
- Finding Resources
- Evaluating Sources
- Doing Research
- Academic Writing
- Referencing
- Book a Workshop

- Signposting and subtitles
- Types of questions
- Choosing words in your essay question
- Defining your question
- Example questions
- Quiz: what makes a good academic question?
- Game: drag-and-drop words
- Introduction, paragraphs and conclusion
- Spider diagrams
- Bullet points, sub-questions and tables
- Video: Introduction to Notetaking
- Video: Language and style
- Game: Proofreading
- Time management
Signposting is a really useful tool to help you structure your essay and provide clarity for your reader.
Signposting can be divided into two broad categories:

Major signposts

Examples of major signposts:
- The aim of this study is to…
- The purpose of this essay is to…
- This essay argues that…
- There is a lot of academic literature about this issue…
- This essay begins by… It will then go on to… Finally…
- This paragraph will focus upon…
- In conclusion…
Linking words and phrases or connectives
These show connections between sentences and paragraphs.
Examples of linking words and phrases:
- Listing: firstly, secondly, finally
- Indicating addition or similarity: also, in addition, furthermore, similarly
- Indicating contrast: however, nevertheless, on the other hand
- Giving a reason: for this reason, because, due to…
- Indicating result or consequence: therefore, as a result, consequently
- Reformulating an idea: in other words, to put it simply, that is…
- Using examples: for example, for instance
Depending on your essay question and/or length, subtitles may be another useful signposting tool. They are a clear indication to the reader about what the following paragraphs will be focusing upon. It is worth checking that your subject discipline encourages the use of subtitles.
Be careful that you use signposting and subtitles correctly as having too many and using them incorrectly can be confusing to the reader and may lose you marks.
- Newcastle University Library
- Accessibility
- About this website
- Contact & feedback

Getting the title right

The title is the first thing you write. It is the moment you decide what is the purpose, focus and message of your article.
The title is also the first thing we will see of your published article. Whether we decide to click and read the abstract, or download the full article depends – at least, partly - on this first impression.
In this blogpost, I share some thoughts on what makes a good title, and how to come up with one. Even if you can´t find a great title for your article, what you can definitely do is avoid a bad one. I start with tips on what to avoid, proceed with properties and examples of good titles and finish with an illustration of how to get a decent title for a paper.
Five big ‘No’s.
A good title should be informative, argumentative and intriguing. And that’s all - any extra words that do not inform us or intrigue us about the argument, question, hypothesis or contribution of your article are redundant.
While it is difficult to come up with strong titles, you can start by avoiding bad ones!
Never do the following (disclosure - I’ve done all five of them):
Don't tell us in the title what is it that you are doing (‘a study of’, ‘lessons from’, ‘insights on’, ‘the case of’, ‘a comparison of’, ‘exploring’, ‘investigating’, ‘assessing’, ‘evaluating’, ‘measuring’). We know that this is a research paper. Go ahead and tell us what you found, not what you did.
Do not add dead words or words that are too general, such as: ‘beyond’, ‘from … to …’, ‘towards a’.
Avoid clichés and platitudes (‘exploring the contradictions of’, ‘integrating the’, ‘revealing the complexity of’). We know that research objects are complex (we wouldn’t study them if they were not), that causal relations in the real world are contradictory, or that integrating is better than separating.
Don´t tell us the method you are using or the approach you are following (‘a survey of’, ‘an econometric panel data analysis of’, ‘a case study of’, ‘an interdisciplinary perspective’). Exception: do it if the innovation of your paper is the method itself - but then tell us what your innovation is, not the name of your method.
Don’t try too hard to be witty. I’ve seen one too many papers that are ‘a tale of two’ .. islands, rivers, case-studies, ethnographies or surveys. I am sure there are also papers that are ‘gone with the wind’, or worst, ‘gone with the sea’.
Ashamed of past sins
Consider this title of an early paper of mine. “The EU water framework directive: measures and implications” .
Terrible. Boring as hell. I don’t want to read this paper and I am the one who wrote it.
What is wrong with this title?
First, it does not inform the reader about the purpose of my research or my argument. The reader only learns that I am analysing a legislative piece called the Water Framework Directive.
Second, ‘measures’ and ‘implications’ are descriptive, redundant terms. I am analysing a legislation, so of course I will describe its measures and talk about its implications.
The reader does not learn what is interesting or new about my analysis – no hint of what I found or what I will argue. I do not intrigue you to read the paper (unless you are a serious water nerd).
The three elements of a good title
What makes a great title?
Let me repeat.
A good title is informative: the core variables, phenomena or concepts you are contributing to, are there. The purpose of your paper is clear.
A better title is also argumentative: your (hypo)thesis, core finding, or politically-relevant conclusion is there. Ideally, this may include the process that connects your core variables, or the empirical pattern you demonstrate for your phenomenon.
A great title is also intriguing (without being cheesy): it attracts the attention of the reader, it promises something interesting and a new argument or explanation that the reader has not encountered before.
Most of us can write good titles. Titles that inform about the research we did (e.g. my “Social metabolism, ecological distribution conflicts, and valuation languages” ). The challenge is to go the extra mile and write great titles – titles that let the reader know not only what you researched, but also what you found. Titles that intrigue the reader to read your paper.
Learn from the champs
Consider two of the most cited titles in environmental studies.
‘ Limits to growth ’. It can´t get better than that. In just three words, the title informs you what this work is about: growth and its limits. The thesis, novelty and contribution are clear: unlike what others claim, this piece will argue that there are limits to growth – unlike others studying the causes of growth, this work studies the limits to growth. And this makes it intriguing.
Or Garett Hardin’s four-worded ‘tragedy of the commons’ . By reading the title you know what it is about: the commons. You also get the process, or hypothesis, Hardin is going to demonstrate and explain – the collapse of the commons.
The argument is intriguing: commons end up in tragedy. Written at the height of the Cold War, Hardin’s paper had an underlying political message: commons (shorthand for communism) end up in tragedy and there is a scientific reason why this is so. Like or dislike his conclusion, you are curious to read his paper and you want to engage with the argument, to support it or refute it.
My own In defence of degrowth tries something similar. It is short. It is politically provocative. And it is informative: the reader knows this paper is going to be about growth and degrowth.
But it lacks something that the limits or tragedy titles have: they make an argument. They have a thesis. My title does not say why or how I defend degrowth. (I could add a subtitle to capture this, but then some of the intrigue would be lost – see further on about subtitles and title length).
This is fine. We can´t be perfect. Rules can be broken. If your title is informative and intriguing enough, I think you can excuse yourself if you cannot capture also the thesis within the title.
Create some suspense with a question
Good research papers have good research questions. And good questions can be effective titles. Question titles lack an argument, but they intrigue with suspense.
Consider Daron Acemoglu’s and James Robinson’s ‘Why nations fail’ . You sure want to know why nations fail!
The book deals with the study of so-called ‘state failure’ – corruption and the collapse of government institutions. Instead of using this academic terminology, it uses simple language that speaks to everyone, while hinting to academics what it is about.
Another good question-title my ex-classmate Nathan McClintock came up with is ‘Why farm the city?’
I’ve seen scores of recent articles on urban agriculture (or urban gardening). I would never read one called ‘Beyond existing explanations of urban agriculture: lessons and contradictions’. But I am intrigued to learn why so many people suddenly farm in cities.
Often a subtitle follows a main, shorter title. ´Why nations fail´ for example, is followed by ‘The origins of power, prosperity and poverty´. ‘Why farm the city’ is followed by the more esoteric ‘Theorizing urban agriculture through the lens of metabolic rift’.
A subtitle explains or provides context to a shorter main title, it sets the place and time under study or the method used, and adds substance if your main title is a catchy visual cue, verbal quote or open question.
If you can avoid a subtitle, and your title is powerful enough on its own, I would say avoid it. Hardin did. Adding the place, time or method of your research weakens the generality of your claim – the reader will find this information in the abstract or the paper anyway. Darwin did not have to explain that his study of the origin of species covered millions of years and was based on specimens collected in England and the Galapagos.
Too short or too long?
One reason I am sceptical of subtitles is because very long headings tend to be confusing. As a rule of thumb, a title, including the subtitle, should be between 5 and 15 words.
I am personally fan of ‘short is beautiful’. If you can say it in three or four words, go for it!
Why nations fail? Why farm the city? The tragedy of the commons. The origin of species. You don’t need to say more than that.
Fair enough: you may feel you are not Darwin yet. A longer title with many dead words diminishes your claim to contribution and makes you feel safer. But time to get out of your comfort zone and stake the relevance of your research. If it is not relevant, why did you do it? And why do you want us to read it?
Lively titles
A common title structure used in the social sciences is “Lively cue: informative title”.
The lively cue takes the form of a visual cue, a metaphor, a pun, a literary reference or a quote from something someone said.
As I wrote, if you have to try hard to be witty, then don’t. Do it only if the cue comes naturally to you and only if it is your thesis.
Consider Robert Putnam’s ‘Bowling alone: America's declining social capital’ .
The thesis, and core finding of the book - that social bonds are weakening in the U.S. - is in the title for you to see: a person bowling alone. The subtitle informs you about the phenomenon studied, ‘social capital’ - and the process that is demonstrated empirically: the ‘decline’ of social capital. This is the perfect use of the cue: it really drives home the message of what this book is about, with a visual metaphor that speaks to all of us. The subtitle explains and asserts scientific credibility: make no mistake this is not a book about bowling.
Consider instead the title I chose with my friends Christos Zografos and Erik Gomez for our paper ‘To value or not to value? That is not the question’ .
The paper deals with the monetary valuation of nature: should we try to calculate the worth of a river? Our Shakespearean hint points to the quasi-existential dimension of this dilemma among ecological economists, the audience of this particular article. ‘That is not the question’ summarises our conclusion: the terms of the debate are wrong.
Looking back at it, I find our title somewhat pompous. The rest of the article is an esoteric debate on methods of monetary valuation with arcane academic language. The comparison to a Shakespearean drama makes us good candidates to be covered by the Onion .
My advice: use wit with caution and only if you are 100% sure that you can pull it off. Like an airplane cockpit, journal articles are not the place to be funny - titles even less so. Be aware of the risk when you use literary or other references. You might seem to be exaggerating the importance of your own work (we are the Shakespeares of ecological economics) – not a good idea, more so if you are a starting researcher.
Same principles apply to quotes from interviews. Don’t do it unless the quote is your thesis. Consider a title like “‘Let them die alone’: homelessness and social exclusion in downtown New York” (I imagined this).
‘Let them die alone’ could be a phrase that an officer, businessman or an angry neighbour told you the researcher. If the core thesis of your article is that there is an intentional abandonment of homeless people, and as a result they die, then this quotation is impactful.
If however your article is about something different, say increasing numbers of homelessness and unfair housing policies, or if you touch only peripherally on questions of intentional neglect, then the phrase is just sensational and distractive.
If you end up using a quote, make sure that it is grammatically correct, and that its meaning is crystal clear to everyone. Using quotes in the title is risky if you are not a native speaker. Many of my students are not (I am not either). Translating quotes from interviews they took in Spanish or Greek often times do not make sense in English.
Let’s do this!
You know what your article is going to be about. It's time to baptise it! I have created a workbook with a three step process to help you create better titles. Click on the image below to access the workbook.

If you tried any of this and it worked or didn't work let me know in the comments below. And if you have other tips to share, please let us know!

Written by Giorgos Kallis
Giorgos Kallis is an ICREA professor of environmental science at ICTA in Barcelona. Giorgos has degrees in Chemistry, Economics, Environmental Engineering and Environmental Policy and Planning. Before coming to Barcelona, he was a Marie Curie Fellow at the University of California at Berkeley.

- October 2017
- January 2018
- February 2018
- September 2018
- October 2018
- November 2018
- February 2019
- September 2019
Contribute to the blog

Are you interested in submitting a guest post on the site? Learn more about what we are looking for and next steps by reading our contributor’s guide .
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Choosing a Title
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The title summarizes the main idea or ideas of your study. A good title contains the fewest possible words needed to adequately describe the content and/or purpose of your research paper.
Importance of Choosing a Good Title
The title is the part of a paper that is read the most, and it is usually read first . It is, therefore, the most important element that defines the research study. With this in mind, avoid the following when creating a title:
- If the title is too long, this usually indicates there are too many unnecessary words. Avoid language, such as, "A Study to Investigate the...," or "An Examination of the...." These phrases are obvious and generally superfluous unless they are necessary to covey the scope, intent, or type of a study.
- On the other hand, a title which is too short often uses words which are too broad and, thus, does not tell the reader what is being studied. For example, a paper with the title, "African Politics" is so non-specific the title could be the title of a book and so ambiguous that it could refer to anything associated with politics in Africa. A good title should provide information about the focus and/or scope of your research study.
- In academic writing, catchy phrases or non-specific language may be used, but only if it's within the context of the study [e.g., "Fair and Impartial Jury--Catch as Catch Can"]. However, in most cases, you should avoid including words or phrases that do not help the reader understand the purpose of your paper.
- Academic writing is a serious and deliberate endeavor. Avoid using humorous or clever journalistic styles of phrasing when creating the title to your paper. Journalistic headlines often use emotional adjectives [e.g., incredible, amazing, effortless] to highlight a problem experienced by the reader or use "trigger words" or interrogative words like how, what, when, or why to persuade people to read the article or click on a link. These approaches are viewed as counter-productive in academic writing. A reader does not need clever or humorous titles to catch their attention because the act of reading research is assumed to be deliberate based on a desire to learn and improve understanding of the problem. In addition, a humorous title can merely detract from the seriousness and authority of your research.
- Unlike everywhere else in a college-level social sciences research paper [except when using direct quotes in the text], titles do not have to adhere to rigid grammatical or stylistic standards. For example, it could be appropriate to begin a title with a coordinating conjunction [i.e., and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet] if it makes sense to do so and does not detract from the purpose of the study [e.g., "Yet Another Look at Mutual Fund Tournaments"] or beginning the title with an inflected form of a verb such as those ending in -ing [e.g., "Assessing the Political Landscape: Structure, Cognition, and Power in Organizations"].
Appiah, Kingsley Richard et al. “Structural Organisation of Research Article Titles: A Comparative Study of Titles of Business, Gynaecology and Law.” Advances in Language and Literary Studies 10 (2019); Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; Jaakkola, Maarit. “Journalistic Writing and Style.” In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication . Jon F. Nussbaum, editor. (New York: Oxford University Press, 2018): https://oxfordre.com/communication.
Structure and Writing Style
The following parameters can be used to help you formulate a suitable research paper title:
- The purpose of the research
- The scope of the research
- The narrative tone of the paper [typically defined by the type of the research]
- The methods used to study the problem
The initial aim of a title is to capture the reader’s attention and to highlight the research problem under investigation.
Create a Working Title Typically, the final title you submit to your professor is created after the research is complete so that the title accurately captures what has been done . The working title should be developed early in the research process because it can help anchor the focus of the study in much the same way the research problem does. Referring back to the working title can help you reorient yourself back to the main purpose of the study if you find yourself drifting off on a tangent while writing. The Final Title Effective titles in research papers have several characteristics that reflect general principles of academic writing.
- Indicate accurately the subject and scope of the study,
- Rarely use abbreviations or acronyms unless they are commonly known,
- Use words that create a positive impression and stimulate reader interest,
- Use current nomenclature from the field of study,
- Identify key variables, both dependent and independent,
- Reveal how the paper will be organized,
- Suggest a relationship between variables which supports the major hypothesis,
- Is limited to 5 to 15 substantive words,
- Does not include redundant phrasing, such as, "A Study of," "An Analysis of" or similar constructions,
- Takes the form of a question or declarative statement,
- If you use a quote as part of the title, the source of the quote is cited [usually using an asterisk and footnote],
- Use correct grammar and capitalization with all first words and last words capitalized, including the first word of a subtitle. All nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs that appear between the first and last words of the title are also capitalized, and
- Rarely uses an exclamation mark at the end of the title.
The Subtitle Subtitles are frequently used in social sciences research papers because it helps the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem. Think about what type of subtitle listed below reflects the overall approach to your study and whether you believe a subtitle is needed to emphasize the investigative parameters of your research.
1. Explains or provides additional context , e.g., "Linguistic Ethnography and the Study of Welfare Institutions as a Flow of Social Practices: The Case of Residential Child Care Institutions as Paradoxical Institutions." [Palomares, Manuel and David Poveda. Text & Talk: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Language, Discourse and Communication Studies 30 (January 2010): 193-212]
2. Adds substance to a literary, provocative, or imaginative title or quote , e.g., "Listen to What I Say, Not How I Vote": Congressional Support for the President in Washington and at Home." [Grose, Christian R. and Keesha M. Middlemass. Social Science Quarterly 91 (March 2010): 143-167]
3. Qualifies the geographic scope of the research , e.g., "The Geopolitics of the Eastern Border of the European Union: The Case of Romania-Moldova-Ukraine." [Marcu, Silvia. Geopolitics 14 (August 2009): 409-432]
4. Qualifies the temporal scope of the research , e.g., "A Comparison of the Progressive Era and the Depression Years: Societal Influences on Predictions of the Future of the Library, 1895-1940." [Grossman, Hal B. Libraries & the Cultural Record 46 (2011): 102-128]
5. Focuses on investigating the ideas, theories, or work of a particular individual , e.g., "A Deliberative Conception of Politics: How Francesco Saverio Merlino Related Anarchy and Democracy." [La Torre, Massimo. Sociologia del Diritto 28 (January 2001): 75 - 98]
6. Identifies the methodology used , e.g. "Student Activism of the 1960s Revisited: A Multivariate Analysis Research Note." [Aron, William S. Social Forces 52 (March 1974): 408-414]
7. Defines the overarching technique for analyzing the research problem , e.g., "Explaining Territorial Change in Federal Democracies: A Comparative Historical Institutionalist Approach." [ Tillin, Louise. Political Studies 63 (August 2015): 626-641.
With these examples in mind, think about what type of subtitle reflects the overall approach to your study. This will help the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem.
Anstey, A. “Writing Style: What's in a Title?” British Journal of Dermatology 170 (May 2014): 1003-1004; Balch, Tucker. How to Compose a Title for Your Research Paper. Augmented Trader blog. School of Interactive Computing, Georgia Tech University; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. “Formulating the Right Title for a Research Article.” Journal of Association of Physicians of India 64 (February 2016); Choosing the Proper Research Paper Titles. AplusReports.com, 2007-2012; Eva, Kevin W. “Titles, Abstracts, and Authors.” In How to Write a Paper . George M. Hall, editor. 5th edition. (Oxford: John Wiley and Sons, 2013), pp. 33-41; Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; General Format. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Kerkut G.A. “Choosing a Title for a Paper.” Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology 74 (1983): 1; “Tempting Titles.” In Stylish Academic Writing . Helen Sword, editor. (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012), pp. 63-75; Nundy, Samiran, et al. “How to Choose a Title?” In How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries? A Practical Guide . Edited by Samiran Nundy, Atul Kakar, and Zulfiqar A. Bhutta. (Springer Singapore, 2022), pp. 185-192.
- << Previous: Academic Writing Style
- Next: Making an Outline >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 9:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Mastering Essay Title and Subtitle Formatting 📚
Mastering essay title and subtitle formatting.

Importance of a Strong Title
Apa vs. mla: a comparative guide, common formatting frustrations.

How should you format an essay that includes a title and a subtitle?
Share superior formatting, people also asked.

What is the optimal format for writing an essay paper?

How do you write a title in MLA format?

How should you represent a book title in a handwritten essay?

How should a book title be written in a personal note?

How should you format the title of your own work in essays and creative writing?
Superior formatting articles.

The Power of a Strong Title: How to Write a Book Title in an Essay

Unlocking Creativity: How to Write a Book Title in an Essay for Maximum Engagement
Login to superior formatting.
How to Title an Essay: Basic Guidelines With Examples
9 December 2023
last updated
When writing an essay, a student should take the time to consider the best title. Basically, such a title should reflect the content of a paper with the idea expressed in a thesis statement, being a critical component. For example, there are several rules and strategies that students should consider when titling their works. Moreover, these rules include using an academic tone by avoiding jargon and abbreviations, keeping a title simple and straight-to-the-point, writing a title in bold, and avoiding capitalizing or italicizing a title. In turn, other strategies include brainstorming and discussing ideas about an essay title with a friend, colleague, or mentor. Hence, students need to learn how to title an essay to make it interesting for readers.
General Guidelines of Titling an Essay
Titling is a critical step in essay writing that students must master if they are to produce an excellent document. By definition, a title is a word or phrase that a writer provides at the beginning of their texts, such as an essay, article, report, chapter, or other work. In this case, the purpose of titling an essay is to provide the audience with an idea about the content of a document. Moreover, an essay title is important because it identifies the subject matter, captures the readers’ attention, and determines the tone and substance of the entire writing activity. Sometimes, a title has a subtitle, whose function is to amplify a message expressed in a specific title. Based on this definition, a writer must use a title when writing any document targeted at a specific or even general audience, such as essays, theses, dissertations, books, and journal articles that must have a topic.

Constructing an Essay’s Title: Step-by-Step Guide
When writing any academic text, students observe specific writing conventions to make their work impressive and credible. Basically, some of these rules include formatting and following a detailed essay outline . Although there is no particular rule that guides on the titling of academic texts, students must learn how to construct a topic for their essays. When titling an essay, authors must consider the audience and the content of their papers. In other words, writers need to create a title or rethink it after completing an essay. During the process of perfecting an essay, writers should confirm that a topic is relevant to the content and specific or general audience.
Step 1: Skeleton of an Essay Title
As mentioned in the previous section, a title can be a word or a phrase, which can stand alone or have a subtitle. Like the content that follows an outline, a title should have a structure that is not necessarily visible like the introduction-body-conclusion outline. Moreover, the structure of an essay title denotes the impact that it has on the audience and involves a catchy hook, topic keywords, and focus keywords. Then, the goal of the catchy hook is to get the readers’ attention. For example, a title is an element that introduces an essay to the audience, and a good paper should have a hook that grabs the readers’ attention immediately. In turn, topic keywords help an essay to answer the “What?” question that the audience may have when reading written works. On the other hand, focus keywords answer “When?” or “Where?” questions too.
Step 2: Altering an Essay Title for Different Purposes
When titling an essay, students must consider the structure described above to make the topic impactful on the audience. In essence, three components described above — a catchy hook, topic keywords, and focus keywords — indicate a general outline of an essay title. Basically, students should learn how to tailor the title of their work to the content and needs of the target audience. Moreover, such needs include having a paper that lacks jargon and is straight-to-the-point. Then, writers can alter the title to meet these requirements. Ideally, it is the discipline area that determines the approach that a person should take when titling an essay. For example, when writing about “climate change,” a student uses a different catchy hook, topic keywords, and focus keywords. However, in all contexts, the goal is the same: to grab the readers’ attention immediately to make them interested in reading the entire paper.
Template of an Essay Outline
Standard papers have a template or essay structure that writers should follow every time they have an essay writing assignment. Basically, template components enable writers to emphasize three main features of an essay topic described above. In essence, the body part is longer compared to introduction and conclusion sections because students have to elaborate on the topic or idea expressed in the title. Hence, a simple template structure of an essay looks like:
I. Introduction II. Body Paragraphs III. Conclusion
Content in Each Section
As indicated, three sections of an essay enable writers to emphasize three features of a title — a catchy hook, topic keywords, and focus keywords. In this case, the introduction part is where authors introduce their topics and provide background information. Also, the highlight of this section is a thesis, a statement that defines the purpose of the text. Then, the body is the section where students elaborate on the idea expressed in the topic and exemplified by the thesis statement. Here, scholars should use several paragraphs to emphasize the themes expressed in the introduction. In turn, the conclusion section allows writers to summarize their texts. Here, students restate the thesis, summarize the main points, and make a concluding remark.
1. Tips for Writing an Introduction Part
- Provide background information.
- Create a thesis.
2. Tips for Writing a Body Text
- Use several paragraphs.
- Use the topic and concluding sentences in each paragraph.
- Use supporting facts.
- Observe the Sandwich Rule.
3. Tips for Writing a Conclusion Section
- Restate the thesis.
- Summarize the main points as captured in the main text.
- Do not introduce new information.
- Provide a concluding remark.
Rules for Titling an Essay
- Title the entire document. Before writing or after writing an essay, a student should title their work by using a word or phrase.
- Title every section of the text. When writing an essay, a student should create interesting headings and subheadings to give the main text (body) an identity.
- A title must express the text’s central theme. Authors must choose a title that summarizes an essay.
- Use capitalization as necessary . Scholars must use a title case when titling an essay. In this case, it means capitalizing the first letter of every word in the title. Also, students must not capitalize pronouns, prepositions, and conjunctions.
- Write the title in bold. Writers should write the title in bold for purposes of emphasis.
- Do not underline or italicize the title . Authors should avoid underlining or italicizing the title because this aspect might lead to overemphasis.
- Review the title after completing the first draft . After completing the first draft, students should read and reread their work to ensure any mistakes are noted and corrected. These mistakes include formatting errors, spelling mistakes, and grammatical errors, such as missing or wrong punctuation. It is during this stage that they should review the title to ensure it aligns with the message (the main text) of the text. They should confirm the title is catchy enough to grab the readers’ attention immediately and arouse their interest to read the entire paper.
- Include a subtitle for a long title. Authors should shorten the title of their essays by including a subtitle. Here, they should use a colon after the title and then indicate the subtitle.
- Avoid jargon or slang when titling an essay. A writer should maintain formal language when titling their work. In turn, the use of jargon or slang is a turn-off for many readers, especially those conversant with academic writing conventions.
- Put the title in a title page. When writing an essay, a student should indicate the title in the title page – the page that precedes the paper’s introduction. Also, headings and subheadings should appear from the introduction to the conclusion.
Strategies for Creating an Essay Title
- Title an essay after finishing writing the text. Writers should consider the title of their work after completing the first draft. At this time, students know the structure of their papers and the content in each section. Moreover, they understand how the entire paper emphasizes the central theme captured in the thesis statement. With this understanding, it becomes easy to create a topic that reflects the message of the text.
- Emphasize on an academic tone. When titling an essay, writers should maintain the academic tone that permeates the entire document. In this case, language or words they use must be strict, informative, and persuasive. However, it must also be catchy and warm to arouse the readers’ interest.
- Highlight several keywords. Using keywords or phrases in an essay title optimizes the writer’s work. Basically, this strategy that bloggers use to make their works attract higher online traffic. Moreover, writers should use the same technique to attract the attention of their audience, whether it is an instructor or a college admissions board. In turn, students must ensure that keywords are strict to the point.
- Follow the expert’s opinion. When writing an essay, students should consider the formula expressed by academic experts. For example, when titling their essays, writers should start with creative introductory words followed by a line that directly states the purpose of a paper.
- Identify a quote that corresponds to the essay’s central idea or one of its themes. When titling an essay, a writer can identify a quote that emphasizes the thesis or one of the central themes of a paper and use it to create a title.
- Rewrite the title of a famous book, movie, or album. When titling an essay, students can take the title of a well-known work, such as a book or movie, and rewrite it to make it reflect their works. Moreover, the message of the text must align with themes expressed in such a work, whether it is a book, movie, or album. As a result, this approach makes the title catchy, which is right in the eyes and minds of the audience.
- Answer What, Who, When, or Where questions. One way of making the title of an essay is to take the inquiry approach. In this case, writers must create a title that answers “What?,” “Who?,” “When?,” or “Where?” questions. Also, it is another strategy for making the title catchy and straight to the point.
- Talk it out . When creating a title for an essay, a student can discuss ideas with a friend or mentor. Basically, this approach is effective when it comes to titling an essay that is informative or argumentative.
- Brainstorm . When reviewing the first draft, authors can write down some of the ideas they get about the topic of their works. From the list, students can judge the best title for their works based on the content and the central message.
- Free write . Scholars can write down topics and start writing their essays. Basically, this approach means that authors begin with the topic and let ideas come into their heads about what to write. Moreover, this approach is suitable for personal narratives but not essays that require research, such as informative essays.
Examples of Essay Titles
1. child or spouse abuse.
When writing an essay about domestic violence, a writer can use “Child Abuse” or “Spousal Abuse” as a topic. In this case, authors would spend their time narrating how children or spouses are the primary victims of domestic violence in society. To make a title catchy, they can include a subtitle that describes the kind of abuse, such as sexual violence or emotional abuse.
Suffering is a broad topic. When writing a sociology essay, a writer can use the title “Poverty” to show how a lack of the means to afford basic life amenities creates suffering for a majority of people in developing countries. Here, students can choose a community, country, or region as their target and capture it in the title. Moreover, writers arouse the readers’ interest, seeking to understand more about that environment and how poverty leads to suffering.
3. Plastic Surgery
When writing on themes of beauty, a writer can use the title “Plastic Surgery” to denote the extent to which individuals are willing to go to look “beautiful.” Here, students can select a demographic population, such as celebrities, and show how many people have undergone surgical procedures to alter their physical appearances. Also, writers can elaborate on how this tradition is the basis of the celebrity culture where fans see their idols as role models in the body of their essays.
When writing on themes of emotional health, students can use the title “Stress” to emphasize the adversity of emotional strain. Here, authors can link stressful circumstances to adverse health outcomes, such as anxiety and depression.
5. Procrastination
When writing on subjects of personal discipline, authors can use the title “Procrastination” to denote counterproductive habits. In this case, students can provide a personal anecdote of an instance when procrastination affected an area of their life and use that story as the basis for discouraging the habit.
6. Illegal Immigration
When writing about politics, a writer can use the title “Illegal Immigration” to exemplify issues that have become politically sensitive in recent years. Moreover, students can highlight the complications of applying for refugee or asylum status as the reason for the growing numbers of illegal immigrants in America and European countries.
When writing an essay on mental health, students can use the word “Racism” when titling their essays. For example, the term “Racism” becomes a significant theme of a paper expressed in a title, and the writer’s mission is to link it with mental health. In this case, authors can show how experiences of racism have affected the mental health of African Americans and other minority groups residing in the United States.
When writing an essay about culture, a writer can use the topic “Tattoos” to indicate the recent trend of people getting tattoos on their bodies. In this case, students can try to link the pop culture to this trend.
9. Teen Pregnancy
When writing an essay about the abortion debate, a writer can use the title “Teen Pregnancy” to support or oppose calls for the legalization of abortion. Moreover, if authors support the legalization of abortion, they can show how teen pregnancy jeopardizes the lives of millions of young girls who become pregnant unintentionally. As such, abortion would grant them an opportunity to complete their education. On the other hand, if writers oppose the legalization of abortion, they can argue that young girls can give birth and still go back to school. Also, students can mention the foster care program and its benefits to those who are not ready to become responsible parents.
10. Homelessness
When writing about public policy, students can use the title “Homelessness” to write about how governments have failed in their solemn duty of providing housing to citizens. In this case, authors can pick a city with high numbers of homeless people and use it as an example of a failure by legislators to pass essential laws and policies.
Summing Up on How to Title an Essay
Essay writing is an essential academic exercise for students, as it provides opportunities for perfecting critical thinking skills. More importantly, it helps students to put into use what they have learned in a semester or calendar year. Then, one of the most vital aspects of essay writing is titling an essay. Ideally, it is a title that provides readers with an idea of what a paper is all about. As such, writers of essays need to learn basic rules and strategies of titling an essay. Hence, the following tips are vital:
- pick a theme from the draft and use it to create the title;
- let the title answer What, Who, When, or Where questions;
- use an academic tone by avoiding jargon and abbreviations;
- keep the title simple and straight to the point;
- write the title in bold;
- avoid capitalizing or italicizing the title;
- use a title in every section of a paper.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles
How to write an essay about yourself with tips and examples, how to cite song lyrics in different formats with examples.
Best Tips on How to Title an Essay

How to Make a Good Title for an Essay
The success of an essay heavily depends on its title. This may not come as a surprise given that the essay title is the first aspect to provide the reader with a sneak peek into the text. It piques our interest to read the paper in the first place and gives us a preview of what to expect from the author.
Our research paper writing help prepared a thorough guide on how to title an essay. Here you may find tips and tricks for developing an effective APA or MLA essay title. So, let's dive straight into the article for more exciting details!
Essay Title Format
During your essay writing process, ensure you know the stylistic requirements before beginning an essay. Knowing the format you need to employ is crucial because different style manuals may have varying requirements. Mostly, you could have used an APA or MLA essay title format. Our service, where you can buy essay online , explains these two in more detail below.
Essay Title MLA
If you're required to create an essay title MLA format, check whether your instructor wants you to make a separate cover page. If not, put a heading at the beginning of your work that includes your name, the name of your professor, the course ID, and, lastly, the date.
On the other hand, if you must present a cover page for your essay title MLA, then you need to include the following:
- The name of the college
- The title of your paper
- The subtitle of your paper, if applicable
- Your first and last name
- Your teacher or professor's name
- The class name or course number
- The date the paper is due
The formatting instructions are as follows:
- Double-spaced
- Times New Roman font
- Size 12 font
- Apart from very short terms, each word's initial letter should be capitalized. The initial word, however, must always be uppercase.
- The title page shouldn't include a header with the page numbers.
Essay Title APA
Having discussed the MLA format essay title, let's explore what the APA student title page includes:
- The paper title
- Author names
- Institutional affiliation where the author carried out the study
- Name and number of the course
- Professor name
- Page number
The title of an essay format instructions:
- double-spaced
- 1" margins
- 12-point Times New Roman
- According to APA, your title should be targeted and brief, without unnecessary words or abbreviations
How to Choose a Good Title for an Essay: Important Qualities
Nobody will read a dull headline. Your title should grab your audience's attention and encourage them to read the rest of the work. As it is one of the initial things readers see, having a strong attention grabber is essential when writing an essay from scratch. To fully understand how to come up with a title for essay that is strong and exciting, let's consider a few following factors:
Employ a Catchy Hook - Usually, the title of essay format follows a similar basic structure, especially if they are used for an academic article. The hook serves as a unique component that attracts the reader. It's a captivating statement informing others about the topic of the essay. You can also explore several types of sentences with examples that can help you develop the ideal hook structure.
Consider Topic Keywords - These are essential terms or expressions pertinent to your subject and help your reader understand the focus and body of your article. These focus keywords should serve as a brief, one- to two-word article summary. You can choose some terms from the research topic your instructor gave you, but after your thesis statement is formed, this is where you should hunt for ideas.
Use a Colon - A colon is frequently used in academic titles to separate concepts and sentences. The standard procedure is to place a clever remark or brief quotation before the colon. Although these beginning words offer flavor, they can be overdone. Because of this, some individuals find using the colon to be repugnant. Therefore be careful not to misuse this method.
Ask a Question - To write essay title that is strong, consider asking a question. But, use it with caution because posing a question will make your tone less formal. As long as the question is suitably phrased to meet the subject of your essay, feel free to employ it. Always check to see if the title question still applies to your points in the essay's body. The thesis statement should be appropriately reflected as well.
Find Inspirational Quotes - There is no formula for selecting essay titles from the textual content. You may get playful and choose any quotation, proverb, or catchphrase that applies to your particular publication and works as a title. You may also create a great essay title using well-known expressions or idioms. Doing so will help your readers relate to and feel more comfortable discussing your subject.

Here are other rules for how to create a good title:
- Title every section of writing: In the process of writing, create interesting subheadings to give your paragraphs an identity. Also, they make your text look ordered and clear.
- The title must bear the theme of the text: choose a title that summarizes the essay.
- Capitalize all words with certain exceptions: Capitalize the first letter of every word in the title, but do not capitalize pronouns, articles, prepositions, and conjunctions.
- Avoid underlining the title: Since topics come in boldface, underlining it will amount to overemphasis. Some authorities say that if you must underline it, do not bolden it.
- Review the final version of the title: Do not forget to do a quick review of the final version of the title—check for grammar, structure, spelling and so on. Re-read it to determine if the title has given justice to the essay. Confirm if the topic is catchy enough to attract your reader’s attention.
- When using a colon in your title, follow the rules: Since we are dealing with punctuation rules here, let us talk about the colon – when you have two eye-catching topics, separate them with a colon.
Student’s Guide on How to Come Up with a Title for an Essay
Titling an essay can be easy, but there are a few core principles to be taken into account. The following tips will help you stay on track and avoid any common pitfalls.
Essay Goes First
Never start with a title! If you write it before the rest of the text, it will be based on it, and it should be vice versa. Writing an essay before choosing a heading will give you a clear understanding of what should make sense to the reader. Re-read the finished paper several times to decide on the title. The last thing to create is a title - such strategy will give more time to spend on crafting an essay outline, conducting research, or writing the paper itself.

What are you writing about? What is the style of your paper, and is it an academic essay or a free-form essay like a narrative essay? If the topic of your essay is “Do people who commit heinous crimes deserve the death penalty?” your title should not be humorous; it should be strict and to the point.
If your topic is “Why do people like watching funny cat videos?”, feel free to craft a funny title. Determine the tone of your essay and base your title on it—in consideration with the essay’s topic.
The tone can be:
- Serious - “The implications of global warming”
- Funny - “How cats and dogs love their masters”
- Amiable - “Ways to fight depression”
- Persuasive - “Why positive thinking is a must have skill for every person”
- Informative - “Ten rules for creating a chemical at home”
The main goal of a title is to name its paper. There is no need to tell an entire story in the title, or provide any useless details. Sum up your paper in a few words! Another way to do this is to sum up your thesis statement, as it represents the main idea of your essay. Take your thesis and squeeze it into 3-4 words. Imagine that you are creating a title for your favourite newspaper or a slogan for Coca-Cola.
Don’t use fancy words! Take 2-3 main words (keywords), put them together, and stop wasting your time. Avoid jargon and abbreviations.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is something that can help any student and young writer reap benefits. While working on a title, detect the words related to the central idea of the paper. Type the words into the search field of Google and add the word “quote.” A search engine will show numerous web pages with in-text quotations that could be useful. Select the fragment you like. It is possible to learn how to make a creative title for an essay in this way.
Discover several more tips from experts:
- Never forget the “What,” “Who,” “When,” “How,” “Why,” and “Where” questions (if you start with one of these questions, your title has a chance of getting noticed);
- Come up with an unexpected image not related to the selected topic;
- Sometimes, starting with a lie increases the chances of a title being able to catch an eye;
- Review our catchy essay title examples.
Need Some Help With Your Essay's Title?
Feel free to contact EssayPro and we will provide you with a writing help at a moment’s notice. With the years of essay writing experience, titling becomes second nature, so you no longer need to worry about having a catchy headline on your paper.
Essay Title Examples: Bad vs Good
The strongest essay titles condense lengthy essays into concise statements. When wondering how to make an essay title, think carefully about your stylistic choices and essay format to produce an excellent one. Our dissertation help has provided essay title examples to let you understand the difference between good and bad ones more vividly.

Bad Essay Title Examples
As we discussed how to create an essay title and the specific elements that go into it, you should have a clear idea of how important it is to craft a strong title. In contrast, first, look at weak essay title ideas that can break your paper. This should serve as an example of why your heading should not be like this:
Ex 1: ' How Television Has Changed Our World ' - too vast and not informative
Ex 2: 'The Ara Pacis Augustae' - unclear for those who don't know Latin
Ex 3: 'The Most Poisonous Frog' - does not provide any insight
Ex 4: 'A Brief History of Subcultures and How They Manifest Themselves in a Constantly Changing Socio-Economic Environment' - too long and complicated
Ex 5: 'The Little Mermaid 29 Years Later: Selling a Harmful Sexist Message Through a Naughty Image' - inappropriate language
Good Essay Title Examples
Now that you know what a bad essay title looks like, let's explore good essay title examples as their substitutes. Examine the following essay title format styles that will give you a clear understanding.
Ex 1: ' The Electronic Babysitter: A Social History of Uses of the Television' - gives an exact description of what the essay will be about
Ex 2: ' The Modern Historical Significance of the Ara Pacis Augustae to the City of Rome' - here, the reader can understand what they will be reading about
Ex 3: ' A Deadly Beauty: The Evolution of Skin Coloration and Toxicity of the Poisonous Dart Frog' - clear, informative, and on-point.
Ex 4: 'Reconsidering Counterculture in Contemporary Society' - informative enough and brief
Ex 5: 'The Projection of Gender Stereotypes in The Little Mermaid' - employs appropriate language
Catchy Essay Title Ideas
You now understand that long, complicated headlines do not accurately convey the paper's main idea. Take ample time to consider the word choice before tilting your work. How do you create good essay titles? Think creatively and with common sense. But meanwhile, for your convenience, we compiled title ideas for essays you may use as inspiration.
Persuasive Essay Titles
- Why Receiving College Education is Important: Examining Long-term Benefits
- Face-to-Face Courses Cannot Be Replaced by Online Learning
- An MBA Does Not Ensure Corporate Success.
- Every Company Should Adopt a Green Strategy.
- Energy Drinks Represent a Lucrative Market Segment.
- Aircraft, Excess Weight Charges, Need to be Prohibited.
- Patients' Life Shouldn't be Put to Death by Nurses.
- Google Glasses May Increase the Number of Auto Accidents.
- All of the Conventional Malls Will Soon be Replaced By Online Shopping
- How Do Team-building Exercises Contribute to the Development of Inventions?
- Illegal immigrants are entitled to remain in the US.
Academic Essay Titles
- Several English Dialects: The Link Between Various Cultures
- Instagram: A social media innovation
- Is it possible to reverse drug-induced brain damage, and if so, how?
- What the Future Holds for Humans in the Light of Artificial Intelligence
- The Story of Two Nations after Decades of Conflict: North and South Korea
- Video Games and Their Learning Context in Schools
- Free Wi-Fi: Strategies for Enhancing the City's Economy
Strong Research Paper Titles
- Digital World Cybersecurity
- E-business to Provide New Paths for Booksellers
- Outsourcing for Large Businesses
- Preparing for College Costs for High School Students
- What News Reporters Should Do in the Digital Age and How to Do It: Examples
- The Transformative Power of Music: How Heavy Metal Impacted My Life
Best Essay Titles for College Students
- The Possible Benefits and Risks of Artificial Intelligence for Humans
- The Potential for Time Travel in Virtual Reality
- What Role Has Mathematics Played in Human History?
- How to Succeed in the Real Estate Industry
- E-Commerce: An Empire of Virtual Businesses Worth Millions of Dollars
- How to Achieve Financial Independence in the Digital Age Without Opening a Real Business
More Creative Titles for Essays
- When getting rewarded for their grades, would kids do better left alone?
- How Does Fake News Impact the Mainstream press?
- Homelessness in Contemporary Society: A Dilemma
- What News Reporters' Best Job Is in the Digital Age and How to Uphold It
- Elon Musk: Brilliant Mind or Insane Person?
- Positives and Negatives of Employing a Smoker
- Do We Employ the Appropriate Student Success Metrics?
Professional Academic Help
Now that you know how to make a good title for an essay, you should also understand that you should approach the task as a process. While composing your essay title, you must condense your whole thesis and point of discussion into a single, concise, yet powerful sentence. If you have time before your deadline, give it some thought and don't hurry.
Don't forget that you can always rely on our professional academic assistance, whether you need a reflection paper , ideas for a strong essay title, or any other academic papers. Consider the following words - write my essay for me - magic keywords for delegating your most complex tasks to our skilled writers!
Is the Volume of Schoolwork Getting Out of Hand?
Get essays online to do your work without stress. You may always count on our experienced writers for help with any endeavor!
Related Articles
%20(1).webp)
- How to setup your software
- Sample MLA Paper – normal paper
- Sample MLA Paper – has cover page
- Sample APA Paper
- Sample Chicago Paper
- Sample CSE Paper
- APA Format Guidelines
MLA Format Sub-headings
If you would like to utilize subheadings (subtitles) in your research paper, it is a good idea to first check with your instructor to be 100% sure what subheading format he/she would like you to use.
Depending on how long your paper is, you will need either one level subheadings or several levels subheadings
One Level Subheadings:
Format : centered, capitalize the first letter but not the whole subtitle.

MLA Format One Level Subheading
*Visit this full sample paper for ideas!
Multi-Level Subheadings:
If your paper has subtitles under subtitles, see the format below. Be sure to check with your instructor first if he/she agrees with this format before you decide to use it.
– MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 7th Edition – Writing the Research Paper, 7th Edition.
If you find this website useful, please share with a friend:
super helpful thank you!
Thank you for the information, it really worked for my minerals and rocks research essay
Very helpful 🙂
Thanks for the help my friend.
Leave a Comment
Current ye ignore me @r *
Leave this field empty
Next post: MLA Format Sample Paper, with Cover Page and Outline
Previous post: APA Headings
- The Format of the Research Paper
- MLA Format Cover Page
- MLA Format Headings
- MLA Citations
- MLA Format Works Cited
- MLA Format FAQs
- MLA Format Sample Paper
- MLA Sample Paper w/ Cover and Outline Pages
HOW TO SETUP YOUR SOFTWARE
- MLA Format using Google Docs
- MLA Format Microsoft Word 2016
- MLA Format using Pages on Mac
Copyright © 2011–2024 • MLA Format • All rights reserved. Currently, MLA is at its 8th edition. This website has no official relationship with the Modern Language Association and is not endorsed by the MLA.
Write it Great
an elite ghostwriting firm
- Dec 15, 2022
Title Vs. Subtitle: What's the Difference?
The title and subtitle of a piece of writing play a crucial role in determining its success. Yet, people often struggle to determine the difference between titles and subtitles. Titles and subtitles both serve to convey the message of a piece of writing, but they each have their own purpose.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between titles and subtitles. We will also provide tips and tricks for writing effective titles and subtitles, so you can make the most of these elements in your writing. By the end, you will have a solid understanding of the differences between titles and subtitles and how to use them to your advantage. So, let's get started on our journey to mastering the art of titles and subtitles!
Definition of Titles and Subtitles
A title is the main heading or name given to a piece of writing, typically placed at the top of the page or at the beginning of the text. On the book cover above, the title is " Foresight is 20/20 ." A subtitle , on the other hand, is a secondary heading that provides additional information about the content of the text. The subtitle for the book above is " Unlock Your Past to Create a Better Future ."
Subtitles are usually placed below the main title and help to break up the content into smaller, more manageable sections.
Understanding the differences between titles and subtitles–and knowing how to use them effectively–will help you to take your writing to the next level. Whether you are a seasoned writer or just starting out, this blog post will provide valuable insights and information to help you improve your writing and take your skills to the next level.

The Role of Titles in Writing
The title is the first thing that a reader sees when they pick up a piece of writing. It plays a crucial role in determining whether or not the reader will continue to read the text. The main function of a title is to grab the reader's attention and give them a brief overview of what they’re about to read.
A good title is short, attention-grabbing, and relevant to the content of the text. The title provides the reader with their first impression, so it’s important to make it count.
A good title also establishes the tone of the content, whether it be serious, humorous, or informative. Here are some examples of strong titles that serve their purpose well:
1. " On the Origin of Species " by Charles Darwin
This title falls under the “serious” category. While “On the Origin of Species” gives us some context about what Darwin’s book is about, it’s a little vague. Still, this sweeping title provides the tone for Darwin’s dive into evolutionary biology.
2. " You Can’t Touch My Hair ” by Phoebe Robinson
This title reflects the tone of this New York Times best seller as funny, real, and a little confrontational. It’s a great title for a book written by a stand-up comedian who writes about her experiences with race, gender, and the cultural climate.
3. " The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People " by Stephen Covey
This title doesn’t set much of a tone for the book, but it certainly tells us exactly what we should expect to learn. We know we’re going to learn about highly effective people’s habits, specifically the ones ranking in the Top Seven.
They say not to judge a book by its cover, but it’s hard not to judge a book by its title. A title is the first and most important element of a piece of writing, and its ability to impact readers will determine the writing’s success.
The Role of Subtitles in Writing
A subtitle provides additional information about the content of a piece of writing. Subtitles are usually placed below the main title and serve to break up the content into smaller, more manageable sections. Subtitles provide additional detail and support the main title, making it easier for the reader to understand and engage with the content.
The main function of a subtitle is to provide more specific information about the content than the title does. They help the reader understand the structure and purpose of the writing.
Effective subtitles should be specific, clear, and concise, and they should always relate back to the main title. If we look back at our three previous title examples, we can see how their subtitles make them even easier for readers to understand:

1. “On the Origin of Species: by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life” by Charles Darwin
What a mouthful! Although Darwin’s title is short and serious, his book’s subtitle provides much more information about the content of his writing. Readers who want to know about the scientific theories surrounding natural selection can rejoice, while the ones who were hoping for a sci-fi origin story can safely set the book down.
2. “You Can’t Touch My Hair: And Other Things I Still Have to Explain” by Phoebe Robinson
This subtitle gives us an even stronger sense of tone. The words “still” and “have to” hint at Phoebe’s exasperation with people who want to touch her hair–and do other things! The subtitle still uses plain, confrontational language, but it also reveals more about what the book might have to say.
3. "The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People: Powerful Lessons in Personal Change" by Stephen Covey
This subtitle lets us know we’re not only going to discover these seven habits; we’re also going to learn lessons about them. These lessons will (hopefully) provide us with the tools we need to make a personal change. While Covey’s original title was pretty specific, the subtitle works perfectly to give even more information to curious perusers in bookstores everywhere.
Subtitles provide crucial information and structure to the content of a piece of writing. By understanding the definition of subtitles and their purpose, you can use them effectively to help your writing flow and make it easier for the reader to engage with the content.
Differences Between Titles and Subtitles
Titles and subtitles are both important elements of writing, but they serve different purposes and have different characteristics. While both are used to provide structure and organization to the content, there are some key differences between titles and subtitles that are worth exploring.
The first difference between titles and subtitles is their size. On covers and title pages, titles are typically much larger and more prominent than subtitles, and they are usually placed at the top of the page or at the beginning of the text. Subtitles, on the other hand, are usually smaller and less prominent, and they are placed below the main title.
Another difference between titles and subtitles is their purpose. Titles are designed to grab the reader's attention and give them a brief overview of the content, while subtitles are designed to provide additional information and support for the main title. Titles also set the tone of the content, while subtitles provide specific details to help the reader better understand the content’s structure.
How to use titles and subtitles effectively is a skill every writer must learn. By knowing the specific purposes and characteristics of each, you can use them effectively in your writing to provide structure, organization, and detail to your content. Don't let title confusion hold you back! Knowing the difference between titles and subtitles will help you give your readers the sneak peek they need to tip the scales in your direction when they see your writing.

Using Titles and Subtitles Effectively
One of the keys to successful writing is the effective use of titles and subtitles. When used correctly, titles and subtitles can help to organize your content, make it easier to read and understand, and increase engagement with your audience. Here are some tips for using titles and subtitles effectively:
Keep titles short and to the point. Titles should be concise and easy to read with a maximum of ten words. They should grab the reader's attention and give them an idea of what the content is about.
Make subtitles specific and relevant. Subtitles should be specific and directly related to the main title. They should provide additional information about the content and help the reader understand the structure of the writing.
Use different levels of titles and subtitles . When organizing your content, use different levels of titles and subtitles to distinguish between different sections and topics. This makes it easier for the reader to follow the content and understand the overall structure of the writing.
Consistency is key. When using titles and subtitles, be consistent in your use of capitalization, font size, and style. This makes your writing look professional and organized.
By following these tips and using titles and subtitles effectively, you can make your writing more organized, easier to read, and more engaging. Whether you are writing a novel, an article, or any other type of writing, the effective use of titles and subtitles is an essential skill to master.
Take some time to reflect on your own writing and see if there is room for improvement. Maybe your longer titles would work better split into a title-subtitle combo. Maybe your subtitle is better off as a title by itself! By reviewing your own choices, you'll be able to make changes to give your writing more clarity, structure, and impact, and engage your audience more effectively. Remember, the right use of titles and subtitles can make a big difference in your writing, so make sure to use them wisely!
Recent Posts
How Your Book Will Make You Rich
From Author to Authority: How A Book Establishes You as a Thought Leader
10 Tips For Becoming a Great Writer
What Are Subtitles In A Paper

- How-To Guides
- Tech Setup & Troubleshooting

Introduction
When it comes to writing a paper, there are several elements that contribute to its overall structure and organization. One such element is the use of subtitles. Subtitles, also known as subheadings or headings, are short phrases or titles that provide a concise summary of the content that follows. They serve as a roadmap for readers, helping them navigate through the paper and understand the main points being discussed.
The use of subtitles in a paper is not only a stylistic choice but also an important tool for effective communication. Subtitles help break down complex ideas into smaller, more manageable sections, making it easier for readers to grasp the main ideas and follow the logical flow of the paper. Additionally, subtitles provide visual cues that assist readers in skimming through the paper and quickly locating specific information.
Whether you are writing an essay, research paper, or any other academic document, using subtitles can greatly enhance the reader’s experience and understanding. By structuring your paper with clear and informative subtitles, you can present your ideas in a cohesive and organized manner, making it easier for readers to engage with your content.
In the following sections, we will explore the purpose and importance of subtitles in academic writing, as well as provide guidelines and examples for effectively using subtitles in your paper. But before we delve into those details, let us first understand what exactly subtitles are and how they differ from headings and subheadings.
Definition of Subtitles
Before we delve into the benefits and guidelines for using subtitles in a paper, it is important to establish a clear understanding of what exactly subtitles are and how they differ from headings and subheadings.
Subtitles, also known as subheadings or headings, are concise phrases or titles that provide a brief summary of the content that follows. They are typically used in written materials, such as papers, articles, books, and presentations, to break down the main text into smaller, more manageable sections.
Unlike headings, which are used to designate major sections or chapters within a document, subtitles are used to further divide these sections into more specific categories or topics. They provide a hierarchical structure to the content, allowing readers to easily navigate through the paper and locate relevant information.
Subtitles are often distinguished from headings by their formatting. While headings are typically presented in a larger font size, subtitles are usually formatted with bold text or placed within quotation marks to visually differentiate them from the main text. This visual distinction makes it easier for readers to identify and locate specific sections within a paper.
It is crucial to note that the use of subtitles should be consistent throughout the paper. Ideally, they should be used in a logical and systematic manner, following a clear and coherent structure. This ensures that readers can easily follow the flow of ideas and connect the different sections of the paper.
Now that we have established the definition of subtitles and their role in organizing a paper, let us explore the purpose and importance of using subtitles in academic writing.
Purpose of Subtitles in a Paper
The use of subtitles in a paper serves various purposes that contribute to effective communication and enhanced reader comprehension. Understanding the purpose of subtitles can help you strategically incorporate them into your writing to create a well-structured and engaging document.
One of the primary purposes of subtitles is to guide the reader through the content of the paper. By providing clear and descriptive titles for different sections, subtitles act as signposts, indicating the main ideas or topics covered in each section. This helps readers orient themselves and understand the overall organization of the paper, making it easier for them to navigate through the text and locate specific information.
Furthermore, subtitles facilitate the skimming and scanning of a paper. In academic settings, readers often have limited time and may need to quickly assess the relevance of a document to their research or study. Subtitles provide visual cues that allow readers to skim through the paper and identify sections or subsections that are of particular interest. This not only helps readers save time but also encourages them to engage with the content more effectively.
In addition to aiding navigation and skimming, subtitles also improve the readability of a paper. Breaking down large blocks of text into smaller, subsections with descriptive subtitles makes the content more digestible. This is especially important for academic papers that may contain complex concepts or lengthy discussions. Subtitles provide a logical structure to the content, allowing readers to follow the flow of ideas and maintain focus throughout the paper.
Another purpose of subtitles is to highlight key points or arguments within the paper. By using concise and informative subtitles, you can draw attention to important concepts, findings, or discussions. This helps readers understand the significance of specific sections and enables them to selectively dive deeper into the content that is most relevant to their needs.
Overall, the purpose of subtitles in a paper is to improve readability, facilitate navigation, and enhance the overall comprehensibility of the content. By strategically incorporating subtitles, you can guide your readers through your paper, provide visual cues for efficient skim reading, and create a more engaging and accessible document.
Importance of Subtitles in Academic Writing
Subtitles play a crucial role in academic writing, offering significant benefits for both writers and readers. Recognizing the importance of subtitles can help you improve the clarity, organization, and overall impact of your academic papers.
First and foremost, subtitles help improve the overall structure and organization of academic writing. By breaking down the content into smaller sections with clear subtitles, you create a sense of coherence and logical progression. This not only makes it easier for readers to understand your arguments and ideas but also enables you to organize your thoughts better as a writer. Subtitles help you communicate your main points effectively, ensuring that your paper flows smoothly and is easy to follow.
Additionally, subtitles enhance the readability of academic papers. When readers encounter lengthy paragraphs or dense text, they can quickly become overwhelmed, leading to reduced comprehension. Subtitles provide visual breaks in the text, making the content more accessible and digestible. The use of subtitles allows readers to skim through the paper, locate relevant information, and focus on specific sections that align with their research interests or needs. This not only improves the reader’s experience but also increases the chances of your paper being read and cited by others.
Furthermore, subtitles in academic writing help to improve the overall accessibility and inclusivity of your paper. Different readers may have varying levels of background knowledge or may be approaching your paper from different disciplinary perspectives. Subtitles allow readers to quickly assess the content of each section, enabling them to decide which sections are most relevant to their interests or expertise. This ensures that your paper can be accessed and understood by a wider range of readers, fostering interdisciplinary dialogue and collaboration.
The use of subtitles in academic writing also promotes effective communication of complex ideas. Academic papers often address intricate concepts or present detailed findings. By breaking down these ideas into smaller sections with descriptive subtitles, you can guide readers through the content and help them grasp the main arguments or findings. Subtitles serve as signposts, highlighting the key points and ensuring that readers can follow the logical flow of your paper, even when dealing with intricate subject matter.
In summary, the importance of subtitles in academic writing cannot be overstated. They contribute to the overall structure, readability, accessibility, and clarity of your papers. By incorporating subtitles strategically, you improve the organization of your ideas, enhance the reader’s experience, and increase the impact and reach of your academic work.
Guidelines for Using Subtitles in a Paper
Using subtitles effectively is essential for creating a well-structured and accessible academic paper. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your subtitles enhance the overall organization and readability of your work.
1. Be clear and concise: Subtitles should accurately reflect the content of the section while being concise and informative. Avoid using vague or overly broad titles that may confuse the reader. Instead, choose subtitles that provide a clear and concise summary of what will be discussed in that particular section.
2. Maintain a logical hierarchy: Subtitles should follow a logical hierarchy, with main sections identified by larger headings and subsections labeled with subheadings. This hierarchical structure helps readers grasp the overall organization of your paper and understand the relationships between different sections.
3. Ensure parallelism: When using subtitles for multiple sections within the same level, make sure they have a consistent structure. This means using parallel grammatical form, such as using all nouns, verbs, or phrases, to maintain consistency and clarity.
4. Avoid redundancy: Subtitles should provide new and distinct information from the main heading. Avoid duplicating words or phrases that are already mentioned in the main title. Instead, use the subtitle to add additional details or to focus on a specific aspect of the main topic.
5. Consider your audience: Take into account the background and expertise of your intended audience when crafting subtitles. Use terminology and language that is appropriate for your target readership, ensuring that the subtitles are accessible and understandable to them.
6. Use formatting consistently: Formatting is an important aspect of subtitles. Consistently follow the formatting guidelines provided by your institution or publisher. This may include using bold text, italicization, or quotation marks to distinguish subtitles from the main text.
7. Review for coherence: Once you have incorporated subtitles into your paper, review the overall flow and coherence of the sections. Ensure that the subtitles create a logical progression and help guide the reader through your arguments or findings. Adjust and revise as necessary to create a seamless and well-organized document.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can effectively incorporate subtitles into your academic writing, creating a clear and organized paper that is accessible to your readers.
Formatting Subtitles in a Paper
Formatting subtitles in a paper is essential for visually distinguishing them from the main text and creating a clear hierarchy of information. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your subtitles are formatted consistently and effectively.
1. Use appropriate font size and style: Subtitles should be formatted using a slightly larger font size than the main text to make them stand out. However, they should not be excessively larger, as this may disrupt the flow and visual coherence of the paper. Choose a font style that is clear and easy to read, such as Arial, Times New Roman, or Calibri.
2. Utilize bold or italics: To further emphasize subtitles, you can use bold or italics formatting. Decide on a consistent approach for your subtitles and apply the same formatting throughout the paper. For example, you may choose to use bold for main section subtitles and italics for subsections. This helps visually differentiate the different levels of subtitles.
3. Consider using numbering or lettering: In certain cases, such as when presenting a step-by-step process or outlining multiple points, using numbering or lettering can provide clarity and organization. This helps readers understand the sequence or hierarchy of the information being presented. Ensure that the formatting for the numbering or lettering is clear and easily distinguishable from the main text.
4. Use consistent punctuation: Decide on a consistent style for punctuation in subtitles and apply it throughout the paper. For example, you may choose to use sentence case (capitalizing only the first word and any proper nouns) or title case (capitalizing the first letter of each word). Consistency in punctuation helps maintain the visual coherence and professionalism of your paper.
5. Maintain a clear hierarchy: Formatting should reflect the hierarchical structure of your paper. Use larger headings for major sections and smaller subheadings for subsections. Consider using a different font size or formatting style for each level of subtitles to visually indicate the hierarchy. This makes it easier for readers to navigate your paper and locate specific sections.
6. Follow specific style guidelines: Depending on the academic discipline or publication guidelines, there may be specific rules for formatting subtitles. Familiarize yourself with the recommended style guide, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago style, and adhere to their formatting guidelines for subtitles. This ensures consistency and compliance with academic standards.
7. Proofread for consistency: After formatting your subtitles, take the time to proofread your paper for consistency. Check that the font sizes, styles, and punctuation are applied uniformly throughout the document. Consistent formatting enhances the professional appearance of your paper and facilitates readability for your audience.
By following these formatting guidelines, you can effectively structure and present subtitles in your paper, enhancing readability and aiding in the navigation of your content.
Examples of Subtitles in Different Disciplines
Subtitles in academic writing can vary depending on the specific discipline or field of study. Different disciplines may have their own conventions and expectations for how subtitles are used. Here are some examples of how subtitles are commonly employed in various disciplines:
1. Social Sciences: In social sciences, subtitles are often used to indicate different research questions or hypotheses being addressed within a study. For example:
- “The Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Factors Influencing Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections: A Comparative Study”
2. Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, subtitles are commonly used to outline different stages of an experimental procedure or to present key findings and interpretations. For example:
- “Experimental Setup and Materials”
- “Results and Discussion: Analysis of Growth Patterns”
3. Humanities: In humanities disciplines, subtitles are often employed to present different themes or topics within an overall argument or analysis. For example:
- “Exploring Symbolism in the Novels of Virginia Woolf”
- “The Evolution of Renaissance Art: A Comparative Study of Italian and Flemish Painting”
4. Engineering and Technology: In engineering and technology disciplines, subtitles are frequently used to indicate different stages or components of a design or experimental process. For example:
- “Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip for Drug Delivery”
- “Testing and Evaluation of Mechanical Properties: Tensile Strength and Hardness”
5. Business and Management: In business and management fields, subtitles may be used to outline different aspects of a case study, business plan, or strategic analysis. For example:
- “Case Study: Success Factors in International Market Entry”
- “Strategic Analysis: SWOT Analysis and Competitive Landscape”
These examples provide a glimpse into how subtitles are commonly employed in different disciplines. However, it is important to consult the specific style guidelines or preferences of your field when formatting and structuring subtitles in your own academic writing.
Final Thoughts on Using Subtitles in a Paper
Using subtitles in a paper can greatly enhance its organization, readability, and overall impact. By considering the purpose and following the guidelines for using subtitles effectively, you can create a well-structured and engaging academic document.
Subtitles serve as signposts, guiding readers through the content and aiding in the navigation of the paper. They break down complex ideas into smaller, more manageable sections, making it easier for readers to follow the flow of your arguments or findings.
When incorporating subtitles, it is important to be clear, concise, and consistent. Use descriptive subtitles that accurately reflect the content of each section. Maintain a logical hierarchy and formatting style for your subtitles, ensuring they are visually distinguishable from the main text.
Remember to consider your audience when crafting subtitles, using terminology and language that is appropriate for your readership. Avoid redundancy and ensure that the subtitles add new and distinct information to the overarching title.
Keep in mind that different disciplines may have specific conventions for using subtitles. Familiarize yourself with the guidelines and style requirements of your field to ensure consistency and compliance.
Overall, subtitles play a vital role in improving the organization, readability, and accessibility of academic papers. They facilitate effective communication, aid in skimming and scanning, and enhance the overall reading experience for your audience.
Incorporating subtitles demonstrates your mastery of structuring information and catering to the needs of your readers. By utilizing them strategically, you can effectively convey your ideas, promote understanding, and engage with your audience more effectively.
Remember to proofread your paper for consistency and coherence, ensuring that the subtitles contribute to the overall flow and logical progression of your arguments or findings.
By utilizing and formatting subtitles thoughtfully, you can create a well-organized and impactful paper that captivates readers and effectively communicates your research or ideas.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Crowdfunding
- Cryptocurrency
- Digital Banking
- Digital Payments
- Investments
- Console Gaming
- Mobile Gaming
- VR/AR Gaming
- Gadget Usage
- Gaming Tips
- Online Safety
- Software Tutorials
- Tech Setup & Troubleshooting
- Buyer’s Guides
- Comparative Analysis
- Gadget Reviews
- Service Reviews
- Software Reviews
- Mobile Devices
- PCs & Laptops
- Smart Home Gadgets
- Content Creation Tools
- Digital Photography
- Video & Music Streaming
- Online Security
- Online Services
- Web Hosting
- WiFi & Ethernet
- Browsers & Extensions
- Communication Platforms
- Operating Systems
- Productivity Tools
- AI & Machine Learning
- Cybersecurity
- Emerging Tech
- IoT & Smart Devices
- Virtual & Augmented Reality
- Latest News
- AI Developments
- Fintech Updates
- Gaming News
- New Product Launches
New Step by Step Roadmap for Marijuana News
- Facts About Skycity Online Casino Nz 8211 100 Welcome Bonus Up To 100 Revealed
Related Post
The basic principles of online pokies real money nz ᐈ best slots to play (2024), top guidelines of play pokies online new zealand, related posts.

What Can A 2000mW Laser Engraver Do

How To Cite An eBook Using APA Format

The Man Who Knew Infinity With Subtitles

How To Write An EBook Fast

How Do I Make An EBook Cover

How To Use Subtitles On Windows Media Player

How To Get Subtitles On Kodi

How To Add Subtitles To Gifs
Recent stories.

Facts About Skycity Online Casino Nz – 100% Welcome Bonus Up To $100 Revealed

How to Find the Best Midjourney Alternative in 2024: A Guide to AI Anime Generators

How to Know When it’s the Right Time to Buy Bitcoin

Unleashing Young Geniuses: How Lingokids Makes Learning a Blast!

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

What Is A Subtitle Of A Book And How To Write One
Sometimes, a title says all your cover needs to say (other than your author name).
But more often than not, at least when it comes to nonfiction, a good subtitle can be the difference between publishing success and invisibility .
Why are subtitles necessary, though?
What makes them so powerful?
And how do you write the kind of subtitle that will give your book the edge it needs in a crowded market ?
Let’s find out.
What Is a Subtitle of a Book?
A subtitle in a book is a phrase that often does more to establish your book’s place in the market than your title does.
The title gets more of the spotlight, but the subtitle does most of the work. The title is the hook ; the subtitle is the reel.
So, what is the subtitle’s purpose? What does it actually do?
- Clarifies the focus of your book (which is useful if your title is vague);
- Tells readers why they should read your book—what they’ll get out of it;
- Helps convey the tone of your book (serious, scholarly, funny, lighthearted, etc.);
- Provides context for the title (which can be short and cryptic but memorable);
- Uses keywords to make your book visible to search engines.
Some books have standalone titles that do all the work, making subtitles unnecessary. But effective do-it-all titles are rare.
And as you’ll see in the examples further down, crafting a killer title-subtitle pairing can be a lot of fun—the kind of fun your readers can feel when they see your cover.
That’s the hope, anyway. So, how do you get closer to that?
How to Write a Subtitle that Sells
There’s no set formula for crafting the perfect subtitle for a book. But many of the best subtitles use the following to their advantage:
- Keywords — Book subtitles need targeted keywords to get the attention of both search engines and shoppers. Publisher Rocket can help you find the best ones for your book. Caveat: Don’t overdo it. Keyword cramming is not a good look.
- Cadence — Subtitles that read easily and are even fun to say are more likely to circulate in the minds of shoppers and anyone who happens upon your book cover. Cadence gives your words a balanced, rhythmic flow and melodic feel. It lingers.
- Brevity — Get to the point in as few words as possible without sacrificing essential details. Shorter isn’t always better. But don’t use more words than you need.
- Clarity — Spell out in crystal-clear language exactly how the reader will benefit from reading your book or what problems it will solve for them.
- The Rule of Three — The human brain loves groupings of three, and many subtitles capitalize on that with three goals, ideas, or pain points.
Keeping the above in mind, here are some steps to help get you started on creating the best subtitle for your book:
- Research what’s already working — Look at bestseller lists in newspapers and online bookstores to get a sense of what’s working. What do you notice about the subtitles that stand out for you?
- Identify the keywords you need — Use the keyword tools at your disposal—including search engines (Google, Amazon, etc.) to find the keywords people use to find books like yours.
- Brainstorm a list of at least 20 subtitles — Using the most important keywords, make a list of at least 20 potential subtitles to consider. Allow yourself to write down even the stinkers that come to mind. No filters.
- Identify your top three — Cut your list of 20 down to the three that make the best possible use of the words in them. Write them out where you’ll see them throughout the day.
- Get feedback — Try running them through the CoSchedule Headline Analyzer. Otherwise, try to find your ideal readers (who aren’t friends or family) and ask for their honest, unfiltered feedback.
5 Examples of Subtitles
We’ve found five subtitles examples demonstrating the key elements and considerations described above. Look through them carefully and feel free to click on the links to each book’s sales pages for a closer look.
Example #1: The Five Hour Workday: Live Differently, Unlock Productivity, and Find Happiness by Stephan Aarstol
We’ll start with a subtitle that uses the rule of three and popular keywords to capture the attention of book browsers and search engines alike. While the title offers a strong clue to the book’s message, the subtitle drills down to the three key benefits of reading the book.
Example #2: The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You’re Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You Are by Brené Brown
The title here is vague, but the subtitle more than makes up for it by identifying the book’s aim is clear unambiguous language. The aim is two-fold, but it articulates a goal that resonates with millions. It’s a clear invitation to a better life.
Example #3: Hillbilly Elegy: A Memoir of a Family and Culture in Crisis by J.D. Vance
Here again, the title itself is unclear, though the “elegy” bit does suggest we’re looking at a memoir . It says little, though, about the focus of that memoir, and that’s where the subtitle helps us out. The word “crisis” gives the subtitle a sense of urgency, while “family” and “culture” give it resonance.
Example #4: The Science of Getting Started: How to Beat Procrastination, Summon Productivity, and Stop Self-Sabotage by Patrick King
Here’s another subtitle using the Rule of Three to hammer home the three main goals for this book. Keywords like “procrastination,” “productivity,” and “self-sabotage” make the book searchable and more likely to be found by those searching for help in those areas.
Example #5: The Forks Over Knives Plan: How to Transition to the Life-Saving, Whole-Food, Plant-Based Diet by Alona Pulde and Matthew Lederman OR The Food Revolution: How Your Diet Can Help Save Your Life and Our World by John Robbins
More Related Articles
What Is A Heading In A Book? Here’s What You Need To Know
Writing a Story? 10 Key Parts Of A Story You Must Include
Does A Comma Go Before Or After But?
Both food books use subtitles to make the book’s purpose clearer to the reader. Forks Over Knives uses the three-fold keywords “life-saving,” “whole-food,” and “plant-based” to make the book searchable and create an emotional impact. Food Revolution uses its subtitle to explain the word “Revolution” in the title by driving home the power of one person’s diet.
Now that you know why subtitles are essential and how to create a powerful one for your book, what’s your biggest takeaway from this post?
How many subtitle ideas have already come to mind for your current book? Remember to keep the filter switched off while you’re brainstorming. This is your “rough sketch” of ideas. It’s supposed to look rough. Have fun with it.
How many subtitles can you think up today?
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Latest in science and technology to the in business big stories
Tips and Tricks
- Troubleshooting
- Product Launches
- Technology Trends
- Software and Apps
Home > How-To Guides > Tips and Tricks > What Is A Subtitle In An Essay
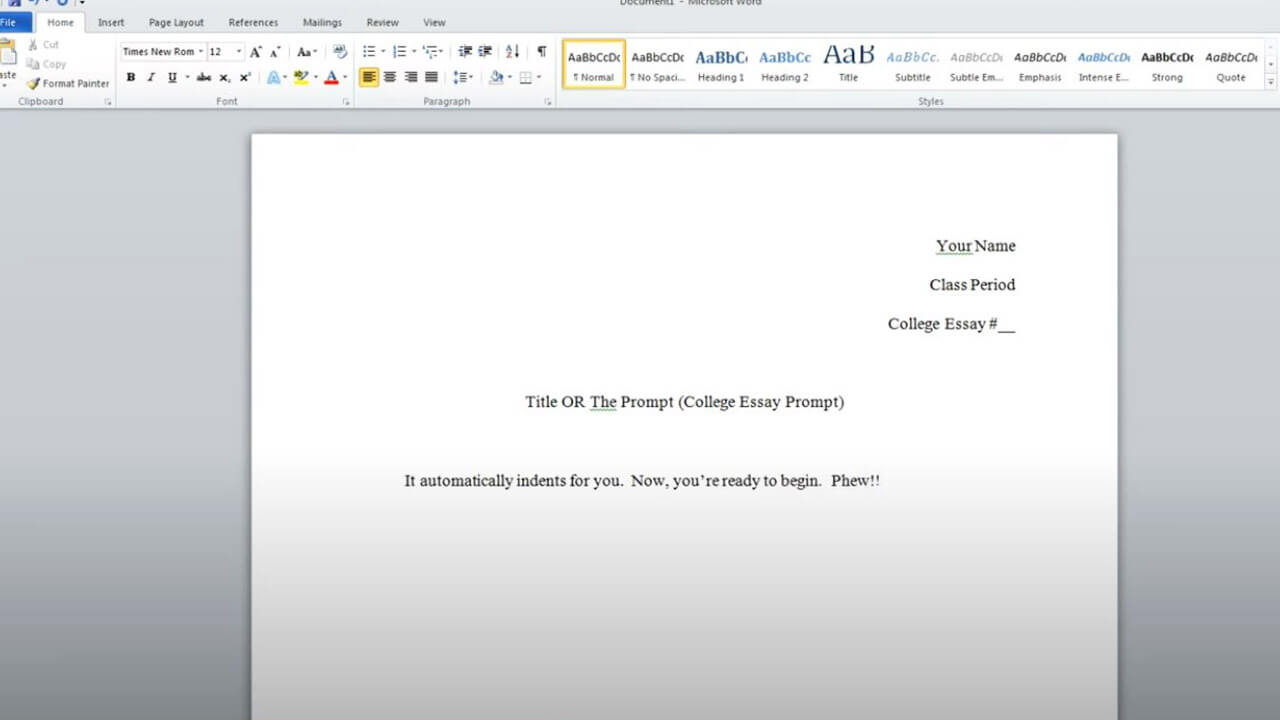
What Is A Subtitle In An Essay
Published: February 22, 2024
Written by: Melitta Newsome
Learn the tips and tricks for using subtitles in an essay effectively. Discover how to make your writing more organized and engaging with subtitles.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Techsplurge.com, at no extra cost. Learn more )
Table of Contents
Importance of using subtitles in essays, guidelines for including subtitles in essays, examples of effective subtitles in essays, common mistakes to avoid when using subtitles in essays, how subtitles enhance the overall structure of an essay.
Subtitles play a crucial role in enhancing the readability and organization of essays. They serve as signposts, guiding readers through the content and providing a clear roadmap of the essay's structure. By breaking down the text into distinct sections, subtitles offer a visual break, making the content more approachable and digestible for the reader.
When used effectively, subtitles can capture the essence of each section, offering a glimpse into the content that follows. This not only piques the reader's interest but also helps them anticipate the information to come. Moreover, subtitles provide a framework for the writer to present their ideas in a coherent and logical manner, ensuring that each section flows seamlessly into the next.
In addition to aiding comprehension, subtitles also contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of an essay. They create a sense of order and organization, transforming lengthy blocks of text into visually appealing segments. This not only makes the essay more visually engaging but also helps in retaining the reader's attention.
From an SEO perspective, subtitles also play a vital role in improving the discoverability of an essay. By incorporating relevant keywords into the subtitles, writers can enhance the search engine optimization of their content, making it more likely to appear in relevant search results.
In essence, the strategic use of subtitles in essays can significantly elevate the overall quality of the content. They facilitate comprehension, improve visual appeal, aid in structuring the essay, and enhance its discoverability. As such, incorporating well-crafted subtitles is a powerful tool for writers to effectively convey their ideas while engaging and guiding their readers through the essay.
Read more : What Is A Subtitle In Powerpoint
When incorporating subtitles in essays, it is essential to adhere to certain guidelines to ensure their effectiveness in enhancing the overall structure and readability of the content. Here are some key guidelines to consider:
Clarity and Relevance : Subtitles should be clear, concise, and directly relevant to the content of the section they introduce. They should provide a glimpse into the main idea or argument of the subsequent text, allowing readers to anticipate the information to follow.
Consistency : Maintain consistency in the formatting and style of subtitles throughout the essay. This includes using the same font, size, and formatting for all subtitles to create a cohesive visual structure.
Hierarchy and Organization : Utilize a hierarchical structure for subtitles to reflect the organization of the essay. This may involve using different levels of headings to denote main sections, subsections, and sub-subsections, thereby creating a clear and logical hierarchy.
Keyword Integration : Incorporate relevant keywords into the subtitles to improve the essay's search engine optimization. By including keywords that align with the essay's topic or theme, writers can enhance the discoverability of their content.
Length and Precision : Keep subtitles succinct and to the point. They should effectively encapsulate the essence of the section without being overly verbose. This ensures that readers can quickly grasp the main idea of each segment.
Parallel Structure : Maintain a parallel structure in the wording of subtitles within the same level. This creates a sense of uniformity and coherence, contributing to the overall professional presentation of the essay.
Avoiding Ambiguity : Subtitles should be unambiguous and clearly reflect the content they introduce. Ambiguous or misleading subtitles can confuse readers and detract from the essay's coherence.
Visual Distinction : Ensure that subtitles are visually distinct from the main body of the text. This can be achieved through the use of bold, italics, or a different font size to clearly demarcate the beginning of each section.
By adhering to these guidelines, writers can effectively integrate subtitles into their essays, enhancing the overall structure, readability, and search engine optimization of their content. This, in turn, contributes to a more engaging and organized reading experience for the audience.
"The Art of Storytelling: Crafting Compelling Narratives"
- This subtitle introduces a section focused on the techniques and elements of storytelling. It sets the stage for discussing the art of crafting engaging narratives, capturing the reader's attention and signaling the exploration of storytelling principles within the essay.
"Unveiling the Power of Renewable Energy: A Sustainable Future"
- Here, the subtitle succinctly encapsulates the theme of sustainable energy and its potential impact. It provides a clear preview of the upcoming content, guiding the reader's expectations toward an exploration of renewable energy's significance in shaping a sustainable future.
"Exploring Cultural Diversity: Embracing Global Perspectives"
- This subtitle hints at a section delving into the rich tapestry of cultural diversity and its broader implications. It offers a glimpse into the forthcoming discussion, inviting readers to anticipate an exploration of global perspectives and the value of embracing diverse cultures.
"Innovation in Technology: Revolutionizing the Digital Landscape"
- By using this subtitle, the essay signals a focus on technological innovation and its transformative impact on the digital realm. It sets the stage for an in-depth examination of technological advancements, enticing readers to delve into the evolving landscape of digital innovation.
"The Quest for Knowledge: Navigating the Depths of Intellectual Curiosity"
- This subtitle hints at a section dedicated to the pursuit of knowledge and intellectual exploration. It provides a captivating glimpse into the thematic content, inviting readers to embark on a journey through the depths of intellectual curiosity within the essay.
"Evolving Business Strategies: Adapting to a Dynamic Market Environment"
- Here, the subtitle foreshadows a discussion on adaptive business strategies within a dynamic market landscape. It offers a clear indication of the upcoming content, guiding readers to anticipate insights into the evolution of business approaches in response to market dynamics.
"The Essence of Leadership: Inspiring Vision and Influence"
- This subtitle sets the stage for a section dedicated to the core attributes of leadership. It offers a compelling preview of the forthcoming discussion, signaling an exploration of the essence of leadership, encompassing vision, inspiration, and influence.
"Environmental Conservation: Preserving Ecosystems for Future Generations"
- By using this subtitle, the essay introduces a section focused on environmental conservation and its long-term impact. It provides a concise preview of the upcoming content, guiding readers to anticipate insights into the imperative of preserving ecosystems for future generations.
These examples illustrate how effective subtitles can succinctly encapsulate the essence of each essay section, offering a glimpse into the thematic content while guiding readers through the structured flow of the essay.
When incorporating subtitles in essays, it is imperative to be mindful of common mistakes that can detract from their effectiveness in enhancing the overall structure and readability of the content. By recognizing and avoiding these pitfalls, writers can ensure that their subtitles fulfill their intended purpose and contribute to a cohesive and engaging essay.
Overly Lengthy Subtitles
One prevalent mistake is the use of excessively long subtitles that overshadow the main content they introduce. Subtitles should be succinct and to the point, providing a clear preview of the section without overwhelming the reader with excessive detail. Lengthy subtitles can disrupt the flow of the essay and diminish the impact of the subsequent content.
Read more : What Is A Subtitle In An Article
Lack of Clarity and Relevance
Subtitles that lack clarity and relevance to the content they introduce can lead to confusion and disengagement among readers. It is essential to ensure that each subtitle concisely encapsulates the main idea of the section it precedes, offering a clear and relevant preview of the forthcoming content. Ambiguous or vague subtitles can undermine the coherence of the essay.
Inconsistent Formatting and Style
Inconsistency in the formatting and style of subtitles can disrupt the visual flow of the essay. Writers should maintain uniformity in the presentation of subtitles, including font, size, and styling, to create a cohesive and professional aesthetic. Deviating from consistent formatting can create visual distractions and detract from the overall reading experience.
Lack of Keyword Integration
Failing to integrate relevant keywords into subtitles can hinder the search engine optimization of the essay. Subtitles present an opportunity to incorporate essential keywords related to the essay's topic or theme, enhancing its discoverability in online searches. Neglecting to optimize subtitles with relevant keywords can limit the essay's visibility and reach.
Ambiguous or Misleading Subtitles
Ambiguity or misleading wording in subtitles can lead to reader confusion and misinterpretation of the subsequent content. Subtitles should accurately reflect the essence of the section they introduce, avoiding vague or misleading language that may misalign with the actual content. Clear and precise subtitles are essential for maintaining reader engagement and comprehension.
Read more : What Is Chromecast
Inadequate Visual Distinction
Subtitles that lack visual distinction from the main body of the text can diminish their effectiveness as organizational signposts. It is crucial to ensure that subtitles are visually differentiated, using formatting techniques such as bold, italics, or a distinct font size to clearly demarcate the beginning of each section. Insufficient visual distinction can impede the reader's ability to navigate the essay's structure.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and actively avoiding them, writers can harness the full potential of subtitles to enhance the organization, readability, and search engine optimization of their essays. This proactive approach contributes to a more cohesive and impactful presentation of ideas, ultimately enriching the reader's experience.
Subtitles serve as a fundamental element in shaping the structural framework of an essay, playing a pivotal role in enhancing its coherence, organization, and overall readability. By strategically integrating subtitles, writers can effectively segment the content, creating a well-defined roadmap that guides readers through the essay's thematic landscape.
One of the primary ways in which subtitles contribute to the essay's structure is by establishing a clear hierarchy of ideas. Through the use of distinct levels of headings and subheadings, the essay's content is systematically categorized into cohesive sections, each addressing specific aspects of the overarching topic. This hierarchical arrangement not only provides a systematic flow but also enables readers to navigate through the essay with ease, gaining a comprehensive understanding of the content's progression.
Furthermore, subtitles facilitate the logical progression of ideas within the essay. By delineating distinct sections, each with its own subtitle, writers can ensure a seamless transition between different themes, arguments, or perspectives. This segmentation allows for a focused exploration of individual subtopics, preventing the content from becoming convoluted or disjointed. As a result, readers can engage with the essay in a structured manner, following the natural flow of ideas from one section to the next.
In addition to enhancing the essay's coherence, subtitles also contribute to its visual appeal. By breaking down the text into manageable segments, each marked by a clear subtitle, the essay becomes more visually inviting and approachable. This visual organization not only alleviates the intimidation of dense, uninterrupted text but also entices readers to delve into the segmented content, fostering a more immersive reading experience.
From an SEO perspective, subtitles play a crucial role in improving the discoverability of an essay. By incorporating relevant keywords into the subtitles, writers can enhance the search engine optimization of their content, making it more likely to appear in relevant search results. This strategic integration of keywords within subtitles amplifies the essay's visibility, ensuring that it reaches a broader audience and resonates with individuals seeking information on related topics.
In essence, the strategic use of subtitles enriches the overall structure of an essay by establishing a clear hierarchy, facilitating the logical progression of ideas, enhancing visual appeal, and optimizing search engine discoverability. Through these multifaceted contributions, subtitles elevate the essay's organization and coherence, ultimately enriching the reader's experience and comprehension of the content.
Was this page helpful?
How To Download YouTube Subtitles
Closed Caption Vs Subtitle: Understanding The Difference
How To Add Subtitles In Premiere Pro
How To Make Subtitles Bigger On Peacock
How To Turn On Subtitles On Disney Plus
Latest articles.
Mastering Subtitles With Final Cut Pro
Written By: Melitta Newsome
Kodi Subtitles: Enhancing Your Viewing Experience
How To Make Subtitles Bigger On Netflix
Creating Concise Subtitles
Converting An SRT File
Related post.

By: Marice Dionne • Tips and Tricks

By: Adelaida Jerome • Gadgets

By: Larisa Hinkle • Software and Apps
By: Vonnie Blevins • Tips and Tricks
By: Doe Maynard • Tips and Tricks
By: Eustacia Buckley • Tips and Tricks

By: Inesita Groves • Technology Trends

By: Celle Costa • Software and Apps
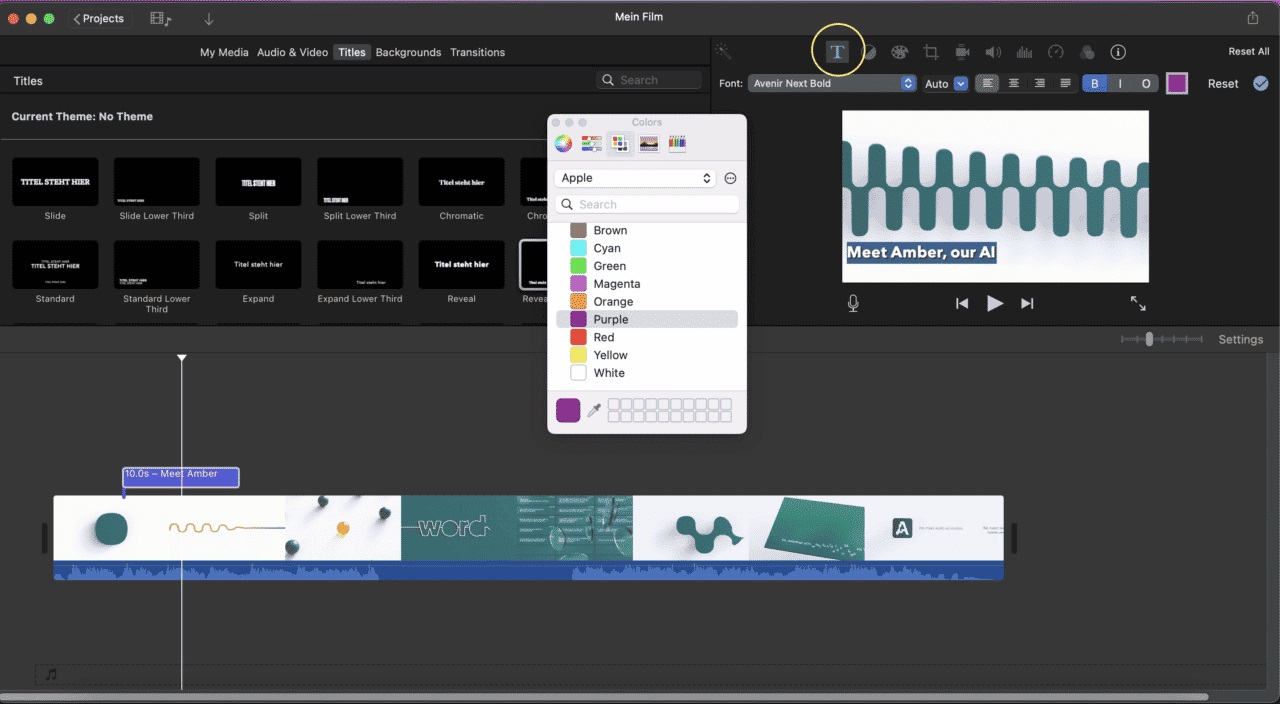
By: Jeanette Clifton • Tips and Tricks

By: Rea Ostrom • Tips and Tricks
By: Anallise Pool • Tips and Tricks

By: Astrix Merino • Software and Apps

By: Isadora Zahn • Software and Apps
Please accept our Privacy Policy.
TechSplurge.com uses cookies to improve your experience and to show you personalized ads. Please review our privacy policy by clicking here .

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
- https://techsplurge.com/how-to-guides/tips-and-tricks/what-is-a-subtitle-in-an-essay/
Ultimate Guide to Writing Your College Essay
Tips for writing an effective college essay.
College admissions essays are an important part of your college application and gives you the chance to show colleges and universities your character and experiences. This guide will give you tips to write an effective college essay.
Want free help with your college essay?
UPchieve connects you with knowledgeable and friendly college advisors—online, 24/7, and completely free. Get 1:1 help brainstorming topics, outlining your essay, revising a draft, or editing grammar.
Writing a strong college admissions essay
Learn about the elements of a solid admissions essay.
Avoiding common admissions essay mistakes
Learn some of the most common mistakes made on college essays
Brainstorming tips for your college essay
Stuck on what to write your college essay about? Here are some exercises to help you get started.
How formal should the tone of your college essay be?
Learn how formal your college essay should be and get tips on how to bring out your natural voice.
Taking your college essay to the next level
Hear an admissions expert discuss the appropriate level of depth necessary in your college essay.
Student Stories
Student Story: Admissions essay about a formative experience
Get the perspective of a current college student on how he approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about personal identity
Get the perspective of a current college student on how she approached the admissions essay.
Student Story: Admissions essay about community impact
Student story: admissions essay about a past mistake, how to write a college application essay, tips for writing an effective application essay, sample college essay 1 with feedback, sample college essay 2 with feedback.
This content is licensed by Khan Academy and is available for free at www.khanacademy.org.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks
Published on February 9, 2015 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023 by Shona McCombes.
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction , focused paragraphs , clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion .
Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence , and each point is directly related to the thesis statement .
As you read, hover over the highlighted parts to learn what they do and why they work.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing an essay, an appeal to the senses: the development of the braille system in nineteenth-century france.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
In France, debates about how to deal with disability led to the adoption of different strategies over time. While people with temporary difficulties were able to access public welfare, the most common response to people with long-term disabilities, such as hearing or vision loss, was to group them together in institutions (Tombs, 1996). At first, a joint institute for the blind and deaf was created, and although the partnership was motivated more by financial considerations than by the well-being of the residents, the institute aimed to help people develop skills valuable to society (Weygand, 2009). Eventually blind institutions were separated from deaf institutions, and the focus shifted towards education of the blind, as was the case for the Royal Institute for Blind Youth, which Louis Braille attended (Jimenez et al, 2009). The growing acknowledgement of the uniqueness of different disabilities led to more targeted education strategies, fostering an environment in which the benefits of a specifically blind education could be more widely recognized.
Several different systems of tactile reading can be seen as forerunners to the method Louis Braille developed, but these systems were all developed based on the sighted system. The Royal Institute for Blind Youth in Paris taught the students to read embossed roman letters, a method created by the school’s founder, Valentin Hauy (Jimenez et al., 2009). Reading this way proved to be a rather arduous task, as the letters were difficult to distinguish by touch. The embossed letter method was based on the reading system of sighted people, with minimal adaptation for those with vision loss. As a result, this method did not gain significant success among blind students.
Louis Braille was bound to be influenced by his school’s founder, but the most influential pre-Braille tactile reading system was Charles Barbier’s night writing. A soldier in Napoleon’s army, Barbier developed a system in 1819 that used 12 dots with a five line musical staff (Kersten, 1997). His intention was to develop a system that would allow the military to communicate at night without the need for light (Herron, 2009). The code developed by Barbier was phonetic (Jimenez et al., 2009); in other words, the code was designed for sighted people and was based on the sounds of words, not on an actual alphabet. Barbier discovered that variants of raised dots within a square were the easiest method of reading by touch (Jimenez et al., 2009). This system proved effective for the transmission of short messages between military personnel, but the symbols were too large for the fingertip, greatly reducing the speed at which a message could be read (Herron, 2009). For this reason, it was unsuitable for daily use and was not widely adopted in the blind community.
Nevertheless, Barbier’s military dot system was more efficient than Hauy’s embossed letters, and it provided the framework within which Louis Braille developed his method. Barbier’s system, with its dashes and dots, could form over 4000 combinations (Jimenez et al., 2009). Compared to the 26 letters of the Latin alphabet, this was an absurdly high number. Braille kept the raised dot form, but developed a more manageable system that would reflect the sighted alphabet. He replaced Barbier’s dashes and dots with just six dots in a rectangular configuration (Jimenez et al., 2009). The result was that the blind population in France had a tactile reading system using dots (like Barbier’s) that was based on the structure of the sighted alphabet (like Hauy’s); crucially, this system was the first developed specifically for the purposes of the blind.
While the Braille system gained immediate popularity with the blind students at the Institute in Paris, it had to gain acceptance among the sighted before its adoption throughout France. This support was necessary because sighted teachers and leaders had ultimate control over the propagation of Braille resources. Many of the teachers at the Royal Institute for Blind Youth resisted learning Braille’s system because they found the tactile method of reading difficult to learn (Bullock & Galst, 2009). This resistance was symptomatic of the prevalent attitude that the blind population had to adapt to the sighted world rather than develop their own tools and methods. Over time, however, with the increasing impetus to make social contribution possible for all, teachers began to appreciate the usefulness of Braille’s system (Bullock & Galst, 2009), realizing that access to reading could help improve the productivity and integration of people with vision loss. It took approximately 30 years, but the French government eventually approved the Braille system, and it was established throughout the country (Bullock & Galst, 2009).
Although Blind people remained marginalized throughout the nineteenth century, the Braille system granted them growing opportunities for social participation. Most obviously, Braille allowed people with vision loss to read the same alphabet used by sighted people (Bullock & Galst, 2009), allowing them to participate in certain cultural experiences previously unavailable to them. Written works, such as books and poetry, had previously been inaccessible to the blind population without the aid of a reader, limiting their autonomy. As books began to be distributed in Braille, this barrier was reduced, enabling people with vision loss to access information autonomously. The closing of the gap between the abilities of blind and the sighted contributed to a gradual shift in blind people’s status, lessening the cultural perception of the blind as essentially different and facilitating greater social integration.
The Braille system also had important cultural effects beyond the sphere of written culture. Its invention later led to the development of a music notation system for the blind, although Louis Braille did not develop this system himself (Jimenez, et al., 2009). This development helped remove a cultural obstacle that had been introduced by the popularization of written musical notation in the early 1500s. While music had previously been an arena in which the blind could participate on equal footing, the transition from memory-based performance to notation-based performance meant that blind musicians were no longer able to compete with sighted musicians (Kersten, 1997). As a result, a tactile musical notation system became necessary for professional equality between blind and sighted musicians (Kersten, 1997).
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Bullock, J. D., & Galst, J. M. (2009). The Story of Louis Braille. Archives of Ophthalmology , 127(11), 1532. https://doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.286.
Herron, M. (2009, May 6). Blind visionary. Retrieved from https://eandt.theiet.org/content/articles/2009/05/blind-visionary/.
Jiménez, J., Olea, J., Torres, J., Alonso, I., Harder, D., & Fischer, K. (2009). Biography of Louis Braille and Invention of the Braille Alphabet. Survey of Ophthalmology , 54(1), 142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2008.10.006.
Kersten, F.G. (1997). The history and development of Braille music methodology. The Bulletin of Historical Research in Music Education , 18(2). Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/40214926.
Mellor, C.M. (2006). Louis Braille: A touch of genius . Boston: National Braille Press.
Tombs, R. (1996). France: 1814-1914 . London: Pearson Education Ltd.
Weygand, Z. (2009). The blind in French society from the Middle Ages to the century of Louis Braille . Stanford: Stanford University Press.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, July 23). Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/example-essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Headings and Seriation

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
APA Style uses a unique headings system to separate and classify paper sections. Headings are used to help guide the reader through a document. The levels are organized by levels of subordination, and each section of the paper should start with the highest level of heading. There are 5 heading levels in APA. Regardless of the number of levels, always use the headings in order, beginning with level 1. The format of each level is illustrated below:
Thus, if the article has four sections, some of which have subsections and some of which don’t, use headings depending on the level of subordination. Section headings receive level one format. Subsections receive level two format. Subsections of subsections receive level three format. For example:
Method (Level 1)
Site of Study (Level 2)
Participant Population (Level 2)
Teachers (Level 3)
Students (Level 3)
Results (Level 1)
Spatial Ability (Level 2)
Test One (Level 3)
Teachers With Experience. (Level 4)
Teachers in Training. (Level 4)
Teaching Assistants . (Level 5)
Test Two (Level 3)
Kinesthetic Ability (Level 2)
In APA Style, the Introduction section never gets a heading and headings are not indicated by letters or numbers. For subsections in the beginning of a paper (introduction section), the first level of subsection will use Level 2 headings — the title of the paper counts as the Level 1 heading. Levels of headings will depend upon the length and organization of your paper. Regardless, always begin with level one headings and proceed to level two, etc.
Special headings called section labels are used for certain sections of a paper which always start on a new page.
- Paper title
- Appendix A (and so on for subsequent appendices)
These labels should be positioned on their own line at the top of the page where the section starts, in bold and centered.
APA also allows for seriation in the body text to help authors organize and present key ideas. For lists where a specific order or numbered procedure is necessary, use an Arabic numeral directly followed by a period, such as:
On the basis of four generations of usability testing on the Purdue OWL, the Purdue OWL Usability Team recommended the following:
- Move the navigation bar from the right to the left side of the OWL pages.
- Integrate branded graphics (the Writing Lab and OWL logos) into the text on the OWL homepage.
- Add a search box to every page of the OWL.
- Develop an OWL site map.
- Develop a three-tiered navigation system.
Numbered lists should contain full sentences or paragraphs rather than phrases. The first word after each number should be capitalized, as well as the first word in any following sentence; each sentence should end with a period or other punctuation.
For lists that do not communicate hierarchical order or chronology, use bullets:
In general, participants found the user-centered OWL mock up to be easier to use. What follows are samples of participants' responses:
- "This version is easier to use."
- "Version two seems better organized."
- "It took me a few minutes to learn how to use this version, but after that, I felt more comfortable with it."
Authors may also use seriation for paragraph length text.
For seriation within sentences, authors may use letters:
On the basis of research conducted by the usability team, OWL staff have completed (a) the OWL site map; (b) integrating graphics with text on the OWL homepage; (c) search boxes on all OWL pages except the orange OWL resources (that is pending; we do have a search page); (d) moving the navigation bar to the left side of pages on all OWL resources except in the orange area (that is pending); (e) piloting the first phase of the three-tiered navigation system, as illustrated in the new Engagement section.
Authors may also separate points with bullet lists:
On the basis of the research conducted by the usability team, OWL staff have completed
- the OWL site map;
- integrating graphics with text on the OWL homepage;
- search boxes on all OWL pages except the orange OWL resources (that is pending; we do have a search page);
- moving the navigation bar to the left side of pages on all OWL resources except in the orange area (that is pending);
- piloting the first phase of the three-tiered navigation system, as illustrated in the new Engagement section.
If your bulleted list is part of the sentence and is not preceded by a colon, treat the bullets like a part of the sentence, adhering to standard capitalization and punctuation. This option is helpful for complex or longer bulleted sentences that may be more difficult to read without the aid of punctuation. For items in a bulleted list that are phrases rather than sentences, no punctuation is necessary.
Advertisement
Read the Florida Supreme Court’s Ruling on the Abortion Ban
- Share full article
The Florida Supreme Court overturned decades of legal precedent in ruling that the State Constitution’s privacy protections do not extend to abortion, effectively allowing Florida to ban the procedure after six weeks of pregnancy.
A PDF version of this document with embedded text is available at the link below:
Download the original document (pdf)
Supreme Court of Florida No. SC2022-1050 PLANNED PARENTHOOD OF SOUTHWEST AND CENTRAL FLORIDA, et al., Petitioners, VS. STATE OF FLORIDA, et al., Respondents. No. SC2022-1127 PLANNED PARENTHOOD OF SOUTHWEST AND CENTRAL FLORIDA, et al., Petitioners, VS. STATE OF FLORIDA, et al., Respondents. April 1, 2024 GROSSHANS, J. The Florida Constitution guarantees "the right to be let alone and free from governmental intrusion into . . . private life.” Art. I,
§ 23, Fla. Const. In this case, we are asked to determine if there is a conflict between the rights secured by this provision and a recently amended statute that shortens the window of time in which a physician may perform an abortion. See ch. 2022-69, § 4, Laws of Fla. (codified at section 390.0111(1), Florida Statutes (2022)). The parties have presented thoughtful arguments as to the scope of this provision, which has traditionally been referred to as the “Privacy Clause." Those legal arguments on the Privacy Clause's meaning are, in our view, distinct from the serious moral, ethical, and policy issues that are implicated in the subject matter of this case. Our analysis focuses on the Privacy Clause’s text, its context, and the historical evidence surrounding its adoption. After considering each of these sources and consistent with longstanding principles of judicial deference to legislative enactments, we conclude there is no basis under the Privacy Clause to invalidate the statute. In doing so, we recede from our prior decisions in which-relying on reasoning the U.S. Supreme Court has rejectedwe held that the Privacy Clause guaranteed the right to receive an abortion through the end of the second trimester. See generally In re T.W., 551 So. 2d 1186 (Fla. 1989); N. Fla. Women's Health & - 2
Counseling Servs., Inc. v. State, 866 So. 2d 612 (Fla. 2003); Gainesville Woman Care, LLC v. State, 210 So. 3d 1243 (Fla. 2017). For this reason, petitioners are not entitled to the temporary injunction granted by the trial court, and we approve the outcome reached by the First District Court of Appeal below.1 I This case involves a constitutional challenge to an amended Florida statute prohibiting abortions “if the physician determines the gestational age of the fetus is more than 15 weeks." § 390.0111(1), Fla. Stat. (2022); ch. 2022-69, § 8, Laws of Fla. (providing effective date of July 1, 2022). This prohibition does not apply if any of the following occurs: (a) Two physicians certify in writing that, in reasonable medical judgment, the termination of the pregnancy is necessary to save the pregnant woman's life or avert a serious risk of substantial and irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function of the pregnant woman other than a psychological condition. (b) The physician certifies in writing that, in reasonable medical judgment, there is a medical necessity for legitimate emergency medical procedures for termination of the pregnancy to save the pregnant woman's life or avert a serious risk of imminent substantial and 1. We have jurisdiction. See art. V, § 3(b)(3), Fla. Const. (express-and-direct conflict). - 3
irreversible physical impairment of a major bodily function of the pregnant woman other than a psychological condition, and another physician is not available for consultation. (c) The fetus has not achieved viability under s. 390.01112 and two physicians certify in writing that, in reasonable medical judgment, the fetus has a fatal fetal abnormality. § 390.0111(1)(a)-(c). Prior to this change, the statute had restricted only late-term abortions. ² After this new law took effect, seven abortion clinics and one medical doctor (collectively Planned Parenthood)³ sued the State and others. Planned Parenthood alleged that the statute violated the Privacy Clause, which was added to the Florida Constitution in 1980. Located within the Declaration of Rights, the clause provides in full: 2. Specifically, the statute said, "No termination of pregnancy shall be performed on any human being in the third trimester of pregnancy unless one of [two] conditions is met." § 390.0111(1), Fla. Stat. (2021) (emphasis added). 3. The eight plaintiffs are Planned Parenthood of Southwest and Central Florida; Planned Parenthood of South, East, and North Florida; Gainesville Woman Care, LLC; A Woman's Choice of Jacksonville, Inc.; Indian Rocks Woman's Center, Inc.; St. Petersburg Woman's Health Center, Inc.; Tampa Woman's Health Center, Inc.; and Dr. Shelly Hsiao-Ying Tien. - 4
SECTION 23. Right of privacy.-Every natural person has the right to be let alone and free from governmental intrusion into the person's private life except as otherwise provided herein. This section shall not be construed to limit the public's right of access to public records and meetings as provided by law. With the complaint, Planned Parenthood filed a motion for temporary injunction, asking the trial court to block enforcement of the statute until it could rule on the merits of the constitutional challenge. In part, Planned Parenthood claimed that it was substantially likely to prevail in the lawsuit because it could demonstrate that the statute violates the Privacy Clause. In addition, Planned Parenthood argued that pregnant Floridians would be irreparably harmed absent a temporary injunction because the statute "would prohibit [them] from obtaining essential medical care and force them to remain pregnant and continue enduring the risks of pregnancy against their will." The statute, Planned Parenthood said, would also cause irreparable harm to itself and its staff by subjecting them to potential punitive consequences and interfering with the doctor-patient relationship. The State opposed Planned Parenthood's request for a temporary injunction. It argued that Planned Parenthood lacked - 5
standing to assert the privacy rights of its patients and, on the merits, could not establish any of the four requirements for a temporary injunction, let alone all four.4 After the State submitted its response, the U.S. Supreme Court issued a landmark decision on abortion in a case involving a Mississippi statute. See Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Org., 597 U.S. 215 (2022). In that decision, the Court ruled that the federal constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion. Id. at 231, 235-63, 292, 295. Based on this holding, the Court overturned Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S. 113 (1973), and Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey, 505 U.S. 833 (1992)—cases which had recognized a broad right to abortion under federal law. Dobbs, 597 U.S. at 292, 302 (expressly overruling Roe and Casey). In overruling those decisions, Dobbs "returned to the people and their elected representatives" "the authority to regulate abortion." Id. at 292. 4. Under Florida law, a party seeking a temporary injunction must prove four things: “(1) a substantial likelihood of success on the merits, (2) the unavailability of an adequate remedy at law, (3) irreparable harm absent entry of an injunction, and (4) that the injunction would serve the public interest." Fla. Dep't of Health v. Florigrown, LLC, 317 So. 3d 1101, 1110 (Fla. 2021). - 6
Several days after Dobbs issued, the trial court in this case held an evidentiary hearing on Planned Parenthood's motion for temporary injunction. Planned Parenthood called one witness and offered several exhibits. The State also presented witness testimony and documentary evidence. Deeming Planned Parenthood's evidence persuasive, the trial court entered a temporary injunction. It found that Planned Parenthood had third-party standing and satisfied all four temporary-injunction elements. In finding a likelihood of success on the merits, the court relied on our abortion jurisprudence. See generally T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1191-94 (Privacy Clause encompasses abortion); N. Fla. Women's Health, 866 So. 2d at 639 (reaffirming T.W.); Gainesville Woman Care, 210 So. 3d at 1246, 1253-55 (relying on T.W.). The court concluded that the statute was subject to strict scrutiny under that case law and determined that it either did not serve compelling interests or, in the alternative, was not the least restrictive means of achieving those interests. For the harm factor, the court ruled that both Planned Parenthood and its patients would suffer sufficient harm to support the requested relief. Rounding out its analysis, the court found no -7
adequate remedy at law and that an injunction would serve the public interests. The State appealed to the First District, triggering an automatic stay of the temporary injunction.5 Planned Parenthood asked the trial court and later the district court to vacate the automatic stay. Both courts, however, denied relief. State v. Planned Parenthood of Sw. & Cent. Fla., 342 So. 3d 863, 865-66 (Fla. 1st DCA 2022). As relevant here, in denying Planned Parenthood's motion to vacate, a divided panel of the First District held that Planned Parenthood could not establish irreparable harm as a result of the stay. Id. at 868-69. A few weeks later, the district court relied on essentially that same reasoning in reversing the temporary injunction—again, one judge dissented. State v. Planned Parenthood of Sw. & Cent. Fla., 344 So. 3d 637, 638 (Fla. 1st DCA 2022) ("[T]he non-final order granting the temporary injunction is reversed as [Planned Parenthood] could not assert irreparable harm on behalf of persons not appearing below."); id. (Kelsey, J., dissenting). 5. Fla. R. App. P. 9.310(b)(2) (automatic-stay provision triggered by filing of timely notice of appeal in certain situations). -8
Following these adverse rulings, Planned Parenthood asked us to review the First District's decisions, arguing that they conflict with our precedent. Accepting this jurisdictional argument, we granted review. II Planned Parenthood asks that we quash the district court's decisions and reinstate the temporary injunction. Relying on our precedent, it argues that the right to an abortion is secured by our constitution’s Privacy Clause. The State disputes Planned Parenthood's interpretation of the provision's text and asks us to reconsider our Privacy Clause jurisprudence or, at the very least, the abortion-related decisions. It argues that T.W.—our first case recognizing a right to abortion under the Privacy Clause-is flawed 6. In its brief, the State argues that Planned Parenthood lacks standing to challenge the new law. However, at oral argument, the Solicitor General urged us to decide this case on the merits. Oral Arg. at 50:52-51:06 (“We do think that the Court can assume for the sake of argument that the Plaintiffs have standing here and instead reach the merits. . . . That, I think, is what the Court should do.”). We view these statements as an abandonment of the State's standing argument. Thus, we proceed directly to the merits without passing upon any theory of standing articulated by the parties. - 9
in numerous respects, including that it failed to meaningfully consider the actual text of the provision at issue, failed to consider the history of the provision, and failed to give deference to the statute challenged in that case. Mindful of these fundamental concerns, we agree that our holding in T. W. should be reexamined.7 In T. W., this Court assessed a Privacy Clause challenge to a law that required unmarried minors to obtain parental consent or a substitute for consent to have an abortion. We held the challenged law to be incompatible with the protections afforded by the Privacy Clause, concluding that the right to abortion was embodied within the provision. T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1188, 1192-96; id. at 1197, 1201 7. As our discussion will show, we also emphasize the uniqueness of the competing interests implicated in abortion and the fact that the Supreme Court repudiated Roe and its underlying understanding of privacy. Because these factors relate to T. W. in a particularized way, we do not take up the State's invitation now to revisit the question of whether the Privacy Clause protects only "informational privacy" interests. Our jurisprudence before and after T. W. has understood the Privacy Clause to encompass certain decisional or autonomy rights, and today we do not revisit our precedents outside the abortion context. - 10
(Ehrlich, C.J., concurring specially).8 In the majority opinion, we discussed Roe v. Wade at length and ultimately adopted its definition of privacy along with its trimester and viability rules. See id. at 1190-94. Integral to the majority's analysis, T. W. emphasized recent Florida cases (primarily from the district courts) equating privacy with the right of personal decision-making in the specific context of refusing unwanted medical treatment. Id. at 1192. We also relied on Winfield v. Division of Pari-Mutuel Wagering, 477 So. 2d 544 (Fla. 1985)-a case involving privacy in financial institution records—to conclude that the provision “embraces more privacy interests" and "extends more protection to the individual in those interests, than does the federal Constitution." T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1192. Building on that, this Court made the following broad pronouncement: 8. Three justices, however, concluded that the challenged statute could be given a constitutional construction, though they accepted or assumed that the Privacy Clause conferred a right to abortion. T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1201-02 (Overton, J., concurring in part and dissenting in part); id. at 1202-04 (Grimes, J., concurring in part and dissenting in part); id. at 1204-05 (McDonald, J., dissenting). - 11 -
Florida's privacy provision is clearly implicated in a woman's decision of whether or not to continue her pregnancy. We can conceive of few more personal or private decisions concerning one's body that one can make in the course of a lifetime, except perhaps the decision of the terminally ill in their choice of whether to discontinue necessary medical treatment. Of all decisions a person makes about his or her body, the most profound and intimate relate to two sets of ultimate questions: first, whether, when, and how one's body is to become the vehicle for another human being's creation; second, when and how-this time there is no question of "whether"-one's body is to terminate its organic life. [Laurence H.] Tribe, American Constitutional Law 133738 (2d ed. 1988). The decision whether to obtain an abortion is fraught with specific physical, psychological, and economic implications of a uniquely personal nature for each woman. See Roe, 410 U.S. at 153. The Florida Constitution embodies the principle that “[f]ew decisions are more personal and intimate, more properly private, or more basic to individual dignity and autonomy, than a woman's decision . . . whether to end her pregnancy. A woman's right to make that choice freely is fundamental.” T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1192-93 (second alteration in original) (some citations omitted). This pronouncement was flawed in several respects. T. W. associated the language of the Privacy Clause with Roe's understanding of privacy; but it did not justify how that concept of privacy aligned with our constitution's text—i.e., “the right to be let alone and free from government intrusion into private life." T. W. - 12 -
also did not ask how Florida voters would have understood the text of the provision and how that understanding would be informed by Florida's long history of proscribing abortion. As a result of its analytical path, T. W. did not look to dictionaries, contextual clues, or historical sources bearing on the text's meaning. Instead, overlooking all these probative sources, it adopted Roe's notions of privacy and its trimester framework as matters of Florida constitutional law.9 Compounding these errors, the T.W. majority failed to apply longstanding principles of judicial deference to legislative enactments and failed to analyze whether the statute should be given the benefit of a presumption of constitutionality. Since Roe featured prominently in T. W., we think it fair to also point out that the T. W. majority did not examine or offer a reasoned response to the existing criticism of that decision or consider 9. In his dissent, Justice Labarga emphasizes "that T. W. was decided on state law grounds." Dissenting op. at 90. We agree that T.W. was not applying federal law to the challenged statute. However, T.W. relied heavily on Roe in interpreting the meaning of our constitution's Privacy Clause. Indeed, T. W. cited Roe over twenty times, it accepted Roe's concept of privacy without analysis, and it enacted a viability-trimester system that closely paralleled Roe's, without citing to any Florida precedent supporting that framework. - 13 -
whether it was doctrinally coherent. This was a significant misstep because Roe did not provide a settled definition of privacy rights. Controversial from the moment it was released, “Roe's constitutional analysis was far outside the bounds of any reasonable interpretation of the various constitutional provisions to which it vaguely pointed." Dobbs, 597 U.S. at 268. What's more, Roe "failed to ground its decision in text, history, or precedent.” Id. at 270. This left even progressive legal scholars baffled at how such a right could be gleaned from the constitution's text. Akhil R. Amar, Intratextualism, 112 Harv. L. Rev. 747, 778 (1999) ("As a precedent-follower, Roe simply stringcites a series of privacy cases involving marriage, procreation, contraception, bedroom reading, education, and other assorted topics, and then abruptly announces with no doctrinal analysis that this privacy right is broad enough to encompass' abortion. . . . But as the Court itself admits a few pages later [in the opinion], the existence of the living fetus makes the case at hand ‘inherently different’ . . . from every single one of these earlier-invoked cases. And as a precedent-setter, the Court creates an elaborate trimester framework that has struck many critics as visibly (indeed, nakedly) . . . more legislative than - 14 -
judicial." (footnotes omitted)); see also Laurence H. Tribe, Foreword: Toward a Model of Roles in the Due Process of Life and Law, 87 Harv. L. Rev. 1, 4 (1973) (noting that "[o]ne reads the Court's explanation [of the viability line] several times before becoming convinced that nothing has inadvertently been omitted”). Indeed, just three years after T.W. (and well before Dobbs), the U.S. Supreme Court abandoned Roe's position that the right to abortion was grounded in any sort of privacy right. See Casey, 505 U.S. at 846 (joint opinion) (“Constitutional protection of the woman's decision to terminate her pregnancy derives from the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment."); cf. Dobbs, 597 U.S. at 279 ("The Court [in Casey] abandoned any reliance on a privacy right and instead grounded the abortion right entirely on the Fourteenth Amendment's Due Process Clause."). This demonstrates the tenuous connection between “privacy” and abortion an issue that, unlike other privacy matters, directly implicates the interests of both developing human life and the pregnant woman. In light of T. W.'s analytical deficiencies and subsequent U.S. Supreme Court decisions rejecting the Roe framework on which - 15 -
T.W.'s reasoning depended, our assessment of the challenged statute requires us to examine the Privacy Clause and, for the first time in the abortion context, consider the original public meaning of the text as it was understood by Florida voters in 1980.10 III A We begin by recognizing the standard that governs our review. Because this case requires us to review both “the constitutionality of a statute and the interpretation of a provision of the Florida Constitution," our review is de novo. Lewis v. Leon Cnty., 73 So. 3d 151, 153 (Fla. 2011) (citing Crist v. Fla. Ass’n of Crim. Def. Laws., Inc., 978 So. 2d 134, 139 (Fla. 2008)); see also Florigrown, LLC, 317 So. 3d at 1110. We have long recognized that “statutes come clothed with a presumption of constitutionality and must be construed whenever possible to effect a constitutional outcome." Lewis, 73 So. 3d at 10. We decided two other significant cases involving abortion after T. W., but in those cases, we did not provide additional doctrinal justifications for T.W.'s adoption of Roe's privacy framework. - 16
153 (citing Fla. Dep't of Revenue v. City of Gainesville, 918 So. 2d 250, 256 (Fla. 2005)). Indeed, nearly a century ago, we said: (1) On its face every act of the Legislature is presumed to be constitutional; (2) every doubt as to its constitutionality must be resolved in its favor; [and] (3) if the act admits of two interpretations, one of which would lead to its constitutionality and the other to its unconstitutionality, the former rather than the latter must be adopted . . . Gray v. Cent. Fla. Lumber Co., 140 So. 320, 323 (Fla. 1932); see also Savage v. Bd. of Pub. Instruction for Hillsborough Cnty., 133 So. 341, 344 (Fla. 1931); Chatlos v. Overstreet, 124 So. 2d 1, 2 (Fla. 1960); In re Caldwell's Estate, 247 So. 2d 1, 3 (Fla. 1971); Franklin v. State, 887 So. 2d 1063, 1073 (Fla. 2004); Florigrown, LLC, 317 So. 3d at 1111; Statler v. State, 349 So. 3d 873, 884 (Fla. 2022). And to overcome the presumption of constitutionality, “the invalidity must appear beyond reasonable doubt." Franklin, 887 So. 2d at 1073 (quoting State ex rel. Flink v. Canova, 94 So. 2d 181, 184 (Fla. 1957)); see also Waybright v. Duval Cnty., 196 So. 430, 432 (Fla. 1940) ("[W]e will . . . determine if, beyond a reasonable doubt, violence was done [to] any provisions of the organic law in the passage of the challenged act, and in doing so will not deal with the - 17 -
merits of the measure, that being the exclusive concern of the Legislature."). B Our approach to interpreting the constitution reflects a commitment to the supremacy-of-text principle, “recognizing that '[t]he words of a governing text are of paramount concern, and what they convey, in their context, is what the text means. Coates v. R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co., 365 So. 3d 353, 354 (Fla. 2023) (alteration in original) (quoting Levy v. Levy, 326 So. 3d 678, 681 (Fla. 2021)) (interpreting statutory text); see also Advisory Op. to Governor re Implementation of Amend. 4, The Voting Restoration Amend. (Amendment 4), 288 So. 3d 1070, 1081 (Fla. 2020) (interpreting constitutional text). The goal of this approach is to ascertain the original, public meaning of a constitutional provision-in other words, the meaning as understood by its ratifiers at the time of its adoption. See City of Tallahassee v. Fla. Police Benevolent Ass'n, Inc., 375 So. 3d 178, 183 (Fla. 2023) ("[W]e give the words of the constitution their plain, usual, ordinary, and commonly accepted meanings at the time they were written.”). In construing the meaning of a constitutional provision, we do not - 18 - 999
seek the original intent of the voters or the framers. Instead, we ask how the public would have understood the meaning of the text in its full context when the voters ratified it. See Amendment 4, 288 So. 3d at 1081-82. To answer this question of public meaning, we consider the text, see Alachua Cnty. v. Watson, 333 So. 3d 162, 169-70 (Fla. 2022), contextual clues, see id., dictionaries, see Somers v. United States, 355 So. 3d 887, 891 (Fla. 2022), canons of construction, see Conage v. United States, 346 So. 3d 594, 598-99 (Fla. 2022), and historical sources, including evidence related to public discussion, see Tomlinson v. State, 369 So. 3d 1142, 1147-51 (Fla. 2023); Dist. of Columbia v. Heller, 554 U.S. 570, 614 (2008). IV With these background principles fixed, we now focus our attention on the Privacy Clause itself. Article I, section 23 is entitled: "Right of privacy." Our constitution, though, tells us that in construing the meaning of constitutional text, we are not to use titles and subtitles. See art. X, § 12(h), Fla. Const. Accordingly, we look at the operative text, which guarantees the right “to be let - 19 -
alone and free from governmental intrusion into the person's private life." Art. I, § 23. As is apparent at first glance, the provision does not explicitly reference abortion at all. Thus, if Planned Parenthood is to prevail, we must find that the public would have understood the principle embodied in the operative text to encompass abortion, even though the clause itself says nothing about it. To this end, the parties have marshaled era-appropriate dictionary definitions of key terms in the Privacy Clause. Based on the dictionaries we consulted, we know that in 1980 the right to be "let alone" could be defined as the right to be left "in solitude," free from outside "interfer[ence]” or “attention." See Let Alone, Oxford English Dictionary 213 (1st ed. 1933) (reprinted in 1978). And the latter phrase "free from governmental intrusion” into “private life”—can convey a similar meaning. “Intrusion” meant “[i]llegal entry upon or appropriation." Intrusion, American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language 688 (1st ed. 1969); see also Intrusion, American Heritage Dictionary 674 (2d Coll. ed. 1982) (same); Intrude, American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language 687 (1st ed. 1969) ("To interpose (oneself or something) - 20 -
without invitation, fitness, or leave."); Intrude, American Heritage Dictionary 674 (2d Coll. ed. 1982) (similar). And the word "private" carried the idea of being "[s]ecluded from the sight, presence, or intrusion of others," the chief example being “a private bathroom." Private, American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language 1042 (1st ed. 1969); Private, American Heritage Dictionary 986 (2d Coll. ed. 1982) (same). These accepted definitions do not seem to us to be natural ways of describing the abortion procedures of 1980. The decision to have an abortion may have been made in solitude, but the procedure itself included medical intervention and required both the presence and intrusion of others. See, e.g., Roe, 410 U.S. at 172 (Rehnquist, J., dissenting) (“A transaction resulting in an operation such as [abortion] is not 'private' in the ordinary usage of that word."); Thornburgh v. Am. Coll. of Obstetricians & Gynecologists, 476 U.S. 747, 792 (1986) (White, J., dissenting) (noting that even the Roe majority recognized a "pregnant woman cannot be isolated in her privacy” because “the termination of a - 21
pregnancy typically involves the destruction of another entity: the fetus" (quoting Roe, 410 U.S. at 159)).11 Next, we see if contextual clues could offer guidance. Looking at the complete text of the provision allows us to consider the physical and logical relation of its parts, as they might have been viewed by a voter. See Lab'y Corp. of Am. v. Davis, 339 So. 3d 318, 324 (Fla. 2022). 11. The dissent cites Griswold v. Connecticut, 381 U.S. 479 (1965) (invalidating on privacy grounds a state law criminalizing the use of contraception in the marital context), to support the assertion that the involvement of others does not prevent an activity or procedure from being a private matter. Dissenting op. at 67-68 (stressing that the law at issue in Griswold “operate[d] directly on an intimate relation of husband and wife and their physician's role in one aspect of that relation" (quoting Griswold, 381 U.S. at 482)). But the Court in Griswold "only invalidated the section of the state law which prohibited the use of contraception, rather than outlawing the manufacture, distribution, or sale of contraceptives." Alyson M. Cox & O. Carter Snead, “Grievously and Egregiously Wrong": American Abortion Jurisprudence, 26 Tex. Rev. L. & Pol. 1, 16-17 (2022). Indeed, as we noted above, Roe itself acknowledged that abortion was "inherently different" from the situations involved in cases like Griswold. Roe, 410 U.S. at 159. Thus, we do not share the dissent's concern "that parties will rely on the majority's reasoning that the involvement of 'others' in an abortion procedure defeats privacy—in attempts to undermine the broad privacy protections that are extended in the medical context.” Dissenting op. at 68. - 22
The first sentence sets forth the protected right, i.e., "to be let alone and free from governmental intrusion into . . . private life." The second sentence then provides that “[t]his section shall not be construed to limit the public's right of access to public records and meetings as provided by law." Art. I, § 23. By its terms, this latter sentence covers “public records and meetings.” That phrase which relates only to accessing public informationdoes not implicate or apply to the subject of abortion. We do not give great weight to this observation, but we note it here to emphasize that contextual clues do not lend support to a claim that voters clearly understood abortion to be part and parcel of the rights recognized in the Privacy Clause. V Dictionary definitions and immediate context, although informative, do not provide a full picture of the text's meaning. We also consider the historical background of the phrases contained within the operative text. See Tomlinson, 369 So. 3d at 1146 ("[W]hen (as often happens) a word had more than one accepted meaning at that time, we decide which one is the law by looking to the context in which it appears, and what history tells us about - 23 -
how it got there."); Antonin Scalia & Bryan Garner, Reading Law: The Interpretation of Legal Texts 33 (2012) ("[C]ontext embraces not just textual purpose but also . . . a word's historical associations acquired from recurrent patterns of past usage . ."); see also Heller, 554 U.S. at 605 (noting the critical importance in constitutional interpretation of examining “a variety of legal and other sources to determine the public understanding of a legal text in the period after its enactment or ratification"); TransUnion LLC v. Ramirez, 594 U.S. 413, 424 (2021) (relying on historical sources in determining constitutional text's meaning); N.Y. State Rifle & Pistol Ass’n, Inc. v. Bruen, 597 U.S. 1, 26-27 (2022) (historical sources integral to Court's holding). A Before examining the Privacy Clause's specific history and public debate, we explore the settled use of the "right to be let alone" in the context of Florida law, cognizant that technical meanings might bear upon the public understanding of the constitutional text. 12 12. In construing constitutional provisions that have an acquired meaning, “[w]e cannot understand these provisions unless - 24
The phrase "to be let alone" carries with it a rich legal tradition. In Cason v. Baskin, we discussed the common-law right to privacy and explained that in substance it was "the right to be let alone, the right to live in a community without being held up to the public gaze if you don't want to be held up to the public gaze." 20 So. 2d 243, 248 (Fla. 1944) (quoting Laurence H. Eldredge, Modern Tort Problems 77 (1941)).¹3 This right “to be let alone,” which was we understand their history; and when we find them expressed in technical words, and words of art, we must suppose these words to be employed in their technical sense." Thomas M. Cooley, A Treatise on the Constitutional Limitations which Rest upon the Legislative Power of the States of the American Union 93-94 (7th ed. 1903). Indeed, “[t]he technical sense in these cases is the sense popularly understood, because that is the sense fixed upon the words in legal and constitutional history where they have been employed for the protection of popular rights." Id. at 94 (emphasis added). 13. We recognize that this phrase “the right to be let alone” is likely sourced from the seminal 1890 law-review article, The Right to Privacy. Samuel D. Warren & Louis D. Brandeis, The Right to Privacy, 4 Harv. L. Rev. 193 (1890); cf. Stall v. State, 570 So. 2d 257, 265 (Fla. 1990) (Kogan, J., dissenting) (recognizing significance of this article). The authors of that article elaborated on the "right to be let alone" and free from “intrusion upon the domestic circle." Warren & Brandeis, supra, at 195-96 (borrowing label for this right from a tort treatise by Judge Thomas Cooley). The right, however, “had little to do with the autonomy of an individual to make decisions . . . free from government control." Jeffrey M. Shaman, The Right of Privacy in State Constitutional Law, 37 Rutgers L.J. 971, 990 (2006). It described a "different sort of privacy"-one - 25 -
often used interchangeably with the "right to privacy," was a prominent feature in Florida tort law. See, e.g., Battaglia v. Adams, 164 So. 2d 195, 197 (Fla. 1964) (“An unauthorized use of a person's name in this respect is recognized as a violation of his right of privacy."); Jacova v. S. Radio & Television Co., 83 So. 2d 34, 36 (Fla. 1955) (reiterating that Florida recognized a common-law claim for invasion of privacy and noting that "[when] one, whether willingly or not, becomes an actor in an occurrence of public or general interest,” “he emerges from his seclusion, and it is not an invasion of his right of privacy' to publish his photograph with an account of such occurrence" (quoting Metter v. L.A. Exam'r, 95 P.2d 491, 494 (Cal. Ct. App. 1939))); Harms v. Mia. Daily News, Inc., 127 So. 2d 715, 717 (Fla. 3d DCA 1961) (noting in the tort context that "[t]he "directed to keeping personal information from being exposed to the public, rather than to keeping decision-making within the control of an individual." Id. To Warren and Brandeis, the “right to be let alone" and free from “intrusion" safe-guarded against the publication of private facts. Warren & Brandeis, supra, at 195-96, 207-12. - 26
right of privacy is defined as the right of an individual to be let alone and to live a life free from unwarranted publicity"). 14 Significantly, throughout the decades in which the "right to be let alone" was developed and applied in Florida, two distinct propositions were true in the law and harmonious: first, the right "to be let alone” existed and had a discernable and enforceable meaning; and second, the Legislature had the authority to comprehensively regulate abortion before and after viability. Indeed, from at least 1868 to 1972, abortion was for the most part prohibited in our state. 15 And although litigants, prior to the 14. Florida law in this respect appears consistent with that of other jurisdictions. See W.E. Shipley, Annotation, Right of Privacy, 14 A.L.R.2d 750 (1950) (noting acts of intrusion into one's private affairs may also constitute violations of the right of privacy, such as eavesdropping, examination of private records or papers, or publications of personal material identified with the complainant as would using the complainant's name or likeness in almost any form of distributive publication). 15. See ch. 1637, subc. 3, § 11, subc. 8, § 9, Laws of Fla. (1868) (outlawing most abortions); Rev. St. 1892, §§ 2387, 2618 (same); §§ 782.10, 797.01, Fla. Stat. (1941) (repealed 1972) (same); §§ 782.10, 797.01, Fla. Stat. (1971) (repealed 1972) (same). In 1972, this Court determined that the abortion statute in effect at that time was unconstitutionally vague. State v. Barquet, 262 So. 2d 431, 438 (Fla. 1972). Immediately following that decision, the Legislature passed a more specific law, still banning abortion at all times during pregnancy except in certain limited circumstances. - 27 -
adoption of the Privacy Clause, sought to curtail government action by arguing they had the "right to be let alone," we are not aware of litigants invoking that particular right to challenge abortion restrictions in Florida. We also stress that this “right to be let alone” was modified by a limiting principle: the right did not permit an individual to inflict harm on herself or others. See State v. Eitel, 227 So. 2d 489, 491 (Fla. 1969) (rejecting a challenge to helmet laws based on a right "to be let alone," stressing that "no person is an entirely isolated being" and that “it is impossible for a person to do anything seriously or permanently hurtful to himself, without mischief reaching at least to his near connections, and often far beyond them") (cleaned up). Indeed, our Privacy Clause jurisprudence outside the abortion context recognizes that the right does not authorize harm to third parties. See, e.g., Beagle v. Beagle, 678 So. 2d 1271, 1276 (Fla. 1996) (parents' privacy right to raise their children yields to need to protect children from harm). Because the "right to be let alone" was limited in this way, it is not surprising that when litigants Ch. 72-196, § 2, Laws of Fla. (codified at section 458.22 of the Florida Statutes (Supp. 1972)) (repealed 1976). - 28
challenged the 1972 abortion statute in this Court, they did not do so based on the "right to be let alone." Instead, they argued a right to privacy grounded in substantive due process under the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. See Barquet, 262 So. 2d at 434. B We also acknowledge that the public understanding of the term "privacy" was, to some extent, informed by the U.S. Supreme Court's 1973 decision in Roe v. Wade. Following that decision, the phrase “right to privacy” gained new connotations that, for the first time, included the choice to have an abortion. See Roe, 410 U.S. at 154 ("We, therefore, conclude that the right of personal privacy includes the abortion decision .”). In Planned Parenthood's view, this aspect of federal privacy jurisprudence should control our analysis here. Specifically, Planned Parenthood argues that Florida voters would have internalized Roe's definition of privacy when they voted for the privacy amendment. Indeed, Planned Parenthood has repeatedly asserted that the public understanding of this privacy definition was so engrained by 1980 that even without a specific mention of the term abortion, the Privacy Clause unequivocally - 29 -
included such a right by implication. Agreeing with this argument, the dissent cites case law, newspaper articles, a news clip, and more to support the contention that Americans, and Floridians in particular, would have naturally understood privacy to encompass abortion. 16 Though this argument has some force, we cannot agree with Planned Parenthood or the dissent that the backdrop of Roe conclusively establishes how a voter would have understood the provision. In Roe, the Supreme Court did not consider language comparable to the operative text of Florida's Privacy Clause-that is, the “right to be let alone.” That phrase is found only once in Roe, and that single mention is in Justice Stewart's concurrence quoting Katz v. United States, 389 U.S. 347 (1967), in support of the proposition that there is no federal right to privacy. Roe, 410 U.S. 16. This evidence consists primarily of media coverage surrounding the Roe decision and subsequent evidence that discussed the abortion debate and associated a right of privacy with abortion. We accept that Roe had some bearing on the public's understanding of privacy rights in 1980. But, unlike the dissent, we do not find that it is dispositive. We are unwilling to disregard other probative evidence of public meaning, much of which is focused specifically on the amendment itself. The dissent, in our view, gives little attention to such evidence. - 30
at 167 n.2 (Stewart, J., concurring). So, while the Roe majority may have deemed abortion to be part of a “right to privacy," it would require an analytical leap to say that the public would have instinctively associated “the right to be let alone and free from governmental interference into one's private life" with abortion. E.g., Louis Henkin, Privacy and Autonomy, 74 Colum. L. Rev. 1410, 1424 (1974) (decisional autonomy “is not at all what most people mean by privacy,” which instead concerns “my freedom from official intrusion into my home, my person, my papers, my telephone”). This point is reinforced by the fact that the specific phrase used in the Privacy Clause had a consistent meaning in Florida law and had never once been interpreted to cover abortion rights. And as a final point here, we reiterate that Roe did not settle the scope of privacy rights as Planned Parenthood insists. As we discussed earlier, Roe's privacy-based reasoning was questioned soon after the opinion issued and was eventually rejected in a decision that completely detached abortion rights from the concept of privacy. See Casey, 505 U.S. at 846 (joint opinion). Thus, even if it is possible that voters would have understood the Privacy Clause to protect certain individual autonomy interests, it is by no means - 31
clear that those interests would have included the controversial subject of abortion, which uniquely involves the interests of prenatal life. Consequently, while Roe is relevant to our analysis of public meaning, it is not dispositive. Having considered dictionary definitions, context, and technical meanings that could have informed the original public meaning, we now turn to a critical piece of our historical analysis where we answer the following relevant questions: How did this provision make its way to the ballot, what was the focus of the debate surrounding its adoption, and how were the issues framed for the voters? C The origin of our Privacy Clause traces back to the work of a constitution revision commission in the late 1970s. As part of its work, the commission held public meetings throughout Florida and listened to the public's views and concerns. See Daniel R. Gordon, Upside Down Intentions: Weakening the State Constitutional Right to Privacy, a Florida Story of Intrigue and a Lack of Historical Integrity, 71 Temp. L. Rev. 579, 588 (1998); Transcript of Fla. C.R.C. proceedings at D:003272-73 (Jan. 9, 1978) (discussion of - 32 -
committee's work regarding privacy proposal). Eventually, the commission agreed upon the following language: Every natural person has the right to be let alone and free from governmental intrusion into his private life except as otherwise provided herein. Patricia A. Dore, Of Rights Lost and Gained, 6 Fla. St. U. L. Rev. 609, 650 n.248 (1978) (quoting Fla. C.R.C., Rev. Fla. Const. art. I, § 23 (May 11, 1978)). That proposed amendment, along with roughly 80 others, was submitted to the public as a package deal in the 1978 election. Gordon, supra, at 588. This package, in addition to containing the privacy proposal, also included amendments ensuring access to (1) public records, (2) meetings of non-judicial public bodies, (3) judicial hearings and records, and (4) proceedings and records of the judicial nominating commissions. Gerald B. Cope, Jr., To Be Let Alone: Florida's Proposed Right of Privacy, 6 Fla. St. U. L. Rev. 671, 675-77 (1978). Of note, proposals specifically addressing state abortion rights were rejected by the commissioners and never made it to the ballot. See Fla. Const. Revision Comm'n, Summary of Proposed Revisions to the Florida Constitution 1-2 (Sept. 27, 1977) (available in the Florida State University College of Law Research - 33 -
Center); cf. Mary Ann Lindley, A New Constitution Takes Shape, Palm Beach Post-Times, Apr. 9, 1978, at D1. For our purposes, though, we focus on statements made by commissioners in describing the reason or need for the proposal.17 On this subject, Justice Overton said: [W]ho, ten years ago, really understood that personal and financial data on a substantial part of our population could be collected by government or business and held for easy distribution by computer operated information systems? There is a public concern about how personal information concerning an individual citizen is used, whether it be collected by government or by business. The subject of individual privacy and privacy law is in a developing stage. . . . It is a new problem that should probably be addressed. Transcript of Fla. C.R.C. proceedings D:000020-21 (July 6, 1977). 17. See McDonald v. City of Chicago, 561 U.S. 742, 828-29 (2010) (Thomas, J., concurring in part and concurring in the judgment) (“When interpreting constitutional text, the goal is to discern the most likely public understanding of a particular provision at the time it was adopted. Statements by legislators can assist in this process to the extent they demonstrate the manner in which the public used or understood a particular word or phrase. They can further assist to the extent there is evidence that these statements were disseminated to the public. In other words, this evidence is useful not because it demonstrates what the draftsmen of the text may have been thinking, but only insofar as it illuminates what the public understood the words chosen by the draftsmen to mean.”). - 34 -
Justice Overton was not alone in this respect. Commissioner Jon Moyle (sponsor of the privacy proposal) spoke of government surveillance, technological advances, and society's dependence on such technology—characterizing them as threats to an individual's privacy. Transcript of Fla. C.R.C. proceedings at D:003273, 327678 (Jan. 9, 1978). He also noted that records about private life were becoming more common. Id. at D:003277-81. According to him, states were “very much involved in the business of keeping records about their residents.” Id. at D:003276. But the states, in his view, had not done “their part” in protecting such records. Id. at D:003277. In line with Commissioner Moyle's sentiments, Commissioners Lew Brantley and Dexter Douglass both noted specific government-surveillance efforts as sources of privacy concerns. Id. at D:003325 (remarks of Lew Brantley); id. at D:003336 (remarks of Dexter Douglass). This historical survey is illustrative of the commission's focus in terms of privacy. Various commissioners publicly expressed concern for informational privacy. However, as best as we can tell from their statements, that pressing concern did not extend to abortion. - 35
The proposals failed, and less than two years later, we held that there was no state constitutional right of privacy that would prevent public disclosure of confidential papers prepared by a consultant for an electric authority. Shevin v. Byron, Harless, Schaffer, Reid & Assocs., Inc., 379 So. 2d 633, 639 (Fla. 1980); cf. Laird v. State, 342 So. 2d 962, 963 (Fla. 1977) (no constitutional right of privacy to smoke marijuana in confines of home). Months after Shevin was decided, the Legislature revived the idea of a privacy clause and ultimately agreed on a proposal that said: Every natural person has the right to be let alone and free from governmental intrusion into [the person's] private life except as otherwise provided herein. This section shall not be construed to limit the public's right of access to public records and meetings as provided by law. Editorial, Guaranteeing Our Privacy, Boca Raton News, Oct. 29, 1980, at 6A (setting forth language to appear on 1980 ballot); Patrick McMahon, State Constitutional Amendments, St. Petersburg Times, Oct. 30, 1980, at 22 (noting ballot title). In overwhelming numbers, legislators from both political parties voted to approve it for placement on the ballot. Out of the - 36
138 legislators who voted on it, only 6 did not support the proposal. See Lorraine Cichowski, House Votes to Propose Guaranteeing Right to Privacy, Fort Myers News-Press, May 7, 1980, at 8B; Jim Walker, Senators Clash over Privacy Amendment, Tampa Tribune, May 15, 1980, at 6-A. Of additional note, during the floor debate, there was virtually no discussion of abortion. And when abortion was brought up, the Senate sponsor assured other senators that the proposal would have no effect on that subject. Audio Tape: Proceedings of the Fla. S., Tape 2 at 17:40 (May 14, 1980) (available at Fla. Dep't of State, Fla. State Archives, Tallahassee, Fla., Series S1238, Box 57). As best as we can tell, no commissioner or legislator ever claimed (at least publicly between 1977-80) that abortion was part of the rights guaranteed by the Privacy Clause.¹8 See, e.g., Gordon, 18. To the extent that Planned Parenthood relies on Representative Jon Mills's later statement in the 1990s that he subjectively hoped that the privacy proposal would cover abortion, such reliance is misplaced. See Heller, 554 U.S. at 577 (proper approach to interpretation does not consider hidden or secret meaning "that would not have been known to ordinary citizens in the founding generation”). Similarly, Planned Parenthood and one amicus misplace reliance on how voters handled two later proposed amendments—one in 2004 and the other in 2012. The understanding of voters over 20 years after the privacy amendment offers little value in determining what the voters in 1980 would have understood the privacy proposal to mean. Indeed, at oral - 37 -
supra, at 590 n.148 ("Nowhere did revision commissioners in 1978 refer to abortion . ."). Indeed, Planned Parenthood does not claim otherwise. D Like the history of the privacy proposal, the public debate surrounding the amendment also did not focus on abortion. Once the privacy proposal was approved for placement on the ballot in 1980, the public engaged in significant and robust debate over whether that proposal should be approved. Advocates for homosexual rights, proponents of legalized marijuana use, and various editorial boards advocated in favor of the amendment. Mary Hladky, Commissioners Table Vote on State Privacy Amendment, Fort Lauderdale News, Oct. 1, 1980, at 8B; Mary Lavers, Privacy Amendment Advocated by Kunst, Tampa Times, Oct. 23, 1980, at 10-A; Associated Press, Privacy Amendment Caught in Swirl of Controversy, Sentinel Star (Orlando), Oct. 24, 1980, at 2-C; Editorial, Amendment 2-Vote Yes, argument, Planned Parenthood conceded as much. See Oral Arg. at 22:59-23:02 (“2012 isn't evidence of what [the privacy amendment] meant in 1980.”). - 38 -
Bradenton Herald, Nov. 1, 1980, at A-4; Craig Matsuda, State Questions Are a Mix of Roads, Water, Privacy, Miami Herald, Nov. 2, 1980, at 8E; Amendments, St. Petersburg Times, Nov. 1, 1980, at 12B. These groups presented sweeping views of what the amendment would accomplish. Some, for instance, claimed that the amendment would decriminalize marijuana as well as certain intimate sexual conduct occurring inside the confines of a home. Julius Karash, Psychologist Stumps for Amendment, News-Press Local, Oct. 3, 1980, at B1; Steve Piacente, Gay Rights Activist Speaks for Privacy Act, Tampa Tribune, Oct. 24, 1980, at 2-B. Opponents of the measure included some political conservatives, various law enforcement officers, an association of prosecutors, and the then-serving governor. Prosecutors Condemn Privacy Amendment, Florida Today, Oct. 28, 1980, at 4B; Attorneys' Group Fights Privacy Amendment, Palm Beach Post, Oct. 28, 1980, at B26; Amendments under Attack as Vote Nears, Bradenton Herald, Oct. 29, 1980, at B-5; Graham Hit on Privacy, Florida Today, Oct. 29, 1980, at 6B; Amendment Opposition by Graham Criticized, Palm Beach Post, Oct. 29, 1980, at A11; Lawyer Raps Constitution Revision Plan, Fort Lauderdale News, Oct. 29, 1980, at 17A; Michael - 39 -
Harrell, Advertisement, Fort Lauderdale News, Oct. 29, 1980, at 16A; Amendments, St. Petersburg Times, Nov. 1, 1980, at 12B. Some opponents expressed concern that the open-ended language would permit courts to expansively interpret the amendment. Sensing that growing concern, House sponsors of the privacy proposal weighed in on the public debate. Taking to the newspapers, they reassured the public that concerns about whether the amendment would accomplish sweeping policy changes were unfounded. For instance, sponsors said that the proposed amendment arose from concerns “about technological advances that could enable the government to compile extensive computer files on citizens." Privacy Amendment Caught in Swirl of Controversy, supra, at 2-C; see also Associated Press, Privacy Measure Stirs Controversy, Pensacola News-Journal, Nov. 2, 1980, at 14C. Indeed, one sponsor said that the proposal was "necessary to ward off a growing government whose curiosity about people's private lives also is increasing." R. Michael Anderson, Amendment Guaranteeing Right to Privacy Debated, Florida Times-Union Jacksonville Journal, Oct. 26, 1980, at B-1. That same sponsor characterized the proposal as "quite conservative," predicting that - 40 -
"Florida judges wouldn't use it to overturn many existing laws." Privacy Amendment Caught in Swirl of Controversy, supra, at 2-C. And the other sponsor called expansive views of the proposed amendment “garbage.” See id. Of note, in looking at the extensive discussion surrounding the privacy amendment, little to nothing was said about abortion in print or in public comment. The debate-as framed to the publicoverwhelmingly associated the Privacy Clause's terms with concerns related to government surveillance and disclosure of private information to the public. Consistent with this observation, prolife and prochoice groups did not join in the fray. These groups are not politically bashfulnot now, and not in 1980. If the public understanding of the privacy proposal was that it included a silent-but almost unfettered-right to abortion, we would expect such groups to have engaged in the robust public debate. But based on all sources brought to our attention, we simply see no evidence of that. See James W. Fox, Jr., A Historical and Originalist Defense of Abortion in Florida, 75 Rutgers U. L. Rev. 393, 443-44 (2023) (acknowledging that these groups were silent on this topic; but - 41 -
discounting significance of such fact); cf. Oral Arg. at 13:02-13:39 (counsel for Planned Parenthood acknowledging that silence in the historical record). The dissent downplays the significance of this scope-of-debate evidence. Dissenting op. at 86. Accepting the logic of a law review article, the dissent claims that “[a]bortion would only have been debated if its coverage within the right to privacy were in dispute or were not yet established in law." Dissenting op. at 86 (quoting Fox, supra, at 442-43). We, however, cannot agree with this speculation. A person's understanding of the amendment's purpose would certainly inform whether he or she supported the adoption of the amendment. And, critically, it would inform how that person would persuade others to adopt their position. The debate over the privacy amendment was vigorous, yet there is virtually no evidence that anyone publicly connected the privacy amendment proposal with abortion rights. And as referenced by the dissent, newspapers during this same period were still discussing the controversy surrounding abortion, so it was far from a settled issue. Dissenting op. at 81-82 (noting that "Florida newspapers" in 1980 "covered statements by pro-choice activists and by pro-life activists" - 42 -
involving the abortion debate). We are unwilling to presume, as the dissent does, that abortion was so intertwined with the term "privacy" and so unquestionably accepted by society that its complete absence from the public debate surrounding this amendment should be expected. In sum, the scope of the privacy-proposal debate, both in terms of topics and participants, underscores that the public would not have understood, or assumed, the language of the Privacy Clause to encompass abortion. E Finally, we consider two additional sources of historical evidence, both of which show a contemporaneous understanding that the Privacy Clause did not enshrine abortion rights in our constitution. The first is concurrent legislative action. There were several Florida statutes passed between 1978 and 1980 regulating or restricting access to abortion in substantial ways. See ch. 78382, §§ 2, 4-10, Laws of Fla. (empowering Department of Health and Rehabilitative Services to create rules regulating abortion clinics; setting forth licensing requirement and framework; prohibiting abortion by unlicensed clinics); ch. 79-302, § 1, Laws of - 43 -
Fla. (requiring parental consent for unmarried minors); ch. 80-208, § 1, Laws of Fla. (fetal remains to be disposed of in "sanitary and appropriate manner"; establishing crime for violations of this standard); ch. 80-413, § 1, Laws of Fla. (additional regulations on abortion clinics; imposing standard governing disposal of fetal remains); cf. Amicus Brief of Former State Representative John Grant at 25-28 (noting concurrent legislation on abortionparticularly the abortion law passed during the same session as the privacy proposal). Based on this significant body of abortion regulation—some of which would be struck down as violative of Roe¹⁹ it seems unlikely to us that the Legislature in 1980 would put to the people a proposal crafted to imperil that recent work. The second source of evidence is what legislators of the time expressed with respect to adding a right-to-life amendment to the U.S. Constitution. See Fla. S. Comm. on HRS SM 737 (1978) Staff Analysis 1 (Fla. May 9, 1978) (available at Fla. Dep’t of State, Fla. State Archives, Tallahassee, Fla.); Fla. H.R., H.M. 388, 11th Sess. (Fla. 1979) (available at Dep't of State, Fla. State Archives, 19. See, e.g., Fla. Women's Med. Clinic, Inc. v. Smith, 536 F. Supp. 1048, 1059 (S.D. Fla. 1982). - 44 -
Tallahassee, Fla.); Fla. S., S.M. 118, 11th Sess. (Fla. 1979) (available at Fla. Dep't of State, Fla. State Archives, Tallahassee, Fla.). Of significance here, twenty-seven legislators who voted for the privacy proposal had, within the prior two years, openly supported the adoption of a federal amendment to "protect unborn human[s]” in response to Roe v. Wade. Compare H.R. Journal, 12th Sess., at 318 (Fla. 1980), with H.R. Journal, 11th Sess., at 48 (Fla. 1979); compare S. Journal, 11th Sess., at 21 (Fla. 1979), with S. Journal, 12th Sess., at 313 (Fla. 1980). To us, it seems quite unlikely that so many legislators would have tried to remove abortion rights as a matter of federal constitutional law only to restrict legislative power on abortion just two years later by way of a state constitutional amendment. F We pause to summarize the textual, contextual, and historical evidence we have discussed so far. The Privacy Clause of the Florida Constitution does not mention abortion or include a word or phrase that clearly incorporates it. Era-appropriate dictionary definitions and contextual clues suggest that abortion does not naturally fit within the rights at issue. Reliable historical sources, - 45 -
like the technical meaning of the terms contained in the provision, the origin of the amendment, and the framing of the public debate, similarly do not support a conclusion that abortion should be read into the provision's text. Roe is also relevant to our analysis of the public meaning of the Privacy Clause. But speculation as to Roe's effect on voter understanding does not overcome the combined force of the substantial evidence we have examined above. Thus, we cannot conclude that in 1980 a voter would have assumed the text encompassed a polarizing definition of privacy that included broad protections for abortion. VI We have established the background legal principles that govern our review and analyzed the original public meaning of the Privacy Clause as it relates to the subject of abortion. Now, we must address how those considerations apply here-namely, can Planned Parenthood demonstrate conflict between the challenged statute and the constitutional protections secured by the Privacy Clause? The statute we review prohibits abortions after 15 weeks of pregnancy, subject to certain exceptions. This statute "come[s] - 46 -
clothed with a presumption of constitutionality and must be construed" if possible "to effect a constitutional outcome." Crist, 978 So. 2d at 139. To overcome this presumption, the challenger must establish invalidity (or conflict) "beyond reasonable doubt." Id. Based on our analysis finding no clear right to abortion embodied within the Privacy Clause, Planned Parenthood cannot overcome the presumption of constitutionality and is unable to demonstrate beyond a reasonable doubt that the 15-week ban is unconstitutional. 20 This conclusion brings us into tension with our precedent, primarily T. W. in which we derived a right to abortion from the Privacy Clause's text and invalidated a statute on that basis. 551 So. 2d at 1188; see also N. Fla. Women's Health, 866 So. 2d at 639 (reaffirming T.W.); Gainesville Woman Care, 210 So. 3d at 1253-56, 20. Even if we gave significantly greater weight to Roe's effect on the original public meaning of the Privacy Clause (as urged by the dissent) and gave less weight to the other meaningful sources of evidence discussed above, we would still be left without a definition of privacy and considerable ambiguity as to the breadth of the provision. In that instance, we would reach the same conclusion, because a statute is presumed constitutional unless shown to be invalid beyond a reasonable doubt. Franklin, 887 So. 2d at 1073. The dissent fails to address what effect, if any, this longstanding principle of law should have here. - 47 -
1260 (relying on T.W.). In deciding how to resolve that tension, we again emphasize that T. W. failed to acknowledge the longstanding principle that statutes are presumed to be constitutional. This error led the Court to read additional rights into the constitution based on Roe's dubious and immediately contested reasoning, rather than evaluate what the text of the provision actually said or what the people of Florida understood those words to mean. The decision to extend the protections of the Privacy Clause beyond what the text could reasonably bear was not ours to make. As a result, we removed substantial authority from the people's elected representatives to regulate abortion-a profoundly unique and complicated issue that affects society in many significant ways. Accordingly, for the reasons given above, we find T.W. to be clearly erroneous. Based on our established test for assessing stare-decisis issues, we now ask whether there is a valid reason not to recede from T.W. See State v. Poole, 297 So. 3d 487, 506-07 (Fla. 2020) (outlining a two-part framework on stare-decisis issues). We have said that reliance is a critical consideration. Id. But as noted by the State, the Supreme Court's reasoning in Dobbs shows why reliance does not justify keeping T.W. In conducting a - 48 -
stare-decisis analysis in that case, the Supreme Court stressed that "[t]raditional reliance interests arise where advance planning of great precision is most obviously a necessity.'” Dobbs, 597 U.S. at 287 (first quoting Casey, 505 U.S. at 856 (joint opinion); and then citing Payne v. Tennessee, 501 U.S. 808, 828 (1991)). The Court went on to state that “those traditional reliance interests [a]re not implicated because getting an abortion is generally ‘unplanned activity,' and ‘reproductive planning could take virtually immediate account of any sudden restoration of state authority to ban abortions."" Id. at 288 (quoting Casey, 505 U.S. at 856). Finally, the Court rejected application of a more malleable and undefined form of reliance that focused on the relative social and economic effects of abortion. Id. at 288-89. In its view, this type of reliance was irrelevant to a proper stare-decisis framework. Id. We think that this analysis from Dobbs is in keeping with Poole. Indeed, in Poole, we expressed wariness for tests that are "malleable and do not lend themselves to objective, consistent, and predictable application." 297 So. 3d at 507 (criticizing North Florida Women's Health's multi-factor stare-decisis framework). And in the years since Poole issued, we have not employed the more malleable - 49 -
form of reliance that Dobbs declined to apply—the same sort of societal reliance interests now being advanced by Planned Parenthood. Apart from arguing reliance, Planned Parenthood does not offer any other valid reasons for keeping T.W. Accordingly, because Planned Parenthood has failed to demonstrate a valid reason for retaining T. W., we recede from it. We also recede from Gainesville Woman Care and North Florida Women's Health, which both applied T.W.'s flawed reasoning and offered no additional doctrinal justification for locating a right to abortion in the Privacy Clause. VII We now return to the specific facts of this case. Below, the trial court granted a temporary injunction, finding that Planned Parenthood would likely succeed in its constitutional challenge. Our holding, however, displaces the doctrinal justification for the trial court's decision. Planned Parenthood cannot demonstrate a likelihood of success on the merits of its claim, which alleged that the newly enacted statute was facially invalid under the Privacy Clause of the Florida Constitution. And since Planned Parenthood fails on this prong, it is not entitled to a temporary injunction. - 50 -
Although we do not adopt the reasoning of the First District, we approve the result it reached below. It is so ordered. MUÑIZ, C.J., and CANADY, COURIEL, and FRANCIS, JJ., concur. SASSO, J., concurs with an opinion. LABARGA, J., dissents with an opinion. NOT FINAL UNTIL TIME EXPIRES TO FILE REHEARING MOTION AND, IF FILED, DETERMINED. SASSO, J., concurring. I join the majority opinion because it correctly holds that the Florida Constitution does not contain a right to elective abortion. I write separately to explain why I believe it is appropriate to reach that decision considering the standing arguments raised by the State in the lower court proceedings and on appeal and as highlighted by Amici in this Court. In doing so, I will start with some observations regarding this Court's standing jurisprudence. I will then explain why I agree with the majority's decision to accept the State's waiver of any standing arguments here. Finally, I will explain why I believe, in the proper case, this Court should reconsider its standing precedent. - 51 -
I. Standing is the legal doctrine that defines when a litigant has a stake in a controversy sufficient to obtain judicial resolution of that controversy. The doctrine keeps us in our constitutional lane by ensuring we do not become “roving commissions assigned to pass judgment on the validity of the [State's] laws." See Broadrick v. Oklahoma, 413 U.S. 601, 611 (1973). At the federal level, standing requirements are derived from Article III of the United States Constitution's Case or Controversy Clause. Constitutional in origin, standing is therefore a jurisdictional prerequisite to a plaintiff's right to sue in federal court. See Indus. Servs. Grp., Inc. v. Dobson, 68 F.4th 155, 167 (4th Cir. 2023) ("It is axiomatic that standing is a threshold jurisdictional issue that must be determined before a court can consider the merits of a case." (citing Steel Co. v. Citizens for a Better Env't, 523 U.S. 83, 88 (1998))). For that reason, federal courts have the ability, and indeed the obligation, to address standing sua sponte even if a defendant has not raised the issue. See United States v. Hays, 515 U.S. 737, 742 (1995) ("[W]e are required to address [standing] even if the courts - 52 -
below have not passed on it, and even if the parties fail to raise the issue before us." (first alteration in original) (quoting FW/PBS, Inc. v. City of Dallas, 493 U.S. 215, 230-31 (1990))); Cent. States Se. & Sw. Areas Health & Welfare Fund v. Merck-Medco Managed Care, L.L.C., 433 F.3d 181, 198 (2d Cir. 2005) ("Because the standing issue goes to this Court's subject matter jurisdiction, it can be raised sua sponte."). Likewise, the question of standing is not subject to waiver. Hays, 515 U.S. at 742. At the state level, it is different. As it relates to standing, the Florida Constitution is textually distinct from the Federal Constitution because it does not contain an explicit cases and controversies clause. It should go without saying, then, that federal law does not control standing requirements in state courts. See ASARCO Inc. v. Kadish, 490 U.S. 605, 617 (1989) (noting that the constraints of Article III do not apply to state courts, and accordingly state courts are not bound by the limitations of a case or controversy). Even so, this Court has at times reflexively adopted federal standing tests without examining whether the Florida Constitution demands similar requirements. See, e.g., State v. J.P., 907 So. 2d 1101, 1113 n.4 (Fla. 2004) (adopting three-part standing - 53 -
test established by the United States Supreme Court in Lujan v. Defenders of Wildlife, 504 U.S. 555 (1992)); Alterra Healthcare Corp. v. Est. of Shelley, 827 So. 2d 936, 941 (Fla. 2002) (adopting thirdparty standing test recognized by the United States Supreme Court). We have not done so consistently, though. At times, we have concluded that standing in Florida is less restrictive than at the federal level. For example, in Department of Revenue v. Kuhnlein, 646 So. 2d 717, 720 (Fla. 1994), we said that the doctrine of standing does not exist in Florida "in the rigid sense employed in the federal system." See also Coal. for Adequacy & Fairness in Sch. Funding, Inc. v. Chiles, 680 So. 2d 400, 403 (Fla. 1996) (noting that in Florida, unlike the federal system, the doctrine of standing has not been rigidly followed). Consistent with this observation, we have sometimes applied state-specific standing rules. See, e.g., Johnson v. State, 78 So. 3d 1305, 1314 (Fla. 2012) (holding a litigant has standing if "he or she reasonably expects to be affected by the outcome of the proceedings, either directly or indirectly” (quoting Hayes v. Guardianship of Thompson, 952 So. 2d 498, 505 (Fla. 2006))). Other times we have, either explicitly or implicitly, - 54 -
bypassed a standing analysis altogether. See, e.g., J.P., 907 So. 2d at 1113 ("Because the Second District never determined whether these juveniles have standing to assert the constitutional rights of their parents, we decline to rule on these claims." (footnote omitted)).21 Our inconsistent approach is especially evident in the context of third-party standing. Traditionally, this Court considered as well-settled the rule that one who is not himself denied some constitutional right or privilege cannot be heard to raise constitutional questions on behalf of some other person who may at some future time be affected. See, e.g., Steele v. Freel, 25 So. 2d 501, 503 (Fla. 1946). Eventually, though, we carved out exceptions. For example, in Jones v. State, 640 So. 2d 1084 (Fla. 1994), we determined that criminal defendants could raise the privacy rights 21. Despite the inconsistent application of various tests to determine whether a party has standing to pursue its claims, our standing precedent has been steady in one respect. We have always held that standing can be waived. See, e.g., Krivanek v. Take Back Tampa Pol. Comm., 625 So. 2d 840, 842 (Fla. 1993); Cowart v. City of West Palm Beach, 255 So. 2d 673, 675 (Fla. 1971). However, this is somewhat logically inconsistent, because we oftentimes have adopted federal standards ostensibly derived from the Federal Constitution without adopting the corresponding rule that standing is jurisdictional in nature and therefore not subject to waiver. - 55 -
of the female minors with whom they had sexual relations because the criminal defendants "st[oo]d to lose from the outcome of this case and yet they ha[d] no other effective avenue for preserving their rights." Id. at 1085 (referencing Stall v. State, 570 So. 2d 257 (Fla. 1990), for "vicarious standing" requirements). Later, in Alterra, we applied a federal test to determine when parties can sue on behalf of rights belonging to others. 827 So. 2d at 941-42. The test, as laid out in Alterra, goes like this: a litigant may bring an action on behalf of a third party if 1) the litigant suffered an “injury in fact,” thus giving him or her a "sufficiently concrete interest" in the outcome of the issue in dispute; 2) the litigant has a close relation to the third party; and 3) there is some hindrance to the third party's ability to protect his or her own interests. Id. (quoting Powers v. Ohio, 499 U.S. 400, 410-11 (1991)). But we applied this test in Alterra without explicitly adopting it as doctrine and without addressing our previous application of the Stall standard in Jones. Only a year after Alterra was decided, we again backed away from applying federal standing tests at all in Allstate Insurance Co. v. Kaklamanos, 843 So. 2d 885 (Fla. 2003). There, we reiterated - 56
that the doctrine of standing does not exist in Florida "in the rigid sense employed in the federal system." Id. at 895 (quoting Kuhnlein, 646 So. 2d at 720). This made room for our conclusion that an insured could maintain an action against the insurer for nonpayment of personal injury protection automotive insurance benefits even though the insured had not paid the medical bills in question and the medical provider had not instituted legal action against the insured for nonpayment. Id. at 897. And later, we appeared to cabin Alterra to the employment context in Weaver v. Myers, 229 So. 3d 1118, 1129 (Fla. 2017). In that same case, we also cited favorably the “vicarious standing" test from Jones, a case that preceded Alterra.2² Id. 22. Our doctrinal inconsistency in third-party standing cases is not the only aspect of our standing jurisprudence that has been unclear. For example, as noted above we adopted the three-part standing test established by the United States Supreme Court in Lujan v. Defenders of Wildlife, 504 U.S. 555, in J.P. But a few years later in Johnson, we stated broadly that “standing ‘requires a would-be litigant to demonstrate that he or she reasonably expects to be affected by the outcome of the proceedings, either directly or indirectly.'" 78 So. 3d at 1314 (quoting Hayes, 952 So. 2d at 505). We did so without any reference to our previous adoption of the Lujan test and over the dissenting justices' observation that the moving party would have met that standing requirement. And although we have, with more consistency, adhered to the Rickman v. Whitehurst, 74 So. 205 (Fla. 1917), rule when litigants have - 57 -
II. With that background in mind, I now return to this case. It serves as a prime example of the challenges our doctrinal inconsistencies create for litigants and lower courts. In the trial court, the State argued Planned Parenthood lacked standing to challenge HB 5 because none of the plaintiffs could assert a personal right to privacy—instead, the plaintiffs sought to assert the privacy rights of their patients and/or customers. Working off the Alterra test, the State then argued Planned Parenthood could not meet the requirements for overcoming the general bar to third-party standing. In doing so, though, the State conceded that the second prong of the Alterra test (the close relationship requirement) was satisfied. In response, Planned Parenthood accepted the State's framing of the issue, arguing it could satisfy the Alterra test. This framework carried over to the trial court's order granting the challenged government action, we continue to carve out exceptions without a textual explanation justifying a new exception. See, e.g., Dep't of Admin. v. Horne, 269 So. 2d 659 (Fla. 1972) (citing federal precedent to carve out exception for "ordinary citizens and taxpayers" to pursue constitutional claims in certain circumstances even absent a showing of special injury to themselves). - 58 -
temporary injunction, where it applied the Alterra test and concluded that Planned Parenthood has "third-party standing to bring this suit on behalf of their actual and potential patients." Planned Parenthood of Sw. & Cent. Fla. v. State, No. 2022-CA-912, 2022 WL 2436704, at *17 (Fla. 2d Cir. Ct. July 5, 2022). But, in the First District, the court concluded that it did not need to address Petitioners' standing argument. Instead, the First District decided that Petitioners had not suffered irreparable harm sufficient to support the issuance of a temporary injunction. State v. Planned Parenthood of Sw. & Cent. Fla., 342 So. 3d 863, 867-68 (Fla. 1st DCA 2022). That takes us to the parties' briefing filed in this Court. The State reasserted its argument as to Planned Parenthood's standing to pursue its claims. But as the majority opinion notes, the State essentially conceded the issue of standing at oral argument, urging this Court to reach the merits. So why do we accept that concession? First, as the majority notes, this case has been litigated under the umbrella of this Court's abortion jurisprudence. See, e.g., Gainesville Woman Care, LLC v. State, 210 So. 3d 1243, 1253-54 (Fla. 2017); N. Fla. Women's - 59 -
Health & Counseling Servs., Inc. v. State, 866 So. 2d 612, 620 (Fla. 2003); In re T. W., 551 So. 2d 1186, 1188-89 (Fla. 1989). And our abortion jurisprudence falls into the category of cases where we have, without explaining why, skipped over a standing analysis altogether. As a result, we have neither directly addressed standing nor applied the Alterra test in any of our abortion cases. Instead, to the extent standing was considered, we seem to have collapsed the analysis into the grounds for obtaining a temporary injunction without considering which standing test to apply or whether an abortion provider can meet that test. See Gainesville Woman Care, 210 So. 3d at 1247 (“Petitioners have established a substantial likelihood of success on the merits, one of the requirements of granting a temporary injunction, as well as all other grounds for the entry of a temporary injunction.” (emphasis added)). For that reason, addressing standing alone here would have only added to the inconsistencies in our cases. Second, both parties have asked us to apply the federal thirdparty standing test as applied in Alterra. But as explained above, we have applied that test once. And, for many reasons, I question the wisdom of perpetuating the standard here. For one, I do not - 60
think we should apply federal standards to textually distinct provisions of the Florida Constitution without considering whether that standard is independently justified on state law grounds. For another, reflexively adopting the federal third-party standing test is particularly troublesome because, in federal courts, it has been inconsistently applied and widely criticized. See, e.g., June Med. Servs. L. L. C. v. Russo, 140 S. Ct. 2103, 2142-46 (2020) (Thomas, J., dissenting) (noting the test's inconsistent application, criticizing the characterization of third-party standing as prudential in nature, and concluding that third-party standing is inconsistent with the case-or-controversy requirement of Article III). Finally, and critically, neither party has challenged our characterization of standing as waivable rather than jurisdictional. Similarly, no party has offered an alternative standard to apply in the absence of Alterra or an argument as to whether Planned Parenthood fails to meet any alternative standard. As a result, I believe this Court properly reaches the merits of this case. III. While the State's concession takes care of this case, in future cases we should reconsider our standing precedents. Most - 61
fundamentally, we should consider from where our standing requirements are derived (spoiler alert-it is not the Federal Constitution). For example, is standing in Florida derived only from article V's conception of "judicial power"? See, e.g., Sons of Confederate Veterans v. Henry Cnty. Bd. of Comm'rs, 880 S.E.2d 168, 185-86 (Ga. 2022) (concluding that standing requirement arises from the Georgia Constitution's judicial power provision). Or does the access to courts provision of article I, section 21 have anything to say as to standing? Once decided, we will need to clarify the scope of any standing requirements, such as whether parties may assert both legal and factual injuries or whether only a legal injury will suffice. See, e.g., F. Andrew Hessick, Standing, Injury in Fact, and Private Rights, 93 Cornell L. Rev. 275, 280-81 (2008) (noting that at common law "factual harm without a legal injury was damnum absque injuria and provided no basis for relief"). We will also need to examine whether standing requirements are truly subject to waiver, or instead whether they are jurisdictional in nature. And finally, we will need to provide a principled methodology to help litigants understand which tests to apply when. - 62 -
To decide these and other issues related to standing, we will need the benefit of the adversarial process and thorough briefing. For that reason, and in the proper case, I encourage parties to critically assess these and other standing issues and present argument to this Court should the opportunity arise. LABARGA, J., dissenting. When the United States Supreme Court's decision in Dobbs23 “returned to the people and their elected representatives” “the authority to regulate abortion,” the decision did not force the state of Florida into uncharted territory. Instead, as history reveals and the majority acknowledges, the right to an abortion as a matter of Florida law was decided decades ago following two significant postRoe24 developments: (1) Florida voters' 1980 approval of an amendment to the Florida Constitution expressly providing a right of privacy, and (2) this Court's 1989 decision in In re T. W., 551 So. 2d 1186 (Fla. 1989), holding that Florida's express right of privacy 23. Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Org., 597 U.S. 215, 292 (2022). 24. Roe v. Wade, 410 U.S. 113 (1973). - 63
encompasses the right to an abortion. Nonetheless, today's majority decision recedes from decades of this Court's precedent and holds that "there is no basis under [Florida's express right of privacy] to invalidate” “a recently amended statute that shortens the window of time in which a physician may perform an abortion." Majority op. at 2. I strongly dissent. The Right of Privacy Adopted by Florida voters in 1980, article I, section 23 of the Florida Constitution provides: “Every natural person has the right to be let alone and free from governmental intrusion into the person's private life except as otherwise provided herein. This section shall not be construed to limit the public's right of access to public records and meetings as provided by law." Contrary to the majority, I am convinced that in 1980, a Florida voter would have understood that the proposed privacy amendment “included broad protections for abortion." Id. at 46. The right of privacy is no novel concept. More than 100 years ago, former Michigan Supreme Court Justice and noted legal scholar Thomas Cooley described “[t]he right to one's person" as the right "to be let alone." Thomas M. Cooley, A Treatise on the Law of - 64 -
Torts or the Wrongs Which Arise Independent of Contract 29 (2d ed. 1888). When the right "to be let alone" was discussed by Samuel D. Warren and Louis D. Brandeis in their Harvard Law Review article The Right to Privacy, the article primarily discussed the tort of invasion of privacy. See Samuel D. Warren & Louis D. Brandeis, The Right to Privacy, 4 Harv. L. Rev. 193 (1890). However, the authors also made the following salient observation: THAT the individual shall have full protection in person and in property is a principle as old as the common law; but it has been found necessary from time to time to define anew the exact nature and extent of such protection. Political, social, and economic changes entail the recognition of new rights, and the common law, in its eternal youth, grows to meet the demands of society. Id. at 193. Thus, even in early considerations of the right of privacy, scholars recognized that the right would be one that would evolve over time and it did. During the twentieth century, political, social, and economic changes led to a host of changes in the legal landscape, resulting in an expansion of the right of privacy far beyond a right to be free from unwanted public exposure. Without question, one of the most significant legal developments was the United States Supreme Court's recognition in Roe of an implicit right of privacy - 65 -
guaranteeing the right to an abortion as a matter of federal law. However, the right of privacy in the context of decisional autonomy took hold several years earlier in Griswold v. Connecticut, 381 U.S. 479 (1965) (holding that a state statute prohibiting the use of contraceptives violated the right to marital privacy). It is relevant to the analysis of the public understanding of the right of privacy that Griswold's expansion of privacy to reach decisional autonomy occurred more than seven years before Roe and fifteen years before Florida voters' adoption of the right of privacy as a matter of state constitutional law. The State's argument, that the sole context for Florida's right of privacy is informational privacy, seems to have been a step too far even for the majority. Nonetheless, the majority concludes that the language of "shall not be construed to limit the public's right of access to public records and meetings as provided by law" provides context that "do[es] not lend support to a claim that voters clearly understood abortion to be part and parcel of the rights recognized" under the right of privacy. Majority op. at 23. What is more, it reaches this conclusion despite substantial evidence that - 66 -
overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that the public understood the right of privacy to encompass the right to an abortion. Abortion as a Private Matter Before turning to the public understanding of the right of privacy, I write to address the majority's suggestion that abortion is ultimately not a private matter because “the procedure itself include[s] medical intervention and require[s] both the presence and intrusion of others.” Id. at 21 (citing Roe, 410 U.S. at 172 (Rehnquist, J., dissenting)). The majority acknowledges that an abortion "include[s] medical intervention,” see id., but beyond merely “includ[ing] medical intervention,” Florida’s statutes regulating abortion—then and now-require that the procedure be performed by a physician. See § 390.0111(2), Fla. Stat. (2023) (requiring that a termination of pregnancy be performed by a physician); Wright v. State, 351 So. 2d 708 (Fla. 1977) (pre-1980 decision from this Court upholding the conviction of a registered nurse who performed an abortion in violation of statute requiring that the procedure be performed by a physician). The “others” required to be present and involved in the procedure are physicians and medical personnel. In the interest of - 67 -
patient privacy, medical matters, including countless forms of medical procedures, are broadly afforded confidentiality protections with narrowly tailored exceptions. And notably, the involvement of a physician was not fatal to the privacy issue in Griswold, where the United States Supreme Court said: "This law [prohibiting the use of contraceptives], however, operates directly on an intimate relation of husband and wife and their physician's role in one aspect of that relation.” 381 U.S. at 482 (emphasis added). As a matter of necessity, physicians and medical personnel are routinely involved in a wide range of medical procedures, decisions, and other medical matters. The majority attempts to limit today's decision to the issue of abortion. See majority op. at 10 note 7 ("[T]oday we do not revisit our precedents outside the abortion context."). However, I fear that parties will rely on the majority's reasoning that the involvement of "others" in an abortion procedure defeats privacy-in attempts to undermine the broad privacy protections that are extended in the medical context. - 68
The Public Understanding of Roe v. Wade and the Right of Privacy The majority "acknowledge[s] that the public understanding of the term 'privacy' was, to some extent, informed by the United States Supreme Court's 1973 decision in Roe v. Wade," observing that "[following that decision, the phrase ‘right to privacy' gained new connotations that, for the first time, included the choice to have an abortion." Majority op. at 29 (emphasis added). The majority continues: In Planned Parenthood's view, this aspect of federal privacy jurisprudence should control our analysis here. Specifically, Planned Parenthood argues that Florida voters would have internalized Roe's definition of privacy when they voted for the privacy amendment. Indeed, Planned Parenthood has repeatedly asserted that the public understanding of this privacy definition was so engrained by 1980 that even without a specific mention of the term abortion, the Privacy Clause unequivocally included such a right by implication. Though this argument has some force, we cannot agree with Planned Parenthood that the backdrop of Roe conclusively establishes how a voter would have understood the provision. Id. at 29-30 (emphasis added). The majority concludes that "[c]onsequently, while Roe is relevant to our analysis of public meaning, it is not dispositive.” Id. at 32. I could not disagree more. - 69 -
The majority correctly recognizes the significant impact of Roe but stops short of the reality that Roe, having fundamentally changed the landscape of abortion rights on a national scale by redefining the scope of the right of privacy, was key to the public understanding of the right of privacy. During the seven-year interval between Roe and Florida voters' adoption of the right of privacy, I find it inconceivable that Americans and more specifically, Floridians were not aware that the right of privacy encompassed the right to an abortion. I agree with the petitioners that "the public understanding of [Roe's] privacy definition was so engrained by 1980 that even without a specific mention of the term abortion, the Privacy Clause unequivocally included such a right by implication." Id. at 29-30. In fact, the majority notes the controversial impact of Roe's reasoning, which reinforces that the public would have understood the right of privacy encompassed the right to an abortion. See id. at 14 (stating that Roe "left even progressive legal scholars baffled at how such a right could be gleaned from the constitution's text," and quoting Dobbs, 597 U.S. at 268 (“Roe's constitutional analysis was far outside the bounds of any reasonable interpretation of the - 70 -
various constitutional provisions to which it vaguely pointed.")). Contrary to the majority's position, evidence of the discussion surrounding Roe's reasoning is probative that the public understood the right of privacy to encompass the right to an abortion, and to so conclude does not require the "analytical leap" that the majority suggests it does. See id. at 31. Roe's opponents strenuously disapproved of basing the right to an abortion on the right of privacy; just as strenuously, Roe's supporters agreed with the Supreme Court's analysis. The common denominator is the understanding that the right to an abortion was tied to the right of privacy. The Nationwide Understanding of Roe and the Right of Privacy A decision that triggered pervasive national coverage, Roe was publicly discussed and debated in a way that most judicial decisions-even those decided by the United States Supreme Court are not. Media outlets across the nation reported on the landmark decision. On the day that Roe was decided, Associated Press articles announcing the seminal decision were published on the front pages of newspapers nationwide, many explaining that the decision "was - 71 -
based predominantly on what [Justice] Blackmun called a right of privacy."25 The nightly news programs on the major television networks also reported on Roe to an audience of tens of millions of viewers. The CBS Evening News with Walter Cronkite-a news program with, at that time, a consistent audience of twenty million or more viewers-covered the decision in a segment lasting more than three minutes, noting that “[t]he nine justices made abortion 25. See, e.g., Associated Press, Abortion Law Out, Mexico Ledger, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Barry Schweid, Abortion Law Struck by Court, The Courier News (Blytheville), Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Abortions Allowed During 1st 6 Months, The Daily Chronicle (Centralia), Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Barry Schweid, Blackmun Cites 'Right of Privacy' Court Bars Restricting Three-Month Abortions, The Index-Journal (Greenwood), Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Court Strikes Down Abortion Law, The Neosho Daily News, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Court Strikes Down Abortion Law, Aiken Standard, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Court Strikes Down Texas Abortion Law, The Daily Times-News (Burlington), Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Barry Schweid, Decision Will Affect 44 States, Del Rio News-Herald, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, High Court Upholds Medical Abortions, Waukesha Daily Freeman, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Key Abortion Ruling by Supreme Court, Santa Cruz Sentinel, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Rule on Abortions, The Sedalia Democrat, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, States Can't Block Early Abortions, The Bismarck Tribune, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Supreme Court Upholds Women's Abortion Rights, Fairbanks Daily News-Miner, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Texas Law Struck Down, 7-2, The Vernon Daily Record, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1-2. - 72 -
largely a private matter." CBS Evening News with Walter Cronkite, featuring George Herman in Washington (CBS television broadcast Jan. 22, 1973), https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dccagy905yk (available on the CBS News YouTube channel). Throughout the nation, local journalists also published articles announcing and explaining Roe, as did opinion writers in making their arguments.26 In some articles, even the titles emphasized that the right to an abortion was based on the right of privacy. See, e.g., Supreme Court: Right of Privacy Includes Abortion, The Georgia Bulletin, Feb. 22, 1973, at 2 (calling Roe "one of the biggest news stories of the year"); Chicago Daily News Services, 'Privacy' is Reason for Abortion Ruling, Omaha World-Herald, 26. See, e.g., Bonni McKeown, Abortion's Status in West Virginia: Legal Question Affects Availability, Beckley Post-Herald, June 21, 1976, at 5 (explaining that Roe invalidated most states' abortion laws based on the balancing of the state's interests versus a woman's right of privacy); Washington Post, Editorial, Abortion: 19th Century, The Evening Times (Sayre), Feb. 3, 1973, at 4 (same); Joseph Kraft, Opinion, The High Court Speaks Up for Privacy, The Greensboro Record, Jan. 29, 1973, at 20 (same); Joseph Kraft, Opinion, Ruling Revealed Conservative Court, The Montana Standard, Jan. 28, 1973, at 6 (same); Joseph Kraft, Opinion, The Abortion Ruling, The Roanoke Times, Jan. 27, 1973, at 6 (same); Mary Smith, Abortion Ruling Draws Varied Reactions Here, The Lawton Constitution, Jan. 23, 1973, at 4 (same). - 73 -
Jan. 23, 1973, at 18; Associated Press, 'Right of Privacy' Cited in Action Against States, Reno Gazette-Journal, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1. Roe and its extensive coverage informed legislators and their constituents that the right of privacy under the U.S. Constitution protected the right to an abortion. Far from an issue that faded after one or two news cycles, abortion remained a prevalent issue during the seven years between Roe and the 1980 adoption of Florida's privacy amendment. The three-trimester framework laid out in Roe balanced the state's interests against the mother's right of privacy, and based on that balancing test, abortion laws in multiple states, including Florida, were struck down on federal privacy grounds. See Fla. Women's Med. Clinic, Inc. v. Smith, 478 F. Supp. 233 (S.D. Fla. 1979) (holding unconstitutional, on federal privacy grounds, administrative rules implementing Florida abortion statute); Jones v. Smith, 474 F. Supp. 1160 (S.D. Fla. 1979) (granting, on federal privacy grounds, a preliminary injunction against the enforcement of Florida abortion statute); Coe v. Gerstein, 376 F. Supp. 695 (S.D. Fla. 1973) (holding Florida abortion statute unconstitutional on federal privacy grounds). - 74 -
As courts, legislatures, and the public continued to confront the topic of abortion, the media continued to cover Roe, noting the historical and legal context: “In the famous 1973 Roe vs. Wade case, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that choosing abortion was part of a woman's right to privacy";27 "The Supreme Court legalized abortions in 1973, basing its landmark ruling on a woman's right to privacy."28 In 1980, only two months before Florida's privacy amendment vote, a United States district court judge struck down North Dakota's new abortion law regulating first trimester abortions, applying Roe and stating that "[t]he decision to obtain an abortion free from governmental interference is a fundamental right founded 27. Kevin M. Russell, Letter to the Editor, Does The Bill Regulating Abortions Deny Women Their Rights?, The Record (Hackensack), June 17, 1979, at 105. 28. Associated Press, Top Court to Decide Abortion Law Rule, Gettysburg Times, Nov. 28, 1979, at 6; Associated Press, Abortion Issue Back Before Supreme Court, The Index-Journal (Greenwood), Nov. 27, 1979, at 8; Associated Press, Abortion Issue Goes Back to High Court, News-Journal (Mansfield), Nov. 27, 1979, at 7; Associated Press, Abortion Issue is Back Before the Supreme Court, Poughkeepsie Journal, Nov. 27, 1979, at 6; Associated Press, High Court to Rule on Abortion Issue, Daily Sitka Sentinel, Nov. 27, 1979, at 2. - 75 -
in the right of privacy implicit in the Constitution." Leigh v. Olson, 497 F. Supp. 1340, 1343 (D.N.D. 1980); Associated Press, Most of Abortion Law Tossed Out, The Bismarck Tribune, Sept. 30, 1980, at 1 (front-page newspaper article in North Dakota quoting the court's decision). Following Roe, pro-choice advocates praised the decision for recognizing a woman's right of privacy, while Catholic bishops and other pro-life advocates spoke out against Roe, asserting that the decision let the right of privacy outweigh the right to life: “In effect, the Court is saying that the right of privacy takes precedence over the right to life." U.S. Bishops Issue Message on Abortion, Panama City News-Herald, Mar. 4, 1973, at 40; Bishops Reject High Court's Abortion Ruling, Issue Pastoral Applications for Catholics, The True Voice (Omaha), Feb. 16, 1973, at 1.29 at 29. See also Katherine Lunine, Letter to the Editor, Preserve Constitutional Rights, The Journal News (Hamilton), Feb. 1, 1977, 4 (showing that pro-choice actors argue that government interference with abortion is limited by a woman's right of privacy); Associated Press, Abortion Ban Voted by House, The Corbin TimesTribune, Sept. 17, 1976, at 12 (same); Associated Press, Betty Anne Williams, Anti-Abortionists Stage Ban Rally in Washington, The Robesonian (Lumberton), Jan. 22, 1976, at 2 (same); Associated Press, 'March for Life' Again Seeks Amendment to Ban Abortion, The Index-Journal (Greenwood), Jan. 22, 1976, at 3 (same); Associated - 76
Ultimately, whether they supported the Supreme Court's decision in Roe or not, Americans in 1980 would have understood that the right of privacy encompassed the right to an abortion. The Public Understanding of Florida Voters in 1980 More specifically, and especially relevant to the present case, Florida media coverage after Roe illustrates that in 1980 Florida voters would have understood the privacy amendment to encompass the right to an abortion. The wealth of primary sources from Florida strongly indicates what voters would have known. Newspapers across Florida began reporting on Roe the day it was decided: January 22, 1973. In explaining the decision, these articles discussed the federal right of privacy as the basis for the right to an abortion. Adam Richardson, The Originalist Case for Why the Florida Constitution's Right of Privacy Protects the Right to an Abortion, 53 Stetson L. Rev. 101, 125 (2023). Like newspapers throughout the nation, Florida newspapers published an Associated Press, Washington Rally Marks Abortion Anniversary, The Times Record (Troy), Jan. 22, 1976, at 3 (same); United Press International, High Court 7-2 Ruling on Abortion Praised, Condemned, Traverse City Record-Eagle, Jan. 23, 1973, at 24 (same). - 77 -
Press article quoting Roe's pronouncement that the right of privacy "is broad enough to encompass a woman's decision whether or not to terminate her pregnancy." See, e.g., Associated Press, Court Strikes Down Abortion Laws, The Pensacola News, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, High Court KOs Ban on Abortion, Tallahassee Democrat, Jan. 22, 1973, at 1. Coverage of Roe and of this broad privacy right also made the front pages of newspapers in Orlando and Fort Myers. See Washington Post Dispatch, High Court Nullifies Abortion Laws, Sentinel Star (Orlando), Jan. 23, 1973, at 1; Associated Press, Six-Month Abortions Upheld, Fort Myers NewsPress, Jan. 23, 1973, at 1. In 1980, the right of privacy and its inextricable connection to the right to an abortion continued to permeate Florida news. When Justice Douglas died in January 1980, Florida newspapers reported his legacy with mention of his majority opinion in Griswold as a precursor to Roe. Richardson, supra, at 131; James W. Fox Jr., A Historical and Originalist Defense of Abortion in Florida, 75 Rutgers U. L. Rev. 393, 427-28 (2023). For example, a Miami Herald article noted that after Griswold, "the [United States Supreme] court moved to rule, in 1973, that a woman in early pregnancy has a - 78 -
constitutional right of privacy to choose abortion without government interference." Aaron Epstein, William O. Douglas: Champion of Underdogs, Unpopular Ideas, The Miami Herald, Jan. 27, 1980, at 5-E. Florida news coverage of the United States Supreme Court continued with reports of abortion cases―and their right of privacy issues. In discussing the Supreme Court's 1980 oral arguments in H. L. v. Matheson, 450 U.S. 398 (1981), which involved parental notification of abortion, the Miami Herald reported that “[o]ut of this conflict between a minor's right to privacy and her parents' obligation to care for her has emerged a constitutional issue that was accepted Monday for review by the U.S. Supreme Court." Aaron Epstein, Court Will Examine Parents' Notification for Minor's Abortion, The Miami Herald, Feb. 26, 1980, at 10-A. And explaining the Court's decision in Harris v. McRae, 448 U.S. 297 (1980), which upheld the Hyde Amendment's restrictions on the use of federal funds to pay for an abortion, the Pensacola News reported that the decision "had nothing to do with the legality of abortion itself" because “[t]he Supreme Court legalized abortion in its landmark 1973 decision” in which "the court said a woman's right to privacy - 79 -
makes her decision to have an abortion a matter only for her and her doctor during the first three months of her pregnancy." Associated Press, High Court Rules on Abortions, The Pensacola News, June 30, 1980, at 1. Florida newspapers covered major party platforms, including their stances on abortion. These articles linked the abortion issue with the right of privacy. The Fort Lauderdale News and other Florida newspapers published a syndicated column indicating that although the Republican platform did not yet have a consensus on abortion, the Supreme Court had made its determination in 1973 by, in the author's view, “forging from a ‘privacy right' a scythe to mow down state laws that expressed various community judgments about abortion." See George Will, Opinion, Bridges to Cross; Bridges to Burn, Fort Lauderdale News, July 17, 1980, at 18A; Richardson, supra, at 132 n. 177 (observing that the column ran in Florida Today, Fort Myers News-Press, Palm Beach Post, Pensacola News, Sentinel Star (Orlando), St. Lucie News Tribune, St. Petersburg Times, Stuart News, and Tallahassee Democrat). Covering the Democratic platform, the St. Petersburg Times reported that delegates had voted for a platform statement opposing "government - 80 -
interference in the reproductive decisions of Americans" and "restrictions on funding for health services for the poor that deny poor women especially the right to exercise a constitutionallyguaranteed right to privacy." Charles Stafford, Kennedy Stirs Democrats with Rousing Call to Arms, St. Petersburg Times, Aug. 13, 1980, at 1-A (quoting the statement under the label “ABORTION”). Florida newspapers also covered statements by pro-choice activists and by pro-life activists that demonstrate both groups' understanding of abortion as part of the right of privacy. See Associated Press, Planned Parenthood Waving the Flag, The Tampa Tribune, Oct. 4, 1980, at 7-D (“In recent years we have faced an increasingly vocal and at times violent minority which seeks to deny all of us our fundamental rights of privacy and individual decisionmaking."); Carol Jeffares, Her Love of Life Makes Her Stand, Fight for It, The Tampa Tribune, Sept. 20, 1980, at 5-Pasco ("The abortion law is based on the woman's right to privacy. It says ‘a woman's right to privacy supersedes the fetus's life." "); Richardson, supra, at 132. With inflammatory language, both pro-choice and pro-life letters to the editor in Florida newspapers further demonstrate this understanding. See Joyce Tarnow, Letter to the Editor, Vote Out - 81
Anti-Abortionists, Fort Lauderdale News, Jan. 29, 1980, at 26-A ("The U.S. Constitution guarantees each of us the right of privacy, the right of religious freedom and the right to pursue happiness however we define it. Compulsory pregnancy is a denial of each of these rights."); Hugh Pope, Letter to the Editor, The Tampa TribuneTimes, Nov. 2, 1980, at 2-C (“There cannot be a more compelling reason for intelligent and patriotic Americans to vote Republican than to save lives! Stripped of all its sugarcoated slogans-freedom of choice[,]' [] 'woman's right to privacy[,]' [] etc., etc., abortion is legalized murder.”). The foregoing primary sources from Florida and from across the United States are examples of many. These sources should not be overlooked, and their impact should not be undervalued. In a quest to uncover the original public meaning of the Florida Constitution's Privacy Clause, they reveal that Roe was widely known for its holding and for its reasoning. Thus, in 1980, Florida voters would have understood the right of privacy as encompassing the right to an abortion. I hasten to add that the coverage discussed above, specifically connecting Roe and the right to an abortion to the right of privacy, - 82 -
occurred at a time when Americans relied heavily on print media and national news broadcasts. Florida Courts Acknowledge Right of Privacy Under Roe By the time Florida voters adopted the privacy amendment in 1980, Florida court decisions had repeatedly acknowledged the right of privacy expanded under federal law by Roe. While these decisions did not conclude that a right of privacy existed on state law grounds, they do provide further support that the public would have understood the link between the right to an abortion and the right of privacy. In 1977, this Court stated that “Justice Blackmun's articulation in Roe v. Wade of the limited scope of the right to privacy remains the current state of the law." Laird v. State, 342 So. 2d 962, 965 (Fla. 1977) (emphasis added) (rejecting argument that a right of privacy protected the possession of marijuana in the home). Even the dissenting opinion in Laird observed: "A constitutional right to privacy has been clearly established by the United States Supreme Court in . . . Roe . . . .” Id. at 966 (Adkins, J., dissenting) (emphasis added). - 83 -
In Jones v. Smith, 278 So. 2d 339 (Fla. 4th DCA 1973), cert. denied, Jones v. Smith, 415 U.S. 958 (1974), a case involving the abortion context, the Fourth District Court of Appeal rejected the claim of a putative father that he was entitled to prevent the mother from obtaining an abortion. The district court rejected that argument, saying: The recent decisions of the United States Supreme Court in Roe v. Wade . . . and Doe v. Bolton [410 U.S. 179 (1973)], while dealing with the constitutionality of statutes, set forth what we perceive to be the essential and underlying factor in the determination of this appeal. That factor is the "right of privacy” of the mother. Id. at 341 (emphasis added). Additionally, in discussing the right of privacy, the district court noted an observation made by the United States Supreme Court in Union Pacific Railway Co. v. Botsford, 141 U.S. 250, 251 (1891): “As well said by Judge Cooley, The right to one's person may be said to be a right of complete immunity to be let alone."" 278 So. 2d at 342 (quoting Babbitz v. McCann, 310 F. Supp. 293, 299 (E.D. Wisc. 1970)). Moreover, in Wright, the statute at issue required that an abortion be performed by a physician and at an approved facility. The petitioner, a registered nurse, challenged the approved facility - 84 -
requirement on the basis that under Roe and other federal decisions, the requirement violated the right of privacy. 351 So. 2d at 710. This Court ultimately upheld the petitioner's conviction on the ground that the statute constitutionally prohibited nonphysicians from performing an abortion. Despite concluding that the approved facility requirement was unconstitutional, this Court rejected the petitioner's privacy argument, stating: “The right to privacy in the abortion decision, recognized in Roe . . . as belonging to the pregnant woman in consultation with her physician, gives way to state power to regulate as the embryo or fetus develops." Id. at 710.30 30. Other decisions not involving abortion-related issues also recognized the right of privacy established in Roe. See, e.g., Rodriguez v. State, 378 So. 2d 7, 8 n.2 (Fla. 2d DCA 1979) (“In Roe, the court balanced the fundamental right to privacy of a woman's decision whether or not to terminate pregnancy against state interest to limit that right to safeguard health and potential life.”); Franklin v. White Egret Condo., Inc., 358 So. 2d 1084, 1089 (Fla. 4th DCA 1977) (observing on motion for rehearing that “[t]he right to be free of unwarranted interference with the decision to have children has been identified on numerous occasions by the United States Supreme Court as one of the matters protected by the right of privacy"); Day v. Nationwide Mut. Ins. Co., 328 So. 2d 560, 562 (Fla. 2d DCA 1976) (“The decision to have an abortion during the first trimester has been held to be private and personal to the individual woman. The primary interest, at least in the early stages of pregnancy, is that of the woman and her right to privacy." (citations - 85
Roe and the Privacy Amendment Debate According to the majority, the relative absence of the topic of abortion from the debate over Florida's proposed privacy amendment is evidence that the public did not understand that the right to an abortion was included in the scope of the proposed right of privacy. See majority op. at 41-42 (citing Fox, supra, at 443-44). However, Professor Fox explains why the topic of abortion was not a part of the amendment debate: Abortion would only have been debated if its coverage within the right to privacy were in dispute or were not yet established in law. But as of 1980 the protection of abortion through the right to privacy was the established law. It would hardly make sense for debates about section 23 to invest time and effort re-arguing the reasoning of Roe, let alone arguing that the terms “right to privacy," "right to be let alone," and "free from governmental intrusion" would plainly mean what they already meant in federal law. Fox, supra, at 442-43 (emphasis omitted). Indeed, Roe's extension of the right of privacy to the abortion context so dominated the abortion discussion that it would have been well understood that omitted)). Again, these cases are relevant to demonstrate that after Roe, and before voters adopted Florida's privacy amendment, the right to an abortion as a matter of a right of privacy would have been well understood. - 86 -
the right of privacy adopted by Florida voters included the right to an abortion. In re T.W. [S]tate courts cannot rest when they have afforded their citizens the full protections of the federal Constitution. State constitutions, too, are a font of individual liberties, their protections often extending beyond those required by the Supreme Court's interpretation of federal law. The legal revolution which has brought federal law to the fore must not be allowed to inhibit the independent protective force of state law-for without it, the full realization of our liberties cannot be guaranteed. William J. Brennan, Jr., State Constitutions and the Protection of Individual Rights, 90 Harv. L. Rev. 489, 491 (1977). Indeed, "[t]he citizens of Florida opted for more protection from governmental intrusion when they approved article I, section 23 of the Florida Constitution. This amendment is an independent, freestanding constitutional provision which declares the fundamental right to privacy." Winfield v. Div. of Pari-Mutuel Wagering, 477 So. 2d 544, 548 (Fla. 1985). The amendment "was intentionally phrased in strong terms . in order to make the privacy right as strong as possible." Id. It was in the context of Florida's broad right of privacy that almost thirty-five years ago, this Court held as a matter of state - 87 -
constitutional law that "Florida's privacy provision is clearly implicated in a woman's decision of whether or not to continue her pregnancy." T. W., 551 So. 2d at 1192. T.W. explained: “[W]e have said that the [privacy] amendment provides ‘an explicit textual foundation for those privacy interests inherent in the concept of liberty which may not otherwise be protected by specific constitutional provisions."" Id. (quoting Rasmussen v. S. Fla. Blood Serv., 500 So. 2d 533, 536 (Fla. 1987)). Unfortunately, the majority's decision to recede from T. W. and its progeny constitutes the rejection of a “decades-long line of cases hold[ing] that the Privacy Clause ‘embraces more privacy interests, and extends more protection to the individual in those interests, than [does] the federal Constitution."" Petitioners' Opening Brief at 41 (emphases omitted) (quoting T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1192). The decision is an affront to this state's tradition of embracing a broad scope of the right of privacy.31 31. In 2012, Florida reaffirmed this tradition when voters rejected a state constitutional amendment that would have narrowed protections for abortion rights in Florida by requiring that the protections be no greater than those provided under federal law. Additionally, the amendment would have overruled T. W. and other decisions concluding that Florida protections for abortion rights - 88 -
In deciding to reexamine T. W. and ultimately to recede from T.W. and its progeny, the majority states: "Since Roe featured prominently in T.W., we think it fair to also point out that the T. W. majority did not examine or offer a reasoned response to the existing criticism of that decision or consider whether it was doctrinally coherent. This was a significant misstep because Roe did not provide a settled definition of privacy rights." Majority op. at 13-14. I disagree. T. W. did acknowledge that "the workability of the trimester system and the soundness of Roe itself have been seriously questioned in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services, 492 U.S. 490 (1989).” T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1190. However, this Court correctly exceed those provided under federal law. In a decisive vote, more than fifty-five percent of Florida voters rejected the amendment. See Initiative Information: Prohibition on Public Funding of Abortions; Construction of Abortion Rights, Fla. Dep't of State, Division of Elections, https://dos.elections.myflorida.com/initiatives/initdetail.asp?accou nt=10&seqnum=82 (last visited Mar. 19, 2024). While the petitioners conceded during the oral argument in this case that Florida voters' rejection of the abortion amendment in 2012 was not relevant to the public understanding of the right of privacy adopted in 1980, the 2012 amendment rejection is still relevant to an understanding of Florida's tradition with respect to the right of privacy. - 89 -
observed that “[Roe] for now remains the federal law." See id. As such, this Court was not obligated in T.W. to “examine or offer a reasoned response to the existing criticism of [Roe] or consider whether it was doctrinally coherent." Majority op. at 13-14. It was "three years after T. W." and almost twelve years after Florida voters' 1980 adoption of the right of privacy that “the U.S. Supreme Court abandoned Roe's position that the right to abortion was grounded in any sort of [federal] privacy right." See id. at 15 (emphasis added) (citing Planned Parenthood of Se. Penn. v. Casey, 505 U.S. 833, 846 (1992)). Even then, the United States Supreme Court did not abandon Roe's “essential holding." Casey, 505 U.S. at 846. I reemphasize that T. W. was decided on state law grounds and with a clear understanding of the breadth of Florida's right of privacy as discussed in Winfield. To be certain, Roe was fundamental to the public understanding of the right of privacy as encompassing the right to an abortion. However, T. W. did not rely on Roe or the federal constitution to determine that Florida's right of privacy included the right to an abortion. See T.W., 551 So. 2d at 1196 ("We expressly decide this case on state law grounds and cite federal precedent only to the extent that it illuminates Florida - 90 -
law."). Because this Court based its decision squarely on Florida law, there is no basis for upending decades of precedent that give effect to Florida's broad right of privacy. Beyond Today's Decision The impact of today's decision extends far beyond the fifteenweek ban at issue in this case. By operation of state statute, the majority's decision will result in even more stringent abortion restrictions in this state. While not before this Court in the present case, it is an irrefutable effect of today's decision that chapter 202321, Laws of Florida, also known as the Heartbeat Protection Act, will take effect in short order. Chapter 2023-21 amends section 390.0111, Florida Statutes (among other statutes), and with limited exceptions, it bans abortions beyond the gestational age of six weeks. The Act provides that the ban will take effect thirty days after any of the following events: (1) a decision by this Court holding that Florida's constitutional right to privacy does not include a right to abortion; (2) a decision by this Court in the present case allowing the fifteen-week ban to remain in effect; (3) an amendment to the Florida Constitution clarifying that Florida's constitutional right of privacy - 91 -
does not include the right to an abortion; or (4) a decision from this Court after March 7, 2023, that recedes in whole or part from any of the following: T.W., North Florida Women's Health v. State, 866 So. 2d 612 (Fla. 2003), and Gainesville Woman Care, LLC v. State, 210 So. 3d 1243 (Fla. 2017). See ch. 2023-21, § 9, Laws of Fla. Today's decision implicates three of these four events, meaning that the Act's six-week ban will take effect in thirty days. “The document that the [majority] releases [today] is in the form of a judicial opinion interpreting a [provision of the Florida Constitution]. Bostock v. Clayton Co., 590 U.S. 644, 683 (2020) (Alito, J., dissenting). However, I lament that what the majority has done today supplants Florida voters' understandingthen and now that the right of privacy includes the right to an abortion. Conclusion "" The majority concludes that the public understanding of the right of privacy did not encompass the right to an abortion. However, the dominance of Roe in the public discourse makes it inconceivable that in 1980, Florida voters did not associate abortion with the right of privacy. - 92 -
Because of this, and with deep dismay at the action the majority takes today, I dissent. Application for Review of the Decision of the District Court of Appeal Direct Conflict of Decisions First District - Case No. 1D22-2034 (Leon County) Whitney Leigh White, Jennifer Dalven, and Johanna Zacarias of American Civil Liberties Union Foundation, New York, New York, for Petitioners Gainesville Woman Care, LLC, Indian Rocks Woman's Center, Inc., St. Petersburg Woman's Health Center, Inc., and Tampa Woman's Health Center, Inc., Autumn Katz and Caroline Sacerdote of Center for Reproductive Rights, New York, New York, for Petitioner A Woman's Choice of Jacksonville, Inc. Jennifer Sandman of Planned Parenthood Federation of America, New York, New York, for Petitioners Planned Parenthood of Southwest and Central Florida, Planned Parenthood of South, East, and North Florida, and Shelly Hsiao-Ying Tien, M.D., M.P.H. April A. Otterberg and Shoba Pillay of Jenner & Block LLP, Chicago, Illinois; and Daniel Tilley of American Civil Liberties Union Foundation of Florida, Miami, Florida; Benjamin James Stevenson, American Civil Liberties Union Foundation of Florida, Pensacola, Florida, and Nicholas L.V. Warren of American Civil Liberties Union Foundation of Florida, Inc., Tallahassee, Florida, for Petitioners - 93 -
Ashley Moody, Attorney General, Henry C. Whitaker, Solicitor General, Jeffrey Paul DeSousa, Chief Deputy Solicitor General, Daniel William Bell, Chief Deputy Solicitor General, Nathan A. Forrester, Senior Deputy Solicitor General, David M. Costello, Deputy Solicitor General, Darrick W. Monson, Assistant Solicitor General, Zachary Grouev, Solicitor General Fellow, John M. Guard, Chief Deputy Attorney General, James H. Percival, Chief of Staff, and Natalie P. Christmas, Assistant Attorney General, Office of the Attorney General Tallahassee, Florida, for Respondent Brad F. Barrios of Turkel Cuva Barrios, P.A., Tampa, Florida, for Amici Curiae Law Professors Jonathan B. Miller and Hilary Burke Chan of Public Rights Project, Oakland, California; and Matthew A. Goldberger of Matthew A. Goldberger, P.A., West Palm Beach, Florida, for Amici Curiae Current and Former Elected Representatives for Reproductive Justice Kimberly A. Parker, Lesley F. McColl, and Aleksandr Sverdlik of Wilmer Cutler Pickering Hale and Dorr LLP, Washington, District of Columbia, and Meghan G. Wingert of Wilmer Cutler Pickering Hale and Dorr LLP, New York, New York; and Sean Shaw of Swope Rodante, Tampa, Florida, for Amici Curiae American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Medical Association, and Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Miranda Schiller, Sarah M. Sternlieb, Robert Niles-Weed, and Elizabeth McLean of Weil, Gotshal & Manges LLP, New York, New York, Charlotte McFaddin and Caroline Elvig of Weil, Gotshal & Manges LLP, Washington, District of Columbia, and Edward Soto of Weil, Gotshal & Manges LLP, Miami, Florida, - 94 -
for Amicus Curiae Floridians for Reproductive Freedom Angela C. Vigil, Robert H. Moore, and Paul Chander of Baker & McKenzie LLP, Miami, Florida; and Francisca D. Fajana of LatinoJustice PRLDEF, New York, New York, and Emily M. Galindo of LatinoJustice PRLDEF, Orlando, Florida, for Amici Curiae LatinoJustice PRLDEF, Florida Access Network, National Latina Institute for Reproductive Justice, Esperanza United, and A.L. Brian J. Stack and Robert Harris of Stack Fernandez & Harris, P.A., Miami, Florida; and Sarah B. Gutman, Lilianna Rembar, and Caroline Soussloff of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton, New York, New York, and Jennifer Kennedy Park of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton, San Francisco, California, for Amici Curiae Sanctuary for Families, Legal Momentum, The National Organization for Women Foundation, The Rapid Benefits Group Fund, Women for Abortion and Reproductive Rights, Margaret A. Baldwin, JD, Professor Cyra Choudhury, Professor Donna K. Coker, Professor Zanita E. Fenton, Doctor Kathryn M. Nowotny, PhD, and Jodi Russell Eugene M. Gelernter and Caitlin A. Ross of Patterson Belknap Webb & Tyler LLP, New York, New York; and Courtney Brewer of The Mills Firm, P.A., Tallahassee, Florida, for Amici Curiae National Council of Jewish Women, Religious Coalition for Reproductive Choice, Catholics for Choice, Metropolitan Community Churches, National Council of Jewish Women - Greater Miami Section, National Council of Jewish Women - Palm Beach Section, National Council of Jewish Women - Sarasota Manatee Section, National Council of Jewish Women - Kendall Section, National Council of Jewish Women - Valencia Shores Section, Reconstructionist Rabbinical Association, Women's Rabbinic Network, Moving Traditions, Avodah, Bend the Arc: A Jewish Partnership for Justice, Jewish Council for Public Affairs, Jewish Orthodox - 95 -
Feminist Alliance, Union for Reform Judaism, Central Conference of American Rabbis, Men of Reform Judaism, Women of Reform Judaism, Rabbinical Assembly, Society for Humanistic Judaism, Muslim Women's Organization, Hindus for Human Rights, Sadhana: Coalition of Progressive Hindus, Women's Alliance for Theology, Ethics, and Ritual (WATER), SACRED (Spiritual Alliance of Communities for Reproductive Dignity), Faith in Public Life, and Florida Interfaith Coalition for Reproductive Health and Justice Jordan E. Pratt and Christine K. Pratt of First Liberty Institute, Washington, District of Columbia, for Amicus Curiae National Institute of Family and Life Advocates Alan Lawson, Paul C. Huck, Jr., Jason Gonzalez, Amber Stoner Nunnally, and Caroline May Poor of Lawson Huck Gonzalez, PLLC, Tallahassee, Florida, for Amicus Curiae Former State Representative John Grant Christopher Green, University, Mississippi; and Antony B. Kolenc, Naples, Florida, for Amici Curiae Scholars on original meaning in State Constitutional Law Lynn Fitch, Attorney General, Scott G. Stewart, Solicitor General, and Justin L. Matheny, Deputy Solicitor General, Mississippi Attorney General's Office, Jackson, Mississippi; and Samuel J. Salario, Jr. of Lawson Huck Gonzalez, PLLC, Tampa, Florida, for Amici Curiae Mississippi, Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, and West Virginia Stephen C. Emmanuel of Ausley McMullen, Tallahassee, Florida, - 96
for Amici Curiae Florida Conference of Catholic Bishops and the Florida Baptist Convention Jay Alan Sekulow, Jordan Sekulow, and Olivia F. Summers of American Center for Law & Justice, Washington, District of Columbia; and Edward L. White III of American Center for Law & Justice, Ann Arbor, Michigan, for Amicus Curiae Charlotte Lozier Institute Christopher E. Mills of Spero Law LLC, Charleston, South Carolina; and Chad Mizelle, Tampa, Florida, for Amicus Curiae American College of Pediatricians Edward M. Wenger of Holtzman Vogel Baran Torchinsky & Josefiak, PLLC, Washington, District of Columbia, for Amicus Curiae American Cornerstone Institute Carlos A. Rey, General Counsel, Kyle E. Gray, Deputy General Counsel, The Florida Senate, David Axelman, General Counsel, and J. Michael Maida, Deputy General Counsel, The Florida House of Representatives, Tallahassee, Florida, for Amicus Curiae The Florida Legislature Kenneth L. Connor of Connor & Connor, LLC, Aiken, South Carolina, for Amicus Curiae Liberty Counsel Action S. Dresden Brunner of S. Dresden Brunner, P.A., Naples, Florida, for Amicus Curiae The Prolife Center at the University of St. Thomas (MN) Patrick Leduc of Law Offices of Patrick Leduc, P.A., Tampa, Florida, - 97 -
for Amicus Curiae American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists Mathew D. Staver, Anita L. Staver, Horatio G. Mihet, and Hugh C. Phillips of Liberty Counsel, Orlando, Florida, for Amici Curiae Frederick Douglass Foundation, The National Hispanic Christian Leadership Conference, Fiona Jackson Center for Pregnancy, and Issues4life Foundation D. Kent Safriet of Holtzman Vogel Baran Torchinsky & Josefiak, PLLC, Tallahassee, Florida, for Amicus Curiae Susan B. Anthony Pro-Life America Denise M. Harle of Alliance Defending Freedom, Lawrenceville, Georgia, and Joshua L. Rogers of Alliance Defending Freedom, Scottsdale, Arizona, for Amicus Curiae Concerned Women for America - 98 -

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Headings and subheadings provide structure to a document. They signal what each section. is about and allow for easy navigation of the document. APA headings have five possible levels. Each heading level is formatted differently. Note: Title case simply means that you should capitalize the first word, words with four or more letters, and all ...
Titles for academic essays are often very long. Don't be surprised if your title is two or more lines long. Often, titles are split into two parts, the main title and a subtitle, separated by a colon. The main title and subtitle are usually a combination of: Catchy Phrase, Quotation, or Clever Hook Example: It's a Frog's Life
The objective of the whole essay and the main points you want to put across should also be clear to avoid formulating subtitles that do not rhyme with your essay title. In some essays, subtitles should be from the main to the minor. For example, if the title of your essay is "How the Covid-19 pandemic has affected the United States economy ...
Titles and Subtitles. It is common for pieces of academic writing to have both a title and a subtitle. In these works, the title is presented first and separated from the subtitle by a colon. For example: Nixonland: The Rise of a President and the Fracturing of a Nation. The "title: subtitle" format is rarely obligatory in academic writing ...
Writing titles in an essay requires attention to detail and an understanding of writing formats. Whether composing the essay's title and subtitles or citing other works, your titling should remain consistent. Essays inspire and inform the reader, and effective titles reflect the mood and purpose.
Using examples: for example, for instance; Subtitles. Depending on your essay question and/or length, subtitles may be another useful signposting tool. They are a clear indication to the reader about what the following paragraphs will be focusing upon. It is worth checking that your subject discipline encourages the use of subtitles.
Getting the title right. The title is the first thing you write. It is the moment you decide what is the purpose, focus and message of your article. The title is also the first thing we will see of your published article. Whether we decide to click and read the abstract, or download the full article depends - at least, partly - on this first ...
Example of a work with a subtitle. Dreams from My Father: A Story of Race and Inheritance. The exception is when the title ends in a question mark, exclamation point or dash, in which case you keep the original punctuation: ... MLA format for academic papers and essays Apply MLA format to your title page, header, and Works Cited page with our 3 ...
The Subtitle Subtitles are frequently used in social sciences research papers because it helps the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem. Think about what type of subtitle listed below reflects the overall approach to your study and whether you believe a subtitle is needed to emphasize the investigative parameters of your ...
Writing effective headings. Although similar, headings are not the same as titles. Headings head paragraphs and help structure a document. Effective headings make your paper easily scannable. Common high level headings in dissertations and research papers are "Methods", "Research results", and "Discussion". Lower level headings are ...
Start by aligning your title in the center of the page. It should be positioned about one-third of the way down the page. Step 1. Step 2. Step 3. Step 4. Step 5. Perfecting the art of essay writing is not just about content; it's also about presentation. One of the most crucial aspects of this presentation is your essay title and subtitle ...
Step 1: Skeleton of an Essay Title. As mentioned in the previous section, a title can be a word or a phrase, which can stand alone or have a subtitle. Like the content that follows an outline, a title should have a structure that is not necessarily visible like the introduction-body-conclusion outline.
The name of the college. The title of your paper. The subtitle of your paper, if applicable. Your first and last name. Your teacher or professor's name. The class name or course number. The date the paper is due. The formatting instructions are as follows: Double-spaced.
If you would like to utilize subheadings (subtitles) in your research paper, it is a good idea to first check with your instructor to be 100% sure what subheading format he/she would like you to use. ... Format: centered, capitalize the first letter but not the whole subtitle. Example: MLA Format One Level Subheading *Visit this full sample ...
A title is the main heading or name given to a piece of writing, typically placed at the top of the page or at the beginning of the text. On the book cover above, the title is "Foresight is 20/20." A subtitle, on the other hand, is a secondary heading that provides additional information about the content of the text.
Example 4: Fast Company's Work Life category home page. Headline: Work Life. Subtitle: Productivity tips and hacks, inspiring stories of success and failures, career advice, and a look inside the future of work. Why it works: Clarifies the short, generic headline by being specific about what to expect.
Whether you are writing an essay, research paper, or any other academic document, using subtitles can greatly enhance the reader's experience and understanding. ... Here are some examples of how subtitles are commonly employed in various disciplines: 1. Social Sciences: In social sciences, subtitles are often used to indicate different ...
Example #3: Hillbilly Elegy: A Memoir of a Family and Culture in Crisis by J.D. Vance. Here again, the title itself is unclear, though the "elegy" bit does suggest we're looking at a memoir. It says little, though, about the focus of that memoir, and that's where the subtitle helps us out.
They facilitate comprehension, improve visual appeal, aid in structuring the essay, and enhance its discoverability. As such, incorporating well-crafted subtitles is a powerful tool for writers to effectively convey their ideas while engaging and guiding their readers through the essay. Guidelines for Including Subtitles in Essays
College essays are an important part of your college application and give you the chance to show colleges and universities your personality. This guide will give you tips on how to write an effective college essay. ... Sample College Essay 1 with Feedback Read More
How to Write Subtitles in an Essay. A good subtitle should be catchy, informative and relevant to the main topic. ... Though the headings in the sample are titled "First Level," "Second Level," and so on, your paper's headings should be more specifically titled to reflect the content they describe. The first level.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
APA Style uses a unique headings system to separate and classify paper sections. Headings are used to help guide the reader through a document. The levels are organized by levels of subordination, and each section of the paper should start with the highest level of heading. There are 5 heading levels in APA. Regardless of the number of levels ...
The essays in "Ghost Dogs, On Killers and Kin" by Andre Dubus III are pieces of memoir. ... born in Louisiana and most of his "kin," to emphasize the term from his subtitle, are from there ...
For example, as noted above we adopted the three-part standing test established by the United States Supreme Court in Lujan v. Defenders of Wildlife, 504 U.S. 555, in J.P.