Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Brain Drain Essay


Essay on Brain Drain
Brain Drain is defined as the emigration or migration of individuals of talents and skills from developing or under-developed countries to developed ones. It means impoverishment of intellectuals, professionals, and technical resources of one country and enriching another. It is also known as the mass departure of skillful resources from a country. It brings a potential economic decline to the nation. Brain Drain subjects to a vital threat before a country. This migration results in a great loss to the countries where they are born and educated. Higher education is one of the important reasons for permanent emigration.
We, at Vedantu, have provided the students with an essay on brain drain with two perspectives in mind. The first one is the concept of making the students understand what is brain drain and next, to make them develop their essay writing skills which are useful in several ways including the need to write essays for improving their writing skills, for making good answers in the exams, to help the students prepare better result for themselves by going through this process.
The term ‘Brain Drain’ was first used by the United Kingdom in 1960 when the skilled workforce started emigrating from the developing or under-developed countries to the developed countries (first world countries). It refers to the situation when highly qualified and trained people leave his/her own country to permanently settle down in other developed countries. It is also known as human capital flight. With the beginning of globalization, ideas, opinions, skills in the form of labor started being exchanged between the nations.
This concept of Brain Drain is a matter of serious concern for any nation because it takes off individuals from their homeland to another foreign land. Often people go abroad to pursue higher education and settle there because of better work and attractive pay packages. Talented, skilled, and experienced professionals migrate to other countries for better career prospects. They get attracted by better standards of living and quality of life, higher salaries, access to advanced technology, and more stable political conditions in the developed countries which lead to migration from less developed countries.
The factors for the rise of Brain Drain are also called Push and Pull factors. The Push factors are the factors connected to the country of origin and Pull factors are the factors connected with the country of destination.
Push Factors:
The basic facility is not congenial for research and education in the institutions.
Under-employment for thousands of engineering graduates, scientific and technical manpower waiting for respective assignments.
Political instability.
Poor quality of living.
Limited access to health care facilities.
Less economic opportunity.
Pull Factors:
Better Economic prospects.
Better Research facilities.
Employment Opportunities.
Relative Political Stability.
Modern Education System and a better chance of advancement.
There are Three Types of Brain Drain
Geographical Brain Drain: This refers to the emigration of highly skilled professionals to other developing countries in search of better-paying jobs. It creates a negative impact on the economic development of the homeland.
Organizational Brain Drain: This refers to the departure of experienced and talented individuals from one organization to another. This exodus can be very harmful to organizations.
Industrial Brain Drain: This refers to the movement of skilled and trained workers from one industry to another for a better salary. This causes a shortage of experienced workers in the industry from where they depart.
Overall, Brain Drain is a widespread phenomenon these days. Many developing and under-developed countries are suffering from the loss of talents and skilled professionals like India, Africa, and Arab countries. The governments and private firms should take some strict measures to control this by aiming towards a better and friendlier atmosphere. They should provide better working conditions, improve infrastructure in educational institutions, create more employment opportunities, increase salaries and develop rural places. Making laws and strictly implementing them should check discrimination and bias at workplaces. Incentives should be given to youngsters from going abroad in search of work. These action plans can solve the problem of Brain Drain.
10 facts on Brain Drain Essay
The Brain Drain is the migration of talented geniuses from their homeland to other countries in search of a better life and jobs.
It occurs when people go out and settle abroad for their jobs or for making careers.
People often go abroad for their higher studies and after having finished their studies, they settle over there and do not return to their homeland which also causes brain drain.
It is of vital concern especially for developing countries like India, where it can have negative effects.
Countries like India keep losing citizens who have the potential and talent to change the economic conditions of the country.
However, Brain Drain is a call for hope for the countries to which the people migrate for their jobs or studies.
The countries which receive the migrating people from the other countries benefit a lot from them.
The problem of brain drain can be easily solved by providing better working conditions, good pay, and other facilities in the home country to the people.
Political disturbances are amongst one the other causes of brain drain.
Brain Drain also occurs in some countries as a result of poor living conditions for the people which pushes them to migrate to other countries.
Study the different points related to brain drain and compile a good essay on this topic. Learn more about this topic and seek assistance from Vedantu to get the best words on paper. Score well by brilliantly scribing this essay in exams and competitions.

FAQs on Brain Drain Essay
1. What is Brain Drain?
Brain Drain is the mass departure of talented and skilled individuals from a developing or under-developed country to a developing country. The Brain drain in simple words is defined as the migration of personnel in search of a better standard of living, quality of life, higher salaries, access to advanced technology, and more stable political conditions in the different places of the world. It is a condition which is fairly not good for the developing countries as they tend to suffer a major loss due to this.
2. What are Push Factors?
Push Factors are factors that are associated with the country of origin. The push factors are factors that motivate a person to migrate from their country or the region of living to another country in search of better jobs and living. The push factors are often used in a negative connotation, as they often consist of problems, distressing situations, and political or economic failures, depicting the poor conditions of the country. Also, this is a situation of loss for the country.
3. What is Organizational Brain Drain?
Organizational Brain Drain refers to the departure of experienced and talented individuals from one organization to another. This is similar to the original concept of brain drain. The concept involves the shift of employees from one organization to the other due to various reasons which include the movement due to organizational issues like poor working conditions, low pays, unhealthy work environment, etc. due to which the organization faces a challenge in many ways like the building of poor reputation within the industry and the like.
4. How to Prevent Brain Drain?
There are a lot of ways in which both the companies and countries can stop the problem of brain dragon some of which include the following:
To prevent the problem of Brain Drain, the governments of developing and under-developed countries should take stern measures of providing better working conditions to the employees in the form of infrastructure, health, travel, and other such measures.
The government must try to create more employment opportunities in the country itself so the people do not need to move by bringing in projects, developments, etc.
The government must try stopping discrimination with the people in all forms be it in terms of discrimination on the basis of age, gender, culture, religion, and others and any bias among employees.
The government must also work on the development of rural places to generate employment opportunities in the rural areas of the country.
5. Where can I get an Essay on Brain Drain?
The students can easily get essays on brain drain from the website of Vedantu for free of cost. The students will also have the access to many more new concepts which will help them in understanding better the different topics that persist. Vedantu also helps the students by providing them with other study material and resources like sample papers, previous year’s question papers, and other important resources that will help them in preparing for the exam and writing better answers.
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- SRMJEEE Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET Courses List 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Brain Drain Essay
- 100 Words Essay On Brain Drain
The term ‘Brain Drain’ is often used to refer to the emigration of highly educated or skilled individuals from one country to another. The loss of these individuals can have negative effects on the native country, including a shortage of qualified workers and deterioration of the quality of education and research. Brain drain can also lead to a brain gain for the receiving country, as it gains access to a larger pool of skilled workers. The most common reason for brain drain is the quest for better opportunities. Workers may leave their home countries in search of higher wages, better working conditions, or more prestigious positions.
200 Words Essay On Brain Drain
500 words essay on brain drain.

Brain drain is a problem that has been plaguing developing countries for years. It occurs when skilled and educated workers leave their home countries to seek better opportunities elsewhere. This often happens because these workers are not able to find good jobs at home, or because they are lured by higher salaries and better working conditions abroad. The problem of brain drain has been rapidly increasing in India, where many skilled workers have left to work in developed countries. This has had a devastating effect on the continent, as it has deprived India of the human resources it needs to develop its economy.
The loss of skilled workers can have serious consequences for a country's economy. When brain drain occurs, it can lead to shortages of qualified workers and a lack of innovation and creativity. This can ultimately hinder a country's ability to compete on the global stage. There are a number of ways to solve the problem of brain drain. One way is to provide better opportunities and jobs for skilled workers in India. Another way is to encourage the Indian diaspora to return home and share their skills and expertise with the people of their home countries and take part in the country’s holistic development.
There are many factors responsible for brain drain, but some of the most common include a lack of opportunities, poor working conditions, and low pay. When talented people are forced to leave their home countries in search of better opportunities elsewhere, it can have a detrimental effect on the country they leave behind. Not only does it deprive the country of their skills and knowledge, but it can also create a brain drain effect, where the best and brightest leave in search of greener pastures, leaving behind a less-qualified workforce.
Factors Responsible For Brain Drain
There are many factors causing brain drain. One of the most common is a lack of opportunity in the home country. When people feel they can not find good jobs or advance their careers in their own countries, they often look elsewhere.
Other factors include political instability, violence, and poverty. In some cases, people may leave their countries because they do not feel safe living there. Additionally, many people who are highly educated and skilled may choose to leave because they can earn more money elsewhere.
Brain drain can also occur when there is a mismatch between the skills required for available jobs and the skills of the workforce. This often happens in developing countries where jobs are growing faster than the education system can keep up with. As a result, many qualified workers leave to find better opportunities elsewhere.
Brain drain can also be caused by political or economic instability in a worker's home country. If a country is undergoing civil unrest or economic turmoil, its citizens may choose to leave in search of stability elsewhere.
Some workers may also leave their home countries in order to escape discrimination or persecution based on factors such as race, religion, or sexual orientation.
Effects Of Brain Drain
When a country experiences brain drain, it is losing its best and brightest minds to other countries. This can have a number of negative effects on the country.
For one, brain drain can lead to a shortage of skilled workers in the country. This can make it difficult for businesses to find the talent they need to grow and prosper. Additionally, brain drain can make it difficult for the country to attract foreign investment.
Furthermore, brain drain can lead to a loss of social and cultural capital. When the best and brightest leave the country, they take with them their skills, knowledge, and experience. This can leave the country at a disadvantage compared to other nations.
Finally, brain drain can have political consequences. The departure of skilled workers can leave the country short-staffed in critical areas such as healthcare and education. Additionally, brain drain can lead to a loss of tax revenue for the government as skilled workers are often among the highest earners in society.
How To Combat Brain Drain | There are many ways to combat brain drain, but some of the most effective include investing in education and training, creating more opportunities for advancement, and providing better working conditions and compensation. By retaining its best and brightest citizens, a country can ensure that its workforce is qualified and able to meet the demands of the ever-changing global economy.
Applications for Admissions are open.

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

UPES School of Liberal Studies
Ranked #52 Among Universities in India by NIRF | Up to 30% Merit-based Scholarships | Lifetime placement assistance

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd
Enrol in PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd for JEE/NEET preparation

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Brain Drain — Brain Drain: Causes, Consequences, and Solutions
Brain Drain: Causes, Consequences, and Solutions
- Categories: Brain Drain Human Migration
About this sample

Words: 518 |
Published: Sep 7, 2023
Words: 518 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Table of contents
Causes of brain drain, consequences of brain drain, solutions to address brain drain, case study: india's approach.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 748 words
1 pages / 1054 words
2 pages / 879 words
3 pages / 1258 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Brain Drain
Developing economies continue to grapple with the phenomenon of brain drain, where a significant portion of educated and skilled individuals migrate to developed nations seeking better opportunities. This scenario poses severe [...]
The term brain drain is profoundly impactful in the healthcare sector, illustrating the migration of healthcare professionals from less developed regions to more affluent ones. This phenomenon, influenced by various factors [...]
Brain Drain, often described as the emigration of highly skilled and educated individuals from less developed or unstable regions to more developed regions, is a phenomenon deeply ingrained in the global socio-economic [...]
It have some men in this world, they don’t do nothing at all, and you feel that they would dead from starvation, but day after day you meeting them and they looking hale, they laughing and they talking as if they have a million [...]
As we all know Donald Trump had won the presidency against Hillary Clinton in this past election. Trump took office in mid-January and has already made some radical changes throughout the Country. Of these changes, the most [...]
In the short story “The Blossoming of Bongbong,” the main character, Bongbong, moves to America with big hopes to reshape his life and achieve success. This vague notion of the American dream leads to Bongbong’s desire for the [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Brain Drain?
Understanding brain drain.
- Reducing Brain Drain
- Brain Drain FAQs
The Bottom Line
Brain drain: definition, causes, effects, and examples.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/profile_photo-5bfc2a3446e0fb0026012f81.png)
Katrina Ávila Munichiello is an experienced editor, writer, fact-checker, and proofreader with more than fourteen years of experience working with print and online publications.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KatrinaAvilaMunichiellophoto-9d116d50f0874b61887d2d214d440889.jpg)
Investopedia / Mira Norian
Brain drain is a slang term that indicates a substantial emigration or migration of individuals. A brain drain can result from turmoil within a nation, the existence of favorable professional opportunities in other countries, or a desire to seek a higher standard of living . In addition to occurring geographically, brain drain may also occur at the organizational or industrial levels when workers perceive better pay, benefits, or upward mobility within another company or industry.
Key Takeaways
- Brain drain is a slang term indicating substantial emigration or migration of individuals.
- Brain drain can result from political turmoil or the existence of more favorable professional opportunities elsewhere.
- It causes countries, industries, and organizations to lose a core portion of valuable individuals
- Some of the consequences of brain drain include the loss of tax revenue.
- One of the best ways to reduce brain drain is to boost government investment in the local economy.
As noted above, brain drain is the movement of people from one area to another. Brain drain often occurs between countries and cities where they can find better opportunities. They may move to look for work or a better standard of living. Brain drain can also refer to the movement of professionals between corporations and/or industries for better pay or opportunities.
Brain drain causes countries, industries, and organizations to lose a core portion of valuable individuals. The term is often used to describe the departure of certain professionals, including groups of doctors, healthcare workers, scientists, engineers, or financial professionals. When these people leave , the places they leave are harmed in two main ways:
- Expertise is lost with each emigrant, diminishing the supply of that profession.
- The (country's) economy is harmed because each professional represents surplus spending units.
Professionals often earn large salaries, so their departure reduces consumer spending in that region or the country overall.
Geographic, Organizational, and Industrial Brain Drain
Brain drain can occur on several levels: geographic, organizational, and industrial brain drain.
Geographic Brain Drain
Geographic brain drain happens when talented professionals flee one country or region and end up moving to a country that they feel gives them better and more opportunities.
Several common causes precipitate brain drain on the geographic level including political instability, poor quality of life , limited access to health care, and a shortage of economic opportunity. These factors prompt skilled and talented workers to leave source countries for places that offer better opportunities.
Organizational and Industrial Brain Drain
Organizational brain drain involves the mass exodus of talented workers from a company, often because they sense instability, a lack of opportunity within the company, or they may feel that they can realize their career goals more easily at another company. Industrial brain drain happens when skilled workers exit not only a company but an entire industry .
These two forms of brain drain are usually a byproduct of a rapidly evolving economic landscape in which companies and industries unable to keep up with technological and societal changes lose their best workers to those that can.
Causes of Brain Drain
So what causes brain drain? As noted above, there are several underlying factors that lead to this phenomenon. They can vary, though, based on the type of brain drain.
Some of the main reasons why people choose to leave their home countries/regions include:
- Economic opportunities, including new and better jobs, higher standards of living, access to housing and health care
- Political strife and instability
- Persecution based on religion, gender, or sexuality
While most brain drain is geographic, there is some brain drain that occurs as a result of situational factors. For instance, skilled workers may leave companies and industries when machines and technology replace human labor.
Brain drain is also known as a human capital flight,
Effects of Brain Drain
Brain drain can have major consequences. The effects are felt not only in the area where the brain drain occurs but also where the brain gain (where individuals move to) takes place. And it can often have a chain reaction.
Areas affected by brain drain end up with a dearth of human capital . Professionals who go elsewhere end up leaving a large hole to fill—one that isn't always easy to fill. Consider medical professionals in developing nations who move to parts of the developed world for better opportunities. There may not be enough (qualified) people to replace them when they leave, which affects the quality of health care for those left behind.
Another effect on areas that experience brain drain is the loss of revenue . Governments rely on income taxes to fund their social programs and infrastructure projects. A mass exodus leads to a drop in tax receipts which can stunt economic growth and development.
Areas that see brain gain are also impacted. Some of these factors include overcrowding (especially in major metropolitan areas where more opportunities are available). More people in one area puts a strain on resources, which can lead to higher prices and taxes.
Measures to Reduce Brain Drain
While there isn't an easy fix for brain drain, there are some things that business and government leaders can do to reduce or minimize it. These include:
- Increasing investments into certain areas of the economy
- Offering competitive wages
- Paving the way for legal and social reform
- Improving the quality of resources, such as housing and health care
- Providing affordable housing solutions
Examples of Brain Drain
Ukraine brain drain.
War and conflict are big catalysts for brain drain. This was evident following Russia's invasion of Ukraine. Studies conducted by the European Parliament indicate a massive displacement of the country's population across the European Union (EU). One of the main areas the study examined was the movement of students. The number of students leaving Ukraine doubled from 25,000 to 50,000 between 2007 and 2014. That number jumped to about 78,000 by 2019. The majority of these students were enrolled in post-secondary institutions in Poland.
Some professionals leaving Ukraine are having a tough time finding work in their fields in other countries because of a lack of available work or transferrable skills. As such, some are choosing to take on lower-paying jobs to find a sense of security and safety.
But it isn't just Ukraine that's experiencing a brain drain. In fact, Russia is experiencing a flight of human capital, too. Economic sanctions placed on the country by the U.S., the United Kingdom, and Canada, are having a profound impact on Russian citizens. The federal government also has laws in place punishing citizens who support Ukraine. It's estimated that as many as 200,000 Russians left the country.
Puerto Rico Brain Drain
Brain drain was a significant consequence of the ongoing Puerto Rican debt crisis as of 2019. This was particularly evident in the exodus of skilled medical professionals, which hit the island hard. While almost half of Puerto Rico's residents receive Medicare or Medicaid , the island receives significantly fewer federal funds to pay for these programs than similarly sized states on the mainland, such as Mississippi.
This lack of funding combined with the island's dire financial situation precludes its ability to offer competitive compensation to doctors, nurses, and other medical staff. As a result, such professionals were reported to be leaving the island en masse for more lucrative opportunities on the mainland.
This form of brain drain was also exacerbated by Hurricane Maria, which hit the island in September 2017, creating even more incentives for emigration .
What Does Brain Drain Mean?
Brain drain is a slang term that alludes to the loss of human capital from one area to another or from one industry to another. Brain drain usually happens when skilled individuals and professionals leave the home countries (in most cases, developing nations) and go elsewhere to take advantage of better opportunities. It also occurs when individuals leave one area of the workforce and go to another for some of the same reasons.
How Does Economic Growth Help Fight Brain Drain?
Brain drain occurs when there is a lack of opportunity in a certain area. For instance, professionals living in a developing nation may leave in search of better opportunities in parts of the developed world. Making economic investments to boost growth often provides incentives for people to stay, as it means access to better (and more) resources, personal economic prosperity, and the potential for a higher standard of living.
What Impact Does Brain Drain Have on Developing Nations?
Brain drain or the exodus of human capital often has a big impact on developing nations. It often leaves a hole that is hard to fill since there may not be as many people with similar skills to fill that void. It also leads to a loss in tax revenue, which can lead to higher taxation to make up for the shortfall. Citizens may not be able to access quality resources, such as education and health care, which also affects their quality of life.
Human capital is a vital part of the economy. But when conditions get tough, these individuals may look elsewhere for better jobs, higher pay, and an improved standard of living. A mass exodus of people can lead to what's called brain drain. When human capital is depleted from a certain area, it can have lasting effects on the local economy.
European Parliament. " RUSSIA'S WAR ON UKRAINE: UKRAINIAN STUDENTS IN THE EU ."
NBC News. " A brain drain is devastating Ukraine ."
BBC News. " Russia faces brain drain as thousands flee abroad ."
Center on Budget and Policy Procedures. " Puerto Rico's Medicaid Program Needs an Ongoing Commitment of Federal Funds ."
National Provider Identifier (NPI) Dashboard. " 2020 Update -- Aftermath of Hurricane Maria and the Emigration of Health Care Professionals to Mainland US ."
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. " National Hurricane Center, Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Maria ," Page 2.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/home_sale-184314534-5bb93fdec9e77c0058f5d318.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Toggle navigation
- Explore Themes
- Document Library
- Visualisation Gallery
- Methodology
- Data for Sustainable Development - UIS Blog
- Training and Workshops
- UNESCO website
From Brain Drain to Gain: The Benefits Arising from International Knowledge Networks
By Silvia Montoya, Director of the UNESCO Institute for Statistics ( UIS ) This blog was also published by Norrag
Thinking about studying abroad next year or know someone who is? You’re not alone. International student mobility is on the rise and data show that everyone benefits. Rather than depriving developing countries of their best talent through ‘brain drain,’ mobile students are offering ‘brain gain’ by creating a global pool of highly-skilled human capital.
As scientists and researchers, they are forming knowledge networks and increasing collaboration on global policy issues. This improves innovation in research and development (R&D) in host countries and generates results for countries that send students abroad.
When G20 education ministers meet from September 5-6 in Argentina, they will be focusing on the future of jobs, and the skills development needed to go with it. To help inform the discussions, the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) has released a new paper , entitled Skills and Innovation in G20 Countries, which looks at skills development at different levels of education as well as the the impact of cross-border flows of students on R&D and innovation.

University students in Malaysia - Credit: World Bank
Most mobile students go to G20 countries
As enrollment in post-secondary education has grown, the number of students studying abroad has more than doubled from 2.1 million to 4.7 million in the last fifteen years (see Figure 1). UIS data show that two out of every 100 tertiary students pursue their studies abroad.
Figure 1. Long-term trend in the global numbers of internationally-mobile students, 1980-2015

Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics.
More than two-thirds of these mobile students live in G20 countries, with 19% studying in the United States, followed by 9% in the United Kingdom and 6% in Australia.
On the flip side, China is by far the largest source of internationally-mobile students with over 800,000 studying abroad in 2015. India, and to lesser extent Germany, also sends large numbers of students to study internationally (see Figure 2). In fact, a recent study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) suggests that due to demographic trends, India will soon surpass China in the supply of mobile students.
Figure 2. Net flow (inflows minus outflows) of mobile students by country, 2015
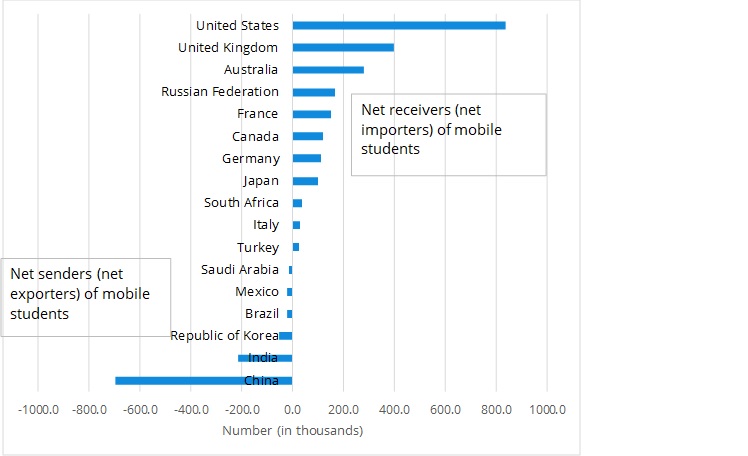
Note: Argentina and Indonesia are not presented due to a lack of data. Source: UNESCO Institute for Statistics.
It is interesting to note that while China sends by far the largest number of students abroad, they account for just 2% of the total number of tertiary students in the country. In contrast, over 5% of university students in Saudi Arabia are internationally mobile. American students, on the other hand, are much less likely to study abroad with less than 1% choosing to do so.
All of this movement means that university campuses are becoming increasingly diverse. In the United Kingdom, for example, internationally mobile students account for almost 19% of the total number of tertiary-level students. Australia is a close runner-up with a foreign student body of 15%.
The rise of global knowledge networks
Both sending and receiving countries hope to benefit from this growing pool of skilled human capital. Host countries eager to build their own research capacities seek international talent. They vie for students by offering affordable, relevant, high-quality course offerings.
Sending countries, who may lack the capacity to educate students beyond secondary school, offer inducements such as scholarships so their students can gain innovation-promoting skill sets in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) subjects – and bring that knowledge back home.
Importantly from a gender perspective, while women now outpace men in overall tertiary educational attainment, they account for less 27% of all researchers in the G20, slightly lower than the global average. Only Argentina and South Africa have achieved gender parity.
Notwithstanding this imbalance, the accumulation of human talent within the G20 has created an impressive knowledge network. Global R&D activities and expenditure are concentrated in this economic region, mainly in the United States and China. However, collaboration within this vast talent pool – many of whom originated abroad – ensures that even the sending countries benefit.
When Ebola broke out in West Africa in 2014, for example, scientists, researchers and health professionals from governments, international organizations and the nonprofit sector worked together to find a solution. And, the UNESCO Science Report points out that climate change is another important area of collaboration as online global data hubs allow researchers around the world to compare work and bridge the gap between global and local efforts.
So, human talent flows can more rightly be seen as a brain gain for everyone: talented human capital that benefits host and home countries alike through collaboration on global issues. This network of internationally mobile students, and the scientists that they become, is arguably a public good.
International policy implications
Policies to promote education and innovation are a key part of global initiatives. The sustainable development goal for education ( SDG 4 ), for example, promotes the expansion of scholarships available to students in developing countries for training in STEM subjects.
But, the significant rise in the number of internationally-mobile students has increased demand for course offerings. Out of the box solutions include online learning, foreign campuses and international joint degree programs so quality assurance systems are necessary to ensure that students are getting what they paid for. To this end, UNESCO and the OECD are developing a global convention for quality control.
When G20 education ministers meet this week, they may want to consider three takeaways for ongoing cooperation and policy initiatives.
- Leaders within the G20 and beyond need to promote inclusive policies to ensure that all groups have access to quality education and lifelong learning. This includes the promotion of gender equality in STEM subjects in education, and as a career choice for women.
- G20 leaders can also encourage the harmonization of education systems and the recognition of qualifications to facilitate access to education for international students.
- Closer collaboration between education and labour ministers could establish linkages between universities and the job market . By encouraging the mobility of researchers, countries can further benefit from innovation activities through intragroup peer learning.
In this era of rising student mobility and greater collaboration between talented individuals around the world, brain gain in science and technology is a net gain for everyone.

Leave a comment
View the discussion thread.
Essay on Brain Drain
Brain drain refers to the movement of highly skilled and educated people from one country to another, where they can work in better conditions and earn more money. People migrate due to the lack of opportunities in their home country. The brain drain reduces economic growth through the depletion of a source country’s human capital assets and, additionally, through loss of return on investment in education. It’s a serious problem that most developing countries like India are facing today. The essay on brain drain will help students to understand the reason behind brain drain and how this problem can be solved. Students can also check out the list of CBSE Essays to practise more essays on different topics and boost their essay writing skills.
500+ Words Essay on Brain Drain
The term “brain drain” refers to the international transfer of human capital resources, and it applies mainly to the migration of highly educated individuals from developing to developed countries. The term is generally used in a narrower sense. It relates more specifically to the migration of engineers, physicians, scientists, and other highly skilled professionals with university training, to developed countries. The brain drain is a serious constraint on the development of poor countries.
Reasons for Brain Drain in India
The major reason behind the brain drain is the lack of career opportunities, investment and lower salaries in home countries. The highly skilled people do not get proper exposure where they can showcase their skills. They don’t get the opportunity to grow higher. This happens because, in many private and government organisations, the managers sitting in higher positions give preference to their relatives and known people. Many times, the hiring team does not use the correct assessment process to recruit people. Moreover, the reservation and reserved quota in government jobs are the major reasons why youth lose interest in appearing in various competitive or government exams.
Brain drain also occurs when an employee loses interest in work. If he continues to do the same task for 5 to 6 years, he becomes saturated with work. He wants some new role and responsibility that excite him and challenges him to do the work. The change in work also sharpens their skills and significantly increases their income. The work culture and environment also play a major role in brain drain. If the work culture is not flexible and reliable, then people start thinking of leaving the organisation and moving to another. Many times office politics, blame games, overwork, no appreciation, and no rewards also compel a person to look for a better opportunity where his skills will be appreciated.
India has skilled and semi-skilled, employed and unemployed human resources. Low salaries and inefficient working conditions trigger the movement of people to countries with better living standards and facilities. There is a huge difference in terms of salary in developed, developing and underdeveloped countries. Most of the students who go abroad for higher studies do not return to India. After seeing the affluent life of foreign countries, they lose all interest in their own country. They get placed in good companies and start living a high-profile life.
How to Stop Brain Drain?
Talent in emerging economies is scarce, expensive, and hard to retain. But, for the balance of power and for the development of the world, it is very important to stop the phenomena of brain drain. This will help a particular country to use all local skilled citizens for development and proliferation. But to hold these skilled workers at their native places, it is also important to provide them with enough work opportunities and living facilities. For this purpose, developed nations should help developing countries with the necessary money and resources. So that each and every human on this planet can have a good standard of living and each and every nation can introduce itself as a developed nation.
Students must have found this essay on brain drain useful for improving their essay-writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

Brain Drain and Brain Gain: The Global Competition to Attract High-Skilled Migrants
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This volume reviews the most recent research on brain drain and brain gain, producing new original results by the means of data sources specifically assembled for this study, and addressing several key policy issues. Part I focuses on brain gain, that is, it takes the standpoint of the recipient country. The first section provides an overview of skill‐selective immigration policies in the main destination countries and of the major shifts in these policies which have been recently observed. It also documents the strong economic gains from immigration of highly skilled migrants. But what drives the decisions of highly skilled migrants as to where to locate? The econometric analyses performed by the authors indicate that it is mainly the labour market that is key to attracting talent, wage premia on education in particular. R&D spending also induces greater inflows of highly skilled migrants, while generous welfare benefits and strict employment protection end up attracting more unskilled workers. Part II is devoted to the consequences of brain drain, taking the point of view of the sending country. This second section provides for the first time a measure of the net global impact of the brain drain on sending countries. The results indicate that most developing countries experience a net gain from skilled emigration. Adverse overall impacts are found to be limited only to a subset of countries exhibiting very high skilled emigration rates. A number of policy recommendations are also offered to increase the benefits of brain drain.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Essay on Brain Drain
Students are often asked to write an essay on Brain Drain in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Brain Drain
Introduction.
Brain drain refers to the migration of skilled professionals from their home country to another for better opportunities. It’s a global issue affecting many nations.
Causes of Brain Drain
Brain drain is caused by several factors including lack of opportunities, low wages, political instability, and poor living conditions in the home country.
Effects of Brain Drain
Brain drain leads to loss of skills and intellectual resources. It can slow down the development of a country and create imbalance in the global distribution of talent.
To combat brain drain, nations need to improve their living conditions, provide better opportunities and create a stable political environment.
Also check:
- Paragraph on Brain Drain
250 Words Essay on Brain Drain
Brain drain refers to the emigration of highly skilled individuals from their home countries to foreign nations, often in search of better opportunities. It is a global phenomenon that affects both developed and developing countries, posing significant socio-economic implications.
The primary cause of brain drain is the quest for improved living conditions. Professionals migrate to countries offering better job prospects, higher wages, and enhanced life quality. Political instability, lack of research opportunities, and inadequate infrastructure in home countries further exacerbate this issue.
Impacts of Brain Drain
Brain drain has a dual impact. The host countries benefit from the influx of skilled professionals contributing to their economic growth. Conversely, the home countries suffer from a loss of human capital, leading to a potential decline in their development pace.
Counteracting Brain Drain
To counteract brain drain, it is crucial for countries to create conducive environments that encourage their citizens to stay. This includes ensuring political stability, offering competitive wages, and investing in research and infrastructure. Implementing policies that promote circular migration can also be beneficial, where emigrants return to their home countries, bringing back new skills and knowledge.
While brain drain poses challenges, it also presents opportunities for global knowledge exchange. The key lies in managing this phenomenon effectively, turning the potential loss into a gain for both home and host countries. This requires concerted efforts from governments, institutions, and individuals alike.
500 Words Essay on Brain Drain
Understanding the phenomenon of brain drain.
Brain Drain, also known as Human Capital Flight, is a phenomenon where skilled and educated individuals migrate from less developed or developing countries to developed nations in search of better opportunities. This migration, while offering personal growth for individuals, often leads to a significant loss for their home countries.
The Driving Forces of Brain Drain
The primary drivers of Brain Drain are socio-economic in nature. The quest for improved living conditions, higher wages, and better career prospects are some of the primary reasons why skilled professionals migrate. Political instability, lack of infrastructure, and limited research opportunities also contribute to this exodus.
The Impact of Brain Drain
The impact of Brain Drain is multifaceted, with both negative and positive outcomes. On the negative side, the departure of skilled professionals leads to a knowledge gap in the home country. It hampers the growth of industries and research, and can even affect the country’s economy.
However, there’s a positive side as well. The remittances sent back home by these professionals can contribute significantly to the home country’s economy. Moreover, if these professionals return home after gaining global exposure, they can bring back valuable skills and knowledge, contributing to the development of their home country.
Brain Drain vs Brain Gain
While Brain Drain is often viewed negatively, it’s important to consider the concept of Brain Gain. This refers to the influx of skilled professionals into a country, which can lead to significant economic and social benefits. Developed countries often experience Brain Gain, which contributes to their continued growth and development.
Addressing the Issue of Brain Drain
Addressing Brain Drain requires comprehensive strategies that focus on improving socio-economic conditions, political stability, and research opportunities in the home country. Governments should invest in education, research, and development, and create an environment that encourages innovation and entrepreneurship.
Moreover, strategies should be developed to attract back the expatriate professionals. For instance, the concept of “Brain Circulation”, where professionals work overseas for a period and then return home, can be promoted.
Brain Drain is a complex issue with both negative and positive impacts. While it can lead to a loss of valuable human capital for developing countries, it can also result in economic benefits through remittances and the return of skilled professionals. Addressing this issue requires a balanced approach that not only prevents the outflow of talent but also encourages their return. The key lies in transforming the Brain Drain into a Brain Gain, thus turning a potential loss into a win-win situation for all involved.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Women Empowerment
- Essay on The Happiest Day of My Life
- Essay on Self Reliance With Integrity
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Essay of the Week: Brain drain in the developing world
Our band nine sample essays give you the opportunity to learn from successful essays that show off the best structure, vocabulary and grammar. This problem and solution type essay is about the complex issue of 'brain drain' in the developing world.
An increasing number of professionals like teachers and doctors are leaving poorer countries where they grew up to work in richer countries. What are some problems this causes and what are some solutions?
In recent years, developed countries have seen an influx of educators and healthcare practitioners from the developing world. In this essay, I will look at two issues this causes and present some solutions. First, that these countries do not recoup their investments in these people’s education, and second, that this leads to an unfair distribution of important workers.
First, professionals leaving the country after graduation is unfair to the countries who train them. When countries train public workers, they are making an investment in their education that they expect to recoup by having well trained staff in important jobs. If these professionals then leave the country for a high salary in the developed world, this means the country fails to get anything back for it’s investment. This is especially problematic for developing countries who have less public money available for education.
Second, this causes a shortage of professionals in those countries. Because these professionals have in-demand skills, it is easy for them to find jobs and visas abroad. This can cause staff shortages as poorer countries can lose staff to countries with more money causing a damaging shortage. For example, a country might lose teachers and then struggle to develop because of a lack of education provision.
To conclude, losing skilled professionals is both unfair and damaging to countries. However, there are several solutions to this problem. Developed countries should focus more on training their own workers rather than relying on the developing world. In addition, poorer countries should make training conditional on trainees working in that country for a period of time.
Related posts
- A Beginner’s Guide to IELTS
- Common Grammar Mistakes [for IELTS Writing Candidates]
Writing Correction Service
- Free IELTS Resources
- Practice Speaking Test
Select Page
Brain Drain [Sample Essays and Vocabulary]
Posted by David S. Wills | Feb 27, 2023 | Model Essays | 2
For today’s English lesson, we are going to look at the topic of “brain drain.” This is a phenomenon that occurs when lots of talented people move from developing countries to developed ones. It is an interesting topic with many issues to debate, so it is possible that you could encounter it in the IELTS writing test.
What is “brain drain” and how could it appear in IELTS?
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, “brain drain” means:
the situation in which large numbers of educated and very skilled people leave their own country to live and work in another one where pay and conditions are better ( source )
This is quite a big issue nowadays and it affects many parts of the world positively and negatively. As the world becomes more interconnected, it seems reasonable that it will continue to be a problem in the future.
This sort of topic is most likely to occur in the IELTS writing test and specifically in task 2. In fact, I’ll show you two sample answers below. You might also see a reading passage about “brain drain” in the reading test and I suppose it is theoretically possible that it could be the subject of section 4 of the listening test.
However, I cannot imagine that you would realistically see questions about this in any part of the IELTS speaking test. It is slightly too specialised and talking about it is a little too difficult.
Language related to “brain drain”
When it comes to the topic of “brain drain,” you should think of this generally as being a sub-topic of work , education , and immigration . Note that IELTS topics often overlap like this.
As such, to talk about this, you should be comfortable with vocabulary related to these areas and specifically the points at which they intersect. Here are some examples:
- advanced economy
- developed country
- developing country
- emigration / emigrant
- immigration / immigrant
- permanent residency
- standard of living
- tertiary education
- tuition fees
Make sure that you know more than just the loose meaning of each word or phrase. It is important that you know precisely how to use them.
Also, I have tried not to include more common words like “abroad” but obviously you should be familiar with them and confident about how to use them.
You can read more about common IELTS topics here .
How to think of ideas about “brain drain”
Sometimes, IELTS questions can be difficult not just because of the language required but because of the topic. While some people have strong opinions about brain drain, others don’t. They simply can’t think of anything to say or worry that their ideas aren’t very developed.
For this reason, it is useful not just to learn vocabulary in preparation for your IELTS test, but also to learn ideas. You can do that in different ways:
- reading articles
- listening to podcasts
- watching videos or documentaries
- engaging in debates
I recently saw this very interesting YouTube video, which goes into detail about why brain drain hurts some countries and why it keeps happening.
I have a whole article about how to generate ideas for IELTS .
Sample Essays
Ok, now let’s look at some sample questions and answers. These are quite similar but the types of question are different and so I have written different answers.
Brain Drain Essay: Problems and Solutions
Here is our first question:
An increasing number of professionals, such as doctors and teachers, are leaving their own poorer countries to work in developed countries. What problems does this cause? What can be done to deal with this situation?
As you can see, this is a problems and solutions question . That means you need to firstly explain the problems caused by brain drain and then suggest some solutions.
Sample Answer
In the modern era, it is common for people to move around the world for various reasons, including immigration purposes. This sometimes results in people leaving a poor country to go to a richer one, in a phenomenon that is sometimes known as “brain drain.” This essay will look into the reasons for this and also suggest some solutions.
The allure of wealthy countries is naturally going to appeal to many people from poorer nations. They look to these places and see opportunities for themselves and their families, as well as clean environments and high-quality homes and goods. It is natural, then, that these people will aspire to leave their own country and move to a more developed one in the hope of a better life. They study hard and take every possible chance to give themselves a brighter future, and once they are able to emigrate, they leave their home country and travel to their new home. This is usually a positive step for them, but it tends to trap poor countries in a cycle of poverty.
Solving this problem is clearly not easy because it is a pretty natural phenomenon and people will always want to give themselves a better life. However, if there was a way to encourage doctors and other professionals to stay in their home nation, they could help to build it into a much more prosperous society, ultimately resulting in generations of educated people with no real desire to leave. Another option is for that nation to attempt to attract doctors and teachers from other countries as a way of filling the knowledge gap. This would not be easy, but again if it were achieved it would result in a strengthened nation that would no longer encourage its citizens to leave.
In conclusion, it is a natural occurrence that people want to move to cleaner, more developed places with safer streets and better standards of living, which is why educated people flee from poor nations. However, solving this problem will not be easy and may require some creative action by various governments.
Notes on the Answer
I have a simple but effective structure here:
In terms of language, I will note some useful phrases:
- The allure of wealthy countries
- see opportunities for themselves
- high-quality homes and goods
- take every possible chance
- a brighter future
- a cycle of poverty
- a much more prosperous society
- filling the knowledge gap
- a natural occurrence
You will see that my solutions are not very definite but that’s because there are no easy solutions. Some students write things like “The government should pay doctors more money.” However, is this a realistic suggestion? If governments had unlimited money and could pay doctors more, they probably would. Therefore, use careful thinking and language skills to show reasonable ideas. Don’t worry about your suggestions being weakened by the admission that these ideas might not work. It is better to show that you are aware of this than to confidently make unreasonable suggestions.
Brain Drain Essay: Discuss Both Views
Here is our second question:
Some people believe that professionals, such as doctors and engineers, should be required to work in the country where they did their training. Others believe they should be free to work in another country if they wish. Discuss both these views and give your own opinion.
You can see that this is a “ discuss both views ” question, so it is a little different from the previous one. Also, I suppose it is technically possible that you could answer this without mentioning brain drain, but still the idea is clearly connected.
A small number of people think that highly trained professionals should be required to work in the same country where they did their training, but most people disagree with this. This essay will also disagree, suggesting that they should be free to work where they want.
To begin with, it is understandable that people might argue in favour of professionals working in the country where they trained because in some cases that country has paid for their training. Take, for example, a doctor who received medical training at the government’s expense in a relatively poor country. If they moved to another country, perhaps in order to earn a higher salary, then the government’s investment would have been wasted.
However, there are a few problems with that viewpoint. First of all, professionals of this nature usually pay for their own education, and so if they were required to stay in that country then it would be unfair. A lot of people invest in their education purely to gain the chance of moving to another country for a better life. Then, of course, there is the argument that all people should have some freedom of movement. Particularly in the case of highly trained professionals, who can bring value to different societies, it is beneficial to have them move around the world, sharing their skills and increasing diversity. Perhaps they ought to give something back to the society in which they were trained, but they should not be restricted by any law because that would be a violation of their fundamental rights.
In conclusion, people who have important skills should be free to move to other countries if they wish. They should not have a legal obligation to stay in the nation where they earned their skills, but perhaps for the sake of decency they might consider staying a short while and giving back to that society.
I have not used the phrase “brain drain” here but the essay is still about that because brain drain is what happens when these people leave their home countries in large numbers.
Note that I have discussed both views but sided with the “disagree” perspective. That means I have written a longer paragraph full of “disagree” ideas. I have also made my opinion clear throughout the whole essay, which is also essential. In the introduction , for example, my outline sentence puts my perspective across very clearly.
Here are some more useful words and phrases:
- highly trained professionals
- to earn a higher salary
- the government’s investment
- people invest in their education
- freedom of movement
- a violation of their fundamental rights
- a legal obligation
Finally, note that in both these essays I avoided the trap of repeating the examples from the question. It is a common mistake that IELTS candidates see an example and assume it is the main idea of the question. In fact, you do not need to talk about doctors and engineers. You could talk about any professionals.
About The Author
David S. Wills
David S. Wills is the author of Scientologist! William S. Burroughs and the 'Weird Cult' and the founder/editor of Beatdom literary journal. He lives and works in rural Cambodia and loves to travel. He has worked as an IELTS tutor since 2010, has completed both TEFL and CELTA courses, and has a certificate from Cambridge for Teaching Writing. David has worked in many different countries, and for several years designed a writing course for the University of Worcester. In 2018, he wrote the popular IELTS handbook, Grammar for IELTS Writing and he has since written two other books about IELTS. His other IELTS website is called IELTS Teaching.
Related Posts
Cambridge IELTS 18: Sample Answers
August 28, 2023
Bad Behaviour in Schools [IELTS Task 2]
October 29, 2022
2x Process Diagram Model Essays
June 26, 2017
Model Essay: Bar Chart
July 18, 2017
I have some questions related to IELTS Writing in general and your essays. 1. Have you tried using chatGPT for IELTS Writing? What do you think the quality of the essays it can create and how do IELTS learners use it to improve their writing? 2. In your essays + The first essay – You use near future tense ‘be going to do sth’ in the first sentence of the first body paragraph. Could you explain to me why you use this tense in this sentence? + The second essay – Actually, I see some dictionary mark ‘To begin with’ or ‘To begin’ as an informal phrase. Is it also proper when used in IELTS Writing? – In the second body paragraph, I see you use ‘increasing diversity’ which makes me confused. Could you explain what does this phrase exactly mean? Thank a lot
1. I’ve tested it a few times. It’s fine but not perfect. I haven’t really looked into it as a means of learning to write essays. I know that other AI programmes are terrible at fixing grammar problems, but ChatGPT is a lot smarter, so it’s possible.
2. This is used to mean that something hypothetically does appeal to these people. I suppose it is a strange structure, but it’s quite common in English. It is like imagining a future state.
3. I don’t think “To begin with” is particularly informal.
4. It means that when people travel around, the diversity of the places they go to increases because they have more people from different places.
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Download my IELTS Books
Recent Posts
- How to Improve your IELTS Writing Score
- Past Simple vs Past Perfect
- Complex Sentences
- How to Score Band 9 [Video Lesson]
- Taxing Fast Food: Model IELTS Essay
Recent Comments
- Mariam on IELTS Writing Task 2: Two-Part Questions
- abdelhadi skini on Subordinating Conjunction vs Conjunctive Adverb
- David S. Wills on How to Describe Tables for IELTS Writing Task 1
- anonymous on How to Describe Tables for IELTS Writing Task 1
- David S. Wills on Writing Correction Service
- Lesson Plans
- Model Essays
- TED Video Lessons
- Weekly Roundup

- Specialized Training Manuals

Brain Drain In Pakistan: Pros, Cons and Prevention

Brain Drain, also known as human capital flight, refers to the emigration of highly skilled individuals from one country to another, in search of better opportunities and working conditions. The phenomenon has been prevalent in many countries, including Pakistan, where a significant number of educated and skilled professionals leave the country for foreign shores. In this article, we will explore the Pros, Cons, and the steps that can be taken to prevent the issue of Brain Drain in Pakistan.
Pros of Brain Drain in Pakistan
- Increased income and standard of living: The migration of skilled professionals to foreign countries results in an increase in their income and standard of living. This can have a positive impact on the economy of the host country and the quality of life of the individuals who emigrate.
- Brain Gain for host countries: The emigration of skilled professionals to foreign countries can result in a Brain Gain for the host country. The influx of highly skilled individuals can lead to an increase in innovation and the development of new technologies.
Cons of Brain Drain in Pakistan
- Loss of human capital: The departure of highly skilled individuals from Pakistan results in a loss of human capital for the country. This can have a negative impact on the economy, as the potential for innovation and growth is limited.
- Brain Waste for the origin country: The emigration of highly skilled individuals from Pakistan can result in a Brain Waste for the country. This is because the country has invested resources in the education and training of these individuals, only for them to leave and contribute to the development of another country.
- Negative impact on the economy: The departure of highly skilled individuals can result in a shortage of skilled professionals in certain fields, leading to a decline in the quality of services and products in the country. This can have a negative impact on the economy and the standard of living of the population.
Prevention of Brain Drain in Pakistan
- Encouragement of entrepreneurship: The government can encourage entrepreneurship by providing incentives and support to individuals who start their own businesses. This will create new job opportunities and reduce the need for skilled professionals to seek employment abroad.
- Investment in research and development: The government can invest in research and development to create new technologies and innovations. This will attract highly skilled professionals to stay in the country and contribute to its growth.
- Improvement in working conditions: The government can improve working conditions in the country by increasing wages, providing better benefits, and ensuring safe and healthy working environments. This will make the country a more attractive place for skilled professionals to work.
Conclusion Brain Drain is a persistent issue in Pakistan, with many highly skilled professionals leaving the country for better opportunities abroad. The Pros of Brain Drain include increased income and standard of living, as well as a Brain Gain for the host country. However, the Cons of Brain Drain include the loss of human capital, Brain Waste, and a negative impact on the economy. To prevent the issue of Brain Drain in Pakistan, the government can encourage entrepreneurship, invest in research and development, and improve working conditions. These steps will make the country a more attractive place for highly skilled professionals to work, reducing the need for them to seek employment abroad.

Bespoke HR Outsourcing Solutions
People is the leading HR outsourcing firm in the Middle East and South-Central Asia with two decades of specialized experience
Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
Our Partners
- People Perfect Advisory UAE
- People Perfect Advisory KSA
- People Perfect Advisory UK
- Heritage Luxury Suites
People 1-C, Jehlum Block, Green Fort-2, Lahore – Pakistan. [email protected] 042-111-000-737
dalilaltelmidh.net
Jeudi 7 janvier 2021, brain drain | bac essays | writing bac | anglais | english.

Sujets similaires - Similar topics
0 commentaires, enregistrer un commentaire, top topics - popular posts.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Brain Drain. Brain Drain is defined as the emigration or migration of individuals of talents and skills from developing or under-developed countries to developed ones. It means impoverishment of intellectuals, professionals, and technical resources of one country and enriching another. It is also known as the mass departure of skillful ...
100 Words Essay On Brain Drain. The term 'Brain Drain' is often used to refer to the emigration of highly educated or skilled individuals from one country to another. The loss of these individuals can have negative effects on the native country, including a shortage of qualified workers and deterioration of the quality of education and ...
The term ―brain drain‖ dominates popular discourse on high-skilled migration, and for this reason we use it in this article. However, as Harry Johnson (1965, p. 299) noted, the term brain drain ―is obviously a loaded phrase, involving implicit definitions of economic and social welfare, and implicit assertions about facts.
Brain Drain, often described as the emigration of highly skilled and educated individuals from less developed or unstable regions to more developed regions, is a phenomenon deeply ingrained in the global socio-economic landscape. This occurrence has both positive and negative effects, which bear scrutiny.
The United Nations defines brain drain as a one-way movement of highly skilled people from developing to developed countries that only benefits the industrialized world. In Zimbabwe, brain drain has been put forward as a key contributor to the country's weak health system over the past two decades [, , , ]. High vacancy rates in the ...
Consequences of Brain Drain. 1. Loss of Human Capital: Brain drain results in the loss of highly skilled individuals, which can hinder a country's economic and technological development. 2. Impact on Health and Education: The emigration of healthcare professionals and educators can have a detrimental impact on healthcare systems and educational ...
However, some academic observers (e.g., Mountford, 1997; Beine, Docquier and Rapoport, 2001) have argued that brain drain is beneficial. They posit that the possibility of migration encourages investment in education because of the potential high returns abroad from educated migrants. Arguably, brain drain can thus eventually increase income ...
Brain drain, disadvantage, and migration constraints. The dynamic of skilled migration from developing to developed countries is sometimes captured by the phrase 'the perverse subsidy' (Labonté, Packer, and Klassen Citation 2006; Kollar and Buyx Citation 2013).The basic point here is simple and can be exemplified using the main domain in which discussions about brain drain arise ...
Brain drain is a slang term for a significant emigration of educated or talented individuals. A brain drain can result from turmoil within a nation, from there being better professional ...
JOHNSON: "BRAIN DRAIN" IN THE CARIBBEAN 2 "Brain Drain" is in fact legitimate phenomenon. Finally, I will end by discussing some possible solutions to the counter possible effects of the 'Brain Drain' on the Caribbean and show the importance of moving from a mindset of "Brain Drain" to one of "Mutual Gain."
Abstract. Brain drain is defined as the migration of health personnel in search of the better standard of living and quality of life, higher salaries, access to advanced technology and more stable political conditions in different places worldwide. This migration of health professionals for better opportunities, both within countries and across ...
Rather than depriving developing countries of their best talent through 'brain drain,' mobile students are offering 'brain gain' by creating a global pool of highly-skilled human capital. As scientists and researchers, they are forming knowledge networks and increasing collaboration on global policy issues. This improves innovation in ...
The essay on brain drain will help students to understand the reason behind brain drain and how this problem can be solved. Students can also check out the list of CBSE Essays to practise more essays on different topics and boost their essay writing skills. 500+ Words Essay on Brain Drain.
Introduction to Brain Drain. "Knowledge exists, nations suffer the cost of brain drain.". Brain Drain, a significant global issue, refers to the mass migration of skilled individuals from their native countries in pursuit of better opportunities overseas. Driven by economic, professional, and political factors, this phenomenon presents ...
Part II is devoted to the consequences of brain drain, taking the point of view of the sending country. This second section provides for the first time a measure of the net global impact of the brain drain on sending countries. The results indicate that most developing countries experience a net gain from skilled emigration. Adverse overall ...
Executive Board paper discussing the causes, consequences and remedies to brain drain from the developing to the developed countries, overviews the work accomplished by UNESCO and other UN System Agencies, proposing possible remedial action, outlines an integrated international programme of action on brain drain, and UNESCO's role therein
The brain-drain from certain areas/countries leads to the creation of imbalance at the international level, where rich countries are becoming richer and the poor poorer (Bhagwati & Rodriguez, 1975). The third movement was created in the 1990s and observes the issue differently.
500 Words Essay on Brain Drain Understanding the Phenomenon of Brain Drain. Brain Drain, also known as Human Capital Flight, is a phenomenon where skilled and educated individuals migrate from less developed or developing countries to developed nations in search of better opportunities. This migration, while offering personal growth for ...
Essay of the Week: Brain drain in the developing world. Our band nine sample essays give you the opportunity to learn from successful essays that show off the best structure, vocabulary and grammar. This problem and solution type essay is about the complex issue of 'brain drain' in the developing world. An increasing number of professionals ...
Sample Answer. In the modern era, it is common for people to move around the world for various reasons, including immigration purposes. This sometimes results in people leaving a poor country to go to a richer one, in a phenomenon that is sometimes known as "brain drain.". This essay will look into the reasons for this and also suggest some ...
The Pros of Brain Drain include increased income and standard of living, as well as a Brain Gain for the host country. However, the Cons of Brain Drain include the loss of human capital, Brain Waste, and a negative impact on the economy. To prevent the issue of Brain Drain in Pakistan, the government can encourage entrepreneurship, invest in ...
Details on Brain Drain. Brain drain is defined as the movement of health professionals from one country to another in quest of a better standard of living and quality of life, greater incomes, access to sophisticated technologies, and more stable political situations. Human capital flight refers to those who have earned advanced training at ...
Brain Drain | Bac essays | Writing Bac | anglais | English. - janvier 07, 2021 Writing. The migration of highly qualified and trained employees, in my view, produces both advantages and problems. For certain workers, willing to change their financial condition or to avoid economic or political problems in their own countries at an individual ...
Indonesia is considering offering dual citizenship to people of Indonesian descent in order to attract more skilled workers to the country, a senior cabinet minister said yesterday. Speaking at a ...