step 3: Controls Assessment and Implementation
Once risks have been identified and analyzed, controls that address or partially address those risks should be mapped. Any risks that don’t have associated controls, or that have controls that are inadequate to mitigate the risk, should have controls designed and implemented to do so.
Step 4: Resource and Budget Allocation
This step, the resource and budget allocation step, doesn’t get included in a lot of content about risk management. However, many businesses find themselves in a position where they have limited resources and funds to dedicate to risk management and remediation. Developing and implementing new controls and control processes is timely and costly; there’s usually a learning curve for employees to get used to changes in their workflow.
Using the risk register and corresponding risk scores, management can more easily allocate resources and budget to priority areas, with cost-effectiveness in mind. Each year, leadership should re-evaluate their resource allocation as part of annual risk lifecycle practices.
Step 5: Risk Mitigation
The risk mitigation step of risk management involves both coming up with the action plan for handling open risks, and then executing on that action plan. Mitigating risks successfully takes buy-in from various stakeholders. Due to the various types of risks that exist, each action plan may look vastly different between risks.
For example, vulnerabilities present in information systems pose a risk to data security and could result in a data breach. The action plan for mitigating this risk might involve automatically installing security patches for IT systems as soon as they are released and approved by the IT infrastructure manager. Another identified risk could be the possibility of cyber attacks resulting in data exfiltration or a security breach. The organization might decide that establishing security controls is not enough to mitigate that threat, and thus contract with an insurance company to cover off on cyber incidents. Two related security risks; two very different mitigation strategies.
One more note on risk mitigation — there are four generally accepted “treatment” strategies for risks. These four treatments are:
- Risk Acceptance: Risk thresholds are within acceptable tolerance, and the organization chooses to accept this risk.
- Risk Transfer : The organization chooses to transfer the risk or part of the risk to a third party provider or insurance company.
- Risk Avoidance : The organization chooses not to move forward with that risk and avoids incurring it.
- Risk Mitigation : The organization establishes an action plan for reducing or limiting risk to acceptable levels.
If an organization is not opting to mitigate a risk, and instead chooses to accept, transfer, or avoid the risk, these details should still be captured in the risk register, as they may need to be revisited in future risk management cycles.
Step 6: Risk Monitoring, Reviewing, and Reporting
The last step in the risk management lifecycle is monitoring risks, reviewing the organization’s risk posture, and reporting on risk management activities. Risks should be monitored on a regular basis to detect any changes to risk scoring, mitigation plans, or owners. Regular risk assessments can help organizations continue to monitor their risk posture. Having a risk committee or similar committee meet on a regular basis, such as quarterly, integrates risk management activities into scheduled operations, and ensures that risks undergo continuous monitoring. These committee meetings also provide a mechanism for reporting risk management matters to senior management and the board, as well as affected stakeholders.
As an organization reviews and monitors its risks and mitigation efforts, it should apply any lessons learned and use past experiences to improve future risk management plans.
Examples of Risk Management Strategies
Depending on your company’s industry, the types of risks it faces, and its objectives, you may need to employ many different risk management strategies to adequately handle the possibilities that your organization encounters.
Some examples of risk management strategies include leveraging existing frameworks and best practices, minimum viable product (MVP) development, contingency planning, root cause analysis and lessons learned, built-in buffers, risk-reward analysis, and third-party risk assessments.
Leverage Existing Frameworks and Best Practices
Risk management professionals need not go it alone. There are several standards organizations and committees that have developed risk management frameworks, guidance, and approaches that business teams can leverage and adapt for their own company.
Some of the more popular risk management frameworks out there include:
- ISO 31000 Family : The International Standards Organization’s guidance on risk management.
- NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) : The National Institute of Standards and Technology has released risk management guidance compatible with their Cybersecurity Framework (CSF).
- COSO Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) : The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations’ enterprise risk management guidance.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Development
This approach to product development involves developing core features and delivering those to the customer, then assessing response and adjusting development accordingly. Taking an MVP path reduces the likelihood of financial and project risks, like excessive spend or project delays by simplifying the product and decreasing development time.
Contingency Planning
Developing contingency plans for significant incidents and disaster events are a great way for businesses to prepare for worst-case scenarios. These plans should account for response and recovery. Contingency plans specific to physical sites or systems help mitigate the risk of employee injury and outages.
Root Cause Analysis and Lessons Learned
Sometimes, experience is the best teacher. When an incident occurs or a risk is realized, risk management processes should include some kind of root cause analysis that provides insights into what can be done better next time. These lessons learned, integrated with risk management practices, can streamline and optimize response to similar risks or incidents.
Built-In Buffers
Applicable to discrete projects, building in buffers in the form of time, resources, and funds can be another viable strategy to mitigate risks. As you may know, projects can get derailed very easily, going out of scope, over budget, or past the timeline. Whether a project team can successfully navigate project risks spells the success or failure of the project. By building in some buffers, project teams can set expectations appropriately and account for the possibility that project risks may come to fruition.
Risk-Reward Analysis
In a risk-reward analysis, companies and project teams weigh the possibility of something going wrong with the potential benefits of an opportunity or initiative. This analysis can be done by looking at historical data, doing research about the opportunity, and drawing on lessons learned. Sometimes the risk of an initiative outweighs the reward; sometimes the potential reward outweighs the risk. At other times, it’s unclear whether the risk is worth the potential reward or not. Still, a simple risk-reward analysis can keep organizations from bad investments and bad deals.
Third-Party Risk Assessments
Another strategy teams can employ as part of their risk management plan is to conduct periodic third-party risk assessments. In this method, a company would contract with a third party experienced in conducting risk assessments, and have them perform one (or more) for the organization. Third-party risk assessments can be immensely helpful for the new risk management team or for a mature risk management team that wants a new perspective on their program.
Generally, third-party risk assessments result in a report of risks, findings, and recommendations. In some cases, a third-party provider may also be able to help draft or provide input into your risk register. As external resources, third-party risk assessors can bring their experience and opinions to your organization, leading to insights and discoveries that may not have been found without an independent set of eyes.
Components of an Effective Risk Management Plan
An effective risk management plan has buy-in from leadership and key stakeholders; applies the risk management steps; has good documentation; and is actionable. Buy-in from management often determines whether a risk management function is successful or not, since risk management requires resources to conduct risk assessments, risk identification, risk mitigation, and so on. Without leadership buy-in, risk management teams may end up just going through the motions without the ability to make an impact. Risk management plans should be integrated into organizational strategy, and without stakeholder buy-in, that typically does not happen.
Applying the risk management methodology is another key component of an effective plan. That means following the six steps outlined above should be incorporated into a company’s risk management lifecycle. Identifying and analyzing risks, establishing controls, allocating resources, conducting mitigation, and monitoring and reporting on findings form the foundations of good risk management.
Good documentation is another cornerstone of effective risk management. Without a risk register recording all of a company’s identified risks and accompanying scores and mitigation strategies, there would be little for a risk team to act on. Maintaining and updating the risk register should be a priority for the risk team — risk management software can help here, providing users with a dashboard and collaboration mechanism.
Last but not least, an effective risk management plan needs to be actionable. Any activities that need to be completed for mitigating risks or establishing controls, should be feasible for the organization and allocated resources. An organization can come up with the best possible, best practice risk management plan, but find it completely unactionable because they don’t have the capabilities, technology, funds, and/or personnel to do so. It’s all well and good to recommend that cybersecurity risks be mitigated by setting up a 24/7 continuous monitoring Security Operations Center (SOC), but if your company only has one IT person on staff, that may not be a feasible action plan.
Executing on an effective risk management plan necessitates having the right people, processes, and technology in place. Sometimes the challenges involved with running a good risk management program are mundane — such as disconnects in communication, poor version control, and multiple risk registers floating around. Risk management software can provide your organization with a unified view of the company’s risks, a repository for storing and updating key documentation like a risk register, and a space to collaborate virtually with colleagues to check on risk mitigation efforts or coordinate on risk assessments. Get started building your ideal risk management plan today!

Emily Villanueva, MBA, is a Senior Manager of Product Solutions at AuditBoard. Emily joined AuditBoard from Grant Thornton, where she provided consulting services specializing in SOX compliance, internal audit, and risk management. She also spent 5 years in the insurance industry specializing in SOX/ICFR, internal audits, and operational compliance. Connect with Emily on LinkedIn .
Related Articles

How to Make Risk Management Presentations Engaging and Actionable Across Your Organization

Life is full of risk. We face risks from the moment we wake up in the morning until we fall asleep at night. Will the alarm fail to sound? Will I get into a car accident on my way to work? Will I catch a virus when I go to dinner? Heck, there’s a risk— no matter how small— that we will die in our sleep during each night.
Risk is simply an inherent element of everything we do, and business is no exception. Will a vital employee quit, or will there be a labor shortage? What will happen in the stock market, and how will it impact the economy? What if there is an accident or a lawsuit involving the company? What happens if a new product fails? What actions will be taken in the event of a security breach or equipment failure?
We might not be able to prevent risk, but we can manage it. Managing business risk requires identifying and understanding risks while seeking ways to reduce risk in a way that also supports other business goals.
Companies heavily invest every year in ways to mitigate and respond to risk. But how do they make sure everyone is on board?
There might be a variety of ways to communicate a risk management plan to all the relevant players, but a visual presentation can be effective in not only presenting the risk management plan, but also ensuring that it is engaging and actionable across your organization.
What to include when you prepare a risk management plan:
A written risk management plan for business should not only include a listing of possible risks, but it also should feature plans to manage risk and respond to incidents.
- Identify risks
Risk management refers to a variety of business aspects, both internal weaknesses, and external threats. Like much in life, knowing is half the battle, and therefore identifying risks is key in addressing them.
Risk management should be considered before embarking on any new task or project, and everyone connected to a business should be encouraged to identify additional risks. Not only should the risk itself be considered, but companies also should identify possible consequences to better prepare to address each one.
- Minimize risks
A variety of strategies are available to manage and minimize risks once they are identified. One popular method of mitigating risk involves the 4Ts:
- Transfer risk by assigning a responsible team or party to each identified risk.
- Tolerate risk by monitoring it before taking further action.
- Treat risk by taking actions that reduce the likelihood that it will occur.
- Terminate risk by adopting or amending processes that eliminate it.
- Assign roles
Staff members should be assigned to each potential risk or risk category. These individuals will be responsible for mitigating their assigned risks, as well as reporting and responding to applicable incidents. A list of these roles should be included in the risk management plan.
- Plan recovery
Each risk included in the management plan must be followed by a strategy for preventing and addressing issues. An effective risk management plan will include a compilation of business projects, the risk applicable to each and an operational plan to respond and recover from incidents. Part of that plan also should include updating mitigation efforts following an incident to prevent it from repeating.
- Communicate plan
A risk management plan can’t be effective unless everyone within a company is on board. In addition to presenting the plan to principle players, be sure that it is also published somewhere that the full risk management plan can be accessed and understood by anyone within the company at any time.
- Rinse and repeat
The most effective risk management plans are living documents, continually updated with new or changed risks and new strategies to address them. Each risk outlined in the plan should be periodically reevaluated and new risks identified. The plan also should be monitored along with staff turnover to ensure no tasks fall through the cracks.
Tips to make risk management presentations engaging and actionable across your organization:
Audience engagement is vital to a successful risk management training presentation. After all, if staff and executives are asleep they will hardly become familiar with the plan and their assigned roles.
- Include visual assets
About 90 percent of human thought is visually-based. Therefore, it’s no shocker that including visual assets within a presentation is one of the most effective strategies for engaging all types of audiences .
Releasing the risk management plan through a visual presentation is a great start, but the content within the slide deck is just as important. After all, the average PowerPoint slide includes 40 words , which is entirely too many. Instead, include more images, videos and animations within a financial risk management presentation or any other risk management training presentations.
- Illustrate data
Data is one of the most convincing sorts of content that can be presented to an audience. As anyone can attest— at least in most cases— numbers don’t lie. In fact, they can tell their own stories. A crowded slide full of stats and figures is a quick way to send your audience off to Dreamland.
Instead, illustrate your data through infographics. Beautiful.ai offers a host of various infographics through our smart slide templates. Just input your data and watch our artificial intelligence-powered presentation software design the infographic accordingly. Choose from infographics like scattergraphs , process diagrams , pie charts and bar graphs to tell the story of different risks and strategies to address them.
- Tell a story
According to the 2018 State of Attention survey, almost 90 percent of respondents said a strong narrative or story backing a presentation is critical in maintaining audience engagement. Sure, facts and data can persuade audiences and get them on board, but only if people are paying attention.
Stories have kept audiences engaged since before recorded history. Tell the story of your risk management plan by including real-life examples or by creating a character for hypothetical scenarios. Those unsure how to incorporate a story into the structure of their presentation can look to Beautiful.ai’s various presentation templates for inspiration.
- Include your audience
If you really want to keep your audience engaged with your risk management presentation slides, be sure you talk with people, not at them. Include your audience in your presentation by asking questions, taking surveys or presenting group activities. Of course, the first step is identifying who makes up that audience. You won’t necessarily present the same content to an executive board as to a room full of new hires.
One effective way to engage an audience with a risk management plan presentation from the very start is through a pre-presentation quiz or survey that gauges how much participants already know about risk management, like this example from the U.S. Small Business Association. Not only will the activity engage the audience, but it will alert participants to what they don’t know from the very start. Other engagement tools include Q&A sessions, humor and gamification.
As mentioned, the average PowerPoint slide consists of 40 words… way too many to keep audiences engaged. Remember, your presentation should be based on an outline of your plan, not a verbatim recitation of it.
Not only are uncluttered slides more effective, but shorter presentations also are more effective than longer ones, based on both audience attention and respect for time. Especially when delivering a risk management board presentation, it’s vital to respect your audience’s time. Beautiful.ai’s library of presentation templates can serve as a guideline to effective presentation lengths for a variety of topics.

Samantha Pratt Lile
Samantha is an independent journalist, editor, blogger and content manager. Examples of her published work can be found at sites including the Huffington Post, Thrive Global, and Buzzfeed.
Recommended Articles
Tips for running a successful webinar, real estate marketing strategies to improve listings and close more deals, how to craft a thought leadership marketing strategy to become a subject matter expert, what is cross channel marketing and how to lead your team to do it successfully.

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Introduction To Risk Management Powerpoint Presentation Slides
Demonstrate that you are genuinely a champion with our Introduction To Risk Management Powerpoint Presentation Slides. You will definitely earn the garlands.

These PPT Slides are compatible with Google Slides
Compatible With Google Slides

- Google Slides is a new FREE Presentation software from Google.
- All our content is 100% compatible with Google Slides.
- Just download our designs, and upload them to Google Slides and they will work automatically.
- Amaze your audience with SlideTeam and Google Slides.
Want Changes to This PPT Slide? Check out our Presentation Design Services
Get Presentation Slides in WideScreen
Get This In WideScreen
- WideScreen Aspect ratio is becoming a very popular format. When you download this product, the downloaded ZIP will contain this product in both standard and widescreen format.

- Some older products that we have may only be in standard format, but they can easily be converted to widescreen.
- To do this, please open the SlideTeam product in Powerpoint, and go to
- Design ( On the top bar) -> Page Setup -> and select "On-screen Show (16:9)” in the drop down for "Slides Sized for".
- The slide or theme will change to widescreen, and all graphics will adjust automatically. You can similarly convert our content to any other desired screen aspect ratio.
- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
Do you want to remove this product from your favourites?
PowerPoint presentation slides
Presenting this set of slides with name - Introduction To Risk Management Powerpoint Presentation Slides. This is a one stage process. The stages in this process are Introduction To Risk Management, Risk Management Overview, Risk Management Outline.
People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- Business Slides , Flat Designs , Strategic Planning Analysis , Complete Decks , All Decks , Risk Management , General , Management , Risk Management
- Introduction To Risk Management ,
- Risk Management Overview ,
- Risk Management Outline
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1 : This slide presents Introduction To Risk Management with imagery. State Your Company Name and get started. Slide 2 : This slide presents Risk Management- Introduction with the following content- Minimize, Monitor, Control, Probability and / or impact of unfortunate events, Realization of opportunities, Maximize Resources, Identification of Risks, Prioritization of Risks, Assessment of Risks. This is a framework showing the outcome of risk management for a firm which involves minimizing, monitoring & controlling unfavorable events and maximizing the opportunities. Slide 3 : This slide presents Types Of Risks segregated as- External Risks (Demand, Regulatory, Economical, Socio- Political, Environment). Internal Risks Enablers: (People, Financial, Technology, Infrastructure). Operational: (Access to Services, Processes, Business Interruption, Emergency response). Strategic: (Governance, Strategic Planning, Ethics & Values, Stakeholder Relations) Slide 4 : This slide also presents a detailed Types Of Risks for- Strategic: Demand shortfall, Customer Retention, Integration problems, Pricing Pressure, Regulation, R&D, Industry or sector downturn, JV or partner losses. Operational: Cost overrun, Operating controls, Poor capacity management, Supply chain issues, Employee issues incl. fraud, Bribery & Corruption, Regulation, Commodity prices. Hazard: Macroeconomic, Political issues, Legal issues, Terrorism, Natural disasters. Financial: Debt & Interest Rates, Poor financial management, Asset issues, Goodwill & amortisation, Accounting problems. Below are four broad categories of risk and the various factors associated with the same. You can modify them as per your needs. Slide 5 : This slide displays Risk Categories for- System/ Software Product Design Manufacturing Quality Project Management All Other We have mentioned the six broad categories of risk and few factors associated with them. You can alter them as per your requirements. Slide 6 : This slide presents Identify The Risk Categories in tabular form- Risk Score By Risk Category Risk Category Risk Sub-Category in terms of Likelihood & Risk Level Once you have listed down the risk categories. Identify the level of risk associated with each one of them. Slide 7 : This slide presents Stakeholders Risk Appetite graph in terms of- Likelihood and Impact. Obtain an estimate of the risk appetite of the shareholders with the help of the below bar graph. This will help in assessing the acceptable risk level. Slide 8 : This is the first slide on Risk Tolerance. Estimate the Risk tolerance level of the stakeholders on the basis of the below mentioned criteria. You can modify these as per your requirements. Slide 9 : This is the second slide on Risk Tolerance. Below is a heat map showing the risk tolerance limit of the stakeholders, where the redline shows the boundary between risks that are acceptable & those that are not. Slide 10 : This slide shows a Risk Assessment Plan with- Business Name, ABN, Activity, Steps, Potential Hazards/ Risks, Risk Rating, Risk Control Measures, Risk Rating, Person Responsible, Time Frame. Slide 11 : This is Introduction To Risk Management Icon Slide. Use icons as per your need. Slide 12 : This is a Coffee break slide to halt. You can change the slide content as per need. Slide 13 : This slide is titled Charts & Graphs to move forward. Slide 14 : This is a Bar Chart slide. State specifications, comparison of products/entities here. Slide 15 : This is a Line Chart slide. State specifications, comparison of products/entities here. Slide 16 : This is an Area Chart slide. State specifications, comparison of products/entities here. Slide 17 : This slide is titled Additional Sides to move forward. You can change the slide content as per need. Slide 18 : This is Our Mission slide with Mission and Goals. State them here. Slide 19 : This slide presents Our Team with name, designation and image box. Slide 20 : This is a Comparison slide to show comparison, information etc. Slide 21 : This is a Financial score slide in terms of minimum, medium and maximum. State financial aspects here. Slide 22 : This is a Timeline slide to show milestone, growth highlights, evolution etc. Slide 23 : This is a Magnifying glass image slide. State specifications, information here. Slide 24 : This is a Bulb/Idea image slide. State specifications, information, innovative aspects here. Slide 25 : This is a Thank You slide with Address, Street number, city, state, Contact Numbers, Email Address.
Introduction To Risk Management Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 25 slides:
Display genuine interest in identifying the cause with our Introduction To Risk Management Powerpoint Presentation Slides. Be able to investigate the incident.

Ratings and Reviews
by Amal Al Jardani
November 12, 2022
by Connor Lopez
July 19, 2021
by Liam Perez
July 18, 2021

Risk Management Training Presentation
Duration: 20 minutes | format: editable ppt/pdf.
Whether we are driving to work, crossing the road, investing in financial products, or making a change in our lifestyle, risk is all around us. In an increasingly fast-paced world, the risk we have to manage is constantly evolving.
In the corporate world, risk management involves understanding and analysing risk to ensure that organisations meet their objectives.
Our free training aid is a short, interactive presentation that you can use to teach your employees all about risk management and the role they play in controlling risk across your organisation.

- What is risk?
- What is risk management?
- The types of risk
- Assessing and managing risk
- Company and employee responsibilities
Download this free training aid
Share this training aid.
Home Blog Business Risk Management Techniques
Risk Management Techniques

Risk and business cannot be separated! For an entrepreneur, the possibility of a loss is as real as the possibility of profitability; what lies in between the two is risk. In simple terms, the risk is the possibility of loss for a business, with financial implications. There are risks that are avoidable and risks that need to be better managed to reduce the likelihood of negative consequences.
Basic Elements of Risk Management
Risk management is the identification, assessment, and controlling of risks. Businesses around the world plan and spend a significant amount of money in managing risks. However, risk management has implications beyond business. Risk management is applicable for businesses and disaster management and can even be used by an individual at the household level . The latter can be a form of financial management, retirement-related risks, and identification of financial shocks that can affect a household.
Risk management broadly has five basic elements, covering the structure of how it can be incorporated for anticipating and controlling risks.
1. Identify Threats
In order to anticipate and manage risks, one must first identify what might be deemed as a risk. For a business, it can include the possibility of financial loss, an injury to an employee, the possibility of a lawsuit, accidents affecting customers, etc. These risks can arise due to a number of factors, be it economic conditions of a country, competition from competitors, lack of safety measures at the workplace for employees, faulty products, and the like.
2. Assess Vulnerability of Critical Assets
The next step includes an evaluation and assessment of risks. This is to identify the vulnerability of critical assets due to the risk. For example, if there is a production process that can lead to an employee’s injury or death, there seems to be a high probability of such an accident occurring. Such a process needs to be changed or replaced.
3. Determine the Threat the Risk Poses
Different risks can pose different types of threats. An injury caused due to a hazardous production process can lead to a lawsuit by the employee, cause reputation damage, and might even lead to a decline in sales due to bad reputation.
4. Reducing Risks
There are several ways that businesses can reduce risks. If a production process has the potential to cause harm, it might be worth revising how the process is carried out or finding alternative methods for performing certain tasks to make the process safe. There might even be a need for safety equipment or machinery and regular equipment inspection and maintenance that can help manage such a risk in a better way by reducing the probability of an accident. Some risks however can be hard to reduce. This might include accounting for an economic meltdown, economic policy changes due to a change of government in a country, or viz majors like the COVID-19 pandemic or an unforeseen natural disaster.
5. Risk Reduction Measures
Risks can be categorized, (e.g., low, medium, or high). It isn’t necessary for a business to try to manage all types of risks, since the possibility of some risks might be negligible, and committing resources for them might be very expensive. Risk reduction is a process that cannot be viewed in isolation. Organizations need to perpetually monitor risks and account for course correction if and when necessary.
Managing Different Types of Risks
Risk management entails various types of strategies, such as risk reduction, risk avoidance, risk sharing, and risk retaining. We covered these strategies in detail in our previous post about risk management and risk assessment . In the section below, we will provide you with examples of different types of risks a business might face and what can be a few ways of managing such risks.
Market Risk
When it comes to imagining risks, investors usually consider the term synonymous with market risk. Market risk is the possibility of investors losing money due to a decrease in the value of their investment. The most common strategy for investors to manage market risk is by diversifying investment portfolios to avoid tying too many assets in a single business entity. Furthermore, buying at various intervals and investing in less correlated investments, such as real estate, bonds, and other commodities can be another method to avoid market risks.
Inflation Risk
Inflation can affect a business in a number of ways. The cost of inputs can suddenly rise, whereas a business engaged in export of goods can find the real value of the currency decline, leading to a loss in selling goods at a previously agreed rate. Similarly, an increase in the price of imports due to a shift in exchange rate can adversely affect the price the business can charge for its products in the local market.
There are a number of ways businesses can manage inflation-related risks, such as by localization of production parts to avoid exchange rate volatility and owing ancillary firms. Likewise, an investor might choose to invest in assets that can offer a real rate of return above inflation. This might include real estate, mineral resources, or government-issued bonds.
Liquidity Risk
You might come across a house that you intend to buy to sell later on. The location of the house might be in an area that has good market value and is likely to increase in the near future. However, how long might it take you to sell the house? Is the property too expensive for an average buyer? Will your assets get tied up for too long after purchasing the property? This is an example of how a liquidity risk can occur. Businesses can end up with assets that are tied up for too long, leading to the risk of owning assets that can be hard to cash out.
A liquidity risk can be avoided by avoiding the purchase of assets that might be difficult to cash out. Some businesses might avoid giving products on credit to local retailers or selling raw material at deferred payments to avoid a liquidity risk.

Longevity Risk
As people receive better healthcare and lifestyles, it is expected that they might live longer. While this is good news, the increase in the lifespan of such individuals means that pensions and policyholders will live longer, leading to a higher payout ratio. Longevity risk is viewed differently by different individuals. For a business, a long lifespan of policyholders or pensioners will lead to an increase in the amount of money they need to pay. Whereas people receiving such benefits will be able to live longer with the assurance of the benefits they have worked hard for.
Many organizations, be it profitable businesses or government-run organizations operating on a loss for several years, have different coping mechanisms for such a risk. Many organizations now hire employees on a contractual basis, whereas pensioners in some cases might be paid out an amount after a ‘plan termination’ by the employer. Some countries might also look to encourage people to work longer and delay social security to rationalize pension plans.
Opportunity Risk
Let’s assume you have a large sum of money placed safely in a safe at home. While the money might appear secure, it might lose value over time due to inflation. You might also run the risk of missing out on a profitable opportunity because you failed to invest in the venture. Businesses can be risk-averse , leading to a competitor taking more of the market share by investing in R&D to improve their product.
An opportunity risk, therefore, requires careful consideration. Businesses might choose to keep a sum for cost overruns, emergency needs or to avoid losing money tied up in assets hard to liquidate while investing the rest to avoid an opportunity risk.
For any business, taxes, especially an increase in them, can lead to a reduction in profitability and loss of sales due to higher prices for their commodities. There’s also the issue of sales tax compliance as the company expands to new states or countries. For an investor, it is essential to determine which portfolio to invest in, considering the rate of tax applicable in relation to the anticipated rate of return. Some investors might opt for tax-deferred accounts to cope with tax risks, whereas businesses might try to reduce tac risks by investing in offers by the government in products which are less heavily taxed.
Many countries are offering fewer taxes on electric cars to help improve the air quality of cities and reduce the negative implications of cars running on petroleum-based products. Some countries have even announced a ban on petrol and diesel-based vehicles by 2035 .
Sequence of Returns Risk
An investor might invest in a portfolio or venture that gives it a return of 5% one year and a loss of 5% the following year. To avoid negative portfolio returns, investors might spend conservatively and account for spending flexibility. An investor might also avoid selling stocks on a loss and use a reserve to fund for a buffer stock to avoid short-term losses due to a sale of stocks at a loss when the chips are down. To have smart investment strategies, start using an all-in-one investment app , which allows you to prevent risks.
Using Different Techniques for Identifying and Presenting Risks
There are a number of techniques that businesses use to identify risks. If you need to create a PowerPoint presentation about risk management, you can use a number of handy templates and techniques listed below.
Risk Matrix
A risk matrix is used during the process of assessing risks to categorize them and determine the possibility of the occurrence of the risks. The matrix can be a very handy mechanism for visually identifying high-priority risks for important management decisions.
RAIDAR Model
RAIDAR model is a risk management model used to assess risks, assumptions, issues, dependencies, action, and repairs. The model can be useful for assessing project risks and for their effective management.
PEST or PESTEL Analysis
A PEST analysis looks at the political-economic, social and technological environment for macro-environmental factors. The analysis is often extended to also include environmental and legal factors, extending the term PEST to PESTEL. This strategic management component is used for the scanning for the aforementioned factors to determine the potential for market growth, decline, and the direction that the business needs to take.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT Analysis is a famous strategic planning technique used for identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Be it a competitor, economic uncertainty, natural disasters, market volatility, or the potential of an opportunity risk, a SWOT analysis can be a handy tool to use in identifying and mitigating risks.
Decision Tree
A decision tree is used to support decisions by placing options and anticipating possible consequences in a tree-like structure. A decision tree can be used by businesses to assess chance events, resource costs, risks, and payoffs.
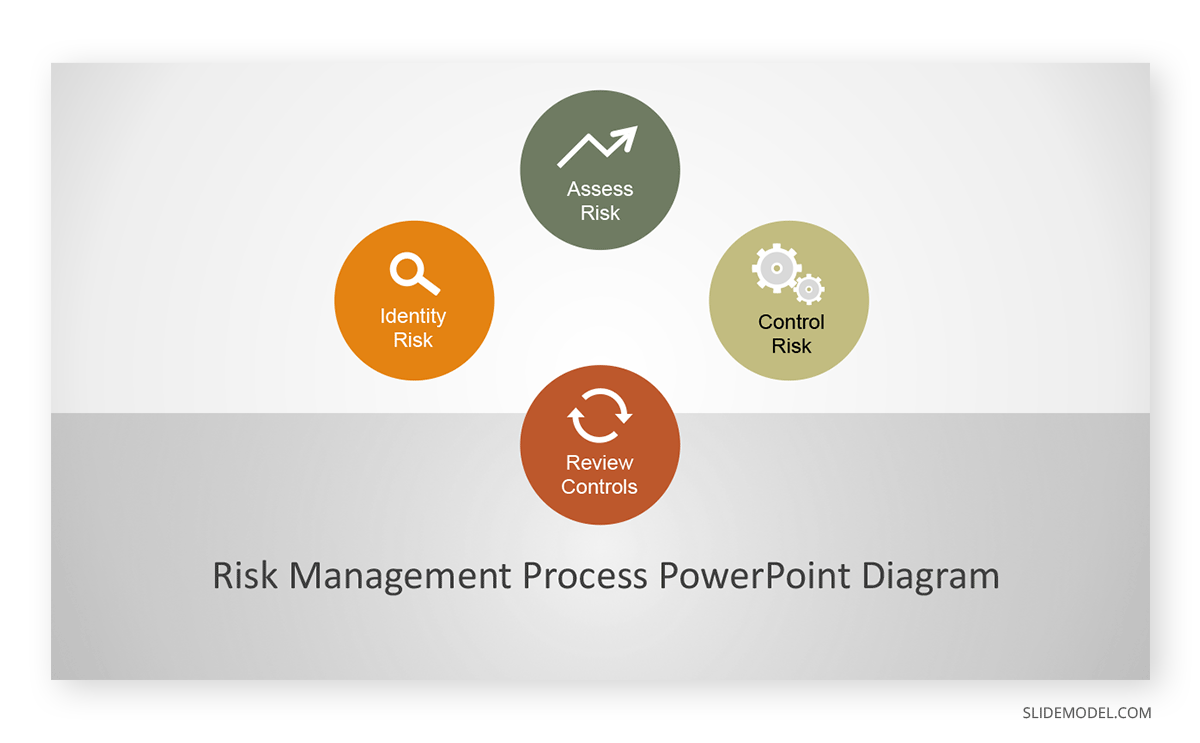
Final Words
There are risks that a business can account for and manage and risks that remain perpetual. Risks that might be associated with the national economy, a natural disaster, or sudden change in government policy can be hard to account for and need constant monitoring. This is different from risks that can be managed by changing a hazardous production process to a safer alternative or diversification of portfolio to avoid losses.
Risk management is a practice that businesses would ideally do away with if it were ever possible. As distasteful as it might be, it is impossible to avoid anticipating risks for business continuity and managing them, even if it comes with a burden of heavy costs that are sometimes unavoidable.
1. Enterprise Risk Management PowerPoint Template
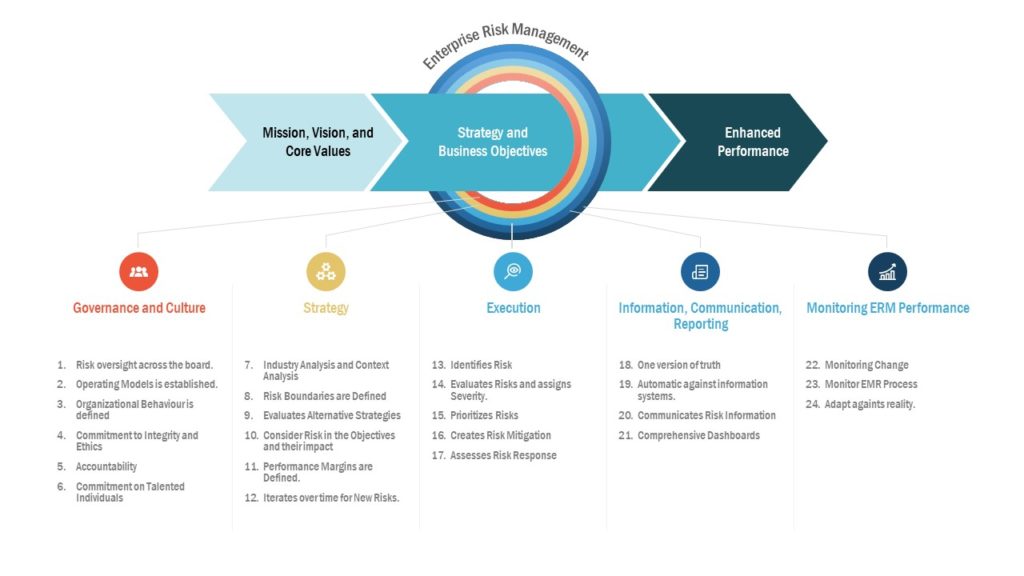
The Enterprise Risk Management PowerPoint Template allows you to create a visual representation that is useful for any business presentation.
Use This Template

Like this article? Please share
Business Diagrams, Business Intelligence, Business Planning, Business Presentations, Financial Risks, Risk Management Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Business • February 7th, 2024
How to Create & Present a Competitive Landscape Slide for Your Pitch Deck
Get to know how to properly create a winning competitive landscape slide for your pitch deck. Boost your pitch performance now.

Filed under Business • February 2nd, 2024
Business Plan Presentations: A Guide
Learn all that’s required to produce a high-quality business plan presentation in this guide. Suggested templates and examples are included.

Filed under Business • January 31st, 2024
How to Create a Sponsorship Deck (Guide + Examples)
Impress your audience and secure deals by knowing the insights on how to create a winning Sponsorship Deck. Step-by-step instructions + templates.
Leave a Reply

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Risk Management 101 An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks.
Published by Charlene Perry Modified over 7 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Risk Management 101 An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks."— Presentation transcript:

Trieschmann, Hoyt & Sommer Introduction to Risk Chapter 1 ©2005, Thomson/South-Western.

Raising Entrepreneurial Capital

Museum Presentation Intermuseum Conservation Association.

Assignment Six Risk Control and Premium Auditing.

Section Objectives Explain why risk is inevitable.

Dr. James Kallman, ARM 6-1 Advanced PowerPoint Presentation ©2009 The National Underwriter Company.

Managing Risk in Academic Placement Agreements Joseph C. Risser, CPCU, ARM-P Director, Risk Management California Polytechnic State University.

“This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under Workforce Innovation in Regional Economic Development (WIRED) as implemented by the U.S. Department.

Lecture No. 3 Insurance and Risk.

An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks

WHAT IS RISK MANAGEMENT? Risk management attempts to identify and manage threats that could be the downfall of an organization.

© 2000 International Risk Control America, Inc. Risk Management Presentation — 1 International Risk Control America IRCA

Chapter 2 Insurance and Risk.

The Australian/New Zealand Standard on Risk Management

Copyright © 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Chapter 3 Introduction to Risk Management.

Introduction to Risk Management

PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook The University of West Alabama Copyright © 2006 Thomson Business & Professional Publishing. All rights reserved.

1 Construction Engineering 221 Construction Insurance.

Identify exposures relevant to all U of I operations To protect the Students, Faculty, Staff, Board of Regents and the State Board of Education To protect.

Chapter 3: Risk Management
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Risk Management

Download and customize this and 500+ other business templates
Start here ⬇️
Voila! You can now download this Presentation
Risk is unavoidable, but this doesn't mean that risk can't be planned for. To make better-calculated strategic choices, set clear expectations and always be prepared for different outcomes, use our Risk Management presentation. This presentation allows you to roll with the punches at all times and outline ways to monitor and control unpredictable events.
Slide highlights
Go over your risk assessment with this slide. List the hazards, and explain why and how they may affect your venture, propose precautions, introduce risk management strategy and obtain feedback to make necessary changes.

One of the risk assessment tools to consider is the risk assessment matrix . Identify risks, calculate consequences, determine risk rating, create an action plan, then plug data into your risk assessment matrix.

Introduce your risk mitigation plan to your audience with this slide. A risk mitigation plan helps to eliminate or minimize the impact of the hazards events and develop options and actions to enhance opportunities and reduce threats.

According to Risk Management , there are three categories of risk:
- Preventable risksn – these are internal risks, arising from within the organization, that are controllable and ought to be eliminated or avoided. Examples of preventable risks include the risks from employees' and managers' unauthorized, illegal, unethical, incorrect or inappropriate actions and the risks from breakdowns in routine operational processes.
- Strategy risks – companies voluntarily accept some risk in order to generate superior returns from their strategies. "A bank assumes credit risk, for example, when it lends money; many companies take on risks through their research and development activities," the experts say.
- External risks – some risks arise from events outside the company and are beyond its influence or control, such as natural and political disasters and major macroeconomic changes. External risks require unique approach. Because companies cannot prevent such events from occurring, their management must focus on identification and mitigation of their impact.

Application
To develop a risk management strategy, use this six-step process, recommended by business solution platform, EDC:
- Identify the risk – identify risks with regular brainstorming sessions that involve staff from all departments. The experts say it's crucial to look at current risks and have the vision to identify future risks.
- Analyze the risk – conduct an in-depth risk analysis. It can be difficult if you don't have all the information, but the checklist can best prepare you to identify those risks and how they can potentially impact your business in both operational and financial terms.
- Prioritize the risk – a large list of risks can be overwhelming, so it's critical to prioritize the risks so you can address the most pressing of them first. Once you have the checklist, go one step further and classify risks as high, medium or low.
- Assign responsibility to the risk – ensure there is someone in the organization that's going to own and oversee the risk management. "Determining who will be responsible is an internal company decision; it could be someone who works in a specific risk area who is best suited to tackle the risk or an arbitrary choice. It's a best practice to develop a risk management team consisting of both internal and, if applicable, external people in your supply chain," the experts say.
- Respond to the risk – develop a strong risk management plan that covers: risk management team, market information and market entry information, contracts and getting paid, quality and performance systems and processes, insurance and cash flow protection.
- Monitor the risk – things will change in your company and so will the risks. "As these changes occur, it's critical to update your plan to ensure that you don't become complacent or lose sight of potential threats to your business. Incorporating an ongoing review of your risk management plan into the company's planning activities will ensure you are on top of any potential risks," the EDC team says.

When COVID-19 crept up on the world, companies like Apple ended up being "especially vulnerable because of their large customer base in China and the dependence of their supply chain on Chinese manufacturers," Amiyatosh Purnanandam, professor of finance at the Ross School of Business, University of Michigan, writes in his article for Forbes .
Tim Cook named the impact of coronavirus as a significant source of uncertainty in the company during Q1 2020 earnings call. At the time, Apple had restricted employee travel and shut one store in China due to the virus outbreak, and was cutting back on retail store hours in China as well.
Purnanandam meditates on the question of what can the managers do to control risks that are not even identifiable? "Unlike exchange rates or commodity prices, there are no market-based derivatives contracts that can be used to hedge such a threat," Purnanandam writes. He's answer is cash balance. Cash balance is the best vaccine against unpredictable events such as the pandemic, Purnanandam writes. Moreover, he believes that cash is actually the best hedge against any risk that cannot be identified or quantified ahead of time. So in case of Apple, a $200 billion pile of cash is what makes it resistant to the risk.
Risk Management Basics Presentation
( june, 2019 ).
Slide set for the UVM Extension Growing Place's course Risk Management 101 presentation.
Filed Under
- Production Risk
- Marketing Risk
- Financial Risk

More by University of Vermont Extension
- Hemp production webinar series on youtube
- Guide to Navigating Vermont's Agritourism Regulations
- HPAI and Agritourism Factsheet
Related Materials
Included In
- @if (collection.IsToolbox) { @Html.ActionLink("Toolbox: " + collection.CollectionName, "index", "Toolbox", new { area = "", id = collection.FriendlyPath }, new { id = collection.FriendlyPath }) } else { @Html.ActionLink("Collection: " + collection.CollectionName, "Collection", "Library", new { area = "", id = collection.FriendlyPath }, new { id = collection.FriendlyPath }) }

Risk Management 101
Mar 11, 2019
260 likes | 379 Views
Risk Management 101. An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks. Definition of Risk. danger possibility peril chance exposure jeopardy consequence hazard menace threat gamble
Share Presentation
Risk management.
- internal external
- general liability
- risk management authority
- foreign travel liability program

Presentation Transcript
Risk Management 101 An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks
Definition of Risk danger possibility peril chance exposure jeopardy consequence hazard menace threatgamble We are concerned with the potential loss, including economic loss, human suffering, or that which may prevent the organization from being able to achieve its goals.
WHAT IS RISK MANAGEMENT? • A conscious effort of planning,organizing, directing, and controlling resources and activities. • To minimize the adverse effects of accidental loss at the LEAST POSSIBLE ACCEPTABLE COST.
Risk Management Decision Process Monitor results/ Modify methods Identify exposures Implement selected method Evaluate loss potential Select method
Types of Risk and Loss • General Liability • Workers’ Compensation • Property Loss – building & contents • Athletic Injury • Business Interruption • Institutional Reputation and Image Loss • Contractual Activities • Vehicle
Types of Risk and Loss continued • Financial Risk • Legal Liability • Environmental Health & Safety • Information Management • Intellectual Property • Student Activities • Auxiliary Enterprises
California State University Risk Management Authority CSURMA • Joint powers authority (JPA) formed under CA Gov’t Code section 6500 et seq.; ultimately allows CSURMA to provide insurance programs, self-insurance programs, and related services to the 23 campuses, Chancellor’s Office, and auxiliaries. • Separate legal entity from the CSU. • Subject to open meetings (Bagley-Keene Meeting Act).
Programs in the CSURMA • General Liability Program • Workers’ Compensation Program • Master Property Program • IDL/NDI/UI Program • Athletic Injury Medical Expense Program (AIME)
Programs in the CSURMA continued • Property – Inland Marine Program • AGPIP – Auxiliary Group Purchase Insurance Program – create market clout among the CSU Auxiliary Organizations to drive premium costs down through group purchase of insurance. • Student Health Insurance Program (CSUSHI) • Foreign Travel Liability Program
Campus Risk Exposures • On the Job Safety (internal & external) • EPL • Vehicle Accidents • Vendors (contracts & product) • Building Maintenance (repairs, IAQ, general maintenance, etc.) • Facilities Use (internal & external) • Reputation (internal & external)
Headlines: Eight killed in Utah State University Van Rollover By Paul Foy ASSOCIATED PRESS 10:09 p.m. September 26, 2005 TREMONTON, Utah – A Utah State University van returning to campus from a field trip blew a tire on Interstate 84 and rolled over, killing seven agriculture students and an instructor. Three other students were hospitalized. The van overturned Monday on the freeway near Tremonton, about 65 miles northwest of Salt Lake City. All 11 occupants were thrown from the van. The students were underclassmen, mostly freshmen. "Some have only been on campus a couple of weeks," university President Stan Albrecht said, calling the deaths an "incredible tragedy." No one in the 16-passenger van, driven by the instructor, was wearing a seatbelt, the Utah Highway Patrol said. Six men were pronounced dead at the scene. Two others died at hospitals. Two of the survivors were in critical condition at McKay-Dee Hospital in Ogden, hospital supervisor Robert Miller said. A third was taken to Ogden Regional Medical Center. .... The single-vehicle crash occurred at about 4:30 p.m. It appeared the left rear tire on the eastbound van had blown as it tried to pass another vehicle, said patrol Lt. Ed Michaud. The Dodge van rolled four times, coming to rest on its wheels about six feet from a 50-foot-deep ravine, troopers said. The van's roof was collapsed to the windows. Parts of the vehicle and personal belongings littered the area near the freeway. "It was a horrific, nasty accident," said Trooper Jason Jensen. "It was one of those things you don't want to drive up on." Albrecht said the students had been on a field trip to look at harvest equipment near Tremonton, west of the Logan campus. Utah State University has about 21,000 students. .....A similar rollover shocked the school in April 2001. Six members of the men's volleyball club were injured when their Dodge van flipped over near Laramie, Wyoming. The crash prompted a government safety warning for large-sized vans.
What we think…. The usual reality.. Field Trips
Obligations • Know where the students are going. • Prepare them for an emergency. • Know in advance if there are health issues that may have to be dealt with. • Review acceptable actions and unacceptable actions.
Student Travel • Approval = Acknowledged benefit • Prepare the students for the travel – risks, expectations, contacts • Waivers versus Informed Consents • Know who is where • Options for those with disabilities
The Accident • Have your contact information handy. • Report the accident to the campus (your supervisor or the Police) as soon as you can. • Do Not Admit Fault. • Do Not make promises.
The Claim • Their’s Victim’s Compensation & Government Claims • Your’s Victim’s Compensation & Government Claims • Our’s CSU Risk Management – Program Administrators
Government Claim Booklet • State of California Victim’s Compensation & Government Claims Program • Includes Instructions & Claim Form http://www.governmentclaims.ca.gov/
METHODS OF CONTROLLING RISK • Avoidance • Transfer of Risk • Retention of Risk • Reduce Risk through Loss Reduction Efforts • Finance Retained Risk • Define Meaningful Standards and Expectations
EVALUTE LOSS POTENTIAL • Evaluation Techniques • Frequency/Severity of Claims • Publications/Periodicals/Other Universities • Political/Litigation Climate • Anticipate
The Challenges We Face • Internal • “We’ve never had that kind of loss” • “What, change my procedure, I’ve always done it this way!” • “I’ve taught this class for 20 years without a problem!” • “All Risk Management has is: bad news with higher price tags!” • No communication!
The Challenges We All Face • External: • The Insurance Market • Your vendors • Your constituents • Unions • Auxiliary Organizations • Foundations • Athletic Corporations • Bookstores • Food Services • Health Centers
OTHER RISKS TO CAUSE YOU WORRY • Liability • General, a wide variety of exposures, including civil liability arising out of accidents resulting from the premises or operations of a public university • Employment- the trifecta of risk • Expensive to defend • Awarding of compensatory, special damages • Awarding of plaintiff’s attorney fees • Automobile • Public Officials’ Errors and Omissions
Risk Management’s Role • Manages insurance and claims • Looks for process improvement through feedback • Consults • Reviews • Forecasts • Play “what ifs” • Thinks worst case scenarios • Recommends
Let’s Team Up! RM&S Takes an Active Role: • G.O. • Observe • Inquire • Alert • Collaborate
Most Risks Do Have a Reward! Be prepared in order to enjoy.
- More by User

Risk Management
Youth Sports Programs. Charitable Organizations. Common Transfer Options. file://localhost ... by federal, state or local organizations such as schools and city ...
928 views • 24 slides

Insurance & Risk Management 101
Insurance & Risk Management 101. Insurance & Risk Management 101. Presenters: Kymberlee Keefe, National Director of Elder Services, Aon Risk Services Judy Cangealose, Atlanta Healthcare Practice Leader, Aon Risk Services
738 views • 33 slides

Risk Management. F29SO1 Software Engineering. Monica Farrow EM G30 [email protected] www.vision.hw.ac.uk. Risk Management. Risk concerns future happenings For today and yesterday, we are reaping what we sowed by our past actions/inactions
890 views • 29 slides

2. ????? ??????? ?????? ????? ???? ??????? ?? ????? ??? ?? ??? ?????? ???? ??? ? ???? ?? ???? ?????? : . ????? ?????? ???? risk management ????? ???? ?? ??? ??????? uncertainty ?? ?????? ????? chance of loss????? ???? ???? pure risk ?? ???? ??? ? ???? speculative risk????? ??????? ??????? ???
937 views • 62 slides

Clinical Risk Management: 101
1.36k views • 108 slides

Risk Management “101” Terminology
Risk Management “101” Terminology. Presented for Wisconsin 4-H Youth Development Staff. Youth Emphasis April 2005. Potential Liability Risks. Negligence
234 views • 8 slides

1.41k views • 25 slides

Risk Management 101. Presented at:. Illinois ASBO 61 st Annual Conference May 16, 2012. Presented by:. Michael McHugh Area Executive Vice President Arthur J. Gallagher Risk Management Services, Inc. Introductions. 31+ Years Insurance and Brokerage Experience
632 views • 33 slides

“Management 101”
“Management 101”. Tim Smith President, Gwinnett Cemeteries. I. The Most Important Aspect of Managing People Is …CONSISTENCY!. Examples: GOD PARENTS COACHES TEACHERS
322 views • 20 slides

Risk management
174 views • 4 slides
Risk Management. Mrs. Smith 2/10/2014. Recession. A Period of temporary economic decline. Trade and Industrial activity are reduced During recessions jobs are scarce and companies are doing everything they can to protect their reputations. Inflation Warranty Guarantee. What is Risk?.
245 views • 7 slides

Risk Management. John Watt. Overview. An introduction to risk management standards and frameworks.
409 views • 16 slides
Risk Management. Speculative risk Pure risk Everyday life Business risk Occupational safety and health is ONE business risk. Risk Management for OSH Hazard Risk Control. Identify the hazard Assess the risk Control the risk Avoid Retain and / or Reduce Transfer. Likelihood.
516 views • 8 slides

Risk Assessment 101
Risk Assessment 101. Anna Tomassacci , Kendal McGillycuddy and Teddi Wilcox. objectives. Perform a basic risk assessment Design a system of internal controls. agenda. Risk Assessment Bazinga Internal Controls Overview Group Exercise:
427 views • 17 slides

risk management 101 measuring, managing & monitoring risk: a km approach kmworld09
risk management 101 measuring, managing & monitoring risk: a km approach kmworld09. [email protected]. why should km care about risk?. “The purpose of knowledge management is to provide support throughout the organization for improved:
338 views • 17 slides

Risk Management. Proactive strategies for minimizing the effects of bad things. Software Risk Management: Principles and Practices. Barry Boehm IEEE Software, Jan1991 text pp443-452. Survey. 35% of 600 firms “had at least one runaway software project”
214 views • 12 slides

ERM 101 Risk Management and the Actuarial Profession
ERM 101 Risk Management and the Actuarial Profession. Management of Risks Actuaries (and others) have been managing specific risks as part of business as long as there have been businesses Risks have often been managed risk-by-risk, in silos Management by profession or occupation
246 views • 22 slides

Risk Management. Instructor: Vassilis Athitsos. This presentation was derived from the textbook used for this class, McConnell, Steve, Rapid Development , Chapter 5. The presentation was prepared by Mr. Mike O'Dell and modified by Vassilis Athitsos. Systems Design Project Are Risky.
655 views • 18 slides

Risk management theory and practice
577 views • 7 slides

Running a successful bar is a balancing act of managing expenses while ensuring a safe and enjoyable environment for patrons. One crucial aspect often overlooked is bar insurance. In this article, we will delve into the hidden costs of not having proper bar insurance coverage and conduct a risk analysis to shed light on the potential financial pitfalls that can arise. To safeguard your bar from the hidden costs of being uninsured, itu2019s imperative to invest in comprehensive bar insurance coverage. At RMS Insurance, we specialize in providing tailored policies that address unique needs.
11 views • 3 slides
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

solar eclipse
25 templates

16 templates

12 templates

18 templates

41 templates

thanksgiving
38 templates
Risk Management Infographics
Free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Every project has its risks. Assess them and show all the information that you’ve gathered in the form of infographics. All of the designs are ready for you to edit accordingly. As a bonus, we’ve included the real deal, a risk management matrix, totally modifiable and customizable.
Features of these infographics
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 30 different infographics to boost your presentations
- Include icons and Flaticon’s extension for further customization
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Microsoft PowerPoint and Keynote
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Include information about how to edit and customize your infographics
How can I use the infographics?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute the infographics?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Risk Management Cycle - Step 5. Monitor & Report. Use a standard format for capturing risk data e.g. a "Risk Register". Review all risks at least annually. Serious risks to be reviewed more often depending on circumstances. Report on risk to senior management / Board.
The six risk management process steps that we've outlined below will give you and your organization a starting point to implement or improve your risk management practices. In order, the risk management steps are: Risk identification. Risk analysis or assessment. Controls implementation.
Tips to make risk management presentations engaging and actionable across your organization: Audience engagement is vital to a successful risk management training presentation. After all, if staff and executives are asleep they will hardly become familiar with the plan and their assigned roles. Include visual assets
Presentation Transcript. Risk Management 101 An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks. Definition of Risk danger possibility peril chance exposure jeopardy consequence hazard menace threatgamble We are concerned with the potential loss, including economic loss, human suffering, or that which may prevent the organization from ...
Slide 1: This slide presents Introduction To Risk Management with imagery.State Your Company Name and get started. Slide 2: This slide presents Risk Management- Introduction with the following content- Minimize, Monitor, Control, Probability and / or impact of unfortunate events, Realization of opportunities, Maximize Resources, Identification of Risks, Prioritization of Risks, Assessment of ...
Risk Management Training Presentation. Duration: 20 minutes | Format: Editable PPT/PDF. Whether we are driving to work, crossing the road, investing in financial products, or making a change in our lifestyle, risk is all around us. In an increasingly fast-paced world, the risk we have to manage is constantly evolving.
If you need to create a PowerPoint presentation about risk management, you can use a number of handy templates and techniques listed below. Risk Matrix. A risk matrix is used during the process of assessing risks to categorize them and determine the possibility of the occurrence of the risks. The matrix can be a very handy mechanism for ...
Download ppt "Risk Management 101 An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks." Similar presentations . Trieschmann, Hoyt & Sommer Introduction to Risk Chapter 1 ©2005, Thomson/South-Western. Raising Entrepreneurial Capital. Museum Presentation Intermuseum Conservation Association.
Presenting this set of slides with name - Introduction To Risk Management Powerpoint Presentation Slides. This is a one stage process. The stages in this pro...
This presentation features include how risks are identified, how potential impacts of risks are assessed as a function of multiple evaluation criteria, and how identified risks are scored to produce a most-to-least critical risk ranking. Methods are described for evaluating risk mitigation progress and visually displaying risk status to decision-makers.
Risk Management is one of the core skillsets within the wider profession of Project Management. Whether your project is purely predictive, or absolutely agil...
101 guide to learn more. Risk management programs can be invaluable to your business as you work to avoid accidents. Not only can they help you reduce losses by preventing problems in the first place, they are also designed to reveal potential safety hazards and help you create risk-reducing procedures. As important as these programs are, it ...
To make better-calculated strategic choices, set clear expectations and always be prepared for different outcomes, use our Risk Management presentation. This presentation allows you to roll with the punches at all times and outline ways to monitor and control unpredictable events. Download and customize this and 500+ other business templates.
Slide set for the UVM Extension Growing Place's course Risk Management 101 presentation. Slide set for the UVM Extension Growing Place's course Risk Management 101 presentation. ... Risk Management Basics Presentation ( June, 2019 ) Go Back Go To This Bookmark This Report This. Summary. Slide set for the UVM Extension Growing Place's course ...
Risk Management 101. Jul 12, 2014. 370 likes | 631 Views. Risk Management 101. Presented at:. Illinois ASBO 61 st Annual Conference May 16, 2012. Presented by:. Michael McHugh Area Executive Vice President Arthur J. Gallagher Risk Management Services, Inc. Introductions. 31+ Years Insurance and Brokerage Experience. Download Presentation.
Presentation Transcript. Risk Management 101 An Introductory Guide to Risk Management and Managing Risks. Definition of Risk danger possibility peril chance exposure jeopardy consequence hazard menace threatgamble We are concerned with the potential loss, including economic loss, human suffering, or that which may prevent the organization from ...
Summary. This training presentation is designed for heads of ERM to present to executives and members of the board to illustrate what the ERM function does and why it is valuable to the organization. The presentation is customizable to allow heads of ERM to update the deck with company-specific information.
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Every project has its risks. Assess them and show all the information that you've gathered in the form of infographics. All of the designs are ready for you to edit accordingly. As a bonus, we've included the real deal, a risk management matrix, totally modifiable and customizable.