- All Products

Fetal Pole(फीटल पोल) क्या होता है और प्रेगनेंसी में कब दिखाई देता है ? Fetal Pole and Early Pregnancy Ultrasound
Fetal Pole(फेटल पोल) गर्भवती महिलाओ के गर्भ में दिखने वाला वो पहला स्ट्रक्चर होता है जो प्रेगनेंसी के पहले अल्ट्रासाउंड के दौरान दिखाई देता है और यही स्ट्रक्चर आगे जाकर बच्चे का रूप लेता है |
जब प्रेगनेंसी के लगभग 6 हफ्तों के बाद पहला अल्ट्रासाउंड कराया जाता है तो योल्क सैक के अन्दर एक ओवल के शेप की स्ट्रक्चर दिखाई देती है जो एक बीज की तरह होती है यही स्ट्रक्चर Fetal Pole (फेटल पोल) कहलाती है दरअसल ये बच्चा या भ्रूण होता है जो अपने शुरुआती स्टेज में होता है और अभी इसका विकास शुरू हुआ होता है इस भ्रूण को मेडिकल की भाषा में embryo कहा जाता है जिसे पोषण देने के लिए योल्क सैक का निर्माण होता है |

Table of Contents
पहला अल्ट्रासाउंड:- क्या दिखाई देता है :-
प्रेगनेंसी का पहला अल्ट्रासाउंड साधारणतया 5-6 हफ्तों के बाद कराया जाता है जिसमे मुख्यता तीन चीजो के होने को जांचा जाता है :-
फेटल पोल :- Fetal Pole वो भ्रूण जो अभी विकसित हो रहा होता है |
योल्क सैक :- भ्रूण को कवर करने वाली एक झिल्ली जो बच्चे को जरूरी nutrition प्रदान करती है |
अम्निओटिक फ्लूइड :- एक प्रकार का लिक्विड जो योल्क सैक के अन्दर भरा होता है और इसके अन्दर बच्चा 9 महीने तक सुरक्षित रहता है |
गेस्तेशनल सैक :- एक प्रकार की झिल्ली जो फेटल पोल और योल्क सैक दोनों को कवर करके रखती है |
इन सब चीजो का ठीक से दिखाई देना इस और इशारा करता है की प्रेगनेंसी में कोई परेशानी नहीं है और बच्चे का विकास सही से हो रहा है |
अगर प्रेगनेंसी में एक से ज्यादा भ्रूण है तो फेटल पोल भी एक से ज्यादा दिखाई देते है |
क्राउन रुम्प लेंग्थ :-
अल्ट्रासाउंड ( ultrasound ) के दौरान फेटल पोल की लम्बाई भी नापी जाती है यह लम्बाई क्राउन रम्प लेंग्थ कहलाती है इस योल्क सैक के अन्दर स्थित ओवल समान आकार की कुल लम्बाई के द्वारा गर्भावस्था की अवधि पता लगाई जाती है जो gestational पीरियड कहलाता है |
फेटल पोल की लम्बाई को क्राउन रम्प लेंग्थ कहलाने का मुख्य कारण ये होता है क्युकी भ्रूण का सिर वाला सिरा (क्राउन) अंग्रेजी के “C” लैटर की तरह दिखता है और पैर वाला सिरा (रुम्प) पूंछ की तरह दिखता है इसलिए इसे सिर से लेकर पैर की लम्बाई में आँका जाता है |
यही फेटल पोल प्रेगनेंसी के 9 महीनो तक लगातार विकसित होता है और एक बच्चे के रूप में पैदा होता है | गर्भावस्था की अवधि भी इसी फेटल पोल की लम्बाई से मापी जाती है |
अगर Fetal Pole दिखाई न दे ?
प्रेगनेंसी अल्ट्रासाउंड में Fetal Pole (फेटल पोल) के दिखाई न देने के पीछे कई कारण हो सकते है जैसे :-
डेट गलत बताना :- कई बार महिला को अपने आखिरी पीरियड की तारीख याद नहीं रहती है जिससे वो सही तारीख नहीं बता पाती है और इस वजह से gestational सैक तो बन जाता है पर उसमे Fetal Pole (फेटल पोल) दिखाई नहीं देता है एसी स्थिति में डॉक्टर एक या दो हफ्तों के बाद फिर से अल्ट्रासाउंड कराने की सलाह देते है |
Ectopic Pregnancy :- ये एक रेयर पाई जाने वाली कंडीशन होती है जिसमे एग uterus के अन्दर fertilize नहीं होता है बल्कि uterus के बाहर कही जैसे फल्लोपियन ट्यूब में fertilize हो जाता है और इस वजह से HCG हार्मोन तो बढ़ जाता है जिसकी वजह से प्रेगनेंसी हुई होती है परन्तु फेटल पोल नहीं बन पता है |
मिसकैरिज हो जाना :- ये एक कॉमन कारण हो सकता है की आप अल्ट्रासाउंड कराने गए जब तक बच्चे का शुरुआती स्टेज में ही मिस कैरिज हो गया हो | एसा तब होता है जब Fetal Pole (फेटल पोल) की CRL 7 mm या उससे ज्यादा होती है तो बच्चा सरवाइव नहीं कर पता है और मिस कैरिज हो जाता है |
प्रेगनेंसी इस संसार की सबसे खुबसूरत फीलिंग होती है एक माँ होने का अनुभव काफी मनोरंजक होता है पर अगर किन्ही कारणों की वजह से प्रेगनेंसी में रिस्क पैदा होती है या बच्चा विकसित नहीं हो पता है तो निराश नहीं होना चाहिए बल्कि पॉजिटिव थॉट और शुद्ध भावनाओ के साथ फिर से प्रयास करने चाहिए | अपने डॉक्टर से हमेशा बात करते रहे और उनकी सलाह माने और पॉजिटिव रहे |
पूछे जाने वाले सवाल :-
Q1 . फीटल पोल इज नॉट सीन इसका क्या मतलब है , ans. फीटल पोल इज नॉट सीन का मतलब यह है की आप का बच्चा अभी अल्ट्रासाउंड में दिखाई नहीं दे रहा है इसके सलूशन के लिए आप कुछ हफ्तों बाद फिर से ultrasound कराये या फिर ट्रांस वेजाइनल ultrasound भी करा सकते है |, q2. measure not possible aur fetal sac not seen aur yolck not seen iska matlab kya hota hai, ans. इसका मतलब है की अभी सैक और फेटल पोल दोनों ही दिखाई नहीं दिए है इसलिए इनका मेज़रमेंट करना पॉसिबल नहीं है |, q3 . is it ok to have no fetal pole in 5 week 3 day ultrasound.
Ans. In an early pregnancy scan of about 5-6 weeks pregnancy, gestational sack, yolk sack and fetal pole should be visible in trans-vaginal ultrasound. Visible fetal pole is the 1st sure sign of pregnancy, and a developing embryo. A fetal heart should also be visible by that time. Sometimes, it is difficult to see a fetal pole and a fetal heart at this time between 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, because sometimes the sinologist interpretation or the machine resolution. There is no other signs of fetal abortion, one can wait for about 2 weeks, it also may be caused by wrong dates, so there is no harm in waiting for about 2 weeks, and in an anxious patient, serum beta HCG, a pregnancy hormone can be checked, and it can be repeated after 48 hours to look for doubling of the values, which is a confirming sign of pregnancy. It will also be wise to rule out any atrophic pregnancy or hetrotrophic pregnancy i.e simultaneous pregnancy in the tubes and ovaries or elsewhere outside the uterus. By Dr. Shashi Agrawal
Q4 फीटल पोल इज नॉट सीन मतलब क्या होता है?
Ans. कभी-कभी प्रेगनेंसी में फीटल पोल दिखाई नहीं देता है इसका मुख्य कारण हो सकता है कि आपके अनुसार आपकी प्रेगनेंसी 7 वीक की हो रही हो लेकिन एग्जैक्ट में आपकी जो प्रेगनेंसी है वह 7 वीक की पूरी ना हुई हो । आप परेशान ना हो आप जब दोबारा से अपना अल्ट्रासाउंड करवाने जाएंगे तो हो सकता है कि तब तक आप का फैटल पोल दिखाई देने लगे । और आपके डॉक्टर ने आपको जो मैडिसिन सजेस्ट की है आप उसका भी सेवन करती रहे।
Q5. फीटल इको क्या है?
Ans. फीटल इको टेस्ट अल्ट्रासाउंड या सोनोग्राफी की तरह ही होता है जो कि एक विकसित होते भ्रूण के दिल को बेहतर तरीके से देखने के काम करता है। फीटल इको की मदद से एक डॉक्टर जान पाता है कि भ्रूण के हृदय की संरचना कैसी है और वह ठीक से काम कर पा रहा है या नहीं।
अपने विचार कमेंट करके बताये |
Related Articles

गर्भावस्था में मूड स्विंग (Mood Swing ) क्यों होता है ? सही कारण एवं निवारण |

Pregnancy Diet Chart:- इस तरह बनायेगे डाइट चार्ट तो बच्चा पैदा होगा बिलकुल तंदुरुस्त |

प्रेगनेंसी टेस्ट कितने प्रकार के होते है ? घर में टेस्ट कैसे करे ?

गर्भावस्था में सर्दी जुकाम की दवाई लेना सही है?

कीगल एक्सरसाइज क्या होती है ? कीगल एक्सरसाइज करने के तरीके | Kegel exercise To Tight Sex Organs.

गर्भकालीन मधुमेह | कारण एवं उपाय | gestational diabetes in pregnancy | all about it.

प्रेगनेंसी में ये स्टाइलिश ड्रेसेस पेहन कर लगे सबसे अलग |List Of Stylish Pregnancy Dresses.

ये 10 तरीके अपनाकर आप एक अच्छे पिता बन सकते है | prepare to become a father by following these tips.
Join our youtube channel -.
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Key Points |
Abnormal fetal lie or presentation may occur due to fetal size, fetal anomalies, uterine structural abnormalities, multiple gestation, or other factors. Diagnosis is by examination or ultrasonography. Management is with physical maneuvers to reposition the fetus, operative vaginal delivery , or cesarean delivery .
Terms that describe the fetus in relation to the uterus, cervix, and maternal pelvis are
Fetal presentation: Fetal part that overlies the maternal pelvic inlet; vertex (cephalic), face, brow, breech, shoulder, funic (umbilical cord), or compound (more than one part, eg, shoulder and hand)
Fetal position: Relation of the presenting part to an anatomic axis; for transverse presentation, occiput anterior, occiput posterior, occiput transverse
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse
Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position.
Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with
Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
Fetal congenital anomalies
Uterine structural abnormalities (eg, fibroids, synechiae)
Multiple gestation
Several common types of abnormal lie or presentation are discussed here.

Transverse lie
Fetal position is transverse, with the fetal long axis oblique or perpendicular rather than parallel to the maternal long axis. Transverse lie is often accompanied by shoulder presentation, which requires cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation
There are several types of breech presentation.
Frank breech: The fetal hips are flexed, and the knees extended (pike position).
Complete breech: The fetus seems to be sitting with hips and knees flexed.
Single or double footling presentation: One or both legs are completely extended and present before the buttocks.
Types of breech presentations
Breech presentation makes delivery difficult ,primarily because the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge. Having a poor dilating wedge can lead to incomplete cervical dilation, because the presenting part is narrower than the head that follows. The head, which is the part with the largest diameter, can then be trapped during delivery.
Additionally, the trapped fetal head can compress the umbilical cord if the fetal umbilicus is visible at the introitus, particularly in primiparas whose pelvic tissues have not been dilated by previous deliveries. Umbilical cord compression may cause fetal hypoxemia.

Predisposing factors for breech presentation include
Preterm labor
Uterine abnormalities
Fetal anomalies
If delivery is vaginal, breech presentation may increase risk of
Umbilical cord prolapse
Birth trauma
Perinatal death

Face or brow presentation
In face presentation, the head is hyperextended, and position is designated by the position of the chin (mentum). When the chin is posterior, the head is less likely to rotate and less likely to deliver vaginally, necessitating cesarean delivery.
Brow presentation usually converts spontaneously to vertex or face presentation.
Occiput posterior position
The most common abnormal position is occiput posterior.
The fetal neck is usually somewhat deflexed; thus, a larger diameter of the head must pass through the pelvis.
Progress may arrest in the second phase of labor. Operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
Position and Presentation of the Fetus
If a fetus is in the occiput posterior position, operative vaginal delivery or cesarean delivery is often required.
In breech presentation, the presenting part is a poor dilating wedge, which can cause the head to be trapped during delivery, often compressing the umbilical cord.
For breech presentation, usually do cesarean delivery at 39 weeks or during labor, but external cephalic version is sometimes successful before labor, usually at 37 or 38 weeks.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.

Variation in fetal presentation
- Report problem with article
- View revision history
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
At the time the article was last revised Yuranga Weerakkody had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
- Delivery presentations
- Variation in delivary presentation
- Abnormal fetal presentations
There can be many variations in the fetal presentation which is determined by which part of the fetus is projecting towards the internal cervical os . This includes:
cephalic presentation : fetal head presenting towards the internal cervical os, considered normal and occurs in the vast majority of births (~97%); this can have many variations which include
left occipito-anterior (LOA)
left occipito-posterior (LOP)
left occipito-transverse (LOT)
right occipito-anterior (ROA)
right occipito-posterior (ROP)
right occipito-transverse (ROT)
straight occipito-anterior
straight occipito-posterior
breech presentation : fetal rump presenting towards the internal cervical os, this has three main types
frank breech presentation (50-70% of all breech presentation): hips flexed, knees extended (pike position)
complete breech presentation (5-10%): hips flexed, knees flexed (cannonball position)
footling presentation or incomplete (10-30%): one or both hips extended, foot presenting
other, e.g one leg flexed and one leg extended
shoulder presentation
cord presentation : umbilical cord presenting towards the internal cervical os
- 1. Fox AJ, Chapman MG. Longitudinal ultrasound assessment of fetal presentation: a review of 1010 consecutive cases. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2006;46 (4): 341-4. doi:10.1111/j.1479-828X.2006.00603.x - Pubmed citation
- 2. Merz E, Bahlmann F. Ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology. Thieme Medical Publishers. (2005) ISBN:1588901475. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Obstetric curriculum
- Cord presentation
- Polyhydramnios
- Footling presentation
- Normal obstetrics scan (third trimester singleton)
Promoted articles (advertising)
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
By Section:
- Artificial Intelligence
- Classifications
- Imaging Technology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiography
- Central Nervous System
- Gastrointestinal
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Head & Neck
- Hepatobiliary
- Interventional
- Musculoskeletal
- Paediatrics
- Not Applicable
Radiopaedia.org
- Feature Sponsor
- Expert advisers

- Getting Pregnant
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
- Birth Clubs
- See all in Community
- Ovulation Calculator
- How To Get Pregnant
- How To Get Pregnant Fast
- Ovulation Discharge
- Implantation Bleeding
- Ovulation Symptoms
- Pregnancy Symptoms
- Am I Pregnant?
- Pregnancy Tests
- See all in Getting Pregnant
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Pregnant Sex
- Weight Gain Tracker
- Signs of Labor
- Morning Sickness
- COVID Vaccine and Pregnancy
- Fetal Weight Chart
- Fetal Development
- Pregnancy Discharge
- Find Out Baby Gender
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- See all in Pregnancy
- Baby Name Generator
- Top Baby Names 2023
- Top Baby Names 2024
- How to Pick a Baby Name
- Most Popular Baby Names
- Baby Names by Letter
- Gender Neutral Names
- Unique Boy Names
- Unique Girl Names
- Top baby names by year
- See all in Baby Names
- Baby Development
- Baby Feeding Guide
- Newborn Sleep
- When Babies Roll Over
- First-Year Baby Costs Calculator
- Postpartum Health
- Baby Poop Chart
- See all in Baby
- Average Weight & Height
- Autism Signs
- Child Growth Chart
- Night Terrors
- Moving from Crib to Bed
- Toddler Feeding Guide
- Potty Training
- Bathing and Grooming
- See all in Toddler
- Height Predictor
- Potty Training: Boys
- Potty training: Girls
- How Much Sleep? (Ages 3+)
- Ready for Preschool?
- Thumb-Sucking
- Gross Motor Skills
- Napping (Ages 2 to 3)
- See all in Child
- Photos: Rashes & Skin Conditions
- Symptom Checker
- Vaccine Scheduler
- Reducing a Fever
- Acetaminophen Dosage Chart
- Constipation in Babies
- Ear Infection Symptoms
- Head Lice 101
- See all in Health
- Second Pregnancy
- Daycare Costs
- Family Finance
- Stay-At-Home Parents
- Breastfeeding Positions
- See all in Family
- Baby Sleep Training
- Preparing For Baby
- My Custom Checklist
- My Registries
- Take the Quiz
- Best Baby Products
- Best Breast Pump
- Best Convertible Car Seat
- Best Infant Car Seat
- Best Baby Bottle
- Best Baby Monitor
- Best Stroller
- Best Diapers
- Best Baby Carrier
- Best Diaper Bag
- Best Highchair
- See all in Baby Products
- Why Pregnant Belly Feels Tight
- Early Signs of Twins
- Teas During Pregnancy
- Baby Head Circumference Chart
- How Many Months Pregnant Am I
- What is a Rainbow Baby
- Braxton Hicks Contractions
- HCG Levels By Week
- When to Take a Pregnancy Test
- Am I Pregnant
- Why is Poop Green
- Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp
- Insemination
- UTI During Pregnancy
- Vitamin D Drops
- Best Baby Forumla
- Postpartum Depression
- Low Progesterone During Pregnancy
- Baby Shower
- Baby Shower Games
Breech, posterior, transverse lie: What position is my baby in?

Fetal presentation, or how your baby is situated in your womb at birth, is determined by the body part that's positioned to come out first, and it can affect the way you deliver. At the time of delivery, 97 percent of babies are head-down (cephalic presentation). But there are several other possibilities, including feet or bottom first (breech) as well as sideways (transverse lie) and diagonal (oblique lie).
Fetal presentation and position
During the last trimester of your pregnancy, your provider will check your baby's presentation by feeling your belly to locate the head, bottom, and back. If it's unclear, your provider may do an ultrasound or an internal exam to feel what part of the baby is in your pelvis.
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery.
Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Medical illustrations by Jonathan Dimes

Head down, facing down (anterior position)
A baby who is head down and facing your spine is in the anterior position. This is the most common fetal presentation and the easiest position for a vaginal delivery.
This position is also known as "occiput anterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the front (anterior) of your pelvis.
Head down, facing up (posterior position)
In the posterior position , your baby is head down and facing your belly. You may also hear it called "sunny-side up" because babies who stay in this position are born facing up. But many babies who are facing up during labor rotate to the easier face down (anterior) position before birth.
Posterior position is formally known as "occiput posterior" because the back of your baby's skull (occipital bone) is in the back (posterior) of your pelvis.
Frank breech
In the frank breech presentation, both the baby's legs are extended so that the feet are up near the face. This is the most common type of breech presentation. Breech babies are difficult to deliver vaginally, so most arrive by c-section .
Some providers will attempt to turn your baby manually to the head down position by applying pressure to your belly. This is called an external cephalic version , and it has a 58 percent success rate for turning breech babies. For more information, see our article on breech birth .
Complete breech
A complete breech is when your baby is bottom down with hips and knees bent in a tuck or cross-legged position. If your baby is in a complete breech, you may feel kicking in your lower abdomen.
Incomplete breech
In an incomplete breech, one of the baby's knees is bent so that the foot is tucked next to the bottom with the other leg extended, positioning that foot closer to the face.
Single footling breech
In the single footling breech presentation, one of the baby's feet is pointed toward your cervix.
Double footling breech
In the double footling breech presentation, both of the baby's feet are pointed toward your cervix.
Transverse lie
In a transverse lie, the baby is lying horizontally in your uterus and may be facing up toward your head or down toward your feet. Babies settle this way less than 1 percent of the time, but it happens more commonly if you're carrying multiples or deliver before your due date.
If your baby stays in a transverse lie until the end of your pregnancy, it can be dangerous for delivery. Your provider will likely schedule a c-section or attempt an external cephalic version , which is highly successful for turning babies in this position.
Oblique lie
In rare cases, your baby may lie diagonally in your uterus, with his rump facing the side of your body at an angle.
Like the transverse lie, this position is more common earlier in pregnancy, and it's likely your provider will intervene if your baby is still in the oblique lie at the end of your third trimester.
Was this article helpful?
What to know if your baby is breech

What's a sunny-side up baby?

Too much amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios)

How your twins’ fetal positions affect labor and delivery

BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies .
Ahmad A et al. 2014. Association of fetal position at onset of labor and mode of delivery: A prospective cohort study. Ultrasound in obstetrics & gynecology 43(2):176-182. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23929533 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Gray CJ and Shanahan MM. 2019. Breech presentation. StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448063/ Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Hankins GD. 1990. Transverse lie. American Journal of Perinatology 7(1):66-70. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2131781 Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]
Medline Plus. 2020. Your baby in the birth canal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002060.htm Opens a new window [Accessed September 2021]

Where to go next


- Mammary Glands
- Fallopian Tubes
- Supporting Ligaments
- Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Placental Development
- Maternal Adaptations
- Menstrual Cycle
- Antenatal Care
- Small for Gestational Age
- Large for Gestational Age
- RBC Isoimmunisation
- Prematurity
- Prolonged Pregnancy
- Multiple Pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Recurrent Miscarriage
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Breech Presentation
- Abnormal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Placenta Praevia
- Placental Abruption
- Pre-Eclampsia
- Gestational Diabetes
- Headaches in Pregnancy
- Haematological
- Obstetric Cholestasis
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy
- Induction of Labour
- Operative Vaginal Delivery
- Prelabour Rupture of Membranes
- Caesarean Section
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Cord Prolapse
- Uterine Rupture
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Primary PPH
- Secondary PPH
- Psychiatric Disease
- Postpartum Contraception
- Breastfeeding Problems
- Primary Dysmenorrhoea
- Amenorrhoea and Oligomenorrhoea
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial Cancer
- Adenomyosis
- Cervical Polyps
- Cervical Ectropion
- Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia + Cervical Screening
- Cervical Cancer
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Ovarian Cysts & Tumours
- Urinary Incontinence
- Genitourinary Prolapses
- Bartholin's Cyst
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Vulval Carcinoma
- Introduction to Infertility
- Female Factor Infertility
- Male Factor Infertility
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Barrier Contraception
- Combined Hormonal
- Progesterone Only Hormonal
- Intrauterine System & Device
- Emergency Contraception
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Genital Warts
- Genital Herpes
- Trichomonas Vaginalis
- Bacterial Vaginosis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Obstetric History
- Gynaecological History
- Sexual History
- Obstetric Examination
- Speculum Examination
- Bimanual Examination
- Amniocentesis
- Chorionic Villus Sampling
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial Ablation
- Tension-Free Vaginal Tape
- Contraceptive Implant
- Fitting an IUS or IUD
Abnormal Fetal lie, Malpresentation and Malposition
Original Author(s): Anna Mcclune Last updated: 1st December 2018 Revisions: 12
- 1 Definitions
- 2 Risk Factors
- 3.2 Presentation
- 3.3 Position
- 4 Investigations
- 5.1 Abnormal Fetal Lie
- 5.2 Malpresentation
- 5.3 Malposition
The lie, presentation and position of a fetus are important during labour and delivery.
In this article, we will look at the risk factors, examination and management of abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition.
Definitions
- Longitudinal, transverse or oblique
- Cephalic vertex presentation is the most common and is considered the safest
- Other presentations include breech, shoulder, face and brow
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) – this is ideal for birth
- Other positions include occipito-posterior and occipito-transverse.
Note: Breech presentation is the most common malpresentation, and is covered in detail here .
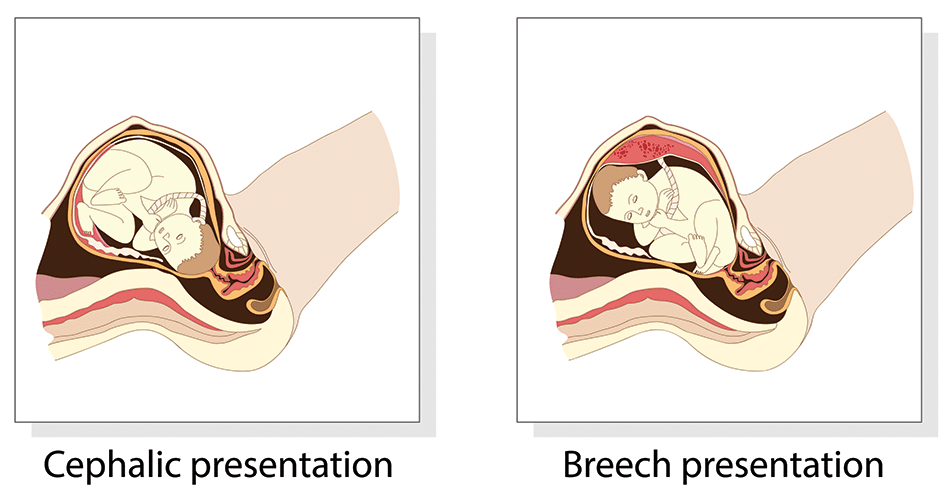
Fig 1 – The two most common fetal presentations: cephalic and breech.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for abnormal fetal lie, malpresentation and malposition include:
- Multiple pregnancy
- Uterine abnormalities (e.g fibroids, partial septate uterus)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Placenta praevia
- Primiparity
Identifying Fetal Lie, Presentation and Position
The fetal lie and presentation can usually be identified via abdominal examination. The fetal position is ascertained by vaginal examination.
For more information on the obstetric examination, see here .
- Face the patient’s head
- Place your hands on either side of the uterus and gently apply pressure; one side will feel fuller and firmer – this is the back, and fetal limbs may feel ‘knobbly’ on the opposite side
Presentation
- Palpate the lower uterus (above the symphysis pubis) with the fingers of both hands; the head feels hard and round (cephalic) and the bottom feels soft and triangular (breech)
- You may be able to gently push the fetal head from side to side
The fetal lie and presentation may not be possible to identify if the mother has a high BMI, if she has not emptied her bladder, if the fetus is small or if there is polyhydramnios .
During labour, vaginal examination is used to assess the position of the fetal head (in a cephalic vertex presentation). The landmarks of the fetal head, including the anterior and posterior fontanelles, indicate the position.
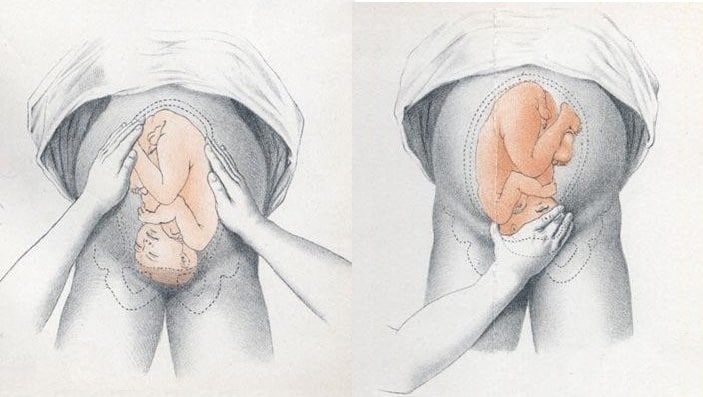
Fig 2 – Assessing fetal lie and presentation.
Investigations
Any suspected abnormal fetal lie or malpresentation should be confirmed by an ultrasound scan . This could also demonstrate predisposing uterine or fetal abnormalities.
Abnormal Fetal Lie
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted – ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen.
It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women. Only 8% of breech presentations will spontaneously revert to cephalic in primiparous women over 36 weeks gestation.
Complications of ECV are rare but include fetal distress , premature rupture of membranes, antepartum haemorrhage (APH) and placental abruption. The risk of an emergency caesarean section (C-section) within 24 hours is around 1 in 200.
ECV is contraindicated in women with a recent APH, ruptured membranes, uterine abnormalities or a previous C-section .
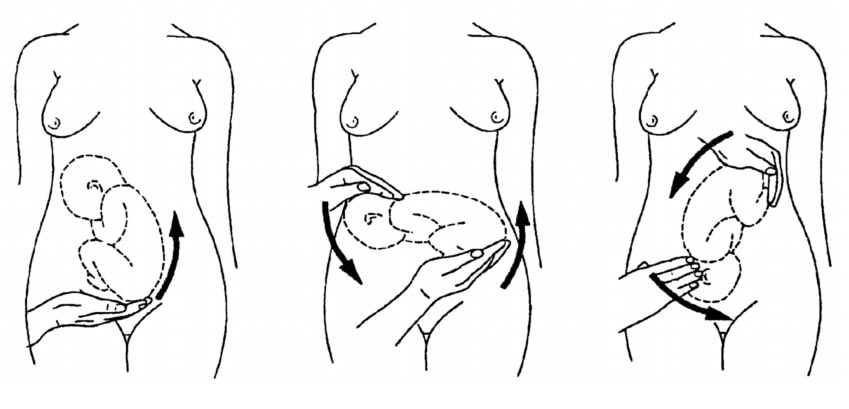
Fig 3 – External cephalic version.
Malpresentation
The management of malpresentation is dependent on the presentation.
- Breech – attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
- Brow – a C-section is necessary
- If the chin is anterior (mento-anterior) a normal labour is possible; however, it is likely to be prolonged and there is an increased risk of a C-section being required
- If the chin is posterior (mento-posterior) then a C-section is necessary
- Shoulder – a C-section is necessary
Malposition
90% of malpositions spontaneously rotate to occipito-anterior as labour progresses. If the fetal head does not rotate, rotation and operative vaginal delivery can be attempted. Alternatively a C-section can be performed.
- Usually the fetal head engages in the occipito-anterior position (the fetal occiput facing anteriorly) - this is ideal for birth
If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation.
- Breech - attempt ECV before labour, vaginal breech delivery or C-section
Found an error? Is our article missing some key information? Make the changes yourself here!
Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site.
We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy .
Privacy Overview
- MSD careers
Fetal Presentation, Position, and Lie (Including Breech Presentation)
- Variations in Fetal Position and Presentation |
During pregnancy, the fetus can be positioned in many different ways inside the mother's uterus. The fetus may be head up or down or facing the mother's back or front. At first, the fetus can move around easily or shift position as the mother moves. Toward the end of the pregnancy the fetus is larger, has less room to move, and stays in one position. How the fetus is positioned has an important effect on delivery and, for certain positions, a cesarean delivery is necessary. There are medical terms that describe precisely how the fetus is positioned, and identifying the fetal position helps doctors to anticipate potential difficulties during labor and delivery.
Presentation refers to the part of the fetus’s body that leads the way out through the birth canal (called the presenting part). Usually, the head leads the way, but sometimes the buttocks (breech presentation), shoulder, or face leads the way.
Position refers to whether the fetus is facing backward (occiput anterior) or forward (occiput posterior). The occiput is a bone at the back of the baby's head. Therefore, facing backward is called occiput anterior (facing the mother’s back and facing down when the mother lies on her back). Facing forward is called occiput posterior (facing toward the mother's pubic bone and facing up when the mother lies on her back).
Lie refers to the angle of the fetus in relation to the mother and the uterus. Up-and-down (with the baby's spine parallel to mother's spine, called longitudinal) is normal, but sometimes the lie is sideways (transverse) or at an angle (oblique).
For these aspects of fetal positioning, the combination that is the most common, safest, and easiest for the mother to deliver is the following:
Head first (called vertex or cephalic presentation)
Facing backward (occiput anterior position)
Spine parallel to mother's spine (longitudinal lie)
Neck bent forward with chin tucked
Arms folded across the chest
If the fetus is in a different position, lie, or presentation, labor may be more difficult, and a normal vaginal delivery may not be possible.
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when
The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids .
The fetus has a birth defect .
There is more than one fetus (multiple gestation).

Position and Presentation of the Fetus
Variations in fetal position and presentation.
Some variations in position and presentation that make delivery difficult occur frequently.
Occiput posterior position
In occiput posterior position (sometimes called sunny-side up), the fetus is head first (vertex presentation) but is facing forward (toward the mother's pubic bone—that is, facing up when the mother lies on her back). This is a very common position that is not abnormal, but it makes delivery more difficult than when the fetus is in the occiput anterior position (facing toward the mother's spine—that is facing down when the mother lies on her back).
When a fetus faces up, the neck is often straightened rather than bent,which requires more room for the head to pass through the birth canal. Delivery assisted by a vacuum device or forceps or cesarean delivery may be necessary.
Breech presentation
In breech presentation, the baby's buttocks or sometimes the feet are positioned to deliver first (before the head).
When delivered vaginally, babies that present buttocks first are more at risk of injury or even death than those that present head first.
The reason for the risks to babies in breech presentation is that the baby's hips and buttocks are not as wide as the head. Therefore, when the hips and buttocks pass through the cervix first, the passageway may not be wide enough for the head to pass through. In addition, when the head follows the buttocks, the neck may be bent slightly backwards. The neck being bent backward increases the width required for delivery as compared to when the head is angled forward with the chin tucked, which is the position that is easiest for delivery. Thus, the baby’s body may be delivered and then the head may get caught and not be able to pass through the birth canal. When the baby’s head is caught, this puts pressure on the umbilical cord in the birth canal, so that very little oxygen can reach the baby. Brain damage due to lack of oxygen is more common among breech babies than among those presenting head first.
In a first delivery, these problems may occur more frequently because a woman’s tissues have not been stretched by previous deliveries. Because of risk of injury or even death to the baby, cesarean delivery is preferred when the fetus is in breech presentation, unless the doctor is very experienced with and skilled at delivering breech babies or there is not an adequate facility or equipment to safely perform a cesarean delivery.
Breech presentation is more likely to occur in the following circumstances:
Labor starts too soon (preterm labor).
The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains abnormal growths such as fibroids .
Other presentations
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.
In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.
Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor. If they do not, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
In transverse lie, the fetus lies horizontally across the birth canal and presents shoulder first. A cesarean delivery is done, unless the fetus is the second in a set of twins. In such a case, the fetus may be turned to be delivered through the vagina.

- Cookie Preferences

Copyright © 2024 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and its affiliates. All rights reserved.
The evolution of fetal presentation during pregnancy: a retrospective, descriptive cross-sectional study
Affiliations.
- 1 1st Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland.
- 2 Teaching Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Ruda Slaska, Medical University of Silesia, Ruda Slaska, Poland.
- PMID: 25753199
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.12626
We investigated changes in the frequencies of four primary types of singleton fetal lie/presentation for each gestational week from 18 to 39 weeks in a retrospective, cross-sectional study which analyzed ultrasound examination records of fetal positions, in the outpatient prenatal diagnosis clinics in two cities in Poland. We calculated the prevalence and 95% confidence intervals for each type of lie/presentation. We then identified the gestational age after which no statistically significant changes in terms of prevalence were observed, by comparing the results at each week with the prevalence of cephalic presentation at 39(+0) weeks, used as reference. A total of 18 019 ultrasound examinations were used. From 22 to 36 weeks of gestation, the prevalence of cephalic presentation increased from 47% (45-50%) to 94% (91-96%), before and after which times plateaus were noted. Spontaneous change from breech to cephalic is unlikely to occur after 36 weeks of gestation.
Keywords: Fetal lie; breech; cephalic; external version; fetal presentation.
© 2015 Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Publication types
- Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
- Cross-Sectional Studies
- Gestational Age
- Labor Presentation*
- Retrospective Studies
- Ultrasonography, Prenatal

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Social media links - Like on my Facebook page - https://www.facebook.com/N.G.MedicalsFollow on Instagram -https://www.instagram.com/n.g.medicals/ Fetal Prese...
Fetus in Utero relates its status when lying in womb, there are various terms that describe here in Hindi like Lie, Presentation, Attitude, Denominator, Pres...
In face presentation, the baby's neck arches back so that the face presents first rather than the top of the head.. In brow presentation, the neck is moderately arched so that the brow presents first.. Usually, fetuses do not stay in a face or brow presentation. These presentations often change to a vertex (top of the head) presentation before or during labor.
Visible fetal pole is the 1st sure sign of pregnancy, and a developing embryo. A fetal heart should also be visible by that time. Sometimes, it is difficult to see a fetal pole and a fetal heart at this time between 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, because sometimes the sinologist interpretation or the machine resolution. ... Dual Marker Test In Hindi ...
Fetal lie: Relation of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus; longitudinal, oblique, or transverse. Normal fetal lie is longitudinal, normal presentation is vertex, and occiput anterior is the most common position. Abnormal fetal lie, presentation, or position may occur with. Fetopelvic disproportion (fetus too large for the pelvic inlet)
There can be many variations in the fetal presentation which is determined by which part of the fetus is projecting towards the internal cervical os. This includes: cephalic presentation: fetal head presenting towards the internal cervical os, considered normal and occurs in the vast majority of births (~97%); this can have many variations ...
The vertex presentation describes the orientation a fetus should be in for a safe vaginal delivery. It becomes important as you near your due date because it tells your pregnancy care provider how they may need to deliver your baby. Vertex means "crown of the head.". This means that the crown of the fetus's head is presenting towards the ...
N.G. Medicals posted a video to playlist OBG Lectures. Fetal Presentation - Full Explanation in Hindi - By N.G. Medicals
The data included a patient study identity code, date of examination, GA at examination, number of fetuses and fetal presentation. Examinations were performed between December 2004 and November 2011. Because the medical management of abnormal fetal presentations renders data after 39 +0 weeks unreliable, we analyzed data only up to that GA ...
Fetal position refers to whether the baby is facing your spine (anterior position) or facing your belly (posterior position). Fetal position can change often: Your baby may be face up at the beginning of labor and face down at delivery. Here are the many possibilities for fetal presentation and position in the womb.
Presentation of twins in Der Rosengarten ("The Rose Garden"), a standard medical text for midwives published in 1513. In obstetrics, the presentation of a fetus about to be born specifies which anatomical part of the fetus is leading, that is, is closest to the pelvic inlet of the birth canal. According to the leading part, this is identified as a cephalic, breech, or shoulder presentation.
Fetal presentation is a reference to the part of the fetus that is overlying the maternal pelvic inlet. The most common relationship between fetus and mother is the longitudinal lie, cephalic presentation. ... Mean +2 SD. 20. 1.055. 1.178. 1.305. 24. 1.030. 1.145. 1.265. 28. 1.000. 1.110. 1.225 ... Fetal heart rate patterns, particularly in the ...
Possible fetal positions can include: Occiput or cephalic anterior: This is the best fetal position for childbirth. It means the fetus is head down, facing the birth parent's spine (facing backward). Its chin is tucked towards its chest. The fetus will also be slightly off-center, with the back of its head facing the right or left.
Abnormal Fetal Lie. If the fetal lie is abnormal, an external cephalic version (ECV) can be attempted - ideally between 36 and 38 weeks gestation. ECV is the manipulation of the fetus to a cephalic presentation through the maternal abdomen. It has an approximate success rate of 50% in primiparous women and 60% in multiparous women.
प्रसूति तंत्र- FETAL LIE, ATTITUDE, PRESENTATION, POSITION
The term presentation refers to that part of the fetus presenting to the lower pole of the uterus. It can more precisely be defined by the presenting part, i.e., that part of the presentation that lies in close proximity to the internal os of the cervix. Thus the usual presentation is cephalic, and the presenting part is the vertex or occiput.
Fetal malpresentation and fetal malposition are frequently interchanged; however, fetal malpresentation refers to a fetus with a fetal part other than the head engaging the maternal pelvis. Fetal malposition in labor includes occiput posterior and occiput transverse positions. Both fetal malposition and malpresentation are associated with significant maternal and neonatal morbidity, which have ...
Variations in fetal presentation, position, or lie may occur when The fetus is too large for the mother's pelvis (fetopelvic disproportion). The uterus is abnormally shaped or contains growths such as fibroids Uterine Fibroids A fibroid is a noncancerous tumor of the uterus that is composed of muscle and fibrous tissue.
Ms. Hasan is a Medical Student, Dr. Bystry is Assistant Professor, and Dr. Morosky is Associate Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, UConn Health, 263 Farmington Ave, Farmington, CT 06030; E-mail: [email protected]. The authors, faculty, and staff in a position to control the content of this CME/CNE activity, and their spouses/life partners (if any), have disclosed that they ...
We investigated changes in the frequencies of four primary types of singleton fetal lie/presentation for each gestational week from 18 to 39 weeks in a retrospective, cross-sectional study which analyzed ultrasound examination records of fetal positions, in the outpatient prenatal diagnosis clinics in two cities in Poland.
ब्रीच (breech meaning in hindi) जिसमे शिशु का नीचला हिस्सा पहले या पैर नीचे की तरफ हो| यह हमेशा घबराने की बात नहीं क्यूंकि शिशु अपनी पोज़िशन गर्भावस्था के दौरान बदलता ...
Compilation presentation on the topic of fetal circulation and garbha poshana in Hindi according to the 3rd year BAMS syllabus. Video is exclusively recorded...